Page 1
ALLEN-BRADLEY
Bulletin 2755
Hand-Held Scanner
with RS-232 Option
(Catalog No. 2755-G3-D or -G6-D)
User Manual
Page 2

Important User Information
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics
differing from those of electromechanical equipment.
“Application Guidelines for Application, Installation, and
Maintenance of Solid State Controls” (Publication
SGI-1.1) describes some important differences between
solid state equipment and hard–wired electromechanical
devices. Because of this difference, and also because of the
wide variety of uses for solid state equipment, all persons
responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy
themselves that each intended application of this
equipment is acceptable.
In no event will the Allen-Bradley Company be
responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages
resulting from the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included
solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many
variables and requirements associated with any particular
installation, the Allen-Bradley Company cannot assume
responsibility or liability for actual use based on the
examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Allen-Bradley Company
with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or
software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in
part, without written permission of the Allen-Bradley
Company is prohibited.
PHOTOSWITCH is a registered trademark of Allen-Bradley Company, Inc.
Page 3

Table of Contents
g
Hand-Held Scanner with RS-232 Option
A–B
Using
this Manual
Overview
of Scanner
Chapter 1
Chapter Objectives 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contents of Package 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intended Audience 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview of Manual 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Warnings and Cautions 1–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Related Publications 1–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2
Chapter Objectives 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Function of Scanner 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Modes 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hand-Held Mode 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Autosense Mode 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Setup Parameters 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Setup 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Communication 2–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Message Format 2–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symbology 2–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Commands 2–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ordering a Scanner 2–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanner Accessories 2–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Usin
the Scanner
Chapter 3
Chapter Objectives 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Physical Description 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LED Indicators 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safety Labels 3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanning Ranges 3–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Scanner 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Beep 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Tips 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting 3–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
i
Page 4

Table of Contents
G
Hand-Held Scanner with RS-232 Option
Setup
Instructions
eneral
Setup
Parameters
Chapter 4
Chapter Objectives 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting Scanner to Host 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing Interface Cable 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing Interface Cable 4–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing Power Supply 4–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanner Configuration Guidelines 4–5. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanner Default Settings 4–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Resetting Factory Defaults 4–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5
Chapter Objectives 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Status 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Consumption 5–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Beeper Operation 5–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Capture Count 5–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Spotter Beam 5–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Autosense Mode 5–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Trigger Operation 5–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial
Communication
Parameters
ii
Chapter 6
Chapter Objectives 6–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baud Rate 6–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Data Transmission Parameters 6–3. . . . . . . . . . .
Protocol 6–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
XON/XOFF 6–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CTS 6–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RTS 6–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intercharacter Delay 6–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Transmit Buffer 6–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Full Buffering 6–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Buffering 6–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
One Label Buffering 6–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 5

Table of Contents
ym
Hand-Held Scanner with RS-232 Option
Message
Format
Parameters
S
bologies
Chapter 7
Chapter Objectives 7–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Message Format 7–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prefix 7–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Suffix 7–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanner Identifier 7–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Code Identifier 7–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preamble or Postamble 7–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preamble 7–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Postamble 7–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Read Message 7–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 8
Chapter Objectives 8–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Label Lengths 8–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Code 39 8–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modulo 43 Check Character 8–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Stop/Start Characters 8–3. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Length 8–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Length 8–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UPC (A and E) 8–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Supplements 8–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expanded UPC-E 8–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Number System Digit 8–6. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Check Digit 8–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UPC to EAN Translation 8–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EAN/JAN 8–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Supplements 8–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Number System Digit 8–9. . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Check Digit 8–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interleaved 2 of 5 8–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Check Digit 8–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Length 8–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Length 8–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard 2 of 5 8–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Length 8–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Length 8–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iii
Page 6

Table of Contents
f
Hand-Held Scanner with RS-232 Option
Code 128 8–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Length 8–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Length 8–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Codabar 8–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmit Stop/Start Characters 8–14. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Length 8–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Length 8–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial
Commands
ications
Speci
Chapter 9
Chapter Objectives 9–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Command Format 9–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Scanning Interaction 9–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ACK/NAK Protocol 9–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Standby and Serial Commands 9–4. . . . . . . . . .
Communication Parameter Changes 9–4. . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 10
Appendix A Bar Code Test Symbols
Appendix B Digit Selection Symbols
Appendix C Autosense Mode
Appendix D Interface Cable Pinouts
Appendix E Maintenance
Appendix F Scanner Commands
Glossary
iv
Index
Page 7

3.1
.
.
.
.
.A
.A
.A7.B9.A
4
4
4
C
2
2.B
3
3.B
4.A
7
Table of Contents
Hand-Held Scanner with RS-232 Option
Figures
Scanning Ranges 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
2
3
1
System Connections 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing Interface Cable 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing Interface Cable 4–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Autostand C–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tables
Interface Cables 2–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanner Accessories 2–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LED Indicators 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scanning Ranges: Standard/Long Range Scanner 3–4
Scanner Default Settings 4–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Code Identifier Characters 7–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hexadecimal Conversion Table 7–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Programming Command Examples 9–2. . . . . . .
v
Page 8

Chapter
I
Using this Manual
1
A–B
Chapter Objectives
Contents of Package
ntended
Audience
This chapter gives an overview of the manual
including:
• Contents of Package
• Intended Audience
• Overview of Manual
• Warnings and Cautions
• Related Publications
You should receive the following items when
ordering the Catalog No. 2755-G3-D or
2755-G6-D Scanner:
• Scanner
• Scanner Holder
• User Manual
No special knowledge is required to read this manual
or use the scanner. However, this manual does not
show you how to generate an application program on
the host computer to receive the scanned data.
1–1
Page 9
Chapter 1
Using this Manual
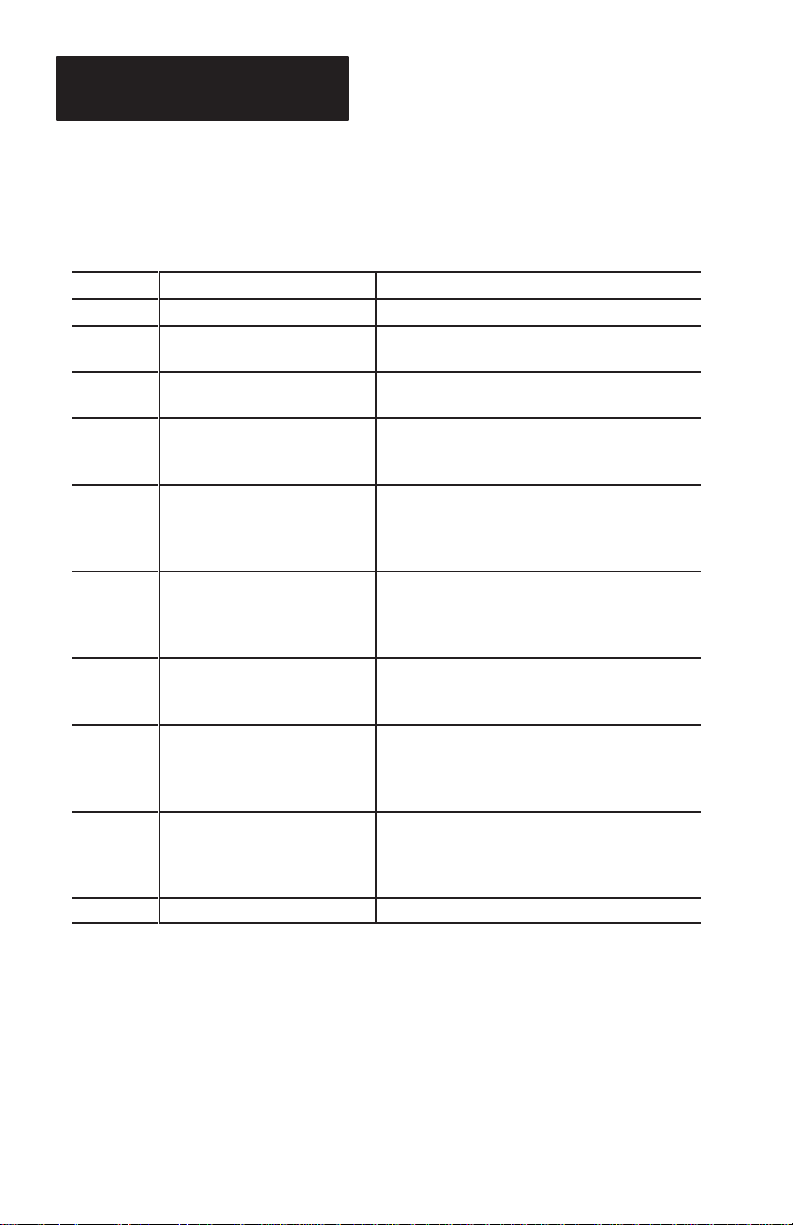
Overview of Manual
This manual shows how to set up and use the scanner
with an RS-232 serial device for non-contact scan-
ning applications. The contents of each chapter are:
Chapter Title Purpose
1 Using this Manual Provides an overview of this manual.
2 Overview of Scanner
3 Using the Scanner
4 Setup Instructions
5
6
7
8 Symbology Parameters
9 Serial Commands
10 Specifications Details specifications of the scanners.
Communication Parameters
General
Operating Parameters
Serial
Message
Format Parameters
Gives an overview of scanner functions, operating modes, and scanner setup parameters.
Provides basic instructions on how to use the
scanner for non-contact scanning.
Shows how to connect the scanner to the
serial host device and how to select scanner
operating parameters.
Covers parameters specific to the operation of
the scanner including beeper, power consumption, and capture count. Parameters are
selected by scanning bar code labels.
Covers parameters that control serial
communications between the scanner and the
host device. Parameters are selected by
scanning bar codes.
Covers parameters that control the format of
messages transmitted to the host. Parameters
are selected by scanning bar codes.
Covers parameters that enable bar code
symbologies the scanner is capable of reading. Symbologies are disabled or enabled by
scanning bar codes.
Describes serial commands and communications between the scanner and host computer.
It also covers precautions when operating in
serial communication mode.
1–2
Page 10
Chapter 1
W
R
Using this Manual
arning and
Caution Symbols
elated
Publications
This manual contains the following caution and
warning symbols.
CAUTION:
A laser caution symbol that appears
where laser light is present.
WARNING
A warning symbol means people might
!
be injured if procedures are not followed.
CAUTION
A caution symbol is used when equip-
!
ment may be damaged if procedures are
not followed.
Below is a list of related publications you may need
to refer to when using the scanners.
• Publication No. 2755-921
Bar Code Basics
Describes bar code symbologies, equipment, and
typical applications.
• Publication No. 2755-2.44
Product Data for
Visible Laser Diode Hand-Held Scanners
1–3
Page 11

Chapter
F
2
Overview of Scanner
A–B
Chapter Objectives
unction
of Scanner
This chapter gives an overview of the scanner
including:
• Function of Scanner
• Operating Modes
• Scanner Setup Parameters
• Serial Commands
• Accessories
The scanner is capable of scanning, decoding, and
transmitting bar code data to devices equipped with
RS-232 serial communication ports, including
personal computers and terminals.
You configure the scanner for serial communications
by modifying the built-in setup parameters of the
scanner. Parameters are selected based on the
requirements of the host device and the types of bar
codes used in your application.
The scanner is easily configured by scanning the
appropriate bar code labels in Chapters 4 through 8 of
this manual. When a configuration label is scanned,
the scanner sends a 1 or 2 line acknowledgement
message to your terminal display.
Important: It is your responsibility to provide the
application program on the host device that will
receive and store the data.
2–1
Page 12

Chapter 2
g
Overview of Scanner
Operatin
Modes
The scanner functions in one of two operating modes:
Hand-Held mode or Autosense mode.
Hand-Held Mode
In hand-held mode, you hold the scanner in your
hand and press the trigger every time you want to
scan a bar code symbol.
Chapter 3 provides details on using the scanner in
hand-held mode.
Autosense Mode
In this mode the scanner operates in an optional
Autostand (Catalog No. 2755-NS2) for hands-free
operation. The scanner uses a low level laser beam as
an internal object sensor.
When the scanner is placed in the stand it becomes
immediately active for reading any bar code label
presented to it. The scanner is triggered when the
scan beam path (between the reflector on the stand
and the scanner) is broken.
You also have the option of removing the scanner
from the stand and using it as a conventional
hand-held scanner. The low level beam will not
interfere with hand-held use of the scanner.
2–2
When replaced in the stand the scanner reverts
automatically to the Autosense mode.
Note: Autosense mode can also be set up using a
PHOTOSWITCH reflector. See Accessories.
Page 13

Chapter 2
Overview of Scanner
Setup Parameters
The built-in setup parameters of the scanner fall into
four general categories:
• General Setup
• Serial Communication
• Message Format
• Symbologies
Each category controls parameters that relate to
specific functions of scanner operations or
communications with the host device.
General Setup Parameters
General setup parameters are basic to the operation
of the scanner. These parameters control:
• System Status
• Power Consumption
• Beeper Operation
• Capture Count
• Spotter Beam
• Autosense Mode
• External Trigger
General parameters are set by scanning bar code
labels in Chapter 5.
Serial Communication Parameters
The serial communication parameters define how the
scanner will communicate with the host computer
through its serial interface including:
• Baud Rate
• Serial Data Parameters
• Intercharacter Delay
• Protocol
• Serial Transmit Buffer
Serial Communication parameters are set by scanning
bar code labels in Chapter 6.
2–3
Page 14

