Page 1

SMC™-Flex
BULLETIN 150
USER MANUAL FOR SERIES B
Page 2
Important User Information
ATTENTION
!
IMPORTANT
Because of the variety of uses for the products described in this publication,
those responsible for the application and use of this control equipment must
satisfy themselves that all necessary steps have been taken to assure that
each application and use meets all performance and safety requirements,
including any applicable laws, regulations, codes and standards.
The illustrations, charts, sample programs and layout examples shown in
this guide are intended solely for purposes of example. Since there are many
variables and requirements associated with any particular installation,
Allen-Bradley does not assume responsibility or liability (to include
intellectual property liability) for actual use based upon the examples shown
in this publication.
Allen-Bradley publication SGI-1.1, Safety Guidelines for the Application,
Installation and Maintenance of Solid-State Control (available from your
local Allen-Bradley office), describes some important differences between
solid-state equipment and electromechanical devices that should be taken
into consideration when applying products such as those described in this
publication.
Reproduction of the contents of this copyrighted publication, in whole or
part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, is prohibited.
Throughout this manual we use notes to make you aware of safety
considerations:
Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage
or economic loss
Attention statements help you to:
• identify a hazard
• avoid a hazard
• recognize the consequences
Identifies information that is critical for successful
application and understanding of the product.
Trademark List
Accu-Stop, Allen-Bradley Remote I/O, RSNetworx, PLC, PowerFlex, SLC, SMC, SMC-2,
SMC-Flex, SMC PLUS, SMC Dialog Plus, SMB, and STC are trademarks of Rockwell
Automation. ControlNet is a trademark of ControlNet International, Ltd. DeviceNet and the
DeviceNet logo are trademarks of the Open Device Vendors Association (ODVA). Ethernet is a
registered trademark of Digital Equipment Corporation, Intel, and Xerox Corporation. Modbus is
a trademark or registered trademark of Schneider Automation Inc. Profibus is a registered
trademark of Profibus International.
Page 3

European Communities (EC)
Directive Compliance
If this product has the CE mark it is approved for installation within the
European Union and EEA regions. It has been designed and tested to meet
the following directives.
EMC Directive
This product is tested to meet the Council Directive 89/336/EC
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) per EN/IEC 60947-4-2.
This product is intended for use in an industrial environment.
Low Voltage Directive
This product is tested to meet Council Directive 73/23/EEC Low Voltage,
per EN/IEC 60947-4-2.
This equipment is classified as open equipment and must be mounted in an
enclosure during operation to provide safety protection.
Page 4

Notes
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1
Product Overview
Other Related Documents ........................................................................... 1-1
Description .................................................................................................1-1
Operation ....................................................................................................1-2
Modes of Operation (Standard) ....................................................................1-2
Soft Start ..............................................................................................1-2
Selectable Kickstart ..............................................................................1-3
Current Limit Start ................................................................................1-3
Dual Ramp Start ...................................................................................1-4
Full Voltage Start ..................................................................................1-4
Preset Slow Speed ...............................................................................1-5
Linear Speed Acceleration.....................................................................1-6
Soft Stop ..............................................................................................1-7
Control Options ...........................................................................................1-8
Modes of Operation (Pump Control) .............................................................1-8
Pump Control Option ............................................................................1-8
Modes of Operation (Braking Control) ..........................................................1-9
SMB Smart Motor Braking Option .........................................................1-9
Accu-Stop Option ...............................................................................1-10
Slow Speed with Braking Option .........................................................1-10
Protection and Diagnostics ........................................................................1-11
Overload ............................................................................................1-11
Underload ...........................................................................................1-11
Undervoltage ......................................................................................1-13
Overvoltage ........................................................................................1-13
Unbalance ..........................................................................................1-13
Stall Protection and Jam Detection .....................................................1-14
Ground Fault ......................................................................................1-15
Ground Fault Trip ...............................................................................1-16
Ground Fault Alarm ............................................................................1-16
Thermistor/PTC Protection ..................................................................1-17
PTC Trip .............................................................................................1-17
Excessive Starts/Hour .........................................................................1-18
Overtemperature ................................................................................1-18
Open Gate ..........................................................................................1-18
Line Faults .........................................................................................1-18
Metering ...................................................................................................1-19
I/O ............................................................................................................1-19
Communication .........................................................................................1-20
Programming ............................................................................................1-20
Status Indication .......................................................................................1-21
Chapter 2
Installation
Degree of Protection ...................................................................................2-1
Receiving ....................................................................................................2-1
Unpacking ...................................................................................................2-1
Inspecting ...................................................................................................2-1
Storing ........................................................................................................2-1
Page 6

Lifting .........................................................................................................2-2
General Precautions .................................................................................... 2-3
Heat Dissipation ..........................................................................................2-3
Enclosures ..................................................................................................2-4
Mounting ....................................................................................................2-5
Power Factor Correction Capacitors .......................................................... 2-12
Protective Modules ................................................................................... 2-13
Motor Overload Protection .........................................................................2-13
Two-speed Motors .............................................................................2-13
Multi-motor Protection .......................................................................2-13
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ......................................................... 2-14
Enclosure ...........................................................................................2-14
Wiring ................................................................................................2-14
Additional Requirements ....................................................................2-14
Chapter 3
Wiring
Terminal Locations .....................................................................................3-1
Power Structure .......................................................................................... 3-3
Power Wiring .......................................................................................3-3
Line Connected ....................................................................................3-4
Delta Connected ..................................................................................3-4
Power Lugs ................................................................................................3-5
Control Power .............................................................................................3-7
Control Wiring ......................................................................................3-7
Controllers rated 5…480 A ..................................................................3-7
Controllers rated 625…1250 A ............................................................3-7
Control Wire Specifications ................................................................3-11
Fan Power ................................................................................................3-11
Fan Terminations ...............................................................................3-11
Control Terminal Designations ..................................................................3-12
Standard Controller Wiring Diagrams ........................................................ 3-13
