Page 1

X11SRM-F
X11SRM-VF
USER'S MANUAL
Revision 1.0b
Page 2

The information in this user’s manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be accurate. The manufacturer
assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document, and makes no commitment
to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to notify any person or organization of the updates.
Please Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual, please see our website at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. ("Supermicro") reserves the right to make changes to the product described in this manual
at any time and without notice. This product, including software and documentation, is the property of Supermicro and/
or its licensors, and is supplied only under a license. Any use or reproduction of this product is not allowed, except
as expressly permitted by the terms of said license.
IN NO EVENT WILL Super Micro Computer, Inc. BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT
OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPER
MICRO COMPUTER, INC. SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED
OR USED WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING,
INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and customer shall be governed by the laws of Santa Clara County in the
State of California, USA. The State of California, County of Santa Clara shall be the exclusive venue for the resolution
of any such disputes. Supermicro's total liability for all claims will not exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference with radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference, in which case you will be required to correct the interference at your own expense.
California Best Management Practices Regulations for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning applies only
to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells. “Perchlorate Material-special handling may apply.
See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate”.
WARNING: Handling of lead solder materials used in this product may expose you to lead, a
chemical known to the State of California to cause birth defects and other reproductive harm.
The products sold by Supermicro are not intended for and will not be used in life support systems, medical equipment,
nuclear facilities or systems, aircraft, aircraft devices, aircraft/emergency communication devices or other critical
systems whose failure to perform be reasonably expected to result in signicant injury or loss of life or catastrophic
property damage. Accordingly, Supermicro disclaims any and all liability, and should buyer use or sell such products
for use in such ultra-hazardous applications, it does so entirely at its own risk. Furthermore, buyer agrees to fully
indemnify, defend and hold Supermicro harmless for and against any and all claims, demands, actions, litigation, and
proceedings of any kind arising out of or related to such ultra-hazardous use or sale.
Manual Revision 1.0b
Release Date: October 14, 2019
Unless you request and receive written permission from Super Micro Computer, Inc., you may not copy any part of this
document. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies referred
to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 2019 by Super Micro Computer, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 3

Preface
Preface
About This Manual
This manual is written for system integrators, IT technicians and knowledgeable end users.
It provides information for the installation and use of the X11SRM-F/-VF motherboard.
About This Motherboard
The Supermicro X11SRM-F/-VF supports an Intel® Xeon® W-2200/2100 (Socket R4)
processor with up to 18 cores and a thermal design power (TDP) of up to 165W. Built with
the Intel C422 chipset, the X11SRM-F/-VF supports 4-channel, 4-DIMM DDR4 ECC RDIMM/
LRDIMM memory with speeds of up to 2933MHz. This motherboard oers features such as
SATA 3.0 ports, a M.2 slot, dual 1G Base-T ports, SuperDOM connectors, a Trusted Platform
Module (TPM) header, and a built-in PCIe storage solution enhancement via Intel VROC. The
X11SRM-F/-VF is the perfect solution for data centers, cloud, embedded, storage servers,
and high performance computing (HPC). Please note that this motherboard is intended to
be installed and serviced by professional technicians only. For processor/memory updates,
please refer to our website at http://www.supermicro.com/products/.
Note: Intel VROC requires a separate hardware key to enable.
Note 2: 2933MHz memory is supported on selected SKUs.
Conventions Used in the Manual
Warning! Indicates important information given to prevent equipment/property damage
or personal injury.
Warning! Indicates high voltage may be encountered while performing a procedure.
Important: Important information given to ensure proper system installation or to
relay safety precautions.
Note: Additional Information given to dierentiate various models or provides infor-
mation for proper system setup.
3
Page 4

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email: marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Website: www.supermicro.com
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
's-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
Email: sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Website: www.supermicro.nl
Asia-Pacic
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
3F, No. 150, Jian 1st Rd.
Zhonghe Dist., New Taipei City 235
Taiwan (R.O.C)
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3992
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Website: www.supermicro.com.tw
4
Page 5

Preface
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Checklist ...............................................................................................................................8
Quick Reference ...............................................................................................................12
Quick Reference Table ......................................................................................................13
Motherboard Features .......................................................................................................15
1.2 Processor and Chipset Overview .......................................................................................19
1.3 Special Features ................................................................................................................19
Recovery from AC Power Loss .........................................................................................19
1.4 System Health Monitoring ..................................................................................................19
Onboard Voltage Monitors ................................................................................................19
Fan Status Monitor with Firmware Control .......................................................................20
Environmental Temperature Control .................................................................................20
System Resource Alert......................................................................................................20
1.5 ACPI Features ....................................................................................................................20
1.6 Power Supply .....................................................................................................................21
1.7 Serial Port ...........................................................................................................................21
Chapter 2 Installation
2.1 Static-Sensitive Devices .....................................................................................................22
Precautions .......................................................................................................................22
Unpacking .........................................................................................................................22
2.2 Motherboard Installation .....................................................................................................23
Tools Needed ....................................................................................................................23
Location of Mounting Holes ..............................................................................................23
Installing the Motherboard.................................................................................................24
2.3 Processor and Heatsink Installation ...................................................................................25
Installing a CPU ...............................................................................................................25
Installing a Passive CPU Heatsink ...................................................................................28
Removing the CPU and the Heatsink ...............................................................................29
2.4 Memory Support and Installation .......................................................................................30
Memory Support ................................................................................................................30
General Guidelines for Optimizing Memory Performance ................................................31
5
Page 6

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
DIMM Installation ..............................................................................................................32
DIMM Removal .................................................................................................................32
2.5 Rear I/O Ports ....................................................................................................................33
2.6 Front Control Panel ............................................................................................................38
2.7 Connectors .........................................................................................................................43
Power Connections ...........................................................................................................43
Headers .............................................................................................................................45
2.8 Jumper Settings .................................................................................................................55
How Jumpers Work ...........................................................................................................55
2.9 LED Indicators ....................................................................................................................59
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3.1 Troubleshooting Procedures ..............................................................................................62
Before Power On ..............................................................................................................62
No Power ..........................................................................................................................62
No Video ...........................................................................................................................63
System Boot Failure .......................................................................................................63
Memory Errors ..................................................................................................................63
Losing the System's Setup Conguration .........................................................................64
When the System Becomes Unstable ..............................................................................64
3.2 Technical Support Procedures ...........................................................................................66
3.3 Frequently Asked Questions ..............................................................................................67
3.4 Battery Removal and Installation .......................................................................................68
Battery Removal ................................................................................................................68
Proper Battery Disposal ....................................................................................................68
Battery Installation .............................................................................................................68
3.5 Returning Merchandise for Service ....................................................................................69
Chapter 4 UEFI BIOS
4.1 Introduction .........................................................................................................................70
4.2 Main Setup .........................................................................................................................71
4.3 Advanced Setup Congurations .........................................................................................72
4.4 Event Logs .........................................................................................................................95
4.5 IPMI ....................................................................................................................................97
4.6 Security .............................................................................................................................100
6
Page 7

Preface
4.7 Boot .................................................................................................................................104
4.8 Save & Exit .......................................................................................................................107
Appendix A UEFI BIOS Codes
Appendix B Software Installation
B.1 Installing Software Programs ........................................................................................... 111
B.2 SuperDoctor® 5 .................................................................................................................112
Appendix C Standardized Warning Statements
Battery Handling ..............................................................................................................113
Product Disposal .............................................................................................................115
Appendix D UEFI BIOS Recovery
7
Page 8

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Chapter 1
Introduction
Congratulations on purchasing your computer motherboard from an industry leader.
Supermicro motherboards are designed to provide you with the highest standards in quality
and performance.
In additon to the motherboard, several important parts that are included in the retail box are
listed below. If anything listed is damaged or missing, please contact your retailer.
1.1 Checklist
Main Parts List
Description Part Number Quantity
Supermicro Motherboard X11SRM-F/-VF 1
I/O Shield MCP-260-00042-0N 1
SATA Cables CBL-0044L 6
Quick Reference Guide MNL-1967-QRG 1
Important Links
For your system to work properly, please follow the links below to download all necessary
drivers/utilities and the user’s manual for your server.
• Supermicro product manuals: http://www.supermicro.com/support/manuals/
• Product drivers and utilities: https://www.supermicro.com/wftp/driver/
• Product safety info: http://www.supermicro.com/about/policies/safety_information.cfm
• If you have any questions, please contact our support team at: support@supermicro.com
This manual may be periodically updated without notice. Please check the Supermicro website
for possible updates to the manual revision level.
8
Page 9
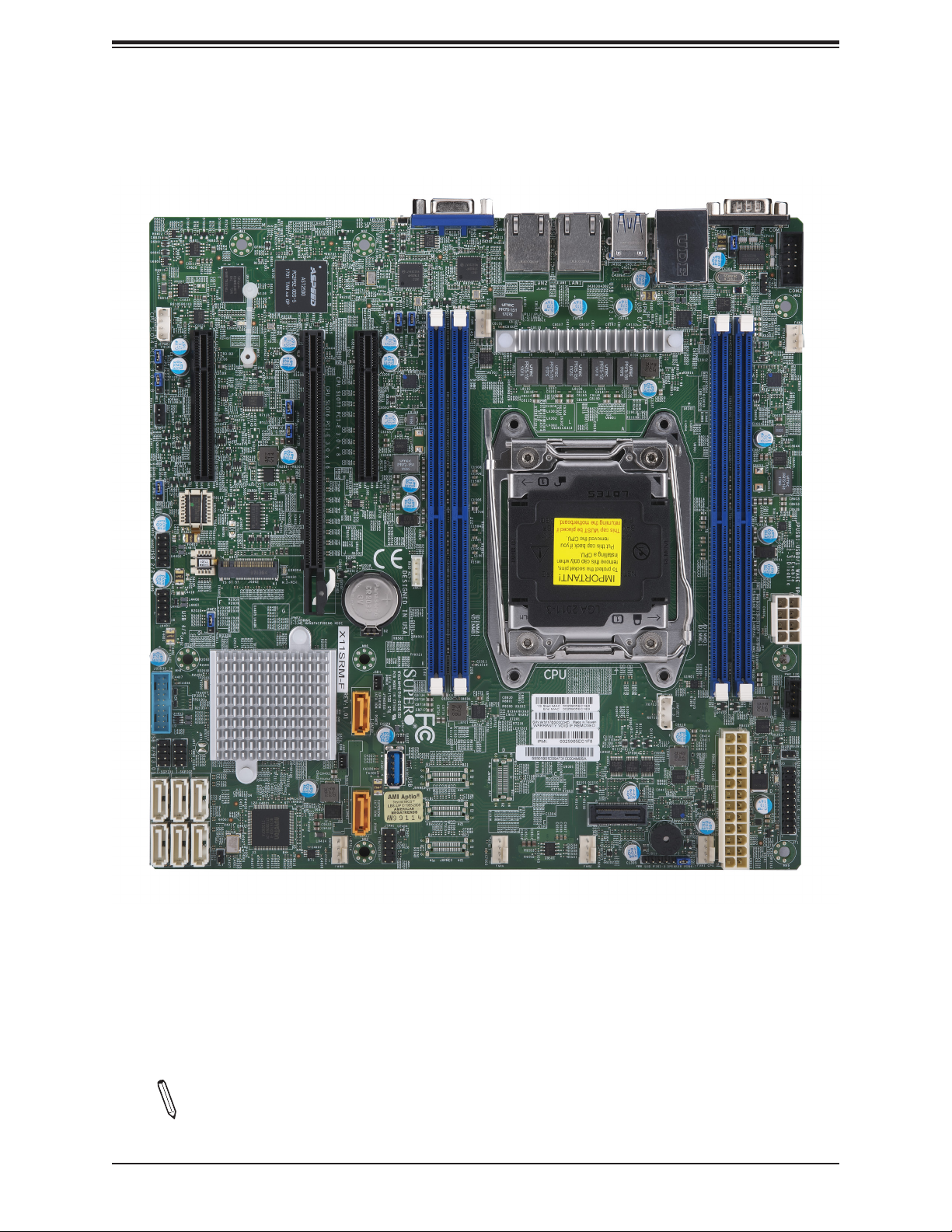
Figure 1-1. X11SRM-F Motherboard Image
Chapter 1: Introduction
Note: All graphics shown in this manual were based upon the latest PCB revision
available at the time of publication of the manual. The motherboard you received may
or may not look exactly the same as the graphics shown in this manual.
9
Page 10
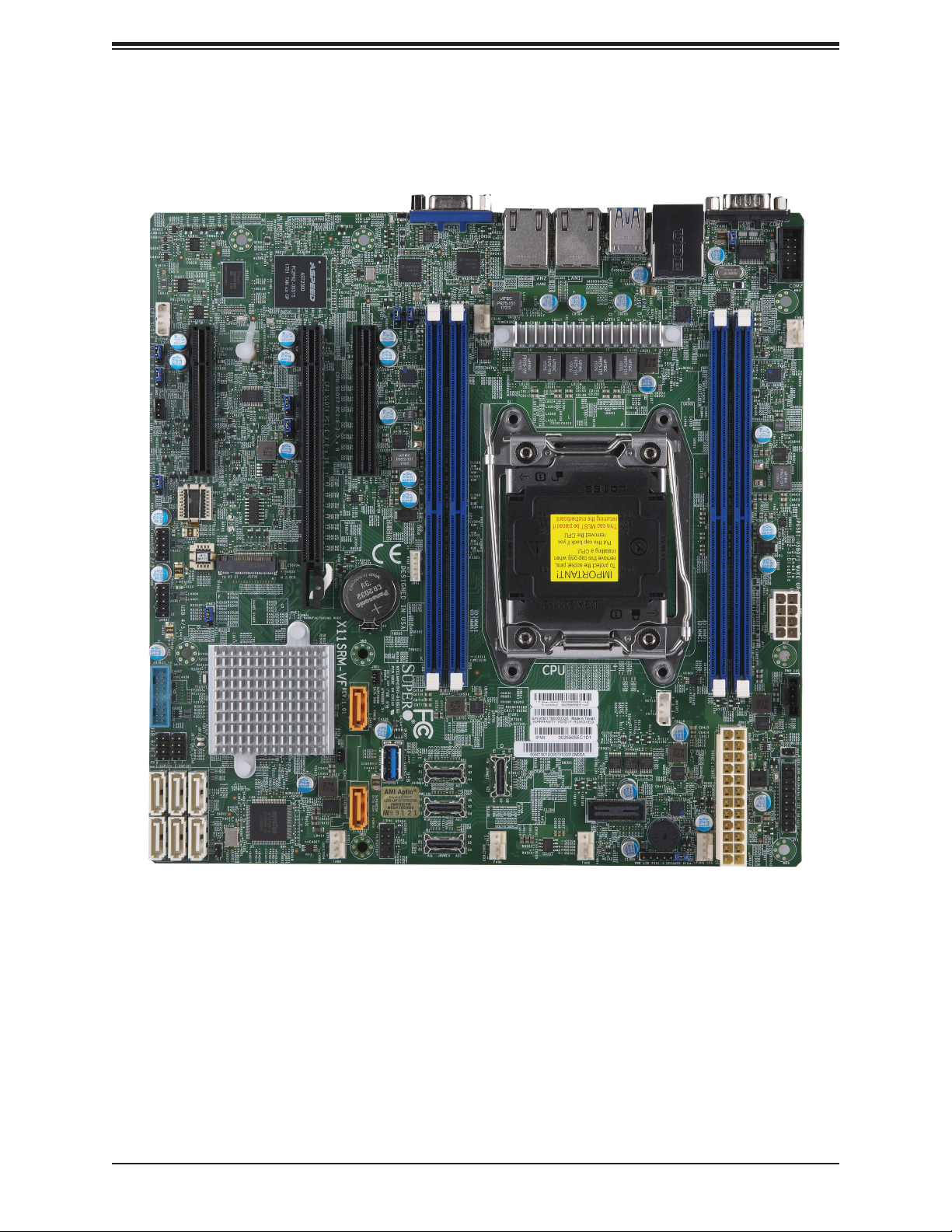
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Figure 1-2. X11SRM-VF Motherboard Image
10
Page 11
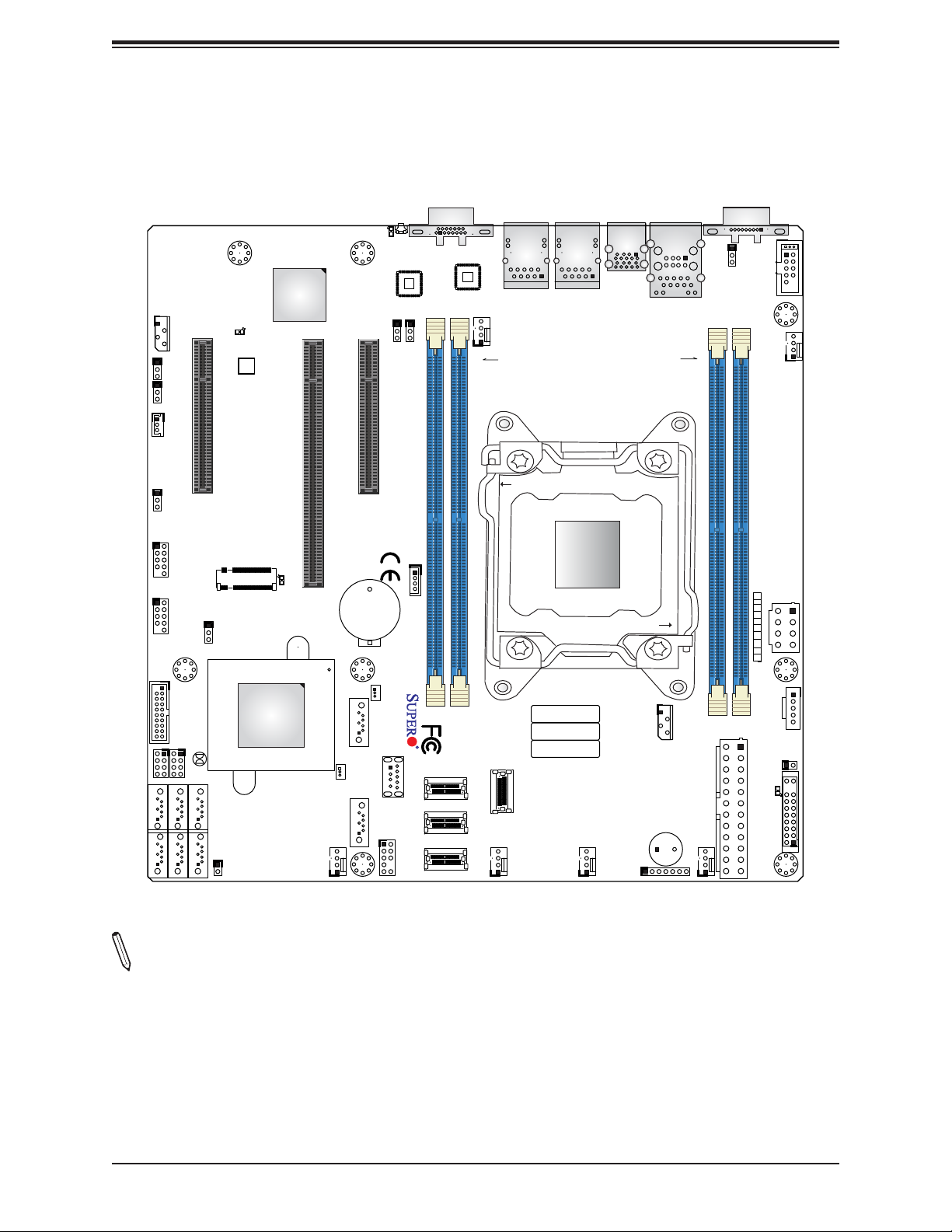
Chapter 1: Introduction
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Figure 1-3. X11SRM-F/-VF Motherboard Layout
(not drawn to scale)
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JRK1
JPL2
Intel
i210
1
FAN4
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
LAN2
CLOSE 1st
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
CPU
OPEN 1st
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
COM2
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
ON
FAN3
JPWR2
JF1
1
1
I-SATA1
I-SATA0
JSD2
JSD1
JTPM1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
1
JD1
JNVI2C1
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
1
1
I-SGPIO1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA4
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
FANB
Notes:
• The image above combines both X11SRM-F and X11SRM-VF models. See pages 9-10
for a more accurate representation of each motherboard.
• X11SRM-VF Only: NVMe PCI-Express 3.0 x4 Connectors (JNVME0~3)
• Components not documented are for internal testing only.
11
Page 12
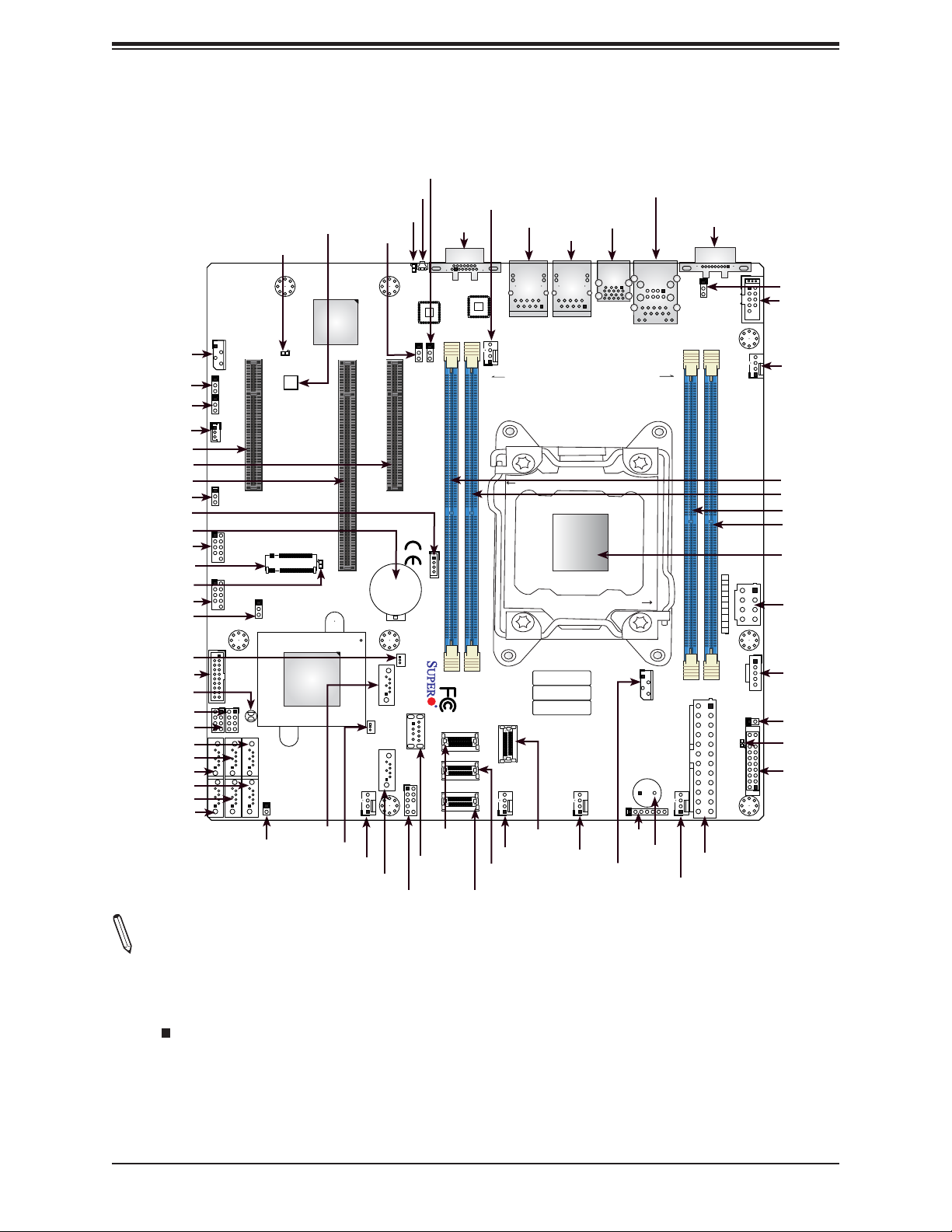
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Quick Reference
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
SLOT4
SLOT7
SLOT6
JPB1
JRK1
B2
USB 2/3
M.2-PCH
LED6904
USB 4/5
JPME2
JSD1
USB 8/9 (3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SGPIO1
I-SATA5
I-SATA6
I-SATA7
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
I-SGPIO1
JIPMB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
LED6301
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA4
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
I-SATA0
JL1
MH10
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
JSD2
FANB
FANB
JPL2
JUIDB1
UID-LED
JPL1
UID-LED
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
JTPM1
USB10
I-SATA1
JTPM1
VGA
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
i210
JPL2
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
USB 10(3.0)
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME3
(3.0)
JNVME0
FAN4
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
JNVME2
FANA
JNVME1
LAN2
LAN2
CLOSE 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FANA
JNVME2
LAN1
LAN1
FAN2
1
FAN2
USB 6/7
(3.0)
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
JNVI2C1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
OPEN 1st
SP1
+
JD1
JD1
SP1
COM1
JPUSB1
1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JNVI2C1
JPW1
FAN1 CPU
1
JPW1
FAN1 CPU
COM1
COM2
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
LED7201
FAN3
JF1
1
JOH1
1
JPUSB1
COM2
FAN3
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
CPU
JPWR2
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JF1
Notes:
• See Chapter 2 for detailed information on jumpers, I/O ports, and JF1 front panel con-
nections.
• " " indicates the location of Pin 1.
• Jumpers/LED indicators not indicated are used for testing only.
• Use only the correct type of onboard CMOS battery as specied by the manufacturer. Do
not install the onboard battery upside down to avoid possible explosion.
12
Page 13

