Page 1
Triguard SC300E
MDO16FNS
16-Channel Digital Output Module
120Vac/dc
(MDO16FNS
Issue 4
INTRODUCTION
PURPOSE
The 120Vac/dc Digital Output Module MDO16FNS provides the output control interface
between the SC300E processing environment and up to 16 high-voltage field items. All field
outputs from the module are galvanically isolated from the system.
October 2005
)
Circuit triplication and voting procedures make the module single-fault tolerant and latent
testing ensures that the failure of a normally ‘ON’ (energised) or ‘OFF’ channel will be
recognised and reported to the system. Front panel indicators show the state of all channels,
the circuit ‘on-line’ status and the health of the module.
The module, which is compatible with ‘dual slot hot repair’, can be fitted in any of the ten I
slots in the SC300E chassis. ‘wrong slotting’ is prevented by physical coding. The SC300E
MPP software software identifies the module via a built-in hardware identifier.
Channel outputs leave the module via the DIN 41612 ‘rear plug-up’ system on the ch
backplane.
The MDO16FNS has relatively high power dissipation which may place some constraints upon
its use.
This document is intended to provide a general understanding of the function of the module
sufficient to enable basic maintenance operations to be effected in the field.
ASSOCIATED DOCUMENTATION
/O
assis
Reference No
008-5097
008-5128
Title
Chassis User Manual
TDO16AIB 16 Termination Card User Manual DIN to Screw
008-5148
Channel Digital Output
Page 2

2
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
Terminals, Internally Powered, High Voltage
User Manual
Mechanical
block (Upper)
coding
Connector J1
Common
Module
Connector J2
Interface
(CI)
Fig
ure 1-1 General view and front panel detail
Connector J3
Protective
Mechanical
block (Lower)
Cover
coding
Page 3

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
3
Triguard
SPECIFICATION
Model
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
MDO16FNS
Channels
Architecture
Indicators:
Outp ut d river FET
Voltage range
Voltage drop
Maximum d
Surge limiting
Isolation
Module power consumption excluding field
power dissipation in module
Module power consumption including field
power dissipation in module
Overall size (mm)
Overall size (inches)
Input
Modules
rive
16
TMR
One per point
Health, 3 x On Line
99 to 132Vac/dc
Less than 4V
Resistive load: 0.50A per channel
Tungsten load: 0.125A per channel
3A peak
1kVdc field to system, commoned supply
12mA (24mA if dual slot hot repair)
4W
2W @ minimum load
36W @ maximum load
400(9U)H x 397L x 28W
15.75H x 15.63L x 1.1W
Weight
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIF
The maximum ambient temperature measured at the hottest point within the Triguard system
shall
Temperature operating:
Temperature
Humidity
EMC/RFI Immunity
Vibration/Shock
Certification:
General Certification: Ref. SC300E TMR Product Guide (ref 008-5209).
ICATIONS
not be greater than 60 degrees centigrade.
storage:
+5°C to +60°C
-
25°C to +70°C
5% to 95% non-condensing at ambient <40°C
Tested and certified to IEC 1131-Part 2 1994
Tested and certified to IEC 1131-Part 2 1994
2.1kg
Page 4