Chapter 2
Overview of Scanner
Message Format Parameters
Parameters that control the format of messages
transmitted to the host include:
• Prefix
• Suffix
• Scanner Identifier
• Code Identifier
• Preamble
• Postamble
Message Format parameters are enabled or disabled
by scanning bar codes in Chapter 7.
Symbology Parameters
The symbology parameters enable or disable the
types of bar codes the scanner is capable of reading.
The scanner supports the following symbologies:
2–4
Serial Commands
• Code 39 • UPC
• Interleaved 2 of 5 • EAN/JAN
• Standard 2 of 5 • Code 128
• Codabar
Symbologies are selected based on the requirements
of the application.
You enable or disable symbologies by scanning bar
codes in Chapter 8.
The scanner also supports a set of serial commands
that can be sent from the host to configure scanner
operations and communications between the scanner
and host device.
The serial commands perform the same functions as
scanning the menus of bar code labels. Chapter 9
covers topics related to serial programming.
Page 15
Chapter 2
g
Overview of Scanner
Orderin
a Scanner
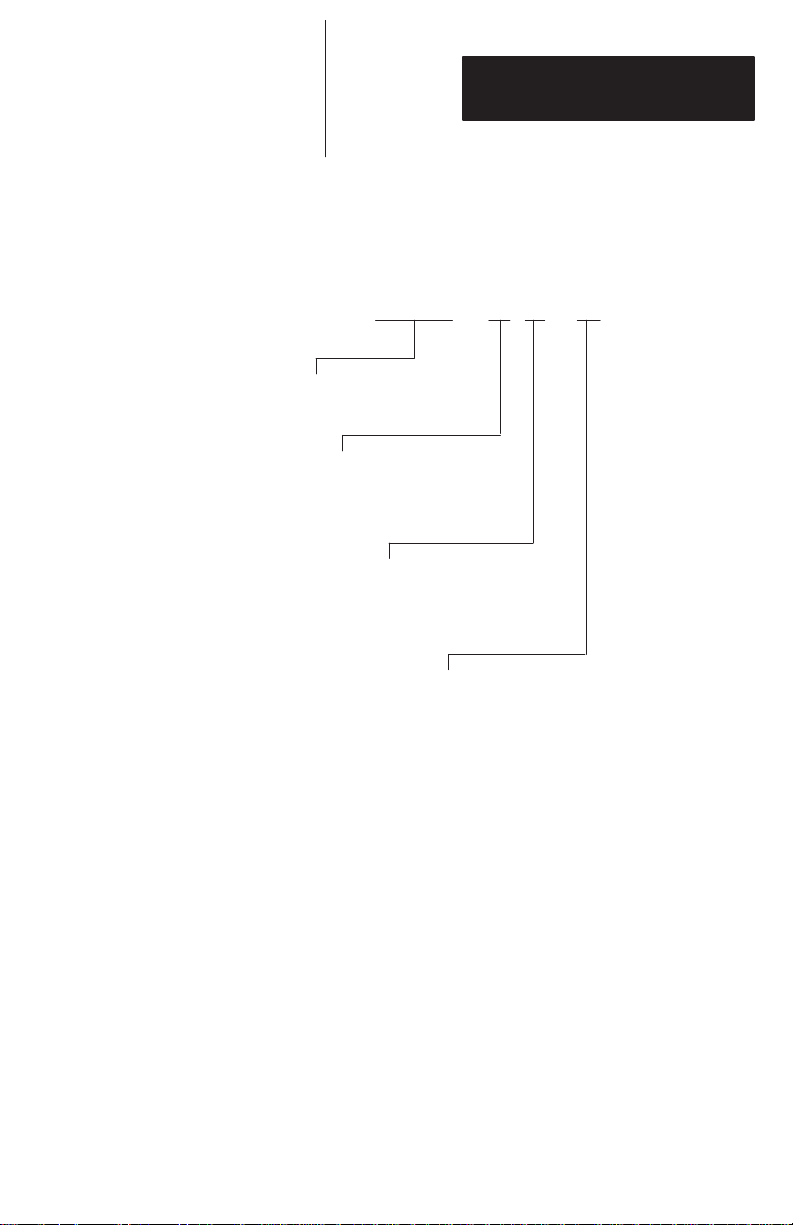
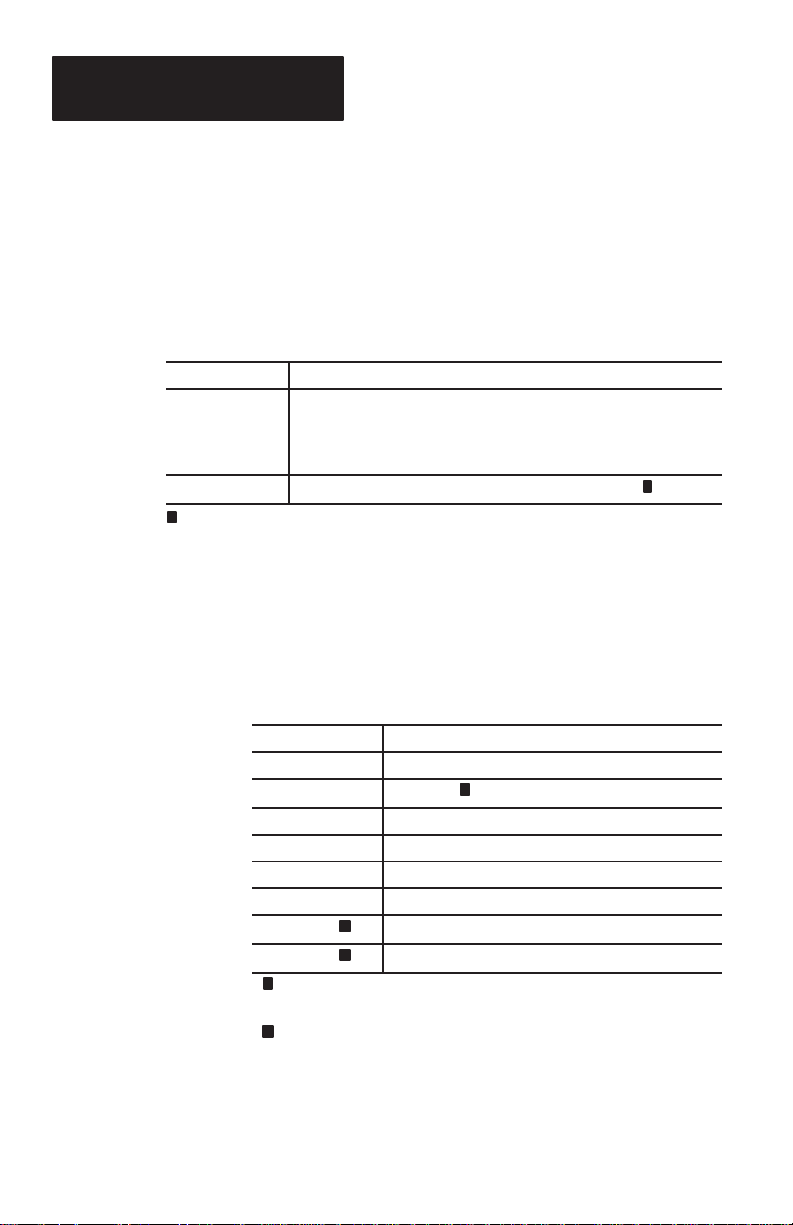
The following figure shows the catalog number
breakdown for ordering a scanner.
2755 - G 3 - D
Bulletin Number
Device TypeDevice Type
G = Gun
Scan Range
3 = Standard Range
6 = Long Range
Decoder Type
D = RS-232
2–5
Page 16
Chapter 2
Overview of Scanner
Scanner Accessories
Catalog No.
2755-NCR1 RS-232 DCE, Female, 8 Foot (2.4 Meter) Coiled Cable
2755-NCR2
1
This cable is compatible with the AUX port on the Single and Dual-Head
Enhanced Bar Code Decoders (Cat. No. 2755-DS1A, -DD1A).
T able 2.A lists the RS-232 interface cables available
for the scanners. Cables are available with different
pinouts to support either DTE or DCE configurations.
Appendix D lists the pinouts for each cable.
Table 2.A
Interface Cables with 25 Pin D-Type Connector
Description
This cable is typically used with IBM PC compatible computers.
You may have to use an adapter with this cable if your
computer has a 9-pin port.
RS-232 DTE, Male, 8 Foot (2.4 Meter) Coiled Cable
1
T able 2.B lists other accessories for the scanners.
Table 2.B
Scanner Accessories
Catalog No.
2755-NS1 Scanner Holder (included with scanner).
2755-NS2
Autostand
2755-GB1 Holster Belt
2755-GH5 Scanner Holster (can function on belt or sling).
2755-PW1 5V Power Supply, 110 VAC, 60 Hz
2755-NT1 Reflective Tape, 2 inch (50.8 mm) square
2
92-39
92-47
1
Reflective tape is supplied with Autostand. Additional reflective
Circular Reflector, 3 inch (76.2 mm) diameter
2
Circular Reflector, 1 1/4 inch (31.8 mm) diameter
tape is available by ordering Catalog No. 2755-NT1.
2
Allen-Bradley PHOTOSWITCH part number.
Description
11
2–6
Page 17
Chapter
Phy
Using the Scanner
3
A–B
Chapter Objectives
sical
Description
This chapter covers some basic topics on the
operation and use of the scanner including:
• Physical Description
• LED Indicators
• Safety Labels
• Scanning Ranges
• Operating Scanner
• Beep
• Operating Tips
• Troubleshooting
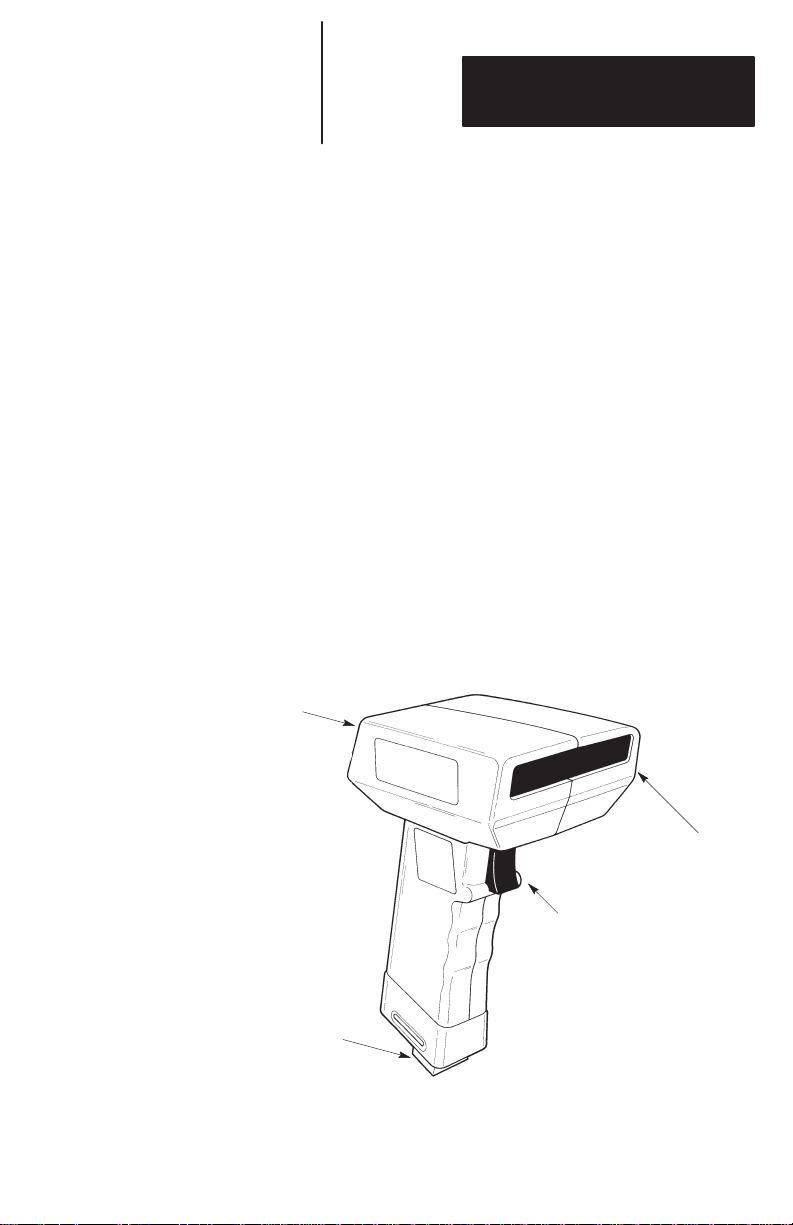
The scanners use a low power visible laser diode light
source for non-contact scanning applications.
The trigger in the handle of the scanner turns on the
light beam. The beam exits the window on the front
of the scanner.
LED Indicators
Scanning Window
Trigger
Cable Connection
Note: If your scanner is enabled for Autosense
mode, the internal object sensor is automatically
triggered when bar codes are presented to it.
3–1
Page 18
Chapter 3
LED
Using the Scanner
Indicators
Light, reflected off the bar code symbols, passes back
through the window and is detected by light sensors.
When a label is read, the laser is automatically turned
off until the next pull of the trigger.
The laser beam looks like a narrow red line of light. It
is actually a tiny spot of light traveling very fast. The
laser spot moves across the bar code symbol at
approximately 35 scans/second. The bar code is
scanned many times in a short period of time.
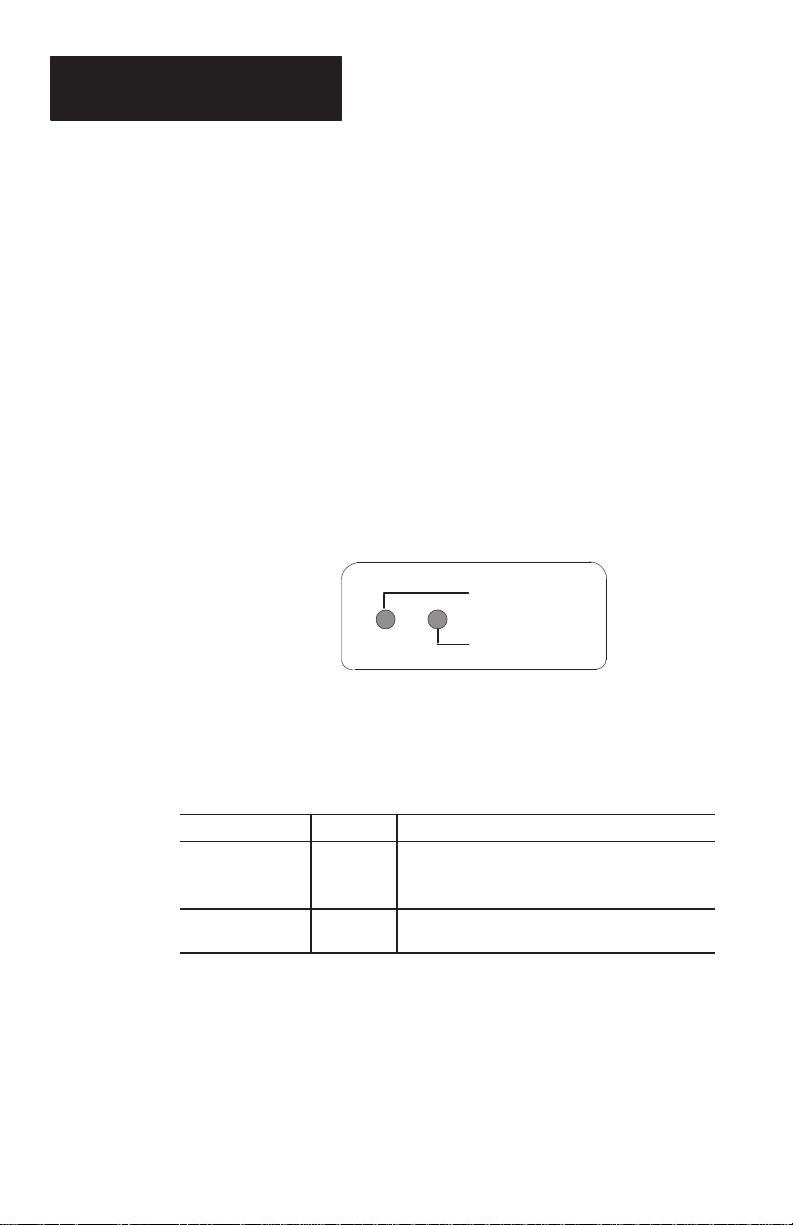
The rear of the scanner has two indicators that
provide a visual indication of scanner operation.
GOOD READ
SCANNING
3–2
T able 3.A defines the color and function of each
LED indicator.
Table 3.A
LED Indicators
LED Label
GOOD READ Green
SCANNING Yellow
Color Function
The GOOD READ light momentarily turns on
(and you will hear a beep) when a bar code
symbol has been successfully decoded.
The SCANNING light turns on when the
device is scanning.
Page 19
Chapter 3
y
Using the Scanner
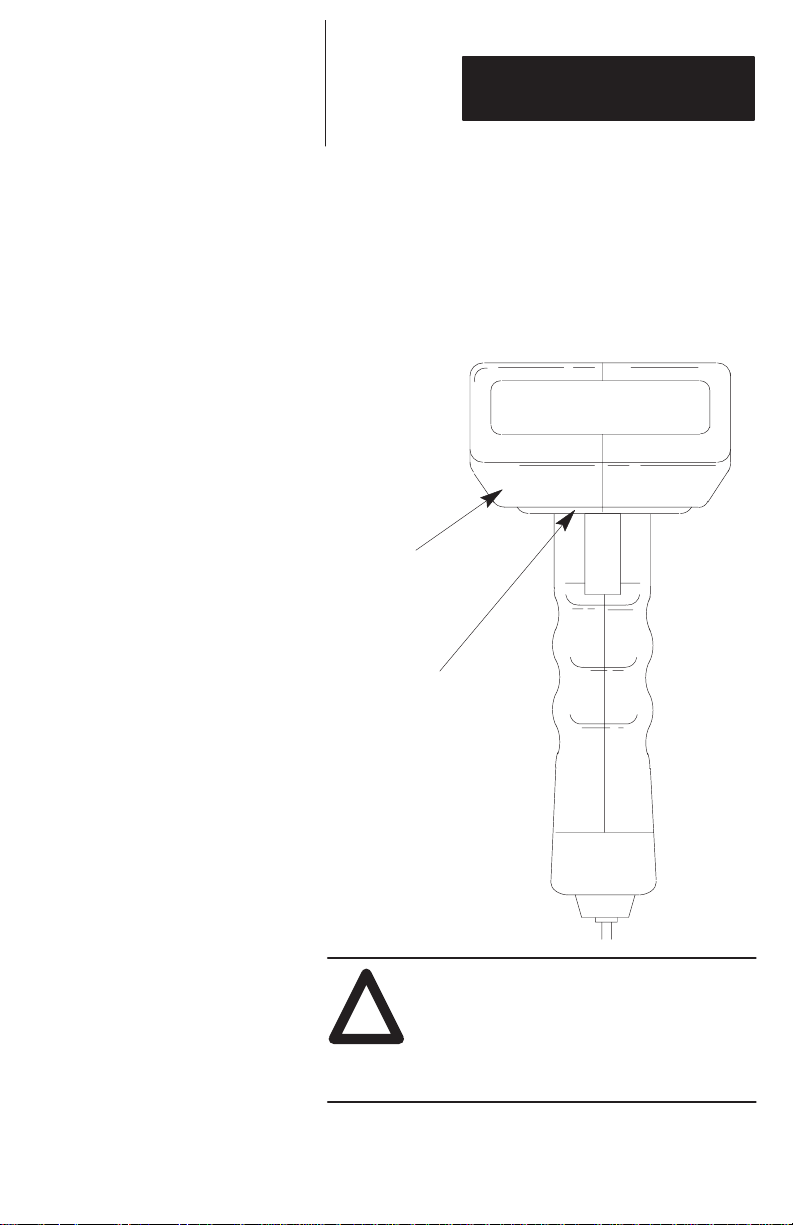
Safet
Labels
The scanners use a low power visible laser diode. As
with any bright light source, such as the sun, you
should avoid staring directly into the beam.
Momentary exposure to a CDRH Class II laser is not
known to be harmful.
The following figure shows the location of all safety
labels as they appear on the scanner.
CAUTION
Use of controls, adjustments, or perform-
!
ance of procedures other than those
specified herein may result in hazardous
visible light exposure.
3–3
Page 20
Chapter 3
g
Using the Scanner
Scannin
Ranges
The scanners can read bar code labels at various
distances depending on the bar code width (width of
narrowest element in bar code, either bar or space).
T able 3.B defines the scanning ranges for both the
standard and long range scanner. Scanning ranges are
listed for symbols with bar code widths from 6.0 mil
to 55.0 mil (.15 mm to 1.40 mm).
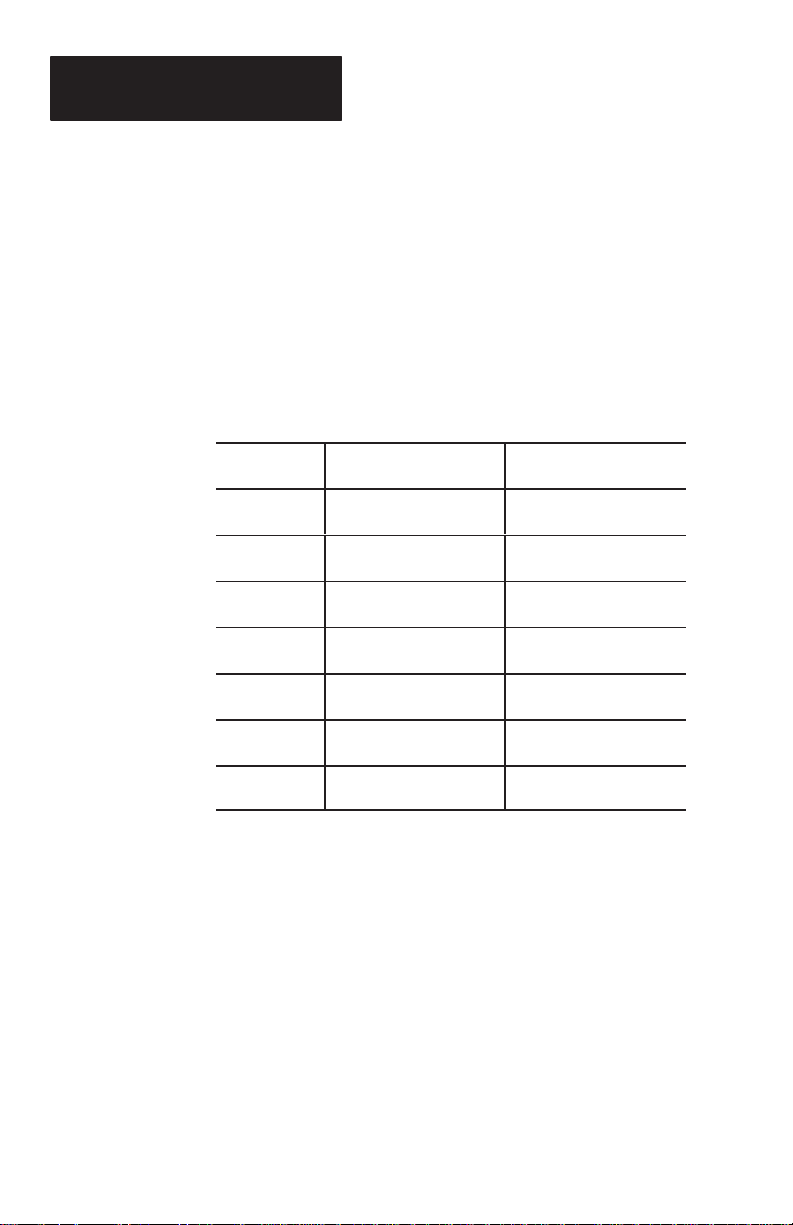
Table 3.B
Scanning Ranges: Standard and Long Range Scanners
Bar Code
Width
6.0 mil
(.15 mm)
7.5 mil
(.19 mm)
10.0 mil
(.25 mm)
15.0 mil
(.38 mm)
20.0 mil
(.51 mm)
40.0 mil
(1.02 mm)
55.0 mil
(1.40 mm)
Standard Range
(2755-G3-D)
3.0 in - 5.0 in
7.6 cm - 12.7 cm
2.5 in - 7.5 in
6.4 cm - 19.0 cm
1.0 in - 10.0 in
2.5 cm - 25.4 cm
1.5 in - 14.0 in
3.8 cm - 35.6 cm
2.5 in - 18.0 in
6.4 cm - 45.7 cm
9.0 in - 25.0 in
22.9 cm - 63.5 cm
12.0 in - 30.0 in
30.5 cm - 76.2 cm
Long Range
(2755-G6-D)
N.A.
N.A.
N.A.
8.0 in - 22 in
20.3 cm - 55.9 cm
12 in - 36 in
30.5 cm - 91.4 cm
23 in - 60 in
58.4 cm - 152.4 cm
23 in - 66 in
58.4 cm - 167.6 cm
3–4
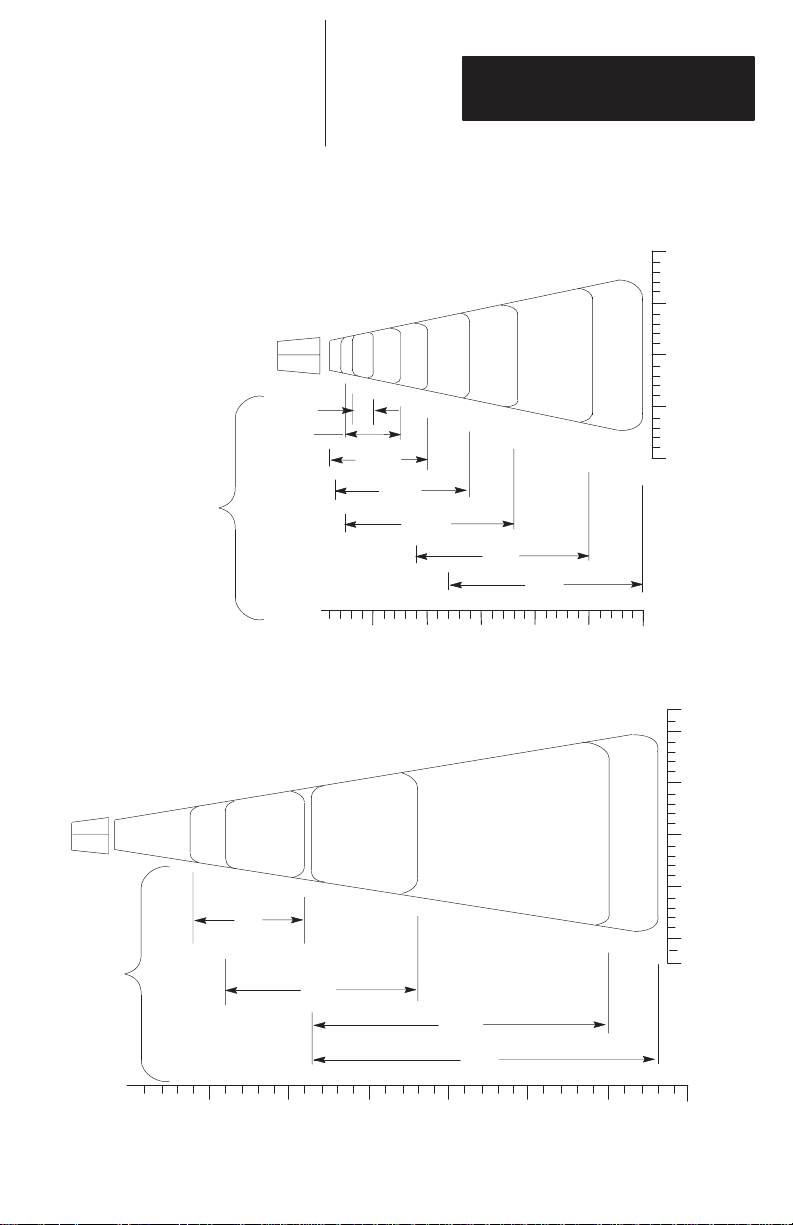
Figure 3.1 illustrates the scanning ranges in graphic
form. The figure shows that the scanning range of
the standard range scanner for a 40.0 mil (1.02 mm)
bar code width is 9.0 - 25.0 inches (22.9 - 63.5 cm).
The scanning range of the long range scanner for the
40.0 mil (1.02 mm) bar code width is 23 - 60 inches
(58.4 - 152.4 cm).
Page 21
Standard Range Scanner
Catalog No. 2755-G3-D
Narrow
Bar Width
Scanner
0.006 in
(0.15mm)
0.0075 in
(0.19mm)
inches
centimeters
0
Figure 3.1
Scanning Ranges
0.010 in
(0.25mm)
0.015 in
(0.38mm)
0.020 in
(0.51mm)
10 20 30
5
25.4 50.8 76.2
12.7
Chapter 3
Using the Scanner
0.040 in
(1.02 mm)
(1.40 mm)
15
38.1
Depth of Field
0.055 in
63.5
10
5
Width
of
0
Scanning
Beam
(inches)
5
10
25
Long Range Scanner
Catalog No. 2755-G6-D
Scanner
Narrow
Bar Width
0
inches
centimeters
15.0 mil
(0.38 mm)
20.0 mil
(0.51mm)
40.0 mil
(1.02 mm)
55.0 mil
(1.40 mm)
25.4 50.8 76.2 101.6 127.0
2010
Depth of Field
10
5
Width
of
0
Scanning
Beam
(inches)
5
10
504030
60 70
152.4 177.8
3–5
Page 22
Chapter 3
g
Using the Scanner
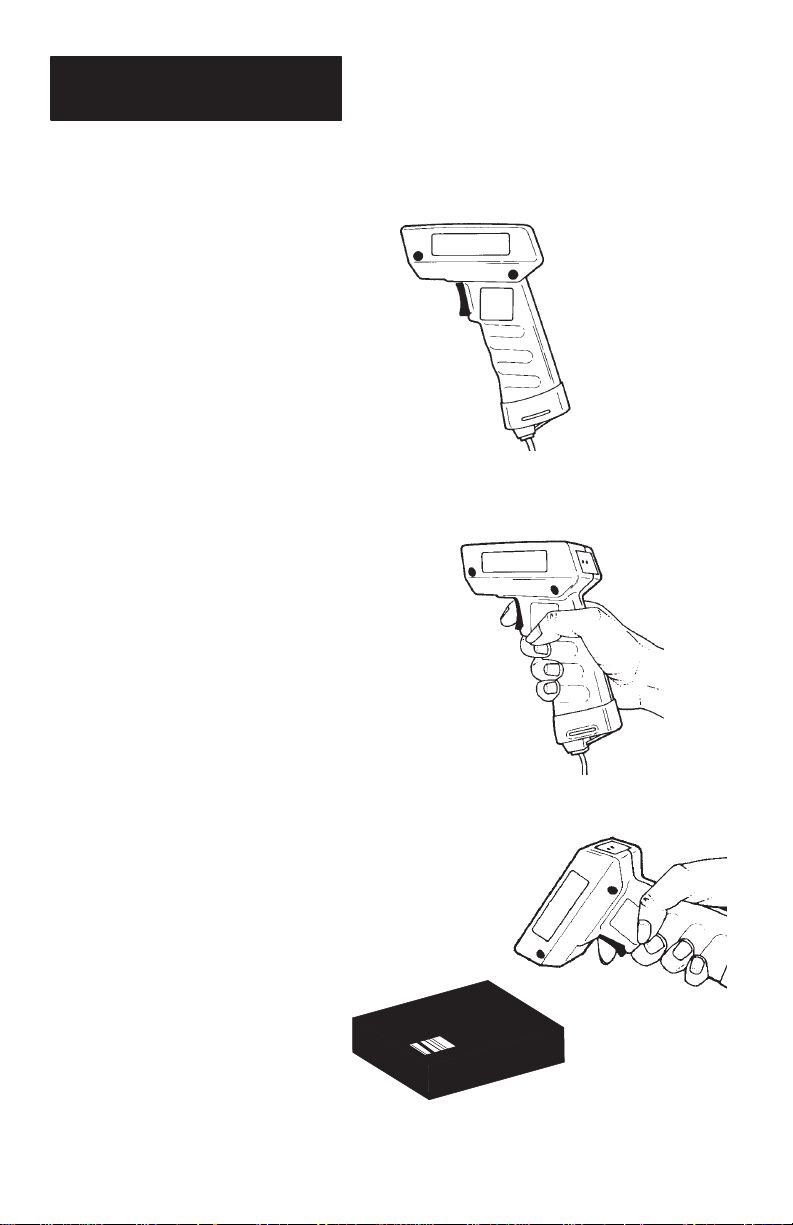
Operatin
Follow these basic steps to operate scanner.
Scanner
1. Check
Before using the scanner, check
all cable connections to make
sure they are secure.
Chapter 4 defines connections
between scanner, power supply,
and serial communication device.
2. Test
Aim the scanner at the work
surface and press the trigger.
You should see the red beam on
the work surface, and the SCANNING indicator on the back of
the unit should be on.
2. Scan
Aim the scanner at the bar code and
press the trigger. Adjust the scanner
position so the beam is centered on the
bar code and overlaps it on both sides.
When the scanner has read the symbol:
• You will hear a beep and/or ...
• The GOOD READ indicator
will turn on momentarily.
• The red scan beam will turn off.
If you fail to scan, see the Trouble-
shooting section.
3–6
Page 23
Chapter 3
B
g T
RIGHT
Using the Scanner
eep
Operatin
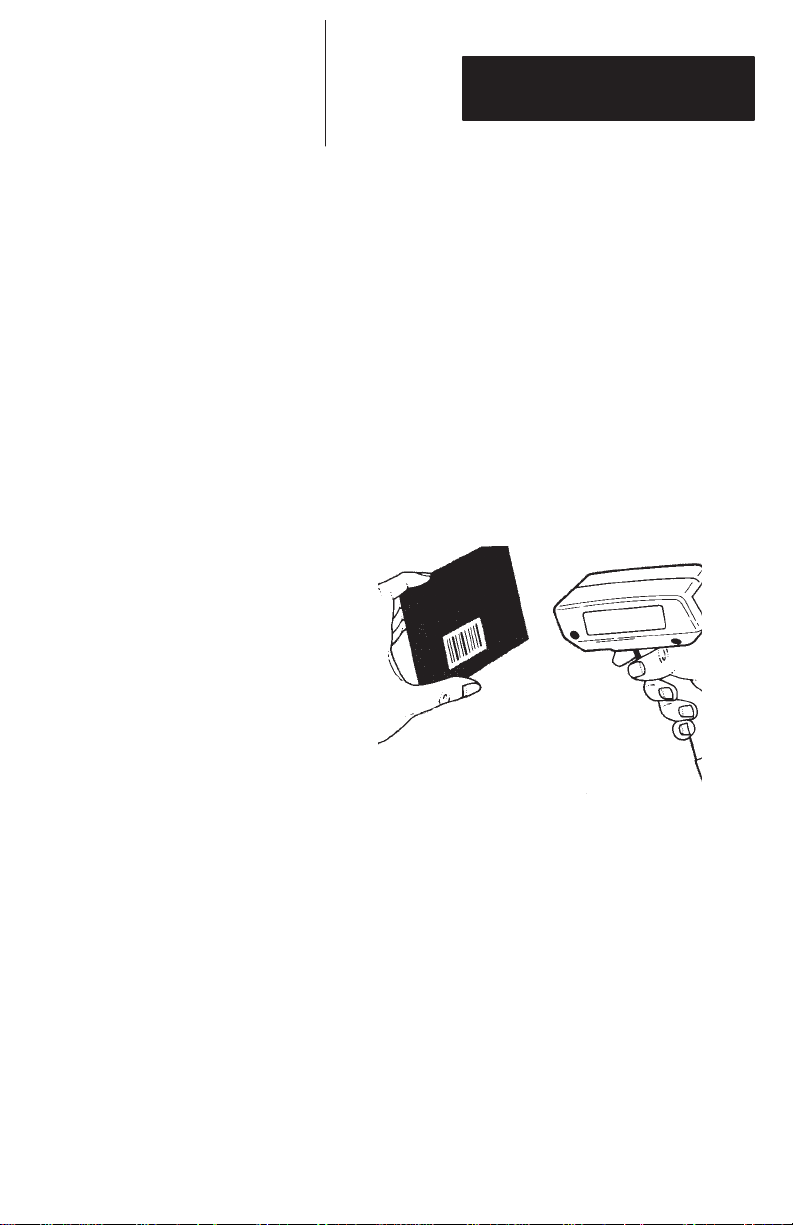
ips
When scanning a bar code symbol, listen for one
short, high tone. It means the bar code has been
decoded successfully.
A low-high-medium sequence of beeps on power up
means the scanner has been configured in a
continuous power mode for operation with serial
communication devices.
Hold at an Angle
Do not hold the scanner directly over the bar code. In
this position light can reflect back into the scanner
and prevent decoding. Angle the scanner slightly.
Scan the Entire Symbol
• Move the scanner so the beam crosses every bar
and space on the symbol.
• The larger the symbol the farther away you should
hold the scanner.
RIGHT
• Hold the scanner closer for symbols with bars that
are close together.
• If you have difficulty reading a label hold the
scanner beyond the recommended range in T able
3.B and then move the scanner closer.
WRONG
3–7
Page 24

