
TLC320AD58C
Data Manual
Sigma-Delta Stereo Analog-to-Digital Converter
SLAS102
May 1995
Printed on Recycled Paper

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products or to discontinue any
semiconductor product or service without notice, and advises its customers to obtain the latest
version of relevant information to verify , before placing orders, that the information being relied
on is current.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products and related software to the specifications
applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard warranty . T esting and other quality
control techniques are utilized to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty.
Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily performed, except those
mandated by government requirements.
Certain applications using semiconductor products may involve potential risks of death,
personal injury , or severe property or environmental damage (“Critical Applications”).
TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, INTENDED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT APPLICATIONS, DEVICES
OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS.
Inclusion of TI products in such applications is understood to be fully at the risk of the customer.
Use of TI products in such applications requires the written approval of an appropriate TI officer .
Questions concerning potential risk applications should be directed to TI through a local SC
sales office.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and
operating safeguards should be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural
hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software
performance, or infringement of patents or services described herein. Nor does TI warrant or
represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright,
mask work right, or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination,
machine, or process in which such semiconductor products or services might be or are used.
Copyright 1995, Texas Instruments Incorporated

Contents
Section Title Page
1 Introduction 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Features 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Functional Block Diagram 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Terminal Assignments 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Ordering Information 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Terminal Functions 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Detailed Description 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Power-Down and Reset Functions 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.1 