Soft Stop, Pump Control, and SMB Smart Motor Braking ...........................3-24
Preset Slow Speed .................................................................................... 3-28
Slow Speed with Braking ..........................................................................3-30
Sequence of Operation ..............................................................................3-31
Special Application Considerations ............................................................3-36
Use of Protective Modules ..................................................................... 36
Multi-motor Applications ........................................................................... 3-38
SMC-Flex Controller as a Bypass to an AC Drive .......................................3-39
SMC-Flex Controller with a Bulletin 1410 Motor Winding Heater ...............3-40
Chapter 4
Programming
Overview ....................................................................................................4-1
Keypad Description .....................................................................................4-1
Programming Menu ....................................................................................4-1
Password ....................................................................................................4-5
Parameter Management .............................................................................4-6
Random Access Memory (RAM) ...........................................................4-6
Read-only Memory (ROM) ....................................................................4-6
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-only Memory (EEPROM)....... 4-6
Parameter Modification................................................................................ 4-7
Soft Start .................................................................................................... 4-8
Page 7

Current Limit Start ......................................................................................4-8
Dual Ramp Start ..........................................................................................4-9
Full Voltage Start .......................................................................................4-10
Linear Speed .............................................................................................4-10
Programming Parameters .........................................................................4-11
Standard ............................................................................................4-11
Pump Control .....................................................................................4-12
Braking Control ..................................................................................4-12
Basic Set Up .............................................................................................4-14
Motor Protection .......................................................................................4-15
Example Settings ......................................................................................4-16
Undervoltage ......................................................................................4-16
Overvoltage ........................................................................................4-16
Jam ...................................................................................................4-16
Underload ..........................................................................................4-16
Chapter 5
Metering
Chapter 6
Optional HIM Operation
Chapter 7
Communications
Overview .....................................................................................................5-1
Viewing Metering Data ................................................................................5-1
Overview .....................................................................................................6-1
Human Interface Module .............................................................................6-1
Standard .............................................................................................. 6-1
Pump Control .......................................................................................6-2
Braking Control ....................................................................................6-2
Overview .....................................................................................................7-1
Communication Ports ..................................................................................7-1
Human Interface Module............................................................................. 7-2
Keypad Description .............................................................................. 7-2
Connecting the Human Interface Module to the Controller ....................7-4
HIM Control Enable ...............................................................................7-4
Control Enable .............................................................................................7-6
Loss of Communication and Network Faults ................................................7-6
SMC-Flex Specific Information ....................................................................7-6
Default Input/Output Configuration ..............................................................7-7
Variable Input/Output Configuration .............................................................7-7
SMC — Flex Bit Identification ..................................................................... 7-8
Reference/Feedback ...................................................................................7-9
Parameter Information ................................................................................7-9
Scale Factors for PLC Communication .........................................................7-9
Read Example ......................................................................................7-9
Write Example ......................................................................................7-9
Display Text Unit Equivalents ....................................................................7-10
Configuring DataLinks ...............................................................................7-10
Rules for Using DataLinks ..................................................................7-10
Updating Firmware ....................................................................................7-10
Chapter 8
Diagnostics
Overview .....................................................................................................8-1
Protection Programming .......................................................................8-1
Page 8

Fault Display ...............................................................................................8-1
Clear Fault ..................................................................................................8-2
Fault Buffer .................................................................................................8-2
Fault Codes ..........................................................................................8-3
Fault and Alarm Auxiliary Indication for Fault or Alarm ................................8-3
Fault Definitions .......................................................................................... 8-4
Chapter 9
Troubleshooting
Appendix A
Specifications
Appendix B
Parameter Information
Appendix C
Renewal Parts
Appendix D
Accessories
Introduction ................................................................................................9-1
Power Module Check ..................................................................................9-7
Shorted SCR Test .................................................................................9-7
Functional Design Specifications .................................................................A-1
Electrical Ratings ........................................................................................A-2
Short Circuit Protection ...............................................................................A-3
Environmental .............................................................................................A-5
Mechanical .................................................................................................A-5
Other ..........................................................................................................A-6
Approximate Dimensions and Shipping Weights ..........................................A-6
Open Type Controllers ..........................................................................A-6
Enclosed Type Line-Connected Controllers ...........................................A-7
Parameter Information................................................................................ B-1
Renewal Parts ............................................................................................C-1
Contactor Replacement Installation Instructions for
625…1250 A units
...................................................................................... D-1
Appendix E
Accessories
Appendix F
Renewal Parts Cross Reference
Accessories ................................................................................................ E-1
Renewal Part Cross Reference ....................................................................F-1
Page 9

Product Overview
Chapter 1
Other Related Documents • Quick Start — Publication 150-QS001_
• Renewal Part Instructions — 41053-277-01 (5…85 A)
41053-328-01 (108…135 A)
41053-228-01 (201…480 A)
41053-367-01 (625…1250 A)
• Selection Guide — Publication 150-SG009_
• Application Guide — Publication 150-AT002_
①
-EN-P
①
-EN-P
①
-EN-P
Description The SMC™-Flex controller offers a full range of starting modes as
standard:
• Soft Start with Selectable Kickstart
• Current Limit with Selectable Kickstart
• Dual Ramp Start with Selectable Kickstart
• Full Voltage Start
• Preset Slow Speed
• Linear Speed Acceleration with Selectable Kickstart (requires
Tach feedback)
• Soft Stop
Other features that offer further user benefit include:
• Expanded protective features
• Metering
•I/O
• Communication capability
Innovative starting and stopping options provide enhanced
performance:
• Pump Control
• Braking Control
• Smart Motor Braking (SMB™)
• Accu-Stop™
• Slow Speed with Braking
These modes, features, and options are further described in this
chapter.
➀ Latest revision
Page 10
1-2 Product Overview
Percent Voltage
100%
Initial
Torque
Time in Seconds
Start
Run
Ramp Time
Current Limit
Operation The SMC-Flex controller can operate standard squirrel-cage
induction motors rated 1…1250 A or Star-delta (wye-delta) type
motors rated 1.8…1600 A; up to 690V AC, 50/60 Hz. Depending
upon the controller type ordered, the control power input can range
from 100…240V AC to 24V AC/DC. Please verify voltage on
product, before applying power.