4
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
TRANSPORT AND HANDLING
The MDO16FNS must be transported and stored in its original packing material which should
be retained for this purpose.
Page 5
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
5
Triguard
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTIO
N
PHYSICAL
The MDO16FNS is a 9U high PCB with integral front panel and rear connectors. A plug-in
daughterboard carries the common interface circuits. The board faces are protected by
detachable
the location of the connectors, covers and front panel details.
covers (see Section 3.1, Scope). Figure 1-1 shows the general layout, including
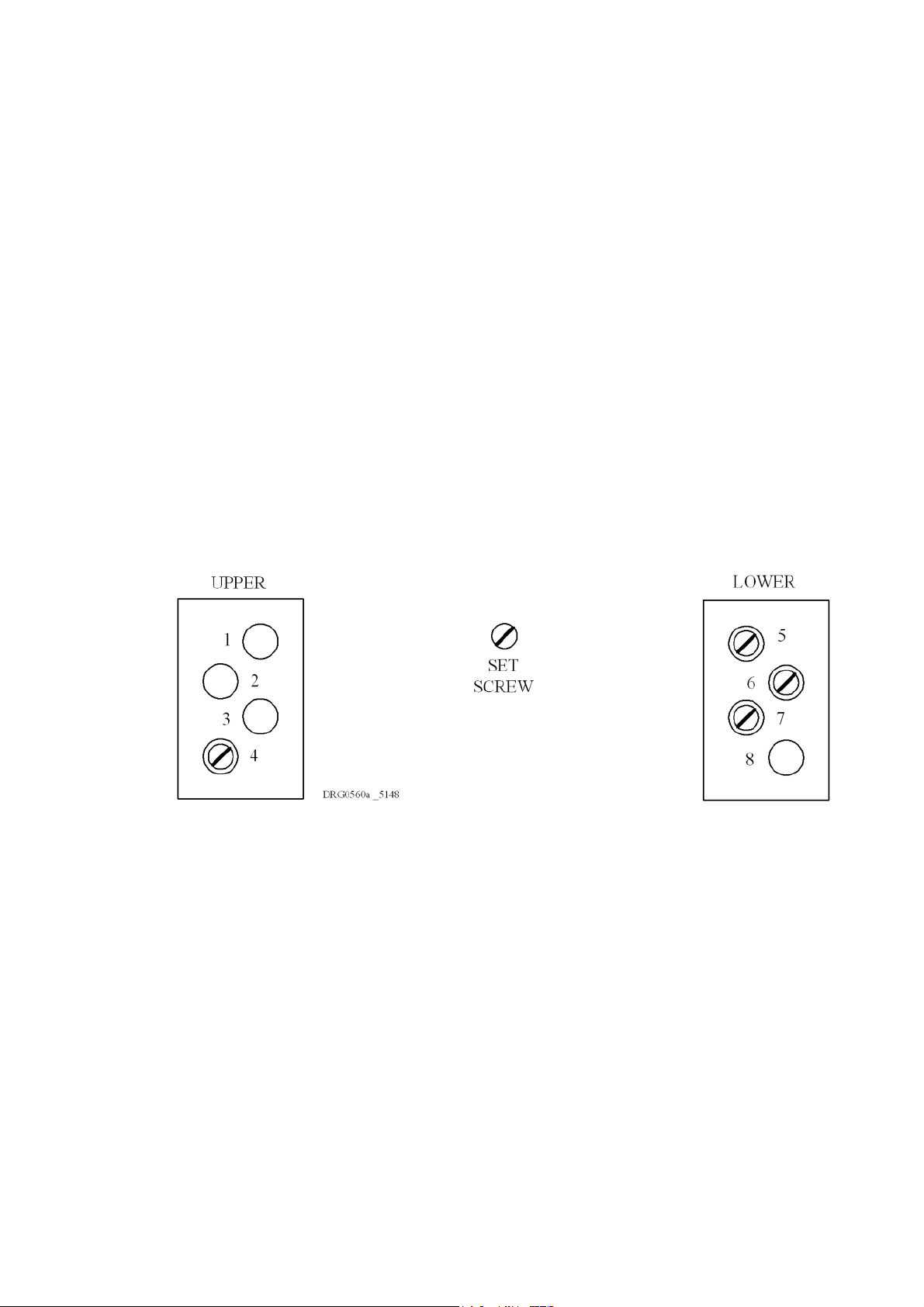
Mechanical coding blocks
All Input/Output modules carry two coder blocks equipped with pins which mate with holes in
corresponding blocks in the chassis and prevent the module being inserted into the wrong slot.
The
pins in the module blocks are factory installed in a pattern determined by the module and
corresponding
holes
are plugged with set screws. The chassis slot coder block configuration for this module
is shown in Figure 2-1.
set screws are removed from the chassis coder blocks to enable fitting. Unused
Figure 2-1 Chassis slot coder blocks configuratio
n
EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS
Field circuits
The field load circuit shown in Figure 2-2 is the typical required for the safe connection of field
loads
to
the MDO16FNS. For any unused channel a dummy field load (value 4.7k ohm) should
be used. We however, recommend the use of their 16-Channel Digital Output Termination
Cards TDO16AIB which offer full connection facilities with indicating fuses, and alarm outputs
(See
Section 1.2, Associated documentation).
Page 6

6
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
Figure 2-2 Basic field load circuit
Module connectors
The system bus connector is J1 and the common interface is connected via J4 and J5 (not
shown).
diagram (Figure 2-3 ) the following symbols are used:
Lethal voltages earth. All other pins on J3 are connected to field supply return but this field supply
return
All the digital outputs are routed through connector J2. In the external connection
0
x = Connector pin
Earth =
+ve
-
ve
O/P = Channel output
may not be at earth potential.
=
First mate (
long pin)
Connected to chassis
=
= Field supply return
Field supply in
WARNING
Live pins on Connector J3 rear of chassis J3 pin 1c is connected to
Page 7

