Page 1

QUICK START
ARMORSTART® DISTRIBUTED
MOTOR CONTROLLER —
SAFETY VERSION
Getting Started
BULLETIN 284G
Introduction This guide provides the basic information required to start up your
®
ArmorStart
and information regarding installing, programming, and DeviceNet™
Node Commissioning are described here. For detailed information on
specific product features or configurations, refer to the ArmorStart
user manual, Publication 284G-UM001*.
This guide is intended for qualified service personnel responsible for
setting up and servicing these devices. You must have previous
experience with and a basic understanding of electrical terminology,
configuration procedures, required equipment, and safety precautions.
You should understand DeviceNet network operations, including how
slave devices operate on a network and communicate with a
DeviceNet master. You should also be familiar with RSNetWorx™
for DeviceNet. You must use RSNetWorx for DeviceNet revision
3.21 service pack 2 or later. This software package is referred to
often in this manual. Rockwell Automation product EDS files are
available on the internet at: http://www.ab.com/networks/eds
Note: The Bulletin 284G Safety ArmorStart is suitable for safety
Distributed Motor Controller. Factory default settings
applications up to Safety Category 4PL e (T
per ISO 13849-1:2008). T
upon request.
ÜV compliance letter is available
ÜV assessment
.
Page 2
2
Installation The ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller is convection cooled.
Operating temperature must be kept between -20…40°C (-4…104°F).
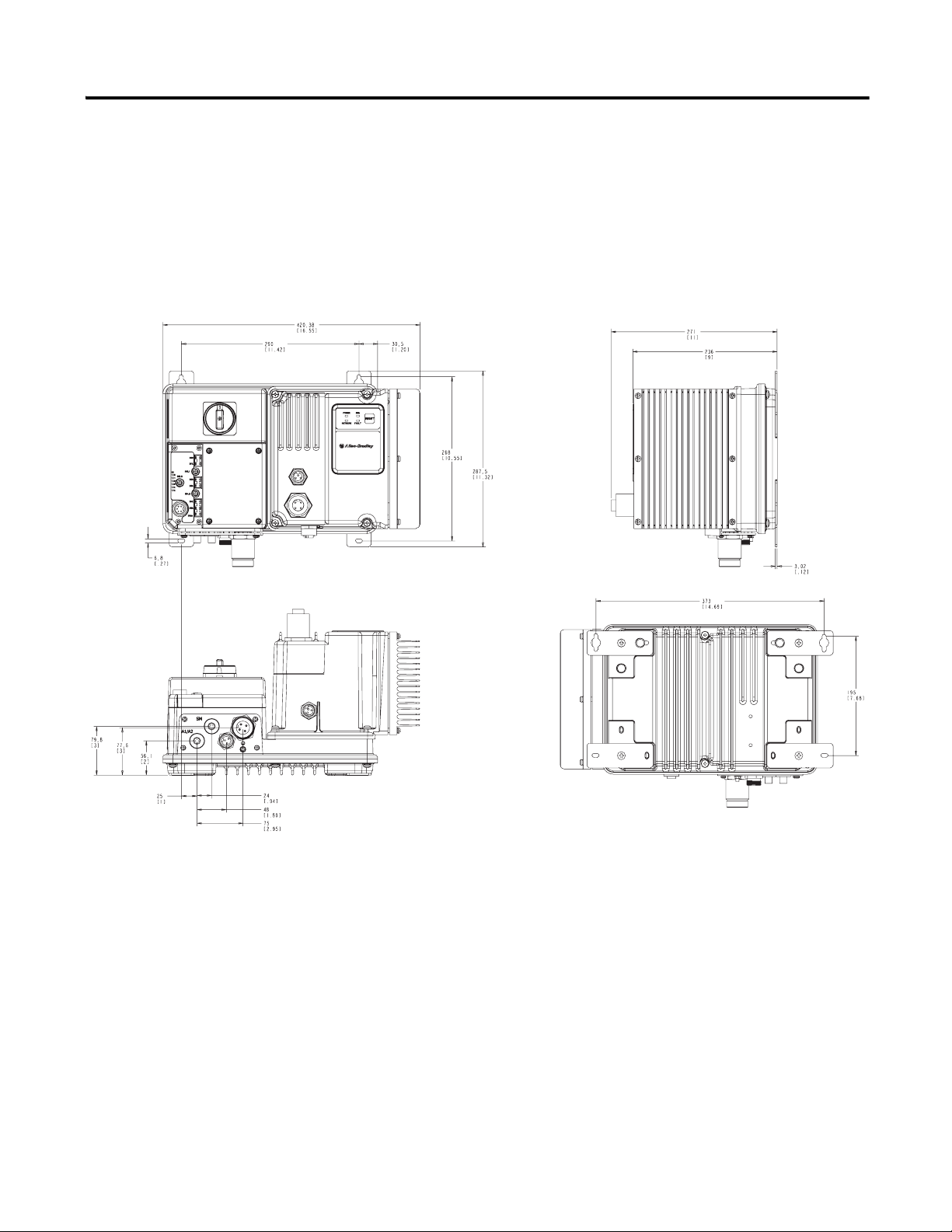
Dimensions Dimensions are shown in millimeters (inches). Dimensions are not intended
to be used for manufacturing purposes. All dimensions are subject to
change.
Figure 1 Dimensions for 2 Hp and below @ 460V AC, IP67/NEMA Type 4
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 3
3
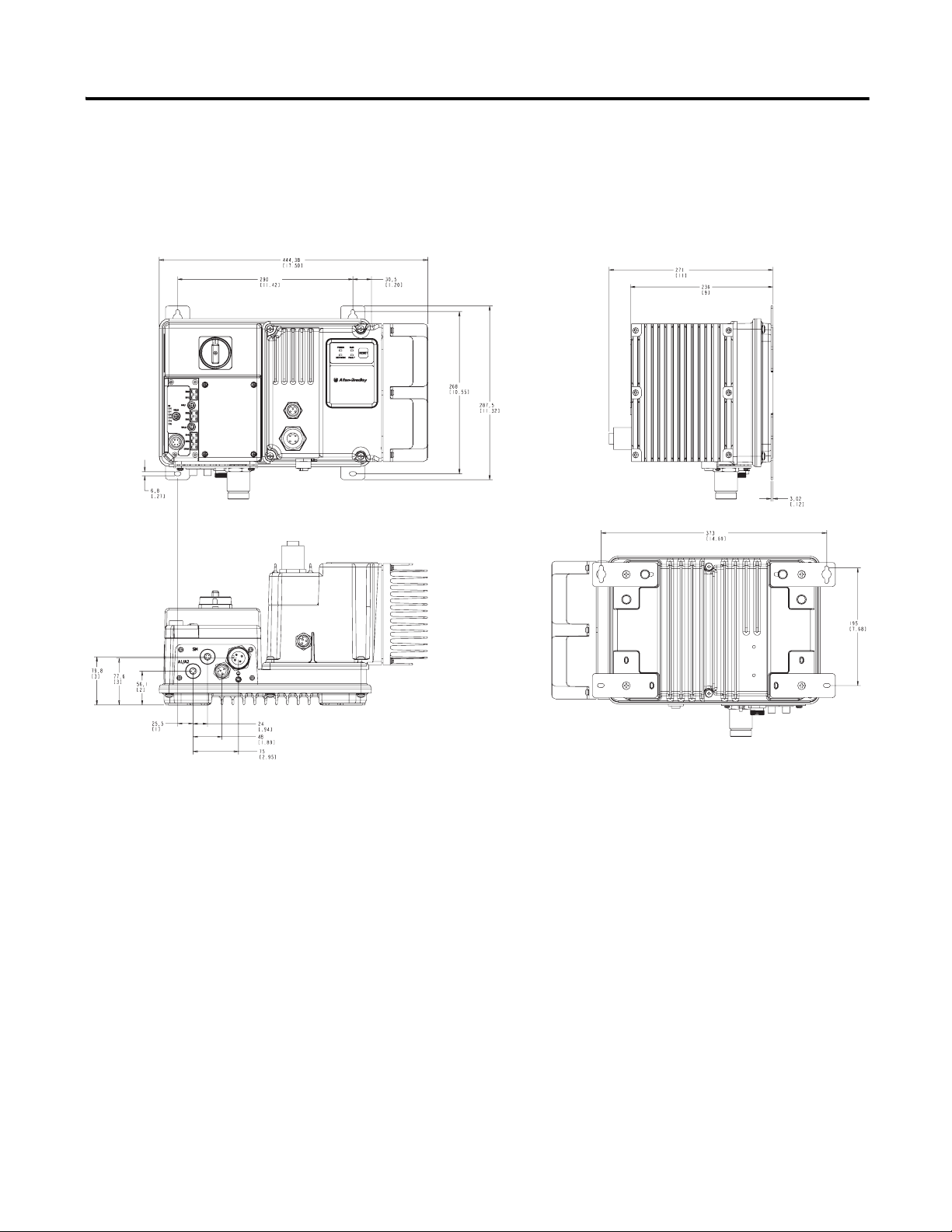
Dimensions, Continued Dimensions are shown in millimeters (inches). Dimensions are not intended
to be used for manufacturing purposes. All dimensions are subject to
change.
Figure 2 Dimensions for 3 Hp and above @ 460V AC, IP67/NEMA Type 4
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 4
4
Wiring Power, Control, and Ground Wiring
Table 1 provides the power, control, safety monitor inputs, and ground wire
capacity and the tightening torque requirements. The power, control, and
ground terminals will accept a maximum of two wires per terminal.
Table 1 Power, Control, Ground Wire Size, and Torque Specifications
Terminals Wire Size Torque Wire Strip Length
