Suzuki GRAND VITARA JB416, GRAND VITARA JB420 SERVICE MANUAL

IMPORTANT
WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE
Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the words
!
WARNING
lighted by these signal words.
!
WARNING
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in death or injury.
!
CAUTION
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in vehicle damage.
NOTE:
Indicates special information to make maintenance easier or instructions clearer.
!
WARNING
This service manual is intended for authorized Suzuki dealers and qualified service technicians only.
Inexperienced technicians or technicians without the proper tools and equipment may not be able to
properly perform the services described in this manual.
Improper repair may result in injury to the technician and may render the vehicle unsafe for the driver
and passengers.
!
, and NOTE have special meanings. Pay special attention to the messages high-
CAUTION
!
WARNING
For vehicles equipped with a Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
• Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing service on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Service Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
• If the air bag system and another vehicle system both need repair, Suzuki recommends that the air
bag system be repaired first, to help avoid unintended air bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel, instrument panel or any other air bag system component on or
around air bag system components or wiring. Modifications can adversely affect air bag system
performance and lead to injury.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93 °C (200 °F), for example, during a paint baking
process, remove the air bag system components, that is air bag (inflator) modules, SDM and/or seat
belt with pretensioner, beforehand to avoid component damage or unintended activation.
The circle with a slash in this manual means “Don’t do this” or “Don’t let this happen”.

FOREWORD
This SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICE MANUAL is a supplement to GRAND VITARA (JB416/JB420) SERVICE
MANUAL.
It has been prepared exclusively for the following applicable model.
Applicable model:
GRAND VITARA (JB416/JB420) vehicles
This supplementary ser vice manual describes only different service information of the above applicable model
as compared with GRAND VITARA (JB416/JB420) SERVICE MANUAL. Therefore, whenever servicing the
above applicable models, consult this supplement first. And for any section, item or description not found in this
supplement, refer to the related manual below.
When replacing parts or servicing by disassemb ling , it is recommended to use SUZUKI genuine parts, tools and
service materials as specified in each description.
All information, illustrations and specifications contained in this literature are based on the latest product information available at the time of publication approv al. And used as the main subject of description is the vehicle of
standard specifications among others.
Therefore, note that illustrations may differ from the vehicle being actually serviced.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time without notice.
Related Manuals:
Manual Name Manual No.
GRAND VITARA (JB416/JB420 ) SERVICE MANUAL 99500-64J00-01E
© COPYRIGHT SUZUKI MOTOR CORPORATION 2005

RECOMMENDATON OF GENUINE SUZUKI PARTS AND ACCESSORIES USE
SUZUKI strongly recommends the use of genuine SUZUKI parts* and accessories. Genuine SUZUKI parts and
accessories are built to the highest standards of quality and performance, and are designed to fit the vehicle's
exact specifications.
A wide variety of non-genuine replacement parts and accessories for SUZUKI vehicles are currently availabl e in
the market. Using these par ts and accessories can affect the vehicle performance and shorten its useful life.
Therefore, installation of non-genuine SUZUKI parts and accessories is not covered under warranty.
Non-Genuine SUZUKI Parts and Accessories
Some parts and accessories may be approved by certain authorities in your country.
Some parts and accessories are sold as SUZUKI a uthorized replacement par ts and accessor ies. Some genuine SUZUKI parts and accessor ies are sold as re-use parts and accessories. These par ts and acce ssories are
non-genuine Suzuki parts and accessories and use of these parts are not covered under warranty.
Re-use of Genuine SUZUKI Parts and Accessories
The resale or re-use of the following items which could give rise to safety hazards for users is expressly forbidden:
1) Air bag components and all other pyrotechnic items, including their components (e.g. cushion, control
devices and sensors)
2) Seatbelt system, including their components (e.g. webbing, buckles, and retractors)
The air bag and seat belt pretensioner components contain explosive chemicals. These components should be
removed and disposed of properly by SUZUKI authorized service shop or scrap yard to avoid unintended explosion before scrapping.
*The parts remanufactured under SUZUKI's approval can be used as genuine SUZUKI parts in Europe.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
NOTE
For the screen toned sections with asterisk (*) in the “TABLE OF CONTENTS” below, refer to the same
sections of the service manual mentioned in the “FOREWORD” of this manual.
00
0
Precautions............................................................... 00-i
Precautions ............................................................ 00-1
General Information ................................................... 0-i
General Information ............................................... 0A-1
Maintenance and Lubrication ..................................0B-*
Engine ......................................................................... 1-i
Precautions ............................................................... 1-*
Engine General Information and Diagnosis ...........1A-1
Aux. Emission Control Devices ...............................1B-*
Engine Electrical Devices....................................... 1C-*
Engine Mechanical................................................. 1D-*
Engine Lubrication System .....................................1E-*
Engine Cooling System...........................................1F-*
Fuel System ........................................................... 1G-*
Ignition System....................................................... 1H-*
Starting System........................................................ 1I-*
Charging System..................................................... 1J-*
Exhaust System ......................................................1K-*
Suspension................................................................. 2-i
Precautions ............................................................... 2-*
Suspension General Diagnosis...............................2A-*
Front Suspension ................................................... 2B-1
Rear Suspension.................................................... 2C-*
Wheels and Tires ................................................... 2D-*
Driveline / Axle ........................................................... 3-i
Precautions ............................................................... 3-*
Drive Shaft / Axle ....................................................3A-*
Differential ...............................................................3B-*
Transfer.................................................................. 3C-1
Propeller Shafts...................................................... 3D-*
Brakes ......................................................................... 4-i
Precautions .............................................................. 4-1
Brake Control System and Diagnosis ....................4A-1
Front Brakes........................................................... 4B-1
Rear Brakes ........................................................... 4C-*
Parking Brake......................................................... 4D-*
ABS ........................................................................ 4E-1
Electronic Stability Program ................................... 4F-1
Transmission / Transaxle .......................................... 5-i
Precautions ............................................................... 5-*
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle ........................5A-1
Manual Transmission/Transaxle ............................ 5B-*
Clutch ..................................................................... 5C-*
Steering....................................................................... 6-i
Precautions ............................................................... 6-*
Steering General Diagnosis ................................... 6A-*
Steering Wheel and Column ..................................6B-1
Power Assisted Steering System ........................... 6C-*
HVAC ........................................................................... 7-i
Precautions ............................................................... 7-*
Heater and Ventilation............................................ 7A-1
Air Conditioning System.........................................7B-1
Restraint...................................................................... 8-*
Precautions ............................................................... 8-*
Seat Belts............................................................... 8A-*
Air Bag System ...................................................... 8B-*
Body, Cab and Accessories ...................................... 9-i
Precautions .............................................................. 9-1
Wiring Systems ...................................................... 9A-*
Lighting Systems.................................................... 9B-1
Instrumentation / Driver Info. / Horn .......................9C-1
Wipers / Washers...................................................9D-1
Glass / Windows / Mirrors ...................................... 9E-*
Security and Locks..................................................9F-*
Seats ...................................................................... 9G-*
Interior Trim............................................................ 9H-*
Sun Roof / T-Top / Convertible Top .........................9I-*
Hood / Fenders / Doors........................................... 9J-*
Body Structure ....................................................... 9K-*
Paint / Coatings....................................................... 9L-*
Exterior Trim...........................................................9M-*
Control systems ....................................................... 10-i
Precautions ............................................................. 10-*
Cruise Control System .........................................10A-1
Body Electrical Control System ............................10B-1
Immobilizer Control System .................................10C-1
Keyless Start System ........................................... 10E-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11


Table of Contents 00- i
Section 00
Precautions
CONTENTS
NOTE
For the items with asterisk (*) in the “CONTENTS” below, refer to the same section of the service manual
mentioned in the “FOREWORD” of this manual.
00
Precautions ...............................................00-1
Precautions........................................................... 00-1
Precautions for Vehicles Equipped with
a Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System ...... 00-*
General Precautions ............................................ 00-*
Precaution in Servicing Full-Time 4WD
Vehicle ............................................................... 00-*
Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP®
System ............................................................. 00-1
Precautions for Catalytic Converter .....................00-*
Precaution for CAN Communication System ....... 00-*
Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service .............00-*
Precautions for Installing Mobile
Communication Equipment ................................ 00-*
Air Bag Warning ...................................................00-*
Discharge Headlight Warning ..............................00-*
A/C System Caution.............................................00-*
Fastener Caution.................................................. 00-*
Suspension Caution ............................................. 00-*
Wheels and Tires Caution....................................00-*
Brakes Caution and Note .................................... 00-1
Differential Gear Oil Note .....................................00-*
Repair Instructions ...............................................00-*
Electrical Circuit Inspection Procedure ................00-*
Intermittent and Poor Connection Inspection .......00-*
00-1 Precautions:
Precautions
Precautions
Precaution for Vehicle Equipped with ESP®
System
S5JB0E0000020
• When testing with any of the following equipments
(when vehicle is tested by rotating wheels (tires)
under vehicle stop), be sure to deactivate ESP®
system referring to “Precautions in Speedometer Test
or Other Tests: in Section 4F” to obtain correct data.
When vehicle acceleration is not sensed and wheels
are rotating, ESP® control module judges that wheels
are in slip condition and controls engine torque to
reduce by TCS control.
– 2 or 4-wheel chassis dynamometer
– Speedometer tester
– Brake tester
–Etc.
ESP® control module
• When ESP® control module is removed / installed, do
not use impact wrenches which generate shock or
impact to avoid damaging sensors in ESP® control
module.
• When any of the following operation is done, calibrate
steering angle sensor, G sensor and master cylinder
pressure sensor (in ESP® control module) referring to
“Sensor Calibration: in Section 4F”.
– When battery or dome fuse is removed.
– When steering angle sensor is replaced.
– When ESP® control module is removed.
– When yaw rate / G sensor assembly is removed.
Brakes Caution and Note
!
CAUTION
All brake fasteners are important attaching
parts in that they could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/
or could result in major repair expense. They
must be replaced with one of same part
number or with an equivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use
a replacement part of lesser quality or
substitute design. Torque values must be
used as specified during reassembly to
assure proper retention of all parts. There is
to be no welding as it may result in extensive
damage and weakening of the metal.
NOTE
Before inspecting and servicing brakes for
vehicle equipped with ABS (ESP®), make
sure that ABS (ESP®) is in good condition.
S5JB0E0000014

