SURVEYING INSTRUMENTS
H18.09.21
Series SRX
SRX1
SRX2
SRX3
SRX5
Total Station
Class 3R Laser Product
Class 1 LED Product
OPERATOR'S MANUAL

Li-ion
S Li-ion
This is the mark of the Japan Surveying
Instruments Manufacturers Association.
SURVEYING INSTRUMENTS
Series SRX
SRX1
SRX2
SRX3
SRX5
Total Station
Class 3R Laser Product
Class 1 LED Product
• Thank you for selecting the SRX1/2/3/5.
• Before using the instrument, please read this operator’s manual carefully.
• Verify that all equipment is included.
"26. STANDARD EQUIPMENT"
• SRX has a function to output data saved in Program mode (SDR) to a connected
host computer. Command operations from a host computer can also be
performed. For details, refer to “Interfacing with the SOKKIA SDR Electronic Field
Book” and “Command Explanations” manuals and ask your Sokkia agent.
• The specifications and general appearance of the instrument may be altered at
any time and may differ from those appearing in brochures and this manual.
• Some of the diagrams shown in this manual may be simplified for easier
understanding.
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
HOW TO READ THIS MANUAL
Regarding other manuals
• Manuals 2, 3, and 4 below are electronic manuals provided on a CD-ROM in PDF format (
• The SRX comes equipped with 4 manuals for operation information:
1. SRX Operator’s Manual (this manual):
Explains basic operation and functions of the SRX.
2. Series SRX SDR Software Reference Manual :
Explains advanced measurement operations using the SRX in Program mode (SDR), and
methods for managing measured data.
3. SFX Dial-Up Program Explanations :
Explains how to send and receive data using the SFX function
4. Series SRX Quick Manual :
Simplified explanations of operations such as Auto-Tracking to allow users to get started
straight away.
Symbols
The following conventions are used in this manual.
Indicates precautions and important items which should be read before
:
operations.
: Indicates the chapter title to refer to for additional information.
: Indicates supplementary explanation.
).
[Softkey] etc. : Indicates softkeys on the display and window dialog buttons.
{Key} etc. : Indicates keys on the operation panel.
<Setting out> etc.: Indicates screen titles.
Notes regarding manual style
• Except where stated, “SRX” means “SRX1/SRX2/SRX3/SRX5” in this manual.
• Screens and illustrations appearing in this manual are of SRX3.
• Location of softkeys in screens used in procedures is based on the factory setting. It is possible to
change the allocation of softkeys.
: Indicates an explanation for a particular term or operation.
Softkey allocation: "21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
• Kodak Gray Card: KODAK is a registered trademark of Eastman Kodak Company.
ii

SURVEYING INSTRUMENTS
• Bluetooth: Bluetooth® is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
• Windows CE® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
• All other company and product names featured in this manual are registered trademarks of each
respective organization.
Operation procedure
• Learn basic operations in "4. PRODUCT OUTLINE" and "5. BASIC OPERATION" before you read
each measurement procedure. An overview of the available SRX functions is given in
"4.1 Functions". For selecting options and inputting figures, see "5.1 Basic Key Operation".
• For Auto Tracking measurement, read this manual in conjunction with the On-demand Remote
Control System Manual.
• Measurement procedures are based on continuous measurement. Some information about
procedures when other measurement options are selected can be found in “Note” (
).
iii

CONTENTS
1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFE OPERATION ................. 1
2. PRECAUTIONS........................................................... 4
3. LASER SAFETY INFORMATION ............................... 6
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE .................................................8
4.1 Functions ........................................................................... 8
4.2 Parts of the Instrument .................................................... 10
4.3 Mode Configuration ......................................................... 15
4.4 Bluetooth Wireless Technology ....................................... 16
5. BASIC OPERATION ................................................. 18
5.1 Basic Key Operation ....................................................... 18
5.2 Display Functions ............................................................ 23
5.3 Inputting Characters using SIP Code (Input Panel) ........ 29
5.4 SETTINGS Mode ............................................................ 30
6. USING THE CF CARD SLOT ................................... 32
6.1 Inserting/Removing the CF Card ..................................... 32
7. USING THE BATTERY ............................................34
8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES ............... 36
8.1 Wireless Communication using Bluetooth Technology ... 36
8.2 Communication between the SRX and Companion Device
......................................................................................... 40
8.3 Connection via RS-232C cable ....................................... 42
8.4 Connecting to USB devices ............................................ 42
9. SETTING UP THE INSTRUMENT ........................... 44
9.1 Centering ......................................................................... 44
9.2 Levelling .......................................................................... 45
10. POWER ON/OFF .....................................................48
10.1 Resolving Software Issues .............................................. 49
10.2 Configuring the Touch Panel ........................................... 49
10.3 Powering the SRX ON/OFF from an External Instrument 50
11. TARGET SIGHTING .................................................51
11.1 Auto Pointing Settings ..................................................... 52
11.2 Auto-Pointing Function for Target Sighting ..................... 54
11.3 Manually Sighting the Target .......................................... 55
12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING ............. 56
iv

CONTENTS
12.1 Auto Tracking Settings .................................................... 56
12.2 Measurement with Auto Tracking .................................... 57
13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT ........................................60
13.1 Measuring the Horizontal Angle between Two Points
(Horizontal Angle 0°) ....................................................... 60
13.2 Setting the Horizontal Angle to a Required Value (Horizontal
Angle Hold) ..................................................................... 62
13.3 Turning the Instrument from the Reference Angle to a
Specified Angle ............................................................... 64
13.4 Angle measurement and Outputting the Data ................. 65
14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT ..................................66
14.1 Returned Signal Checking .............................................. 66
14.2 Distance and Angle Measurement .................................. 68
14.3 Using the Guide Light ...................................................... 68
14.4 REM Measurement ......................................................... 70
14.5 Distance Measurement and Outputting the Data ............ 70
15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT ............................. 73
15.1 Entering Instrument Station Data .................................... 73
15.2 Azimuth Angle Setting ..................................................... 74
15.3 3-D Coordinate Measurement ......................................... 77
16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT ................................79
16.1 Coordinate Resection Measurement ............................... 80
16.2 Height Resection Measurement ...................................... 84
17. SETTING-OUT MEASUREMENT ............................ 89
17.1 Using the Guide Light ...................................................... 89
17.2 Distance Setting-out Measurement ................................. 90
17.3 Coordinates Setting-out Measurement ........................... 96
17.4 REM Setting-out Measurement ....................................... 99
18. OFFSET MEASUREMENT .................................... 102
18.1 Single-distance Offset Measurement ............................ 102
18.2 Angle Offset Measurement ........................................... 104
18.3 Two-distance Offset Measurement ............................... 106
19. MISSING LINE MEASUREMENT .......................... 109
19.1 Measuring the Distance between 2 or more Points ...... 109
19.2 Changing the Starting Point .......................................... 111
20. SURFACE AREA CALCULATION ......................... 113
v

CONTENTS
21. CHANGING THE SETTINGS .................................118
21.1 Observation Conditions ................................................. 118
21.2 Instrument Configuration ............................................... 120
21.3 EDM Settings ................................................................ 123
21.4 Allocating User-defined Tabs ........................................ 126
21.5 Customizing Screen Controls ........................................ 129
21.6 Allocating Key Functions ............................................... 131
21.7 Units .............................................................................. 134
21.8 Date and Time ............................................................... 135
21.9 Changing Password ...................................................... 135
21.10 Restoring Default Settings ............................................ 136
22. WARNING AND ERROR MESSAGES .................. 137
23. CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS ............................140
23.1 Plate Level .................................................................... 140
23.2 Circular Level ................................................................ 141
23.3 Tilt Sensor ..................................................................... 142
23.4 Collimation .................................................................... 145
23.5 Reticle ........................................................................... 147
23.6 CCD reticle .................................................................... 149
23.7 Optical Plummet ............................................................ 151
23.8 Additive Distance Constant ........................................... 152
24. Power Supply System ............................................154
25. Target System ........................................................ 155
26. STANDARD EQUIPMENT ..................................... 157
27. Optional Accessories ..............................................159
28. SPECIFICATIONS ..................................................161
29. REGULATIONS ......................................................168
30. EXPLANATION ......................................................173
30.1 Manually Indexing the Vertical Circle by Face Left, Face
Right Measurement ....................................................... 174
30.2 Atmospheric Correction for High Precision Distance
Measurement ................................................................ 175
31. INDEX ....................................................................177
vi

1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFE OPERATION
For the safe use of the product and prevention of injury to operators and other persons as well as
prevention of property damage, items which should be observed are indicated by an exclamation point
within a triangle used with WARNING and CAUTION statements in this operator’s manual.
The definitions of the indications are listed below. Be sure you understand them before reading the
manual’s main text.
Definition of Indication
General
WARNING
CAUTION
This symbol indicates items for which caution (hazard warnings inclusive) is urged.
Specific details are printed in or near the symbol.
This symbol indicates items which are prohibited. Specific details are printed in or near
the symbol.
This symbol indicates items which must always be performed. Specific details are printed
in or near the symbol.
Warning
Do not use the unit in areas exposed to high amounts of dust or ash, in areas where there
is inadequate ventilation, or near combustible materials. An explosion could occur.
Do not perform disassembly or rebuilding. Fire, electric shock, burns, or hazardous
radiation exposure could result.
Never look at the sun through the telescope. Loss of eyesight could result.
Do not look at reflected sunlight from a prism or other reflecting object through the
telescope. Loss of eyesight could result.
Direct viewing of the sun during sun observation will cause loss of eyesight. Use a solar
filter (option), such as that in "27. OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES", for sun observation.
When securing the instrument in the carrying case make sure that all catches, including
the side catches, are closed. Failure to do so could result in the instrument falling out
while being carried, causing injury.
Ignoring this indication and making an operation error could possibly
result in death or serious injury to the operator.
Ignoring this indication and making an operation error could possibly
result in personal injury or property damage.
Caution
Do not use the carrying case as a footstool. The case is slippery and unstable so a
person could slip and fall off it.
1

1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFE OPERATION
Do not place the instrument in a case with a damaged catch, belt or handle. The case or
instrument could be dropped and cause injury.
Do not wield or throw the plumb bob. A person could be injured if struck.
Do not touch the instrument or look through the telescope eyepiece while the motor drive
is in operation. Hands could be caught in moving parts or an eye could be struck by the
telescope and cause injury.
Secure handle to main unit with handle locks. Failure to properly secure the handle could
result in the unit falling off while being carried, causing injury.
Tighten the adjustment tribrach clamp securely. Failure to properly secure the clamp
could result in the tribrach falling off while being carried, causing injury.
Power Supply
Warning
Do not disassemble, rebuild, mutilate, incinerate, heat or short circuit the battery and
charger. Fire, electric shock, burns or an explosion could result.
Do not use voltage other than the specified power supply voltage. Fire or electrical shock
could result.
Do not use damaged power cords, plugs or loose outlets. Fire or electric shock could
result.
Do not use power cords other than those designated. Fire could result.
Do not place articles such as clothing on the battery charger while charging batteries.
Sparks could be induced, leading to fire.
Use only the specified battery charger to recharge batteries. Other chargers may be of
different voltage rating or polarity, causing sparking which could lead to fire or burns.
Do not heat or throw batteries into fire. An explosion could occur, resulting in injury.
To prevent shorting of the battery in storage, apply insulating tape or equivalent to the
terminals. Otherwise shorting could occur resulting in fire or burns.
Do not use batteries or the battery charger if wet. Resultant shorting could lead to fire or
burns.
Do not connect or disconnect power supply plugs with wet hands. Electric shock could
result.
Do not use the battery, charger or AC (power) cable for any other equipment or purpose.
Fire or burns caused by ignition could result.
Do not short circuit the battery. Fire or burns caused by heat or ignition could result.
2

Caution
Do not touch liquid leaking from batteries. Harmful chemicals could cause burns or
blisters.
Tripod
Caution
When mounting the instrument to the tripod, tighten the centering screw securely. Failure
to tighten the screw properly could result in the instrument falling off the tripod, causing
injury.
Tighten securely the leg fixing screws of the tripod on which the instrument is mounted.
Failure to tighten the screws could result in the tripod collapsing, causing injury.
Do not carry the tripod with the tripod shoes pointed at other persons. A person could be
injured if struck by the tripod shoes.
Keep hands and feet away from the tripod shoes when fixing the tripod in the ground. A
hand or foot stab wound could result.
Tighten the leg fixing screws securely before carrying the tripod. Failure to tighten the
screws could lead to the tripod legs extending, causing injury.
Bluetooth wireless technology
1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFE OPERATION
Warning
Do not use within the vicinity of hospitals. Malfunction of medical equipment could
result.
Use the instrument at a distance of at least 22 cm from anyone with a cardiac
pacemaker. Otherwise, the pacemaker may be adversely affected by the
electromagnetic waves produced and cease to operate as normal.
Do not use onboard aircraft. The aircraft instrumentation may malfunction as a result.
Do not use within the vicinity of automatic doors, fire alarms and other devices with
automatic controls as they may be adversely affected by the electromagnetic waves
produced resulting in malfunction and injury.
3

2. PRECAUTIONS
Tribrach Clamp
• When the instrument is shipped, the tribrach clamp is held
firmly in place with a locking screw to prevent the
instrument from shifting on the levelling base. Before using
the instrument the first time, loosen this screw with a
screwdriver. And before transporting it, tighten the locking
screw to fasten the tribrach clamp in place so that it will not
shift on the levelling base.
• The SRX handle can be removed. When operating the
SRX with the handle attached, always make sure that the
handle is securely fixed to the SRX body with the handle
lock levers.
Precautions concerning water and dust resistance
SRX conforms to IP64 specifications for waterproofing and dust resistance when the battery cover is
closed and connector caps are attached correctly.
• Be sure to correctly attach the connector caps to protect the SRX from moisture and dust particles.
• Make sure that moisture or dust particles do not come in contact with the terminal or connectors.
Contact with these parts may cause damage to the instrument.
• Make sure that the inside of the carrying case and the instrument are dry before closing the case.
If moisture is trapped inside the case, it may cause the instrument to rust.
Charging the battery
• The battery (BDC58) was not charged at the factory. Charge the battery fully before using the SRX.
The Lithium Battery
The lithium battery is used to maintain the SRX Calendar & Clock function. It can back up data for
approximately 5 years of normal use, but its lifetime may be shorter depending on circumstances.
Other precautions
• Never place the instrument directly on the ground. Sand or dust may cause damage to the screw
holes or the centering screw on the base plate.
• Do not aim the telescope at the sun. Use the solar filter to avoid causing internal damage to the
instrument when observing the sun.
"27. OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES"
• Do not perform automatic vertical rotation of the telescope when using the lens hood, diagonal
eyepiece, or solar filter. Such accessories may strike the SRX causing damage.
• Protect the instrument from heavy shocks or vibration.
• Protect the instrument from rain or drizzle with an umbrella or waterproof cover.
• When the operator leaves the instrument attached to the tripod, the vinyl cover should be placed on
the instrument.
• Never carry the instrument on the tripod to another site.
• Turn the power off before removing the battery.
• When placing the SRX in its case, first remove its battery and place it in the case in accordance with
the layout plan.
4