Three-phase
Power
and
Ground
Control Power and
Safety Monitor Inputs
Primary/Secondary
Terminal:
1.5…4.0 mm
(#16 …#10 AWG)
1.0 mm
(#18…#10 AWG)
2
2
…4.0 mm2
Primary Terminal:
10.8 lb•in. (1.2 N•m)
Secondary Terminal:
4.5 lb•in (0.5 N•m)
6.2 lb•in
(0.7 N•m)
0.35 in. (9 mm)
0.35 in. (9 mm)
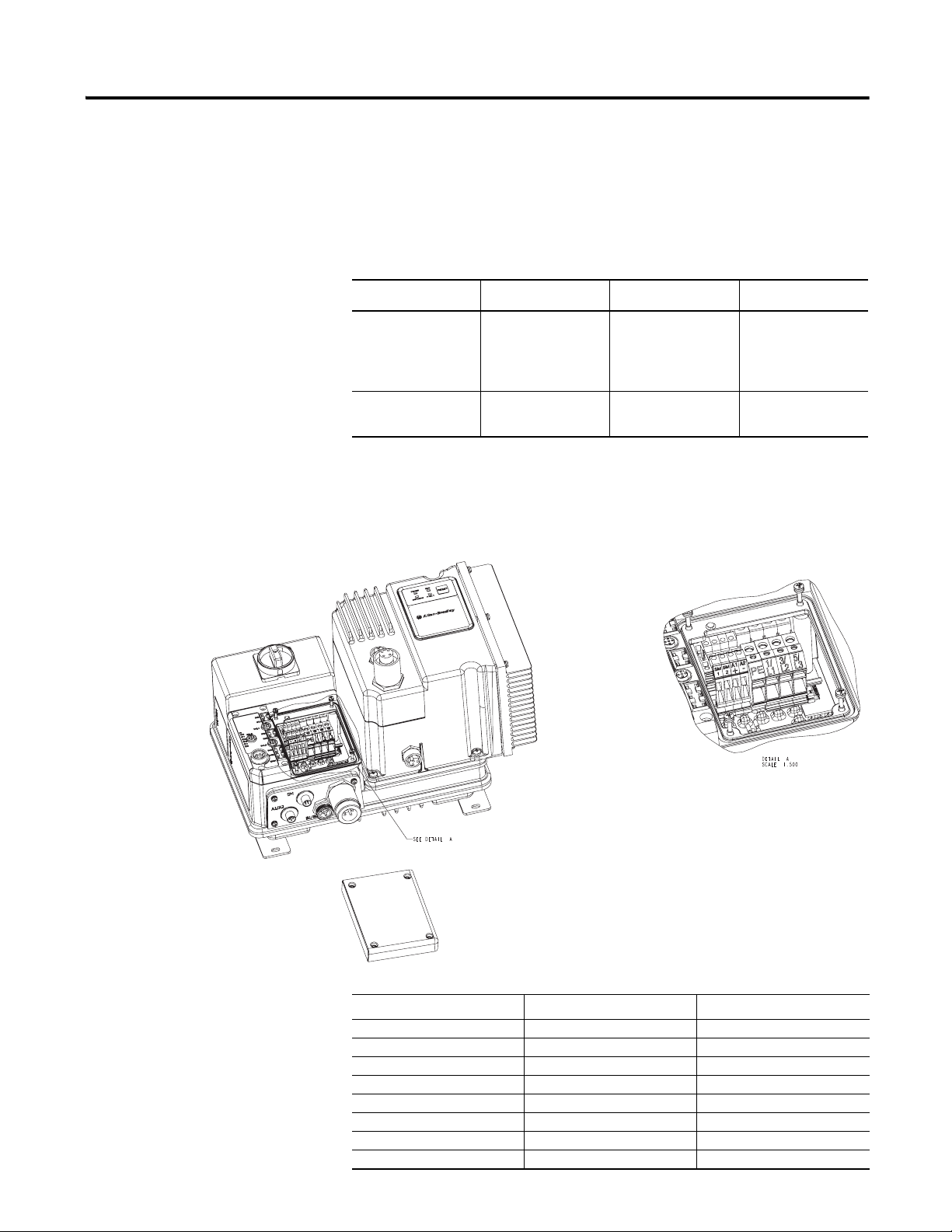
Terminal Designations As shown in Figure 3, the ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller contains
terminals for power, control, safety monitor inputs, and ground wiring.
Access can be gained by removing the terminal access cover plate.
Figure 3 ArmorStart Power, Control, Safety Monitor Inputs, and Ground Terminals
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Table 2 Power, Control, Safety Monitor, and Ground Terminal Designations
Terminal Designations No. of Poles Description
SM1 2 Safety I/O Input
SM2 2 Safety I/O Input
A1 (+) 2 Control Power Input
A2 (-) 2 Control Power Common
PE 2 Ground
1/L1 2 Line Power Phase A
3/L3 2 Line Power Phase B
5/L5 2 Line Power Phase C
Page 5
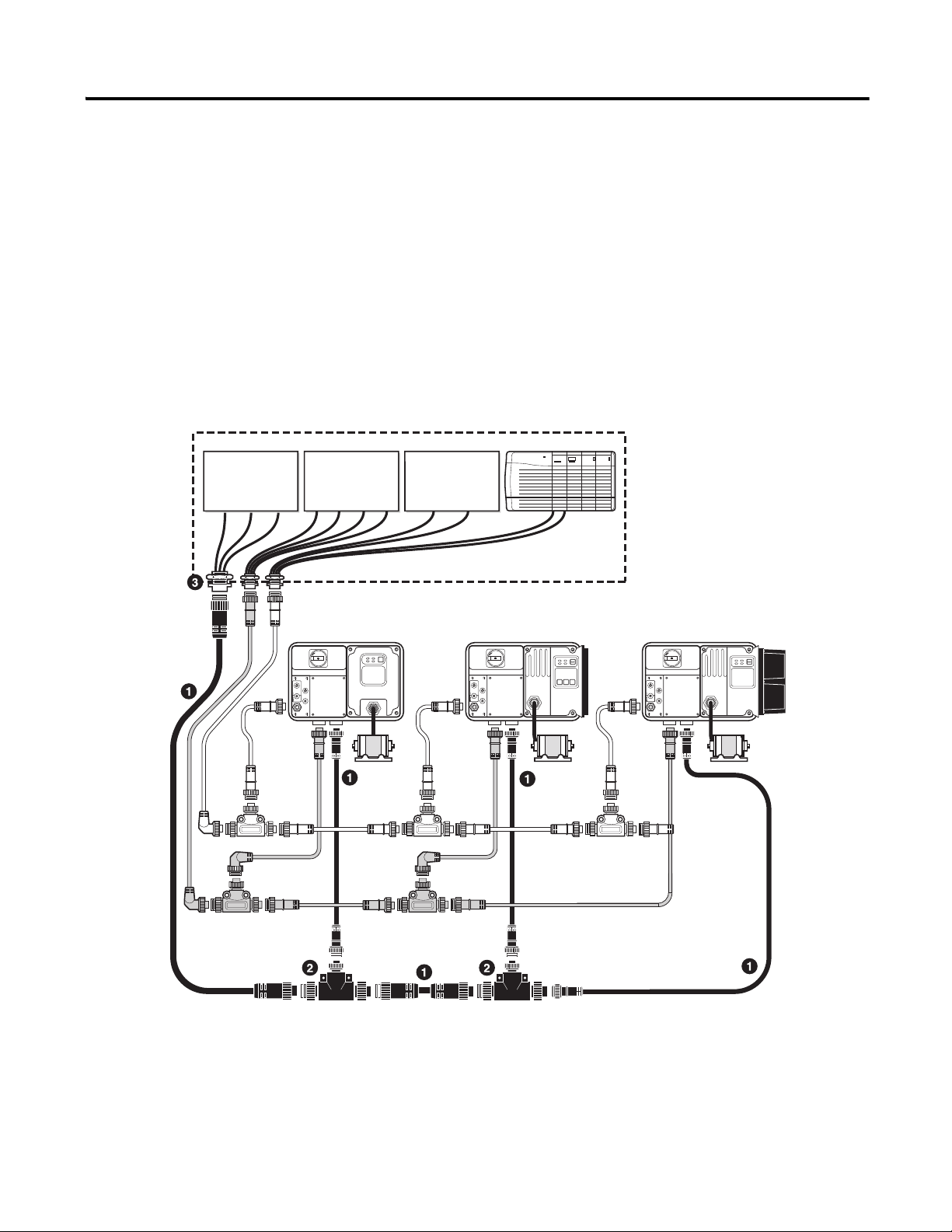
ArmorConnect Power Media Description
Encl
The ArmorStart Power Media offers both three-phase and control power
cable system of cordsets, patchcords, receptacles, tees, reducers and
accessories to be utilized with the ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller.
These cable system components allow quick connection of ArmorStart
Distributed Motor Controllers and reduce installation time. They provide
for repeatable, reliable connection of the three-phase and control power to
the ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller and motor by providing a plug
and play environment that also avoids system mis-wiring. When specifying
power media for use with the ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controllers
(Bulletins 280G/281G and 284G) use only Bulletin 280 ArmorConnect™
power media.
Figure 4 Three-Phase Power System Overview
osure
Branch Circuit
Protective Device
120 V AC
Control
Powe r
1606-XLSDNET4
Power Supply
5
PLC
DeviceNet
Bulletin 280/281
ArmorStart
RESET
Bulletin 283
ArmorStart
Bulletin 284
ArmorStart
OFF
➊ Three-Phase Power Trunk- PatchCord cable with integral female or male connector on each end. (Example Part Number: 280-PWR35A-M*)
➋ Three-Phase Drop Cable- PatchCord cable with integral female or male connector on each end. (Example Part Number: 280-PWR35A-M*)
➌ Three-Phase Power -
Tee connects to a single drop line to trunk with quick change connectors – Part Number: 280-T35
➍ Three-Phase Power Receptacles -