Chapter 1: Introduction
Quick Reference Table
Jumper Description Default Setting
JBT1 CMOS Clear Open (Normal)
JPB1 BMC Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JPG1 VGA Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JPL1, JPL2 LAN1/LAN2 Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JPME2 ME Manufacturing Mode Pins 1-2 (Normal)
JPUSB1 USB 0/1 Wake Up Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JWD1 Watchdog Timer Pins 1-2 (Reset)
LED Description Status
LED6301 BMC Heartbeat LED Blinking Green: BMC Normal
LED6904 M.2 LED Blinking Green: Device Working
LED7201 Onboard Power LED Solid Green: Power On
UID-LED Unit Identier (UID) LED Solid Blue: Unit Identied
Connector Description
B2 Onboard Battery
COM1, COM2 COM Port, COM Header
FAN1 ~ FAN4, FANA, FANB CPU/System Fan Headers
IPMI_LAN Dedicated IPMI LAN Port
I-SATA0 ~ I-SATA7
I-SGPIO1, I-SGPIO2 Serial Link General Purpose I/O Connection Headers
JD1 Speaker/Power LED Indicator (Pins 1-3: Power LED, Pins 4-7: Speaker)
JF1 Front Control Panel Header
JIPMB1 4-pin BMC External I2C Header (for an IPMI card)
JL1 Chassis Intrusion Header
JNVME0~3 NVM Express (NVMe) PCI-Express 3.0 x4 Connectors (-VF only)
JNVI2C1 NVMe I2C Header
JOH1 Overheat LED Indicator
JPI2C1 Power System Management Bus (SMB) I2C Header
JPW1 24-pin ATX Power Connector
JPWR2 8-pin 12V CPU Power Connector
JRK1 Intel RAID Key Header
JSD1, JSD2 SATA DOM Power Connectors
JSTBY1 Standby Power Header
JTPM1 Trusted Platform Module/Port 80 Connector
JUIDB1 Unit Identier (UID) Switch
Intel® PCH SATA 3.0 Ports (with RAID 0, 1, 5, 10)
I-SATA0 and I-SATA1 support SuperDOM (Disk on Module) devices
Note: Table is continued on the next page.
13
Page 14

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Connector Description
LAN1, LAN2 1 GbE LAN (RJ45) Ports
M.2-PCH M.2 PCI-E 3.0 x4 Slot (Supports M-Key 2280)
MH10 M.2 Mounting Hole
SLOT4, SLOT7 CPU PCI-E 3.0 x8 Slots
SLOT6 CPU PCI-E 3.0 x16 Slot
SP1 Internal Speaker/Buzzer
USB 0/1 Back Panel Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 Ports
USB 2/3, USB 4/5 Front Accessible USB 2.0 Headers
USB 6/7 Back Panel USB 3.0 Ports
USB 8/9 Front Accessible USB 3.0 Header
USB 10 USB 3.0 Type-A Header
VGA VGA Port
14
Page 15
Chapter 1: Introduction
Motherboard Features
Motherboard Features
CPU
• Supports an Intel® Xeon® W-2200/2100 series (Socket R4) processor with up to 18 cores and a thermal design power
(TDP) of up to 165W
Memory
• Up to 256GB of RDIMM and 512GB of LRDIMM DDR4 (288-pin) ECC memory with speeds of up to 2933MHz in four
memory slots
Note: Memory speed support depends on the processors used in the system.
Note: 2933MHz memory is supported on selected SKUs.
DIMM Size
• Up to 128GB at 1.2V
Note: For the latest CPU/memory updates, please refer to our website at http://www.supermicro.com/products/
motherboard.
Chipset
• Intel PCH C422
Expansion Slots
• Two (2) PCI-Express 3.0 x8 Slots (CPU SLOT4, SLOT7)
• One (1) PCI-Express 3.0 x16 Slot (CPU Slot 6) (Supports NVMe SSD)
• One (1) M.2 Slot for PCI-Express 3.0 x4 (Supports M-Key 2280)
Network
• Intel Ethernet Controller i210 for Dual 1G BASE-T Ports
• One (1) Dedicated IPMI LAN located on the rear I/O panel
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC)
• ASpeed AST2500 BMC
Graphics
• Graphics controller via ASpeed AST2500 BMC
I/O Devices
• Serial (COM) Port
• SATA 3.0 (6Gb/s)
• One (1) serial port on the rear I/O panel (COM1)
• One (1) front accessible serial port header (COM2)
Eight (8) SATA 3.0 ports:
• Six (6) SATA 3.0 ports via AHCI controller with RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 (I-SATA2~7)
• Two (2) SATA 3.0 ports with SATA DOM power (I-SATA0, I-SATA1)
• Video (VGA) Port • One (1) VGA connection on the rear I/O panel
Note: The table above is continued on the next page.
15
Page 16

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Motherboard Features
Peripheral Devices
• Two (2) USB 2.0 ports on the rear I/O panel (USB 0/1)
• Two (2) USB 3.0 ports on the rear I/O panel (USB 6/7)
• Two (2) front accessible USB 2.0 headers with two (2) USB connections (USB 2/3, USB 4/5)
• One (1) front accessible USB 3.0 header with two (2) USB connections (USB 8/9)
• One (1) USB 3.0 Type-A header (USB 10)
BIOS
• 256Mb AMI BIOS
• ACPI 6.0, Plug and Play (PnP), SPI dual speed support, and SMBIOS 3.0 or later
Power Management
• ACPI power management
• Power button override mechanism
• Power-on mode for AC power recovery
• Power supply monitoring
®
SPI Flash UEFI BIOS
System Health Monitoring
• Onboard voltage monitoring for +1.8V, +3.3V, +5V, +/-12V, +3.3V Stby, +5V Stby, VBAT, HT, memory, PCH temperature,
system temperature, and memory temperature
• 5 CPU switch phase voltage regulator
• CPU thermal trip support
• Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)/TSI
Fan Control
• Fan status monitoring via IPMI connections
• Single cooling zone
• Low-noise fan speed control
• Six (6) 4-pin fan headers
System Management
• Trusted Platform Module (TPM) support
• SuperDoctor® 5
• Redundant power supply unit detection sensor
• Chassis intrusion header and detection
• Intel® Management Engine
LED Indicators
• CPU/system overheat LED
• Power/suspend-state indicator LED
• Fan failed LED
• UID/remote UID
• HDD activity LED
• LAN activity LED
Note: The table above is continued on the next page.
16
Page 17
Motherboard Features
Dimensions
• 9.6" (W) x 9.6" (L) Micro-ATX (243.84mm x 243.84mm)
Note 1: The CPU maximum thermal design power (TDP) is subject to chassis and
heatsink cooling restrictions. For proper thermal management, please check the chas-
sis and heatsink specications for proper CPU TDP sizing.
Note 2: For IPMI conguration instructions, please refer to the Embedded IPMI Conguration User's Guide available at http://www.supermicro.com/support/manuals/.
Note 3: It is strongly recommended that you change BMC log-in information upon initial system power-on. The manufacture default username is ADMIN and the password
is ADMIN. For proper BMC conguration, please refer to http://www.supermicro.com/
products/info/les/IPMI/Best_Practices_BMC_Security.pdf
Chapter 1: Introduction
17
Page 18
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
System Block Diagram
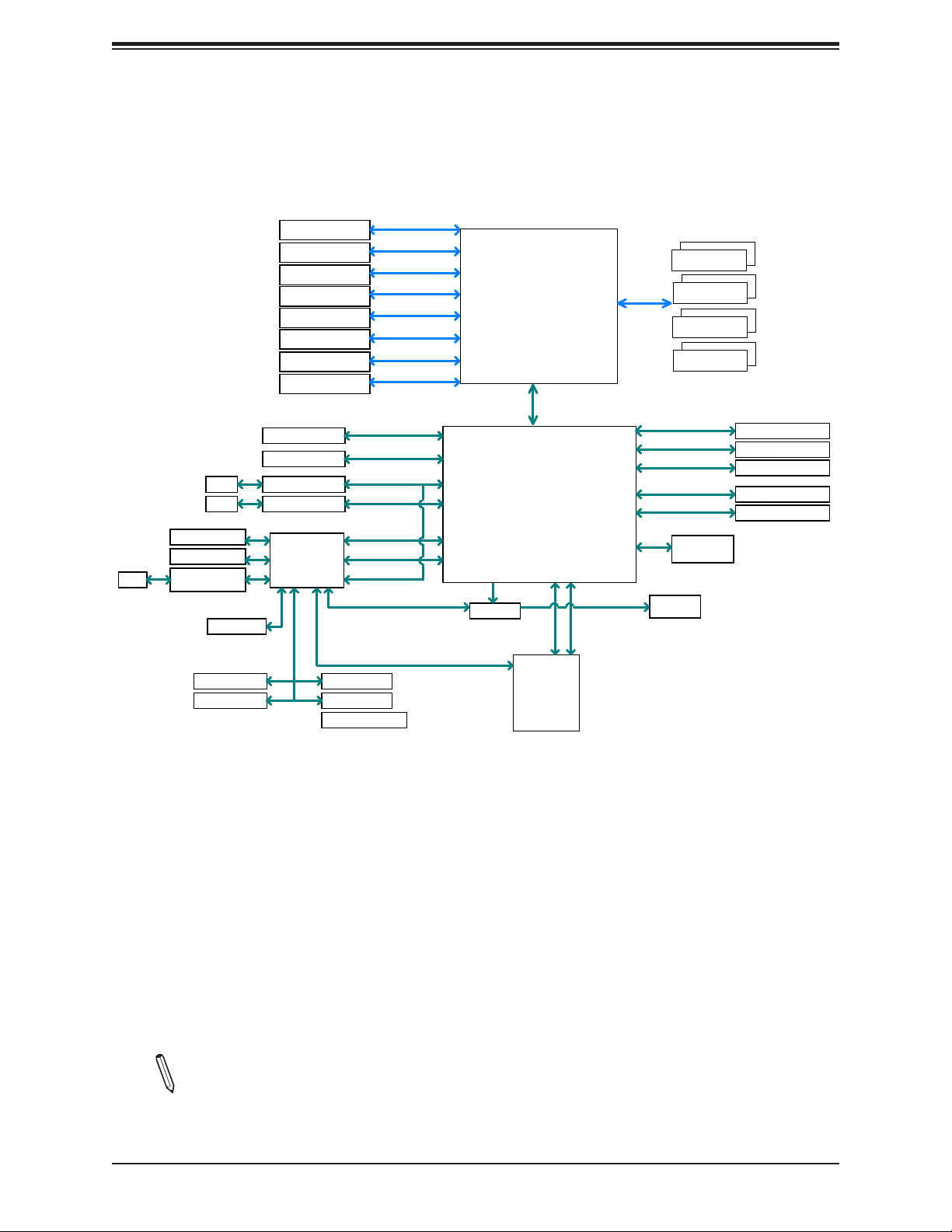
Figure 1-4.
RJ45
RJ45
RJ45
DDR4
BMC Boot Flash
LAN3
RTL8211E-VB-CG
VGA CONN
PCIe x8 SLOT #4
PCIe x16 SLOT #6
PCIe x8 SLOT #7
OCLINK-1 CONN
OCLINK-2 CONN
OCLINK-3 CONN
OCLINK-4 CONN
SKX-X : VR13
8X SATA-III
M.2 SOCKET SSD
GLAN1 i210
GLAN2 i210
BMC
AST2500
PCIe3.0_x8
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x16
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x8
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
SATA-III
6Gb/s
PCIe3.0_x4
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
USB2.0 x2
RMII
SVID
SWITCH
Xeon W
(C422)
SPI
Intel
PCH
x4 DMI
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
USB2.0 x2
DDR4 (1DPC)
ECC RDIMM/LRDIMM
DIMMA0
DIMMB0
DIMMC0
DIMMD0
USB3.0
5Gbps
USB3.0
5Gbps
USB3.0
5Gbps
USB2.0
480Mbps
USB2.0
480Mbps
SPI
TPM Header
Debug card
SPISPI
FLASH
SPI ROM
2 X USB 3.0 Rear
1 X USB 3.0 TYPE-A
2 X USB 3.0 Header
2 X USB 2.0 Rear
4 X USB 2.0 Header
Voltage monitor
Temp Sensor
COM1 CONN
COM2 Header
FAN SPEED CTRL
NCT6792D-B
LPC I/O
Note: This is a general block diagram and may not exactly represent the features on
your motherboard. See the previous pages for the actual specications of your motherboard.
18
Page 19