2. PRECAUTIONS
• Make sure that the instrument and the protective lining of the carrying case are dry before closing
the case. The case is hermetically sealed and if moisture is trapped inside, the instrument could
rust.
• Consult your Sokkia agent before using the instrument under special conditions such as long
periods of continuous use or high levels of humidity. In general, special conditions are treated as
being outside the scope of the product warranty.
Maintenance
• Wipe off moisture completely if the instrument gets wet during survey work.
• Always clean the instrument before returning it to the case. The lens requires special care. First,
dust it off with the lens brush to remove tiny particles. Then, after providing a little condensation by
breathing on the lens, wipe it with the wiping cloth.
• If the display is dirty, carefully wipe it with a soft, dry cloth. To clean other parts of the instrument or
the carrying case, lightly moisten a soft cloth in a mild detergent solution. Wring out excess water
until the cloth is slightly damp, then carefully wipe the surface of the unit. Do not use any organic
solvents or alkaline cleaning solutions.
• Store the instrument in a dry room where the temperature remains fairly constant.
• Check the tripod for loose fit and loose screws.
• If any trouble is found on the rotatable portion, screws or optical parts (e.g. lens), contact your Sokkia
agent.
• When the instrument is not used for a long time, check it at least once every 3 months.
"23. CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS"
• When removing the instrument from the carrying case, never pull it out by force. The empty carrying
case should be closed to protect it from moisture.
• Check the instrument for proper adjustment periodically to maintain the instrument accuracy.
5
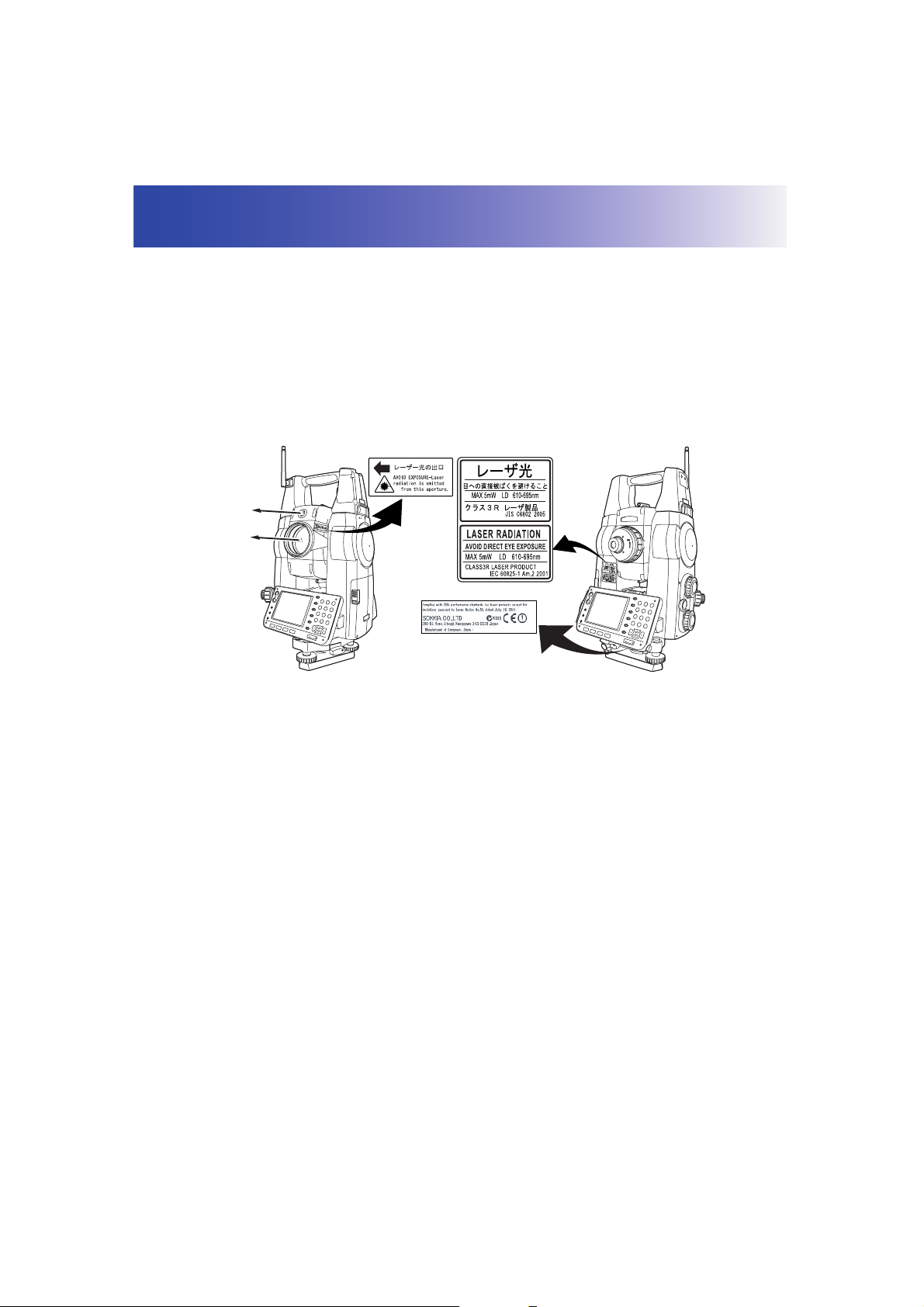
3. LASER SAFETY INFORMATION
SRX is classified as a Class 3R Laser Product and Class 1 LED Product according to IEC Standard
Publication 60825-1 Amd. 2: 2001 and United States Government Code of Federal Regulation FDA
CDRH 21CFR Part 1040.10 and 1040.11 (Complies with FDA performance standards for laser
products except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No.50, dated July 26, 2001.)
• EDM device in objective lens: Class 3R Laser Product
• (When using prism or reflective sheet as target Class 1 Laser Product
or when in Auto Tracking mode)
• Auto pointing device in objective lens: Class 1 Laser Product
• Guide light: Class 1 LED product
LED beam
emitted from
here
Laser beam
emitted from
here
• EDM device is classified as Class 3R Laser Product when reflectorless measurement is selected.
When the prism or reflective sheet is selected as target, the output is equivalent to the safer class 1.
• The cumulative output during distance measurement and tracking in Auto Tracking mode is
equivalent to class 1.
Warning
• Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may
result in hazardous radiation exposure.
• Follow the safety instructions on the labels attached to the instrument as well as in this manual to
ensure safe use of this laser and LED product.
Caution
• Perform checks at start of work and periodic checks and adjustments with the laser beam emitted
under normal conditions.
• When the instrument is not being used, turn off the power and replace the lens cap.
• When disposing of the instrument, destroy the battery connector so that the laser beam cannot be
emitted.
• Operate the instrument with due caution to avoid injuries that may be caused by the laser beam
unintentionally striking a person in the eye. Avoid setting the instrument at heights at which the path
of the laser beam may strike pedestrians or drivers at head height.
6

3. LASER SAFETY INFORMATION
• Never point the laser beam at mirrors, windows or surfaces that are highly reflective. The reflected
laser beam could cause serious injury.
• When using the laser-pointer function, be sure to turn OFF the output laser after distance
measurement is completed. Even if distance measurement is canceled, the laser-pointer function is
still operating and the laser beam continues to be emitted. (After turning ON the Laser-pointer, the
laser beam is emitted for 5 minutes, and then automatically switches OFF. )
• Only those who have been received training as per the following items shall use this product.
• Read the Operator’s manual for usage procedures for this product.
• Hazardous protection procedures (read this chapter).
• Requisite protective gear (read this chapter).
• Accident reporting procedures (stipulate procedures beforehand for transporting the injured and
contacting physicians in case there are laser induced injuries).
• Persons working within the range of the laser beam are advised to wear eye protection which
corresponds to the laser wavelength of the instrument being used
• Areas in which the lasers are used should be posted with laser warning notices.
• If Search or Track is selected in the Motor configuration "A.T. Setting", the laser beam will be emitted
from the objective lens when tracking a moving prism or searching for the center of the prism.
Tracking settings: "12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
• The LED beam is emitted when the guide light is set to ON and the power is turned ON. Before
turning ON the power check that there are no persons in the LED beam path. Alternatively, always
set the guide light to OFF when you have finished measurement.
Guide light settings for tasks other than setting-out: "14.2 Using the Guide Light"
Guide light settings for setting-out: "14.2 Using the Guide Light"
7

4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
4.1 Functions
SRX has the following features to make operation more efficient.
1. Auto Tracking
The SRX will automatically follow a moving prism when the target is being moved to
the next measurement point, making surveying operations such as setting out faster
and smoother. Even when an obstacle causes the SRX to momentarily lose the
target, the On-demand Remote Control system allows the operator at the target to
move the SRX via remote control and re-acquire the target position.
"12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING"
2. Bluetooth wireless technology
Bluetooth technology removes the need for cumbersome cables and provides
wireless communication functionality between the SRX and the On-demand
Remote Control system, data collectors and computers for even greater efficiency
gains in the field. Bluetooth device address and passkey settings afford greater
security when transmitting data wirelessly.
"8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES"
3. High accuracy with reflectorless measurement
Sokkia’s own optics, electrical circuits, and processing algorithms combine to
provide superior reflectorless accuracy at distances as short as 30cm.
4. Various interface options
Data link options for the SRX include both a CF card slot and USB ports.
5. Full colour touch panel display
Not only does the colur screen improve usability, but the Graphic option allows the
user to visualise the current survey point during operation. In addition to the
operation keys, the touch panel with stylus pen offers another user-friendly method
for selecting screens and inputting characters.
"5.2 Display Functions"
8