Female receptacles are a panel mount connector with flying leads – Part Number: 280-M35F-M1
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 6
6
RESET
Bulletin 280/281
ArmorStart
Bulletin 284
ArmorStart
RESET
Bulletin 280/281
ArmorStart
PLC
Bulletin 1492FB
Branch Circuit
Protective Device
Enclosure
Bulletin 1606
Power Supply
1606-XLSDNET4
DeviceNet
Power Supply
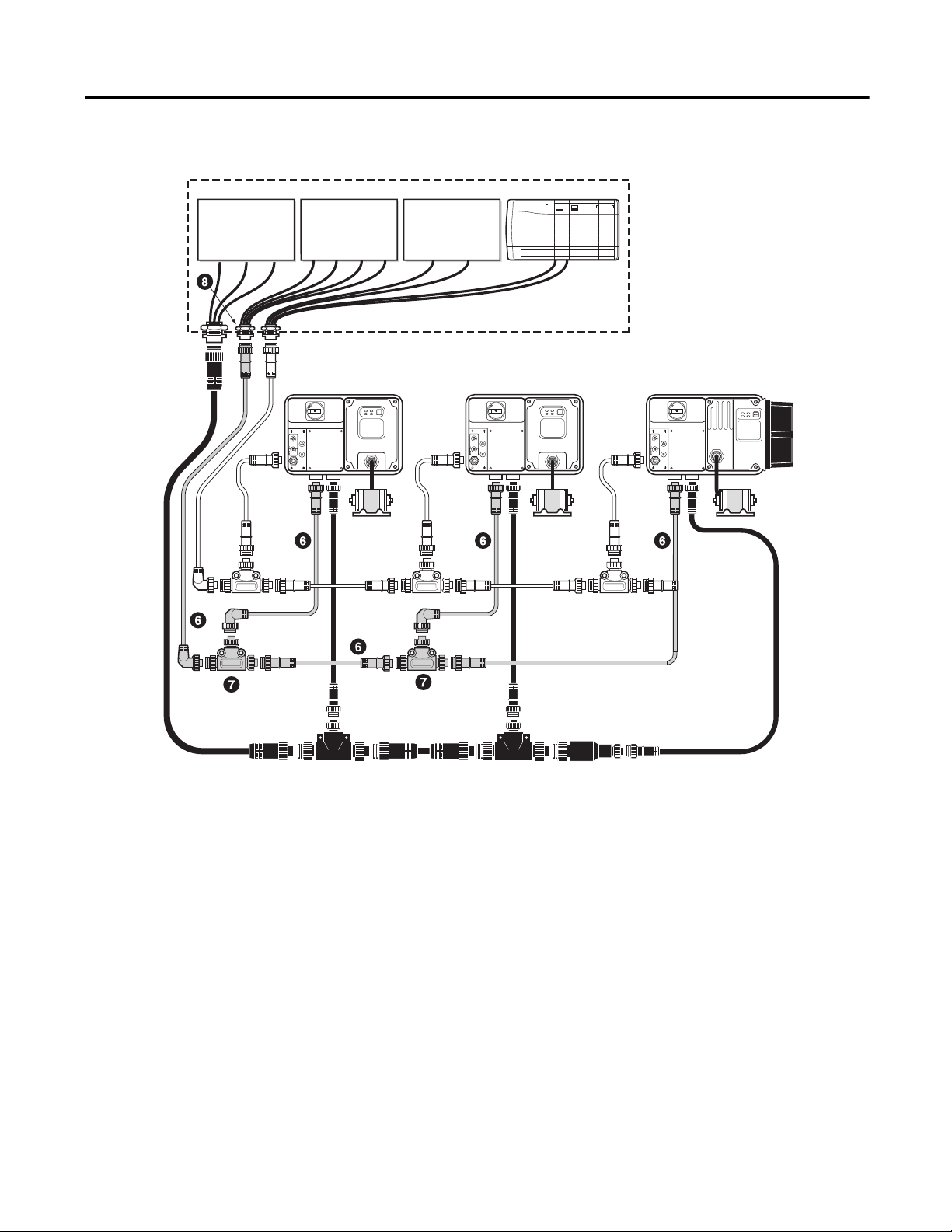
Figure 5 Control Power Media System Overview
➏ Control Power Media Patchcords - PatchCord cable with integral female or male connector on each end
Example Part Number: 889N-F3AFNU-*F
➐ Control Power Tees - The control power tee (Part Number: 898N-33PB-N4KF) is used to connect to the ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller using a
control power media patchcord.
➑ Control Power Receptacles - Female receptacles are a panel mount connector with flying leads –
Part Number: 888N-D3AF1-*F
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 7
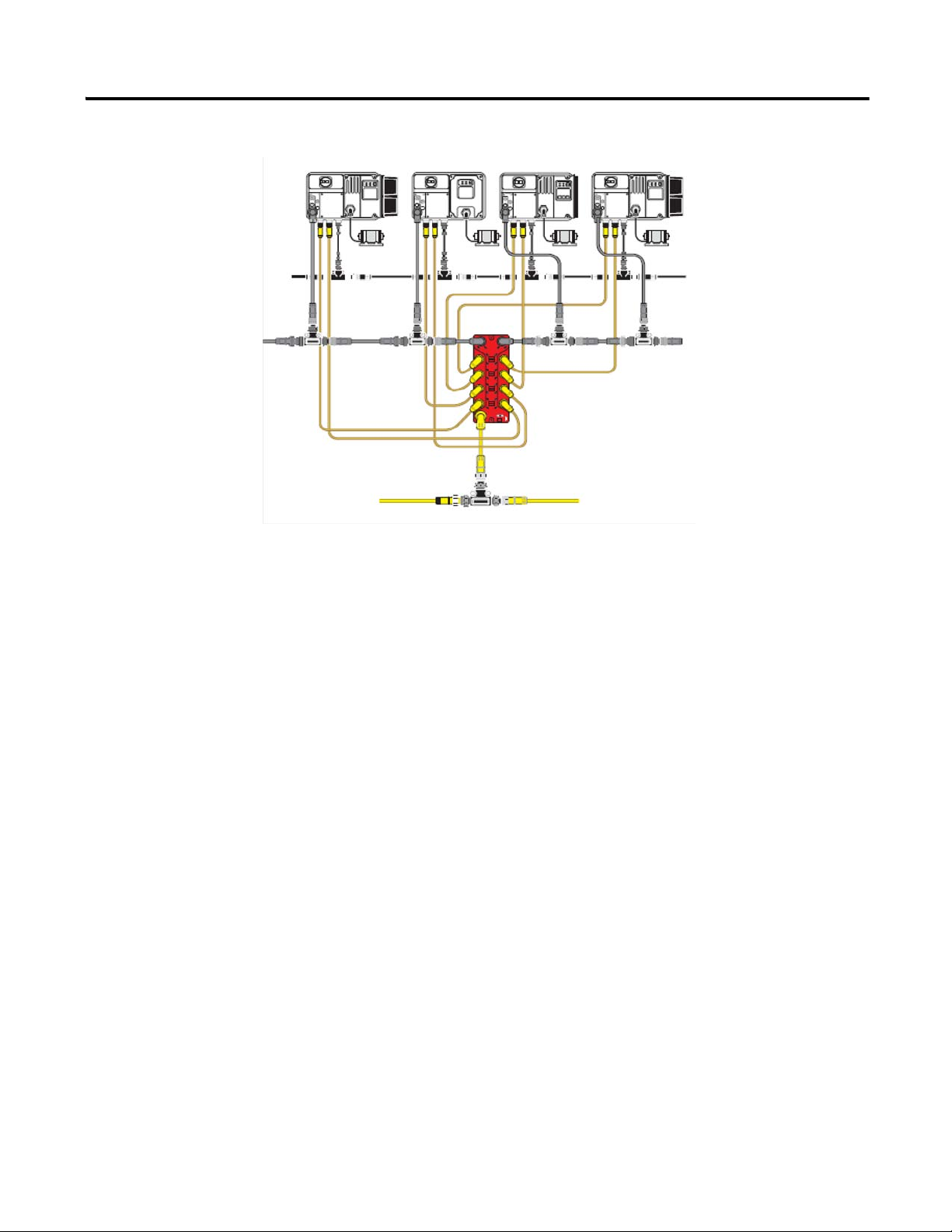
Figure 6 Safety System Overview
DeviceNet Media
I/O input
I/O output
Aux. Power
Three-Phase Power Media
The 1732DS Safety I/O module outputs to
provided 24V DC power for control power
to the ArmorStart - A1/A2 control power
The 1732DS Safety I/O module inputs will monitor the status of the safety-rated contactors inside the ArmorStart -SM safety monitor input.
input
7
Configuration of the
1732DS-IBXOBV4 Safety I/O
Note: To comply with TÜV, the 1732DS-IBXOBV4 Safety I/O module
must be configured as indicated below:
Configure the output that is connected to the I/O output cable assembly for:
• Dual (bipolar mode)
• Safety Pulse Test
Configure the input that is connected to the I/O Input cable assembly as
follows:
• Channel = Single
• Mode = Pulsed Test Input from test output X
• Source = Pulsed output from X
Safety PLC Program The program must:
• Force the output contactors to the open state when a safety-related stop
is demanded.
• Force the output contactors to remain in the open state if the SM
feedback is open after a safety-related stop is executed (see Notes).
Note: The program must inhibit the contactor closure to satisfy safety
Category 4 of 13849-1.
Note: The SM feedback logic should be implemented only after a
safety-related stop for the Bulletin 284G controllers. It should be
ignored during normal operation. One of the series contactors is
used for the normal stop/start function for these controllers.
Therefore, a malfunctioning contactor circuit cannot be
distinguished from a normal running state.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 8