Power Down 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.2 Reset Function 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Differential Input 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Sigma-Delta Modulator 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4 Decimation Filter 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 High-Pass Filter 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6 Master-Clock Circuit 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7 T est 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8 Serial Interface 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8.1 Master Mode 2–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8.2 Slave Mode 2–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Specifications 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Free-Air Temperature Range 3–1. . . . .
3.2 Recommended Operating Conditions 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Electrical Characteristics 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.1 Digital Interface, T
3.3.2 Analog Interface 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3.3 Channel Characteristics, T
f
= 48 kHz 3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Switching Characteristics 3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
s
= 25°C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
= 25°C, AVDD = DVDD = 5 V,
A
4 Parameter Measurement Information 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Application Information 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A Mechanical Data A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iii

List of Illustrations
Figure Title Page
2–1. Power-Down Timing Relationships 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–2. Differential Analog Input Configuration 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–3. Serial Master Transfer Modes 2–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–4. Serial Slave Transfer Modes 2–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–1. SCLK to Fsync and DOUT – Master Mode 3 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–2. SCLK to Fsync, DOUT, and LRClk – Master Modes 4 and 6 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–3. SCLK to Fsync, DOUT, and LRClk – Master Mode 5 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–4. SCLK to Fsync, DOUT, and LRClk – Master Mode 7 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–5. SCLK to LRClk and DOUT – Slave Mode 0, Fsync High 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–6. SCLK to Fsync, LRClk, and DOUT – Slave Mode 2, Fsync Controlled 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . .
5–1. TLC320AD58C Configuration Schematic 5–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–2. TLC320AD58C External Digital Timing and Control-Signal Generation Schematic 5–3.
5–3. TLC320AD58C External Analog Input Buffer Schematic 5–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of Tables
Table Title Page
2–1. Master-Clock to Sample-Rate Comparison 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv
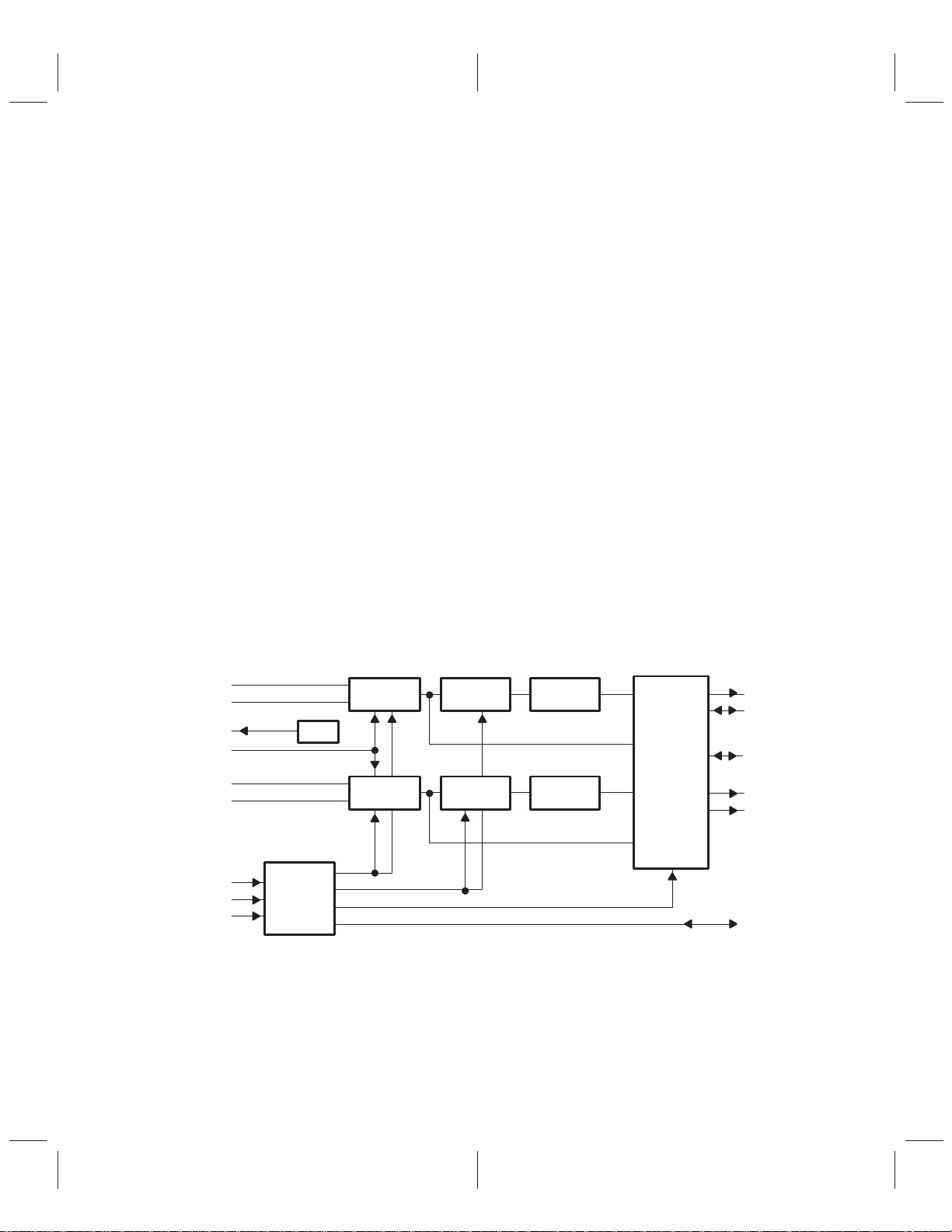
1 Introduction
The TLC320AD58C provides high-resolution signal conversion from analog to digital using oversampling
sigma-delta technology. This device consists of two synchronous conversion paths. Also included is a
decimation filter after the modulator as shown in the functional block diagram. Other functions provide
analog filtering and on-chip timing and control.
A functional block diagram of the TLC320AD58C is included in Section 1.2. Each block is described in the
detailed description section.
1.1 Features
• Single 5-V Power Supply
• Sample Rates up to 48 kHz
• 18-Bit Resolution
• Signal-to-Noise Ratio (EIAJ) of 97 dB
• Dynamic Range of 95 dB
• Total Signal-to-Noise+Distortion of 95 dB
• Internal Reference Voltage (V
• Serial-Port Interface
• Differential Architecture
• Power Dissipation of 200 mW. Power-Down Mode for Low-Power Applications
• One-Micron Advanced LinEPIC1Z Process
1.2 Functional Block Diagram
ref
)
INLP
INLM
REFO
REFI
INRP
INRM
MCLK
CMODE
MODE(0–2)
CONTROL
VREF
Sigma-Delta
Modulator
Sigma-Delta
Modulator
Decimation
Filter
Decimation
Filter
LinEPIC1Z is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
High-Pass
Filter
High-Pass
Filter
Serial
Interface
DOUT
Fsync
LRClk
OSFR
OSFL
SCLK
1–1
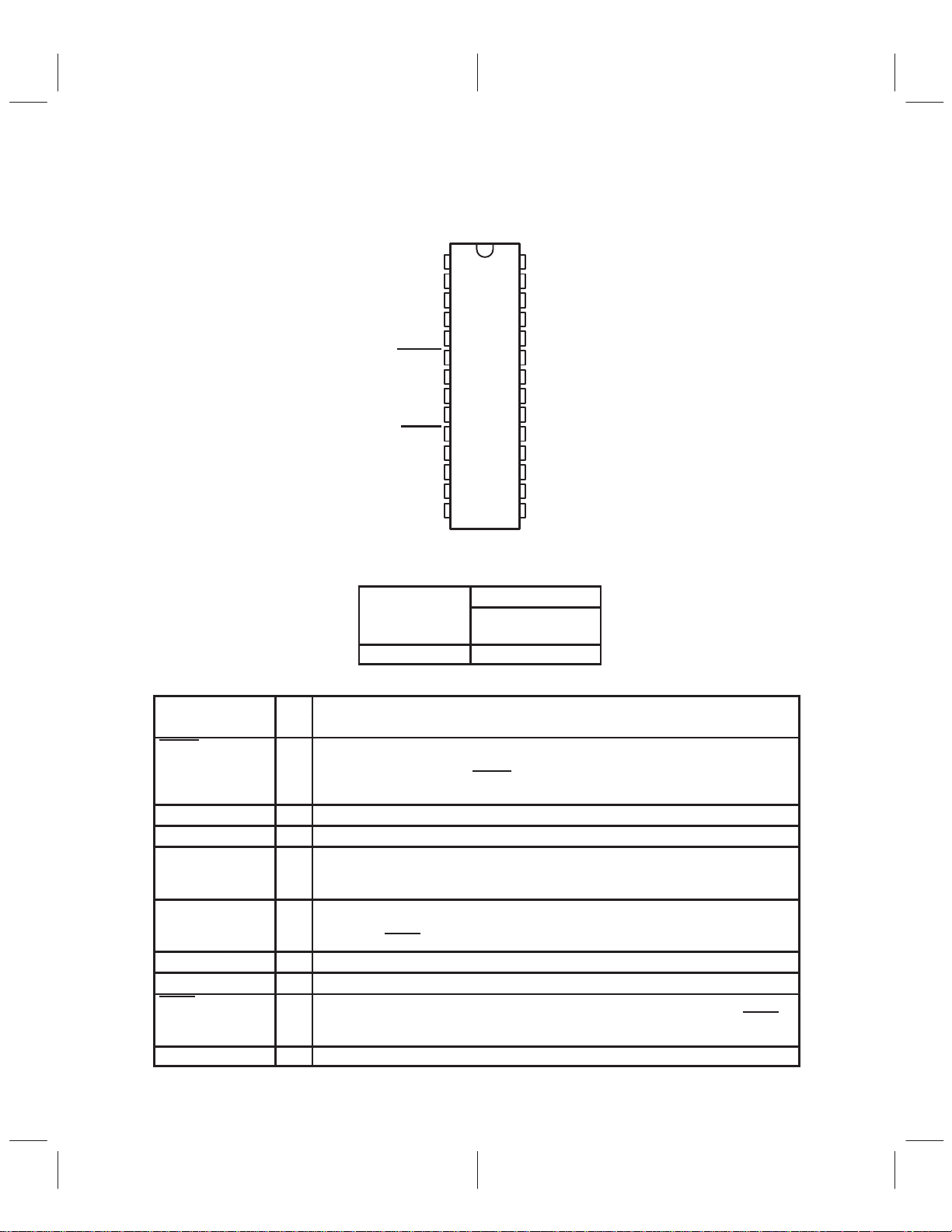
1.3 Terminal Assignments
I/O
DESCRIPTION
DW PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
INLP
1
INLM
REFI
AV
AV
AnaPD
TEST1
MODE2
OSFL
DigPD
TEST2
CMODE
MODE0
LRClk
NC – No internal connection
DD
SS
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
INRP
INRM
REFO
LGND
Vlogic
NC
MODE1
OSFR
MCLK
DV
SS
DV
DD
Fsync
DOUT
SCLK
1.4 Ordering Information
PACKAGE
T
A
0°C to 70°C TLC320AD58CDW
SMALL OUTLINE
(DW)
1.5 Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
AnaPD 6 I Analog power-down mode. The analog power-down mode disables the analog
AV
DD
AV
SS
CMODE 12 I Clock mode. CMODE is used to select between two methods of determining the master
DOUT 16 O Data output. DOUT is used to transmit the sigma-delta audio ADC output data to a DSP
DV
DD
DV
SS
DigPD 10 I Digital power-down mode. The digital power-down mode shuts down the digital filters and
Fsync 17 I/O Frame sync. Frame sync is used to designate the valid data from the ADC.