4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
6. Guide light
Setting-out measurement etc. can be carried out effectively using the guide light.
The guide light is composed of a light that is divided into a red and a green light. A
poleman can ascertain whether to move to the right or left by checking the guide
light color.
"14.2 Using the Guide Light"
7. Sighting the target and performing distance measurement using Auto Pointing
Use the peep sight to bring the target roughly into the field of view. Then, press
[SRCH] to automatically sight the center of the target. The instrument and telescope
can be rotated manually by hand or, for more precise adjustments, by turning the
vertical and horizontal jogging knobs.
The instrument can be set to automatically measures the distance after Auto
Pointing has been completed. The search range can be set beforehand.
"11.2 Auto-Pointing Function for Target Sighting" and "21.3 EDM Settings"
8. Trigger Key for Easier Operation
Each screen contains a number of softkeys. Softkeys displayed in bold type control
the flow of measurement operation. Pressing the trigger key located on the side of
the SRX will perform exactly the same operation as the bolded softkey in the current
screen. This allows the user to continue operation without having to return to the
display to press softkeys, making operations such as resection measurement even
simpler.
"4.2 Parts of the Instrument Trigger key"
9. Wide range of advanced programs
One touch of the {PROGRAM} key allows the user to switch from Basic mode to
Program mode (SDR) in order to use advanced measurement programs. The
position of menus and softkeys can be user-defined for greater ease-of-use.
Switching modes: "4.3 Mode Configuration", rearranging softkeys:
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
10. SETTINGS Mode
One-touch of the {SETTINGS} key allows the user to jump to and from the
SETTINGS mode during operation without exiting measurement.
"4.3 Mode Configuration"
11.Sokkia’s original Independent Angle Calibration System (IACS) technology
Unaffected by errors in collimation and instrument setup, this internal calibration
technology provides an even higher level of stability and reliability for angle
measurement.
Independent angle calibration cannot be performed by the user. Consult your
Sokkia agent.
9
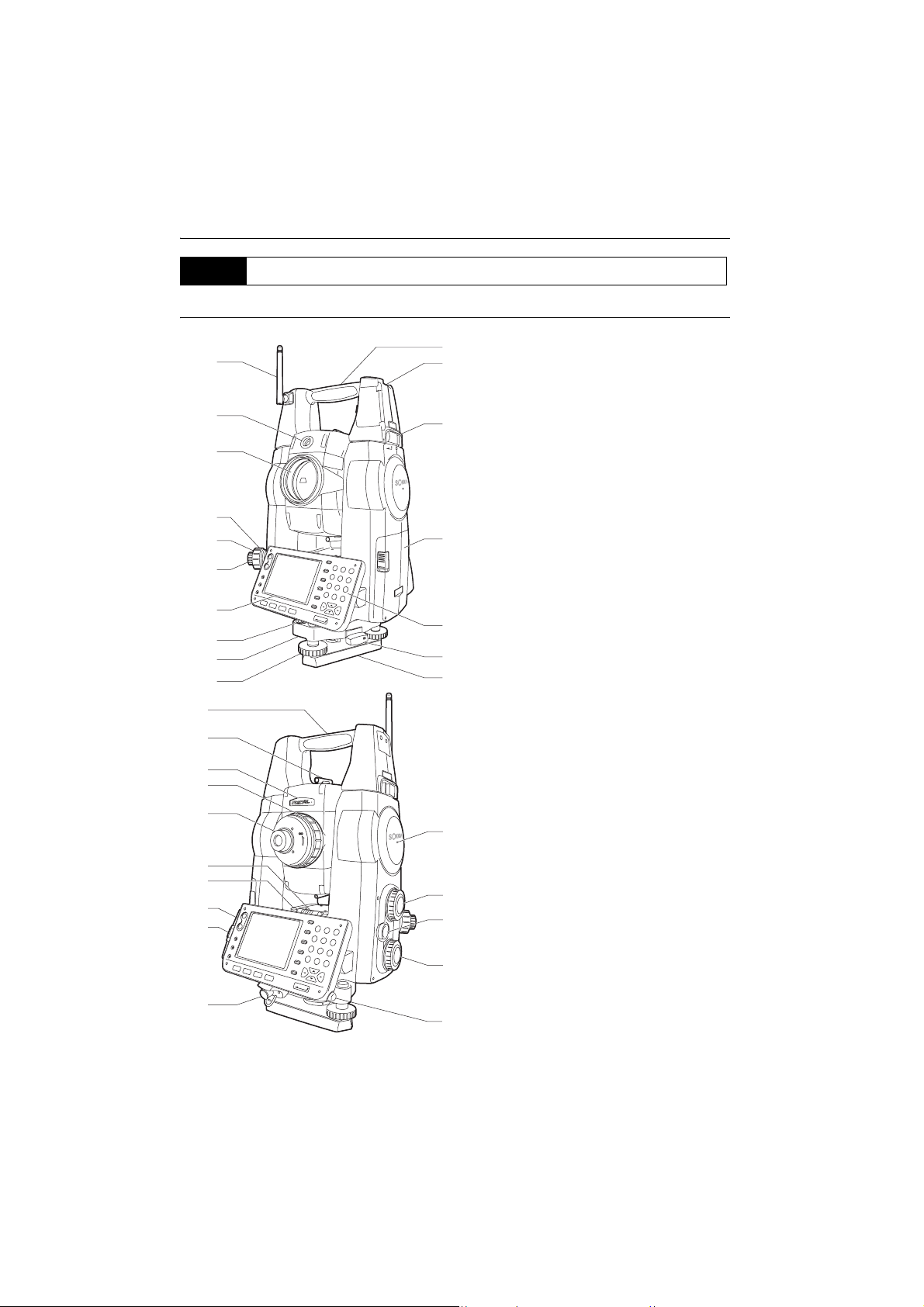
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
4.2 Parts of the Instrument
Parts and functions of the instrument
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
1 Handle
1
2 Tubular compass slot
2
3 Handle lock
4 Battery holder
5 Keyboard
6 Tribrach clamp
3
7 Base plate
8 Levelling foot screw
9 Circular level adjusting screws
10 Circular level
11 D isp lay
12 Optical plummet eyepiece
13 Optical plummet reticle cover
4
14 Optical plummet focussing ring
15 Objective lens
(Includes " Laser-pointer
function")
16 Guide light
17 Bluetooth antenna
5
6
7
18 Instrument height mark
19 Vertical jogging knob
20 Trigger key
21 Horizontal jogging knob
22 Stylus pen holder
23 Combined communications and
power supply connector
24 CF card slot
18
"6. USING THE CF CARD SLOT"
25 USB ports
"8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL
DEVICES"
26 Plate level adjusting screw
19
27 Plate level
28 Telescope eyepiece screw
20
29 Telescope focussing ring
30 Laser radiation warning
21
indicator
31 Peep sight
32 Instrument center mark
22
10
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
Vertical and Horizontal jogging knobs
The instrument and telescope can be rotated manually by hand or, for more precise adjustments,
by turning the vertical and horizontal jogging knobs.
The faster the jogging knobs are turned, the faster the instrument and telescope rotate.
Guide light
Setting-out measurement etc. can be carried out effectively using the guide light. The guide light
is composed of a light that is divided into a red and a green light. A poleman can ascertain the
present position by checking the guide light color.
green
red
Guide light status
Light status Meaning
Red (From position of poleman) Move target left
Green (From position of poleman) Move target right
Red and Green Target is at correct horizontal position
The guide light indicator is lit or flashes depending on the status of the guide light.
Laser radiation warning indicator
Laser radiation warning indicator is red when laser beam is emitted or laser-pointer is used,
allowing the status laser beam of the laser beam to be ascertained from the telescope eyepiece
side.
Peep sight
Use peep sight to aim the SRX in the direction of the measurement point.
Turn the instrument until the triangle in the peep sight is aligned with the target.
Instrument height mark
The height of the SRX is 236mm (from tribrach dish to this mark). "Instrument height" is input
when setting instrument station data and is the height from the measuring point (where SRX is
mounted) to this mark.
Trigger key
When the Trigger key is pressed SRX carries out the operation indicated by the softkey in bold
type on the screen. This allows the user to continue operation without having to return to the
display to press softkeys, making operations such as resection measurement even simpler.
Laser-pointer function
A target can be sighted with a red laser beam in dark locations without the use of the telescope.
Removing the handle (RC-TS3)
11
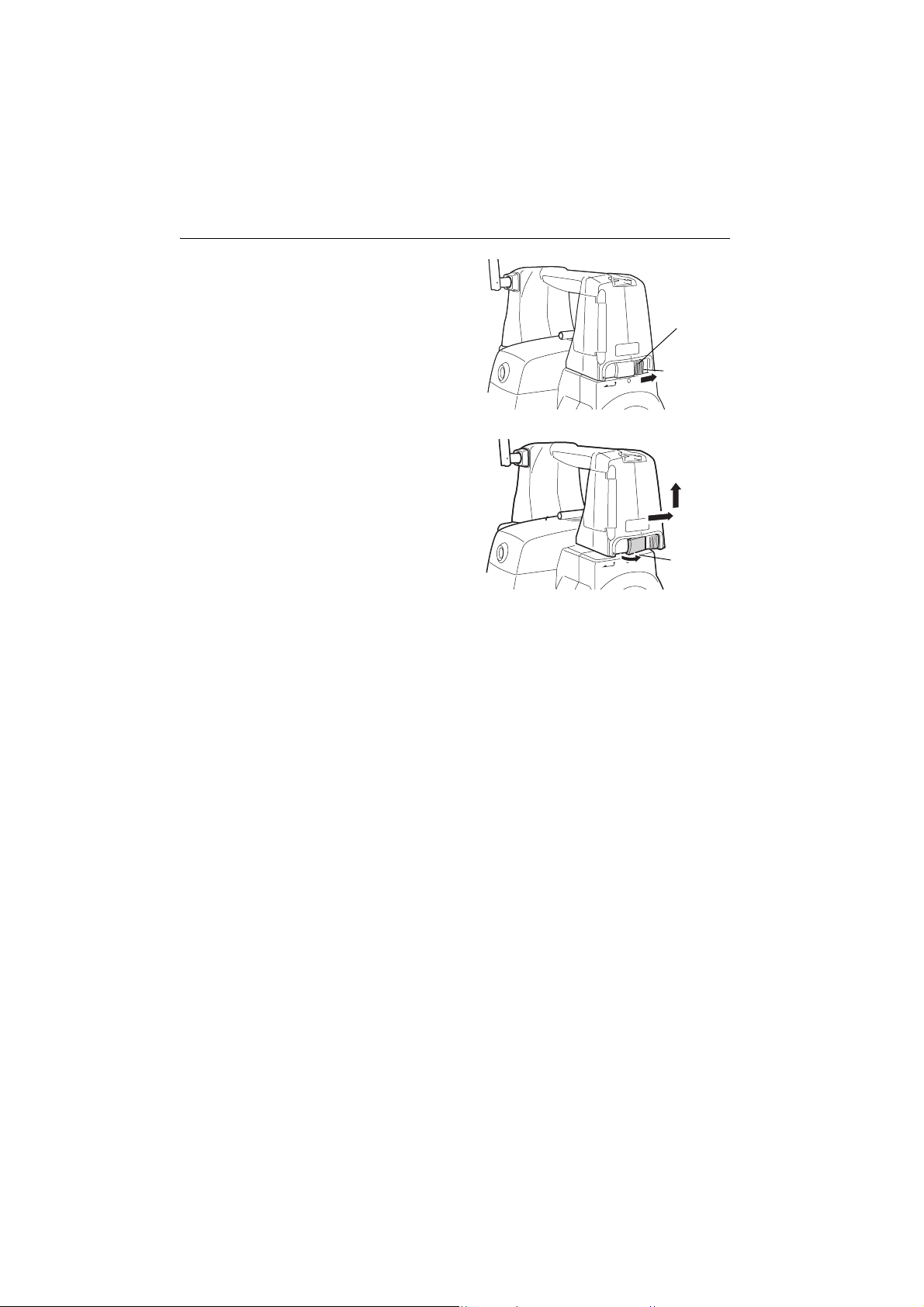
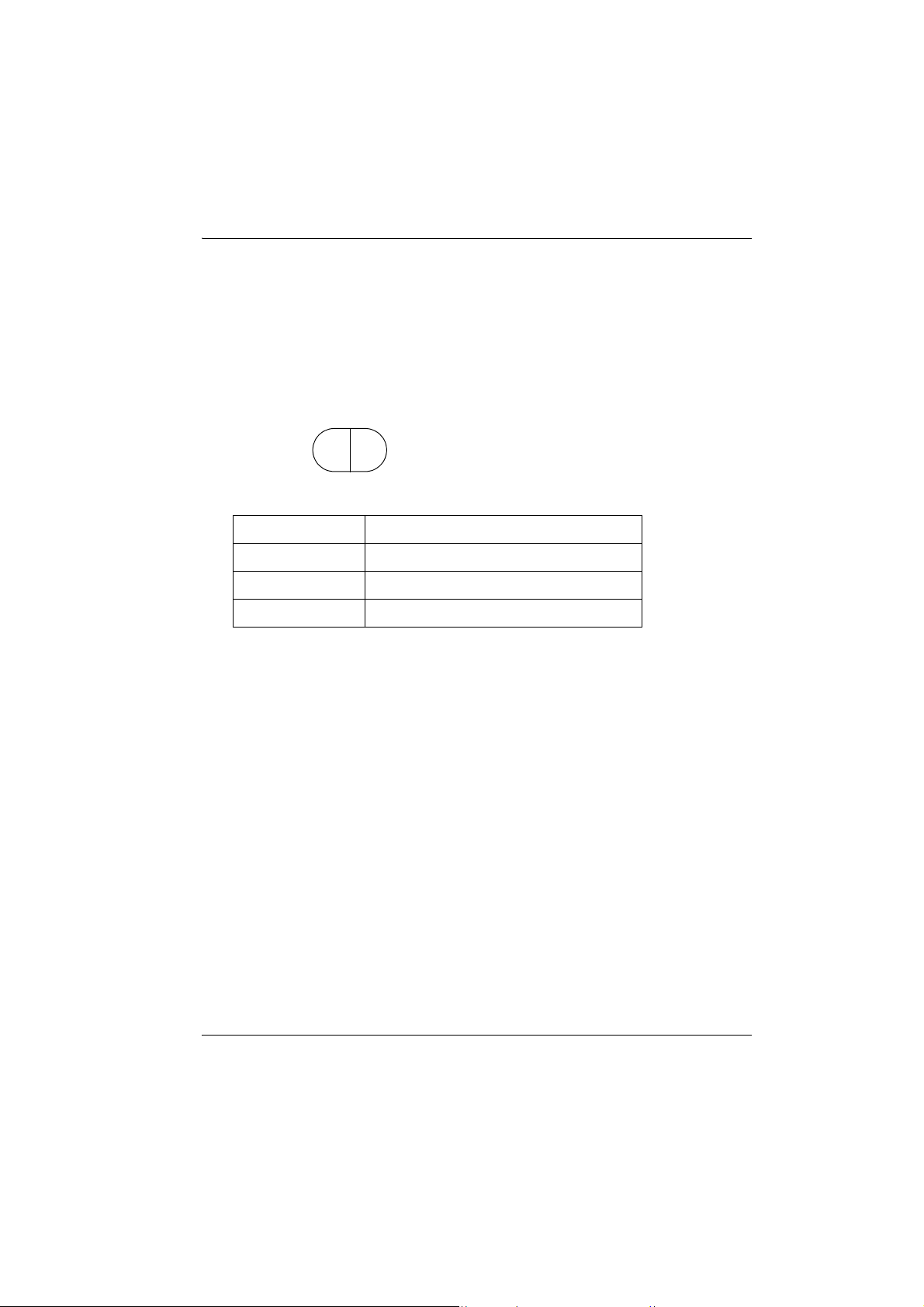
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
1. Slide the handle locks in the direction as
shown at right until a click is heard. The
handle are now unlocked.
2. Pull the lock levers towards you and slide the
handle back and up to remove.
The handle lock levers, once released, will
return to the original position.
Make sure that the handle does not fall
while being removed. Removing the
handle requires a certain amount of force.
As a result, always hold firmly when
removing.
Handle
lock
Green indicates
locked state
Lock lever
12
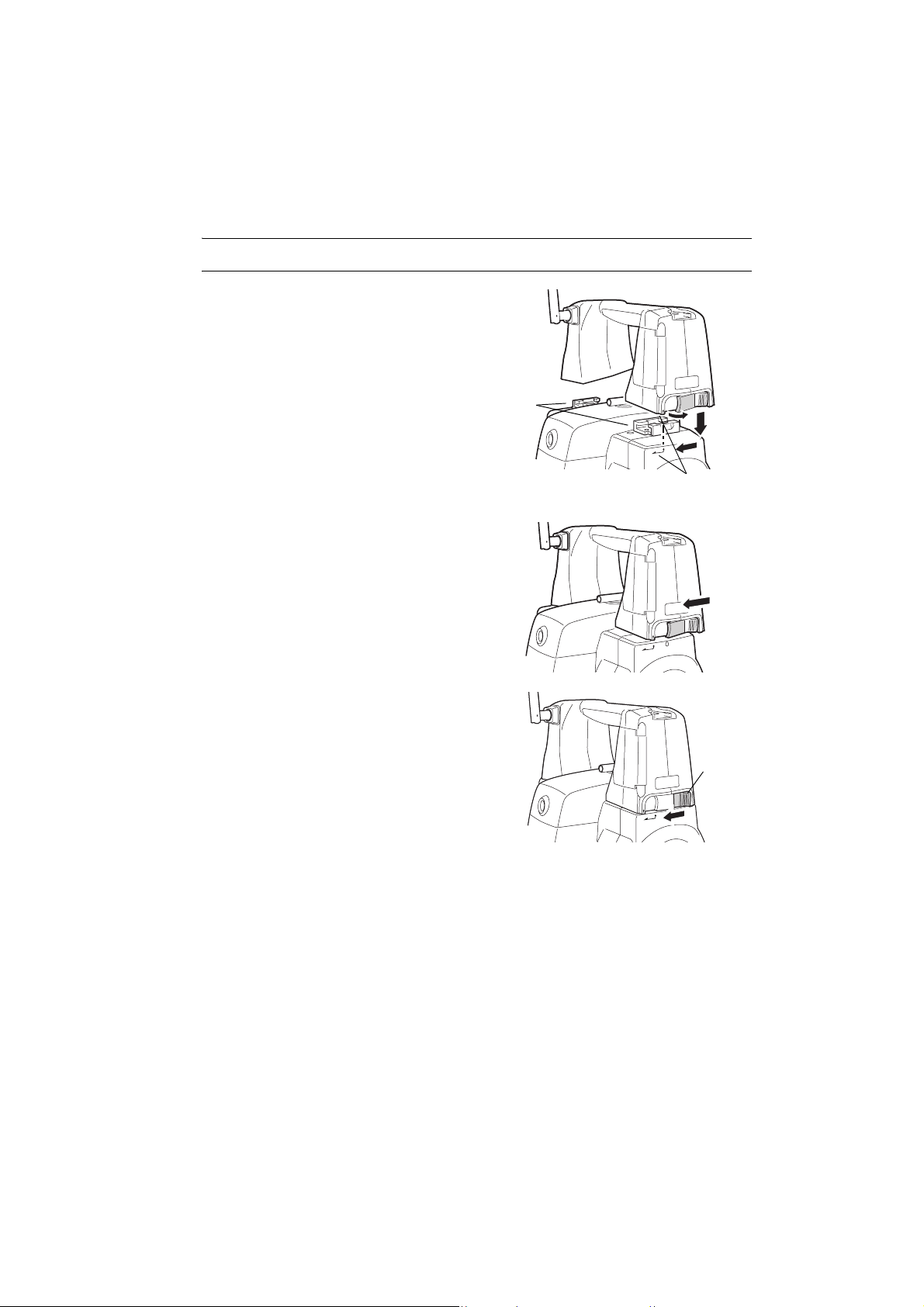
Attaching the handle (RC-TS3)
1. Align the handle with the mounting brackets.
2. Slide the handle onto the mounting position
until a click is heard. Check that the handle
lock levers, once released, return to the closed
position.
Mounting
brackets
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
Handle mounting
position
3. Slide the handle locks away from you to lock
the handle. Check that the green sections of
the handle locks are showing.
• Securely lock the handle in place before
starting measurement.
Handle
locked
13
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
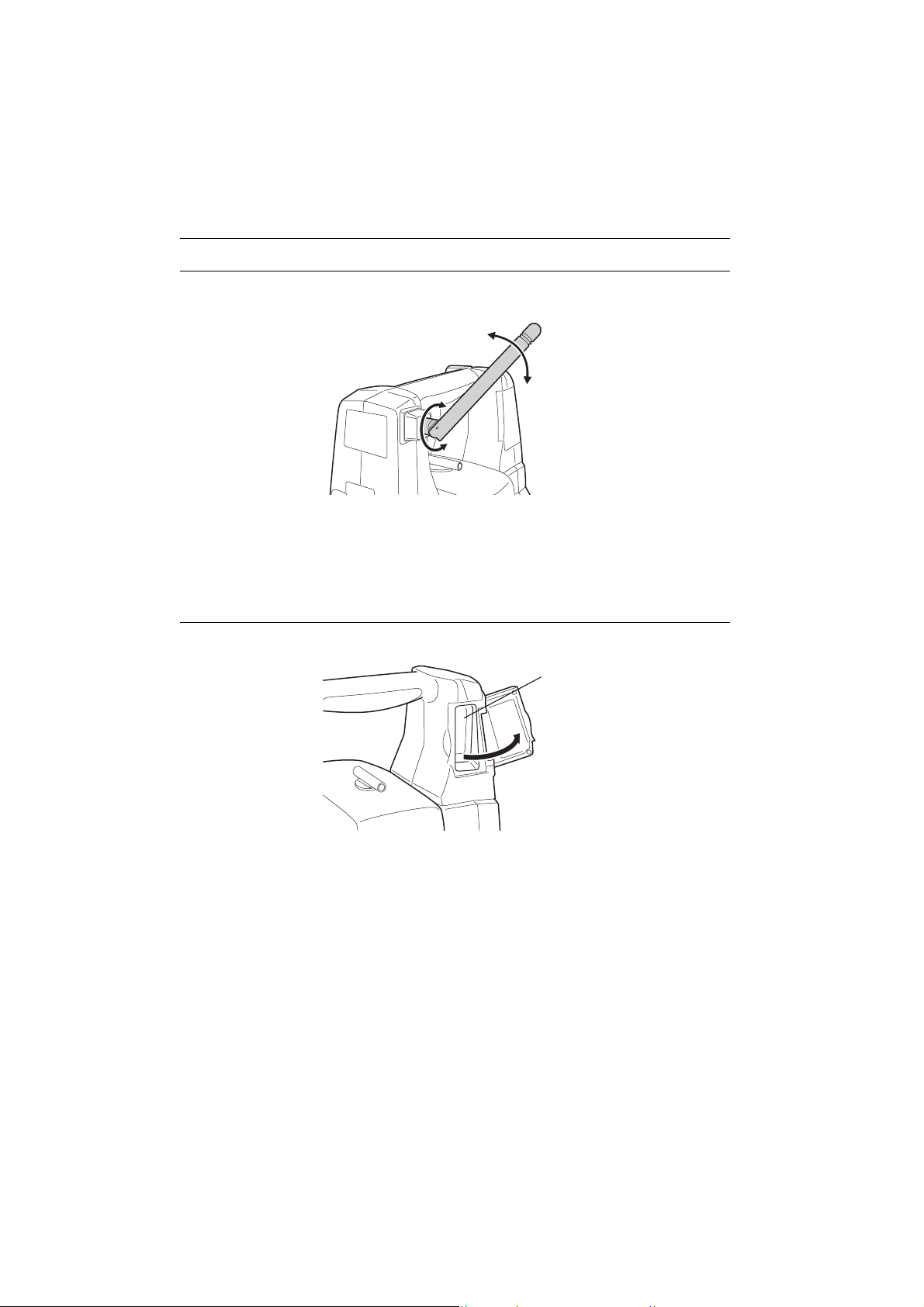
Bluetooth antenna
When performing communication using Bluetooth wireless technology, the antenna must be directed
towards the intended companion device.
Handle the antenna with care and be aware of the following points when operating.
• An extended antenna may be damaged if struck during operation.
• The antenna may be damaged if forcibly bent in an incorrect direction. The antenna cannot be bent
to angles exceeding 90°.
Beam detector for On-demand Remote Control System
Always open the beam detector cover when using the On-demand Remote Control system.
Beam
detector
• The beam detector cover can be damaged if forced open beyond a certain angle. Always close the
beam detector cover before moving the instrument.
• Never touch the beam detector. The ability of the system to perform Turning may be adversely
affected.
14
4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
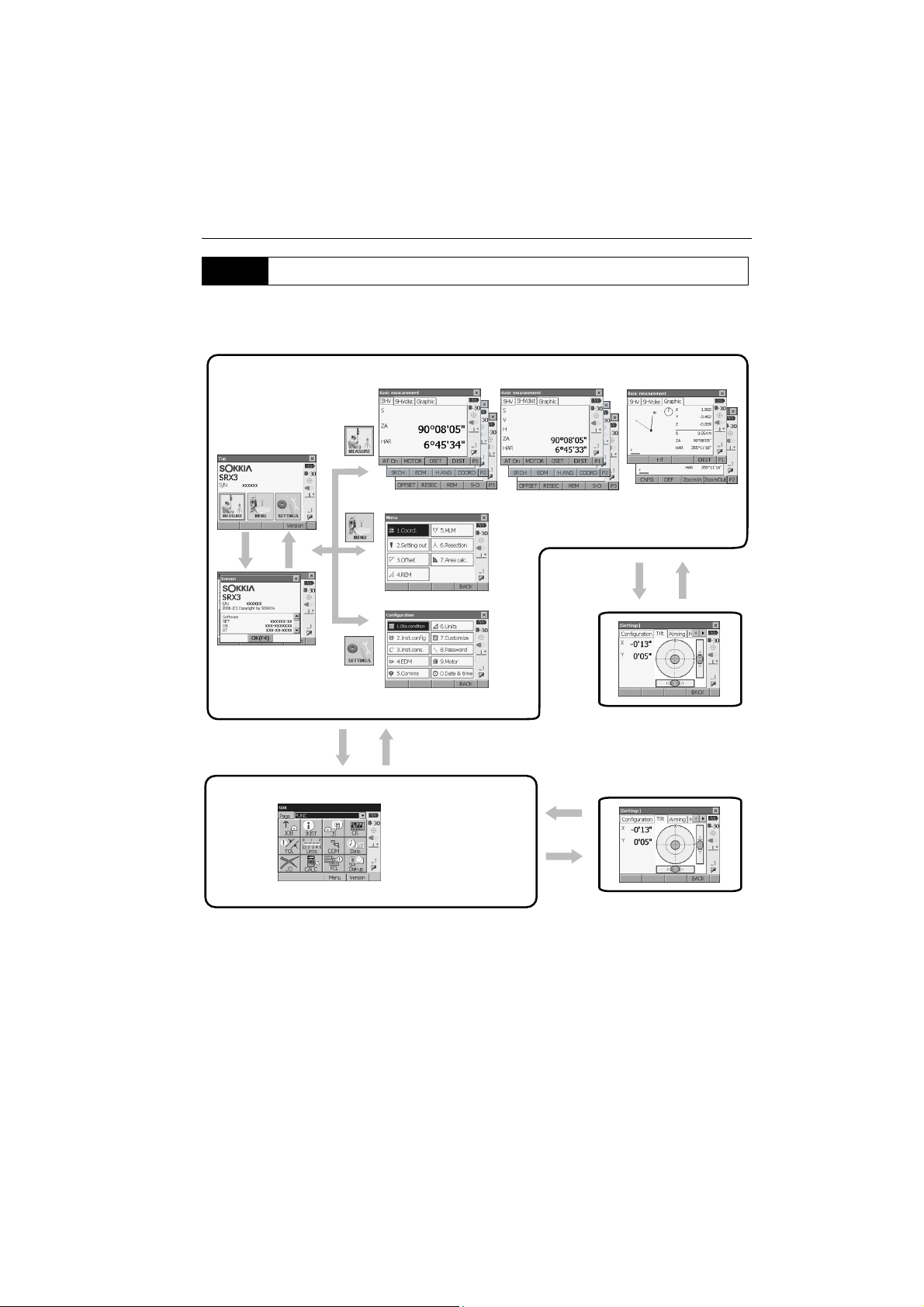
4.3 Mode Configuration
The diagram below describes the different modes of the SRX and key operations for navigating
between them. Managing data functions are contained in Program mode (SDR).
Basic mode
Status screen
[Version]
[OK]
{ESC}
{PROGRAM}
Meas mode (Navigable with tabs)
Program mode
Settings mode
Chapter 21
Program mode (SDR)
Series SRX SDR
Software Reference
Manual
Chapters 15-20
{SETTINGS}
"5.2 Display Functions"
{SETTINGS}
SETTINGS mode
"5.4 SETTINGS Mode"
• Switching between modes is not possible during distance measurement or while the motor is in
operation.
15