Table of Contents 0- i
Section 0
General Information
CONTENTS
NOTE
For the items with asterisk (*) in the “CONTENTS” below, refer to the same section of the service manual
mentioned in the “FOREWORD” of this manual.
0
General Information ................................ 0A-1
General Description .............................................0A-1
Abbreviations ...................................................... 0A-1
Symbols ...............................................................0A-*
Wire Color Symbols .............................................0A-*
Fastener Information............................................0A-*
Vehicle Lifting Points............................................0A-*
Engine Supporting Points ....................................0A-*
Vehicle Identification Number ..............................0A-*
Engine Identification Number ...............................0A-*
Transmission Identification Number.....................0A-*
Component Location ........................................... 0A-*
Warning, Caution and Information Label
Location .............................................................0A-*
Maintenance and Lubrication..................0B-*
Precautions........................................................... 0B-*
Precautions for Maintenance and
Lubrication .........................................................0B-*
Scheduled Maintenance ...................................... 0B-*
Maintenance Schedule under Normal
Driving Conditions..............................................0B-*
Maintenance Recommended under Severe
Driving Conditions..............................................0B-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 0B-*
Engine Accessory Drive Belt Inspection ..............0B-*
Engine Accessory Drive Belt Replacement..........0B-*
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ......................0B-*
Engine Oil and Filter Change ...............................0B-*
Engine Coolant Change .......................................0B-*
Exhaust system Inspection ..................................0B-*
Spark Plugs Replacement ...................................0B-*
Air Cleaner Filter Inspection.................................0B-*
Air Cleaner Filter Replacement ............................0B-*
Fuel Lines and Connections Inspection ...............0B-*
Fuel Filter Replacement.......................................0B-*
Fuel Tank Inspection............................................0B-*
Crankcase Ventilation Hoses and
Connections Inspection (Vehicle without
A/F Sensor) ....................................................... 0B-*
PCV Valve Inspection ......................................... 0B-*
Fuel Evaporative Emission Control System
Inspection.......................................................... 0B-*
Brake Discs and Pads Inspection ....................... 0B-*
Brake Drums and Shoes Inspection.................... 0B-*
Brake Hoses and Pipes Inspection ..................... 0B-*
Brake Fluid Change ............................................ 0B-*
Parking Brake Lever and Cable Inspection......... 0B-*
Clutch Fluid Inspection........................................ 0B-*
Tire / Wheel Inspection and Rotation .................. 0B-*
Wheel Discs Inspection....................................... 0B-*
Wheel Bearing Inspection ................................... 0B-*
Suspension System Inspection ........................... 0B-*
Steering System Inspection ................................ 0B-*
Propeller Shafts and Drive Shafts
Inspection.......................................................... 0B-*
Manual Transmission Oil Inspection ................... 0B-*
Manual Transmission Oil Change ....................... 0B-*
Automatic Transmission Fluid Inspection............ 0B-*
Automatic Transmission Fluid Change ............... 0B-*
Automatic Transmission Fluid Cooler Hose
Inspection.......................................................... 0B-*
Transfer Oil Inspection (If Equipped) .................. 0B-*
Differential Oil Inspection .................................... 0B-*
Transfer (If Equipped) and Differential Oil
Change.............................................................. 0B-*
Power Steering (P/S) System Inspection ............ 0B-*
All Hinges, Latches and Locks Inspection........... 0B-*
HVAC Air Filter Inspection (If Equipped)............. 0B-*
HVAC Air Filter Replacement (If Equipped) ........ 0B-*
Final Inspection for Maintenance Service ........... 0B-*
Specifications....................................................... 0B-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 0B-*
Special Tools and Equipment ............................. 0B-*
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants................. 0B-*
Special Tool ........................................................ 0B-*
0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Description
Abbreviations
S5JB0E0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
ATDC: After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid
A/T: Automatic Transmission
AWD: All Wheel Drive
B:
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CKT: Circuit
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Control Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
(Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
ELR: Emergency Locking Retractor
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
ESP®: Electronic Stability Program
EVAP: Evaporative Emission
EVAP Canister: Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)
F:
FWD: Front Wheel Drive
4WD: 4 Wheel Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
H:
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
HVAC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
IMT: Intake Manifold Tuning
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator (Motor)
L:
LH: Left Hand
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor,
AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Multipoint Fuel Injection)
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
Min: Minimum
M/T: Manual Transmission
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
OCM: Occupant Classification module
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
P/S: Power Steering
R:
RH: Right Hand
S:
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
SDM: Sensing and Diagnostic Module (Air Bag
Controller, Air bag Control Module)

SFI: Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection
SOHC: Single Over Head Camshaft
T:
TBI: Throttle Body Fuel Injection (Single-Point Fuel
Injection, SPI)
TCC: Torque Converter Clutch
TCM: Transmission Control Module (A/T Controller, A/T
Control Module)
TPMS: Tire Pressure Monitoring System
TP Sensor: Throttle Position Sensor
TVV: Thermal Vacuum Valve (Thermal Vacuum
Switching Valve, TVSV, Bimetal Vacuum Switching
Valve, BVSV)
TWC: Three Way Catalytic Converter (Three Way
Catalyst)
2WD: 2 Wheel Drive
V:
VIN: Vehicle Identification Number
VSS: Vehicle Speed Sensor
VVT: Variable Valve Timing (Camshaft Position Control)
W:
WU-OC: Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter
WU-TWC: Warm Up Three Way Catalytic Converter
General Information: 0A-2

0A-3 General Information:

Section 1
Engine
CONTENTS
Table of Contents 1- i
NOTE
For the items with asterisk (*) in the “CONTENTS” below, refer to the same section of the service manual
mentioned in the “FOREWORD” of this manual.
Precautions ................................................. 1-*
Precautions.............................................................. 1-*
Precautions for Engine........................................... 1-*
Engine General Information and
Diagnosis ................................................. 1A-1
Precautions...........................................................1A-1
Precautions on Engine Service ............................1A-*
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble ..................... 1A-1
Precautions For DTC Troubleshooting.................1A-*
Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection.................1A-*
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration.............................................1A-*
General Description .............................................1A-2
Statement on Cleanliness and Care ....................1A-*
Engine Diagnosis General Description ................1A-*
On-Board Diagnostic System Description........... 1A-2
Engine and Emission Control System
Description ........................................................1A-5
CAN Communication System Description........... 1A-5
Air Intake System Description ..............................1A-*
Description of Electric Throttle Body System .......1A-*
Description of Electric Throttle Body
System Calibration.............................................1A-*
Generator Control System Description ................1A-*
A/F Sensor Description ........................................1A-*
Electronic Control System Description................ 1A-7
Engine and Emission Control Input / Output
Table ...............................................................1A-15
Schematic and Routing Diagram......................1A-16
Engine and Emission Control System
Diagram .......................................................... 1A-16
Component Location .........................................1A-17
Electronic Control System Components
Location .......................................................... 1A-17
Diagnostic Information and Procedures..........1A-19
Engine and Emission Control System
Check.................................................................1A-*
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Check .............1A-*
DTC Check ..........................................................1A-*
DTC Clearance ....................................................1A-*
DTC Table......................................................... 1A-19
Fail-Safe Table.....................................................1A-*
Scan Tool Data ....................................................1A-*
Visual Inspection ................................................. 1A-*
Engine Basic Inspection...................................... 1A-*
Engine Symptom Diagnosis ................................ 1A-*
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Does Not Come
ON with Ignition Switch ON and Engine
Stop (but Engine Can Be Started)................... 1A-25
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Remains ON
after Engine Starts ..........................................1A-27
DTC P0010: Camshaft Position Actuator
Circuit (For M16 Engine) ................................... 1A-*
DTC P0011 / P0012: Camshaft Position -
Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance
/ -Retarded (For M16 Engine) ........................... 1A-*
DTC P0030: HO2S Heater Control Circuit
(Sensor-1) ......................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0031 / P0032: HO2S Heater Control
Circuit Low / High (Sensor-1) ............................ 1A-*
DTC P0037 / P0038: HO2S Heater Control
Circuit Low / High (Sensor-2) ............................ 1A-*
DTC P0101: Mass Air Flow Circuit Range
/ Performance.................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0102: Mass Air Flow Circuit Low
Input .................................................................. 1A-*
DTC P0103: Mass Air Flow Circuit High
Input .................................................................. 1A-*
DTC P0106: Manifold Absolute Pressure
Range / Performance ........................................ 1A-*
DTC P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure
Circuit Low Input ............................................... 1A-*
DTC P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure
Circuit High Input............................................... 1A-*
DTC P0111: Intake Air Temperature Circuit
Range / Performance ........................................ 1A-*
DTC P0112: Intake Air Temperature
Sensor Circuit Low ............................................ 1A-*
DTC P0113: Intake Air Temperature
Sensor Circuit High ........................................... 1A-*
DTC P0116: Engine Coolant Temperature
Circuit Range / Performance............................. 1A-*
DTC P0117: Engine Coolant Temperature
Circuit Low ........................................................ 1A-*
DTC P0118: Engine Coolant Temperature
Circuit High........................................................ 1A-*
DTC P0122: Throttle Position Sensor
(Main) Circuit Low ............................................. 1A-*
1