Chapter 1: Introduction
1.2 Processor and Chipset Overview
Built upon the functionality and capability of the Intel® Xeon® W-2200/2100 series (Socket R4)
processor and the Intel C422 chipset, the X11SRM-F/-VF motherboard provides system
performance, power eciency, and feature sets to address the needs of next-generation
computer users.
With the support of the new Intel Microarchitecture 14nm Process Technology, the
X11SRM-F/-VF dramatically increases system performance for a multitude of server
applications.
The Intel C422 chipset provides Enterprise SMbus support, including the following features:
• DDR4 288-pin memory support
• Support for Management Engine (ME)
• Support of SMBus speeds of up to 400KHz for BMC connectivity
• Improved I/O capabilities to various storage congurations
• SPI Enhancements
• BMC supports remote management, virtualization, and the security package for enterprise
platforms
1.3 Special Features
Recovery from AC Power Loss
The Basic I/O System (BIOS) provides a setting that determines how the system will respond
when AC power is lost and then restored to the system. You can choose for the system to
remain powered o (in which case you must press the power switch to turn it back on), or
for it to automatically return to the power-on state. See the Advanced BIOS Setup section
for this setting. The default setting is Last State.
1.4 System Health Monitoring
Onboard Voltage Monitors
An onboard voltage monitor will scan the voltages of the onboard chipset, memory, CPU,
and battery continuously. Once a voltage becomes unstable, a warning is given, or an error
message is sent to the screen. The user can adjust the voltage thresholds to dene the
sensitivity of the voltage monitor.
19
Page 20

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Fan Status Monitor with Firmware Control
The system health monitor embedded in the BMC chip can check the RPM status of the
cooling fans. The CPU and chassis fans are controlled via lPMI.
Environmental Temperature Control
System Health sensors monitor temperatures and voltage settings of onboard processors
and the system in real time via the IPMI interface. Whenever the temperature of the CPU or
the system exceeds a user-dened threshold, system/CPU cooling fans will be turned on to
prevent the CPU or the system from overheating.
Note: To avoid possible system overheating, please be sure to provide adequate air-
ow to your system.
System Resource Alert
This feature is available when used with SuperDoctor 5® in the Windows OS or in the Linux
environment. SuperDoctor is used to notify the user of certain system events. For example,
you can congure SuperDoctor to provide you with warnings when the system temperature,
CPU temperatures, voltages and fan speeds go beyond a predened range.
1.5 ACPI Features
ACPI stands for Advanced Conguration and Power Interface. The ACPI specication denes
a exible and abstract hardware interface that provides a standard way to integrate power
management features throughout a computer system, including its hardware, operating
system and application software. This enables the system to automatically turn on and o
peripherals such as CD-ROMs, network cards, hard disk drives and printers.
In addition to enabling operating system-directed power management, ACPI also provides a
generic system event mechanism for Plug and Play, and an operating system-independent
interface for conguration control. ACPI leverages the Plug and Play BIOS data structures,
while providing a processor architecture-independent implementation that is compatible with
Windows operating systems.
20
Page 21

Chapter 1: Introduction
1.6 Power Supply
As with all computer products, a stable power source is necessary for proper and reliable
operation. It is even more important for processors that have high CPU clock rates where
noisy power transmission is present.
The X11SRM-F/-VF motherboard accommodates a 24-pin ATX power supply. Although most
power supplies generally meet the specications required by the CPU, some are inadequate.
In addition, one 12V 8-pin power connection is also required to ensure adequate power supply
to the system.
Warning: To avoid damaging the power supply or the motherboard, be sure to use a
power supply that contains a 24-pin and an 8-pin power connector. Be sure to connect
the power supplies to the 24-pin power connector (JPW1), and the 8-pin power connector (JPWR2) on the motherboard. Failure in doing so may void the manufacturer
warranty on your power supply and motherboard.
It is strongly recommended that you use a high quality power supply that meets ATX power
supply Specication 2.02 or above. It must also be SSI compliant. (For more information,
please refer to the website at http://www.ssiforum.org/).
1.7 Serial Port
The X11SRM-F/-VF motherboard supports two serial communication connections. COM Ports
1 and 2 can be used for input/output. The UART provides legacy speeds with a baud rate of
up to 115.2 Kbps as well as an advanced speed with baud rates of 250 K, 500 K, or 1 Mb/s,
which support high-speed serial communication devices.
21
Page 22

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Chapter 2
Installation
2.1 Static-Sensitive Devices
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) can damage electronic com ponents. To avoid damaging your
system board, it is important to handle it very carefully. The following measures are generally
sucient to protect your equipment from ESD.
Precautions
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent static discharge.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the antistatic bag.
• Handle the motherboard by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral chips,
memory modules or gold contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the motherboard and peripherals back into their antistatic bags when not in use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure that your computer chassis provides excellent conduc-
tivity between the power supply, the case, the mounting fasteners and the motherboard.
• Use only the correct type of onboard CMOS battery. Do not install the onboard battery
upside down to avoid possible explosion.
Unpacking
The motherboard is shipped in antistatic packaging to avoid static damage. When unpacking
the motherboard, make sure that the person handling it is static protected.
22
Page 23
Chapter 2: Installation
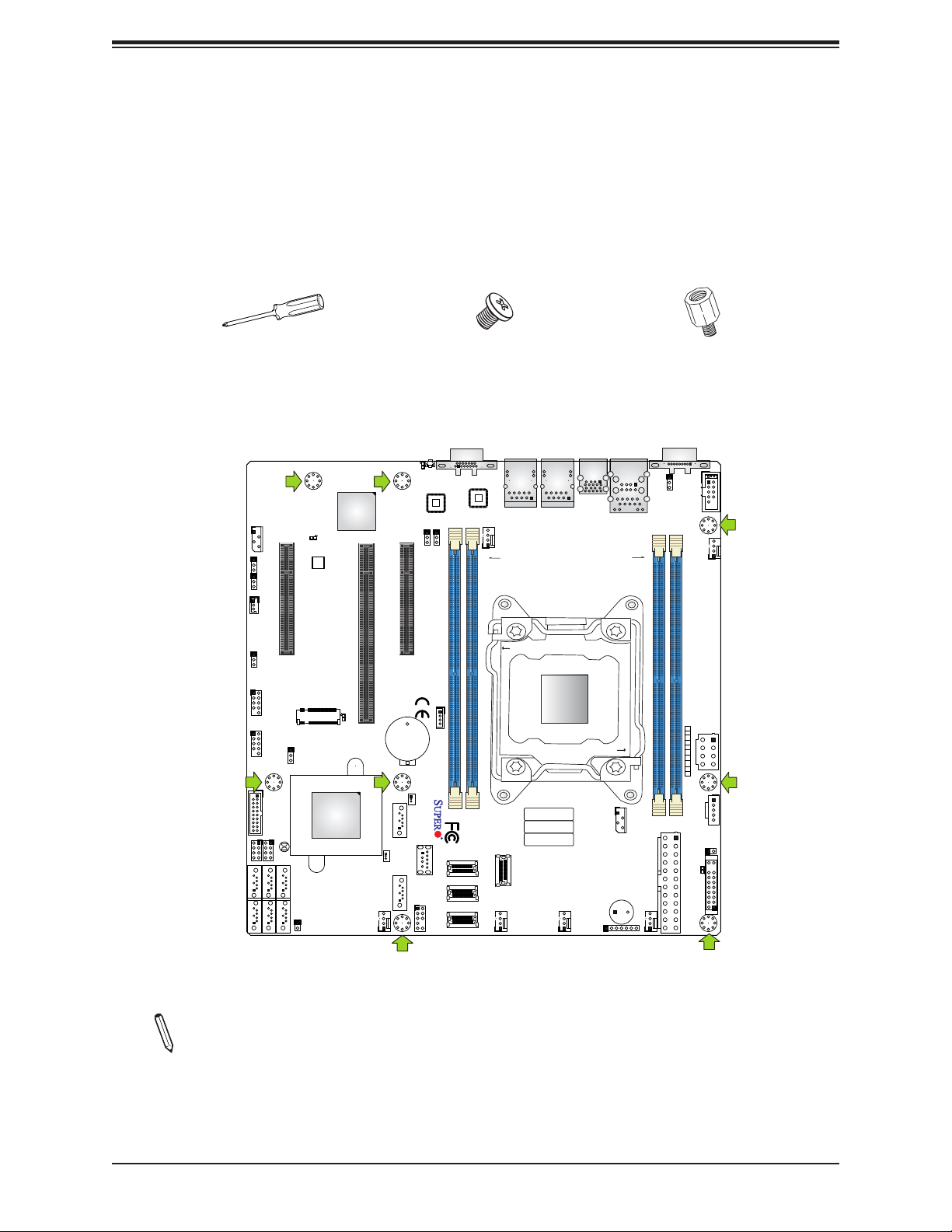
2.2 Motherboard Installation
All motherboards have standard mounting holes to t dierent types of chassis. Make sure
that the locations of all the mounting holes for both the motherboard and the chassis match.
Although a chassis may have both plastic and metal mounting fasteners, metal ones are
highly recommended because they ground the motherboard to the chassis. Make sure that
the metal standos click in or are screwed in tightly.
Phillips
Screwdriver
(1)
Tools Needed
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
I-SGPIO1
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA4
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
FANB
UID-LED
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
JTPM1
Phillips Screws
(8)
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
i210
JPL2
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
USB 10(3.0)
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
1
FAN4
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
JNVME2
CLOSE 1st
FANA
LAN2
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
LAN1
Standos (8)
Only if Needed
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
1
+
JD1
COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
Location of Mounting Holes
Note: 1) To avoid damaging the motherboard and its components, please do not use
force greater than 8 lb-f/in on each mounting screw during motherboard installation.
2) Some components are very close to the mounting holes. Please take precautionary measures to avoid damaging these components when installing the motherboard
to the chassis.
23
Page 24
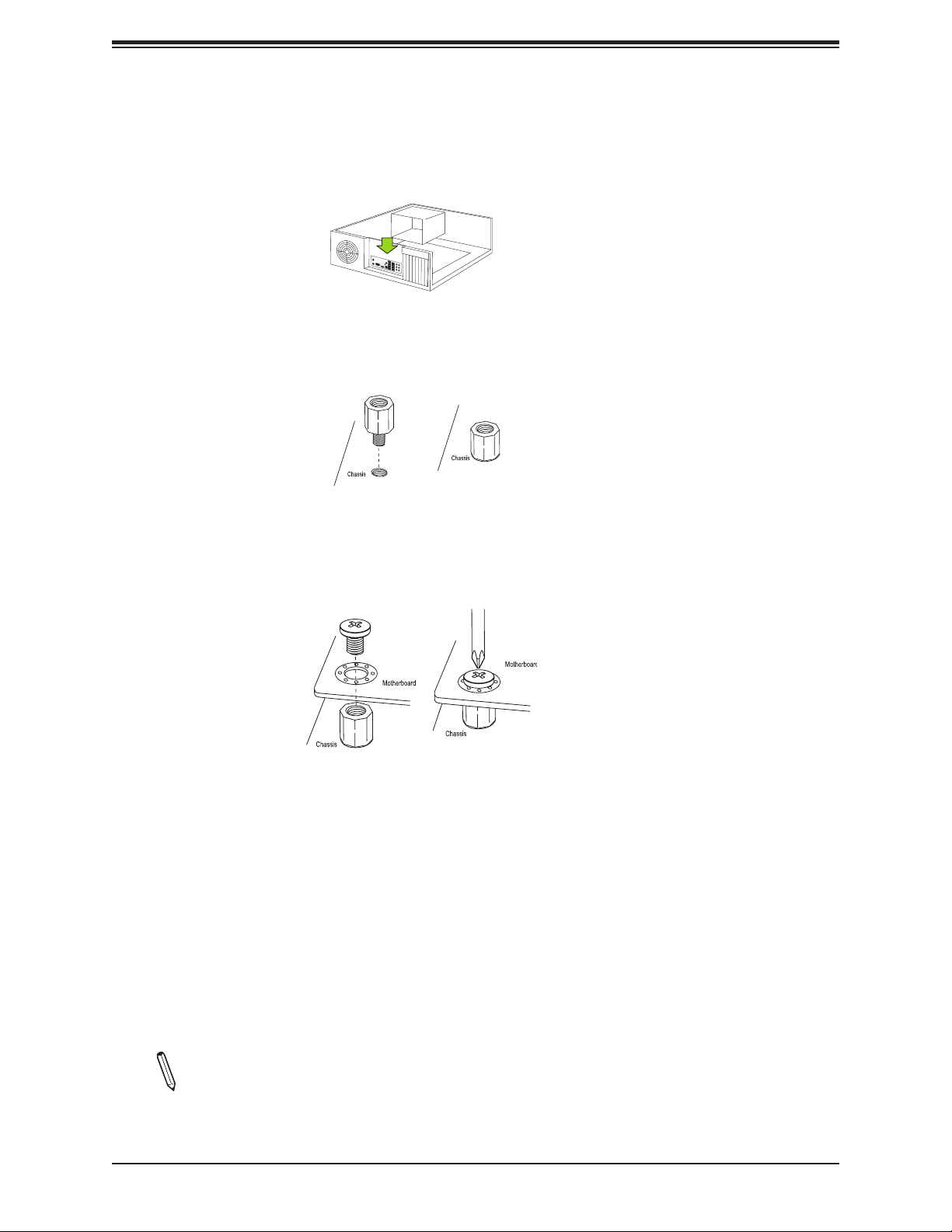
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Installing the Motherboard
1. Install the I/O shield into the back of the chassis, if applicable.
2. Locate the mounting holes on the motherboard. See the previous page for the location.
3. Locate the matching mounting holes on the chassis. Align the mounting holes on the
motherboard against the mounting holes on the chassis.
4. Install standos in the chassis as needed.
5. Install the motherboard into the chassis carefully to avoid damaging other motherboard
components.
6. Using the Phillips screwdriver, insert a pan head #6 screw into a mounting hole on the
motherboard and its matching mounting hole on the chassis.
7. Repeat Step 5 to insert #6 screws into all mounting holes.
8. Make sure that the motherboard is securely placed in the chassis.
Note: Images displayed are for illustration only. Your chassis or components might
look dierent from those shown in this manual.
24
Page 25
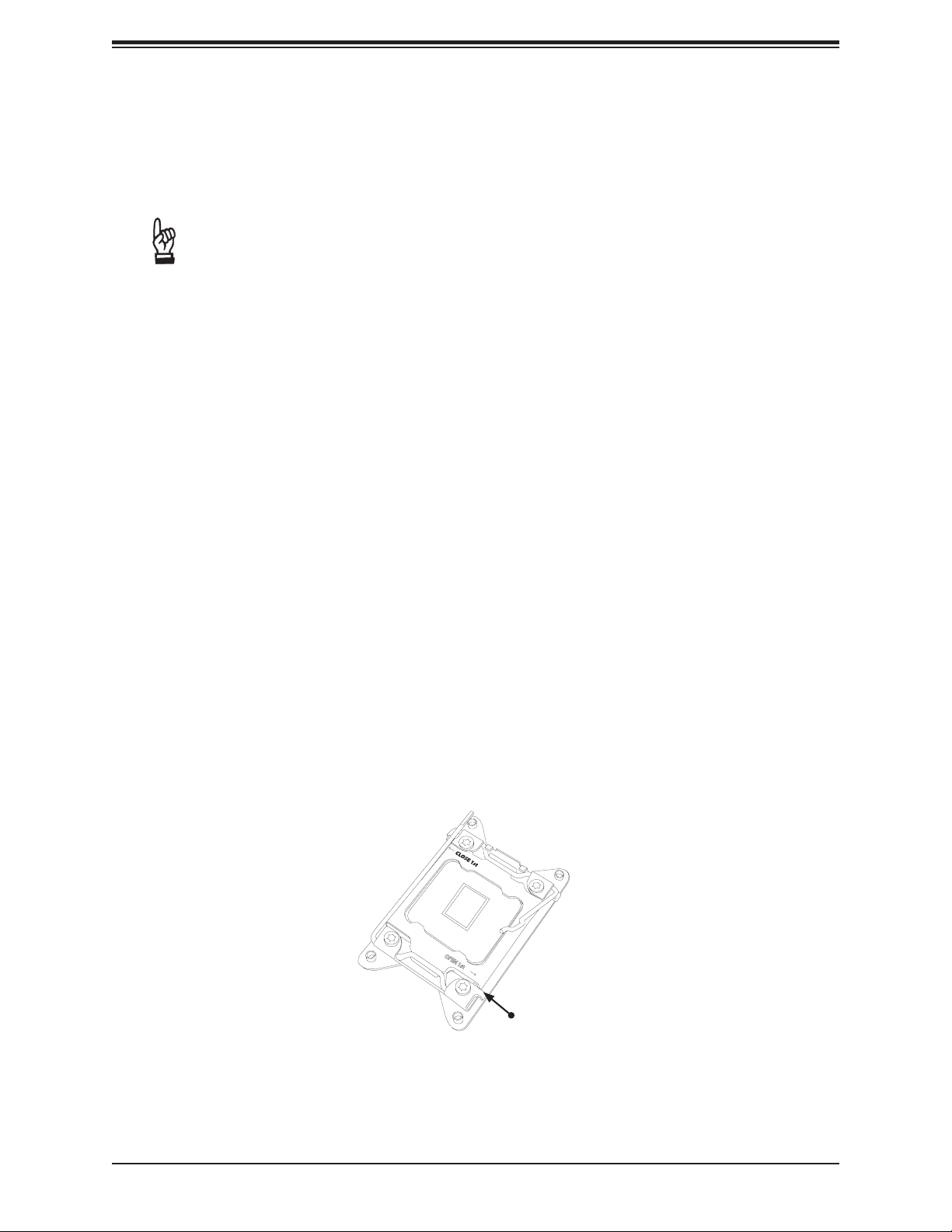
Chapter 2: Installation
2.3 Processor and Heatsink Installation
Warning: When handling the processor package, avoid placing direct pressure on the label
area of the fan.
Important:
• Always connect the power cord last, and always remove it before adding, removing or
changing any hardware components. Make sure that you install the processor into the
CPU socket before you install the CPU heatsink.
• If you buy a CPU separately, make sure that you use an Intel-certied multi-directional
heatsink only.
• Make sure to install the motherboard into the chassis before you install the CPU heatsink.
• When receiving a motherboard without a processor pre-installed, make sure that the plastic
CPU socket cap is in place and none of the socket pins are bent; otherwise, contact your
retailer immediately.
• Refer to the Supermicro website for updates on CPU support.
Installing a CPU
1. There are two load levers on the LGA 2066 socket. To open the socket cover, press and
release the load lever labeled "Open 1st".
1
OPEN 1st
Press down on
load lever labeled
"Open 1st"
25
Page 26
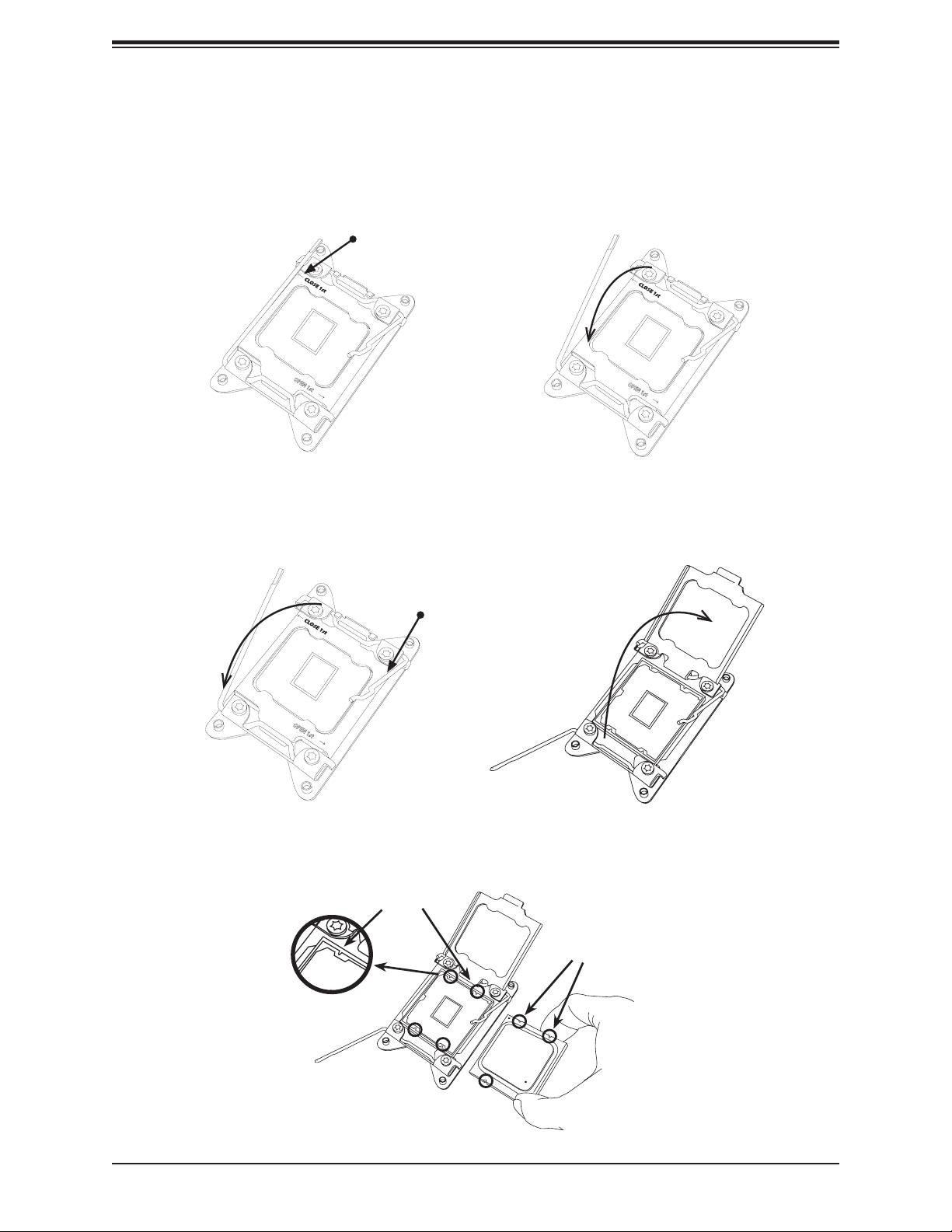
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
2. Press the second load lever labeled "Close 1st" to release the load plate that covers the
CPU socket from its locking position.
1
3. With the "Close 1st" lever fully retracted, gently push down on the "Open 1st" lever to
open the load plate. Lift the load plate to open it completely.
Press down on
OPEN 1st
1
load lever
"Close 1st"
Gently push down
to pop the load
plate open
2
Pull lever away from
socket
OPEN 1st
2
OPEN 1st
4. Use your thumb and index nger to hold the CPU by its edges. Align the CPU keys,
which are semi-circle cutouts, against the socket keys.
Socket Keys
CPU Keys
26
Page 27
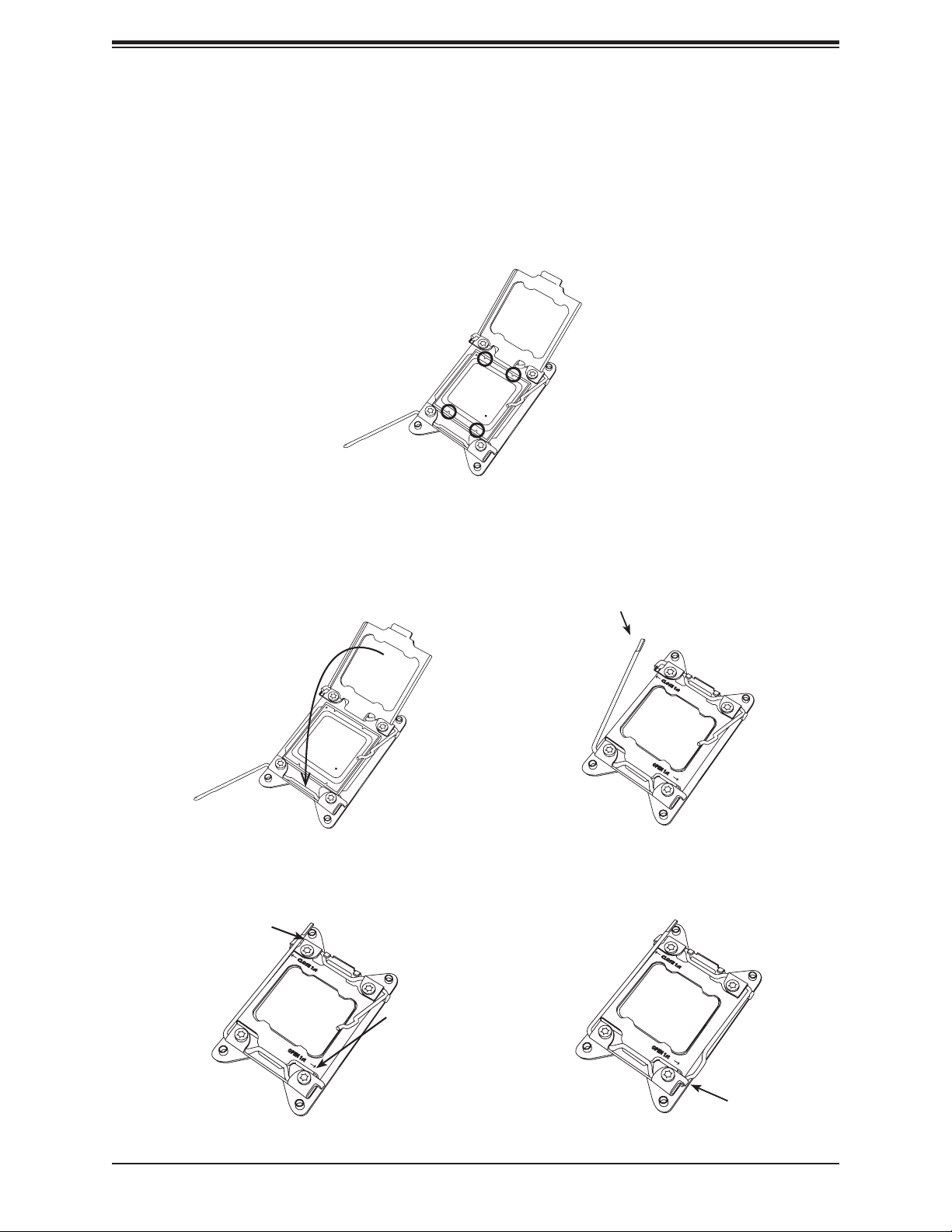
Chapter 2: Installation
5. Once they are aligned, carefully lower the CPU straight down into the socket. To avoid
damaging the CPU or socket, do not drop the CPU onto the socket, move it horizontally
or vertically, or rub it against the socket pins. Note that you can only install the CPU
inside the socket in one direction.
6. With the CPU inside the socket, inspect the four corners of the CPU to make sure that it
is properly installed.
7. Close the load plate with the CPU inside the socket. Lock the "Close 1st" lever rst,
then lock the "Open 1st" lever second. Gently push the load levers down to the lever
locks.
1
3
Lever Lock
Gently close
the load plate
Push down and lock the
2
lever labeled "Close 1st"
OPEN 1st
4
OPEN 1st
Push down and
lock the lever
labeled "Open
1st"
27
OPEN 1st
Lever Lock
Page 28