4 I Analog supply voltage
5 I Analog ground
18 I Digital supply voltage
19 I Digital ground
modulators. The single-bit modulator outputs become invalid, rendering the outputs of the
digital filters invalid. When AnaPD
resumed.
clock frequency. When CMODE is high, the master clock input is 384× the conversion
frequency. When CMODE is low , the master clock input is 256× the conversion frequency .
serial port or other compatible serial interface and is synchronized to SCLK. This output
is low when DigPD
clock generators. All digital outputs are brought to unasserted states. When DigPD
pulled high, normal operation of the device is resumed.
is high.
is pulled high, normal operation of the device is
is
1–2
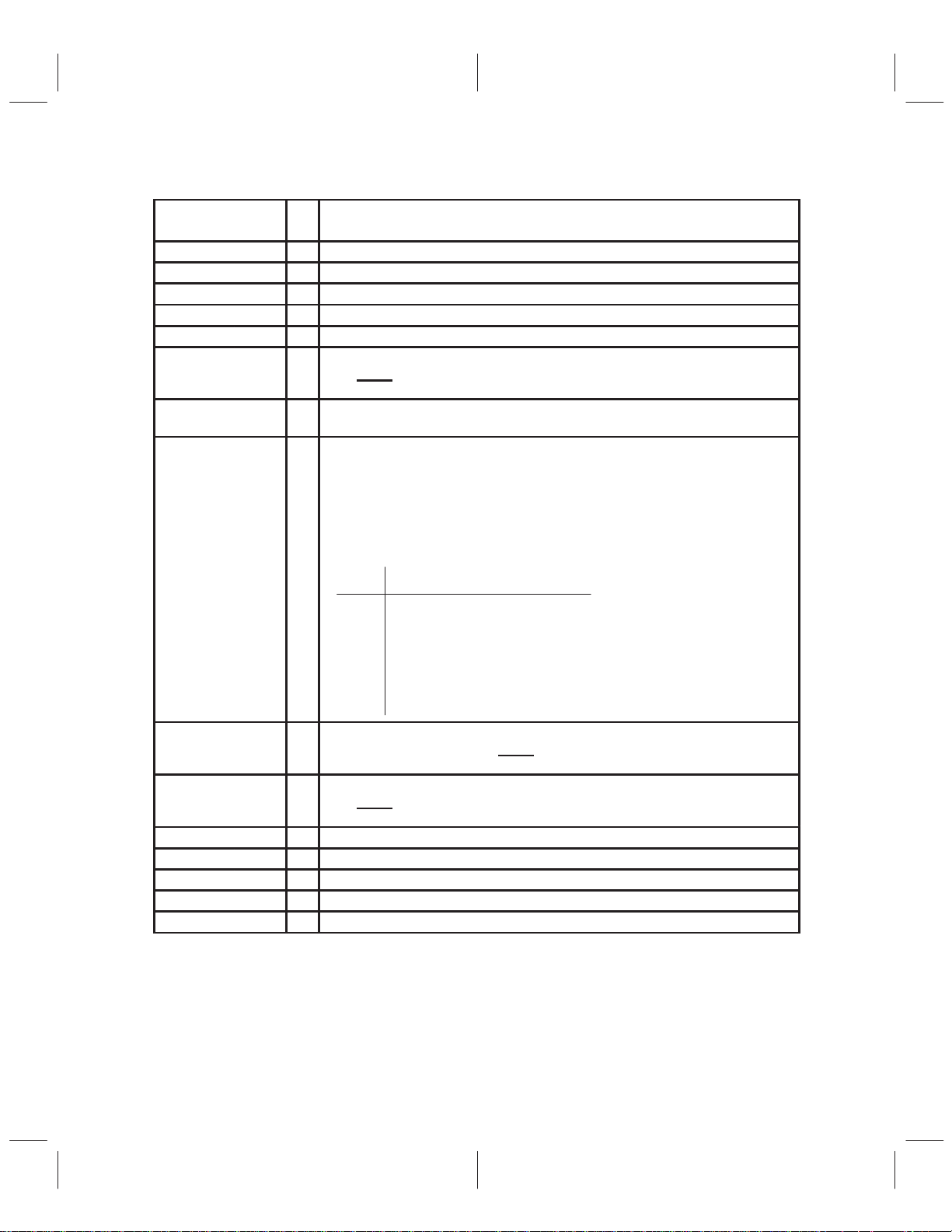
1.5 Terminal Functions (Continued)
I/O
DESCRIPTION
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
INLM 2 I Inverting input to left analog input amplifier
INLP 1 I Noninverting input to left analog input amplifier
INRM 27 I Inverting input to right analog input amplifier
INRP 28 I Noninverting input to right analog input amplifier
LGND 25 I Logic power supply ground for analog modulator
LRClk 14 I/O Left/right clock. LRClk signifies whether the serial data is associated with the left channel
MCLK 20 I Master clock. MCLK is used to derive all the key logic signals of the sigma-delta audio
MODE(0–2) 13, 22,8I Serial modes. MODE(0–2) configure this device for many different modes of operation.
