Page 1
FO-2970MU
SERVICE MANUAL
No. 00ZFO2970USME
FACSIMILE
MODEL FO-2970M
SELECTION CODE DESTINATION
U U.S.A.
Chapters 1, 3, 7 and 8 of this manual are omitted because they are partly common to the FO-2950MU. Please refer to
previous service manual UX-4000MU/FO-2950MU/C (00ZUX4000USME) for these chapters.
Difference between FO-2970MU and FO-2950MU
FO-2970MU FO-2950MU
Control PWB DCEKC182PSCZZ DCEKC388NSCZZ
TEL/LIU PWB DCEKL259CSC01 DCEKL222CSC01
Modem speed 33,600 bps 14,400 bps
CAUTION
This laser facsimile is a class 1 laser product that complies with 21CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 of the CDRH or IEC60825-1 standard.
This means that this machine does not produce a hazardous laser radiation. The use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
This laser radiation is not a danger to the skin, but when an exact focusing of the laser beam is achieved on the eyes retina, there is
danger of spot damage to the retina.
The following cautions must be observed to avoid exposure of the laser beam to your eyes at the time of servicing.
1) When a problem in the laser optical unit has occurred, the whole optical unit must be exchanged as a unit, not an individual part.
2) Do not look into the machine with the main switch turned on after removing the toner/developer unit and drum cartridge.
3) Do not look into the laser beam exposure slit of the laser optical unit with the connector connected when removing and installing
the optical system.
4) The cover of Laser Printer Unit contains the safety interlock switch.
Do not defeat the safety interlock by inserting wedges or other items into the switch slot.
Laser Wave Length : 780 ±15 nm
Laser Pulse Times
Laser Output Power : 0.4 mW ± 0.05mW
Parts marked with " " is important for maintaining the safety of the set. Be sure to replace these parts with specified ones for maintaining the safety and performance of the set.
: (13.95 ± 3 µs)/7mm
SHARP CORPORATION
This document has been published to be used
for after sales service only.
The contents are subject to change without notice.
Page 2

FO-2970MU
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
[2] Operation panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
[3] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[4] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[5] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[6] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[7] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
[1] Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
[3] Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
[4] Error code table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
CHAPTER 3. MECHANICAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[2] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
[1] Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
[2] Wiring diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
[3] Point-to-point diagram and connector signal name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
[2] Circuit description of control PWB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-21
[4] Circuit description of power supply PWB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-23
[5] Circuit description of CIS UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-24
CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMATICS AND PARTS LAYOUT
[1] Control PWB circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
[2] TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
[3] Printer PWB circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
[4] Power supply PWB circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
[5] Operation panel PWB circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-20
CHAPTER 7. OPERATION FLOWCHART
[1] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[2] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
CHAPTER 8. OTHERS
[1] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
[2] Refer to the service manual of FO-2950MU
PARTS GUIDE
Page 3

CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications
FO-2970MU
• GENERAL
Automat ic dialing Rapid Key Dialing: 20 numbers
Speed Dialing: 100 numbers
Memo ry siz e* 4 MB (approx. 300 pages)
Mode m speed 33,600 bps (max.)
Automatic fallback to lower speeds.
Transmission time* Approx. 3 seconds
Toner cartridge yield Initial starter cartridge (included with
(4% page coverage, letter paper)
Replacement cartridge (FO-29ND):
Drum car tridge yield Initial starter cartridge (included with
fax machine): 20,000 pages (avg.)
Replacement cartridge (FO-29DR):
Scanning resolution Fax/copy:
Horizontal: 203 pels/inch (8 pels/mm)
Vertical:
Standard: 98 lines/inch (3.85 lines/mm)
Fine /Halftone: 196 lines/inch
(7.7 lines/mm)
Super fine: 391 lines/inch
(15.4 lines/mm)
PC: Enhanced 600 dpi
Automatic d ocument 20 pages max. (20-lb. letter paper)
feeder
Halftone (grayscale) 64 levels (PC scan: 256 levels)
Paper tray capacity 200 sheets (20-lb. letter paper)
Compression scheme MMR, MR, MH, Sharp (H2)
Applicable telephone line Public switched telephone network
Compatibility ITU-T (CCITT) G3 mode
fax machine): Approx. 1,875 pages
Approx. 3,750 pages
20,000 pages (avg.)
Effective Scanning width 8.3" (210 mm) max.
Effectiv e Printing width 8.0" (208 mm) max.
Recepti on mo de s Fax/Tel/A.M.
Scanning speed 8 ppm (letter paper)
Full Dual Access Yes
Copy function Single/Multi/Sort (99 copies/page)
Power requirements 120 V AC, 60 Hz
Operating temperature 50 - 86°F (10 - 30°C)
Humidity 20 to 85% RH
Power consumption Standby: 8.1 W
Maximum: 650 W
Dimensions Width: 15.2" (386 mm)
Depth: 15.7" (398 mm)
Height: 6.7" (169 mm)
Weight Approx. 13.8 lbs. (6.3kg)
* Based on ITU-T Test Chart #1 at standard resolution in Sharp special
mode, excluding time for protocol signals (i.e., ITU-T phase C time
only).
Important:
• This facsimile machine is not designed for use on a line which has call
waiting, call forwarding, or certain other special services offered by
your telephone company. If you attempt to use the fax machine in
conjunction with any of these services, you may experience errors
during transmission and reception of facsimile messages.
• This facsimile machine is not compatible with digital telephone systems.
Printing resolution Horizontal: 406 lines/inch (16 lines/mm)
Vertical: 391 lines/inch (15.4 lines/mm)
PC Printing: 600 dpi (enhanced 1,800 dpi)
Input document size Automatic feeding:
Width: 5.8 to 8.5" (148 to 216mm)
Length: 5.5 to 11" (140 to 279mm)
Manual feeding:
Width: 5.8 to 8.5" (148 to 216mm)
Length:5.5 to 39.4" mm (140 to 1,000mm)
As a part of our policy of continuous improvement, SHARP reserves the right to make design and specification changes for product
improvement without prior notice. The performance specifications figures indicated are nominal values of production units. There may be some
deviations from these values in individual units.
1 – 1
Page 4
FO-2970MU
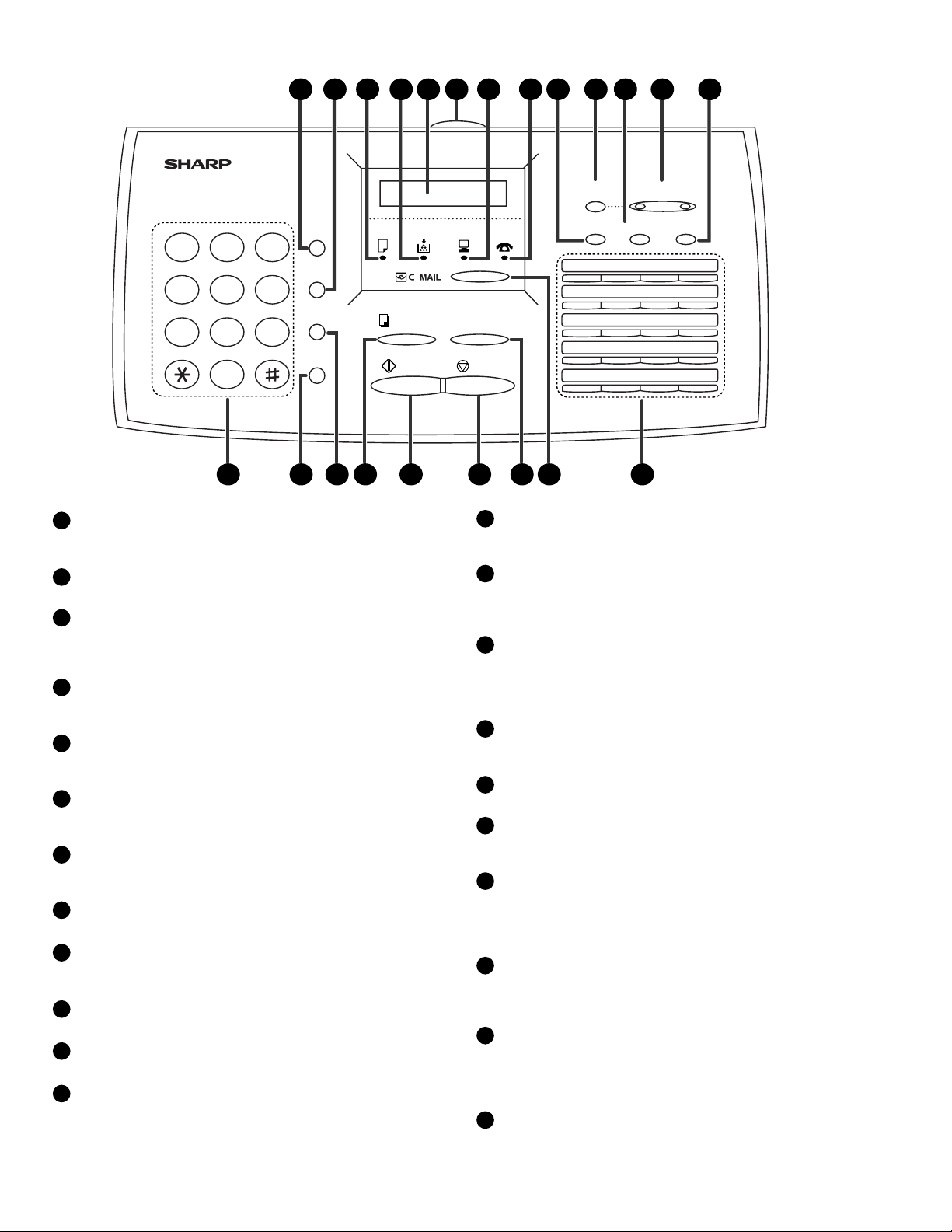
[2] Operation panel
GHI MNO
PQRS WXYZ
ABC21DEF
JKL
54
TUV
87
0
1 2 3 4 7 8 9 13
FAX
TEL
A.M.
SPEED
DIAL
PAPER
CHECK
TONER
EMPTYPCIN USE
LINE
IN USE
3
REDIAL
10 11 125 6
FUNCTION
RECEPTION
MODE
01
RESOLUTION
02
VOLUME
DOWN
03 04
6
HOLD/
SEARCH
COPY/HELP
9
SPEAKER
START
REDUCTION/
ENLARGEMENT
STOP
13
15
14
UP
BROADCAST
08070605
12111009
16/POLL
20/G419/G318/G217/G1
SPEED DIAL key
1
Press this key to dial a fax or voice number using an
abbreviated 2 digit Speed Dial number.
REDIAL key
2
Press this key to automatically redial the last number dialed.
PAPER CHECK indicator
3
This lights when the paper tray is out of paper, the paper has
jammed, the printer compartment cover is open, or a paper
size error has occurred.
TONER EMPTY indicator
4
This blinks when the toner cartridge nears empty and lights
steadily when the toner cartridge needs replacement.
Display
5
This displays messages and prompts during operation and
programming.
Panel release
6
Grasp this release and pull toward you to open the operation
panel.
PC IN USE light
7
This blinks when data is being sent to or from the computer
connected to the fax machine.
LINE IN USE light
8
This lights when the fax machine is using the telephone line.
RECEPTION MODE key
9
Press this key to select the reception mode. An arrow in the
display will point to the currently selected reception mode.
FUNCTION key
10
Press this key to select special functions and settings.
RESOLUTION Keys
11
Press this key to adjust the resolution for faxing or copying.
VOLUME (UP/DOWN) keys
12
Press these keys to adjust the volume of the speaker when the
SPEAKER key has been pressed, the volume of the handset
when the handset is lifted, or the volume of the ringer at all
other times. The keys can also be used to scroll through
FUNCTION key settings.
14151620 1921 171822
BROADCAST key
13
Press this key to send a document to a group of receiving fax
machines.
Rapid Dial Keys
14
Press one of these keys to dial a fax number automatically, or
send a document as an E-mail attachment to a preset E-mail
address.
E-MAIL key
15
Press this key to send a document as an E-mail attachment.
After you press the key, your specified E-mail program will
open to let you enter the E-mail address, a subject, and a
message if desired.
REDUCTION/ENLARGEMENT key
16
Press this key to select an enlargement or reduction setting
when making a copy of a document.
STOP key
17
Press this key to cancel an operation before it is completed.
START key
18
Press this key to begin transmission when using Speed Dialing,
Direct Keypad Dialing, or Normal Dialing.
COPY/HELP key
19
When a document is in the feeder, press this key to make a
copy of a document. At any other time, press this key to print
out the Help List, a quick reference guide to the operation of
your fax machine.
HOLD/SEARCH key
20
When dialing, press this key to search for an auto-dial fax
number. During a phone conversation, press this key to put the
other party on hold.
SPEAKER key
21
Press this key to listen to the line and fax tones through the
speaker when faxing a document.
Note: this is not a speakerphone. You must pick up the
handset to talk with the other party.
Number Keys
22
Use these keys to dial numbers, and enter numbers and letters
when storing auto-dial numbers.
1 – 2
Page 5
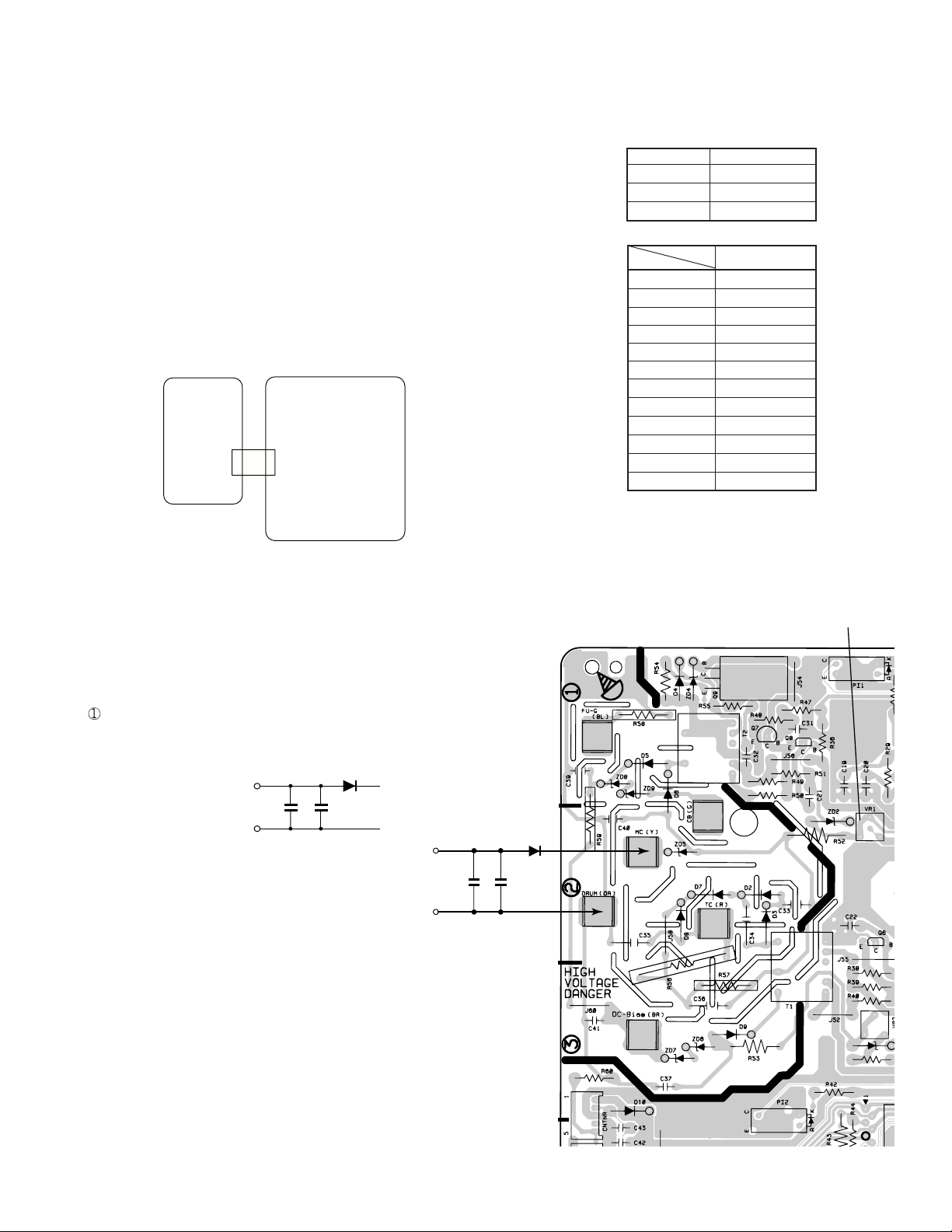
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
[1] Adjustments
FO-2970MU
General
Since the following adjustments and settings are provided for this model,
make adjustments and/or setup as necessary.
1. Adjustments
Adjustments of output voltage (FACTORY ONLY)
1. Install the power supply unit in the machine.
2. Set the recording paper and document.
3. When the document is loaded, power is supplied to the output lines.
Confirm that outputs are within the limits below.
Output voltage settings
Power
Printer PWB
Supply
PWB
12
1
1
CNPWCN101
12
Fig. 1
Output Voltage limits
+5V 4.75V~5.25V
+24VH 23.04V~24.96V
+24V* 23.04V~24.96V
Connector
PIN No.
1 +5V
2DG
3DG
4 +24VH
5MG
6MG
7 +24VS
8 PWRLY–
9 HLON–
10 +24V
11 +24V
12 ZC
No.
CNPW
2. High voltage power adjustments
The high voltage power adjustments are composed of the MC output
voltage adjustment and the DC bias output voltage adjustment. Either
adjustment is performed with the diag function. (MAIN CHG ADJUST
MODE)
1
MC output voltage adjustment
In the measurement circuit shown below, adjust VR1 to be –1050V ~
–1200V (aim at –1100V)
Measure with the high
voltage tester
(effective value meter).
• Capacitor: 1000pF/3KV (VCKYQY3FB102K)
• Diode: SHV-03 (VHDSHV03///-1)
MC
DRUM
MC output
voltage check
+
–
VR1 (MC output voltage adjustment volume)
2 – 1
Fig. 3
Fig.2
Page 6
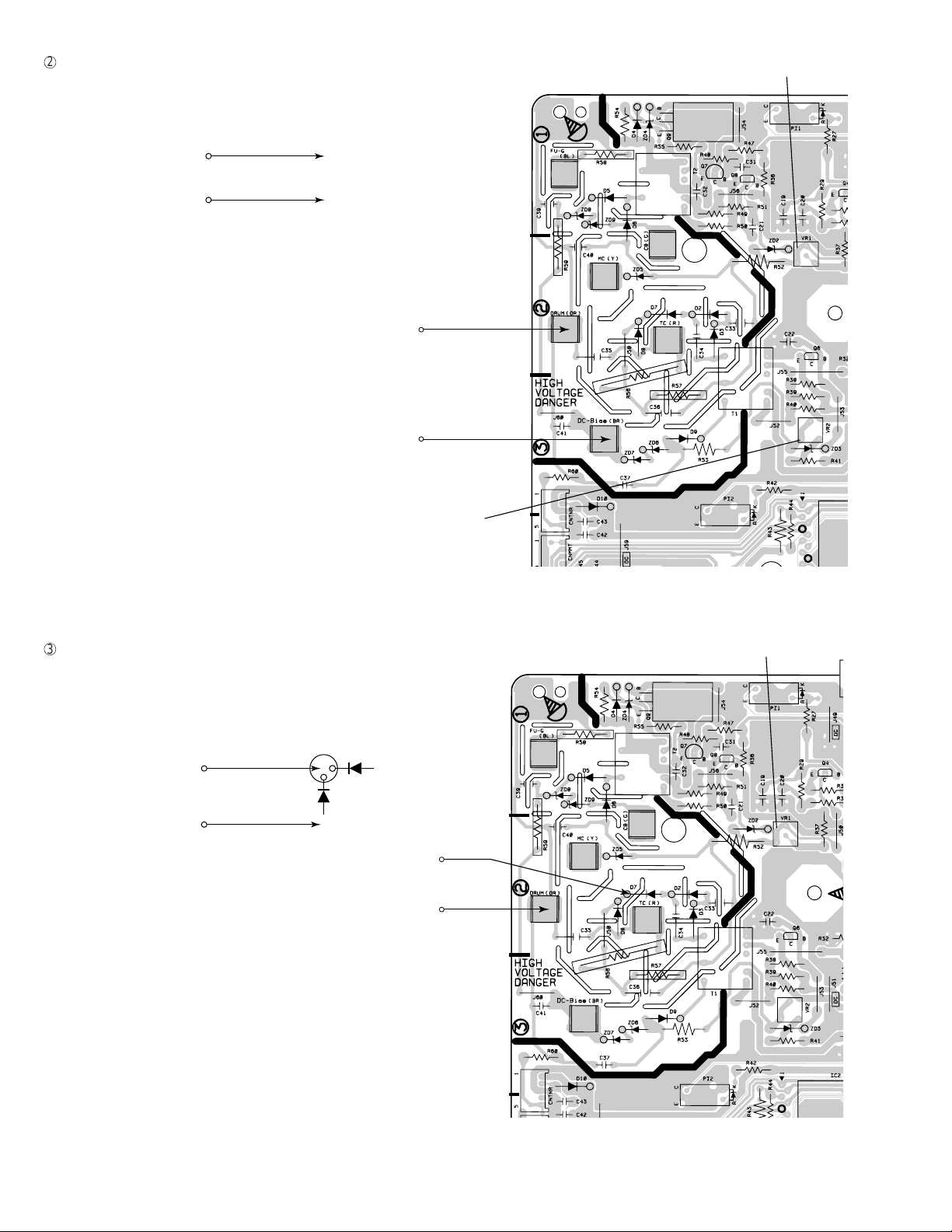
FO-2970MU
DC bias output voltage adjustment
2
Adjust VR2 so that the output voltage is –310V ±5V
For measurement, use the high voltage tester (effective value meter).
VR1 (MC output voltage adjustment volume)
DC-Bias
Output voltage check
–
+
DRUM
DC-Bias
–
DC-Bias
Output voltage check
+
VR2
(DV bias output adjustment volume)
Fig.3
3
Transfer charger voltage check
After MC output voltage adjustment and DC bias output voltage adjustment, check transfer charger voltage.
Check that the output voltage is +3200V ~ +3700V.
For measurement, use a high voltage tester (effective value meter).
+
Transfer charger
Output voltage check
–
D7
D8
DRUM
Transfer changer
Output voltage check
Note: For measurement, do not remove Printer PWB from the bottom
plate.
VR1 (MC output voltage adjustment volume)
+
–
2 – 2
Fig.4
Page 7
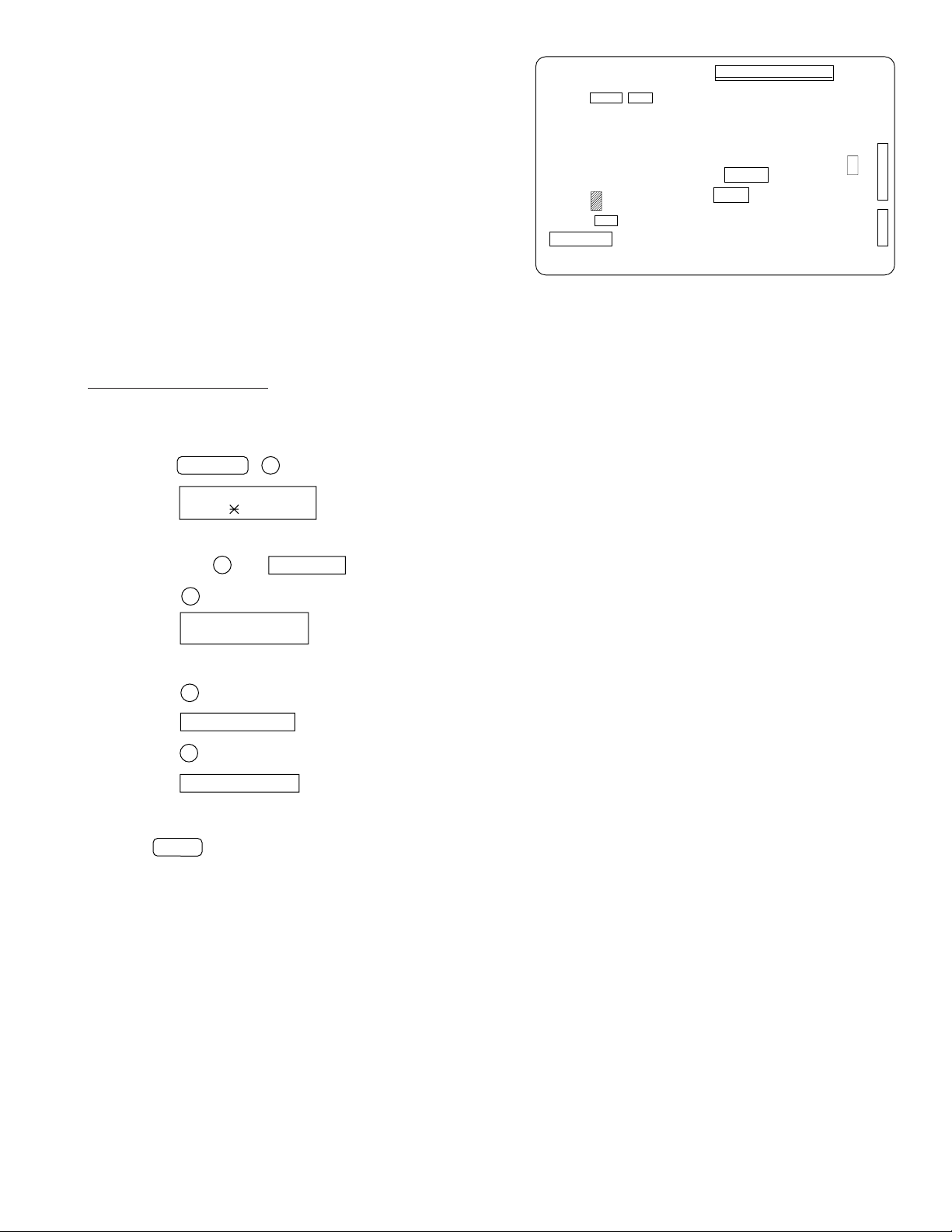
3. IC protectors replacement
ICPs (IC Protectors) are installed to protect the TX motor drive circuit
and verification stamp drive circuit. ICPs protect various ICs and electronic circuits from an overcurrent condition.
The location of ICPs are shown below:
(1) F100 (ICPS10) is installed in order to protect IC’s from and
overcurrent generated in the verification stamp drive circuit. If F100
is open, replace it with a new one.
CNRTH
F100
CNFUSE
CNMT
FO-2970MU
CNPRT
CNLIUA
CNPN
CNSP
CNCIS
4. Settings
(1) Dial mode selector
OPTION SETTING: DIAL MODE (Soft Switch No. SW2 DATA No. 1)
Use this to set the fax machine to the type of telephone line you are on.
• The factory setting is "TONE".
(step 1) Select "OPTION SETTING".
KEY:
DISPLAY:
(step 2) Select "DIAL MODE".
KEY:
DISPLAY:
(step 3) Select, using "1" or "2".
KEY:
FUNCTION 4
OPTION SETTING
PRESS or #
Push # until " DIAL MODE " is
indicated because the number of
# s changes by the models.
DIAL MODE
1= TONE, 2= PULSE
1
IC6
Control PWB (Bottom side)
Fig.5
CNLIUB
DISPLAY: TONE SELECTED
KEY:
DISPLAY:
2
PULSE SELECTED
(step 4) End, using the "STOP" key.
KEY:
STOP
2 – 3
Page 8
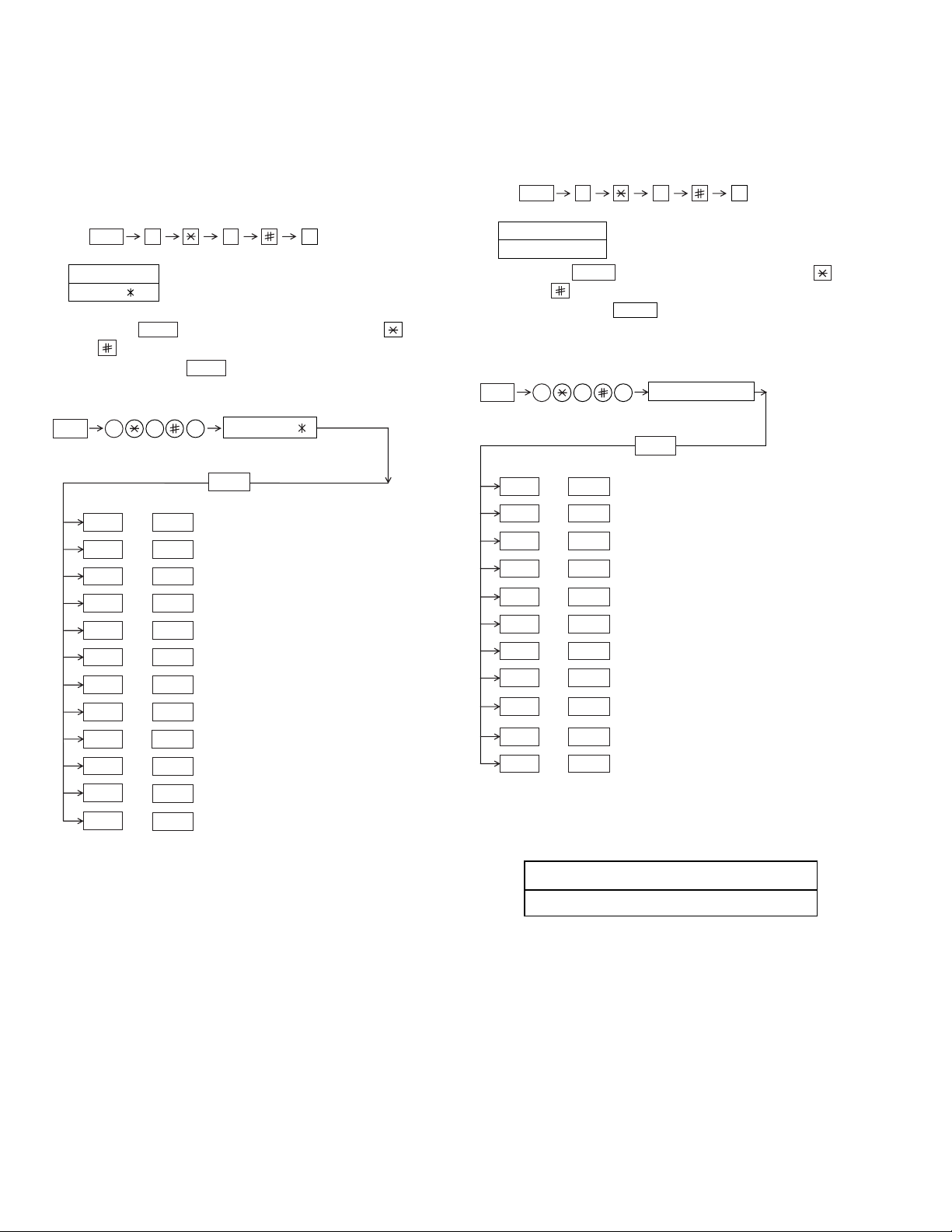
FO-2970MU
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switches
1. Operating procedure
Two kinds of diagnoses are supported.
1-1. Fax diagnosis
This diagnosis is concerned with the main body of fax which is used
for production and service support.
Entering the diagnostic mode
FUNC
Press
display will appear.
DIAG MODE
ROM:
FBF0
Then press the
and the key or select with the rapid key.
Enter the mode with the
(Diag
•
specifications)
FUNC
02
04
05
07
08
10
9 8
START
key. Select the desired item with the
START
key.
9 8 7
START01 SOFT SWITCH MODE
START
START03
START
START
START06
START
START
START09
START
ROM: FBF0
START
ROM & RAM CHECK
AGING MODE
PANEL KEY TEST
OPTICAL ADJUST MODE
CHECK PATTERN MODE
SIGNAL SEND MODE
MEMORY CLEAR MODE
AUTO FEEDER MODE
MOTOR AGING MODE
7
, and
the
following
key
1-2. Print diagnosis
This diagnosis is concerned with the print which is used for
production and service support.
Entering the diagnostic mode
FUNC
Press
display will appear.
PRINT DIAG MODE
PRESS START KEY
Then press the
key andthe key or selectwith the rapid key.
Enterthe modewith the key.
(Diag•specifications)
FUNC
01
02
03
08
09
9 8
START
9 8 6
START
START
START
START04
START05
START06
START07
START
START
START10
START11
6
, and
key. Select the desired item with the
START
PRINT DIAG MODE
START
AREA PRINT MODE
CHECK PATTERN 1
CHECK PATTERN 2
CHECK PATTERN 3
PAPER FEED AGING
LIFE SET MODE
LIFE ALL CLEAR
LIFE ENTRY MODE
TOP ADJUST MODE
LIFE CLEAR MODE
MAIN CHARGER ADJUST
the
following
11
START
TEL. NUMBER SET
Memory clear when power is turned on
12
START
SIGNAL SEND MODE 2
Pressing the START and STOP keys, turn on the main power, and the
following message will be displayed.
MEMORY CLEAR?
YES: START
Press STAR T key, the memory will be cleared to be ready for operation.
Press COPY key, the memory will be cleared to be ready for process
check.
If press the other keys, it will continue ready for operation as it is.
2 – 4
Page 9
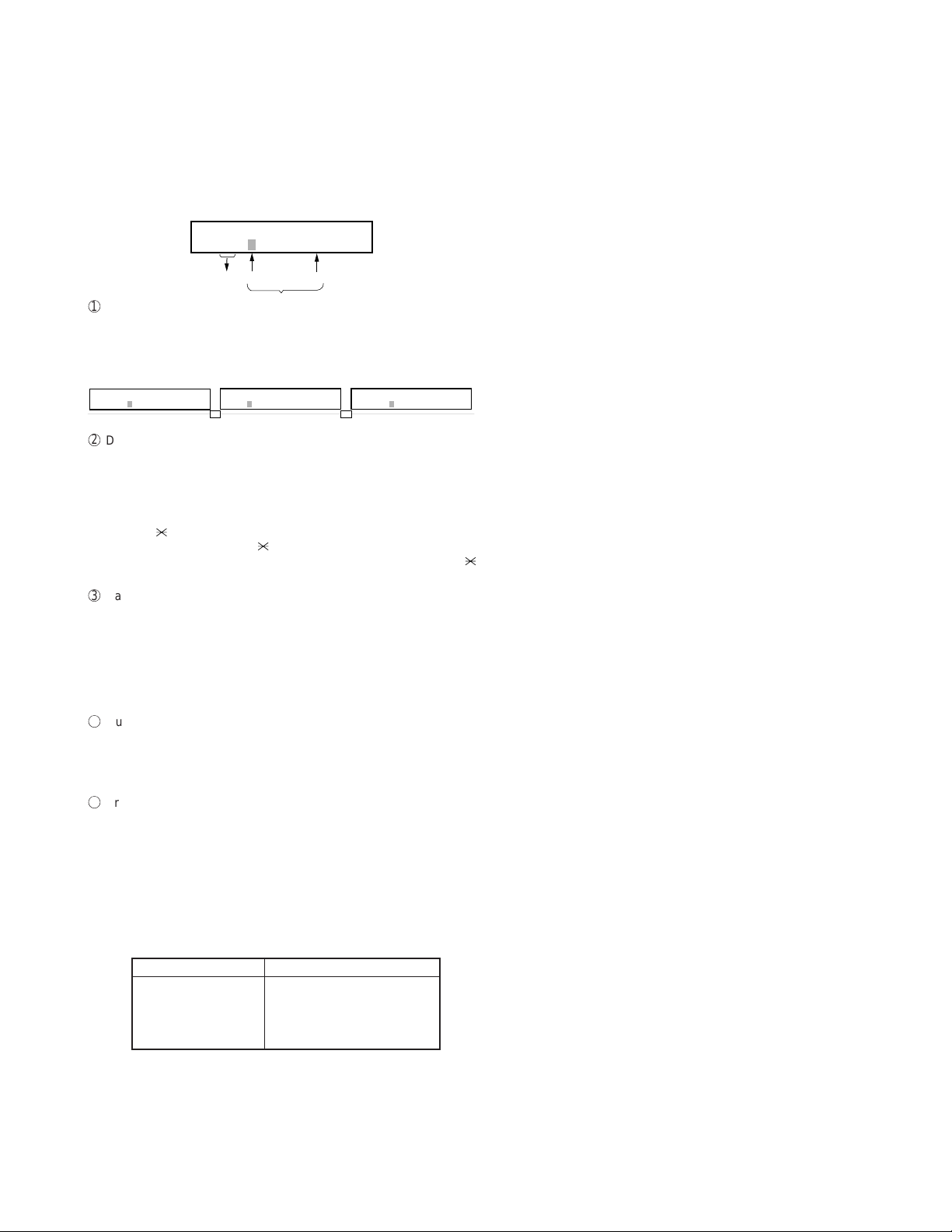
FO-2970MU
2. Diagnostic items description
2-1. Fax diagnosis
1) Soft switch mode
The soft switches are provided so that each operation mode can be set
by using the operation panel.
In this mode, these switches can be checked and set.
The contents of these switches are backed up.
Soft switch mode screen
S O F T S W I T C H M O D E
S W 0 1 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8
Data
1
Switch number selection
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 :DATA No.
Switch
No.
• Press START key for setting of the next soft switch. If the soft
switch number is the final, pressing START key will exit the soft
switch mode.
• Enter two digits of a soft switch number to set the switch number.
S O F T S W I T C H M O D E
S W 0 1 = 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2
Data number selection
S O F T S W I T C H M O D E
S W 1
1 6
The cursor position shows the data to be set.
Pressing # key moves the cursor to the right. If, however, the cursor
is on data number 8, pressing # key shifts the cursor to data number
1 of the next switch number. If the switch number is the final, pressing # key will exit the soft switch mode.
Pressing key moves the cursor to the left. If, however, the cursor is
on data number 1, pressing key shifts the cursor to data number 1
of the former switch number. If the switch number is 1, pressing
key will not move the cursor and the error buzzer will sound.
3
Data setting method
Press the FUNCTION key, and the data at the position of the cursor
will be reversed to 0 when it is 1, or to 1 when it is 0. (If the soft switch
can not be changed at the bit the error buzzer will sound with the
process not received.), When you press the STAR T key or the # key
and the cursor moves to the next switch position, the changes in the
contents of the previous switch position will be saved. If you do not
want to save your changes, press the STOP key.
4
Outputting method of soft switch list
In the soft switch mode, press the COPY/HELP key, and the soft
switch list will be output.
If the recording paper runs out or is clogged, condition is held until
recording paper is prepared, and an error buzzer doesn’t ring.
5
Prohibition against changing individual pieces of data and synchro-
nized data changes
At present, there is no prohibition against changing data individually
and there is also no capability to make synchronized changes to data.
(The ECM may be turned on or off while using image memory.)
2) ROM & RAM check
ROM executes the sum check, and RAM executes the matching test.
If any error occurs, the buzzer will inform it. (Refer to the following table).
Finally, the result will be printed.
Number of buzzer sounds Device checked
1 time <Short sound> MAIN ROM
2 times <Short sounds> S-RAM
3 times <Short sounds> D-RAM
4 times <Short sounds> CPU integrated ROM/RAM
The buzzer beep pattern is: on for 0.25 seconds and then off for 0.25
seconds.
S O F T S W I T C H M O D E
S W 1 6 = 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
4) Panel key test
This is used to check whether each key is normally operated or not.
According to the key input, LCD is displayed.
1) When the START key is pressed while PANEL KEY TEST is being
displayed, a test will start. Since all of the LEDs will light up in sequence until the test is finished, the LED operation can be checked
as well.
2) Press all of the keys one at a time, but do not press the STOP key.
Every time a key is pressed, the name of that key will appear in the
display.
3) Finally , press the ST OP key. If there was a key you pressed that was
not detected when the STOP key is pressed, PANEL TEST NG! will
be displayed. When all of the keys have been pressed and detected,
PANEL TEST OK! will be displayed.
Then the display will go blank, which is OK. If there was an NG, any
key which was not pressed or not detected will be printed in the result table. (For details about the printout format, see the list function
specifications.)
5) Optical adjust mode
In this mode, the optical system is adjusted. Document feeding can be
started by pressing the STAR T key two times. It can be stopped by pressing the STOP key.
6) Check pattern mode
The effective printing area used will be according to the size specified.
A copy of a pattern will be printed, and the printing will be complete.
7) Signal send mode
This mode is used to send various signals to the circuit during FAX communication. Every push of START key sends a signal in the following
sequence.
[ 1] No signals (CML-ON)
[ 2] 14400bps (V. 33)
[ 3] 12000bps (V. 33)
[ 4] 14400bps (V. 17)
[ 5] 12000bps (V. 17)
[ 6] 9600bps (V. 17)
[ 7] 7200bps (V. 17)
[ 8] 9600bps (V. 29)
[ 9] 7200bps (V. 29)
[10] 4800bps (V27ter)
[11] 2400bps (V27ter)
[12] 300bps (FLAG)
[13] 2100Hz (CED)
[14] 1100Hz (CNG)
[15] END
8) Memory clear mode
This mode is used to clear the backup memory and to reset to the factory default setting.
The content of each setting will be cleared. Then, the initialized list be
output.
3) Aging mode
If any document is set up in the first state (when started), copying will be
executed. If it is not set up, "check pattern" of the print diagnosis is output at the intervals of 1 sheet/5 minutes. (A total of 10 sheets are output.)
2 – 5
Page 10
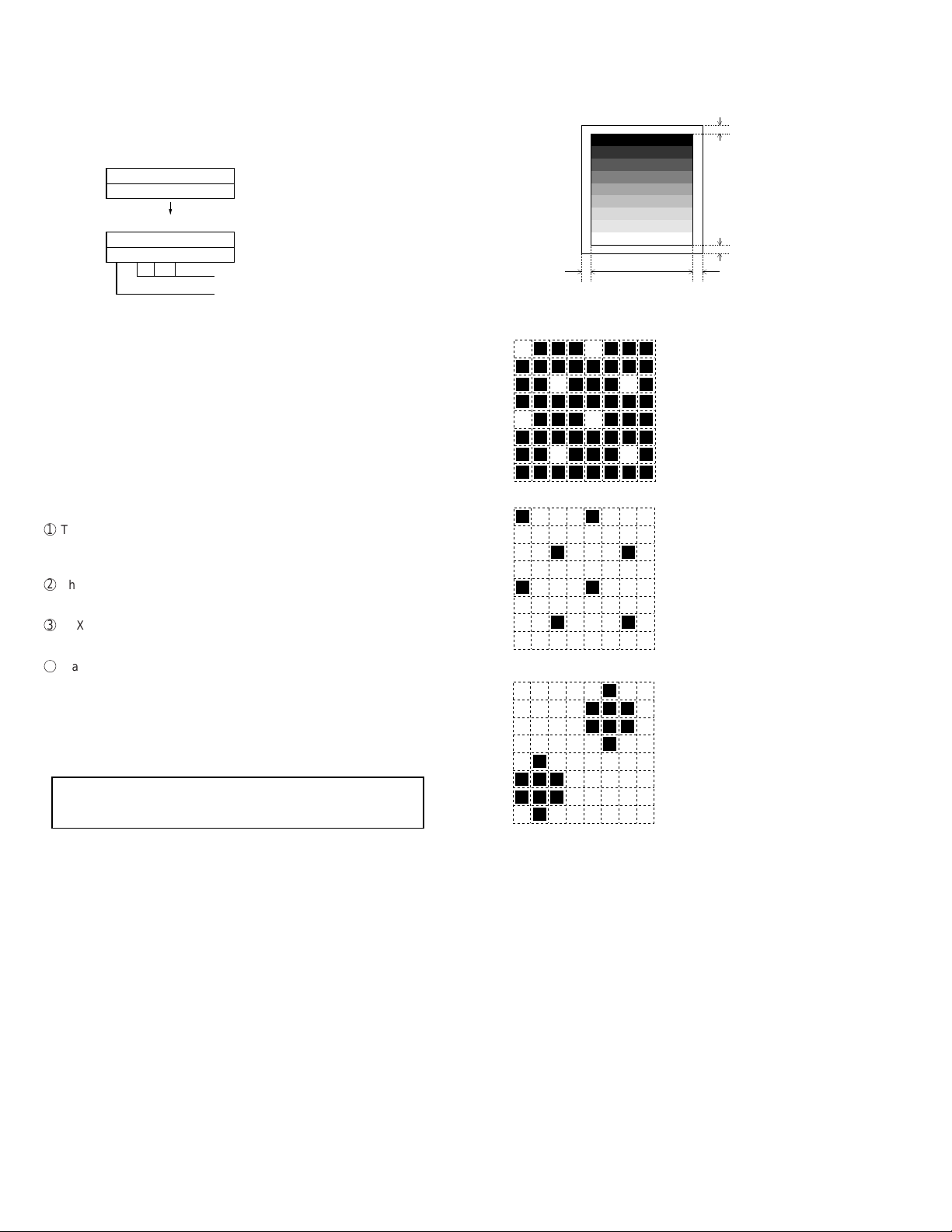
FO-2970MU
9) Auto feeder mode
The auto feed function can be checked by inserting and discharging the
document. (After entering this mode, when a document is placed in the
machine and the START key is pressed, the operation will start.)
After this mode is activated, the document size A4(A4 ) and
sensor information A4(A4 ORG) are displayed when the document
sensor is turned.
AUTO FEEDER MODE
( )
After setup of the document
AUTO FEEDER MODE
A4 (A4 ORG)
Only the sensor which is
activated (fallen down) is displayed.)
The paper sheet size (A4) is
displayed.
10) Motor aging mode
Regardless of the presence or absence of a document, the transmission system motor will continue to run until the STOP key is pressed.
When the STAR T key is pressed after this mode has been selected, the
motor will run at the STANDARD mode speed. Then, when the image
quality is changed using the RESOLUTION key, the motor will run at the
speed used for that image quality.
(When HALF-TONE is selected, the motor will run at the FINE
modespeed.)
11) TEL. number set
The function is used to simplify the registration of FAX/TEL No. during
aging.
1
The diagnosis mode is activated. If anything is not registered in the
Rapid number 01 or any program or group is registered, it will pass
the diagnosis without doing anything.
2
The FAX number (including the substitutive destination) of the Rapid
number 01 is copied to the Rapid numbers 02 thru 19.
3
FAX number of the Rapid number 01 is copied to SPEED key numbers 00 thru 99.
4
If any chain dial is not set in the Rapid number 01, the Rapid numbers 01 thru 19 and SPEED key numbers 00 thru 10 are registered in
the group number 04.
If any chain dial is set, the group will be not produced but the chain
dial setting alone of the Rapid number 01 will be reset.
(In all others except the Rapid number 01, the chain dials will be
continuously set as they are.)
2-2. Print diagnosis
Rapid key 01: Area print mode
The effective printing area frame is printed in the specified sheet size.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
4mm
208mm
1. [Full black pattern]
2. [Intermediate tone 2 pattern]
3. [Intermediate tone 1 pattern]
4. [Mesh point pattern]
4mm
4mm
4mm
The left pattern is repeated.
The left pattern is repeated.
The left pattern is repeated.
Rapid key
SPEED key
RXX
SXX
XXXX: Rapid number
: Speed key number
(12th and subsequential letters of the destination name registered in the
Rapid number 01 will be discarded.)
12) Signal Send Mode 2
The signals concerned with V.34 & V.8 are checked.
After this mode is activated, press the START key, and the signals will
be sent in the following sequence.
It can be used to check the modem.
[ 1] No signals (CML-ON) [10] 14400bps (V.34)
[ 2] 33600bps (V.34) [11] 12000bps (V.34)
[ 3] 31200bps (V.34) [12] 9600bps (V.34)
[ 4] 28800bps (V.34) [13] 7200bps (V.34)
[ 5] 26400bps (V.34) [14] 4800bps (V.34)
[ 6] 24000bps (V.34) [15] 2400bps (V.34)
[ 7] 21600bps (V.34) [16] 0-300bps (V.21)
[ 8] 19200bps (V.34) [17] ANsam (V.8)
[ 9] 16800bps (V.34) [18] END
5. [Longitudinal strip 2 pattern]
Black 2 dot and white 2 dot are repeated in line.
6. [Lateral strip 2 pattern]
Black 2 line and white 2 line are repeated.
7. [Longitudinal strip 1 pattern]
Black 1 dot and white 1 dot are repeated in line.
8. [Lateral strip 1 pattern]
Black 1 line and white 1 line are repeated.
9. [Full White pattern]
Rapid key 02: Check pattern 1
The lateral stripe 2 pattern is printed on one sheet.
(Black 2 line and white 2 line are repeated.)
Rapid key 03: Check pattern 2
The lateral stripe 2 pattern is printed on multiple pages.
Press the STOP key to end the printing.
Rapid key 04: Check pattern 3
The intermediate tone 1 is printed on one sheet.
2 – 6
Page 11
FO-2970MU
LI FE1= 00123
LI FE2= 00123
LI FE3= 00123
0
0
0
# key
key
Rapid key 05: Paper feed aging
The mode is used for aging related to the printing. In this mode, the
following modes are provided.
1
Blank paper aging mode (ALL WHITE AGING)
2
Whole black print aging mode (ALL BLACK AGING)
3
4% printing aging mode (4% AGING)
After selecting the paper-feed aging mode in the print diagnosis mode,
input the number of each mode above with the ten-key, and the mode
will be executed. The detailed specifications of each mode are described
as follows. Here, the operation in each mode is stopped only when the
STOP key is pressed by the operator or a printing-impossible error occurs.
• Blank paper aging mode (ALL WHITE AGING)
In the mode, printing is continued in the whole white (white paper)
printing pattern until the STOP key is pressed by the operator . (In the
printing area)
• Whole black printing aging mode (ALL BLACK AGING)
In the mode, printing is continued in the whole black (whole black)
printing pattern until the STOP key is pressed by the operator . (In the
printing area)
Rapid key 06: Life set mode
The mode is used to set the life counter of the printer and the counter of
the auto feeder at desired values. For setting, proceed with the following procedure.
1
When the life counter setting mode is selected, the following will be
is displayed.
Rapid key 07: Life all clear
The mode is used to clear the life counter of the printer of the counter
of the auto feeder.
Note: The counter shows the operational state of the printer (e.g. how
many sheets have been printed since start of use?). The ordinary memory does not reset the counter. Accordingly, it is necessary to reset this counter in addition to the ordinary memory
clear if the content in the memory on the control PWB is broken
because of PWB repair, etc. (In the production stage, it is necessary to execute this in the last process.)
Rapid key 08: Life entry mode
(For Serviceman temporary counter)
The mode is used to set a desired value for the judgment value (alarm
judgment counter value) of the general purpose life counters 1 thru 3 of
the printer. If the life of a consumable part (developer, imprinter, etc) is
set, the model which has the error display and RMS function will inform
RMS when the counter reaches the set value. For setting, proceed with
the following procedure.
1
When the life counter entry mode is selected, the following will be
displayed.
IFE1
L
= 00123
0
= 00123
0
= 00123
0
= 00123
0
= 00123
0
0
F
key
# key
MACHINE
DRUMLLIFE
LIFE2
LLIFFE3
FEEDER = 00123
OT NER = 001230
The cursor blinks at the top data.
Seven counters can be selected with the "#" and " " keys.
2
In the state 1, input a desired setting number of 6 digits with the tenkey.
3
After input of 6 digits, shift to another counter with the "#" and " "
keys as necessary. When all necessary counters are completely input, press the START key.
4
"STORED" will be displayed with the set values stored into the
memory. For checking, retry this mode.
Note:
This counter indicates the printer use conditions such as numbers of
printed pages from the beginning of use. In the normal memory clear
condition, the counter will not be reset.
In conditions including damaged memory contents caused by repairing
the panel, this counter should be reset or cleared in addition to the ordinary memory clear.
The cursor blinks at the top data.
Three counters can be selected with the "#" and " " keys.
2
In the state 1 , input a desired setting number of 6 digits with the tenkey.
3
After input of 6 digits, shift to another counter with the "#" and " "
keys as necessary. When all necessary counters are completely input, press the START key.
4
"STORED" will be displayed with the set values stored into the
memory. For checking, retry this mode.
Note: The counter shows the operational state of the printer (how many
sheets have been printed since start of use? and others). The
ordinary memory does not reset the counter. Accordingly, it is
necessary to reset the counter or do the clear process in addition to the ordinary memory clear if the content in the memory
on the control PWB is broken because of PWB repair, etc. (In
the production stage, it is necessary to execute this in the last
process.)
Rapid key 9: Top adjust mode
Adjust the top margin for printing on a page. You can enter any value
from 0 to 99 using the ten-key keypad.
The standard (initial) value is 50.
When the setting is increased, the print start position will be moved closer
to the beginning of page.
When the setting is decreased, the print start position will be moved
further away from the beginning of page.
2 – 7
Page 12
FO-2970MU
Rapid key 10: Life clear mode
The mode is used to respectively clear the life counter of the printer and
the counter of the auto feeder. For setting, proceed with the following
procedure.
1
When the life counter clearing mode is selected, the following will be
is displayed.
Seven counters can be selected with the "#" and " " keys.
LF
LEAR
MACHINE
C
DRUM
# key
FEEDER LF LEAR
TONER L I FE LEAR
2
In the state of 1, select the counter value you want to clear using the
LIFE
L
IFE1
LIFE2
LIFE3
LEAR
C
LEAR
C
LEAR
C
LEAR
C
C
C
key
"#" key or the " " key, and then press the START key.
3
"CLEARED " will be displayed, and the counter value will be cleared.
After clearing the counter value, another counter value can be cleared
using the # or key, if desired. Press the ST OP key to exit from the
mode.
Note: The counter shows the operational state of the printer (how many
sheets have been printed since start of use? and others). The
ordinary memory does not reset the counter. Accordingly, it is
necessary to reset the counter or do the clear process in addition to the ordinary memory clear if the content in the memory
on the control PWB is broken because of PWB repair, etc. (In
the production stage, it is necessary to execute this in the last
process.)
Rapid key 11: Main charger adjust
This mode is used to control voltage of main charger.
2 – 8
Page 13
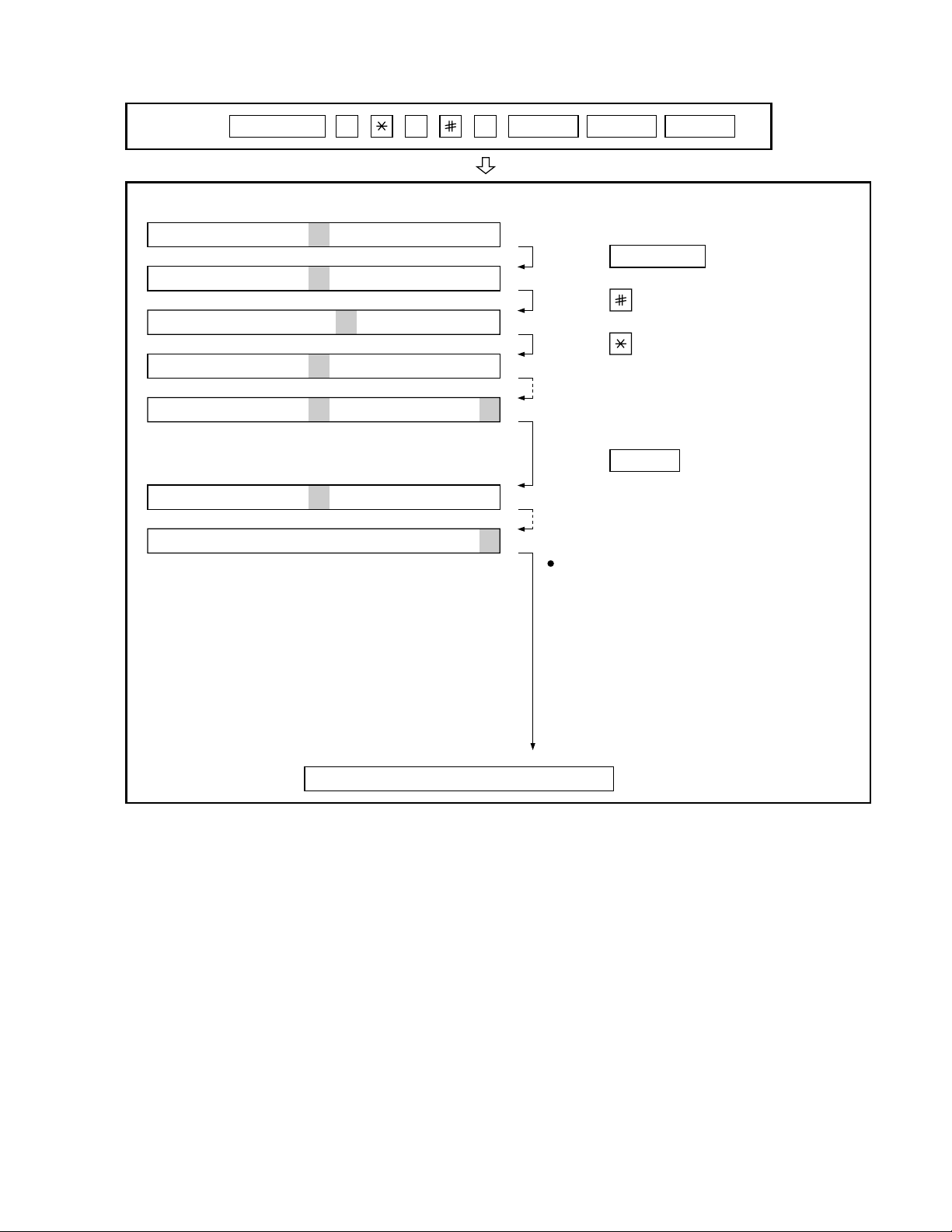
3. How to make soft switch setting
To enter the soft switch mode, make the following key entries in sequence.
FO-2970MU
Press
FUNCTION
9 8 7 START 0 1START
S F T S W 1 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 2 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T S W 65 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Press FUNCTION key.
Press key.
Press key.
Bit1 - 8 are set.
Press key during setting.
START
Soft SW2 - 65 are set.
To finish the settings halfway between
SW 1 and SW65, press the STOP key.
In this case, the setting being done to
the SW No. on display will be nullified
while settings done to the preceding
SW Nos. remain in effect.
The soft switch mode is terminated.
2 – 9
Page 14
FO-2970MU
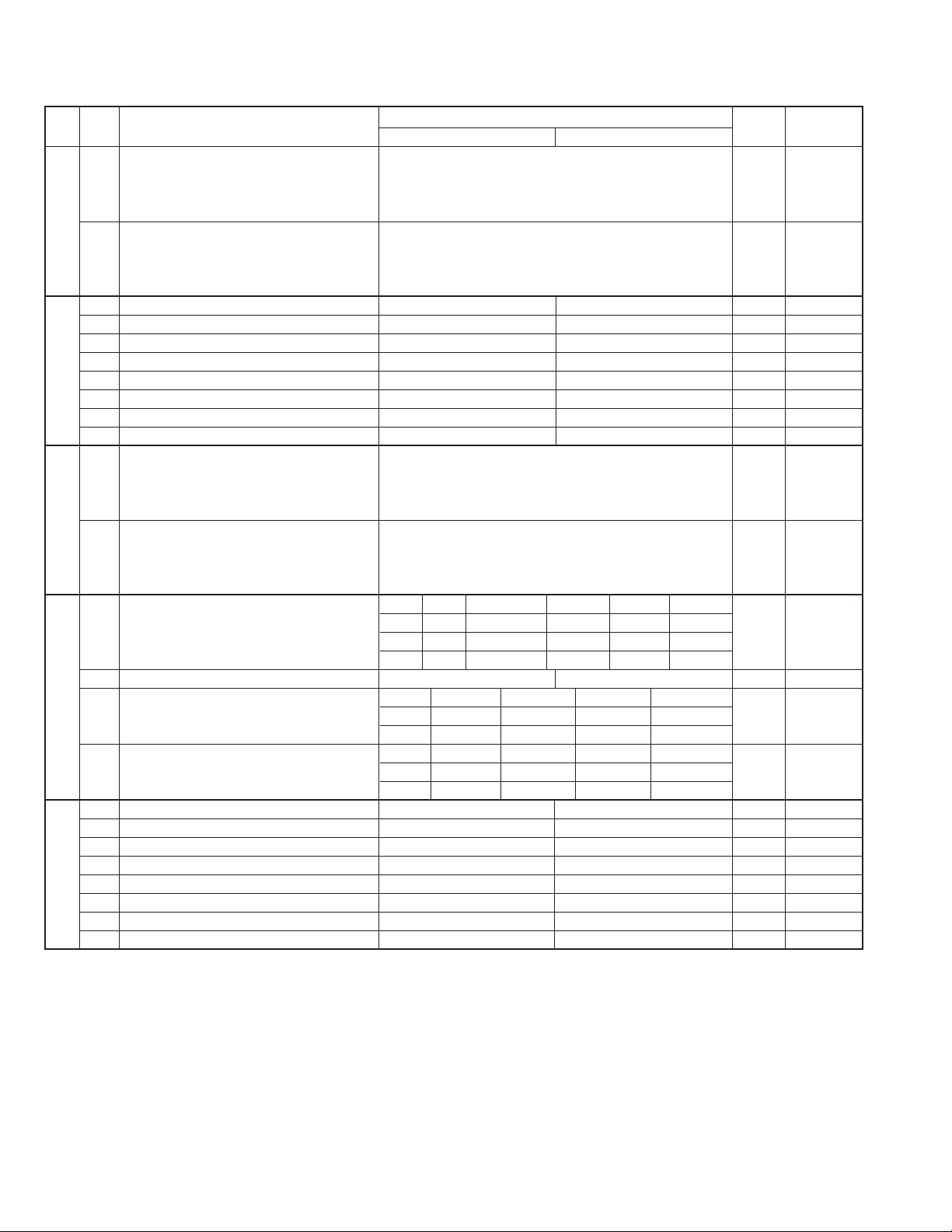
4. Soft switch description
• Soft switch
DATA
SW
NO.
NO.
1 Recall interval Binary input 8421 0 OPTION
2 No. = 1234 1 Set to 01~15
3 0101(5 x 60 sec = 5 min) 0
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4 Delay timer of after line connect in auto dial 3.6 sec 3.0 sec 1.7 sec 3.0 sec
SW5
4 1
5 Recall times Binary input 8421 0 OPTION
6 No. = 5678 0 Set to 0~10
7 0010(Twice) 1
8 0
1 Dial mode Pulse Tone 0 OPTION
2 Reception mode Auto Manual 1 Recep key
3 ECM mode No Yes 0 OPTION
4 CNG detection in stand-by mode No Yes 0 OPTION
5 Polling security On Off 0 FUNC +3
6 Automatic cover sheet No Yes 1 OPTION
7 Junk fax function in manual reception Yes No 0
8 Anti junk fax function Yes No 0 OPTION
1 Number of rings for auto receive Binary input 8421 0 OPTION
2 No. = 1234 1
3 0100(4 times) 0
4 0
5 Automatic switching manual to auto receive Binary input 8421 0
6 mode No. = 5678 0
7 (0: OFF) 0000(off) 0
8 0
Communication results printout Error Err/Tmr/Mem Send only No print Always OPTION
1 (transaction report) No. 1 0 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 0 1 0 1 0
3 No. 3 1 0 0 0 0 1
4 Delay timer before line connect in auto dial 3 sec 0 sec 0
5 No. 5 1 1 0 0 0
6 No. 6 1 0 1 0 1
Number of CNG detect (STAND-BY mode) 1 pulse 2 pulses 3 pulses 4 pulses
7 No. 7 0 0 1 0 0
8 No. 8 0 1 0 0 1
1 Time format 24-hours 12-hours 0
2 Date format Month-Day-Year Day-Month-Year 1
3 Sender’s information transmit Off On 0
4 Footer print On Off 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Substitute reception Off On 0
7 Substitute reception conditions Reception disable without TSI Reception enable without TSI 0
8 CSI transmission Off On 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 10
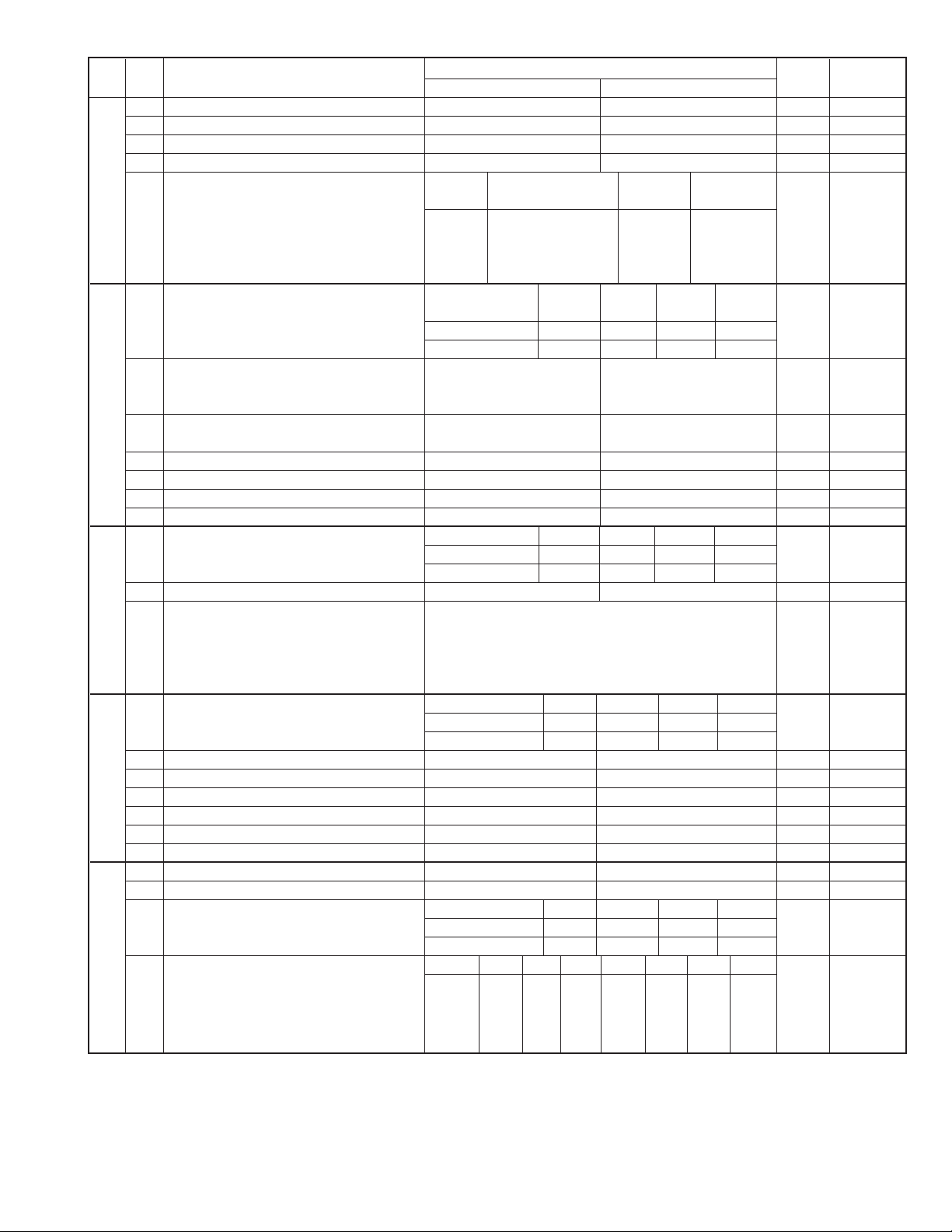
Page 15
FO-2970MU
DATA
SW
NO.
NO.
1 H2 mode No Yes 0
2 MH fixed Yes No
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
SW6
SW7
SW8
SW9 4 Equalizer freeze conditions All 7200 bps 0
SW10
Modem speed V.17 V. 29
(DCS data reception speed)
5 No. 5 1111 0 0 0 0 1
6 No. 6 0000 0 0 0 0 0
7 No. 7 0101 0 1 1 0 0
8 No. 8 0011 1 1 0 0 0
Reception speed fixed NO V. 17- V. 29- V. 27 ter-
1 No. 1 0 1 0 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 1 0 0
3 DIS receive acknowledgement during Twice 0 0
G3 transmission
4 Non modulated carrier for V.29 On Off 0
transmission mode
5 EOL detect timer 25 sec 13 sec 0
6 Protocol monitor On Off 0
7 Line monitor On Off 0
8 Length limitation of copy/send/receive No limit Copy/Send:1m Receive:1.5 m 0
Digital line equalization setting 0 Km 1.8 Km 3.6 Km 7.2 Km
1 (Reception) No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
3 Dial pausing (sec/pause) 2sec 4sec 1
4 Signal transmission level Binary input 16 8 4 2 1 0
5 No. = 45678 1
6 01001 (–9 dBm) 0
7 0
8 1
CED tone signal interval 75 ms 500 ms 750 ms 1000 ms
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
3 Equalizer freeze control (MODEM) On Off 0
5 CED detection time 500 ms 1000 ms 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Busy tone detection (after auto dial) Yes No 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
CI off detection timer 1200 ms 1000 ms 700 ms 350 ms
3 (Distinctive ring setting off only) No. 3 0 1 0 1 0
4 No. 4 0 0 1 1 1
Distinctive ringing setting OFF STD
5 Factory setting : OFF No. 5 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
6 No. 6 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 Canada
7 No. 7 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 Only
8 No. 8 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
14400 12000
9600 7200 9600 7200 4800 2400
RING1 RING2 RING3 RING4 RING5 OPTION
0
(depends on remote machine)
V. 27ter
14400 bps 9600 bps 4800 bps
setting
Initial
0
Remarks
When 14400 bps
modem used,
setting to
14400 bps is
ignored.
RING4/RING5
2 – 11
Page 16
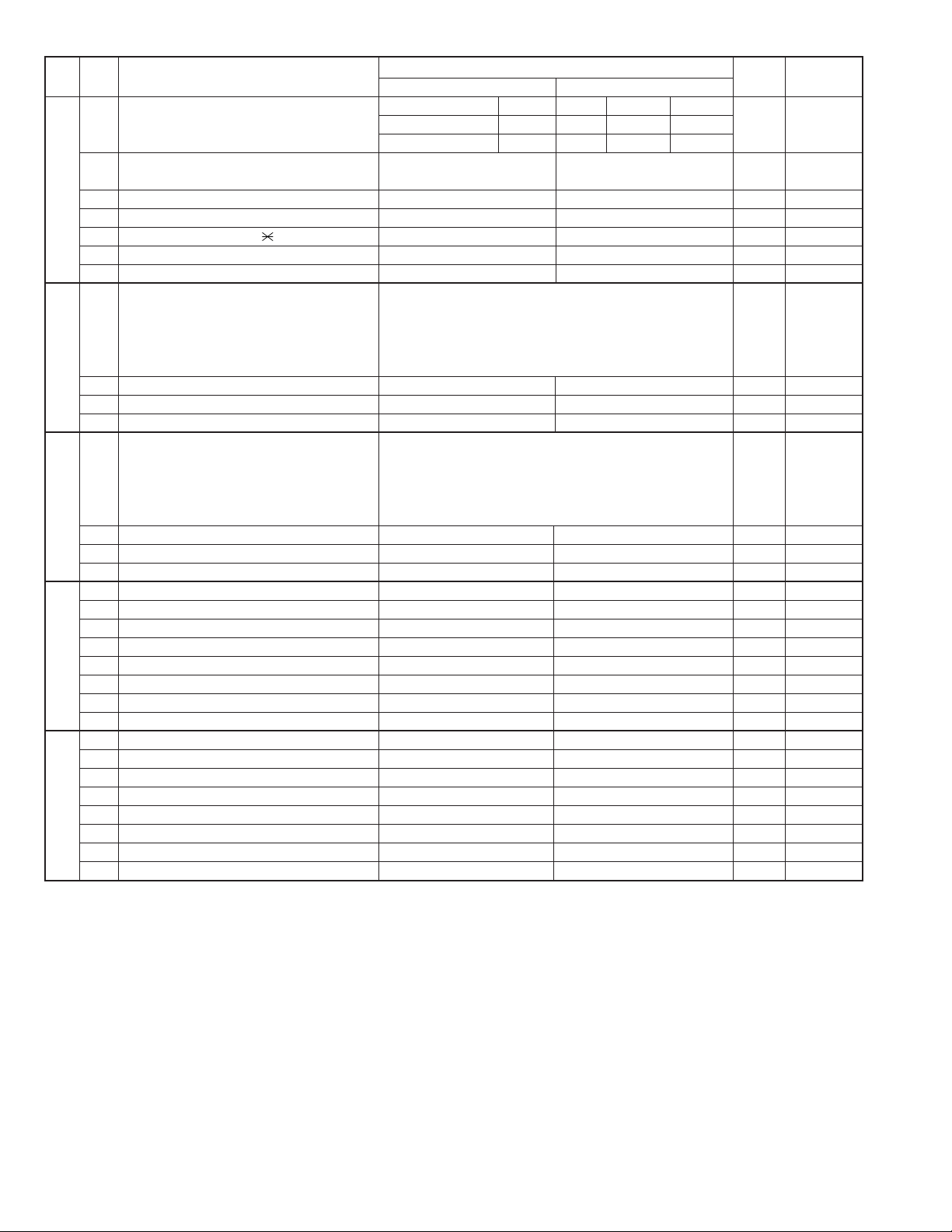
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW11
SW12
SW13
SW14
SW15
DATA
NO.
End buzzer 3 sec 1 sec No Beep No Beep OPTION
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
3 Communication error treatment No communication error Communication error 0
in RTN sending mode (reception)
4 CNG transmission after auto dialing No Yes 0
5 Error criterion 10 ~ 20 % 5 ~ 10 % 0
6 Pulse to tone change by key On Off 0
7 CNG transmission in manual transmission No Yes 0
8 Reserved 0
1 DTMF signal transmission level (Low) Binary input 16 8 4 2 1 0
2 No. = 12345 1
3 01100 (–6 dBm) 1
4 0
5 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 DTMF signal transmission level (High) Binary input 16 8 4 2 1 0
2 No. = 12345 1
3 01000 (–4 dBm) 0
4 0
5 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 12
Page 17
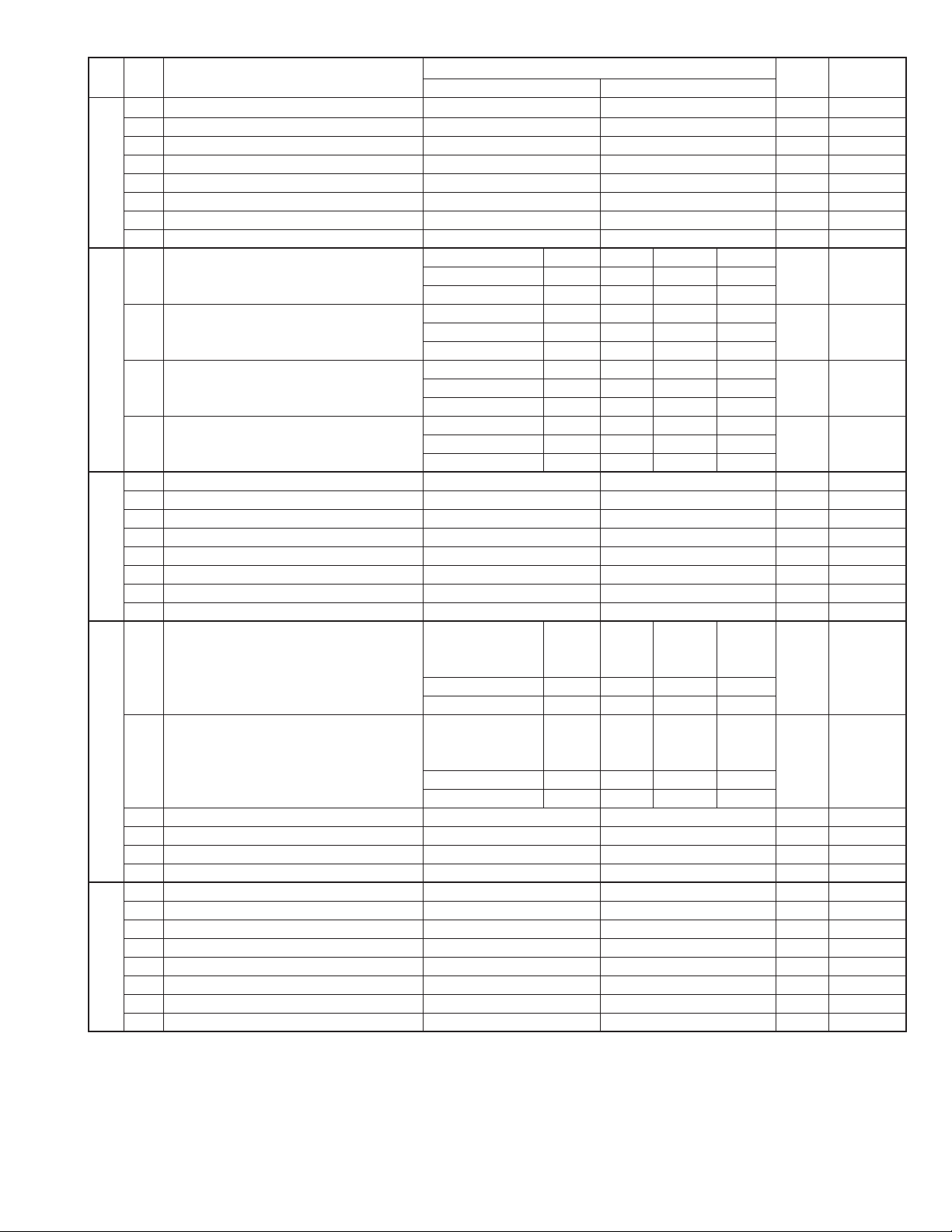
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW16
SW17
SW18
SW19
SW20
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
Speaker volume (3 stages) High High Middle Low Using
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 1 Volume
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0 key
Hand-set receiver volume (3 stages) High High Middle Low Using
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 1 Volume
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 0 key
Ringer volume (4 stages) Off High Middle Low Using
5 No. 5 0 0 1 1 1 Volume
6 No. 6 0 1 0 1 0 key
Key volume Off High Low Low
7 No. 7 0 0 1 1 1
8 No. 8 0 1 0 1 0
1 Reserved 1
2 Auto reception in PC I/F mode FAX PC 1 FUNC + #
3 Summer time setting No Yes 1 FUNC + 3
4 Sender’s phone number setting Cannot change Change allowed 0
5 Polling key Yes No 0 OPTION
6 Activity report print Automatic printout No printout when memory full 0 OPTION
7 Total communication hours and pages print Off On 0
8 Line density selection Fine Standard 0 OPTION
Density adjustment (when Fine/STD mode) Normal Faint Deep Deep
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
Density adjustment (when Half-tone mode) Normal Faint Deep Deep
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 0
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 F.A.S.T (RMS) mode On Off 1
8 Quick on-line Yes No 1 OPTION
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
(when Dark
mode)
(when Dark
mode)
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 13
Page 18
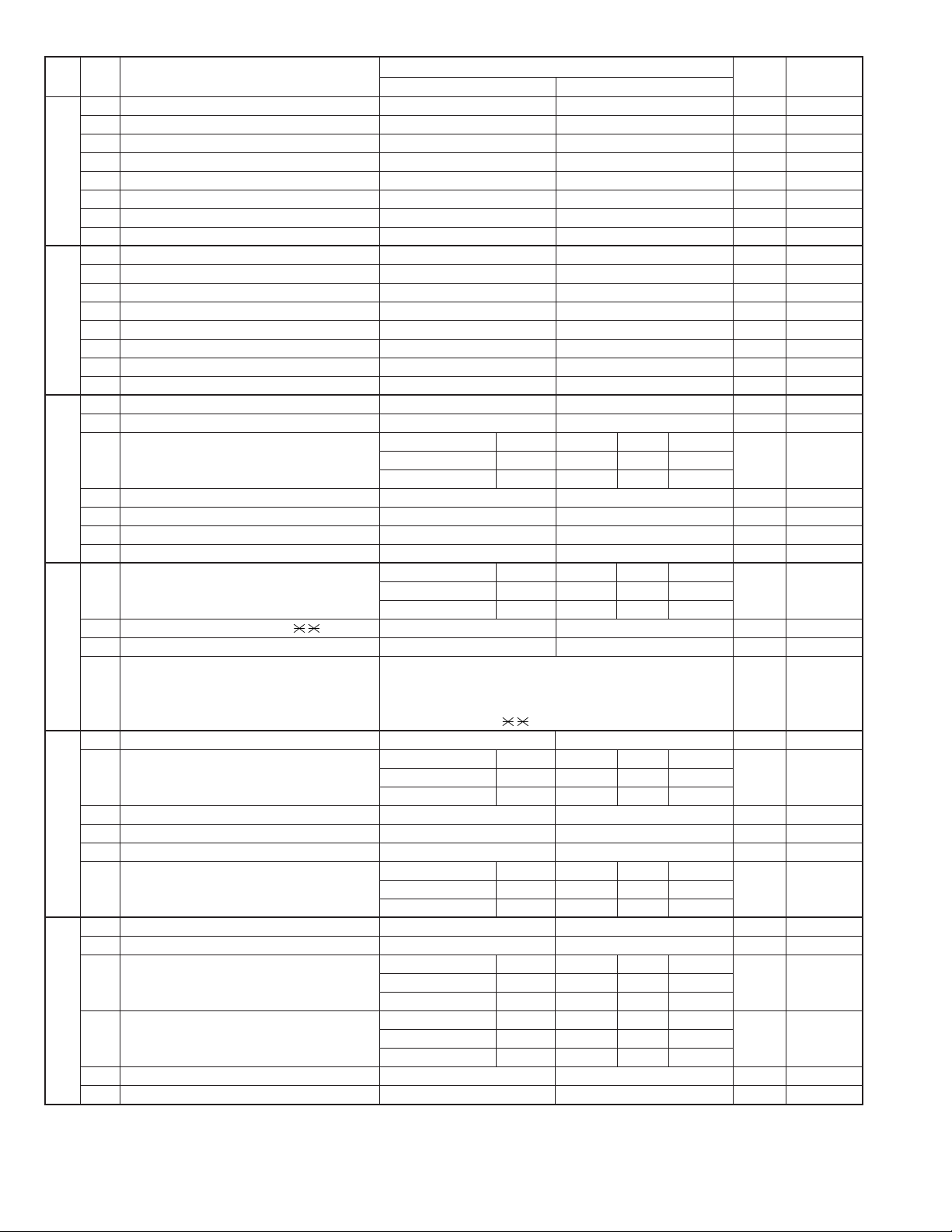
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW21
SW22
SW23
SW24
SW25
SW26
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Automatic reduce of receive Auto 100% 1 OPTION
2 Cut off mode (COPY mode) Continue Cut-off 0 OPTION
Paper set size Letter Legal A4 Letter OPTION
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 0
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
DTMF detection time 50 ms 80 ms 100 ms 120 ms
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
3
Protection remote reception (5 ) detect
4 Reserved 0
5 Remote operation code figures by external Binary input 8421 0 OPTION
6 tel (0 ~ 9) No. = 5678(Data No.) 1
7 EX 0101 0
8 eg. 5 1
1
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Shorter duration)
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time 650 ms 900 ms 2700 ms 900 ms
2 (Longer duration) No. 2 0 0 1 1 0
3 No. 3 0 1 0 1 1
4 Busy tone continuous sound detect time 10 sec 5 sec 1
5 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect No Yes 0
6 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect No Yes 0
Busy tone detection pulse number 2 pulses 4 pulses 6 pulses 10 pulses
7 No. 7 0 0 1 1 0
8 No. 8 0 1 0 1 1
1 TAD connect Yes No 0 Recep key
2 Fax switching when A.M. full Yes No 0 OPTION
Selection time of quiet detection 30 sec 40 sec 50 sec 60 sec
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 0
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 1
Number of CNG detect (AM mode) 1 pulse 2 pulses 3 pulses 4 pulses
5 No. 5 0 0 1 1 0
6 No. 6 0 1 0 1 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 1
ITEM
Yes No 0 OPTION
350ms 150 ms 0
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 14
Page 19
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW27
SW28
SW29
SW30
SW31
DATA
NO.
1 Quiet detect time Binary input 8421 0 OPTION
2 No. = 1234 1
3 0100(4 sec) 0
4 0
5 Quiet detect start timing Binary input 8421 0
6 No. = 5678 1
7 0101(5 sec) 0
8 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 15
Page 20
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW32
SW33
SW34
SW35
SW36
SW37
SW38
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 1
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 1
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 16
Page 21
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW39
SW40
SW41
SW42
SW43
SW44
SW45
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 17
Page 22
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW46
SW47
SW48
SW49
SW50
SW51
SW52
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 18
Page 23
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW53
SW54
SW55
SW56
SW57
SW58
SW59
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 1
1 V.34 mode sending speed Sending speed = 2400 (bps) x N 1
2 Example: 1
3 2400 (bps) x 12 = 28800 (bps) 1
4 2400 (bps) is set for N = 0. 0
5 V.34 mode receiving speed Receiving speed = 2400 (bps) x N 1
6 Example: 1
7 2400 (bps) x 12 = 28800 (bps) 1
8 2400 (bps) is set for N = 0. 0
1
V.34 mode function in case of manual communication
2 V.34 mode function On Off 1
3 V.34 control channel communication speed 2400 bps 1200 bps 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
33600 (bps) is set for N = 15.
33600 (bps) is set for N = 15.
On Off 1
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 19
Page 24
FO-2970MU
SW
NO.
SW60
SW61
SW62
SW63
SW64
SW65
DATA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 1
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 1
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 1
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 1
7 Reserved 1
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 1
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 1
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 20
Page 25
FO-2970MU
• Soft switch function description
SW1 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Recall interval
Choice is made for a recall interval for speed, rapid dial numbers, ten
key +START and search + START. Use a binary number to program
this. If set to 0 accidentally, 1 will be assumed.
SW1 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Recall times
Choice is made as to how many recall times should be made. Use a
binary number to program this.
SW2 No. 1 Dial mode
Switch the type according to the telephone circuit connected to the facsimile.
0: TONE DIAL
1: PULSE DIAL
SW2 No. 2 Reception mode
Auto/manual receiving mode is set.
SW2 No. 3 ECM mode
Used to determine ECM mode function. Refer to the following table.
SW2- No. 3 ECM mode 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 011111111
SW6- No. 2 MH fixed 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 101010101
Compression method ECM MMR mode Yes No Yes No No No No No No No No No No No No No
ECM MR mode Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No No No No No No No No No
ECM MMH mode Yes Yes No No Yes Yes No No No No No No No No No No
ECM MH mode Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No No No No No No No No
MR mode Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No
MH mode Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
(Depending on remote machine)
SW2 No. 4 CNG detection in stand-by mode
The CNG signal detection function during stand-by stops.
0: Y es
1: No
SW2 No. 5 Polling security
This switch is employed to enable or disable the polling operation using
the ID code verification function, in order to prevent unauthorized polling operation.
SW2 No. 6 Automatic cover sheet
When "0" (=YES) is selected, the cover sheet is automatically sent after
transmission of the original to notify the receiver of the number of original sheets transmitted.
SW2 No. 7 Junk fax function in manual reception
It is set whether JUNK-FAX is functioned in the manual receiving mode
or not.
SW2 No. 8 Anti junk fax function
This function is used to receive data from a specific remote machine
(station registered in entry mode). It is the function that refused a reception in the case that TSI of remote machine matched with fax number of
the station registered.
0: No
1: Y es
SW3 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Number of rings for auto receive
When the machine is set in the auto receive mode, the number of rings
before answering can be selected. It may be set from one to nine rings
using a binary number. If the soft switch was set to 1, a direct connection is made to the facsimile. If it was set to 0 accidentally, receive ring is
set to 1. If it was above 9, receive rings are set to 9.
SW3 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Automatic switching manual to auto receive mode
(0: OFF)
This setting allows machine to switch from manual to Auto Receive mode.
Setting this number to 0 forces machine to stay in Manual receive mode.
Entering the binary number 0 forces the machine to remain in the manual
answer mode. If a number between 1 and 9 is entered, the machine will
go into the answer mode after the given number of rings. However, it
can be used as an ordinary telephone if the handset is taken off the
hook before this programmed number is finished. If entry of a number
above 9 by accident, it will be set to 9. In this case, it must be corrected
to the proper number.
SW4 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Communication results printout
(transaction report)
Every communication, the result can be output. As usual, it is set to print
the timer sending communication error alone. If No.1 : 1 No.2 : 1 No.3 :
0 are set, printing is always on (printed ever if it is normally ended).
000 : Error, timer and memory sending/receiving
010 : Sending
110 : Continuous printing
100 : Not printed
001 : Communication error
SW4 No. 4 Delay timer before line connect in auto dial
Delay time between the dial key input and line connection under the
auto dial mode.
SW4 No. 5, No. 6 Delay timer of after line connect in auto dial
Delay time between the line connection and dial data output under the
auto-dial mode.
SW4 No. 7, No. 8 Number of CNG detect (STAND-BY mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW5 No. 1 Time format
When this switch is set to "0", time is displayed in 12-hour system.
When set to "1", 24-hour system.
2 – 21
Page 26