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Installing a Passive CPU Heatsink
1. Do not apply any thermal grease to the heatsink or the CPU die -- the required amount
has already been applied.
2. Place the heatsink on top of the CPU so that the four mounting holes are aligned with
those on the motherboard and the heatsink bracket underneath.
3. Screw in two diagonal screws (e.g., the #1 and the #2 screws) until just snug. Do not
over-tighten the screws to avoid damaging the CPU and the motherboard.
4. Finish the installation by fully tightening all four screws.
Screw #1
Direction of the
OPEN 1st
airow
Screw #2
Mounting Holes
Note: For optimal airow, please follow your chassis airow direction to correctly install
the CPU heatsink. Graphic drawings included in this manual are for reference only.
They might look dierent from the components installed in your system.
28
Page 29
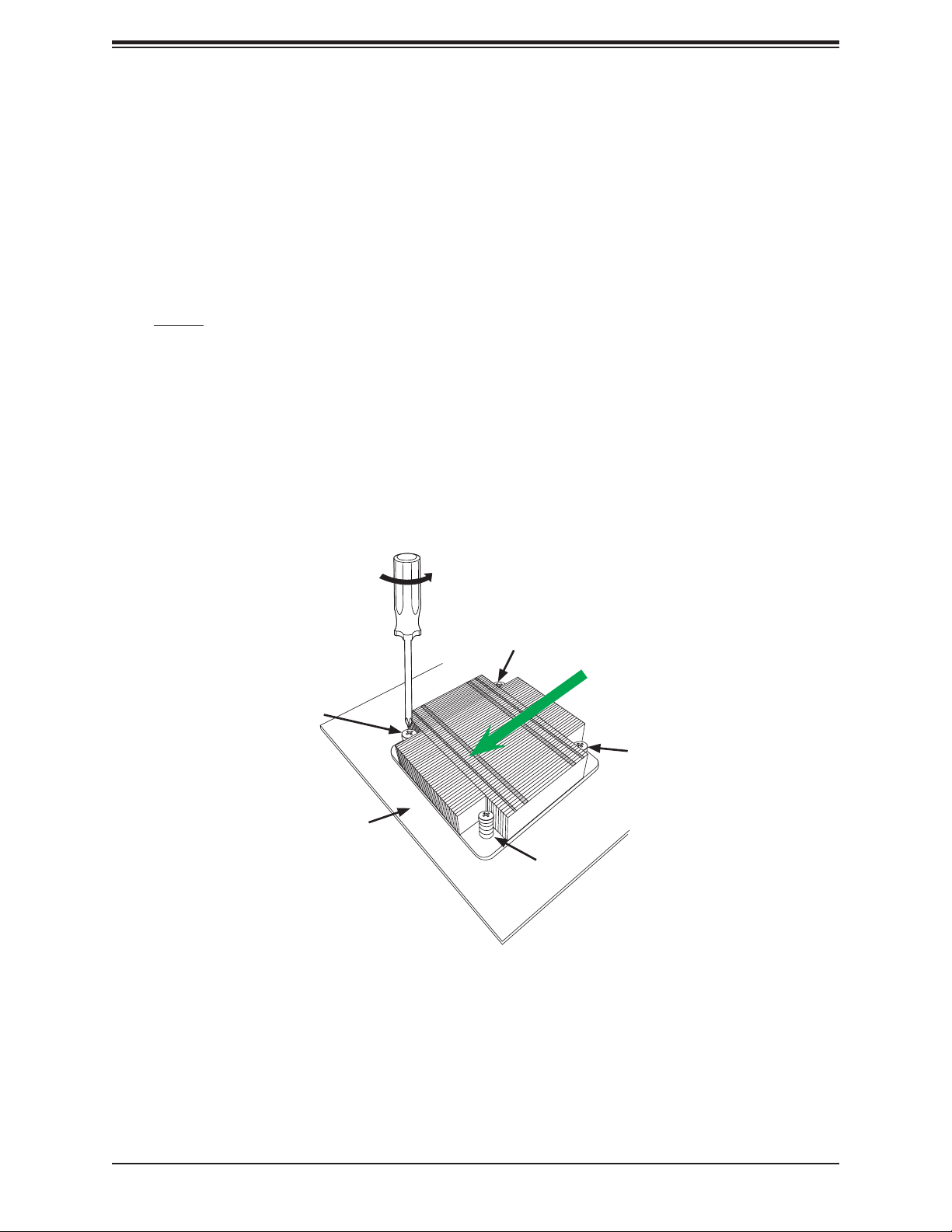
Chapter 2: Installation
Removing the CPU and the Heatsink
Warning: We do not recommend that the CPU or the heatsink be removed. However, if you
do need to uninstall the CPU or the heatsink, please follow the instructions below to uninstall
the heatsink to avoid damaging the CPU or other components.
1. Unscrew the heatsink screws from the motherboard in the sequence as shown in the
illustration below.
2. Gently wriggle the heatsink to loosen it from the CPU. Do not use excessive force when
loosening the heatsink.
3. Once the heatsink is loosened from the socket, remove the heatsink from the CPU
socket. Next, remove the CPU from the socket if needed.
4. Remove the used thermal grease and clean the surface of the CPU and the heatsink.
Reapply the proper amount of thermal grease on the surface before reinstalling the CPU
and the heatsink.
Loosen screws in
the sequence as
shown
Screw #1
Motherboard
Screw #4
Direction of the
airow
Screw #2
Screw #3
29
Page 30
Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
2.4 Memory Support and Installation
Note: Check the Supermicro website for recommended memory modules.
Important: Exercise extreme care when installing or removing DIMM modules to pre-
vent any possible damage.
Memory Support
The X11SRM-F/-VF supports up to 256GB of RDIMM and 512GB of LRDIMM DDR4 (288-pin)
ECC memory with speeds of up to 2933MHz in four memory slots. Refer to the tables below
for the recommended DIMM population order and additional memory information.
1 CPU, 4-DIMM Slots
Number of DIMMs Memory Population Sequence
1 DIMMA1
2 DIMMA1 / DIMMC1
3 DIMMB1 / DIMMA1 / DIMMC1
4 DIMMB1 / DIMMA1 / DIMMC1 / DIMMD1
DIMM Capacity
DIMM Type
RDIMM SRx4 8GB 16GB 16GB
RDIMM SRx8 4GB 8GB 32GB
RDIMM DRx8 8GB 16GB 32GB
RDIMM DRx4 16GB 32GB 64GB
LRDIMM QRx4 32GB 64GB 128GB
Ranks Per DIMM
and Data Width
4Gb 8Gb 16Gb 1.2V 1.2V 1.2V
(GB)
DRAM Density 1DPC 1DPC 2DPC
*DDR4 2933 only supported on select SKU.
Speed (MT/s), Voltage (V),
Slot Per Channel (SPC),
and DIMM Per Channel (DPC)
1 Slot Per
Channel
2933* 2933* 2666
2 Slots Per Channel
30
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installation
General Guidelines for Optimizing Memory Performance
• Always use DDR4 memory of the same type, size and speed.
• Mixed DIMM speeds can be installed. However, all DIMMs will run at the speed of the
slowest DIMM.
• The motherboard will support odd-numbered modules (one or three modules installed).
However, to achieve the best memory performance, a balanced memory population is
recommended.
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Aspeed
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
1
1
AST2500
LED6301
MH10
Intel
i210
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
FAN4
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
LAN2
LAN1
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
COM2
FAN3
1
1
JPB1
I-SGPIO1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA4
CLOSE 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
CPU
1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JD1
OPEN 1st
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPW1
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JF1
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
JTPM1
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
USB 10(3.0)
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
FANA
LED6904
M.2-PCH
B2
Intel
C422
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
31
Page 32

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
DIMM Installation
1. Insert the desired number of DIMMs
into the memory slots based on the
recommended DIMM population table on
page 30.
2. Push the release tabs outwards on both
ends of the DIMM slot to unlock it.
3. Align the key of the DIMM module with the
receptive point on the memory slot.
4. Align the notches on both ends of the
module against the receptive points on the
ends of the slot.
I-SGPIO1
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
JSD1
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JNVME3
JNVME1
JTPM1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
LAN1
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
CPU
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
JNVME2
FAN2
FANA
1
Aspeed
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
1
JIPMB1
USB 8/9(3.0)
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
AST2500
LED6301
MH10
LED6904
M.2-PCH
Intel
C422
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
FANB
JL1
1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 6/7(3.0)
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
FAN3
1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
OPEN 1st
JD1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JNVI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
5. Press the notches on both ends of the
module straight down into the slot until the
module snaps into place.
6. Press the release tabs to the lock positions
to secure the DIMM module into the slot.
DIMM Removal
Press both release tabs on the ends of the
DIMM module to unlock it. Once the DIMM
module is loosened, remove it from the
memory slot.
Notches
Release Tabs
Press both notches
straight down into
the memory slot.
32
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
2.5 Rear I/O Ports
See Figure 2-1 below for the locations and descriptions of the various I/O ports on the rear
of the motherboard.
UID-LED
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
VGA
Intel
i210
JPL2
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
FAN3
1
JNVME2
CLOSE 1st
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
JPW1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
1
JD1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
LED6904
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
I-SATA1
FANB
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
Figure 2-1. I/O Port Locations and Denitions
2
5
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
ON
LED7201
JPWR2
JF1
JPI2C1
JOH1
JF1
1
3
4
# Description # Description
1 COM Port 1 6 USB6 (3.0)
2 Dedicated IPMI LAN 7 LAN1
3 USB1 8 LAN2
4 USB0 9 VGA Port
5 USB7 (3.0) 10 UID Switch
33
876
9
10
Page 34

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
COM Ports
Two COM connections (COM1, COM2) are located on the motherboard. COM1 is located on
the I/O back panel. COM2 is located next to FAN3.
COM Port
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 DCD 6 DSR
2 RXD 7 RTS
3 TXD 8 CTS
4 DTR 9 RI
5 Ground 10 N/A
VGA Port
A video (VGA) port is located next to LAN2 on the I/O back panel. Refer to the board layout
below for the location.
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
2
1. COM1
2. COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
3. VGA Port
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
3
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
OPEN 1st
1
JD1
34
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
LAN Ports
Two Gigabit Ethernet ports (LAN1, LAN2) are located on the I/O back panel. In addition, a
dedicated IPMI LAN is located above the USB0/1 ports on the back panel. All of these ports
accept RJ45 cables. Please refer to the LED Indicator section for LAN LED information.
LAN Port
Pin Denition
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 TD0- 11 P3V3_Dual
2 TD0+ 12 Act LED (Yellow)
3 TD1- 13
4 TD1+ 14
Link 1000
(Amber)
Link 100 LED
(Green)
5 TD2- 15 GND
6 TD2+ 16 GND
7 TD3- 17 GND
8 TD3+ 18 GND
9 COMMCT
10 GND
123
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
Aspeed
AST2500
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
JPL2
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
IPMI LAN
Pin Denition
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
9 19 GND
10 TD0+ 20
11 TD0- 21
12 TD1+ 22
Act LED
(Yellow)
Link 100 LED
(Green)
Link 1000 LED
(Amber)
13 TD1- 23 SGND
14 TD2+ 24 SGND
15 TD2- 25 SGND
16 TD3+ 26 SGND
17 TD3-
18 GND
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. IPMI LAN
2. LAN1
FAN3
1
3. LAN2
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
CLOSE 1st
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
SP1
FAN2
FANA
+
1
JD1
I-SATA1
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
LED6904
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
FANB
JL1
35
Page 36

