Page 1

Lab Scope Plug-in
User Manual
September 2010
EAZ0007E07G Rev. A
Page 2

T rademark Acknowledgments
Snap-on, Fast-Track, Scanner, and MODIS are trademarks of Snap-on Incorporated.
All other marks are trademarks or registered tr ademarks of th eir resp ective hold ers.
Copyright Information
©2010 Snap-on Incorporated. All rights rese rved.
Disclaimer
The information, specifications and illustrations in this manual are based on the latest information available at the
time of printing.
Snap-on reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice.
Visit our website at:
www.snapon.co m/solus (Nor th America)
snapondiag.com (Europe)
sun-diagnostics.com (Europe)
For Technical Assistance
CALL 1-800-424-7226 (North America )
CALL +44 (0) 845 601 4736 (United Kingdom)
E-mail DiagnosticsUKproductsupport@snapon.com (United King dom)
For technical assistance in all other markets, cont act your selling agent.
Page 3

Safety Information
!
DANGER
!
WARNING
For your own safety and the safety of others, and to prevent damage to the equipment an d
vehicles upon which it is used, it is important that the accompanying Safety Information be read
and understood by all persons operating, or coming into contact with, the equ ipment. We suggest
you store a copy the book near the unit in sight of the oper ator
This product is intended for use by properly trained and ski lled pro fessional automo tive
technicians. The safety messages presented throughout this manual are reminders to the
operator to exercise extreme care when using this test instrument.
There are many variations in procedures, techniques, tools, and p art s for servicing vehicles, as
well as in the skill of the individual doing the work. Because of the vast number of test applications
and variations in the products that can be tested with this instrument, we cannot possibly
anticipate or provide advice or safety messages to cover every situation. It is the automotive
technician’s responsibility to be knowledgeable of the system being tested. It is essential to use
proper service methods and test procedures. It is import ant to perform tests in an appropriate and
acceptable manner that does not endanger your sa fety, the safety of others in the work area, the
equipment being used, or the vehicle being tested.
It is assumed that the operator has a thorough underst anding of vehicle systems before using this
product. Understanding of these system principl es and oper ating theor ies is nece ssary for
competent, safe and accurate use of this instrument.
Before using the equipment, always refer to and follow the safety messages and app licable te st
procedures provided by the manufacturer of the vehicle or equipment being tested. Use the
equipment only as described in this manual.
Read, understand and follow all safety messag es and instructio ns in this manual, the
accompanying safety manual, and on the test equi pment.
Safety Message Conventions
Safety messages are provided to help prevent personal injury and equipm ent damage. All safety
messages are introduced by a signal word indicating the haza rd level.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury to the operator or to bystanders.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if n ot avoided, could result in death o r serious
injury to the operator or to bystanders.
iii
Page 4
Safety Information Important Safety Instructio ns
!
CAUTION
!
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not a voided, may r esult in modera te or mino r
injury to the operator or to bystanders.
Safety messages contain three different type styles.
• Normal type states the hazard.
• Bold type states how to avoid the hazard.
• Italic type states the possible consequences of not avoid ing th e hazard.
An icon, when present, gives a graphical description of the potential hazard.
Example:
Risk of unexpected vehicle movement.
• Block drive wheels before performing a test with engine running.
A moving vehicle can cause injury.
Important Safety Instructions
For a complete list of safety mess ages, refer to the accomp anying safety manual.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Safety Information..................................................................................................................... iii
Safety Message Conventions.......................................................................................................iii
Important Safety Instructions...................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ..............iv
Table of Contents....................................................................................................................... v
Chapter 1: Using This Manual................................................................................................... 1
Conventions.................................................................................................................................. 1
Bold Text................................................................................................................................ 1
Symbols ................................................................................................................................. 1
Terminology ........................................................................................................................... 2
Note and Important Messages............................................................................................... 2
Procedures............................................................................................................................. 2
Additional Manuals........... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ........... 3
Tool Help...................................................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 2: Getting Started......................................................................................................... 4
Powering the MODIS™ Unit.........................................................................................................4
Connecting Leads and Adapters................ ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ........................ 4
Channel One Lead............ ... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... .................................. 4
Channel Two Lead........ .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ...................................... ..... 5
Channel Three Lead ......................................... ... ... .... ...................................... ... .... ... ...........6
Channel Four Lead ........................................ ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... .............. 6
Secondary Coil Adapter Lead................................................................................................ 7
Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter .............................................................................................. 8
Chapter 3: Introduction.............................................................................................................. 9
Functional Description...................................... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...................................... .... ... ......... 10
Technical Specifications............................................................................................................. 10
Capabilities................................................................................................................................. 11
Leads, Probes and Adapters......................................................................................................12
Channel 1 Lead............. .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ...... 12
Channel 2 Lead............. .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ...... 13
Channel 3 Lead ................... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ...... 13
Channel 4 Lead............. .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ...... 13
Alligator Clips....................................................................................................................... 13
Test Probes.......................................................................................................................... 14
Secondary Coil Adapter Lead.............................................................................................. 14
Secondary Ignition Clip-on Wire Adapter............................................................................. 14
Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter ............................................................................................ 14
Chapter 4: Navigation .............................................................................................................. 15
Screen Layout ............................................................................................................................ 15
Upper Toolbar......................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ......................... 15
Main Body............................................................................................................................ 16
v
Page 6

Table of Content s
Lower Toolbar......................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... .... ... ......................... 16
Making Selections ...................................................................................................................... 17
Chapter 5: Multimeter Operations........................................................................................... 18
Selecting Multimeter Software.................................................................................................... 18
Graphing Meter.................................................................................................................... 19
Digital Meter......................................................................................................................... 20
Performing Multimeter Tests ............................ ....................................... ... .... ... ......................... 20
Changing Views................................................................................................................... 20
Pausing Data ....................................................................................................................... 21
Using Zoom..........................................................................................................................22
Using Cursors ...................................................................................................................... 22
Taking Snapshots ................................................................................................................23
Resetting Gauges .......................................... ...................................... .... ... ... ......................24
Saving Data ......................................................................................................................... 24
Printing................................................................................................................................. 25
Using Setup ......................................................................................................................... 25
Calibration Indicator............................................................................................................. 27
Adjusting Channel Settings.................................................................................................. 27
Setting the Sweep Time.................... ... ... ... ....... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ....... ... ... ... 30
Chapter 6: Scope Operations.................................................................................................. 31
Selecting Scope Software .......................................................................................................... 31
Lab Scope............................................................................................................................ 32
Ignition Scope ...................................................................................................................... 32
Performing Scope Tests... ... .... ... ....................................... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ...... 35
Changing View..................................................................................................................... 35
Saving Data ......................................................................................................................... 36
Using Setup ......................................................................................................................... 36
Adjusting Channel Settings.................................................................................................. 38
Displaying Triggers .............................................................................................................. 39
Using Presets............................................................................................................................. 41
Identifying Saved Presets .................................................................................................... 42
Loading Saved Presets........................................................................................................ 42
Editing Presets..................................................................................................................... 42
Deleting Presets................................................................................................................... 43
Copying and Moving Presets............................................................................................... 44
Selecting Multiple Presets.................................................................................................... 44
Appendix A: Testing Tips........................................................................................................45
General Tips........................................ .... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ............................ 45
Using the Split Lead Adapter...................................................................................................... 45
Connecting the Pressure Transducer .................................................................................. 46
Connecting the Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter................................................................... 47
Appendix B: Using Peak Detect.............................................................................................. 48
When To Use Peak Detect.........................................................................................................48
Example—Testing Secondary Ignition................................................................................. 48
Example—Testing a TPS for Glitches.................................................................................. 50
When Not to Use Peak Detect.................................................................................................... 52
Example—Testing an Oxygen Sensor................................................................................. 52
vi
Page 7

Table of Content s
Peak Detect and the Graphing Meter......................................................................................... 53
Appendix C: Using Noise Filter............................................................................................... 54
When to Use Filter...................................................................................................................... 54
Using the Filter with the Graphing Meter.............................................................................. 54
Using the Filter with the Scope ...................................... ...................................... .... ... ......... 57
Appendix D: Using Sensitivity Adjustment............................................................................ 59
When To Use Sensitivity Adjustment ......................................................................................... 59
Improper Sensitivity Adjustments .. .... ... ... ... .... ...... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ...... ... ... 59
Some Common Ignition Problems.............................................................................................. 62
Example–Vehicle With A Shorted Spark-Plug ..................................................................... 62
Example–Vehicle With A Coil Not Firing.............................................................................. 63
Index.......................................................................................................................................... 65
vii
Page 8

Chapter 1 Using This Manual
This manual contains tool usage instructions.
Some of the illustrations shown in this manual may contain modules and optional equipment that
are not included on your system. Contact a sales representative for availability of other modules
and optional equipment.
1.1 Conventions
1.1.1 Bold Text
Bold emphasis is used in procedures to highlight select able items such as butto ns and menu
options.
Example:
• Press the Y/a button.
1.1.2 Symbols
The following types of arrows are used.
The “greater than” arrow (>) indicates an abbreviated set o f se lection instructions.
Example:
• Select Utilities > T ool Setup > Date.
The above statement abbreviates the following procedu re:
1. Navigate to the Utilities button.
2. Use the Thumb Pad to navigate to and highlight the Tool Setup submenu.
3. Use the Thumb Pad to navigate to and highlight the Date option from the submenu.
4. Press Y/a to confirm the selection.
The solid arrows (e, c, d, b) are navigational instructions referring to the four directions of the
Thumb Pad.
Example:
• Press the down d arrow.
1
Page 9

Using This Manual Conventions
NOTE:
IMPORTANT:
1.1.3 Terminology
The term “select” means highlighting a button or menu item u sing the Thumb Pad and pressing
the Y/a button to confirm the selection.
Example:
• Select Reset.
The above statement abbreviates the following procedu re:
1. Navigate to and highlight the Reset button.
2. Press the Y/a button.
1.1.4 Note and Important Messages
The following messages are used.
Note
A NOTE provides helpful information such as additional explanations, tips, and comment s.
Example:
i For additional information refer to...
Important
IMPORTANT indicates a situation which, if not avoided, may result in damage to the test
equipment or vehicle.
Example:
Do not force the CompactFlash® card into the slot.
1.1.5 Procedures
An arrow icon indicates a procedure.
Example:
z To change screen views:
1. Select View.
The drop-down menu displays.
2. Select an option from the menu.
The screen layout changes to the format you selected.
2
Page 10