FO-2970MU
SW5 No. 2 Date format
Used to select date display/print formats.
0: DAY-Month-Year
1: Month-DAY-Year
SW5 No. 3 Sender’s information transmit
When it is set at 0, sender’s name, sending page number and so on
are automatically printed in the recording paper on the receiving side
during transmission. Thus, the sender can be known on the receiving
side.
0: Applied
1: Not applied
SW5 No. 4 Footer print
When set to "1", the date of reception, the sender machine No., and the
page No. are automatically recorded at the end of reception.
SW5 No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW5 No. 6 Substitute reception
Selection of substitute reception in the case of recording paper exhausted or paper jam. If set to "NO", auto receive is disabled even when
the receive memory is ready to receive.
Substitute reception is not performed even during receive operation.
SW5 No. 7 Substitute reception conditions
Selection of substitute reception according to existence of TEL number
from transmitting side. Initial setting allows substitute reception without
CSI. If set to "no", the receiver cannot receive any documents
SW5 No. 8 CSI transmission
CSI signal contains the sender’s phone number registered in the machine. If this switch is set to "1", no sender’s name will be printed at the
receiving side.
SW6 No. 1 H2 mode
Used to determine reception of H2 mode (15 sec transmission mode).
When set to OFF , H2 mode reception is inhibited even though the transmitting machine has H2 mode function.
SW6 No. 2 MH fixed
Normally set to allow automatic selection of MH and MR mode according to the remote side.
If set to 1, the mode is fixed to MH and is useful if the remote side is a
MH only unit ; or a lot of image distortion is met due to a bad line.
SW6 No. 3, No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW6 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Modem speed (DCS data reception speed)
Used to determine the initial modem speed. The default is
14400BPS(V.17). It may be necessary to program it to a slower speed
when frequent line fallback is encountered, in order to save the time
required for the fallback procedure.
SW7 No. 1, No. 2 Reception speed fixed
The transferable speed of modem in the receiving mode is set.
SW7 No. 3 DIS receive acknowledgement during G3 transmission
Used to make a choice of whether reception of NSF (DIS) is acknowledged after receiving two NSFs (DISs) or receiving one NSF (two DISs).
It may be useful for overseas communication to avoid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW7 No. 4 Non modulated carrier for V.29 transmission mode
Though transmission of a non-modulated carrier is not required for transmission by the V29 modem according to the CCITT Recommendation,
it may be permitted to send a non-modulated carrier before the image
signal to avoid an echo suppression problem.
It may be useful for overseas communication to avoid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW7 No. 5 EOL detect timer
25 seconds or 13 seconds are selected for the detection timer of EOL
(end of line). This is effective against communication trouble on a specific type of long EOL.
0: 13 seconds
1: 25 seconds
SW7 No. 6 Protocol monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", communication can be checked, in case
of troubles, without using a G3 tester or other tools.
When communication FSK data transmission or reception is made, the
data is taken into buffer. When communication is finished, the data
analyzed and printed out. When data is received with the line monitor
(SW7-No.7) set to "1" the reception level is also printed out.
SW7 No. 7 Line monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", the transmission speed and the reception level are displayed on the LCD. Used for line tests.
SW7 No. 8 Length limitation of copy/send/receive
Used to set the maximum page length.
To avoid possible paper jam, the page length is normally limited to 1m
for copy or transmit, and 1.5 meters for receive.
It is possible to set it to "No limit" to transmit/receive a long document,
such as a computer print form, etc. (In this case, the receiver/transmitter must also be set to no limit.)
SW8 No. 1, No. 2 Digital line equalization setting (Reception)
The specific line equalizer is inserted.
No. 1 No. 2
0 0 The line equalizer built in the modem is turned off.
0 1 Line equalizer corresponding to 1.8 km
1 0 Line equalizer corresponding to 3.6 km
0 1 Line equalizer corresponding to 7.2 km
SW8 No. 3 Dial pausing (sec/pause)
Pauses can be inserted between telephone numbers of direct dial connection. Selection of 4 sec or 2 sec pause is available.
SW8 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Signal transmission level
Used to control the signal transmission level in the range of –0dB to
–31dB.
SW9 No. 1, No. 2 CED tone signal interval
For international communication, the 2100Hz CED tone may act as an
echo suppresser switch, causing a communication problem. Though this
soft switch is normally set to "00", it should be change the time between
CED tone and DIS signal from 75ms to 1000ms to eliminate the communication problem caused by echo.
SW9 No. 3 Equalizer freeze control (MODEM)
This switch is used to perform reception operation by fixing the equalizer control of modem for the line which is always in an unfavorable
state and picture cannot be received. Usually, the control is executed
according to the state of line where the equalizer setting is changed
always.
SW9 No. 4 Equalizer freeze conditions
Setting which specifies SW9 No.3 control only in condition of 7200bps
modem speed.
SW9 No. 5 CED detection time
The detection time of the CED signal from the called side in the auto
calling mode is set.
SW9 No. 6, No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW9 No. 8 Busy tone detection (after auto dial)
this is used to set busy tone detection in auto dialing.
SW10 No.1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 22
Page 27
FO-2970MU
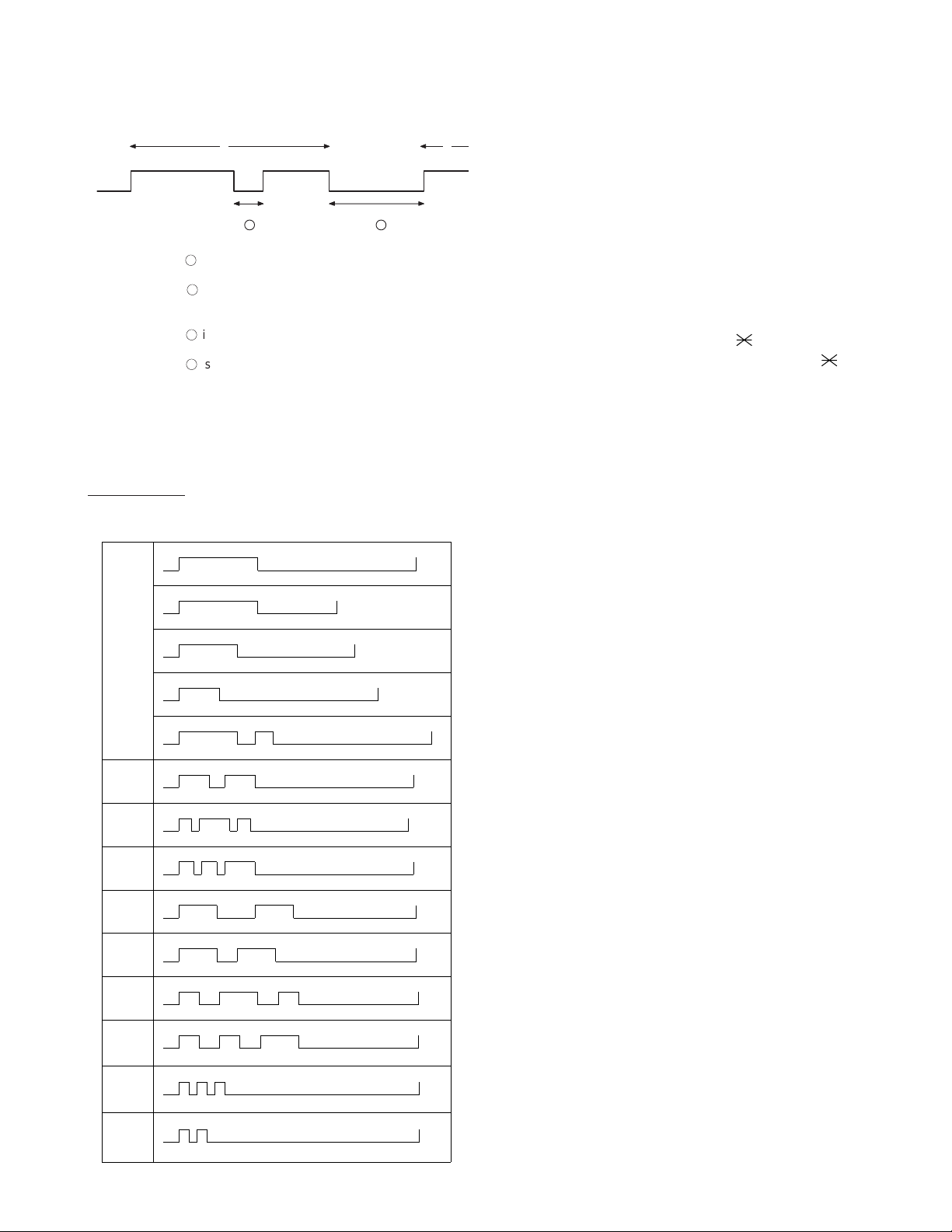
SW10 No. 3, No. 4 CI off detection timer
(Distinctive ring setting off only)
Set the minimum time period of CI signal interruption which affords to be
judged as a CI OFF section with 50ms steps.
(Example)
A B
400msec
1
2000msec
2
01 : 700ms (CI interruption>700ms:Judged as a CI OFF section)
The section 1 is not judged as a CI OFF section, the CI signal A is
counted as one signal.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section, the CI signal B is
considered as the second signal.
11: 350ms (CI interruption>350ms: Judged as a CI OFF section)
The section 1 is judged as a CI OFF section, and the CI signal A
is counted as two signals.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section, and the CI signal B
is considered as the third signal.
SW10 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Distinctive ringing
Factory setting : OFF
When the ringing setting is turned off, all of the CI signal are received.
When any of the standard, and ring patterns 1 through 4 or 5 is selected
for the ringing setting, only the selected CI signal is received.
CI signal patterns
The CI signal patterns consists of the standard pattern, and ring pat-
terns 1 through 9. The standard pattern is the conventional one.
2S
4S
2S
4S
4S
4S
4S
3S
3.5S
3S
3S
4.8S
5.3S
STANDARD
RING
PATTERN 1
for USA
RING
PATTERN 2
for USA
RING
PATTERN 3
for USA
RING
PATTERN 4
for USA
RING
PATTERN 1
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 2
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 3
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 4
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 5
for CANADA
0.8S
0.3S
0.2S
0.4S
0.5S
0.5S
0.25S
0.2S 0.2S
0.25S
0.2S
2S
1.5S
1S
1.5S
0.4S
1S
0.2S
0.4S 0.8S
0.2S 0.2S
1S
1S
0.5S
0.5S
0.25S 0.25S
0.25S
3S
4S
0.5S
0.5S
0.8S
0.3S
1S
1S
1S
1S 0.5S
0.5S0.5S
1S
0.5S0.5S
SW11 No. 1, No. 2 End buzzer
The sounding length of the buzzer for normal end of operation set.
SW11 No. 3 Communication error treatment in RTN setting mode
(reception)
Used to determine communication error treatment when RTN is sent by
occurrence of a received image error in G3 reception. When it is set to
“1”, communication error is judged as no error.
SW11 No. 4 CNG transmission after auto dialing
When set to “0”, this model allows CNG transmission by pressing the
Start key in the key pad dialing mode. When set to “1”, CNG transmission in the key pad dialing mode cannot be performed. In either case.
CNG transmission can be performed in the auto dial mode.
SW11 No. 5 Error criterion
Used to select error criterion for sending back RTN when receiving image data.
SW11 No. 6 Pulse to tone change by
When setting to 1, the mode is changed by pressing the key from the
pulse dial mode to the tone dial mode.
SW11 No. 7 CNG transmission in manual transmission
CNG signal sending ON/OFF in case of manual transmission is set.
SW11 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW12 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level (Low)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (lower frequency)
00000 : 0 dBm
↓
11111 : -15.5 dBm
SW12 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW13 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level (High)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (higher frequency)
00000 : 0 dBm
↓
11111 : -15.5 dBm
SW13 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW14 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW14 No. 4 , No. 5 Reserved
Set to “1”.
SW14 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW15 No.1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW16 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW16 No. 2 ~ No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW16 No. 5 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW16 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 23
Page 28