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports
There are two USB 2.0 ports (USB 0/1) and two USB 3.0 ports (USB 6/7) located on the
I/O back panel. The motherboard also has two front access USB 2.0 headers (USB 2/3 and
USB 4/5) and one front access USB 3.0 header (USB 8/9). The USB 10 header is USB 3.0
Type-A. The onboard headers can be used to provide front side USB access with a cable
(not included).
Back Panel USB 0/1 (2.0)
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 +5V 5 +5V
2 USB_N 6 USB_N
3 USB_P 7 USB_P
4 Ground 8 Ground
Back Panel USB 6/7 (3.0)
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
A1 VBUS B1 Power
A2 D- B2 USB_N
A3 D+ B3 USB_P
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 Stda_SSRX- B5 USB3_RN
A6 Stda_SSRX+ B6 USB3_RP
A7 GND B7 GND
A8 Stda_SSTX- B8 USB3_TN
A9 Stda_SSTX+ B9 USB3_TP
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
C422
Intel
AST2500
LED6904
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
6
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
2
USB 4/5
3
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
5
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
i210
1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
DIMMB1
JNVME2
FAN4
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
FANA
LAN2
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
Front Panel USB 2/3, 4/5 (2.0)
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 +5V 2 +5V
3 USB_N 4 USB_N
5 USB_P 6 USB_P
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 Key 10 NC
Front Panel USB 8/9 (3.0)
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1
VBUS 19 Power
2
Stda_SSRX- 18 USB3_RN
3
Stda_SSRX+ 17 USB3_RP
4
GND 16 GND
5
Stda_SSTX- 15 USB3_TN
6
Stda_SSTX+ 14 USB3_TP
7
GND 13 GND
8
D- 12 USB_N
9
D+ 11 USB_P
4
USB 6/7(3.0)
1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
FAN3
10 x
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1
1 VBUS 5 SSRX-
Type A USB 10 (3.0)
Pin Denitions
2 USB_N 6 SSRX+
3 USB_P 7 GND
4 Ground 8 SSTX-
9 SSTX+
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
SP1
+
1
JD1
1. USB0/1
2. USB2/3
3. USB4/5
4. USB6/7
5. USB8/9
6. USB10
36
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
Unit Identier Switch/UID LED Indicator
A Unit Identier (UID) switch and an LED Indicator are located on the motherboard. The UID
switch is located at JUIDB1, which is next to the VGA port on the back panel. The UID LED
is located next to the switch. When you press the UID switch, the UID LED will be turned
on. Press the UID switch again to turn o the LED indicator. The UID Indicator provides easy
identication of a system unit that may be in need of service.
Note: UID can also be triggered via IPMI on the motherboard. For more information
on IPMI, please refer to the IPMI User's Guide posted on our website at http://www.
supermicro.com.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
AST2500
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
UID Switch
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Ground
2 Ground
3 Button In
4 Button In
1
2
UID-LED
JUIDB1
Aspeed
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
UID LED
Pin Denitions
Color Status
Blue: On Unit Identied
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
1. UID Switch
2. UID LED
FAN3
1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
JPL2
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
CLOSE 1st
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
SP1
FAN2
FANA
+
1
JD1
I-SATA1
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
LED6904
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
FANB
37
Page 38

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
2.6 Front Control Panel
JF1 contains header pins for various buttons and indicators that are normally located on a
control panel at the front of the chassis. These connectors are designed specically for use
with Supermicro chassis. See the gure below for the descriptions of the front control panel
buttons and LED indicators.
UID-LED
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
VGA
Intel
i210
JPL2
1
FAN4
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
LAN2
LAN1
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
COM2
1
FAN3
1
I-SGPIO1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA4
M.2-PCH
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
PWR
Reset
CLOSE 1st
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
Intel
C422
LED6904
B2
I-SATA1
FANB
Figure 2-2. JF1 Header Pins
1 2
Power Button
Reset Button
3.3V
Ground
Ground
Power Fail LED
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN2
1
FAN1 CPU
+
JD1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
UID LED
3.3V Stby
3.3V Stby
UID SW
3.3V Stby
NMI
OH/Fan Fail LED
NIC2 Active LED
NIC1 Active LED
HDD LED
PWR LED
X
X
Ground
19
20
38
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installation
Power Button
The Power Button connection is located on pins 1 and 2 of JF1. Momentarily contacting both
pins will power on/o the system. This button can also be congured to function as a suspend
button (with a setting in the BIOS - see Chapter 4). To turn o the power when the system
is in suspend mode, press the button for 4 seconds or longer. Refer to the table below for
pin denitions.
Power Button
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pins Denition
1 Signal
2 Ground
Reset Button
The Reset Button connection is located on pins 3 and 4 of JF1. Attach it to a hardware reset
switch on the computer case to reset the system. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
Reset Button
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pins Denition
3 Reset
4 Ground
1 2
PWR
1
Reset
2
Power Button
Reset Button
3.3V
UID LED
3.3V Stby
3.3V Stby
UID SW
Ground
Ground
Power Fail LED
OH/Fan Fail LED
NIC2 Active LED
NIC1 Active LED
HDD LED
1. PWR Button
2. Reset Button
3.3V Stby
NMI
PWR LED
X
19
20
X
Ground
39
Page 40

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Power Fail LED
The Power Fail LED connection is located on pins 5 and 6 of JF1. Refer to the table below
for pin denitions.
Power Fail LED
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
5 3.3V
6 PWR Supply Fail
UID/Overheat (OH)/Fan Fail
Connect an LED cable to UID/OH/Fan Fail connections on pins 7 and 8 of JF1 to provide
front UID LED indication and warnings of overheating or fan failure. Refer to the tables below
for pin denitions.
PWR
Reset
OH/Fan Fail Indicator
Status (JF1)
State Denition
O Normal
On Overheat
Flashing Fan Fail
Power Button
Reset Button
3.3V
UID LED
3.3V Stby
3.3V Stby
1 2
Ground
Ground
Power Fail LED
OH/Fan Fail LED
NIC2 Active LED
NIC1 Active LED
OH/Fan Fail LED
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
7 Blue LED
8 OH/Fan Fail LED
1. Power Fail LED
2. OH/Fan Fail LED
1
2
UID SW
3.3V Stby
NMI
HDD LED
PWR LED
X
19
20
X
Ground
40
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installation
NIC1/NIC2 (LAN1/LAN2)
The NIC (Network Interface Controller) LED connection for LAN port 1 is located on pins
11 and 12 of JF1, and LAN port 2 is on pins 9 and 10. Attach the NIC LED cables here to
display network activity. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
LAN1/LAN2 LED
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
9,11 3.3V LAN
10 NIC 2 Activity LED
12 NIC 1 Activity LED
HDD LED/UID Switch
The HDD LED/UID Switch connection is located on pins 13 and 14 of JF1. Attach a cable
to pin 14 to show hard drive activity status. Attach a cable to pin 13 to use the UID switch.
PWR
Reset
Power Button
Reset Button
3.3V
UID LED
3.3V Stby
3.3V Stby
UID SW
1 2
Ground
Ground
Power Fail LED
OH/Fan Fail LED
NIC2 Active LED
NIC1 Active LED
HDD LED
HDD LED
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pins Denition
13 3.3V Stdby
14 HDD Active
1. NIC2 LED
2. NIC1 LED
3. HDD LED
1
2
3
3.3V Stby
NMI
PWR LED
X
19
20
X
Ground
41
Page 42

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Power LED
The Power LED connection is located on pins 15 and 16 of JF1. Refer to the table below
for pin denitions.
Power LED
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pins Denition
15 3.3V
16 PWR LED
NMI Button
The non-maskable interrupt (NMI) button header is located on pins 19 and 20 of JF1. Refer
to the table below for pin denitions.
PWR
Reset
Power Button
Reset Button
3.3V
UID LED
3.3V Stby
1 2
Pins Denition
19 Control
20 Ground
Ground
Ground
Power Fail LED
OH/Fan Fail LED
NIC2 Active LED
NMI Button
Pin Denitions (JF1)
1. PWR LED
2. NMI
3.3V Stby
UID SW
3.3V Stby
NMI
2
NIC1 Active LED
HDD LED
PWR LED
X
19
20
X
Ground
1
42
Page 43

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
2.7 Connectors
Power Connections
ATX Power Supply Connector
The 24-pin power supply connector (JPW1) meets the ATX SSI EPS 12V specication. You
must also connect the 8-pin (JPWR2) processor power connector to the power supply.
ATX Power 24-pin Connector
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
13 +3.3V 1 +3.3V
14 -12V 2 +3.3V
15 Ground 3 Ground
16 PS_ON 4 +5V
17 Ground 5 Ground
18 Ground 6 +5V
19 Ground 7 Ground
20 Res (NC) 8 PWR_OK
21 +5V 9 5VSB
22 +5V 10 +12V
23 +5V 11 +12V
24 Ground 12 +3.3V
Required Connection
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
Intel
C422
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
1
SP1
FAN2
FANA
1
FAN1 CPU
+
JD1
1
COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
1. 24-Pin ATX PWR
43
Page 44

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
8-Pin Power Connector
JPWR2 is an 8-pin 12V DC power input for the CPU that must be connected to the power
supply. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
8-pin Power
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 - 4 Ground
5 - 8 P12V (12V Power)
Required Connection
Important: To provide adequate power supply to the motherboard, be sure to connect
the 24-pin ATX PWR and the 8-pin CPU PWR connectors to the power supply. Failure
to do so may void the manufacturer warranty on your power supply and motherboard.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
1
COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
1
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1. 8-Pin PWR
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
JD1
44
Page 45

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
Headers
Fan Headers
There are six 4-pin fan headers (FAN1 ~ FAN4, FANA, FANB) on the motherboard. All
these 4-pin fan headers are backwards compatible with the traditional 3-pin fans. However,
fan speed control is available for 4-pin fans only by Thermal Management via the IPMI 2.0
interface. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
Fan Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Ground (Black)
2 2.5A/+12V (Red)
3 Tachometer
4 PWM_Control
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
2
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
1. FANA
2. FANB
FAN3
5
1
3. FAN1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
6
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
4. FAN2
CLOSE 1st
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
3
1
OPEN 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
JNVME2
SP1
FAN2
FANA
1
+
4
1
JD1
5. FAN3
6. FAN4
45
Page 46

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
SGPIO Headers
There are two Serial Link General Purpose Input/Output (I-SGPIO1, I-SGPIO2) headers
located on the motherboard. Refer to the tables below for pin denitions.
SGPIO Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 NC 2 NC
3 Ground 4 Data
5 Load 6 Ground
7 Clock 8 NC
NC = No Connection
Disk-On-Module Power Connector
Two power connectors for SATA DOM (Disk-On-Module) devices are located at JSD1 and
JSD2. Connect appropriate cables here to provide power support for your Serial Link DOM
devices.
DOM Power
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 5V
2 Ground
3 Ground
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
C422
Intel
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
LED6904
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
3
USB 10(3.0)
4
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
1
JD1
OPEN 1st
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. I-SGPIO1
2. I-SGPIO2
FAN3
1
3. JSD1 (DOM PWR)
4. JSD2 (DOM PWR)
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
46
Page 47

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
TPM/Port 80 Header
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM)/Port 80 header is located at JTPM1 to provide TPM support
and Port 80 connection. Use this header to enhance system performance and data security.
Refer to the table below for pin denitions. Please go to the following link for more information
on the TPM: http://www.supermicro.com/manuals/other/TPM.pdf.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
AST2500
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
Aspeed
UID-LED
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
JUIDB1
Trusted Platform Module Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 +3.3V 2 SPI_CS#
3 RESET# 4 SPI_MISO
5 SPI_CLK 6 GND
7 SPI_MOSI 8 NC
9 +3.3V Stdby 10 SPI_IRQ#
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
FAN3
1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
JPL2
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
1. TPM Header
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
CLOSE 1st
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
SP1
FAN2
FANA
+
1
JD1
I-SATA1
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
1
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
LED6904
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
FANB
47
Page 48

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
Standby Power
The Standby Power header is located at JSTBY1 on the motherboard. You must have a card
with a Standby Power connector and a cable to use this feature. Refer to the table below
for pin denitions.
Standby Power
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 +5V Standby
2 Ground
3 No Connection
Internal Speaker/Buzzer
The Internal Speaker/Buzzer (SP1) is used to provide audible indications for various beep
codes. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
Internal Buzzer
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Pos (+) Beep In
2 Neg (-) Alarm Speaker
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
C422
Intel
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
LED6904
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
2
1
JD1
OPEN 1st
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. Standby Power
2. Internal Speaker
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
48
Page 49

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
Power SMB (I2C) Header
The Power System Management Bus (I2C) connector (JPI2C1) monitors the power supply,
fan, and system temperatures. Refer to the table below for pin denitions.
Power SMB Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Clock
2 Data
3 PMBUS_Alert
4 Ground
5 +3.3V
4-pin BMC External I2C Header
A System Management Bus header for IPMI 2.0 is located at JIPMB1. Connect the appropriate
cable here to use the IPMB I2C connection on your system. Refer to the table below for pin
denitions.
External I2C Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Data
2 Ground
3 Clock
4 No Connection
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
C422
Intel
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
LED6904
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
2
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
1
JD1
OPEN 1st
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. Power SMB Header
2. BMC External Header
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
49
Page 50

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
Chassis Intrusion
A Chassis Intrusion header is located at JL1 on the motherboard. Attach the appropriate cable
from the chassis to inform you of a chassis intrusion when the chassis is opened. Refer to
the table below for pin denitions.
Chassis Intrusion
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Intrusion Input
2 Ground
M.2 Slot
The X11SRM-F/-VF motherboard has one M.2 slot. M.2 was formerly known as Next
Generation Form Factor (NGFF) and serves to replace mini PCI-E. M.2 allows for a variety of
card sizes, increased functionality, and spatial eciency. The M.2 socket on the motherboard
supports PCI-E 3.0 x4 (32 Gb/s) SSD cards in the 2280 form factor.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
2
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
1
COM2
1. Chassis Intrusion
2. M.2 Slot
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
JD1
50
Page 51

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
NVMe I2C Header
Connector JNVI2C1 is a management header for the Supermicro AOC NVMe PCI-E peripheral
cards. Please connect the I2C cable to this connector.
NVMe Connector
JNVME0 ~ JNVME3 are Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) connectors that provide four
connections for devices like solid state drives. The NVMe interface provides lower data latency
for increased eciency and performance. It supports up to 64K commands per queue. The
NVMe connectors also serve as OCuLink connectors for Intel Virtual RAID on Chip (VROC)
support, which is only available for the X11SRM-VF.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
5
3
JTPM1
2
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
1. NVMe I2C Header
2. JVNME0
FAN3
1
3. JVNME1
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
4. JVNME2
5. JVNME3
JNVME2
CLOSE 1st
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
4
FAN2
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
1
SP1
+
1
JD1
51
Page 52

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Power LED/Speaker
Pins 1-3 of JD1 are used for power LED indication, and pins 4-7 are for the speaker. Please
note that the speaker connector pins (4-7) are used with an external speaker. If you wish to
use the onboard speaker, you should close pins 6-7 with a cap. Refer to the tables below
for pin denitions.
PWR LED Connector
Pin Denitions
Pin# Signal
1 JD1_PIN1
2 FP_PWR_LED
3 FP_PWR_LED
Speaker Connector
Pin Denitions
Pin# Signal
4 P5V
5 Key
6 R_SPKPIN_N
7 R_SPKPIN
Overheat/Fan Fail LED Header
The JOH1 header is used to connect an LED indicator to provide warnings of chassis
overheating and fan failure. This LED will blink when a fan failure occurs. Refer to the tables
below for pin denitions.
Overheat LED Header
Status
State Denition
Solid Overheat
Blinking Fan Fail
Pin# Signal
1
2 OH Active
Overheat LED
Pin Denitions
Pull high to +3.3V
power through 330-ohm
resistor
1
1
1
1
I-SGPIO1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
1. Power LED/ Speaker Header
2. Overheat/Fan Fail LED
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
2
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
Header
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
JD1
52
Page 53

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
SATA Ports
The X11SRM-F/-VF has eight SATA 3.0 ports (I-SATA0 ~ I-SATA7) supported by the Intel PCH
C422 chipset. These SATA ports support RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10. SATA ports provide serial-link
signal connections, which are faster than the connections of Parallel ATA. Refer to the table
below for pin denitions.
Note: Supermicro SuperDOMs are yellow SATADOM connectors with power pins built
in and do not require separate external power cables. These connectors are backwards
compatible with non-Supermicro SATADOMS that require an external power supply.
SATA 3.0 Port
Pin Denitions
Pin# Signal
1 Ground
2 SATA_TXP
3 SATA_TXN
4 Ground
5 SATA_RXN
6 SATA_RXP
7 Ground
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
8 7
1
I-SATA7
I-SATA4
564 3
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
1
JL1
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
1
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
COM2
1. I-SATA0
2. I-SATA1
FAN3
1
3. I-SATA2
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
4. I-SATA3
5. I-SATA4
6. I-SATA5
7. I-SATA6
8. I-SATA7
JNVME2
CLOSE 1st
FANA
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
SP1
+
1
JD1
53
Page 54

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
Intel RAID Key Header
The JRK1 header allows the user to enable RAID functions for NVMe connections. Refer to
the table below for pin denitions.
Intel RAID Key Header
Pin Denitions
Pin# Dention
1 GND
2 PU 3.3V Stdby
3
4
GND
PCH RAID KEY
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
1
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JPUSB1
1
COM1
DIMMD1
1
1
COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1. Intel RAID Key
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
JD1
54
Page 55

Chapter 2: Installation
2.8 Jumper Settings
How Jumpers Work
To modify the operation of the motherboard, jumpers can be used to choose between optional
settings. Jumpers create shorts between two pins to change the function of the connector.
Pin 1 is identied with a square solder pad on the printed circuit board. See the diagram
below for an example of jumping pins 1 and 2. Refer to the motherboard layout page for
jumper locations.
Note: On two-pin jumpers, "Closed" means the jumper is on and "Open" means the
jumper is o the pins.
Connector
Pins
Jumper
Setting
3 2 1
3 2 1
CMOS Clear
JBT1 is used to clear CMOS, which will also clear any passwords. Instead of pins, this jumper
consists of contact pads to prevent accidentally clearing the contents of CMOS.
To Clear CMOS
1. First power down the system and unplug the power cord(s).
2. Remove the cover of the chassis to access the motherboard.
3. Remove the onboard battery from the motherboard.
4. Short the CMOS pads with a metal object such as a small screwdriver for at least four
seconds.
5. Remove the screwdriver (or shorting device).
6. Replace the cover, reconnect the power cord(s), and power on the system.
Note: Clearing CMOS will also clear all passwords.
Do not use the PW_ON connector to clear CMOS.
JBT1 contact pads
55
Page 56