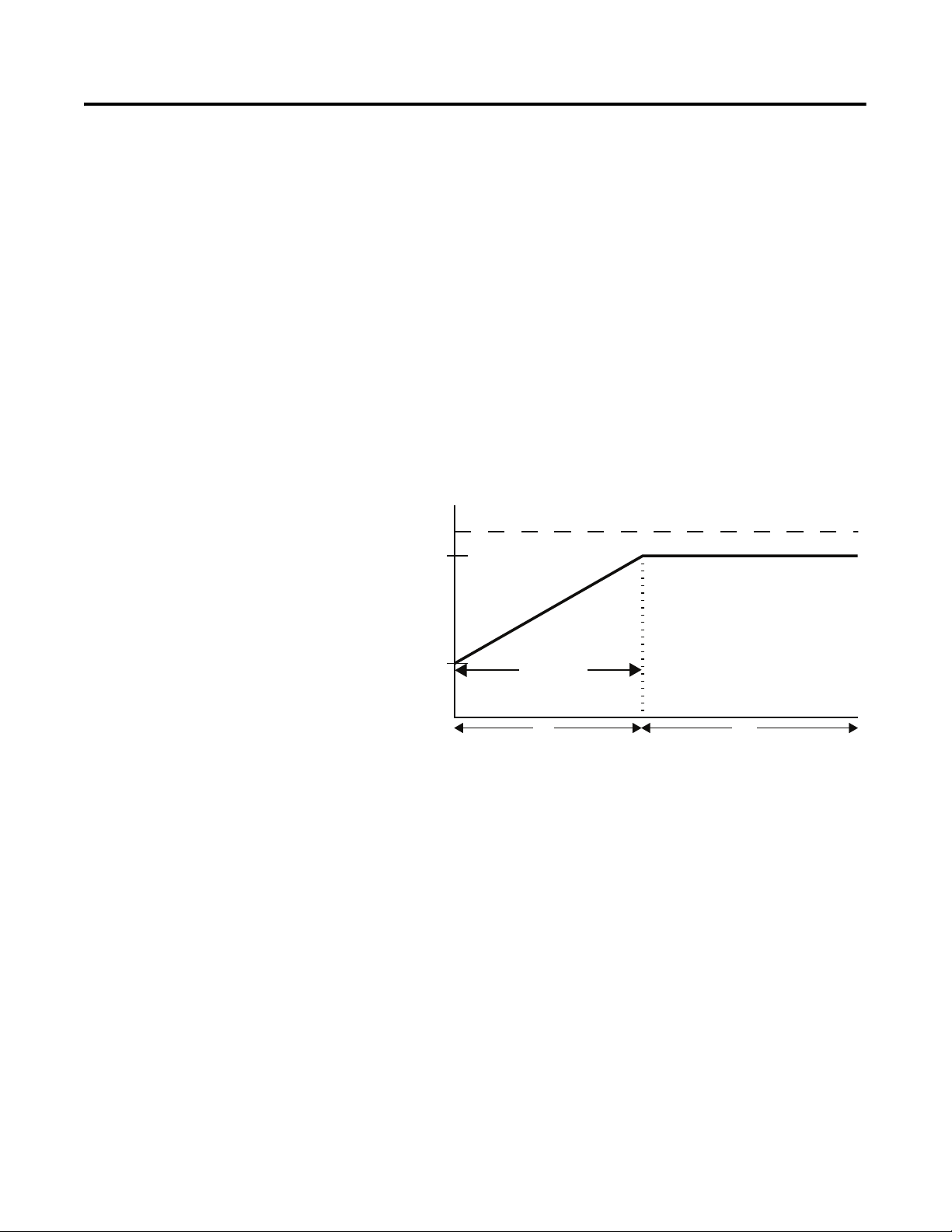
Modes of Operation (Standard) Soft Start
This mode has the most general application. The motor is given an
initial torque setting, which is user-adjustable from 0…90% of locked
rotor torque. From the initial torque level, the output voltage to the
motor is steplessly increased during the acceleration ramp time. The
acceleration ramp time is user-adjustable from 0…30 seconds. If the
SMC-Flex controller senses that the motor has reached the up-tospeed condition during the voltage ramp operation, the internal
bypass contactor will be pulled in.
Figure 1.1 Soft Start
①
➀ Kickstart is also available with Soft Start.
Page 11
Product Overview 1-3
S
t
un
00%
que
ge
)
S
t
p
C
t
p
S
t
600%
50%
C
t
)
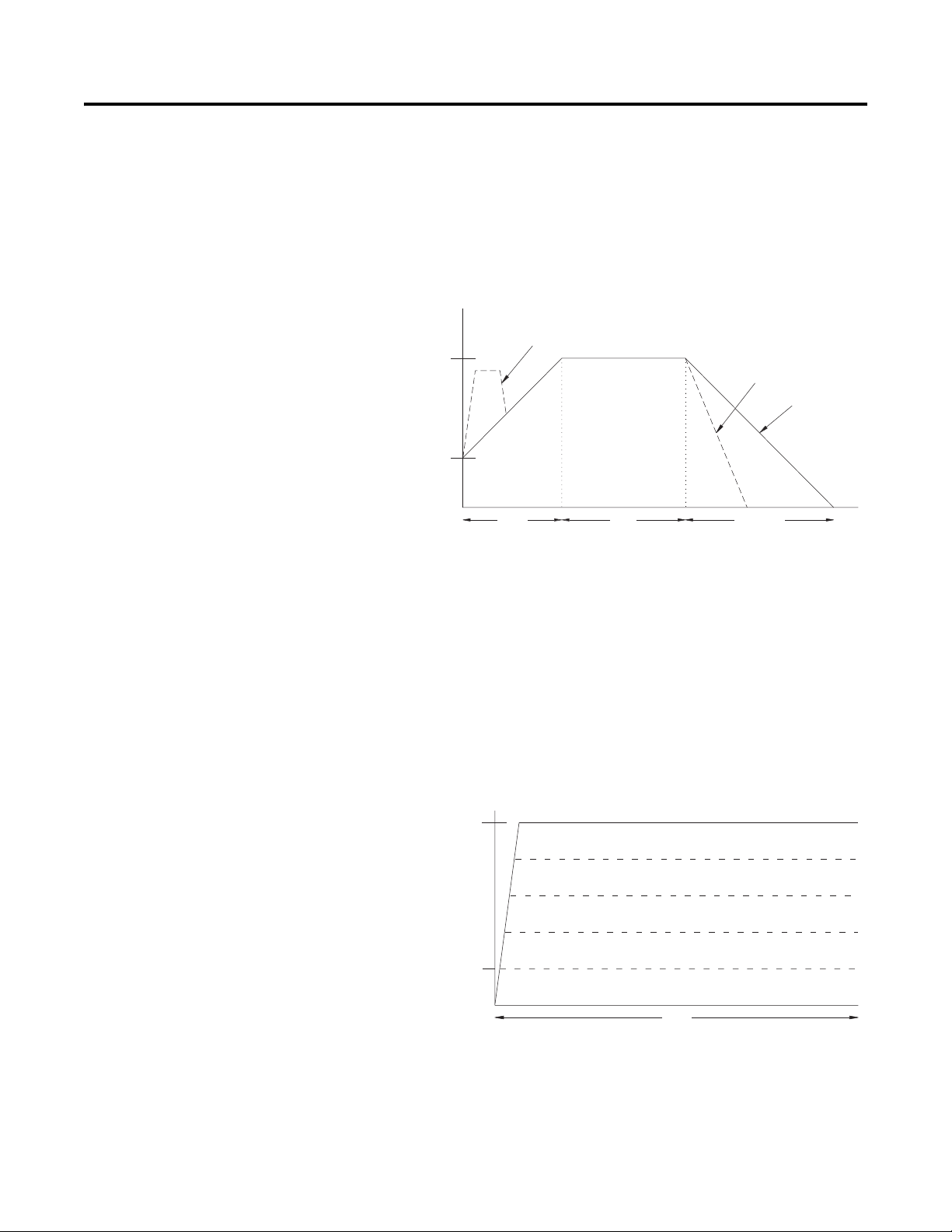
Selectable Kickstart
This feature provides a boost at startup to break away loads that
require a pulse of high torque to get started. This is intended to
provide a pulse of current that is selectable from 0…90% of locked
rotor torque. Selectable kickstart is user-adjustable from
0.0…2.0 seconds.
Figure 1.2 Selectable Kickstart
Percent
Volta
1
Initial
Tor
electable Kickstar
oast-to-res
Soft Sto