FO-2970MU
SW17 No. 1, No. 2 Speaker volume (3 stages)
Used to adjust sound volume from a speaker.
SW17 No. 3, No. 4 Hand-set receiver volume (3 stages)
Used to adjust sound volume from a handset receiver volume.
SW17 No. 5, No. 6 Ringer volume (4 stages)
Used to adjust ringing volume.
SW17 No. 7, No. 8 Key volume
Key buzzer volume:
The sound volume of key inputting buzzer and other buzzers is set.
SW18 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW18 No. 2 Auto reception in PC I/F mode
Automatic receiving of I/F mode:
Which receives the call is determined.
SW18 No. 3 Summer time setting
The day light saving function ON/OFF is set.
SW18 No. 4 Sender’s phone number setting
Whether the registered sender’s phone number can be changed or not
is selected. If it is set at 1, the phone number of the sender can not be
registered or changed. Set 1 in order to prevent careless change of the
sender’s phone number.
0: Change allowed
1: Cannot change
SW18 No. 5 Polling key
If this switch is set to 1, the last of Rapid key works as polling key.
SW18 No. 6 Activity report print
Whether the communication record table is automatically printed or not,
it is selected if the number of communication data is excessive. Regardless of the setting of this selection, communication record table can be
printed at all times by operating the keys.
FUNCTION + “2” + “#” + “START”
When the communication record table is printed, the memorized content of the data sent and received up to now will be all cleared (erased).
If No (non-printing) is set, the oldest data will be erased when the number
of memorized items is excessive.
0: No (first data lost when memory is full)
1: YES (when memory is full)
SW18 No. 7 Total communication hours and pages print
Whether the total time of communication and total number of sheets are
recorded in the communication record table or not is selected.
0: Recorded.
1: Not recorded.
SW18 No. 8 Line density selection
Used to set the transmission mode which is automatically selected when
the Resolution Key is not pressed. In the copy mode, however, the fine
mode is automatically selected unless the Resolution key is manually
set to another mode.
SW19 No. 1 , No. 2 Density adjustment (when Fine/STD mode)
This is used for density adjustment in fine/standard mode. Adjust the
density according to that of frequently used original.
Set to “Dark” for darker reading (either in the auto or the dark mode) of
light original. Set to “Light” for lighter reading (either in the auto or the
dark mode) of dark original.
Set to “Dark only in dark mode” for darker reading only in the dark mode.
SW19 No. 3 , No. 4 Density adjustment (when Half-tone mode)
This is used for density adjustment in the half tone. Setting procedures
are the same as SW19 No. 1, No. 2.
SW19 No. 5, No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW19 No. 7 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW19 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW20 No. 1 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW20 No. 7 F.A.S.T (RMS) mode
Used to determine a function of remote maintenance system (F .A.S.T).
SW20 No. 8 Quick on-line
It is selected whether auto dial call is activated in the memory input
mode when one document is completely read or when all pages are
completely read.
SW21 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW21 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW21 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW22 No.1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW23 No. 1 Automatic reduce of receive
If set to 1, it is reduced automatically.
SW23 No. 2 Cut off mode (COPY mode)
When in copy, if the scanned data is out of the range of recording, the
operator has one of the choices below using the switch
1: Continue: Data is printed onto the next page with the last 20mm
also printed at the beginning of the next page
0: Cut off. Data scanned out of the limit is cut off (a page is printed.)
SW23 No. 3, No. 4 Paper set size
At present a size of the record paper.
00: LETTER
01: LEGAL
10: A4
SW23 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW24 No. 1, No. 2 DTMF detection time
Used to set detect time of DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) used in
remote reception (5 ). The longer the detection time is, the error
detection is caused by noises.
SW24 No. 3 Protection remote reception (5 ) detect
Used to set the function of remote reception (5 ). When set to “1”,
the remote reception function is disabled.
SW24 No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW24 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Remote operation code figures by external tel
(0 ~ 9)
Remote operation codes can be changed from 0 through 9. if set to
greater than 9, it defaults to 9. The “5 ” is not changed.
2 – 24
Page 29

FO-2970MU
SW25 No. 1 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Shorter duration)
The initial value of detection is set according to electric condition.
The set value is changed according to the local switch board. (Erroneous detection of sound is reduced.)
Normally the upper limit is set to 900msec. and the lower limit to 150msec.
If erroneous detection is caused by sound, etc., adjust the detection
range.
The lower limit can be set in the range of 350msec to 150msec.
SW25 No. 2, No. 3 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Longer
duration)
Similarly to SW-25 No.1, the set value can be varied.
The upper limit can be set in the range of 650msec to 2700msec.
SW25 No. 4 Busy tone continuous sound detect time
Set detecting time busy tone for 5 seconds or as is PTT.
SW25 No. 5 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect
Used to select detection of the continuous sound of certain frequency.
SW25 No. 6 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect
Used to select detection of the intermittent sound of certain frequency.
SW25 No. 7, No. 8 Busy tone detection pulse number
Used to set detection of Busy tone intermittent sounds.
SW26 No. 1 TAD connect
When connecting the answering machine to the extension telephone
jack.
SW26 No. 2 Fax switching when A.M. full
If the answering machine’s memory (tape) is full and there is no response, the machine automatically switches to Fax reception.
SW26 No. 3, No. 4 Selection time of quiet detection
The switch which sets the time from the start of detection function to the
end of the function.
SW26 No. 5, No. 6 Number of CNG detect (AM mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW26 No. 7, Reserved
Set to "0".
SW26 No. 8, Reserved
Set to "1".
SW27 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Quiet detect time
When an answering machine is connected, if a no sound status is detected for a certain period of time, the machine judges it as a transmission from a facsimile machine and automatically switches to the FAX
mode.
SW27 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Quiet detect start timing
Inserts a pause before commencing quit detection.
0000: 0 seconds
1111 : 15 seconds
SW28 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW29 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW30 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW31 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW32 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW33 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW33 No. 2 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW33 No. 3 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW34 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW34 No. 5, No. 6 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW34 No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW34 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW35 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW35 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW35 No. 4 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW35 No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW35 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW36 No. 1 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW36 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW37 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW38 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW39 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW40 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW41 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW42 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW43 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW44 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW45 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW46 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW47 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW48 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW49 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "1".
2 – 25
Page 30

FO-2970MU
SW49 No. 2 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW50 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW51 No. 1 ~ No.8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW52 No. 1 ~ No.3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW52 No. 4, No. 5 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW52 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW52 No. 7 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW52 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW53 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW53 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW53 No. 4 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW53 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW54 No. 1 ~ No. 4 V.34 mode sending speed
Used to determine the initial modem speed when communication method
is V.34 sending mode.
SW54 No. 5 ~ No. 8 V.34 mode receiving speed
Used to determine the initial modem speed when communication method
is V.34 reception mode.
SW55
No. 1 V.34 mode function in case of manual communication
Used to select whether the V .34 mode is made valid when automatically
transmitting/receiving.
SW55 No. 2 V.34 mode function
Used to select the V .34 mode for communication when set to "1", communication method is V.34 mode.
SW55 No. 3 V.34 control channel communication speed
Used to select the control channel communication speed for V.34 mode.
SW55 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW56 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW56 No. 2, No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW56 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW57 No. 1 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW57 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW58 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW59 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW59 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW60 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW60 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW60 No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW60 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW61 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW61 No. 5 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW61 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW62 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW62 No. 2, No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW62 No. 4 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW62 No. 5, No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW62 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW63 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW63 No. 2 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW63 No. 3 ~ No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW63 No. 6, No. 7 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW63 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW64 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW64 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW64 No. 4 ~ No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW64 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW65 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW65 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "1".
SW65 No. 4 ~ No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW65 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "1".
2 – 26
Page 31

[3] Troubleshooting
y
FO-2970MU
1. Fax troubleshooting
Refer to the following actions to troubleshoot any of the problems mentioned in 1-4.
[1] A communication error occurs.
[2] Image distortion produced.
[3] Unable to do overseas communication.
[4] Communication speed slow due to FALLBACK.
• Increase the transmission level SOFT SWITCH 8-4, 5, 6, 7, 8
May be used in case [1] [2] [3].
• Apply line equalization SOFT SWITCH 8-1, 2
May be used in all cases.
• Slow down the transmission speed SOFT SWITCH 6-5, 6, 7, 8
May be used in case [2] [3].
• Replace the LIU PWB.
May be used in all cases.
• Replace the control PWB.
May be used in all cases.
* If transmission problems still exist on the machine, use the following
format and check the related matters.
• Decrease the transmission level SOFT SWITCH 8-4, 5, 6, 7, 8
May be used in case [3].
TO: ATT: Ref.No. :
CC: ATT: Date :
FM: Dept :
Sign :
***** Facsimile communication problem *****
From: Mr. Fax Tel No.:
Our customer Name T el No.
Address Fax No.
Contact person Model name
Other party Name T el No.
Address Fax No.
Contact person Model name
Problem mode Line: Domestic / international Mode: G3 Phase: A. B. C. D.
Reception / Transmission
Frequency: % ROM version:
Confirmation
item
Our customer
Automatic reception / Manual reception
Automatic dialing / Manual dialing / Others
B1
Other party
B2
Please mark problem with an X
No problem is: 0
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 E2
Ref.No.:
Date:
A1 A2
C1 D2
C2 D1
E1
E2
Our service
Comment
Countermeasure
**** Please attach the G3 data and activity report on problem. ****
Other part
's service
Transmission level setting is ( ) dB at our
customer
Transmission level ( ) dBm
Reception level ( ) dBm
By level meter at B1 and B2
2 – 27
Page 32

FO-2970MU
[4] Error code table
1. Communication error code table
G3 Transmission
Code Final received signal Error Condition (Receiver side)
0 Incomplete signal frame Cannot recognize bit stream after flag
1 NSF, DIS Cannot recognize DCS signal by echo etc.
Cannot recognize NSS signal (FIF code etc)
2 CFR Disconnects line during reception (carrier missing etc)
3 FTT Disconnects line by fallback
4 MCF Disconnects line during reception of multi page
Cannot recognize NSS, DCS signal in the case of mode change
5 PIP or PIN The line is hung up without replying to telephone request from the receiving party.
6 RTN or RTP Cannot recognize NSS, DCS signal after transmit RTN or RTP signal.
7 No signal or DCN No response on receiver side or DCN signal received* (transmitter side)
8 − Owing to error in some page the error could not be corrected although the specified number of
error retransmission was attempted.
11 − Error occurred after or while reception by the remote (receiving) machine was revealed to be
impossible.
12 − Error occurred just after fallback.
13 − Error occurred after a response to retransmission end command was received.
G3 Reception
Code Final received signal Error Condition (Receiver side)
0 Incomplete signal frame Cannot recognize bit stream after flag
1 NSS, DCS Cannot recognize CFR or FTT signal
Disconnects line during transmission (line error)
2 NSC, DTC Cannot recognize NSS signal (FIF code etc)
3 EOP Cannot recognize MCF, PIP, PIN, RTN, RTP signal
4 EOM Cannot recognize MCF, PIP , PIN, RTN, RTP signal in the case of mode change
5 MPS The line is hung up without replying to communication request.
6 PR1-Q Cannot recognize PIP, PIN signal in the case of TALK request
7 No signal or DCN No response in transmitter (cannot recognize DIS signal) or DCN signal received* (receiver side)
8 − Error occurred upon completion of reception of all pages.
9 − Error occurred when mode was changed or Transmission/Reception switching was performed.
10 − Error occurred during partial page or physical page reception.
11 − Error occurred after or during inquiry from the remote (transmitting) machine as to whether
reception is possible or not.
12 − Error occurred during or just after fallback.
13 − Error occurred after the retransmission end command was received.
14 − Error occurred after the voice communication command was received.
2 – 28
Page 33

Super G3 mode
Error Code Transmission Errors Reception Errors
E-16 Same as E-0 Same as E-0
E-17 Same as E-1 Same as E-1
E-18 Same as E-2 Same as E-2
E-19 − Same as E-8
E-20 Same as E-4 Same as E-9
E-21 − Same as E-10
E-22 −−
E-23 Same as E-7 Same as E-7
E-24 Same as E-8 −
E-25 Same as E-11 Same as E-11
E-26 Same as E-12 Same as E-12
E-27 Same as E-13 Same as E-13
E-28 − Same as E-14
E-29
E-30 Error occured during handshaking for super G3 mode
E-31
<Reference> Details of E-29 ~ 31
E-29 Handshaking error in V.8 negotiation procedure
E-30 Handshaking error in V.34 line probing procedure
E-31 Handshaking error in V.34 HDX training procedure
FO-2970MU
2. Service call error massage
The following service call errors may occur in FO-2970MU.
Message Description
1 POLYGON ERROR Cause: When the recognition of the laser beam detection signal (HSYNC) is impossible after the printing is
2 HEATER ERROR Cause: When the disconnection of the thermistor is counted 8 times (80ms).
3 HEATER HIGH ERROR Cause: When the temperature of the heater lamp exceeds 188°C during 200 ms.
4 HEATER LOW ERROR Cause: When the temperature does not exceed 97°C within 15 seconds after the heater lump is ON, or it is
Only the power on and off can be restored when the service error occurs.
started.
[HSYNC interruption is usually done once every 846.7µS for PC printing and once every 1298.7524µS for
other printing (copying, reception and list).]
less than 97°C even while printing.
2 – 29
Page 34

FO-2970MU
CPU
SH7041
SRAM
1M bit
ROM
8M bit
MODEM
33.6k bps
DRAM
1M x 16bit x 3
SCAN LSI
LC82103
RTC
4M bit DRAM
ONLY PC-PRINT
THERMISTER
TEL/LIU
PWB
CIS
SCANNER MOTOR
CNRTH
CNLIU
CNCIS
OPERATION PANEL
PWB
LCD
CNMT
CNPN
SPEAKER
CNSP
ASIC
LR38784
TONER
SENSOR
PICK UP
SOLENOID
LASER UNIT
PAPER FEED MOTOR
FAN
MOTOR
PRINTER
PWB
PERSONAL
COMPUTER
CNPL
CNTNR
CNLSU
CNMMT
POWER
PWB
HEATER
LAMP
CNFM
CNHT
CNPW
CONTROL PWB
CNPRT
SENTRONICS CABLE
BAT
CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
[1] Block diagram
4 – 1
Page 35

[2] Wiring diagram
CNPN
CNLIUA
FJ
CNMT
CNPRT
CNPRT
CNMMT
CNLSU
CNTNR
CNPL
CNPC
CN101
CNPW
CN2
CN1
LINEEXT.TEL
HANDSET
HIGH VOLTAGE
CIRCUIT
INTERLOCK
SWITCH
AC 120V/60HZ
CNFM
CNHS1
CNLIUA
CNHS2
TONER
SENSOR
CNSP
CNCIS
CIS
TX
MOTOR
7
2
22
OPERATION
PANEL
PWB
LCD
14
6
CONTROL PWB
50
PRINTER PWB
PRINTER
MOTOR
4
AUTO POWER
CONTROL
PWB
9
5
3
LASER
SCANING
MOTOR
BEAM DETECTOR
PWB
LSU UNIT
PICKUP
SOLENOID
5
2
36
FAN
MOTOR
3
PC
12
2
HEATER
LAMP
2
POWER SUPPLY
UNIT
CNFUSE
THERMAL
FUSE UNIT
3
CNRTH
THERMISTOR
2
HOOK
SWITCH
PWB
2
TEL LINE
TEL/LIU PWB
12
SPEAKER
CNLCD
FO-2970MU
4 – 2
Page 36

FO-2970MU
CNFUSE
+24VMG+24VS
123
CNRTH
+5V
RTH
1
2
CNSP
SP+
SP–
1
2
CNMT
12345
6
TPA
TPB
TPA-
TPB-
+24V
+24V
CNCIS
1234567
AODG5VSHCISCLK
GLED
VLED
TEL/LIU PWB
CNLIUACNLIUA
+24VDG+5VA
CML
CI-
HS-
RHS-
TXOUT
RXIN
TELMUTE
TELOUT
TELIN
+24VADG+5VA
CML
CI-
HS-
RHS-
TXOUT
RXIN
TELMUTE
TELOUT
TELIN
1234567891011
12
1234567891011
12
OPERATION
PANEL
PWB
CNPN
CNPN
123456789101112131415161718192021
22
123456789101112131415161718192021
22
DG
+5VDG+5VRSE
LD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
P-CHK
TONER
PC IN USE
TEL LINE
FRTSNS
ORGSNS
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
B4SNS
DG
+5VDG+5VRSE
LD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
P-CHK
TONER
PC IN USE
TEL LINE
FRTSNS
ORGSNS
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
B4SNS
CNLCD
CNHS1
12345678910111213
14
DG
+5VVORS
R/WEN.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
LD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
1
2
RHS-
DG
CNHS2
1
2
RHS-
DG
LCD
HOOK
SW PWB
CNFM
123
VFMOUT
N.C.
MG
PRINTER
PWB
POWER SUPPLY
CNPW
CN101
CN2
CN1
+5VDGDG
+24VHMGMG
+24VS
PWRLY-
HLON-
+24V
+24V
ZC
+5VDGDG
+24VHMGMG
+24VS
PWRLY-
HLON-
+24V
+24V
ZC
1234567891011
12
1234567891011
12
HLL
N.C.
HLN
123
L
N.C.
N
123
CNPL
1
2
+24V
PUS
CNMMT
123
4
MA
MA-MBMB-
CNLSU
123456789
+24VDGVIDEO
SAMP
SYNC-
APCSTT
PMCLK
PMD-
PE
CNPC
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435
36
NSTOROBE
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8
NACK
BUSY
PERROR
SELECT
NAUTOFD
N.C.DGDG
PLHDGDGDGDGDGDGDGDGDGDGDGDG
NINIT
NFAULT
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
NSELECTON
CNTNR
12345
+5V
TSENDGN.C.
FG
POUT-
PWMSIN
PIN-
DOP-
TSEN
24VS
MEN-MAMB
VIDEO
SAMP
SYNC-
APCSTT
PMCLK
PMD-PEMCOM
PUS
TC/BIASON
HLON
PWRLY
NSTOROBE
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8DGZC
NACK
BUSY
PERROR
SELECT
NFAULT
NAUTOFD
NINIT
NSELECTIN
+5V
+5VDGDG
+24VH
+24V
VFM-
+24VMGMG
POUT-
PWMSIN
PIN-
DOP-
TSEN
24VS
MEN-
MA
MB
VIDEO
SAMP
SYNC-
APCSTT
PMCLK
PMD-
PE
MCOM
PUS
TC/BIASON
HLON
PWRLY
NSTOROBE
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8
DG
ZC
NACK
BUSY
PERROR
SELECT
NFAULT
NAUTOFD
NINIT
NSELECTIN
+5V
+5V
DG
DG
+24VH
+24V
VFM-
+24V
MG
MG
1a1b2a2b3a3b4a4b5a5b6a6b7a7b8a8b9a9b10a
10b
11a
11b
12a
12b
13a
13b
14a
14b
15a
15b
16a
16b
17a
17b
18a
18b
19a
19b
20a
20b
21a
21b
22a
22b
23a
23b
24a
24b
25a
25b
1a1b2a2b3a3b4a4b5a5b6a6b7a7b8a8b9a
9b
10a
10b
11a
11b
12a
12b
13a
13b
14a
14b
15a
15b
16a
16b
17a
17b
18a
18b
19a
19b
20a
20b
21a
21b
22a
22b
23a
23b
24a
24b
25a
25b
CNPRTCNPRT
CIS
PICK UP
SOLENOID
PRINTER
MOTOR
LSU
UNIT
TONER
SENSOR
PC
FAN MOTOR
TX
MOTOR
THERMAL
FUSE UNIT
HEATER
LAMP
THERMISTOR
SPEAKER
CONTROL PWB
[3] Point- to-point diagram and connector signal name
4 – 3
Page 37

FO-2970MU
CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description
1. General description
The compact design of the control PWB is obtained by using Risc Processor (CPU) in the main control section and high density printing of
surface mounting parts. Each PWB is independent according to its function as shown in Fig. 1.
2. PWB configuration
FAN
MOTOR
PRINTER
CONTROL
CIS
OPERATION
PANEL PWB
HEATER
LAMP
LINE CABLE
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
TEL/LIU
PWB
HOOK
SW
PWB
AC CORD
Fig. 1
(1) Control PWB
The control PWB controls peripheral PWBs, mechanical parts, transmission, and performs overall control of the unit.
This machine employs a 1-chip modem (FM336) which is installed on
the control PWB.
(2) TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB
This PWB controls connection of the telephone line to the unit.
(3) Power supply PWB
This PWB provides voltages of +5V, VREG and +24V to the another
PWB.
PWB
PWB
PC
LSU UNIT
PICK UP SOLENOID
PRINTER MOTOR
TONER SENSOR
THERMAL FUSE UNIT
THERMISTOR
SPEAKER
TX
MOTOR
LCD
3. Operational description
Operational descriptions are given below:
• Transmission operation
When a document is loaded in stand-by mode, the state of the document sensor is sensed via the ASIC (IC15).
If the sensor signal was on, the motor is started to bring the document into the standby position. With depression of the STAR T key in
the off-hook state, transmission takes place.
Then, the procedure is sent out from the modem and the motor is
rotated to move the document down to the scan line. In the scan
processor, the signal scanned by the CIS is sent to the internal image processor and the AD converter to convert the analog signal into
binary data. This binary data is transferred from the scan processor
to the image buffer within the RAM and encoded and stored in the
transmit buffer of the RAM. The data is then converted from parallel
to serial form by the modem where the serial data is modulated and
sent onto the line.
• Receive operation
There are two ways of starting reception, manual and automatic.
Depression of the START key in the off-hook mode in the case of
manual receive mode, or CI signal detection by the LIU in the automatic receive mode.
First, the CPU(SH2) controls the procedure signals from the modem
to be ready to receive data. When the program goes into phase C,
the serial data from the modem is converted to parallel form in the
modem interface of the 1 fax CPU(SH2) which is stored in the receive buffer of the RAM. The data in the receive buffer is decoded
software-wise to reproduce it as binary image data in the image buffer.
The data is DMA transferred to the recording processor within the
ASIC (IC15) and sent to the LSU on printer PWB.
CPU (SH2) and ASIC (IC15) control printing data, LSU, main motor,
high-voltage circuit, heater control and fan motor.
• Copy operation
T o make a copy on this facsimile, the COPY key is pressed when the
machine is in stand-by with a document on the document table and
the telephone set is in the on-hook state.
First, depression of the COPY key advances the document to the
scan line. Similar to the transmitting operation, the image signal from
the CIS is converted to a binary signal in the DMA mode via the
reading processor which is then sent to the image buffer of the RAM.
Next, the data is transferred to the ASIC in the DMA mode to send
the image data to the printer PWB in order to print. The copying takes
place as the operation is repeated.
(4) Panel PWB
The panel PWB allows input of the operation keys.
(5) Printer PWB
This PWB controls the printer mechanical parts.
This PWB employs 8 bit CPU that is installed on printer PWB.
This CPU control a printer mechanical parts.
(6) LCD PWB
This PWB controls the LCD display.
5 – 1
Page 38

FO-2970MU
,
,
[2] Circuit description of control PWB
1. General description
Fig. 2 shows the functional blocks of the control PWB, which is composed of 5 blocks.
MAIN
CONTROL
BLOCK
MODEM/
CONTROL
BLOCK
IMAGE
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
Fig. 2 Control PWB functional block diagram
2. Description of each block
(1) Main control block
The main control block is composed of HITACHI CPU (SH2),
ROMX1 (8M bit), SRAMX1 (1M bit), DRAMX3 (16M bit).
Devices are connected to the bus to control the whole unit.
1) SH7041 (IC5) : pin-144 QFP
The CPU Integrated Facsimile Controllers.
SH7041, contains an internal 32 bit microprocessor with an external 16
bit address space and dedicated circuitry optimized for facsimile image
processing and facsimile machine control and monitoring.
PA18/BREQ/DRAK0
PA19/BACK/DRAK1
PA21/CASHH
PA20/CASHL
PA23/WRHH
PA22/WRHL
RES/VPP
MDTOVF
MD3
MD2
MD1
MD0
NMI
EXTAL
XTAL
PLLVCC
PLLCAP
PLLVSS
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
AVCC
AVSS
AVREF
PF/AN7
PA17/WAIT
PF5/AN5
PF6/AN6
PA16/AH
P
L
L
PF3/AN3
PF4/AN4
PA14/RD
PA15/CK
PF1/AN1
PF2/AN2
ASIC/PRINTING
CONTROL
BLOCK
PA13/WRH
PA12/WRL
PA10/CS0
PA11/CS1
PROM/MASKROM
128KB/64KB
CPU
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
SERIAL COMMUNICATION
INTERFACE
(X2CHANNELS)
COMPARE MATCH TIMER
(X2CHANNELS)
PF0/AN0
PA8/TCLKC/IRQ2
PA9/TCLKD/IRQ3
PA6/TCLKA/CS2
PA7/TCLKB/CS3
USER
BREAK
PA5/SCK1/DREQ1/IRQ1
PA4/TXD1
PE14/TIOC4C/DACK0/AH
PE15/TIOC4D/DACK1/IRQOUT
2) M27C800-90F1 (IC14): pin-42 DIP (ROM)
EPROM of 8M bit equipped with software for the main CPU.
3) W24010S-70LET (IC1): pin-32 SOP (RAM)
Line memory for the main CPU system RAM area and coding/decoding
process. Used as the transmission buffer.
Memory of recorded data such as daily report and auto dials. When the
power is turned off, this memory is backed up by the lithium battery.
4) MSM5118165D (IC11, IC13, IC22): pin-42 SOJ (DRAM)
Image memory for recording process.
• Memory for recording pixel data at without paper.
PA2/SCK0/DREQ0/IRQ0
PA0/RXD0
PA3/RXD1
PA1/TXD0
RAM/CACHE
4KB/1KB
DATA TRANSFER
CONTROLLER
DIRECT MEMORY
ACCESS CONTROLLER
BUS STATE
CONTROLLER
MULTI FUNCTION
TIMER PULSE UNIT
CONVERTER
PE10/TIOC3C
PE11/TIOC3D
PE8/TIOC3A
PE9/TIOC3B
PE12/TIOC4A
PE13/TIOC4B/MRES
PB5/IRQ3/POE3/RDWR
PB9/IRQ7/A21/ADTRG
WATCHDOG
PE7/TIOC2B
PB4/IRQ2/POE2/CASH
PB7/IRQ5/A19/BREQ
PB6/IRQ4/A18/BACK
PB8/IRQ6/A20/WAIT
TIMER
PE2/TIOC0C/DREQ1
PE3/TIOC0D/DRAK1
PE5/TIOC1B
PE6/TIOC2A
PE4/TIOC1A
PB3/IRQ1/POE1/CASL
PB2/IRQ0/POE0/RAS
PB1/A17
PB0/A16
PE1/TIOC0B/DRAK0
PE0/TIOC0A/DREQ0
PC15/A15
PC14/A14
PC13/A13
PC12/A12
PC11/A11
PC10/A10
PC9/A9
PC8/A8
PC7/A7
PC6/A6
PC5/A5
PC4/A4
PC3/A3
PC2/A2
PC1/A1
PC0/A0
PD31/D31/ADTRG
PD30/D30/IRQOUT
PD29/D29/CS3
PD28/D28/CS2
PD27/D27/DAK1
PD26/D26/DACK0
PD25/D25/DREQ1
PD24/D24/DREQ0
PD23/D23/IRQ7
PD22/D22/IRQ6
PD21/D21/IRQ5
PD20/D20/IRQ4
PD19/D19/IRQ3
PD18/D18/IRQ2
PD17/D17/IRQ1
PD16/D16/IRQ0
PD15/D15
PD14/D14
PD13/D13
PD12/D12
PD11/D11
PD10/D10
PD9/D9
PD8/D8
PD7/D7
PD6/D6
PD5/D5
PD4/D4
PD3/D3
PD2/D2
PD1/D1
PD0/D0
: PERIPHERAL ADDRESS BUS(32BIT)
: PERIPHERAL DATA BUS(16BIT)
: INTERNAL ADDRESS BUS(32BIT)
: INTERNAL HIGH-ORDER DATA(16BIT)
: INTERNAL LOW-ORDER DATA(16BIT)
Fig. 3
5 – 2
Page 39

FO-2970MU
SH7041 (IC5) Terminal descriptions
Classification Code Terminal No. I/O Name Function
Power Vcc 12,26,40, I Power Connect Vcc terminals with the power source for all systems.
Vss 6,14,28, I Ground Connect to the ground.
Vpp I
Clock PLL Vcc 104 I PLL power Power source for the built-in PLL oscillator.
PLL Vss 106 I PLL ground Ground for the built-in PLL oscillator.
PLLCAP 105 I PLL capacity External capacity terminal for the built-in PLL oscillator.
EXTAL 96 I External clock
XTAL 94 I Crystal Connected with the crystal oscillator.
CK 107 O System clock Supplied to peripheral devices.
System control RES 108 I Power-on-reset When impressing low level onto this terminal, power-on-reset
MRES 144 I Manual reset When applying low level to this terminal, manual reset condition
WDTOVF 44 O Watch dog timer Overflow output signal from WDT.
BREQ 33,38 I Bus right demand Low level obtained when external device demands to release
BACK 30,37 O Bus right demand Shows that the bus right has been released to the external device.
Operation MD0~ 95,97 I Mode setting The terminal to determine operation modes.
mode control MD3 102,103 Do not change the input value during operation.
Interrupt NMI 98 I Non-maskable Non-maskable interruption demand terminal. Receiving on either
IRQ0 ~ 31,32,34 I Interruption demand Maskable interruption demand terminal. Level input and edge
IRQ7 37~39 0 to 7 input can be selected.
IRQOUT 5,46 O Interruption demand Shows that the interrupt factor has occurred.
Address bus A0~A21 7~11,13, O Address bus Outputs address.
63,77,85, If any open terminal remained, operation is impossible.
99,112,135
35,42,55, Connect Vss terminals with the ground for all systems.
61,71,79, If any open terminal remained, operation is impossible.
87,93,117,
129,141
41,51,52
64~69
70,72
132,
136
15~24,25,
27,29,30,
37~39,41
Program power source Connected with the power source (Vcc) for normal operation.
overflow
acknowledge The device outputting signal BREQ can acknowledge the pass
interrupt leading edge or trailing edge can be selected.
output During bus release, interrupt occurred can be known.
In case of PROM mode, apply 12.5 V.
Connected with the crystal oscillator. By EXTAL terminal the external
clock can be input.
condition is attained.
is obtained.
the bus right.
right gained by receiving signal BACK.
5 – 3
(Continuing)
Page 40

FO-2970MU
SH7041 (IC5) Terminal descriptions
Classification Code Terminal No. I/O Name Function
Data bus D0 ~ D15 45,46 O Data bus Bilateral data bus for 16 bit (Pin plate QFP-112 ) or 32 bit (Pin plate
Bus control CS0~CS3 49,50,53 O Chip select 0 to 3 Chip select signals for external memory or device.
Multi function TCLKA 51~54 I MTU timer clock input External clock input terminal for MTU counter.
timer pulse unit TCLKB
Direct memory DREQ0, 60,62,109, I DMA transfer demand Input terminal for external DMA transfer demand.
access control DREQ1 111,132,136 (Channels 0 and 1)
(DMAC) DRAK0, 2,30,33,110, O DREQ demand Outputs sampling acceptance of external DMA transfer demand
(QFP-112) 56~60, QFP-144).
D0 ~ D31 62,64~70
(QFP-144) 72~76,78
RD 43 O Read-out Shows reading-out from the external device.
WRH 47 O Higher side writing Shows writing in higher 8 bits (bits 15 to 8).
WRL 48 O Lower side writing Shows writing in lower 8 bits (bits 7 to 0).
WAIT 39,101 I Wait T o insert wait cycle into the bus cycle when accessing external space.
RAS 31 O Low address strobe Timing signal for low address strobe of DRAM.
CASH 34 O
CASL 32 O Lower column address Timing signal for column address strobe of DRAM.
RDWR 36 O DRAM read/write Strobe signal for DRAM writing.
AH 2,100 O Address hold Address hold timing signal for the device using multiplex bus of
WRHH 1 O HH writing Shows writing of bits 31 to 24 of external data.
(QFP-144)
WRHL 3 O HL writing Shows writing of bits 23 to 16 of external data.
(QFP-144)
CASHH 4 O HH column address Timing signal for column address strobe of DRAM.
(QFP-144) strobe It is output when accessing bits 31 to 24 of data.
CASHL 29 O HL column address Timing signal for column address strobe of DRAM.
(QFP-144) strobe It is output when accessing bits 23 to 16 of data.
TCLKC
TCLKD
TIOC0A 109~111, I/O MTU input capture/ Channel 0 terminal for inputting Input Capture/outputting Output
TIOC0B 113 output conveyer Conveyer/outputting PWM.
TIOC0C (Channel 0)
TIOC0D
TIOC1A 114,115 I/O MTU input capture/ Channel 1 terminal for inputting Input Capture/outputting Output
TIOC1B output conveyer Conveyer/outputting PWM.
TIOC2A 116,117 I/O MTU input capture/ Channel 2 terminal for inputting Input Capture/outputting Output
TIOC1B output conveyer Conveyer/outputting PWM.
TIOC3A 138~140, I/O MTU input capture/ Channel 3 terminal for inputting Input Capture/outputting Output
TIOC3B output conveyer Conveyer/outputting PWM.
TIOC3C (Channel 3)
TIOC3D
TIOC4A 2,5,143,144 I/O MTU input capture/ Channel 4 terminal for inputting Input Capture/outputting Output
TIOC4B output conveyer Conveyer/outputting PWM.
TIOC4C (Channel 4)
TIOC4D
DRAK1 113 acceptance (Channels input.
DACK0, 5,58,59 O DMA transfer strobe Outputs strobe to external I/O of external DMA transfer demand.
DACK1 (Channels 0 and 1)
80~84
86,88~92
54,56,57
Higher column address
strobe It is output when accessing higher eight bits of data.
strobe
(Channel 1)
(Channel 2)
0 and 1)
Timing signal for column address strobe of DRAM.
address/data.
5 – 4
(Continuing)
Page 41

