Page 1

Operation Manual
Page 2

Cristina Bachmann, Heiko Bischoff, Marion Bröer, Sabine Pfeifer, Heike Schilling
Thanks to: Ashley Shepherd
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part
of Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH. The software described by this document is subject to a License Agreement
and may not be copied to other media except as specifically allowed in the License Agreement. No part of this publica
tion may be copied, reproduced, or otherwise transmitted or recorded, for any purpose, without prior written permission
by Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH. Registered licensees of the product described herein may print one copy of
this document for their personal use.
All product and company names are ™ or ® trademarks of their respective owners. Windows 7 is a registered trademark or
trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. The Mac logo is a trademark used under li
cense. Macintosh and Power Macintosh are registered trademarks. MP3SURROUND and the MP3SURROUND logo are
registered trademarks of Thomson SA, registered in the US and other countries, and are used under license from Thomson
Licensing SAS.
Release Date: December 16, 2010
© Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH, 2010.
All rights reserved.
-
-
Page 3

Table of Contents
Page 4

11 Part I: Getting into the details
12 About this manual
13 Welcome!
14 Setting up your system
15 Setting up audio
20 Setting up MIDI
22 Connecting a synchronizer
22 Setting up video
22 Optimizing audio performance
25 VST Connections
26 About this chapter
26 The VST Connections window
26 Setting up busses
29 Setting up group and FX channels
30 About monitoring
30 External instruments/effects (Cubase only)
34 Editing operations
36 The Project window
37 Window Overview
39 The track list
39 The Inspector
42 The toolbar
43 The status line
43 The info line
44 The overview line
44 The ruler
45 The Snap function
47 Auto-Scroll
48 Working with projects
49 Creating new projects
50 Opening projects
50 Closing projects
50 Saving projects
52 The Archive and Backup functions
54 Startup Options
54 The Project Setup dialog
56 Zoom and view options
58 Audio handling
58 Auditioning audio parts and events
59 Scrubbing audio
59 Editing parts and events
66 Range editing
68 Region operations
68 The Edit History dialog
69 The Preferences dialog
71 Working with tracks and lanes
72 Setting up tracks
74 Editing tracks
76 Working with lanes
79 Organizing tracks in folder tracks
81 Dividing the track list
82 Playback and the Transport panel
83 Background
84 Operations
86 Options and Settings
88 The Virtual Keyboard
89 Recording
90 Background
90 Basic recording methods
92 Audio recording specifics
100 MIDI recording specifics
105 Options and Settings
108 Quantizing MIDI and audio
109 Introduction
110 Quantize functions
110 Advanced Quantize functions
111 The Quantize Panel
114 Quantizing multiple audio tracks (Cubase only)
4
Table of Contents
Page 5

117 Fades, crossfades and envelopes
118 Creating fades
120 The Fade dialogs
121 Creating crossfades
121 The Crossfade dialog
122 Auto fades and crossfades
123 Event envelopes
124 The arranger track
125 Introduction
125 Setting up the arranger track
126 Working with arranger events
128 Flattening the arranger chain
129 Live mode
130 Arranging your music to video
131 The transpose functions
132 Introduction
132 Transposing your music
135 Other functions
138 Using markers
139 Introduction
139 The Marker window
141 The marker track
143 Marker key commands
143 Exporting and importing markers
145 The Mixer
146 Overview
148 Configuring the Mixer
152 Basic mixing procedures
155 Audio-specific procedures
164 Routing
166 MIDI-specific procedures
167 Utilities
169 VST Mixer Diagrams
172 Control Room (Cubase only)
173 Virtual Control Room – The concept
173 Configuring the Control Room
177 The Control Room Mixer
182 Studios and Studio Sends
185 The Control Room Overview
186 Direct Monitoring and latency
187 Audio effects
188 About this chapter
188 Overview
189 Insert effects
194 Send effects
198 Using the side-chain input
200 Using external effects (Cubase only)
200 Editing effects
200 Effect presets
203 Installing and managing effect plug-ins
206 VST instruments and instrument
tracks
207 Introduction
207 VST instrument channels vs. instrument tracks
207 VST instrument channels
209 Instrument tracks
211 What do I need? Instrument channel or instrument
track?
211 Instrument Freeze
212 VST instruments and processor load
212 Using presets for VSTi configuration
215 About latency
216 External instruments (Cubase only)
217 Surround sound (Cubase only)
218 Introduction
219 Preparations
220 Using the SurroundPanner V5
226 Exporting a surround mix
227 Automation
228 Introduction
228 Working with automation curves
228 Enabling and disabling the writing of automation
data
229 Writing automation data
230 Editing automation events
232 Automation track operations
235 The Automation panel (Cubase only)
241 Automation Preferences
241 Hints and further options
241 MIDI controller automation
5
Table of Contents
Page 6

244 Audio processing and functions
245 Background
245 Audio processing
253 Applying plug-ins (Cubase only)
254 The Offline Process History dialog
255 Freeze Edits
256 Detect Silence
257 The Spectrum Analyzer
259 Statistics
259 About time stretch and pitch shift algorithms
261 The Sample Editor
262 Window overview
266 General functions
272 Warping audio
276 Working with hitpoints and slices
281 VariAudio (Cubase only)
292 Flattening realtime processing
294 The Audio Part Editor
295 Background
295 Opening the Audio Part Editor
295 Window overview
296 Operations
298 Options and Settings
299 The Pool
300 Background
300 Window overview
302 Operations
311 The MediaBay
312 Introduction
313 Working with the MediaBay
314 The Define Locations section
315 The Locations section
316 The Results list
318 Previewing files
321 The Filters section
323 The Attribute Inspector
327 The Loop Browser, Sound Browser, and Mini
Browser windows
327 Preferences
328 Key commands
328 Working with MediaBay-related windows
329 Working with Volume databases
331 Working with track presets
332 Introduction
332 Types of track presets
333 Applying track presets
335 Creating a track preset
336 Creating tracks from track presets or VST presets
337 Track Quick Controls
338 Introduction
338 Assigning parameters to quick controls
339 Connecting quick controls with remote controllers
340 Quick controls and automatable parameters
342 Remote controlling Cubase
343 Introduction
343 Setting Up
344 Operations
345 The Generic Remote device
347 Track Quick Controls
347 Apple Remote (Macintosh only)
348 MIDI realtime parameters and effects
349 Introduction
349 The Inspector – general handling
349 The Inspector sections
353 MIDI effects
355 Managing plug-ins
356 Using MIDI devices
357 Background
357 MIDI devices – general settings and patch
handling
362 About Device panels (Cubase only)
364 About Studio Connections
366 MIDI processing
367 Introduction
368 Making your settings permanent
369 Dissolve Part
370 Bounce MIDI
370 Repeat Loop
371 Other MIDI functions
6
Table of Contents
Page 7

374 The MIDI editors
375 Introduction
375 Opening a MIDI editor
377 The Key Editor – Overview
380 Key Editor operations
396 The In-Place Editor
397 The Drum Editor – Overview
398 Drum Editor operations
400 Working with drum maps
403 Using drum name lists
404 The List Editor – Overview
405 List Editor operations
407 Working with SysEx messages
409 Recording SysEx parameter changes
409 Editing SysEx messages
411 The basic Score Editor – Overview
412 Score Editor operations
419 Expression maps (Cubase only)
420 Introduction
421 Using expression maps in Cubase
424 Creating and editing expression maps
428 Note Expression (Cubase only)
429 Introduction
430 Setting up the Note Expression Inspector tab
431 Mapping controllers
432 Recording
434 Editing Note Expression data
437 Note Expression and MIDI
439 HALion Sonic SE
440 The Logical Editor, Transformer, and
Input Transformer
441 Introduction
441 Opening the Logical Editor
442 Window overview
442 Setting up filter conditions
447 Selecting a function
447 Specifying actions
450 Applying the defined actions
450 Working with presets
450 The Input Transformer
452 The Project Logical Editor
(Cubase only)
453 Introduction
453 Opening the Project Logical Editor
453 Window overview
454 Setting up filter conditions
458 Specifying actions
460 Selecting a function
460 Applying Macros
460 Applying the defined actions
460 Working with presets
462 Editing tempo and signature
463 Background
463 Tempo and signature display
465 Editing tempo and signature
467 Process Tempo (Cubase only)
467 The Process Bars dialog (Cubase only)
468 The Beat Calculator
469 Merge Tempo From Tapping (Cubase only)
469 The Time Warp tool (Cubase only)
473 Tempo Detection (Cubase only)
476 Adjusting the audio to the project tempo
477 The Project Browser (Cubase only)
478 Window Overview
479 Editing tracks
484 Export Audio Mixdown
485 Introduction
485 Mixing down to audio files
486 The Export Audio Mixdown dialog
489 The available file formats
493 Synchronization
494 Background
494 Timecode (positional references)
496 Clock sources (speed references)
496 The Project Synchronization Setup dialog
500 Synchronized operation
500 Example scenarios (Cubase only)
501 Working with VST System Link
503 Activating VST System Link
7
Table of Contents
Page 8

509 Video
510 Introduction
510 Before you start
511 Preparing a video project in Cubase
513 Video files in the Project window
514 Playing back video
516 Editing video
516 Extracting audio from a video file
516 Replacing the audio in a video file
517 ReWire
518 Introduction
518 Launching and quitting
519 Activating ReWire channels
519 Using the transport and tempo controls
520 How the ReWire channels are handled in Cubase
520 Routing MIDI via ReWire2
520 Considerations and limitations
521 File handling
522 Importing audio
525 Exporting and importing OMF files (Cubase only)
527 Exporting and importing standard MIDI files
529 Exporting and importing MIDI loops
529 Exporting and importing track archives (Cubase
only)
531 Customizing
532 Background
532 Workspaces
534 Using the Setup options
535 Customizing track controls
536 Appearance
537 Applying colors in the Project window
539 Where are the settings stored?
541 Key commands
542 Introduction
542 Setting up key commands
545 Setting up tool modifier keys
546 The default key commands
550 Part II: Score layout and printing
(Cubase only)
551 How the Score Editor works
552 About this chapter
552 Welcome!
552 How the Score Editor operates
552 MIDI notes vs. score notes
553 Display Quantize
555 Entering notes by hand vs. recording notes
556 The basics
557 About this chapter
557 Preparations
557 Opening the Score Editor
557 The project cursor
557 Playing back and recording
558 Page Mode
558 Changing the zoom factor
559 The active staff
559 Making page setup settings
559 Designing your work space
561 About the Score Editor context menus
561 About dialogs in the Score Editor
562 Setting clef, key, and time signature
565 Transposing instruments
566 Printing from the Score Editor
566 Exporting pages as image files
567 Working order
567 Force update
568 Transcribing MIDI recordings
569 About this chapter
569 About transcription
569 Getting the parts ready
569 Preparing parts for score printout
570 Staff settings
570 Situations which require additional techniques
571 Inserting Display Quantize changes
572 The Explode function
572 Using “Scores Notes To MIDI”
8
Table of Contents
Page 9

573 Entering and editing notes
574 About this chapter
574 Score settings
575 Note values and positions
576 Adding and editing notes
578 Selecting notes
579 Moving notes
580 Duplicating notes
580 Cut, copy, and paste
581 Editing pitches of individual notes
582 Changing the length of notes
582 Splitting a note in two
583 Working with the Display Quantize tool
583 Split (piano) staves
583 Strategies: Multiple staves
584 Inserting and editing clefs, keys, or time signatures
585 Deleting notes
586 Staff settings
587 About this chapter
587 Staff settings
587 Making settings
587 Working with staff presets
588 Staff names
588 Key and clef
588 Display Quantize and Interpretation Options
591 Display Transpose
591 The Options tab
592 The Polyphonic tab
592 The Tablature tab
603 Additional note and rest formatting
604 About this chapter
604 Background: Note stems
604 Setting stem direction
605 Stem length
606 Accidentals and enharmonic shift
606 Changing the note head shape
607 Other note details
608 Coloring notes
608 Copying settings between notes
608 Handling beaming
612 About tied notes
614 Graphic moving of notes
614 Cue notes
615 Grace notes
616 Tuplets
618 Working with symbols
619 About this chapter
619 Background: The different layers
620 The Symbols Inspector
621 Important! – Symbols, staves, and voices
622 Adding symbols to the score
628 Selecting symbols
629 Moving and duplicating symbols
632 Changing length, size, and shape
633 Deleting symbols
633 Copy and paste
633 Alignment
634 Symbol details
593 Polyphonic voicing
594 About this chapter
594 Background: Polyphonic voicing
595 Setting up the voices
597 Strategies: How many voices do I need?
597 Entering notes into voices
597 Checking which voice a note belongs to
598 Moving notes between voices
599 Handling rests
599 Voices and Display Quantize
600 Creating crossed voicings
601 Automatic polyphonic voicing – Merge All Staves
602 Converting voices to tracks – Extract Voices
Table of Contents
640 Working with chords
641 About this chapter
641 Inserting Chord symbols
643 Global chord settings
645 Working with text
646 About this chapter
646 Adding and editing text symbols
648 Different types of text
652 Text functions
9
Page 10

655 Working with layouts
656 About this chapter
656 Background: Layouts
656 Creating a layout
656 Opening a layout
656 Layout operations
657 Using layouts – an example
658 Marker Track to Form
659 Working with MusicXML
660 Introduction
661 Importing and exporting MusicXML files
663 Designing your score:
additional techniques
664 About this chapter
664 Layout settings
665 Staff size
665 Hiding/showing objects
666 Coloring notes
667 Multiple rests
667 Editing bar lines
668 Creating upbeats
669 Setting the number of bars across the page
670 Moving bar lines
670 Dragging staves
672 Adding brackets and braces
672 Auto Layout
674 Reset Layout
674 Breaking bar lines
684 The score and MIDI playback
685 About this chapter
685 Scores and the Arranger mode
685 Working with mapped dynamics
688 Tips and Tricks
689 Overview
689 Useful editing techniques
690 Frequently asked questions
692 If you wish you had a faster computer
693 Index
676 Scoring for drums
677 About this chapter
677 Background: Drum maps in the Score Editor
677 Setting up the drum map
679 Setting up a staff for drum scoring
679 Entering and editing notes
679 Using “Single Line Drum Staff”
680 Creating tablature
681 About this chapter
681 Creating tablature automatically
682 Creating tablature manually
682 Tablature number appearance
683 Editing
683 Note head shape
10
Table of Contents
Page 11

Part I:
Getting into the details
Page 12

1
About this manual
Page 13

Welcome!
This is the Operation Manual for Steinberg’s Cubase.
Here you will find detailed information about all the features and functions in the program.
About the program versions
The documentation covers two program versions, Cubase
and Cubase Artist, for two different operating systems or
“platforms”, Windows and Mac OS X.
Some features described in the documentation are only
applicable to the Cubase version. Whenever this is the
case this will be clearly indicated in the heading of the re
lated subject.
Some features and settings are also specific to one of the
platforms. This is clearly stated in the applicable cases. If
nothing else is said, all descriptions and procedures in the
documentation are valid for all Cubase versions for both
Windows and Mac OS
The screenshots are taken from the Windows version of
Cubase.
Key command conventions
Many of the default key commands in Cubase use modifier
keys, some of which are different depending on the oper
ating system. For example, the default key command for
Undo is [Ctrl]-[Z] under Windows and [Command]-[Z] under Mac OS X.
When key commands with modifier keys are described in
this manual, they are shown with the Windows modifier
key first, in the following way:
[Win modifier key]/[Mac modifier key]-[key]
For example, [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Z] means “press [Ctrl]
under Windows or [Command] under Mac OS X, then
press [Z]”.
Similarly, [Alt]/[Option]-[X] means “press [Alt] under Windows or [Option] under Mac OS X, then press [X]”.
Ö This manual often refers to right-clicking, for example, to
open context menus. If you are using a Mac with a singlebutton mouse, hold down [Ctrl] and click.
X.
-
-
13
About this manual
Page 14

2
Setting up your system
Page 15
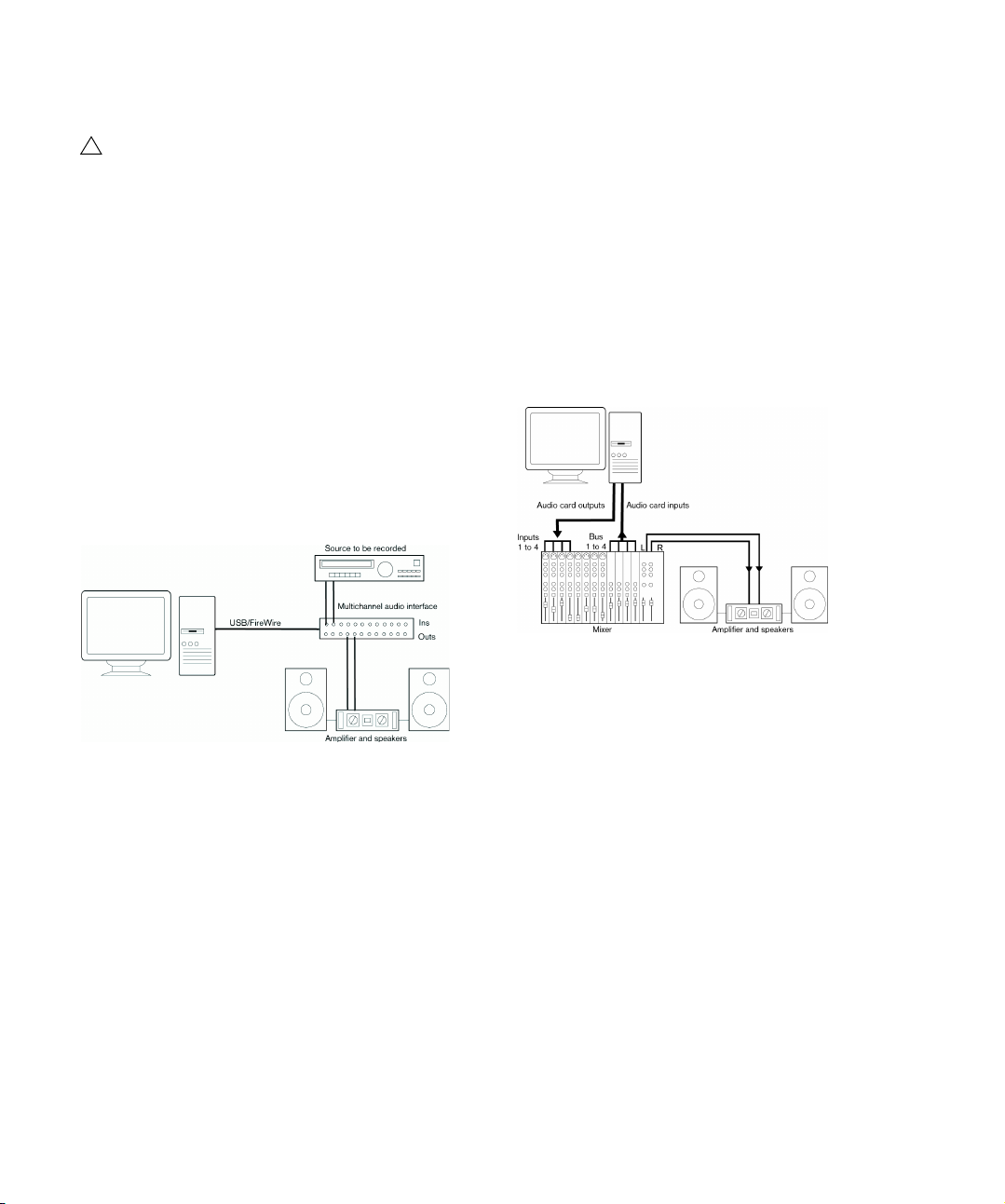
Setting up audio
!
Make sure that all equipment is turned off before
making any connections!
Connecting audio
Exactly how to set up your system depends on many different factors, e. g. the kind of project you wish to create,
the external equipment you want to use, or the computer
hardware available to you. Therefore, the following sec
tions can only serve as examples.
How you connect your equipment, i. e. whether you use
digital or analog connections, also depends on your indi
vidual setup.
Stereo input and output – the simplest connection
If you only use a stereo input and output from Cubase, you
can connect your audio hardware, e. g. the inputs of your
audio card or your audio interface, directly to the input
source and the outputs to a power amplifier and speaker.
-
Multi-channel input and output
Most likely however, you will have other audio equipment
that you want to integrate with Cubase, using several input and output channels. Depending on the equipment
available to you, there are two ways to go: either mixing
using an external mixing desk, or mixing using the Mixer in
side Cubase.
• External mixing means having a hardware mixing device
with a group or bus system that can be used for feeding
inputs on your audio hardware.
In the example below, four busses are used for feeding signals to the audio hardware’s inputs. The four outputs are connected back to the mixer
for monitoring and playback. Remaining mixer inputs can be used for
-
connecting audio sources like microphones, instruments, etc.
-
A multi-channel audio setup using an external mixer
Ö When connecting an input source (like a mixer) to the
audio hardware, you should use output busses, sends or
similar that are separate from the mixer’s master output to
avoid recording what you are playing back. You may also
A simple stereo audio setup
have mixing hardware that can be connected via FireWire.
This is probably the simplest of all setups – once you have
set up the internal input and output busses, you can con
nect your audio source, e. g. a microphone, to your audio
interface and start recording.
15
Setting up your system
Page 16
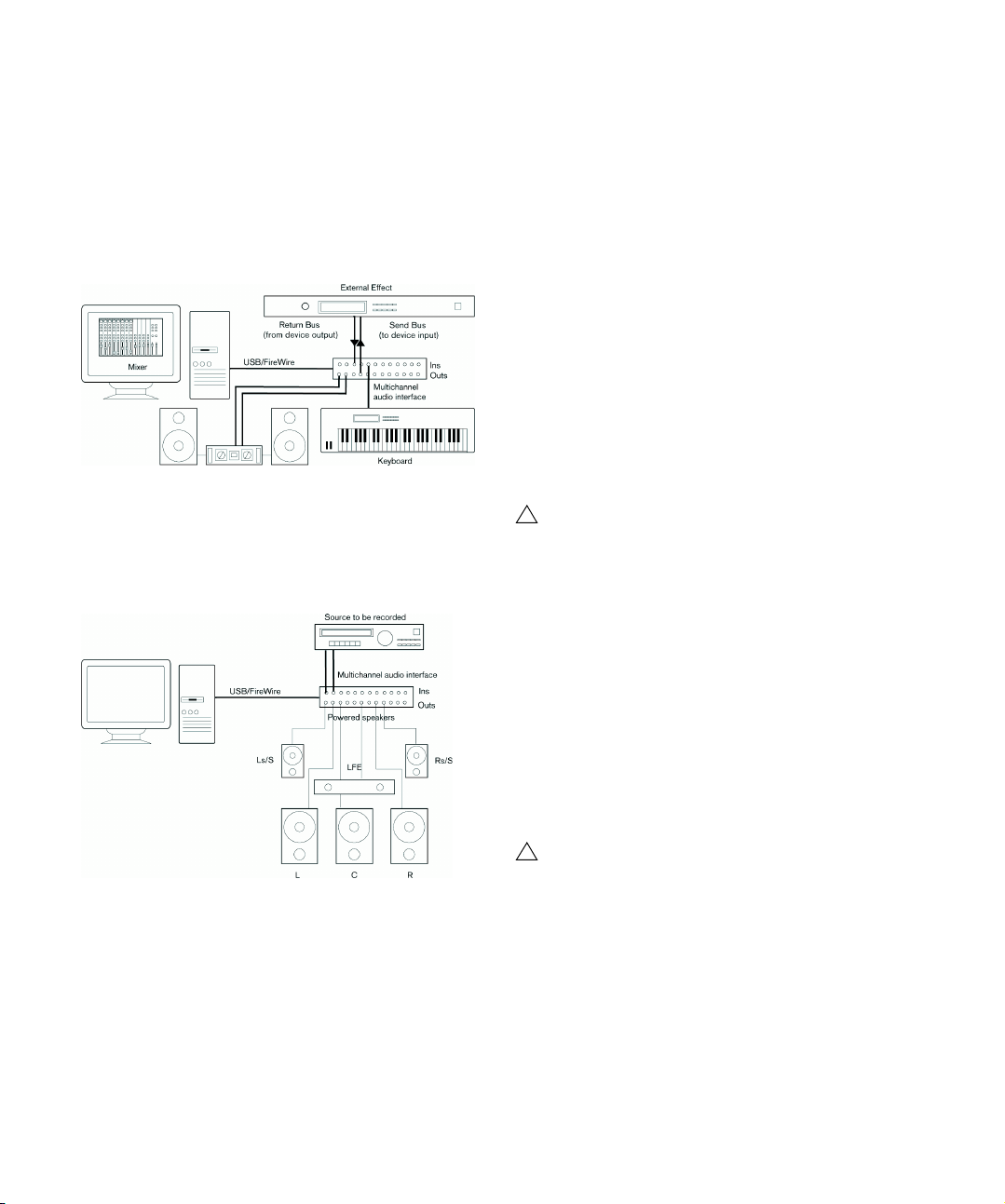
• When using the Mixer inside Cubase, you can use the
!
!
inputs on your audio hardware to connect microphones
and/or external devices. Use the outputs to connect your
monitoring equipment.
Cubase only: You can create very complex setups using external instruments and external effects, and integrate Cubase seamlessly with all
your external equipment using the Control Room feature (see the chap
ters “VST Connections” on page 25 and “Control Room (Cubase only)”
on page 172).
Mixing inside Cubase
Recording from a CD player
Most computers come with a CD-ROM drive that can also
be used as a regular CD player. In some cases the CD
player is internally connected to the audio hardware so
that you can record the output of the CD player directly
into Cubase (consult the audio hardware documentation if
-
you are uncertain).
• All routing and level adjustments for recording from a
CD (if available) are done in the audio hardware setup application (see below).
• You can also grab audio tracks directly from a CD in
Cubase (see the chapter
“File handling” on page 521).
Word clock connections
If you are using a digital audio connection, you may also
need a word clock connection between the audio hardware and external devices. Please refer to the documentation that came with the audio hardware for details.
Connecting for surround sound (Cubase only)
If you plan to mix for surround sound, you can connect the
audio outputs to a multi-channel power amplifier, driving a
set of surround channels.
A surround sound playback configuration
Cubase supports surround formats with up to 6 speaker
channels. The figure above shows a 5.1 surround setup.
It is very important that word clock synchronization is
done correctly or there might be clicks and crackles
in recordings that you make!
About recording levels and inputs
When you connect your equipment, you should make sure
that the impedance and levels of the audio sources and in
puts are matched. Typically, different inputs may be designed for use with microphones, consumer line level
dBV) or professional line level (+4 dBV), or you may
(-10
be able to adjust input characteristics on the audio interface or in its control panel. Please check the audio hardware documentation for details.
Using the correct types of input is important to avoid distortion or noisy recordings.
Cubase does not provide any input level adjustments
for the signals coming in to your audio hardware,
since these are handled differently for each card. Ad
justing input levels is either done in a special application included with the hardware or from its control
panel (see below).
-
-
16
Setting up your system
Page 17
Making settings for the audio hardware
!
!
Most audio cards come with one or more small applications that allow you to configure the inputs of the hardware to your liking. This includes:
• Selecting which inputs/outputs are active.
• Setting up word clock synchronization (if available).
• Turning monitoring via the hardware on/off (see “About moni-
toring” on page 19).
• Setting levels for each input. This is very important!
• Setting levels for the outputs, so that they match the equip-
ment you use for monitoring.
• Selecting digital input and output formats.
• Making settings for the audio buffers.
In many cases all available settings for the audio hardware
are gathered in a control panel, which can be opened from
within Cubase as described below (or opened separately,
when Cubase isn’t running). In some cases, there may be
several different applications and panels – please refer to
the audio hardware documentation for details.
Plug and Play support for ASIO devices
The Steinberg MR816 hardware series supports Plug and
Play in Cubase. These devices can be plugged in and
switched on while the application is running. Cubase will
automatically use the driver of the MR816 series and will
re-map the VST connections accordingly.
Steinberg cannot guarantee that this will work with other
hardware. If you are unsure of whether your device sup
ports plug and play, please consult its documentation.
If a device that does not support Plug and Play is
connected/disconnected while the computer is run
ning, it may get damaged.
-
Selecting a driver and making audio settings
in Cubase
The first thing you need to do is select the correct driver in
Cubase to make sure that the program can communicate
with the audio hardware:
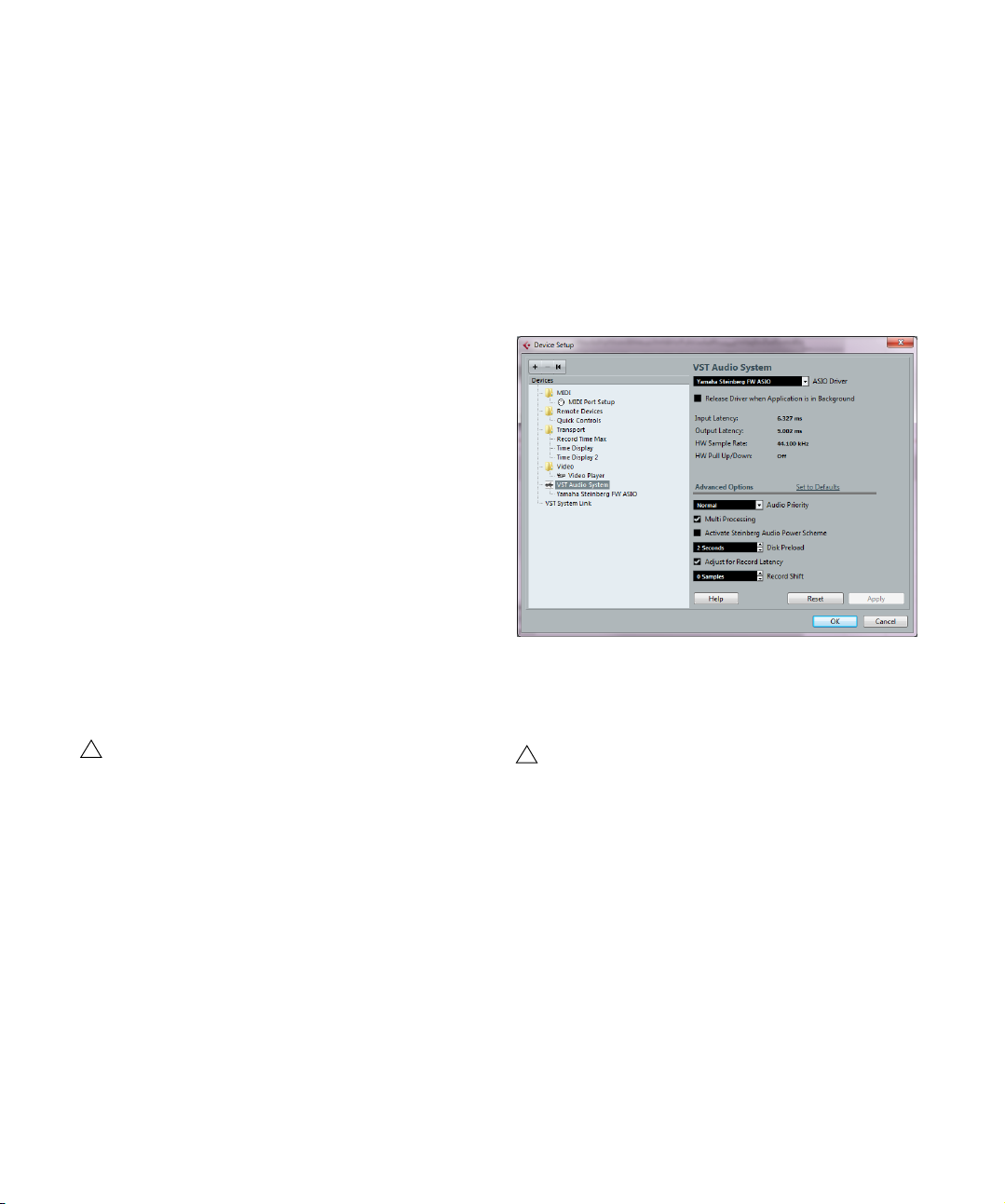
1. Launch Cubase and select Device Setup from the
Devices menu.
2. In the Devices list to the left, click on “VST Audio System”.
The VST Audio System page is shown.
3. On the ASIO Driver menu, select your audio hardware
driver.
There may be several options here that all refer to the same audio hardware. When you have selected a driver, it is added to the Devices list.
-
Under Windows, we strongly recommend that you access your hardware via an ASIO driver written specifically for the hardware. If no ASIO driver is installed,
we recommend that you check with your audio hardware manufacturer if they have an ASIO driver available, for example, for download via the Internet. You
can use the Generic Low Latency ASIO driver if no
specific ASIO driver is available.
4. Select the driver in the Devices list to open the driver
settings for your audio hardware.
5. Bring up the control panel for the audio hardware and
adjust the settings as recommended by the audio hardware manufacturer.
17
Setting up your system
Page 18