8
Ground
Term in al
Three-Phase
Power
Receptacle
120V AC
Aux. Power
for
Control Brake
Safety Monitor
Input from
1732DS Safety
I/O Module Input
A1/A2 -24V DC
Control Power from
1732DS Safety
I/O Module Output
Term in al
Designations
Description Color Code
SM1 Safety Monitor Input Brown
SM2 Safety Monitor Input White
A1 (+) Control Power Input Brown
A2 (-) Control Power Common Blue
PE Ground Green/Yellow
1/L1 Line Power - Phase A Black
3/L2 Line Power - Phase B White
5/L3 Line Power - Phase C Red
ArmorStart Safety with
ArmorConnect Connectivity
Terminal Designations
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 9

ArmorConnect Cable Ratings The ArmorConnect Power Media cables are rated per UL Type TC
600V 90 °C Dry 75 °C Wet, Exposed Run (ER) or MTW 600V 90 °C or
STOOW 105 °C 600V - CSA STOOW 600V FT2. For additional
information regarding ArmorConnect Power Media see the ArmorStart
User Manual.
9
Branch Circuit Protection
Requirements for
ArmorConnect™ Three-Phase
Power Media
Group Motor Installations for
USA and Canada Markets
Wiring and Workmanship
Guidelines
When using ArmorConnect Three-Phase Power Media, fuses can be used
for the motor branch circuit protective device, for the group motor
installations. The recommended fuse types are the following: Class CC, T,
or J type fuses, (100 A max.). For additional information, see the
ArmorStart User Manual. A circuit breaker can be used for the motor
branch protective device, for the group motor installations when using only
the following ArmorConnect power media components: 280-M35M-M1,
280-M35F-M1, 280-T35, and 280-PWRM35*-M*. For additional
information, see the ArmorStart User Manual.
The ArmorStart Distributed Motor controllers are listed for use with each
other in group installations per NFPA 79, Electrical Standard for Industrial
Machinery. When applied according to the group motor installation
requirements, two or more motors, of any rating or controller type, are
permitted on a single branch circuit. Group Motor Installation has been
successfully used for many years in the USA and Canada.
In addition to conduit and seal-tite raceway, it is acceptable to utilize cable
that is dual rated Tray Cable, Type TC-ER and Cord, STOOW, for power
and control wiring on ArmorStart installations. In the USA and Canada
installations, the following guidance is outlined by the NEC and NFPA 79.
In industrial establishments where the conditions of maintenance and
supervision ensure that only qualified persons service the installation, and
where the exposed cable is continuously supported and protected against
physical damage using mechanical protection, such as struts, angles, or
channels, Type TC tray cable that complies with the crush and impact
requirements of Type MC (Metal Clad) cable and is identified for such use
with the marking Type TC-ER (Exposed Run)* shall be permitted between
a cable tray and the utilization equipment or device as open wiring. The
cable shall be secured at intervals not exceeding 1.8 m (6 ft) and installed in
a “good workman-like” manner. Equipment grounding for the utilization
equipment shall be provided by an equipment grounding conductor within
the cable.
*Historically cable meeting these crush and impact requirements were
designated and marked “Open Wiring”. Cable so marked is equivalent to the
present Type TC-ER and can be used.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 10