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Watchdog
Watchdog (JWD1) is a system monitor that can reboot the system when a software application
hangs. Close pins 1-2 to reset the system if an application hangs. Close pins 2-3 to generate
a non-maskable interrupt (NMI) signal for the application that hangs. Refer to the table below
for jumper settings. The watchdog must also be enabled in the BIOS.
Watchdog
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Reset
Pins 2-3 NMI
Open Disabled
VGA Enable/Disable
Jumper JPG1 allows the user to enable the onboard VGA connector. The default setting is
pins 1-2 to enable the connection. Refer to the table below for jumper settings.
VGA Enable/Disable
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Enabled
Pins 2-3 Disabled
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
Intel
C422
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
LED6904
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
2
JWD1
1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
I-SGPIO1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
OPEN 1st
1
JD1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
+
JNVI2C1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. Watchdog
2. VGA Enable
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
56
Page 57

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
ME Manufacturing Mode
Close pins 2-3 of jumper JPME2 to bypass SPI ash security and force the system to operate
in the manufacturing mode, which will allow the user to ash the system rmware from a
host server for system setting modications. Refer to the table below for jumper settings.
The default setting is Normal.
Manufacturing Mode
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Normal
Pins 2-3 Manufacturing Mode
BMC Enabled
JPB1 allows you to enable or disable the BMC (Baseboard Management Control) chip and
the onboard IPMI connection for remote system management/monitoring purpose. This jumper
is used together with the IPMI settings in the BIOS. After the BMC is disabled, IPMI health
monitoring and remote management functions are no longer supported.
Note: Please always keep BMC enabled to make sure the platform operates reliably
with the health monitor.
BMC Enable
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Enabled (Default)
Pins 2-3 Disabled
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
C422
Intel
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
LED6904
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
1
JIPMB1
1
JPG1
JWD1
1
JSTBY1
1
JPB1
2
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
1
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
1
JD1
OPEN 1st
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
COM2
1. Manufacturing Mode
2. BMC Enable
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
57
Page 58

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
I-SGPIO1
LAN Port Enable/Disable
Change the setting of jumpers JPL1 for LAN1 and JPL2 for LAN2 to enable or disable the
LAN ports. The default setting is Enabled.
LAN Port Enable/Disable
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Enabled
Pins 2-3 Disabled
USB Wake Up
Use the JPUSB1 jumper to enable system "wake up" via a USB device. This jumper allows
you to "wake up" the system by pressing a key on the USB keyboard or by clicking the USB
mouse of your system. The JPUSB1 jumper is used together with the USB Wake Up function
in the BIOS. Enable both the jumper and the BIOS setting to activate this function. See the
table below for jumper settings and jumper connections.
Note: The default jumper setting is Enabled. When the "USB Wake Up" function is
enabled, it will be active on all USB ports.
USB Wake Up
Jumper Settings
Jumper Setting Denition
Pins 1-2 Enabled (Default)
Pins 2-3 Disabled
UID-LED
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
+
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
VGA
Intel
i210
LAN2
FAN4
2
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
CPU
1
JD1
OPEN 1st
+
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
SP1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
DIMMD1
FAN1 CPU
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
3
COM2
1. LAN 1 Enable
2. LAN 2 Enable
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
3. USB Wake Up
58
Page 59

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
2.9 LED Indicators
LAN LEDs
Two LAN ports (LAN 1 and LAN 2) are located on the I/O back panel of the motherboard.
Each Ethernet LAN port has two LEDs. The green LED indicates activity, while the other Link
LED may be green, amber, or o to indicate the speed of the connection. Refer to the tables
below for more information.
LAN1/2 Activity LED (Right)
LED State
Color Status Denition
Green Flashing Active
LED Color Denition
Green 100 Mbps
LAN1/2 Link LED (Left)
LED State
Yellow/Amber 1 Gbps
Unit ID LED
A rear UID LED indicator (UID-LED) is located near the UID switch on the I/O back panel.
This UID indicator provides easy identication of a system unit that may need service.
UID LED
LED Indicator
LED Color Denition
Blue: On Unit Identied
1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
COM2
FAN3
1
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
USB 6/7(3.0)
LAN1
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
1. LAN 1/2 LED
2. UID LED
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
AST2500
LED6301
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
MH10
Aspeed
2
UID-LED
Intel
i210
JPL1
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
i210
JPL2
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
CLOSE 1st
CPU
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
OPEN 1st
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
SP1
FAN2
FANA
+
1
JD1
I-SATA1
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
B2
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
I-SATA0
USB 10(3.0)
JSD2
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
JNVME2
LED6904
M.2-PCH
1
JPME2
Intel
C422
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
JL1
FANB
59
Page 60

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
IPMI LAN LEDs
In addition to LAN1 and LAN2, an IPMI LAN is also located on the I/O back panel. The amber
LED on the right indicates activity, while the green LED on the left indicates the speed of the
connection. Refer to the table below for more information.
IPMI LAN
Activity LEDLink LED
Link (left)
IPMI LAN LEDs
Color/State Denition
Green: Solid
Amber: Solid
100 Mbps
1Gbps
Activity (Right) Amber: Blinking Active
M.2 LED
An M.2 LED is located at LED6904 on the motherboard. When LED6904 is blinking, M.2
functions normally. Refer to the table below for more information.
M.2 LED State
LED Color Denition
Green: Blinking Device Working
1
1
1
1
I-SGPIO1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
MH10
M.2-PCH
C422
Intel
2
Aspeed
AST2500
LED6904
UID-LED
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
B2
I-SATA0
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
JUIDB1
Intel
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
Intel
i210
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
VGA
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
DIMMD1
CPU
OPEN 1st
JNVI2C1
SP1
FAN1 CPU
+
1
JD1
1
COM2
1. IPMI LAN LED
2. M.2 LED
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
JOH1
LED7201
JPW1
JF1
1
60
Page 61

Chapter 2: Installation
I-SGPIO1
Onboard Power LED
The Onboard Power LED is located at LED7201 on the motherboard. When this LED is on,
the system is on. Be sure to turn o the system and unplug the power cord before removing
or installing components. Refer to the table below for more information.
Onboard Power LED Indicator
LED Color Denition
System O
O
(power cable not
connected)
Green System On
BMC Heartbeat LED
A BMC Heartbeat LED is located at LED6301 on the motherboard. When LED6301 is blinking,
the BMC is functioning normally. Refer to the table below for more information.
1
1
1
1
JIPMB1
JPG1
JWD1
JSTBY1
JPB1
USB 2/3
USB 4/5
1
USB 8/9(3.0)
1
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
1
JPME2
JBT1
I-SGPIO2
I-SATA7
I-SATA6
I-SATA3
I-SATA4
1
LED6301
I-SATA5
I-SATA2
JL1
2
M.2-PCH
BMC Heartbeat LED Indicator
LED Color Denition
Green:
Blinking
UID-LED
JUIDB1
VGA
Intel
Intel
Aspeed
AST2500
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16
MH10
LED6904
B2
Intel
I-SATA0
C422
JSD2
I-SATA1
FANB
i210
JPL1
JPL2
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8
JRK1
DESIGNED IN USA
+
JSD1
REV:1.01
X11SRM-F
USB 10(3.0)
JTPM1
JNVME3
JNVME1
JNVME0
i210
LAN2
FAN4
1
DIMMB1
DIMMA1
CLOSE 1st
JNVME2
FANA
LAN1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
IPMI CODE
FAN2
USB 6/7(3.0)
IPMI_LAN
CPU
OPEN 1st
SP1
+
1
JD1
USB 0/1
DIMMC1
JNVI2C1
FAN1 CPU
DIMMD1
1
JPUSB1
1
COM1
JPW1
BMC Normal
1
COM2
FAN3
1
NMI
X
PWR
LED
LED
HDD
JPWR2
NIC
1
NIC
2
UID
LED
FAIL
PS
RST
PWR
JF1
ON
JPI2C1
1
JOH1
LED7201
JF1
1. Onboard Power LED
2. BMC Heartbeat LED
61
Page 62

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Chapter 3
Troubleshooting
3.1 Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures to troubleshoot your system. If you have followed all of the
procedures below and still need assistance, refer to the ‘Technical Support Procedures’ and/
or ‘Returning Merchandise for Service’ section(s) in this chapter. Always disconnect the AC
power cord before adding, changing or installing any non hot-swap hardware components.
Before Power On
1. Make sure that there are no short circuits between the motherboard and chassis.
2. Disconnect all ribbon/wire cables from the motherboard, including those for the keyboard
and mouse.
3. Remove all add-on cards.
4. Install the CPU (making sure it is fully seated) and connect the front panel connectors to
the motherboard.
No Power
1. Make sure that there are no short circuits between the motherboard and the chassis.
2. Make sure that the ATX power connectors are properly connected.
3. Check that the 115V/230V switch, if available, on the power supply is properly set.
4. Turn the power switch on and o to test the system, if applicable.
5. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to verify that it still supplies
~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new one.
62
Page 63

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
No Video
1. If the power is on, but you have no video, remove all add-on cards and cables.
2. Use the speaker to determine if any beep codes are present. Refer to Appendix A for
details on beep codes.
3. Remove all memory modules and turn on the system (if the alarm is on, check the
specs of memory modules, reset the memory or try a dierent one).
System Boot Failure
If the system does not display POST (Power-On-Self-Test) or does not respond after the
power is turned on, check the following:
1. Check for any error beep from the motherboard speaker.
• If there is no error beep, try to turn on the system without DIMM modules installed. If there
is still no error beep, replace the motherboard.
• If there are error beeps, clear the CMOS settings by unplugging the power cord and con-
tacting both pads on the CMOS clear jumper (JBT1). Refer to Section 2-8 in Chapter 2.
2. Remove all components from the motherboard, especially the DIMM modules. Make
sure that system power is on and that memory error beeps are activated.
3. Turn on the system with only one DIMM module installed. If the system boots, check for
bad DIMM modules or slots by following the Memory Errors Troubleshooting procedure
in this chapter.
Memory Errors
When a no-memory beep code is issued by the system, check the following:
1. Make sure that the memory modules are compatible with the system and that the
DIMMs are properly and fully installed. (For memory compatibility, refer to the memory
compatibility chart posted on our website at http://www.supermicro.com.)
2. Check if dierent speeds of DIMMs have been installed. It is strongly recommended that
you use the same RAM type and speed for all DIMMs in the system.
3. Make sure that you are using the correct type of ECC DDR4 modules recommended by
the manufacturer.
4. Check for bad DIMM modules or slots by swapping a single module among all memory
slots and check the results.
63
Page 64

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
5. Make sure that all memory modules are fully seated in their slots. Follow the instructions
given in Section 2-4 in Chapter 2.
6. Please follow the instructions given in the DIMM population tables listed in Section 2-4
to install your memory modules.
Losing the System's Setup Conguration
1. Make sure that you are using a high-quality power supply. A poor-quality power supply
may cause the system to lose the CMOS setup information. Refer to Chapter 2 for
details on recommended power supplies.
2. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to verify that it still supplies
~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new one.
3. If the above steps do not x the setup conguration problem, contact your vendor for
repairs.
When the System Becomes Unstable
A. If the system becomes unstable during or after OS installation, check the following:
1. CPU/BIOS support: Make sure that your CPU is supported and that you have the latest
BIOS installed in your system.
2. Memory support: Make sure that the memory modules are supported by testing the
modules using memtest86 or a similar utility.
Note: Refer to the product page on our website at http:\\www.supermicro.com for
memory and CPU support and updates.
3. HDD support: Make sure that all hard disk drives (HDDs) work properly. Replace the
bad HDDs with good ones.
4. System cooling: Check the system cooling to make sure that all heatsink fans and CPU/
system fans, etc., work properly. Check the hardware monitoring settings in the IPMI
to make sure that the CPU and system temperatures are within the normal range. Also
check the front panel Overheat LED and make sure that it is not on.
5. Adequate power supply: Make sure that the power supply provides adequate power to
the system. Make sure that all power connectors are connected. Please refer to our
website for more information on the minimum power requirements.
6. Proper software support: Make sure that the correct drivers are used.
64
Page 65

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
B. If the system becomes unstable before or during OS installation, check the following:
1. Source of installation: Make sure that the devices used for installation are working
properly, including boot devices such as CD/DVD.
2. Cable connection: Check to make sure that all cables are connected and working
properly.
3. Using the minimum conguration for troubleshooting: Remove all unnecessary
components (starting with add-on cards rst), and use the minimum conguration (but
with the CPU and a memory module installed) to identify the trouble areas. Refer to the
steps listed in Section A above for proper troubleshooting procedures.
4. Identifying bad components by isolating them: If necessary, remove a component in
question from the chassis, and test it in isolation to make sure that it works properly.
Replace a bad component with a good one.
5. Check and change one component at a time instead of changing several items at the
same time. This will help isolate and identify the problem.
6. To nd out if a component is good, swap this component with a new one to see if the
system will work properly. If so, then the old component is bad. You can also install the
component in question in another system. If the new system works, the component is
good and the old system has problems.
65
Page 66

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
3.2 Technical Support Procedures
Before contacting Technical Support, please take the following steps. Also, please note that as
a motherboard manufacturer, Supermicro also sells motherboards through its channels, so it
is best to rst check with your distributor or reseller for troubleshooting services. They should
know of any possible problems with the specic system conguration that was sold to you.
1. Please go through the Troubleshooting Procedures and Frequently Asked Questions
(FAQ) sections in this chapter or see the FAQs on our website (http://www.supermicro.
com/FAQ/index.php) before contacting Technical Support.
2. BIOS upgrades can be downloaded from our website (http://www.supermicro.com/
ResourceApps/BIOS_IPMI_Intel.html).
3. If you still cannot resolve the problem, include the following information when contacting
Supermicro for technical support:
• Motherboard model and PCB revision number
• BIOS release date/version (This can be seen on the initial display when your system rst
boots up.)
• System conguration
4. An example of a Technical Support form is on our website at http://www.supermicro.com/
RmaForm/.
• Distributors: For immediate assistance, please have your account number ready when
placing a call to our Technical Support department. We can be reached by email at support@supermicro.com.
66
Page 67

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3.3 Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What type of memory does my motherboard support?
Answer: The motherboard supports DDR4 ECC RDIMM and LRDIMM modules. To enhance
memory performance, do not mix memory modules of dierent speeds and sizes. Please
follow all memory installation instructions given on Section 2-4 in Chapter 2.
Question: How do I update my BIOS?
Answer: It is recommended that you do not upgrade your BIOS if you are not experiencing
any problems with your system. Updated BIOS les are located on our website at http://
www.supermicro.com/ResourceApps/BIOS_IPMI_Intel.html. Please check our BIOS warning
message and the information on how to update your BIOS on our website. Select your
motherboard model and download the BIOS le to your computer. Also, check the current
BIOS revision to make sure that it is newer than your BIOS before downloading. Please
unzip the BIOS le onto a bootable USB device. Run the batch le using the format FLASH.
BAT lename.rom from your bootable USB device to ash the BIOS. Then, your system will
automatically reboot.
Warning: Do not shut down or reset the system while updating the BIOS to prevent possible
system boot failure!
Note: The SPI BIOS chip used on this motherboard cannot be removed. Send your
motherboard back to our RMA Department at Supermicro for repair. For BIOS Recovery
instructions, please refer to the AMI BIOS Recovery Instructions posted at http://www.
supermicro.com/support/manuals/.
67
Page 68

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
3.4 Battery Removal and Installation
Battery Removal
To remove the onboard battery, follow the steps below:
1. Power o your system and unplug your power cable.
2. Locate the onboard battery as shown below.
3. Using a tool such as a pen or a small screwdriver, push the battery lock outwards to
unlock it. Once unlocked, the battery will pop out from the holder.
4. Remove the battery.
Proper Battery Disposal
Warning: Please handle used batteries carefully. Do not damage the battery in any way; a
damaged battery may release hazardous materials into the environment. Do not discard a used
battery in the garbage or a public landll. Please comply with the regulations set up by your
local hazardous waste management agency to dispose of your used battery properly.
Battery Installation
1. To install an onboard battery, follow steps 1 and 2 above and continue below:
2. Identify the battery's polarity. The positive (+) side should be facing up.
3. Insert the battery into the battery holder and push it down until you hear a click to
ensure that the battery is securely locked.
Warning: When replacing a battery, be sure to only replace it with the same type.
OR
68
Page 69

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3.5 Returning Merchandise for Service
A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is required before any
warranty service will be rendered. You can obtain service by calling your vendor for a
Returned Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number. When returning the motherboard to
the manufacturer, the RMA number should be prominently displayed on the outside of the
shipping carton, and the shipping package is mailed prepaid or hand-carried. Shipping and
handling charges will be applied for all orders that must be mailed when service is complete.
For faster service, you can also request a RMA authorization online (http://www.supermicro.
com/RmaForm/).
This warranty only covers normal consumer use and does not cover damages incurred in
shipping or from failure due to the alternation, misuse, abuse or improper maintenance of
products.
During the warranty period, contact your distributor rst for any product problems.
69
Page 70

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Chapter 4
UEFI BIOS
4.1 Introduction
This chapter describes the AMIBIOS™ Setup utility for the motherboard. The BIOS is stored
on a chip and can be easily upgraded using a ash program.
Note: Due to periodic changes to the BIOS, some settings may have been added
or deleted and might not yet be recorded in this manual. Please refer to the Manual
Download area of our website for any changes to the BIOS that may not be reected
in this manual.
Starting the Setup Utility
To enter the BIOS Setup Utility, hit the <Delete> key while the system is booting-up. (In
most cases, the <Delete> key is used to invoke the BIOS setup screen. There are a few
cases when other keys are used, such as <F1>, <F2>, etc.) Each main BIOS menu option
is described in this manual.
The Main BIOS screen has two main frames. The left frame displays all the options that can
be congured. “Grayed-out” options cannot be congured. The right frame displays the key
legend. Above the key legend is an area reserved for a text message. When an option is
selected in the left frame, it is highlighted in white. Often a text message will accompany it.
(Note that the BIOS has default text messages built in. We retain the option to include, omit,
or change any of these text messages.) Settings printed in Bold are the default values.
A " " indicates a submenu. Highlighting such an item and pressing the <Enter> key will
open the list of settings within that submenu.
The BIOS setup utility uses a key-based navigation system called hot keys. Most of these
hot keys (<F1>, <F2>, <F3>, <Enter>, <ESC>, <Arrow> keys, etc.) can be used at any time
during the setup navigation process.
70
Page 71

Chapter 4: BIOS
4.2 Main Setup
When you rst enter the AMI BIOS setup utility, you will enter the Main setup screen. You
can always return to this screen by selecting the Main tab at the top of the screen. The Main
setup screen is shown below and the following items will be displayed:
System Date/System Time
Use this option to change the system date and time. Highlight System Date or System Time
using the arrow keys. Enter new values using the keyboard. Press the <Tab> key or the arrow
keys to move between elds. The date must be entered in MM/DD/YYYY format. The time
is entered in HH:MM:SS format.
Note: The time is in the 24-hour format. For example, 5:30 P.M. appears as 17:30:00.
The date's default value is the BIOS build date after RTC reset.
Supermicro X11SRM-VF
BIOS Version
This item displays the version of the BIOS ROM used in the system.
Build Date
This item displays the date of when the BIOS ROM version used in the system was built.
Memory Information
Total Memory
This item displays the total size of memory available in the system.
71
Page 72