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
7
Triguard
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
Figure 2-3 Field output connector J2 pinouts
Connector J3 pin 1c is connected to earth.
All other pins on J3 are connected to field supply return.
THEORY OF OPERATION
In accordance with TMR practice, channel output command information from the MPP follows
three
identical paths through the MDO16FNS (see Figure 2-4 ), each path at the command of
its own microcontroller in the common interface. In order to minimise the number of data
connections
form before entering the module from the common interface. In this manner 16 output channels
can
be
The three data streams are each applied to opto-isolators which mark the interface between
the system and field sides of the circuit and provide a system-to-field channel isolation of 1kV.
across the 1kV system-to-field barrier, the channel data are converted to serial
served by just three paths instead of 48.
Page 8

8
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
The data streams are then applied to the 16-bit output shift registers. The serial bits are
clocked successively into the shift registers until the 16th bit has been received. The registers
then latch the data and present it on the 16-bit busses (CHANA, CHANB and CHANC) to the
output switches. The data is con
of the SC300E system.
The output switch for each channel comprises six FETs connected in the series/parallel
network shown and providing 2 out of 3 majority voting between the three paths A, B and C. A
front panel LED at the switch output is lit when the switch is closed. Voltage and current
monitoring circuits are also connected to the switches to provide outputs for the Latent Fault
Detection
registers and opto-isolators. The feedback information confirms that the output has switched to
the
Testing of the output switches by the LFD circuits is co-or
the common interface. When all outputs are in the healthy condition and the microcontrollers
confirm
turn to switch its output alone to the opposite state and confirm the correct operation of its
individual output switch.
The module power requirements are served from two different sources. The power for the
output-side circuits is derived from the chassis 12V supply via dc/dc converters. All of the
supplies are monitored. Electronic fuse circuits sense the current in each output path and cut
off the upper FET if the current exceeds a predetermined limit.
(LFD) system. These outputs are fed back to the microcontrollers via dedicated shift
commanded state and that the line is not open or short circuit.
no
faults present, the SC300E processors (MPPs) will instruct each microcontroller in
tinuously refreshed in this manner and updated at each scan
dinated by the microcontrollers on
An On/Off Line Request switch on the front panel enables a request to be sent to the SC300E
system
module contains a hardware identity circuit that enables system identification of the module,
and three manual links 1, 2 and 3. Link 1 allows the module to be set up for 321 or 320 mode
operation
while still preserving overall operation. 320 mode means that the system will continue to
function with two out of three serviceable circuits. If the number falls to one out of three the last
read
serviceable
line.
Link 2 (HLV/GTZ) determines whether, in the event of a failure due to 321/320 action, the last
read values are held (HLV) or are set to zero (GTZ). Link 2 is only active however, if Link 3
(ICCB/HW)
by software.
that the module be taken off-line for maintenance purposes or returned on-line. The
which sets the threshold that determines how much of the circuit can be degraded
data is maintained. In 321 mode the system will continue to function with one out of three
circuits. If that fails the last read data is maintained and the module is taken off
is
set to HW. If Link 3 is set to ICCB Link 2 is ignored and its function determined
-
Page 9

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
9
Triguard
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
Figure 2-4 MDO16FNS -
Block diagram
Page 10

10
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
Common Interface
The three discrete control circuits in the common interface (A, B, and C) are each responsible
for the control of the corresponding one third of the I/O module circuits. Each control circuit
comprises a microcontroller with a dedicated watchdog, data buffers and shared RAM. The
circuit is powered via the module and permits live insertion of replacement modules.
The microcontrollers co-ordinate I/O signal processing, signal path diagnostics, on-line/off-line
status and signal status read/write cycles to and from the SC300E processors via an I/O
communications bus. All I/O modules have an identification code which is read by the common
interface and passed to the MPPs for verification. The on-line/off-line status is determined by
the MPPs. If, for maintenance purposes, the On/Off Line Request switch on the front of the
module is operated, the action is read by all three microcontrollers and the request passed to
the MPPs which may then grant the request. The watchdog on each microcontroller
extinguishes
failure, LFD failure or a voting discrepancy.
the Health LED on the I/O module front panel in the event of a microcontroller
Page 11