4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
4.4 Bluetooth Wireless Technology
Precautions concerning Bluetooth wireless technology
• Use of this technology must be authorized according to telecommunications regulations of the
country where the instrument is being used. Contact your Sokkia agent in advance.
• Sokkia is not liable for the content of any transmission nor any content related thereto. When
communicating important data, run tests beforehand to ascertain that communication is operating
normally.
• Do not divulge the content of any transmission to any third party.
Radio interference when using Bluetooth technology
Bluetooth communication with the SRX uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This is the same band used
by industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) equipment such as microwaves, portable premises radio
equipment (license required) and portable specified low-power radio equipment (license-exempt)
used in factory production lines, etc.
• Before starting transmission, check that operation will not take place within the vicinity of portable
premises radio equipment or specified low-power radio equipment.
• In the case that the instrument causes radio interference with portable premises radio equipment,
terminate the connection immediately and take measures to prevent further interference (e.g.
connect using an interface cable).
• In the case that the instrument causes radio interference with portable specified low-power radio
equipment, contact your Sokkia agent.
Although a radio station license is not required for this instrument, bear in mind the following points
when using Bluetooth technology for communication.
● Do not use within the vicinity of the following:
•Industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) equipment such as microwaves and pacemakers.
• portable premises radio equipment (license required) used in factory production lines etc.
• portable specified low-power radio equipment (license-exempt)
•IEEE802.11b/IEEE802.11g standard wireless LAN devices
The above devices use the same frequency band as Bluetooth communications. As a result, using
the SRX within proximity to the above devices may result in interference causing communication
failure or reduction of transmission speed.
• Refrain from using the SRX within proximity to televisions and radios
Televisions and radios use a different frequency band to Bluetooth communications.
However, even if the SRX is used within proximity to the above equipment with no adverse effects with
regard to transmission, moving a Bluetooth-compatible device (including the SRX) closer to said
equipment may result in electronic noise in sound or images.
16

4. PRODUCT OUTLINE
Precautions regarding transmission
● For best results
•When using the On-demand Remote Control system, perform communication within a line-ofsight distance of approximately 300m. The usable range becomes shorter when obstacles block
the line of sight, or devices other than the On-demand Remote Control system, such as PDAs or
computers, are used. Wood, glass and plastic will not impede
range becomes shorter. Moreover, wood, glass and plastic containing metal frames, plates, foil
and other heat shielding elements as well as coatings containing metallic powders may adversely
affect Bluetooth communication and concrete, reinforced concrete, and metal will render it
impossible. Use a vinyl or plastic cover to protect the instrument from rain and moisture.
•The direction of the Bluetooth antenna can have adverse effects upon usable range. For best
results make sure that the antennas of both the SRX and the companion device are as vertical
as possible and visible to one another. When this is not possible, better results can be obtained
by pointing the antenna vertically towards the ground.
communication but the usable
• Perform communication at a distance of 2m or more from electrical devices such as audio-visual
equipment and office automation equipment. In the case of microwave ovens, which are especially
su scept ible to int erfer ence, this d ista nce sh ould be inc rease d to 3m .
Moreover, operation near televisions and radios may lead to problems with reception.
• Ensure that cellular phones are at least 20cm from the SRX Bluetooth module during operation.
• Change location when proximity to a wireless device or broadcast station results in communication
failure.
When using the SRX near IEEE802.11b or IEEE802.11g standard wireless LAN devices or other
devices that operate on the 2.4GHz ISM band, interference may result, causing transmission speed
to slow or even disrupting the connection completely. Turn off all devices not being used.
● Reduced range due to atmospheric conditions
The radio waves used by the SRX may be absorbed or scattered by water and airborne moisture. The
signal may be weakened by exposure to rain, fog, and moisture from the human body with the limit of
usable range becoming much lower as a result. Moreover, as wireless devices lose signal strength
when close to the ground, perform communication at as high a position as possible.
17
5. BASIC OPERATION
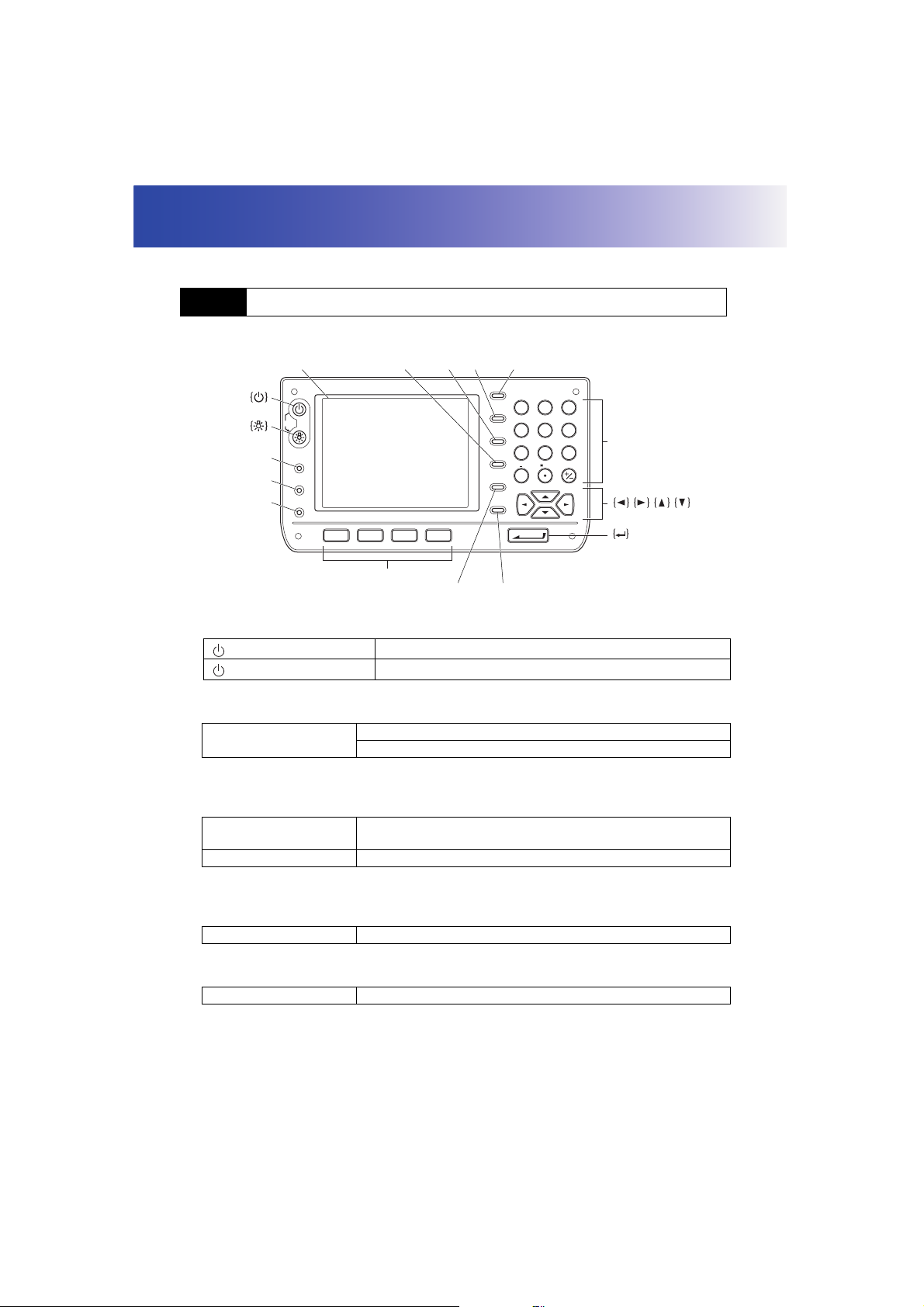
Learn basic key operations here before you read each measurement procedure.
5.1 Basic Key Operation
Display
{SETTINGS}
{PROGRAM}
{TARGET}
{BACKSPACE}
OFF
SETTINGS
PROGRAM
TARGET
F 1 F 2 F 3 F 4
{SHIFT} {ESC}
{TAB}
ESC
SHIFT
TAB
BACKSPACE
SPACE
FUNC CTRL
ABC DEF GHI
7
8
JKL MNO
5
4
STU
2
1
/&
?$
0
ENTER
PQR
#%@
9
6
{0} to {9}
YZ!VWX
{.} to {+/-}
3
Softkey selection
{FUNC CTRL}
●
Power ON/OFF
{SPACE}
Power ON
(while pressing) + {}
Power OFF
● Lighting up the reticle/keys and selecting screen backlight brightness
{}
"21.2 Instrument Configuration"
Switching to SETTINGS mode
●
Switches the reticle illumination/key backlight ON/OFF
Switches the screen backlight brightness setting
{SETTINGS} Switches to screens for tilt correction, returned signal checking,
motor operation, fixed velocity rotation,and general configuration
{SETTINGS}/{ESC} Returns to the previous screen (mode)
"5.4 SETTINGS Mode"
● Switching to Program mode (SDR)
{PROGRAM} Switches between Basic mode and Program mode (SDR)
● Switching target type
{TARGET} Switches between target types
"21.3 EDM Settings"
18
5. BASIC OPERATION
• Changes can also be made by tapping the status bar icon with the stylus pen.
"5.2 Display Functions"
● Switching the laser-pointer/guide light ON/OFF
{} (Press and hold until
a beep sounds)
Turns the laser-pointer/guide light ON/OFF
Selecting laser-pointer/guide light after pressing {}: "21.3 EDM Settings"
•After turning ON the laser-pointer/guide light, the laser beam is emitted for 5 minutes, and then
automatically switches OFF.
• Changes can also be made by tapping the status bar icon with the stylus pen.
"5.2 Display Functions"
● Softkey operation
Softkeys are displayed on the bottom line of the screen.
{F1} to {F4} Select the function matching the softkeys
{FUNC CTRL} Toggles between softkey pages
● Inputting letters/figures
Character input method can be selected from upper case alphabetic, lower case alphabetic and
numeric characters.
•A selection can also be made by tapping the status bar icon with the stylus pen.
{0} to {9} Input numeral or symbol printed above the key (during numeric
input mode)
Input alphabetic character in the order they are listed (in
alphabetic input mode)
{.} Input a decimal point (during numeric input mode)
{+/-} Input a plus or minus sign (during numeric input mode)
{ESC} Cancel the input data
{TAB} Shift to the next item
{BACKSPACE} Delete the character to the left
{SPACE} Input a blank space
{}/{} Move the cursor left/right during character input
{ ▲ }/{ ▼ }
{} Select/accept input word/value
Move the cursor up/down during character input
19