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
4.3 Advanced Setup Congurations
Use the arrow keys to select the Advanced menu and press <Enter> to access the submenu
items:
Warning: Take caution when changing the Advanced settings. An incorrect value, a very high
DRAM frequency, or an incorrect DRAM timing setting may make the system unstable. When
this occurs, revert to default manufacturer settings.
PCH-FW Conguration
The following rmware information will display:
• ME Firmware Version
• ME Firmware Mode
• ME Firmware SKU
• ME File System Integrity Value
• ME Firmware Status 1
• ME Firmware Status 2
72
Page 73

Chapter 4: BIOS
ME FW Image Re-Flash
Use this feature to update the Management Engine (ME) rmware. The options are Enabled
and Disabled.
CPU Conguration
The following CPU information will display:
• Processor BSP Revision
• Processor ID
• Processor Frequency
• Processor Max Ratio
• Processor Min Ratio
• Microcode Revision
• L1 Cache RAM
• L2 Cache RAM
• L3 Cache RAM
• Processor 0 Version
Hyper-Threading (ALL) (Available when supported by the CPU)
Select Enable to support Intel Hyper-threading Technology to enhance CPU performance.
The options are Disable and Enable.
Max CPUID Value Limit
This feature allows the user to set the maximum CPU ID value. Enable this function to boot
the legacy operating systems that cannot support processors with extended CPUID functions.
The options are Disable and Enable.
Execute Disable Bit (Available if supported by the OS & the CPU)
Use this feature to enable the Execute Disable Bit, which will allow the processor to designate
areas in the system memory where an application code can execute and where it cannot, thus
preventing a worm or virus from ooding illegal codes to overwhelm the processor or damage
the system during an attack. The options are Disable and Enable. (Refer to the Intel® and
Microsoft® websites for more information.)
73
Page 74

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Intel (VMX) Virtualization Technology
Select Enable to support Intel Virtualization Technology, which will allow one platform to
run multiple operating systems and applications in independent partitions, creating multiple
"virtual" systems in one physical computer. The options are Disable and Enable.
Note: If a change is made to this setting, you will need to reboot the system for the
change to take eect. Refer to Intel’s website for detailed information.
PPIN Control
Select Unlock/Enable to use the Protected Processor Inventory Number (PPIN) in the system.
The options are Unlock/Disable and Unlock/Enable.
Hardware Prefetcher (Available when supported by the CPU)
If set to Enable, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of data and instructions from
the main memory to the L2 cache to improve CPU performance. The options are Disable
and Enable.
Adjacent Cache Prefetch (Available when supported by the CPU)
The CPU prefetches the cache line for 64 bytes if this feature is set to Disabled. The CPU
prefetches both cache lines for 128 bytes as comprised if this feature is set to Enable. The
options are Enable and Disable.
DCU Streamer Prefetcher (Available when supported by the CPU)
Select Enable to enable the DCU (Data Cache Unit) Streamer Prefetcher, which will stream
and prefetch data and send it to the Level 1 data cache to improve data processing and
system performance. The options are Disable and Enable.
DCU IP Prefetcher (Available when supported by the CPU)
Select Enable for DCU (Data Cache Unit) IP Prefetcher support, which will prefetch IP
addresses to improve network connectivity and system performance. The options are Enable
and Disable.
LLC Prefetch
If set to Enable, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of data and instructions from
the main memory to the L3 cache to improve CPU performance. The options are Disable
and Enable.
DCU Mode
Use this feature to set the data prefetching mode. A write of "1" selects the DCU mode as
16KB 4-way with ECC. The options are 32KB 8Way Without ECC and 16KB 4Way With ECC.
74
Page 75

Chapter 4: BIOS
Extended APIC
Select Enable to activate Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) support. The
options are Disable and Enable.
AES-NI
Select Enable to use the Intel Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) New Instructions (NI) to
ensure data security. The options are Disable and Enable.
APIC Physical Mode
Use this feature to enable the APIC physical destination mode. The options are Disable and
Enable.
Advanced Power Management Conguration
CPU P State Control
This feature allows the user to congure the following CPU power settings:
SpeedStep (Pstates)
Intel SpeedStep Technology allows the system to automatically adjust processor voltage
and core frequency to reduce power consumption and heat dissipation. The options are
Disable and Enable.
EIST PSD Funtion
This feature allows the user to choose between Hardware and Software to control the
processor's frequency and performance (P-state). In HW_ALL mode, the processor
hardware is responsible for coordinating the P-state, and the OS is responsible for keeping the P-state request up to date on all Logical Processors. In SW_ALL mode, the OS
Power Manager is responsible for coordinating the P-state and must initiate the transition
on all Logical Processors. In SW_ANY mode, the OS Power Manager is responsible for
coordinating the P-state and may initiate the transition on any Logical Processors. The
options are HW_ALL, SW_ALL, and SW_ANY.
Turbo Mode
This feature will enable dynamic control of the processor, allowing it to run above stock
frequency. The options are Disable and Enable.
75
Page 76

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Hardware PM State Control
Hardware P-States
This setting allows the user to select between OS and hardware-controlled P-states.
Selecting Native Mode allows the OS to choose a P-state. Selecting Out of Band Mode
allows the hardware to autonomously choose a P-state without OS guidance. Selecting
Native Mode with No Legacy Support functions as Native Mode with no support for older
hardware. The options are Disable, Native Mode, Out of Band Mode, and Native Mode
with No Legacy Support.
CPU C State Control
Autonomous Core C-State
Enabling this setting allows the hardware to autonomously choose to enter a C-state
based on power consumption and clock speed. The options are Disable and Enable.
CPU C6 Report
Select Enable to allow the BIOS to report the CPU C6 State (ACPI C3) to the operating
system. During the CPU C6 State, the power to all cache is turned o. The options are
Disable, Enable, and Auto.
Enhanced Halt State (C1E)
Select Enable to use Enhanced Halt State technology, which will signicantly reduce the
CPU's power consumption by reducing its clock cycle and voltage during a Halt state.
The options are Disable and Enable.
Package C State Control
Package C State
This feature allows the user to set the limit on the C State package register. The options
are C0/C1 State, C2 State, C6 (Non Retention) State, C6 (Retention) State, No Limit,
and Auto.
Chipset Conguration
Warning: Setting the wrong values in the following features may cause the system to malfunction.
North Bridge
This feature allows the user to congure the following North Bridge settings.
76
Page 77

Chapter 4: BIOS
Memory Conguration
Enforce POR
Select POR (Plan of Record) to enforce POR restrictions on DDR4 frequency and voltage programming. The options are Auto, POR and Disable.
Memory Frequency
Use this feature to set the maximum memory frequency for onboard memory modules.
The options are Auto, 1066, 1333, 1666, 1866, 2133, 2666, and 2933.
Custom Refresh Enable
Use this feature to enable a custom memory controller refresh rate. The options are
Disable and Enable.
MC BGF Threshold
Use the HA to MC BGF threshold feature to schedule MC requests in bypass condition.
The default value is 0.
DLL Reset Test
Use this feature to set the number of loops to execute the Dynamic Link Library (DLL)
reset test. The test will execute the Rank Margin Test (RMT) for the provided number of
loops without DLL resets. Then it will execute RMT for the same number of loops with
DLL resets. The default value is 0.
Memory Topology
This item displays the information of onboard memory modules as detected by the
BIOS.
Memory RAS Conguration
Static Virtual Lockstep Mode
Select Enable to run the system's memory channels in lockstep mode to minimize
memory access latency. The options are Disable and Enable.
Mirror Mode
This feature allows memory to be mirrored between two channels, providing 100%
redundancy and consequently reducing the memory capacity by half. The options are
Disable, Mirror Mode 1LM, and Mirror Mode 2LM.
77
Page 78

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
ADDDC Sparing
Adaptive Double Device Data Correction (ADDDC) Sparing detects when the predetermined threshold for correctable errors is reached, copying the contents of the failing
DIMM to spare memory. The failing DIMM or memory rank will then be disabled. The
options are Disable and Enable.
Patrol Scrub
Patrol Scrub is a process that allows the CPU to correct correctable memory errors
detected on a memory module and send the correction to the requestor (the original
source). When this item is set to Enable, the IO hub will read and write back one cache
line every 16K cycles if there is no delay caused by internal processing. By using this
method, roughly 64 GB of memory behind the IO hub will be scrubbed every day. The
options are Disable and Enable.
Patrol Scrub Interval
This feature allows the user to decide how many hours the system should wait before
the next complete patrol scrub is performed. Use the keyboard to enter a value from
0-24. The default setting is 24.
Patrol Scrub Address Mode
Use this feature to select the Patrol Scrub Address mode. The options are Reverse
Address and System Physical Address.
IIO Conguration
EV DFX Features
When this feature is set to Enable, the EV_DFX Lock Bits that are located on a processor will always remain clear during electric tuning. The options are Disable and Enable.
Isoc Mode
Isochronous (Isoc) mode allows time-sensitive processes to be given priority. The options
are Disable, Enable, and Auto.
CPU Conguration
IOU0 (II0 PCIe Br1) / IOU1 (II0 PCIe Br2) / IOU2 (II0 PCIe Br3)
This item congures the PCI-E port Bifuraction setting for a PCI-E port specied by the
user. The options are x4x4x4x4, x4x4x8, x8x4x4, x8x8, x16, and Auto.
78
Page 79

Chapter 4: BIOS
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16 / CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8 / CPU SLOT7
PCI-E 3.0 x 8 / JNVME0 / JNVME1 / JNVME2 / JNVME3
Link Speed
Use this item to select the link speed for the PCI-E port specied by the user. The
options are Auto, Gen 1 (2.5 GT/s), Gen 2 (5 GT/s), and Gen 3 (8 GT/s).
PCI-E Port Max Payload Size
Selecting Auto for this feature will enable the motherboard to automatically detect
the maximum Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) size for the connected PCI-E device,
allowing for maximum I/O eciency. Selecting 128B or 256B will designate maximum
packet size of 128 or 256. If possible, select max payload size to 256B. The options
are 128B, 256B, and Auto.
IOAT Conguration
Disable TPH
Transparent Huge Pages (TPH) is a Linux memory management system that enables
communication in larger blocks (pages). Enabling this feature will increase performance. The options are No and Yes.
Prioritize TPH
Use this feature to enable Prioritize TPH support. The options are Enable and Disable.
Relaxed Ordering
Select Enable to enable Relaxed Ordering support, which will allow certain transactions to violate the strict-ordering rules of PCI bus for a transaction to be completed
prior to other transactions that have already been enqueued. The options are Disable
and Enable.
Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d)
Intel® VT for Directed I/O (VT-d)
Select Enable to use Intel Virtualization Technology for Direct I/O VT-d support by
reporting the I/O device assignments to the VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor) through
the DMAR ACPI tables. This feature oers fully protected I/O resource sharing across
Intel platforms, providing greater reliability, security and availability in networking and
data sharing. The options are Enable and Disable.
79
Page 80

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Interrupt Remapping
Use this feature to enable Interrupt Remapping support, which detects and controls
external interrupt requests. The options are Enable and Disable.
PassThrough DMA
Use this feature to allow devices such as network cards to access the system memory
without using a processor. Select Enable to use the Non-Isoch VT_D Engine Pass
Through Direct Memory Access (DMA) support. The options are Enable and Disable.
ATS
Use this feature to enable Non-Isoch VT-d Engine Address Translation Services (ATS)
support. ATS translates virtual addresses to physical addresses. The options are En-
able and Disable.
Posted Interrupt
Use this feature to enable VT_D Posted Interrupt. The options are Enable and Disable.
Coherency Support (Non-Isoch)
Use this feature to maintain setting coherency between processors or other devices.
Select Enable for the Non-Isoch VT-d engine to pass through DMA to enhance system
performance. The options are Enable and Disable.
Intel® VMD Technology
Note: After you’ve enabled VMD on a PCI-E slot of your choice, this PCI-E slot
will be dedicated for NVMe storage devices use only, and it will no longer support PCI-E devices of other functionalities. To re-activate this slot for PCI-E use,
please disable VMD.
Intel® VMD for Volume Management Device on CPU
VMD Cong for PStack0
Intel® VMD for Volume Management
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this stack.
The options are Disable and Enable.
*If the item above is set to Enable, the following items will become available
for conguration:
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x 16 VMD (Available when the device is detected by
80
Page 81

Chapter 4: BIOS
the system)
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this spe-
cic root port. The options are Disable and Enable.
Hot Plug Capable (Available when the device is detected by the system)
Use this feature to enable hot plug support for PCIe root ports 1A~1D. The options
are Disable and Enable.
VMD Cong for PStack1
Intel® VMD for Volume Management
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this stack.
The options are Disable and Enable.
*If the item above is set to Enable, the following items will become available
for conguration:
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x 8 VMD / CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x 8 VMD (Available
when the device is detected by the system)
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this spe-
cic root port. The options are Disable and Enable.
Hot Plug Capable (Available when the device is detected by the system)
Use this feature to enable hot plug support for PCIe root ports 2A~2D. The options
are Disable and Enable.
VMD Cong for PStack2
Intel® VMD for Volume Management
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this stack.
The options are Disable and Enable.
*If the item above is set to Enable, the following items will become available
for conguration:
JNVME0 VMD / JNVME1 VMD / JNVME2 VMD / JNVME3 VMD (Available when
the device is detected by the system)
Select Enable to use the Intel Volume Management Device Technology for this spe-
cic root port. The options are Disable and Enable.
Hot Plug Capable (Available when the device is detected by the system)
Use this feature to enable hot plug support for PCIe root ports 3A~3D. The options
are Disable and Enable.
81
Page 82

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
PCI-E Completion Timeout Disable
Use this feature to enable PCI-E Completion Timeout support for electric tuning. The
options are Yes, No, and Per-Port.
South Bridge
The following USB information will display:
• USB Module Version
• USB Devices
Legacy USB Support
This feature enables support for USB 2.0 and older. The options are Enabled, Disabled,
and Auto.
XHCI Hand-o
When this feature is disabled, the motherboard will not support USB 3.0. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
Port 60/64 Emulation
This feature allows legacy I/O support for USB devices like mice and keyboards. The options
are Enabled and Disabled.
RSA Support
Use this feature to enable Rack Scale Architecture (RSA) support. The options are Disabled
and Enabled.
SATA and RST Conguration
When this submenu is selected, the AMI BIOS automatically detects the presence of the
SATA devices that are supported by the Intel PCH chipset and displays the following items:
SATA Controller(s)
This item enables or disables the onboard SATA controller supported by the Intel PCH chipset.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Congure SATA as
Select AHCI to congure a SATA drive specied by the user as an AHCI drive. Select RAID
to congure a SATA drive specied by the user as a RAID drive. The options are AHCI and
RAID.
82
Page 83

Chapter 4: BIOS
Aggressive Link Power Management
When this item is enabled, the SATA AHCI controller manages the power usage of the SATA
link. The controller will put the link in a low power mode during extended periods of I/O inactivity, and will return the link to an active state when I/O activity resumes. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Storage Option ROM/UEFI Driver
This feature controls which option ROM to execute for the storage device. The options are
Disabled, EFI, and Legacy.
Serial ATA Port 0~7
This item displays the information detected on the installed SATA drive on the particular SATA
port.
• Model number of drive and capacity
• Software Preserve Support
Port 0~7 Hot Plug
Set this item to Enable for hot plug support, which will allow the user to replace a SATA
drive without shutting down the system. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Port 0~7 Spin Up Device
On an edge detect from 0 to 1, set this item to allow the PCH to initialize the device. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
Port 0~7 SATA Device Type
Use this item to specify if the SATA port specied by the user should be connected to a Solid
State drive or a Hard Disk Drive. The options are Hard Disk Drive and Solid State Drive.
Trusted Computing
The X11SRM-F/-VF supports TPM 1.2 and 2.0. The following Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
information will display if a TPM 2.0 module is detected:
• Vendor Name
• Firmware Version
Security Device Support
If this feature and the TPM jumper on the motherboard are both set to Enabled, onboard
security devices will be enabled for TPM (Trusted Platform Module) support to enhance data
integrity and network security. Please reboot the system for a change on this setting to take
eect. The options are Disable and Enable.
83
Page 84

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
• Active PCR Bank
• SHA256 PCR Bank
*If the item above is set to Enable, "SHA-1 PCR Bank" and "SHA256 PCR Bank" will
become available for conguration:
SHA-1 PCR Bank
Use this item to disable or enable the SHA-1 Platform Conguration Register (PCR) bank for
the installed TPM device. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
SHA256 PCR Bank
Use this item to disable or enable the SHA256 Platform Conguration Register (PCR) bank
for the installed TPM device. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Pending Operation
Use this item to schedule a TPM-related operation to be performed by a security device for
system data integrity. Your system will reboot to carry out a pending TPM operation. The
options are None and TPM Clear.
Platform Hierarchy
Use this item to disable or enable platform hierarchy for platform protection. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Storage Hierarchy
Use this item to disable or enable storage hieararchy for cryptographic protection. The options
are Disabled and Enabled.
Endorsement Hierarchy
Use this item to disable or enable endorsement hierarchy for privacy control. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
PH Randomization
Use this item to disable or enable Platform Hiearchy (PH) Randomization. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
BIOS-Based TPM Provision Support
Use this feature to enable TPM Provision support. Enabling this feature will lock your TPM.
Once locked, the NV indexes will not be able to be deleted. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
TXT Support
Intel Trusted Execution Technology (TXT) helps protect against software-based attacks and
ensures protection, condentiality, and integrity of data stored or created on the system. Use
this feature to enable or disable TXT Suppport. The options are Disable and Enable.
84
Page 85

Chapter 4: BIOS
ACPI Settings
WHEA Support
Select Enabled to support the Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) platform and
provide a common infrastructure for the system to handle hardware errors within the Windows
OS environment to reduce system crashes and to enhance system recovery and health
monitoring. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
High Precision Event Timer
Select Enabled to activate the High Precision Event Timer (HPET) that produces periodic
interrupts at a much higher frequency than a Real-time Clock (RTC) does in synchronizing
multimedia streams, providing smooth playback and reducing the dependency on other
timestamp calculation devices, such as an x86 RDTSC Instruction embedded in the CPU.
The High Performance Event Timer is used to replace the 8254 Programmable Interval Timer.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Native PCIE Enable
Use this feature to enable PCI-E Native Hot Plug/Power Management Events controls. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
Native ASPM
Use this feature to select which system will control the Active State Power Management
(ASPM). Select Eanbled for OS-controlled ASPM. Select Disabled for BIOS-controlled ASPM.
The options are Auto, Enabled, and Disabled.
Numa
This setting enables or disables Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA), a feature that improves memory-to-processor communication and performance. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Boot Feature
Fast Boot
Use this feature to reduce boot time by initializing a minimal set of devices required to launch
an active boot option. Enabling this feature has no eect on BBS boot options. The options
are Disabled and Enabled.
Quiet Boot
Use this feature to select the screen display between the POST messages and the OEM logo
upon bootup. Select Disabled to display the POST messages. Select Enabled to display the
OEM logo instead of the normal POST messages. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
85
Page 86