Chapter 3
T
g
Using the Scanner
roubleshootin
This section provides a list of things to check if you
are having problems scanning.
Note: Scanning problems are most often caused
by poor quality bar code symbols. If scanning
problems arise, test your bar code system using
the high quality bar code test symbols supplied in
Appendix A.
• Make sure the scanner is configured to read the
the type of bar codes you are trying to scan.
• Check if the bar code symbol is worn or damaged.
• Verify that you are holding the scanner at an angle.
• Make sure the beam crosses every bar and space
on the symbol.
• Check for loose cable connections.
• Check that there is power to the scanner and serial
communication device.
If you perform these checks and the symbol still does
not scan, contact your Allen-Bradley representative.
3–8
Page 25
Chapter
g
Setup Instructions
4
A–B
Chapter Objectives
Connectin
Scanner to Host
Host
Device
This chapter provides setup instructions including:
• Connecting Scanner to Host
• Scanner Configuration Guidelines
• Scanner Default Settings
• Resetting Factory Defaults
Before configuring parameters of the scanner, you
must connect the scanner to the host device using the
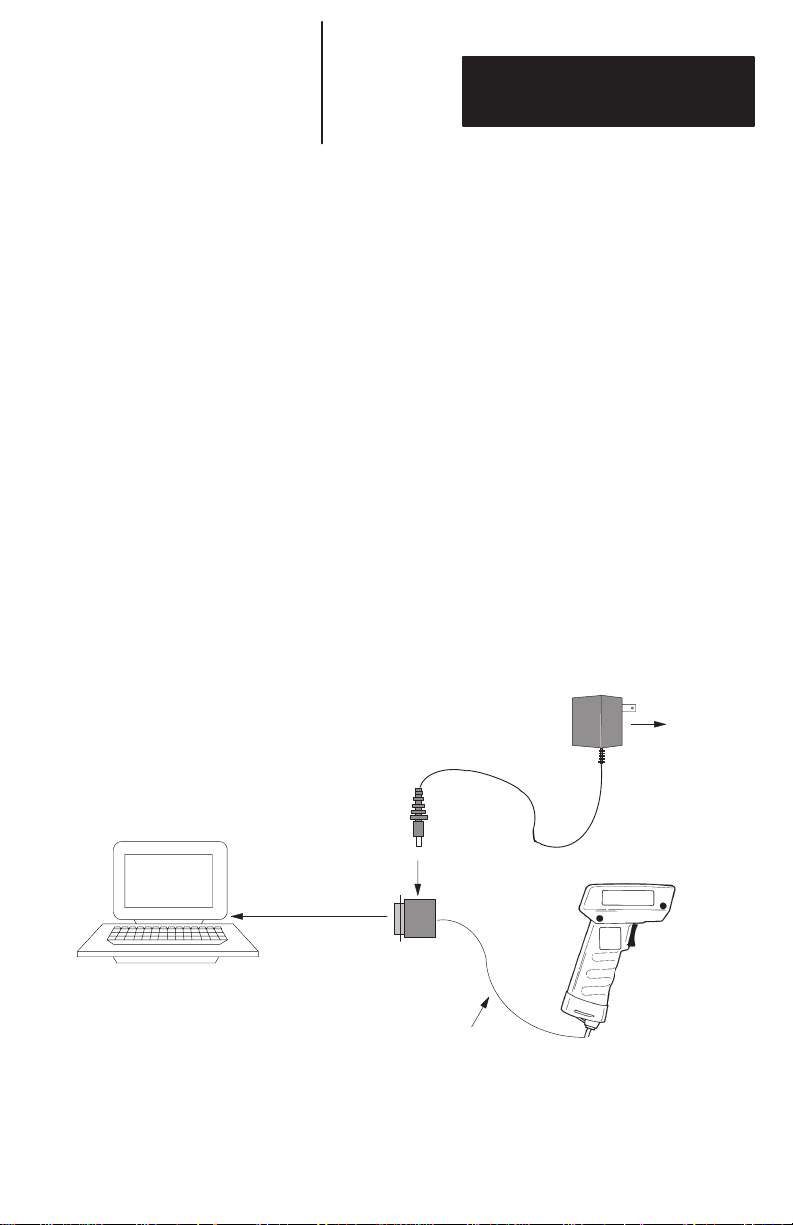
appropriate interface cable and power supply. Figure
4.1 shows the connections.
Figure 4.1
System Connections
Power Supply
Catalog No. 2755-PW1
Scanner
Cat. No. 2755-G3-D or
2755-G6-D
RS-232 Serial Port
Power Supply
Receptacle
AC
Power Source
D-Type
Connector
Cat. No. 2755-NCR1 or -NCR2
4–1
Page 26
Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
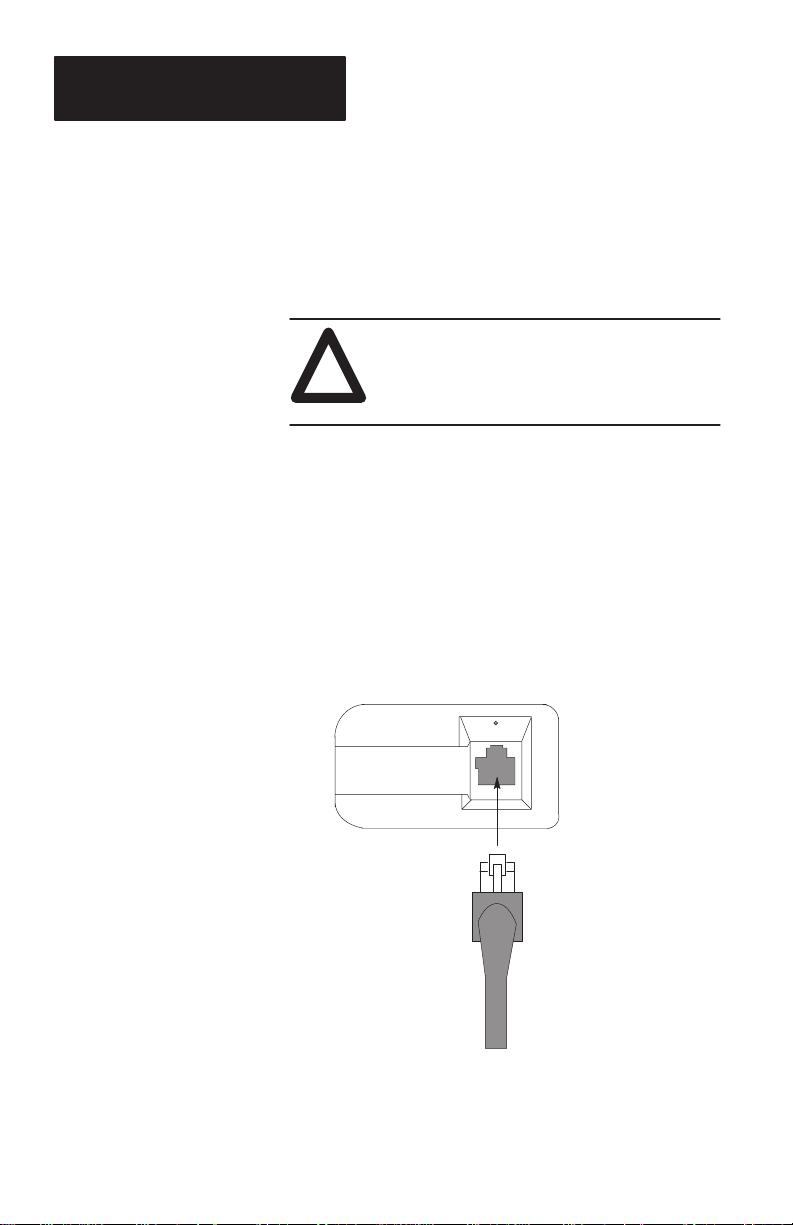
Installing Interface Cable
The interface cable has a modular plug (resembling a
telephone connector) on one end and a 25 pin D-T ype
connector on the other end. The available interface
cables are listed in T able 2.A.
CAUTION:
Do not connect scanner to host until host
!
device is turned off. Failure to do this could
result in damage to the scanner.
T o install the interface cable:
1. Turn power to host computer OFF.
2. Insert the modular plug into the opening at the
bottom of the scanner’s handle (see Figure 4.2).
The modular plug is keyed to insure proper insertion. Press firmly until the plug clicks into place.
4–2
Figure 4.2
Installing Interface Cable
3. Plug the 25 pin D-Type connector into the
RS-232 receiving port of the host device.
Note: You may need an adapter if your
computer has a 9-pin port.
Page 27
Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
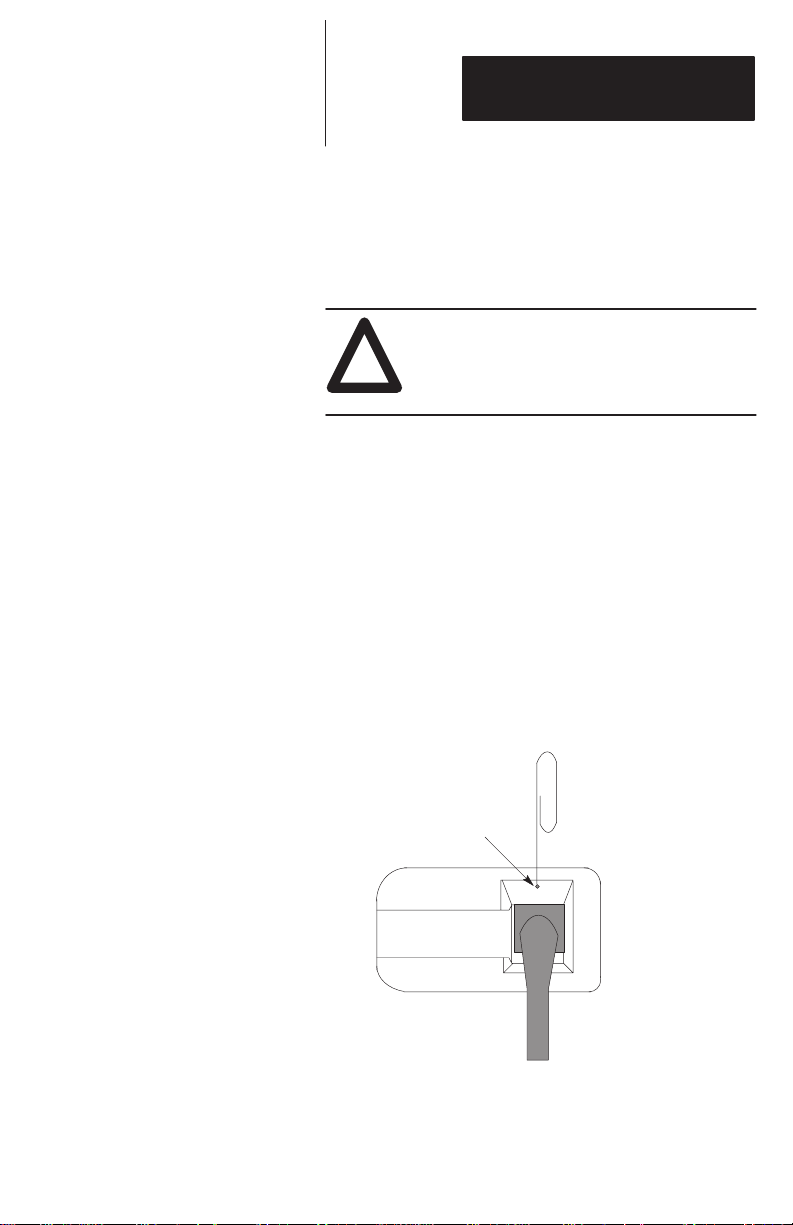
Removing Interface Cable
At some point you may have to replace the interface
cable with another cable.
T o remove the interface cable, follow these steps.
CAUTION:
Do not remove the interface cable until host
!
device is turned off. Failure to do this could
result in damage to the scanner.
1. Turn power to host device off.
2. Disconnect power supply from AC power source.
3. Disconnect scanner from host device.
4. Insert a straightened paper clip into the cable
release hole as shown in Figure 4.3.
5. Press down firmly on the paper clip to release the
retainer and gently pull the connector out of the
scanner.
Figure 4.3
Removing Interface Cable
Cable Release Hole
4–3
Page 28
Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Installing Power Supply
The external power supply (Catalog No. 2755-PW1)
provides power to the scanner. One end connects to a
standard AC receptacle supplying the appropriate
voltage level. The other end plugs into the power receptacle of the 25 pin D-T ype connector.
CAUTION:
The Catalog No. 2755-PW1 Power Supply
!
has the following polarity:
+
+5 V Ground
If using another power supply, the polarity
must be the same.
T o install the power supply:
1. Power to the host device must be turned off.
4–4
CAUTION:
Do not connect power supply until the host
!
device is turned off. Failure to follow this
caution could result in damage to the
scanner or host device.
2. Plug the circular connector into the power supply
receptacle of the 25-pin connector.
3. Plug the power supply into a standard AC
power source.
4. Review all connections. At this point all
components of the system should be connected.
Power on the host device.
5. Aim the scanner down at the work surface and
press the trigger. You should see the red beam
and the SCANNING indicator on the back
of the unit should be on.
Before configuring the scanner, review the next two
sections of this chapter.
Page 29

Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Scanner Configuration Guidelines
Configuration is the process of enabling or disabling
scanner operating parameters. The host system and
the types of bar codes that will be encountered will
determine which parameters should be enabled
or disabled.
Follow three basic steps when selecting parameters:
1. Review the rest of this manual to familiarize
yourself with each group of scanner parameters.
2. Review the requirements of your host system and
application. This will enable you to determine if
the factory defaults must be changed.
3. Enable or disable the relevant parameters by
scanning the bar codes in Chapters 5 through 8.
The section that follows describes this process.
All configuration bar code labels in this manual
are Code 128, Character Set B.
Scanning Menu Labels
The scanner does not have a distinct configuration
mode. Instead, it automatically recognizes and reacts
to labels you scan. You do not scan a label to enter
or exit configuration mode.
Most parameters are set by scanning one label. For
example, assume that to be compatible with your host
system, the scanner’s baud rate setting must be
changed from its default value of 9600 to 2400 baud.
T o make this change, locate the baud rate bar code
menu in Chapter 5 and scan the label to the left of
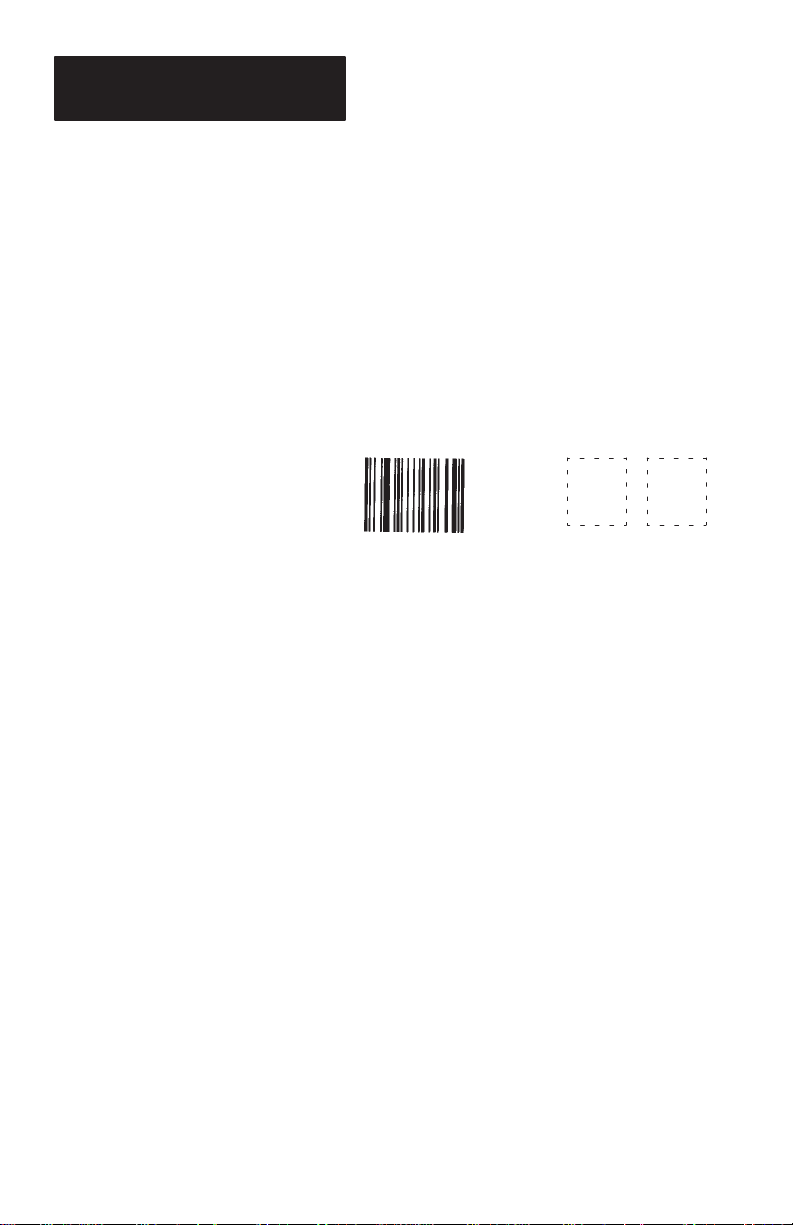
2400 Baud. The correct label is shown below.
DD
A successful scan is indicated by two short-high
beeps. An unsuccessful scan produces no beeps and
requires you to rescan the bar code.
Most parameters are modified in this way. When you
are finished with modifications you can resume
normal bar code scanning.
2400 Baud
4–5
Page 30
Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Note: When enabling or disabling a parameter, be
sure the scanner beam illuminates only one symbol at
a time. The layout of this manual minimizes the
accidental scanning of multiple labels.
Some parameters require that you scan multiple
labels to modify a setting. An example is the
Intercharacter Delay parameter. To set the
intercharacter delay to 5 milliseconds (msec):
1. Scan the Intercharacter Delay (GB) label and listen
for one short beep.
GB
+
Intercharacter Delay=xx msec
The dotted boxes to the right of the label indicate
that you must scan two additional labels; one for
the digit 0 and the second for the digit 5.
2. After the beep, scan the bar code beside 0 in
Appendix B, and listen for one short-high beep.
3. Scan the bar code beside 5 in Appendix B and
listen for two short beeps. The two beeps indicate
that you scanned the last parameter argument.
If you scan the Intercharacter Delay (GB) label and
then scan a normal data label (instead of 0 and 5), a
normal tone is emitted in response to the data label,
and the programming command is ignored. No exit
code is required to resume normal operations.
4–6
Page 31

Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Scanner Default Settings
Parameter
Power Consumption Enable Continuous Full Power
Enable Standby
Beeper Operation Beeper Off
Beeper On; Volume Low
Beeper On; Volume Medium
Beeper On; Volume Loud
Capture Count 1 or 2 1
External Trigger Disable
External Trigger (+)
External Trigger (–)
Spotter Beam Enable or Disable Disable
Autosense Mode Enable or Disable Disable
Parameter
Prefix None, STX, or SOH None
Suffix None, ETX, CR, LF, HT, or
Scanner Identifier Disable or a number (01- 99) Disable
Code Identifier Disable or Enable Disable
Preamble None or 1-4 characters None
Postamble None or 1-4 characters None
T able 4.A lists the factory default settings for each
group of scanner parameters.
Table 4.A
Scanner Default Settings
General Scanner Setup
Options Default
Enable Standby
Beeper On; Volume Loud
Disable
Message Format
Options Default
CR and LF
CR and LF
4–7
Page 32

Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Table 4.A (continued)
Scanner Default Settings
Serial Communication
Parameters
Baud Rate 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600,
19200
Serial Data
Transmission
(Start Bit, Data Bits,
Stop Bits, Parity)
Intercharacter Delay User Defined Delay (in msec) or
Protocol XON/XOFF, CTS, RTS or None None
Serial Transmit Buffer Full Buffering, No Buffering,
7 Data Bits/1Stop Bit/Odd Parity
Space Parity
7 Data Bits/2 Stop Bit/Odd Parity
8 Data Bits/1Stop Bit/Odd Parity
8 Data Bits/2Stop Bit/No Parity
No Intercharacter Delay
One Label Buffering
Options Default
Even Parity
Mark Parity
Even Parity
Mark Parity
Space Parity
Even Parity
Mark Parity
Space Parity
No Parity
9600
7 Data Bits/1Stop Bit/
Space Parity
No Intercharacter Delay
Full Buffering
Code
Code 39 Disable Code 39
4–8
Symbologies
Options Default
Enable Standard Code 39
Enable Full ASCII Code 39
Enable or Disable Modulo 43
Check Character
Enable or Disable Transmission
of Start/Stop Characters
Minimum Label Length 1
Maximum Label Length 32
Enable Standard Code 39
Disable
Disable
Page 33

Chapter 4
Setup Instructions
Table 4.A (continued)
Scanner Default Settings
Symbologies
Code
UPC (A and E) Disable UPC (A and E)
Enable with 2 or 5 Digit Supplements
Enable without 2 or 5 Digit Supplements
Enable or Disable Expanded UPC-E Disable
Enable or Disable Transmission
of Number System Digit
Enable or Disable Transmission
of Check Digit
Enable/Disable UPC to EAN Translation Disable
EAN/JAN (8 or 13 digit) Disable EAN/JAN (8 or 13 digit)
Enable with 2 or 5 Digit Supplements
Enable without 2 or 5 Digit Supplements
Enable or Disable Transmission
Number System Digit
Enable or Disable Transmission
of Check Digit
Interleaved 2 of 5 Disable Interleaved 2 of 5
Enable without Check Digit
Enable with Check Digit
Minimum Label Length 2
Maximum Label Length 32
Standard 2 of 5 Enable or Disable Standard Code 2 of 5 Disable
Minimum Label Length 4
Maximum Label Length 32
Code 128 Enable or Disable Code 128 Enable
Minimum Label Length 1
Maximum Label Length 32
Codabar Enable or Disable Codabar Disable
Enable or Disable Transmission
Start/Stop Characters
Minimum Label Length 1
Maximum Label Length 32
Options Default
Enable without
2 or 5
Digit Supplements
Enable
Enable
Disable
Enable
Enable
Disable
Disable
4–9
Page 34

Chapter 4
R
g
Setup Instructions
esettin
Factory Defaults
T o reset the scanner to the factory default settings,
scan label ZA.
ZA
Note: Scanning this label produces a bi-level tone.
Reset to
Factory Defaults
4–10
Page 35

Chapter
y
m
5
General Setup Parameters
A–B
Chapter Objectives
S
ste
Status
This chapter describes parameters specific to the
operation of the scanner including:
• System Status
• Power Consumption
• Beeper Operation
• Capture Count
• Spotter Beam
• Autosense Mode
• External Trigger Operation
T o set specific operating parameters, scan the
appropriate bar code labels in each section.
Note: Throughout this chapter, default settings for
parameters are flagged by an asterisk (*).
The labels in this section allow you to examine the
configuration of your system.
T o send a list of currently programmed parameters to
the display device, scan option ZB. A sample display
is shown on the top of the next page.
Note: Scanning ZB may interfere with your terminal
software, depending on your application.
ZB
Display Configuration
5–1
Page 36

Chapter 5
General Setup Parameters
Display Configuration Example (ZB Command)
Model 5312
Power
Data Bits
Char Delay
Scanner ID
Preamble
Code ID Char
Serial Buffr
*
Armed
ASCII
*
Addendum
Xmit S/S
Check Ch
Send Sys #
Send Ck Ch
UPCE Expand
Limits
Redundant Scan=Capture Count, Armed=Enabled, Addendum=Supplements
*
Shaded parameters are not supported in this product.
Standby
8
00
None
None
No
Full
39Parameter
Yes
No
–
No
No
–
–
–
01–32
UPC
Yes
–
No
–
–
Yes
Yes
No
–
Beeper
Parity
Protocol
Prefix
Postamble
Labels
Display Duplex Half
Symbology
EAN
No
–
No
–
–
Yes
Yes
–
–
I 2/5
No
–
–
–
No
–
–
–
02–32
Loud
None
Off
Off
None
Unbuffred
S 2/5
No
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
04–32
128
Yes
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
01–32
V ersion
Baud Rate
Stop Bits
RTS
Suffix
*
Redundant Scan
Label Delay
Auto Label Bfr Off
Codabr
No
–
–
No
–
–
–
–
01–32
Scan option ZC to send the program version number
followed by carriage return-line feed (CR-LF) to the
display device. The version number is sent in the
form ##.## (1.00, for example).
2.51
9600
1
Rcv Rdy+
CR/LF
No
00
5–2
ZC Transmit Version Number
Scan option @C to send an identification code which
verifies the specific program type of the scanner to
the display device.
@C Transmit Program ID
Note: Options ZC and @C are used for
troubleshooting to identify the scanner.
Page 37

Chapter 5
P
General Setup Parameters
ower
Consumption
You can select one of two power consumption modes
for the scanner. Option @A supplies full power to the
scanner at all times. Option @B allows the scanner to
revert to standby mode after a successful read. This
mode is a power conservation feature whereby the
scanner uses extremely low power (microwatts).
T o supply full power to the scanner at all times, scan
label @A.
@A
Enable Continuous
Full Power
Note: The scanner automatically uses full power
when configured to operate in Autosense mode.
T o allow the scanner to revert to standby mode after a
successful read, scan label @B.
@B
Enable
Standby Power *
5–3
Page 38

Chapter 5
B
General Setup Parameters
eeper
Operation
T o disable or set the volume of the beeper, scan the
appropriate option below.
AA
AB
AC
AD
Beeper Off
Beeper On;
Volume Low
Beeper On;
Volume Medium
Beeper On;
Volume Loud *
5–4
Page 39

Chapter 5
General Setup Parameters
Capture Count
Capture Count determines the number of successful,
identical decodes that must occur for a valid read.
You can use the capture count to enhance the security
of the bar code reader.
Option BC sets the capture count to 1 which requires
one successful decode.
BC
Scan option BD to set the capture count to 2. Two
identical decodes must occur for a valid read.
BD Capture Count = 2
Because the laser scans a label many times a second,
you will notice little or no change in the speed of the
decode.
Capture Count = 1 *
5–5
Page 40

Chapter 5
m
General Setup Parameters
Spotter Bea
You can enable the scanner to use a spotter beam
which helps when aiming the scanner. Each time the
scanner is triggered it generates a bright laser spot for
a fixed duration, after which the scanner beam is
activated.
The spotter beam is recommended for long range
applications.
Scanning label NP disables the spotter beam. Hold
the trigger for two seconds after scanning.
NP
Disable
Spotter Beam *
T o enable the spotter beam, scan label NQ, then scan a
digit from 0 – 9 (Appendix B), holding the trigger
for two seconds after scanning the digit. Each
digit enables the spotter beam for a specified duration
as shown in the table below. For example, to enable
the spotter beam for 200 milliseconds, scan the NQ
label, then scan code 3 in Appendix B.
NQ
+
5–6
Enable Spotter Beam=xx msec
This Digit Enables Spotter Beam for:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Note: Spotter beam and Autosense mode are
mutually exclusive parameters. Only one of these
parameters can be enabled at a time.
Page 41

Chapter 5
A
General Setup Parameters
utosense Mode
In Autosense mode, the scanner has an internal object
sensor allowing you to operate the scanner in an
optional Autostand (Catalog No. 2755-NS2) for
hands-free operation.
When the scanner is placed in the Autostand it
becomes immediately active for reading any bar code
label presented to it. The scanner is triggered when a
bar code label breaks the scan beam path between the
reflective label on the stand and the scanner.
T o activate Autosense mode, scan the Enable
Autosense (NO) label. You must hold the trigger
down for two seconds after scanning the label.
NO
Enable
Autosense Mode
The scanner will respond by emitting a continuous,
low level, red beam of light.
Note: The scanner is automatically configured to use
full power (not standby power) in Autosense mode.
For details on how to set up the scanner to operate in
the optional Autostand, see Appendix C.
T o deactivate Autosense mode, scan the Disable
Autosense symbol (NN). You must hold the trigger
down for two seconds after scanning the label.
NN
Disable
Autosense Mode *
Note: Spotter Beam and Autosense Mode are
mutually exclusive parameters. Only one of these
parameters can be enabled at a time.
5–7
Page 42

Chapter 5
Ex
General Setup Parameters
ternal Trigger
Operation
External trigger operation enables an external device
to control scanning. External trigger is controlled by
applying an external trigger signal to the CTS
input (refer to Appendix D) with external triggering
enabled. When active, this signal causes scanning to
begin just as if the scanner’s trigger were pressed.
Scanning continues until a label is decoded or the
external signal is deactivated.
Note: CTS protocol cannot be used when external
triggering is enabled.
When a decode occurs, the trigger signal must be
deactivated for a minimum of 50 milliseconds before
another scan can be attempted (tying the trigger
signal active does not cause continuous scanning and
decoding).
When External Trigger (+) is scanned, scanning begins
when a low level input is applied to the CTS input.
Conversely, when External Trigger (–) is scanned,
scanning begins when a high level is applied to CTS.
When CTS is not connected, it is treated as if a low
level is applied.
HA Disable External Trigger *
5–8
HE
HF External Trigger (–)
External Trigger (+)
Page 43