5. BASIC OPERATION
● Selecting options
{ ▲ }/{ ▼ }
{}/{}
{TAB} Shift to the next item
{SPACE} Display other options
{}
● Selecting tabs
{ ▲ }/{ ▼ }
{}/{}
● Other operation
{ESC} Return to previous screen
{}/{}
Tabs:
Example: Entering "computer" (lower case) as the name of a new device
1. Tap the input mode icon in the status bar (second
from bottom) until "_a" is displayed.
"5.2 Display Functions"
Move the cursor/selection item up/down
Move the cursor/selection item left/right or selects other option
Select/accept the option
Move tab/cursor in tab up/down
Display next tab at left/right
Moves tab left/right
2. Press {7} three times.
"c" is displayed.
20

3. Press {5} three times.
"o" is displayed.
4. Press {}.
Press {5} twice. "m" is displayed.
5. Continue to input letters. Press {} to
complete inputting.
5. BASIC OPERATION
Example: selecting a reflector type
(Method 1)
1. Select
2. Move to "Reflector" using {}/{}/{TAB}.
mode or
[EDM]
in the second page of Measure
"EDM" in SETTINGS mode.
21

5. BASIC OPERATION
3. Press {SPACE} to display a list of all options.
4. Select an option using {}/{}.
5. Press {} to confirm selection.
(Method 2)
1. Select
2. Move to "Reflector" using {}/{}/{TAB}.
3. Switch between Prism, 360° Prism, Sheet, and
4. Press {} to confirm selection.
[EDM]
mode or
Reflectorless using {}/{}.
in the second page of Measure
"EDM" in
SETTINGS mode.
.
22

5. BASIC OPERATION
5.2 Display Functions
Screens can be selected/operated using the keys on the keyboard or the touch panel. The touch panel
can be operated using either the stylus pen provided or your fingers.
• Do not scratch the display or use any sharp implement other than the stylus pen to operate the
touch panel.
Using the stylus
The stylus pen can be used to select menus and buttons on the screen and operate the scroll bar. The
touch panel supports "tap", "double tap", and "drag" operations.
Operation Method
Tap Lightly tap the display once. This operation is equivalent to that of clicking
Double tap Lightly tap the display twice on the same point.This operation is equivalent
Drag Lightly apply the point of the stylus pen to the display and move in the
Displaying and operating screens
a mouse button when using a computer.
to the "double-click" for a computer mouse.
desired direction, maintaining contact between the stylus and display all
the time.
• To close a screen, tap the cross in the top right corner, or press {ESC}.
• Tabs, softkey allocations, displayed tab items, and character sizes can all be changed in
accordance with user preferences.
"21. CHANGING THE SETTINGS"
● Status screen
Instrument name
Serial No.
Application software version
23

5. BASIC OPERATION
● Basic measurement screen
(1) Distance
(2) Vertical angle
(3) Horizontal angle
(1) Distance
Press [/SHV] to switch between the SHV and SHVdist tabs. An SHVdist tab will be created when
one does not exist.
"21.1 Observation Conditions"
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
(2) Vertical angle
The Vertical angle display can be switched between Zenith (Z=0°)/Horiz (H=0°)/Horiz (H=±90°)
To switch vertical angle/slope in %, press [ZA/%] when allocated to the Meas mode screen. The
capitalized letter in the softkey indicates the currently selected mode.
"21.1 Observation Conditions"
(3) Horizontal angle
Press [R/l] when allocated to the Meas mode screen to switch the display status. The capitalized
letter in the softkey indicates the currently selected mode.
HAR : Horizontal angle right
HAL : Horizontal angle left
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
● Input screen/configuration screen
Display all options
Scroll down for more
items
Values can be input/
edited
24

5. BASIC OPERATION
● Graphic tab
Arrow indicates north
Target point
Instrument station
Scale
(units: m)
The Graphic tab display can be modified using the softkeys in the second page.
[CNFG]: In <Graphic configuration> the user can specify the orientation of the graphic tab
[DEF.]: Returns to the original orientation display.
[ZoomIn]: Zooms in.
[ZoomOut]:Zooms out.
● Selecting menus
To select a menu, tap the touch panel or press the relevant number key.
display and which point, target or station, to set at the center of the display.
Number
25

5. BASIC OPERATION
● Status bar
Indicates the current status of the instrument.
Tapping icons (1) to (7) will switch between the
relevant options for that item Tapping and holding
will display a list of all available options for that
item and, in certain cases, a link to the
configuration screen for that item.
Settings: "21. CHANGING THE SETTINGS"
(1)Remaining battery power
Remaining battery power indicator and configuration of auto-power function (BDC58/external
battery BDC61, Temperature = 25°, EDM on).
The remaining batter power displayed when distance measurement is in progress may differ to
that displayed at other times.
: Level 3 Full power
: Level 2 Plenty of power remains
: Level 1 Half or less power remains
Level 0 Little power remains. (Flashes red and black)
: No power (Red display in the center of the screen) Stop measurement and charge the
battery
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
SIP code
"7. USING THE BATTERY"
(2) Target display
Selection of target type and configuration of prism constant.
: Prism (-30mm)
: 360° Prism (-7mm)
: Sheet (0mm)
: Reflectorless
Target information can be edited/recorded in <Reflector setting>.
"21.3 EDM Settings"
26

5. BASIC OPERATION
(3) Motor configuration
Configuration of Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking status.
: Auto Tracking ON
: Auto Pointing ON
: Both Auto Tracking and Auto Pointing OFF
: Start Auto Tracking."AT Off" is displayed when in "Prism wait"
status. Press to quit Auto Tracking.
One of the following icons will be displayed while the motor is in operation to indicate the current
status of the SRX.
: Rotating
: Rotating at fixed velocity
: Searching
: Auto Tracking in progress (when Auto Tracking set)
: Target lost (when Auto Tracking set)
: (Flashes red) Waiting for prism (when Auto Tracking set)
Motor settings: "11.1 Auto Pointing Settings", "12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
• Auto Tracking and Auto Pointing cannot be performed when "Reflectorless" has been selected as
the target type. Auto Tracking cannot be performed when "Sheet" has been selected as the target
type. will be displayed.
• An arrow indicating turn direction will be displayed when the SRX is rotating at a fixed velocity.
Fixed velocity rotation: "5.4 SETTINGS Mode ● Fixed velocity rotation"
(4) Laser-pointer/guide light
Configuration of laser-pointer/guide light status.
Switching the laser-pointer/guide light ON/OFF: "5.1 Basic Key Operation"
: Guide light ON
: Guide light OFF
: Laser-pointer ON
: Laser-pointer OFF
• The laser-pointer will be automatically switched OFF during distance measurement.
27

5. BASIC OPERATION
(5) Tilt angle compensation
The vertical and horizontal angles are automatically compensated for small tilt errors usng the
SRX's dual-axis tilt sensor. This icon displays the status of this function.
: Horizontal and vertical tilt angles compensated (blue)
: No compensation
: Only horizontal tilt angle compensated (green)
• is displayed when the instrument is out of level.
(6) Communication status
Selection and configuration of communication status with external devices. This icon is not
displayed in Program mode (SDR).
: Connection via RS-232C cable
: Connection via Bluetooth (SRX set as "Master" device) (blue antenna)
: Connection via Bluetooth (SRX set as "Slave" device) (green antenna)
• When Bluetooth is selected (SRX set as "Master" device) a connection can be initiated/canceled
by tapping / .
• An arrow symbol is displayed while data is being transmitted.
• This icon is not displayed in Program mode (SDR).
Connection status is displayed as follows.
i) Connection via Bluetooth
When SRX is set as the "Master" device the antenna mark is blue. When the SRX is set as the
"Slave" device the antenna mark is green.
: Connecting
: Cancelling connection
: Inquiring about other Bluetooth devices (only when SRX is set as "Master" device)
ii) : Connection via RS-232C cable
(7) Input mode
Selection of input mode
_1 Inputting numbers and symbols
_A Inputting upper case alphabetic characters
_a Inputting lower case alphabetic characters
28

5. BASIC OPERATION
5.3 Inputting Characters using SIP Code (Input Panel)
Tap to display <Input Panel>. This keyboard can be used to input numeric and alphabetic
characters as well as symbols. Tap the icon again to close.
• When <Input panel> is covering the icon of the status bar, use the stylus pen to drag the input
panel to another part of the screen so that you can access the icon.
Input panel
Esc : Deletes all input characters
Tab : Moves the cursor to the next text box
CAP :Alternates between upper and lower case alphabetic characters and numbers/
Shift :Alternates between upper and lower case alphabetic characters and numbers/
Ctl :No function
Del/A : Delete the character to the left/right or deletes the entire text in the active section
←→ :Move the cursor left/right
: Accept input characters
Space : Input a blank space
áü :Accesses further Latin/Germanic characters/symbols
symbols
symbols. Is canceled after inputting a single character.
29

5. BASIC OPERATION
5.4 SETTINGS Mode
Press {SETTINGS} to switch to screens for tilt correction, returned signal checking, motor operation,
fixed velocity rotation,and general configuration
Performing settings: "21. CHANGING THE SETTINGS", Tilt settings: "9.2 Levelling", Returned
signal checking: "14.1 Returned Signal Checking"
● Motor settings
The instrument can be automatically rotated to a desired vertical and/or horizontal angle by
specifying the angle in the "Motor" tab and selecting [ROTATE].
• The following operations can be performed using the softkeys in the second page.
[READ] : Read in coordinates from Program mode (SDR) and set as the desired angle.
[COORD] : Specify rotation angle by inputting coordinates in <Key in coord>.
[TURN] : Rotate the SRX 180°.
[CNFG] : Perform Motor configuration settings.
30
"12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"

5. BASIC OPERATION
● Fixed velocity rotation
The SRX horizontal angle and telescope can be rotated using the controls in the Fixed velocity
rotation tab. Speed settings are from 1 to 16.
Tap the touch panel in the desired rotation direction.
Press {ESC} or tap the red center circle to stop rotation.
31

6. USING THE CF CARD SLOT
CF (Compact Flash) cards, for saving surveying and other data, are supported by the SRX. However,
users with SD cards will need to use an CF card slot adapter.
Management of JOB and survey data is done in Program mode (SDR).
Series SRX SDR Software Reference Manual
• Contact your Sokkia agent for details regarding communication formats for CF card input/output.
• Data can also be transferred to an external device for storage and/or editing using the SRX’s US
ports.
"8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES"
6.1 Inserting/Removing the CF Card
• Do not remove the CF card during data read/write.
• Make sure the eject button is fully depressed when a CF card is inserted. A protruding eject button
will be depressed when the card cover is closed causing the card to be ejected.
• Always close the card cover before moving the instrument. The card cover can be damaged if
forced open beyond a certain angle.
PROCEDURE Inserting the CF card
1. Push the catch on the card cover to open.
B
2. Insert the CF card until a click is heard.
3. Close the card cover.
32
Card cover
Eject button
Card
slot
Catch

PROCEDURE Removing the CF card
1. Push the catch on the card cover to open.
6. USING THE CF CARD SLOT
2. Press the eject button once to release. Once
the eject button is fully protruded, press once
more to remove the card from the card slot.
3. Close the card cover.
Card cover
Catch
Eject button
33

7. USING THE BATTERY
Mount the charged battery (BDC58).
Types of power source: "24. POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM"
• Remove the battery when the instrument is not being used.
• Before removing the battery, turn off the power to the instrument. If the battery is removed while
the power is switched on, a warm boot occurs. File and folder data may be lost as a result.
• When installing/removing the battery, make sure that moisture or dust particles do not come in
contact with the inside of the instrument.
PROCEDURE Mounting the battery
1. Slide down the catches on the battery cover to
open.
Battery cover
2. Insert the battery in the direction of the arrow
printed on the side.
3. Close the battery cover. A click is heard when
the cover is secure.
34
Battery

7. USING THE BATTERY
PROCEDURE Removing the battery
1. Slide down the catches on the battery cover to
open.
2. Retract the battery.
3. Close the battery cover. A click is heard when
the cover is secure.
• Battery cover
If the battery cover is open during power ON, SRX notifies you by displaying the screen below and
beeping.
• When the battery cover is closed, the previous screen is restored.
35