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Bootup Num-Lock
Use this feature to set the Power-on state for the <Numlock> key. The options are On and O.
Option ROM Messages
Use this feature to set the display mode for the Option ROM. Select Keep Current to display
the current AddOn ROM setting. Select Force BIOS to use the Option ROM display set by
the system BIOS. The options are Force BIOS and Keep Current.
INT19 (Interrupt 19) Trap Response
Interrupt 19 is the software interrupt that handles the boot disk function. When this item is
set to Immediate, the ROM BIOS of the host adaptors will "capture" Interrupt 19 at bootup
immediately and allow the drives that are attached to these host adaptors to function as
bootable disks. If this item is set to Postponed, the ROM BIOS of the host adaptors will not
capture Interrupt 19 immediately and allow the drives attached to these adaptors to function
as bootable devices at bootup. The options are Immediate and Postponed.
Port 61h Bit-4 Emulation
Select Enabled to enable the emulation of Port 61h bit-4 toggling in SMM (System Management
Mode). The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Wait For "F1" If Error
Use this feature to force the system to wait until the "F1" key is pressed if an error occurs.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Re-try Boot
If this item is enabled, the BIOS will automatically reboot the system from a specied boot
device after its initial boot failure. The options are Disabled, Legacy Boot, and EFI Boot.
Watch Dog Function
If enabled, the Watch Dog Timer will allow the system to reset or generate NMI based on
jumper settings when it is expired for more than ve minutes. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Power Button Function
This feature controls how the system shuts down when the power button is pressed. Select 4
Seconds Override for the user to power o the system after pressing and holding the power
button for 4 seconds or longer. Select Instant O to instantly power o the system as soon
as the user presses the power button. The options are Instant O and 4 Seconds Override.
86
Page 87

Chapter 4: BIOS
AC Loss Policy Depend On
Use this feature to set the power state after a power outage. Select Stay Off for
the system power to remain o after a power loss. Select Power On for the system
power to be turned on after a power loss. Select Last State to allow the system to
resume its last power state before a power loss. The options are Stay O, Power On,
and Last State.
EuP Support
Use this feature to enable Energy Using Product (EuP) support to maintain the system's
power consumption. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Super IO Conguration
The following Super IO information will display:
• Super IO Chip AST2500
Serial Port 1 Conguration
This submenu allows the user to congure the settings of Serial Port 1.
Serial Port 1
Select Enabled to enable the selected onboard serial port. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Device Settings
This item displays the status of a serial part specied by the user.
Change Settings
This feature species the base I/O port address and the Interrupt Request address of a
serial port specied by the user. Select Auto to allow the BIOS to automatically assign the
base I/O and IRQ address.
The options for Serial Port 1 are Auto, (IO=3F8h; IRQ=4;), (IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
9, 10, 11, 12;), (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;), (IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
9, 10, 11, 12;), and (IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;).
Serial Port 2 Conguration
This submenu allows the user to congure the settings of Serial Port 2.
Serial Port 2
Select Enabled to enable the selected onboard serial port. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
87
Page 88

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Device Settings
This item displays the status of a serial part specied by the user.
Change Settings
This feature species the base I/O port address and the Interrupt Request address of a
serial port specied by the user. Select Auto to allow the BIOS to automatically assign the
base I/O and IRQ address.
The options for Serial Port 1 are Auto, (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3;), (IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
9, 10, 11, 12;), (IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;), (IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
9, 10, 11, 12;), and (IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;).
Serial Port 2 Attribute
Select SOL to use COM Port 2 as a Serial Over LAN (SOL) port for console redirection.
The options are SOL and COM.
Serial Port Console Redirection
COM1 Console Redirection
Select Enabled to enable console redirection support for a serial port specied by the user.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following items will become available for
conguration:
COM1 Console Redirection Settings
Use this feature to specify how the host computer will exchange data with the client
computer, which is the remote computer used by the user.
COM1 Terminal Type
This feature allows the user to select the target terminal emulation type for Console
Redirection. Select VT100 to use the ASCII Character set. Select VT100+ to add color
and function key support. Select ANSI to use the Extended ASCII Character Set. Select
VT-UTF8 to use UTF8 encoding to map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The
options are VT100, VT100+, VT-UTF8, and ANSI.
COM1 Bits Per Second
Use this feature to set the transmission speed for a serial port used in Console Redirection.
Make sure that the same speed is used in the host computer and the client computer. A
lower transmission speed may be required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600,
19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200 (bits per second).
88
Page 89

Chapter 4: BIOS
COM1 Data Bits
Use this feature to set the data transmission size for Console Redirection. The options are
7 Bits and 8 Bits.
COM1 Parity
A parity bit can be sent along with regular data bits to detect data transmission errors. Select
Even if the parity bit is set to 0, and the number of 1's in data bits is even. Select Odd if
the parity bit is set to 0, and the number of 1's in data bits is odd. Select None if you do
not want to send a parity bit with your data bits in transmission. Select Mark to add a mark
as a parity bit to be sent along with the data bits. Select Space to add a Space as a parity
bit to be sent with your data bits. The options are None, Even, Odd, Mark, and Space.
COM1 Stop Bits
A stop bit indicates the end of a serial data packet. Select 1 Stop Bit for standard serial
data communication. Select 2 Stop Bits if slower devices are used. The options are 1 and 2.
COM1 Flow Control
Use this feature to set the ow control for Console Redirection to prevent data loss caused
by buer overow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop sending data when the receiving buer
is full. Send a "Start" signal to start sending data when the receiving buer is empty. The
options are None and Hardware RTS/CTS.
COM1 VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
Select Enabled to enable VT-UTF8 Combination Key support for ANSI/VT100 terminals.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
COM1 Recorder Mode
Select Enabled to capture the data displayed on a terminal and send it as text messages
to a remote server. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
COM1 Resolution 100x31
Select Enabled for extended-terminal resolution support. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
COM1 Legacy OS Redirection Resolution
Use this feature to select the number of rows and columns used in Console Redirection
for legacy OS support. The options are 80x24 and 80x25.
COM1 Putty KeyPad
This feature selects the settings for Function Keys and KeyPad used for Putty, which
is a terminal emulator designed for the Windows OS. The options are VT100, LINUX,
XTERMR6, SC0, ESCN, and VT400.
89
Page 90

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
COM1 Redirection After BIOS POST
Use this feature to enable or disable legacy console redirection after BIOS POST. When
set to Bootloader, legacy console redirection is disabled before booting the OS. When set
to Always Enable, legacy console redirection remains enabled when booting the OS. The
options are Always Enable and Bootloader.
COM2/SOL Console Redirection
Select Enabled to use the SOL port for Console Redirection. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following items will become available for
conguration:
COM2/SOL Console Redirection Settings
Use this feature to specify how the host computer will exchange data with the client
computer, which is the remote computer used by the user.
COM2 Terminal Type
Use this feature to select the target terminal emulation type for Console Redirection.
Select VT100 to use the ASCII Character set. Select VT100+ to add color and function key
support. Select ANSI to use the Extended ASCII Character Set. Select VT-UTF8 to use
UTF8 encoding to map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The options are ANSI,
VT100, VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
COM2 Bits Per Second
Use this feature to set the transmission speed for a serial port used in Console Redirection.
Make sure that the same speed is used in the host computer and the client computer. A
lower transmission speed may be required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600,
19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200 (bits per second).
COM2 Data Bits
Use this feature to set the data transmission size for Console Redirection. The options are
7 Bits and 8 Bits.
COM2 Parity
A parity bit can be sent along with regular data bits to detect data transmission errors. Select
Even if the parity bit is set to 0, and the number of 1's in data bits is even. Select Odd if
the parity bit is set to 0, and the number of 1's in data bits is odd. Select None if you do
not want to send a parity bit with your data bits in transmission. Select Mark to add a mark
as a parity bit to be sent along with the data bits. Select Space to add a Space as a parity
bit to be sent with your data bits. The options are None, Even, Odd, Mark, and Space.
90
Page 91

Chapter 4: BIOS
COM2 Stop Bits
A stop bit indicates the end of a serial data packet. Select 1 Stop Bit for standard serial
data communication. Select 2 Stop Bits if slower devices are used. The options are 1 and 2.
COM2 Flow Control
Use this feature to set the ow control for Console Redirection to prevent data loss caused
by buer overow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop sending data when the receiving buer
is full. Send a "Start" signal to start sending data when the receiving buer is empty. The
options are None and Hardware RTS/CTS.
COM2 VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
Select Enabled to enable VT-UTF8 Combination Key support for ANSI/VT100 terminals.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
COM2 Recorder Mode
Select Enabled to capture the data displayed on a terminal and send it as text messages
to a remote server. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
COM2 Resolution 100x31
Select Enabled for extended-terminal resolution support. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
COM2 Legacy OS Redirection Resolution
Use this feature to select the number of rows and columns used in Console Redirection
for legacy OS support. The options are 80x24 and 80x25.
COM2 Putty KeyPad
This feature selects Function Keys and KeyPad settings for Putty, which is a terminal
emulator designed for the Windows OS. The options are VT100, LINUX, XTERMR6, SCO,
ESCN, and VT400.
COM2 Redirection After BIOS POST
Use this feature to enable or disable legacy Console Redirection after BIOS POST. When
set to Bootloader, legacy Console Redirection is disabled before booting the OS. When
set to Always Enable, legacy Console Redirection remains enabled when booting the OS.
The options are Always Enable and Bootloader.
Legacy Console Redirection
Legacy Serial Redirection Port
Use this feature to select a COM port to display redirection of Legacy OS and Legacy OPROM
messages. The options are COM1 and COM2/SOL.
91
Page 92

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Serial Port for Out-of-Band Management / Windows Emergency Management
Services (EMS) Console Redirection
Select Enabled to use a COM port selected by the user for EMS Console Redirection. The
options are Enabled and Disabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following items will become available for
conguration:
EMS Console Redirection Settings
This feature allows the user to specify how the host computer will exchange data with the
client computer, which is the remote computer used by the user.
Out-of-Band Mgmt Port
The feature selects a serial port in a client server to be used by the Microsoft Windows
Emergency Management Services (EMS) to communicate with a remote host server. The
options are COM1 and COM2/SOL.
Terminal Type
Use this feature to select the target terminal emulation type for Console Redirection.
Select VT100 to use the ASCII character set. Select VT100+ to add color and function
key support. Select ANSI to use the extended ASCII character set. Select VT-UTF8 to use
UTF8 encoding to map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The options are VT100,
VT100+, VT-UTF8, and ANSI.
Bits Per Second
This item sets the transmission speed for a serial port used in Console Redirection. Make
sure that the same speed is used in the host computer and the client computer. A lower
transmission speed may be required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600, 19200,
57600, and 115200 (bits per second).
Flow Control
Use this item to set the ow control for Console Redirection to prevent data loss caused
by buer overow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop sending data when the receiving buer
is full. Send a "Start" signal to start sending data when the receiving buer is empty. The
options are None, Hardware RTS/CTS, and Software Xon/Xo.
Data Bits, Parity, Stop Bits
92
Page 93

Chapter 4: BIOS
PCIe/PCI/PnP Conguration
Option ROM Execution
SR-IOV Support
Use this feature to enable or disable Single Root IO Virtualization support. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
MMCFG Size
Use this item to select the MMCFG size. The options are 64M, 128M, 256M, 512M, 1G, and
2G.
MMIOHBase
Use this item to select the base memory size according to memory-address mapping for the
IO hub. The options are 56T, 40T, 24T, 16T, 4T, and 1T.
MMIO High Granularity Size
Use this item to select the high memory size according to memory-address mapping for the
IO hub. The options are 1G, 4G, 16G, 64G, 256G, and 1024G.
Above 4G Decoding (Available if the system supports 64-bit PCI decoding)
Select Enabled to decode a PCI device that supports 64-bit in the space above 4G Address.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Onboard Video Option ROM
Use this item to select the Onboard Video Option ROM type. The options are Legacy and
UEFI.
PCIe/PCI/PnP Conguration
CPU SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 x8 OPROM
Use this feature to select which rmware type to be loaded for the add-on card in this slot.
The options are Disabled, Legacy, and UEFI.
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x16 OPROM
Use this feature to select which rmware type to be loaded for the add-on card in this slot.
The options are Disabled, Legacy, and UEFI.
CPU SLOT7 PCI-E 3.0 x8 OPROM
Use this feature to select which rmware type to be loaded for the add-on card in this slot.
The options are Disabled, Legacy, and UEFI.
93
Page 94

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
Onboard LAN Option ROM Type
Use this feature to select which rmware type to be loaded for onboard LAN ports. The
options are Legacy and UEFI.
Onboard LAN1 Option ROM
Use this feature to select which rmware function to be loaded for LAN Port 1. The options
are Disabled, PXE, and ISCSI.
Onboard LAN2 Option ROM
Use this feature to select which rmware function to be loaded for LAN Port 2. The options
are Disabled and PXE.
Network Stack
Select Enabled to enable PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) or UEFI (Unied Extensible
Firmware Interface) for network stack support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Ipv4 PXE Support
Select Enabled to enable IPv4 PXE boot support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Ipv4 HTTP Support
Select Enabled to enable IPv4 HTTP boot support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Ipv6 PXE Support
Select Enabled to enable IPv6 PXE boot support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Ipv6 HTTP Support
Select Enabled to enable IPv6 HTTP boot support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
PXE Boot Wait Time
Use this option to specify the wait time to press the ESC key to abort the PXE boot. Press
"+" or "-" on your keyboard to change the value. The default setting is 0.
Media Detect Count
Use this option to specify the number of times media will be checked. Press "+" or "-" on your
keyboard to change the value. The default setting is 1.
94
Page 95

4.4 Event Logs
Use this feature to congure Event Log settings.
Chapter 4: BIOS
Change SMBIOS Event Log Settings
Enabling/Disabling Options
SMBIOS Event Log
Change this item to enable or disable all features of the SMBIOS Event Logging during system
boot. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Erasing Settings
Erase Event Log
If No is selected, data stored in the event log will not be erased. Select Yes, Next Reset, data
in the event log will be erased upon next system reboot. Select Yes, Every Reset, data in
the event log will be erased upon every system reboot. The options are No, Yes, Next reset,
and Yes, Every reset.
When Log is Full
Select Erase Immediately for all messages to be automatically erased from the event log
when the event log memory is full. The options are Do Nothing and Erase Immediately.
95
Page 96

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
SMBIOS Event Log Standard Settings
Log System Boot Event
This option toggles the System Boot Event logging to enabled or disabled. The options are
Enabled and Disabled.
MECI
The Multiple Event Count Increment (MECI) counter counts the number of occurences that
a duplicate event must happen before the MECI counter is incremented. This is a numeric
value. The default value is 1.
METW
The Multiple Event Time Window (METW) denes the number of minutes that must pass
between duplicate log events before MECI is incremented. This is in minutes, from 0 to 99.
The default value is 60.
Note: After making changes on a setting, be sure to reboot the system for the changes
to take eect.
View SMBIOS Event Log
Select this submenu and press enter to see the contents of the SMBIOS event log. The
following categories will be displayed: Date/Time/Error Code/Severity.
96
Page 97

Chapter 4: BIOS
4.5 IPMI
Use this feature to congure Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) settings.
BMC Firmware Revision
This item indicates the IPMI rmware revision used in your system.
IPMI Status (Baseboard Management Controller)
This item indicates the status of the IPMI rmware installed in your system.
System Event Log
Enabling/Disabling Options
SEL Components
Select Enabled for all system event logging at bootup. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
Erasing Settings
Erase SEL
Select Yes, On next reset to erase all system event logs upon next system reboot. Select
Yes, On every reset to erase all system event logs upon each system reboot. Select No to
keep all system event logs after each system reboot. The options are No, Yes, On next reset,
and Yes, On every reset.
97
Page 98

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
When SEL is Full
This feature allows the user to decide what the BIOS should do when the system event log
is full. Select Erase Immediately to erase all events in the log when the system event log is
full. The options are Do Nothing and Erase Immediately.
Note: After making changes on a setting, be sure to reboot the system for the changes
to take eect.
Custom EFI Logging Options
Log EFI Status Codes
Use this feature to select how EFI status codes are logged. The options are Disabled, Both,
Error code, and Progress code.
BMC Network Conguration
BMC Network Conguration
Congure IPV4 Support
This section displays conguration features for IPV4 support.
IPMI LAN Selection
This item displays the IPMI LAN setting. The default setting is Failover.
IPMI Network Link Status
This item displays the IPMI Network Link status. The default setting is Dedicated LAN.
Update IPMI LAN Conguration
Select Yes for the BIOS to implement all IP/MAC address changes at the next system boot.
The options are No and Yes.
*If the item above is set to Yes, the following items will become available for
conguration:
Conguration Address Source
This feature allows the user to select the source of the IP address for this computer. If Static
is selected, you will need to know the IP address of this computer and enter it to the system
manually in the eld. If DHCP is selected, the BIOS will search for a DHCP (Dynamic Host
Conguration Protocol) server in the network that is attached to and request the next available
IP address for this computer. The options are DHCP and Static.
*If the item above is set to Static, the following items will become available for
conguration:
98
Page 99

Chapter 4: BIOS
Station MAC Address
This item displays the Station MAC address for this computer. Mac addresses are 6 two-digit
hexadecimal numbers.
Station IP Address
This item displays the Station IP address for this computer. This should be in decimal and in
dotted quad form (i.e., 192.168.10.253).
Subnet Mask
This item displays the sub-network that this computer belongs to. The value of each threedigit number separated by dots should not exceed 255.
Gateway IP Address
This item displays the Gateway IP address for this computer. This should be in decimal and
in dotted quad form (i.e., 172.31.0.1).
VLAN
This item displays the virtual LAN settings. The options are Disable and Enable.
Congure IPV6 Support
This section displays conguration features for IPV6 support.
LAN Channel 1
IPV6 Support
Use this item to display conguration settings for IPV6 support. The options are Enabled
and Disabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following item will become available for
conguration:
Conguration Address Source
This feature allows the user to select the source of the IP address for this computer. If Static
is selected, the user will need to know the IP address of this computer and enter it to the
system manually in the eld. If DHCP is selected, the BIOS will search for a DHCP (Dynamic
Host Conguration Protocol) server in the network that it is attached to and request the next
available IP address for this computer. If Unspecied is selected, the BMC network paramters
will not be modied during the BIOS phase. The options are Unspecied, Static, and DHCP.
*If the item above is set to Static, the following items will become available for
conguration:
• Station IPV6 Address
• Prex Length
• IPV6 Router1 IP Address
99
Page 100

Super X11SRM-F/-VF User's Manual
4.6 Security
This menu allows the user to congure the following security settings for the system.
Administrator Password
Press Enter to create a new, or change an existing, Administrator password.
User Password
Press Enter to create a new, or change an existing, User password.
Password Check
Select Setup for the system to check for a password at Setup. Select Always for the system
to check for a password at bootup or upon entering the BIOS Setup utility. The options are
Setup and Always.
Secure Boot
This section displays the contents of the following secure boot features:
• System Mode
• Vendor Keys
Secure Boot Enable
Use this item to enable secure boot. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
100
 Loading...
Loading...