tar
Current Limit Start
R
Time (seconds
➀
Soft Sto
This starting mode provides a true current limit start; it is used when
limiting maximum starting current is necessary. The Current Limit
level is user-adjustable from 50…600% of the motor full load ampere
rating; and the current limit time is user-adjustable from 0…30
seconds. If the SMC-Flex controller senses that the motor has reached
the up-to-speed condition during the current limit starting mode, the
internal bypass contactor will be pulled in.
Figure 1.3 Current Limit Start
Percent Full
urren
Load
tar
Time (seconds
➀ Kickstart is also available with Current Limit Start.
Page 12
1-4 Product Overview
Ramp #2
Ramp #1
Time in Seconds
Percent Voltage
100%
Initial
Torque #2
Initial
Torque #1
Start #1
Start #2
Run #1
Run #2
Current Limit 2
Current Limit 1
100%
Percent Voltage
Time in Seconds
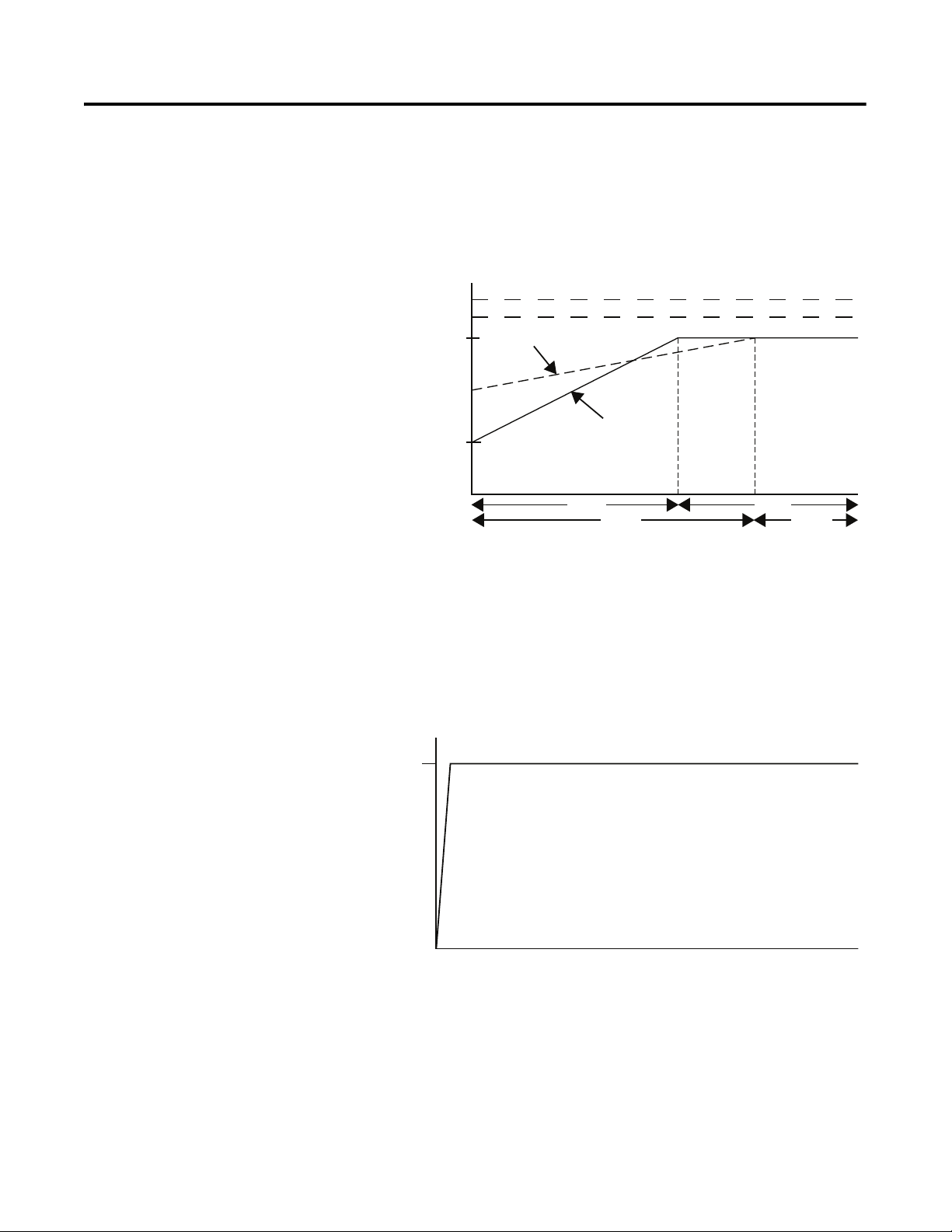
Dual Ramp Start
➀
This starting mode is useful on applications that have varying loads
(and therefore varying starting torque requirements). Dual Ramp Start
allows the user to select between two separate start profiles with
separately adjustable ramp times and initial torque settings.