Chapter
6
A–B
Serial Communication Parameters
Chapter Objectives
This chapter covers parameters that control serial
communications between the scanner and the host
device including:
• Baud Rate
• Data Transmission Parameters
• Intercharacter Delay
• Protocol
• Serial Transmit Buffer
Serial communication parameters are selected by
scanning appropriate bar code labels in each section.
Note: Throughout this chapter, default settings for
parameters are flagged by an asterisk (*).
6–1
Page 44

Chapter 6
B
Serial Communication Parameters
aud Rate
The serial communication baud rate selections are
listed below. Your scanner and the serial host
computer must be set at the same baud rate. Scan the
appropriate rate.
DA 300 Baud
DB 600 Baud
DC 1200 Baud
DD 2400 Baud
6–2
DE 4800 Baud
DF 9600 Baud *
DG 19200 Baud
Page 45

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
Serial Data Transmission Parameters
Serial transmission data consists of three or four
different elements depending on the host system
requirements. These elements are:
• Start Bit
• Data Bits (7 or 8)
• Optional Parity Bits
• Stop Bits (1 or 2)
In this manual, these elements are represented
graphically in the following manner:
Start Bit
7 Bits
Word Bits
or 8 Bits
Stop Bits
The Parity bit is used for error detection (e.g., data
altered in transmission), but is not required by all
systems. A parity bit, if required will be in one of the
following four formats:
or
Odd
Even
Mark
Space O
=
=
=
=
O
E
1
6–3
Page 46

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
ED
EC
EB
7 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Parity Check
If your system requires a word length of 7 Data bits, a
single Stop bit, and Parity check, scan the appropriate
label below.
7 Bits
O
7 Bits
E
7 Bits
1
6–4
EA *
7 Bits
O
Page 47

EH
EG
EF
Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
7 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, Parity Check
If your system requires a word length of 7 Data bits,
2 Stop bits, and Parity check, scan the appropriate
label below.
7 Bits
O
7 Bits
E
7 Bits
1
EE
EM
7 Bits
O
8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, No Parity Check
If your system requires a word length of 8 Data bits,
1 Stop bit, and no Parity check, scan the label below.
8 Bits
6–5
Page 48

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
EL
EK
EJ
8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Parity Check
If your system requires a word length of 8 Data bits,
1 Stop bit, and Parity check, scan the appropriate
label below.
8 Bits
O
8 Bits
E
8 Bits
1
6–6
EI
EN
8 Bits
O
8 Data Bits and 2 Stop Bits
If your system requires a word length of 8 Data bits
and 2 Stop bits, scan the label below. Parity check is
not possible with this combination of data bits and
stop bits.
8 Bits
Page 49

Chapter 6
P
Serial Communication Parameters
rotocol
Protocol controls data flow between your scanner and
the serial host computer. The protocol options are:
None, XON/XOFF, CTS, RTS.
XON/XOFF
When selecting XON/XOFF protocol, the scanner
recognizes the ASCII XON/XOFF characters. The
host may then stop transmission with XOFF and
resume with XON.
Controlled data flow is achieved between devices
when the receiving device sends ASCII XON/XOFF
codes to the transmitting device. When the receiving
device is unable to accept data, it sends an XOFF
code to inform the host to temporarily suspend data
transmission. When the receiving device catches up,
it sends an XON code to inform the host that it is
again ready to accept data.
XON/XOFF protocol does not require additional
hardware for implementation; only transmit, receive,
and signal ground are required.
CTS Protocol
Like XON/XOFF protocol, CTS protocol is a
mechanism used to control data flow out. The CTS
input is used to inform the scanner that the host
terminal is ready to accept scanned data.
When CTS (+) protocol is selected, the scanner
waits for a high level on its CTS input before
transmitting data.
When CTS(–) is selected, the signal polarities are
reversed and a low level indicates data may be
transmitted. The CTS protocol may be programmed
independently of the RTS protocol, however the
signal polarities must be the same. You may not
select CTS(+) and RTS(–).
Note: CTS protocol cannot be used if external
triggering is enabled. See page 5–8 for details.
6–7
Page 50

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
RTS Protocol
The RTS output from the scanner may be programmed to operate in one of three different modes.
1. In the default mode, RTS signals when the
scanner is ready to receive commands or data.
2. RTS is in a fixed state.
3. RTS signals when the scanner has data to
transmit.
The RTS modes are independent of the CTS protocol.
However, you must select the same active state for
RTS as for CTS. You may not select CTS(–) and
RTS fixed high. If CTS(–) is selected, then the active
state for RTS will be low.
Scan the appropriate protocol option.
CTS Protocol=None *
HA
RTS high indicates
scanner ready to
receive data
6–8
HB Protocol=XON/XOFF
HC
Protocol=CTS(+)
HD Protocol=CTS(–)
Page 51

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
HG
RTS always high
HH RTS always low
HI
HJ
HK
RTS high indicates
scanner has data
to transmit
RTS low indicates
scanner has data
to transmit
RTS low indicates
scanner ready to
to receive data
6–9
Page 52

Chapter 6
I
Serial Communication Parameters
ntercharacter
Delay
Certain terminals and computers require an
intercharacter delay to simulate the effects of
keystroke delays. Selecting an intercharacter delay
causes the characters to be sent at the slower rate
required by the device to which you are interfacing.
Scanning label GA disables intercharacter delay .
GA
T o set Intercharacter Delay to a value other than zero,
scan label GB, then two separate digits from
Appendix B. The intercharacter delay cannot
exceed 31 milliseconds.
GB
For example, to set the delay to 15 milliseconds, scan
the GB label, then scan codes 1 and 5 in Appendix B.
+
Intercharacter Delay=xx msec
No Intercharacter
Delay *
6–10
Page 53

Chapter 6
Serial Communication Parameters
Serial Transmit Buffer
The scanner supports three levels of serial buffering:
Full Buffering, No Buffering, One Label Buffering.
Full Buffering
With Full Buffering (the default) selected, the scanner
will place all scanned labels into a 64 byte serial
transmit buffer if the host is unavailable to receive
data. This allows you to continue scanning even
though the previous label may not have been
transmitted yet. Scanning will continue normally
until the buffer is full, then scanning will stop.
Scanning will continue when enough space is
available for the current message.
Note: The buffer holds other message parameters, so
you must consider the total message length (including
label) to determine how many labels can be buffered.
See Chapter 7, Message Format Parameters.
No Buffering
When No Buffering is selected, scanning is stopped
until the current label is completely transmitted.
One Label Buffering
When One Label Buffering is selected, the scanner
will allow you to scan one more label in addition to
the label already in the transmit buffer.
NE
Full Buffering *
NF No Buffering
NG
One Label Buffering
6–11
Page 54

Chapter
g
7
Message Format Parameters
A–B
Chapter Objectives
Messa
Format
e
Prefix Scanner Identifier Code Identifier Data Postamble SuffixPreamble
This chapter defines parameters that control the
format of transmitted bar code messages including:
• Prefix and Suffix
• Scanner Identifier
• Code Identifier
• Preamble and Postamble
A message transmitted from the scanner upon a
successful decode has the following format:
Some of these message parameters may not be
required or may vary from one host system to
another. You select parameters based on the
requirements of your application and the host system.
T o select message parameters, you scan the
appropriate bar code labels in each section.
Note: Throughout this chapter, default settings for
parameters are flagged by an * (asterisk).
7–1
Page 55

Chapter 7
Prefix
Message Format Parameters
A prefix is a subset of the preamble normally
formatted to some industry standard. It is represented
by a specific ASCII code. An example of a prefix is
the STX (Start of Transmission) code.
Scan the appropriate prefix label.
IA
Prefix=None *
IB Prefix=STX
IC Prefix=SOH
7–2
Page 56

Chapter 7
x
Message Format Parameters
Suffi
A suffix is a subset of the postamble. Like the prefix,
it is normally assigned to a specific ASCII code.
Examples of suffixes are CR (Carriage Return) and
LF (Line Feed).
Scan the suffix appropriate for your application.
MA
Suffix=None
MB Suffix=ETX
MC
Suffix=CR
MD
Suffix=LF
ME Suffix=HT
MF Suffix=CR and LF *
7–3
Page 57

Chapter 7
Message Format Parameters
Scanner Identifier
Scanner ID characters are used to identify individual
scanners when more than one scanner is interfaced
with the host system. Options available are none
(Disabled) or digits 01 through 99.
Scanning label JA disables the scanner identifier.
JA
Disable
Scanner Identifier *
T o enter a scanner ID, scan label JB and then two
separate digits from Appendix B. The ID character
cannot exceed 99.
JB
+
Enable Scanner Identifier
plus two characters
For example, to enter a scanner ID of 01, scan the JB
label, then scan codes 0 and 1 in Appendix B.
7–4
Page 58

Chapter 7
Message Format Parameters
Code Identifier
A single-character code identifier may optionally be
transmitted with a message. This option allows the
host computer to identify the type of bar code
scanned, as well as the encoded information.
Scan option FA to disable the code identifier.
FA
Disable
Code Identifier *
Scan option FB to enable the code identifier.
FB
Enable
Code Identifier
T able 7.A shows the code identifier character
assignments.
Table 7.A
Code Identifier Characters
Symbology
Code 39 a
Interleaved 2 of 5 b
Standard 2 of 5 c
UPC/EAN/JAN d
Code 128 f
Codabar h
Code Identifier
7–5
Page 59

Chapter 7
P
Message Format Parameters
reamble
or Postamble
Preambles and postambles consist of up to four
ASCII characters. Each ASCII character is encoded
as two hexadecimal characters. Use T able 7.B,
Hexadecimal Conversion Table, to look up the
hexadecimal equivalent.
T o use the conversion table:
1. Find each ASCII character in the table and locate
the corresponding bold hexadecimal equivalent
character in the top row and the left column of the
table. For example, the ASCII character ”Q” is
represented by the hexadecimal numbers 5 (top)
and 1 (left).
2. Scan the bar code symbols that correspond to the
hexadecimal equivalent characters. First scan the
bar code symbol that corresponds to the bold hex
character at the top. Then scan the bar code
symbol that corresponds to the bold hex character
at the left.
For example, for the ASCII character ”Q”, first
scan the bar code symbol labeled 5, then scan the
bar code symbol labeled 1. If your preamble or
postamble contains an ”N”, first scan 4 and then E.
3. Repeat this procedure for each ASCII character
you want to enter.
7–6
Note: If you select a preamble or postamble you
must scan four ASCII characters, even if the
preamble or postamble is less than four characters in
length. Do this by scanning null (NUL) characters
for the additional characters.
For example, if your preamble is ”AB” (in ASCII
code), enter A, B, and two null characters by
scanning the hexadecimal characters 4,1 4,2 0,0 0,0.
Because each ASCII character is represented by two
hexadecimal characters, you need eight
scans.
Page 60

Chapter 7
P
P
Message Format Parameters
reamble
ostamble
KB
A preamble is a string of characters that prefixes a
message that is transmitted to the host. The preamble
may be used to identify the scanner that sent the
message. The maximum preamble length is four
ASCII characters.
KA
T o enter a preamble, scan the KB label, then refer to
T able 7.B to enter the four ASCII characters. The
procedure on the previous page explains how to enter
preamble characters.
+
Preamble = 4 ASCII (8 Hex) characters
A postamble is similar to a preamble, except it is
appended to the message which is transmitted to the
host. Its maximum length is four ASCII characters.
Preamble=None*
LA
T o enter a postamble, scan the LB label, then refer to
T able 7.B to enter the four ASCII characters. The
procedure on the previous page explains how to enter
preamble characters.
LB
+
Postamble = 4 ASCII (8 Hex) characters
Postamble=None *
7–7
Page 61

Chapter 7
Message Format Parameters
0
1
2
3
4
5
Table 7.B
Hexadecimal Conversion Table
0 1 2 3
0 NUL DLE SP 0
1 SOH DC1 ! 1
2 STX DC2 ” 2
3 ETX DC3 # 3
4 EOT DC4 $ 4
5 ENQ NAK % 5
6 ACK SYN & 6
7 BEL ETB ’ 7
8 BS CAN ( 8
9 HT EM ) 9
A LF SUB * :
B VT ESC + ;
C FF FS , <
D CR GS – =
E SO RS . >
F SI US / ?
6
7–8
7
Page 62

Table 7.B (continued)
Hexadecimal Conversion Table
4 5 6 7
0 @ P ‘ p
1 A Q a q
2 B R b r
3 C S c s
4 D T d t
5 E U e u
6 F V f v
7 G W g w
8 H X h x
9 I Y i y
A J Z j z
B K [ k {
C L \ l |
D M ] m }
E N ^ n ~
F O _ o DEL
Chapter 7
Message Format Parameters
8
9
A
B
C
D
7–9
E
F
Page 63

Chapter 7
No R
Message Format Parameters
ead Message
When the scanner is triggered, the scan beam is
active until:
1. a label is decoded
2. the trigger is released
3. the scan beam timeout period has elapsed
If the No Read Message is enabled, case 2 and 3 will
cause the scanner to substitute NR (No Read) for the
bar code data in the host message.
Bar code data ”12345” transmitted in host message
Prefix Scanner Identifier Code Identifier 12345 Postamble SuffixPreamble
NR substituted for bar code data in host message
Prefix Scanner Identifier Code Identifier NR Postamble SuffixPreamble
The No Read Message is disabled as the default state.
Scan label NY to enable the No Read Message.
No Read Message disabled
No Read Message enabled
7–10
NY
Enable
No Read Message
Scan label NX to disable the No Read Message.
NX
Disable
No Read Message*
Page 64

Symbologies
L
Chapter
8
A–B
Chapter Objectives
abel Lengths
This chapter shows how to enable bar code symbologies the scanner is capable of reading including:
• Code 39
• UPC-A and UPC-E
(with optional 2 or 5-digit supplements)
• EAN-8 and EAN-13
(with optional 2 or 5-digit supplements)
• Interleaved 2 of 5
• Standard 2 of 5
• Code 128
• Codabar
T o disable or enable specific bar code symbologies,
scan the appropriate bar code labels in each section.
Note: We recommend that you disable all
symbologies not used by your application.
Throughout this chapter, the default symbology
selections are flagged by an asterisk (*).
The minimum label lengths are set to 1 character,
except for Interleaved 2 of 5 which is set to 2
characters and Standard 2 of 5 which is set to 4
characters. The maximum label length for all
symbologies is set to 32 characters. You can set
minimum and maximum label lengths.
Note: The minimum length must be less than or
equal to the maximum length for scanning to occur.
8–1
Page 65

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Code 39
T o disable Code 39, scan label OA .
OA
Disable Code 39
T o enable Code 39, scan option OB or OC. After
enabling Code 39, make any additional required
selections from options OD through OI.
OB Enable Standard Code 39 *
OC Enable Full ASCII Code 39
8–2
Page 66

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Modulo 43 Check Character
Options OD and OE allow you to enable or disable the
Modulo 43 check character for Code 39. T o enable
the Modulo 43 check character, scan label OE. To
disable the Modulo 43 check character, scan label OD.
OD
OE
Disable Modulo 43 *
Check Character
Enable Modulo 43
Check Character
Transmit Start/Stop Characters
You can transmit or suppress the Start and Stop
characters in Code 39. T o suppress transmission of
the Start and Stop characters, scan label OF.
OF
Do Not Transmit *
Start and Stop
T o enable transmission of the Start and Stop
characters, scan label OG.
OG
Transmit
Start and Stop
8–3
Page 67