FO-2970MU
SH7041 (IC5) Terminal descriptions
Classification Code Terminal No. I/O Name Function
Serial TxD0, 131, O Transmitting data Output terminal for transmitting data of SC10 to 1.
communication TxD1 134 (Channels 0 and 1)
interface (SCI)
A/D converter AVcc 128 I Analog power source Vcc potential is connected by analog power source.
I/O port POE0~ 31,32,34,36 I Port output enable Input terminal to enable general port to control driving of port
RxD0, 130, I Receiving data Input terminal for receiving data of SC10 to 1.
RxD1 133 (Channels 0 and 1)
SCK0, 132, I/O Serial clock Input/output terminal for clock of SC10 to 1.
SCK1 136 (Channels 0 and 1)
AVss 124 I Analog ground Vss potential is connected by analog power source.
AVref 127 I Analog reference Input terminal for analog reference power source.
(QFP-144) power source
AN0~AN7 118~123, I Analog input Analog signal input terminal.
ADTRG 41,45 I A/D conversion External trigger input to start A/D conversion.
POE3 terminal in case of setting output.
PA0~PA15 1,3,4,33,43, I/O General port
(QFP-112) 47~54,100,
PA0~PA23 101,107,
(QFP-144) 130~134,136
PB0~PB9 25,27,31,32, I/O General port
PC0~PC15
PD0~PD15
(QFP-112) 73~76,78,
PD0~PD31
(QFP-144) 88~92
PE0~PE15
PF0~PF7 118~123, I General port General input port terminal.
125,126
trigger input
General input/output port terminal to specify input/output by every bit.
34,36~39,41
45,46,57~60, I/O General port
62,64~70,72, I/O General port General
80~84,86,
2,5,109~111, I/O General port
113~116
137~140
142~144
125,126
General input/output port terminal to specify input/output by every bit.
General input/output port terminal to specify input/output by every bit.
General input port terminal to specify input/output by every bit.
input/output port terminal to specify input/output by every bit.
5 – 5
Page 42

FO-2970MU
(2) Panel control block
The following controls are performed by the Gate array (LR38784).
• Operation panel key scanning
• Operation panel LCD display
(3) ASIC/Printing control block
1) ASIC [LR38784A 208pin (embedded gate array)
functions(IC15)
1
Mapper
Mapping can connect the modem and image handing LSI to a domain of CS2 (Chip Select 2).
2
Real-time-clock interface
This interface has the clock-synchronous type serial transfer mode
and can write and read to the CLOCK IC (SM8578BV or NJU6355).
3
Image handing LSI interface
This interface has parallel or serial transfer mode with the image
handing LSI.
4
GDI ASIC
This function GDI i/f for PC printing only.
5
IEEE1284
This function IEEE 1284 i/f for PC scanning and PC fax.
6
Sending motor control
This function outputs the sending motor control signals of 2 or 1-2
phase excitation to the motor driver.
7
Buzzer and Ringer control
This function outputs a buzzer (1042Hz) or a ringer (controlled signal) signal.
8
Laser signal control
This function controls to output laser beam.
9
Protection circuits
LR38784A has protection circuits for a pick-up-solenoid and a heater .
LR38784A (IC15) Terminal description
Pin No. I/O Signal name
1 – GND
2 – GND
3 I LCPD3
4 I LCPD4
5 I LCDREQ
6 TO LEDDV4
7 TO LEDDV3
8 TO LEDDV2
9 TO LEDDV1
10 TO RS
11 O LCDACKZ
12 TO E
13 IOR LD3
14 – GND
15 IOR LD2
16 IOR LD1
17 IOR LD0
18 IU SEN4Z
19 IU SEN3Z
20 IU SEN2Z
21 IU SEN1Z
22 IU SEN0Z
23 I FRSNS
24 I ORGSNS
25 I B4SNS
26 I MDMINTZ
27 O MDMRDZ
28 O MDMWRZ
29 O MDMCSZ
30 O MDMRSTZ
31 – GND
32 IS CK16M
33 O OE3Z
34 O WE3Z
35 O BZOUT
36 I LCINT
37 O LCRDZ
38 O LCWRZ
39 I SD
40 I SDE
41 I SDCK
42 ID MTST
43 I DACK0Z
44 I DACK1Z
45 I DRAK0
5 – 6
Page 43

LR38784A (IC15) Terminal description
Pin No. I/O Signal name
46 I DRAK1
47 O DREQ0Z
48 O DREQ1Z
49 – GND
50 IS SHCK
51 – GND
52 – GND
53 – VDD
54 – VDD
55 O RESET2Z
56 O USOUT
57 O2M INT1Z
58 O INT2Z
59 O2M INT3Z
60 O2M INT4Z
61 O INT5Z
62 I RDZ
63 I WRHZ
64 I WRLZ
65 I CS2Z
66 I CSIZ
67 IS WDTOVFZ
68 O RTCIO
69 O RTCCE
70 – GND
71 O RTCCK
72 IOR RTCDT
73 ID TEST1
74 IU CASHZ
75 IU CASLZ
76 IU RASZ
77 IU RDWRZ
78 O BREQZ
79 I BACKZ
80 IOR PD0
81 IOR PD1
82 IOR PD2
83 IOR PD3
84 – GND
85 OR PA9
86 OR PA0
87 I LCPD0
88 I LCPD1
89 I LCPD2
90 OR PA1
91 OR PA2
FO-2970MU
Pin No. I/O Signal name
92 OR PA3
93 OR PA4
94 OR PA5
95 – GND
96 OR PA6
97 OR PA7
98 OR PA8
99 IOR PD4
100 IOR PD5
101 IOR PD6
102 IOR PD7
103 – VDD
104 – VDD
105 – GND
106 – GND
107 OSC3M PEPCKO
108 OSCI PEPCKI
109 IU EXINT1Z
110 IS RESETZ
111 O PCASZ
112 O PWRZ
113 O PRASZ
114 O TPA
115 O TPB
116 O TPAZ
117 O TPBZ
118 – GND
119 O OE1Z
120 O WE1Z
121 O OE2Z
122 O WE2Z
123 O CASLOZ
124 O RASOZ
125 O CASHOZ
126 – GND
127 O PWRLY
128 O HLON
129 O TC_BIASON
130 O PUS
131 O MCON
132 I PE
133 O PMDZ
134 O APCSTT
135 ICS SYNCZ
136 O SMAP
137 – GND
5 – 7
Page 44

FO-2970MU
LR38784A (IC15) Terminal description
Pin No. I/O Signal name
138 – VDD
139 IOR MA
140 IOR MB
141 I DOPZ
142 I PINZ
143 I POUTZ
144 I XBPSTB
145 IO12MR BPBD7
146 O VIDEO
147 – GND
148 IO12MR BPBD6
149 IO12MR BPBD5
150 IO12MR BPBD4
151 – GND
152 IO12MR BPBD3
153 IO12MR BPBD2
154 IO12MR BPBD1
155 – GND
156 – GND
157 – VDD
158 – VDD
159 IO12MR BPBD0
160 I XBPAF
161 O12M XBPOACK
162 O12M BPOBY
163 I XBPINI
164 – GND
165 O12M BPOPE
166 O12M BPOSE
167 O12M XBPOFT
168 I XBPSEI
169 – GND
170 – VDD
171 IS PRTCLK
172 IOR D0
173 IOR D1
174 IOR D2
175 IOR D3
176 IOR D4
177 IOR D5
178 IOR D6
179 IOR D7
180 – GND
181 IOR D8
182 IOR D9
183 IOR D10
Pin No. I/O Signal name
184 IOR D11
185 IOR D12
186 IOR D13
187 IOR D14
188 IOR D15
189 – GND
190 I A21
191 I A20
192 I A13
193 I A12
194 I A11
195 IOR A10
196 IOR A9
197 IOR A8
198 IOR A7
199 IOR A6
200 – GND
201 IOR A5
202 IOR A4
203 IOR A3
204 IOR A2
205 IOR A1
206 I A0
207 – VDD
208 – VDD
5 – 8
Page 45

2) Printing control (PCU)
The CPU and ASIC control printing.
1. Blockdiagram
Main motor
Heater lamp
control circuit
Driver
Motor
driver
CPU
(SH7041)
and
ASIC
(LR38784A)
Laser scanning unit
Laser start
position
sensor
Laser diode
Scanning motor
IEEE1284
I/F Connector
FO-2970MU
Host
computer
Thermistor
Driver
High
voltage
generating
circuit
Driver
Solenoid
PUS
The PCU controls the following functions and items:
1
Rotation of the main motor (pulse motor)
2
High voltage output
3
Fusing temperature
4
Optical system (polygon motor/ laser APC circuit start)
5
400/600DPI resolution automatic selection
6
Temperature correction of fusing temperature and high voltage
output
Driver
Reset circuit
PIN sensor
POUT sensor
PE sensor
Door switch
Fig. 4
5 – 9
Page 46

FO-2970MU
3) Unit control
a. Main motor drive circuit
This machine uses the 4-phase pulse motor, and is driven by the following pulses and the circuit
24VP
IC2
VBB
ENABLE1
ENABLE2
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
OUT4
( Printer PWB)
MM
MA
MAMB
MB-
CNMMT
1
2
3
4
(Drive waveform)
Stop Rotation
MCA
MCB
MEN-
Fig. 5
b. Paper feed controller
Basically, the feed roller is rotated 1.5 times.
If interval between PUS and PIN is within 0.5 sec., it is rotated 1 time.
The procedure of clutch control
1
Timer is cleared by PUS ON according to clutch control demand.
2
PUS OFF 100 ms after PUS ON
3
PUS ON again 450 ms after the procedure 1 above.
4
If paper is remained in PIN 500 ms after the procedure 1, the third
PUS ON is stopped.
5
PUS OFF 1.25s after the procedure 1. Clutch control demand OFF
if additional control is cancelled.
6
PUS ON again 1.534s after the procedure 1.
7
PUS OFF 2.334s after the procedure 1.
8
Clutch control demand OFF 3.366s after the procedure 1.
If the paper is not fed normally and the paper in detector signal (PIN_) is
not outputted even with the above operation, the PCU judges it as a
paper jam display is made.
The paper in detector signal (PIN_) is used for the top margin control
signal in addition to jam detection.
The diagram below shows timings of clutch operation.
PUS
0.1
0.45
0.8
1.534
0.8
IN1
IN2
5V
14
7
13
MA
MEN-
8
MB
116
60
137
( Control PWB)
IC5
c. Electrical connection
In the paper feed and transportation system, drive parts and sensors
are connected as shown in the figure below.
CPU
(SH7041)
ASIC
(LR38784A)
CONTROL PWB
116 MA
60 MEN137 MB
130 PUS
142 PIN- 3
143 POUT- 3
132
PE
CNPRT
PRINTER PWB
13
7,14
IC2
Motor
8
driver
413
IC1
4
PI2
4
PI1
+5V
1
17
4
2
1
2
1
2
+24V
PAPER IN
SENSOR
+5V
PAPER OUT
SENSOR
CNMMT
MA1
MA-2
MB3
MB-4
CNPL
+24V1
PUS-2
CNLSU
PE9
MAIN MOTOR
PAPER
PICK-UP SOLENOID
LSU PWB
CN601
PE9
PD601
PAPER
EMPTY
SENSOR
+24V
Fig. 7
• The main motor , which is the drive source for the paper feed and transportation system, is a 4-phase stepping motor in 2-phase excitement
bipolar system, The step angle is 7.5°.
• The pick-up solenoid operates on 24V to turn on/off paper feed.
• There are following kinds of sensors.
Paper empty sensor (Transmission photo transistor) :
The paper empty sensor is positioned on the LSU PWB, and is used to
detect presence of paper on the multi-purpose paper tray.
Paper in sensor: (Transmission photo transistor):
This sensor is used to detect the paper feed timing of the next paper
(in prefeed) and to make synchronization between paper transport and
image forming on the drum. This sensor is also used to detect paper
jams.
Paper out sensor: (Transmission photo transistor):
This sensor senses paper exit, and paper jam.
PIN
0.5
0.5 1.25 1.534
0.991
Fig. 6
2.334
3.366
5 – 10
Page 47

d. High voltage unit control
The high voltage unit outputs the following voltages:
• Main charger voltage (DC-950V + AC600V peak to peak)
• Transfer charger voltage (DC+2100V + AC600V peak to peak)
• Developing bias voltage (DC-390V)
The following signals are outputted from the CPU (ASIC) to control the
above voltages.
• MCON
This signal is to turn on/off the main charger.
When this signal is outputted, Q7 is driven to the high impedance state.
Then Q9 conducts to drive transformer T2.
As a result, the main charger voltage is outputted to the secondary
side of the transformer.
• TC/BIASON
This signal is to turn on/off the transfer charger and the developing
bias voltage.
When this signal is outputted, Q3 is driven to the high impedance state.
Then Q5 is conducted to drive T1 to output the transfer charger voltage and developing bias voltage to the secondary side of the transformer.
• PWMSIN
This signal is to control the main charger voltage and the transfer
charger voltage. The PWM pulse of 295.28Hz is outputted.
This pulse waveform adds the AC component to the main charger volt-
age and the transfer charger voltage.
By changing the pulse duty of this signal, the main charger voltage
and the transfer charger voltage are controlled (during temperature
correction operation).
When the pulse duty of this signal is changed, the collector currents of
Q4 and Q8 are changed. Therefore, the base current of Q9 and the
drive current of transformer T2 are changed to change the main charger
voltage and the transfer charger voltage.
R29, R31, C19, and C20 from a filter circuit which dulls the waveform
of PWMSIN signal.
FO-2970MU
e. Electrical connection
CONTROL PWB PRINTER PWB
ASIC
IC15
(LR38784A)
CPU
(SH7041)
131
129
115
MCON
TC/Bias ON
PW MSIN
512
Q7
Driver
IC1
314
Q3 Q5
Q4
Q9
Q8
+24VP
+24VP
Q6
T2
Transformer
T1
Transformer
MC
TC
DC
Bias
Charger
roller
OPC
DRUM
Separation electrode
Transfer roller
100V
Doctor
Supply rollier
Developing
roller
CNPRT
Fig. 8
5 – 11
Page 48

FO-2970MU
f. Laser scanning unit
This unit controls the laser beam power and laser beam scanning.
The control is performed with the signals inputted outputted to or from
the CPU and ASIC.
R609
10K
R606
10K
R603
30K
D601
PD481PI
5
So6Vcc7Vps
INH
+5VL
+5VL
4
GND
Q601
A1015
R604
820
R605
240
8
OUT
IC601
IR3C07
Cp
IM
1
2
3
Q602
C1815
BD CIRCUIT
CN604
1
+5VL
2
SYNC-
3
GND
BD
APC CIRCUIT
C607
2200p
+
C606
220uF/10V
IC603
2
BU4S66
+5VL
O/I
CN603
BD
4
Vdd5CONT
3
+5VL
SYNC-
GND
I/O
GND
IC602
R607
1K
C602
0.1uF
VR601
15K
LDPD
LNC702
3
D602
7805
+5VL+5VL
OUT
1
IN
GND
2
R613
180
21
R610
9.1
Q603
A1206
+5VL
1
2
+
3
1
C608
4700p
R608
30
C605
0.1uF
C601
47uF/10V
R601
130ohm/2W
C603
0.1uF
3
4
R611
750
R612
510
PD601
GP1S53
+24V
+24V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
CN601
LSU
CN602
PM
+24V
GND
VIDEO
SAMP
SYNCAPCSTT
PMCLK
PMDPE
GND
PMD+24V
PMCLK
GND
1) Signal functions
PMCLK
Clock signal for driving the scanning (polygon) motor . (1.18KHz/770Hz)
PMD
Scanning motor ON/OFF signal.
APCSTT
Used to start the laser beam generation circuit.
SYNC
This signal is outputted when the laser beam scanned by the laser
beam sensor signal is sensed by sensor (Photo diode D601).
Used for the left margin control.
VIDEO
This signal is used to control the laser diode emitting.
Not only when the laser beam is emitted to perform the LEND proc-
ess, but also when the laser beam is emitted as image data, ASIC
controls and the signal is outputted from video terminal.
Fig. 9
2) Laser beam power control
The laser beam power is controlled in the laser emitting unit PWB.
This circuit functions to keep the laser beam output power at a constant
level.
The laser beam output is monitored with photo diode D602 for monitor.
When the laser beam output rises above the specified value, the impedance of photo diode D602 is decreased to decrease the monitor input
(3PIN) voltage of the laser diode control IC (IC601).
Then the laser diode (LTO28GS) drive voltage is decreased to decrease
the laser beam output to the specified level.
When the laser beam output is decreased below the specified level, the
contrary operation are performed.
5 – 12
Page 49

FO-2970MU
3) Starting operation
Warm-up operation of laser scanning is described below.
The operation is made when the cover is closed from the open state,
and is made before starting printing.
The PMCLK signal is the clock signal for scanner motor speed control.
It is rectangular waveform of 1.18kHz.
1
The PMD_signal is to turn on/off the scanner motor . When this signal
is outputted, the scanner motor is operated.
2
After 2 sec of starting the scanner motor, the laser power control
signal APCSTT and the laser diode ON signal VIDEO (LEND) are
outputted to output laser beams.
3
After 0.5sec from outputting the VIDEO (LEND) signal and turning
on the laser diode, the LEND process operation is started.
Clock of 1,18KHz is always outputted.
0.5sec
After about 0.5sec of turning on the LEND_ signal,
the LEND process is started.
PMCLK
PMD_
(Scanning motor)
APCSTT
(Laser power control)
LEND_
Stop
Start
2.0sec
Fig. 10
4) LEND process operation
The LEND process operation means outputting the HSYNC (HSYNC_)
signal for left margin control.
To control the left margin, the scanning position of the scanning mirror
on the virtual area of the left side out of the margin must be precisely
detected when the scanning motor reaches the stable rpm. Therefore,
the dummy laser beam must be outputted to detect the position.
The laser beam scanning position is detected by the laser beam sensor,
and the SYNC signal is outputted.
The dummy laser beam is outputted for every scanning of one line only
when the scanning position of the scanning mirror is outside the left
area of virtual paper. (The laser is forcibly turned on by the PCU when
the laser beam scanned by the scanning mirror come in front of the
laser beam sensor (left margin reference).)
Note: The laser beam is not outputted continuously during printing op-
eration of one paper. It repeated ON and OFF for every scanning
of one line.
The laser beam is outputted only when the LEND process for controlling the print left margin is made and when the print image is
drawn on the photoconductor.
• Laser control signal
LEND signal is controlled based on HSYNC signal.
For simultaneous APC control, SAMP signal is also controlled.
These timings are made by ASIC. The line-end-of f section is set by the
register.
A
B
SYNC
VIDEO
SAMP
LEND_
1st dot 2nd dot last dot
CD
1 line data
2 µs
Line end off
Keep low level.
Next line
2 µs
Fig. 1 1
1
When the LEND_ signal is on, the dummy laser beam is outputted,
and the scanned laser beam is detected by the laser beam sensor to
output the SYNC signal. When the SYNC signal is outputted, the
CPU detects the scanning position.
2
At the rising of the SYNC signal, the CPU turns off the LEND_signal.
By this, the dummy laser beam is turned off. When the CPU detects
the scanning position with the SYNC signal, the dummy laser beam
becomes unnecessary.
3
The draw signal Video_ is made from the DDA TA_ signal of one line
outputted from the ASIC. When it is outputted, the laser beam is turned
on off accordingly. This corresponds to the making of latent electrostatic images on the photoconductor drum.
4
When making of latent electrostatic images for one line is completed,
the CPU turns on the LEND_ signal before the output timing of the
SYNC.
Procedures 1~4 are repeated.
Time
Resolution
600dpi 846.7µs
406.4x
ABCD
1298.7524µs
3 ~ 10µSec
4.6 ~15.3µSec
(29.97µSec)
(45.971µSec)
(84.3nSec) 510µs
(190.907nSec)
Line end off
720µs
391.16dpi
5) Automatic acknowledgment of resolution
The CPU control 600dpi/400dpi when starting the LEND process.
When the scanner motor rotation is stabilized, the SYNC interval is
judged.
5 – 13
Page 50

FO-2970MU
g. Electrical connection
CONTROL PWB PRINTER PWB
ASIC
(LR38784A)
136 SAMP
146 VIDEO
135
134 APCSTT
133 PMD-
CPU
(SH7041)
SYNC-
65
114 PMCLK
SYNC-
CNPRT
+24V
CNLSU
+24V1
DG
2
VIDEO
3
SAMP
4
SYNC-
5
APCSTT
6
PMCLK
7
PMD-8
CN601
+24V1
DG
2
VIDEO
3
SAMP
4
SYNC-
5
APCSTT
6
PMCLK
7
PMD-8
(APC circuit)
4
GND
+5VL
LSU PWB
IC603
31
3-terminal
regulator
2
CN603
2
+24V
CN602
2
3
4
5GND
Q603
15
INH
OUT
VPS
IM
3
VR601
IC601
VCC
78
54
SYNC_
PMD-
PMCLK
LD
/PD
Laser beam detecting PWB
(Start position detecting PWB)
CN604
+5VL1
GND3
GND1
+5VL1
SYNC_
2
GND3
Scanning motor
+24V
The laser diode control board is driven in synchronization with the VIDEO
signal sent from the CPU board.
By the operation of the laser diode control board, infrared laser beams
of 780nm are outputted from the laser diode and made in parallel by the
collimator lens, and focused onto the scanning motor by the first cylinder lens.
The scanning mirror rotation is controlled by the scanning motor to be
constant at 11811rpm (600dpi) and 8000rpm (400dpi), and the laser
beam is directed to the main scanning direction.
The scanning motor is of six-surface, and six-line print is made for one
rotation of the scanning motor. The laser beam reflected by the scanning mirror is directed to the curved mirror by the first reflection mirror.
Before reaching the curved mirror, the laser beam enters the photo sensor on the start position detector board, making vertical synchronization
and print data synchronization (generating the SYNC signal).
The curved mirror directs the laser beam to the second reflection mirror
in parallel and in even interval regardless of difference in angles of incidence from the first reflection mirror. The laser beam reflected by the
second reflection mirror ia passed through the second cylinder lens to
reach the photoconductor drum.
The second cylinder lens corrects blur of the images caused by variations in the installing angle due to the two-surface scanning mirror, providing stable laser beams to the photoconductor drum for each line.
3
GND O/I
CONT
IC603
I/O
VDD
2
1
Fig. 12
h. Fusing unit control
The fusing section is heated by the heater lamp (400W). The heater
lamp is controlled (turned on/off) to keep the optimum temperature. The
following signals are outputted by the ASIC and CPU for control.
1) Signal functions
• HLON
This signal is to turn on/off the heater lamp. When this signal is
outputted, photo triac PD101 turns on to turn on triac T2. Then an AC
power is supplied to the heater lamp to turn on the heater lamp.
• RTH
This is the output signal of the thermistor which detects the surface
temperature of the heat roller. It is inputted to the CPU. The heater
lamp is turned on/off depending on the value of RTH voltage.
5 – 14
Page 51

FO-2970MU
2) Protect against overheat
Though the heater lamp ON signal (HLON) is normal, if triac PD101 and
T2 are kept ON, overheat may result.
To prevent against this, temperature fuses are used.
When the fusing roller surface temperature exceeds about 187 degrees
C, the temperature fuse blows off to open the 12V power line which
drives the power relay RY101, opening the power line for the photo triac
PD101 and triac T2. Therefore, the power is not supplied to the heater
lamp.
A temperature fuse is also provided in the heater lamp power line. In
case of overheating, the heater lamp power line is opened directly.
3) Timing of temperature detection and heater control
As shown by the following timings, four values of software thermistor
voltage are input as A/D conversion values. The mean value of two
medians among these four is regarded as the newest thermistor value
(temperature).
• The value is compared with the temperature (155°C) control value
every 100 ms.
• If the value is higher than 155°C, the heater becomes OFF. If lower,
the heater becomes ON.
• The heater ON timing is in accordance with the timing of Power Zero
Cross interrupt.
Heater ON/OFF Control
Heater ON/OFF Control
• After printing, temperature is not controlled.
• Fan motor starts revolving from the beginning of temperature control
and stops 120 seconds after printing is finished.
T emperature control is not started from the start of printing because the
first copying time should be within 28 seconds.
HLON
FAN
CDPAGE
(Base machine Printing started)
In case of the base machine printing
(Single sheet continuous printing)
155°C
Preparation of printing
data started
Temperature control started
Printing started
Printing finished
120s
OFF
Fig. 14
T (x 10ms)
Inputting thermistor values
Timings of thermistor value input and heater control
Fig. 13
4) Heater control (Temperature control)
Control method
1
Base machine printing (Copy, List, Receiving)
• Temperature control is started when data to be printed are produced
(or when slips are to be prepared).
• Temperature is controlled at 155 °C. (Heater OFF over 155 °C. Heater
ON below 155 °C.)
• After printing, temperature is not controlled. (Heater is not turned
ON.)
• Fan motor starts revolving from the beginning of temperature control
and stops 120 seconds after printing is finished.
2
PC printing
• Temperature control is started when PC starts printing.
• Temperature is controlled at 155 °C. (Heater OFF over 155 °C. Heater
ON below 155 °C.
Printing started
HLON
FAN
CDPAGE
(PC printing started)
In case of PC printing
(Single sheet/continuous)
155°C
The Heater ON timing is set during Zero Cross interrupt.
Printing finished
Temperature control started
120s
Fig. 15
OFF
5 – 15
Page 52

FO-2970MU
i. Electrical connection
Heater lamp: The 400W halogen lamp is used.
This spring presses the pressure roller with a 690g
pressure on one side.
Thermistor: Thermistor of chip type with good response is
T emperature fuse 1 T emperature fuse 1 is installed to the fusing cover .
(132°C): It blows off when the ambient temperature of the
Temperature fuse 2 Temperature fuse 2 is in close contact with the
(187°C): heat roller. It blows off when the heat roller tem-
used to respond to rapid heating (rapid warm-up
of about 8 sec) of the heat roller.
fusing cover rises abnormally (132°C).
perature rises abnormally high (187°C).
ASIC
(LR38784A)
CPU
(SH7041)
CNPRT
PRINTER PWB POWER PWBCONTROL PWB
131
HLON
PWRLY
127 1 16
RTH
118
2 15 HLON-
IC1
Driver
+5V
+24V+24VS
PWRLY-
CNRTH
+5V1
2 RTH
CNFUSE
+24V1
3 +24VS
CNPW
CNLN
ACL1
2ACN
CNHT
CNHT
HLL1
Temperature
fuse (132 °C)
HLN3
Heater
lamp
Thermistor
Temperature
fuse (187 °C)
• The heat roller surface temperature is maintained to the optimum level
by controlling ON/OFF of the heater lamp according to the temperature data (voltage) from the thermistor. The heat roller surface temperature is controlled to 155°C. Two temperature fuses are provided
to protect the heat machine from an abnormally high temperature in
the fusing section. The heater lamp is lighted by the AC power.
Fig. 16
5 – 16
Page 53

FO-2970MU
j. Timing chart
• Printing process
Pre-revolution processing
Timing from DPAGE (internal signal of ASIC) to BIAS ON (pre-revolu-
tion processing) is specified.
Before rotation of printing (unit:sec)
MM
PMD
APCSTT
LEND_
HSYNC_
LDATAEN
LD_
0.7
1.03
68%DC ON
unit(µs)
44%DC ON
AC SIN
0.98
ACSIN
TC/Bias
HLON
DREADY_
DPAGE_
MC
PU
AC 68%
AC 44%
143.9
93.1
3.5
211.7
Fig. 17
Laser control becomes hard control from the movement when HSYNC
interruption was permitted.
Post-revolution processing
Timings from POUT to motor stop (post-revolution processing for print-
ing) are specified.
After rotation of printing (unit:sec)
MM
PMD
APCST
LEND
HSYNC_
LDATAEN
LD_
MC
Sine wave form output
ACSCN
TC/Bias output
POUT
DREADY
DPAGE
Harf line discharge(20Line)
0.47
Harf line discharge(20Line)
TC output
0.54
Cleaning
OFF
After rotation of printing
50% DC ON
4.8
68% DC ON
0.5
OFF
3.0
OFF
OFF
STOP
OFF
OFF
Continuous printing processing
*1 Waiting according to fixing temperature (Environmental tempera-
ture)
*2 Top margin
READY
DPAGE
VSYNC
PRSTT
MM
PMD
APCSTT
LEND
HSYNC
LDATAEN
LD_
MCON
ACSIN
Tc/BiasON
PUS
PIN
POUT
3.5
Min1.0(*1)
Before rotation
of printing
1.25Typ.
4.0mm(*2)
0.28
0.68
(Letter Size)
(0.5)
0.54
After rotation
of printing
Fig. 19
Revolution before cleaning when power is on and cover is closed
Unit: second
MM
PMD
APCSTT
LEND_
HSYNC_
LDATAEN
LD_
MC
ACSIN
TC/Bias
output voltage
TC/Bias
HLON
DREADY_
DPAGE_
3.5
ON
5.6
ON
LEND_ Hard control start
ON
1.0
OFF
68%DC ON
LEND_ Hard control end
Generation
(5.0)
OFF
Cleaning
3.0
OFF
Fig. 20
3.0
Fig. 18
5 – 17
Page 54

FO-2970MU
k. Top margin control
T op margin is set according to the number of lines (the number of HSYNC
interrupt) from detail paper Pin On to LASER input.
The interval between Pin On and point D is 52.6747 mm.
The interval between Point D and point B is: 27.33 (C-D) + 8.3769 (B-C)
= 35.7069 mm
If top margin is 4 mm,
52.6747 - 35.7069 + 4 = 20.9678 m
In case of the actual software processing, chattering of the sensor is
considered to be observed for 9 msec.
The processing speed is 50 mm/sec; while chattering is being observed,
paper is fed by 0.45 mm (9 x 50/1000 = 0.45 mm).
In order to gain top margin of 4 mm, printing data should be processed
after paper is fed by 20.5178 mm (20.9678 – 0.45 = 20.5178 mm) following PIN On detection.
The base machine resolution in the sub-scanning direction is 391.16
dpi; If the value 20.5178 mm is converted into the number of lines, 315.9
lines are obtained from 391.16 x 20.5178/25.4. Accordingly the software set value is considered to be based on 316 lines.
Similarly, considering from the fact that resolution of PC printing is 600
dpi, the number of lines is 484.6 lines (600 x 20.5178/25.4=484.6).
The software set value is based on 485 lines.
Process speed 50mm/sec
B
OPC drum
Diameter ø24mm
D
LASER
OPC drum speed 49mm/sec=(50x0.98)
8.3769mm(B-C)
C
Developing
roller
nip 2.7693mm
27.33mm(C-D)
52.6747mm(from Pin On)
40.0697mm(from Pin Off)
Paper feed
roller
37.2mm
(until Pin On)
Pin sensor
Pout sensor
Paper exit roller
Discharge
brush
nip 5.7523mm
Fusing
9.3389mm(A-B)
A
30.3522mm(D-A)
Transfer
roller
ø13.4(13.7)
100.4mm(from Pin On)
123.8410mm(from Pin On until Pout On)
207.875mm(from Pin Off)
Fig. 21
(4) MODEM control block
1) INTRODUCTION
Conexant's FM336 modem is a V.34 half-duplex modem. It supports
Group 3 facsimile transmission/reception at speeds up to 33,600bps in
the V.34 half-duplex mode. In order to optimize the modem configuration for the line conditions, this modem uses V.34 technology. It connects at an optimally selected data rate so that speeds from 2,400bps to
33,600bps can be supported.
This modem can be used on the general public telephone network using
a network control unit (NCU) line termination device. This modem conforms to ITU-T V .17, V.21, V.23, V.27ter, V .29, and V.34 specifications. It
also complies with V.8 and T.30 binary signaling conditions. This modem supports HDLC internally. Therefore, products using built-in error
correction and the T.30 protocol do not need an external serial input/
output (SIO) line on DTE. This modem can execute HDLC framing, as
specified in T.30, at all data rates. Since it can perform zero insertion/
deletion and CRC tasks, this allows enhanced SDLC/HDLC frame operation. The FSK flag pattern detector facilitates FSK detection during
high-speed reception.
This modem features a programmable DTMF transmitter/receiver that
operates in tone mode, and three programmable tone detectors. This
modem is primarily suited to use in small system designs in such environments as work plants, offices, and homes because of its low power
consumption and small size. This modem is packaged in a 100-pin PQFP .
2) FEATURES
• Two-wire, half-duplex fax modem that supports transmission/recep
tion speeds up to 33,600bps
- V.17, V.27ter, V.29, V.34, and V.21 2 channel
- Short train option in V.17 and V.27ter
• Two-wire, full-duplex data modem mode
V.21 and V.23 (75bps TX/1,200bps RX or 1,200bps TX/75bps RX)
• PSTN session start
- V.8 signaling
• HDLC supported at all the speeds
- Flag sending, 0 bit insertion, ITU CRC-16 or CRC-32 calculation
and sending
- Flag detection, 0 bit deletion, ITU CRC-16 or CRC-32 checksum
error detection
- FSK flag pattern detection (during high-speed reception)
• Tone mode and function
- Programmable single or dual tone transmission
- DTMF reception
- Tone detection using three programmable tone detectors
• Serial synchronous data
• Parallel synchronous data
• V.34 half-duplex and Automatic Rate Adaptation (ARA)
• TTL- and CMOS-compatible DTE interface
- ITU-T V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E) (data/control)
- Microprocessor bus (data/configuration/control)
• Reception dynamic range: 0dBm ~ –43dBm (V .17, V .33, V.29, V.27ter ,
and V.21)
–9dBm ~ –43dBm (V.34 half-duplex)
• Programmable RLSD turn-on and turn-off thresholds
• Programmable transmission level: 0 ~ –15dBm
• Adjustable speaker output for monitoring communication signals
• DMA support interrupt line
• 16 byte FIFO data buffer (2) for transferring burst data, can be ex
panded up to 255 bytes
• NRZ1 encoding/decoding
• Diagnostic function
• +3.3V operation (+5V input possible)
• +5V analog signal interface
• Standard power consumption:
- Sleep mode: 20mW
- Normal mode: 250mW
• 100-pin PQFP package
5 – 18
Page 55