Figure 1.4 Dual Ramp Start
➀ Dual Ramp Start is available only with the standard controller.
Full Voltage Start
This starting mode is used for applications requiring across-the-line
starting. The output voltage to the motor will reach full voltage within
1/4 second.
Figure 1.5 Full Voltage Start
Page 13
Product Overview 1-5
S
t
un
00%
peed
)
gh
w
w
gh
d
se
ATTENTION
!
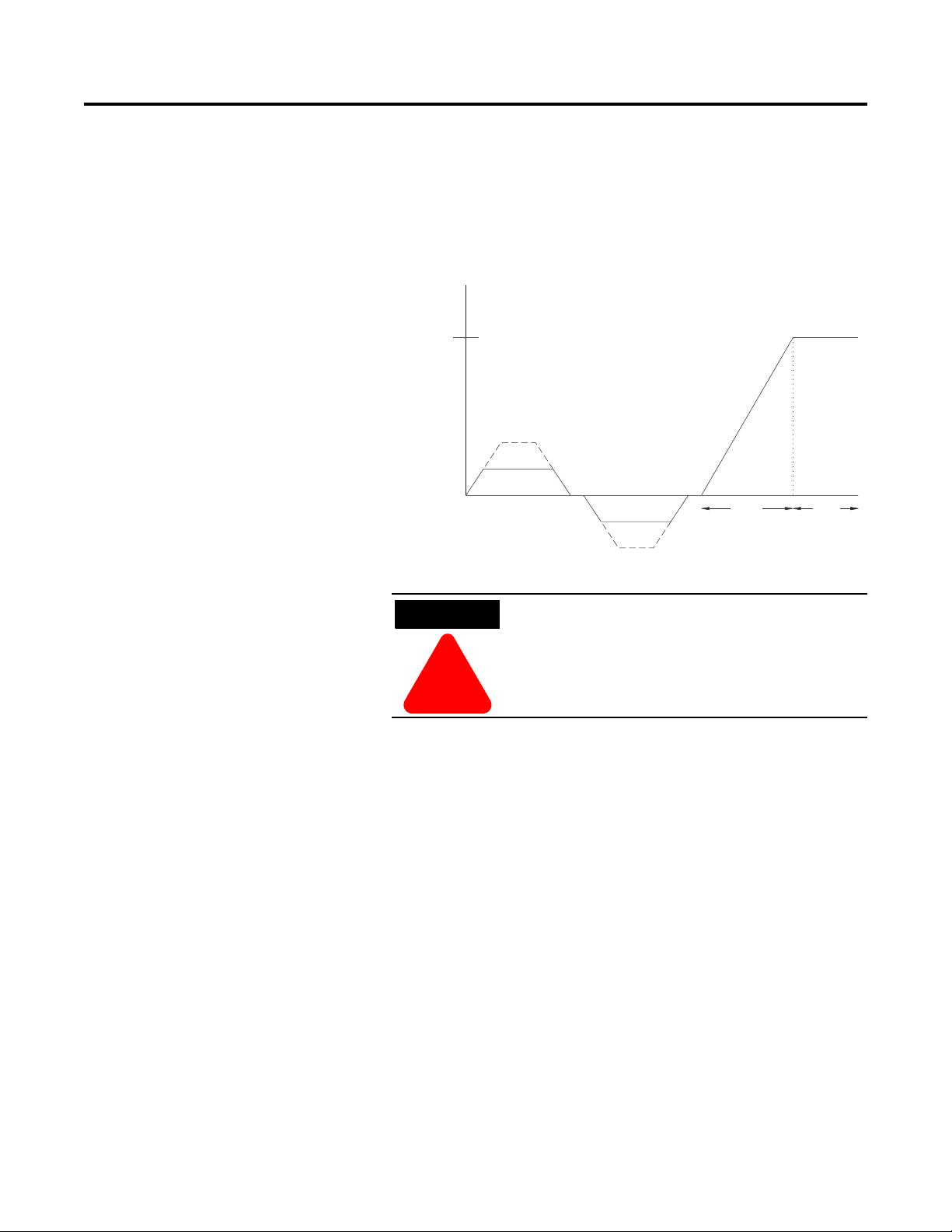
Preset Slow Speed
This option can be used in applications that require a slow speed jog
for general purpose positioning. Preset Slow Speed provides either
7% of base speed (low) or 15% of base speed (high) settings in the
forward direction. Reverse can also be programmed and offers 10%
of base speed (low) and 20% of base speed (high) settings.
Figure 1.6 Preset Slow Speed
1
Motor
S
Forwar
15% - Hi
7% - Lo
10% - Lo
20% - Hi
Time (seconds
Rever
tar
R
Slow speed running is not intended for continuous
operation due to reduced motor cooling.
Page 14
1-6 Product Overview
S
t
00%
peed
)
un
Stop
ATTENTION
!