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Code 39
(continued)
Minimum Length
The minimum length of Code 39 is set by scanning
label OH and then two digits (01 - 32) in Appendix B.
OH
+
Minimum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
For example, to enter a minimum length of 05, scan
the OH label, then scan codes 0 and 5 in Appendix B.
Maximum Length
The maximum length of Code 39 is set by scanning
label OI and then two digits (01 - 32) in Appendix B.
OI
+
Maximum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
8–4
For example, to enter a maximum length of 05, scan
the OI label, then scan codes 0 and 5 in Appendix B.
If the minimum and maximum lengths are set
equal, only codes of that exact length are read.
Page 68

Chapter 8
E)
Symbologies
UPC (A and
T o disable all UPC labels, scan label QA .
QA
Disable UPC (A and E)
Supplements
Option QB or option QC enable both UPC-A and
UPC-E. T o enable scanning of UPC labels with the 2
or 5 Digit supplements, scan label QB.
Enable UPC
QB
with 2 or 5 Digit
Supplement Enabled
T o enable scanning of UPC labels with the 2 or 5
Digit supplements disabled, scan label QC.
QC
Enable UPC *
with 2 or 5 Digit
Supplement Disabled
Expanded UPC-E
You can enable/disable expansion of E labels to A
labels. T o disable expanded UPC-E, scan label QH .
QH
Disable *
Expanded UPC-E
T o enable expansion of E labels to A labels, scan
label QI.
QI
Enable
Expanded UPC-E
8–5
Page 69

Chapter 8
E)
Symbologies
UPC (A and
(continued)
Transmit Number System Digit
You can enable or disable the transmission of the first
character in a UPC symbol (the number system
character). T o disable transmission of the first
character in a UPC symbol, scan label QD.
QD
Disable Transmission
Number System Digit
T o enable transmission of the first character in a UPC
symbol (the number system character), scan label QE.
QE
Enable Transmission *
Number System Digit
Transmit Check Digit
You can enable or disable the transmission of the last
character in a UPC symbol (the check digit). T o
disable transmission of the check digit in a UPC
symbol, scan label QF.
8–6
QF
Disable Transmission
of Check Digit
T o enable transmission of the check digit in a UPC
symbol, scan label QG.
QG
Enable Transmission
of Check Digit *
Page 70

Chapter 8
Symbologies
UPC to EAN Translation
You can cause UPC labels to be transmitted as
EAN-13 labels. T o enable UPC to EAN translation,
scan label QJ.
QJ
Enable UPC to EAN
Translation
T o disable UPC to EAN translation, scan label QK.
QK
Disable UPC to EAN
Translation *
8–7
Page 71

Chapter 8
EAN/JAN
Symbologies
Scan label RA to disable EAN/JAN (8 or 13 digit).
RA
Disable EAN/JAN *
(8 or 13 digit)
Supplements
Option RB or option RC enables both EAN 8-digit
and EAN 13-digit. EAN/JAN labels can be read with
or without supplements. T o enable scanning of
EAN/JAN labels with the 2 or 5 digit supplements,
scan label RB.
Enable EAN/JAN
RB
with 2 or 5 Digit
Supplement Enabled
T o enable scanning of EAN/JAN labels with the 2 or
5 Digit supplements disabled, scan label RC.
Enable EAN/JAN
RC
with 2 or 5 Digit
Supplement Disabled
8–8
Page 72

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Transmit Number System Digit
You can enable or disable the transmission of the first
character in an EAN/JAN symbol (the number system
character). T o disable transmission of the first
character in an EAN/JAN symbol, scan label RD.
RD
Disable Transmission
Number System Digit
T o enable transmission of the first character in an
EAN/JAN symbol, scan label RE.
RE
Enable Transmission *
Number System Digit
Transmit Check Digit
You can enable or disable the transmission of the last
character in an EAN/JAN symbol (the check digit).
T o disable transmission of the check digit in an
EAN/JAN symbol, scan label RF.
RF
Disable Transmission
of Check Digit
T o enable transmission of the check digit in an
EAN/JAN symbol, scan label RG.
RG
Enable Transmission
of Check Digit *
8–9
Page 73

Chapter 8
I
Symbologies
nterleaved 2 of 5
Scan label PA to disable Interleaved 2 of 5.
PA
Disable
Interleaved 2 of 5 *
Check Digit
You can enable Interleaved 2 of 5 with or without the
check digit. T o enable Interleaved 2 of 5 without the
check digit, scan label PB.
PB
Enable
Interleaved 2 of 5
without Check Digit
T o enable Interleaved 2 of 5 with the check digit,
scan label PC.
PC
Enable
Interleaved 2 of 5
with Check Digit
8–10
Page 74

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Minimum Length
T o set a minimum length (other than two) for
Interleaved 2 of 5, scan label PD and then two digits
(02-32) in Appendix B. The value of the number
you scan must be even. Odd numers are ignored.
PD
+
Minimum Length
(Specified by two digits 02-32)
For example, to enter a minimum length of 12, scan
the PD label, then scan codes 1 and 2 in Appendix B.
Maximum Length
T o set a maximum length for Interleaved 2 of 5, scan
label PE and then two digits (02-32) in Appendix B.
The value of the number you scan must be even.
PE
+
Maximum Length
(Specified by two digits 02-32)
For example, to enter a maximum length of 12, scan
the PE label, then scan codes 1 and 2 in Appendix B.
If the minimum and maximum lengths are set
equal, only codes of that exact length are read.
8–11
Page 75

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Standard 2 of 5
Scan label PF to disable Standard Code 2 of 5.
PF
Disable *
Standard 2 of 5
T o enable Standard Code 2 of 5, scan label PG.
PG
Enable
Standard 2 of 5
Minimum Length
T o set a minimum length (other than 4) for Standard
Code 2 of 5, scan label PH and then two digits
(04-32) in Appendix B.
PH
+
Minimum Length
(Specified by two digits 04–32)
8–12
Maximum Length
T o set a maximum length for Standard Code 2 of 5,
scan label PI and then two digits (04-32) in
Appendix B.
PI
+
Maximum Length
(Specified by two digits 04–32)
If the minimum and maximum lengths are set
equal, only codes of that exact length are read.
Page 76

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Code 128
Scan label TA to disable Code 128.
TA Disable Code 128
Scan option TB to enable Code 128.
TB Enable Code 128 *
Minimum Length
T o set a minimum length for Code 128, scan label TC,
then two digits (01-32) in Appendix B.
TC
+
Minimum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
Maximum Length
T o set a maximum length for Code 128, scan TD, then
two digits (01-32) in Appendix B.
TD
+
Maximum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
If the minimum and maximum lengths are set
equal, only codes of that exact length are read.
8–13
Page 77

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Codabar
Scan label VA to disable Codabar.
VA
Disable Codabar *
Scan option VB to enable Codabar.
VB
Enable Codabar
Transmit Start/Stop Characters
You can enable or disable the transmission of the
Start and Stop characters in Codabar. To disable
transmission of the Start and Stop characters, scan
label VC.
VC
Disable Transmission *
Start/Stop Characters
8–14
T o enable transmission of the Start and Stop
characters, scan label VD.
VD
Enable Transmission
Start/Stop Characters
Page 78

Chapter 8
Symbologies
Minimum Length
T o set a minimum length for Codabar, scan label VE
and then two digits (01-32) in Appendix B.
VE
+
Minimum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
For example, to enter a minimum length of 05, scan
the VE label, then scan codes 0 and 5 in Appendix B.
Maximum Length
T o set a maximum length for Codabar messages, scan
label VF, and then two digits (01-32) in Appendix B.
VF
+
Maximum Length
(Specified by two digits 01-32)
For example, to enter a minimum length of 05, scan
the VF label, then scan codes 0 and 5 in Appendix B.
If the minimum and maximum lengths are set
equal, only codes of that exact length are read.
8–15
Page 79

Chapter
Serial Commands
9
A–B
Chapter Objectives
Serial Command Format
This chapter covers serial commands that can be sent
from the host to configure the scanner including:
• Serial Command Format
• Manual Scanning Interaction
• ACK/NAK Protocol
• Power Standby and Serial Commands
• Communication Parameter Changes
The format of serial commands is as follows:
STX ESC LT1 LT2 <optional parameters> ETX
Note: STX= Ctrl-B ETX= Ctrl-C
STX, ESC, and ETX are ASCII codes whose values
are 02H, 1BH, and 03H, respectively.
LT1 and LT2 are uppercase ASCII letters that
represent a serial command. LT1 is the first letter of
the command; LT2 is the second letter of the
command. Each bar code label in this manual is
preceded by a two character serial command.
The ESC code that follows the STX code identifies
this as a command.
Some commands require parameters such as
minimum and maximum code lengths, and strings of
hexadecimal characters. When parameters are
required by the command they immediately follow
LT2. Serial commands never contain spaces.
T able 9.A shows some serial programming command
examples and the corresponding functions. For a
complete list of serial commands, see Appendix F.
9–1
Page 80

Chapter 9
Serial Commands
Table 9.A
Serial Programming Command Examples
Command
STX ESC PC ETX Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 with check digit.
STX ESC PD12 ETX Set Interleaved 2 of 5 minimum length to 12.
STX ESC PE14 ETX Set Interleaved 2 of 5 maximum length to 14.
1
STX ESC KB31323334 ETX
STX ESC LB6162364 ETX
Each ASCII character is encoded as two hexadecimal characters. For example:
1
1=31, 2=32, 3=33, 4=34 and a=61, b=62, c=63, d=64.
Manual Scanning Interaction
The scanner firmware makes no attempt to resolve
conflicts between serial programming commands and
manually scanned menu labels. If you plan to scan
Set Preamble to ’1234’.
1
Set Postamble to ’abcd’.
Function
menu labels, do not attempt serial programming, and
vice versa.
Serial commands are given priority over pending
menu labels. For example, if you scan the menu label
PD (which sets a minimum length for Interleaved 2 of
5 labels) and the scanner is waiting for a two-digit
minimum length code when a serial command is
issued, the serial command is acted upon and the
pending manual command (PD – Set Interleaved 2 of 5
Minimum Length) is ignored.
9–2
Page 81

ACK/NAK
Protocol
Chapter 9
Serial Commands
The scanner provides ACK/NAK protocol during
serial programming to provide feedback to the host
computer which is programming the scanner.
ACK/NAK protocol provides two functions.
• It provides the host with positive acknowledge-
ment that its commands are being accepted and
acted upon.
• It ensures the host will not issue commands to the
scanner faster than the scanner can process them.
For example, every time the scanner receives a
correct command, it modifies its internal EEPROM, a
function that takes about one second. At 9600 baud,
the host can easily issue commands to the scanner
faster than they can be processed.
If, after issuing each command, the host waits to
receive an ACK or NAK code before issuing the next
command the scanner cannot be overrun.
If XON/XOFF or CTS/RTS protocol is being used,
the scanner cannot be overrun by programming
commands. However, the host is not provided with
feedback as to the outcome of its commands.
The ACK/NAK Protocol is quite simple. Whenever
the scanner receives a correctly formatted command,
it sends a confirmation message followed by an ACK
(06H) code. The following example shows the command and response for the BEEPER OFF command.
Command from Host:
STX ESC AA ETX
Response from Scanner:
BEEPER OFF CR–LF ACK
If the scanner receives an unknown command or
improperly formatted command, or if the required
parameters are missing or out-of-range, it sends a
NAK (15H) code.
9–3
Page 82

Chapter 9
P
y
Serial Commands
ower Standb
and Serial
Commands
Communication Parameter Changes
When the scanner is programmed for standby power
operation (@B), the first character of the command is
used to wake-up the scanner; it will not be recognized
by the scanner’s CPU. When there is any possibility
that the scanner is in standby mode, an extra space
code should be transmitted before STX to ensure the
scanner is awake before sending commands to it.
If you are not operating the scanner in standby mode,
the space has no effect on commands (space prefixed
commands are properly decoded).
Having sent the space code to wake-up the scanner, a
150 to 200 millisecond pause must be observed to
allow the scanner’s CPU to complete its initialization
tasks, during which time it is unable to accept serial
commands before issuing the programming
command. Failure to observe this delay causes the
scanner to ignore the incoming command.
All commands which affect serial communication are
acted upon immediately. When changing communication parameters (such as baud rate, word length,
parity), the scanner will send the ACK code, using
the newly implemented communication parameters.
9–4
There should be a delay after the host sends a
communication parameter setup command. This
delay allows the host computer to modify its internal
parameters and correctly receive the ACK code from
the scanner. This is due to the internal, one second
delay required for the scanner to update its internal
EEPROM.
Page 83

Chapter
Specifications
10
A–B
Hand-Held Scanners
Catalog No. 2755-G3-D
Catalog No. 2755-G6-D
Optical
Nominal Scan Rate 35 scans/second
Wavelength (nominal) 670 nm
Maximum Pitch ±55 degrees
Maximum Skew ±65 degrees
Scanning Range
Minimum
Bar Width
6.0 mil
(.15 mm)
7.5 mil
(.19 mm)
10.0 mil
(.25 mm)
15.0 mil
(.38 mm)
20.0 mil
(.51 mm)
40.0 mil
(1.02 mm)
55.0 mil
(1.40 mm)
Standard Range
(2755-G3-D)
3.0 in - 5.0 in
7.6 cm - 12.7 cm
2.5 in - 7.5 in
6.4 cm - 19.0 cm
1.0 in - 10.0 in
2.5 cm - 25.4 cm
1.5 in - 14.0 in
3.8 cm - 35.6 cm
2.5 in - 18.0 in
6.4 cm - 45.7 cm
9.0 in - 25.0 in
22.9 cm - 63.5 cm
12.0 in - 30.0 in
30.5 cm - 76.2 cm
Long Range
(2755-G6-D)
N.A.
N.A.
N.A.
8.0 in - 22 in
20.3 cm - 55.9 cm
12 in - 36 in
30.5 cm - 91.4 cm
23 in - 60 in
58.4 cm - 152.4 cm
23 in - 66 in
58.4 cm - 167.6 cm
Scanning Range
Autosense Mode 36 in (91.4 cm) maximum
(to reflective label or tape)
Electrical
Supply Voltage 4.75 to 14 VDC
Current Consumption
While Scanning 200 mA maximum
Standby Power 100 A maximum
Continuous Full Power 200 mA maximum
1
Autosense mode automatically uses continuous full power.
1
10–1
Page 84

Chapter 10
Specifications
Mechanical
Dimensions
Inches 4.0(L) x 2.8(W) x 6.6(H)
Millimeters 102(L) x 71(W) x 168(H)
Weight 8.0 oz (0.23 kg)
LED Indicators
Good Read Green
Scanning Yellow
Environmental
Operating T emperature 0° to 122° F
-18° to
+50° C
Storage T emperature -40° to 158° F
-40° to +70° C
Relative Humidity 5 to 95% (noncondensing)
Electrostatic Discharge 15kv to any
external surface
Drop T est 5 feet (1.27 meter)
on concrete
Dust and Rain MIL STD 810D
Sections 510.2I & 506.2II
10–2
Interface
RS-232
Certification
Dept. of Health and Class II laser product.
Human Services (DHHS) Complies with DHHS
radiation performance
standards, 21 DFR
subchapter J.
Page 85

Appendix
A
A–B
Bar Code Test Symbols
Use the following labels to insure that your scanner is functioning
properly. The only label the long range scanner can read below is
the Interleaved 2-of-5 (15 mil) label.
A–1
Page 86

Appendix
B
Digit Selection Symbols
A–B
B–1
Page 87

Appendix
C
A–B
Autosense Mode
T o set up the scanner to operate in Autosense mode
using the optional Autostand follow the steps below
while referring to Figure C.1.
1. Enable the scanner to operate in Autosense mode
by scanning the Enable Autosense (NO) label in
Chapter 5.
2. Attach the Stand Riser to the Stand Base
using two of the supplied #6-32 thumb screws.
. Attach the Scanner Holder to the top of the Stand
3
Riser using the other two #6-32 thumb screws.
4. Verify that the reflective label is affixed to the
Stand Base.
5. Place the scanner in the stand as shown in
Figure C.1.
6. Check that the red beam of light is aimed at the
reflective label on the stand.
The Autostand is now ready to read bar code labels
presented to it.
While the scanner is activated in Autosense mode
you are able to remove the scanner from its holder
and use it for hand-held applications. When the
scanner is removed from the Autostand the scanning
beam is turned on automatically to read a bar code
label. If the scanner does not see a label the scanning
beam will turn off after four seconds. Scanning is
re-initiated by manually pulling the trigger. The
scanner can then be placed into the stand once again
and it will function in Autosense mode.
C–1
Page 88