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
11
Triguard
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
Figure 2-5 Common interface -
Block diagram
System Configuration
The Digital Output module requires adequate ventilation to operate at its full capacity. For
convection
and the hot repair partner slot should
system
adequate
cooled systems the output module should be fitted in the lowest module chassis
not be occupied. When forced air cooling is applied to a
these limitations are removed. We recommend that the module be derated by 50% if
ventilation is not provided.
Page 12

12
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
SERVICING
SCOPE
Repair is by module replacement. Faulty modules are not repairable in the field. They should
be replaced by new modules and returned for repair.
WARNING
Lethal voltages are present in this equipment.
The protective covers are to prevent access to circuits. There are no user-serviceable
components under the covers
For your safety:
Do not remove the covers.
Do not touch any exposed circuits or insert objects such as test probes through the covers
while
the module is connected to the chassis backplane.
CAUTION 1
Before fitting a new module ensure that the setting of all three links is the same as that on the
old
module.
This module contains components that may be electrostatically sensitive. It should be
transported and stored in its original packaging material.
CAUTION 2
DIAGNOSIS
The TriBuild works
Health LED on the faulty module will be extinguished.
tation is used for fault diagnosis. In the case of an Input/Output fault the
PREPARATION
To ascertain whether the chassis I/O slot containing the faulty module has been allocated a
hot repair partner, use one of the following methods:
•
Check the system drawings
• Check the chassis wiring configuration
• Use the I/O chassis Configuration Report on the TriBuild workstation.
Page 13

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
13
Triguard
Where there is a hot repair partner allocation, use the ‘Dual-slot hot repair’ procedure,
otherwise
use the ‘Single-slot hot repair’ procedure.
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
Page 14

14
MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
Triguard
SC300E
CONFIGURATION
Before fitting a new module ensure that 321/320 link setting is the same as that on the old
module.
REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT
CAUTION 3
Failure to take the faulty module off-line before removing it from the chassis could trigger a fault
alarm
or
cause plant shutdown.
When inserting a module ensure that it is aligned with the markings on the chassis rails and
that it engages with the top and bottom guides. Improper insertion may cause damage to the
module and/or chassis connectors.
CAUTION 4
SINGLE-SLOT HOT REPAIR
1.
Operate the On/Off Line Request switch on the faulty module. The three On Line LEDs
should
all extinguish to indicate that the MPPs have recognised the request and taken
the module off-line. The last read data input from the module will be maintained until
the new module is on-line.
2.
Slacken the two module securing screws and use the black ejection levers (top and
bottom) to draw the module from its slot.
3.
Insert
in the chassis. The top and bottom chassis rails carry alignment marks to assist. Pull
out the ejection levers and as the module is pushed back engage the levers on the
chassis rails. The levers should then be used to draw the module into position, some
resistance
in position with the securing screws.
4.
Operate the On/Off Line Request switch and check that the three On Line LEDs
illuminate for one second, extinguish for one second and then illuminate permanently
to indicate that the module has been put on-line. If the LEDs do not illuminate either
the
considered faulty.
the new module ensuring that it engages properly in the upper and lower guides
will be felt as the rear connector pins engage. The module should be fixed
first or second time or fail to remain illuminated, then the module must be
Page 15

MDO16FN
S
October
2005–
Issue 4
15
Triguard
SC300E MDO16FNS 16-Channel D/O Module 120Vac/dc
DUAL-SLOT HOT REPAIR
1.
Insert the new module into the vacant hot repair slot ensuring that it engages properly
in the upper and lower guides in the chassis. The top and bottom chassis rails carry
2.
3.
alignment marks to
back engage the levers on the chassis rails. The levers should then be used to draw
the module into position, some resistance will be felt as the rear connector pins
engage. The module should be fixed in position with the securing screws.
Operate the On/Off Line Request switch on the new module. Ascertain that the three
On
Line LEDs on the new module illuminate for one second, extinguish for one second
and then illuminate permanently as the LEDs on the old module extinguish. This
sequence indicates that the new module has been put on line and the old module
taken off-line. If the LEDs on the new module do not illuminate either the first or second
time or fail to remain illuminated, th
module’s
If the new module is serviceable slacken the screws on the old module and use its
ejection levers to remove it from the chassis.
LEDs should remain illuminated indicating that it is still on-line.
assist. Pull out the ejection levers and as the module is pushed
e new module must be regarded as faulty. The old
PREVENTIVE MAINTENAN
No preventive maintenance is necessary.
SERVICE SUPPORT
CE
SPARES
Spare parts and technical advice can be obtained f
rom your local area offices.
 Loading...
Loading...