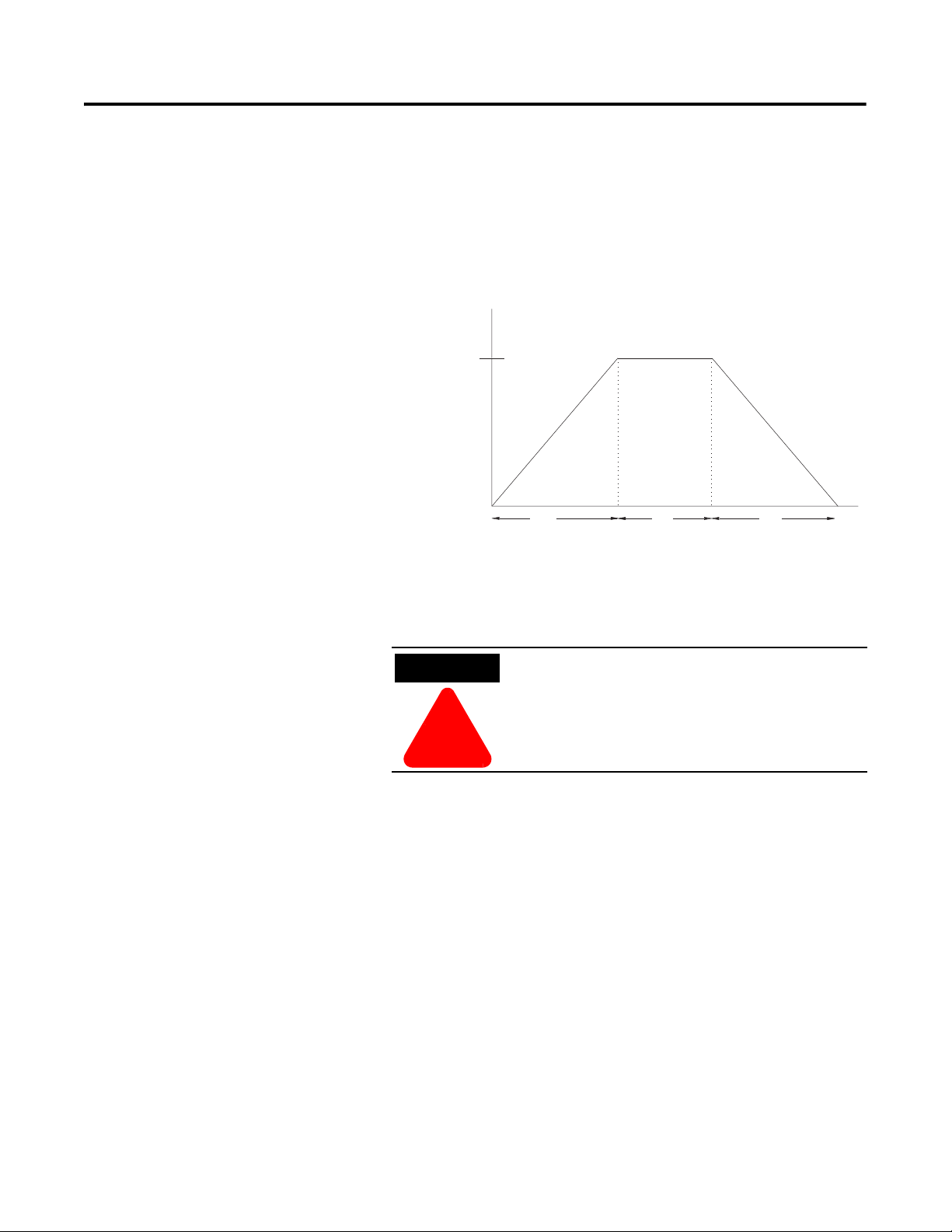
Linear Speed Acceleration
➀
The SMC-Flex has the ability to control the motor speed during
starting and stopping maneuvers. A tach input (0…5V DC) is
required to perform this start mode. The start time is selectable from
0…30 seconds and determines the time the motor will ramp from 0
speed to full speed. Kickstart is available with this option.
Figure 1.7 Linear Speed Acceleration
Percent
S
1
tar
R
Time (seconds
➀ Kickstart is also available with Linear Speed Acceleration.
Linear Stop is not intended to be used as an
emergency stop. Refer to the applicable standards
for emergency stop requirements.
The Linear Stop does not need to be set up even if the linear start has
been programmed. The Linear Stop can not brake the motor/load and
reduce the stopping time.
Page 15
Product Overview 1-7
S
t
un
00%
que
ge
)
S
t
p
C
t
p
ATTENTION
!