• Under Windows, you open the control panel by clicking
!
the Control Panel button.
The control panel that opens when you click this button is provided
by
the audio hardware manufacturer – not Cubase (unless you use
DirectX, see below). Hence it will be different for each audio card brand
and model.
The control panels for the ASIO DirectX driver and the Generic Low Latency ASIO Driver (Windows only) are exceptions, in that they are provided by Steinberg and described in the dialog help, opened by clicking
the Help button in the dialog. See also the notes on DirectX below.
• Under Mac OS X, the control panel for your audio hardware is opened by clicking the “Open Config App” button
on the settings page for your audio device in the Device
Setup dialog.
Note that this button is available only for some hardware products. If
“Open Config App” is not available in your setup, refer to the documen
tation that came with your audio hardware for information on where to
make hardware settings.
6. If you plan to use several audio applications simultaneously, you may want to activate the “Release Driver when
Application is in Background” option on the VST Audio
System page. This will allow another application to play
back via your audio hardware even though Cubase is run
ning.
The application that is currently active (i. e. the “top window” on the desktop) gets access to the audio hardware. Make sure that any other audio
application accessing the audio hardware is also set to release the ASIO
(or Mac OS X) driver so Cubase can use it when it becomes the active
application again.
7. If your audio hardware receives clock signals from an
external sample clock source, you may want to activate
the “Externally Clocked” option on the page for the driver.
This is described in detail in the section “If your hardware setup is based
on an external clock source” on page 18.
8. If your audio hardware and its driver support ASIO
Direct Monitoring, you may want to activate the Direct
Monitoring checkbox on the page for the driver.
Read more about monitoring later in this chapter and in the chapter “Re-
cording” on page 89.
9. Click Apply and then OK to close the dialog.
If your hardware setup is based on an external clock
source
For proper audio playback and recording, it is essential
that you set the project’s sample rate to the sample rate of
the incoming clock signals. If you load a project with a
sample rate that is different from your clock source, the
program will try to change the settings of the clock
source, which may not be what you want.
By activating the “Externally Clocked” option, you “tell”
Cubase that it receives external clock signals and there
fore derives its speed from that source. The program will
not try to change the hardware sample rate any longer.
The sample rate mismatch is accepted and playback will
therefore be faster or slower. For more information about
-
the Sample Rate setting, see
“The Project Setup dialog”
on page 54.
Ö When a sample rate mismatch occurs, the Record
Format field on the status line is highlighted in a different
color.
If you are using audio hardware with a DirectX driver
-
(Windows only)
A DirectX driver is the next best option to a specific
ASIO driver and the Generic Low Latency ASIO
driver.
Cubase comes with a driver called ASIO DirectX Full Duplex, available for selection on the ASIO Driver pop-up
menu (VST Audio System page).
Ö To take full advantage of DirectX Full Duplex, the audio
hardware must support WDM (Windows Driver Model) in
combination with DirectX version 8.1 or higher. In all other
cases, the audio inputs will be emulated by DirectX (see
the dialog help for the ASIO DirectX Full Duplex Setup di
alog for details about how this is reported).
Ö During the installation of Cubase, the latest DirectX
version will be installed on your computer.
-
-
18
Setting up your system
Page 19
When the ASIO DirectX Full Duplex driver is selected in
!
the Device Setup dialog, you can open the ASIO Control
Panel and adjust the following settings (for more details,
click the Help button in the control panel):
• Direct Sound Output and Input Ports
In the list on the left in the window, all available Direct Sound output and
input ports are listed. In many cases, there will be only one port in each
list. To activate or deactivate a port in the list, click the checkbox in the
left column. If the checkbox is ticked, the port is activated.
• You can edit the Buffer Size and Offset settings in this
list if necessary, by double-clicking on the value and typing in a new value.
In most cases, the default settings will work fine. Audio buffers are used
when audio data is transferred between Cubase and the audio card.
While larger buffers ensure that playback will occur without glitches, the
latency (the time between the moment Cubase sends out the data and
when it actually reaches the output) will be higher.
• Offset
If a constant offset is audible during playback of Audio and MIDI recordings, you can adjust the output or input latency time using this value.
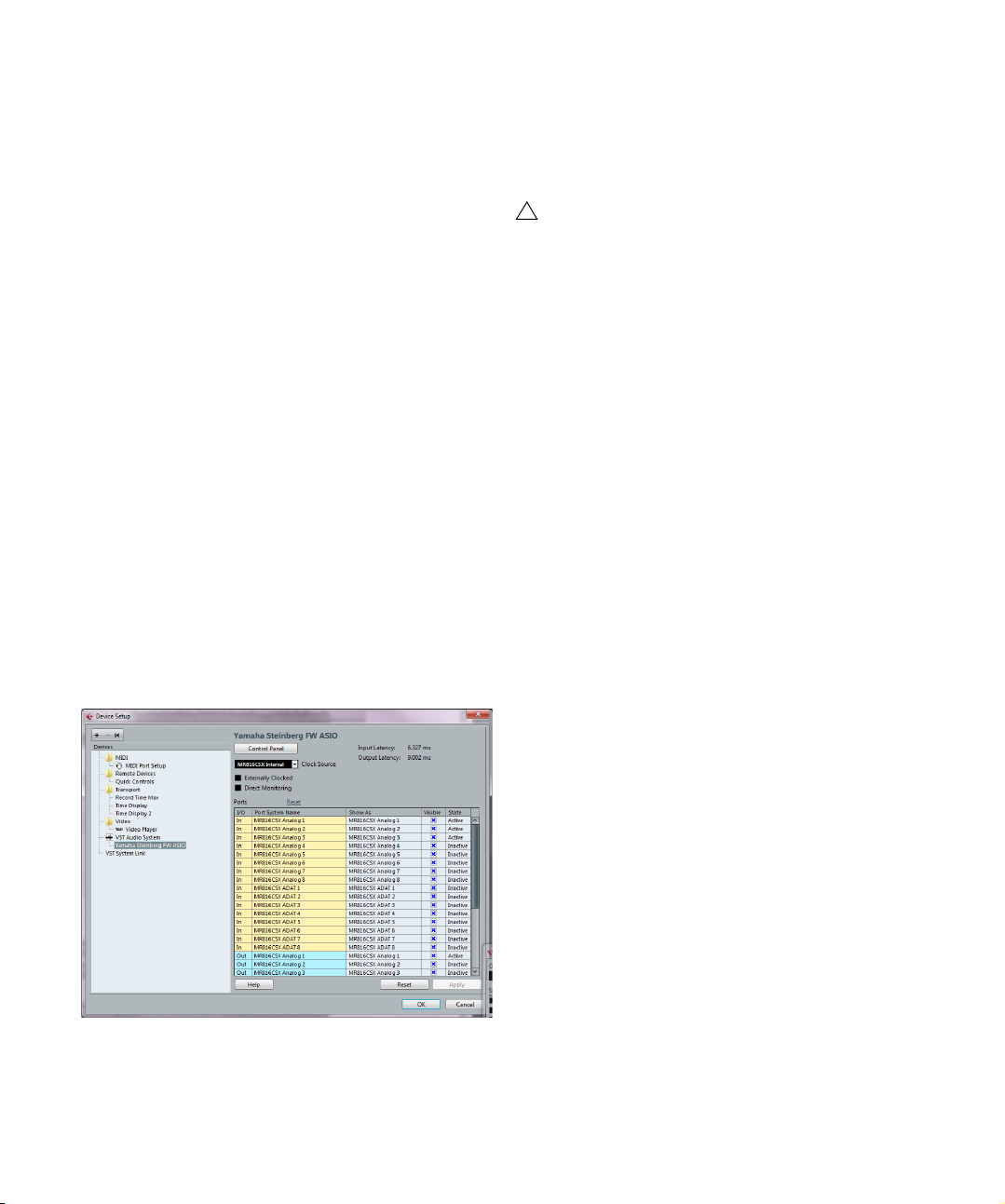
Setting up the input and output ports
Once you have selected the driver and made the settings
as described above, you need to specify which inputs and
outputs will be used and name these:
1. In the Device Setup dialog, select your driver in the
Devices list on the left to display the driver settings for
your audio hardware.
2. To hide a port, click in the “Visible” column for the port
(deselecting the checkbox).
Ports that are not visible cannot be selected in the VST Connections
window where you set up your input and output busses – see the chap
ter “VST Connections” on page 25.
If you attempt to hide a port that is already used by a
bus you will be asked whether this is really what you
want – note that this will disable the port!
3. To rename a port, click on its name in the “Show as”
column and type in a new name.
• It is a good idea to give your ports names that are related to the channel configuration (rather than to the actual hardware model)!
For example, if you are using a 5.1 surround audio setup (Cubase only),
you could name the six ports Left, Right, Center, Lfe, Left Surround, and
Right Surround. This makes it easier to transfer your projects between
different computers, e.g. in different studios – if the same port names are
used on both computers, Cubase will automatically handle the bus con
nections properly when you open the project on the other computer.
4. Click OK to close the Device Setup dialog and apply
your changes.
About monitoring
In Cubase, monitoring means listening to the input signal
while preparing to record or while recording. There are
three ways to monitor:
External monitoring
External monitoring (listening to the input signal before it
goes into Cubase) requires an external mixer for mixing
the audio playback with the input signal. This can be a
classic mixing desk or a mixer application for your audio
hardware, if this has a mode in which the input audio is
sent back out again (usually called “Thru”, “Direct Thru” or
similar).
-
-
Via Cubase
In this case, the audio passes from the input into Cubase,
possibly through Cubase effects and EQ and then back to
the output. You control monitoring via settings in Cubase.
This allows you to control the monitoring level from Cubase and add effects to the monitored signal only.
All input and output ports on the audio hardware are listed.
19
Setting up your system
Page 20
ASIO Direct Monitoring
!
!
If your audio hardware is ASIO 2.0 compatible, it may support ASIO Direct Monitoring (this feature may also be
available for audio hardware with Mac OS X drivers). In
this mode, the actual monitoring is done in the audio hard
ware, by sending the input signal back out again. However, monitoring is controlled from Cubase. This means
that the audio hardware’s direct monitoring feature can be
turned on or off automatically by Cubase.
Monitoring is described in detail in the chapter “Record-
ing” on page 89. However, when setting up, there is one
thing to note:
• If you want to use the external monitoring via your audio
hardware, make sure that the corresponding functions are
activated in the card’s mixer application.
Ö If you are using RME Audio Hammerfall DSP audio
hardware, make sure that the pan law is set to -3
dB in the
card’s preferences.
ule is used for playback only. Using Cubase’s MIDI Thru
feature (described later) you will be able to hear the correct sound from the sound module while playing the keyboard or recording.
-
Setting up MIDI
Make sure that all equipment is turned off before
making any connections!
This section describes how to connect and set up MIDI
equipment. If you have no MIDI equipment, you can skip
this section. Note that this is only an example – you might
need or want to hook things up differently!
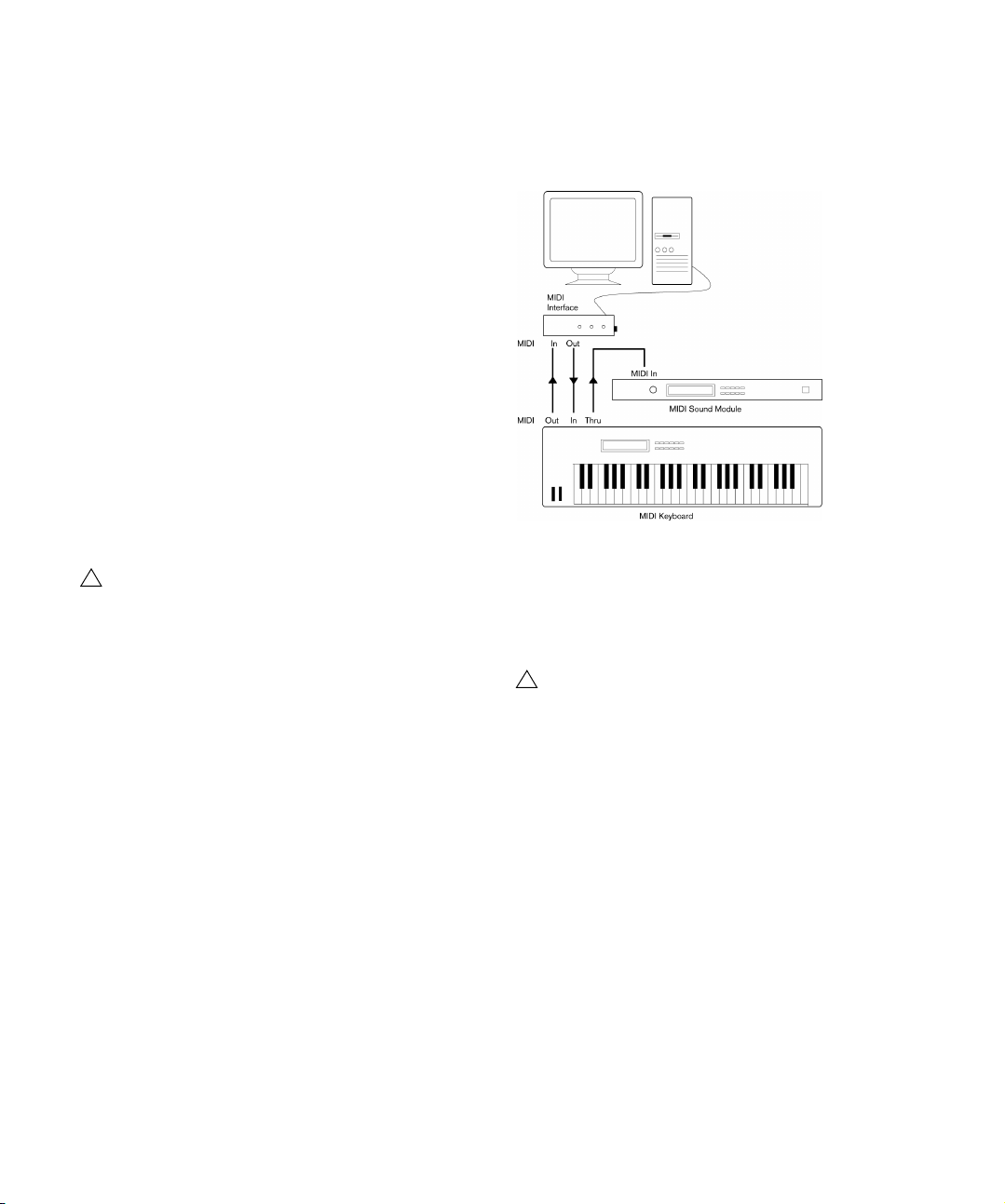
Connecting the MIDI equipment
In this example we assume that you have a MIDI keyboard
and an external MIDI sound module. The keyboard is used
both for feeding the computer with MIDI messages for re
cording and for playing back MIDI tracks. The sound mod-
A typical MIDI Setup
If you want to use even more instruments for playback, simply connect MIDI Thru on the sound module to MIDI In on
the next instrument, and so on. In this hook-up, you will al
ways play the first keyboard when recording. But you can
still use all your devices for providing sounds on playback.
If you plan to use more than three sound sources, we
recommend that you either use an interface with
more than one output, or a separate MIDI Thru box
instead of the Thru jacks on each unit.
Setting MIDI Thru and Local On/Off
On the MIDI page in the Preferences dialog (located on
the File menu under Windows and on the Cubase menu
under Mac OS X), you will find a setting called “MIDI Thru
Active”. This is related to a setting in your instrument
called “Local On/Off” or “Local Control On/Off”.
• If you use a MIDI keyboard instrument, as described earlier in
this chapter, MIDI Thru should be activated and that instru
ment should be set to Local Off (sometimes called Local Control Off – see the instrument’s operation manual for details).
-
-
20
Setting up your system
Page 21
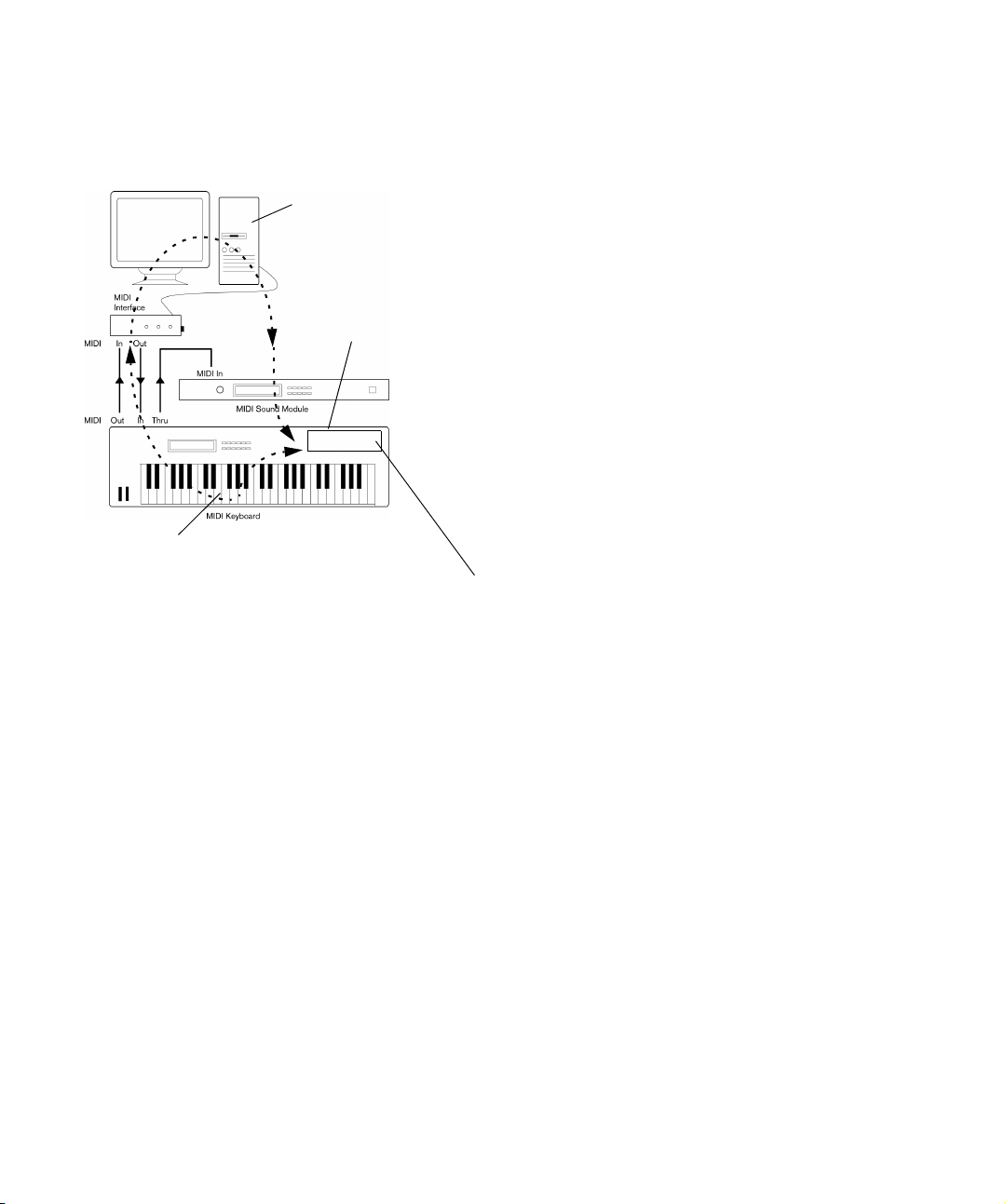
The MIDI signal from the keyboard will be recorded in Cubase
When “MIDI Thru” is active in
Cubase, MIDI data received is
immediately “echoed” back out.
When you press a key, it is sent out via MIDI to Cubase.
MIDI data coming in to
the instrument is played
by the “Synth” inside it.
When Local Control is turned on in the instrument, the keys you press
will be played by the “Synth” inside the instrument. When Local Control
is turned off, this connection is cut off.
“Synth”
and at the same time be re-routed back to the instrument so
that you hear what you are playing, without the keyboard “trig
gering” its own sounds.
• If you use a separate MIDI keyboard – one that does not produce any sounds itself – MIDI Thru in Cubase should also be
activated, but you don’t need to look for any Local On/Off setting in your instruments.
• The only case where MIDI Thru should be deactivated is if you
use Cubase with only one keyboard instrument and that instrument cannot be set to Local Off mode.
• MIDI Thru will be active only for MIDI tracks that are record enabled and/or have the Monitor button activated. See the chapter “Recording” on page 89 for more information.
Setting up MIDI ports in Cubase
The Device Setup dialog lets you set up your MIDI system
as follows:
Ö When you change MIDI port settings in the Device
Setup dialog, these are automatically applied.
Showing or hiding MIDI Ports
The MIDI ports are listed in the Device Setup dialog on the
MIDI Port Setup page. By clicking in the “Visible” column
for a MIDI input or output, you can specify whether or not
it is listed on the MIDI pop-up menus in the program.
If you are trying to hide a MIDI port which is already selected for a track or a MIDI device, a warning message will
appear, allowing you to hide – and disconnect – the port
or to cancel the operation and keep the MIDI port visible.
Setting up the “All MIDI Inputs” option
When you record MIDI in Cubase, you can specify which
MIDI input each recording MIDI track should use. How
ever, you can also select the “In ‘All MIDI Inputs’” option
for an input port, which causes any MIDI data from any
MIDI input to be recorded.
The “In ‘All MIDI Inputs’” option on the MIDI Port Setup
page allows you to specify which inputs are included when
you select All MIDI Inputs for a MIDI track. This can be es
pecially useful if your system provides several instances of
the same physical MIDI input – by deactivating the dupli
cates you make sure only the desired MIDI data is recorded.
Ö If you have a MIDI remote control unit connected, you
should also make sure to deactivate the “In ‘All MIDI Inputs’” option for that MIDI input. This will avoid accidentally
recording the data from the remote control when the “All
MIDI Inputs” option is selected as input for a MIDI track.
-
-
-
21
Setting up your system
Page 22

Connecting a synchronizer
!
!
Make sure that all equipment is turned off before
making any connections!
When using Cubase with external tape transports, you will
most likely need to add a synchronizer to your system. All
connections and setup procedures for synchronization are
described in the chapter
“Synchronization” on page 493.
Setting up video
Cubase plays back video files in a number of formats,
such as AVI, QuickTime, or MPEG. QuickTime is used as
playback engine. Which formats can be played back de
pends on the video codecs installed on your system, see
the chapter
There are several ways to play back video, e. g. without any
special hardware, using a FireWire port, or using dedicated
video cards, see
If you plan to use special video hardware, install it and set
it up as recommended by the manufacturer.
Before you use the video hardware with Cubase, we recommend that you test the hardware installation with the
utility applications that came with the hardware and/or the
QuickTime Player application.
“Video” on page 509.
“Video output devices” on page 511.
-
Optimizing audio performance
This section gives you some hints and tips on how to get
the most out of your Cubase system, performance-wise.
Some of this text refers to hardware properties and can be
used as a guide when upgrading your system. This text is
very brief. Look for details and current information on the
Cubase web site!
Two aspects of performance
There are two distinct aspects of performance with respect to Cubase.
Short response times (latency)
Another aspect of performance is response time. The term
“latency” refers to the “buffering”, i. e. the temporary storing, of small chunks of audio data during various steps of
the recording and playback process on a computer. The
more and larger those chunks, the higher the latency.
High latency is most irritating when playing VST instruments and when monitoring through the computer, i. e.
when listening to a live audio source via the Cubase Mixer
and effects. However, very long latency times (several
hundred milliseconds) can also affect other processes like
mixing, e.
only after a noticeable delay.
While Direct Monitoring and other techniques reduce the
problems associated with very long latency times, a sys
tem that responds fast will always be more convenient to
work with.
• Depending on your audio hardware, it may be possible
to “trim” your latency times, usually by lowering the size
and the number of buffers.
For details, refer to the audio hardware documentation, or, if you are using a DirectX driver under Windows, the dialog help.
g. when the effect of a fader movement is heard
-
System factors that affect performance
RAM
Generally speaking, the more RAM is installed in your
computer, the better.
On computers running a Windows 32-bit operating
system, a running application can address a maximum of 2 GB of RAM. On a Macintosh computer
running Mac OS
The 64-bit versions of Windows and Mac OS X are
able to assign considerably more than 4
to a running 64-bit application.
This limitation is imposed by the operating system, and it
is independent of the amount of RAM that you may have
installed in your computer!
X, this limit is 4 GB.
GB of RAM
Tracks and effects
Simply put: the faster your computer, the more tracks, effects and EQ you will be able to play. Exactly what constitutes a “fast computer” is almost a science in itself, but
some hints are given below.
22
Setting up your system
Page 23

Some program functions may “eat up” all the available
!
!
memory, e. g. recording, the use of effect plug-ins, and the
pre-loading of samples (see also
“RAM requirements for
recording” on page 92 and “Smart plug-in processing” on
page 188).
When a function has used up all the memory made
available by the operating system, the computer will
crash.
Always keep in mind the RAM limitation of your operating
system when setting up your projects.
CPU and processor cache
It goes without saying that the faster the computer processor, the better. But there are a number of factors that affect
the apparent speed of a computer: the bus speed and type
(PCI is strongly recommended), the processor cache size
and of course, the processor type and brand. Cubase relies
heavily on floating point calculations. When shopping for a
processor, please make sure that you get one that is pow
erful in calculating floating point arithmetics.
Note also that Cubase features full support for multi-processor systems. So, if you own a computer system with
more than one processor, Cubase can take advantage of
the total capacity and evenly distribute the processing
load to all available processors. For further information,
“Multi processing” on page 24.
see
Hard disk and controller
The number of hard disk tracks you can record and play
back at the same time also depends on the speed of your
hard disk and hard disk controller. If you use E-IDE disks
and controllers, make sure that the transfer mode is DMA
Busmaster. Under Windows, you can check the current
mode by launching the Windows Device Manager and
looking for properties of the IDE ATA/ATAPI Controller’s
primary and secondary channel. DMA transfer mode is en
abled by default, but may be turned off by the system
should hardware problems occur.
Audio hardware and driver
The hardware and its driver can have some effect on regular performance. A badly written driver can reduce the
performance of your computer. But where the hardware
driver design makes the most difference is with latency.
Again, we strongly recommend that you use audio
hardware for which there is a specific ASIO driver!
This is especially true when using Cubase for Windows:
• Under Windows, ASIO drivers written specifically for
the hardware are more efficient than the Generic Low Latency ASIO Driver or a DirectX driver and produce shorter
latency times.
• Under Mac OS X, audio hardware with properly written
Mac OS X (Core Audio) drivers can be very efficient and
produce very low latency times.
However, there are additional features currently only available with ASIO
drivers, such as the ASIO Positioning Protocol.
-
Making settings that affect performance
Audio buffer settings
Audio buffers affect how audio is sent to and from the audio hardware. The size of the audio buffers affects both
the latency and the audio performance. Generally, the
smaller the buffer size, the lower the latency. On the other
hand, working with small buffers can be demanding for the
computer. If the audio buffers are too small, you may get
clicks, pops or other audio playback problems.
• Under Mac OS X, you can adjust the size of the buffers
on the VST Audio System page in the Device Setup dia
log.
You may also find buffer settings in the control panel for the audio hardware.
• Under Windows, you adjust the buffer size settings in
-
the control panel for the audio hardware (opened by click
ing the Control Panel button on the driver page in the Device Setup dialog).
-
-
23
Setting up your system
Page 24

Optimizing processor scheduling (Windows only)
To get the lowest possible latencies when using ASIO under Windows (on a single-CPU system), the “system performance” has to be optimized for background tasks:
1. Open the Control Panel and select the System settings.
2. On the left, select the “Advanced system settings”
option.
The System Properties dialog opens.
3. Select the Advanced tab and click the “Settings…”
button in the Performance section.
The Performance Options dialog opens.
4. Select the Advanced tab and activate the “Adjust for
best performance of: Background services” option.
5. Click OK to close the dialogs.
Multi processing
On the VST Audio System page you will find the “Advanced options” section. Here you find advanced settings
for the VST Engine, including a Multi Processing option.
When this is activated and there is more than one CPU in
your system, the processing load is distributed evenly to
all available CPUs, allowing Cubase to make full use of the
combined power of the multiple processors.
• The ASIO meter (at the top) shows the ASIO time usage, i. e. the time required to complete the current processing tasks. The more tracks, effects, EQ, etc. you use
in your project, the longer processing will take, and the
longer the ASIO meter will show activity.
If the overload indicator (on the far right) lights up, you need to decrease
the number of EQ modules, active effects, and/or audio channels playing
back simultaneously.
• The lower bar graph shows the hard disk transfer load.
If the overload indicator (on the far right) lights up, the hard disk is not
supplying data fast enough to the computer. You may need to reduce the
number of tracks playing back by using the Disable Track function (see
“About track disable/enable” on page 86). If this does not help, you need
a faster hard disk.
Ö The overload indicator may occasionally blink, e. g.
when you locate during playback. This does not indicate a
problem, but happens because the program needs a mo
ment for all channels to load data for the new playback position.
Ö The ASIO and Disk load meters can also be shown on
the Transport panel (as “Performance”) and on the Project
window toolbar (as “Performance Meter”). There they are
shown as two miniature vertical meters (by default at the
left side of the panel/toolbar).
-
About the VST Performance window
The VST Performance window is opened from the Devices menu. The window shows two meter displays: The
ASIO meter, which indicates CPU load, and the Disk me
ter, which shows the hard disk transfer rate. It is recommended that you check this from time to time, or keep it
always open. Even if you have been able to activate a
number of audio channels in the project without getting
any warning, you may run into performance problems
when adding EQ or effects.
Setting up your system
-
24
Page 25