Using This Manual Additional Manuals
1.2 Additional Manuals
Tools that work in conjunction with various hardware and so f tware m odules have sep ara te
manuals available for each of the modules.
1.3 T ool Help
Your unit has Tool Help containing reference and procedural info rmation fou nd in this and othe r
tool related user’s manuals. From the main menu, access T ool Help on the Utilities menu.
3
Page 11
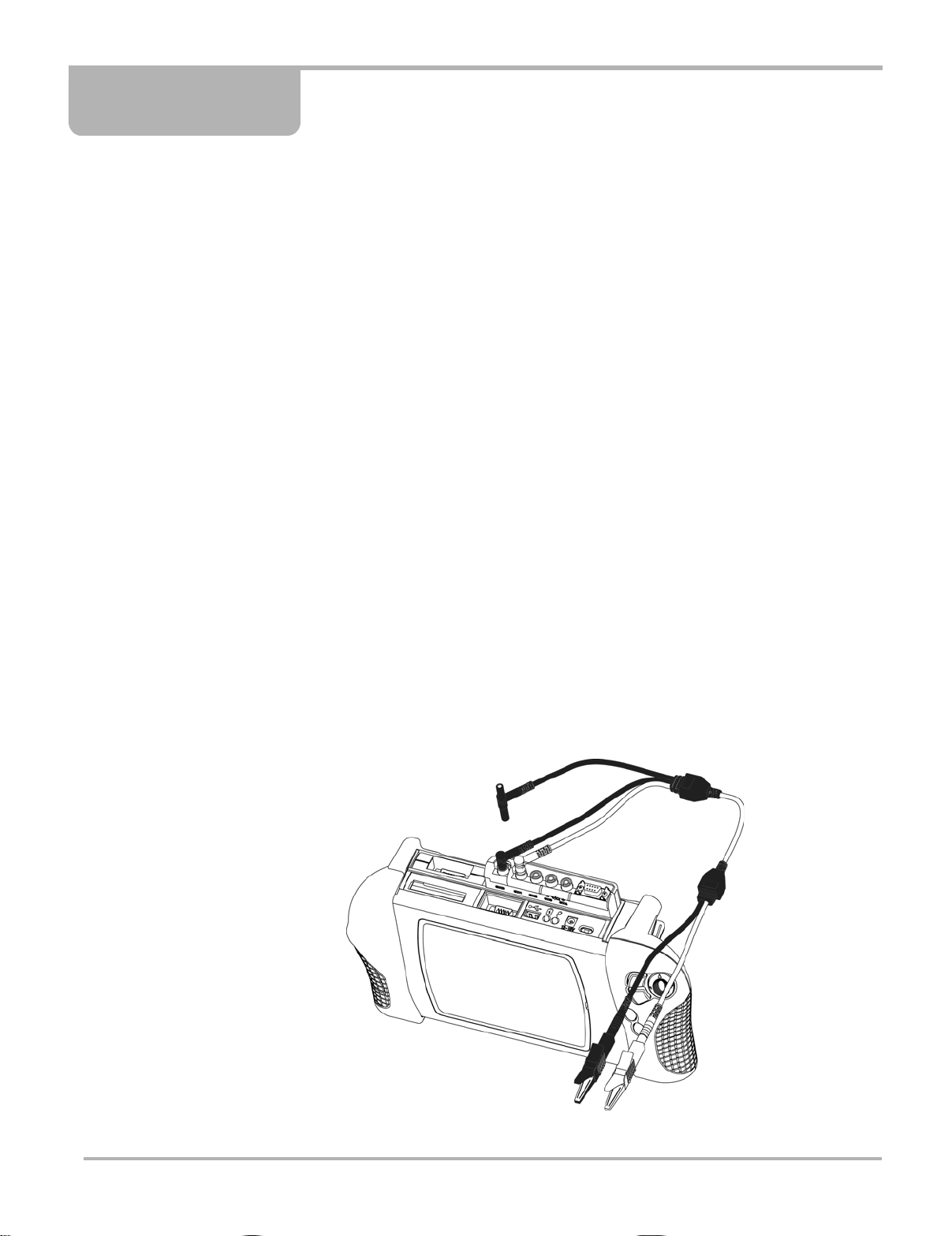
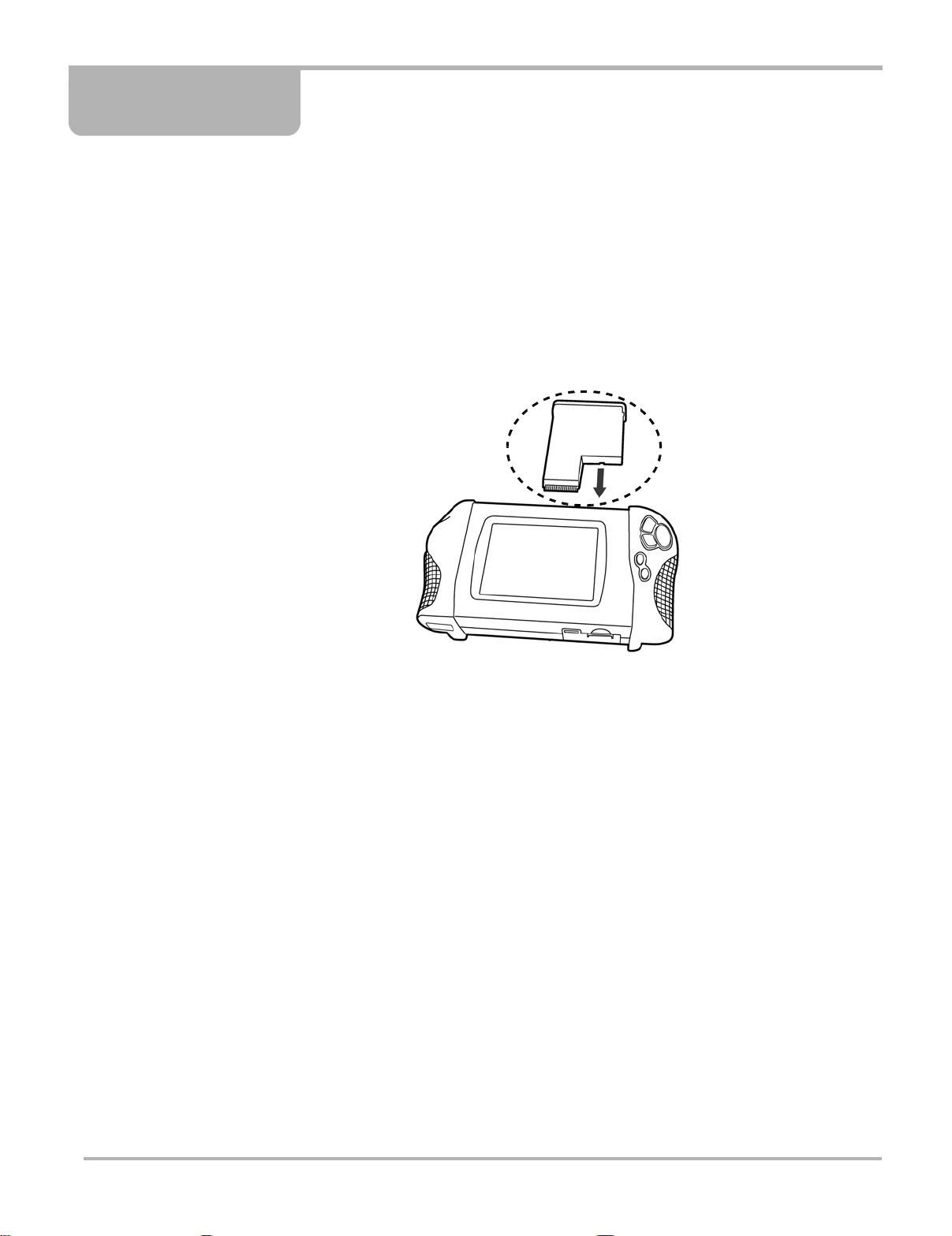
Chapter 2 Getting Started
This section explains how to get started using your MODIS™ Lab Scope Plug -in.
Before you can use your MODIS™ Lab Scope Plug-in, you must do the following:
1. Power the MODIS™ unit.
2. Connect leads and adapters, as needed.
2.1 Powering the MODIS™ Unit
Refer to your MODIS™ Display User Manual for more unit powering information.
z To power on the unit:
• Press the Power button.
2.2 Connecting Leads and Adapters
The following section explains how to connect the provided Lab Scope Plug-in lea ds and
adapters, as needed.
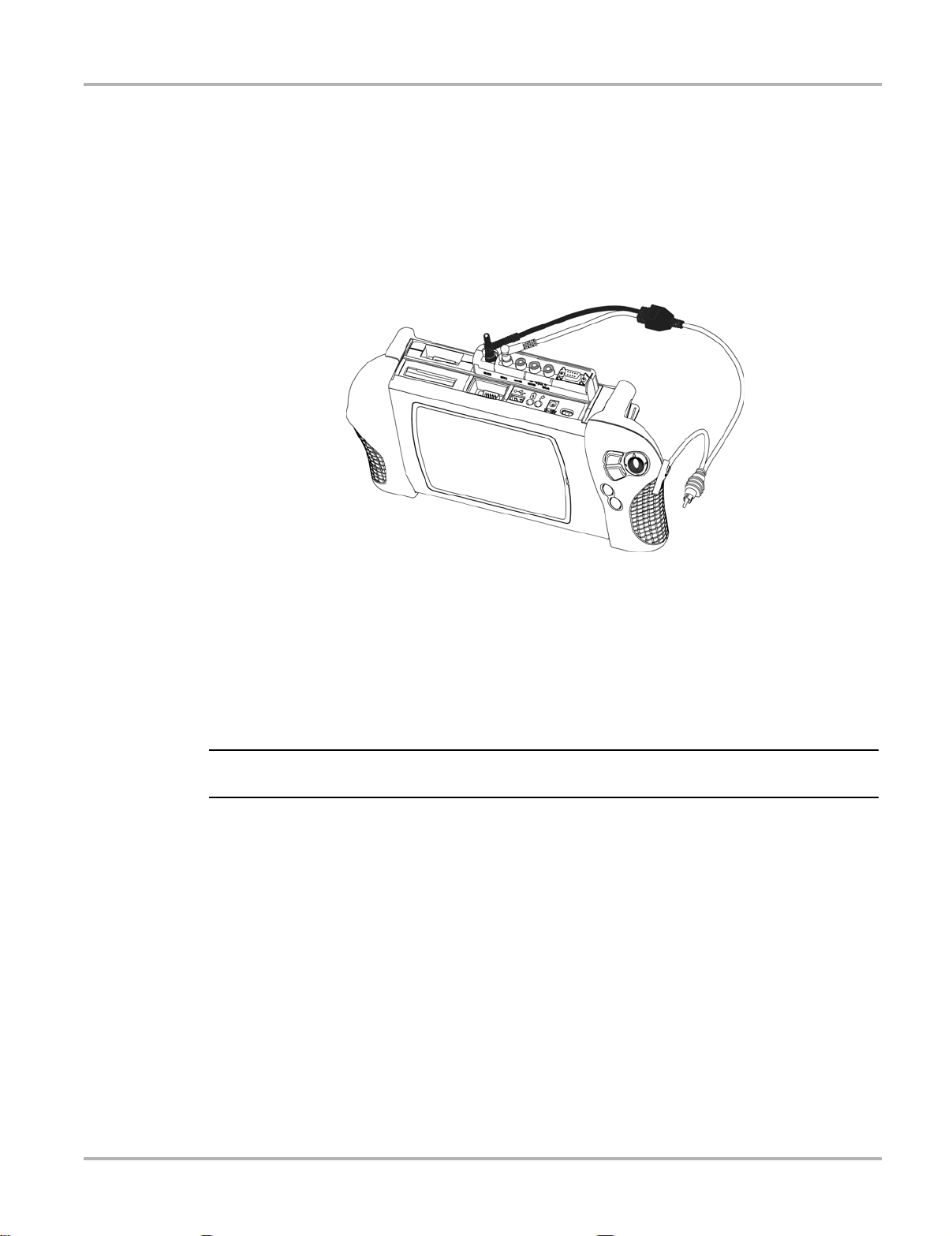
2.2.1 Channel One Lead
Figure 2-1 Sample yellow lead connection
4
Page 12
Getting Started Connecting Leads and Adapters
IMPORTANT:
z To connect the Channel 1 lead:
1. Plug the right-angled black ground plug to th e common gro und socke t on the Lab Sco pe
Plug-in. The black stackable plug is not connecte d to the lab scop e. It is used when
connecting another lead that requires a connectio n to the commo n ground so cket.
2. Plug the right-angled yellow connector into the socket labeled CH1.
3. Attach the yellow alligator clip to the yellow straight end of the lead and the black alligator clip
to the black straight end of the lead.
4. Connect both of the alligator clip ends to the test vehicle, as needed .
When another lead requires a connection to the lab scope common groun d socket, conne ct its
black common ground plug to the loose CH1 black sta ckable le ad. T his method allows m ultiple
common ground leads to be connected to the lab scope common ground socket. It also avoid s a
stack of common ground plugs sticking up from th e lab sco pe module. Refer to Figure2-2,
Figure 2-3 and Figure 2-4 for details.
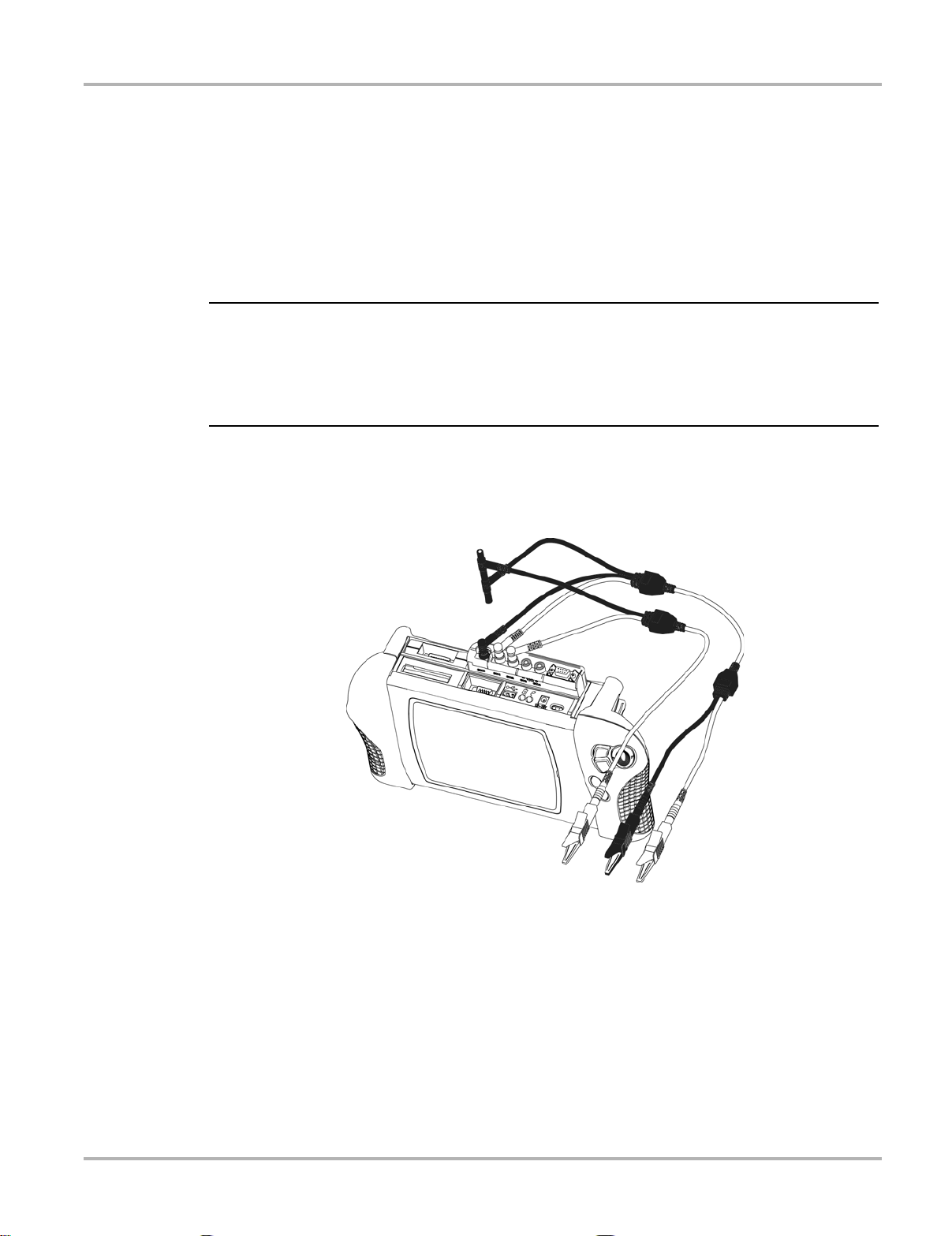
2.2.2 Channel Two Lead
z To connect the Channel 2 lead:
1. Plug the black ground plug of the Channel 2 lead into the stackable common ground plug of
the Channel 1 lead.
This ground connection shields the Channel 2 lead.
2. Plug the right-angled green connector into the socket labeled CH2 .
3. Attach the green alligator clip to the straight end of the Channel 2 lead.
4. Connect the alligator clip end to the test vehicle, as needed.
Figure 2-2 Sample green lead connection
5
Page 13
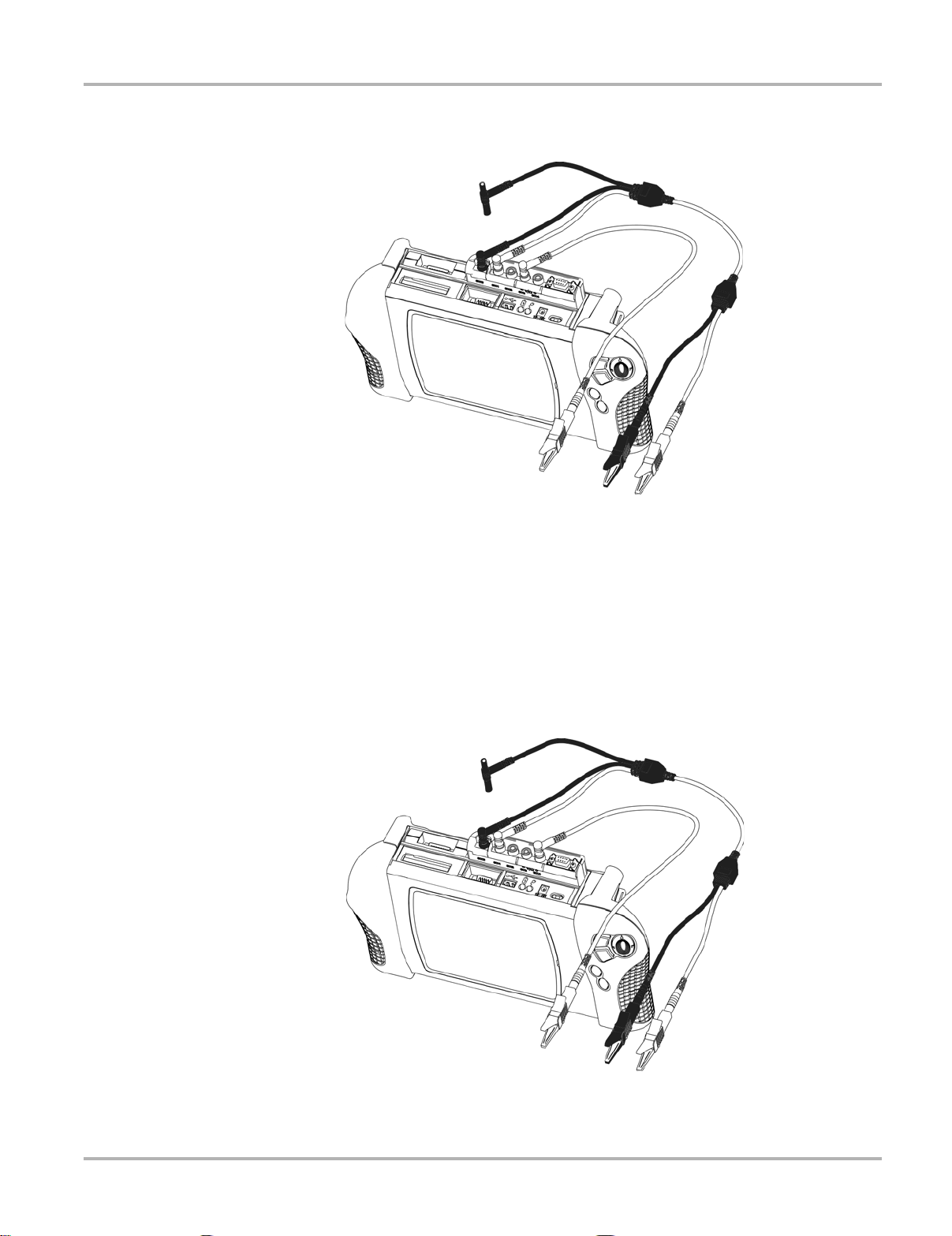
Getting Started Connecting Leads and Adapters
2.2.3 Channel Three Lead
Figure 2-3 Sample blue lead connection
z To connect the Channel 3 lead:
1. Plug the blue connector into the socket labeled CH3.
2. Attach the right-angled blue alligator clip to the straight end of the lead.
3. Connect the alligator clip end to the test vehicle, as needed.
2.2.4 Channel Four Lead
Figure 2-4 Sample red lead connection
6
Page 14
Getting Started Connecting Leads and Adapters
NOTE:
z To connect the Channel 4 lead:
1. Plug the red connector into the socket labeled CH4.
2. Attach the right-angled red alligator clip to the straight-end of the lead.
3. Connect the alligator clip end to the test vehicle, as needed.
2.2.5 Secondary Coil Adapter Lead
Figure 2-5 Sample Secondary Coil Adapter lead connection
z To connect the Secondary Coil Adapter lead:
1. Plug the right-angled black ground plug into the groun d socket on the Lab Scope Plug-in.
2. Plug the right-angled yellow connector into the socket labeled CH1.
3. Connect the ground clip to a good vehicle ground.
4. Connect the phono (RCA) plug into the clip -on coil wire adapter or coil adapters as needed for
the vehicle being tested.
i If you need to extend the length of the ground clip using a jumper wire, keep it as short as possible.
7
Page 15