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
The SRX supports both USB and Bluetooth wireless technology for communication with data
collectors, computers, cellular phones, and the On-demand Remote Control system.
Read this manual in conjunction with the operator’s manual for the relevant external device.
Bluetooth communication: "4.4 Bluetooth Wireless Technology"
Transferring data using the SFX function: SFX Dial-Up Program Explanations, Output
format and command operations: Interfacing with the SOKKIA SDR Electronic Field
Book and Command Explanations manuals
8.1 Wireless Communication using Bluetooth Technology
The Bluetooth module incorporated in the SRX can be used for communication with Bluetooth devices
other than the SRX.
Security functions such as Bluetooth device address and passkey can be used to provide a level of
protection for wireless communication.
Bluetooth device address
This is a number unique to one particular Bluetooth device used to identify devices during
communication. This number consists of 12 characters (numbers 0 to 9 and letters from A to F).
Some devices may be referred to by their Bluetooth device address.
SRX Bluetooth antenna: "4.2 Parts of the Instrument Bluetooth antenna"
Bluetooth connections
Communication between a pair of Bluetooth devices requires one device to be set as the
"Master" and the other as the "Slave". To initiate connections from the SRX side, set the SRX
as the "Master" device. To initiate connections from the paired device side, set the SRX as the
"Slave" device. The factory setting is "Slave".
36

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
PROCEDURE Necessary settings for Bluetooth communication
1. Select "Comms" in SETTINGS mode. Set Comms
mode in the Comms setup tab to "Bluetooth".
2. Select a mode for the SRX in the Bluetooth tab.
To initiate connections from the SRX side, set the
SRX as the "Master" device. To initiate
connections from the paired device side, set the
SRX as "Slave".
The factory setting is "Slave".
Register companion devices.
•"Master" cannot be selected when no companion
devices have been registered.
3. Select, in "Link", a companion device from among
the Bluetooth devices already registered in the
SRX.
Registering devices: "PROCEDURE
Registering Bluetooth companion devices"
•Companion devices cannot be selected when the
SRX is set as "Slave".
4. Set "Authentication" to "Yes" or "No".
37

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
5. When "Authentication" is set to "Yes", input the
same passkey as that for the intended companion
device. Even if "Authentication" is set to "No", a
passkey is requested when authentication is set
on the companion device being used.
• Up to 16 numeral characters can be input. Input
characters will be displayed as asterisks (e.g.
"*****"). The passkey was set to "0123" at the
factory.
6. Press [OK] to finish settings.
38

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
PROCEDURE Registering Bluetooth companion devices
1. Power on the companion device.
2. Select "Comms" in SETTINGS mode.
3. Select "Link" in the Bluetooth tab. and press
[LIST] to display a list of all registered devices.
Data collector devices can be set in the Serial tab
and devices for use with the SFX Dial-Up Program
in the SFX (Dial-Up) tab.
4. Register your Bluetooth device(s).
Press
[Add]
device name and Bluetooth address and press
[OK]
to display <Add device>. Input the
. Up to 12 hexadecimal digits can be input.
39

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
Press [Inquire] to inquire about Bluetooth devices
in the immediate vicinity of the SRX and display
their device name and address in a list. Select a
device from this list and press [OK] to add to the
Link device list in step 3.
Press [Delete] to delete the selected device
name. Deleted device names cannot be retrieved.
• Select a device and press
page
to update the device name and/or device
address.
5. Press [OK] to complete registration and return to
the screen in step 2.
[Edit]
in the second
PROCEDURE Displaying Bluetooth information for the SRX
1. Select "Comms" in SETTINGS mode.
2. Press [Info] in the Bluetooth tab to display the
device name and Bluetooth address for the SRX
Bluetooth module. Register the Bluetooth address
displayed here in the paired device.
8.2 Communication between the SRX and Companion Device
• Bluetooth communication causes SRX battery power to be depleted at a higher than average rate.
Under the "Slave" setting, the SRX is constantly being searched for by communicable devices and
therefore consumes an ever greater amount of power.
• Check that the companion device (data collector, computer, cellular phone, or On-demand Remote
Control system etc.) is turned on and the relevant Bluetooth settings are complete.
• All communication settings will be changed to factory settings when a cold boot is performed.
Comms setup will need to be performed again.
"8.1 Wireless Communication using Bluetooth Technology"
40

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
1. Complete the necessary SRX settings for
Bluetooth communication.
"8.1 Wireless Communication using
Bluetooth Technology"
• To initiate connections from the SRX side, set
SRX as the "Master" device. To initiate
connections from the paired device side, set
SRX as "Slave".
2. Start communication
When SRX is set as the "Master" device, the
[Connect]
of Meas mode. When
SRX searches for the device selected in "Link"
and a connection starts. When a connection has
been successfully established is displayed
in the status bar.
softkey is allocated to the fourth page
[Connect]
is pressed the
• When SRX is set as the "Slave" device, the establishing of a connection can only be initiated/
canceled by the companion device set as "Master".
• The establishing of a connection can also be initiated by tapping in the status bar.
Status bar, communication status:
3. Press [Cancel] in the fourth page of Meas mode
to terminate the connection.
"5.2 Display Functions"
• A connection can also be terminated by tapping in the status bar.
41

8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
8.3 Connecting to USB devices
SRX has two different USB ports.Sokkia cannot guarantee that all USB devices are compatible with
the SRX USB ports.
Each port is used for connection to different types of devices.
Port name Device type
USB port 1 USB memory devices etc.
USB port 2 computers etc.
USB port 1
USB port 2
8.4 Connection via RS-232C cable
PROCEDURE Basic cable settings
1. Connect the cable.
Cables: "27. OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES"
2. Select "Comms" in SETTINGS mode.
Set communication conditions in the Comms
setup tab.Set "Comms mode" to "RS232C".
42

3. Set options in the RS232C tab according to the
selection made in the Comms setup tab.
*: factory settings
Baud rate:
1200*/2400/4800/9600/19200/38400bps
Data bits: 8*/7 bits
Parity: Not set*/Odd/Even
Stop bit: 1*/ 2 bits
8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES
43

9. SETTING UP THE INSTRUMENT
• Mount the battery in the instrument before performing this operation because the instrument will tilt
slightly if the battery is mounted after levelling.
9.1 Centering
PROCEDURE
1. Set up the tripod
Make sure the legs are spaced at equal intervals
and the head is approximately level.
Set the tripod so that the head is positioned over
the surveying point.
Make sure the tripod shoes are firmly fixed in the
ground.
2. Place the instrument on the tripod head.
Supporting it with one hand, tighten the centering
screw on the bottom of the unit to make sure it is
secured to the tripod.
3. Looking through the optical plummet eyepiece,
turn the optical plummet eyepiece to focus on
the reticle.
Turn the optical plummet focusing ring to focus
on the surveying point.
44
Focussing on the survey point
Focussing on
the reticle
Centering screw

9.2 Levelling
Instrument can be levelled using the screen.
“ Levelling on the screen”
PROCEDURE
1. Adjust the levelling foot screws to center the
surveying point in the optical plummet reticle.
2. Center the bubble in the circular level by either
shortening the tripod leg closest to the offcenter
direction of the bubble or by lengthening the
tripod leg farthest from the offcenter direction of
the bubble. Adjust one more tripod leg to center
the bubble.
9. SETTING UP THE INSTRUMENT
Tripod legs
adjustment
3. Turn the upper part of the instrument until the
plate level is parallel to a line between levelling
foot screws A and B.
Center the air bubble using levelling foot screws
A and B.
The bubble moves towards a clockwise rotated
levelling foot screw.
4. Turn the upper part of the instrument though
90°.
The plate level is now perpendicular to a line
between levelling foot screws A and B.
Center the air bubble using levelling foot screw
C.
45

9. SETTING UP THE INSTRUMENT
5. Turn another 90° and check bubble position
Turn the upper part of the instrument a further
90° and check to see if the bubble is still in the
center of the plate level. If the bubble is offcenter, perform the following:
a.Turn levelling foot screws A and B equally in
opposite directions to remove half of the
bubble displacement.
b.Turn the upper part a further 90°, and use
levelling foot screw C to remove half of the
displacement in this direction.
Or adjust the plate level.
.
"23.1 Plate Level"
6. Turn the instrument and check to see if the air
bubble is in the same position in all directions.
If it is not, repeat the levelling procedure.
7. Loosen the centering screw slightly.
Looking through the optical plummet eyepiece,
slide the instrument over the tripod head until the
surveying point is exactly centered in the reticle.
Retighten the centering screw securely.
8. Check again to make sure the bubble in the
plate level is centered
If not, repeat the procedure starting from step 3.
PROCEDURE Levelling on the screen
1. Press {} to power on.
"10. POWER ON/OFF"
2. Press {SETTINGS} to enter SETTINGS mode.
46

3. Select the Tilt tab to display the circular level on
the screen.
“z” indicates the bubble in circular level. The
range of the inside circle is ±3' and the range of the
outside circle is ±4.5'.
4. Center “z” in the circular level.
"9.2 Levelling" steps 1 to 2
5. Turn the instrument until the telescope is parallel
to a line between levelling foot screws A and B.
6. Set the tilt angle to 0° using foot screws A and B
for the X direction and levelling screw C for the Y
direction.
7. Press {ESC} to return to Meas mode.
9. SETTING UP THE INSTRUMENT
47

10.POWER ON/OFF
PROCEDURE Power ON
1. Press .
When the power is switched on, a self-check is run.
The Meas mode screen is displayed.
If "Out of range" is displayed, the instrument tilt
sensor is indicating that the instrument is out of level.
Level the instrument once again and the horizontal
and vertical angles will be displayed.
• "Tilt crn." in "Obs. condition" should be set to "No" if the display is unsteady due to vibration or strong
wind.
"21.1 Observation Conditions"
Resume function
The Resume function redisplays the screen appearing before the instrument was powered OFF
when the instrument is powered back ON. All parameter settings are also saved. Even if
remaining battery power is completely depleted, this function will remain active for 1 minute,
after which it is canceled. Replace a depleted battery as soon as possible.
PROCEDURE Power OFF
Press {} while pressing {}.
• When there is almost no battery power remaining,
the battery mark in the status bar will start to
blink.In this event, stop measurement, switch off
the power and charge the battery or replace with a
fully charged battery.
• To save power, power to the SRX is automatically
cut off if it is not operated for a fixed period of time.
This time period can be set in "Power off" in
<Inst.config.>.
"21.2 Instrument Configuration"
48

10. POWER ON/OFF
10.1 Configuring the Touch Panel
When using for the first time, or after performing a cold
boot, the screen for configuring the touch panel will be
displayed.
Follow the instructions on the screen. Tap the crosshairs at the center of the display with the stylus pen.
Tap 5 times. Press {} to complete touch panel
configuration. Press {ESC} to retain previous settings.
For units with a display on both the F1 and F2 faces:
After tapping 5 times the display backlight wi
dim and the display on the reverse face will
illuminate. Tap the cross-hairs on the reverse
fac
e display a further 5 times.
ll
• Touch panel configuration can be performed at any time by pressing [PNL CAL] in <Inst.config.>.
Reset: "10.2 Resolving Software Issues"
10.2 Resolving Software Issues
If you are experiencing problems with the SRX and suspect a fault in the program, you should try a
warm boot. A warm boot will not erase surveying data in Program mode (SDR) but will cancel the
resume function. Whenever possible transmit the data to a personal computer before rebooting.
If the problem is not resolved with a warm boot the next step is to perform a cold boot.
PROCEDURE
1. Power OFF the instrument.
2. Press { } while pressing {}.
The instrument is reset and powers ON as normal.
Cold boot
If the problem is not resolved with a warm boot the next step is to perform a cold boot. A cold
boot will not erase surveying data in Program mode (SDR) but all the parameters will be
changed to the factory settings. If the data in the memory is necessary, BE SURE TO
TRANSFER IT TO A PERSONAL COMPUTER BEFORE PERFORMING A COLD BOOT.
To perform a cold boot, while holding {F3}, {F1}, and {BACKSPACE}, press
The instrument is reset and powers ON as normal.
{}
"21.10 Restoring Default Settings"
Problems Powering OFF
.
49

10. POWER ON/OFF
When the instrument cannot be powered OFF as normal, depress the reset button with the tip
of the stylus pen. Then, power ON as normal.
•Do not press the reset button while accessing programs. File and folder data may be lost as a
result.
Reset button
10.3 Powering the SRX ON/OFF from an External Instrument
The SRX can be powered ON/OFF from an external device such as a computer or control terminal.
When the SRX is powered OFF from a paired
Bluetooth device during Bluetooth communication, the
screen shown at right will be displayed.
Powering ON the SRX from the paired device or by
pressing on the SRX itself redisplays the screen
appearing before the instrument was powered OFF.
Powering OFF the SRX during Bluetooth
communication will cancel the Bluetooth connection. If
this screen is displayed continuously for 30 minutes,
power to the SRX is automatically cut off.
"12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
50

11.TARGET SIGHTING
The target can be automatically sighted using the Auto Pointing function or manually sighted by the
operator using the peep sight and telescope. The Auto Pointing function automatically sights the target
and does not require you to focus the telescope. The SRX analyses the image of the prism in the field
of view and moves the telescope to sight the center of this prism.
•The search method can be set.
"12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
Caution
• The instrument emits a laser beam until the center of the prism is sighted.
• Auto Pointing can only be performed when a prism or sheet is used as the target. For reflectorless
measurement, the target must be sighted manually.
• Use reflective prisms/reflective sheets from Sokkia for higher precision measurement.
• Auto Pointing cannot be performed if the prism is located at the zenith. In this case, manually sight
the target.
"11.3 Manually Sighting the Target"
• If more than one prism is located in the field of sight during Auto Pointing, an operation error will
occur and the SRX will not be able to find the target.
• A prism beyond glass cannot be searched because a measurement error occurs.
• If an obstacle blocks the laser beam path between the SRX and the prism, SRX cannot find the
target correctly.
• If strong light shines directly into the objective lens, measurement cannot be performed correctly.
• Position the prism in alignment with the objective lens. In short distance measurement especially,
make sure to align the prism with the objective lens (within 10 to 15°) to obtain the correct result. A
prism with a prism constant of -40mm can eliminate the error caused by tilted prism.
Aspect of the 360° Prism
The 360° Prism should be set up so that a pair of hexagonal points on the rubber flanges of the
prism are aligned with the sighting direction of the SRX (see the diagram below).
51

11. TARGET SIGHTING
11.1 Auto Pointing Settings
1. Select "Motor" in <Configuration>.
Set Auto Pointing functions in the Configuration
tab.
Set "A.T. Setting" to "Search".
Settings and Options
(*: factory settings)
(1) Accu. search
Fine*/Rapid
(2) A.T. Setting
None/Search*/Track
(3) Srch method
G.S.*/R.C.
Accu. search
Compared to Digital Imaging Mode ("Rapid" setting), the analysis of the prism image in Optical
Imaging Mode ("Fine" setting) is finer and the criteria for completing sighting are more stringent.
"Rapid" mode should be used when supporting the pole by hand if "Time out" is displayed before
the SRX completes sighting as a result of vibration, or, completing Auto Pointing takes too long.
Srch method
Selects search before distance measurement option.
When set to "G.S." the SRX will search for the target in the area specified in the Search area
tab. When set to "R.C.", the SRX will wait for a Turning command to be issued from the RC
Controller before starting Auto Pointing. Both methods can be used to sight the target.
52

2. Set the area in which to perform target sighting in
the Search area tab. Drag the box to specify the
desired or area or input vertical and horizontal
angle values.
Angle values can only be specified in 1°30’ steps
(e.g. 15°00’, 16°30’, 18°00’ etc.). Input values not
conforming to this format will be automatically
rounded up.
3. Press [OK].
11. TARGET SIGHTING
53