10
While the ArmorStart is intended for installation in factory floor
environments of industrial establishments, the following must be taken into
consideration when locating the ArmorStart in the application: Cables,
including those for control voltage including 24V DC and communications,
are not to be exposed to an operator or building traffic on a continuous
basis. Location of the ArmorStart to minimize exposure to continual traffic
is recommended. If location to minimize traffic flow is unavoidable, other
barriers to minimize inadvertent exposure to the cabling should be
considered. Routing cables should be done in such a manner to minimize
inadvertent exposure and/or damage.
Additionally, if conduit or other raceways are not used, it is recommended
that strain relief fittings be utilized when installing the cables for the control
and power wiring through the conduit openings.
The working space around the ArmorStart may be minimized as the
ArmorStart does not require examination, adjustment, servicing or
maintenance while energized. In lieu of this service, the ArmorStart is
meant to be unplugged and replaced after proper lockout/tag-out procedures
have been employed.
DeviceNet Network Installation The ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller contains the equivalent of
30 in. (0.76 m) of Device Net drop cable's electrical characteristics and
therefore 30 in. of drop cable must be included in the DeviceNet drop cable
budget for each ArmorStart in addition to actual drop cable required for the
installation.
Other DeviceNet System Design
Considerations
Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC)
The separation of the control power and DeviceNet power is recommended
as a good design practice. This minimizes the load on the DeviceNet supply,
and prevents transients which may be present on the control power system
from influencing the communication controls.
The following guidelines are provided for EMC installation compliance.
General Notes
• The motor Cable should be kept as short as possible in order to avoid
electromagnetic emission as well as capacitive currents
• Conformity of the drive with CE EMC requirements does not guarantee
an entire machine installation complies with CE EMC requirements.
Many factors can influence total machine/installation compliance.
• Using an EMI filter with any drive rating, may result in relatively high
ground leakage currents. Therefore, the filter must only be used in
installations and solidly grounded (bonded) to the building power
distribution ground. Grounding must not rely on flexible cables and
should not include any form of plug or socket that would permit
inadvertent disconnection. Some local codes may require redundant
ground connections. The integrity of all connections should be
periodically checked.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 11

11
Grounding
Connect a grounding conductor to the terminal provided as standard on each
ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller. Refer to Table 2 for grounding
provision location. There is also an externally available ground terminal.
Refer to Figure 10.
LED Status Indication The LED Status Indication provides 4 status LEDs and a Reset button. The
LEDs provide status indication for the following:
• POWER LED
The LED is illuminated solid green when control power is present and
with the proper polarity
• RUN LED
This LED is illuminated solid green when a start command and control
power are present
•NETWORK LED
This bi-color (red/green) LED indicates the status of the
communication link
•FAULT LED
Indicates Controller Fault (trip) condition
The “Reset Button” as a local trip reset.
Figure 7 LED Status Indication and Reset
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 12

12
ATTENTION
!
DeviceNet Node Commissioning
Three-phase power must be applied to the Bulletin 284G
Distributed Motor Controller to gain access to drive
parameters.
Establishing a DeviceNet Node Address
The ArmorStart is shipped with a default node address of 63 and Autobaud
enabled. Each device on a DeviceNet network must have a unique node
address or MAC ID which can be set to a value from 0…63. Keep in mind
that most DeviceNet systems use address 0 for the master device (Scanner)
and node address 63 should be left vacant for introduction of new slave
devices. The ArmorStart offers two methods for node commissioning as
shown in the following pages.
Node Commissioning using Software
To set the node address of the ArmorStart using software or other handheld
tools, leave the hardware rotary switches in their default position (99) or
insure that they are set to something greater then (63). With the hardware
switches set, use the software or handheld tool to change the address.
When using software to node commission a device, it may be necessary to
have the EDS file stored on the computer. The EDS file defines how the
software such as RSNetWorx for DeviceNet will communicate to the
ArmorStart. Rockwell Automation product EDS files are available on the
internet at: http://www.ab.com/networks/eds
for DeviceNet Revision 3.21 Service Pack 2 or later.
. You must use RSNetWorx
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 13