1-ii Table of Contents
DTC P0123: Throttle Position Sensor
(Main) Circuit High ............................................ 1A-*
DTC P0131 / P0132 / P0134: O2 Sensor
(HO2S) Circuit Low Voltage / High Voltage
/ No Activity Detected (Sensor-1)...................... 1A-*
DTC P0133: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit
Slow Response (Sensor-1) ............................... 1A-*
DTC P0137 / P0138: O2 Sensor (HO2S)
Circuit Low Voltage / High Voltage
(Sensor-2) ......................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0140: O2 Sensor (HO2S) Circuit No
Activity Detected (Sensor-2) ............................. 1A-*
DTC P0171 / P0172 / P2195 / P2196: Fuel
System Too Lean / Rich / Stuck Lean /
Stuck Rich ......................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0222: Throttle Position Sensor (Sub)
Circuit Low ........................................................ 1A-*
DTC P0223: Throttle Position Sensor (Sub)
Circuit High ....................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 /
P0304: Random Misfire Detected / Cylinder
1 / Cylinder 2 / Cylinder 3 / Cylinder 4
Misfire Detected ................................................ 1A-*
DTC P0327 / P0328: Knock Sensor Circuit Low
/ High................................................................. 1A-*
DTC P0335: Crankshaft Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit (For J20 Engine)........................ 1A-*
DTC P0335: Crankshaft Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit (For M16 Engine)....................... 1A-*
DTC P0340: Camshaft Position (CMP)
Sensor Circuit ................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0401 / P0402: Exhaust Gas
Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected /
Excessive Detected .......................................... 1A-*
DTC P0403: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Control Circuit ................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency
below Threshold................................................ 1A-*
DTC P0443: Evaporative Emission System
Purge Control Valve Circuit............................... 1A-*
DTC P0462: Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Low........ 1A-*
DTC P0463: Fuel Level Sensor Circuit High....... 1A-*
DTC P0480: Fan 1 (Radiator Cooling Fan)
Control Circuit ................................................... 1A-*
DTC P0500: Vehicle Speed Sensor
(VSS) Malfunction ...........................................1A-28
DTC P0504: Brake Switch “A”/“B” Correlation
(For J20 Engine) ............................................... 1A-*
DTC P0532: A/C Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor Circuit Low ............................................ 1A-*
DTC P0533: A/C Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor Circuit High ........................................... 1A-*
DTC P0601 / P0602 / P0607: Internal
Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
/ Control Module Programming Error /
Control Module Performance ............................ 1A-*
DTC P0616: Starter Relay Circuit Low................ 1A-*
DTC P0617: Starter Relay Circuit High............... 1A-*
DTC P0620: Generator Control Circuit ............... 1A-*
DTC P0625 / P0626: Generator Field
Terminal Circuit Low / High ............................... 1A-*
DTC P0660: Intake Manifold Tuning Valve
Control Circuit / Open (For J20 Engine)............ 1A-*
DTC P1501 / P1502: Electric Load Current
Sensor Circuit Low / High.................................. 1A-*
DTC P1510: ECM Back-Up Power Supply
Malfunction........................................................ 1A-*
DTC P1603: TCM Trouble Code Detected
(For J20 Engine) ............................................. 1A-29
DTC P1674: CAN Communication (Bus Off
Error) ...............................................................1A-31
DTC P1676: CAN Communication
(Reception Error for TCM (for A/T model))......1A-35
DTC P1678: CAN Communication
(Reception Error for BCM) ..............................1A-38
DTC P1685: CAN Communication
(Reception Error for ABS or ESP® Control
Module) ..........................................................1A-42
DTC P2101: Throttle Actuator Control
Motor Circuit Range / Performance................... 1A-*
DTC P2102: Throttle Actuator Control
Motor Circuit Low .............................................. 1A-*
DTC P2103: Throttle Actuator Control
Motor Circuit High ............................................. 1A-*
DTC P2111: Throttle Actuator Control System
- Stuck Open ..................................................... 1A-*
DTC P2119: Throttle Actuator Control
Throttle Body Range / Performance.................. 1A-*
DTC P2122: Pedal Position Sensor (Main)
Circuit Low Input ............................................... 1A-*
DTC P2123: Pedal Position Sensor (Main)
Circuit High Input............................................... 1A-*
DTC P2127: Pedal Position Sensor (Sub)
Circuit Low Input ............................................... 1A-*
DTC P2128: Pedal Position Sensor (Sub)
Circuit High Input............................................... 1A-*
DTC P2135: Throttle Position Sensor (Main
/ Sub) Voltage Correlation................................. 1A-*
DTC P2138: Pedal Position Sensor (Main /
Sub) Voltage Correlation................................... 1A-*
DTC P2227 / P2228 / P2229: Barometric
Pressure Circuit Malfunction ............................. 1A-*
Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits ....................1A-46
ECM Power and Ground Circuit Check............... 1A-*
Fuel Injector Circuit Check .................................. 1A-*
Fuel Pump and Its Circuit Check......................... 1A-*
Fuel Pressure Check........................................... 1A-*
A/C System Circuits Check ...............................1A-68
Electric Load Signal Circuit Check ....................1A-71
Radiator Cooling Fan Low Speed Control
System Check ................................................... 1A-*
Radiator Cooling Fan High Speed Control
System Check ................................................... 1A-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1A-*
Idle Speed and IAC Throttle Valve Opening
Inspection.......................................................... 1A-*
Special Tools and Equipment ...........................1A-72
Special Tool ......................................................1A-72

Table of Contents 1-iii
Aux. Emission Control Devices .............. 1B-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1B-*
EGR System Inspection .......................................1B-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1B-*
EVAP Canister Purge Inspection .........................1B-*
EVAP Canister Purge Valve and Its Circuit
Inspection...........................................................1B-*
Vacuum Passage Inspection ...............................1B-*
Vacuum Hose and Purge Valve Chamber
Inspection...........................................................1B-*
EVAP Canister Purge Valve Inspection ...............1B-*
EVAP Canister Inspection....................................1B-*
EGR Valve Removal and Installation ...................1B-*
EGR Valve Inspection ..........................................1B-*
PCV Hose Inspection ...........................................1B-*
PCV Valve Removal and Installation ...................1B-*
PCV Valve Inspection ..........................................1B-*
Specifications....................................................... 1B-*
Tightening Torque Specifications.........................1B-*
Special Tools and Equipment ............................. 1B-*
Recommended Service Material ..........................1B-*
Special Tool .........................................................1B-*
Engine Electrical Devices ........................1C-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1C-*
Engine Control Module (ECM) Removal
and Installation.................................................. 1C-*
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-*
Electric Throttle Body Assembly
On-Vehicle Inspection....................................... 1C-*
Electric Throttle Body System Calibration........... 1C-*
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection ...................... 1C-*
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Removal and Installation .................. 1C-*
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Assembly Inspection ......................................... 1C-*
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Removal and Installation................................... 1C-*
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
Sensor Inspection ............................................. 1C-*
Air Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-*
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S-2) Heater
On-Vehicle Inspection....................................... 1C-*
Air Fuel Ratio (A/F) Sensor, Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S-2) Removal and Installation ...... 1C-*
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Removal
and Installation.................................................. 1C-*
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-*
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Removal and Installation................................... 1C-*
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-*
Knock Sensor Removal and Installation ............. 1C-*
Control Relay Inspection ..................................... 1C-*
Mass Air Flow (MAF) and Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection.......................................................... 1C-*
Mass Air Flow (MAF) and Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1C-*
Mass Air Flow (MAF) and Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Inspection............... 1C-*
Vacuum Tank Assembly Inspection (For
J20 Engine) ....................................................... 1C-*
Electric Load Current Sensor On-Vehicle
Inspection (For J20 Engine) .............................. 1C-*
Electric Load Current Sensor Removal
and Installation (For J20 Engine) ...................... 1C-*
Specifications....................................................... 1C-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1C-*
Engine Mechanical ...................................1D-*
For M16A Engine with VVT..................................... 1D-*
General Description ............................................. 1D-*
Engine Construction Description......................... 1D-*
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable
Valve Timing) System Description .................... 1D-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1D-*
Compression Check............................................ 1D-*
Engine Vacuum Check........................................ 1D-*
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ..................... 1D-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1D-*
Air Cleaner Filter Removal and Installation......... 1D-*
Air Cleaner Filter Inspection and Cleaning.......... 1D-*
Cylinder Head Cover Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1D-*
Throttle Body and Intake Manifold
Components...................................................... 1D-*
Throttle Body On-Vehicle Inspection................... 1D-*
Electric Throttle Body Assembly Removal
and Installation .................................................. 1D-*
Throttle Body Cleaning........................................ 1D-*
Intake Manifold Removal and Installation ........... 1D-*
Engine Mountings Components .......................... 1D-*
Engine Assembly Removal and Installation ........ 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Components ....................... 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Inspection ........................... 1D-*
Oil Control Valve Removal and Installation......... 1D-*
Oil Control Valve Inspection................................ 1D-*
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Components...................................................... 1D-*
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Removal and Installation................................... 1D-*
Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Components .......... 1D-*
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1D-*
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection .............. 1D-*
Valves and Cylinder Head Components ............. 1D-*

1-iv Table of Contents
Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation......................................................... 1D-*
Valves and Cylinder Head Disassembly
and Assembly ................................................... 1D-*
Valves and Valve Guides Inspection................... 1D-*
Cylinder Head Inspection .................................... 1D-*
Valve Spring Inspection ...................................... 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Components............................... 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Removal and Installation............ 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly ....... 1D-*
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
Piston Pins and Connecting Rods
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder
Block Components............................................ 1D-*
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder
Block Removal and Installation ......................... 1D-*
Crankshaft Inspection ......................................... 1D-*
Main Bearings Inspection.................................... 1D-*
Sensor Plate Inspection ...................................... 1D-*
Rear Oil Seal Inspection ..................................... 1D-*
Flywheel Inspection............................................. 1D-*
Cylinder Block Inspection.................................... 1D-*
Specifications....................................................... 1D-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1D-*
Special Tools and Equipment ............................. 1D-*
Recommended Service Material ......................... 1D-*
Special Tool ........................................................ 1D-*
For J20 Engine ........................................................ 1D-*
General Description ............................................. 1D-*
Engine Construction Description......................... 1D-*
Air Cleaner Element Introduction ........................ 1D-*
IMT (Intake Manifold Tuning) System ................. 1D-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1D-*
Compression Check............................................ 1D-*
Engine Vacuum Check........................................ 1D-*
Valve Lash (Clearance) Inspection ..................... 1D-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1D-*
Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and
Installation......................................................... 1D-*
Air Cleaner Filter Removal and Installation......... 1D-*
Air Cleaner Filter Inspection and Cleaning.......... 1D-*
Throttle Body and Intake Manifold
Components...................................................... 1D-*
Throttle Body On-Vehicle Inspection................... 1D-*
Electric Throttle Body Assembly Removal
and Installation .................................................. 1D-*
Throttle Body Cleaning........................................ 1D-*
Intake Manifold Removal and Installation ........... 1D-*
Cylinder Head Cover Removal and
Installation......................................................... 1D-*
Engine Mountings Components .......................... 1D-*
Engine Assembly Removal and Installation ........ 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Components ....................... 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1D-*
Timing Chain Cover Cleaning and
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
2nd Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Components...................................................... 1D-*
2nd Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Removal and Installation................................... 1D-*
2nd Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
1st Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Components...................................................... 1D-*
1st Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Removal and Installation................................... 1D-*
1st Timing Chain and Chain Tensioner
Inspection.......................................................... 1D-*
Camshafts, Tappet and Shim Components ........ 1D-*
Camshafts, Tappet and Shim Removal
and Installation .................................................. 1D-*
Camshaft, Tappet and Shim Inspection .............. 1D-*
Valves and Cylinder Head Components ............. 1D-*
Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1D-*
Valves and Cylinder Head Disassembly
and Assembly.................................................... 1D-*
Valves and Valve Guides Inspection................... 1D-*
Cylinder Head Inspection .................................... 1D-*
Valve Spring Inspection ...................................... 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Components............................... 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Removal and Installation............ 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly ....... 1D-*
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods
and Cylinders Inspection and Cleaning............. 1D-*
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder
Block Components ............................................ 1D-*
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder
Block Removal and Installation ......................... 1D-*
Main Bearings, Crankshaft and Cylinder
Block Inspection ................................................ 1D-*
Specifications....................................................... 1D-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1D-*
Special Tools and Equipment ............................. 1D-*
Recommended Service Material ......................... 1D-*
Special Tool ........................................................ 1D-*
Engine Lubrication System ..................... 1E-*
For M16A Engine with VVT..................................... 1E-*
General Description ............................................. 1E-*
Engine Lubrication Description ........................... 1E-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1E-*
Oil Pressure Check ............................................. 1E-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1E-*
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Components....... 1E-*
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Removal
and Installation .................................................. 1E-*