3
VST Connections
Page 26

About this chapter
Setting up busses
This chapter focuses on the settings you can perform in
the VST Connections window. Here you can set up input
and output busses, group and FX channels, external effects, and external instruments. Furthermore you can use
this window to configure the Control Room (Cubase only)
and access the Control Room itself.
Since input and output busses are vital for working with
Cubase, a large part of this chapter concentrates on busses and this is also the reason why you find this chapter at
the beginning of the Operation Manual. How to use the
busses is described in detail in the section
page 164.
“Routing” on
The VST Connections window
The VST Connections window is opened from the Devices menu. It contains the following tabs:
• The Inputs and Outputs tabs allow you to set up and configure
input and output busses, see
• The Group/FX tab allows you to create group and FX chan-
nels/tracks and to make output assignments for these, see
“Setting up group and FX channels” on page 29.
• The External FX tab (Cubase only) allows you to create effect
send/return busses for connecting external effects which can
then be selected via the effect pop-up menus from inside the
program. For further information, see
fects (Cubase only)” on page 30 and “Using external effects
(Cubase only)” on page 200.
• The External Instruments tab (Cubase only) allows you to cre-
ate input/output busses for connecting external instruments.
For further information, see “External instruments/effects (Cu-
base only)” on page 30 and the chapter “VST instruments and
instrument tracks” on page 206.
• The Studio tab (Cubase only) is where you enable and config-
ure the Control Room, see “VST Connections – Studio tab”
on page 174.
“Setting up busses” on page 26.
“External instruments/ef-
Cubase uses a system of input and output busses to transfer audio between the program and the audio hardware.
• Input busses let you route audio from the inputs on your audio
hardware into the program. This means that when you record
audio, you will always do this through one or several input
busses.
• Output busses let you route audio from the program to the
outputs on your audio hardware. When you play back audio,
you will always do this through one or several output busses.
Once you understand the bus system and know how to
set up the busses properly, it will be easy to go on with
recording, playing back, mixing, and doing surround work
(Cubase only).
Strategies
The bus configuration is saved with the project – therefore
it is a good idea to add and set up the busses you need
and save these in a template project (see “Save as Tem-
plate” on page 51).
When you start working on new projects, you start from
this template. That way you get your standard bus config
uration without having to make new bus settings for each
new project. If you need to work with different bus configurations in different projects, you can either create several
different templates or store your configurations as presets
(see “Presets” on page 29). The templates can of course
also contain other settings that you regularly use – sample
rate, record format, a basic track layout, etc.
So, which type of busses do you need? This depends on
your audio hardware, your general audio setup (e. g. surround speaker setup) and what kind of projects you work
with.
-
26
VST Connections
Page 27

Let’s say you are using audio hardware with eight analog
!
inputs and outputs and digital stereo connections (10 inputs and outputs all in all). Furthermore, you work with a
surround setup in 5.1 format (Cubase only). In this scenario, you may want to add the following busses:
Input busses
• Most likely you need at least one stereo input bus assigned to
an analog input pair. This will let you record stereo material. If
you want to be able to record in stereo from other analog input
pairs as well, you add stereo input busses for these, too.
• Although you can record mono tracks from one side of a stereo input, it may be a good idea to add a dedicated mono input bus. This can be assigned to an analog input to which you
have connected a dedicated microphone pre-amp, for exam
ple. Again, you can have several different mono busses.
• You probably want a dedicated stereo input bus assigned to
the digital stereo input, for digital transfers.
• Cubase only: If you want to transfer surround material directly
to a surround track, e.
g. from surround-configured location recording equipment, you need an input bus in that surround
format – in this example, this will be a 5.1 input bus.
Output busses
• You probably want one or several stereo output busses for
monitoring and listening to stereo mixes.
• For digital transfers, you need a stereo bus assigned to the
digital stereo output as well.
• Cubase only: You need a surround bus in the format of your
speaker configuration (in this example, 5.1) assigned to the
correct outputs (which in turn are connected to the correct
speakers). You may want additional surround busses if you
tend to work in different surround formats.
Different busses can use the same inputs/outputs on
the audio hardware! For example, you may want a
stereo output bus assigned to the same outputs as
the front stereo channels in your surround bus – this
enables you to listen to stereo mixes without having
to reconnect your speakers.
Preparations
Before you set up busses, you should name the inputs
and outputs on your audio hardware. For example, if you
are using a 5.1 surround speaker setup, you should name
the outputs according to which speaker they are con
nected to (Left, Right, Center, and so on).
The reason for this is compatibility – it makes it easier to
transfer projects between different computers and setups.
For example, if you move your project to another studio,
the audio hardware may be of a different model. But if
both you and the other studio owner have given your in
puts and outputs names according to the surround setup
(rather than names based on the audio hardware model),
Cubase will automatically find the correct inputs and out
puts for your busses and you will be able to play and re-
cord without having to change the settings.
To assign names to the inputs and outputs of your audio
hardware, proceed as follows:
1. Open the Device Setup dialog from the Devices menu.
2. On the VST Audio System page, make sure that the
correct driver for your audio hardware is selected.
If this is the case, your audio card is listed in the Devices list on the left of
the Device Setup window.
3. In the Devices list, select your audio card.
The available input and output ports on your audio hardware are listed on
the right.
4. To rename a port, click on its name in the Show As
column and enter a new name.
• If needed, you can also disable ports by deactivating
them in the Visible column.
Disabled ports are not shown in the VST Connections window. If you attempt to disable a port that is used by a bus, you will be asked whether
this is really what you want – note that this will remove the port from the
bus!
5. Click OK to close the Device Setup dialog.
Ö If you open a project created on another computer and
the port names do not match (or the port configuration is
not the same – e.
with multi-channel i/o and you open it on a stereo in/out
system), the Missing Ports dialog will appear. This allows
you to manually re-route ports used in the project to ports
available in your system.
g. the project is created on a system
-
-
-
27
VST Connections
Page 28
Mac OS X only: Port selection and activation
!
On the settings page for your audio card (opened via the
Device Setup dialog, see above), you can specify which
input and output ports are active. This allows you to use
the Microphone input instead of the Line input or even to
deactivate the audio card input or output completely, if re
quired.
Ö This function is only available for Built-In Audio, standard USB audio devices and a certain number of other
audio cards.
Adding input and output busses
Depending on whether you have selected the Inputs or
the Outputs tab in the VST Connections window, the corresponding busses are listed, with the following information:
Column Description
Bus Name Lists the busses. You can select and rename busses by
Speakers Indicates the speaker configuration (mono, stereo, sur-
Audio Device This shows the currently selected ASIO driver.
Device Port If a bus entry is expanded to show all speaker channels,
Click (Outputs
tab only)
clicking on them in this column.
round formats (Cubase only)) of each bus.
this column shows which physical inputs/outputs on your
audio hardware are used by the bus. If the bus entry is
collapsed, only the first port used by this bus is visible
here.
You can route the click to a specific output bus, regardless of the actual Control Room output, or even when the
Control Room is disabled.
3. Select a (channel) configuration.
The Configuration pop-up menu contains a Mono and a Stereo option as
well as several surround formats (Cubase only). Additional surround for
mats are listed on the “More…” submenu.
• Alternatively, you can right-click in the VST Connections
window and add a bus in the desired format directly from
the context menu.
The new bus appears with the ports visible.
4. For each of the speaker channels in the bus, click in
the Device Port column to select a port on your audio
hardware.
The pop-up menu that opens lists the ports with the names you have assigned in the Device Setup dialog.
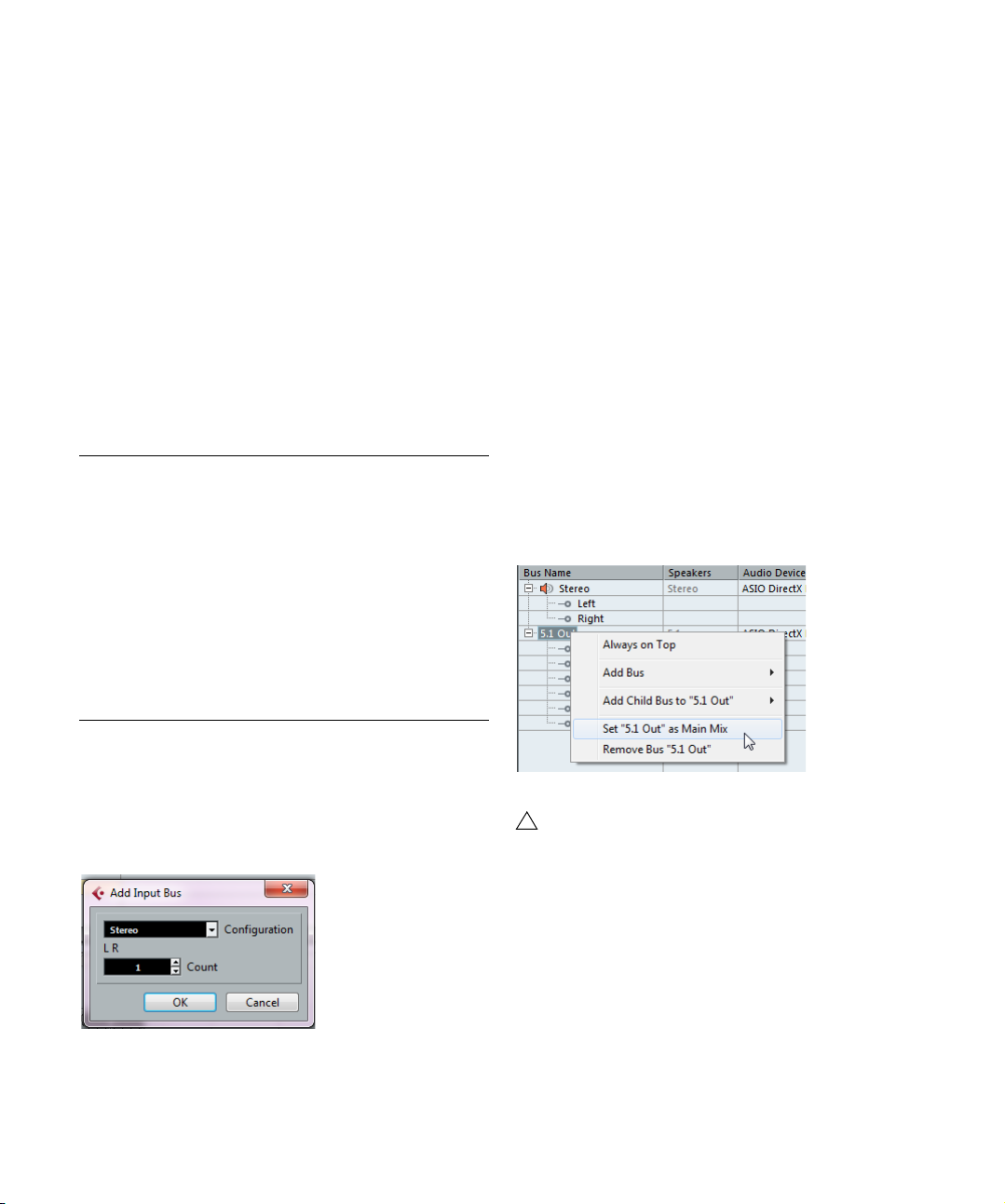
Setting the Main Mix bus (the default output
bus)
The Main Mix is the output bus that each new audio, group
or FX channel is automatically routed to.
Any of the output busses in the VST Connections window
can be the default output bus. By right-clicking on the
name of an output bus, you can set it as the Main Mix bus.
-
To add an input or output bus, proceed as follows:
1. Open the Inputs or Outputs tab depending on the type
of bus that you want to add.
2. Click the Add Bus button.
A dialog opens.
VST Connections
Setting the default output bus.
The Main Mix is indicated by an orange colored
speaker icon next to its name.
28
Page 29
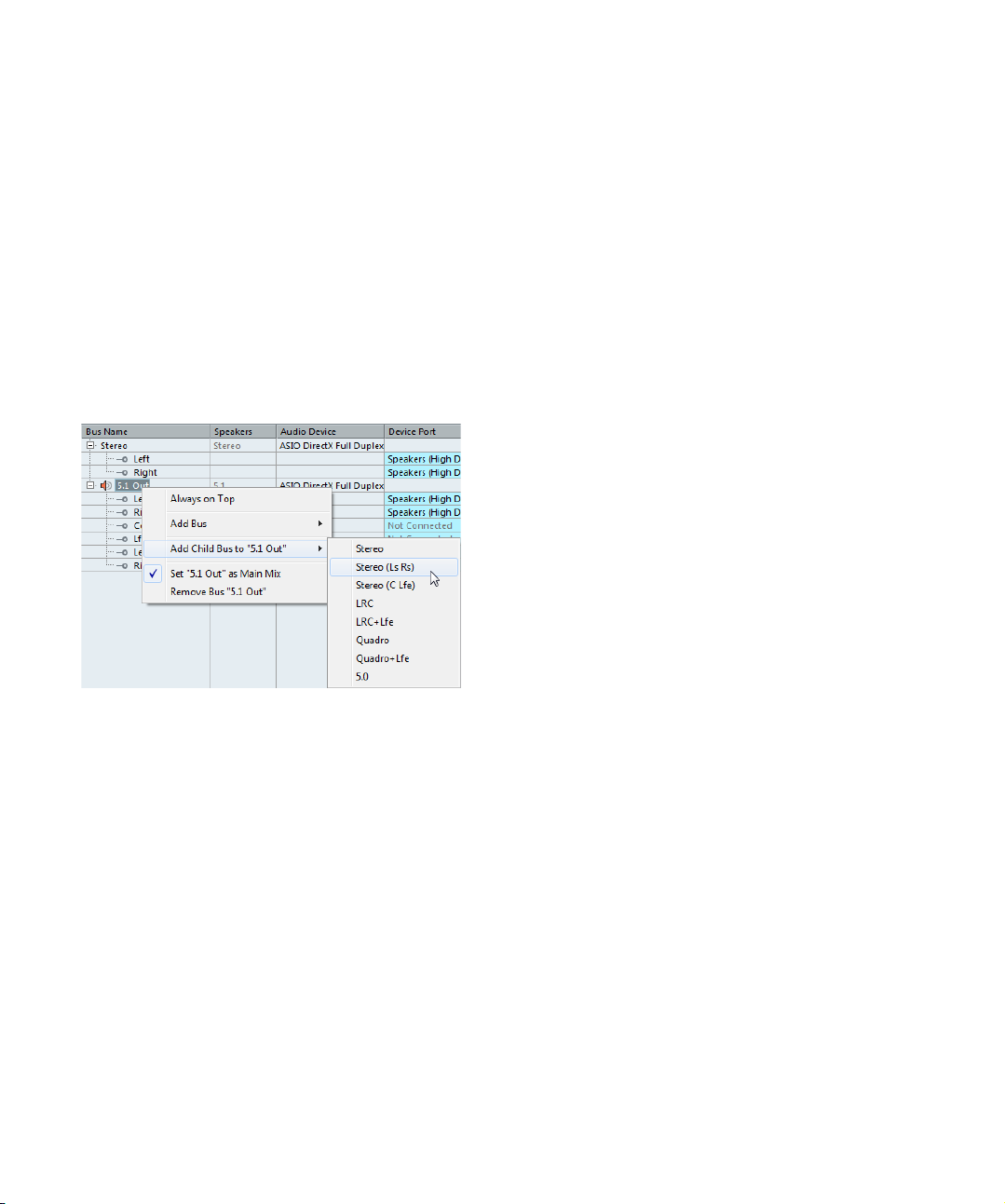
Adding child busses (Cubase only)
A surround bus is essentially a set of mono channels –
6 channels in the case of the 5.1 format. If you have a
mono track in the project, you can route it to a separate
speaker channel in the bus (or route it to the parent sur
round bus and use the SurroundPanner to position it in
the surround image). But what if you have a stereo track
that you simply want to route to a stereo channel pair
within the bus (Left and Right or Left Surround and Right
Surround, for example)? For this you need to create a
child bus.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Bus Name column, select the surround bus and
right-click on it to open the context menu.
-
Presets
On the Inputs and Outputs tabs you will find a Presets
menu. Here you can find three different types of presets:
• A number of standard bus configurations.
• Automatically created presets tailored to your specific
hardware configuration.
On startup, Cubase analyzes the physical inputs and outputs provided
by your audio hardware and creates a number of hardware-dependent
presets with the following possible configurations:
• One stereo bus.
• Various combinations of stereo and mono busses.
• A number of mono busses.
• Cubase only: one 5.1 bus (if you have 6 or more inputs).
• Cubase only: various combinations of 5.1 and stereo busses
(if you have 6 or more inputs).
• Cubase only: various combinations of 5.1 and mono busses (if
you have 6 or more inputs).
• Your own user presets that you can save by clicking the
Store button (“+” symbol). You can then select the stored
configuration directly from the Presets pop-up menu at
any time. To remove a stored preset, select it and click the
Delete button (“-” symbol).
Setting up group and FX channels
2. Select a channel configuration from the “Add Child
Bus” submenu.
As you can see, you can create stereo child busses (routed to various
speaker channel pairs in the surround bus) or other surround bus formats
(with fewer channels than the “parent bus”).
The child bus that you created will be available for routing
in the Mixer. It is a part of the parent surround bus, which
means that it has no separate channel strip.
Although child busses are probably most useful in output
busses, you can also create child busses within a sur
round input bus – for example if you want to record a stereo channel pair (e. g. front left-right) in the surround bus
to a separate stereo track.
VST Connections
The Group/FX tab in the VST Connections window shows
all group channels and FX channels in your project. You
can create new group or FX channels by clicking the cor
responding Add button. This is the same as creating
group channel tracks or FX channel tracks in the Project
window (see
“Using group channels” on page 165 and
the chapter “Audio effects” on page 187).
However, the VST Connections window also allows you
to create child busses for group and FX channels (Cubase only). This is useful if you have group or FX channels
in surround format and want to route stereo channels to
specific channel pairs in these.
Creating a child bus for a group or FX channel in surround
format is similar to creating a child bus for input and out
put busses, see “Adding child busses (Cubase only)” on
page 29.
29
-
-
Page 30

About monitoring
!
!
The VST Connections window allows you to set up the
busses used for monitoring, activate/deactivate the Control Room and open the Control Room Mixer. For details
about using the Control Room and setting up the Studio
tab in the VST Connections window, see the chapter
“Control Room (Cubase only)” on page 172.
When the Control Room is disabled on the Studio tab of
the VST Connections window, the Main Mix bus is used
for monitoring. In this case you can adjust the monitoring
level in the regular Project Mixer, see the chapter
Mixer” on page 145.
Ö In Cubase Artist, the Main Mix bus is always used for
monitoring.
“The
External instruments/effects (Cubase only)
Cubase supports the integration of external effect devices
and external instruments, e. g. hardware synthesizers, into
the sequencer signal flow.
You can use the External Instruments tab and the External
FX tab in the VST Connections window to define the
necessary send and return ports and access the instru
ments/effects through the VST Instruments window.
External instruments and effects are indicated by an
“x” icon in the list next to their names in the respective pop-up menus.
-
Connecting the external effect/instrument
To set up an external effect or instrument, proceed as
follows:
1. Connect an unused output pair on your audio hardware to the input pair on your external hardware device.
In this example, we assume that the hardware device has stereo inputs
and outputs.
2. Connect an unused input pair on your audio hardware
to the output pair on your hardware device.
Please note that it is possible to select input/output
ports for external effects/instruments that are already
used (i.
e. that have been selected as inputs/outputs
in the VST Connections window). If you select a
used port for an external effect/instrument, the exist
ing port assignment will be broken. Note that you will
not get a warning message!
Once the external device is connected to the audio hardware of your computer, you have to set up the input/output busses in Cubase.
Setting up external effects
To set up an external effect in the VST Connections window, proceed as follows:
1. Open the External FX tab and click the “Add External
FX” button.
A dialog opens.
-
Requirements
• To use external effects, you need audio hardware with
multiple inputs and outputs. To use external instruments, a
MIDI interface must be connected to your computer.
An external effect will require at least one input and one output (or input/
output pairs for stereo effects) in addition to the input/output ports you
use for recording and monitoring.
• As always, audio hardware with low-latency drivers is a
good thing to have.
Cubase will compensate for the input/output latency and ensure that the
audio processed through external effects is not shifted in time.
VST Connections
2. Enter a name for the external effect and specify the
send and return configurations.
Depending on the type of effect, you can specify mono, stereo or surround configurations.
30
Page 31

• You also need a MIDI device that corresponds with the
Measure Effect’s Loop Delay button
external effect. You can then click the “Associate MIDI
Device” button to connect the two.
You can use the MIDI Device Manager to create a new MIDI device for
the effect. Note that delay compensation will only be applied for the ef
fect when you use MIDI devices. For information about the MIDI Device
Manager and user device panels see the chapter
on page 356.
“Using MIDI devices”
3. Click OK.
This adds a new external FX bus.
4. Click in the Device Port column for the “left” and
“right” ports of the Send Bus and select the outputs on
your audio hardware that you want to use.
5. Click in the Device Port column for the “left” and
“right” ports of the Return Bus and select the inputs on
your audio hardware that you want to use.
6. If you like, make additional settings for the bus.
These are found in the columns to the right. Note that you can adjust
these while actually using the external effect – which may be easier as
you can hear the result.
The following options are available:
Setting Description
Delay If your hardware effect device has an inherent delay (la-
Send Gain Allows you to adjust the level of the signal being sent to
Return Gain Allows you to adjust the level of the signal coming in from
MIDI Device When you click in this column, a pop-up menu opens
Used Whenever you insert an external effect into an audio
tency), enter this value here, as it allows Cubase to compensate for that delay during playback. You can also let
the delay value be determined by the program: Rightclick the Delay column for the effect and select “Check
User Delay”. Note that you do not have to take the latency
of the audio hardware into account – this is handled auto
matically by the program.
the external effect.
the external effect.
Note however that excessive output levels from an external
effect device may cause clipping in the audio hardware.
The Return Gain setting cannot be used to compensate for
this – you have to lower the output level on the effect de
vice instead.
where you can disconnect the effect from the associated
MIDI device, select a MIDI device, create a new device or
open the MIDI Device Manager to edit the MIDI device.
When Studio Manager 2 is installed, you may also select
an OPT editor to access your external effect.
track, this column shows a checkmark (“x”) to indicate
that the effect is being used.
Ö Note that external device ports are exclusive, see
“Connecting the external effect/instrument” on page 30.
How to use the external effect
-
If you now click an insert effect slot for any channel, you
will find the new external FX bus listed on the “External
Plug-ins” submenu.
When you select it, the following happens:
• The external FX bus is loaded into the effect slot just like a
regular effect plug-in.
• The audio signal from the channel is sent to the outputs on the
audio hardware, through your external effect device and back
to the program via the inputs on the audio hardware.
• A parameter window opens, showing the Delay, Send Gain and
Return Gain settings for the external FX bus. You can adjust
these as necessary while playing back. The parameter window
also provides the “Measure Effect’s Loop Delay for Delay Com
pensation” button. This is the same function as the “Check User
Delay” option in the VST Connections window. It provides Cubase with a Delay value to be used for delay compensation.
When you have defined a MIDI device for the effect, the corre
sponding Device window will be opened. When Studio Manager 2 is installed, and you have set up a corresponding OPT
editor, this OPT editor is displayed.
-
The default parameter window for an external effect
Like any effect, you can use the external FX bus as an insert effect or as a send effect (an insert effect on an FX
-
channel track). You can deactivate or bypass the external
effect with the usual controls.
-
-
31
VST Connections
Page 32

Setting up external instruments
!
To set up an external instrument in the VST Connections
window, proceed as follows:
1. Open the External Instrument tab and click the “Add
External Instrument” button.
A dialog opens.
2. Enter a name for the external instrument and specify
the number of required mono and/or stereo returns.
Depending on the type of instrument, a specific number of mono and/or
stereo return channels is required.
• You also need a MIDI device that corresponds with the
external instrument. You can then click the “Associate
MIDI Device” button to connect the two.
You can use the MIDI Device Manager to create a new MIDI device. For
information about the MIDI Device Manager and user device panels, see
the chapter
3. Click OK.
This adds a new external instrument bus.
4. Click in the Device Port column for the “left” and
“right” ports of the Return Bus and select the inputs on
your audio hardware to which you connected the external
instrument.
5. If you like, make additional settings for the bus.
These are found in the columns to the right. Note that you can adjust
these while actually using the external instrument – which may be easier
as you can hear the result. The following options are available:
Setting Description
Delay If your hardware device has an inherent delay (latency),
“Using MIDI devices” on page 356.
enter this value here. This allows Cubase to compensate
for that delay during playback. Note that you do not have
to take the latency of the audio hardware into account –
this is handled automatically by the program.
Setting Description
Return Gain Allows you to adjust the level of the signal coming in from
MIDI Device When you click in this column, a pop-up menu opens
Used Whenever you insert the external instrument into a VST
the external instrument.
Note however that excessive output levels from an external device may cause clipping in the audio hardware. The
Return Gain setting cannot be used to compensate for
this – you have to lower the output level on the device in
stead.
where you can disconnect the instrument from the asso
ciated MIDI device, select a MIDI device, create a new
device or open the MIDI Device Manager to edit the MIDI
device.
When Studio Manager 2 is installed, you may also select
an OPT editor to access your external instrument.
instrument slot, this column shows a checkmark (“x”) to
indicate that the instrument is being used.
Ö Note that external device ports are exclusive, see
“Connecting the external effect/instrument” on page 30.
How to use the external instrument
Once you have set up the external instrument in the VST
Connections window, you can use it as a VST instrument.
Open the VST Instruments window and click on an empty
instrument slot. On the Instrument pop-up menu, your ex
-
ternal instrument is listed on the External Plug-ins submenu.
When you select the external instrument in the VST Instruments window, the following happens:
• A parameter window for the external device opens automatically. This may either be the Device window, allowing you to
create a generic device panel, an OPT editor window or a de
fault editor. For information about the Device window, the
MIDI Device Manager and User device panels, see the chap
ter “Using MIDI devices” on page 356.
To send MIDI notes to the external instrument, open
the Output Routing pop-up menu in the Inspector for
the corresponding MIDI track and select the MIDI
device to which the external instrument is connected.
This ensures use of delay compensation. The instru
ment will now play any MIDI notes it receives from
this track and return them to Cubase through the re
turn channel(s) you have set up.
The external instrument will behave like any other VST instrument in Cubase.
-
-
-
-
-
-
32
VST Connections
Page 33

About the Favorites buttons
!
!
In the VST Connections window, both the External FX tab
and the External Instruments tab feature a Favorites button.
Favorites are device configurations that you can recall at
any time, like a library of external devices that are not con
stantly connected to your computer. They also allow you
to save different configurations for the same device, e.
multi-effect board or an effect that provides both a mono
and a stereo mode.
To save a device configuration as a favorite, proceed as
follows:
• When you have added a new device in the VST Connections window, select it in the Bus Name column and
click the Favorites button.
A context menu is displayed showing an option to add the selected effect or instrument to the Favorites.
• You can recall the stored configuration at any time by
clicking the Favorites button and selecting the device
name from the context menu.
g. a
To reestablish the broken connection to the external device, simply right-click the entry for the device in the Bus
Name column and select “Connect External Effect”. The
icon is removed, and you can use the external device
within your project as before.
Note that busses set up for external effects or external instruments are saved “globally”, i. e. for your particular computer setup.
-
Freezing external effects/instruments
Just as when working with regular VST instruments and
effects, you can also choose to freeze external effects and
instruments. The general procedure is described in detail
in the chapters
“Audio effects” on page 187 and “VST in-
struments and instrument tracks” on page 206.
Note that you have to perform Freeze in realtime.
Otherwise external effects will not be taken into ac
count.
When freezing external instruments or effects, you can adjust the corresponding tail value in the Freeze Channel
Options dialog:
-
About the “plug-in could not be found”
message
When you open a project that uses an external effect/instrument, you may get a “plug-in could not be found” message. This will happen when you remove an external
device from the VST Connections window although it is
used in a saved project, or when transferring a project to
another computer on which the external device is not de
fined. You may also see this message when opening a
project created with an earlier version of Cubase.
In the VST Connections window, the broken connection
to the external device is indicated by an icon in the Bus
Name column.
VST Connections
• Use the arrow buttons next to the Tail Size value field to
set the desired Tail length, i. e. the range after the part
boundary is also to be included in the freeze. You can also
-
click directly in the value field and enter the desired value
manually (the maximum value being 60
s).
• When the Tail Size is set to 0 s (default), the freezing will
only take into account the data within the Part boundaries.
33
Page 34

Editing operations
!
On the different tabs of the VST Connections window the
corresponding busses or channels are shown in a table
containing a tree view with expandable entries. After you
have set up all the required busses for a project it might
be necessary to edit the names and/or change port as
signments. Cubase provides a number of features to make
such tasks easier.
Expanding and collapsing entries
• Bus entries can be expanded or collapsed to show or
hide the corresponding speaker channels or sub-busses
by clicking the “+” or “-” sign in front of the corresponding
list entry.
• To expand or collapse all entries on a tab at the same
time, use the “+ All” button or the “- All” button (respectively) above the tree view.
Determining how many busses a device port is
connected to
To give you an idea how many busses a given port is already connected to, the busses are shown in square
brackets on the Device Port pop-up menu, to the right of
the port name.
Up to three bus assignments can be displayed in this way.
If more connections have been made, this is indicated by a
number at the far right.
Therefore, if you see the following:
Adat 1 [Stereo1] [Stereo2] [Stereo3] (+2)…
this means that the Adat 1 port is already assigned to
three stereo busses plus two additional busses.
Identifying exclusive port assignments
In some cases (i. e. for certain channel types such as Studio channels), the port assignment is exclusive. Once a
port has been assigned to such a bus or channel, it must
not be assigned to another bus, otherwise the connection
to the first bus will be broken.
To help you identify such exclusive port assignments and
avoid accidental reassignment, the corresponding ports
are marked in red on the Device Port pop-up menu.
-
Selecting/Deselecting multiple entries
• Using the key commands [Ctrl]/[Command]-[A] (Select
All) and [Shift]-[Ctrl]/[Command]-[A] (Select None), you
can select and deselect all entries in the Bus Name column.
Note that for this to work, the table on the current tab needs to have the
focus. This can be achieved by clicking anywhere on the background of
the table.
• By holding [Shift] when selecting entries in the Bus
Name column, you can select multiple entries at the same
time.
This is useful for automatic renaming or changing the port assignments
globally, see below.
Ö If you select a subentry (e. g. a speaker channel in a
bus) the parent entry is automatically selected as well.
Selecting entries by typing the name
In the Bus Name list you can jump to an entry by typing the
first letter of the bus name on the keyboard.
This will only work if the table has the focus. To do
this, simply select any list entry.
Navigating the Bus Name list using the [Tab] key
By pressing the [Tab] key you can jump to the next entry in
the Bus Name list, allowing you to rename your busses
quickly. Similarly, by pressing [Shift]-[Tab] you can return
to the previous list entry.
Automatically renaming selected busses
You can rename all the selected busses at once using incrementing numbers or letters.
• To use incrementing numbers, select the busses that
you want to rename and enter a new name for one of the
busses, followed by a number.
For example, if you have eight inputs that you want to be named “In 1,
In
2, …, In 8”, you select all the busses and enter the name “In 1” for the
first bus. All other busses are then renamed automatically.
34
VST Connections
Page 35