13
LSDLSD
MSDMSD
Node Commissioning using Hardware
The ArmorStart is shipped with the hardware rotary switches set to a value
of (99). If the switches are set to a value of (64) or above, the device will
automatically configure itself to the software node address. If the switches
are set to a value of (63) or less, the device will be at the node address
designated by the switch configuration.
To set an address using the hardware rotary switches, simply set the
switches to the desired node address. To access the node address rotary
switches, three-phase and control power should be turned off. Then remove
the starter module from the base unit. The rotary node address switches are
located on the back side of the starter module. Change the switches to the
desired node address. Re-install the starter module to the base unit. Reapply
power and the device will re-start at the new address.
Figure 8 Rotary Node Address Configuration
System Configuration
Information
The following information is provided to identify the default method for
setting up communication to the ArmorStart. Additional configuration
information and advanced settings help can be found in the ArmorStart User
Manual, Publication 284G-UM001*.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 14

14
Using Automap Feature with Default Input and Output (I/O) Assemblies
The Automap feature available in all Rockwell Automation scanners will
automatically map the information as shown below. If manual mapping is
required, the information below can be used to map a device based on the
default configuration.
Table 3 Default I/O Messaging Data
Default
Message type Polled
Consumed data size 4 byte (Rx)
Produced data size 4 bytes (Tx)
Default Input and Output (I/O) Assembly Formats
The I/O assembly formats for the ArmorStart are identified by the value in
Parameter 11 (Consumed IO Assy.) and Parameter 12 (Produced IO Assy.).
These values determine the amount and arrangement of the information
communicated to the master scanner. The tables below identify the default
information produced and consumed by Bulletin 284G devices. For
additional formats and advance configurations please reference the user
manual:
Defaults for Bulletin 284G Distributed Motor Controllers
Table 4 Instance 164 — Default Consumed Inverter Type Distributed Starter
(4 bytes)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Not
Not
Not
0
Used
Used
Drive
In 4
Drive
In 3
1
2 Comm Frequency Command (Low) (xxx.x Hz)
3 Comm Frequency Command (High) (xxx.x Hz)
Table 5 Instance 165 — Default Produced Inverter Type Distributed Starter
(4 bytes)
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
1 Reserved
2 Output Frequency (Low) (xxx.x Hz)
3 Output Frequency (High) (xxx.x Hz)
➊ Refers to control brake contactor status..
At
Reference
140M On
Contactor 1 ➊Input 5Input
Used
Drive
In 2
Jog
Rev
Drive
In 1
Jog Fwd Fault Reset Run Rev Run Fwd
Decel Rate 2
Net Ctl
Status
Enable
Ready
Decel Rate 1
Enable
Running
Rev
Input 3 Input 2 Input 1 Input 0
4
Accel Rate 2
Running
Fwd
Enable
Warning Tri pped
Accel Rate 1
Enable
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 15

15
Setting the Motor OL Current
The product should now be configured and communicating on the network.
The last step is to program the proper motor OL current setting
(Parameter 133). This can be accomplished by using software such as
RSNetWorx for DeviceNet or a handheld DeviceNet tool.
Use the software to access the device parameters screen. By default the
motor OL current is set to the minimum motor OL current setting for the
device. Set this parameter to the desired value and download to the device.
Select Motor OL Current (Parameter 133) and enter a value that
corresponds to the FLA of the motor connected to the ArmorStart. Make
sure the Single radio button is selected and then select Download to Device.
The proper motor protection is now in place.
Figure 9 RSNetWorx Parameter Screen
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 16

16
IMPORTANT
Table 6 Basic Program Group for Sensorless Vector Control
Parameter
Number
131 ➊ Motor NP Volts 1 VAC
132 ➊ Motor NP Hz 1 Hz 15/400 Hz 60 Hz
133
134 Minimum Freq. 0.1 Hz 0.0/400 Hz 0.0 Hz
135 ➊
136 ➊ Start Source
137 Stop Mode
138
139 Accel Time 1 0.1 Secs 0.0/600.0 Secs 10.0 Secs
140 Decel Time 1 0.1 Secs 0.0/600.0 Secs 10.0 Secs
141 ➊
Parameter
Description
Motor OL
Current
Maximum
Freq.
Speed
Reference
Reset to
Default
Display/
Options
0.1 A
0.1 Hz 0.0/400 Hz 60 Hz
0 = Keypad ➋
1 = 3-Wire ➋
2 = 2-Wire
3 = 2-W Lvl Sens
4 = 2-W Hi Speed
5 = Comm Port
0 = Ramp, CF
1 = Coast, CF
2 = DC Brake, CF
3 = DCBrkAuto, CF
4 = Ramp
5 = Coast
6 = DC Brake
7 = DC BrakeAuto
8 = Ramp + EM B, CF
9 = Ramp + EM Brk
0 = Drive Pot ➋
1 = InternalFreq
2 = 0…10V Input ➋
3 = 4…20 mA Input ➋
4 = Preset Freq
5 = Comm Port
6 = Stp Logic
7 = Anlg in Mult ➋
0 = Ready/Idle
1 = FactoryRset
Min./
Max.
20/Drive Rated
Volts
0.0/(Drive Rated
Amps x 2)
0/5 5
0/9 9
0/7 5
0/1 0
Defaults
Settings
Based on
Based on
Driving
Rating
Driving
Rating
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
➊ Stop drive before changing this parameter.
➋ See Important below:
These drive parameters options will cause the
Bulletin 284G ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller
to become disabled.
Page 17

17
Quick Reference
Troubleshooting
There are four LEDs on the front of the ArmorStart that can provide an
indication as to the health of the device. The following is a brief explanation
of the operation of each LED.
Table 7 LED Status Indication
LED Definition
Power
Run
Network
Fault
Table 8 Network LED Status Indication
Network Status LED Definition Possible Causes
Off The device has not completed the initialization, is
not on an active network, or may not be powered up.
Flashes green-red-off While waiting to detect the network baud rate, the
LED will flash this pattern about every 3 seconds.
Solid Green The device is operating in a normal condition, and is
communicating to another device on the network.
Flashing Green The device is operating in a normal condition, is
on-line, but with no connection to another device.
This is the typical state for new devices.
Flashing Red Recoverable fault has occurred. Check to make sure the PLC™ and scanner are operating correctly
Solid Red The device has detected a major error that has
rendered it incapable of communicating on the
network (Duplicate MAC ID, Bus-off, media issue).
Flashing Red and
Green
The device is in a communication faulted state. Power cycling the device may resolve the problem; however, if the
This LED will be illuminated solid green when control power is present and with
the proper polarity.
This LED will be illuminated solid green when a start command and control
power are present.
This bi-color LED is used to indicate the status of the DeviceNet network. See
the Network Status LED table below for additional information.
This LED is used to indicate the fault status of the ArmorStart. When the unit is
faulted, the unit will respond with a specific blink pattern to identify the fault.
See the Fault LED table below for additional information.
Check to make sure the product is properly wired and configured on
the network.
If the product stays in this state it means that there is no set baud
rate. Insure that at least one device on the network has a set baud
rate.
No action required.
The device may need to be mapped to a master scanner, placed in a
scanlist, or have another device communicate to it.
and that there are no media/cabling issues. Check to see if other
networked devices are in a similar state.
Troubleshooting should be done to ensure that the network is correct
(terminators, lengths, etc.) and there is not a duplicate node problem.
If other devices on the network appear to be operating fine and power
cycling the device does not work, contact Technical Support.
problem continues, it may be necessary to contact Technical Support.
Fault Definitions Some of the Bulletin 284G ArmorStart Distributed Motor Controller faults
are detected by the internal hardware of the ArmorStart, while others are
detected by the internal drive. For internal drive faults, the internal hardware
of the ArmorStart simply polls the drive for the existence of faults and
reports the fault state. No fault latching is done by the internal hardware of
the ArmorStart for these faults. The Pr FltReset Mode parameter
(Parameter 23) determines the Auto Resettability of only the faults that are
detected on the main control board. These faults are listed as “param 23”
autoresettable in Table 9. The Auto Resettability of the faults that are
detected in the internal drive is controlled by internal drive parameters.
These faults are listed as drive controlled in Table 9.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 18