Table of Contents 1-v
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning..............1E-*
Oil Pump Components .........................................1E-*
Oil Pump Removal and Installation......................1E-*
Oil Pump Disassembly and Reassembly .............1E-*
Oil Pump Inspection .............................................1E-*
Specifications........................................................1E-*
Tightening Torque Specifications.........................1E-*
Special Tools and Equipment ..............................1E-*
Recommended Service Material ..........................1E-*
Special Tool .........................................................1E-*
For J20 Engine .........................................................1E-*
General Description ..............................................1E-*
Engine Lubrication Description ............................1E-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures.............1E-*
Oil Pressure Check ..............................................1E-*
Repair Instructions ...............................................1E-*
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Components........1E-*
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Removal
and Installation...................................................1E-*
Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer Cleaning..............1E-*
Oil Pump Components .........................................1E-*
Oil Pump Removal and Installation......................1E-*
Oil Pump Disassembly and Assembly .................1E-*
Oil Pump Inspection .............................................1E-*
Specifications........................................................1E-*
Tightening Torque Specifications.........................1E-*
Special Tools and Equipment ..............................1E-*
Recommended Service Material ..........................1E-*
Special Tool .........................................................1E-*
Engine Cooling System ........................... 1F-*
General Description ..............................................1F-*
Cooling System Description .................................1F-*
Coolant Description..............................................1F-*
Schematic and Routing Diagram.........................1F-*
Coolant Circulation...............................................1F-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures.............1F-*
Engine Cooling Symptom Diagnosis....................1F-*
Repair Instructions ...............................................1F-*
Cooling System Components ..............................1F-*
Coolant Level Check............................................1F-*
Engine Cooling System Inspection and
Cleaning.............................................................1F-*
Cooling System Draining ..................................... 1F-*
Cooling System Flush and Refill ..........................1F-*
Cooling Water Pipes or Hoses Removal
and Installation...................................................1F-*
Thermostat Removal and Installation (For
M16 Engine Model)............................................1F-*
Thermostat Removal and Installation (For
J20 Engine Model) .............................................1F-*
Thermostat Inspection .........................................1F-*
Radiator Cooling Fan Motor On-Vehicle
Inspection...........................................................1F-*
Radiator Cooling Fan Relay Inspection................1F-*
Radiator Cooling Fan Assembly Removal
and Installation...................................................1F-*
Radiator On-Vehicle Inspection and
Cleaning.............................................................1F-*
Radiator Removal and Installation .......................1F-*
Water Pump Removal and Installation (For
M16 Engine Model) ............................................1F-*
Water Pump Removal and Installation (For
J20 Engine Model) .............................................1F-*
Water Pump Inspection........................................1F-*
Specifications........................................................1F-*
Tightening Torque Specifications.........................1F-*
Special Tools and Equipment ..............................1F-*
Recommended Service Material ..........................1F-*
Fuel System ..............................................1G-*
Precautions........................................................... 1G-*
Precautions on Fuel System Service ..................1G-*
General Description ............................................. 1G-*
Fuel System Description ..................................... 1G-*
Fuel Delivery System Description ....................... 1G-*
Fuel Pump Description........................................ 1G-*
Schematic and Routing Diagram........................ 1G-*
Fuel Delivery System Diagram............................ 1G-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1G-*
Fuel Pressure Inspection .................................... 1G-*
Fuel Cut Operation Inspection ............................ 1G-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1G-*
Fuel System Components................................... 1G-*
Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting ......1G-*
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure .......................... 1G-*
Fuel Leakage Check Procedure.......................... 1G-*
Fuel Lines On-Vehicle Inspection ....................... 1G-*
Fuel Pipe Removal and Installation..................... 1G-*
Fuel Injector On-Vehicle Inspection .................... 1G-*
Fuel Injector Removal and Installation ................ 1G-*
Fuel Injector Inspection ....................................... 1G-*
Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1G-*
Fuel Pressure Regulator Inspection.................... 1G-*
Fuel Filler Cap Inspection ................................... 1G-*
Fuel Tank Inlet Valve Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1G-*
Fuel Tank Inlet Valve Inspection ......................... 1G-*
Fuel Tank Removal and Installation.................... 1G-*
Fuel Tank Inspection........................................... 1G-*
Fuel Tank Purging Procedure ............................. 1G-*
Fuel Pump On-Vehicle Inspection....................... 1G-*
Fuel Pump Assembly Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1G-*
Main Fuel Level Sensor Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1G-*
Fuel Pump Inspection ......................................... 1G-*
Sub Fuel Level Sensor Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1G-*
Sub Fuel Level Sensor Inspection ...................... 1G-*
Specifications....................................................... 1G-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1G-*
Special Tools and Equipment .............................1G-*
Recommended Service Material ......................... 1G-*
Special Tool ........................................................ 1G-*
Ignition System.........................................1H-*

1-vi Table of Contents
General Description ............................................. 1H-*
Ignition System Construction .............................. 1H-*
Schematic and Routing Diagram........................ 1H-*
Ignition System Wiring Circuit Diagram............... 1H-*
Component Location ........................................... 1H-*
Ignition System Components Location................ 1H-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1H-*
Ignition System Symptom Diagnosis................... 1H-*
Reference Waveform of Ignition System............. 1H-*
Ignition System Check ........................................ 1H-*
Ignition Spark Test .............................................. 1H-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1H-*
High-Tension Cord Removal and Installation
(For M16 Engine) .............................................. 1H-*
High-Tension Cord Inspection (For M16
Engine).............................................................. 1H-*
Spark Plug Removal and Installation .................. 1H-*
Spark Plug Inspection ......................................... 1H-*
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Removal and Installation................................... 1H-*
Ignition Coil Assembly (Including ignitor)
Inspection.......................................................... 1H-*
Ignition Timing Inspection ................................... 1H-*
Specifications....................................................... 1H-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1H-*
Special Tools and Equipment ............................. 1H-*
Starting System ..........................................1I-*
Precautions.............................................................1I-*
Cranking System Note ..........................................1I-*
General Description ............................................... 1I-*
Cranking Circuit Introduction................................. 1I-*
Starting Motor Circuit Description ......................... 1I-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures.............. 1I-*
Cranking System Symptom Diagnosis.................. 1I-*
Starting Motor Performance Test .......................... 1I-*
Repair Instructions ................................................ 1I-*
Starting Motor Dismounting and
Remounting......................................................... 1I-*
Starting Motor Components .................................. 1I-*
Starting Motor Inspection ...................................... 1I-*
Specifications......................................................... 1I-*
Starting Motor Specifications ................................1I-*
Tightening Torque Specifications.......................... 1I-*
Special Tools and Equipment ...............................1I-*
Recommended Service Material ........................... 1I-*
Charging System...................................... 1J-*
General Description .............................................. 1J-*
Battery Description............................................... 1J-*
Generator Description .......................................... 1J-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............. 1J-*
Battery Inspection ................................................ 1J-*
Generator Symptom Diagnosis ............................ 1J-*
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery
Check)................................................................ 1J-*
Generator Test (Overcharged Battery
Check)................................................................ 1J-*
Repair Instructions ...............................................1J-*
Jump Starting in Case of Emergency................... 1J-*
Battery Dismounting and Remounting ................. 1J-*
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
Removal and Installation (For M16 Engine)....... 1J-*
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
Tension Inspection and Adjustment (For
M16 Engine)....................................................... 1J-*
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
On-Vehicle Inspection (For J20 Engine) ............ 1J-*
Water Pump and Generator Drive Belt
Removal and Installation (For J20 Engine) ........ 1J-*
Generator Dismounting and Remounting............. 1J-*
Generator Components........................................ 1J-*
Generator Inspection............................................ 1J-*
Specifications........................................................ 1J-*
Charging System Specifications .......................... 1J-*
Tightening Torque Specifications......................... 1J-*
Exhaust System........................................1K-*
General Description ............................................. 1K-*
Exhaust System Description ............................... 1K-*
Diagnostic Information and Procedures............ 1K-*
Exhaust System Check ....................................... 1K-*
Repair Instructions .............................................. 1K-*
Exhaust System Components............................. 1K-*
Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation
(For M16 Engine Model) ................................... 1K-*
Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation
(For J20 Engine Model)..................................... 1K-*
Exhaust Pipe and Muffler Removal and
Installation ......................................................... 1K-*
Specifications....................................................... 1K-*
Tightening Torque Specifications........................ 1K-*
Special Tool ........................................................ 1H-*
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-1
Engine General Information and Diagnosis
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing Trouble
S5JB0E1100002
• Don’t disconnect couplers from ECM, battery cable
from battery, ECM ground wire harness from engine
or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ECM memory.
Such disconnection will erase memorized information
in ECM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in ECM memory can be
cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool or OBD generic scan tool (Vehicle without
diagnosis connector). Before using scan tool, read its
Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have good
understanding as to what functions are available and
how to use it.
It is indistinguishable which module turns on MIL
because not only ECM but also TCM (for A/T model)
turns on MIL (For details of on-board diagnostic
system for A/T model, refer to “On-Board Diagnostic
System Description: in Section 5A in related manual”.
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM (for A/T model)
for DTC when MIL lights on.
When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– OBD generic scan tool displays DTC detected by
each of ECM and TCM (for A/T model)
simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instruction in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel
system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too
rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304
(Misfire detected)
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit
Service: in Section 00 in related manual” before
inspection and observe what is written there.
• ECM replacement:
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays and actuators is as
specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, electric load current sensor (for J20
engine), A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if
equipped with A/C), accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor, TP sensor and CO adjust resistor (if
not equipped with A/F sensor) are in good condition
and none of power circuits of these sensors is
shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, combination meter,
keyless start control module (if equipped), ABS /
ESP® control module, 4WD control module (if
equipped), steering angle sensor (if equipped) and
TCM (for A/T model) is established by CAN
(Controller Area Network). (For more detail of CAN
communication for ECM, refer to “CAN
Communication System Description: ”). Therefore,
handle CAN communication line with care referring to
“Precaution for CAN Communication System: in
Section 00 in related manual”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM:
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code with ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement: in Section 10C in related
manual”.
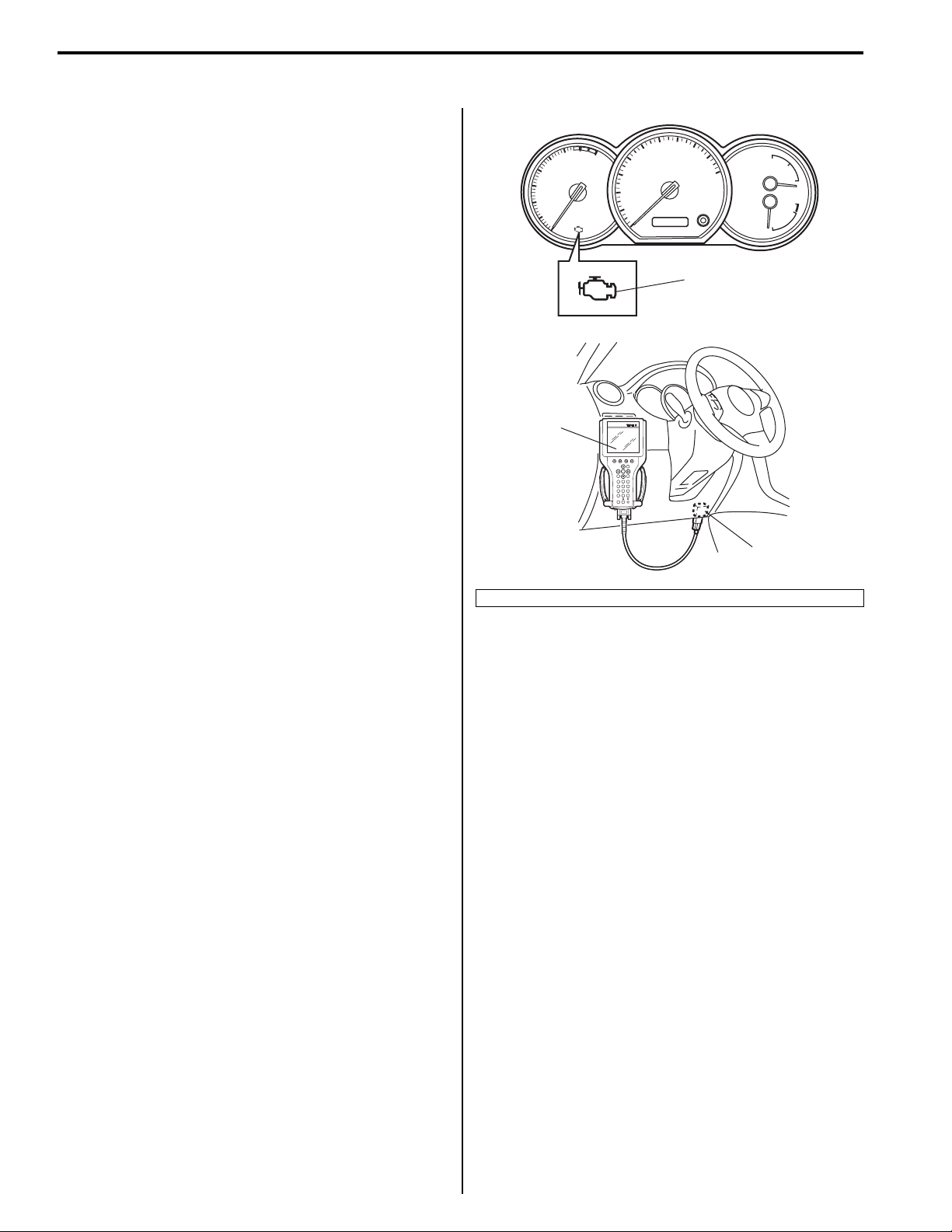
1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
General Description
On-Board Diagnostic System Description
S5JB0E1101003
Vehicle not Equipped with Diagnosis Connector
ECM in this vehicle has the following functions.
• When the ignition switch is turned ON with the engine
at a stop, malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) turns
ON to check the circuit of the malfunction indicator
lamp (1).
• When ECM detects a malfunction which gives an
adverse effect to vehicle emission while the engine is
running, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (1) in
the meter cluster of the instrument panel turn ON or
flash (flashing only when detecting a misfire which
can cause damage to the catalyst) and stores the
malfunction area in its memory.
(If it detects that continuously 3 driving cycles are
normal after detecting a malfunction, however, it
makes MIL (1) turn OFF although DTC stored in its
memory will remain.)
• As a condition for detecting a malfunction in some
areas in the system being monitored by ECM and
turning ON the malfunction indicator lamp (1) due to
that malfunction, 2 driving cycle detection logic is
adopted to prevent erroneous detection.
• When a malfunction is detected, engine and driving
conditions then are stored in ECM memory as freeze
frame data. (For the details, refer to description on
“Freeze Frame Data (Vehicle Not Equipped with
Diagnosis Connector): ”.)
• It is possible to communicate by using not only
SUZUKI scan tool (2) but also OBD generic scan tool.
(Diagnostic information can be accessed by using a
scan tool.)
1
2
3
I5JB0A110002-01
3. DLC
Vehicle Equipped with Diagnosis Connector
ECM diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area
including the following parts when the ignition switch is
ON and the engine is running, and indicates the result by
turning on or flashing malfunction indicator lamp (1).
• A/F sensor (if equipped)
• Heated oxygen sensor (if equipped)
• ECT sensor
• TP sensor
• MAF sensor
• IAT sensor
• MAP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CKP sensor
• Knock sensor
• Wheel speed sensor
• CPU (Central Processing Unit) of ECM
• APP sensor
• Oil control valve (for M16 engine)
• Radiator cooling fan relay