OSFL,
OSFR
SCLK 15 I/O Shift clock. If SCLK is configured as an input, SCLK is used to clock serial data out of
TEST1 7 I Test mode 1. TEST1 should be low for normal operation.
TEST2 11 I Test mode 2. TEST2 should be low for normal operation.
REFI 3 I Input voltage for modulator reference (normally connected to REFO, terminal 26).
REFO 26 I Internal voltage reference
Vlogic 24 I Logic power supply voltage (5 V) for analog modulator
9, 21 O Over scale flag left/right. If the left/right channel digital output exceeds full scale output
ADC (when LRClk is high) or the right channel ADC (when LRClk is low). LRClk is low
when DigPD
ADC. The nominal input frequency range is 18.432 MHz to 256 kHz.
The different configurations are:
Master versus slave
16 bit versus 18 bit
MSB first versus LSB first
Slave: Fsync controlled versus Fsync high
Each of these modes is described in the serial interface section along with timing
diagrams.
MODE MASTER/ MSB/LSB
0 1 2 SLAVE BITS FIRST
0 0 0 slave up to 18 MSB
0 0 1 slave 18 LSB
0 1 0 slave up to 18 MSB
0 1 1 master 16 MSB
1 0 0 master 18 MSB
1 0 1 master 18 LSB
1 1 0 master 16 MSB
1 1 1 master 16 LSB
range for two consecutive conversions, this flag is set high for 4096 LRClk periods.
OSFL and OSFR are low when DigPD
the sigma-delta audio ADC. If SCLK is configured as an output, SCLK stops clocking
when DigPD
is low.
is low.
is low.
1–3

1–4
2 Detailed Description
The sigma-delta converter allows for simple antialias external filtering. Typically, a first order RC filter is
sufficient.
2.1 Power-Down and Reset Functions
2.1.1 Power Down
The power-down state is comprised of a separate digital and analog power down. The power consumption
of each is detailed in the electrical characteristics section.
The digital power-down mode shuts down the digital filters and clock generators. All digital outputs are set
to an unasserted level. When the digital power-down terminal is pulled high, normal operation of the device
is initiated. In slave mode, the conversion process must synchronize to an input on the LRClk terminal as
well as the SCLK terminal. Therefore, the conversion process is not initiated until the first rising edges of
both SCLK and LRClk are detected after DigPD
conversions are performed at a fixed LRClk rate [MCLK/256 (CMODE low) or MCLK/384 (CMODE high)]
after the initial synchronization. After the digital power-down terminal is brought high, the output of the digital
filters remains invalid for 50 LRClk cycles [see Figures 2–1(a) and 2–1(b)].
In master mode, LRClk is an output; therefore, the conversion process initiates based on internal timing.
The first valid data out occurs as shown in Figure 2–1(c).
The analog power-down mode disables the analog modulators. The single-bit modulator outputs become
invalid which renders the outputs of the digital filters invalid. When the analog power-down terminal is
brought high, the modulators are brought back online; however, the outputs of the digital filters require 50
LRClk cycles for valid results.
2.1.2 Reset Function
The conversion process is not initiated until the first rising edges of both SCLK and LRClk are detected after
DigPD is pulled high. This synchronizes the conversion cycle; all conversions are performed at a fixed LRClk
rate [MCLK/256 (CMODE low) or MCLK/384 (CMODE high)] after the initial synchronization.
is pulled high. This synchronizes the conversion cycle; all
2–1
 Loading...
Loading...