• To use letters from the alphabet, proceed as with num-
!
!
bers, but enter a capital letter instead of a number.
For example, if you have three FX channels that you want to be named
“FX A, FX B, and FX C”, you select all the channels and enter the name
“FX
A” for the first. All other channels are then renamed automatically.
The last letter that can be used is Z. If you have more selected entries
than there are letters available, the remaining entries will be skipped.
When using letters instead of numbers, it is important to note that these must be preceded by a space.
If you leave out the space before the letter or if you
do enter neither a letter nor a number, only the first
selected entry is renamed.
Ö You do not have to begin renaming with the topmost
selected entry. The renaming will start from the bus where
you edit the name, will go down the list to the bottom and
then continue from the top until all selected busses have
been renamed.
Changing the port assignment for a single bus
To change the port assignment for a single bus, you proceed as when you added it: Make sure that the channels
are visible and click in the Device Port column to select
ports.
Changing the port assignment for multiple busses
To change the port assignment (or the output routing in
case of groups/FX channels) for multiple entries in the
Bus Name column at the same time, you need to select
the corresponding busses first.
• To assign different ports to the selected busses, press
[Shift], open the Device Port pop-up menu for the first se
lected entry (i. e. the topmost bus) and select a device
port.
All subsequent busses are automatically connected to the next available
port.
Removing busses
To remove a bus you do not need, select it in the list, rightclick and select Remove Bus from the pop-up menu, or
press [Backspace].
-
Cubase only: Exclusive ports (e. g. ports already assigned to Control Room channels) will be skipped!
• To assign the same port to all selected busses, press
[Shift]-[Alt]/[Option], open the Device Port pop-up menu
for the first selected entry (i.
e. the topmost bus) and select
a device port.
Ö You can also set all selected busses or channels to
Not Connected.
35
VST Connections
Page 36

4
The Project window
Page 37

Window Overview
Project
overview
The event display, showing audio parts and events, MIDI parts, automation, markers, etc.
Inspector
Ruler
Status line
Toolbar
The track list with various track types
Info line
The Project window is the main window in Cubase. This provides you with an overview of the project, allowing you to
navigate and perform large scale editing. Each project has one Project window.
About tracks
The Project window is divided vertically into tracks, with a
timeline running horizontally from left to right. The follow
ing track types are available:
Track type Description
Audio For recording and playing back audio events and audio
Folder Folder tracks function as containers for other tracks, mak-
parts. Each audio track has a corresponding audio chan
nel in the Mixer.
An audio track can have any number of automation tracks
for automating Mixer channel parameters, effect settings,
etc.
ing it easier to organize and manage the track structure.
They also allow you to edit several tracks at the same
“Organizing tracks in folder tracks” on page 79.
time, see
-
The Project window
Track type Description
FX Channel FX channel tracks are used for adding send effects. Each
-
Group
Channel
37
FX channel can contain up to eight effect processors – by
routing effect sends from an audio channel to an FX chan
nel, you send audio from the audio channel to the effect(s)
on the FX channel. Each FX channel has a corresponding
channel strip in the Mixer – in essence an effect return
channel, see the chapter
All FX channel tracks are automatically placed in a special
FX channel folder in the track list, for easy management.
An FX channel can also have any number of automation
tracks for automating Mixer channel parameters, effect
settings, etc.
By routing several audio channels to a Group channel,
you can submix them, apply the same effects to them, etc.
“Using group channels” on page 165).
(see
A Group channel track contains no events as such, but
displays settings and automation curves for the corre
sponding Group channel. Each Group channel track has
a corresponding channel strip in the Mixer. In the Project
window, Group channels are organized as tracks in a
special Group Tracks folder.
“Audio effects” on page 187.
-
-
Page 38

Track type Description
Instrument This allows you to create a track for a dedicated instru-
MIDI For recording and playing back MIDI parts. Each MIDI
Marker Marker tracks display markers which can be moved and
Arranger The arranger track is used for arranging your project, by
Ruler Ruler tracks contain additional rulers, displaying the time-
Signature Time signature events can be added and edited on the
Tempo You can create tempo changes within a project using the
Transpose The transpose track allows you to set global key changes.
Video For playing back video events. A project can only have
ment, making VST instrument handling easier and more intuitive. Instrument tracks have a corresponding channel
strip in the Mixer. Each instrument track can have any num
ber of automation tracks in the Project window. However,
Volume and Pan are automated from within the Mixer. It is
possible to edit instrument tracks directly in the Project
window, using the Edit In-Place function (see
Place Editor” on page 396). For more information on in-
strument tracks, see the chapter “VST instruments and in-
strument tracks” on page 206.
track has a corresponding MIDI channel strip in the Mixer.
It is possible to edit MIDI tracks directly in the Project
window, using the Edit In-Place function (see
Place Editor” on page 396).
A MIDI track can have any number of automation tracks
for automating Mixer channel parameters, insert and send
effect settings, etc.
renamed directly in the Project window (see the chapter
“Using markers” on page 138). A project can have only
one marker track.
marking out sections in the project and determining in
which order they are to be played back. See the chapter
“The arranger track” on page 124 for details.
line from left to right. You can use any number of ruler
tracks, each with a different display format if you wish.
“The ruler” on page 44 for more information about
See
the ruler and the display formats.
signature track, or in the Tempo Track Editor. A project
can have only one signature track. See the chapter
ing tempo and signature” on page 462 for details.
tempo track. A project can have only one tempo track.
See the chapter
462 for details.
A project can have only one transpose track, see the
chapter
one video track.
“Editing tempo and signature” on page
“The transpose functions” on page 131.
“The In-
“The In-
“Edit-
About parts and events
The tracks in the Project window contain parts and/or
events. Events are the basic building blocks in Cubase.
-
Different event types are handled differently in the Project
window:
• Video events and automation events (curve points) are always
viewed and rearranged directly in the Project window.
• MIDI events can always be found in MIDI parts, which are containers for one or more MIDI events. MIDI parts are rearranged
and manipulated in the Project window. To edit the individual
MIDI events in a part, you have to open the part in a MIDI edi
tor (see “The MIDI editors” on page 374).
• Audio events can be displayed and edited directly in the Project window, but you can also work with audio parts containing
several events. This is useful if you have a number of events
which you want to treat as one unit in the project. Audio parts
also contain information about the time position in the project.
An audio event and an audio part
Getting on-the-fly info with the Arrow tool
If the “Select Tool: Show Extra Info” option is activated in
the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tools page), a tooltip will
be shown for the Arrow tool, displaying information de
pending on where you point it. For example, in the Project
window event display, the tool will show the current pointer
position and the name of the track and event you are point
ing at.
-
-
-
38
The Project window
Page 39

The track list
The track list displays all the tracks used in a project. It contains name fields and settings for the tracks. Different track
types have different controls in the track list. To see all
available controls, you may have to resize the track in the
track list (see
The track list showing a MIDI track, an audio track with an automation
track, and a VST instrument track
“Resizing tracks” on page 73).
• Using the Track Controls Settings dialog you can decide which controls are visible for each track type, see
“Customizing track controls” on page 535.
The Inspector
2. In the gray area in the middle, activate the Inspector
option.
Inspector handling
For most track classes, the Inspector is divided into a
number of sections, each containing different controls for
the track. Which sections are available in the Inspector
depends on the selected track.
• You can hide or show sections by clicking on their
names.
Clicking the name for a hidden section brings it into view and hides the
other sections. [Ctrl]/[Command]-clicking the section name allows you
to hide or show a section without affecting the other sections. [Alt]/[Op
tion]-clicking a section name shows or hides all sections in the Inspector.
-
The area to the left of the track list is called the Inspector.
This shows additional controls and parameters for the
track you have selected in the track list. If several tracks
are selected, the Inspector shows the setting for the first
(topmost) selected track.
Opening the Inspector
To show the Inspector, proceed as follows:
1. On the toolbar, click the “Set up Window Layout”
button.
A transparent pane appears, covering the Project window.
The Project window
• You can also use key commands to show different In-
spector sections.
These are set up in the Key Commands dialog, see “Setting up key com-
mands” on page 542.
Ö Hiding a section does not affect its functionality. For
example, if you have set up a track parameter or activated
an effect, your settings will still be active even if you hide
the respective Inspector section.
39
Page 40

Not all Inspector tabs are shown by default. You can
show/hide Inspector sections by right-clicking on an Inspector tab and activating/deactivating the desired options on the Inspector Setup context menu.
Ö Make sure that you right-click on an Inspector tab and
not on the empty area below the Inspector, as this will
open the Quick context menu instead.
Inspector sections
The Inspector contains the controls that can be found on
the track list, plus some additional buttons and parame
ters. In the table below, these additional settings and the
different sections are listed. Which sections are available
for which track type is described in the following sections.
Parameter Description
Auto Fades
Settings
button
Edit Channel
Settings
Volume Use this to adjust the level for the track. Changing this
Pan Use this to adjust the panning of the track. As with the
Delay This adjusts the playback timing of the audio track. Positive
Input
Routing
Opens a dialog in which you can make separate Auto
Fade settings for the audio track, see
settings for individual tracks” on page 123.
Opens the Channel Settings window for the track, allowing you to view and adjust effect and EQ settings, etc.,
see
“Using Channel Settings” on page 158.
setting will move the track’s fader in the Mixer window,
and vice versa. See
152 to learn more about setting levels.
Volume setting, this corresponds to the Pan setting in the
Mixer.
values delay the playback while negative values cause the
track to play earlier. The values are set in milliseconds.
This lets you specify the input bus or MIDI input for the
track. See
tion about input busses.
“Setting volume in the Mixer” on page
“Setting up busses” on page 26 for informa-
“Making Auto Fade
-
Parameter Description
Output
Routing
Inserts section Allows you to add insert effects to the track, see the chap-
Equalizers
section
Equalizer
Curve section
Sends section Allows you to route an audio track to one or several FX
Studio Sends
(Cubase only)
Surround Pan
(Cubase only)
Channel
section
Notepad
section
User Panel
(Cubase only)
Quick Controls Here you can configure quick controls, e. g. to use remote
Here you decide to which output the track is routed. For
audio tracks you select an output bus (see
busses” on page 26) or Group channel, for MIDI tracks
you select a MIDI output and for instrument tracks, you
select the instrument to which it is routed.
ters “Audio effects” on page 187 and “MIDI realtime pa-
rameters and effects” on page 348. The Edit button at the
top of the section opens the control panels for the added
insert effects.
Lets you adjust the EQs for the track. You can have up to
four bands of EQ for each track, see
tings” on page 159. The Edit button at the top of the sec-
tion opens the Channel Settings window for the track.
Lets you adjust the EQs for the track graphically, by clicking and dragging points in a curve display.
channels, see the chapter
The Edit button above a slot opens the control panel for
the first effect in each FX channel.
For MIDI tracks, this is where you assign MIDI send effects. Clicking the Edit button above a slot opens the
control panel for the corresponding MIDI effect.
The Studio Sends are used to route cue mixes to Control
Room Studios. For a detailed description of Studios and
Studio Sends, see the chapter
only)” on page 172.
When the SurroundPanner is used for a track, this is also
available in the Inspector. For further information, see
“Using the SurroundPanner V5” on page 220.
Shows a duplicate of the corresponding Mixer channel
strip. The channel overview strip to the left lets you acti
vate and deactivate insert effects, EQs and sends.
This is a standard text notepad, allowing you to jot down
notes about the track. If you open the File menu and se
lect “Notepad Data…” from the Export submenu, your
data will be exported as text file and opened in an external
text editor from where you can print it. Note that you have
to save your project first.
If you have entered any notes about a track, the icon next
to the “Notepad” heading will light up to indicate this.
Moving the pointer over the icon will display the Notepad
text in a tooltip.
Here you can display device panels, e. g. for external MIDI
devices, audio track panels or VST insert effect panels.
For information on how to create or import MIDI device
and user panels, see the separate PDF document “MIDI
Devices”.
devices, see the chapter
337.
“Audio effects” on page 187.
“Control Room (Cubase
“Track Quick Controls” on page
“Setting up
“Making EQ set-
Audio tracks
For audio tracks, all settings and sections listed above are
available.
-
-
40
The Project window
Page 41

Instrument tracks
As explained in the chapter “VST instruments and instru-
ment tracks” on page 206, the Inspector for an instrument
track shows some of the sections from VST instrument
channels and MIDI tracks.
MIDI tracks
When a MIDI track is selected, the Inspector contains a
number of additional sections and parameters, affecting the
MIDI events in realtime (e.
g. on playback). Which sections
are available for MIDI tracks is described in the chapter
“MIDI realtime parameters and effects” on page 348.
Arranger track
For the arranger track, the Inspector displays the lists of
available arranger chains and arranger events. See the
chapter “The arranger track” on page 124 for details.
Folder tracks
When a folder track is selected, the Inspector shows the
folder and its underlying tracks, much like a folder structure in the Windows Explorer or Mac OS X Finder.
Ö You can click one of the tracks shown under the folder
in the Inspector to have the Inspector show the settings
for that track. This way, you do not have to “open” a folder
track to make settings for tracks within it.
FX channel tracks
When an FX channel track is selected, the following controls and sections are available:
• Edit button
• Volume control
• Pan control
• Output Routing pop-up menu
• Inserts section
• Equalizers section
• Equalizer Curve section
• Sends section (Cubase only)
• Studio Sends section (Cubase only)
• Surround Pan section (Cubase only)
• Channel section
•Notepad section
FX channel tracks are automatically placed in a special
folder, for easier management. When this folder track is
selected, the Inspector shows the folder and the FX chan
nels it contains. You can click one of the FX channels
shown in the folder to have the Inspector show the settings for that FX channel – this way you do not have to
“open” a folder track to access the settings for the FX
channels in it.
Group channel tracks
When a group channel track is selected, the following
controls and sections are available:
• Edit button
• Volume control
•Pan control
• Output Routing pop-up menu
• Inserts section
• Equalizers section
• Equalizer Curve section
• Sends section
• Studio Sends section (Cubase only)
• Surround Pan section (Cubase only)
• Channel section
• Notepad section
Just like FX channel tracks, all group channel tracks are
placed in a separate folder – when this is selected, the Inspector shows the folder and the group channels it contains. You can click one of the group channels shown in the
folder to have the Inspector show the settings for that group
channel – this way, you do not have to “open” a folder track
to access the settings for the group channels in it.
Marker tracks
When the marker track is selected, the Inspector shows
the marker list. For more information, see the chapter
“Us-
ing markers” on page 138.
Ruler tracks
For ruler tracks, the Inspector is not used.
Transpose track
When the transpose track is selected, the following controls and sections are available:
• Mute button
• Keep Transpose in Octave range
-
41
The Project window
Page 42

• Toggle Time Base button
• Lock button
•Notepad section
The transpose track controls are described in detail in the
chapter
“The transpose functions” on page 131.
Signature track and tempo track
For the signature track and the tempo track, the Inspector
displays a list of all time signature events or tempo events.
See the chapter
“Editing tempo and signature” on page
462 for details.
Video tracks
When a video track is selected, the Inspector contains a
lock button for locking the track (see the section
“Locking
events” on page 65), a Mute button for interrupting video
playback and two settings for video thumbnails: Show
Frame Numbers and Show Thumbnails (see the section
“Video files in the Project window” on page 513).
Video tracks make use of the Notepad Inspector tab.
The toolbar
The toolbar contains tools and shortcuts for opening other
windows and various project settings and functions.
You can show/hide most of the toolbar elements (except
the Activate Project and “Set up Window Layout” buttons)
by activating/deactivating the corresponding options on
the context menu. The following options are available:
Option Description
Constrain Delay
Compensation
Media & Mixer
Windows
Performance Meter When this is activated, meters for ASIO time usage
Automation Mode When this is activated, the automation mode and a
This is described in the section “Constrain Delay
Compensation” on page 216.
When this is activated, buttons for opening or closing the MediaBay, the Pool, the Mixer, and the Control Room Mixer (Cubase only) are displayed on the
toolbar.
and hard disk transfer load are displayed, see
the VST Performance window” on page 24.
button to open/close the Automation panel are dis
played on the toolbar. For details, see the chapter
“Automation” on page 227.
“About
Option Description
Auto-Scroll When this is activated, buttons for the options “Auto-
Locators When this is activated, the left and right locator posi-
Transport Buttons When this is activated, the transport buttons from the
Arranger Controls When this is activated, the controls used when work-
Time Display When this is activated, the Transport panel’s time
Markers When this is activated, the Transport panel’s marker
Snap to Zero
Crossing
Tool Buttons When this is activated, tool buttons for editing in the
Color menu This shows/hides the color pop-up menu, see “Ap-
Nudge Palette Activate this to display the nudge buttons. These
Project Root Key Activate this to display the Project Root Key. For de-
Snap/Quantize These options are described in the sections “The
Scroll” and “Suspend Auto-Scroll when Editing” are
displayed, see
tions are displayed on the toolbar.
Transport panel are also displayed on the toolbar.
ing with the arranger track are displayed, see the
chapter
display is displayed on the toolbar.
buttons are displayed on the toolbar.
This is described in the section “Snap to Zero
Crossing” on page 47.
Project window are displayed on the toolbar. The
tools are also accessible via the toolbox, see
the toolbox” on page 42.
plying colors in the Project window” on page 537.
buttons can be used to nudge events or parts in the
Project window or for trimming (see
on page 61 and “Resizing events” on page 63).
tails, see the chapter “The transpose functions” on
page 131.
Snap function” on page 45 and “Quantizing MIDI
and audio” on page 108.
“Auto-Scroll” on page 47.
“The arranger track” on page 124.
“Moving events”
Ö How to further set up the toolbar is described in the
section
“Using the Setup options” on page 534.
Using the toolbox
The toolbox can be opened instead of the standard context menus in the event display and editors. It makes the
editing tools from the toolbar conveniently available at the
mouse pointer position.
• To open the toolbox by right-clicking (Win)/[Ctrl]-clicking (Mac), activate the “Popup Toolbox on Right Click”
option in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tools page).
When this option is activated, you need to press any modifier key and
right-click (Win)/[Ctrl]-click (Mac) to open the context menu. When it is
-
deactivated, you need to press a modifier key to open the toolbox instead
of the context menu.
“Using
42
The Project window
Page 43

• To change the number of rows in which the tools are
!
arranged on the toolbox, keep the right mouse button
pressed on the toolbox until the mouse pointer changes to
a double arrow, and drag to the bottom or right.
The tools can be arranged in one, two, or three horizontal or vertical
rows.
The info line
The info line is displayed below the status line in the Project window.
The status line
The status line is displayed below the toolbar in the Project window.
It displays the following information:
Option Description
Record Time Max This displays the time you have left for recording,
Record Format This displays the sample rate and the bit resolution
Project Frame Rate This displays the frame rate used in the project.
Project Pan Law This displays the current Pan Law setting.
Ö Clicking on any of the fields except the Record Time
Max display opens the Project Setup dialog, where you
can adjust the settings (see
page 54).
Cubase permits different sample rate settings for a
project and the audio hardware. However, as a result
the audio files in a project will not play back in their
original pitch. If the “Record Format” field is high
lighted in a different color, there is a sample rate
mismatch and you should check the settings in the
Project Setup dialog.
• To show or hide the status line, click the “Set up Window Layout” button on the toolbar and activate or deactivate the Status Line option.
depending on your project settings and the avail
able hard disk space. Click in this field to display
the remaining record time in a separate window.
used for recording.
“The Project Setup dialog” on
-
The info line shows information about the currently selected event or part in the Project window. You can edit almost all values on the info line using regular value editing.
Length and position values are displayed in the format cur
rently selected for the ruler (see “The ruler” on page 44).
• To show or hide the info line, click the “Set up Window
Layout” button on the toolbar and activate or deactivate
the Info Line option.
The following elements can be selected for display and
-
editing on the info line:
• Audio events
•Audio parts
• MIDI parts
• Video events
•Markers
• Automation curve points
• Transpose events
• Arranger events
When several elements are selected
• If you have selected several elements, the info line shows
information about the first item in the selection. The values
are displayed in color to indicate that several elements are
selected.
• If you edit a value on the info line, the value change is
applied to all selected elements, relatively to the current
values.
If you have selected two audio events, the first being one bar long and the
second two bars, the info line shows the length of the first event (one bar).
If you now change this value to 3 bars in the info line, the other event will be
resized by the same amount – and will thus be 4 bars long.
• To enter absolute values for the selected elements,
press [Ctrl]/[Command] while modifying the value on the
info line. In the example above, both events would be re
sized to 3 bars.
[Ctrl]/[Command] is the default modifier key for this – you can change
this in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tool Modifiers page, in the Info
Line category).
-
-
43
The Project window
Page 44

Editing transpose and velocity for MIDI parts
When one or several MIDI parts are selected, the info line
contains Transpose and Velocity fields.
• Adjusting the Transpose field transposes the selected
parts in semitone steps.
Note that this transposition does not change the actual notes in the part
– it is just a “play parameter”, affecting the notes on playback. The trans
position you specify for a part on the info line is added to the transposition set for the whole track. For more information on transposing, see the
chapter
“The transpose functions” on page 131.
• Adjusting the Velocity field shifts the velocity for the selected parts – the value you specify is added to the velocities of the notes in the parts.
Again, this velocity shift only affects the notes on playback, and again,
the value you specify is added to the Vel.Shift. value set for the whole
MIDI track in the Inspector.
The overview line
The overview line is displayed below the info line in the
Project window. In the overview line, events and parts on
all tracks are displayed as boxes.
• To show/hide the overview line, proceed as for the info
line (see above), but activate the Overview Line option instead.
You can use the overview line to zoom in or out, and for
navigating to other sections of the project. This is done by
moving and resizing the track view rectangle in the over
view line:
• The track view rectangle indicates the section of the
project currently displayed in the event display.
• You zoom in or out horizontally by resizing the rectangle.
Resize it by dragging the edges of the rectangle.
-
• You can drag the track view rectangle to view other
sections of the project.
This can also be done by clicking anywhere in the upper part of the overview – the track view rectangle will be moved to where you clicked.
The ruler
-
The ruler at the top of the event display shows the timeline. Initially, the Project window ruler uses the display format specified in the Project Setup dialog (see “The
Project Setup dialog” on page 54), as do all other rulers
and position displays in the project. However, you can select an independent display format for the ruler by clicking
the arrow button to the right of it and selecting an option
from the pop-up menu (you can also bring up this pop-up
menu by right-clicking anywhere in the ruler).
Option Positions and lengths displayed as
Bars+Beats Bars, beats, sixteenth notes and ticks. By default there
Seconds Hours, minutes, seconds and milliseconds.
Timecode This format displays hours, minutes, seconds, and
Samples Samples.
fps (User) Hours, minutes, seconds and frames, with a user-defin-
Time Linear When this is selected, the ruler will be linear relative to
Bars+Beats
Linear
• The selection you make here affects the ruler, the info
line and tooltip position values (which appear when you
drag an event in the Project window).
You can also select independent formats for other rulers and position
displays.
are 120 ticks per sixteenth note, but you can adjust this
with the “MIDI Display Resolution” setting in the Prefer
ences dialog (MIDI page).
frames. The number of frames per second (fps) is set in
the Project Setup dialog with the Frame Rate pop-up
menu (see
able number of frames per second. You set the desired
number of fps in the Preferences dialog (Transport page).
time. This means that if there are tempo changes on the
tempo track, the distance between the bars will vary in
Bars+Beats mode.
When this is selected, the ruler will be linear relative to
the meter position – bars and beats. This means that if
there are tempo changes on the tempo track, there still
will be the same distance between bars in Bars+Beats
mode. If the ruler is set to a time-based mode, the dis
tance between seconds will vary depending on the
tempo changes.
“The Project Setup dialog” on page 54).
-
-
44
The Project window
Page 45

• To set the display format globally (for all windows), use
the primary display format pop-up on the Transport panel,
or hold down [Ctrl]/[Command] and select a display for
mat in any ruler.
• If you use the “Timecode” or “User” options and the
“Show Timecode Subframes” option are activated in the
Preferences dialog (Transport page), the frames will also
display subframes.
There are 80 subframes per frame.
-
Using multiple rulers – ruler tracks
As described above, the Cubase Project window contains
a main ruler at the top of the event display, displaying the
timeline from left to right.
If needed, you can have several rulers in the Project window, by adding ruler tracks to the project. Each ruler track
contains an additional ruler.
• To add a ruler track, open the “Add Track” submenu
from the Project menu and select “Ruler”.
A ruler track showing an additional ruler is added to the track list.
You can add any number of ruler tracks to a project, and
position them as needed by dragging them up or down in
the track list. Each of the rulers can show a separate display format.
• To select a display format for a ruler track, click on its
name in the track list and select an option from the pop-up
menu.
Note that ruler tracks are completely independent from the
main event display ruler, as well as rulers and position displays in other windows. This means that:
• Each ruler track in a project can have its own display format.
• Ruler tracks are not affected by the display format setting in
the Project Setup dialog (see “The Project Setup dialog” on
page 54).
• Ruler tracks are not affected if you set the display format globally with the primary time display in the Transport panel.
Ö Ruler tracks are affected by the “Show Timecode
Subframes” option in the Preferences dialog (Transport
page, see above).
The Snap function
The Snap function helps you to find exact positions when
editing in the Project window. It does this by restricting
horizontal movement and positioning to certain positions.
Operations affected by Snap include moving, copying,
drawing, sizing, splitting, range selection, etc.
• You turn Snap on or off by clicking the Snap icon on the
toolbar.
When you are moving audio events with Snap activated, it
is not necessarily the beginning of the event that is used
as Snap position reference. Instead, each audio event has
a snap point, which you can set to a relevant position in
the audio (such as a downbeat, etc.).
The snap point is preferably set in the Sample Editor since
it allows for a higher degree of precision (see
the snap point” on page 268). However, you can also set
the snap point directly in the Project window, in the following way:
1. Select an event.
2. Place the project cursor at the desired position within
the selected audio event.
“Adjusting
45
The Project window
Page 46

3. Pull down the Audio menu and select “Snap Point To
Cursor”.
The snap point is set at the cursor position.
The snap point for an event is displayed as a vertical line in the Project
window.
The Snap Type pop-up menu
To determine how the Snap function works, open the
Snap Type pop-up menu and select one of the available
options.
In the Snap Type pop-up menu the following options are
available:
Grid
If you select this Snap type, the Snap positions are set
with the Grid Type pop-up menu. The options depend on
the display format selected for the ruler. For example, if the
ruler is set to show bars and beats, the grid can be set to
bars, beats, or the quantize value set with the selected
quantize preset. If a time or frame-based ruler format is se
lected, the Grid Type pop-up menu contains time or
frame-based grid options, etc.
Grid Relative
If you select this Snap type, events and parts will not be
“magnetic” to the grid. Rather, the grid determines the
step size for moving the events. This means that a moved
event will keep its original position relative to the grid.
For example, if an event starts at the position 3.04.01 (one
beat before bar 4), Snap is set to Grid Relative and the Grid
Type pop-up menu is set to “Bar”, you can move the event
in steps of one bar – to the positions 4.04.01, 5.04.01 and
so on. The event will keep its relative position to the grid, i.
stay one beat before the bar lines.
• This only applies when dragging existing events or parts
– when you create new events or parts this snap type
works like “Grid”.
Events
This grid type makes the start and end positions of other
events and parts become “magnetic”. This means that if
you drag an event to a position near the start or end of another event, it is automatically aligned with the start or end
of the other event. For audio events, the position of the
snap point is also magnetic (see “Adjusting the snap
point” on page 268).
• Note that this includes marker events on the marker
track.
This allows you to snap events to marker positions, and vice versa.
Shuffle
Shuffle is useful when you want to change the order of adjacent events. If you have two adjacent events and drag
the first one to the right, past the second event, the two
events will change places.
-
e.
When Seconds is selected as ruler format, the Grid Type pop-up menu
contains time-based grid options.
The Project window
46
Page 47

The same principle works when changing the order of
12345
52431
Dragging event 2 past event 4…
…changes the order of events 2, 3 and 4.
more than two events:
Magnetic Cursor
This grid type lets the project cursor become “magnetic”.
Dragging an event near the cursor causes the event to be
aligned with the cursor position.
Grid + Cursor
This is a combination of “Grid” and “Magnetic Cursor”.
Events + Cursor
This is a combination of “Events” and “Magnetic Cursor”.
Events + Grid + Cursor
This is a combination of “Events”, “Grid” and “Magnetic
Cursor”.
Snap to Zero Crossing
When this option is activated on the toolbar, splitting and
sizing of audio events is done at zero crossings (positions
in the audio where the amplitude is zero). This helps you
avoid pops and clicks which might otherwise be caused
by sudden amplitude changes.
Auto-Scroll
When the Auto-Scroll option is activated, the waveform
display will scroll during playback, keeping the project cursor visible in the window. You can find the Auto-Scroll button on the toolbars of the Project window and all editors.
“Auto-Scroll” and “Suspend Auto-Scroll when Editing” are activated
• If the “Stationary Cursors” option is activated in the
Preferences dialog (Transport page), the project cursor
will be positioned in the middle of the screen (if possible).
Suspending Auto-Scroll
When editing parts or events during playback with AutoScroll enabled, you may suddenly “lose sight” of the ed
ited material as the display follows the project cursor.
If you do not want the Project window display to change
when editing during playback, you can activate the “Suspend Auto-Scroll when Editing” button. You will find this
button right next to the Auto-Scroll button. When this op
tion is enabled, auto-scrolling is suspended as soon as
you click anywhere in the event display during playback.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open a project that contains audio or MIDI parts/
events.
2. Enable both the “Auto-Scroll” and the “Suspend Auto-
Scroll when Editing” buttons.
3. Start playback.
4. Edit an audio or MIDI part/event of your project (e. g.
click and drag it to a different location on its track).
The Auto-Scroll button turns orange.
Auto-Scrolling is now suspended, i. e. when the project
cursor moves to the right edge of the Project window, the
display will not follow to keep the cursor visible.
As soon as playback stops or when you click the AutoScroll button again, Cubase will return to the normal AutoScroll behavior.
-
-
47
The Project window
Page 48