Getting Started Connecting Leads and Adapters
2.2.6 Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter
Figure 2-6 Sample Inductive RPM Pickup adapter connection
z To connect the Inductive RPM Pickup adapter:
1. Connect the DB9F connector to the AUX port on the Lab Scope Plug-in.
2. Connect the RPM Pickup to the spark plug wire on cylinder number one.
8
Page 16
Chapter 3 Introduction
The Lab Scope Plug-in enables the following MODIS™ functions:
• Component Tests (Refer to your Component Tests User Manual for det ails.)
• Graphing Meter
• Digital Meter
• Lab Scope
• Ignition Scope
Figure 3-1
MODIS™ Lab Scope Plug-in
9
Page 17
Introduction Functional Description
3.1 Functional Description
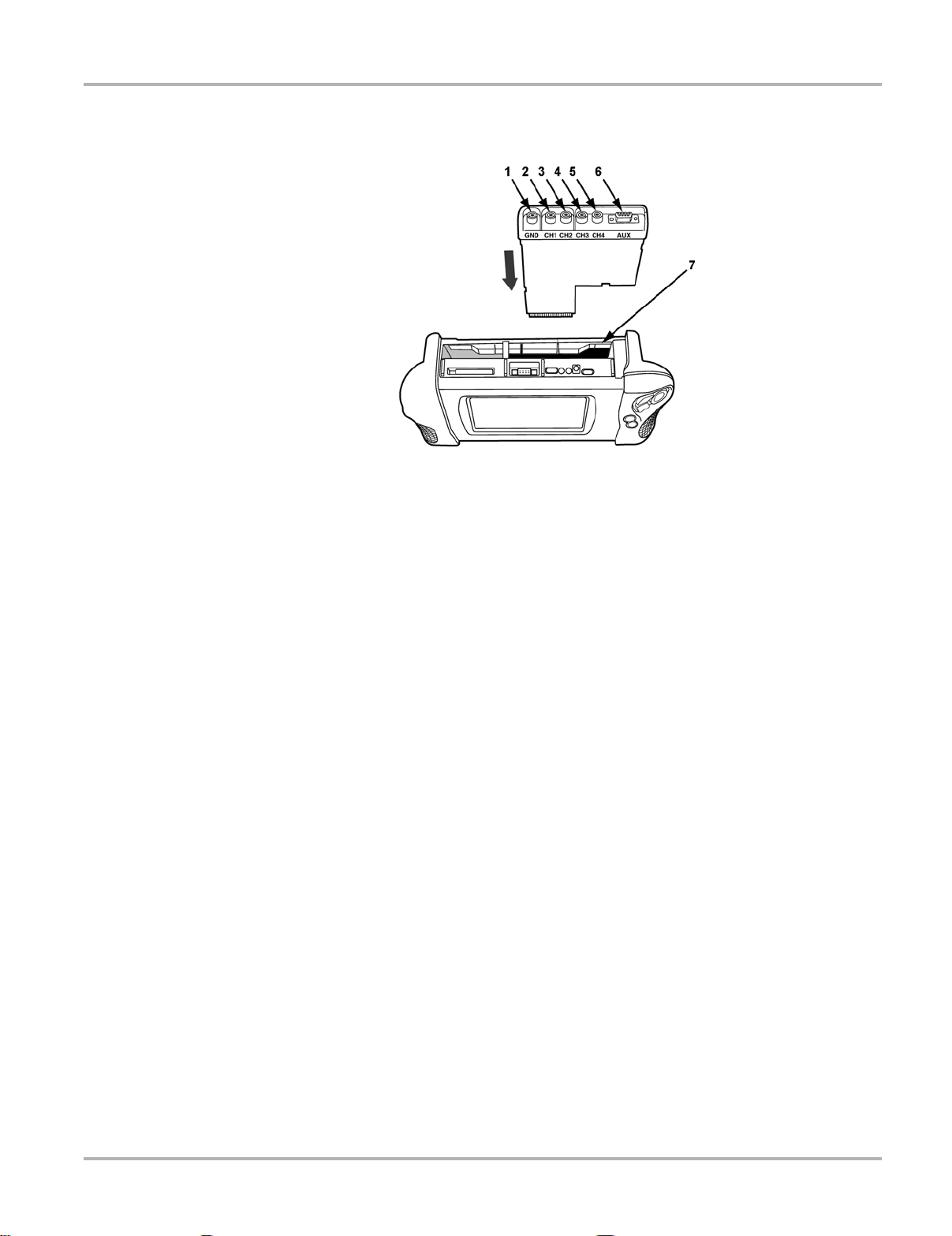
Figure 3-2 Top of MODIS™ unit and Lab Scope Plug-in
1— Common Ground socket
2— Channel 1 socket
Analog scope channel
3— Channel 2 socket
Analog scope channel
4— Channel 3 socket
Analog scope channel or DVOM minus lead
5— Channel 4 socket
Analog scope channel or DVOM plus lead
6— Aux Port (DB-9 PIN Female Connector)
Connection for an inductive RPM pickup or pressure/vacuum probe(s)
7— Lab Scope Plug-in slot
3.2 T echnical S pecifications
Dimensions:
Height:
7 1/2 inches
190.5 mm
Width:
5 3/4 inches
146.1 mm
Depth:
1 inch
25.4 mm
10
Page 18
Introduction Capabilities
Weight:
8.1 oz
229 g
Fuse:
5A (Buss® ATC, Littlefuse® ATO, or equivalent)
Operating Temperature Range (ambient):
At 0 to 90% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
32 to 104°F
0 to 40°C
Storage Temperature (ambient):
At 0 to 70% Relative Humidity (non-condensing)
–4 to 122°F
–20 to 50°C
3.3 Capabilities
The following tables detail the MODIS™ Lab Scope Plug-in capabilities.
Table 3-1
Channels 1–2 Common Grounds
Sample Rate
Bandwidth DC–3 MHz 3 db point @ 3 MHz
Input Impedance
V dc (Full Scale) 75 V maximum
V ac (Full Scale) Peak to
Peak Voltage
Table 3-2 Digital Meter Ohms and Diode Continuity tests
Channels 3–4
Input Impedance 10 M
Glitch capture Approximately 50 uS
Ohms 400
Diode Test 2 V Scale
Multimeter
Function Range Accuracy/Comments
Function Range Accuracy/Comments
6 MSPS
1.5 MSPS
@ DC
10 M
@ 3 MHz
5.8 k
50 V maximum
–40 M
Simultaneous
Continuous per channel
MSPS = mega samples
per second
All channels
Inputs between channels
3 (–) and 4 (+)
Fixed scales or Auto
Ranging
11
Page 19
Introduction Leads, Probes and Adapters
IMPORTANT:
Table 3-3
Channels 1–4 Common grounds
Sample Rate
Bandwidth DC–3 MHz 3 db point @ 3 MHz
Input Impedance
V dc (Full Scale) 100 mV–400 V
V ac (Full Scale) Peak to
Peak Voltage
Scope
Function Range Accuracy/Comments
CH1 = 6 MSPS
CH2 = 3 MSPS
CH3–4 = 1.5 MSPS
@ DC
10 M
@ 3 MHz
5.8 k
100 mV–400 V
Continuous
MSPS = mega samples
per second
All channels
3.4 Leads, Probes and Adapters
The Lab Scope Plug-in uses standard safety banana plu gs that ar e comp atib le with many
accessories. Your kit comes with the various leads, probes, clips, and adapters explained in this
section. See “Connecting Leads and Adapters” on page 4 for more information.
When removing leads from their sockets, do not pull on the wire because it can damage the leads.
Pull on the plug.
3.4.1 Channel 1 Lead
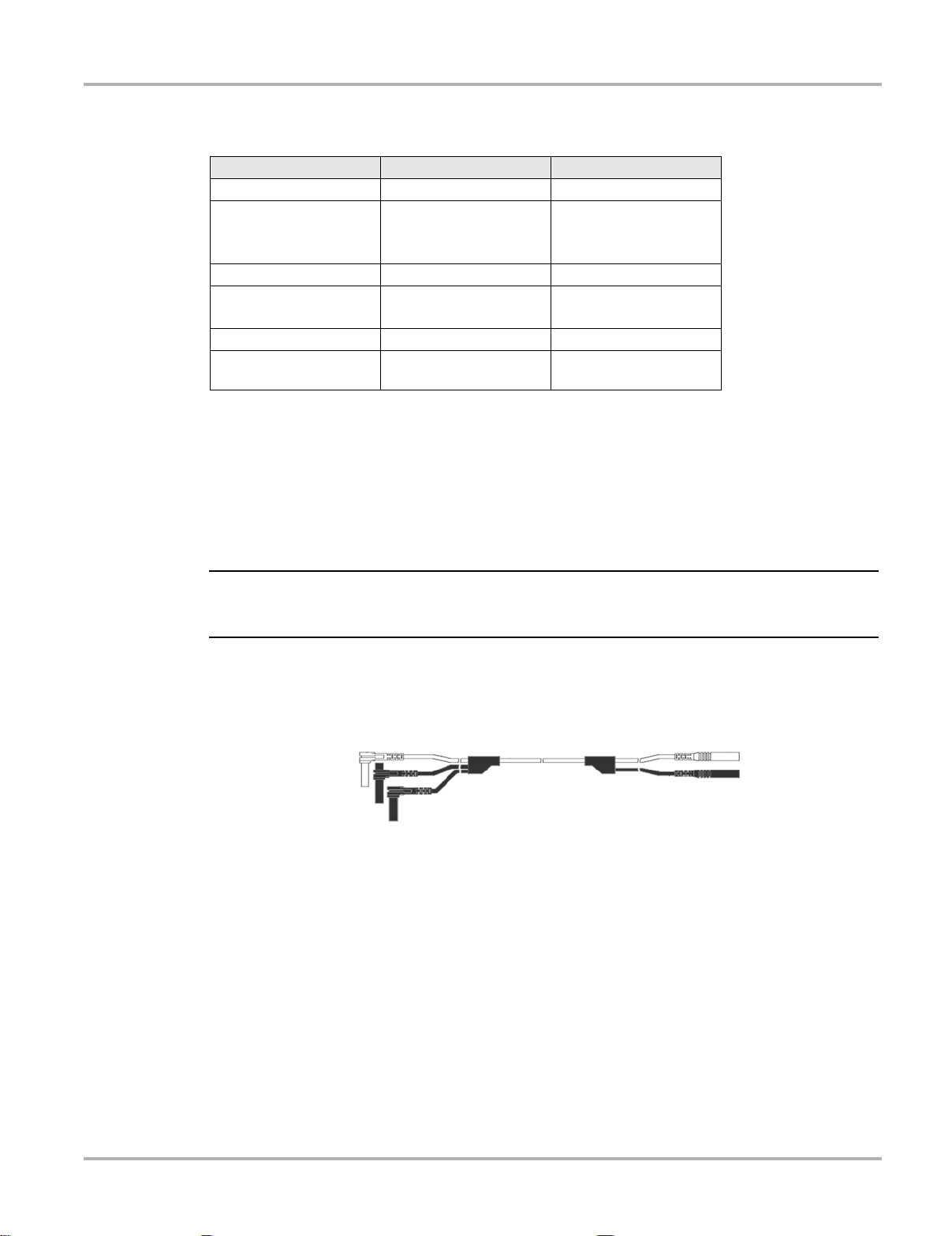
The shielded yellow lead is used for Channel 1 (Figure 3-3) and other channel connections that
need additional grounding. The lead color matches the color of the CH1 socket on the L ab Scope