ECM and malfunction indicator lamp (1) operate as
follows.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (1) lights when the ignition
switch is turned ON (but the engine at stop) with the
diagnosis switch terminal ungrounded regardless of
the condition of Engine and Emission control system.
This is only to check the malfunction indicator lamp (1)
in the combination meter and its circuit.
• If the above areas of Engine and Emission control
system is free from any trouble after the engine start
(while engine is running), malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turns OFF.
• When ECM detects a trouble which has occurred in
the above areas, it makes malfunction indicator lamp
(1) turn ON while the engine is running to warn the
driver of such occurrence of trouble and at the same
time it stores the trouble area in ECM back-up
memory. (The memory is kept as it is even if the
trouble was only temporary and disappeared
immediately. And it is not erased unless the power to
ECM is shut off for specified time or it is cleared by
SUZUKI scan tool (2).)
In addition, DTC can be read by not only using
SUZUKI scan tool but also displayed on odometer (5)
of the combination meter. (i.e. when diagnosis switch
terminal (3) is grounded with a service wire (4) and
ignition switch is turned ON.) For further detail of the
checking procedure, refer to “DTC Check: in related
manual”.
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-3
5
1
2
6
3
4
I5JB0A110003-01
6. Diagnosis connector
Warm-Up Cycle
A warm-up cycle means sufficient vehicle operation such
that the coolant temperature has risen by at least 22 °C
(40 °F) from engine starting and reaches a minimum
temperature of 70 °C (160 °F).
Driving Cycle
A “Driving Cycle” consists of engine startup and engine
shutoff.
2 Driving Cycle Detection Logic
The malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is
stored in ECM memory (in the form of pending DTC) but
the malfunction indicator lamp does not light at this time.
It lights up at the second detection of same malfunction
also in the next driving cycle.
Pending DTC
Pending DTC means a DTC detected and stored
temporarily at 1 driving cycle of the DTC which is
detected in the 2 driving cycle detection logic.