5
Working with projects
Page 49

Creating new projects
Category
bar
Template
list
Location
options
Open Other button
The Project Assistant dialog is opened by selecting the
“New Project…” command on the File menu. In this dialog
you can access recently opened projects and create new
projects, which can either be empty or based on a template.
The Project Assistant dialog will also open in the following
cases:
• If you launch Cubase with the “Show Project Assistant”
option selected on the “On Startup” pop-up menu in the
Preferences dialog (General page).
• If you hold down [Ctrl]/[Command] while launching Cubase.
Opening recent projects
The Recent category in the category bar of the Project Assistant dialog contains a list of recently opened projects.
When you select an item in this category, the Create but
ton changes to “Open”, allowing you to open the corresponding project. This list is similar to the list in the
Recent Projects submenu of the File menu.
Choosing a template
In the category bar of the Project Assistant dialog, the
available factory templates are sorted into the predefined
categories Recording, Production, Scoring, and Mastering. Furthermore, there is a More category which contains
the default project template (see “Setting up a default
template” on page 51) and all templates that are not as-
signed to any of the other categories.
When you click on one of the category items, the list below the category bar shows the available factory templates for this category that were installed with Cubase.
Any new templates that you create (see “Save as Tem-
plate” on page 51) are added at the top of the corre-
sponding list for convenient access.
• To create an empty project that is not based on a tem-
plate, select the “Empty” entry in the More category and
click the Create button.
An empty project is also created if no template is selected in the currently shown category.
• You can rename or delete a template by right-clicking it
in the list and selecting the corresponding option on the
context menu.
• To open the folder in which the selected template is
stored in the Windows Explorer/Mac OS Finder, rightclick the template in the list and select “Show in Explorer”
(Win) or “Reveal in Finder” (Mac).
Choosing a project location
The options in the lower part of the dialog allow you to
specify where the project is stored.
• Select “Use default location” to create the project in the
default project location (as shown in the path field), and
click Create.
In the “Project folder” field you can specify a name for the project folder.
If you do not specify a project folder here, the project will reside in a
folder named “Untitled”.
Ö To change the default project location, simply click in
the path field. A file dialog opens, allowing you to specify a
new default location.
• Select “Prompt for project location” and click Continue
to create the project in a different location.
In the dialog that appears, specify a location and a project folder.
49
Working with projects
Page 50

Open Other
!
The “Open Other” button allows you to open any project
file on your system. This is identical to using the Open
command from the File menu, see below.
Opening projects
The “Open…” command on the File menu is used for opening saved project files. Project files created with Cubase
(file extension “.cpr”), Nuendo (file extension “.npr”) and
Sequel (extension “.steinberg-project”) can be opened.
Ö If you open a project from a different program version
that contains data for functions not available in your ver
sion, this data may get lost when saving the project with
your version.
• Several projects can be open at the same time.
This is useful if you want to copy parts or entire sections from one project
to another.
• If there is already an open project, you will be asked if
you want to activate the new project.
• Click No to open the project inactive.
This significantly reduces load times, especially for large projects.
• Click Activate to open and activate the new project.
The active project is indicated by the lit Activate Project button in the upper
left corner of the Project window. To activate a different project, simply
click its Activate Project button.
-
• You can drag projects from the MediaBay into the Cubase application window (not into an existing Project window) to open them.
About the “Missing Ports” dialog
If you open a Cubase project created on a different system (other audio hardware), the program tries to find
matching audio inputs and outputs for the i/o busses (this
is one of the reasons why you should use descriptive, ge
neric names for your input and output ports – see “Prepa-
rations” on page 27).
If the program cannot resolve all audio/MIDI inputs and
outputs used in the project, a Missing Ports dialog will
open. This allows you to manually re-route any ports spec
ified in the project to ports available in your system.
Closing projects
The Close command on the File menu closes the active
window. If a Project window is active, selecting this closes
the corresponding project.
• If the project contains unsaved changes, you are asked
whether you want to save it before closing.
If you select “Don’t Save” and have recorded or created new audio files
since saving, you will be asked if you want to delete or keep these.
Saving projects
-
-
Save and Save As
The commands Save and Save As allow you to save the
active project as a project file (file extension “.cpr”). The
Save command stores the project under its current name
and location, while Save As allows you to rename and/or
relocate the file. If a project has not been saved yet or if it
has not been changed since it was last saved, only Save
• You can also open project files by selecting an entry
from the “Recent Projects” submenu of the File menu.
This submenu lists the projects you have recently worked with, with the
most recent at the top of the list. The list can also be found in the Project
Assistant dialog, see
• You can also set Cubase to automatically open a project
when you launch the program (see
page 54).
“Creating new projects” on page 49.
“Startup Options” on
Working with projects
As is available.
Generally, we recommend that you save project files
in their project folders, to keep the projects as
manageable as possible.
50
Page 51

A word about file extensions
Under Windows, file types are indicated by three letter file
name extensions (such as *.cpr for Cubase project files).
Under Mac OS X, it is not necessary to use file name extensions, since the file types are stored internally in the
files. However, if you want your Cubase projects to be
compatible with both platforms, make sure that the “Use
File Extension in File Dialog” option is activated in the
Preferences dialog (General page). When this is acti
vated, the proper file name extension is automatically
added when you save a file.
Save New Version
This function is only available as a key command, by default [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Alt]/[Option]-[S]. When you use
this function, an identical, new project file is being created
and activated.
The new file will get the same name as the original project,
but with an incremental number attached. For example, if
your project is called “My Project”, you will get new ver
-
sions called “My Project-01”, “My Project-02”, and so on.
Save New Version is useful if you are experimenting with
edits and arrangements and want to be able to go back to
a previous version at any time. The newest versions are always listed on the Recent Projects submenu of the File
menu for instant access (see also “Opening recent proj-
ects” on page 49).
Save as Template
This function allows you to save the current project as a
template. When you create a new project, the available
templates are listed, allowing you to base the new project
on a template.
Proceed as follows:
1. Set up a project.
2. Select “Save As Template…” from the File menu and
enter a name for the new project template.
• In the Attribute Inspector section you can assign the
template to one of the four template categories shown in
the Project Assistant dialog (see
on page 49) and/or enter a description for the template.
Simply select a category value from the Template Category pop-up
menu and/or enter a description in the Content Summary field.
“Creating new projects”
Ö If you do not choose a Template Category attribute,
the new template will be shown in the More category in
the Project Assistant dialog.
3. Click OK to save the template.
• Templates can contain clips and events just like regular
projects.
If this is not what you want, make sure to remove all clips from the Pool
before you save the project as a template.
Templates are always stored in the Templates folder, see
“Where are the settings stored?” on page 539.
Setting up a default template
If you always want the same default project to open when
you launch Cubase, you can save a default template. Proceed as follows:
1. Set up a project.
2. Select “Save As Template…” from the File menu and
save the project template with the name “default”.
3. Open the Preferences dialog and select the General
page.
4. Open the “On Startup” pop-up menu and select
“Open ‘Default’ Template”.
The next time you launch Cubase, the default template will
automatically be opened. For details on the other Startup
options, see
“Startup Options” on page 54.
Ö In the Project Assistant dialog, the default project template is found in the More category.
Reverting to the last saved version
If you select “Revert” from the File menu, you will be asked
whether you really want to revert to the last saved version
of the project. If you click “Revert”, all changes you have
made since saving will be discarded.
If you have recorded or created new audio files since saving, you will be asked whether you want to delete or keep
these.
51
Working with projects
Page 52

Auto Save
!
!
If you activate the Auto Save option in the Preferences dialog (General page), Cubase will automatically save backup
copies of all open projects with unsaved changes.
These backup copies are named “<project name>-xx.bak”,
where xx is an incremental number. Unsaved projects are
backed up in a similar way as “UntitledX-xx.bak”, with X
being the incremental number for unsaved projects. All
backup files are saved in the project folder.
• Use the “Auto Save Interval” setting to specify the time
intervals in which a backup copy will be created.
• Use the “Maximum Backup Files” option to specify how
many backup files will be created with the Auto Save
function.
When the maximum number of backup files is reached, the existing files
will be overwritten (starting with the oldest file).
Ö With this option only the project files themselves will
be backed up. If you want to include the files from the Pool
and save your project in a different location, you need to
use the “Back up Project” function.
The Archive and Backup functions
Once you have performed a Prepare Archive operation,
you can use the “Back Up Project” function to create a
backup of the project file, containing copies of all neces
sary media files (with the exception of VST Sound content,
see below).
It is not necessary to archive the Images folder, since
these images can be recreated by Cubase. You may also
find a file with the extension “.csh” in the project folder.
This contains image information for edited clips and other
data that can be recreated, so it can safely be deleted.
Video clips are always referenced and not stored in
the project folder.
Back up Project
This function is very useful if you want to create a backup
copy of a project for your archive. It can also be used to
prepare projects for delivery so that they only contain the
necessary work data (while leaving the original project un
touched). When you back up a project, all media files (except those coming from VST Sound archives) can be
included as a copy.
VST Sound content provided by Steinberg is copyprotected and will not be included in the backup
project. If you want to use a backup copy of a project
using such data on a different computer, make sure
that the corresponding content is also available on
that computer.
-
Prepare Archive
The “Prepare Archive” function verifies that every clip referenced in the project is located in the same folder, and
takes actions if that is not the case:
• Any files that are located outside the current project
folder will be copied into it.
Please note that audio files residing within the project folder are not copied to the audio folder. Therefore, you have to copy them there manually
before backing up the audio folder or save them separately during
backup, see below.
• If any processing has been applied, you will be asked
whether you want to Freeze Edits.
If you do this, you do not have to archive the Edits folder. Everything belonging to the project will be contained in the project file and the Audio
folder.
52
Working with projects
Page 53

1. Select “Back up Project…” from the File menu.
A file dialog opens in which you can choose an existing empty folder or
create a new folder to save the project.
2. Click OK.
The “Back up Project Options” dialog opens.
This dialog contains the following options:
Option Description
Project Name Enter a project name if you want to change it from the de-
Keep Current
Project Active
Minimize Audio
Files
Freeze Edits This will perform a Freeze Edits operation, making all pro-
Remove
Unused Files
Do Not Back
up Video
fault (the current name of the project).
When this option is activated, the current project will still
be the active project after clicking OK. If you wish to switch
to the new backup project instead, deactivate this option.
If this is activated, only the audio file portions that are actually used in the project will be included. This can significantly reduce the size of the project folder (if you are using
small sections of large files), but it also means you cannot
use other portions of the audio files if you continue working
with the project in its new folder.
cessing and applied effects permanent to each clip in the
“Freeze Edits” on page 255.
Pool, see
When this is activated, only files in the Pool that are actually used in the project will be stored in the new folder.
When this is activated, any video clips on the video track
or in the Pool of the current project will not be included in
the backup project.
3. Make the desired settings.
4. Click OK.
A copy of the project is saved in the new folder. The original project is
not affected.
Cleanup
The Cleanup function on the File menu helps you to save
hard disk space by locating and – if you like – deleting unused audio files in the project folders on your disk.
1. Select “Cleanup…” from the File menu.
If there are any open projects, an alert shows. Clicking “Close” closes all
open projects and brings up the dialog “Cleanup Cubase Project Folders”.
2. To restrict the Cleanup function to a certain folder,
click the “Search Folder” button and select the folder.
The default setting is that the Cleanup function is applied to all folders on
all hard disks. Only select a specific folder if you are certain it does not
contain audio files used in other projects (outside the folder), see below.
You can reset the function to search all folders by opening the “Search
Folder” dialog again and clicking “Cancel”.
3. Click the Start button.
Cubase will now scan the selected folder (or all hard disks) for Cubase
project folders and check for audio and image files (in the Audio, Edits
and Images subfolders) that are not used by any project. The found files
are listed in the dialog.
4. When the scan is complete, you can select files by
clicking in the list.
Use [Ctrl]/[Command]-click to select several files, and [Shift]-click to select a range of files. You can also click the Select All button to select all
files in the list.
In the following situations, the Cleanup function will list
files that are not unused:
• If you have moved or renamed files or folders (without updat-
ing the project files to use the new paths), there is no way for
Cubase to know that these files are used in a project.
• If you perform the Cleanup function on a folder in which there
are audio files belonging to other projects (outside the folder),
these files will be considered “unused”.
• Also, make sure that you do not delete any files used in
other applications, or files that you generally want to keep!
However, you can always safely delete image files since
these can be reconstructed by the program, if necessary.
5. Delete any files you do not want to keep by selecting
them and clicking Delete.
6. Close the dialog by clicking the Close button.
53
Working with projects
Page 54

Startup Options
The Project Setup dialog
The “On Startup” pop-up menu in the Preferences dialog
(General page) allows you to specify what happens when
you launch Cubase.
The following options are available:
Option Description
Do Nothing Cubase launches without opening a project.
Open Last
Project
Open ‘Default’
Template
Show Open
Options Dialog
Show Project
Assistant
The last saved project is opened on launch.
The default template is opened, see “Setting up a de-
fault template” on page 51.
The Open dialog opens on launch, allowing you to manually locate and open the desired project.
The Project Assistant dialog opens on launch, allowing
you to open a recently opened project or to create a
new project from one of the templates (see
new projects” on page 49).
“Creating
General settings for the project are made in the Project
Setup dialog. This is opened by selecting “Project
Setup…” from the Project menu.
Ö If the “Run Setup on Create New Project” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (General page), the Project Setup dialog will open automatically when you create
a new project.
The following settings are available in the Project Setup
dialog:
Setting Description
Author Here you can add a name that will be written as the project
Company Here you can add a name that will be written as the com-
54
Working with projects
author into the iXML chunk when exporting audio files with
the corresponding option activated (see
page 489). The default setting for this can be set in the
Preferences dialog (General–Personalization page).
pany name into the iXML chunk when exporting audio files
with the corresponding option activated (see
on page 489). The default setting for this can be set in the
Preferences dialog (General–Personalization page).
“AIFF files” on
“AIFF files”
Page 55

Setting Description
!
Start The start time of the project. Allows you to have the project
Length The length of the project.
Frame Rate This setting determines both the timecode standard and
Display Format This is the global display format used for all rulers and po-
Display Offset Offsets the time positions displayed in the ruler, etc., al-
Bar Offset This works just like “Display Offset” described above, in
start at another time than zero. Also used for setting the
sync start position when synchronizing Cubase to external
devices (see the chapter
The format of this value is always in timecode. When you
change this setting you will be asked whether you want to
keep the project content at its timecode positions. “Yes”
means that all events will stay at their original timecode po
sitions – i. e. they will be moved in relation to the start of the
project. “No” means that all events keep their position rela
tive to the project start.
frame rate for the project, see the section
standards” on page 495. The frame rate of a video file
used in a project should match the frame rate set for a
project. The “Get From Video” button allows you to set
the project frame rate to the frame rate of an imported
video file, see the section
on page 512. When synchronizing Cubase to an external
device, make sure that this setting corresponds to the
frame rate of any incoming timecode. However, there
might be situations where perfect synchronization does
not matter to you and you do not want to change the proj
ect frame rate. In this case, the frame rate mismatch will
be indicated on the Transport panel in the Sync section.
sition displays in the program, except ruler tracks (see
“Ruler tracks” on page 41). However, you can make inde-
pendent display format selections for the individual rulers
and displays if you like.
For descriptions of the different display format options,
“The ruler” on page 44.
see
lowing you to compensate for the Start position setting.
Typically, if you synchronize Cubase to an external source
starting at a frame other than zero, you set the Start posi
tion to this value. However, if you still want the display in
Cubase to start at zero, set the Display Offset to the
same value.
that it offsets the time positions in the ruler by a number
of bars, allowing you to compensate for the Start position
setting. The difference is that Bar Offset is only used
when the “Bars+Beats” display format is selected (see
“The ruler” on page 44).
“Synchronization” on page 493).
“Timecode
“Adopting the video frame rate”
Setting Description
Sample Rate The sample rate at which Cubase records and plays au-
-
-
Bit Resolution/
Record File
Type
Stereo Pan
Law
dio. The order of the menu items depends on the sample
rates available for your audio hardware. Supported set
tings are displayed in the upper part of the menu, nonsupported settings are displayed in the lower part. Re
garding the sample rate, there are two possible scenarios: Either your audio hardware generates the audio clock
signals itself or it is clocked externally, i.
nals from an external sample clock source (see “If your
hardware setup is based on an external clock source” on
page 18).
If the sample rate is generated internally, the following applies: When you select a sample rate non-supported by
your audio hardware (from the lower part of the menu), it
is highlighted in a different color and the corresponding
tooltip shows a warning. In this case you must set a dif
ferent sample rate to make your audio files play back
properly. When you specify a project sample rate that
your audio hardware supports but which is different from
the current audio hardware sample rate, and you confirm
your settings by clicking OK, the sample rate setting of
the audio hardware is automatically changed to the project sample rate.
When you record audio in Cubase, the files that are created will be of this resolution and file type, see “Selecting
a recording file format” on page 92.
Decides whether panning uses power compensation or
“About the “Stereo Pan Law” setting” on page
not, see
157.
e. receives sig-
While most Project Setup settings can be changed
at any time, you should set the sample rate directly
after creating a new project! If you change the sam
ple rate at a later stage, you must convert all audio
-
files in the project to the new sample rate to make
them play back properly.
-
-
-
-
55
Working with projects
Page 56

Zoom and view options
!
Click here…
…to open the context
menu.
Zooming in the Project window is done according to the
standard zoom techniques, with the following special notes:
• When you are using the Zoom tool (magnifying glass),
the result depends on the “Zoom Tool Standard Mode:
Horizontal Zooming Only” option in the Preferences dialog
(Editing–Tools page).
If this is activated and you drag a selection rectangle with the Zoom tool,
the window will only be zoomed horizontally (track height will not change).
If the option is off, the window will be zoomed both horizontally and verti
cally.
• When using the vertical zoom sliders, the tracks are
scaled relatively.
In other words, if you have made any individual track height adjustments
(see below), the relative height differences are maintained.
You find the following options are available on the Zoom
submenu on the Edit menu:
Option Description
Zoom In Zooms in one step, centering on the project cursor.
Zoom Out Zooms out one step, centering on the project cursor.
Zoom Full Zooms out so that the whole project is visible. “The
Zoom to
Selection
Zoom to Selection (Horiz)
Zoom to Event This option is available only in the Sample Editor (see
Zoom In Vertically Zooms in one step vertically.
Zoom Out
Vertically
Zoom In Tracks Zooms in on the selected track(s) one step vertically.
Zoom Out Tracks Zooms out the selected track(s) one step vertically.
Zoom Selected
Tracks
Undo/Redo
Zoom
whole project” means the timeline from the project
start to the length set in the Project Setup dialog (see
above).
Zooms in horizontally and vertically so that the current
selection fills the screen.
Zooms in horizontally so that the current selection fills
the screen.
“Zooming” on page 266).
Zooms out one step vertically.
This zooms in vertically on the selected track(s) and
minimizes the height of all other tracks.
These options allow you to undo/redo the last zoom
operation.
-
• You can zoom the contents of parts and events vertically, using the waveform zoom slider in the top right corner of the event display.
This is useful when viewing quiet audio passages.
To get an approximate reading on the level of the audio events by viewing the waveforms, make sure this
slider is all the way down. Otherwise, zoomed waveforms may be mistaken for clipped audio.
• If you activate the option Quick Zoom in the Preferences
dialog (Editing page), the contents of parts and events will
not be continuously redrawn when you zoom manually.
Instead, the contents are redrawn once you have stopped changing the
zoom – activate this if screen redraws are slow on your system.
Zoom presets and cycle markers
The pop-up menu to the left of the horizontal zoom control
allows you to select, create and organize zoom presets.
These are useful if you want to toggle between different
zoom settings (e.
played in the project window and another with a high
zoom factor for detailed editing). With this pop-up menu,
you can also zoom in on the area between cycle markers
in the project.
g. one where the whole project is dis-
• If the “Zoom while Locating in Time Scale” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (Transport page), you
can also zoom by clicking in the ruler and dragging up or
down with the mouse button pressed.
Drag up to zoom out; drag down to zoom in.
56
Working with projects
Page 57

The upper part of the menu lists the zoom presets:
!
!
• To store the current zoom setting as a preset, select
Add from the pop-up menu.
A dialog opens, allowing you to type in a name for the preset.
• To select and apply a preset, select it from the pop-up
menu.
• The “Zoom Full” preset is always available. Selecting
this option zooms out so that the whole project is visible.
“The whole project” means the timeline from the project
start to the length set in the Project Setup dialog (see
“The Project Setup dialog” on page 54).
• If you want to delete a preset, select “Organize…” from
the pop-up menu.
In the dialog that opens, select the preset in the list and click the Delete
button. The preset is removed from the list.
• If you want to rename a preset, select “Organize…”
from the pop-up menu.
In the dialog that opens, select the desired preset in the list and click the
Rename button. A second dialog opens, allowing you to type in a new
name for the preset. Click OK to close the dialogs.
Zoom presets are global for all projects, i. e. they are
available in all projects you open or create.
The middle part of the pop-up menu lists any cycle markers you have added to the project:
• If you select a cycle marker from this menu, the event
display is zoomed in to encompass the marker area.
• You cannot edit the cycle markers in this pop-up menu.
For information on editing markers, see
“The Marker win-
dow” on page 139.
Only the cycle markers you create in the current project are available on the menu.
The Zoom history
Cubase maintains a history of recent zoom stages, allowing you to undo and redo zoom operations. This way you
can zoom in several steps and then easily go back to the
zoom stage at which you started.
There are two ways to invoke Undo Zoom and Redo
Zoom:
• Use the items on the Zoom submenu on the Edit menu.
You can also assign key commands for these.
• Double-click with the Zoom tool (magnifying glass) to
Undo Zoom.
Press [Alt]/[Option] and double-click to Redo Zoom.
Adjusting how parts and events are shown
The Preferences on the File menu (the Cubase menu, under Mac OS X) contains several settings for customizing
the display in the Project window.
The Event Display page contains common settings for all
track types:
Option Description
Show Event
Names
Show Data on
Small Track
Heights
The Event Display–Audio page contains settings for audio
events:
Option Description
Interpolate
Audio Images
Show Event
Volume Curves
Always
Show
Waveforms
Background
Color
Modulation
The Event Display–MIDI page contains settings for MIDI
parts:
Option Description
Default Edit
Action
Part Data
Mode
Show
Controllers
Determines whether the names of parts and events are
shown in the Project window.
If this is activated, the contents of events and parts will be
shown, even if the height of a track is very small.
If the option is deactivated, single sample values are drawn
as “steps”. If the option is activated they are interpolated to
form “curves”.
If this is activated the “volume curves” created with the
volume and fade handles are always shown – if not, the
curves are only shown for selected events.
Determines whether audio waveforms are shown at all.
When this is activated, the backgrounds of audio waveforms are displayed in a different way, reflecting the
waveform dynamics. This is especially useful to get an
overview when working with small track heights.
Determines which editor is opened when you doubleclick a MIDI part, or select it and press [Ctrl]/[Com
mand]-[E]. Note that this setting is overridden for tracks
with drum maps if the “Edit as Drums when Drum Map is
assigned” option (see below) is activated.
Determines if and how events in MIDI parts are shown in
the Project window: as lines, as score notes, as drum
notes, or as blocks. If “No Data” is selected, events will
not be shown at all. Note that this setting is overridden for
tracks with drum maps if the “Edit as Drums when Drum
Map is assigned” option (see below) is activated.
Governs whether non-note events (controllers, etc.) are
shown in MIDI parts in the Project window.
-
57
Working with projects
Page 58

Option Description
!
Edit as Drums
when Drum
Map is
assigned
Note Name
Style
If this is activated, parts on MIDI tracks with drum maps
assigned will be shown with drum note symbols in the
Project window. Also, the parts will automatically open in
the Drum Editor when double-clicked (overriding the De
fault Edit Action setting above).
Determines how MIDI note names (pitches) are displayed in editors, etc.
Audio handling
When you work with audio files, it is crucial to understand
how audio is handled in Cubase:
When you edit or process audio in the Project window,
you always work with an audio clip that is automatically
created on import or during recording. This audio clip re
fers to an audio file on the hard disk that itself remains untouched. This means, that audio editing and processing is
“non-destructive”, in the sense that you can always undo
changes or revert to the original versions.
An audio clip does not necessarily refer to just one original audio file! If you apply some processing to a specific
section of an audio clip, for example, this will create a new
audio file containing only this section. The processing will
then be applied to the new audio file only, leaving the orig
inal audio file unchanged. Finally, the audio clip is automatically adjusted, so that it refers both to the original file
and to the new, processed file. During playback, the pro
gram will switch between the original file and the processed file at the correct positions. You will hear this as a
single recording, with processing applied to one section
only. This feature makes it possible to undo processing at
a later stage, and to apply different processing to different
audio clips that refer to the same original file.
An audio event is the object that you place on a time position in Cubase. If you make copies of an audio event and
move them to different positions in the project, they will
still all refer to the same audio clip. Furthermore, each au
dio event has an Offset value and a Length value. These
determine at which positions in the clip the event will start
and end, i.
back by the audio event. For example, if you resize the audio event, you will just change its start and/or end position
in the audio clip – the clip itself will not be affected.
e. which section of the audio clip will be played
An audio region is a section within a clip with a length
value, a start time, and a snap point. Audio regions are
shown in the Pool and are best created and edited in the
Sample Editor.
-
Ö If you want to use one audio file in different contexts,
or if you want to create several loops from one audio file,
convert the corresponding regions of the audio clip to
events and bounce them into separate audio files. This is
necessary since different events that refer to the same clip
access the same clip information.
Auditioning audio parts and events
Audio parts and events can be auditioned in the Project
window with the Play tool:
-
When auditioning, audio will be routed directly to the
Control Room (Cubase only), if the Control Room is
activated. When the Control Room is deactivated,
the audio will be routed to the default output bus,
bypassing the audio channel’s settings, effects and
EQs. In Cubase Artist, the Main Mix bus is always
used for monitoring.
1. Select the Play tool.
-
-
2. Click where you want playback to start, and keep the
mouse button pressed.
Only the track on which you click is played back, starting at the click position.
3. Release the mouse button to stop playback.
-
58
Working with projects
Page 59

Scrubbing audio
Editing parts and events
The Scrub tool allows you to locate positions in the audio
part or event by playing back, forwards or backwards, at
any speed:
1. Select the Play tool and click a second time on the
icon.
A pop-up menu opens.
2. Select “Scrub”.
3. Click at the desired position of your audio event or
part and keep the mouse button pressed.
The project cursor moves to the position where you click. The mouse
pointer is not visible anymore.
4. Drag to the left or right.
The project cursor moves correspondingly and the audio is played back.
The speed and thus the pitch of the playback depend on how fast you
move the mouse.
You can adjust the volume of the Scrub function in the
Preferences dialog (Transport–Scrub page).
Ö When scrubbing with the mouse, insert effects are always bypassed.
Ö It is also possible to “scrub” all audio and video tracks
of your project with the Jog wheel and Shuttle Speed con
trol on the Transport panel see “Playing back with the
shuttle speed control” on page 85.
Scrubbing can be quite a burden on your system. If playback problems occur, try deactivating the “Use High
Quality Scrub Mode” option in the Preferences dialog
(Transport–Scrub page). The resampling quality will then
be lower, but scrubbing will be less demanding on the
processor. This can be useful when scrubbing in large
projects.
This section describes techniques for editing in the Project window. If not explicitly stated, all descriptions apply
to both events and parts, even though we use the term
“event” for convenience.
Ö When you are using the tools for editing, you can in
many cases get additional functions by pressing modifier
g. pressing [Alt]/[Option] and dragging with the
keys (e.
Arrow tool creates a copy of the dragged event).
On the following pages, the default modifier keys are described – you can customize these in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tool Modifiers page), see “Setting up tool
modifier keys” on page 545.
Selecting events
Selecting events is done using any of the following
methods:
• Use the Arrow tool.
The standard selection techniques apply.
• Use the Select submenu on the Edit menu.
The options are:
Option Description
All Selects all events in the Project window.
None Deselects all events.
Invert Inverts the selection – all selected events are dese-
-
In Loop Selects all events that are partly or wholly between
From Start to
Cursor
From Cursor to
End
Equal Pitch These are available in the MIDI Editors (see “Select-
Select Controllers
in Note Range
All on Selected
Tracks
Events under
Cursor
lected and all events that were not selected are selected instead.
the left and right locator.
Selects all events that begin to the left of the project
cursor.
Selects all events that end to the right of the project
cursor.
ing notes” on page 383) and the Sample Editor (see
“Using the Select menu” on page 269).
This is available in the MIDI Editors (see “Selecting
controllers within the note range” on page 384).
Selects all events on the selected track.
Automatically selects all events on the selected
track(s) that are “touched” by the project cursor.
59
Working with projects
Page 60

!
Option Description
Select Event This is available in the Sample Editor (see “Window
Left/Right Selection Side to Cursor
overview” on page 262).
These two functions are only used for range selection
editing (see
“Creating a selection range” on page 66).
Note that these functions work differently when the
Range Selection tool is selected (see
“Creating a
selection range” on page 66).
• Select all events on a track by right-clicking on it in the
track list and selecting “Select All Events” from the con
-
text menu.
• It is also possible to select ranges, regardless of the
event and track boundaries.
This is done using the Range Selection tool (see “Range editing” on
page 66).
• Use the arrow keys on the computer keyboard to select
the closest event to the left, right, above, or below.
If you press [Shift] and use the arrow keys, the current selection will be
kept, allowing you to select several events.
By default, tracks are selected with the up/down arrow keys
on the computer keyboard. Therefore using these to select
events, too, can be confusing. If you want to use the navigation controls for track selection only (a most vital operation
in both editing and mixing), you can activate the “Use Up/
Down Navigation Commands for selecting Tracks only” option in the Preferences dialog (Editing page). The following
applies:
• When this option is deactivated and no event/part is selected
in the Project window, the up/down arrow keys on the com
puter keyboard are used to step through the tracks in the track
list.
• When this option is deactivated and an event/part is selected
in the Project window, the up/down arrow keys still step
through the tracks in the track list – but on the currently se
lected track, the first event/part will automatically be selected
as well.
• When this option is activated, the up/down arrow keys are
only used to change the track selection – the current event/
part selection in the Project window will not be altered.
• If the “Auto Select Events under Cursor” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (Editing page), all events
on the selected track(s) that are “touched” by the project
cursor are automatically selected.
This can be helpful when rearranging your project, because it allows you
to select whole sections (on all tracks) by selecting all tracks and moving
the project cursor.
Using the cross hair cursor
Also in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tools page), you
can find the Cross Hair Cursor section. When enabled, a
cross hair cursor is displayed when working in the Project
window and in the editors, facilitating navigation and edit
ing, especially when arranging large projects. You can set
up the colors for the line and the mask of the cross hair
cursor, and define its width. The cross hair cursor works
as follows:
• When the Selection tool (or one of its subtools) is selected, the cross hair cursor appears when you start moving/copying a part/event, or when using the event trim
handles.
• When the Pencil tool, the Scissors tool, or any other
tool that makes use of this function is selected, the cross
hair cursor appears as soon as you move the mouse over
the event display.
• The cross hair cursor is only available for tools where
such a function is of any use. The Mute tool, for example,
does not use a cross hair cursor, as you have to click directly on an event to mute it.
-
60
Working with projects
Page 61