Plug-in unit and the trace color of Ch 1 on the test screens. This yellow lead includes a black, r ightangle, common ground plug and a black, st acka ble, right- angle, commo n ground plug.
Figure 3-3 Yellow Channel 1 Lead
12
Page 20
Introduction Leads, Probes and Adapters
3.4.2 Channel 2 Lead
Figure 3-4 Green Channel 2 lead
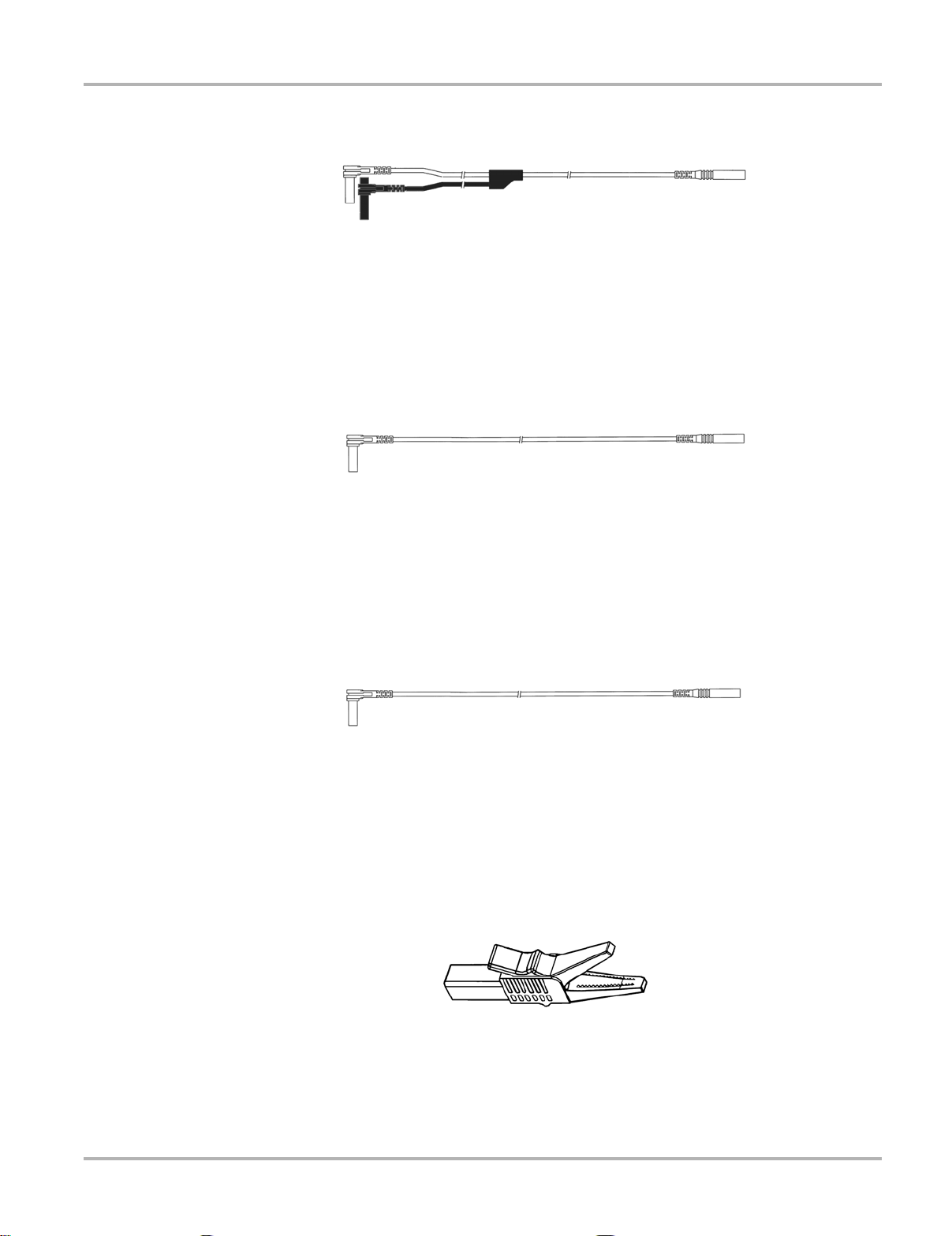
The shielded green lead (Figure 3-4) is used for Channel 2. The lead color matches the color of
the CH2 socket on the Lab Scope Plug-in and the trace color of Ch 2 on the test scre ens. This
green lead includes a stacka ble, black, right- angle, gr ound pl ug.
3.4.3 Channel 3 Lead
Figure 3-5 Blue Channel 3 lead
The non-shielded blue lead (Figure 3-5) is used for Channel 3 or Digital Meter minus (-). The lead
color matches the color of the CH3 socket on the Lab Scope Plug-in and the trace color of Ch 3
on the Lab Scope test screen.
3.4.4 Channel 4 Lead
The non-shielded red lead (Figure 3-6) used for Channel 4 or Digita l Meter plus (+). The lead color
matches the color of the CH4 socket on the Lab Scope Plug-in and the trace color of Ch 4 on the
Lab Scope test screen.
3.4.5 Alligator Clips
Figure 3-6 Red Channel 4 lead
Figure 3-7 Alligator clip
Four insulated alligator clips are included and colored to match each test lead, plus a black clip for
the common ground lead (Figure 3-7). Each clip plugs into the straight end of the channel leads.
13
Page 21
Introduction Leads, Probes and Adapters
3.4.6 Test Probes
Figure 3-8 Test probe
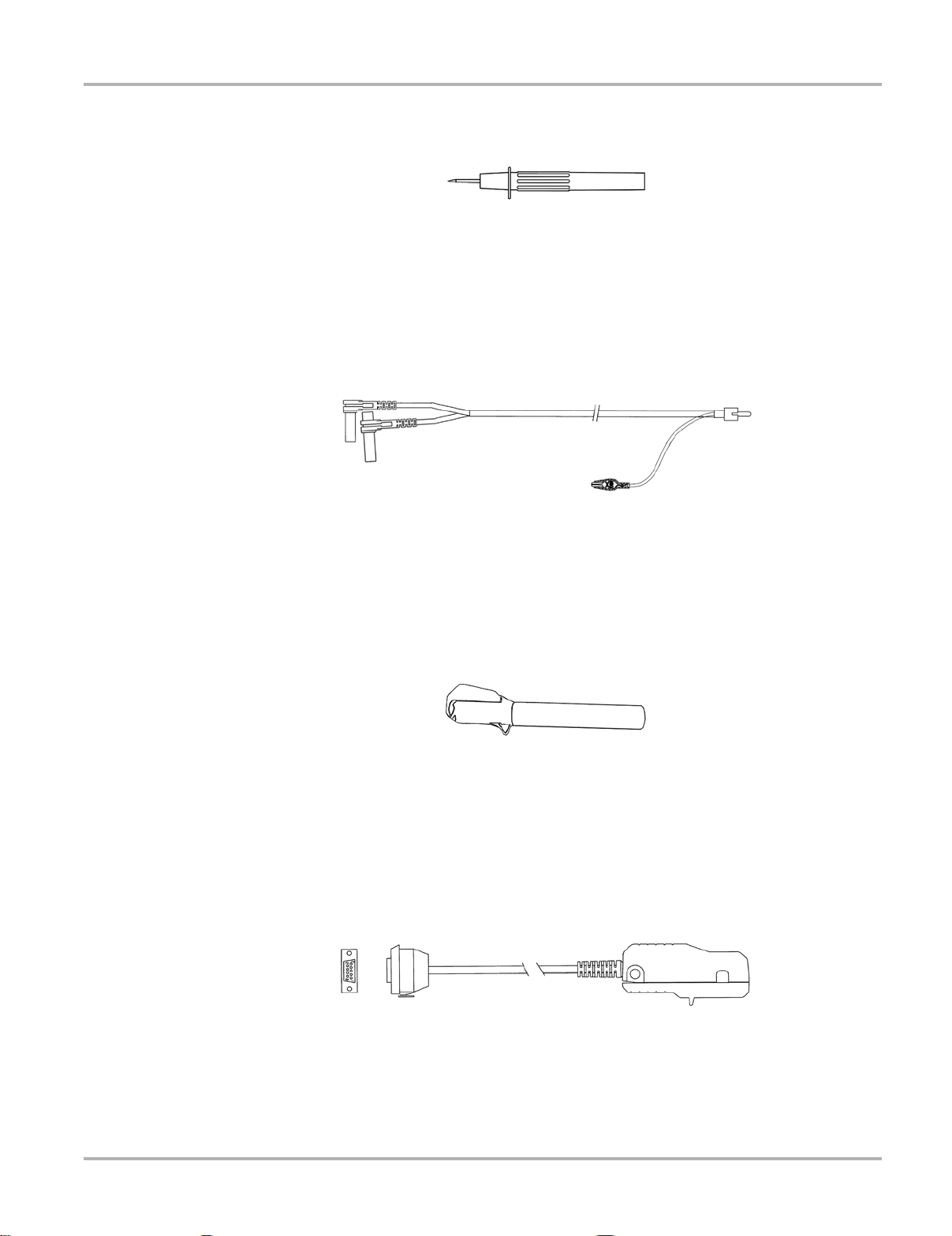
Two te st probes are included, one black a nd one red (Figure 3-8) and plug into the straight end of
the test leads.
3.4.7 Secondary Coil Adapter Lead
Figure 3-9 Secondary Coil Adapter lead
The Secondary Coil Adapter lead (Figure 3-9) connects to the clip-on secondary wire adapter,
coil-in-cap adapter or coil-on-plug adapter to display secondary waveforms.
3.4.8 Secondary Ignition Clip-on Wire Adapter
Figure 3-10 Secondary Ignition Clip-on Wire Adapter
The Secondary Ignition Clip-on Wire Adapter (Figure 3-10) connects the Secondary Coil Adapter
lead to the vehicle Secondary wire to display ignition patterns.
3.4.9 Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter
Figure 3-11 Inductive RPM Pickup adapter
The Inductive RPM Pickup adapter (Figure 3-11) connect s to the AUX port with a DB9F p lug to
trigger a waveform or display RPM. When used with the Ignition Scope, it conn ect s to cylinder
number one to establish proper cylinder order.
14
Page 22
Chapter 4 Navigation
This section provides Lab Scope Plug-in navigation information . For det a iled info rmation on
general MODIS™ navigation, refer to the MODIS™ Display User Manual.
4.1 Screen Layout
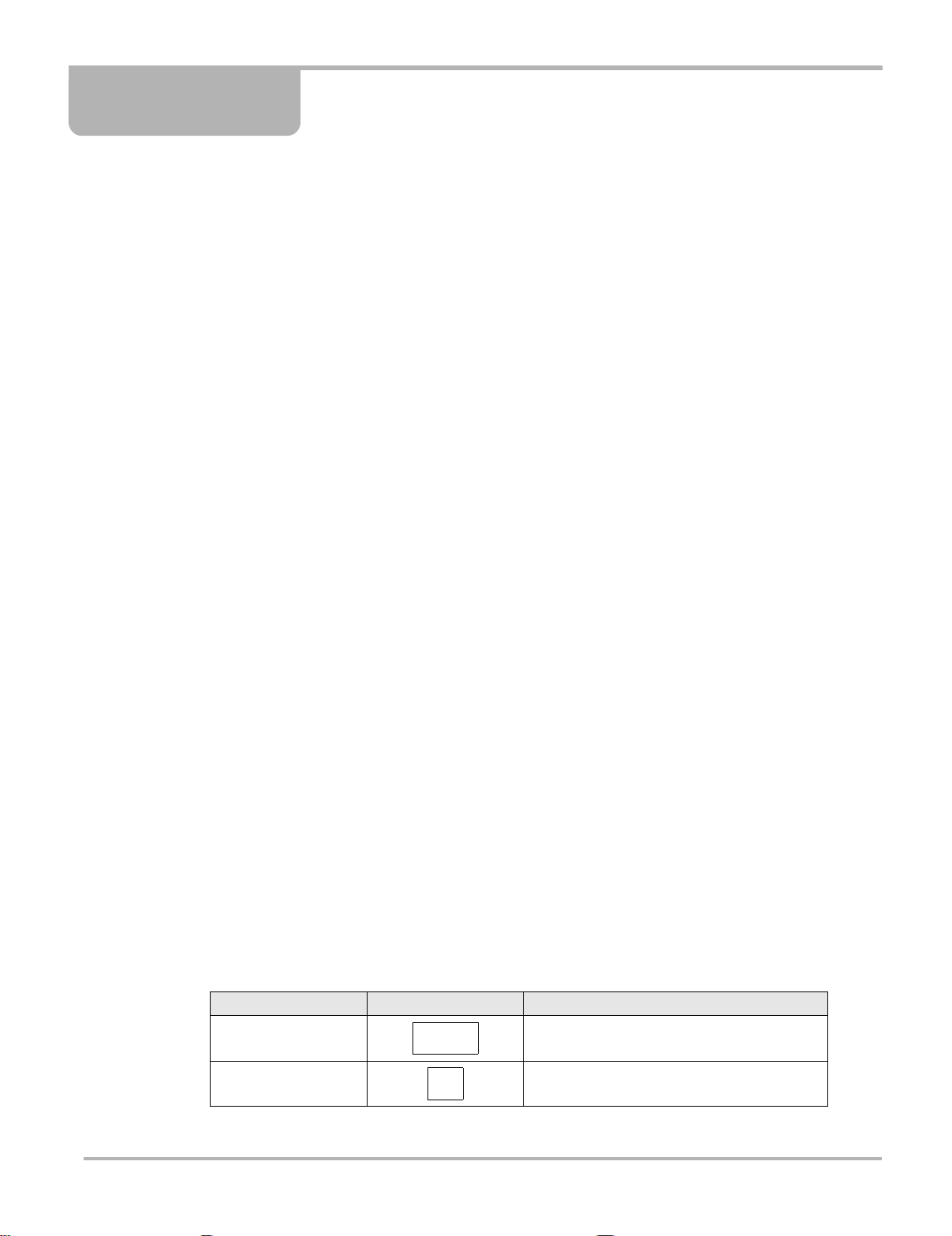
The Scope screens (Figure 4-1) include an upper toolbar , a main bo dy, and a lower toolbar.
Available buttons and controls vary depending on the active mode an d st age of op eration.
1— Upper toolbar
2— Main body
3— Lower toolbar
4.1.1 Upper Toolbar
The upper toolbar controls vary depending on the modu le and st ag e of oper ations ( Table 4-1).
Table 4-1 Upper toolbar controls (part 1 of 2)
Name Button Description
View Lets you change the way data displays
Pause
Figure 4-1
15
Sample Lab Scope Plug-in screen
Stops data collection and lets you review the
buffered data
Page 23