11. TARGET SIGHTING
11.2
Auto-Pointing Function for Target Sighting
PROCEDURE
1. Use the peep sight to aim the objective lens in the
general direction of the target. The vertical and
horizontal jogging knobs can be used for precise
adjustments of the instrument and telescope.
2. Select [SRCH] in any Meas mode screen. The
telescope and top half of the instrument rotate
and target auto-search begins. When the target is
found, the instrument sights the center of the
prism and stops.
Allocating the
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
[SRCH]
softkey:
• The following softkeys can also be used for Auto Pointing when "A.T. Setting" in <Motor
configuration> is set to "Search".
Motor settings: "12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
Softkey Function
[DIST] Performs Auto Pointing then distance and angle measurement
[SRCH] Performs Auto Pointing then distance and angle measurement
[H.ANG] Performs Auto Pointing then sets current angle to the specified angle
[0 SET] Performs Auto Pointing then sets current angle to 0
[RC] Rotates in the direction specified by the On-demand Remote Control
[<-RC] Rotates in a counterclockwise direction (from the point of view of the
[RC->] Rotates in a clockwise direction (from the point of view of the RC
[ROTATE] Automatically rotates the instrument to the specified vertical and
[TURN] Rotates the SRX 180
system then performs Auto Pointing
RC Controller) then performs Auto Pointing
Controller) then performs Auto Pointing
horizontal angles then performs Auto Pointing
°
then performs Auto Pointing
54

11. TARGET SIGHTING
11.3 Manually Sighting the Target
• When sighting the target, strong light shining directly into the objective lens may cause the
instrument to malfunction. Protect the objective lens from direct light by attaching the lens hood.
XPROCEDURE
1. Look through the telescope eyepiece at a bright and
featureless background.
Turn the eyepiece clockwise, then counterclockwise
little by little until just before the reticle image becomes
focussed.
Using these procedures, frequent reticle refocussing is
not necessary, since your eye is focussed at infinity.
2. Use the peep sight to bring the target into the field of
view. Turn the vertical and horizontal jogging knobs for
fine sighting adjustments.
3. Turn the telescope focussing ring to focus on the
target.
Turn the vertical and horizontal fine motion screws to
align the target with the reticle.
The last adjustment of each fine motion screw should
be in the clockwise direction.
4. Readjust the focus until there is no parallax
Readjust the focus with the focussing ring until there is
no parallax between the target image and the reticle.
Eliminating parallax
This is the relative displacement of the target image with respect to the reticle when the
observer's head is moved slightly before the eyepiece.
Parallax will introduce reading errors and must be removed before observations are taken.
Parallax can be removed by refocussing the reticle.
55

12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING
With the Auto Tracking function, an SRX, sighted on the target using Auto Pointing, will following that
target as it is moved from measurement point to measurmeent point. The On-demand Remote Control
System is recommended for high performance Auto Tracking measurement.
Caution
• The instrument emits a laser beam during Auto Pointing and Auto Tracking operation.
• Auto Pointing can only be performed when a prism is used as the target. Auto Tracking is not
possible with reflective sheet and reflectorless measurement
• Use reflective prisms from Sokkia for higher precision measurement.
• If more than one prism is located in the field of sight during Auto Tracking, an operation error will
occur and the SRX will not be able to find the target.
• The prism beyond the glass can not be searched because measurement error occurs.
• If an obstacle blocks the laser beam path between the SRX and the prism, SRX cannot find the
target correctly.
• Position the prism in alignment with the objective lens. In short distance measurement especially,
make sure to align the prism with the objective lens (within 10 to 15°) to obtain the correct result. A
prism with a prism constant of -40mm can eliminate the error caused by tilted prism.
360 Prism: "11. TARGET SIGHTING Aspect of the 360° Prism"
12.1 Auto Tracking Settings
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Motor" in <Configuration>.
Set Auto Tracking functions in the Configuration
tab.
Set "A.T. Setting" to "Track".
56

12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING
Configuration tab:"11.1 Auto Pointing Settings"
2. Set the area in which to perform target sighting in
the Search area tab. Drag the box to specify the
desired or area or input vertical and horizontal
angle values.
Angle values can only be specified in 1°30’ steps
(e.g. 15°00’, 16°30’, 18°00’ etc.). Input values not
conforming to this format will be automatically
rounded up.
3. Press [OK].
12.2 Measurement with Auto Tracking
PROCEDURE
1. Use the peep sight to aim the objective lens in the
general direction of the target. (The vertical and
horizontal jogging knobs can be used for precise
adjustments of the instrument and telescope.)
2. Select [DIST], [RC Cont], or [SRCH] in any Meas
mode screen. The telescope and top half of the
instrument rotate and target auto-search begins.
When the target is found, the instrument sights
the center of the prism and Auto Tracking starts.
Allocating softkeys: "21.6 Allocating Key
Functions"
3. Press [AT Off] in a Meas mode screen to stop
Auto Tracking.
• When [STOP] is pressed, distance measurement
will stop but Auto Tracking will remain active.
57

12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING
Lost Prism
In the event that an obstacle prevents the SRX sighting the target during Auto Tracking, the
instrument will predict the direction in which the target will travel and continue Auto Tracking
based on this prediction. If the SRX re-acquires the target in this predicted direction, Auto
Tracking continues without change. If the target is not re-acquired however, Auto Tracking will
stop and the SRX will enter
field of view or a Turning command is received from the RC Controller during "prism wait", the
SRX will perform Auto Pointing, then resume Auto Tracking. If the target is not re-acquired
during the "prism wait" period, the target is considered "lost" and sighting terminates.
Start Auto Tracking procedure again from step 1.
Auto Tracking
Obstacle
Direction predicted
Ta rg e t
not found
"Prism wait"
Ta rg e t
not found
Target "lost"
"prism wait" status for a period of 60 second
Target found
Target found
s.If the target enters the
• The following softkeys can also be used for Auto Pointing when "A.T. Setting" in <Motor
configuration> is set to "Track".
Softkey Function
[DIST] Performs Auto Pointing then Auto Tracking/distance measurement
[SRCH] Performs Auto Pointing then Auto Tracking/distance measurement
[H.ANG] Sets current angle to a specified angle then performs Auto Pointing/
[0 SET] Sets current angle to 0 then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
[RC] Rotates in the direction specified by the On-demand Remote Control
[<-RC] Rotates in a counterclockwise direction (from the point of view of the
[RC->] Rotates in a clockwise direction (from the point of view of the RC
58
Auto Tracking
System then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
RC Controller) then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
Controller) then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking

12. MEASUREMENT WITH AUTO TRACKING
[RC Cont] Nullifes the current measurement position, continues Turning
[AT On] Performs Auto Pointing then Auto Tracking
[ROTATE] Automatically rotates the instrument to the specified vertical and
[TURN] Rotates the SRX 180
operation, then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
horizontal angles then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
°
then performs Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
59

13.ANGLE MEASUREMENT
This section explains the procedures for basic angle measurement in Basic mode.
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in measurement menus to suit various applications and the ways
that different operators handle the instrument.
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
13.1 Measuring the Horizontal Angle between Two Points
(Horizontal Angle 0°)
Use the “0SET” function to measure the included angle between two points. The horizontal angle can
be set to 0 at any direction.
PROCEDURE
1. Sight the first target as at right.
"10.3 TARGET SIGHTING"
2. In the first page of the Meas mode screen, press
[0SET].
[0SET] will flash, so press [0SET] again.
The horizontal angle at the first target becomes 0°.
3. Sight the second target.
60

The displayed horizontal angle (HAR) is the
included angle between two points.
13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT
61

13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT
13.2 Setting the Horizontal Angle to a Required Value
(Horizontal Angle Hold)
You can reset the horizontal angle to a required value and use this value to find the horizontal angle
of a new target.
PROCEDURE
1. Sight the first target.
2. In the second page of Basic mode, press
[H.ANG]. <Set H angle> is displayed.
3. Enter the angle you wish to set, then press [OK].
The value that is input as the horizontal angle is
displayed.
•Press [SRCH] to rotate the SRX in the direction
of the desired angle.
• The same setting can also be performed with
coordinate and azimuth input.
"15.2 Azimuth Angle Setting"
4. Press [OK] to confirm the input value and display
the new horizontal angle.
5. Sight the second target.
The horizontal angle from the second target to the
value set as the horizontal angle is displayed.
Current angle
62

13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT
• Pressing [HOLD] performs the same function as above.
•Press [HOLD] to set the displayed horizontal angle. Then, set the angle that is in hold status to the
direction you require.
Allocating [HOLD]: "21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
63

13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT
13.3 Turning the Instrument from the Reference Angle to a
Specified Angle
The SRX automatically turns from the reference direction to the specified angle (target).
• SRX also turns to the target coordinates when reference angle is omitted.
• Rotation may not be completed correctly when specifiying an angle near the zenith or nadir if "Tilt
crn." or "Coll. crn" is set to "Yes" in "Obs.condition".
PROCEDURE
1. Sight the point you will use as the reference angle
and set it as the reference angle.
Sight the reference point and press [0SET], or
input the reference point angle.
"13.1 Measuring the Horizontal Angle
between Two Points (Horizontal Angle 0°)"/
"13.2 Setting the Horizontal Angle to a
Required Value (Horizontal Angle Hold)"
2. Press {SETTINGS} to switch to SETTINGS
mode.
64

13. ANGLE MEASUREMENT
3. Enter the vertical and horizontal angles in the
Motor tab.
• Pressing [READ] in the second page displays
the coordinates data recorded in Program mode
(SDR). This data can be recalled and used for
settings.
Series SRX SDR Software Reference
Manual
• The target angle can be obtained from the
entered instrument station and target
coordinates. Instrument station data is entered
on the second page. Press [OK] to calculate
both the horizontal and vertical angle from the
coordinates.
4. After confirming the coordinates, press
[ROTATE]. The SRX moves to the point (target)
entered in step 3.
13.4 Angle measurement and Outputting the Data
The following explains angle measurement and the features used to output measurement results to a
computer or other external devices.
"6.1 CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES", Cables: "27. OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES",
Output format and command operations: Interfacing with the SOKKIA SDR Electronic Field Book
and Command Explanations manuals
PROCEDURE
1. Connect SRX and external device.
2. Sight the target point.
3. Press [HV out] in Meas mode to output target
measurement results to the external device.
65

14.DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
Perform the following settings as preparation for distance measurement in Basic mode.
• Distance measurement mode
• Target type
• Prism constant correction value
• Search area
• Auto Pointing/Auto Tracking
"11.1 Auto Pointing Settings", "12.1 Auto Tracking Settings", "21.3 EDM Settings"
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in measurement menus to suit various applications and the ways
that different operators handle the instrument.
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
Caution
• When using the laser-pointer function, be sure to turn OFF the output laser after distance
measurement is completed. Even if distance measurement is canceled, the laser-pointer function is
still operating and the laser beam continues to be emitted. (After turning ON the laser-pointer, the
laser beam is emitted for 5 minutes, and then automatically switches OFF.)
• Make sure that the target setting on the instrument matches the type of target used. SRX
automatically adjusts the intensity of the laser beam and switches the distance measurement
display range to match the type of target used. If the target does not correspond to the target
settings, accurate measurement results cannot be obtained.
• Accurate measurement results cannot be obtained if the objective lens is dirty. Dust it off with the
lens brush first, to remove minute particles. Then, after providing a little condensation by breathing
on the lens, wipe it off with the wiping cloth.
• During reflectorless measurement, if an object with a high reflective factor (metal or white surface)
is positioned between the SRX and the target, accurate measurement results may not be received.
• Scintillation may affect the accuracy of distance of measurement results. Should this occur, repeat
measurement several times and use the averaged value of the obtained results.
14.1 Returned Signal Checking
Check to make sure that sufficient reflected light is returned by the target sighted by the telescope.
Checking the returned signal is particularly useful when performing long distance measurements.
Caution
• The laser beam is emitted during returned signal checking.
• Manually sight the target when checking the returned signal.
• When the light intensity is sufficient even though the center of the reflective prism and the reticle
are slightly misaligned (short distance etc.), “
measurement is impossible. Therefore make sure that the target center is sighted correctly.
66
” will be displayed in some cases, but in fact, accurate

PROCEDURE
1. Accurately sight the target manually.
"11.3 Manually Sighting the Target"
2. Press {SETTINGS} to switch to SETTINGS mode
and select the Aiming tab or press [AIM] in Meas
mode.
Allocating [AIM]: "21.6 Allocating Key
Functions"
When [AIM] is pressed, a gauge indicating light
intensity is displayed.
• The more displayed, the greater the
quantity of reflected light.
• If “” is displayed, only enough light for the
measurement is returned.
• When “” is not displayed, accurately resight
the target.
[BEEP]/[OFF]: Sets a buzzer sound when
measurement is possible. Press to switch on
and off.
[DIST]: Returns to Meas mode and starts
distance measurement. This softkey is not
displayed when the returned signal checking
function is accessed from Program mode (SDR).
14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
3. Press [OFF] to finish signal checking.
Press
{ESC}
or tap the cross in the top-right
corner to return to the previous screen.
• When is displayed persistently, contact your Sokkia agent.
• If no key operations are performed for two minutes, the display automatically returns to the previous
screen.
67

14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
14.2 Using the Guide Light
The color and flashing speed of the guide light indicates the status of the SRX and can be known when
the user is located at a distance from the instrument.
Switching the guide light ON/OFF "5.1 Basic Key Operation"
• The pattern of the guide light can be changed.
"21.2 Instrument Configuration"
• The guide light will turn off, even when set to ON, during distance measurement and returned signal
checking.
Light status Meaning
Slow flashing (Red and green
simultaneously)
Fast flashing (Red and green
simultaneously)
Green and red alternate
flashing
14.3 Distance and Angle Measurement
Waiting
Searching/returned signal checking in progress
Measuring (continuous measurement)
Search error (error screen only)
Distance measurement error (no signal, sighting error)
An angle can be measured at the same time as distance.
• The search range can be set.
"12.1 Auto Tracking Settings"
Caution
• The laser beam is emitted during Auto Pointing and Auto Tracking.
PROCEDURE
1. Face the SRX in the direction of the target
Use the peep sight to aim the SRX and telescope
toward the target.
"11. TARGET SIGHTING"
68

2. Start measurement.
Press [DIST] in the first page of Meas mode to
start measurement.
The measured distance data (S), vertical angle
(ZA), and horizontal angle (HAR) are displayed.
14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
3. .Press [STOP] to quit distance measurement.
• If the single measurement mode is selected, measurement automatically stops after a single
measurement.
• During fine average measurement, the distance data is displayed as S1, S2,... to S9. When the
designated number of measurements has been completed, the average value of the distance is
displayed in the "SA" line.
• The distance and angle that are most recently measured remain stored in the memory until the
power is off and can be displayed at any time by pressing [RCL].
Allocating [RCL]: "21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
69

14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
14.4 Distance Measurement and Outputting the Data
The following explains distance measurement and the features used to output measurement data to
a computer or external devices.
"8. CONNECTING TO EXTERNAL DEVICES", Communication cables: "27. OPTIONAL
ACCESSORIES". Output format and command operations: Interfacing with the SOKKIA SDR
Electronic Field Book and Command Explanations manuals
PROCEDURE
1. Connect SRX and external device.
2. Sight the target point.
3. Press [HVD out] in Meas mode to start distance
measurement. Target measurement results are
output to the external device.
Output type: "21.6 Allocating Key Functions",
"21.1 Observation Conditions"
4. Press [STOP] to finish data output and return to
the Meas mode.
14.5 REM Measurement
An REM measurement is a function used to measure the height to a point where a target cannot be
directly installed such as power lines, overhead cables and bridges, etc.
The height of the target is calculated using the following formula.
Ht = h
+ h
1
h2 = S sinz1 x cotz2 - S cos
Zenith
Zenith
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in the REM measurement menu to suit various applications and
the ways that different operators handle the instrument.
2
z1
70