1A-4 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Freeze Frame Data (Vehicle Not Equipped with
Diagnosis Connector)
ECM stores the engine and driving conditions (in the
form of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the
detection of a malfunction in its memory. This data is
called “Freeze frame data”.
Therefore, it is possible to know engine and driving
conditions (e.g., whether the engine was warm or not,
where the vehicle was running or stopped, where air/fuel
mixture was lean or rich) when a malfunction was
detected by checking the freeze frame data. Also, ECM
has a function to store each freeze frame data for three
different malfunctions in the order as each malfunction is
detected. Utilizing this function, it is possible to know the
order of malfunctions that have been detected. Its use is
helpful when rechecking or diagnosing a trouble.
[A]
I3RB0A110002-01
[A]: 1st or 2nd in parentheses here represents which position in the order
the malfunction is detected.
Priority of freeze frame data:
ECM has 4 frames where the freeze frame data can be stored. The first frame stores the freeze frame data of the
malfunction which was detected first. However, the freeze frame data stored in this frame is updated according to the
priority described. (If malfunction as described in the upper square “1” is detected while the freeze frame data in the
lower square “2” has been stored, the freeze frame data “2” will be updated by the freeze frame data “1”.)
Priority Freeze frame data in frame 1
1
Freeze frame data at initial detection of malfunction among misfire detected (P0300 – P0304), fuel
system too lean (P0171) and fuel system too rich (P0172)
2 Freeze frame data when a malfunction other than those in “1” is detected
In the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each malfunction is stored in the order as each malfunction
is detected. These data are not updated.
Shown in the table are examples of how freeze frame data are stored when two or more malfunctions are detected.
Frame
Malfunction detected order
Frame 1 Frame 2 Frame 3 Frame 4
Freeze frame data to
be updated
1st freeze frame
data
2nd freeze frame
data
3rd freeze frame
data
No malfunction No freeze frame data
P0401 (EGR)
1
detected
P0171 (Fuel system)
2
detected
P0300 (Misfire)
3
detected
P0301 (Misfire)
4
detected
Data at P0401
detection
Data at P0171
detection
Data at P0171
detection
Data at P0171
detection
Data at P0401
detection
Data at P0401
detection
Data at P0401
detection
Data at P0401
detection
——
Data at P0171
detection
Data at P0171
detection
Data at P0171
detection
—
Data at P0300
detection
Data at P0300
detection
Freeze frame data clearance:
The freeze frame data is cleared at the same time as clearance of DTC.
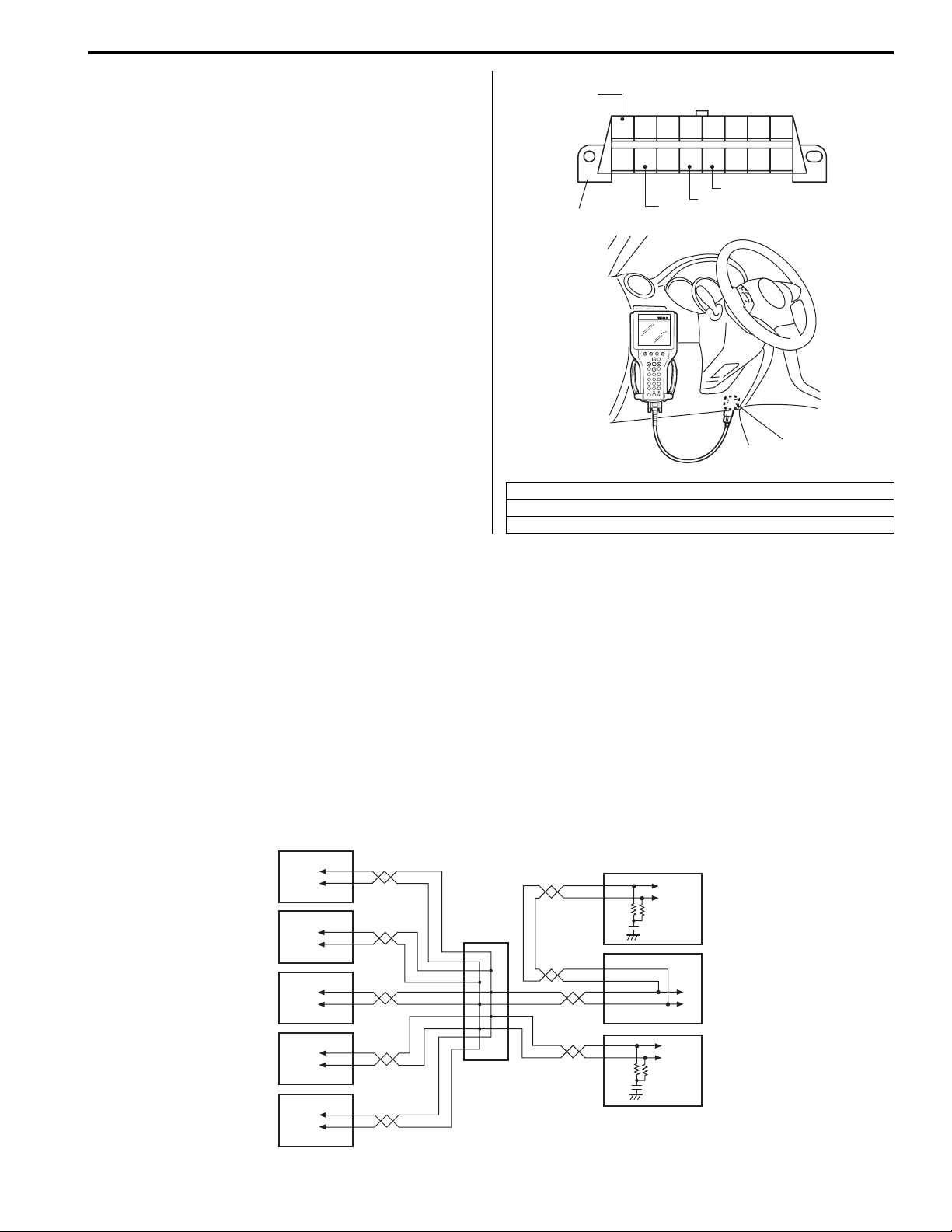
Data Link Connector (DLC)
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAE J1962 in the shape of
connector and pin assignment.
OBD serial data line (3) (K line of ISO 9141) is used for
SUZUKI scan tool or OBD generic scan tool to
communicate with ECM, Air bag SDM, immobilizer
control module (in ECM), BCM (Body electrical Control
Module), TCM (Transmission Control Module (for A/T
model)), 4WD control module (if equipped) and ABS /
ESP® control module.
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-5
2
910111213141516
12345678
5
4
1
2. B + (Unswitched vehicle battery positive)
4. ECM ground (Signal ground)
5. Vehicle body ground (Chassis ground)
3
1
I5JB0A110004-01
Engine and Emission Control System Description
S5JB0E1101004
The engine and emission control system is divided into 4 major sub-systems: air intake system, fuel delivery system,
electronic control system and emission control system.
Air intake system includes air cleaner, throttle body, and intake manifold.
Fuel delivery system includes fuel pump, delivery pipe, etc.
Electronic control system includes ECM, various sensors and controlled devices.
Emission control system includes EGR, EVAP and PCV system.
CAN Communication System Description
S5JB0E1101005
ECM (1), ABS / ESP® control module (2), TCM (for A/T model) (3), BCM (4), 4WD control module (if equipped) (5),
combination meter (6), keyless start control module (if equipped) (7) and steering angle sensor (for vehicle with
ESP®) (8) of this vehicle communicate control data between each control module.
Communication of each control module is established by CAN (Controller Area Network) communication system.
3
1
4
5
2
7
8
6
I6JB01110110-02
1A-6 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
CAN communication system uses the serial communication in which data is transmitted at a high speed. It uses a
twisted pair of two communication lines for the high-speed data transmission. As one of its characteristics, multiple
control modules can communicate simultaneously. In addition, it has a function to detect a communication error
automatically. Each module reads necessary data from the received data and transmits data. ECM communicates
control data with each control module as follows.
ECM Transmission Data
Transmit data of ECM
Engine torque signal
Accelerator pedal position
Engine speed
Throttle position
Stand by to engage air
conditioning compressor
Top gear inhibit
Torque converter clutch
control inhibit
Lock up / slip control
inhibit signal
Immobilizer indication
Engine emissions
related malfunction
Engine coolant
temperature
Fuel level percent
Cruise control signal
(if equipped)
Cruise control system
indication (if equipped)
Vehicle speed
Brake pedal switch
active
Air conditioning compressor
clutch engaged
(if equipped with A/C)
A/C refrigerant pressure
Distance kilometers per
liter of fuel
Engine diagnostic trouble
codes (if equipped with
diagnosis connector)
TCM
(for A/T
model)
ABS hydrauric
unit/control
module assembly
(for vehicle
without ESP )
R
R
ESP
control module
(for vehicle
with ESP )
R
BCM
Combination
meter
4WD control
module
(if equipped)
Keyless start
control module
(if equipped)
I5JB0D110001-02
NOTE
In communication between ECM and combination meter, between ECM and keyless start control
module (if equipped) and between ECM and 4WD control module (if equipped), data is transmitted only
from ECM to combination meter, keyless start control module (if equipped) and 4WD control module (if