Navigation Screen Layout
Table 4-1 Upper toolbar controls (part 2 of 2)
Name Button Description
Play
Continuously captures data and stores it in the
Data Buffer
Cursors
Review
Snapshot
Zoom
Reset
Save Lets you store data and settings in memory
Print Lets you print the displayed screen
Setup
Lets you make digital amplitude, frequency,
and time measurements
Lets you adjust how the paused data scrolls
on-screen for reviewing
Lets you capture data when a problem occurs
while driving, and when you want to capture
data before and after a problem occurs
Lets you change the magnification of the
paused data
Lets you clear the Min/Max data for all digital
gauges
Lets you change the way information appears
on-screen and enter vehicle system
information
Data Buffer
The Data Buffer is located just below the up per toolbar buttons and indicates how mu ch test data
is stored. When the screen is paused, the positio n indicato r displays th e current fr ame nu mber
and the amount of data on the screen relative to the total data captured.
The Data Buffer cannot be highlighted or selected.
4.1.2 Main Body
The main body of Lab Scope Plug-in test screens displays the following:
• Channel status information
• Digital or graphical test results
• Saved data
• Cursors
4.1.3 Lower Toolbar
The lower toolbar controls vary depending on the active mode and stage of operation (Table 4-2).
16
Page 24

Navigation Making Selections
Table 4-2
Channel number Lets you select the channel to adjust
Probe
Scale
cal Indicates when a channel is calibrated or not
Signal Zero Offset
Raster Spacing
Sweep
Trigger Type
Slope
Lower toolbar controls
Name Button Description
Displays the current test connection for the
channel
Displays the current units of measurement for
the channel
Moves the selected channel’s zero (0) position
up or down within the test display area
Adjusts the vertical spacing between the
cylinders in the Ignition Scope Raster pattern
Sets the amount of time displayed across the
screen
Sets the criteria used to start the display of
data–there are three types of Trigger settings:
None, Channel, and Cyl
Lets you change the Trigger edge for the
specified channel from rising to falling
Trigger Position
Sensitivity Adjustment Lets you adjust the ignition scope sensitivity
z To move between the upper and lower toolbars:
• Press the up b and down d arrows.
When Easy Scroll is active, press the N/X button to move to the upper toolba r. Refer to the
MODIS™ Display User Manual for more Easy Scroll information.
4.2 Making Selections
Making selections consists of moving the cursor highlight using the Thumb Pad and pressing the
Y/a to complete the selection. When a right c arrow displays to the right of a menu option, you
can select from a submenu. For more information, refer to the Navigation chapter in your
MODIS™ Display User Manual.
Moves the trigger point for the specified
channel–it can be moved up, down, left, or right
17
Page 25

Chapter 5 Multimeter Operations
This section explains the Multimeter menu and operations.
Figure 5-1
The following is an outline of basic Multimeter softwa re ope ration.
1. Select Multimeter software—Select the type of Multimeter software and a test configuration
for the selected tool. See “Selecting Multimeter Sof twa re” on page 18.
2. Connect test leads—Connect appropriate leads and clips to the Lab Scope Plug-in unit. See
“Connecting Leads and Adapters” on p ag e 4.
3. Connect the Lab Scope Plug-in to the vehicle—Procedures will vary.
4. Perform the test—Set up, test, and evaluate test results. See “Performing Multimeter Tests”
on page 20.
Multimeter selection from main menu
5.1 Selecting Multimeter Software
There are two types of Multimeter tools available:
• Graphing Meter (See “Graphing Meter” on p ag e 19)
• Digital Meter (See “Digital Meter” on page 20)
z To select a Multimeter option:
1. From the main menu, select Multimeter > Graphing Meter or Digital Mete r.
2. Select a test option.
18
Page 26

Multimeter Operations Selecting Multimeter Software
5.1.1 Graphing Meter
Selections from the Graphing Meter menu configure your MODIS™ unit to functio n as a color
graphing meter. Table 5-1 describes the test options available.
Table 5-1
Dual Graphing Meter Displays two channels automatically
Volts DC Measures direct current voltage
Volts DC-A v erage
Volts AC rms
Frequency Measures the number of times a signal repeats itself per second
Pulse Width Measures the on-time of various components
Injector Pulse Width Measures the on-time of the signal that activates the fuel injector
Duty Cycle
Low Amps (20)
Low Amps (40)
MC Dwell (60)
MC Dwell (90)
100 psi Vacuum
100 psi Pressure
500 psi Pressure
5000 psi Pressure
Graphing Meter test options
Option Function
Measures direct current and uses a filter to remove excess noise/
hash on the signal
Measures the effective voltage rather than the Peak or Ave rag e
voltage
Measures the ratio of the pulse width to the complete cycle width,
the on-time of components that cycle on and off like EGR, or
canister purge from 0–100%
Measures current from components like ignition coils, injectors,
fuel pumps and parasitic draw using the Low Amp Probe
Measures current from components like fans and electric motors
using the Low Amp Probe
Measures carburetor Mixture Control Solenoids (0–60°). The duty
cycle of the solenoid is expressed in the dwell angle of a 6
cylinder engine: 100% = 60 deg = 360/6.
Measures fuel system Mixture Control Solenoids (0–90°). The
duty cycle of the solenoid is expressed in the dwell angle of a 4
cylinder engine: 100% = 90 deg = 360/4.
Measures engine vacuum 0–20 inHg using the 0–100 PSI
Transducer
Measures fuel systems, engine oil, and transmissions using the
0–100 PSI Transducer
Measures transmissions, compression, and AC high side
pressure using the 0–500 PSI Transducer
Measures ABS, power steering, and heavy-duty hydraulic
systems using the 0–5000 PSI Transducer
19
Page 27

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
5.1.2 Digital Meter
Selections from the Digital Meter menu configur e your Lab Scop e Plug-in to functi on as a Digit al
Volt Ohm Meter (DVOM). Table 5-2 describes the test options available.
Table 5-2
Volts DC Measures direct current voltage (GND and CH1)
Volts DC-A v erage
Volts AC rms
Ohms Measures electrical resistance (CH3 and CH4)
Diode/Continuity
Low Amps (20)
Low Amps (40)
Description of Digital Meter test options
Option Use
Measures direct current and uses a filter to remove excess noise/
hash on the signal (GND and CH1)
Measures the effective voltage rather than the Peak or Ave rag e
voltage (GND and CH1)
Measures voltage drop across a diode or continuity (CH3 and
CH4)
Measures current from components like ignition coils, injectors,
fuel pumps and parasitic draw using the Low Amp Probe (GND
and CH1)
Measures current from components like fans and electric motors
using the Low Amp Probe (GND and CH1)
5.2 Performing Multimeter T est s
After connecting the Lab Scope Plug-in to the test vehicle, you can proceed with testing. Button
and menu option availability vary depending on your test selection. When performing tests with
the Multimeter, the to olbars an d controls work the sa me as th ose in the Scope .
5.2.1 Changing Views
The VIEW button lets you change the way dat a displays.
z To change screen views:
1. Select View.
The dropdown menu displays (Figure 5-2).
Figure 5-2
2. Select Full Digital, Full Graph or Split Screen, which combin es the disp lay of graph an d
digital data.
The screen changes to reflect your selection.
Sample Graphing Meter VIEW menu
20
Page 28

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
5.2.2 Pausing Data
The Pause button stops data co llection and let s you re view dat a. The screen can b e p aused at
any time.
z To Pause test screen data:
• Press the Pause button.
The displayed data is no longer being updated, and the following three upper toolbar controls also
change:
– The Pause button replaces the Play button.
– The Position Indicator displays in the Data Buffer.
– The Review button is active.
– The Zoom button replaces the Snapshot button.
z To unpause test screen data:
• Press the Play button.
Live data displays and the toolbar controls r evert to their or iginal st a te.
Reviewing Data
The Review button is used with the Thumb Pad to review paused data.
There are two ways to review data:
• Manually
• Automatically
z To manually review data:
1. Select the Pause button.
2. Select the Review button.
3. Use the right c and left e arrows to review data one frame at a time.
4. Use the up b and down d arrows to review data a fraction of a frame at a time when possible.
i You can not r eview fractions of frame s in the Ign ition Scope .
z To automatically scroll paused data:
1. With the Review button selected, press Y/a again to display the menu of scroll options.
2. From the Review menu, select an option.
– Auto Scroll Fast automatically scrolls the data on-screen at full-speed.
– Auto Scroll Slow automatically scrolls the data on-screen at half-speed.
3. Press N/X to close the menu.
The Position Indicator displays the position of the current frame. Zero denotes the frame when the
button was pressed. Frames captured before p ausing are negative (–) ; frames captured af ter are
positive (+).
21
Page 29

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
5.2.3 Using Zoom
The Zoom button let s you choose a macro view of the dat a and appears in place of the Snapshot
button when the display is paused.
z To zoom the view of paused test screens:
1. Select Zoom.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Select an option from the menu.
The screen changes to reflect your selection and the on-screen Zoom Cursor L ine disp lays.
3. To see a point of interest in detail:
a. Select Review.
b. Use the left e and right c arrows to move the Zoom Cursor Line.
c. Select Zoom > 1x.
5.2.4 Using Cursors
The Cursors button lets you make digi t al amplitude , fr equen cy, and time measurements of
paused and live data.
z To use the cursors:
1. Select the Cursors button.
Two vertical cur sor lines display on-screen .
Figure 5-3
2. Press the right c and left e arrows to move the selected cursor line.
3. Press Y/a to change the active cursor.
4. Press N/X when you are finished setting cursors.
A confirmation message displays asking how you want to proceed using cursors.
5. Press Y/a or N/X as desired.
Cursors sample screen
22
Page 30

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
z To turn cursors off:
1. Select Cursors.
2. Press N/X twice.
The cursor lines disappear .
5.2.5 Taking Snapshot s
The Snapshot button let s you capt ure da t a before and after a problem occurs while driving.
z To take a snapshot:
1. Select the Snapshot button.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Select Manual.
The Snapshot button blin ks, indicating that Manual Snapshot mode is armed.
3. Press Y/a to take a snapshot.
The Collecting Snapshot message displays, indicating that Snapshot data is being collected.
When the Snapshot finishes saving, a final confirmation message displays.
When the confirmation message disappears, you are returned to the test scr een with th e
blinking Snapshot button still armed.
4. Press N/X to disarm Snapshot.
i The saved snapshot can be retrieved from Save Data. Refer to the MODIS™ Display User Manual
for details.
Changing Snapshot Settings
You can set up a snapshot in the following ways:
• Select the file type—snapshot images can be saved as a bitmap or jpeg file.
• Adjust the percentage after trigger—snapshots can be between 10% and 90% data
captured after triggering.
• Save to different locations—snapshot s can be saved to the MODIS™ internal m emory or to
the CF card in the top slot.
z To change Snapshot settings:
1. From the MODIS™ main menu, select Utilities > Tool Setup > Save Data.
The Save Data dialog box displays (Figure 5-4).
Figure 5-4
23
Sample Save Data dialog box
Page 31

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
2. Select the File Type d ropdo wn men u.
3. Select a file type setting.
4. Select the % After Tr igger dr opdown m enu.
5. Select a % After Trigger setting.
6. Press N/X to close the dialog box.
5.2.6 Resetting Gauges
The Reset butto n lets you clear the m in/max values recorded for all digit al gauges. Use the Reset
button to:
• Track the variation in a componen t or circuit under a cert ain condition . If the condition
changes, Reset lets you start tracking again to see the change.
• Verify that a connecti on problem you found by looking for a dropout or spike in min/max values
has been fixed.
z To reset the min/max digital values:
• Select Reset.
A confirmation message displays.
When the reset is complete, the confirmation message disappear s.
5.2.7 Saving Data
The Save button lets you store data in memory.
z To save data:
1. Select the Save button.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Select an option:
– Save Movie—This feature allows you to save up to 2000 frames of data (buffered data
plus data transmitted after triggering).
– Save Frame—This feature allows you to save up to 512 frames of buffered data (data
held in scan tool memory).
– Save Image—This feature allows you to capture a single screen as an image. Image files
can be opened with common computer programs, such as Microsoft Pa int.
The Setup Saved Data Notation di alog box di splays.
3. Select from the menus to set preferences as necessary.
The Setup Saved Data Notation dialog box works the same as the Edit Sa ved Da t a Notation
dialog box found in the Saved Data mode. Refe r to the MODIS™ Display User Manual for
operating details.
i If you plan to save many screens from the same vehicle, select Yes for Keep Entries. This
preference retains your settings the next time you select Save.
24
Page 32

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
NOTE:
4. When you are finished setting preferences, select Save.
A confirmation message displays with saved data retrieval instructions.
5. Press Y/a to close the confirmation message.
5.2.8 Printing
The Print button lets you print the displa yed scree n.
i Selecting Inverse Colors from the Setup button menu reduces the amount of ink used by your
printer when printing files.
z To print:
1. Select the Print button.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Press Y/a.
The screen prints according to your printer settings. Refer to th e MODIS™ Display User
Manual for printer setup details.
i Make sure the infrared transceiver on top of the MODIS™ unit is pointed at the infrared
transceiver of the printer and there is nothing in between them.
5.2.9 Using Setup
The Setup button lets you change the way information displays.
z To use Setup:
1. Select the Setup button.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Select one of the following options:
– Units
– Grid
– Scales Display
– Inverse Colors
– Save Data
Units
Selecting Units opens the Units dialog box (Figure 5-5), which lets you change the displayed units
of measurement for vacuum, pressure, and gas concentration.
25
Page 33

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
Figure 5-5 Sample Units dialog box
The Display As dropdown menu sets how the sca le units are displayed on the Scale button and
in the Channel S t atus area. Th e Scale button, on the lower too lbar, displays the scale setting for
the currently selected channel. The Channel Status area, at the top of the test portion of the
screen, displays the scale settings for all channels.
There are three Display As scale unit options:
• Units/Division—the scale value for a major grid division is displayed in the Chann el Status
Area and the Scale button.
• Full Scale—the scale value for the whole grid is displayed in the Channel S tatus Ar ea and the
Scale button.
• Factory Default—the Channel S tatus area displays th e Units/Division for all active channels
and the Scale button displays the full scale value.
i The Units dialog box can also be accessed from the Utilities menu located on the Tool Setup
submenu as described in the MODIS™ Display User Manual.
z To change units:
1. Select Setup > Units.
The Units dialog box displays.
2. Change the unit values as needed.
3. Press N/X to close the dialog box.
Grid
Selecting Grid displays the background grid pattern on all graphing test screens.
z To turn the grid on:
• Select Setup > Grid.
A grid appears in the test area.
Scales Display
Selecting Scales Display displays the scale values on the graph.
z To turn Scales Display on:
• Select Setup > Scales Display.
The scale values appear along the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical) axis of the g raph.
26
Page 34

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
Inverse Colors
Selecting Inverse Colors changes the color scheme.
z To change the color scheme:
• Select Setup > Inverse Colors.
The color scheme changes to a lighter background with da rker traces. This selection reduces
the amount of ink used when printing screens.
Save Data
Selecting Save Data opens the Save Data di alog box, which is u sed to configur e how data is
saved. This allows you to quickly reset save options without returning to the main menu.
5.2.10 Calibration Indicator
The cal LED, in the lower toolbar, indicates whether a channel is calibrated or not during Ohms,
Diodes, Continuity, or Pressure transducers testing. The LED is:
• Green—when calibrated
• Red—when not calibrated (using previous calibration values)
When you select Ohms, Diodes, Continuity, or Pr essure transducers tests, a message similar to
the one below displays with instructions to assist you with the calibration process.
5.2.1 1 Adjusting Channel Settings
The Channel control bar (Figure 5-6) lets you adjust channel settings and viewing characteristics.
Figure 5-6
1— Channel Number
2— Probe
3— Scale
4— Signal Zero Offset
5— Threshold
Sample Channel control bar
Channel Number
The Channel Number button lets you select channel options.
• Channel One (Ch 1) is automatically displayed and cannot be turned off.
• Channel Two (Ch 2 ) can b e manually se lected for displa y.
27
Page 35