Appendix C
Autosense Mode
#6-32 Thumb Screws
Figure C.1
Autostand
Scanner
Scanner Holder
C–2
Stand Riser
#6-32 Thumb Screws
Stand Base
Important: When the scanner is to be powered from
a battery such as in a hand-held terminal, you should
disable Autosense mode. In this application, you may
need to use the power conservation mode (see page
5–3) of the scanner when drawing power from a
battery . Autosense mode will function only in full
power mode.
1
Reflective tape is supplied with the autostand. Additional reflective tape is
available by ordering Catalog No. 2755-NT1.
Reflective
1
Label
Page 89

Appendix
D
A–B
Interface Cable Pinouts
The Catalog No. 2755-NCR1 Cable is typically used
to connect the scanner to IBM PC Compatible
computers. You may have to use an adapter if your
computer has a 9-pin port.
Table D.1
RS232 DCE, 25-Pin, Female, D-Type Connector
Catalog No. 2755-NCR1
Pin
2 RxD Serial data receive input.
3 TxD Serial data transmit output.
4 CTS
5 RTS Request-To-Send
7 Ground Ground pin and reference for both output signals.
External trigger operation is controlled by applying an external signal to the
1
CTS input (with external triggering enabled). CTS protocol and External Trigger
Enabled are mutually exclusive parameters. See Chapter 5 for details on how
to enable the scanner for external trigger operation.
Signal Name Function
Clear-To-Send (or External Trigger)
Handshaking input line.
Handshaking output line.
1
D–1
Page 90

Appendix D
Interface Cable Pinouts
The Catalog No. 2755-NCR2 cable is compatible
with the AUX port on the Single and Dual-Head
Enhanced Bar Code Decoders (Catalog No.
2755-DS1A, -DD1A).
Table D.2
RS232 DTE, 25-Pin, Male, D-Type Connector
Catalog No. 2755-NCR2
Pin
Signal Name Function
2 TxD Serial data transmit output.
3 RxD Serial data receive input.
4
5
RTS
CTS
Request-To-Send
Handshaking output line
Clear-To-Send (or External Trigger)
Handshaking input line
1
7 Ground Ground pin and reference for both output signals.
External trigger operation is controlled by applying an external signal to the
1
CTS input (with external triggering enabled). CTS Protocol and External Trigger Enabled are mutually exclusive parameters. See Chapter 5 for details on
how to enable the scanner for external trigger operation.
D–2
Page 91

Appendix
g
I
g
E
Maintenance
This appendix provides general maintenance
information for your scanner.
A–B
Cleanin
Window
nspectin
Cables
You may need to clean the window of the scanner.
Carefully clean the window by first removing loose
particles of dirt with clean air. Then use an optical
quality cloth moistened with an optical quality
cleaning fluid for plastic lenses and wipe the window
in a single direction (don’t wipe cloth back and forth
across window). Do not leave streaks.
CAUTION:
Do not use abrasive materials (e.g., dis-
!
posable wipes, facial tissue) or solvents
(e.g., alcohol or acetone) on the window.
These items may damage the window or
finish on the scanner.
WARNING:
The scanner has no serviceable parts.
!
Do not open the housing of the scanner.
Periodically inspect the cable on the scanner for wear
and other signs of damage. A worn or damaged cable
may interfere with the operation of the scanner.
Contact your Allen-Bradley representative to order
replacement cables.
E–1
Page 92

Appendix
F
Scanner Commands
Each label in this manual is preceded by two
characters which represent the serial command for a
scanner parameter . The following tables list the
command mnemonic for each scanner parameter and
the page location of the corresponding label.
General Scanner Setup Parameters
Mnemonic
ZA Set Scanner to Factory Defaults 4-10
ZB Display Scanner Configuration 5-1
ZC Transmit Program Version Number 5-2
@C Transmit Program ID 5-2
@A Enable Full Continuous Power 5-3
@B Enable Standby Power 5-3
AA Beeper Off 5-4
AB Beeper On; Volume Low 5-4
AC Beeper On; Volume Medium 5-4
AD Beeper On; Volume Loud 5-4
BC Capture Count=1 5-5
BD Capture Count=2 5-5
NP Disable Spotter Beam 5-6
NQ Enable Spotter Beam 5-6
NO Enable Autosense Mode 5-7
NN Disable Autosense Mode 5-7
HA Disable External Trigger 5-8
HE External Trigger (+) 5-8
HF External Trigger (–) 5-8
Function Page #
A–B
F–1
Page 93

Appendix F
Scanner Commands
Mnemonic
DA Baud Rate = 300 6-2
DB Baud Rate = 600 6-2
DC Baud Rate = 1200 6-2
DD Baud Rate = 2400 6-2
DE Baud Rate = 4800 6-2
DF Baud Rate = 9600 6-2
DG Baud Rate = 19200 6-2
EA 7 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Space Parity 6-4
EB 7 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Mark Parity 6-4
EC 7 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Even Parity 6-4
ED 7 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Odd Parity 6-4
EE 7 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, Space Parity 6-5
EF 7 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, Mark Parity 6-5
EG 7 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, Even Parity 6-5
EH 7 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, Odd Parity 6-5
EI 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Space Parity 6-6
EJ 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Mark Parity 6-6
EK 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Even Parity 6-6
EL 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, Odd Parity 6-6
EM 8 Data Bits, 1 Stop Bit, No Parity 6-5
EN 8 Data Bits, 2 Stop Bits, No Parity 6-6
HA CTS Protocol = None 6-8
HB Protocol = XON/XOFF 6-8
HC Protocol = CTS(+) 6-8
HD Protocol = CTS(–) 6-8
HG RTS always high 6-9
HH RTS always low 6-9
HI RTS high means scanner has data to transmit 6-9
HJ RTS low means scanner has data to transmit 6-9
HK RTS low means scanner ready to receive data 6-9
GA No Intercharacter Delay 6-10
GB Set Intercharacter Delay 6-10
NE Serial Transmit Buffer = Full Buffering 6-11
NF Serial Transmit Buffer = No Buffering 6-11
NG Serial Transmit Buffer = One Label Buffering 6-11
Serial Communication Parameters
Function Page #
F–2
Page 94

Appendix F
Scanner Commands
Message Format Parameters
Mnemonic
IA Prefix = None 7-2
IB Prefix = STX 7-2
IC Prefix = SOH 7-2
MA Suffix=None 7-3
MB Suffix = ETX 7-3
MC Suffix = CR 7-3
MD Suffix = LF 7-3
ME Suffix = HT 7-3
MF Suffix = CR and LF 7-3
JA Disable Scanner Identifier 7-4
JB Enable Scanner Identifier 7-4
FA Disable Code Identifier 7-5
FB Enable Code Identifier 7-5
KA Preamble = None 7-7
KB Preamble = 4 ASCII Characters 7-7
LA Postamble = None 7-7
LB Postamble = 4 ASCII Characters 7-7
Function Page #
Symbology Parameters
Mnemonic
OA Disable Code 39 8-2
OB Enable Standard Code 39 8-2
OC Enable Full ASCII Code 39 8-2
OD Disable Modulo 43 Check Character 8-3
OE Enable Modulo 43 Check Character 8-3
OF Do Not Transmit Code 39 Start/Stop Characters 8-3
OG Transmit Code 39 Start/Stop Characters 8-3
OH Set Minimum Length for Code 39 Labels 8-4
OI Set Maximum Length for Code 39 Labels 8-4
QA Disable UPC (A and E) 8-5
QB Enable UPC (A and E) with 2 or 5 Digit Supplements 8-5
QC Enable UPC (A and E) without 2 or 5 Digit Supplements 8-5
Function Page #
F–3
Page 95

Appendix F
Scanner Commands
Mnemonic
QD Disable Transmission UPC Number System Digit 8-6
QE Enable Transmission UPC Number System Digit 8-6
QF Disable Transmission UPC Check Digit 8-6
QG Enable Transmission UPC Check Digit 8-6
QH Disable Expanded UPC-E 8-5
QI Enable Expanded UPC-E 8-5
QJ Enable UPC to EAN Translation 8-7
QK Disable UPC to EAN Translation 8-7
RA Disable EAN/JAN (8 or 13) 8-8
RB Enable EAN/JAN with 2 or 5 Digit Supplements 8-8
RC Disable EAN/JAN without 2 or 5 Digit Supplements 8-8
RD Disable Transmission EAN/JAN Number System Digit 8-9
RE Enable Transmission EAN/JAN Number System Digit 8-9
RF Disable Transmission EAN/JAN Check Digit 8-9
RG Enable Transmission EAN/JAN Check Digit 8-9
PA Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 8-10
PB Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 without Check Digit 8-10
PC Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 with Check Digit 8-10
PD Set Minimum Length for Interleaved 2 of 5 Labels 8-11
PE Set Maximum Length for Interleaved 2 of 5 Labels 8-11
PF Disable Standard 2 of 5 8-12
PG Enable Standard 2 of 5 8-12
PH Set Minimum Length for Standard 2 of 5 Labels 8-12
PI Set Maximum Length for Standard 2 of 5 Labels 8-12
TA Disable Code 128 8-13
TB Enable Code 128 8-13
TC Set Minimum Length for Code 128 Labels 8-13
TD Set Maximum Length for Code 128 Labels 8-13
VA Disable Codabar 8-14
VB Enable Codabar 8-14
VC Disable Transmission Codabar Start/Stop Characters 8-14
VD Enable Transmission Codabar Start/Stop Characters 8-14
VE Set Minimum Length for Codabar Labels 8-15
VF Set Maximum Length for Codabar Labels 8-15
Symbology Parameters (continued)
Function Page #
F–4
Page 96

Glossary
A–B
ACK: See acknowledgement.
acknowledgement (ACK): An ASCII control character
used to acknowledge the reception and acceptance of a
transmission block.
AIM: Acronym for Automatic Identification
Manufacturers.
alphanumeric: The character set containing letters,
numbers, punctuation marks, and symbols.
ASCII: American Standard Code for Information
Interchange. It is a seven-bit code with an optional parity
bit used to represent alphanumerics, punctuation marks,
and control codes.
bar: The dark element of a printed symbol.
bar code: The parallel bars and spaces found in a bar
code symbol.
bar code density: The number of characters which can be
represented in a linear inch.
bar code label: A label that carries a bar code and is
suitable to be affixed to an article.
bar code symbol: A group of parallel bars that represent
a character or group of characters whose spacing is
determined by a specific set of rules. In most cases,
human readable characters are printed below the bars.
bar length: The bar dimension perpendicular to the
bar width.
bar width: The thickness of a bar measured from the
edge closest to the symbol’s start character to the trailing
edge of the same bar.
baud: A unit of signaling speed equal to the number of
discrete conditions or signal events per second.
character: A single group of bars and spaces representing
an individual number, letter or punctuation mark. A
graphic shape representing a letter, number or symbol.
G–1
Page 97

Glossary
check digit: A digit included within a symbol whose
value is based mathematically on other characters
included in the symbol. It is used to mathematically
check the accuracy of a symbol.
clear area: A clear space, containing no dark marks, that
precedes the start character of a symbol and follows the
stop character.
Codabar: A numeric symbology consisting of 16 data
characters and 4 start/stop characters. Codabar is
primarily used by the medical community.
Code 128: A symbology representing the full 128 ASCII
character set. Numeric data may be represented in a
double density mode where two digits are represented by
one character.
Code 39: An alphanumeric symbology recognized by
most nations, widely used in the manufacturing industry.
code type: See symbology.
G–2
decode: The process of translating a bar code into
data characters using a specific set of rules for each
symbology.
decoder: A device used to decode, or make usable, a
digital or analog signal transmitted from a scanning
device. The scanner contains a decoder.
EAN: Acronym for European Article Numbering
system, the international standard bar code for retail
food packages.
element: Dimensionally the narrowest width in a
character, bar or space.
encoded area: The total linear dimension consisting of all
the characters of a code pattern, including start/stop
characters and data.
guard bars: Bars at the ends and center of a UPC and
EAN symbol. They ensure a complete scan of the
bar code.
Page 98

Glossary
hex: Abbreviated form of the word hexadecimal. See
hexadecimal.
hexadecimal: A base-16 numbering system that uses the
symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F.
horizontal bar code: A bar code or symbol presented in a
manner that its overall length dimension is parallel to the
horizon. The bars look like a picket fence.
Interleaved 2 of 5: A symbology in which characters are
paired together using bars to represent odd number characters and spaces to represent even number characters.
ladder orientation: See vertical bar code.
modulus 43 check character: Used in Code 39 for data
security in addition to the built-in self-checking
characters. The check-character is the modulus 43 sum of
all of the character values in a given message and is the
last character in the code.
NAK: See negative acknowledgement.
negative acknowledgement (NAK): An ASCII control
character transmitted by a receiver as a negative response
to the sender.
orientation: The alignment of bars and spaces to the
scanner. Often referred to as vertical (ladder) or
horizontal (picket fence).
parity bit: An additional non-data bit attached to a binary
word to provide a check of the data integrity by making
the sum of the number of ones in a word always even
or odd.
picket fence code: See horizontal bar code.
scan: The search for a symbol or marks which are to be
optically recognized.
scan area: The area intended to contain a bar code
symbol.
scanner: A device that optically scans bar code symbols
and converts the optical information into digital or analog
form and sends it to a decoder.
G–3
Page 99

Glossary
self-checking: A bar code or symbol using a checking
algorithm which can be applied to each character to guard
against undetected errors. Codes that are not
self-checking may employ a check digit or other
redundancy in addition to the data message.
space: The lighter element of a bar code formed by the
background between bars.
start/stop characters: Bar code characters that provide
the scanner with information on how the code is bounded
and its orientation. The start character is normally at the
left end of a horizontal code and adjacent to the most
significant character . The stop character is normally at the
end of a horizontal code and adjacent to the least
significant character.
symbology: The conventions, or rules, which govern the
formation of characters and strings in bar codes. The
language of the bar code symbol.
symbol density: The number of characters per
linear inch.
G–4
symbol length: The length of the symbol measured from
the beginning of the quiet area adjacent to the start
character to the end of the quiet area adjacent to a stop
character.
UPC: Acronym for Universal Product Code. The
standard bar code for retail food packages in the
United States.
vertical bar code: A code pattern in which the overall
coded area from start to stop is perpendicular to the
horizon. The individual bars appear as rungs of a ladder.
Page 100

Index
A
Accessories, 2–6
ACK/NAK Protocol,
serial programming, 9–3
Autosense Mode, 2–2
disable, 5–7
enable, 5–7
installing autostand, C–1
B
Bar Code T est Symbols, A–1
Baud Rate, 6–2
Beep, 3–7
Beeper Operation, 5–4
C
Cables, 2–6
Capture Count, 5–5
Codabar
disable, 8–14
enable, 8–14
maximum length, 8–15
minimum length, 8–15
start/stop characters, 8–14
Code 128
disable, 8–13
enable, 8–13
maximum length, 8–13
minimum length, 8–13
Standard 2 of 5, 8–12
maximum length, 8–12
minimum length, 8–12
Code 39
disable, 8–2
enable, 8–2
maximum length, 8–4
minimum length, 8–4
modulo 43 check character, 8–3
start/stop characters, 8–3
Code Identifier, 7–5
Configuration of Scanner
default settings, 4–7
guidelines, 4–5
serial programming, 9–1
viewing, 5–1
Continuous Full Power, 5–3, 10–1
CTS Protocol, 6–7
D
Data Bits, 6–3
Digit Selection Symbols, B–1
Display Scanner Configuration, 5–1
E
EAN/JAN
check digit, 8–9
disable, 8–8
enable with or without
supplements, 8–8
number system digit, 8–9
External Trigger Operation
applying external signal to CTS
input, 5–8, 6–7, D–1
disable, 5–8
enable, 5–8
I–1
 Loading...
Loading...