equipped). (Combination meter, keyless start control module (if equipped) and 4WD control module (if
equipped) does not transmit data to ECM.)
ECM Reception Data
Receives data of ECM
Torque reduction request
Slip control signal
Transmission malfunction
indication on
Transmission emissions related
malfunction active
Transmission gear selector
position
Daytime running light active
(if equipped with DRL)
Air conditioning switch ON
(if equipped with A/C)
A/T mode status
Electric load active (low beam)
Electric load active (high beam)
Electric load active (tail light)
Electric load active (rear defogger)
Blower fan step
Torque up request
Wheel speed pulse (rear right)
Wheel speed pulse (rear left)
Electronic stability program
system active
Electronic stability program
system off
Antilock brake system active
TCM
(for A/T model)
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-7
R
ABS hydraulic
unit/control module
assmbly (for vehicle
without ESP )
R R
ESP
control module
(for vehicle
with ESP )
BCM
I5JB0D110002-02
Electronic Control System Description
S5JB0E1101011
The electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving conditions, 2)
ECM which controls various devices according to the signals from the sensors and 3) various controlled devices.
Functionally, it is divided into the following sub systems:
• Fuel injection control system
• Ignition control system
• Intake manifold tuning valve control system (for J20 engine)
• Electric Throttle Body Control System
• Fuel pump control system
• Radiator cooling fan control system
• Evaporative emission control system (if equipped)
• EGR system
• A/F sensor heater control system (if equipped)
• Oxygen sensor heater control system (if equipped)
• A/C control system (if equipped with A/C)
• Camshaft position control system (for M16 engine)
• Immobilizer control system (if equipped)
• Generator control system (for J20 engine)
• Controller (computer) communication system
Especially, ECM (Engine Control Module), BCM (Body electrical Control Module), combination meter, TCM
(Transmission Control Module (For A/T model)), ABS / ESP® control module, 4WD control module (if equipped),
keyless start control module (if equipped) and steering angle sensor (for vehicle with ESP®) intercommunicate by
means of CAN (Controller Area Network) communication.
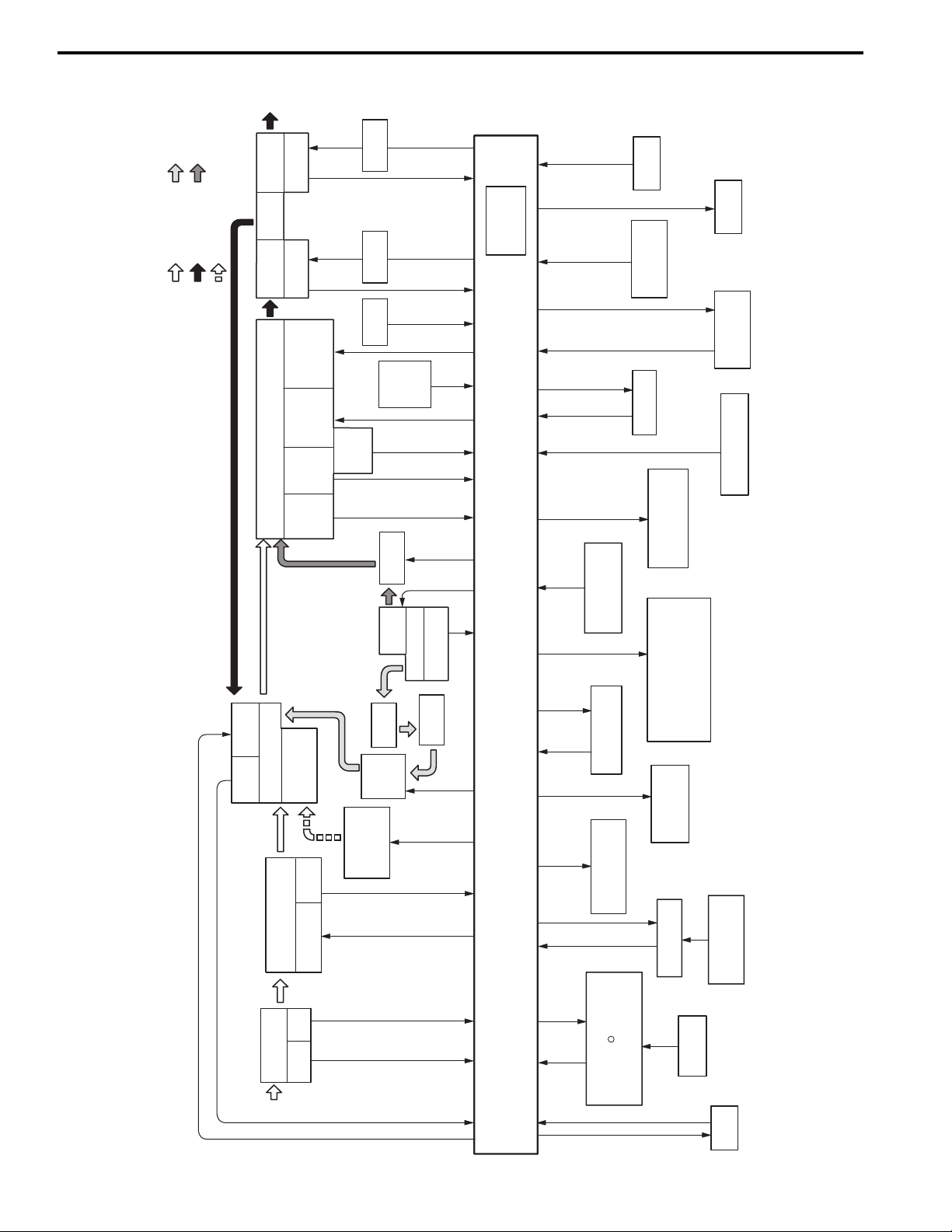
1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Engine and Emission Control System Flow Diagram
VAP OR
AIR
FUEL
VACUUM
EXHAUST GAS
PIPE
EXHAUST
CATALYST
THREE WAY
EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
ENGINE
HO2S-2
(IF EQUIPPED)
A/F SENSOR
(IF EQUIPPED)
VALVE
(FOR M16
OIL CONTROL
CMP ACTUATOR
COIL
IGNITION
WITH IGNITER
CKP
SENSOR
CMP
SENSOR
ENGINE)
KNOCK
SENSOR
HEATER
CONTROL
HEATER
CONTROL
ECT
SENSOR
SENSOR
(FOR J20
CURRENT
FUEL
INJECTOR
ENGINE)
SENSOR
PRESSURE
BAROMETRIC
SWITCH
STOP LAMP
SWITCH
PUMP PRESSURE
POWER STEERING
GENERATOR
CLUTCH
A/C COMPRESSOR
(IF EQUIPPED WITH A/C)
FAN
RADIATOR
IMMOBILIZER
(IF EQUIPPED)
COIL ANTENNA
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION (APP) SENSOR
EGR
VALVE
MAP
SENSOR
INTAKE
MANIFOLD
THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
AIR
CLEANER
IMT VALVE
(FOR J20 ENGINE)
TP
SENSOR
THROTTLE
ACTUATOR
MAF
SENSOR
IAT
SENSOR
FUEL
VALVE
CHECK
EVAP
PURGE
CANISTER
IMT VACUUM
SOLENOID VALVE
(FOR J20 ENGINE)
PUMP
VALVE
FUEL TANK
EVAP
SENSOR
FUEL LEVEL
CANISTER
ECM
A/C REFRIGERANT
PRESSURE SENSOR
(IF EQUIPPED WITH A/C)
COMBINATION METER
TCM (FOR A/T MODEL)
(IF EQUIPPED)
4WD CONTROL MODULE
R
MODULE
ABS / ESP CONTROL
· MIL
· COOLANT TEMP.
· IMMOBILIZER INDICATOR LAMP
(IF EQUIPPED)
KEYLESS START
CONTROL MODULE
BCM
· TACHOMETER
· SPEEDOMETER
ELECTRIC LOAD
A/C SWITCH ON
·
·
SENSOR (VSS)
WHEEL SPEED
(IF EQUIPPED WITH A/C)
DLC
I5JB0D110003-01
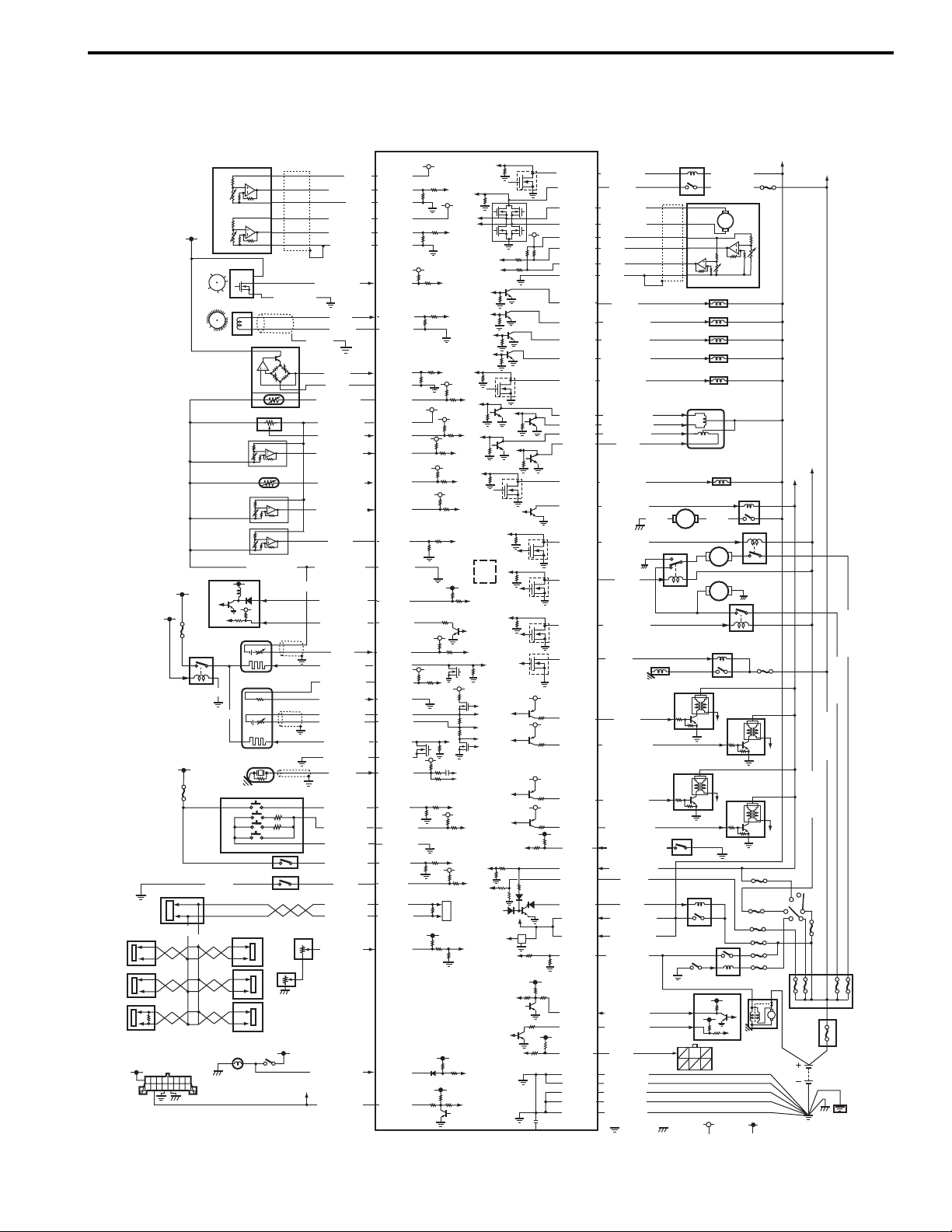
ECM Input / Output Circuit Diagram
For J20 engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-9
+BB
2
1
+B
WHT
WHT/BLU
ORN
ORN/BLU
BLU/GRN
BLUYEL
E23-56
E23-55
E23-54
E23-53
E23-52
E23-51
3
WHT/RED
5
7
9
10
11
BLK/YEL
6
8
GRY/GRN
14
2
BLU
BLK
RED
BLU
LT GR N
GRY/RED
GRN/WHT
RED/WHT
PPL/YEL
GRY/BLK
BLU
GRY/GRN
GRN
BRN/BLK
BRN/BLK
4
+BB
IG1
12
13
BLK/RED
15
BLK
PNK
BLK
16
18
19
IG1
17
20
RED
WHT
23
24
25
21
22
26
+BB
27
28
29
RED/YEL
RED/BLU
2
WHT
PNK/BLU
BLK/YEL
2
BLK/WHT
LT GR N
BLK/YEL
YEL/GRN
WHT/RED
WHT/BLU
76
YEL/RED
77
GRN/WHT
PNK
RED
BLK
WHT
BLU
C37-52
C37-51
C37-36
C37-26
C37-27
C37-25
C37-14
C37-10
C37-55
C37-24
C37-12
C37-9
C37-57
C37-8
C37-28
C37-11
C37-47
C37-35
C37-34
C37-38
C37-37
C37-32
C37-31
C37-56
E23-6
E23-22
E23-21
E23-8
E23-7
E23-4
E23-19
E23-24
E23-20
31
30
PPL/WHT
E23-5
E23-50
E23-17
C37-45
C37-44
C37-53
C37-54
C37-40
C37-41
C37-1
C37-2
C37-16
C37-17
C37-13
C37-5
C37-6
C37-3
C37-4
C37-33
E23-15
E23-46
E23-47
E23-48
E23-49
C37-21
C37-20
C37-19
C37-18
C37-7
E23-29
E23-2
E23-60
E23-1
E23-16
C37-22
E23-28
E23-13
E23-12
C37-15
C37-30
C37-29
C37-48
C37-58
BLU/ORN
GRN
BLU/YEL
BLU/RED
WHT
BLK
RED
GRN
PNK
PNK/BLK
PNK/GRN
PNK/BLU
GRN/BLK
YEL/BLK
YEL/RED
YEL/GRN
YEL
GRY/RED
WHT/GRN
RED/BLK
RED
RED/YEL
PNK
BRN
BRN/BLK
BRN/WHT
BRN/YEL
BLU/ORN
BLK/WHT
WHT
BLU
BLU/BLK
BLU/BLK
BLK/YEL
GRY/BLU
PNK/BLU
YEL
BLK/ORN
BLK/ORN
BLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
52
: 74 : 75
32
BLU/BLK
BLU/RED
2
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
PNKBLK
45
46
47
49
50
51
54
55
56
57
58
60
69
68
71
DN
72
: 5V
+B
+BB
33
34
IG2
IG1
44
48
53
BLU/WHT
BLU/BLK
WHT/GRN
YEL/GRN
59
IG1
IG2
ST
64
65
61
62
63
66
67
70
73
: 12V
I5JB0D110004-01
1A-10 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
1. Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
assembly
2. Shield wire 28. Stop lamp 54. Ignition coil assembly (for No.1 spark plug)
3. CMP sensor 29. DLC 55. Ignition coil assembly (for No.2 spark plug)
4.
CKP sensor
5. MAF and IAT sensor 31. Barometric pressure sensor 57. Ignition coil assembly (for No.4 spark plug)
6. CO adjust resistor (if equipped) 32. Throttle actuator control relay 58. Power steering pump pressure switch
7. MAP sensor 33. “THR MOT” fuse 59. “IG COIL” fuse
8. ECT sensor 34. Electric throttle body assembly 60. Main relay
9. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if