FM336 (IC8) Terminal description
PIN Signal Name I/O Type Interface
1
RESERVED
2 RS2 IA Host interface
3 RS3 IA Host interface
4 RS4 IA Host interface
5 /CS IA Host interface
6 /WR IA Host interface
7 /RD IA Host interface
8 /RDCLK OA DTE Serial interface
9 /RLSD OA DTE Serial interface
10 TDCLK OA DTE Serial interface
11 TXD IA DTE Serial interface
12 /CTS OA DTE Serial interface
13 VDD1 PWR –
14 RESERVED – –
15 RESERVED – –
16 VSS GND –
17 NC – NC
18 /RESET OA Modem interconnect
19 SR4OUT OA Modem interconnect
20 NC – NC
21 SR4IN IA Modem interconnect
22 CLK_OUT OA Modem interconnect
23 EYESYNC OA Diagnosis signal
24 EYECLK OA Diagnosis signal
25 MAVSS GND –
26 MAVDD PWR –
27 SPKR O(DF) Telephone lines interface
28 TXA2 O(DD) Telephone lines interface
29 TXA1 O(DD) Telephone lines interface
30 VREF MI Modem interconnect
31 VC MI Modem interconnect
32 RIN I(DA) Telepone lines interface
33 MAVSS AGND –
34 /POR LA Modem interconnect
35 RESERVED – –
36 RESERVED – –
37 /TALK O(DD) Telephone lines interface
38 VDD PWR –
39 RESERVED – –
40 RESERVED – –
41 NC – NC
42 M_CNTRL_SIN IA Modem interconnect
43 M_CLKIN IA Modem interconnect
44 M_TXSIN IA Modem interconnect
45 M_SCK IA Modem interconnect
46 M_RXOUT IA Modem interconnect
47 M_STROBE IA Modem interconnect
48 RESERVED – –
49 OH O(DD) Telephone lines interface
50 VDD PWR –
Notes:
I/O types: MI = Modem interconnect
IA, IB = Digital input OA, OB = Digital output
I(DA) = Analog input O(DD), O(DF) = Analog output
––
FO-2970MU
3
PIN Signal Name I/O Type Interface
51
RESERVED
52 VSUB GND –
53 VSS GND –
54 NC – NC
55 NC – NC
56 SLEEP MI Modem interconnect
57 VDD1 PWR –
58
RESERVED
59
RESERVED
60 NC – NC
61 SR1IO MI Modem interconnect
62 VCORE PWR –
63 VDD1 PWR –
64 XTCLK IA DTE Serial interface
65 VSS GND –
66
RESERVED
67 RXD OA DTE Serial interface
68 /DTR IA DTE Serial interface
69 VDD1 PWR –
70 IA_SLEEP MI Modem interconnect
71 VGG PWR –
72 YCLK OA Overhead signal
73 XCLK OA Overhead signal
74 EYEXY OA Diagnosis signal
75 /DSR OA DTE Serial interface
76 /RI OA Telephone lines interface
77 RINGD IA Telephone lines interface
78 /RTS IA DTE Serial interface
79 IRQ OA Host interface
80 VSS GND –
81 GPO0 MI Modem interconnect
82 RESERVED – –
83 RESERVED – –
84 VDD1 PWR –
85 XTALI/CLKIN I Overhead signal
86 XTALO O Overhead signal
87 D0 IA/OB Host interface
88 D1 IA/OB Host interface
89 D2 IA/OB Host interface
90 D3 IA/OB Host interface
91 D4 IA/OB Host interface
92 VDD1 PWR –
93 D5 IA/OB Host interface
94 D6 IA/OB Host interface
95 D7 IA/OB Host interface
96 RS0 IA/OB Host interface
97 RS1 IA/OB Host interface
98 PLL VDD PWR –
99 VSS GND –
100 PLL GND GND –
NC = Not connect
RESERVED = No external connection allowed
Interface description: HOST = Modem control unit (Host)
DTE = Data terminal equipment
––
––
––
––
3
5 – 19
Page 56

FO-2970MU
(5) Image signal process block
LOCAL
BUS
CIS
VIDEO
SIGNAL
LC82103
CLOCK
VREF+
VREF–
(IC4)
Fig. 22
The CIS is driven by the LSI (LC82103), and the output video signal
from the CIS in input into the LC82103.
The ADC and buffer are provided in the LC82103, and the digital image
processing is performed.
n. Speaker amplifier
The speaker amplifier monitors the line under the on-hook mode, outputs the buzzer sound generated from the SH7041, ringer sound, DTMF
generated from the modem, and line sound.
o. Adjustment of voice/ringer volume
The voice/ringer volume can be adjusted by using the panel buttons
“UP” and “DOWN”.
• The ringer volume can be adjusted in the Stand-by mode by pressing
the UP/DOWN button.
• The reception level can be adjusted by pressing the UP/DOWN button
when the handset is located in the off-hook state.
• The speaker volume can be adjusted by using the speaker key.
ASIC
5 – 20
Page 57

[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU and Hook
H
L
HS DETECTOR
CML
CI DETECTOR
0:LINE
1:BZ
SPEAKER
LINE
+5VA
+24VA
DG
BZCONT
TELOUT
TEL IN
EXT.
RX
RXIN
TXOUT
CML
HS
0:CID
CONTROL PWBLIU PWB
SIGTX
SIXGRX
1:RX
0:MID
1:HIGH
TEL MUTE
(H:MUTE)
IC15 G.A
LR38784A
SP MUTE
(H:MUTE)
BZOUT
BZCONT
RCVOL
VOL C
VOL B
VOL A
SP MUTE
TEL MUTE
CI
RHS
GAIN-C
CML
HS
IC5 SH2
(7041)
HOOK-SW PWB
TX
GAIN -C
CI
MIC MUTE
IC8
MODEM(FM336)
SPKR
SW PWB
1. TEL/LIU block operation description
(1) Block diagram
FO-2970MU
Fig. 23
(2) Circuit description
The TEL/LIU PWB is composed of the following 9 blocks.
1. Surge protection circuit
2. On-hook status detection circuit
3. Dial pulse generation circuit
4. CML relay
5. Matching transformer
6. Hybrid circuit
7. Signal selection
8. CI detection circuit
9. Power supply and bias circuit
(3) Block description
1) Surge Protection circuit
This circuit protects the circuit from the surge voltage occurring on
the telephone line.
• The AR1 protects the circuit from the 390V or higher line surge
voltages.
• The V A1 and V A2 protect the circuit from the 470V or higher vertical
surge voltage.
2) On-hook status detection circuit
The on-hook status detection circuit detects the status of the hook
switch (RHS) of built-in telephone, and the status of the hook of a
telephone externally connected.
• The status of on-hook switch (RHS) is determined from the logical
level of RHS signal. (RHS is in the hook SW PWB)
RHS LOW: ON-HOOK
RHS HIGH: OFF-HOOK
• External telephone hook status detection circuit (HS)
This circuit comprises the photo-coupler PC1, resistors R1 and R2,
Zener diodes ZD1 and ZD2.
When an external telephone is connected and enters the on-hook
mode, the LED of photo-coupler PC1 emits light and the light receiving element turns on. The status signal HS is input to the pin119 of
(SH7041) (IC5: control PWB).
HS LOW: EXT. TEL OFF-HOOK
HS HIGH:EXT. TEL ON-HOOK
3) Dial pulse generation circuit
The pulse dial generation circuit comprises the CML relay.
4) CML relay
The CML relay switches over connection to the matching transformer
T1 while the FAX or built-in telephone is being used.
5 – 21
Page 58

FO-2970MU
5) Matching transformer
The matching transformer performs electrical insulation from the telephone line and impedance matching for transmitting the TEL/FAX
signal.
6) Hybrid circuit
The hybrid circuit performs 2-wire-to-4-wire conversion using the IC1
of operational amplifier, transmits the voice transmission signal to
the line, and feeds back the voice signal to the voice reception circuit
as the side tone.
7) Signal selection
The following signals are used to control the transmission line of TEL/
FAX signal. For details, refer to the signal selector matrix table.
[Control signals from output port]
Signal Name Description
CML H: Line make
SP MUTE H: Muting (Power down mode)
TEL MUTE H: Muting
RCVOL
(The circuit is located
in the control PWB.)
VOL A VRSEL1 VRSEL2 matrix
VOL B
VOL C
(The circuit is located
in the control PWB.)
GAIN-C Reception gain switching signal
(The circuit is located L: When connected to line, 1: 1 gain
in the control PWB.) H: When not connected to line, HIGH gain
BZCONT Speaker output signal switching
(The circuit is located H: Buzzer signal output
in the control PWB.) L: When monitoring line signal
MIC MUTE Handset mic mute control signal
Line connecting relay and DP generating relay
L: Line break
Speaker tone mute control signal
L: Muting cancel (Normal operation)
Handset reception mute control signal
L: Muting cancel
Handset receiver volume control signal
Volume High Middle Low
RCVOL H L L
Set the line driver of MODEM (FM336)
to – 6 dBm
Speaker volume control signal
VOL A VOL B VOL C
RING./
Receiving
Buzzer DTMF
H L L High — High
L H L Middle — Middle
L L H Low — Low
L L L — Fixed —
H: Muting
L: Muting cancel
[Signals for status recognition according to input signals]
Signal Name Function
RHS H: The handset is in the on-hook state.
(On the HOOK-SW PWB)
L: The handset is in the off-hook state.
CI Incoming call (CI) detection signal.
H: The handset or external telephone is in the
HS
on-hook state.
L: The handset or external telephone is in the
off-hook state.
[Other signals]
Signal Name Function
TEL IN Receiving signal from line or modem
TEL OUT Transfer signal to line
TXOUT
RXIN
Transmission (DTMF) analog signal output
from modem
Reception (DTMF, others) analog signal
input
into modem
No. Signal Name (CNLIU) No. Signal Name (CNLIU)
1 +24V 7
RHS
2 DG 8 TXOUT
3 +5VA 9 RXIN
4 CML 10 TELMUTE
5
CI 11 TELOUT
6 HS 12 TELIN
No.
Signal Name (CNHS 1 and 2)
1 RHS 2
No.
Signal Name (CNHS 1 and 2)
DG
8) CI detection circuit
The CI detection circuit detects the CI signals of 15.3 Hz to 68 Hz.
A CI signal, which is provided to the photo-coupler PC2 through the
C3 (0.82 uF), R3 (22 K), and ZD3 when the ring signal is inputted
from the telephone line.
9) Power supply and bias circuits
The voltages of +5VA and +24V are supplied from the control PWB
unit.
5 – 22
Page 59

(Example: Fax signal send)
FO-2970MU
CONTROL PWBLIU PWB
HS
CML
GAIN -C
EXT.
LINE
CML
HS DETECTOR
RX
TX
SPEAKER
H
L
TEL MUTE
(H:MUTE)
CI DETECTOR
SP MUTE
(H:MUTE)
TEL IN
TELOUT
TXOUT
RXIN
CI
+5VA
+24VA
DG
0:CID
1:RX
0:MID
1:HIGH
BZCONT
0:LINE
1:BZ
HOOK-SW PWB
SIGTX
SIXGRX
SPKR
BZCONT
BZOUT
MIC MUTE
RCVOL
VOL C
VOL B
VOL A
SP MUTE
TEL MUTE
RHS
CI
IC8
MODEM(FM336)
IC15 G.A
LR38784A
IC5 SH2
(7041)
GAIN-C
CML
HS
Fig. 24
[4] Circuit description of power supply
PWB
1. Noise filter circuit
The filter part removes noises generated from the power unit to avoid
noise release outside and prevent external noises from entering.
Excessive surge such as thunder is prevented by varistor Z1.
2. Rectified smoothing circuit
The rectified smoothing circuit rectifies AC input at diodes D10, 11, 12,
and 13, and then smoothens it at capacitor C5 to supply DC voltage to
the switching part.
3. Switching part
This circuit adopts the ringing choke converter system of self-excited
type.
By repeating ON/OFF of MOS FETQ1, this system converts DC voltage
supplied from the rectified smoothing part into high-frequency pulse,
stores energy in the primary winding of transformer T1 during ON period, releases energy to the secondary winding during OFF period, and
supplies power.
Frequency changes according to output load; As load increases, ON
period becomes longer.
Constant voltage is controlled by applying feedback to the control circuit
via photo coupler from 24 V output.
The overcurrent protective circuit detects prolonged ON period caused
by excessive output load, lengthens Q1 OFF period by using the control
circuit, and restricts energy stored in the primary winding of transformer
T1.
Increase of the secondary output voltage 24 V is led to the overcurrent
condition by turning on power zener diode D202 between 24 V output
and GND.
Thus overvoltage is protected by operating the overcurrent protective
circuit of the control circuit.
4. 24 V circuit
To supply output, transformer T1 output is rectified and smoothened
with the use of diode D101 and capacitor C101. Voltage is controlled by
Volume VR101.
5. +5 V circuit
Transformer T1 output is rectified and smoothened with the use of diode
D301 and capacitor C301 to stabilize +5 V output by using 3-terminal
regulator IC301.
6. Heater circuit
To maintain the optimal temperature, the heater lamp is controlled by
HLON signal from the control panel.
This HLON signal is to switch ON/OFF the heater lamp. If this signal is
input LOW, PC2 is switched ON, resulting TRIACK TRA1 ON.
Accordingly, AC power is supplied to the heater lamp to switch the heater
lamp ON.
7. Zero cross circuit
When AC input reaches the zero cross point (0 V), PC3 is switched ON.
When Q501 is switched ON, the zero cross signal is output to the control panel.
5 – 23
Page 60

FO-2970MU
CN1
AC IN
F1
NOISE
FILTER
CIRCUIT
RECTIFIED
SMOOTHING
CIRCUIT
SWITCHING
CIRCUIT
T1
TRANSFORMER
+5V
CIRCUIT
+24V
CIRCUIT
+5V
+24VH
ZERO CROSS CIRCUIT
HEATER CIRCUIT
CN2
[5] Circuit description of CIS UNIT
This CIS unit picks up optical information from the document, converts it
into an electrical (analog) signal and it to the control PWB.
1. Block diagram
SW101
+24V
PC1
ZC
+24VS
HLON
PC2
Fig. 25
2. Description of blocks
(1) CIS
The DL100-05AUJC is highly sensitive charged coupled image sensor
that consists of 1728 picture elements.
SH
CISCLK
VLED
GLED
+5V
GND
AiN
OUTPUT CIRCUIT
(emitter follower)
Fig. 26
SIG
CIS
Receiving two drive signal (SI,CLK) from the control PWB, the transferred photoelectric analog signal SIG is impedance converted, and the
signal AIN, is supplied to the control PWB.
(2) Waveforms
1. CLK, SI, SIG signals within the control PWB.
CLK
SI
SIG
1 2 3 1720 1721 1722
5 msec/line
Fig. 27
5 – 24
Page 61

CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMATICS AND PARTS LAYOUT
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
TP106
876
5
876
5
876
5
876
5
BR23
33 x 4
92
91
90
89
88
86
84
83
82
81
80
78
76
75
74
73
143
142
140
139
138
137
116
115
114
45
46
65
70
69
68
67
66
30
33
62
5049545343484731323436
109
111
110
113
2
5
44
108
107
96
94
105
104
106
127
128
124
126
125
123
122
121
120
119
118
98413938372725242322212019181716151311109879597
102
103
135
112998577634026
12
14
28
42
61
79
87
93
117
141
129
71
55
35
6
57
58
59
60
144
64
56
72
1
3
4
29
101
100
51
52
136
134
133
132
131
130
IC5
SH7041
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
BR8
33 x 4
BR22
33 x 4
BR5
33 x 4
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
CA2
100P x 4
D0
D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D[15:0]
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
CA1
100P x 4
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
CA3
100P x 4
4
3
2
1
5
6
7
8
CA4
100P x 4
DG
A[21:0]
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
C120
C121
C118
C117
C112
C113
C114
C116
C115
C110
C111
C147
C148
C149
C150
C155
C156
C152
C153
C144
C145
C146
18P x 22
R208
100
C183
2200P
R206
10K
DG
USOUT
BR7
33 x 4
123
4
876
5
R125 33
R126 33
BR6
33 x 4
BR24
33 x 4
BR9
100 x 4
BR25
100 x 4
+5VSH
C37
C221
C180
C181
C160
C24
C25
C157
C179
0.1 x 9
DG
DG
+5V
DG
/MEN
MPXC
ZC
R339
0
C324
N.M.
DG
R196
N.M.
R173
1K
R334 270
R341 100
R342 68 PNLON
VFM
BZCONT
TSEN
MIC MUTE
LAMPON
CML
RCVOL
SPMUTE
GAINC
TELMUTE2
R197
N.M.
R232
470
R198
270
R233
470
R231
1K
R199
100
BR11(A)
10K x 4
+5V
R131 100
R129 100
R130 100
R127 68
R128 68
R166 68
R169 100
R170 100
R171 100
R165 100
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
BR2
10K x 4
+5V
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
BR3
10K x 4
+5V
/CS0
/CS1
/CS2
/CS3
/RD
/WRL
/WRH
/RAS
/CASL
/CASH
/RDWR
/DREQ0
/DREQ1
DRAK0
DRAK1
/DACK0
/DACK1
/WDTOVF
R203 68
R202 68
R205 68
R204 68
/RESET
C222
1000P
DG
C220 C219
DG
N.M.
DG
R236
10K
R235
10K
DG
DG
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
BR19
10K x 4
+5V
SHCK
R2
33
R3
33
C63
C62
N.M.
DG
R240
3K
C226
470P
C224 0.1
PLLVCC
PLLVSS
DG
C162
27P
C163
22P
X1
6.912MHz
DG
C217
0.1
+5V
CHK24V
PIN
DG
N.M.
CI
RHSHSRTH
R201
470
R168
270
R200
470
BR11(B)
10K x 4
+5V
D107
DA204K
+5V
R333
2K
DG
+5V
DG
C27
1000P
C26
1000P
C182
1000P
MRES
R172
4.7K
DG
/BREQ
/BACK
DG
+5V
R194
10K
R163
10K
C154
N.M.
/INT1
/INT2
/INT3
/INT4
/INT5
/HSYNC
DG
C161
N.N.
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
BR4
10K x 4
+5V
DG
C123
2200P
C127
2200P
C125
2200P
C124
2200P
C126
2200P
PMCLK
PWMSIN
MA
MB
VOLA
VOLB
VOLC
MPXA
MPXB R195
R228
N.M.
R161 270
R162 270
+5VSH
+5V
R134
0
R132
0
C128 C6
DG
N.M.
CS0
CS1
CS2
CS3RDWRL
WRH
RAS
CASL
CASH
RDWR
DREQ0
DREQ1
DRAK0
DRAK1
DACK0
DACK1
WDTOVF
RESCKEXTAL
XTAL
PLLCAP
PLLVCC
PLLVSS
AVREF
AVCC
AVSS
PF7/AN7
PF6/AN6
PF5/AN5
AN4/PF4
PF3/AN3
PF2/AN2
PF1/AN1
AN0/PF0
PD24
BREQ
BACK
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ1
IRQ6
PD30
PD31
TIOC1A/PE4
TIOC1B/PE5
TIOC2A/PE6
TIOC2B/PE7
PE8
PE9
PE10
PE11
PE12
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PA4
PA5
PA8
PA9
PA16
PA17
PA20
PA21
PA22
PA23
PD16
PD29
IRQ7
PE13
PD25
PD26
PD27
PD28
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
NMI
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
MD3
MD2
MD1
MD0
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
R164
33
R193 270
123
4
123
4
123
4
123
4
6
5
R238
200
R174 3.3K
R234
33
R230
33
R160
100
32bit RISC MICROPROCESSOR
(2-6G)
(3-3D)
(3-3I)
(3-6C)
(3-6F)
(3-6I)
(4-5E)
(5-5D)
(8-3A)
(2-5H)
(2-5H)
(3-3A)
(3-3G)
(3-4D)
(3-5F)
(3-6A)
(3-6D)
(4-5E)
(5-4D)
(8-5A)
(2-3B)
(9-4I)
(9-5E)
(9-3A)
(9-5E)
(6-3F)
(9-4E)
(7-3E)
(6-5A)
(7-2A)
(6-2A)
(9-3A)
(9-5A)
(6-4A)
(9-4A)
(6-3H)
TELMUTE
(9-5A)
(9-5A)
(9-5A)
(9-5A)
(9-1G)
(9-5E)
(2-6B)
(9-3I)
(9-3I)
(2-3G)
(7-5D)
(2-3G)
(2-3H)
(2-4H)
(2-4H)
(2-4H)
(2-4G)
(2-4G)
(2-1E)
(2-1E)
(2-1E)
(2-1E)
(2-4G)(8-4G)
(2-4G)(3-4F)(8-4G)
(2-4G)(3-4D)(3-4F)(8-4G)
(3-4F)
(2-4G)(4-3E)
(2-4G)
(3-4D)
(7-5A)
(2-3H)
(2-3H)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-5C)
(9-5I)
(9-5I)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(6-2F)
(6-2F)
(6-3F)
(9-3A)
(9-3A)
TP107
R371
270
R370
270
1
2
8
7
3
4
FO-2970MU
[1] Control PWB circuit CPU block 1/9
6 – 1
Page 62

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
(3-2A)
(3-2G)
D[15:0]
190
191
192
193
194
206
195
196
197
198
199
201
202
203
204
2056263646566474845464344505758596061787911067554288
208
207
170
158
157
138
104
1035453951
2
14
31
49
51
52
70
84
105
106
118
126
137
147
151
155
156
164
169
180
189
200
76
74
75
77
124
125
123
119
121
120
122
34
89
3
29
30
27
28
26
4
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
32
12
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
87
109
73
68
72
71
25
24
23
168
163
160
167
166
165
162
161
159
154
153
152
150
149
148
145
144
143
142
141
127
130
129
128
131
132
69
135
5
139
140
133
134
136
146
171
102
101
100
9983828180
113
111
112
859897969493929190
86
107
108
117
116
115
114
56
678
9
1819202122131516171011
IC15
LR38784A
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
LCPD0
EXINT1Z
TEST1
RTCIO
RTCCE
RTCDT
RTCCK
B4SNS
ORGSNS
FRTSNS
XBPSEI
XBPINI
XBPAF
XBPOFT
BPOSE
BPOPE
BPOBY
XBPOACK
BPBD0
BPBD1
BPBD2
BPBD3
BPBD4
BPBD5
BPBD6
BPBD7
XBPSTB
POUTZ
PINZ
DOPZ
PWRLY
PUS
TC_BIASON
HLON
MCON
PE
MAMBPMDZ
APCSTT
SAMP
VIDEO
PRTCLK
PD7
PD6
PD5
PD4
PD3
PD2
PD1
PD0
PRASZ
PCASZ
PWRZ
PA9
PA8
PA7
PA6
PA5
PA4
PA3
PA2
PA1
PA0
PEPCKO
PEPCKI
TPBZ
TPAZ
TPB
TPA
USOUT
LEDDV4
LEDDV3
LEDDV2
LEDDV1
SEN4Z
SEN3Z
SEN2Z
SEN1Z
SEN0Z
LD3
LD2
LD1
LD0
RS
11 : LCDACKZ
135 : SYNCZ
5 : LCDREQ
E
CK16M
SDCK
SDE
SD
LCWRZ
LCRDZ
LCINT
BZOUT
LCPD4
MDMINTZ
MDMWRZ
MDMRDZ
MDMRSTZ
MDMCSZ
LCPD3
LCPD2
WE3Z
WE2Z
WE1Z
OE3Z
OE2Z
OE1Z
CASLOZ
CASHOZ
RASOZ
RDWRZ
CASLZ
CASHZ
RASZ
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
VCC
LCPD1
MTST
RESET2Z
WDTOVFZ
RESETZ
BACKZ
BREQ
INT5Z
INT4Z
INT3Z
INT1Z
95 : GND
1 : GND
SHCK
DACK1Z
DACK0Z
DRAK1
DREQ1Z
DREQ0Z
CS1Z
CS2Z
WRLZ
WRHZ
RDZ
A1A2A3A4A5A6A7
A8
DRAK0
INT2Z
A9
A10A0A11
A12
A13
A20
A21
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
LCPD0
+5V
DG
RTCIO
RTCCE
RTCDT
RTCCK
/B4SNS
/ORGSNS
/FRTSNS
NSELECTIN
NINIT
NAUTOFD
NFAULT
SELECT
PERROR
BUSY
NACK
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8
NSTROBE
POUT
PIN
DOP
PWRLY
PUS
TC/BIASON
HLON
MCON
PE
R284
33K
R283
33K
R282
20K
+5V
+5V
C304
680P
DG
R250 470
R253 470
R254 470
R271 47
R275 47
R278 47
R272 47
R273 47
R274 47
R276 47
R277 47
R279 47
R315 47
R301 47
R316 47
R302 47
R317 47
R304 47
R318 47
R305 47
PD7
PD6
PD5
PD4
PD3
PD2
PD1
PD0
PA9
PA8
PA7
PA6
PA5
PA4
PA3
PA2
PA1
PA0
/PRAS
/PCAS
/PWR
VIDEO
SAMP
APCSTT
PMD
MBMALCDREQ
/HSYNCSYNC
DG
C286
470P
+5V
R280
1K
R281
680
R256
68
1213
14
7
DG
+5V
1011
14
7
DG
+5V
R257
0
DG
R259
1M
X4
20.95261MHz
C260
10P
C262
15P
/TPB
/TPA
TPB
TPA
USOUT
LEDDV4
LEDDV3
LEDDV2
LEDDV1
5
678
4
321
BR26
470 x 4
5
678
4
321
BR15
10 x 4
R290
0
R291
1M
R268
200
X5
35.5721237MHz
21
21
C290
0.01
C279
47P
DG
/SEN4
/SEN3
/SEN2
/SEN1
/SEN0
LD3
LD2
LD1
LD0RS/LCDACK0
5
678
4
321
BR17
470 x 4
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
1
BR18
10K x 4
R251
10K
+5V
5
678
4
321
BR16
270 x 4
R261
270
R260
100
33
+5V
C261 0.1
C39 0.1
C38 0.1
C40 0.1
C41 0.1
C34 0.1
/CASLO
/CASHO
/RASO
/RDWR
/CASL
/CASH
/RAS
C276
18P
C275
18P
C277
18P
DG
C249
47P
DG
/MDMWR
/MDMRD
/MDMRST
/MDMCS
LCPD3
LCPD2
/WE2
/WE1
/OE2
/OE1
DG
C244
1000P
/MDMINT
LCINT
BZOUT
LCPD4
R229
10K
DG
/LCRD
/LCWR
LCPD7
LCPD5
LCPD6
CK16M
C248
C246
C218
N.M.
DG
DG
R262
270
R263
3K
E
A[21:0]
A[10:1]
A0
A11
A12
A13
A20
A21
A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9
A10
/DREQ0
/CS1
/CS2
/WRL
/WRH
/RD
/DREQ1
/DACK0
DRAK1
DRAK0
/DACK1
/INT5
/INT4
/INT3
/INT1
SHCK
/INT2
C263
100P
C264
100P
C274
100P
C285
100P
DG
DG
C287
47P
C278
1000P
/BACK
/BREQ
/RESET
LCPD1
MTP
/RESET2
/WDTOVF
C289
0.1
R288
3.9K
R289
20K
DG
+24VS
CHK24V
DATA
CLKCEINTN
XT
XTN
VCC
VSS
RTCDT
RTCCK
RTCCE
RTCIO
765
1
328
4
C306
10P
C305
10P
C291
0.1
X6
32.768KHz
DG
IC16
SM8578BV
+5V
R294
10K
R295
10K
R293
4.7K
DG
R292
N.M.
VBAT
IC18E
74HCU04
IC18F
74HCU04
R258
470
L100
0.47
R252
470
C247
1000P
DG
R287 33
R285 33
R286 33
GATE ARRAY
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
(1-5I)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4A)
(1-4A)
(1-3A)
(1-3A)
(1-3A)
(1-3A)
(1-3A)
(1-6B)
(1-6B)
(1-6B)
(1-6B)
(1-6B)
(1-5A)
(1-5A)
(7-5D)
(2-6E)
(2-6E)
(2-6E)
(2-6E)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(3-4A)
(3-4A)
(3-4A)
(3-4A)
(3-2G)
(3-5A)
(3-2A)
(4-5I)
(4-5I)
(5-3C)
(5-2C)
(5-4C)
(5-4C)
(5-3C)
(4-5I)
(6-1H)
(4-2E)
(4-3E)
(4-3E)
(4-5I)
(4-5I)
(4-5I)
(4-2E)
(9-2A)
(4-5I)
(9-2A)
(9-1A)
(9-1A)
(9-1A)
(9-1A)
(9-2E)
(9-1E)
(9-1E)
(9-1E)
(9-1E)
(9-1A)
(9-2E)
(9-2E)
(9-2E)
(1-5H)
(7-2A)
(7-2A)
(7-2A)
(7-2A)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-3D)
(3-2D)
(3-2D)
(3-2D)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(3-3G)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-5E)
(9-5E)
(9-5E)
(9-5I)
(4-5I)
(9-5I)
(1-2B)
(1-6B)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-5E)
(9-5I)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-5I)
(9-5E)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-4E)
(9-4I)
(9-2E)
(9-2E)
(9-1E)
(2-1F)
(2-1F)
(2-1F)
(2-1F)
(4-5I)
(1-3C)
(4-3E)
(4-5I)
(4-5I)
/WE3
/OE3
C361 1000P
Gate Array block 2/9
6 – 2
Page 63

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
IC13
HY5118164CJC-6
28
27262524232019181731301413
29
1112151632
414039383635343310987543221614237
22
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0LCAS
UCAS
RASWEOE
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
I/O15
I/O14
I/O13
I/O12
I/O11
I/O10
I/O9
I/O8
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
VCC
VCC
VCC
VSS
VSS
VSS
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2
A1
A[10:1]
/WE1
/OE1
R266
100
R267
100
DG
C272 C271
N.M.
/CASLO
/CASHO
/RASO
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
C273
0.1
C268
0.1
C267
0.1
DG
+5V
D[15:0]
IC11
HY5118164CJC-6
28
27262524232019181731301413
29
1112151632
414039383635343310987543216214237
22
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0LCAS
UCAS
RASWEOE
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
I/O15
I/O14
I/O13
I/O12
I/O11
I/O10
I/O9
I/O8
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
VCC
VCC
VCC
VSS
VSS
VSS
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2
A1
A[10:1]
/WE2
/OE2
R265
100
R264
100
DG
C269 C270
N.M.
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
C254
0.1
C253
0.1
C250
0.1
DG
+5V
D[15:0]
IC14
M27C800
1
2
33343536373839
40
34567
1011133242
3028262421191715292725232018161422
31
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10A9A7A6A5A4A3
A0EG
BYTEVPP
N.C.
Q15A-1
Q14
Q13
Q12
Q11
Q10
Q9Q8Q7Q6Q5Q4Q3Q2Q1
Q0
VCC
VSS
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2
A1
A[19:1]
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
+5V
D[15:0]
8
9
/CS0
/RD
A20
R269
N.M.
12
VSS
A2
A1
41
A8
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
C43
0.1
DG
IC21
BS62LV1024
2313284
252326
27
578
9
10
11
242922
30
21201918171514
13
32
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10A9A7A6A5A4A3
A0OEWS1S2
DQ8
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
DQ2
DQ1
VCC
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2
A1
A[16:1]
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
VBAT
D[7:0]
12
/RD
/WRL
TCS1
R336
0
16
GND
A2
A1
6
A8
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
C266
0.1
DG
A0
/CS3
R335
33
R225
100
R337
N.M.
VBAT
N.C.
1
IC17
HM514800-70J
9
201918171613121110
27262524543
2
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
PA0
PA[9:0]
PD7
PD6
PD5
PD4
PD3
PD2
PD1
PD0
+5V
PD[7:0]
PA1
PA2
PA3
PA4
PA5
PA6
PA7
PA8
PA9
C319
0.1
DG
/PRAS
/PCAS
/PWR
R321 33
R319 33
R320 33
C320
0.1
62111415
28
N.C.
N.C.
VCC
VCC
VSS
VSS
RAS
CASWEOE
8237
22
DG
R338
N.M.
1M x 16bit DRAM
1M x 16bit DRAM
EPROM
512K x 8bit DRAM
1Mbit SRAM
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
(1-6I)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(7-4D)
(2-4B)
(2-4B)(1-6I)
(2-4B)
(2-4B)
(2-4B)
(1-5I)
(1-4B)
(1-5B)
(1-5I)
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
(1-5I)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
IC22
HY5118164CJC-6
28
27262524232019181731301413
29
1112151632
414039383635343310987543216214237
22
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0LCAS
UCAS
RASWEOE
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
I/O15
I/O14
I/O13
I/O12
I/O11
I/O10
I/O9
I/O8
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
VCC
VCC
VCC
VSS
VSS
VSS
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2
A1
A[10:1]
/WE3
/OE3
R372
100
R373
100
DG
C362 C363
N.M.
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
C44
0.1
C365
0.1
C366
0.1
DG
+5V
D[15:0]
1M x 16bit DRAM
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
Memory block 3/9
6 – 3
Page 64