Moving events
!
!
!
To move events in the Project window, use the following
methods:
• Click and drag to a new position.
All selected events are moved, maintaining their relative positions. You
can only drag events to tracks of the same type. If Snap is activated, this
determines to which positions you can move the events (see
function” on page 45).
Note also that you can restrict movement to be either horizontal or vertical only, by holding down [Ctrl]/[Command] while dragging.
“The Snap
• Use the Nudge buttons on the toolbar.
These move the selected events to the left or right. The amount of movement depends on the selected display format (see “The Project Setup di-
alog” on page 54) and the value set on the Grid pop-up menu.
You will note that there is a slightly delayed response
when you move an event by dragging. This helps you
avoid accidentally moving events when you click on
them in the Project window. You can adjust this delay
with the Drag Delay setting in the Preferences dialog
(Editing page).
• Select the event and edit the Start position in the info line.
• Use the “Move to” options on the Edit menu.
The following options are available:
Option Description
Cursor Moves the selected event to the project cursor position.
Origin Moves the selected events to their original positions, i. e.
Front/Back This function does not actually change the position of the
If there are several selected events on the same track,
the first event will start at the cursor, and the following
will be lined up end-to-start after the first one.
the positions at which they were originally recorded.
events, but moves the selected events to the front or back,
respectively. This is useful if you have overlapping events
and want to see one that is partially obscured.
For audio events, this is an extra important feature, because only the visible sections of events will be played
back. Moving an obscured audio event to front (or moving
the obscuring event to back) will allow you to hear the
whole event on playback.
Note that it is also possible to use the “To Front” function
on the event context menu for this.
When the Range Selection tool is used, the Nudge
buttons move the selection range (see “Moving and
duplicating” on page 67).
Ö The Nudge buttons are not visible on the toolbar by
default. You can decide which items are visible by rightclicking on the toolbar and activating the corresponding
option on the context menu (see
“The setup context
menus” on page 534).
• Use the Up/Down key commands, found in the Nudge
category in the Key Commands dialog.
These commands allow you to nudge one or more events (except folder
parts) up or down to the nearest track.
Nudging up/down will not create new tracks: If there is no
destination track that matches the track configuration of
the nudged event, nothing happens.
Exceptions
• If you select events in Lane Display mode, these are
moved to the upper or lower lane.
• If you select MIDI events in the In-Place Editor, the MIDI
events are nudged up or down.
Duplicating events
Events can be duplicated in the following ways:
• Hold down [Alt]/[Option] and drag the event to a new
position.
If Snap is activated, this determines to which positions you can copy the
events (see
“The Snap function” on page 45).
If you hold down [Ctrl]/[Command] as well, movement direction is restricted to either horizontal or vertical. That means if you drag an event vertically it
cannot be moved horizontally at the same time.
61
Working with projects
Page 62

• Audio and MIDI parts can also be duplicated by clicking
on the part, pressing [Alt]/[Option]-[Shift], and dragging.
This creates a shared copy of the part. If you edit the contents of a
shared copy, all other shared copies of the same part are automatically
edited in the same way.
• Selecting “Fill Loop” from the Functions submenu on
the Edit menu creates a number of copies starting at the
left locator and ending at the right locator.
The last copy is automatically shortened to end at the right locator position.
Note:
• When you duplicate audio events, the copies are al-
ways shared. This means that shared copies of audio
events always refer to the same audio clip (see “Audio
processing” on page 245).
• You can convert a shared copy to a real copy by select-
ing “Convert to Real Copy” from the Functions submenu on
the Edit menu. This creates a new version of the clip (that
can be edited independently) and adds this to the Pool.
Note that no new files are created by this operation – for
that you need to use the “Bounce Selection” function from
the Audio menu (see
“Exporting regions as audio files” on
page 307).
• Selecting “Duplicate” from the Functions submenu on
the Edit menu creates a copy of the selected event and
places it directly after the original.
If several events are selected, all of these are copied “as one unit”, maintaining the relative distance between the events.
• Selecting “Repeat…” from the Functions submenu on
the Edit menu opens a dialog, allowing you to create a
number of copies (regular or shared) of the selected
events.
This works just like the Duplicate function, but you can specify the number of copies.
• You can also perform the Repeat function by dragging:
Select the events to repeat, press [Alt]/[Option], click the
handle in the lower right corner of the last selected event
and drag to the right.
The longer to the right you drag, the more copies are created (as shown
by the tooltip).
Using Cut, Copy and, Paste
You can cut or copy selected events, and paste them in
again, using the functions on the Edit menu.
• When you paste an audio event, it is inserted on the selected track, positioned so that its snap point is aligned
with the cursor position.
If the selected track is of the wrong type, the event will be inserted on its
original track. See
the snap point.
“The Snap function” on page 45 for information about
• If you use the “Paste at Origin” function on the Function
submenu of the Edit menu, the event is pasted at its origi
nal position (the position from which you cut or copied it).
Renaming events
By default, audio events show the name of their clip, but
you can enter a separate descriptive name for separate
events if you like. This is done by selecting the event and
typing in a new name in the “Description” field on the info
line.
• You can also give all events on a track the same name
as the track by changing the track name, holding down a
modifier key and pressing [Return].
See “Audio handling” on page 58.
Splitting events
You can split events in the Project window in the following
ways:
• Click with the Scissors tool on the event you want to
split.
If Snap is activated, this determines the exact split position (see “The
Snap function” on page 45). You can also split events by pressing [Alt]/
[Option] and clicking with the Arrow tool.
-
62
Working with projects
Page 63

• Select “Split at Cursor” from the Edit menu, Functions
submenu.
This splits the selected events at the position of the project cursor. If no
events are selected, all events (on all tracks) that are intersected by the
project cursor will be split.
• Select “Split Loop” from the Edit menu, Functions sub-
menu.
This splits events on all tracks at the left and right locator positions.
Ö If you split a MIDI part so that the split position intersects one or several MIDI notes, the result depends on the
“Split MIDI Events” option in the Preferences dialog (Editing–MIDI page). If the option is activated, the intersected
notes will be split (creating new notes at the beginning of
the second part). If it is deactivated, the notes will remain
in the first part, but “stick out” after the end of the part.
Gluing events together
You can glue events together using the Glue Tube tool.
There are three possibilities:
• Clicking on an event with the Glue Tube tool glues it to-
gether with the next event on the track. The events do not
have to touch one another.
The result is a part containing the two events, with one exception: If you
first split an event and then glue the two sections together again (without
moving or editing them first), they become a single event again.
• You can select several events on the same track and
click on one of them with the Glue Tube tool.
A single part is created.
• When you hold down [Alt]/[Option] while clicking on an
event with the Glue Tube tool, this event will be glued together with all following events on this track.
You can change the default key command for this in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Tool Modifiers page).
Resizing events
Resizing events means to move their start or end positions
individually. In Cubase, there are three modes for resizing:
Resizing mode Description
Normal Sizing The contents of the event stay fixed, and the start or
end point of the event is moved to “reveal” more or less
of the contents.
Resizing mode Description
Sizing Moves
Contents
Sizing Applies
Time Stretch
The contents follow the moved start or end of the event
(see the figure below).
The contents will be time stretched to fit the new event
length (see the separate section
time stretch” on page 64).
“Resizing events using
To select one of the resizing modes, select the Arrow tool
and then click again on the Arrow tool icon on the toolbar.
This opens a pop-up menu from which you can select one
of the options.
The icon on the toolbar will change, indicating the selected resizing
mode.
The actual resizing is done by clicking and dragging the
lower left or right corner of the event. If Snap is activated,
the Snap value determines the resulting length (see “The
Snap function” on page 45).
Normal sizing
Sizing moves contents
• If several events are selected, all will be resized in the
same way.
63
Working with projects
Page 64

• It is also possible to resize events by using the Trim but-
!
tons (located in the Nudge palette) on the toolbar.
This will move the start or end position of the selected event(s) by the
amount set on the Grid Type pop-up menu. The sizing type currently se
lected applies to this method too, with the exception of “Sizing Applies
Time Stretch” which is not possible with this method. You can also use
key commands for this (by default, press [Ctrl]/[Command] and use the
left and right arrow key).
-
Ö Note that the Nudge palette is not visible on the toolbar by default. See “The setup context menus” on page
534 for instructions on how to show and hide items on the
toolbar.
Ö When resizing events, any automation data will not be
taken into account.
Resizing events using time stretch
If you want to resize a part and make its contents “fit” the
new size, you should use this sizing mode. Proceed as follows:
1. Click the Arrow icon on the toolbar and click again to
select the “Sizing Applies Time Stretch” option from the
pop-up menu.
2. Point close to the end point of the part you want to
stretch.
3. Click and drag left or right.
When you move the mouse, a tooltip shows the current mouse position
and length of the part. Note that the snap value applies, as with any part
operation.
4. Release the mouse button.
The part is “stretched” or “compressed” to fit the new length.
• For MIDI parts, this means that the note events are
stretched (moved and resized).
Note Expression (Cubase only) and controller data will be stretched, too.
• For audio parts, this means that the events are moved,
and that the referenced audio files are time stretched to fit
the new length.
A dialog shows the progress of the time stretch operation.
Ö In the Preferences dialog (Editing–Audio page), you
can adjust which algorithm is used for the time stretch algorithm. For more information about time stretch, see
“Time Stretch” on page 252.
Sliding the contents of an event or part
You can move the contents of an event or part without
changing its position in the Project window. By default,
this is done by pressing [Alt]/[Option]-[Shift], clicking in
the event or part and dragging to the left or right.
When sliding the contents of an audio event, you
cannot slide past the start or end of the actual audio
clip. If the event plays the whole clip, you cannot
slide the audio at all.
Grouping events
Sometimes it is useful to treat several events as one unit.
This can be done by grouping them: Select the events (on
the same or different Tracks) and select “Group” from the
Edit menu.
Grouped events are indicated by a group icon on the right.
If you edit one of the grouped events in the Project window,
all other events in the same group are affected too (if appli
-
cable).
64
Working with projects
Page 65

Group editing operations include:
The padlock symbol indicates that one or
more of the lock options are activated for
the event.
• Selecting events.
• Moving and duplicating events.
• Resizing events.
• Adjusting fade-in and fade-out (audio events only, see “Creat-
ing fades” on page 118).
• Splitting events (splitting one event will automatically split any
other grouped events that are intersected by the split position).
• Locking events.
• Muting events.
• Deleting events.
Locking events
If you want to make sure that you do not edit or move an
event by accident, you can lock it. Locking can affect one
(or any combination) of the following properties:
Lock Options Description
Position If this is locked, the event cannot be moved.
Size If this is locked, the event cannot be resized.
Other If this is locked, all other editing of the event is disabled.
• To specify which of these properties are affected by the
Lock function, use the “Lock Event Attributes” pop-up
menu in the Preferences dialog (Editing page).
• To lock events, select them and select “Lock…” from
the Edit menu.
The events will be locked according to the options specified in the Preferences dialog.
This includes adjusting the fades and event volume, pro
cessing, etc.
• You can adjust the lock options for a locked event by
selecting it and selecting “Lock…” from the Edit menu
again.
This opens a dialog in which you can activate or deactivate the desired
lock options.
• To unlock an event (turn off all lock options), select it
and select “Unlock” from the Edit menu.
• It is also possible to lock a whole track, by clicking the
padlock symbol in the track list or in the Inspector.
This disables all editing of all events on the track.
Muting events
To mute individual events in the Project window, proceed
as follows:
• To mute or unmute a single event, click on it with the
Mute tool.
-
• To mute or unmute several events, select them – either
by using the standard selection techniques, or by using
one of the options on the Select submenu on the Edit
menu – and click on one of the selected events with the
Mute tool.
All selected events will be muted.
• You can also click in an empty area with the Mute tool
and drag a selection rectangle around several events you
want to mute or unmute, and then click on one of them
with the Mute tool.
• You can mute events by selecting them and selecting
“Mute” from the Edit menu.
Similarly, you can unmute the selected events by selecting “Unmute”
from the Edit menu.
• You can also change the mute status of selected events
on the info line.
Muted events can be edited as usual (with the exception
of adjusting fades), but are not played back.
Muted events are “grayed out”.
65
Working with projects
Page 66

• You can also mute whole tracks by clicking the Mute
(“M”) button in the track list, the Inspector or the Mixer.
Clicking the Solo (“S”) button for a track mutes all other tracks. Note that
there are two modes for the track solo function:
If the “Enable Solo on Selected Track” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Project & Mixer page) and you have soloed a
track, selecting another track in the track list will automatically solo that
track instead – the solo state “moves” with the track selection.
If the option is not activated, the track you solo stays soloed, regardless
of the selection.
Removing events
To remove an event from the Project window, use any of
the following methods:
• Click on the event with the Erase tool.
Note that if you press [Alt]/[Option] while you click, all following events
on the same track will be deleted, but not the event you clicked and all
events before it.
• Select the event(s) and press [Backspace], or select
“Delete” from the Edit menu.
Creating new files from events
An audio event plays a section of an audio clip, which in
turn refers to one or more audio files on the hard disk.
However, in some situations you may want to create a new
file that consists only of the section played by the event.
This is done with the function “Bounce Selection” on the
Audio menu:
1. Select one or several audio events.
2. Set up fade in, fade out and event volume (on the info
line or using the volume handle) as desired.
These settings will be applied to the new file. For details on fades and
event volume, see
3. Select “Bounce Selection” from the Audio menu.
You are asked whether you want to replace the selected event or not.
• If you click “Replace”, a new file is created, containing
only the audio in the original event. A clip for the new file is
added to the Pool, and the original event is replaced by a
new event playing the new clip.
• If you click “No”, a new file is created and a clip for the
new file is added to the Pool.
The original event is not replaced.
“Creating fades” on page 118.
You can also apply the Bounce Selection function to an
audio part. In that case, the audio from all events in the
part will be combined into a single audio file. If you choose
“Replace” when asked, the part will be replaced with a
single audio event playing a clip of the new file.
Range editing
Editing in the Project window is not necessarily restricted
to handling whole events and parts. You can also work
with selection ranges, which are independent from the
event/part and track boundaries.
The range selection tool can also be used for comping (see
“Comping operations” on page 77). Furthermore you can
define Edit groups with the range selection tool. These allow you to quickly group events and parts across multiple
tracks without having to select all the events or parts (see
“About Group Editing (Cubase only)” on page 80).
Creating a selection range
To make a selection range, drag with the Range Selection
tool.
When the Range Selection tool is selected, the Select
submenu on the Edit menu has the following items for
making selection ranges:
Option Description
All Makes a selection that covers all tracks, from the start of
None Removes the current selection range.
Invert Only used for event selection (see “Selecting events” on
In Loop Makes a selection between the left and right locator, on
From Start to
Cursor
From Cursor to
End
All on Selected
Tracks
Select Event This is available in the Sample Editor (see “Using the
the project to the end (as defined by the Length setting
in the Project Setup dialog).
page 59).
all tracks.
Makes a selection on all tracks, from the start of the project to the project cursor.
Makes a selection on all tracks, from the project cursor
to the end of the project.
Only used for event selection (see “Selecting events” on
page 59).
Select menu” on page 269).
66
Working with projects
Page 67

Option Description
!
Left Selection
Side to Cursor
Right Selection
Side to Cursor
Moves the left side of the current selection range to the
project cursor position.
Moves the right side of the current selection range to the
project cursor position.
• Double-clicking on an event with the Range Selection
tool creates a selection range encompassing the event.
If you hold down [Shift] you can double-click several events in a row, and
the selection range will expand to encompass them all. Double-clicking a
second time on an event opens it for editing in the Sample Editor.
Making selection ranges for several non-contiguous
tracks
You can create selection ranges that cover several tracks.
It is also possible to exclude tracks from a selection range:
1. Create a selection range from the first to the last de-
sired track.
2. Press [Ctrl]/[Command] and click in the selection
range on the tracks that you want to exclude from the selection.
Editing selection ranges
Adjusting the size of the selection range
You can adjust the size of a selection range in the following ways:
• By dragging its edges.
The pointer takes the shape of a double arrow when you move it over an
edge of the selection range.
• By holding down [Shift] and clicking.
The closest selection range edge will be moved to the position at which
you clicked.
• By adjusting the selection range start or end position on
the info line.
• By using the Trim buttons on the toolbar.
The left Trim buttons will move the start of the selection range and the
right buttons will move the end. The edges will be moved by the amount
specified on the Grid pop-up menu.
• By using the Nudge buttons on the toolbar.
These will move the whole selection range to the left or the right. The
amount of movement depends on the selected display format (see
Project Setup dialog” on page 54) and the value specified on the Grid
pop-up menu.
Note that the contents of the selection are not
moved – using the Nudge buttons is the same as adjusting the start and end of the selection range at the
same time, by the same amount.
“The
Ö The Trim buttons and the Nudge buttons are located
in the Nudge palette, which is not visible on the toolbar by
default.
See “The setup context menus” on page 534 for instructions on how to show and hide items on the toolbar.
3. In the same manner, you can add a track to the selec-
tion range by [Ctrl]/[Command]-clicking in the selection
range area on the track.
Moving and duplicating
• To move a selection range, click and drag it to a new
position.
This will move the contents of the selection range to the new position. If
the range intersected events or parts, these will be split before moving,
so that only the sections within the selection range are affected.
• To duplicate a selection range, hold down [Alt]/[Option]
and drag.
You can also use the Duplicate, Repeat and Fill Loop functions, just as
when duplicating events (see
67
Working with projects
“Duplicating events” on page 61).
Page 68

Using Cut, Copy, and Paste
When working with selection ranges, you can either use
Cut, Copy and Paste on the Edit menu, or use the functions
“Cut Time” and “Paste Time” on the Range submenu on the
Edit menu. These work differently to their related functions
on the Edit menu:
Function Description
Cut Cuts out the data in the selection range and moves it to
Copy Copies the data in the selection range to the clipboard.
Paste Pastes the clipboard data at the start position and track
Paste at
Origin
Cut Time Cuts out the selection range and moves it to the clip-
Paste Time Pastes the clipboard data at the start position and track
Paste Time at
Origin
the clipboard. The selection range is replaced by empty
track space in the Project window, meaning that events
to the right of the range keep their positions.
of the current selection. Existing events are not moved to
make room for the pasted data.
Pastes the clipboard data back at its original position. Existing events are not moved to make room for the pasted
data.
board. Events to the right of the removed range are
moved to the left to fill out the gap.
of the current selection. Existing events are moved to
make room for the pasted data.
Pastes the clipboard data back at its original position. Existing events are moved to make room for the pasted
data.
Deleting selection ranges
Again, you can either use “regular” Delete or “Delete Time”:
• If you use the Delete function on the Edit menu (or press
[Backspace]), the data within the selection range is replaced by empty track space.
Events to the right of the range keep their position.
• If you use “Delete Time” on the Edit menu’s Range sub-
menu, the selection range is removed and events to the
right are moved to the left to close up the gap.
Other functions
On the Range submenu on the Edit menu, you will find
three more range editing functions:
Function Description
Global Copy This copies everything in the selection range.
Split Splits any events or parts that are intersected by the se-
lection range, at the positions of the selection range
edges.
Function Description
Crop All events or parts that are partially within the selection
Insert
Silence
range are cropped, that is, sections outside the selection
range are removed. Events that are fully inside or outside
the selection range are not affected.
Inserts empty track space from the start of the selection
range. The length of the silence equals the length of the
selection range. Events to the right of the selection range
start are moved to the right to “make room”. Events that
are intersected by the selection range start are split, and
the right section is moved to the right.
Region operations
Regions are sections within a clip, with various uses. While
regions are perhaps best created and edited in the Sample
Editor (see
“Working with regions” on page 270), the fol-
lowing region functions are available in the Advanced submenu of the Audio menu:
Function Description
Event or
Range as
Region
Events from
Regions
This function is available when one or several audio events
or selection ranges are selected. It creates a region in the
corresponding clip, with the start and end position of the
region determined by the start and end position of the
event or selection range within the clip.
This function is available if you have selected an audio
event whose clip contains regions within the boundaries
of the event. The function will remove the original event
and replace it with event(s) positioned and sized accord
ing to the Region(s).
The Edit History dialog
In the Edit History dialog you can undo and redo many edit
actions. Actions that can be undone include all functions
in the Project window as well as in the editors. It is also
possible to undo audio processes or applied plug-in ef
fects. However, these are better removed and modified
using the Offline Process History (see “The Offline Pro-
cess History dialog” on page 254).
Ö In the Preferences dialog (General page) you can limit
the Undo function by setting the number in the “Maximum
Undo” field to the desired value. This is useful if you run
out of hard disk space, for example.
-
-
68
Working with projects
Page 69

To undo and redo your actions, proceed as follows:
1. On the Edit menu, select “History…”.
The Edit History dialog opens.
The Preferences dialog
The dialog contains a list of all your edits, with the most
recent action at the bottom of the list. The Action column
displays the name of the action while the Time column
tells you when this action was performed. In the Details
column further details are shown. Here you can enter new
text by double-clicking in the column.
2. Move the horizontal, colored line upwards to the desired position to undo your actions.
You can only undo your actions in reverse order, i. e. the last performed
action is the first action to be undone.
3. Move the line down the List again to redo an action
that was undone previously.
When you open the File menu (the Cubase menu on a
Mac) and select “Preferences…”, the Preferences dialog
opens. This dialog provides a large number of options and
settings that control the global behavior of Cubase.
The dialog has a number of pages, each containing options and settings belonging to a particular topic.
• In the list on the left, click on one of the entries to open
the corresponding page.
• You can find detailed descriptions of all Preferences
options in the dialog help, opened by clicking the Help
button at the bottom left of the dialog.
About preference presets
In the Preferences dialog it is possible to save complete or
partial preference settings as presets. This lets you recall
settings quickly and easily.
69
Working with projects
Page 70

Saving a preference preset
When you have made your preferences settings, proceed
as follows to save all settings as a preset:
1. Make sure that the “Store marked preferences only”
option is not activated.
This is because this option is used for saving partial settings (see below),
as opposed to complete settings.
2. Click the Store button in the lower left section of the
Preferences dialog.
A dialog opens, allowing you to type in a name for the preset.
3. Click OK to save the preset.
Your saved settings are now available from the Preference Presets
pop-up menu.
Loading a preference preset
To load a saved preference preset, simply select a preset
from the Preference Presets pop-up menu. The preset is
applied immediately.
Saving partial preferences settings
It is also possible to save partial preferences settings. This
is useful when you have made settings that only relate to a
certain project or situation, for example. When you apply a
saved partial preference preset, you only change the saved
settings. All other preferences will be left unchanged.
When you have made your specific preferences settings,
proceed as follows to save the partial settings as a preset:
1. Activate “Store marked preferences only”.
A new “Store” column is added to the Preferences list.
2. Click in the Store column of the Preferences items you
wish to save.
Note that if you activate a Preferences page that contains subpages, these
will also be activated. If this is not what you want, simply deactivated the
subpages.
3. Click the Store button in the lower left section of the
Preferences dialog.
A dialog opens, asking you to type in a name for the preset. It is a good
idea to choose a descriptive name for a partial preference preset, prefer
ably relating to the saved settings (for example “Editing–Controls”).
4. Click OK to save.
Your saved settings are now available from the Preference Presets
pop-up menu.
-
70
Working with projects
Page 71

6
Working with tracks and lanes
Page 72

Setting up tracks
Adding tracks
To add a track to the project, proceed as follows:
1. Open the “Add Track” submenu from the Project
menu or from the track list context menu.
The new track is added below the currently selected track in the track
list.
2. Select the desired track type.
If you select the Audio, MIDI, Group Channel, or Instrument option from
the Add Track submenu, a dialog opens, allowing you to insert several
tracks in one go. Just enter the desired number of tracks in the Count
field.
• For audio and group channel tracks, the channel configuration – mono, stereo or surround configuration (Cubase
only) – can be set in the Configuration pop-up menu.
Ö The “Add Track Using Track Preset” option allows you
to select a Track Preset. This is described in the chapter
“Working with track presets” on page 331.
Once you have created tracks, you can manipulate and rearrange them in various ways. This is explained in the following sections.
Removing tracks
To remove tracks, you have the following options:
• Select the track you want to remove, open the Project
menu and select “Remove Selected Tracks”.
• In the track list, right-click on the track you want to remove, and select “Remove Selected Tracks” from the
context menu.
• You can also remove all tracks not containing any
events by selecting “Remove Empty Tracks” from the
Project menu.
Naming tracks
To rename a track, proceed as follows:
1. Double-click in the name field and type in a new name
for the track.
2. Press [Return] to close the name field.
• If you want all events on the track to get the same name,
hold down any modifier while pressing [Return].
• If “Parts get Track names” is activated in the Preferences dialog (Editing page) and you move an event from
one track to another, the moved event will automatically be
named according to its new track. Otherwise the event
will retain the name of the track it was previously on.
Coloring tracks
All tracks are automatically assigned a color.
• To control which colors are used for new tracks, use the
“Auto Track Color Mode” pop-up menu in the Preferences
dialog (Editing–Project & Mixer page).
The available options are described in the section “Applying track colors
automatically” on page 537.
• To change the color for existing tracks, use the Select
Colors pop-up menu on the toolbar.
This is described in detail in the section “About the Select Colors pop-
up menu” on page 538.
• To change the color for a track you can also press
[Ctrl]/[Command], point the mouse at the strip where the
track color is shown and click.
The color strip is shown, allowing you to select the desired color.
This method works in several places where the track color is visible, i. e.
in the track list, the track name field in the Inspector, and the channel
name field in the Mixer.
• To override the track color for individual events and
parts, use the Color tool or the Select Colors pop-up
menu.
For more information, see “Coloring tracks, parts, or events manually” on
page 538.
Working with tracks and lanes
72
Page 73

Resizing tracks
!
• To change the width of the track list area, drag the border between the track list and the event display.
• To change the height of an individual track, click on its
lower border in the track list and drag up or down.
• To change the height of all tracks simultaneously, hold
down [Ctrl]/[Command] and resize one of the tracks in this
way.
If “Snap Track Heights” is activated on the Track Scale pop-up menu
(see below), the track height will change in fixed increments when you
resize it.
This behavior is different when “Enlarge Selected
Track” is activated on the Edit menu (see
Enlarge Selected Track option” on page 73).
“About the
Data display on the tracks
Changing the width and the height of tracks naturally has
an effect on how the track controls and the parts or events
on the track are displayed. The following happens when
you resize a track’s height or width:
• The track controls will be placed where they best “fit in”
by default. The controls shown for tracks in the track list
will adapt to the track size.
If you prefer to have the controls in fixed positions, deactivate the “Wrap
Controls” option in the Track Controls settings dialog (see
track controls” on page 535).
“Customizing
• The contents of events and parts will not be shown if
the height of a track is very small.
You can change this behavior by activating “Show Data on Small Track
Heights” in the Preferences (Event Display).
• To set the number of tracks to view in the current Project
window, use the Track Scale pop-up menu (opened by
clicking the arrow button above the vertical zoom control).
The track height will be adjusted to show only the number of tracks specified on the pop-up menu. By selecting “Zoom N Tracks” from the pop-up
you can manually set the number of tracks to fit in the current Project
window.
By default, lanes (see “Working with lanes” on page 76)
have a track height of 4 rows. If you still have difficulties to
discern the recorded takes, you can size the lanes individually as usual. Lanes can be reordered as usual.
About the Enlarge Selected Track option
When this option is activated on the Edit menu (or in the
Preferences dialog, Editing–Project & Mixer page), the selected track is enlarged automatically. This is useful if you
are stepping through the tracks in the track list, to check
or edit the settings. The tracks will revert to the size they
had before when they are deselected. You can adjust the
size directly in the track list if the default enlargement fac
tor does not suit you.
While this is the program behavior you will want in most
cases, it may be a disadvantage when changing the track
height you started out with for one or more tracks (i. e. their
“original” height, before “Enlarge Selected Track” was ac
tivated). As soon as you try to resize a track, it is selected
and automatically enlarged. Instead of turning off “Enlarge
Selected Track”, resizing the desired track(s) and the acti
vating “Enlarge Selected Track” again, you can resize a
track in the track list without selecting it.
Proceed as follows:
1. Move the mouse pointer over the lower border of the
(unselected) track you want to resize.
The mouse pointer turns into a divider symbol.
2. Hold down [Alt]/[Option] and drag the lower border of
the track until it reaches the desired height.
Now, when you select this track, (and “Enlarge Selected Track” is activated), it will be enlarged. It will revert to the changed size, when you select a different track.
-
-
-
Working with tracks and lanes
73
Page 74

Defining the track time base
!
In the Inspector or track list you can set the time base individually for each track, by clicking on the “Toggle Timebase” button. Tracks can be either musical (tempo) or
linear (time) based or follow the Transport Main display:
• Musical
On a track using musical time base, the positions of events are represented as meter values (bars, beats, 1/16th notes and ticks, with 120
ticks per 1/16th note). If you change the playback tempo, the events will
play back at an earlier or later time. Musical time base is indicated by a
note symbol.
• Time Linear
On a track using linear time base, the events will be positioned on specific time positions – changing the playback tempo will not affect the
time position of events. Linear time base is indicated by a clock symbol.
• Follow Transport Main Display
This uses the primary time format setting on the Transport panel. When
this is set to “Bars+Beats”, tracks with musical time base will be added.
When this is set to any of the other options (Seconds, Timecode, Sam
ples, etc.), all new tracks will use linear time base.
Which time base suits better depends on the type of project and recording situation.
Internally, events on musical time based tracks use the
same high precision for positioning (64 bit floating
point values) as linear time based events. However,
switching between linear and musical time base re
sults in a very small loss of precision (introduced by
the mathematical operations used for scaling values in
the two different formats). Therefore you should avoid
switching repeatedly between the two modes.
Ö In the Preferences dialog (Editing page), you can find
the “Default Track Time Type” option (Cubase only). This
allows you to specify the default track time type for new
tracks (audio, group/FX, MIDI, and marker tracks).
For more information about tempo changes, see the chapter “Editing tempo and signature” on page 462.
-
Editing tracks
Adding events to a track
There are a number of ways to add events to a track:
• By recording (see “Basic recording methods” on page
90).
• By dragging files and dropping them on the track at the
desired position.
You can drag from the following locations: the desktop, the MediaBay
and its related windows (see the chapter
the Pool, a library (a Pool file that is not attached to a project) (Cubase
only), the “Find media” dialog, another open Project window, the Audio
Part Editor, the Sample Editor (press [Ctrl]/[Command] and drag to cre
ate an event of the current selection, or click in the left column of the region list and drag to create an event from a region).
When you drag the clip into the Project window, its position will be indicated by a marker line and a numerical position box.
• By importing an audio or video file using the Import submenu on the File menu.
When you import a file this way, a clip is created for the file and an event
that plays the whole clip is inserted on the selected track, at the position
-
of the project cursor.
• By importing a MIDI file using the Import submenu.
See “Exporting and importing standard MIDI files” on page 527.
• By grabbing audio CD tracks and converting them to audio files.
See “Importing audio CD tracks” on page 522.
• By importing only the audio portion of a video file and
converting it to an audio file.
See “About thumbnail cache files” on page 513.
• By using Copy and Paste on the Edit menu.
This allows you to copy all kinds of events between projects. You can
also copy events within the project, e.
• By drawing.
This is possible for marker and automation tracks e. g. For audio, MIDI
and instrument tracks, you can only draw parts (see
page 75).
“The MediaBay” on page 311),
g. from the Sample Editor.
“Creating parts” on
-
Working with tracks and lanes
74
Page 75