equipped with A/C)
10. Electric load current sensor 36. Throttle position sensor 62. “DOME” fuse
11. Generator 37. Fuel injector No.1 63. “FI” fuse
12. “O2 HTR” fuse 38. Fuel injector No.2 64. Ignition switch
13. HO2S heater relay 39. Fuel injector No.3 65. “IGN” fuse
14. HO2S-2 40. Fuel injector No.4 66. “STR MOT” fuse
15. A/F sensor 41. EVAP canister purge valve 67. “ST SIG” fuse
16. Knock sensor 42. EGR valve 68. Starting motor control relay
17. Cruise control switch (if equipped) 43. IMT vacuum solenoid valve 69. Transmission range switch (for A/T model)
18. Brake pedal switch (for cruise control) 44. Fuel pump relay 70. Starting motor
19. Clutch pedal position switch (for cruise
control)
20. ABS / ESP® control module 46. Radiator cooling fan relay No.1 72. Diagnosis connector (if equipped)
21. BCM 47. Radiator cooling fan relay No.2 73. Battery
22. TCM (for A/T model) 48. Radiator cooling fan relay No.3 74. Engine ground
23. Combination meter 49. Radiator cooling fan motor No.1 75. Body ground
24. 4WD control module (if equipped) 50. Radiator cooling fan motor No.2 76. Main fuel level sensor
25. Keyless start control module (if equipped) 51. A/C compressor relay (if equipped with A/C) 77. Sub fuel level sensor
26. Steering angle sensor (for vehicle with
ESP®)
27. Stop lamp switch 53. “CPRSR” fuse
30. To TCM (for A/T model), BCM, ABS / ESP® control
module and 4WD control module (if equipped)
35. Throttle actuator 61. “IG2 SIG” fuse
45. Fuel pump 71. Immobilizer coil antenna (if equipped)
52. A/C compressor (if equipped with A/C)
56. Ignition coil assembly (for No.3 spark plug)
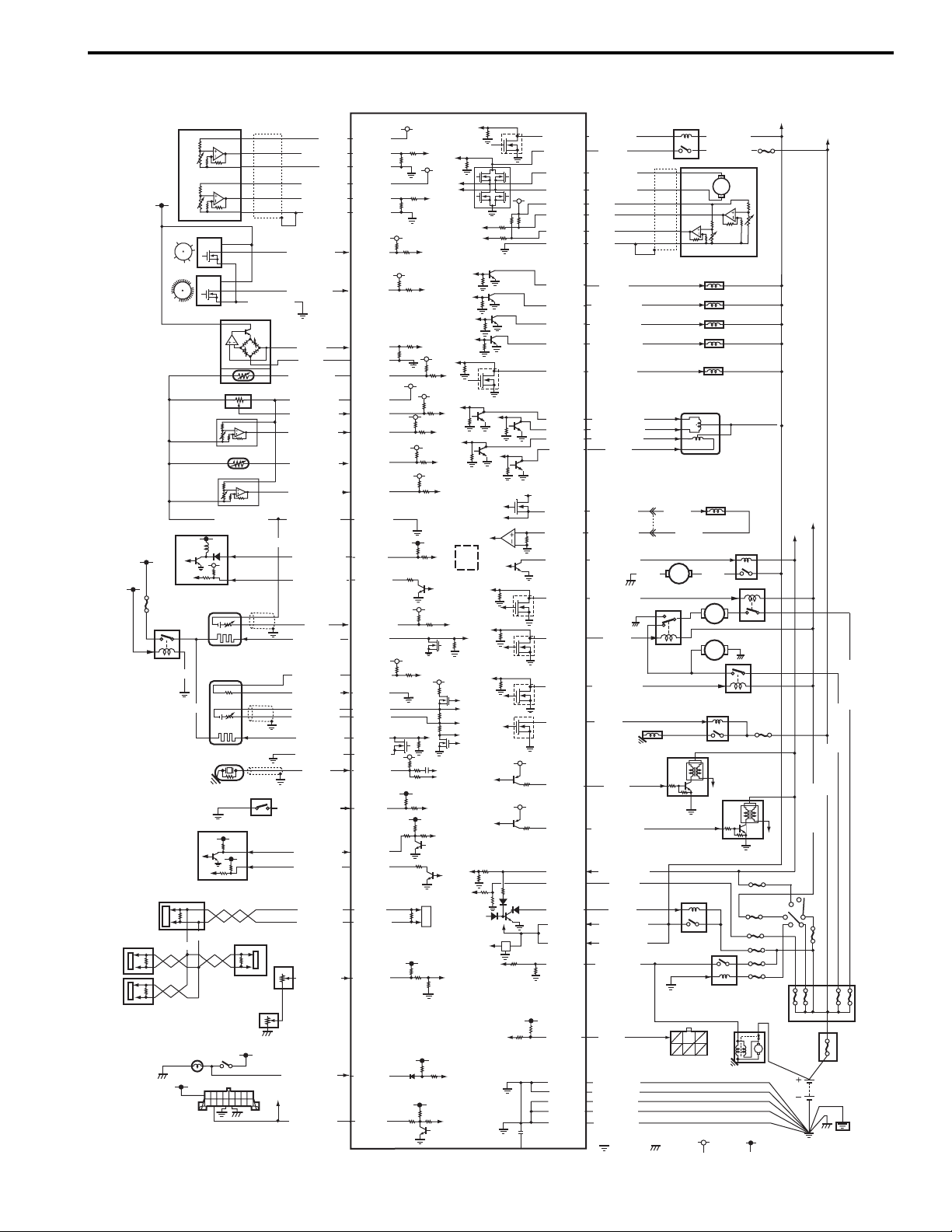
For M16 engine
Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
IG1
+BB
+B
+BB
28
29
IG2
IG1
39
43
BLU/WHT
48
BLU/BLK
WHT/GRN
YEL/GRN
51
IG1
53
54
55
IG2
ST
56
57
58
59
2
42
RED
40
49
27
YEL
BLU/BLK
BLU/RED
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
PNKBLK
41
44
45
46
50
52
60
2
1
+B
WHT
WHT/BLU
ORN
ORN/BLU
BLU/GRN
BLUYEL
E23-56
E23-55
E23-54
E23-53
E23-52
E23-51
3
WHT/RED
C37-52
4
WHT/BLU
BLK/YEL
2
2
GRN
2
RED
BLU
LT GRN
GRY/RED
GRN/WHT
RED/WHT
PPL/YEL
GRY/BLK
GRY/GRN
BRN/RED
BRN/BLK
RED
BLK/RED
RED/YEL
RED/BLU
WHT
BLK
PNK/BLU
BLK/YEL
WHT
BLU/ORN
5
6
7
8
9
GRY/GRN
10
11
13
12
BLK
14
PNK
15
C37-51
C37-26
C37-27
C37-25
C37-14
C37-10
C37-55
C37-24
C37-12
C37-57
C37-8
C37-28
C37-11
C37-47
C37-35
C37-34
C37-38
C37-37
C37-32
C37-31
C37-56
C37-7
26
16
17
18
RED
WHT
20
19
21
GRY/BLU
PNK/BLU
WHT/RED
WHT/BLU
66
YEL/RED
E23-28
E23-13
E23-4
E23-19
E23-24
E23-50
E23-17
C37-45
C37-44
C37-53
C37-54
C37-40
C37-41
C37-1
C37-2
C37-16
C37-17
C37-13
C37-5
C37-6
C37-3
C37-4
C37-60
C37-59
E23-15
E23-46
E23-47
E23-48
E23-49
C37-21
C37-20
E23-29
E23-2
E23-60
E23-1
E23-16
C37-22
BLU/ORN
GRN
BLU/YEL
BLU/RED
WHT
BLK
RED
GRN
PNK
PNK/BLK
PNK/GRN
PNK/BLU
GRN/BLK
YEL/BLK
YEL/RED
YEL/GRN
YEL
BRN/WHT
BRN/YEL
WHT/GRN
RED/BLK
RED
RED/YEL
PNK
BRN
BRN/BLK
BLK/WHT
WHT
BLU
BLU/BLK
BLU/BLK
BLK/YEL
47
67
62
: 5V
61
63
: 12V
I5JB0D110005-01
+BB
+BB
22
23
24
GRN/WHT
25
PPL/WHT
E23-20
E23-5
E23-12
C37-15
C37-30
C37-29
C37-48
C37-58
YEL
BLK/ORN
BLK/ORN
BLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
BLK/YEL
DN
: 64 : 65
1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
1. Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
assembly
2. Shield wire 25. To BCM and ABS / ESP® control module 48. “CPRSR” fuse
3. CMP sensor 26. Barometric pressure sensor 49. Ignition coil assembly (for No.1 and No.4
4. CKP sensor 27. Throttle actuator control relay 50. Ignition coil assembly (for No.2 and No.3
5. MAF and IAT sensor 28. “THR MOT” fuse 51. “IG COIL” fuse
6. CO adjust resistor (if equipped) 29. Electric throttle body assembly 52. Main relay
7. MAP sensor 30. Throttle actuator 53. “IG2 SIG” fuse
8. ECT sensor 31. Throttle position sensor 54. “DOME” fuse
9. A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if equipped
with A/C)
10. Generator 33. Fuel injector No.2 56. Ignition switch
11. “O2 HTR” fuse 34. Fuel injector No.3 57. “IGN” fuse
12. HO2S heater relay 35. Fuel injector No.4 58. “STR MOT” fuse
13. HO2S-2 36. EVAP canister purge valve 59. “ST SIG” fuse
14. A/F sensor 37. EGR valve 60. Starting motor control relay
15. Knock sensor 38. Oil control valve (Camshaft position control) 61. Starting motor
16. Power steering pump pressure switch 39. Fuel pump relay 62. Diagnosis connector (if equipped)
17. Immobilizer coil antenna (if equipped) 40. Fuel pump 63. Battery
18. ABS / ESP® control module 41. Radiator cooling fan relay No.1 64. Engine ground
19. BCM 42. Radiator cooling fan relay No.2 65. Body ground
20. Combination meter 43. Radiator cooling fan relay No.3 66. Main fuel level sensor
21. Steering angle sensor (for vehicle with ESP®) 44. Radiator cooling fan motor No.1 67. Sub fuel level sensor
22. Stop lamp switch 45. Radiator cooling fan motor No.2
23. Stop lamp 46. A/C compressor relay (if equipped with A/C)
24. DLC 47. A/C compressor (if equipped with A/C)
spark plugs)
spark plugs)
32. Fuel injector No.1 55. “FI” fuse
Terminal Arrangement of ECM Coupler (Viewed from Harness Side)
E23 C37
15
14
30
29
44
45 43 41 33
59
60 58
262728
56 48
5557 54 53
8
23
52
5671011
2122
2
11213
15
14
1819
1720
32 31343536374042 39 38
47 46495051
30
1625924
29
44
45 43 41 33
59
60 58
262728
56 48
5557 54 53
834
23
5671011
2122
52
2
34
1819
1720
32 31343536374042 39 38
47 46495051
Connector: C37
Terminal Wire color Circuit Terminal Wire color Circuit
1 PNK Fuel injector No.1 31 BLK/YEL Ground for A/F sensor heater
2 PNK/BLK Fuel injector No.2 32 PNK/BLU Heater output of A/F sensor
3YEL/GRN
4 YEL
5 YEL/BLK
6 YEL/RED
7BLU/ORN
EGR valve (stepper motor coil
3)
EGR valve (stepper motor coil
4)
EGR valve (stepper motor coil
1)
EGR valve (stepper motor coil
2)
Power steering pump pressure
switch signal
33 GRY/RED
34 RED/BLU
35 RED/YEL
36 PNK
37 BLK A/F sensor signal (–)
Intake manifold tuning vacuum
solenoid valve output
(for J20 engine)
Ground for A/F sensor
adjusting resistor
A/F sensor adjusting resistor
signal
Crankshaft position (CKP)
sensor (–)
(for J20 engine)
BRN/RED
(for M16
8
engine) Generator field coil monitor
BRN/BLK
signal
38 WHT A/F sensor signal (+)
(for J20
engine)
11213
1625924
I4RS0A110008-01
 Loading...
Loading...