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
i Both channels automatically display in the Dual Graphing Meter.
The following channel options are available:
• Displayed makes a channel’s waveform visible.
• Peak Detect captures fast events, spikes and glitches for signals going in both positive and
negative directions.
• Filter minimizes unwanted noise in the Graphing Meter.
z To display Channel Two:
1. Select the Channel Number button from the Channel control bar.
The channel setup menu displays.
2. Select Ch 2 > Displayed.
The Channel T wo trace displays.
3. Press N/X to close the menu.
z To change the channel setup:
1. Select the Channel Number button from the Channel control bar.
The channel setup menu displays.
2. Select the channel you want to change (Ch 1 or Ch 2).
3. Select the Peak Detect or Filter channel setup option.
See “When To Use Peak Detect” on page 48 and “When to Use Filter” on page 54 for details.
Probe
The Probe button lets you select a different test.
z To select a different test:
1. Select the Probe button.
The Probe menu displays.
2. Select an option.
The Probe button changes to indicate your selection.
Scale
The Scale button lets you select a measurement scale for each channel.
z To select a measurement scale:
1. Select the Scale button to open the Scale menu.
2. Select an option.
The Scale button and the waveforms on-screen chang e to reflect your selecti on.
28
Page 36

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
Signal Zero Offset
The Signal Zero Offset button moves the zero (0) position of the selected channel up or down.
z To move a zero position:
1. Select the Signal Zero Offset button.
The button appears depressed and highlighted to indicate that the function is on (Figure 5-7).
Figure 5-7
2. Press the up b or down d arrows as needed to move the zero point (Figure 5-8).
3. Press N/X to exit the function.
Sample Signal Zero Offset selection
Figure 5-8
Sample zero position
29
Page 37

Multimeter Operations Performing Multimeter Test s
NOTE:
NOTE:
Threshold
The Threshold button changes the reference point on the wavefor m and is only u sed when
calculating measurements such as frequency, duty cycle, MC dwell and pulse width. There are
two threshold options:
• Auto Threshold Select (ATS)—automatically picks a threshold level in the middle of the
range in which the waveform travels. A TS default s to a falling edge.
• Manual Threshold Select (MTS)—lets you man ually pick a signal le vel and d irection to use
as a reference point. This is used if ATS picks a level that does not give the desired result.
z To change the threshold level:
1. Select the Threshold button.
The Threshold menu displays.
2. Select an option.
z To use the Manual Threshold option:
1. Select Manual Threshold Select as described in the previous procedu re.
The Manual Threshold Select dialog box displays (Figur e 5-9).
Figure 5-9
The Signal Min and Max display to the left and right of the Th reshold value for refer ence.
Measuring the Min and Max may take a few seconds.
2. Change the Threshold value and th e Slope, as ne eded.
Sample Manual Threshold Select dialog box
i Threshold can only be changed to a value that is between the Min and Max of the signal.
3. Press N/X to exit the dialog box.
5.2.12 Setting the Sweep Time
The Sweep button sets the amo unt of time dat a cr ossed the screen fro m lef t to right.
z To change the sweep time:
1. Press the Sweep button.
The dropdown menu displays.
2. Select an option.
i Sweeps shorter than 1 second will collect some frames after the Pause button is selected. The
faster the sweep, the more frames will be collected.
30
Page 38

Chapter 6 Scope Operations
NOTE:
This section explains the Scope menu and operations.
i Most of the Scope toolbars and controls work the same as the Multimeter . Only the differences are
covered in this section.
Figure 6-1
The Scope menu offers the following options (Figu re 6-1):
• Lab Scope
• Ignition Scope
• Presets
The following is an outline of basic Scope software op erati on.
1. Select Scope Software—Select the type of Scope software and a test configuration for the
selected tool. See “Selecting Scope Softwa re” on p ag e 31.
2. Connect test leads—Connect appropriate leads and clips to the Lab Scope Plug-in unit. See
“Connecting Leads and Adapters” on p ag e 4.
3. Connect the Lab Scope Plug-in to the vehicle—Procedures will vary.
4. Perform the test—Set up, test, and evaluate test results. See “Performing Scope Tests” on
page 35.
Scope selection from main menu
6.1 Selecting Scope Software
There are two types of scope tools available:
• Lab Scope (See “Lab Scope” on page 32)
31
Page 39

Scope Operations Selecting Scope Software
• Ignition Scope (See “Ignition Scope” on page 32)
The following procedures explain how to select a scope tool.
z To select scope software:
1. From the main menu, select Scope > Lab Scope or Igniti on Scope .
2. Select a test configuration.
6.1.1 Lab Scope
Selections from the Lab Scope menu configure your Lab Scop e Plug-in to function a s a
four-channel display. Table 6-1 describes the available test options.
Table 6-1
4 Ch Lab Scope Displays four channels automatically
Volts DC Measures direct current voltage
Low Amps (20)
Low Amps (40)
Ignition Probe
100 psi Vacuum Measures engine vacuum 0–20 inHg using the 0–100 PSI Transducer
100 psi Pressure
500 psi Pressure
5000 psi Pressure
Lab Scope test configuration options
Option Function
6.1.2 Ignition Scope
The Ignition Scope module configures the MODIS™ unit to view a secondary waveform using
preset ignition pattern display options:
Measures current from components like ignition coils, injectors, fuel
pumps and parasitic draw using the Low Amp Probe
Measures current from components like fans and electric motors using
the Low Amp Probe
Measures secondary ignition system voltage using a secondary coil
adapter lead and pickups
Measures fuel systems, engine oil, and transmissions using the 0–100
PSI Transducer
Measures transmissions, compression, and AC high side pressure
using the 0–500 PSI Transducer
Measures ABS, power steering, and heavy-duty hydraulic systems
using the 0–5000 PSI Transducer
• Parade
• Cylinder
• Raster
• Superimposed
• Single Cylinder Ignition
Each of these options are explained in “Ignition Patterns” on p ag e 33.
Connecting to all cylinders of an engine at the same time simplifies cylinder co mp ariso n in the
following ways:
• All cylinders can be viewed at once.
32
Page 40

Scope Operations Selecting Scope Software
NOTE:
NOTE:
• Each cylinder is displayed once per screen in firing or der and is displayed in the same location
on-screen.
• The same pattern is displayed regardless of engine RPM.
The Ignition Scope requires the use of two leads.
• Secondary Coil adapter–to display the secondary wavefo rm
• Inductive RPM Pickup adapter–to identify cylinder number one for proper cylinder order
display. Refer to “Connecting Leads and Adapters” on page 4 for more details.
• RPM can be calculated from either the gray Inductive RPM pickup adapter or the Secondary
Coil adapter. If only the RPM or Secondary Coil adapter is used, RPM will be calculated from
whichever lead is connected. If both leads are connected, RPM will be calculated from the
gray Inductive RPM pickup.
i The optional SIA 2000 Adapter Kit is required to connect to multiple cylinders at once on Wasted
Spark distributorless ignition systems. Contact your sales representative for details.
Note the following regarding Ignition Scope synchronization:
• Synchronization to cylinder number one may take seve ral seco nds after the engine starts.
• Cylinder firings may be observed to change position during the synchronizatio n process.
• If the Ignition Scope settings are changed, cylinder synchronization reoccurs.
i When testing Wasted Spark systems, power firings will display on Channel One and wasted on
Channel Two.
Ignition Patterns
Four ignition pattern options are available to view and compare the secondary waveform for all
engine cylinders.
• The Parade pattern displays the secondary waveform for each cylinder in the firing order from
left to right across the screen.
• The Cylinder pattern displays the secondary waveform for the se lected cylinder.
• The Raster pattern displays the secondary wave form for e ach cylinder in th e firing o rder,
starting with cylinder number one at the bottom.
• The Superimposed pattern displays the secondar y waveform for ea ch cylinder in the fir ing
order stacked on top of each other.
The Single Cylinder Ignition option configures the MODIS™ unit to connect to an individ ual
cylinder using a fixed time sweep when a lead is not available to conn ect to all cylinders.
Ignition Scope Probe
The Channel One (Ch 1) Probe button setting is restricted to Ignition Probe. The Channel T wo (Ch
2) Probe button setting is not restricted and functions the same as in the Lab Scope. See “Probe”
on page 39.
33
Page 41

Scope Operations Selecting Scope Software
NOTE:
NOTE:
Sensitivity Adjustment
The Sensitivity Adjustment button at the far right of the lower to olbar let s you set the detection
sensitivity to cylinder firings. The lower the setting, the more sensitive the ignition scope will be for
detecting cylinder firing. Adjusting the sensitivity and improve cylinder detection increases the
range of vehicles that can be tested and the range of secon dary picku ps tha t can be used.
z To adjust cylinder firing detection sensitivity:
1. Select the Sensitivity Adjustment button.
The button appears depressed and remains highlighted to indi cate that the functio n is on.
2. Press the up b or down d arrows as needed to reposition the level indicator on the left of the
graph (x-axis).
i Unless you are having problems detecting cylinders, a sensitivity setting of 2.0 kV is optimal for
many ignition systems.
3. When you are finished setting the sensitivity, press N/X to deselect the button.
i With Wasted Spark ignitio n systems, the sensitivity le vel settin g only displays on Ch annel 1 , but
the setting applies to both channels.
See “Using Sensitivity Adjustment” on page 59 for usage details.
Missed Cylinder Detection
When a cylinder firing is not detected because it is either firing too low to be detected a t the current
setting or is not firing at all, a blank space displays in the on-scre en p atter n.
z To verify a missed cylinder firing:
• Lower the sensitivity setting to verify that the cylinder is firing, but firing too low to be detected
at the current sensitivity setting.
If a cylinder is not firing at all, the blank space on the graph will remain.
See “Sensitivity Adjustment” on page 34 for more details.
Digital kV View
When using the ignition scope, the Digital kV view selection (available from the View button on
the upper toolbar) displays the digital kV readings correspo nding to the selected chann el of the
ignition scope. This provides another way to monitor the second ary ignition system. When testing
Wasted Spark ignition systems, Power firings display on channel one and Wasted Spark firings
display on channel two.
34
Page 42

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
NOTE:
IMPORTANT:
i The digital values are only as good as the source waveform. If there is a problem with the lead
connection or set up and a stable waveform is not displaye d, the d igit al value m ay not be
calculated correctly. If problems are experienced with the digital values, check lead connections
and Ignition Setup. If a measurement cannot be calculated, dashes display in place o f values.
Firing kV, Spar k kV, and S p ark Duration (burn ) measurement s are calculated from the seco ndary
waveform.
• Firing kV (FKV)—voltage required to overcome the rotor and sp ark p lug gap s and est ab lish
a spark across the spark plug electro des.
• Spark kV (SKV)—voltag e require d to maint a in a sp ar k across the sp ar k plug electrodes.
• Spark Durat ion (Bur n)—time the spark is maintained across the spark plug electrodes.
Min/Max and current values for Firing kV, Sp ark kV, and Spark Duration are displayed as digital
values for each cylinder in the firing order. Intermittent problems that happen to o fast to be seen
on the live waveform will be captured in the Min/Max reading, making it possible to spot problems
that can be difficult to see in the live waveform.
Multiple Spark Ignition Systems
On vehicles with multiple spark ignition systems, when more than one spark per cylinder is
present, Firing kV (FKV) is calculated at the start of the first spark and Sp ark kV (SKV) and Burn
are calculated from the last spark.
z To calculate the Digital kV and Burn measurements:
• Select an ignition pattern with a 10 ms sweep, such as Parade 10 ms or Cyl 10 ms when
testing a multiple spark system.
Digital kV cannot be correctly calculated if, in the Ignition Scope view , the end of the last spark for
each cylinder is near the end of the screen or of f o f th e screen.
6.2 Performing Scope T est s
When performing tests with the Scope, the toolbars and controls work the same as those in the
Multimeter . The fo llowing explains the differences.
6.2.1 Changing View
The View button lets you change the way data displays.
z To change screen views:
1. Select View.
The dropdown menu displays.
35
Page 43

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
2. Select an option from the menu.
The screen changes to reflect your selection.
6.2.2 Saving Data
The Save button lets you store dat a and scope setting s.
z To save scope settings:
1. Select Save.
The dropdown menu displays.
2. Select a save option:
– Save Movie—This feature allows you to save up to 2000 frames of data (buffered data
plus data transmitted after triggering).
– Save Frame—This feature allows you to save up to 512 frames of buffered data (data
held in scan tool memory).
– Save Preset—This feature allows you to save the current scope settings as a preset.
– Save Image—This feature allows you to capture a single screen as an image. Image files
can be opened with common computer programs, such as Microsoft Pa int.
Presets
A preset is the configuration of your screen setup prefere nces. Saved p reset s can be used fo r
later testing. See “Using Presets” on pa ge 41 for more information.
z To save a preset:
1. Select Save.
A dropdown menu displays.
2. Select Save Preset.
A confirmation message displays with saved preset retrieval instructions.
3. Press Y/a to close the confirmation message.
6.2.3 Using Setup
The Setup button on the upper toolbar let s you chan ge the way infor mation ap pears on-scre en.
See “Using Setup” on page 25 for information about the previously-covered options: Units, Grid,
Scales Display , Inverse Colors, and Save Dat a.
The following sections cover the Lab Scope-specific Setup menu options Ignition System and
Trigger Display.
36
Page 44

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
Ignition System
Before ignition testing can begin, the ignition system type and relevant parameters should be
selected. Selecting Ignition System displays the Ignition System dialog box (Figure 6-2) that lets
you select the following for the test vehicle:
• Ignition Type
• Cylinders
• Firing Order
• #1 Trigger (Inductive RPM Pickup connection)
• Polarity
• RPM Factor
Figure 6-2
The following ignition types and settings are available:
Sample Ignition System dialog box
• Stan dard (Coil)—The Inductive RPM Pickup connects to the coil wire on a distributor system.
Set the number of cylinders and cylinder firing order.
• Stan dard (Plug)—The Inductive RPM Pickup connect s to a plug wire on a distributor system.
Set the number of cylinders and cylinder firing order.
• Wasted Sp ark—The Inductive RPM Pickup connects to a plug wire on a wasted spark
distributorless system. Set the number of cylinders, cylinder firing order, and polarity.
Be sure the firing order and cylinder firing p olarity values are correctly set up before using the
Ignition Scope to test Wasted S p ark systems.
• Direct—The Inductive RPM Pickup connects to plug wire (if app licable) on a di rect ignition
system. Set the number of cylinders and cylinder firing ord er.
If connecting the inductive RPM lead to display RPM, the lead can be connected to any plug
wire that is accessible. If using the Ignition scope, the lead must be connected to the #1 spark
plug wire so that the cylinders firings are displayed in the correct or der.
• Other—The Inductive RPM Pickup connects to a plug or a coil wire. Set the RPM factor
appropriate for the test vehicle.
The Ignition System dialog box can also be a ccessed fro m the Utilities > Tool Setup menu.
Refer to your MODIS™ Display User Manual for more information.
Inductive RPM Pickup Testing T ips:
•
When only the Inductive RPM Pickup lead is connected to display RPM, the lead can be
connected to any plug wire that is accessible.
• When using the Ignition Scope, the Inductive RPM Pickup lead must be connected to the #1
spark plug wire so that the cylinder firings are displayed in the cor rect order.
37
Page 45