18
Fault LED Indications for
Bulletin 284G ArmorStart
Distributed Motor Controllers
Table 9 Controller Fault LED Definitions
Blink
Pattern
1 Short (140M) — The circuit breaker has tripped. Try to reset the breaker. If the condition continues check the
2 — Overload Fault
3 — Phase Short (Drive Error Codes
4 — Ground Fault (Drive Error Codes
5 — Motor Stalled
6 Control
7 I/O Fault — Depending on the types of modules in the configuration this error could be generated by a
8 — Heatsink Overtemperature
9 — Over-Current
10 DNet Power
11 Internal
12 — DC Bus Fault
13 — EEPROM Fault/Internal Comm
14 — Hardware Fault
15 — Auto Restart Tries
16 — Miscellaneous Fault This fault is actually the logical OR of the drive’s Auxiliary Input fault (Fault Code 2), Heatsink
ArmorStart Drive Controlled
Power
Loss
Comm
Fault Definitions
(Drive Error Codes 7 and 64)
41…43)
13, 38…40)
(Drive Error Code 6)
— The ArmorStart has detected a loss of the control power voltage. Check control voltage, wiring,
(Drive Error Code 8)
(Drive Error Codes 12 and 63)
— DeviceNet power has been lost or has dropped below the 12V threshold. Check the state of the
— This fault occurs when communications between the main board the drive is lost. This fault
(Drive Error Codes 3, 4, and 5)
Flt
(Drive Error Codes 81 and 100)
(Drive Error Codes 2, 70, and
122)
(Drive Error Code 33)
Possible Causes or Remedies
power wiring. This fault cannot be disabled.
An excessive motor load exists. Reduce load so drive output current does not exceed the current
set by Parameter 133 (Motor OL Current) and verify Parameter 184 (Boost Select) setting.
Reduce load or extend Accel Time. This fault cannot be disabled.
The ArmorStart has detected a phase short. Excessive current has been detected between two
of the output terminals. Check the motor for a shorted condition. Replace starter module if fault
cannot be cleared. This fault cannot be disabled.
A current path to earth has been detected at or more of the drive output terminals or a phase to
ground fault has been detected between the drive and motor in this phase. Check the motor for
a grounded condition. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared. This fault cannot be
disabled.
Drive is unable to accelerate motor. Increase Parameter 139 and/or 167 (Accel Time x) or reduce
load so drive output current does not exceed the current by Parameter 189. This fault cannot be
disabled.
and proper polarity. Also check and replace control voltage fuse, if necessary. This fault can be
disabled and is disabled by default.
shorted sensor, shorted input device, wiring mistakes, or a blown output fuse. If this fault
occurs, the offending problem should be isolated or removed prior to restarting the system. This
fault can be disabled and is disabled by default.
Heatsink temperature exceeds a predefined value. Verify that ambient temperature has not
exceeded. This fault cannot be disabled. Replace internal fan.
The ArmorStart has detected a voltage imbalance. Check the power system and correct if
necessary. This fault cannot be disabled.
network power supply and look for DeviceNet media problems. This fault can be disabled and is
disabled by default.
cannot be disabled.
DC bus voltage remained below 85% of nominal. DC bus voltage fell below the minimum value.
DC bus voltage exceeded maximum value. Monitor the incoming AC line for low voltage or line
power interruption. Check input fuses.
Monitor the AC line for high line voltage or transient conditions. Bus overvoltage can also be
caused by motor regeneration. Extend the decel time or install a starter module with the
dynamic brake option. This fault cannot be disabled.
This is a major fault, which renders the ArmorStart inoperable. Possible causes of this fault are
transients induced during EEprom storage routines. If the fault was initiated by a transient,
power cycling should clear the problem. Otherwise replacement of the starter module may be
required. This fault cannot be disabled.
This fault indicates that a serious hardware problem exists. Check for a base/starter module
mismatch. Auxiliary input interlock is open. Failure has been detected in the drive power
section. Failure has been detected in the Drive control and I/O section. Cycle power and replace
drive if fault cannot be cleared. This fault cannot be disabled.
Drive unsuccessfully attempted to reset a fault and resume running for the programmed number
of Parameter 192 (Auto RstrtTries). Correct the cause of the fault. This fault cannot be disabled.
Overtemperature fault (Fault Code 8), Parameter Defaulted fault (Fault Code 48), and SVC
Autotune fault (Fault Code 80), Fan RPM, Fan and DB1 fault. This fault cannot be disabled.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 19

Internal Drive Faults
A fault is a condition that stops the drive. There are two fault types.
Table 10 Internal Drive Fault Types
Typ e Description
Auto-Reset/Run
When this type of fault occurs, and Parameter 192 (Auto Rstrt Tries) Related Parameter(s):
155, 158, 161, 193 is set to a value greater than 0, a user-configurable timer,
1
Parameter 193 (AutoRstrt Delay) Related Parameter(s): 192, begins. When the timer
reaches zero, the drive attempts to automatically reset the fault. If the condition that
caused the fault is no longer present, the fault will be reset and the drive will be restarted.
Non-Resettable
This type of fault may require drive or motor repair, or is caused by wiring or
2
programming errors. The cause of the fault must be corrected before the fault can be
cleared.
Automatically Clearing Faults (Option/Step)
19
Clear a Type 1 fault and restart the drive.
1. Set Parameter 192 (Auto Rstrt Tries) to a value other than 0.
2. Set Parameter 193 (Auto Rstrt Delay) to a value other than 0.
Clear an OverVoltage, UnderVoltage or Heatsink OvrTmp fault without restarting
the drive.
1. Set 192 [Auto Rstrt Tries] to a value other than 0.
2. Set 193 [Auto Rstrt Delay] to 0.
Auto Restart (Reset/Run)
The Auto Restart feature provides the ability of the drive to automatically
perform a fault reset followed by a start attempt without user or application
intervention. This allows remote or unattended operation. Only certain
faults are allowed to be reset. Certain faults (Type 2) that indicate possible
drive component malfunction are not resettable.
Caution should be used when enabling this feature, since the drive will
attempt to issue its own start command based on user selected
programming.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 20