"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
PROCEDURE
1. Set the target directly under or directly over the
object and measure the target height with a tape
measure etc.
Press [HT] and enter the target height.
2. Select "REM" in <Menu>.
3. Sight the target and press [DIST] to start
measurement. Press [STOP] to stop the
measurement.
14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
71

14. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
The measured distance data, vertical angle and
horizontal angle are displayed.
4. Sight the object, then press [REM] to start REM
measurement is started. The height from the
ground to the object is displayed in "Ht.".
Press [STOP] to stop the measurement.
• To re-observe the target, sight the target then
press [DIST].
• To continue REM measurement, press [REM].
• When measurement data already exists, select [REM] in <Menu> as in step 2 to proceed to step
4 and start REM measurement. Press [STOP] to stop the measurement.
72

15.COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
By performing coordinate measurements it is possible to find the 3-dimensional coordinates of the
target based on station point coordinates, instrument height, target height, and azimuth angles of the
backsight station which are entered in advance.
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in measurement menus to suit various applications and the ways
that different operators handle the instrument.
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
15.1 Entering Instrument Station Data
Before performing coordinate measurement, enter instrument station coordinates, instrument height
and target height.
PROCEDURE
1. First measure the target height and instrument
height with a tape measure, etc.
2. Select "Coord." in <Menu>.
73

15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
3. Select "Station setup" and enter instrument
station coordinates, instrument height and target
height.
•Press [READ] to read in coordinate data
registered in Program mode (SDR).
Series SRX SDR Software Reference
Manual
4. Press [OK] to set the input values. <Set H angle>
is displayed again.
15.2 Azimuth Angle Setting
Based on the instrument station coordinates and backsight station coordinates which have already
been set, the azimuth angle of the backsight station is calculated.
74

PROCEDURE Entering coordinates
1. Select "Backsight setup" in <Coordinate>. <Set
H angle> is displayed.
• <Set H angle> can also be displayed from the
screen in step 4 of "15.1 Entering Instrument
Station Data".
2. Select the Key in coord tab and enter the
backsight station coordinates.
15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
• [READ]
:
Reads in coordinate data registered in
Program mode (SDR) .
Series SRX SDR Software Reference
Manual
[SRCH]
: R
•
desired angle.
• Sight the backsight station and press
Press
from coordinates, the measured distance, and
the difference between the two. Press
set the azimuth angle and display <Coord.
measurement>.
•
[None]
method.
3. Press [OK] to set the input values. <Coord.
measurement> is displayed.
otates the SRX in the direction of the
[STOP]
to display the distance calculated
: Switches horizontal angle setting
Horizontal angle settings
[DIST]
[YES]
.
to
75

15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
PROCEDURE Entering angle
1. Select "Backsight setup" in <Coordinate>. <Set
H angle> is displayed.
. <Set H angle> can also be displayed from the
screen in step 4 of "15.1 Entering Instrument
Station Data".
2. Select the Key in angle tab and enter the desired
angle in "H.ang".
•
[SRCH]
: Rotates the SRX in the direction of the
desired angle.
3. Press [OK] to set the input values. <Coord.
measurement> is displayed.
PROCEDURE Entering azimuth
1. Select "Backsight setup" in <Coordinate>. <Set
H angle> is displayed.
. <Set H angle> can also be displayed from the
screen in step 4 of "15.1 Entering Instrument
Station Data".
2. Select the Key in azimuth tab and enter the
desired angle in "H.ang".
• [SRCH]: Rotates the SRX in the direction of the
desired angle.
•
[None]
: Switches horizontal angle setting
method.
"
Horizontal angle settings
3. Press [OK] to set the input values. <Coord.
measurement> is displayed.
"
Horizontal angle settings
76

15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
None (input azimuth angle only)/0 SET (horizontal angle set to 0°)/Azimuth (set both horizontal
and azimuth angles to the same value)/H.ANG (input both horizontal and azimuth angles)
15.3 3-D Coordinate Measurement
The coordinate values of the target can be found by measuring the target based on the settings of the
instrument station and backsight station.
The coordinate values of the target are calculated using the following formulae.
N1 Coordinate = N0 + S x sinZ x cosAz
E1 Coordinate = E0 + S x sinZ x sinAz
Z1 Coordinate = Z0 + S x cosZ + ih - fh
N0: Station point N coordinate S: Slope distance ih: Instrument height
E0: Station point E coordinate Z: Zenith angle fh: Target height
Z0: Station point Z coordinate Az: Direction angle
"Null" coordinates will not be included in calculations. "Null" is not the same as zero.
77

15. COORDINATE MEASUREMENT
PROCEDURE
1. Sight the target at the target point.
"
11. TARGET SIGHTING"
2. Select "Coord." in <Coordinate>.
Press
[DIST]
to start measurement.
to stop the measurement. The coordinates of the
target point are displayed. Select the Graphic tab
to display coordinates on a graph.
• By pressing [HT], the instrument station data can
be reset. When the target height of the next
target is different, reenter the target height
before beginning the observation.
Press [STOP]
3. Sight the next target and press [DIST] to begin
measurement. Continue until all targets have
been measured.
4. When coordinate measurement is completed,
press {ESC} or tap the cross in the top-right
corner to return to <Coordinate>
78

16.RESECTION MEASUREMENT
Resection is used to determine the coordinates of an instrument station by performing multiple
measurements of points whose coordinate values are known. Registered coordinate data can be
recalled and set as known point data. Residual of each point can be checked, if necessary
Entry Output
Coordinates of
known point
Observed
horizontal angle
Observed vertical
angle
Observed distance : Di
: (Ni, Ei, Zi) Station point coordinates : (N0,E0, Z0)
:Hi
:Vi
• Between 2 and 10 known points can be measured by distance measurement, and between 3 and
10 known points by angle measurement.
• The more known points there are and the more points there are whose distance can be measured,
the higher the precision of the coordinate value calculation.
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in the Coord. measurement menu to suit various applications and
the ways that different operators handle the instrument.
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
79

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
16.1 Coordinate Resection Measurement
N, E, Z of an instrument station is determined by the measurement.
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Resection" in <Menu>.
2. Select "NEZ" to display <Resection/Known
point>.
3. Input the known point.
After setting the coordinates and target height for
for the first known point press [OUT] to move to
the second point.
• Press [READ] to read in coordinate data
registered in Program mode (SDR).
•Press
[IN] to return to settings for the previous
point.
When all required known points have been set,
press [OK].
80

4. Sight the first known point and press [DIST] to
begin measurement.
The measurement results are displayed on the
screen.
• When [ANGLE] has been selected, the distance
cannot be displayed.
5. Press [YES] to use the measurement results of
the first known point.
• You can also input target height here.
•Press [NO] to return to the screen in step 3 and
perform measurement again.
6. Repeat procedures 3 to 4 in the same way from
subsequent points.
When the minimum quantity of observation data
required for the calculation is present, [CALC] is
displayed.
16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
7. Press [CALC] or [YES] to automatically start
calculations after observations of all known points
are completed.
• Instrument station coordinates, station elevation,
and standard deviation, which describes the
measurement accuracy, are displayed.
81

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
Standard deviation for the northing and easting
coordinates of each point are displayed in the
Detail tab.
8. If there are problems with the results of a point,
align the cursor with that point and press [BAD].
“BAD” is displayed to the right of the point.
Repeat for all results that include problems.
9. Press [RE CALC] to perform calculation again
without the point designated in step 8. The result
is displayed.
If there are no problems with the result, go to step
10.
If problems with the result occur again, perform
the resection measurement from step 3.
•
Press
[RE OBS]
designated in step 8.
If no points are designated in step 8, all the
points or only the final point can be observed
again.
• Press [ADD] when there is a known point that
has not been measured or when a new known
point is added.
to measure the point
10.
Press [OK] in <Resection/result> to display
<Resection/Set h angle>.
82

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
11. Select an angle mode and press
azimuth angle of the first known point as the
backsight point and return to <Resection/Menu>.
12. Press [NO] to return to <Resection/Menu>
without setting the azimuth angle.
[YES]
to set the
Horizontal angle settings
H (set horizontal angle to measured value)/H=Az (set horizontal angle to the same value as
azimuth angle)/Az (set azimuth angle only)
• It is also possible to perform resection measurement by pressing [RESEC] when allocated to the
Meas mode screen.
Allocating
[RESEC]
: "21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
83

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
16.2 Height Resection Measurement
Only Z (height) of an instrument station is determined by the measurement.
• Known points must be measured by distance measurement only.
• Between 1 and 10 known points can be measured.
PROCEDURE
1. Select "Resection" in <Menu>.
2. Select "Elevation" to display <Resection/Known
point>.
3. Input the known point.
After setting the elevation and target height for for
the first known point press [OUT] to move to the
second point.
• Press [READ] to read in data registered in
Program mode (SDR).
•Press
[IN] to return to settings for the previous
point.
When all required known points have been set,
press [OK].
84

4. Sight the first known point and press [DIST] to
begin measurement.
The measurement results are displayed on the
screen.
• When [ANGLE] has been selected, the distance
cannot be displayed.
5. If measuring two or more known points, repeat
procedures 3 to 4 in the same way from the
second point.
When the minimum quantity of observation data
required for the calculation is present, [CALC] is
displayed
6. Press [CALC] or [YES] to automatically start
calculations after observations of all known points
are completed.
• Instrument station elevation and standard
deviation, which describes the measurement
accuracy, are displayed in the Result tab.
16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
Standard deviation values for each point are
displayed in the Detail tab.
85

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
7. If there are problems with the results of a point,
align the cursor with that point and press [BAD].
“BAD” is displayed to the right of the point.
Repeat for all results that include problems.
8. Press [RE CALC] to perform calculation again
without the point designated in step 8. The result
is displayed.
If there are no problems with the result, go to step
10.
If problems with the result occur again, perform
the resection measurement from step 3.
• Press [RE OBS] to measure the point
designated in step 8.
If no points are designated in step 8, all the points
or only the final point can be observed again.
• Press [ADD] when there is a known point that
has not been measured or when a new known
point is added.
9. Press [OK] to finish resection measurement and
return to Meas mode. Only Z (elevation) of the
instrument station coordinate is set. N and E
values are not overwritten.
86

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
Resection calculation process
The NE coordinates are found using angle and distance observation equations, and the
instrument station coordinates are found using the method of least squares. The Z coordinate
is found by treating the average value as the instrument station coordinates.
87

16. RESECTION MEASUREMENT
Precaution when performing resection
In some cases it is impossible to calculate the coordinates of an unknown point (instrument
station) if the unknown point and three or more known points are arranged on the edge of a
single circle.
An arrangement such as that shown below is desirable.
: Unknown point
: Known point
It is sometimes impossible to perform a correct calculation in a case such as the one below.
When they are on the edge of a single circle, take one of the following measures.
(1) Move the instrument station as close as possible
to the center of the triangle.
(2) Observe one more known point which is not on the
circle.
(3) Perform a distance measurement on at least one
of the three points.
• In some cases it is impossible to calculate the coordinates of the instrument station if the included
angle between the known points is too small. It is difficult to imagine that the longer the distance
between the instrument station and the known points, the narrower the included angle between the
known points. Be careful because the points can easily be aligned on the edge of a single circle.
88

17.SETTING-OUT MEASUREMENT
Setting-out measurement is used to set out the required point.
The difference between the previously input data to the instrument (the setting-out data) and the
measured value can be displayed by measuring the horizontal angle, distance or coordinates of the
sighted point.
The horizontal angle difference distance difference, and coordinate difference are calculated and
displayed using the following formulae.
Horizontal difference
Displayed value (angle) = Horizontal angle of setting-out data - measured horizontal angle
Displayed value (distance) = measured horizontal distance x tan (horizontal angle of setting out data
- measured horizontal angle)
Slope distance difference
Displayed value (slope distance) * = measured slope distance - slope distance setting-out data
* Horizontal distance or height difference can be input in the above formula.
Coordinate difference
Displayed value (coordinates)* measured N setting-out coordinates - N coordinates of setting-out data
* E or Z coordinates can be input in the above formula
Height difference (REM setting out measurement)
Displayed value (height) = measured REM data - REM data of setting out data
• Setting out data can be input in various modes: slope distance, horizontal distance, height
difference, coordinates and REM measurement.
• It is possible to allocate softkeys in the Setting-out measurement menu to suit various applications
and the ways that different operators handle the instrument.
"21.6 Allocating Key Functions"
17.1 Using the Guide Light
When the guide light is set to ON, the flashing speed of the light indicates the status of the SRX and
can be known when the user is located at a distance from the instrument. Also, the flashing colors
relative to the target indicate the direction of the instrument and allow the user to reposition the target.
Turning the Guide light ON/OFF: "5.1 Basic Key Operation"
• The pattern of the guide light can be changed.
"21.2 Instrument Configuration"
• The Guide light will turn off, even when set to ON, during distance measurement and returned signal
checking.
89

17. SETTING-OUT MEASUREMENT
● Guide light status and meaning
Status of SRX
Slow flashing Waiting
Fast flashing Searching
Green and red alternate flashing Search error (error screen only)
Indication for positioning target during setting-out measurement
Increased flashing speed (From position of poleman) Move target away from SRX
Decreased flashing speed (From position of poleman) Move target toward SRX
Fast flashing Target is at correct distance
Red (From position of poleman) Move target left
Green (From position of poleman) Move target right
Red and Green Target is at correct horizontal position
Light status Meaning
Measuring (repeated measurement)
Distance measurement error (no signal, sighting error)
Light status Meaning
17.2 Distance Setting-out Measurement
The point is to be found based on the horizontal angle from the reference direction and the distance
from the instrument station.
90

PROCEDURE
1. Select "Setting out" in <Menu> to display <Setting
out>.
17. SETTING-OUT MEASUREMENT
2. Select "Station setup" to display <Height setting>.
Enter data for the instrument station and press
[OK] to move to Backsight setup.
"15.1 Entering Instrument Station Data"
•Press [READ] to read in coordinate data
registered in Program mode (SDR).
Series SRX SDR Software Reference
Manual
3. Set the azimuth angle for the backsight station.
Press [OK] to return to <Setting out>.
"15.2 Azimuth Angle Setting"
91

17. SETTING-OUT MEASUREMENT
4. Select "SO data setting" In <Setting out> to
display <SO data setting>. Enter the included
angle between the reference point and the
setting-out point in "SO.H.ang", and the distance
(slope distance, horizontal distance or height
difference) from the instrument station to the
position to be set out in "SO.Sdist". Enter the
value in the Distance mode that conforms to your
measurement requirements.
• Each time [/Shvr] is pressed, the distance input
mode changes from "S" (slope distance), "H"
(horizontal distance), "V" (height difference), and
"Ht." (REM).
• When [READ] is pressed, coordinates
registered in Program mode (SDR) can be
recalled and used. The distance selected
according to the selected distance input mode is
calculated using these coordinate values.
Series SRX SDR Software Reference
Manual
• Press [COORD] in the second page and input
coordinates in <Key in coord>. The angle and
distance from these coordinates to the position
to be set out will be calculated.
5. Enter values and press [OK] to display the
screen at right.
Press [H.ROTA] to automatically rotate the SRX
toward the horizontal angle set in step 3 and set
the angle to the setting out point to 0°.
92
 Loading...
Loading...