Creating parts
This track is selected.
Parts are containers for MIDI or audio events, or even for
tracks (see “Working with folder parts” on page 79).
Creating MIDI parts
A MIDI part is automatically created when you record. This
will contain the recorded events. However, you can also
create empty MIDI parts and later add events to them.
There are two ways to do this:
• Draw a part on a MIDI track with the Pencil tool.
You can also draw parts by pressing [Alt]/[Option] and using the Arrow
tool.
• Double-click with the Arrow tool on a MIDI track, between the left and right locator.
To add events to a MIDI part, you use the tools and functions in a MIDI editor (see “The Key Editor – Overview” on
page 377).
Creating audio parts
There is no way of automatically creating audio parts on
recording. On recording audio events are created always.
To create audio parts, you have the following possibilities:
• Use the “Events to Part” function on the Audio menu to
gather existing audio events into a part.
This creates an audio part containing all selected audio events on the
same track. To remove the part and make the events appear as indepen
dent objects on the track again, select the part and use the “Dissolve
Part” function on the Audio menu.
• Draw a part on an audio track with the Pencil tool.
You can also draw parts by pressing [Alt]/[Option] and using the Arrow
tool.
• Double-click with the Arrow tool on an audio track, between the left and right locator.
Ö You can use Copy and Paste or Drag and Drop in the
Audio Part Editor to add events to existing audio parts
(see
“Window overview” on page 295).
Selecting tracks
• To select a track, click on it in the track list.
A selected track is indicated by a light gray color in the track list.
• To select several tracks press [Ctrl]/[Command] and
click on them.
• To select a continuous range of tracks [Shift]-click on
them.
You can also set up Cubase to select tracks on the following actions by activating Preferences:
• Selecting a channel in the mixer
The respective track is automatically displayed in the track list as well.
For this to work you need to activate the “Scroll to Selected Track…” op
tion in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Project & Mixer).
• Selecting an event in the Project Window
The corresponding track is automatically selected, if the “Track Selection
Follows Event Selection” option is activated in the Preferences dialog
(Editing).
• Activating the solo button for the track
The track gets automatically selected, if the “Select Channel/Track on
Solo” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Project &
Mixer).
• Clicking the Edit button (e) for the track
The track gets automatically selected, if the “Select Channel/Track on
Edit Settings” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (Editing–Proj
ect & Mixer).
Duplicating tracks
• To duplicate a track together with all contents and
channel settings, right-click the track list and select “Du
plicate tracks” from the context menu, or select “Duplicate
tracks” from the Project menu.
The duplicated track will appear below the original track.
-
-
-
Working with tracks and lanes
75
Page 76

Moving tracks
Click the “Show Lanes” button…
…to display the recorded takes on different lanes.
• To move a track, click and drag it up or down in the list.
• To move one or several selected tracks to a folder, se-
lect “Move Selected Tracks to New Folder” from the context menu.
Disabling tracks
Audio tracks can be disabled by selecting “Disable Track”
from the track list context menu. Disabling a track is similar
to muting it (see
abled track will not be played back. However, disabling a
track not only “zeroes” the output volume from the track,
but actually shuts down all disk activity for it. For more in
formation, see “About track disable/enable” on page 86.
Track folding
On the Project menu you will find the Track Folding submenu, allowing you to quickly show, hide or invert what is
displayed in the Project window event display. This enables you for example to divide the project into several
parts (by creating several folder tracks for the different
project elements) and showing/hiding their contents by
selecting a menu function (or using a key command). You
can also fold in automation tracks this way. The following
options are available:
• Toggle Selected Track
When you select this menu option, the fold state of the selected track is
reversed, i.
den), it is now unfolded (all subtracks displayed) and vice versa.
• Fold Tracks
Select this menu option to fold in all open folder tracks in the Project window. Please note that the exact behavior of this function depends on the
“Deep Track Folding” setting in the Preferences dialog, see below.
• Unfold Tracks
Select this menu option to unfold all folder tracks in the Project window.
Please note that the exact behavior of this function depends on the
“Deep Track Folding” setting in the Preferences dialog, see below.
• Flip Fold States
Select this menu option to flip the fold states of the tracks in the Project
window. This means that all tracks that were folded in will be unfolded
and all unfolded tracks will be folded in, respectively.
• Move Selected Tracks to New Folder
This menu option is available, if at least one folder track is available. Selecting this option moves all selected tracks to the folder track.
e. if the track was folded in (its elements (subtracks) were hid-
“Muting events” on page 65), since a dis-
Ö You can assign key commands for these menu options
in the Key Commands dialog (Project category).
In the Preferences dialog (Editing–Project & Mixer page),
you can find the following option affecting the track folding
behavior:
• Deep Track Folding
When this is activated, any folding settings you make in the Track Folding submenu of the Project menu also affect the subelements of the
tracks, i.
e. if you fold in a folder track which contains 10 audio tracks 5 of
which have several automation tracks open, all these audio tracks within
the folder track will be folded in as well.
Working with lanes
-
Ö To simplify matters, the descriptions in the following
paragraphs focus on cycle recordings with takes. However, you can also apply lane operations and comping
methods on overlapping events or parts that you assemble on one track!
If you perform a cycle recording in the “Keep History” or in
“Cycle History + Replace” modes (audio) or in the
“Stacked” or “Mix-Stacked” modes (MIDI), the recorded
cycle laps are shown on the track with the last recorded
take active and shown on top.
The “Show Lanes” mode provides a very comfortable working environment and a good overview of all your takes. If you
activate the “Show Lanes” button, the recorded takes are
shown on separate lanes.
Working with tracks and lanes
76
Page 77

Lanes are handled differently, depending on whether you
Double-clicking the range brings it to front.
work with audio or MIDI:
• Audio
As each audio track can only play back one single audio event at a time,
you will only hear the take that is activated for playback (e.
of a cycle recording).
g. the last lap
• MIDI
Overlapping MIDI takes (parts) can be played back simultaneously. For
example, if you recorded in “Mix-Stacked” mode, you hear all takes from
all cycle laps. There is no playback priority between lanes on a MIDI
track.
Lanes can be reordered, sized, and zoomed like regular
tracks.
In the following you will learn how to play back, cut, and
activate different takes on different lanes.
Comping operations
After recording different takes in a cycle recording and activating the “Show Lanes” button to display the recorded
laps on separate lanes, you have several possibilities to
assemble a “perfect” take. This process is often referred to
as comping. You can comp your takes using the Object
Selection or the Range Selection tools.
Comping with the Object Selection tool
With the Object Selection tool selected, you can perform
the following actions:
• To select a take for playback, click on it in the event display.
The selected take is displayed in the current track color on the lane and
on the main track. All other takes are dimmed. On playback, you will only
hear the selected take.
• To audition a certain section of a take, hold down [Ctrl]/
[Command] and click with the Speaker tool.
This works even if the take is not selected for playback.
• To cut a take, hold down [Alt]/[Option] and click at the
desired position.
The cutting affects all lanes of a track. If you cut a MIDI part and the cut
position intersects one or several MIDI notes, the result depends on the
“Split MIDI Events” option in the Preferences dialog, see
events” on page 62.
“Splitting
• To adjust the cut position, position the mouse pointer
over a cut and move the cut point to the left or to the right.
This way you can finetune your edits. If you position the mouse pointer in
the lower part of a cut take, you will adjust the length instead.
• To correct the timing of a take, select the desired take,
hold down [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Alt]/[Option] (the tool modifier for Slip Event) and drag with the mouse.
The mouse pointer changes its shape to indicate that you can change
the timing.
Comping with the Range Selection tool
With the Range Selection tool selected, you can perform
the following actions:
• To bring the selected range to front, select a range on a
lane and double-click it.
Working with tracks and lanes
77
Page 78

• To glue cuts, select a range that spans all the cuts that
Before…
…and after gluing.
you want to glue and double-click.
The gluing affects all the lanes of a track.
• To correct the timing of a range, hold down [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Alt]/[Option] (the tool modifier for Slip Event) and
drag with the mouse.
The mouse pointer changes its shape to indicate that you can change
the timing.
Ö For all comping operations except “Slip Events”, Snap
is taken into account.
Cubase only: You can also perform a multi-track comping
using edit groups (see “About Group Editing (Cubase
only)” on page 80), for example, to comp two guitar tracks
recorded with different microphones.
Ö The Solo button also comes in handy in case you used
the lowermost lane for assembling your “perfect take” instead of using the comping techniques.
Additional steps
After rearranging the overlapping events so that you hear
what you want, you can perform additional steps.
Audio
1. Apply auto fades and crossfades to the comped
events.
2. Select all events and select “Delete Overlaps” from
the Advanced submenu on the Audio menu to put all
events in the top lane and resize the events so that over
lapping sections are removed.
3. Open the Audio menu and select the “Bounce Selection” function to create a new and continuous event of all
selected events.
MIDI
1. Open your takes in a MIDI editor to perform fine adjustments like removing or editing notes.
2. Select all parts in the Project window and use the
“Merge MIDI in Loop” option from the MIDI menu with the
“Erase Destination” option activated to create a single
MIDI part containing your “perfect take”.
-
Comping with the cursor keys
Another way of comping is to use the cursor keys to navigate through the takes and the lanes and the “Move To
Front (Uncover)” key command (by default [U]) to bring
the active take to front.
Using the Solo button
To solo a lane, you can activate the Solo button for it. This
allows you to hear the lane in project context. If you want
to hear the take without project context, you will also have
to activate the main track’s Solo button.
Working with tracks and lanes
78
Page 79

Organizing tracks in folder tracks
A folder track
Tracks in the folder
Creating Folder tracks
Moving tracks into a folder is a way to structure and organize tracks in the Project window. By grouping tracks in
folder tracks, you can solo and mute them in a quicker and
easier way and perform editing on several tracks as one
entity. Folder tracks can contain any type of track includ
ing other folder tracks.
Working with folder tracks
• Creating a folder track
On the Project menu open the “Add Track” submenu and select “Folder”,
or right-click the track list and select “Add Folder Track” from the context
menu.
• Moving tracks into a folder
Open the Project menu and use the “Move Selected Tracks To New
Folder” command from the Track folding submenu, right-click on the
track in the track list and select the command from the context menu or
set up and use the corresponding key command (found in the Project
category of the Key Commands dialog).
-
• Hiding/showing data on folder tracks
Right-click on the folder track to open the context menu and from the
“Show Data on Folder Tracks” submenu select one of the options. This
menu is also available in the Preferences (Editing page). The following
options are available:
Option Description
Always Show Data The data on the folder track is always visible.
Never Show Data The data on the folder track is never visible.
Hide Data When
Expanded
The data on the folder track is only visible if the
folder is not expanded.
• Muting and soloing folder tracks
Click the Mute or Solo button on the folder track to mute or solo all
tracks in the folder as one unit.
• Removing tracks from a folder
Drag a track out of the folder and release it in the track list to remove it
from the folder.
• Hiding/showing tracks in a folder
Click on the “Expand/Collapse Folder” button (the folder icon) to hide or
show the tracks located in a folder or use the corresponding options in
the Track Folding submenu of the Project menu (see
page 76). Hidden tracks are played back as usual.
“Track folding” on
79
Working with tracks and lanes
Working with folder parts
A folder part is a graphic representation of events and
parts on the tracks in the folder. Folder parts indicate the
position and length of the events and parts, as well as on
which track they are (their vertical position). If part colors
are used, these are also shown in the folder part.
Any Project window editing you perform to a folder part
affects all the events and parts it contains. You can select
several folder parts if you like – this allows you to handle
and edit them together. The editing you can perform in
-
cludes:
• Moving a folder part. This will move its contained events and
parts (possibly resulting in other folder parts, depending on
how the parts overlap).
• Using cut, copy and paste.
• Deleting a folder part. This will delete its contained events and
parts.
Page 80

• Splitting a folder part with the Scissors tool.
• Gluing folder parts together with the Glue tube tool. This will
only work if the adjacent folder parts contain events or parts
on the same track.
• Resizing a folder part resizes the contained events and parts
according to the selected resizing method.
• Muting a folder part. This will mute its contained events and
parts.
Tracks inside a folder can be edited as one entity by performing the editing directly on the folder part containing
the tracks. You can also edit individual tracks within the
folder by showing the contained tracks, selecting parts
and opening editors as usual.
Double-clicking a folder part opens the editors for the corresponding track classes present in the folder. The following applies:
• All MIDI parts located on the tracks within the folder are
displayed as if they were on the same track, just like when
opening the Key Editor with several MIDI parts selected.
To be able to easily discern the different tracks in the editor, give each
track a different color in the Project window and use the “Part Colors”
option in the editor (see
“Coloring notes and events” on page 382).
• If the folder contains tracks with audio events and/or au-
dio parts, the Sample and/or Audio Part Editors are opened
with each audio event and audio part in a separate window.
About Group Editing (Cubase only)
One very convenient feature in Cubase is the Group Editing mode for folders. It allows you to quickly group events
and parts across multiple tracks without having to select
all the events or parts. This is useful for multi-track record
ings of drum sets e.g., where you often want to edit the different drum tracks (bass drum, snare, toms, etc.) together.
Edit groups are also useful, if you want to quantize multiple
tracks, see
only)” on page 114.
“Quantizing multiple audio tracks (Cubase
You activate the Group Editing mode by clicking the “=”
button in the track list for a folder or by using the default key
command [K] (“Toggle Edit Group on Selected Tracks“).
If the Group Editing mode is activated and you select an
event, a part or a range on a track inside the folder track,
other events, parts or ranges that have the same start and
end time and the same playback priority, are also selected
and temporarily grouped.
Temporarily means that on every new selection with the
Object Selection or the Range Selection tool, Cubase
looks for corresponding events or parts inside the folder
and groups them. If you edit the start or end point of a sin
gle event or part before activating the “=” button for group
editing, will cause this event or part to be excluded from
the group.
Edit actions in Group Editing mode affect all grouped
events, parts or ranges. If you select another take by using
the small “To Front” arrow at the right side of one event of
an Edit Group e.g., all other tracks inside the Edit Group
also switch to the corresponding take. This is very useful
for comparing takes of a multi-track recording.
Ö The Group Editing setting overwrites any regular group
settings in the edit group. For further information, see
“Grouping events” on page 64.
-
Working with tracks and lanes
80
Page 81

Dividing the track list
It is possible to divide the track list into two parts. Both
sections will have independent zoom and scroll controls (if
needed), but resizing the window vertically will affect the
lower section only (if possible). This is useful if you are
working with a video track along with multi-track audio, for
example. This way, you can place the video track in the
upper track list, letting you scroll the audio tracks sepa
rately in the lower track list, referencing them against the
video track.
• To divide the track list, click the “Divide Track List” button in the top right corner of the Project window just below the ruler.
• To revert to a single track list, click the button again.
When the track list is divided into two parts, the following
applies:
• If you add tracks from the Add Track submenu of the
Project menu, video tracks, marker tracks, and arranger
tracks are automatically placed in the upper part of the
track list.
If the track list already contains tracks any video, marker, or arranger
tracks, these are automatically moved to the upper part when you divide
the track list. All other types of tracks are placed in the lower part.
• If you add tracks from the context menu invoked by
right-clicking the track list, the tracks are added to the part
of the track list in which you click.
• You can move any type of track from the lower track list
to the upper and vice versa by right-clicking it in the track
list and selecting “Toggle Track List” from the context
menu.
• You can resize the upper part by clicking and dragging
the divider between the track list sections.
-
Working with tracks and lanes
81
Page 82

7
Playback and the Transport panel
Page 83

Background
This chapter describes the various methods available for
controlling playback and transport functions in Cubase.
The Transport panel
The Transport panel contains the main transport functions
in Cubase, as well as many other options related to play
back and recording.
The following sections can be shown on the Transport
panel, from left to right:
• Virtual Keyboard, see “The Virtual Keyboard” on page 88.
• Performance, this is related to the VST Performance window,
“About the VST Performance window” on page 24.
see
• Record Mode, see “Recording audio” on page 97 and “Re-
cording MIDI” on page 102.
• Locators, see “Setting the left and right locators” on page 85
and “About Pre-roll and Post-roll” on page 105.
•Jog/Scrub, “Playing back with the shuttle speed control” on
page 85 and “Project scrubbing – the jog wheel” on page 86.
• Main Transport, see below.
• Arranger, see “The arranger track” on page 124.
• Master + Sync, see “Using the metronome” on page 106,
• Marker, see “Using markers” on page 138, “Editing tempo and
signature” on page 462, and “Synchronized operation” on
page 500.
• MIDI Activity, see below.
• Audio Activity, see below.
• Audio Level Control, see below.
The main transport controls
In the Main Transport area you will find the basic transport
controls as well time display options, see
“Setting the time
format in the Transport panel” on page 84.
Ö The main transport functions (Cycle/Stop/Play/Record) can also be shown on the toolbar. In addition, various play options are available on the Transport menu.
-
The MIDI Activity, Audio Activity and Audio Level Control
sections
These sections are useful to monitor the MIDI and audio
input and output signals. The Audio Level Control section
furthermore contains clipping indicators and an output
level control.
Ö The audio activity and clipping indicator as well as the
output level control refer to the Control Room channel (Cubase only), if the Control Room is activated. Otherwise,
these controls refer to the Main Mix Output bus as defined
on the Outputs tab in the VST Connections window. For in
formation on the Control Room, see the chapter “Control
Room (Cubase only)” on page 172. In Cubase Artist, the
Main Mix bus is always used for monitoring.
Hiding and showing the Transport panel
The Transport panel is shown automatically when you
launch a new project. To hide or show it, select “Transport
Panel” on the Transport menu (or use the corresponding
key command – by default [F2]).
Changing the Transport panel setup
You can customize the appearance of the Transport panel
by right-clicking anywhere on the panel and selecting/deselecting the corresponding options on the context menu.
This is described in detail in the section “The setup con-
text menus” on page 534.
The numeric keypad
In the default Key Command settings, various Transport
panel operations are assigned to the numeric keypad on
the computer keyboard. The keypads are slightly different
on PC and Macintosh computers:
Numeric Key Function
[Enter] Play
[+] Fast Forward
[-] Rewind
[*] Record
[÷] (Win)/[/] (Mac) Cycle On/Off
[,] Return to Zero
[0] Stop
[1] Go to Left Locator
-
Playback and the Transport panel
83
Page 84

Numeric Key Function
[2] Go to Right Locator
[3-9] Go to marker 3 to 9
Operations
Setting the project cursor position
There are several ways to move the project cursor position:
• By using Fast Forward and Rewind.
• By using the Jog/Shuttle/Nudge control on the Trans-
port panel (see “Playing back with the shuttle speed con-
trol” on page 85).
• By dragging the project cursor in the lower part of the
ruler.
• By clicking in the ruler.
Double-clicking in the ruler moves the cursor and starts/stops playback.
• If the “Locate when Clicked in Empty Space” option is
activated in the Preferences dialog (Transport page) you
can click anywhere in an empty section of the Project window to move the cursor position.
• By changing the value in any of the position displays.
• By using the position slider above the transport buttons
in the Transport panel.
The range of the slider relates to the Length setting in the Project Setup
dialog. Hence, moving the slider all the way to the right will take you to
the end of the project.
• By using markers (see the chapter “Using markers” on
page 138).
• By using playback options (see “Playback functions” on
page 87).
• By using the arranger function (see “The arranger track”
on page 124).
• By using functions on the Transport menu.
On the Transport menu, the following functions are available:
Function Description
Locate Selection/Locate
Selection End
Locate Next/
Previous Marker
Locate Next/
Previous Event
Moves the project cursor to the beginning or end of the
current selection. For this to be available, you must
have selected one or more events or parts, or made a
selection range.
This moves the project cursor to the closest marker to
the right or left (see
This moves the project cursor forwards or backwards
respectively, to the closest beginning or end of any
event on the selected track(s).
“Marker tracks” on page 41).
Ö If Snap is activated when dragging the project cursor,
the Snap value is taken into account. This is helpful for
finding exact positions quickly.
Ö There are also numerous key commands available for
moving the project cursor (in the Transport category in the
Key Commands dialog). For example, you can assign key
commands to the “Step Bar” and “Step Back Bar” func
tions, allowing you to move the project cursor in steps of
one bar, backwards and forwards.
Setting the time format in the Transport panel
Primary time display (left) and secondary time display (right)
The time unit shown in the ruler can be independent from
the time unit shown in the main time display on the Transport panel. This means that you can display timecode in
the transport position display and bars and beats in the
ruler, for example. In addition, there is a secondary time
display to the right of the primary time display which is
also independent, giving you three different time units
shown at the same time. In the Project window, you can
also create additional ruler tracks – see
rulers – ruler tracks” on page 45.
The following rules apply:
• If you change the time format of the primary time display
on the Transport panel, the time format of the ruler will be
changed as well.
This is the same as changing the display format in the Project Setup.
Therefore, to have different display formats in the ruler and the main time
display you should change the format in the ruler.
“Using multiple
Playback and the Transport panel
84
Page 85
• The primary time display format is set on the pop-up
menu to the right in the main position display.
• This setting also determines the time format displayed
for the left and right locators on the Transport panel.
• The secondary time display is completely independent,
and the display format is set on the pop-up menu to the
right in the secondary time display.
• You can swap time formats between the primary and
secondary time displays by clicking the double arrow symbol (Exchange Time Formats) between them.
Setting the left and right locators
The left and right locators are a pair of position markers
used for specifying punch-in and punch-out positions during recording, and as boundaries for cycle playback and
recording.
Ö When cycle mode is activated on the Transport panel,
the area between the left and right locators will be re
peated (cycled) on playback. However, if the right locator
is positioned before the left, this will work as a “jump” or
“skip mode” – when the project cursor reaches the right
locator it will immediately jump to the left locator position
and continue playback from there.
There are several ways to set locator positions:
• To set the left locator, press [Ctrl]/[Command] and click
at the desired position in the ruler.
Similarly, pressing [Alt]/[Option] and clicking in the ruler sets the right locator. You can also drag the locator “handles” directly in the ruler.
The locators are indicated by the “flags” in the ruler. The area between
the locators is highlighted in the ruler and in the Project window (see
“Appearance” on page 536). Note that if the right locator is before the
left locator, the color of the ruler between the locators will change.
-
• Click and drag in the upper half of the ruler to “draw” a
locator range.
If you click on an existing locator range, you can drag to move it.
• Pressing [Ctrl]/[Command] and pressing [1] or [2] on
the numeric keypad sets the left or right locator to the
project cursor position.
Similarly, you can press [1] or [2] on the numeric keypad (without [Ctrl]/
[Command]) to set the project cursor position to the left or right locator
position. Note that these are default key commands – you can change
these if you like.
• By creating cycle markers you can store any number of
left and right locator positions, which can be recalled by
simply double-clicking on the corresponding marker (see
“Editing markers on the marker track” on page 142).
• The “Locators to Selection” item on the Transport menu
(default key command [P]) sets the locators to encompass
the current selection.
This is available if you have selected one or several events or made a selection range.
• You can also adjust the locators numerically on the
Transport panel.
Clicking the L/R buttons in the locator section on the Transport panel will
move the project cursor to the respective locator. If you press [Alt]/[Op
tion] and click the L or R button, the corresponding locator will be set to
the current project cursor position.
-
Playing back with the shuttle speed control
The shuttle speed control (the outer wheel on the Transport
panel) allows you to play back the project at any speed
(four times the playback speed at maximum), forwards or
backwards. This is a quick way to locate or “cue” to any po
sition in the project.
• Turn the shuttle speed wheel to the right to start playback.
The further to the right you move the wheel, the faster the playback speed.
• If you turn the wheel to the left instead, the project will
play backwards.
The speed depends on how far to the left you turn the wheel.
-
Playback and the Transport panel
85
Page 86

• The “Use Inserts While Scrubbing” option in the Preferences (Transport–Scrub page) allows you to activate insert effects for scrubbing with the shuttle speed control.
By default, insert effects are bypassed.
Ö You can also access the shuttle speed control via a
remote control device.
Project scrubbing – the jog wheel
The middle wheel on the Transport panel serves as a jog
wheel. By clicking and turning it to the right or left you will
move the playback position manually forwards or back
wards – much like scrubbing on a tape deck. This helps
you pinpoint exact locations in the project.
• Note that the jog wheel is an “endless rotary encoder” –
you can turn it as many times as needed to move to the
desired location.
The faster you turn the wheel, the faster the playback speed. The original
playback speed is the fastest speed possible.
• If you click the jog wheel during playback, playback automatically stops and scrubbing starts.
• The “Use Inserts While Scrubbing” option in the Preferences dialog on the Transport–Scrub page allows you to
activate insert effects for scrubbing with the jog wheel.
By default, insert effects are bypassed.
Ö You can also use a jog wheel on a remote controller
for scrubbing.
-
Nudging the project cursor
The “+” and “–” buttons in the middle of the Shuttle/Jog
section allow you to nudge the project cursor position one
frame at a time to the right or left.
Options and Settings
The “Return to Start Position on Stop”
preference
This setting is found on the Transport page in the Preferences dialog (opened from the File menu under Windows,
or the Cubase menu under Mac OS X).
• If “Return to Start Position on Stop” is activated when
you stop playback, the project cursor will automatically
return to the position where recording or playback last
started.
• If “Return to Start Position on Stop” is deactivated, the
project cursor will remain at the position where you stop
playback.
Pressing Stop again will return the project cursor to the position where
recording or playback last started.
About track disable/enable
For audio tracks, the track context menu contains an item
named “Disable Track”. This shuts down all disk activity
for the track, as opposed to using Mute, which merely
turns down the output volume for a track. For example, if
you often record “alternative takes” you can easily build up
a large number of takes on different tracks. Even though
these tracks are muted, they are actually still “playing
back” from the hard disk during playback. Because this
puts an unnecessary load on your disk system, using “Dis
able Track” is recommended for such situations.
• Select “Disable Track” for tracks that you want to keep in
the project for later use but do not want to play back now.
The track color changes to indicate that the track is disabled.
• Select “Enable Track” from the track context menu to
re-enable disabled tracks.
-
Playback and the Transport panel
86
Page 87

Playback functions
!
Apart from the standard transport controls on the Transport panel, you can also find a number of functions on the
Transport menu that can be used to control playback. The
items have the following functionality:
Option Description
Post-roll from
Selection Start/End
Pre-roll to Selection
Start/End
Play from Selection
Start/End
Play until Selection
Start/End
Play until Next
Marker
Play Selection
Range
Loop Selection This activates playback from the start of the current
Starts playback from the beginning or end of the
currently selected range and stops after the time
set in the Post-roll field on the Transport panel.
Starts playback from a position before the start or
end of the currently selected range and stops at
the selection start or end, respectively. The play
back start position is set in the Pre-roll field on the
Transport panel.
Activates playback from the beginning or end of the
current selection.
Activates playback two seconds before the start or
end of the current selection and stops at the selec
tion start or end, respectively.
This activates playback from the project cursor and
stops at the next marker.
This activates playback from the start of the current
selection and stops at the selection end.
selection and keeps starting over again when
reaching the selection end.
-
The functions listed above (except “Play until Next
Marker”) are only available if you have selected one
or more events or made a selection range.
Ö In the Preferences dialog (Editing–Audio page) you
will find the “Treat Muted Audio Events like Deleted” option. When you activate this option, any events overlapped
by a muted event will become audible.
About Chase
Chase is a function that makes sure your MIDI instruments
sound as they should when you locate to a new position
and start playback. This is accomplished by the program
transmitting a number of MIDI messages to your instru
ments each time you move to a new position in the project,
making sure all MIDI devices are set up correctly with re
gard to program change, controller messages (such as
MIDI Volume), etc.
For example, let’s say you have a MIDI track with a program change event inserted at the beginning. This event
makes a synth switch to a piano sound.
-
-
At the beginning of the first chorus you have another program change event which makes the same synth switch to
a string sound.
You now play back the song. It begins with the piano
sound and then switches to the string sound. In the middle
of the chorus you stop and rewind to some point between
the beginning and the second program change. The synth
will now still play the string sound although in this section
it really should be a piano!
The Chase function takes care of that. If program change
events are set to be chased, Cubase will track the music
back to the beginning, find the first program change and
transmit it to your synth, setting it to the correct sound.
The same thing can apply to other event types as well. The
Chase Events settings in the Preferences dialog (MIDI
-
page) determine which event types will be chased when
you locate to a new position and start playback.
Ö Event types for which the checkbox is activated here
will be chased.
• In this section of the Preferences dialog, you will also
find the “Chase not limited to Part Boundaries” option.
When you activate this option, MIDI controllers are also chased outside
the part boundaries, i.
by the cursor as well as on all the parts to the left of it. Please note that
this option should be deactivated for very large projects, as it consider
ably slows down operations such as positioning and soloing. When you
deactivate this option, the MIDI controllers are only chased within the
parts under the position cursor.
e. the Chase will be performed on the part touched
-
Playback and the Transport panel
87
Page 88

The Virtual Keyboard
!
The Virtual Keyboard can be displayed in the Transport
panel. It allows you to play and record MIDI notes by using
your computer keyboard or mouse. This is useful if you have
no external MIDI instrument at hand and you do not want to
draw in notes with the Pencil tool. The Virtual Keyboard can
perform all functions that can be controlled by external MIDI
keyboards, e.
• You can choose between two different keyboard display modes: computer keyboard and piano keyboard. To
switch between these two modes, click the “Change Virtual Keyboard Display Type” button in the lower right corner of the Virtual Keyboard section or use the [Tab] key.
g. playing and recording MIDI notes.
When the Virtual Keyboard is displayed, the usual key
commands are blocked because they are reserved for
the Virtual Keyboard. The only exceptions are: [Ctrl]/
[Command]-[S] (Save), Num [*] (Start/Stop Record),
[Space] (Start/Stop Playback), Num
[1] (Jump to left
locator), [Delete] or [Backspace] (Delete), Num [/]
(Cycle on/off), [F2] (Show/Hide Transport panel), and
[Alt]/[Option]-[K] (Show/Hide Virtual Keyboard).
• You can also press several keys simultaneously to enter
polyphonic parts. The maximum number of notes that can
be played at one time varies between the different operat
ing systems and hardware configurations.
4. Use the fader “Note velocity level” to the right of the
virtual keyboard to adjust the volume.
You can also use the up and down arrow keys for this.
5. Enter the desired notes this way.
6. When you are done, hit the Stop button and close the
Virtual Keyboard.
When the Virtual Keyboard is hidden, all key commands are available
again.
Options and settings
• In piano keyboard mode, you have a wider range of keys
at your disposal, allowing you to enter two voices simultaneously, for example bass and lead voice or bass drums
and HiHats.
In computer keyboard mode, you can use the two rows of keys that are
displayed on the Virtual Keyboard to enter notes. In piano keyboard
mode, you can also use the two rows of keys below these.
• You have seven full octaves at your disposal. Use the
“Octave Offset” buttons at the bottom of the virtual keyboard to offset the octave range of the keyboard.
You can also use the left and right arrow keys to switch the keyboard
range to a lower or higher octave, respectively.
-
The Virtual Keyboard in computer keyboard display mode
The Virtual Keyboard in piano keyboard display mode
To record MIDI using the Virtual Keyboard, proceed as follows:
1. Create or choose a MIDI or an instrument track and
activate the “Record Enable” button for it.
2. Open the Virtual Keyboard by selecting “Virtual Key-
• In piano keyboard mode, you can use the two sliders to
the left of the keyboard to introduce pitchbend (left slider)
or modulation (right slider).
You can also click on a key, hold the mouse button pressed until the
mouse pointer becomes a crosshair tool and drag upwards/downward to
introduce modulation or left/right to create pitchbend.
board” on the Devices menu, by pressing [Alt]/[Option][K] or by right-clicking on the Transport panel and select
-
ing “Virtual Keyboard” on the context menu.
The Virtual Keyboard is displayed in the Transport panel.
3. Activate the Record button and press a key on your
computer keyboard to enter a note.
You can also click on the keys of the Virtual Keyboard to enter notes.
Playback and the Transport panel
88
Page 89