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
z To change Ignition System settings:
1. Select Setup > Ignition System.
The Ignition System dialog box displays.
2. Select the Ignition System values as needed.
3. Press N/X to close the dialog box.
Trigger Display
Selecting Trigger Display turns on the Trigger position values located in the bottom right corne r
of the test area.
When Trigger Display is not selected, trigger position values only display when the trigger
position button is selected on the lower toolbar.
z To display trigger values:
• Select Setup > Trigger Display.
The Trigger values display in the bottom right corner of the test area.
6.2.4 Adjusting Channel Settings
The Channel control bar (Figure 6-3) lets you adjust Lab Scope channel settings and viewing
characteristics for the selected trace.
Figure 6-3
1— Channel Number
2— Probe
3— Scale
4— Signal Zero Offset
5— Raster Spacing
Channel Number
The Channel Number button lets you select channel optio ns. Ther e are fo ur chann els available
for use in the Lab Scope.
In addition to —Displayed and Peak Detect, explained in “Adjusting Channel Settin gs” on
page 27,—Lab Scope also includes:
Sample Lab Scope Channel control bar
• Inverted—flips the selected waveform upside-do wn. This is typically used when testing
secondary ignition or displaying waveforms from the Low Amp s Probe.
38
Page 46

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
NOTE:
NOTE:
• Coupling AC—subtracts the average value of a waveform to see sma ll variatio ns, which is
ideal for viewing alternator ripple or fuel pump amps. Thi s blocks the DC portio ns of an input
signal in order to amplify the AC portions without driving them off the center of the screen.
• Auto Find—picks the best scale to fit the selected signal pattern on the screen. If run on the
same channel as the trigger, the trigger level is set halfway between the minimum and
maximum values of the waveform.
i When testing with the Single Cylinder Ignition scope, the Channel 1 Peak Detect option cannot be
turned off.
Probe
The Probe button lets you select a different test.
i Calculated measurement tests are only available in the Graphing Meter.
Refer to “Probe” on page 28 and “Ignition Scope Probe” on page 33 for more details.
6.2.5 Displaying T riggers
Use the Display Trigger con trol bar (Figur e 6-4) to set the criteria to start the display of dat a .
1— Trigger Type
2— Slope
3— Trigger Position
Trigger Type
Selecting T rigger Type lets you set the criteria used to star t the display of data. A vailable T rigger
Type menu options include:
• None—displays data as fast as it is received.
• Ch 1/2/3/4—triggers the display based on the signal from the selected channel. Av ailable
submenu options include:
– Auto—updates the screen when the signal crosses the trigger thres hold in the selected
direction (rising or falling).
Even if the signal does not cross the trigger threshold, th e screen a utoma tically u pd ates
after a short period so you can see the waveform, which lets you set a threshold to
optimize viewing.
Figure 6-4
Sample Display Trigger control bar
39
Page 47

Scope Operations Performing Scope Test s
NOTE:
NOTE:
– Normal—updates the screen when the signal crosses the trigger threshold in the
selected direction (rising or falling).
If the signal does not cross the trigger threshold, the screen will not update which lets you
capture intermittent events because the screen only updates when the signal meets your
trigger selection.
• Cyl—triggers the scope from the RPM lead signal. The l ead detects the firing on the plug wire
that the lead is connected to and the scope uses this signal to trigger the display. You can only
adjust the time offset for this type of trigger.
– Auto—updates the screen when the scope receives a signal from the RPM lead.
Even if the signal does not receive a signal from the lead, the screen automatically
updates after a short period so you can still see the waveform.
– Normal—updates the screen when scope receives a signal from the RPM lead.
If the scope does not receive a signal from the lead, the screen will not update.
z To select a trigger type:
1. Select the Trigger Type button.
The dropdown menu displays.
2. Select a cylinder triggering option.
With the exception of None, a submenu displays.
3. Select Auto or Normal from the submenu.
– When a Channel trigger (Ch1–4) is selected, a plus sign (+) colored according to the
channel it represents displays in the graph area.
– When the Cyl trigger is selected, a white plus sign (+) displays along the bottom of the
graph area which represents the point in time a cylinder is detected on the RPM lead.
When you are finished setting the trigger modes, press N/X to close the menu.
Trigger Slope
The Trigger Slope button selects the direction the waveform must be going (ri sing or falling) when
crossing the trigger point.
i This button is only available when a Channel is the active trigger type.
Trigger Position
The Trigger Position button is used for moving the trigger point for a specified channel either
along the X (horizontal) or Y (vertical) axis o f the displa y.
i This button is not available when None is the active Trigger type.
z To move the trigger point:
1. Select the Trigger Position button.
The trigger point marker becomes active.
40
Page 48

Scope Operations Using Presets
NOTE:
2. Use the Thumb Pad to move the on-screen marker and select a new Trigger point.
3. When you are finished, press N/X.
6.3 Using Presets
A preset is the configuration of your screen setup. The Presets option gives you access to all of
your custom presets and factory-installed presets for commonly-tested components.
Custom presets can be saved from any of the Scope tool Save m enus. See “Saving Dat a” on
page 36 for more details.
The Presets Management screen (Figure 6-5) displays a list of all the available presets.
Figure 6-5
1— Top slot CompactFlash® card indicator
Displays which CF slot is selected in Setup. The left icon is the Top CF slot and the right
icon is Master CF slot (Internal). The T op CF slot icon will be crossed out if there is no card
in the slot when it is the selected destination.
2— Internal memory indicator
Refers to the Master CF card in the side slot. The check mark indicates the active status
3— Memory usage indicator
Indicates the remaining storage capacity for the active storage memory.
Preset Management screen sample
i Factory-installed presets, which are identified by a lock icon in the Type field, cannot be edited,
deleted, copied or moved.
See “Presets” on page 36 for information on saving a preset.
The Preset Management screen has the following upper to olbar buttons:
• Load opens an active test screen with the selected preset settings.
41
Page 49

Scope Operations Using Presets
• Edit lets you change the file name of a preset a nd add te xt to the note field .
• Delete removes the selected preset from the active storage location.
• Copy lets you copy the selected preset to the inactive storag e memory.
• Move lets you move the selected preset to the in active stor age memor y.
• Select All lets you select all of the files.
• Setup provides a shortcut to the Save Data utility dialog box that lets you set the location
where presets are saved.
z To open the Preset Management screen:
• From the main menu, select Scope > Presets.
The Preset Management screen displays.
z To exit the Preset Management screen:
• Press N/X to return to the main menu.
6.3.1 Identifying Saved Presets
Saved presets have the following characteristics:
• Type is represented as a three-letter identifier, such as LS(C ), where “LS” re present s the
module source (Lab Scope) and “(C)” represents the kind of captured data (Configuration).
Preset source identifiers include:
– LS = Lab Scope
– IS = Ignition Scope
• Size is the percentage of available storag e sp ace used.
• Date/Time is the date and time that the preset was saved.
• File Name is the name given when the preset was saved.
6.3.2 Loading Saved Presets
The load button opens an active test screen with the selected preset.
z To load a preset:
1. From the main menu, select Scope > Presets.
The Preset Management screen displays.
2. Highlight a preset from the list.
3. Select the Load button.
A scope screen displays with your selected preset configuration.
6.3.3 Editing Presets
The Edit button lets you edit preset s in the following ways:
42
Page 50

Scope Operations Using Presets
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
• Add notes
• Change filename
i A USB keyboard (not supplied) is required to edit presets.
z To edit a preset:
1. From the main menu, select Scope > Presets.
The Preset Management screen displays.
2. Connect a USB keyboard to the USB port on top of the MODIS™ unit.
3. Highlight a preset from the list.
4. Select the Edit button.
The Edit Preset Name And Note dialog box displays.
i The Notes and Name icons are not active if a keyboard is not plugged in.
5. Select Notes.
The Additional Information section acti vate s (Figure6-6).
Figure 6-6
6. Using your keyboard, type a text note (7 lines maximum), then press Esc to exit the Additional
Information section.
7. Select Name.
The File Name field is now active.
8. Using your keyboard, type a file name, then press Esc to exit the File Name field.
Sample Note selection
i If you do not provide a file name, a name is automatically created for you.
9. Select Save.
After processing your edits, you return to the Pr eset Manageme nt screen.
6.3.4 Deleting Presets
The Delete button deletes preset files from system memory.
43
Page 51

Scope Operations Using Presets
z To delete presets:
1. From the main menu, select Scope > Preset.
The Preset Management screen displays.
2. Highlight a preset from the list.
3. Select the Delete button.
A confirmation message displays.
4. Permanently remove the preset from memory by pressin g Y/a.
After processing your delete request, you are retur ned to the Pr eset Managem ent screen.
6.3.5 Copying and Moving Presets
The Copy and Move buttons let you change the stor age location of your custom preset s. The se
functions require the use of a CF card in the top slot. Copy and move preset s go to the inactive CF
card, which is the CF card that files are not being saved to.
For example:
If you designate the Top CF as your Save To storage memor y preference, when you use the Copy
and Move buttons, your selected preset goes to the Internal Memory.
z To copy or move data:
1. Insert a CF card in the top slot (not supplied).
2. From the main menu, select Scope > Preset.
The Preset Management screen displays.
3. From the upper toolbar, select Setup.
The Save Data dialog box displays.
4. Select from the Save To options, an d then press N/X to close the dialog box.
This will be the storage memory you will be viewing and copying or moving presets from.
5. When selecting a file from the list on-screen, use the up b and down d arrows.
6. When selecting Copy or Move from the upper toolbar, use the right c and left e arrows.
A confirmation message displays.
7. Press Y/a to close the dialog box and return to the Preset Management screen.
z To verify the preset copied or moved:
1. Leave the top CF card installed.
2. From the upper toolbar, select Setup.
The Save Data dialog box displays.
3. Select from the Save To options, an d then press N/X to close the dialog box.
When the Preset Management screen displays, you should see the preset(s) that you copied
or moved from your source storage memory.
6.3.6 Selecting Multiple Presets
The Select All button highlights all the preset s so you can delete, copy, or move all of them at once.
44
Page 52

Appendix A Testing Tips
Keep the following information in mind when testing with the Lab Scope Plug-in.
A.1 General Tip s
• Refer to the vehicle manufacturer test procedures and specifications before beginning a test.
• When connecting an inductive pickup onto a spark plug wire, make sure the jaws of the p ickup
are firmly seated.
• Always make sure the test leads have clean, tight connections.
• When testing, periodically check the external lead connections to make sure they a re secure.
• Never move the unit by pulling on the test leads.
• Do not drive or roll a vehicle, roll cab, floor jack, engine hoist, etc. over the test leads.
• Never set anything on the display device that could spill on it and allow liquid to run into it.
• Immediately clean any spills from the exterior of the display device, especially substances as
gasoline, brake fluid, battery acid, cleaning solvents, penetrati ng oil, o r other chemical s.
• Connect the ground lead (black booted clip) to a good grou nd source. The ne gative b attery
terminal is the recommended ground connection.
• When testing sensors, actuators, or other circuit components, refer to the manufacturer’s
shop manual or the automotive repair manua l for the pr oper test po int(s).
• Because of the high speed data acquisition capability, the Lab Scope or Graphing Meter
should be used for glitch capture.
• DO NOT position any cables where they can be trapped, snagged, stretched across sha rp
edges, or pose any type of potential ha zard .
• DO NOT place tools or test equipment on vehicle fend ers or oth er places inside the e ngine
compartment.
• Keep test leads away from sources of electrical noise, such as the ignition system, injectors,
and the alternator.
• The shielded Channel 1 and 2 leads can be used to minimize unwante d noise and for testing
high impedance circuits like oxygen sensor signals.
A.2 Using the Split Lead Adapter
The Split Lead adapter is used to connect the Pressure Transducer and the Inductive RPM Pickup
adapter to the Lab Scope Plug-in.Use the following procedur e to conne ct the Split Lead adapter
(Figure A-1) to the Lab Scope Plug-in.
z To connect the Split Lead Adapter:
1. Connect the Split L ead adapter plug to the AUX p ort on the Lab Scop e Plug-in.
2. Connect the banana plugs to the Scope channels be ing used to display the signal.
45
Page 53

Testing Tips Using the Split Lead Adapter
NOTE:
1
2
Figure A-1 Sample Split Lead adapter connection
1— Banana plugs
2— Split Lead adapter plug
i The banana plugs typically connect to the Scope channel of the same color, but can be plugged
into any available Scope channel if necessary.
A.2.1 Connecting the Pressure Transducer
The Pressure Transducer co nnect s to the Lab Sco pe Plug- in throug h the Split Lead adapter
(Figure A-2).
Figure A-2
1— Split Lead adapter
2— Pressure Transduc er
Sample pressure transducer connection
1
2
46
Page 54

Testing Tips Using the Split Lead Adapter
z To connect the Pressure Transducer:
1. Connect the Split Lead adapter to the Lab Scope Plug-in .See “Using the Split Lead Adapter”
on page 45 for more details.
2. Connect the DIN-plug end of the Pressure T ransduce r to socket 1 or 2 of the Split Lead
adapter . The nu mbers and colo rs match the channel on the unit.
A.2.2 Connecting the Inductive RPM Pickup Adapter
The Inductive RPM Pickup adapter can connect to the Lab Scope Plug-in th rough the Split Lead
adapter (Figure A-3).
1
2
Figure A-3 Sample Inductive RPM Pickup connection
1— Split Lead adapter
2— Inductive RPM Pickup
When the Split Lead ad apter is not in use, the Inductive RPM Pickup adapter conne cts directly to
the AUX port (DB9F) on the Lab Scope Plug-in.
z To connect the Inductive RPM Pickup adapter:
1. Connect the Inductive RPM Pickup adapter to the Lab Scope Plug-in . See “Using the Split
Lead Adapter” on page 45 for more details.
2. Connect the Inductive RPM Pickup adapter to the DB9F plug of th e Split Lead adapter.
47
Page 55