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
(1-5I)
(1-6I)
(4-2E)
(1-4B)
(2-1C)
(2-1C)
(2-3G)
(2-1C)
(4-5E)
(2-1C)
(9-5C)
DG
+5V
+5VR
IC4
LC82103
2326272811121314151619
20
123
678
59575847485051
52
45
A12
A11
A10A9A8A7A6A5A3A2A1A0D7
D4
WR
RESET
MTP/PP7
DACK/PP5
DREQ/PP6
PD7/SD
PD6/SDCK
PD5/SDE
PD4/PP4
PD3/PP3
ATAPL
A6A5A4A3A2A1A0
D7D6D5
A[12:0]
4
/CS2
/LCRD
/RESET2
37
DALRL
D6
D5
18
A4
A7
A8A9A10
A11
A12
DG
D4
/LCWR
PD0/PP0
555354
PD2/PP2
PD1/PP1
D3D2D1
D0
REFCSRD
D[7:0]
SH
CLK1
CLK2
RS
ATAPH
TRIG
ICLK
DAHRL
DAHRH
TEST
DVDD
DVDD
DVDD
DGND
DGND
DGND
DGND
CLKIN
SAMP/LININT
AIN
TEMP AVDD
AGND
AGND
5
D3D2D1
D0
R122 100
R121 68
R117 68
R227 68
R346 68
R347 68
R348 68
R349 68
R350 68
R345 100
MTP
LCPD7
LCPD6
LCPD5
LCPD4
LCPD3
LCPD2
LCPD1
LCPD0
LCDREQ
/LCDACK0
C177
N.M.
DG
CISSI
CISCLK
+5V
R119
10K
R124
10K
R123 33
R120 0
TP411
TP412
63626160413130
DALRH
384244
34
+5VR
C108 0.01
C107 0.01
DG
102456
DG
+5V
C64
0.1
C143
0.1
C22
0.1
C9
47/16
91749
64
C142
0.1
C10
47/16
433646
R191 100
R190 100
+5V
222132
35
29
N.M.
C178
DG
AIN
LCINT
+5V
DG
14
9
7
8
IC18D
74HCU04
C259
0.1
CK16M
R223
68
+5V
2
14
1
7
DG
IC18A
74HCU04
R224
0
+5V
4
14
3
7
DG
IC18B
74HCU04
R225
1M
X3
16MHz
21
R226
0
C215
30P
C214
30P
DG DG
R332
0
AIN
+5VR
R116
2.2K
E
B
C
DG
Q100
2SA1037K
+5VR
R340
2.2K
R186
N.M.
E
B
C
Q101
2SA1037K
DG
AO
DG
+5VR
D105
DA204K
R331
N.M.
333940
25
IMAGE SIGNAL PROCESSOR
(2-3G)
(2-2A)
(2-5B)
(2-1C)
(2-1C)
(2-1C)
(2-1C)
(2-1D)
(2-1D)
(2-3G)
(2-6E)
(9-5D)(9-5C)
(9-5D)(9-5C)
Reading block 4/9
6 – 4
Page 65

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
83
73
8
81
87888990919394
95
6
5
21
46
172039
96
97
234
7
D4D5D6
D7
483418
54
/MDMRST
60
19
IRQ
N.C
N.C
N.C
N.C
POR
RESET
N.C
N.C
M_TXSIN
744572
30311
14
32
SR4OUT
M_SCK
EYEXY
RDCLK
YCLK
RIN
VREF
VC
RESERVED
RESERVED
922662
11
67
6875641035404261562347
36
78
12
TP208
TP212
VDD1
MAVDD
VCORED0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7
RS0
RS1
RS2
RS3
RS4RDWRCSM_RXOUT
SR4IN
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
XTCLK
TDCLK
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
M_CNTRL_SIN
SR1IO
SLEEP
M_STROBE
EYESYNC
38507169631357
84
3776497727
TP206
SPKRP
IC8
FM336
33600 bps FAX MODEM
VDD
VDD
VGG
VDD1
VDD1
VDD1
VDD1
VDD1
TALK
RI
OH
RINGD
SPKR
SIGRX
(2-1D)
(6-3A)
(6-3D)
C61
10/50
C388
0.1
TP205
+5V
R382
10K
R383
10K
TP2099TP210
TP207
70
TP211
24
29
28
TXA2
TXA1
(6-5B)
(6-5B)
C60
10/50
C386
0.1
1558596682
513325
98
100
+3.3V
DG
R381
0
L102
0
12
C59
10/50
C53
0.1
MAG
DG
MAG
R384
0
79
41
55
4443228586521653658099
+5V
C45 0.1
C46 0.1
C47 0.1
C48 0.1
C371 0.1
C49 0.1
DG
C50 0.1
C51 0.1
C52 0.1
DG
D3
D2D1D0
D[7:0]
A4
A3A2A1
A0
A[4:0]
/MDMCS
(2-1D)
/MDMWR
(2-1D)
/MDMRD
(2-1D)
R374 100
R375 100
R376 68
TP204
MAG
DG
R380
100
R390
18P
C382
18P
2
1
X2
28.224MHz
C380
2200P
C381
2200P
R379
47K
DG
DG
R398
N.M
+3.3V
DG
/MDMINT
(2-1D)
IC18C
74HCU04
56
R377
4.7K
R378
10
+5VA
MAG
MAG
C379
0.1
C58
22/50
L101
10
+3.3V
DG
C376
0.1
C57
22/50
C322
1
DG
+5V
C104
1
REG1
XC62FP3302P
12
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
DG
C389
0.1
D100
1SS355
KA
2
1
3
+3.3V
N.C
N.C
M_CLKIN
CLK_OUT
XTALI/CLKIN
XTALO
VSUB
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
RLSD
IA_SLEEP
EYECLK
GRO0
XCLK
TXA2
TXA1
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
MAVSS
MAVSS
PLL_VDD
PLL_GND
VSS
Modem block 5/9
6 – 5
Page 66

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
C400
0.1
DG
C405
1000P
N.M.
N.M.
R396
BLM11A102
R397
BLM11A102
DG
N.M.
C401
N.M.
R391
44.2K
+5VA2
C129
1
C7
10/50
C397
R388
6.2K
C395
0.1(K)
IC1A
NJM2902M
–
+
+24VA
2
1
4
11
3
DGDGDG
C391
1000P
R387
10K
C394
1
R393
3.3K
R385
10K
VREF
(2.5V)
R386
0
+5V
5
14
7
4
3
C411
1
+5VA2
CBE
C
B
E
DGDGDG
TEL OUT
R394
1K
MIC MUTE
Q104
DTC114
Q105
2SC2412
R395
4.7K
C392
DG
R330
3.3K
C56
DG
DG
C55
N.M
N.M
C54
N.M
N.M
N.M.
C390
N.M.
IC2B
BU4066
C409
0.1
9
10
8
4
11
TXOUT
R175
3.3K
DGDG
TXA2
R389
22K
+5VA
DGDG
R392
1K
R180
44.2K
C166
330P
C396
0.1(K)
GAINC
0
1
16
9
4
8
5
3
EXTSIG
RXIN
R176
3K
R182
62K
R214
R215
0
N.M.
R177
0
+5V
DG
C35
0.1
DG
IC7A
HCF4053
IC1C
NJM2902M
+24VA
C1
4.7/50
DG
6
5
4
7
11
+24VA
DG
C130
470P
R137
62K
C133
0.1
+5VA
D101
1SS355
K
A
SIGRX
+5VA
R328
10K
R329
10K
DG
VREF (2.5V)
RCVOL
DG
13
12
4
14
11
+24VA
DG
C100
1000P
R101
47K
R327
3.3K
R100
1.5K
TELIN
C131
1
R138
1.5K
IC1B
NJM2902M
IC1D
NJM2902M
0
1
16
10
15
8
2
1
+5V
DG
IC7B
HCF4053
0
1
16
11
14
8
12
13
+5V
DG
IC7C
HCF4053
R183
27K
R218
11K
C197
0.1(K)
SPKRP
C165
0.1(K)
+5V
14 13
12
7
R212
390K
+5V
BZCONT
VOLC
14 12
11 10
7
14 6
89
7
DG
VOLB
VOLA
R150
1M
R148
120K
R149
33K
IC2A
BU4066
IC2D
BU4066
IC2C
BU4066
C196
0.1(K)
C15
47/16
DG
+5V
R245
100K
423
C13
4.7/50
C12
1/50
DG DG DG
C230
330P
R244
150K
5
871
6
R367
R352
SP+
SP–
SPMUTE
BZOUT
C231
4700P
DG
R247
2K
DG
C199
0.01(K)
R217
20K
INH
VDD
VEE
VSS
6
16
7
8
IC7D
HCF4053
DG
+5V
C36
0.1
DG
R178
10K
+5V
TP600
R179
10K
R246
20K
R213
3K
IC9
NJM2113
(9-2E)
(9-1E)
(1-1C)
(1-6E)
(1-6E)
(1-6E)
(2-1C)
(1-1D)
(9-4A)
(9-5A)
(9-5A)
(5-5H)
(5-3H)
(1-1C)
(5-2H)
(1-1D)
(9-5A)
TXA1
(5-2H)
(1-1D)
(9-5A)
Analog block 6/9
6 – 6
Page 67

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFGIHCA
C407
1000P
C408
0.1
N.M.
R368
0
R351 0
C350
C351
15P
FG4 FG2
MG
DG
MRES 1
2
3
C228
1
5
4
M/R
SUB
GND
VCC
VOUT
IC20
PST596
+5V
R241
1K
DG
SW1
C323
N.M.
DG
RESET
C
B
E
+5V
TSC1
R242
4.7K
DG
Q1
2SC4081
R239
10K
VBAT
+24VA
+5V
C21
33/16
R325
10K
R323
10K
R324
10K
D103
HRW0502A
R322
5.6K
D102
1SS355
BAT
CR2032
1
2
DG
DG
TPA
TPB
/TPA
/TPB
LAMPON
123
G COM
45678
R133
10K
DG MG
161514
131211109
IC6
ULN2003A
DG
C189
1000P
N.M.
+24V
ZD2
RD22FB3
F100
KAB2404 801
1
2
TX24V
TXPA
TXPB
/TXPA
/TXPB
GLED
+5VPN
B
EC
Q102
2SA1036
R353
10K
Q103
DTC114
B
E
C
PNLON
DG
R209
R210
R211
R296
0
MGFG1
DG
+5V +5V
R355
N.M.
R354
4.7K
1
2
3
D1
DAP202U
FG3
R369 0
(1-1D)
(1-3C)(2-3H)
(3-4F)
(9-3C)
(9-3C)
(9-3C)
(9-4C)
(9-4C)
(5-5B)(9-5D)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(1-1D)
(1-5B)
Reset/Driver block 7/9
6 – 7
Page 68

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
5678
4321
(1-5I)
(1-6I)
R343
10K
A0A1A2A3A4
A5A6A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A[21:0]
BR1
10K x 4
+5V
BR27
10K x 4
BR21
10K x 4
R270
10K
BR14
10K x 4
BR28
10K x 4
D0D1D2
D3D4D5
D6D7D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D[15:0]
BR12
10K x 4
+5V
BR29
10K x 4
BR13
10K x 4
BR30
10K x 4
C119
C252
C251
N.M.
DG
/WRH
/WRL
/RD
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
(1-4B)
Other block 8/9
6 – 8
Page 69

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
CNLIUA
12R-FJ
1234567891011
12
C195
1000P
C229
1000P
C255
C256
1000P
N.M.
+24VA
+5VA
DG
CMLCIHS
RHS
TXOUT
RXIN
TELMUTE
TELOUT
TELIN
TP1
TP2
TP3
TP4
TP5
TP6
CNLIUB
6R-FJ
12345
6
C194 56P
C193 56P
C190 56P
MPXB
MPXC
RCVOL
C191 56P
DG
MPXA
TELMUTE2
EXTSIG
CNCIS
B7B-PH-K-S
1234567
8
9
10
C175
1000P
+5V
CISSI
CISCLK
GLED
CISCLK
GLED
TELMUTE
+24VH
AO
TP7
DG
C173
0.1
C8
47/16
C172
330P
C174
MGDG
+24VH
DG
R356
0
R357 0
R358 0
R359
0
R360
R361
R362
R363
CISSI
DG
CNMT
B6B-PH-K-S
12345
6
C186
56P
C185
56P
TXPA
TX24V
C187
56P
C188
56P
DG
TXPB
/TXPA
/TXPB
1234567891011
1213141516171819202122
LEDDV2
LEDDV3
LEDDV4
/FRTSNS
/ORGSNS
/SEN0
/SEN1
/SEN2
/SEN3
/SEN4
/B4SNS
R364
10K
R365
10K
R366
10K
+5V
CNPN
B22B-PHDSS-B
C204
0.1
+5VPN
C208 1
C237 1
C209 1
C238 2200P
C210 2200P
C241 1000P
C211 1000P
C242 1000P
C212 1000P
C243 1000P
C213 2200P
DG
C236 1
C207
C235
C206
C234
C205
C233
N.M.
RSELD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
LEDDV1
1a2a3a4a5a6a7a8a9a
10a
11a
12a
13a
14a
15a
16a
17a
18a
19a
20a
21a
22a
23a
24a
25a
1b2b3b4b5b6b7b8b9b
10b
11b
12b
13b
14b
15b
16b
17b
18b
19b
20b
21b
22b
23b
24b
25b
DG
50pin
+24VH
+5V
DATA1
DATA3
DATA5
DATA7
NACK
PERROR
NFAULT
NINIT
VFM
POUT
C315
DG
MG
DG
MG
C313
C312
C309
C17
N.M.
C308
0.1
PIN
TSEN
/MENMBSAMP
APCSTT
PMD
MCON
TC/BIASON
PWRLY
R314 100
R313 100
R312 0
R311 200
R310 0
R309 0
R308 0
R307 0
CNPRT
C343
C344
C330
+24VS
NSTROBE
DATA2
DATA4
DATA6
DATA8
ZC
BUSY
SELECT
NAUTOFD
NSELECTIN
C321
C297
C314
C311
C296
C295
C294
DG
C293
0.1
DG
+5V
MG
DG
+24V
C42
0.1
C19
N.M.
C18
47/16
PLLVCC
PLLVSS
HLON
PUS
PE
PMCLK
SYNC
VIDEO
MA
DOP
PWMSIN
R303 100
R300 100
R299 33
R298 0
R297 0
CNFUSE
B3B-PH-K-S
123
MG
+24V+24VS
CNSP
B2B-PH-K-R
1
2
DG
SP+
SP–
C258
C257
CNRTH
B2B-PH-K-S
1
2
DG
RTH
C20
47/16
R306
20K
C307
0.1
+5V
+24VA+24VH
DG
C16
100/50
C281
0.1
R1
10
DG
TP13
TP12
TP11
TP10
TP14
N.M.
N.M.
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6C)
(2-6C)
(2-6C)
(1-6D)
(2-5A)
(2-5B)
(1-6D)(2-5B)
(2-6C)
(1-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(1-1F)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6E)
(1-3B)
(1-2B)
(2-6C)
(2-6C)(1-2B)
(1-1D)
(1-1E)
(2-5B)(1-6D)
(2-5B)
(2-5B)
(2-5B)
(2-6C)
(2-6C)
(2-6C)
(4-4I)
(4-4I)
(7-2D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(2-6D)
(1-1D)
(4-4A)
(4-4I)
(4-4I)
(7-2D)
(1-1D)
(1-2B)
(1-2B)
(1-2B)
(6-5E)
(6-3E)
(1-1C)
(6-6A)
(6-2A)
(6-4E)
(1-1C)
(1-6E)
(1-6E)
(1-1E)
(1-1D)
(7-2D)
(7-2D)
(7-2D)
(7-2D)
(7-3D)
(2-2A)
(2-1C)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(2-3B)
(2-6E)
(2-6E)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-2A)
(2-3A)
(2-6E)
(6-4H)
(6-3H)
(1-2B)
C410
1000P
C352
2200P
C329
56P
TP8
TP9
N.M.
C325
1000P
C346
C348
DG
C347
1000P
C310
MG
C357
1000P
C360
DG
C345
C342
C298 4700P
C299 4700P
C300 1000P
C301 47P
C303
C341
C340
C339
C338
C337
C336
C335
C334
C333
C332 56P
C331
C317 4700P
C318 4700P
N.M.
C316
N.M.
MG
C192 56P
C326
56P
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
Connector block 9/9
6 – 9
Page 70

FO-2970MU
Control PWB parts layout (Top side)
6 – 10
Page 71

Control PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
FO-2970MU
6 – 11
Page 72

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFGIHCA
CNLUA
+24V1
2345678
9
101112
DG
+5VA
CMLCIHS
RHS
TXOUT
RXIN
TELMUTE
TELOUT
TELIN
CNHS1/2
RHS1
2DG
–
+
–
+
R6
4.7(1/2W)
L1
EL0909RR-102K-2
C5
0.01
C105
3300P
JP5
L7
N.M.
JP6
L8
N.M.
C9
4.7/50
C112
2200P
N.M.
VA3
TNR07G101K
ZD5
1ZC27
R101
13K
Q1
BS108
R4
15(1/2W)
C1
10/50
ZD4
MTZJ6.8B
R102
10K
R5
15(1/2W)
D
G
S
–
+
~
~
1
2
4
3
DB1
0R5G4B42
B
C
E
C
B
E
1
2
TIP
RING
MJ1-3
MJ1-4
AR1
RA-391P-V6-2
1
2
1
2
ARG
VA2
ERZVA5D471
VA1
ERZVA5D471
L2
R-5C
L3
R-5C
R2
30
ZD1
RD2.2FB2
ZD2
RD2.2FB2
PC1
PC814X
CML
OUAZ-SH-124DZ
C
B
M
R7
22K
R3
22K
(1/2W)
D1
1SS133
AK
112
PC2
TLP521-BL
ZD3
HZ27-A
T1
TRTEP17-0411F
C2
2.2
C104
0.033
ZD7
HZ2C1
ZD6
HZ2C1
C7
4.7/50
R107
620
R108
47K
R111
51K
3
2
1
C106 560P
R112 36K
IC1
NJM2904D
+5VA
C111
1
R113
3.3K
CNLIUA-8
CNLIUA-9
TXOUT
RXIN
DG
R109
16K
VREF
MJ2-3
MJ2-4
EX TIP
EX RING
JP2
N.M.
L4
R-5C
JP3
N.M.
L5
R-5C
1
2
3
C100
0.1
CNHS2-1
CNHS2-2
SW1
HOOK SW
B
M
C
RHS
DG
CNLIUA-7
(1-3G)
RHS
CNHS1-1
CNHS1-2
DG
+24VA
AK
D2
1SS133
CNLIUA-4
CML
Q102
DTC114EK
DG
CML
+24VA
CNLIUA-1
+24VA
CNLIUA-3
+5VA
+5VA
VREF
CNLIUA-2
DG
C6
22/50
R106
1K
R105
1K
C4
47/50
DG
CNLIUA-6
HS
3
4
DGDG
C101
1000P
PC1
PC814X
CNLIUA-5
CI
3
4
DGDG
C102
1000P
PC2
TLP521-BL
CNLIUA-11
TELOUT
6
5
7
IC1
NJM2904D
C110
2200P
R118
11K
C108
1000P
R114
3.3K
C107
C109
1000P
R117
1K
C11
2.2/50
VREF
C10
10/50
+5VA
R115
1.5K
R116
1.5K
C103
2200P
Q101
DTC114EK
MJTEL-1
TX+
MJTEL-4
RHS
TX–
(1-2B)
RX–
MJTEL-3
RX+
MJTEL-2
JP4
N.M.
L6
D3
D4
N.M.
+5VA
DG
R8
150
Q103
2SC2412KR
TELIN
CNLIUA-12
TEL MUTE
CNLIUA-10
DG
Q104
DTC114EK
C8
4.7/50
JP1
C3
0.82/250
DG
8
4
HOOK SW PWB(F3134)
DG DG DG
R1
91
DG
R110
0
N.M.
[2] TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB circuit 1/1
6 – 12
Page 73

TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB parts layout (Top side)
FO-2970MU
6 – 13
Page 74

FO-2970MU
TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
6 – 14
Page 75

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFGIHCA
MC
MC
DRUM
DRUM EARTH
FG
FU-G
FU EARTH
FG
R58
200M RK(1/2)
ZD5
1ZB200Y
CB
CB
ZD9
RD100E
ZD8
RD100E
DC-BIAS
DC-BIAS
R59
8.2M RK(1/2)
R52
3.9M(1W)
VR1
RH0165(1M)
1
3
2
R37
470K
C40
150P/2KV
AK
D6
SHV-03
AK
D5
SHV-03
C39
1000P/1KV
FG
C41
1000P/1KV
ZD7
RD100E
ZD6
RD100E
T2
0021GC
R50
560
+24V
F1
ICP-N10
C1
47/35
1
2
MG
ZD2
RD30JS
Q8
A933S
C21
1000P
DG DG
1
2
3
R51
1M
R49
5.1K
+24VP
C32
2200P(F)
R55
62
ZD4
RD2.4ES
D4
DSM1D
R54
3.0(1/2W)
+5V
Q4
A933S
1
3
2
R30
11K(F)
C19
4700P(F)
C20
0.015(F)
DG DG
+5V
R29
100K
R31
20K
R28
10K
1
3
2
Q7
C1815
R48
4.7K
C31
1000P
+24VP
R36
10K
R47
15K
(2-4C)
(2-4C)
(2-4C)
MB
MA
MEN
+5V
R12
10K
14713
8
ENABLE1
ENABLE2
IN1
IN2
E2
SENSE2
E1
SENSE1
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
+5V+24V
5
11
15
9
12
10
R34
680
R20
10K
DGDG
Q9
2SD1264
1
3
2
C11
330P
R19
20K
C9
330P
R18
20K
F2
ICP-N25
12
C25
47/35
C10
0.1
VBB
LOGIC SPLY
VREF
RC2
RC1
GND
IC2
A2918SWH
3
6
18
16
2
4
17
1
R44
1K
R45
1K
CNMMT
MA1
234
MAMBMB
DG
C7
1000P
C6
1000P
C12 1000P
C8 1000P
123
4
S4B-PH-KS
MG MG MG MG
R43
0.56(1W)
R46
0.56(1W)
C24
0.1
C23
0.1
98
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
GCOM
10111213141516
IC1
ULN2003
+24VH
MG
(2-4C)
MCON
(2-3C)
PUS
(2-3C)
TC/BIASON
(2-3C)
HLON
(2-3C)
PWRLY
(2-5C)
PWMSIN
CNPL
+24V1
2 PUS
1
2
S2B-PH-K-E
+24V
C44
1000P
C45
1000P
DG DG
CNPW
+5V1
2345678
9
101112
DGDG+24VHMGMG
+24VS
PWRLY
HLON
+24V
+24V
ZC
R1
N.M.
C2
47/35
+5V
+24VH+24V
DG MG
9176B-12L-TL
(2-4C)
(2-2C)
ZC
24VS
TC
TC
C35
1000P/6KV
D8
SHV-06
R56
250M RM18
FG
R57
100M RK(1/2W)
C36
1000P/6KV
AK
C34
1000P/6KV
D7
SHV-06
KAKAKA
D2
SHV-06
D3
SHV-06
C33
1000P/3KV
DG
KA
D9
SHV-02
R40
560
T1
0022GC
ZD3
RD30JS
C22
1000P
Q6
A933S
1
3
2
R38
1M
R39
5.1K
+24VP
C14
4700P
R33
62
D1
DSM1D
A
K
DG
ZD1
RD2.4ES
Q5
2SD1264
R32
3.0(1/2W)
1
2
3
DGDGDGDG
123
Q3
C1815
R15
4.7K
C5
1000P
R16
15K
R17
10K
+24VP
DG DG
C37
1000P/1KV
FG
R53
3.9M(1/2W)
RCR50
R41
330K
VR2
RH0165(200K)
1
2
3
DG
HIGH VOLTAGE AREA
FG
11
8
251
6
DG
DG
FG
DG
7
10
12
6
251
6
DG DG
A
K
MG
DG
DG DG
DG
MOTOR DRIVER
TRANSISTOR ARRAY
DG
MG
[3] Printer PWB circuit 1/2
6 – 15
Page 76

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
MG
DG
+24V
DG
VIDEO
SAMP
SYNC
APCSTT
PMCLK
PMD
PE
123456789
CNLSU
00 6216 009 100 808(9PIN)
C38
390P
DG
1a
2a
3a
4a
5a
6a
7a
8a
9a
10a
11a
12a
13a
14a
15a
16a
17a
18a
19a
20a
21a
22a
23a
24a
25a
POUT
1b
2b
3b
4b
5b
6b
7b
8b
9b
10b
11b
12b
13b
14b
15b
16b
17b
18b
19b
20b
21b
22b
23b
24b
25b
PWMSIN
DOP
+24VSMAVIDEO
SYNC
PMCLKPEPUS
HLON
NSTOROBE
DATA2
DATA4
DATA6
DATA8ZCBUSY
SELECT
NAUTOFD
NSELECTON
+5VDG+24V
+24V
MG
PIN
TSEN
MENMBSAMP
APCSTT
PMD
MCON
TC/BIASON
PWRLY
DATA1
DATA3
DATA5
DATA7DGNACK
PERROR
NFAULT
NINIT
+5VDG+24VH
VFM
MG
CNPRT
128A-050S2B-L14N(50PIN)
C47
0.1
C46
47/35
DG
+24V
PWMSIN
+24VS
MEN
MA
MB
MCON
PUS
TC/BIASON
HLON
PWRLY
(1-3I)
(1-1F)
(1-6I)
(1-5I)
(1-5I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
ZC
(1-1F)
+5V
+24VH
+24V
+5V
R27
220
R42
220
13
24
DG
13
24
DG
POUT
PIN
+24VP
R14
20K
R13
3.9K
C4
0.1
DGDG
12345
C43
100P
AK
D10
1SS133
+5V
DG
FG
R60
0
C42
0.1
+5V
TSENDGN.C.
FG
CNTNR
S5B-PH-KS
123
45678
9
1011121332
183514
31
36
C28
100P
C17
100P
C16
100P
C15
100P
C13
100P
DG
+5V
R7
1.2K
R5
R8
1.2K
R6
1.2K
R4
1.2K
C30
0.1
C27
C18
390P
C29
390P
C26
390P
N.M.
N.M.
DG
+5V
DG
C3
390P
R9
1.2K
R10
1.2K
R11
1.2K
R21
1.2K
R22
1.2K
R23
1.2K
R24
1.2K
R25
1.2K
R26
1.2K
NSTOROBE
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8
NACK
BUSY
PERROR
SELECT
NFAULT
PLH
VCC
NAUTOFD
NINIT
NSELECTON
DG
153334
R35
N.M.
SG
FG
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
1617192021222324252627
GND28GND29GND
30
DG
CNPC
57RE-40360-830B(D29B)
123
MG
R3
47K
Q2
2SA854S
+24V
VFMOUT
N.C.
MG
CNFM
B3B-PH-K-R
DG
C
E
B
E
C
B
Q1
DTC114
R2
4.7K
PI1
POUT
PI2
PIN
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
Printer PWB circuit 2/2
6 – 16
Page 77

Printer PWB parts layout
FO-2970MU
6 – 17
Page 78

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
T1
CN1
LIVE
NEUTRAL
CN101
11
D101
D301
C101
C103
D202
IC301
Q101
D110
R101
PC1
VR101
R105R102
R103
C105
R106
C302
R507
(OPTION)
R505
(OPTION)
PC3
(OPTION)
R509
(OPTION)
R508
(OPTION)
Q501
(OPTION)
F101
(OPTION)
10
4
SW101
R132
(OPTION)
R131
(OPTION)
R130
(OPTION)
1
12
3
2
6
5
R17
D6
C11
R10R16
PC1
R9
R12
R11
R13
D5
C10
R8
Q2
C9
D7
R7
R6
D4
R5
R3
R2
Q1
R19
BEA1
C8
C7
C5 C15
R51
(OPTION)
R52
(OPTION)
R53
(OPTION)
R54
(OPTION)
PC3
(OPTION)
D52
(OPTION)
D51
(OPTION)
D11
D13
D10D12
NTC1
7
C3
R1
F1
C1
C2
(OPTION)
PC2
D501
RL1
C22
R23
TRA1
C5
PC2 ZC
R20
R21
3
1
CN2
9
8
R501
R502
R503
R504
+24VS
HLON–
PWRLY–
+24V
+24V
+24VH
+5V
ZC
DG
DG
MG
MG
3
1
Z1
F2
L1
R120
C301
[4] Power supply PWB circuit 1/1
6 – 18
Page 79

2
8
1
C
CN1
C5
C15
C7
C10
R13
R12
R9
R131
R102
R101
J103
J101
IC301
R130
R504
R503
R502
R501
R103
D110
C105
R106
R508
D301
R120
Q101
R105
R507
R509
R132
J104
R505
SW101
C101
D202
D101
J105
PC3
Q501
C103
VR101
1
F101
CN101
C302
C301
R6
D4
R7
R17
R8
R3
T1
C8
R19
BEA1
C9
Q2
Q1
D10
D11
D52
R23
C22
R51
R52
R53
R54
C3
NTC1
Z1
F2
C2
L1
R1
C1
D13
R2
D12
D51
TRA1
R20
R21
CN2
1
J1
RL1
C6
PC2
R11
PC1
D5
D6
D7
C11
R10
R5
R16
1
J102
D501
Power supply PWB parts layout
FO-2970MU
6 – 19
Page 80

FO-2970MU
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFGIHCA
CNPN-18
CNPN-19
CNPN-20
CNPN-21
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
LD0
CNPN-8
LD1
CNPN-9
LD2
CNPN-10
LD3
5
0
6
REDIAL
SPEAKER
START
STOP
RECEPTION
Y0Y1Y2
Y3
Y4Y5Y6Y7Y8
1234567910
ABC
D
151413
12
IC1
LS145
CNPN-7
CNLCD
DG1
2345678
9
1011121314
+5VVORS
R/WEN.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
LD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
CNPN
DG
+5VDG+5V
LD0
RSELD1
LD2
LD3
P-CHK
8
RESOLUTION
05
HOLD/
SEARCH
E-MAIL
COPY
16
DOWN
06
11
17
UP
07
12
18
08
13
19
09
14
20
10
15
VCC
GND
123456789
10
11
#
DG
9
4
7
REDUCTION
CNPN-17
SEN0
2
3
SPEED DIAL
FUNCTION 01 02 03 04 BROADCAST1
Y9
11
+5V
TONER
PC IN USE
TEL LINE
FRTSNS
SEN1
ORGSNS
SEN0
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
B4SNS
121314151617181920
21
22
LD0
LD1
LD2
LD3
RS
R/W
E
VO
CNLCD-11
CNLCD-12
CNLCD-13
CNLCD-14
CNLCD-4
CNLCD-5
CNLCD-6
CNLCD-3
+5V
CNLCD-2
DG
CNLCD-1
C3
N.M.
R3
360
R4
6.2K
DGDGDG
RS
E
+5V
DG
CNPN-5
CNPN-6
CNPN-2,4
CNPN-1DGCNPN-3
C1
33/16
FRSNS
CNPN-15
ORGSNS
CNPN-16
B4SNS
CNPN-22
FR SNS
ORG SNS
N.M.
TONER
CNPN-12
P-CHK
CNPN-11
TEL LINE
CNPN-14
PC IN USE
CNPN-13
+5V
R2R1R6
R5
220
220
220
220
121212
12
LED2 RED
LED1 RED
LED4 GREEN
LED3 GREEN
(TONER)
(P-CHK)
(TEL/FAX)
(PC IN USE)
Q4
DTC114ES
Q3
DTC114ES
Q1
DTC114ES
Q2
DTC114ES
16
8
C2
22000P
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
[5] Operation panel PWB circuit 1/1
6 – 20
Note: Since the parts of this PWB cannot be supplied, change it as a unit.
Page 81

PARTS GUIDE
MODEL FO-2970M
SELECTION CODE DESTINATION
U U.S.A.
CONTENTS
FO-2970MU
1 Cabinet, etc.
2 Operation panel unit
3 Document guide upper unit
4 Drive unit
5 Scanner frame unit
6 Printer frame
7 Upper frame
9 Fusing unit
10 Packing material & Accessories
11 Control PWB unit
12 TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB unit
13 Printer PWB unit
14 Power supply PWB unit
15 Operation panel PWB unit
8 Lower frame
Because parts marked with " " is indispensable for the machine safety maintenance and operation, it must be
replaced with the parts specifi to the product specification.
Index
Page 82

FO-2970MU
[1] Cabinet, etc.
B1
B1
32
B1
34
35
36
8
31
28
B6
14
B4
B4
B1
B4
15
27
33
30
B2
47
45
23
48
13
B7
26
Scanner frame unit
Operation
panel unit
42
B1
21
B1
44
24
46
B1
47
19
43
46
22
B8
5
B1
16
B5
45
B5
29
B1
B1
41
Printer unit
B1
25
B3
B1
B7
10
7
B1
B1
40
20
B3
B3
B1
B3
18
38
12
Document guide
upper unit
B1
2
B4
1
4
39
11
6
B1
37
5
17
3
B1
9
– 1 –
Page 83