8
Recording
Page 90

Background
This chapter describes the various recording methods
that you can use in Cubase. As it is possible to record
both audio and MIDI tracks, both recording methods are
covered in this chapter.
Before you start
This chapter assumes that you are reasonably familiar with
certain basic recording concepts, and that the following
initial preparations have been made:
• You have properly set up, connected and calibrated
your audio hardware.
• You have opened a project and set the project setup
parameters to your specifications.
Project setup parameters determine the record format, sample rate, project length, etc. that affect the audio recordings you make during the
course of the project, see
• If you plan to record MIDI, your MIDI equipment has to
be set up and connected correctly.
“The Project Setup dialog” on page 54.
Basic recording methods
This section describes the general methods used for recording. However, there are additional preparations and
procedures that are specific to audio and MIDI recording
respectively. Make sure to read these sections before you
start recording (see
92 and “MIDI recording specifics” on page 100).
“Audio recording specifics” on page
Record-enabling tracks
Cubase can record on a single track or on several tracks
(audio and/or MIDI) simultaneously. To make a track ready
for recording, activate the Record Enable button for the
track in the track list, in the Inspector, or in the Mixer.
Record Enable in the Inspector, track list, and Mixer
Ö If “Enable Record on Selected Audio Track” or “Enable Record on Selected MIDI Track” is activated in the
Preferences dialog (Editing–Project & Mixer page), audio
or MIDI tracks are automatically record-enabled when you
select them in the track list.
Ö You can set up key commands to record-enable all
audio tracks simultaneously and to deactivate Record Enable for all audio tracks (Arm/Disarm all Audio Tracks).
You will find these commands in the Key Commands dia
log, in the Mixer category (see “Setting up key commands”
on page 542).
Ö The exact number of audio tracks you can record simultaneously depends on your computer CPU and hard
disk performance. In the Preferences dialog (VST page),
you can find the “Warn on Processing Overloads” option.
When this is activated, a warning message will be dis
played as soon as the CPU clip indicator (on the Transport panel) lights up during recording.
-
-
90
Recording
Page 91

Activating recording
Activating recording, i e. performing and setting up manual
and automatic punch in recording is identical for audio
and MIDI.
Ö Punching in and out on MIDI recordings with pitchbend or controller data (modulation wheel, sustain pedal,
volume, etc.) may lead to strange effects (apparently
hanging notes, constant vibrato, etc.). If this happens, you
may need to use the Reset item on the MIDI menu (see
“The Reset function” on page 104).
Manually
You activate recording by clicking the Record button on
the Transport panel or toolbar or by using the corresponding key command (by default [*] on the numeric keypad).
Recording can be activated in Stop mode (from the current
cursor position or from the left locator) or during playback:
• If you activate recording in Stop mode, and the “Start
Record at Left Locator” option is activated on the Trans
port menu, recording will start from the left locator.
The pre-roll setting or the metronome count-in will be applied (see
“About Pre-roll and Post-roll” on page 105).
• If you activate recording in Stop mode, and “Start Record
at Left Locator” is deactivated, recording will start from the
current project cursor position.
• If you activate recording during playback, Cubase will
immediately enter Record mode and start recording from
the current project cursor position.
This is known as “manual punch in”.
Ö If you are synchronizing the Cubase transport to external equipment (Sync is activated on the Transport panel)
and you activate recording, the program will go into “record ready” mode (the record button on the Transport
panel will light up). In this case, recording will start when a
valid timecode signal is received (or when you click the
Play button). See the chapter
“Synchronization” on page
493 for more information.
-
Automatically
Cubase can automatically switch from playback to recording at a given position. This is known as “automatic punch
in”. A typical use for this is if you need to replace a section
of a recording, and want to listen to what is already re
corded, up to the recording start position. Proceed as follows:
1. Set the left locator to the position where you want recording to start.
2. Activate the Punch In button on the Transport panel.
Punch In activated
3. Activate playback from some position before the left
locator.
When the project cursor reaches the left locator, recording is automatically activated.
Stopping recording
Again, this can be done automatically or manually:
• If you click the Stop button on the Transport panel (or
use the corresponding key command, by default [0] on the
numeric keypad), recording is deactivated and Cubase
goes into Stop mode.
• If you click the Record button (or use the key command
for recording, by default [*]), recording is deactivated but
playback continues.
This is known as “manual punch out”.
• If the Punch Out button is activated on the Transport
panel, recording will be deactivated when the project cur
sor reaches the right locator.
This is known as “automatic punch out”. By combining this with automatic punch in, you can set up a specific section to record – again very
useful if you want to replace a certain part of a recording (see also
after Automatic Punch Out” on page 105).
“Stop
-
Punch In and Out activated
91
Recording
Page 92

Cycle recording
!
Cubase can record and play back in a cycle – a loop. You
specify where the cycle starts and ends by setting the left
and right locators. When the cycle is active, the selected
section is seamlessly repeated until you hit Stop or deac
tivate cycle mode.
• To activate cycle mode, click the cycle button on the
Transport panel.
Cycle activated
• To record in cycle mode, you can start recording from
the left locator, from before the locators or from within the
cycle, in Stop mode or during playback.
As soon as the project cursor reaches the right locator, it will jump back
to the left locator and continue recording a new lap.
• The results of cycle recording depend on the selected
cycle record mode and are different for audio (see
“Recording audio” on page 97) and MIDI (see “Recording
MIDI” on page 102).
Audio recording specifics
Selecting a recording file format
The format for recorded files is set in the Project Setup dialog on the Project menu. There are three settings: Sample Rate, Bit Resolution, and Record File Type. While the
sample rate is set once and for all when you start working
on a new project, the bit resolution and file type can be
changed at any time.
Record File Type
The Record File Type setting determines which type of
files will be created when you record:
File type Description
Wave File Wave files have the extension “.wav” and are a common
Wave 64 File Wave 64 is a proprietary format developed by Sonic
file format on the PC platform.
Foundry Inc. Audio-wise it is identical to the Wave format,
but the internal file structure makes much larger file sizes
possible. This is useful for long live recordings, where the
audio files can become huge.
File type Description
Broadcast
Wave File
AIFF File Audio Interchange File Format, a standard defined by Ap-
-
In terms of audio content, the same as regular Wave files,
but with embedded text strings for supplying additional
information about the file (see below).
ple Inc. AIFF files have the extension “.aif” and are used
on most computer platforms. Like Broadcast Wave files,
AIFF files can contain embedded text strings (see below).
• If you select Broadcast Wave File or AIFF format, you
can specify Author, Description and Reference text strings
that will be embedded in the recorded file.
This is done on the Record–Audio–Broadcast Wave page in the Preferences dialog.
Bit Resolution
The available options are 16 bit, 24 bit, and 32 bit float.
Use the following guidelines:
• Normally, select the record format according to the bit
resolution delivered by your audio hardware.
For example, if your audio hardware has 20 bit A/D converters (inputs),
you may want to record at 24 bit resolution to capture the full bit resolu
tion. On the other hand, if your hardware has 16 bit inputs, it is pointless
to record with a higher bit resolution – this will only make the audio files
larger, with no difference in audio quality. The exception is if you record
with effects – see
“Recording with effects (Cubase only)” on page 98.
• The higher the bit resolution, the larger the files and the
more strain is put on the disk system.
If this is an issue, you may want to lower the record format setting.
For further information on the options in the Project
Setup dialog, see
“The Project Setup dialog” on
page 54.
RAM requirements for recording
When recording live music performances, you will often
simultaneously record on a large number of tracks at the
same time.
Each track on which you record requires a certain amount
of RAM, and the memory usage increases the longer the
recording lasts.
-
92
Recording
Page 93

Please consider the RAM limitation (see “RAM” on page
!
Click here to select an input bus for
the track.
22) of your operating system when setting up your project
for recording.
When a recording has used up all the memory made
available by the operating system, the computer may
crash.
For each audio channel, 2.4 MB of RAM are required for
mixer settings, etc. One minute of audio recording with a
sample rate of 96 kHz on a mono track will increase memory usage by another 176 KB (Windows Task Manager,
average).
Examples:
• Recording on a 32-bit system with 64 mono tracks at a
sample rate of 44.1
This would require a total of 403 MB of memory – not a problem on a
modern computer.
kHz, lasting 60 minutes.
• Recording on a 32-bit system with 128 mono tracks at
a sample rate of 96 kHz, lasting 60 minutes.
This would require 1658 MB of memory – dangerously close to the 2 GB
limit for RAM on a 32-bit Windows computer.
Ö Also note that the maximum file size for regular Wave
files is 2 GB. If you want to record larger files, use the
Waves 64 format (see
“Record File Type” on page 92).
Setting up the track
Creating a track and selecting the channel configuration
Audio tracks can be configured as mono, stereo, or surround tracks (Cubase only). This allows you to record or
import a file containing multiple channels and treat it as
one entity, with no need to split it up into several mono
files, etc. The signal path for an audio track maintains its
channel configuration all the way from the input bus, via
EQ, level and other Mixer settings to the output bus.
You specify the channel configuration for a track when you
create it:
1. Select “Add Audio Track” from the track list context
menu or the Project menu (or, if an audio track is already
selected, double-click in an empty area of the track list).
A dialog opens with a channel configuration pop-up menu.
2. Select the desired format from the pop-up menu.
In Cubase Artist, you choose between mono and stereo. In Cubase, the
most common formats are listed directly on the pop-up menu, with the
remaining surround formats listed on the “More…” submenu. For a list of
the available surround formats, see
219.
“Output bus configuration” on page
• The Browse item in this dialog allows you to browse
your disks for created track presets, which can be used as
a basis (or template) for tracks.
This is described in detail in the chapter “Working with track presets” on
page 331.
3. Click the Add Track button.
A track is added, set to the specified channel configuration. In the Mixer,
a corresponding channel strip appears. You cannot change the channel
configuration for a track.
Selecting an input bus for a track
Here we assume that you have added and set up the required input busses (see “Setting up busses” on page 26).
Before you record, you need to specify from which input
bus the track will record. You can do this in the Inspector or
in the Mixer.
• In the Inspector, you select an input bus on the Input
Routing pop-up menu in the top section.
As described in the section “The Inspector” on page 39, the Inspector
shows the settings for the selected track.
93
Recording
Page 94

• In the Mixer, you select an input bus on the Input Rout-
Click here to select an input
bus for the track.
Click here to show or hide the
input and output settings.
ing pop-up menu at the top of the track’s channel strip.
If this pop-up menu is not shown, you need to open the Mixer Routing
View by clicking the “Show Routing” button in the extended Mixer com
mon panel or by selecting “Show Routing View” from the Window submenu of the Mixer context menu. See “Configuring the Mixer” on page
148 for more information about the Mixer.
Recording from busses (Cubase only)
You can also select an output bus, a group bus or an FX
channel bus as an Input for your recording.
Let’s assume you want to create a downmix of separate
tracks, e.
g. bass drum, hihats, snare, etc.
Proceed as follows:
1. Set up your separate tracks as desired and add a
group track.
2. For each of the drum tracks, open the Output Routing
pop-up menu and select the Group track as output.
3. Create a new audio track, open the Input Routing popup menu for it and select the Group track as input for this
audio track.
4. Record enable this audio track and start recording.
Now, the output of the group track will be recorded on the
new track and you will get a mix of your separate tracks.
Ö You can also select an FX channel as recording
source. In this case, only the output of the FX channel will
be recorded.
For more information about the routing possibilities, see
“Routing” on page 164.
Selecting a folder for the recorded audio files
Each Cubase project has a project folder containing
(among other things) an “Audio” folder. By default, this is
-
where recorded audio files are stored. However, you can
select record folders independently for each audio track if
needed.
Proceed as follows:
1. To select the same record folder for several audio
tracks, select them by pressing [Shift] or [Ctrl]/[Com
mand] and clicking on them in the track list.
2. Right-click the track list for one of the tracks to bring
up the context menu.
3. Select “Set Record Folder”.
A file dialog opens.
4. Navigate to the desired folder (or create a new folder
with the Create button).
Tip: if you want to have separate folders for different types of material
(speech, ambient sounds, music, etc.), you can create subfolders within
the project’s “Audio” folder and assign different tracks to different sub
folders. This way, all audio files will still reside within the project folder,
which will make managing the Project easier.
• It is possible to have different tracks record to totally different locations, even on different disks. However, if you
need to move or archive the project, there is a risk of missing some files. The solution is to use the “Prepare Archive”
function in the Pool to gather all external files into the proj
ect folder first, see “Prepare Archive” on page 309.
Setting input levels
When recording digital sound, it is important to set the input levels correctly – loud enough to ensure low noise and
high audio quality, but not so loud that clipping (digital distortion) occurs.
Clipping typically occurs in the audio hardware when a
too loud analog signal is converted to digital in the hard
ware’s A/D converters.
• It is also possible to get clipping when the signal from
the input bus is written to a file on your hard disk.
This is because in Cubase, you can make settings for the input bus, adding EQ, effects, etc. to the signal as it is being recorded. This may raise
the level of the signal, causing clipping in the recorded audio file.
-
-
-
-
94
Recording
Page 95

To check the level of the “unprocessed” signal coming
into the audio hardware, you need to switch the level meters to “Meter Input”. In this mode, the input channel level
meters will show the level of the signal at the input of the
bus, before any adjustments such as input gain, EQ, effects, level or pan:
1. Right-click in the Mixer window to open the context
menu.
2. Select the Global Meter Settings submenu and make
sure that “Meter Input” is activated.
3. Play back the audio and check the level meter for the
input channel.
The signal should be as loud as possible without exceeding 0 dB (the
Clipping indicator for the input bus should not light up).
The Clipping indicator
4. If necessary, adjust the input level in one of the following ways:
• Adjust the output level of the sound source or external
mixer.
• Use the audio hardware’s own application program to
set the input levels (if possible).
See the documentation for the audio hardware.
• If your audio hardware supports the ASIO Control Panel
function, it may be possible to make input level settings.
To open the ASIO control panel, open the Device Setup dialog via the Devices menu and, in the list to the left (below “VST Audio System”), select
your audio card. When this is selected, you can open the Control Panel by
clicking the Control Panel button in the settings section to the right.
The next step is to check the level of the audio being written to a file on your hard disk. This is only necessary if you
have made any adjustments to the input channel (level
settings, EQ, insert effects, etc.).
Also note the following:
• If you record in 32-bit float format, the bit resolution will
not be reduced – which means there is no risk of clipping
at this stage.
Also, this preserves the signal quality perfectly. Therefore, you should
consider using 32-bit float format when you are recording with effects
(see
“Recording with effects (Cubase only)” on page 98).
• If you record in 16- or 24-bit format, the available headroom is lower, which means clipping can occur if the signal is too loud. To avoid this, set the signal as described
below.
1. Bring up the Mixer context menu, open and select
Global Meter Settings “Meter Post-Fader”.
2. Set up the input channel, by adding EQ and/or effects.
With some effects you may want to adjust the level of the signal going
into the effect – use the Input Gain knob for this. Note that you need to
press [Shift] or [Alt]/[Option] to adjust the Input Gain.
Adjusting the Input Gain.
3. Play back the audio and check the level meter of the
input channel.
The signal should be reasonably loud without exceeding 0 dB (the Clipping indicator for the input bus should not light up).
4. If necessary, use the input channel fader to adjust the
signal level.
Audio pre-record
This feature allows you to capture up to 1 minute of any incoming audio you play in Stop mode or during playback,
“after the fact”. This is possible because Cubase can capture audio input in buffer memory, even when not recording.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Preferences dialog (Record–Audio page).
2. Specify a time (up to 60 seconds) in the “Audio Pre-
Record Seconds” field.
This activates the buffering of audio input, making Pre-Record possible.
3. Make sure an audio track is record-enabled and receives audio from the signal source.
4. When you have played some audio material you want
to capture (either in Stop mode or during playback), click
the Record button.
95
Recording
Page 96

5. After a few seconds stop the recording.
An audio event is created, starting at where the cursor position was
when you activated recording. If you were in stop mode and the cursor
was at the beginning of the project, you may have to move the event to
the right in the next step. If you were playing along to a project you, leave
the event where it is.
6. Select the Arrow tool and place the cursor on the bottom left edge of the event so that a double arrow appears,
then click and drag to the left.
Now the event is extended and the audio you played before activating record is inserted – this means that if you played along during playback,
the captured notes will end up exactly where you played them in relation
to the project.
Monitoring
In this context, “monitoring” means listening to the input
signal during recording. There are three fundamentally different ways to do this: via Cubase, externally (by listening
to the signal before it reaches Cubase), or by using ASIO
Direct Monitoring (which is a combination of both other
methods – see below).
Monitoring via Cubase
If you monitor via Cubase, the input signal is mixed in with
the audio playback. The advantage of this is that you can
adjust the monitoring level and panning in the Mixer, and
add effects and EQ to the monitor signal just as during
playback (using the track’s channel strip – not the input
bus!).
The disadvantage of monitoring via Cubase is that the
monitored signal will be delayed according to the latency
value (which depends on your audio hardware and driv
ers). Therefore, monitoring via Cubase requires an audio
hardware configuration with a low latency value. You can
check the latency of your hardware in the Device Setup
dialog (VST Audio System page).
Ö If you are using plug-in effects with large inherent delays, the automatic delay compensation function in Cubase
will increase the latency. If this is a problem, you can use the
Constrain Delay Compensation function while recording,
“Constrain Delay Compensation” on page 216.
see
-
When monitoring via Cubase, you can select one of four
Auto Monitoring modes in the Preferences dialog (VST
page):
• Manual
This option allows you to turn input monitoring on or off by clicking the
Monitor button in the Inspector, the track list or in the Mixer.
• While Record Enabled
With this option, you will hear the audio source connected to the channel
input whenever the track is record enabled.
• While Record Running
This option switches to input monitoring only during recording.
• Tapemachine Style
This option emulates standard tapemachine behavior: input monitoring in
Stop mode and during recording, but not during playback.
• In the Preferences dialog (VST–Metering page) you can
find the “Map Input Bus Metering to Audio Track (in Direct
Monitoring)” option.
When Direct Monitoring is activated in the Device Setup dialog, this option allows you to map the input bus metering to monitor-enabled audio
tracks. This gives you the opportunity to watch the input levels of your
audio tracks when working in the Project window.
When Direct Monitoring is activated in the Device Setup
dialog, this function works as follows:
• When “Map Input Bus Metering to Audio Track (in Direct
Monitoring)” is activated, audio tracks show the metering signal from the input bus they are routed to as soon as the track
is record-enabled.
Note that the tracks are mirroring the input bus signal, i. e. you
will see the same signal in both places. When using mapped
metering, any functions (e.
g. trimming) you apply to the audio
track are not reflected in its meters.
• When “Map Input Bus Metering to Audio Track (in Direct
Monitoring)” is not activated, metering works as usual.
96
Recording
Page 97

External monitoring
External monitoring (listening to the input signal before it
goes into Cubase) requires some sort of external mixer for
mixing the audio playback with the input signal. This can
be a stand-alone physical mixer or a mixer application for
your audio hardware, if this has a mode in which the input
audio is sent back out again (usually called “Thru”, “Direct
Thru” or similar).
When using external monitoring, you cannot control the
level of the monitor signal from within Cubase or add VST
effects or EQ to the monitor signal. The latency value of
the audio hardware configuration does not affect the mon
itor signal in this mode.
Ö If you want to use external monitoring, you need to
make sure that monitoring via Cubase is not activated as
well. Select the “Manual” monitoring mode in the Prefer
ences dialog (VST page) and do not activate the Monitor
buttons.
ASIO Direct Monitoring
If your audio hardware is ASIO 2.0 compatible, it may support ASIO Direct Monitoring (this feature may also be available for audio hardware with Mac OS X drivers). In this
mode, the actual monitoring is done in the audio hardware,
by sending the input signal back out again. However, monitoring is controlled from Cubase. This means that the audio
hardware’s direct monitoring feature can be turned on or off
automatically by Cubase, just as when using internal monitoring.
• To activate ASIO Direct Monitoring, open the Device
Setup dialog on the Devices menu and activate the Direct
Monitoring checkbox on the page for your audio hardware.
If the checkbox is grayed out, your audio hardware (or its driver) does not
support ASIO Direct Monitoring. Consult the audio hardware manufac
turer for details.
-
• When ASIO Direct Monitoring is activated, you can select a monitoring mode in the Preferences dialog (VST
page), as when monitoring via Cubase (see
“Monitoring
via Cubase” on page 96).
• Depending on the audio hardware, it may also be possible to adjust the monitoring level and panning from the
Mixer (including the Control Room section, but excluding
the Talkback and External Return channels – Cubase
only) by adjusting the volume faders, and the input gain
controls and the send levels for Control Room studios.
Consult the documentation of the audio hardware if in doubt.
• VST effects and EQ cannot be applied to the monitor
signal in this mode, since the monitor signal does not pass
through Cubase.
• Depending on the audio hardware, there may be special
restrictions as to which audio outputs can be used for di
rect monitoring.
For details on the routing of the audio hardware, see its documentation.
The latency value of the audio hardware configuration
does not affect the monitor signal when using ASIO Direct
Monitoring.
When using Steinberg hardware (MR816 series) in combination with ASIO Direct Monitoring, monitoring will be
virtually latency-free.
Ö If you are using RME Audio Hammerfall DSP audio
hardware, make sure that the pan law is set to -3 dB in the
card’s preferences.
Recording audio
You can record audio using any of the general recording
methods (see “Basic recording methods” on page 90).
When you finish recording, an audio file is created in the
Audio folder within the project folder. In the Pool, an audio
clip is created for the audio file, and an audio event that
plays the whole clip appears on the recording track. Fi
nally, a waveform image is calculated for the audio event. If
the recording was very long, this may take a while.
Ö If the “Create Audio Images During Record” option is
activated in the Preferences dialog (Record–Audio page),
the waveform image will be calculated and displayed dur
ing the actual recording process. This realtime calculation
uses some processing power – if your processor is slow
or if you are working on a CPU-intensive project, consider
deactivating this option.
-
-
-
97
Recording
Page 98

Undoing recording
Click here…
…to open the Audio Record Mode panel.
If you decide that you do not like what you just recorded,
you can delete it by selecting Undo from the Edit menu.
The following will happen:
• The events you just created will be removed from the Project
window.
• The audio clips in the Pool will be moved to the Trash folder.
The recorded audio files will not be removed from the hard
disk. However, since their corresponding clips are moved
to the Trash folder, you can delete the files by opening the
Pool and selecting “Empty Trash” from the Media menu,
“Deleting from the hard disk” on page 303.
see
About overlap and the Audio Record Modes
The Audio Record Mode setting lets you decide what
happens to your recording and to any existing events on
the track where you are recording. This is necessary be
cause you will not always record on an empty track. There
may be situations where you record over existing events –
especially in cycle mode.
To select an Audio Record Mode, proceed as follows:
1. On the Transport panel, click the audio symbol in the
upper left section.
Option Description
Cycle History +
Replace
Replace Existing events (or portions of events) that are over-
Existing events (or portions of events) that are overlapped by a new recording are replaced by the new
recording.
However, if you record in cycle mode, all takes from
the current cycle recording are kept.
lapped by a new recording are replaced by the last recorded take.
3. Click anywhere outside the panel to close the Audio
Record Mode panel.
To learn how to create a “perfect take” by combining the
best parts from the different cycle laps, see “Working with
lanes” on page 76.
Handling overlapping audio
The basic rule for audio tracks is that each track can only
play back a single audio event at a time. If two or more
events overlap, you will only hear one of them: the one that
is actually visible (e.
g. the last lap of a cycle recording).
If you have a track with overlapping (stacked) events/regions, use one of the following methods to select the
event/region that is played back:
• Open the context menu for the audio event in the event
display and select the desired event or region from the “To
Front” or “Set to Region” submenu.
The available options depend on whether you performed a linear or a cycle recording and the record mode you used. When recording audio in
cycle mode, the recorded event is divided in regions, one for each take.
• Use the handle in the middle of a stacked event and select an entry from the pop-up menu that appears.
• Activate the “Show Lanes” button and click on the desired take.
For details about lane editing, see “Working with lanes” on page 76.
2. Activate the desired option.
The following options are available:
Option Description
Keep History Existing events (or portions of events) that are over-
lapped by a new recording are kept.
Recording with effects (Cubase only)
Normally you record the audio signals “dry” and add effects non-destructively during playback as described in
the chapter
base also allows you to add effects (and/or EQ) directly
while recording. This is done by adding insert effects and/
or making EQ settings for the input channel in the Mixer.
This will make the effects become part of the audio file itself – you cannot change the effect settings after recording.
98
Recording
“Audio effects” on page 187. However, Cu-
Page 99

About the record format
When you record with effects, consider setting the bit resolution to 32 Bit Float. This is done in the Project Setup
dialog opened via the Project menu. Note that this is not
required in any way – you can also record with effects in
24 or 16
Bit format. However, there are two advantages to
the 32 Bit Float format:
• You do not risk clipping (digital distortion) in the recorded files.
This can be avoided with 24 or 16 Bit recording as well, but requires
more care with the levels.
• Cubase processes audio internally in 32 Bit Float format – recording in the same format means the audio quality will be kept absolutely pristine.
The reason is that the effect processing in the input channel (as well as any
level or EQ settings you make there) is done in 32 Bit Float format. If you
record at 16 or 24 Bit, the audio will be converted to this lower resolution
when it is written to file – with possible signal degradation as a result.
Ö It does not matter at which actual resolution your audio hardware works. Even if the signal from the audio
hardware is in 16 Bit resolution, the signal will be 32 Bit
Float after the effects are added in the input channel.
An example
This example shows how to apply the “SoftClipper” effect
while recording. The principle is the same for all effects (or
combinations of effects).
1. Set up an audio track for recording and select the desired input bus.
For best results, also activate monitoring as this allows you to hear and
try out your settings before actually recording. See
base” on page 96 for a description of monitoring via Cubase.
“Monitoring via Cu-
2. Open the Mixer and make sure that the full extended
view is shown.
To show the extended Mixer view, either click the arrow icon (“Show Extended Mixer”) in the Common Panel, select “Show Extended View” from
the Window submenu of the Mixer context menu or use a key command
(this can be set in the Key Commands dialog, see
mands” on page 542).
“Setting up key com-
3. Locate the input channel (bus) from which you record.
If the input channels are hidden, click on the Show/Hide Input Channels
button to the left.
4. Check the input level (of the signal coming into the audio hardware) as described in the section “Setting input
levels” on page 94 and adjust the level of the source audio
if necessary.
5. Pull down the View Options pop-up menu for the input
channel and select “Inserts”.
The View Options pop-up menu is opened by clicking the arrow button
between the fader panel and the extended panel.
Now the extended panel for the input channel shows the
insert slots.
6. Click on an insert slot and select an effect from the
context menu.
As you see, the included effects are sorted into submenus – you will find
the SoftClipper effect on the “Distortion” submenu.
The effect is loaded and activated and its control panel is
automatically opened.
7. Adjust the effect parameters to your liking.
For detailed information on the Effect parameters, see the separate PDF
document “Plug-in Reference”.
8. When the effect is set up as desired, you can check
the level of the input channel by setting the Meters to
post-fader (see
Use the input channel fader to adjust the level if needed.
“Setting input levels” on page 94).
99
Recording
Page 100

9. Activate recording.
!
!
Record Enable
button
Monitor
button
10. When you are finished, you can play back the recorded audio track.
As you can hear, the effect you applied is now a part of the actual audio file.
11. If you do not want to record more with the same plugin, deactivate it by clicking in the insert slot and selecting
“No Effect”.
Recovery of audio recordings after system
failure
Normally, when a computer crashes, all changes made to
your current project since you last saved it will be lost.
Usually, there is no quick and easy way to recover your
work.
With Cubase, when your system crashes while you are recording (because of a power cut or other mishap), you will
find that your recording is still available, from the moment
when you started recording to the time when your computer crashed.
When you experience a computer crash during a recording, simply relaunch the system and check the project record folder (by default this is the Audio subfolder inside
the project folder). It should contain the audio file you
were recording at the time of the crash.
This feature does not constitute an “overall” guarantee by Steinberg. While the program itself was improved in such a way that audio recordings can be
recovered after a system failure, it is always possible
that a computer crash, power cut, etc. might have
damaged another component of the computer, mak
ing it impossible to save or recover any of the data.
Please do not try to actively bring about this kind of
situation to test this feature. Although the internal
program processes have been improved to cope
with such situations, Steinberg cannot guarantee
that other parts of the computer are not damaged as
a consequence.
MIDI recording specifics
Activating MIDI Thru
Normally, when working with MIDI, you will have MIDI Thru
activated in Cubase, and Local Off selected in your MIDI
instruments. In this mode, everything you play during re
cording will be “echoed” back out again on the MIDI output and channel selected for the recording track.
1. Make sure that the “MIDI Thru Active” option is activated in the Preferences dialog (MIDI page).
2. Record enable the tracks on which you want to record.
Now, incoming MIDI is “echoed” back out again for all record-enabled
MIDI tracks.
Ö If you just want to use the Thru function for a MIDI
track without recording, activate the monitor button for the
track instead. This is useful, for instance, if you want to try
out different sounds or play a VST instrument in realtime
without recording your playing.
Setting MIDI channel, input, and output
Setting the MIDI channel in the instrument
Most MIDI synthesizers can play several sounds at the
same time, each on a different MIDI channel. This is the
key to playing back several sounds (bass, piano, etc.) from
-
the same instrument. Some devices (such as General
MIDI compatible sound modules) always receive on all 16
MIDI channels. If you have such an instrument, there is no
specific setting you need to make in the instrument. On
other instruments, you will have to use the front panel con
trols to set up a number of “Parts”, “Timbres” or similar so
that they receive on one MIDI channel each. See the manual that came with your instrument for more information.
-
-
100
Recording
 Loading...
Loading...