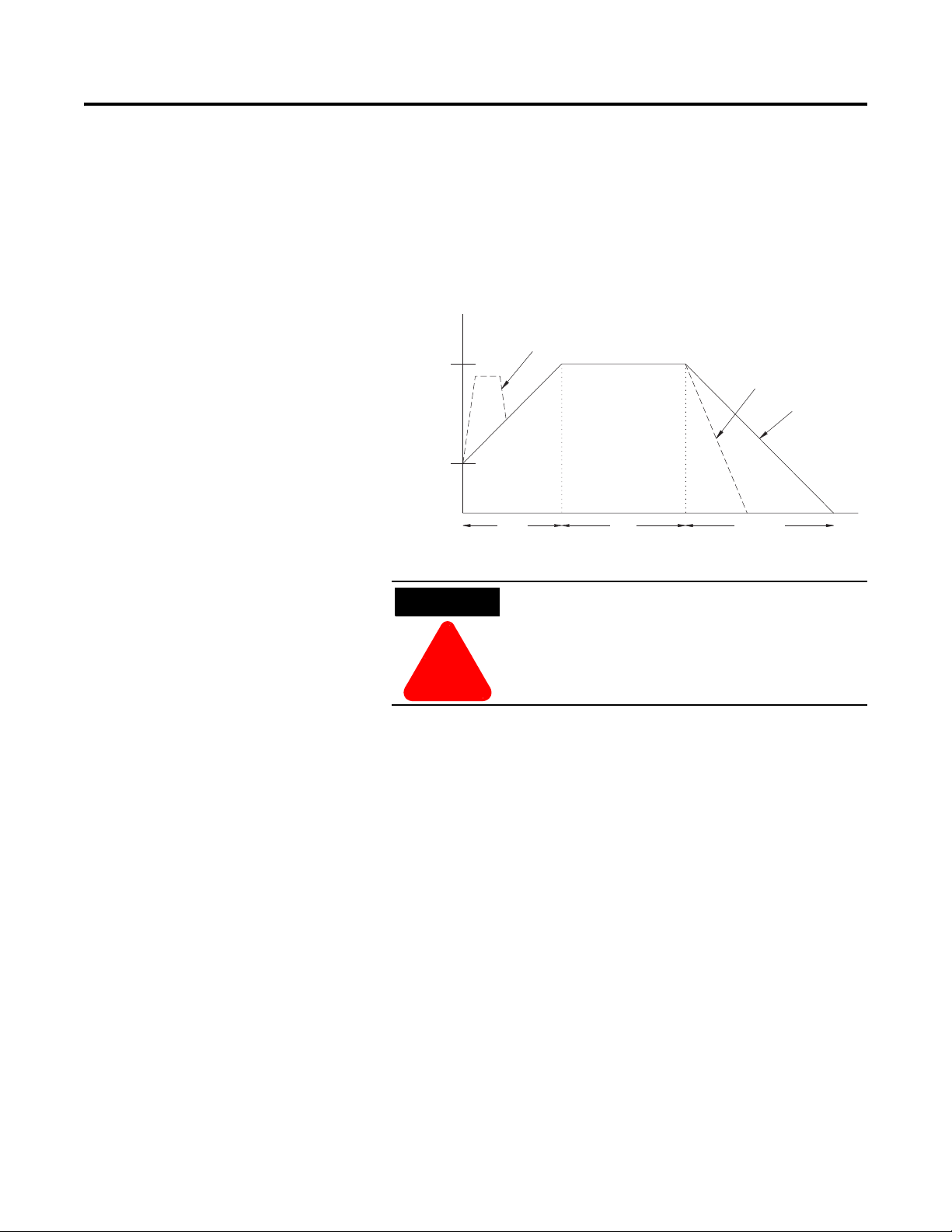
Soft Stop
This option can be used in applications that require an extended stop
time. The voltage ramp down time is user-adjustable from
0…120 seconds and is adjusted independently from the starting time.
The load will stop when the output voltage drops to a point where the
load torque is greater than the developed motor torque.
Figure 1.8 Soft Stop
Percent
Volta
1
Initial
Tor
electable Kickstar
oast-to-res
Soft Sto
tar
R
Time (seconds
Soft Sto
Soft Stop is not intended to be used as an emergency
stop. Refer to the applicable standards for
emergency stop requirements.
Page 16
1-8 Product Overview
100%
Motor Speed
Time in Seconds
Pump Start
Ramp Time
Run
Pump Stop
Stop Time
ATTENTION
!
ATTENTION
!
Control Options The SMC-Flex controller offers the control options described below.
Important: The options listed in this section are mutually exclusive
and must be specified when ordering. An existing
controller may be upgraded to another control option by
replacing the control module. Consult your local
Allen-Bradley distributor.
Modes of Operation
(Pump Control)
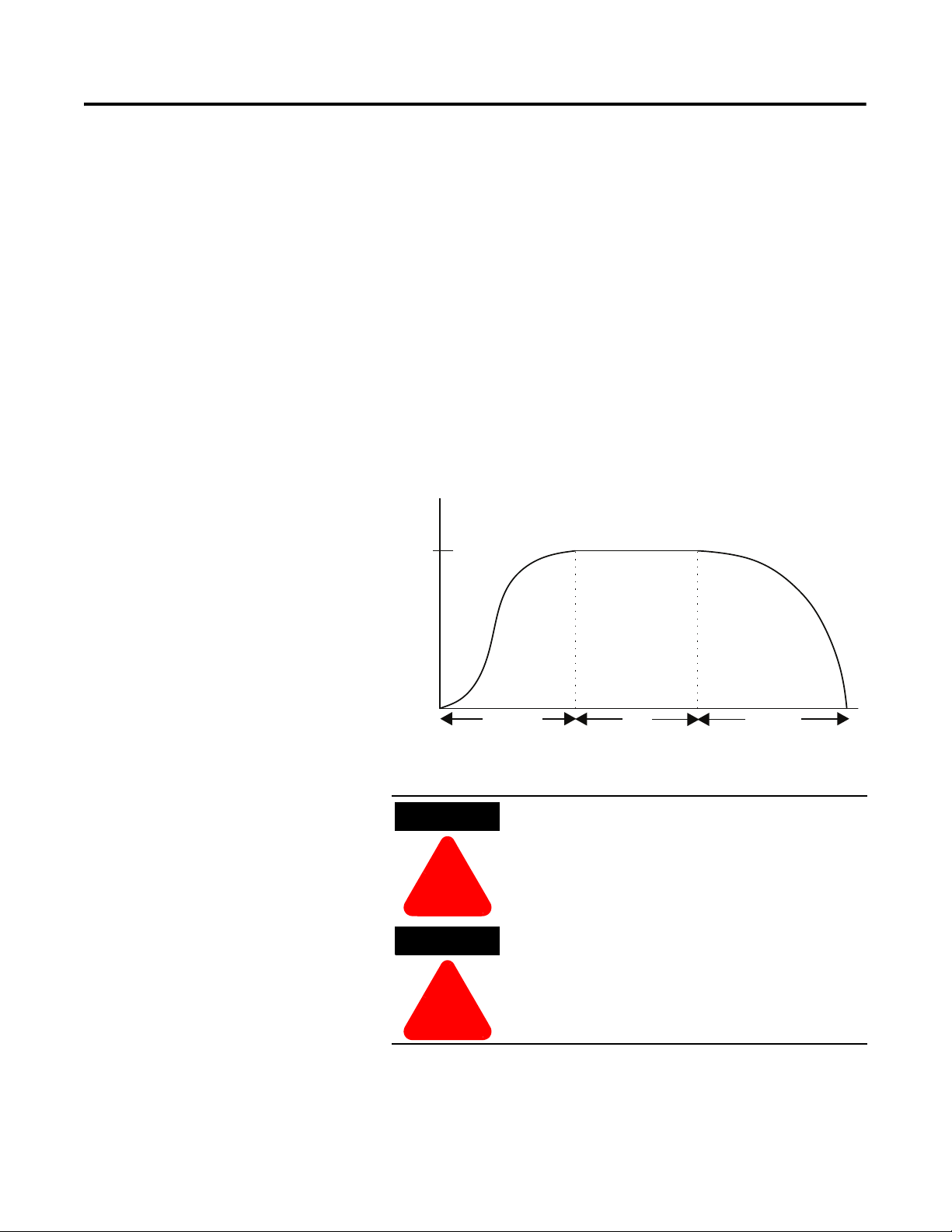
Pump Control Option
This option reduces surges during the starting and stopping of a
centrifugal pump by smoothly accelerating and decelerating the
motor. The microprocessor analyzes the motor variables and
generates commands that control the motor and reduce the possibility
of surges occurring in the system.