Appendix B Using Peak Detect
Peak Detect is used to capture fast events, spik es and glitches for signa ls going in positive and
negative directions. See “Adjusting Channel Settings” on p age 27 and “Adjusting Channel
Settings” on page 38 for more.
B.1 When T o Use Peak Detect
The following section explains when you might want to use Peak Detect a nd how it wo rks.
When Peak Detect is off—the scope collect s ju st enough dat a to plot a wa veform across the
screen. This is the standard mode of operation for ma ny scope s.
Example:
If the Sweep setting is 10 seconds and the screen was 100 point s wide, the sample rate would be
10 times a second. If the Sweep setting is decreased to 1 seco nd, the sample rate would increase
to 100 times a second.
When Peak Detect is on—the scope samples at the maximum rate possible and captures more
sample points than needed to plot the screen. This lets you catch a fast event or glitch.
B.1.1 Example—Testing Secondary Ignition
At a Sweep setting of 1 ms (Figure B-1), firing voltage will be captured even if Peak Detect is off
(the sample rate is relatively fast at this time setting).
Figure B-1
Sample 1 ms Sweep Peak Detect off
48
Page 56

Using Peak Detect When To Use Peak Detect
As the Sweep setting is increased, the firing voltage may be observed to decrease in height and
vary more than usual, and the peak firing voltage will not be captured consistently (Figure B-2).
Figure B-2
Sample 10 ms Sweep—Peak Detect off
At longer sweeps, the sample rate is slower and the peak firing volt age or the e ntire firing can be
missed if it happens between samples (Figure B-3).
Figure B-3
Sample 10 ms Sweep—Peak Detect off
When Peak Detect is on, the firings will be displayed regardless of the Sweep because the scope
is sampling at the maximum rate. The longer the Sweep, the more useful Peak De tect can be.
49
Page 57

Using Peak Detect When To Use Peak Detect
Figure B-4 illustrates a Firing Peak captured at a 10 ms Sweep rate. Compare this illustration with
Figure B-3 on page 49.
Figure B-4
Sample 10 ms Sweep—Peak Detect on
B.1.2 Example—Testing a TPS for Glitches
With a sweep of 5 or 10 seconds, typically used for testing a throttle position sensor (TPS), the
sample rate is relatively slow. When a sweep is longer , the sam ple rate is slower , which increases
the chance that a glitch can be missed because it occurred in between samples.
Figure B-5 illustrates a TPS glitch not captured.
Figure B-5
Sample Slow Sweep—TPS Glitch not captured
To increase the chance of capturing a glitch without Peak Detect, a shorter sweep is neede d.
50
Page 58

Using Peak Detect When To Use Peak Detect
Figure B-6 illustrates a TPS Glitch captured using a faster Sweep.
Figure B-6
Sample Faster Sweep—TPS Glitch captured
Even if the glitch was captured, with a sweep this short the glitch could easily be missed if you
looked away for a moment or even blinked.
When Peak Detect is on, the scope is sampling at the maxim um r ate a sig nal gl it ch ca n be
captured using a longer sweep where it will be easy to see.
Figure B-7 illustrates a TPS Glitch captured using a 10 second sweep. Compare this illustration
with Figure B-5 on page 50.
Figure B-7
Sample 10 Second Sweep—TPS Glitch captured
51
Page 59

Using Peak Detect When Not to Use Peak Detect
B.2 When Not to Use Peak Detect
Peak Detect puts the scope in a high speed sampling mode which can p ick u p and d isplay
unwanted noise from components su ch as injector s and solen oids.
B.2.1 Example—T esting an Oxygen Sensor
An Oxygen sensor (O2S) produces is relatively slow signal that requires, a clean, noise-free
pattern for diagnosis.
Peak Detect should be off when testing an O2 sensor , because the waveform is much cleaner and
easier to evaluate since less noise displays (Figure B-8).
Figure B-8
When Peak Detect is on, more noise is picked up, which makes diagnosis difficult (Figure B-9).
Figure B-9
Sample O2 waveform with Peak Detect off
Sample O2 waveform with Peak Detect on
52
Page 60

Using Peak Detect Peak Detect and the Graphing Meter
B.3 Peak Detect and the Graphing Meter
The Graphing Meter uses a combination of Filter and Peak Detect modes. Filter rem oves the
unwanted ignition and other high frequen cy signals from the display, which gives a better view of
the signal of interest.
The combination of Filter and Peak Detect give s a good b alance be tween detectin g fast glitches
and preventing unwanted noise from displaying. The Noise Filter can be sele cted from the
Channel Control bar as applicable.
For related information, see the following sections:
• “Adjusting Channel Settings” on page 27
• “Using the Filter with the Scope” on page 57
53
Page 61

Appendix C Using Noise Filter
NOTE:
If glitches are being detected and no vehicle problems are observed, noise may be the cause. As
a precaution, do the following:
• Use shielded leads
• Route the leads away from secondary ignition components.
• Verify the test co nnection s.
• If noise is still suspected to be a problem, turn on the Filter. See “Channel Number” on
page 27 for procedures.
i The Filter may also eliminate extremely fast glitches.
C.1 When to Use Filter
The following sections explain when to use the filter with the Graphing Meter and the Scope.
C.1.1 Using the Filter with the Graphing Meter
In the Graphing Meter, the filter minimizes noise by ignoring or smoothing out fast spikes.
Calculated Measurements
When you conduct a calculated measurement test (frequency, pulse wid th, MC Dwe ll Or Duty
Cycle) the filter is used so that very fast spikes (20 uS and faster) from sources like the ignition
system can be ignored.
Figure C-1 illustrates noise from the ignition system when conducting the Graphing Meter
Frequency test with Peak Detect on and Filter off.
54
Page 62

Using Noise Filter When to Use Filter
Figure C-1 Sample of Frequency with Filter off
Figure C-2 illustrates the noise filtered out when conducting the same test with the filter on.
Figure C-2
Sample of Frequency with Filter on
Direct Measurements
When you conduct a direct measurement test in the Graphing Mete r (Volts, Amps, or Pressure),
the filter minimizes the display of very fast spikes by averaging the data. When used together,
Filter and Peak Detect balance captur ing glitches an d minimizing n oise.
55
Page 63

Using Noise Filter When to Use Filter
Figure C-3 illustrates Peak Detect on and Filter off during a TPS Sweep with the key on and
engine off (KOEO).
Figure C-3
Sample Noise Filter off—TPS Sweep (KOEO)
Figure C-4 illustrates Peak Detect on and Filter on during a TPS Sweep with the key on and
engine off (KOEO).
Figure C-4
Sample of Noise Filter on—TPS Sweep (KOEO)
Figure C-5 illustrates Peak Detect on and Filter off during a TPS test. The throttle was snapped
with the engine running (KOER). Compare this wit h Figure C-6, taken under the same conditions
but with the Filter on.
56
Page 64

Using Noise Filter When to Use Filter
Figure C-5 Sample Noise Filter off—TPS Sweep (KOER)
Figure C-6 Sample Noise Filter on—TPS Sweep (KOER)
C.1.2 Using the Filter with the Scope
In the Scope, Filter smooths out spikes and fast variations in the waveform, which provides a good
balance between noise suppression and signal integrity and is most useful on scales of 5 volts and
below. Th e lower the volts scale, the more likely noise could be a problem.
Testing an O2 sensor using a 1 or 2 volt scale or testing with an amps prob e would be examples
of when Filter might be used. Due to the conversion factors used by the probes, a very small volt s
scale is used to measure the output of the probe.
For a probe with a conversion factor of 100 mV/A connected to a 2 amp load, the scop e uses a
200 mV scale to measure the probe output and then convert it to 2 amps for display on the scree n.
57
Page 65

Using Noise Filter When to Use Filter
In Figure C-7, 2 low amps probes were connected to the same inje ctor to comp are the waveform
with Filter on and off.
Figure C-7
Sample Noise Filter—two low amp scope probes
Channel 1 uses the Filter and Channel 2 does not use the Filter.
Notice the difference in readings.
58
Page 66

Appendix D Using Sensitivity Adjustment
Sensitivity Adjustment is used in the Ignition Scope to set the detection sensitivity of cylinder
firings. See “Sensitivity Adjustment” on page 34 and “Missed Cylinder Detection” on page 34 for
more information.
D.1 When T o Use Sensitivity Adjustment
The sensitivity adjustment affects the ability of the ignition scope to detect ignition firings.
Generally it is best to set the sensitivity level just above the spark (Figure D-1).
Figure D-1
Sample of correct sensitivity adjustment
D.1.1 Improper Sensitivity Adjustments
Setting the cylinder firing sensitivity is essential for the proper display of the secondary pattern.
• If the sensitivity is set too high, cylinder firings may not be detected and firing peaks may not
get detected on multiple spark ignition systems.
• If the sensitivity is set too low, events other than the cylind er firings may be falsely detected as
cylinder firings.
The following examples illustrate what happens when the Sensitivity Adjustments are set too high
and too low.
59
Page 67

Using Sensitivity Adjustment When T o Use Sensitivit y Adjustment
NOTE:
Sensitivity Set Too High
Cylinder firings may not be detected consistently if the sensitivity setting is too high. A blank space
will display in place of a cylinder that is not detected. Lowering the setting allows the scope to
detect the firings consistently (Figure D-2).
Figure D-2
Sample missed cylinder detection
i If a cylinder is not firing at all, it cannot be displayed and remains a blank space on-screen
Multiple Spark Systems
When testing a multiple spark ignition system, if the sensitivity is set too high, firing peaks can be
intermittently missed and the Digital kV measurement do es not calcula te correctly (Fig ure D-3).
Figure D-3
60
Sample of missing peaks
Page 68

Using Sensitivity Adjustment When T o Use Sensitivit y Adjustment
Lowering the scope sensitivity captures all of the firing peaks consistently and calculates the
Digital kV measurement correctly (Figure D-4).
Figure D-4
Sample of properly set sensitivity for Multiple Spark systems
Sensitivity Set Too Low
When other events are detected as cylinder firings, the detection sensitivity may be se t too low.
The setting should be increased until the ignition scope consistently detect s e ach cylinder firin g.
Figure D-5 illustrates the detection sensitivity level set at 500V which is too low because the start
of Dwell is being displayed as the firing of cylinders 3 and 2.
Figure D-5
Sample of sensitivity adjustment set too low
61
Page 69

Using Sensitivity Adjustment Some Common Ignition Problems
Figure D-6 illustrates another view of the secondary waveform and highlights the start of the dwell
that was being falsely detected as a cylinder firing in Figure D-5, where the setting was too low.
Figure D-6
Sample of sensitivity adjustment set too low
D.2 Some Common Ignition Problems
This section explains how to set the sensitivity level pr operly when you encou nter some common
ignition system problems.
D.2.1 Example–Vehicle With A Shorted Spark-Plug
Figure D-7 illustrates inaccurate cylinder firing detection on a vehicle with a carbon fouled
spark-plug. The spark-plug on cyl inder 3 was se verel y carbon fouled. In the ill ustration , the
detection sensitivity level is set too high and the cylinder is not being detected consistently.
Figure D-7
62
Sample sensitivity set too high
Page 70

Using Sensitivity Adjustment Some Common Ignition Problems
Decreasing the detection sensitivity to 1.5 kV , as illustrated in Figure D-8, results in the consistent
detection of the shorted cylinder.
Figure D-8
Sample shorted spark-plug detected
D.2.2 Example–Vehicle With A Coil Not Firing
Figure D-9 illustrates cylinder firing detection on a vehicle with the 6/3 coil not firing. Lowering the
detection sensitivity will not help because there are no firings from the 6/3 coil to detect.
Figure D-9
Sample 6/3 coil not firing and not detected
63
Page 71

Using Sensitivity Adjustment Some Common Ignition Problems
The actual cylinder spacing can be seen by changing to the 2 00 ms fixed time sweep and viewing
the raw waveform on channels 1 and 2. The cylinder spacing (long/sh ort/long/short) verifies a coil
is not firing (Figure D-10).
Figure D-10
Sample raw waveform of coil not firing
64
Page 72

Index
Numerics
100 psi Pressure 19, 32
100 psi Vacuum 19
4 Ch Lab Scope 32
500 psi Pressure 19
5000 psi Pressure 19
, 32
, 32
, 32
A
alligator clips 13
auto scroll 21
aux port 10
B
bold text 1
C
cables 12–14
channel 1 12
channel 2 13
channel 3 13
channel 4 13
connecting 4
inductive RPM pickup 14
secondary coil adapter 14
secondary ignition clip-on wire adapter 14
capabilities, hardware 11
channel 1 socket 10
channel 2 socket 10
channel 3 socket 10
channel 4 socket 10
channel control bar 27
channel number 27
common ground socket 10
connecting cables 4
channel 1 4
channel 2 5
channel 3 6
channel 4 6
pressure transducer 45
secondary coil adapter 7
cursors 22
–7
–7
, 47
D
deleting data 43
digital meter 13
dimensions,plug-in 10
Diode/Continuity 20
, 20
display as 26
display trigger 39
dual graphing meter 19
Duty Cycle 19
DVOM 10
and digital meter 20
connection location 10
–40
F
filter 53, 54–58
Frequency 19
fuse 11
G
grid 26
ground socket 10
H
hardware overview 10–12
I
ignition patterns 33
Ignition Probe 32
ignition scope 32
ignition system 37
inductive RPM pickup adapter 14
Injector Pulse Width 19
inverse colors 27
–34
L
lab scope 32
leads. See test leads
loading data 42
Low Amps (20) 19
Low Amps (40) 19
, 20, 32
, 20, 32
M
manual conventions 1–3
manuals, additional 3
MC Dwell (60) 19
MC Dwell (90) 19
messages 2
important 2
note 2
65
Page 73

Index N
multimeter 18–30
graphing meter 19
performing tests 20
selecting software 18
noise filter 28, 53, 54–58
Ohms 20
pausing data 21
peak detect 28
plug-in capabilities 11
plug-in slot 10
powering 4
presets 36
copying and moving 44
deleting 43
editing 42
identifying 42
loading 42
management screen 41
selecting all 44
using 41
pressure transducer 46
print 25
printing screens 25
probe 28
test 14
procedures 2
Pulse Width 19
reset 24
review 21
Safety iii–iv
safety
information iii
save 24
saving data 24
scale 28
scales display 26
scope 31
ignition scope 32
performing tests 35
selecting software 31
secondary coil adapter 14
setup button 25
, 48–53
–44
, 33, 34, 39
–25
–44
N
O
P
R
S
setup options 25
grid 26
ignition system 37
inverse colors 27
scales display 26
trigger display 38
units 25
signal zero offset 29
snapshot 16
changing settings 23
split lead adapter 45
sweep
setting 30
symbols 1
, 21, 22, 23–24
T
technical specifications 10
temperature range
operating 11
storage 11
terminology 2
test leads 12
connecting 4
test probes 14
testing tips 45
threshold 30
Auto Threshold Select (ATS) 30
Manual Threshold Select (MTS) 30
tool help 3
toolbars 15
trigger display 38
trigger. See display trigger
–14
–7
–16
U
units 25
USB keyboard 43
V
view options 20
full digital 20
full graph 20
split screen 20
Volts AC rms 20
Volts AC-RMS 19
Volt s DC 19
Volts DC-Average 19
, 20, 32
, 20
W
weight,plug-in 11
Z
zoom 22
66
 Loading...
Loading...