20
Table 11 Fault Types, Descriptions, and Actions
No. Fault
Typ e
➊
Description Action
F2 Auxiliary Input 1 Auxiliary input interlock is open. 1. Check remote wiring.
2. Verify communications.
F3 Power Loss 2 DC bus voltage remained below
85% of nominal.
F4 UnderVoltage 1 DC bus voltage fell below the
1. Monitor the incoming AC line for low voltage or line power interruption.
2. Check input fuses.
Monitor the incoming AC line for low voltage or line power interruption.
minimum value.
F5 OverVoltage 1 DC bus voltage exceeded
maximum value.
Monitor the AC line for high line voltage or transient conditions. Bus
overvoltage can also be caused by motor regeneration. Extend the decel time
or install dynamic brake option.
F6 Motor Stalled 1 Drive is unable to accelerate motor. Increase Parameter 139…167 (Accel Time x) or reduce load so drive output
current does not exceed the current set by Parameter 189 (Current Limit 1).
F7 Motor Overload 1 Internal electronic overload trip 1. An excessive motor load exists. Reduce load so drive output current
does not exceed the current set by Parameter 133 (Motor OL Current).
2. Verify Parameter 184 (Boost Select) setting
F8 Heatsink
OvrTmp
1 Heatsink temperature exceeds a
predefined value.
1. Check for blocked or dirty heat sink fins. Verify that ambient
temperature has not exceeded 40°C.
2. Replace internal fan.
F12 HW OverCurrent 2 The drive output current has
exceeded the hardware current
limit.
F13 Ground Fault 2 A current path to earth ground has
been detected at one or more of the
Check programming. Check for excess load, improper programming of
Parameter 184 (Boost Select), DC brake volts set too high, or other causes of
excess current.
Check the motor and external wiring to the drive output terminals for a
grounded condition.
drive output terminals.
F33 Auto Rstrt Tries Drive unsuccessfully attempted to
Correct the cause of the fault and manually clear.
reset a fault and resume running
for the programmed number of
Parameter 192 (Auto Rstrt Tries).
F38
Phase U to Gnd
F39
Phase V to Gnd
F40
Phase W to Gnd
F41
Phase UV Short
F42
Phase UW Short
F43
Phase VW Short
2 A phase to ground fault has been
detected between the drive and
motor in this phase.
2 Excessive current has been
detected between these two output
terminals.
1. Check the wiring between the drive and motor.
2. Check motor for grounded phase.
3. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared.
1. Check the motor and drive output terminal wiring for a shorted
condition.
2. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
➊ See Table 10 for internal drive fault types.
Page 21

Table 12 Fault Types, Descriptions, and Actions (Continued)
21
No. Fault
F48 Params
Defaulted
F63 SW
OverCurrent
F64 Drive
Overload
Typ e
➊
Description Action
2 The drive was commanded to write
default values to EEPROM.
2 Programmed Parameter 198 [SW
Current Trip] has been exceeded.
2 Drive rating of 150% for 1 min. or
200% for 3 sec. has been
exceeded.
F70 Power Unit 2 Failure has been detected in the
drive power section.
F80 SVC Autotune The autotune function was either
cancelled by the user or failed.
F81 Comm Loss 2 RS485 (DSI) port stopped
communicating.
F100 Parameter
Checksum
2 The checksum read from the board
does not match the checksum
calculated.
F122 I/O Board Fail 2 Failure has been detected in the
drive control and I/O section.
➊ See Table 10 for internal drive fault types.
1. Clear the fault or cycle power to the drive.
2. Program the drive parameters as needed.
Check load requirements and Parameter 198 (SW Current Trip) setting.
Reduce load or extend Accel Time.
1. Cycle power.
2. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared.
Restart procedure.
1. Turn off using Parameter 205 (Comm Loss Action).
2. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared.
Set Parameter 141 (Reset To Defaults) to option 1 Reset Defaults.
1. Cycle power.
2. Replace starter module if fault cannot be cleared.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 22

22
Motor
Connection
DeviceNet
Connection
(Mini/M18)
Local Disconnect
6 Inputs
(Micro/M12)
Dynamic Brake
3-Phase Power
LED Status
Indication
A1/A2
Aux. Power
SM
Control Brake
Figure 10 Bulletin 284G Safety ArmorStart
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 23

23
Accessories Table 12 DeviceNet Media
0
Description Length m (ft) Cat. No.
KwikLink pigtail drops are Insulation
Displacement Connector (IDC) with integral Class
1 round cables for interfacing devices or power
supplies to flat cable
DeviceNet Mini- T-Port Tap
Gray PVC Thin Cable
Thick Cable
➊
Mini Straight Female
Mini Straight Male
Mini Straight Female
Mini Right Angle Male
Mini Right Angle Female
Mini Straight Male
Mini Right Angle Female
Mini Straight Male
Mini Straight Female
Mini Straight Male
Mini Straight Female
Mini Right Angle Male
Mini Right Angle Female
Mini Straight Male
Mini Right Angle Female
Mini Straight Male
1 m (3.3)
2 m (6.5)
3 m (9.8)
6 m (19.8)
Right Keyway
Left Keyway
Connector
Sealed
1485P-P1E4-B1-N5
1485P-P1E4-B2-N5
1485P-P1E4-B3-N5
1485P-P1E4-B6-N5
1485P-P1N5-MN5NF
1485P-P1N5-MN5KM
Cat. No.
1485G-P➋N5-M5
1485G-P➋W5-N5
1485G-P➋M5-Z5
1485G-P➋W5-Z5
1485C-P➌N5-M5
1485C-P➌W5-N5
1485C-P➌M5-Z5
1485C-P➌W5-Z5
See Publication M116-CA001A-EN-P for complete cable selection information.
➊
Replace symbol with desired length in meters (Example: 1485G-P1N5-M5 for a 1 m cable). Standard cable lengths: 1 m, 2 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m, and 6 m.
➋
Replace symbol with desired length in meters (Example: 1485C-P1N5-M5 for a 1 m cable). Standard cable lengths: 1 m, 2 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m, 6 m, 8 m, 10 m, 12 m,
➌
18 m, 24 m, and 30 m.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 24

24
DC Micro Patchcord
DC Micro V-Cable
Table 13 Sensor Media
0
Description
0
ArmorStart I/O
Connection
➊
Pin Count Connector Cat. No.
Straight Female
Straight Male
Input 5-Pin
Straight Female
0
0
Right Angle Male
Straight Female
Input 5-pin
Right Angle Male
0
See Publication M116-CA001A-EN-P for complete cable selection information.
➊
Replace symbol with desired length in meters (Example: 889D-F4ACDM-1 for a 1 m cable). Standard cable lengths: 1 m, 2 m, 5 m, and 10 m.
➋
889D-F4ACDM-
889D-F4AACDE-
879D-F4ACDM-
879D-R4ACM-
➋
➋
➋
➋
Table 14 Sealing Caps
Description Used on I/O Connection Cat. No.
Plastic Sealing Cap (M12) Input 1485A-M12
➌ To achieve IP67 rating, sealing caps must be installed on all unused I/O connections.
Table 15 ArmorBlock Guard I/O Recommended Compatible Cables and Connectors
Description Cat. No.
DC Micro (M12) Male Cordset 889D-F4HJ-➊
DC Micro Style Patchcord 889D-F4HJDM-➊
M12 Terminal Chamber, Straight Male 871A-TS4-DM
➌
M12 Terminal Chamber, Right Angle Male
➊ Replace symbol with 1 (1 m), 2 (2 m), 5 (5 m), or 10 (10 m) for standard cable length.
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
871A-TR4-DM
Page 25

Notes:
25
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 26

26
Notes:
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 27

Notes:
27
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P - May 2009
Page 28

Registered Trademark List
ArmorPoint and ArmorStart are registered trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Tr ademark List
ArmorConnect, RSLogix5000, PLC, RSNetWorx, and SLC are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc. ControlNet is a trademark of ControlNet
International, LTD. DeviceNet and the DeviceNet logo are trademarks of the Open Device Vendors Association (ODVA).
Publication 284GS-QS001A-EN-P — May 2009 PN-29252
Copyright ©2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Printed in USA.
 Loading...
Loading...