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[1] Cabinet,etc.
1 CCNW-270ASC01 AN C Speaker ass’y
2 GDAI-2074XHZZ AK C Handset holder upper
3 GDAI-2075XHZZ AE C Handset holder lower
4 DCEKC182PSCZZ CF N E Control PWB unit
5 DCEKL259CSC01 BG N E TEL/LIU and Hook SW PWB unit
6 MLEVP2332SCZZ AD C Hook switch lever
7 GCABA2350SCZA AU D Upper cabinet
8 GCABB2351SCZA AN C Document guide lower
9 GCABC2352SCZA AW D Bottom cabinet
10 GCABD2353SCYA AM D Inner cabinet
11 GCOVA2418SCZA AL D Back cover
12 LBSHZ2007HCZZ AB C SW spacer
13 HPNLH2398SCZZ AK C Decoration panel
14 LANGA2828SCZZ AD C Stopper bracket,left
15 LANGA2830SCZZ AD C Stopper bracket,right
16 QCNW-285ASCZZ AH C Ground cable B
17 LBNDJ2006SCZZ AA C Band(100mm)
18 TCAUS2034SCZZ AD D Laser caution label
19 PGUMS2169SCZZ AE C FD guide sheet
20 LSTPP0022GCZZ AD C DV protector
21 LANGH2829SCZZ AG C Scanner strengthen plate
22 PGIDM2584SCYA AD C Feed guide
23 LPLTP3089SCZA AD C Shading plate
24 PSHEZ3534SCZZ AC C SF insulation sheet M
25 LANGR2833SCZZ AC C Earth bracket
26 MSPRC3161SCZZ AC C Stopper spring
27 MSPRC3165SCZZ AC C Clutch spring
28 MSPRC3166SCZZ AB C Hopper spring
29 QCNW-342ASCZZ AC C Ground cable C
30 NGERH2363AXZZ AC C Paper feed gear
31 NGERP2318XHZZ AD C Pinion gear
32 NROLR2333XHZZ AP C Paper feed roller
33 NSFTZ2321SCZZ AE C Paper feed roller shaft
34 PCOVP2127SCZA AK D ROM cover
35 PGIDM2585SCZA AF C Hopper guide,left
36 PGIDM2586SCZA AF C Hopper guide,right
37 PSHEZ3508SCZZ AE C Jack sheet
38 PSHEZ3522SCZZ AD C Reset sheet
39 PSLDM2063SCZZ AF C Shield plate
40 PSHEZ3531SCZZ AD C Shading sheet
41 QCNW-343ASCZZ AC C Ground cable D
42 MSPRC3177SCZZ AA C CIS earth spring
43 PSHEZ3529SCZZ AE C SF insulation sheet L
44 PSHEZ3530SCZZ AD C SF insulation sheet R
45 MSPRP3054XHFJ AD C Panel lock spring
46 NROLP2332XHZZ AD C Paper out pinch roller
47 MSPRC3154SCZZ AB C Paper out pinch spring
48 RCORF2125XHZZ AE B Core
!
B1 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
B2 XEBSD30P30000 AA C Screw(3x30)
B3 XEBSE30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B4 XEBSF30P12000 AA C Screw(3x12)
B5 XHBSE30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6)
B6 LX-BZ2138XHZZ AB C Screw(2x6)
B7 LX-BZ2205SCZZ AB C Screw(3x8)
B8 LX-BZ1006LC03 AA C Screw
DESCRIPTION
– 2 –
Page 84

FO-2970MU
[2] Operation panel unit
3
901
6
8
9
2
5
7
4
10
1
B1
[3] Document guide upper unit
B2
B2
B1
B1
7
B2
14
14
10
16
10
15
12
12
B1
11
B1
13
4
6
6
2
9
19
11
5
17
3
8
21
– 3 –
11
8
21
1
18
1
20
Page 85

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[2] Operation panel unit
1 DCEKP223CSC01 BF E Operation panel PWB unit(without sensor)
2 GCASP2121SCZG AQ N D Panel case
3 JBTN-2282SCZA AE C 10 key
4 JBTN-2283SCZA AE C Direct key
5 JBTN-2284SCZZ AC C Start key
6 JBTN-2285SCZA AC C Copy,reduction key
7 JBTN-2286SCZA AC C Stop key
8 JBTN-2287SCZZ AC C E-mail key
9 JBTN-2288SCZA AK C Function key
10 QCNW-268ASCZZ AN C Panel cable
11 QSW-Z2262AXZZ AE C FR sensor switch
12 QSW-M2294XHZZ AE C ORG sensor switch
B1 XUBSD20P06000 AA C Screw(2x6)
901 CCASP2121SC08 BH N E Operation panel unit
(Unit)
DESCRIPTION
[3] Document guide upper unit
1 LANGF2827SCZZ AD C Back bracket
2 LPLTG2707XHZZ AE C Separation rubber plate
3 LPLTM3090SCZZ AG C Document paper guide plate
4 LPLTP2790XHZZ AD C Separate plate
5 QCNW-285ASCZZ AH C Ground cable B
6 MARMP2025SCZZ AC C FD arm
7 MLEVP2331SCZA AC C Release lever
8 MSPRC3153SCZZ AA C Back spring 2
9 MSPRC3163SCZZ AB C LC-RT spring
10 MSPRC3164SCZZ AB C Pinch roller spring
11 MSPRP3152SCZZ AE C Back spring 1
12 MSPRT3162SCZZ AB C Separate spring
13 MSPRT3168SCZZ AC C Feed spring
14 NROLP2334XHZA AC C Pinch roller
15 NSFTZ2322SCZZ AC C Pinch roller shaft 1
16 NSFTZ2323SCZZ AC C Pinch roller shaft 2
17 PBRS-2050SCZZ AH C Paper brush
18 PGIDM2583SCZZ AK C Back guide
19 PGIDP2582SCZZ AP C Document guide upper
20 PSHEZ3497SCZZ AE C Back sheet
21 PSHEZ3591SCZZ AG N C Rear plate earth sheet
B1 XHBSD30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6)
B2 LX-BZ2205SCZZ AB C Screw(3x8)
– 4 –
Page 86

FO-2970MU
[4] Drive unit
B1
[5] Scanner frame unit
B1
8
9
7
2
5
1
6
4
3
10
8
13
4
1
12
6
7
10
11
B1
14
B1
2
11
Drive unit
3
9
5
– 5 –
Page 87

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[4] Drive unit
1 LPLTM3091SCZZ AD C Radiator plate
2 LPLTP3094SCZZ AG C Drive frame
3 NGERH2277XHZZ AC C Reduction gear B
4 NGERH2279XHZZ AC C Idler gear
5 NGERH2380XHZZ AC C Reduction gear(17/36Z)
6 NGERH2395AXZZ AD C Gear,White(15/23Z)
7 PSHEZ3528SCZZ AC C Motor sheet
8 RMOTZ2150SCZZ AU B Transfer motor
9 QCNW-342ASCZZ AC C Ground cable C
B1 XEBSE30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
DESCRIPTION
[5] Scanner frame unit
1 QCNW-269ASCZZ AG C CIS cable
2 LBSHP2121SCZZ AB C Transfer roller bearing
3 LFRM-2213SCZC AQ C Scanner frame
4 LHLDZ2180XHZZ AC C CIS holder,left
5 LHLDZ2181XHZZ AC C CIS holder,right
6 RUNTZ2057SCZZ BE E CIS(Contact image sensor)unit
7 NROLR2435SCZZ AL C Transfer roller 1
8 NROLR2436SCZZ AK C Transfer roller 2
9 PSHEZ3540SCZZ AC C CIS earth sheet
10 NBRGP2141XHZZ AH C Transfer bearing
11 NGERH2275XHZZ AC C Transfer gear
12 RCORF2124XHZZ AE B Core
!
13 PSHEZ3498SCZZ AD C CIS sheet
14 MSPRC3234SCZZ AC N C Roller earth spring
B1 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
– 6 –
Page 88

FO-2970MU
[6] Printer frame
B1
B2
34
23
36
33
B2
24
Upper frame
10
B2
12
9
11
15
21
28
8
10
3
37
A
B4
5
B2
18
7
22
19
B4
26
B2
13
14
B3
1
Fusing unit
30
B2
B6
B6
B6
B2
1
B6
25
B4
Lower frame
20
4
17
6
16
2
B3
B3
31
B6
B1
B6
A
37
29
B5
B6
35
32
27
27
– 7 –
Page 89

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[6] Printer frame
1 JKNBZ0004GCZZ AC C Fusing knob
2 LPLTM0159GCZ1 AD C Gear plate
3 LPLTM0282GCZ2 AD C Heat sink plate
4 MLEVP0037GCZZ AB C Fusing clutch lever
5 MLEVP0093GCZZ AD C Tray lock lever
6 MSPRC0135GCAZ AB C Fusing clutch spring
7 MSPRC3151SCZZ AA C SW lever spring
8 MSPRT0307GCZZ AA C Lock lever spring
9 NBLTH0008GCA1 AC C Fan belt
10 NBRGP0106GCZZ AF C Fusing bearing
11 NBRGP0108GCZZ AD C Fan bearing
12 NFANP0005GCZZ AE C Cooling fan
13 NGERH0071GCZZ AC C Motor idle gear
14 NGERH0072GCZ1 AD C Drum idle gear
15 NGERH0076GCZZ AC C Developer drive gear B
16 NGERH0077GCZZ AC C Fusing clutch gear A
17 NGERH0078GCZZ AC C Fusing clutch gear B
18 NGERH0094GCZZ AC C PU idle gear A
19 NGERH0096GCZZ AC C PU idle gear C
20 NGERH0171GCZ1 AE C Fusing idle gear
21 NGERH0172GCZZ AH C Developer drive gear A
22 NGERH0173GCZZ AD C PU idle gear B2
23 PCUSG2136SCZZ AD C Speaker cushion
24 NROLP0109GCZZ AY C Fusing roller
25 NROLP2442SCZZ AF C Paper exit roller upper A
26 PCOVP0086GCZZ AD C Fusing gear cover
27 GLEGG2075SCZZ AK C Gum leg
28 PRNGP0088FCZZ AB C G ring
29 DCEK-224CSC01 BG E Printer PWB unit
30 RDENT2148SCZZ BH E Power supply PWB unit
!
31 QACCD2027XHZZ AR C AC cord
!
32 LPLTM3083SCZZ AP C Bottom plate
33 MSPRP3150SCZZ AD C Speaker spring
34 NROLP2443SCZZ AF C Paper exit roller upper B
35 RMOTZ2153SCZZ AU B Fan motor
36 MLEVP2330SCZZ AE C Interlock sw lever
37 QCNW-387ASCZZ AD C Ground cable D2
B1 XBPSN40P06K00 AA C Screw(4x6)
B2 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
B3 XEPSD30P08X00 AA C Screw(3x8)
B4 XHBSE30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B5 LX-BZ2252SCZZ AB C Screw
B6 XHBSE30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6)
DESCRIPTION
– 8 –
Page 90

FO-2970MU
[7] Upper frame
B1
23
10
21
12
8
6
23
20
16
11
9
7
1
4
B2
3
19
13
3
2
B2
15
W1
W2
B3
W3
5
22
18
14
17
– 9 –
Page 91

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[7] Upper frame
1 DHAI-0139GCZZ AF C MM harness
2 LBOSZ0058GCZ1 AE C Paper feed roller boss
3 LFIX-0003GCZZ AC C DV fixer
4 LPLTM0273GCZZ AF C MM heat sink
5 PMLT-0124GCZZ AB C FFC protect molt
6 RCORF7013XCZZ AH B Core
!
7 RMOTN0039GCZZ AZ B Main motor
8 RPLU-0004GCZZ AN C Paper feed solenoid
9 MLEVP0046GCZZ AE C Sleeve release lever
10 MLEVP0088GCZZ AC C PE lever
11 MSPRC0149GCAZ AA C DV press spring
12 MSPRC0159GCAZ AB C Lever release spring
13 MSPRC0319GCZZ AB C DV spring
14 MSPRT0137GCAZ AC C Clutch spring
15 NGERH0080GCZ1 AE C Paper feed clutch gear
16 NROLP0112GCZZ AR C Paper feed roller
17 PPIPP0003GCZ1 AC C Clutch sleeve
18 PPIPP0006GCZ2 AC C Clutch R sleeve
19 PSHEP0166GCZZ AC C Shading sheet C
20 PSHEP0320GCZ1 AF C Shading sheet 1
21 PSHEZ0335GCZZ AD C Shading sheet 2
22 PSPAZ0049GCZZ AC C Spacer
23 CFRM-2214SC51 BZ E Optical unit
B1 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B2 XHBSD30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6)
B3 LX-BZ0187FCZ1 AA C Screw(3x8)(Red,Left type)
W1 LX-WZ0017GCZZ AC C Washer
W2 LX-WZ0018GCZZ AC C Washer
W3 LX-WZ0019GCZZ AC C Washer
DESCRIPTION
– 10 –
Page 92

FO-2970MU
[8] Lower frame
25
27
14
24
W3
22
29
5
26
14
18
16
21
B2
1
17
8
3
30
17
32
1
30
7
22
W3
11
W1
B3
31
12
15
B1
4
W2
20
B1
2
W2
6
B1
9
10
23
19
– 11 –
13
28
Page 93

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[8] Lower frame
1 CPLTP0274PS51 AL C Separate plate ass’y
2 DUNTK0152PSZZ AE C DV bias
3 LFRM-0045GCZ1 AY C Lower frame
4 LPLTM0163GCZZ AE C Separation electrode
5 LPLTM0275GCZ1 AK C Lift plate
6 QSLP-0028GCZZ AE C Earth terminal
7 MLEVP0038GCZZ AC C DR lock lever R
8 MLEVP0039GCZZ AC C DR lock lever L
9 MLEVP0040GCZZ AC C PIN actuator
10 MLEVP0089GCZZ AC C POUT actuator
11 MLEVP0090GCBZ AE C Tray release lever
12 MLEVP0091GCZZ AC C SB release lever
13 MSPRC0133GCA1 AB C High voltage terminal DR-MC spring
14 MSPRC0155GCA2 AB C Pressure spring
15 QSLP-0032GCZZ AD C DV bias electrode
16 MSPRC0305GCZ2 AD C Tray spring
17 MSPRC0306GCZZ AA C Separate spring
18 MSPRC0309GCZZ AB C Fusing spring L
19 MSPRC0312GCZZ AB C Fusing guide spring
20 MSPRC0313GCZZ AB C DV bias spring
21 MSPRC0314GCZZ AB C Fusing spring R
22 MSPRP0158GCAZ AB C DR lock spring
23 MSPRP0304GCZZ AC C High voltage terminal TC
24 NBRGP0104GCZZ AC C Transfer bearing R
25 NBRGP0105GCZZ AC C Transfer bearing L
26 NGERH0169GCZZ AC C Transfer gear
27 NROLP7046XCZZ AX C Transfer roller
28 PCOVP0038GCAZ AA C Cover
29 PGIDM0078GCZZ AM C Fusing guide
30 PMLT-0120GCZZ AC C Dumper 1
31 XPLUW20-14000 AC C Pin
32 PSHEZ0190GCZZ AC C TR sheet
B1 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B2 XEBSD30P18000 AA C Screw(3x18)
B3 XEBSD30P30000 AA C Screw(3x30)
W1 XWHSD30-05080 AA C Washer
W2 XWSSD30-07000 AA C Washer
W3 LX-WZ0044FCZZ AA C Washer(CS-3)
DESCRIPTION
– 12 –
Page 94

FO-2970MU
[9] Fusing unit
18
11
B2
17
2
901
4
15
7
12
10
B1
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[9] Fusing unit
1 CHLDZ0040PS73 AR E Temperature fuse holder
2 QSLP-0030GCZZ AD C Fusing AC terminal C
3 RDTCT0014GCZZ AP B Thermistor
4 MSPRT0308GCZZ AA C Fusing separate spring
5 RLMPU0021GCZZ AX B Heater lamp
6 NBRGC0035GCZ1 AE C Fusing bearing R
7 NBRGP0082GCZZ AB C Fusing bearing L
8 NGERH0083GCZZ AC C Fusing gear(27T)
9 NGERH0174GCZZ AD C Paper out idler gear
10 NROLM0108GCZ1 AV C Heat roller
11 TCAUH0992FCZZ AE D Caution label
12 PBARM0001GCA1 AD C Fusing bar
13 PCOVP0091GCZZ AW C Fusing cover
14 PSHEP0161GCZ2 AC C Fuse sheet
15 PTME-0022GCZZ AF C Separate nail
16 QFS-T0005GCZZ AQ A Temperature fuse
!
17 QSLP-0029GCZZ AD C Fusing terminal
18 XNGSN30-18000 AC C Nut(M3)
B1 XBPSN30P05K00 AA C Screw(3x5)
B2 XBPSN30P06KS0 AA C Screw(3x6)
B3 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B4 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
B5 XEPSD30P06X00 AA C Screw(3x6)
B6 LX-BZ0030GCZZ AB C Screw
B7 LX-BZ3004SC0B AA C Screw
W1 XWVUW30-04000 AA C Washer
901 DUNTW221CSC01 BL E Fusing unit
(Unit)
14
15
18
13
9
4
B5
18
B7
W1
B6
6
16
3
1
B4
5
B3
8
B1
DESCRIPTION
– 13 –
Page 95

[10] Packing material & Accessories
FO-2970MU
6
10
14
7
18
15
8
9
1
2
16
4
AC Cord
17
5
19
3
11
12
13
Front
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[10] Packing material & Accessories
1 CPLTP3084SC02 AF N C Original document support ass’y
2 CPLTP3088SC02 AH C Received document tray ass’y
3 DUNTK369BSCOG AR E Handset unit
4 CPLTP3085SC02 AT C Paper tray ass’y
5 DUNT-205CSCZA BL S Toner cartridge(Initial starter cartridge)
6 TLABM311BSCZA AE D Rapid key labels
7 UDSKA2024SCZA AK E Sharp laser multifunction CD-ROM
8 QCNW-289ASCOG AG C Handset cord
!
9 QCNW-290ASCZZ AE C Telephone line cord
!
10 SPAKA315BSCZZ AK D Add.,left
11 SPAKA316BSCZZ AK D Add.,right
12 SPAKA317BSCZZ AE D Add.
13 SPAKC229CSCCZ AS N D Packing case
14 SPAKP355BSCZZ AE D Body cover
15 SSAKA2340QCZZ AA D Bag,operation manual
16 SSAKA3001CCZZ AA D Bag(140x360mm)
17 TCAUZ2035SCZZ AC D Caution sheet
18 TINSE4147SCCZ AZ N D Operation manual
19 SPAKA266CSCZZ AC D DV-pad
DESCRIPTION
– 14 –
Page 96

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[11] Control PWB unit
1 UBATL2049SCZZ AF B Battery(CR2032T23) [BAT]
2 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR1]
3 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR2]
4 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR3]
5 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR4]
6 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR5]
7 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR6]
8 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR7]
9 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR8]
10 RR-TZ3012SCJ0 AB C Resistor array(100Ωx4) [BR9]
11 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR11]
12 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR12]
13 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR13]
14 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR14]
15 RR-TZ3012SC10 AB C Resistor array(10Ωx4) [BR15]
16 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Resistor array(270Ωx4) [BR16]
17 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Resistor array(470Ωx4) [BR17]
18 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR18]
19 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR19]
20 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR21]
21 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR22]
22 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR23]
23 RR-TZ3016SCZZ AA C Resistor array(33Ωx4) [BR24]
24 RR-TZ3012SCJ0 AB C Resistor array(100Ωx4) [BR25]
25 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Resistor array(470Ωx4) [BR26]
26 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR27]
27 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR28]
28 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR29]
29 RR-DZ1115AFZZ AC C Resistor array(10KΩx4) [BR30]
30 VCEAJA1HW475M AB C Capacitor(50WV 4.7µF) [C1]
31 VCEAJA1HW106M AB C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C7]
32 VCEAGA1CW476M AB C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C8]
33 VCEAGA1CW476M AB C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C9]
34 VCEAGA1CW476M AB C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C10]
35 VCEAGA1HW105M AB C Capacitor(50WV 1µF) [C12]
36 VCEAGA1HW475M AA C Capacitor(50WV 4.7µF) [C13]
37 VCEAGA1CW476M AB C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C15]
38 VCEAGA1HW107M AA C Capacitor(50WV 100µF) [C16]
39 VCEAEA1CW476M AA C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C18]
40 VCEAEA1CW476M AA C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C20]
41 VCEAEA1CW336M AB C Capacitor(16WV 33µF) [C21]
42 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C22]
43 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C24]
44 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C25]
45 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C26]
46 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C27]
47 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C34]
48 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C35]
49 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C36]
50 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C37]
51 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C38]
52 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C39]
53 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C40]
54 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C41]
55 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C42]
56 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C43]
57 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C44]
58 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C45]
59 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C46]
60 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C47]
61 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C48]
62 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C49]
63 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C50]
64 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C51]
65 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C52]
66 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C53]
67 VCEAJA1HW226M AC N C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C57]
68 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C58]
69 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C59]
70 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C60]
71 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C61]
72 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C64]
73 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C100]
74 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C104]
75 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C107]
76 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C108]
77 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C110]
78 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C111]
79 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C112]
80 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C113]
– 15 –
Page 97

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[11] Control PWB unit
81 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C114]
82 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C115]
83 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C116]
84 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C117]
85 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C118]
86 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C120]
87 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C121]
88 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C123]
89 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C124]
90 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C125]
91 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C126]
92 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C127]
93 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C129]
94 VCCCCY1HH471J AA C Capacitor(50WV 470PF) [C130]
95 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C131]
96 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C133]
97 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C142]
98 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C143]
99 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C144]
100 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C145]
101 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C146]
102 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C147]
103 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C148]
104 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C149]
105 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C150]
106 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C152]
107 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C153]
108 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C155]
109 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C156]
110 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C157]
111 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C160]
112 VCCCCY1HH270J AA C Capacitor(50WV 27PF) [C162]
113 VCCCCY1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C163]
114 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C165]
115 VCCCCY1HH331J AB C Capacitor(50WV 330PF) [C166]
116 VCCCCY1HH331J AB C Capacitor(50WV 330PF) [C172]
117 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C173]
118 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C175]
119 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C179]
120 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C180]
121 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C181]
122 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C182]
123 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C183]
124 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C185]
125 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C186]
126 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C187]
127 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C188]
128 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C189]
129 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C190]
130 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C191]
131 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C192]
132 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C193]
133 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C194]
134 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C195]
135 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C196]
136 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C197]
137 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C199]
138 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C204]
139 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C208]
140 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C209]
141 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C210]
142 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C211]
143 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C212]
144 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C213]
145 VCCCCY1HH300J AB C Capacitor(50WV 30PF) [C214]
146 VCCCCY1HH300J AB C Capacitor(50WV 30PF) [C215]
147 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C217]
148 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C221]
149 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C222]
150 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C224]
151 VCCCCY1HH471J AA C Capacitor(50WV 470PF) [C226]
152 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C228]
153 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C229]
154 VCCCCY1HH331J AB C Capacitor(50WV 330PF) [C230]
155 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C231]
156 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C236]
157 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C237]
158 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C238]
159 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C241]
160 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C242]
– 16 –
Page 98

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[11] Control PWB unit
161 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C243]
162 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C244]
163 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C247]
164 VCCCCY1HH470J AA C Capacitor(50WV 47PF) [C249]
165 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C250]
166 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C253]
167 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C254]
168 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C256]
169 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C259]
170 VCCCCY1HH100J AA C Capacitor(50WV 10PF) [C260]
171 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C261]
172 VCCCCY1HH150J AB C Capacitor(50WV 15PF) [C262]
173 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C263]
174 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C264]
175 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C266]
176 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C267]
177 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C268]
178 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C273]
179 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C274]
180 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C275]
181 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C276]
182 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C277]
183 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C278]
184 VCCCCY1HH470J AA C Capacitor(50WV 47PF) [C279]
185 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C281]
186 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C285]
187 VCCCCY1HH471J AA C Capacitor(50WV 470PF) [C286]
188 VCCCCY1HH470J AA C Capacitor(50WV 47PF) [C287]
189 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C289]
190 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C290]
191 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C291]
192 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C293]
193 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C298]
194 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C299]
195 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C300]
196 VCCCCY1HH470J AA C Capacitor(50WV 47PF) [C301]
197 VCCCCY1HH681J AA C Capacitor(50WV 680PF) [C304]
198 VCCCCY1HH100J AA C Capacitor(50WV 10PF) [C305]
199 VCCCCY1HH100J AA C Capacitor(50WV 10PF) [C306]
200 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C307]
201 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C308]
202 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C317]
203 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C318]
204 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C319]
205 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C320]
206 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C322]
207 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C325]
208 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C326]
209 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C329]
210 VCCCCY1HH560J AA C Capacitor(50WV 56PF) [C332]
211 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C347]
212 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C349]
213 VCCCCY1HH150J AB C Capacitor(50WV 15PF) [C351]
214 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C352]
215 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C357]
216 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C358]
217 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C359]
218 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C361]
219 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C365]
220 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C366]
221 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C371]
222 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C376]
223 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C379]
224 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C380]
225 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C381]
226 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C382]
227 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C386]
228 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C388]
229 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C389]
230 VCCCCY1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C390]
231 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C391]
232 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C394]
233 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C395]
234 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C396]
235 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C400]
236 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C405]
237 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C407]
238 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C408]
239 VCKYCY1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C409]
240 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C410]
– 17 –
Page 99

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[11] Control PWB unit
241 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C411]
242 RC-KZ0001RCZZ AD C Ceramic capacitor array(100PFx4) [CA1]
243 RC-KZ0001RCZZ AD C Ceramic capacitor array(100PFx4) [CA2]
244 RC-KZ0001RCZZ AD C Ceramic capacitor array(100PFx4) [CA3]
245 RC-KZ0001RCZZ AD C Ceramic capacitor array(100PFx4) [CA4]
246 QCNCM7014SC0G AB C Connector(7pin) [CNCIS]
247 QCNCM7014SC0C AA C Connector(3pin) [CNFUSE]
248 QCNCW2500SC1B AF C Connector(12pin) [CNLIUA]
249 QCNCM7014SC0F AB C Connector(6pin) [CNMT]
250 QCNCM2482SC2B AE C Connector(22pin) [CNPN]
251 QCNCM2436SC5J AB C Connector(50pin) [CNPRT]
252 QCNCM7014SC0B AD C Connector(2pin) [CNRTH]
253 QCNCM2401SC0B AA C Connector(2pin) [CNSP]
254 VHDDAP202U/-1 AB B Diode(DAP202U) [D1]
255 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D100]
256 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D101]
257 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D102]
258 VHDHRW0502A-1 AD B Diode(HRW0502ATR) [D103]
259 VHDDA204K//-1 AC B Diode(DA204K) [D105]
260 VHDDA204K//-1 AC B Diode(DA204K) [D107]
261 QFS-P2010SCZZ AD B IC protector(KAB2402) [F100]
262 VHINJM2902M-1 AF B IC,OPERATIONAL AMP.(NJM2902M) [IC1]
263 VHIBU4066BCF1 AD B IC,ANALOG SW(BU4066) [IC2]
264 VHILC82103/-1 BA B IC,IMAGE SIGNAL PROCESSOR(LC82103) [IC4]
265 VHISH7041/28A BE B IC,32bit RISC MICROPROCESSOR(SH7041) [IC5]
266 VHIULN2003AN/ AE B IC,DRIVER(ULN2003A) [IC6]
267 VHIHCF4053M1T AG B IC,ANALOG SW(HCF4053) [IC7]
268 VHIFM336///-1 BN N B IC,33600bps FAX MODEM(FM336) [IC8]
269 VHINJM2113M-1 AG B IC,SPEAKER AMP(NJM2113) [IC9]
270 VHI1M16E//J-6 AZ B IC,1Mx16bit DRAM(HY5118164CJC-6) [IC11]
271 VHI1M16E//J-6 AZ B IC,1Mx16bit DRAM(HY5118164CJC-6) [IC13]
272 QSOCZ2067SC42 AE C IC socket(42pin) [IC14]
273 VHI27080FBF0A BQ N B IC,EPROM(8Mbit) [IC14]
274 VHILR38784/-1 BD B IC,GATE ARRAY(LR38784A) [IC15]
275 VHISM8578BV-1 AK B IC,REAL TIME CLOCK(SM8578BV) [IC16]
276 RH-IX2129SCZZ AY B IC,512Kx8bit DRAM(HM514800-70J) [IC17]
277 VHI74HCU04S-1 AF B IC,INVERTER(74HCU04) [IC18]
278 VHIPST596CMT1 AF B IC,SYSTEM RESET(PST596) [IC20]
279 RH-IX2164XHZZ AY N B IC,1Mbit SRAM(BS62LV1024) [IC21]
280 VHI1M16E//J-6 AZ B IC,1Mx16bit DRAM(HY5118164CJC-6) [IC22]
281 RCILZ0006GCZZ AC C Coil [L100]
282 VRS-CY1JB100J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10Ω ±5%) [L101]
283 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [L102]
284 VS2SC4081R/-1 AB B Transistor(2SC4081R) [Q1]
285 VS2SA1037KS-1 AB B Transistor(2SA1037) [Q100]
286 VS2SA1037KS-1 AB B Transistor(2SA1037) [Q101]
287 VS2SA1036KR-1 AC B Transistor(2SA1036) [Q102]
288 VSDTC114EK/-1 AB B Transistor(DTC114EK) [Q103]
289 VSDTC114EK/-1 AB B Transistor(DTC114EK) [Q104]
290 VS2SC2412KR-1 AD B Transistor(2SC2412KR) [Q105]
291 VRD-HT2EY100J AA C Resistor(1/4W 10Ω ±5%) [R1]
292 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R2]
293 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R3]
294 VRS-CY1JB152J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.5KΩ ±5%) [R100]
295 VRS-CY1JB473J AA C Resistor(1/10W 47KΩ ±5%) [R101]
296 VRS-CY1JB222J AA C Resistor(1/10W 2.2KΩ ±5%) [R116]
297 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R117]
298 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R119]
299 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R120]
300 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R121]
301 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R122]
302 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R123]
303 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R124]
304 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R125]
305 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R126]
306 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R127]
307 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R128]
308 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R129]
309 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R130]
310 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R131]
311 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R132]
312 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R133]
313 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R134]
314 VRS-CY1JB623J AA C Resistor(1/10W 62KΩ ±5%) [R137]
315 VRS-CY1JB152J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.5KΩ ±5%) [R138]
316 VRS-CY1JB124J AA C Resistor(1/10W 120KΩ ±5%) [R148]
317 VRS-CY1JB333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R149]
318 VRS-CY1JB105J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1MΩ ±5%) [R150]
319 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R160]
320 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R161]
– 18 –
Page 100

FO-2970MU
NO.
PAR TS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[11] Control PWB unit
321 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R162]
322 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R163]
323 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R164]
324 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R165]
325 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R166]
326 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R168]
327 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R169]
328 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R170]
329 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R171]
330 VRS-CY1JB472J AA C Resistor(1/10W 4.7KΩ ±5%) [R172]
331 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R173]
332 VRS-CY1JB332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R174]
333 VRS-CY1JB332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R175]
334 VRS-CY1JB302J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3KΩ ±5%) [R176]
335 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R177]
336 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R178]
337 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R179]
338 VRSCY1JD4422F AA N C Resistor(1/10W 44.2KΩ ±1%) [R180]
339 VRS-CY1JB623J AA C Resistor(1/10W 62KΩ ±5%) [R182]
340 VRS-CY1JB273J AA C Resistor(1/10W 27KΩ ±5%) [R183]
341 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R190]
342 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R191]
343 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R193]
344 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R194]
345 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R198]
346 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R199]
347 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R200]
348 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R201]
349 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R202]
350 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R203]
351 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R204]
352 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R205]
353 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R206]
354 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R208]
355 VRS-CY1JB394J AA C Resistor(1/10W 390KΩ ±5%) [R212]
356 VRS-CY1JB302J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3KΩ ±5%) [R213]
357 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R215]
358 VRS-CY1JB203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R217]
359 VRS-CY1JB113J AA C Resistor(1/10W 11KΩ ±5%) [R218]
360 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R223]
361 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R224]
362 VRS-CY1JB105J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1MΩ ±5%) [R225]
363 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R226]
364 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R227]
365 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R229]
366 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R230]
367 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R231]
368 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R232]
369 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R233]
370 VRS-CY1JB330J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33Ω ±5%) [R234]
371 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R235]
372 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R236]
373 VRS-CY1JB201J AA C Resistor(1/10W 200Ω ±5%) [R238]
374 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R239]
375 VRS-CY1JB302J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3KΩ ±5%) [R240]
376 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R241]
377 VRS-CY1JB472J AA C Resistor(1/10W 4.7KΩ ±5%) [R242]
378 VRS-CY1JB154J AA C Resistor(1/10W 150KΩ ±5%) [R244]
379 VRS-CY1JB104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R245]
380 VRS-CY1JB203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R246]
381 VRS-CY1JB202J AA C Resistor(1/10W 2KΩ ±5%) [R247]
382 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R250]
383 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R251]
384 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R252]
385 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R253]
386 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R254]
387 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R255]
388 VRS-CY1JB680J AA C Resistor(1/10W 68Ω ±5%) [R256]
389 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R257]
390 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R258]
391 VRS-CY1JB105J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1MΩ ±5%) [R259]
392 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R260]
393 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R261]
394 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R262]
395 VRS-CY1JB302J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3KΩ ±5%) [R263]
396 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R264]
397 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R265]
398 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R266]
399 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R267]
400 VRS-CY1JB201J AA C Resistor(1/10W 200Ω ±5%) [R268]
– 19 –
 Loading...
Loading...