The starting time is programmable from 0…30 seconds, and the
stopping time is programmable from 0…120 seconds.
Figure 1.9 Pump Control Option
➀
➀ Kickstart is also available with Pump Control.
Pump stopping is not intended to be used as an
emergency stop. Refer to the applicable standard for
emergency stop requirements.
Pump stopping may cause motor heating depending
on the mechanical dynamics of the pumping system.
Therefore, select the lowest stopping time setting
that will satisfactorily stop the pump.
Page 17
Product Overview 1-9
100%
Motor Speed
Smart Motor
Braking
Coast-to-Rest
Time in Seconds
Automatic Zero
Speed Shut-Off
Start
Run
Brake
Stop
Time
ATTENTION
!
Modes of Operation
(Braking Control)
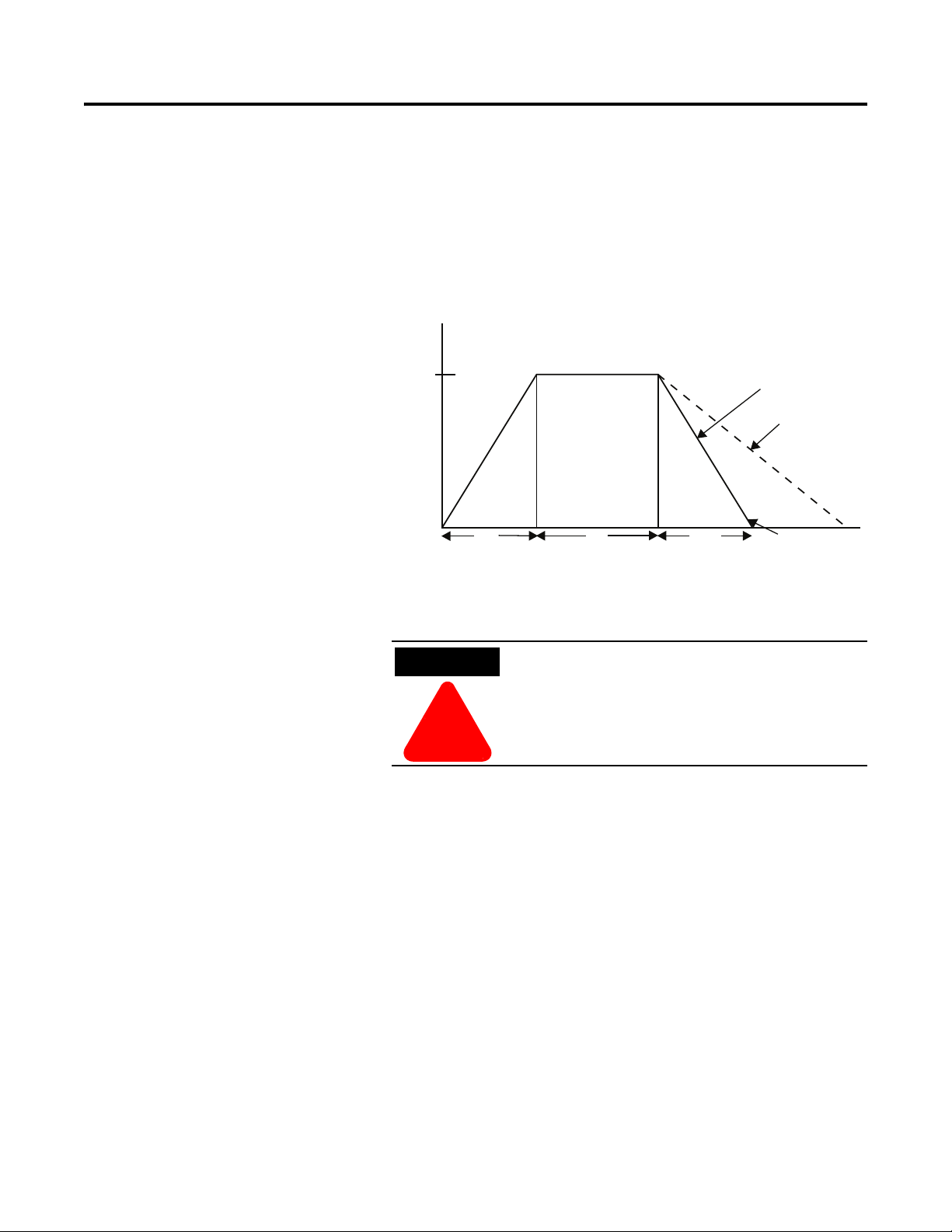
SMB™ Smart Motor Braking Option
This option can be used in applications that require reduced stopping
times. The SMC-Flex controller incorporates a microprocessor-based
system that applies braking current to a motor without any additional
equipment. This option offers a user-adjustable braking current
setting from 0% to 400% of the motor’s full load current rating.
Further, it provides automatic shut-off at zero speed detection.
Figure 1.10 SMB Smart Motor Braking Option
Note: All braking current settings in the range of 1…100% will
provide 100% braking current to the motor.
SMB Smart Motor Braking is not intended to be used
as an emergency stop. Refer to applicable standards
for emergency stop requirements.
Page 18
1-10 Product Overview
ATTENTION
!
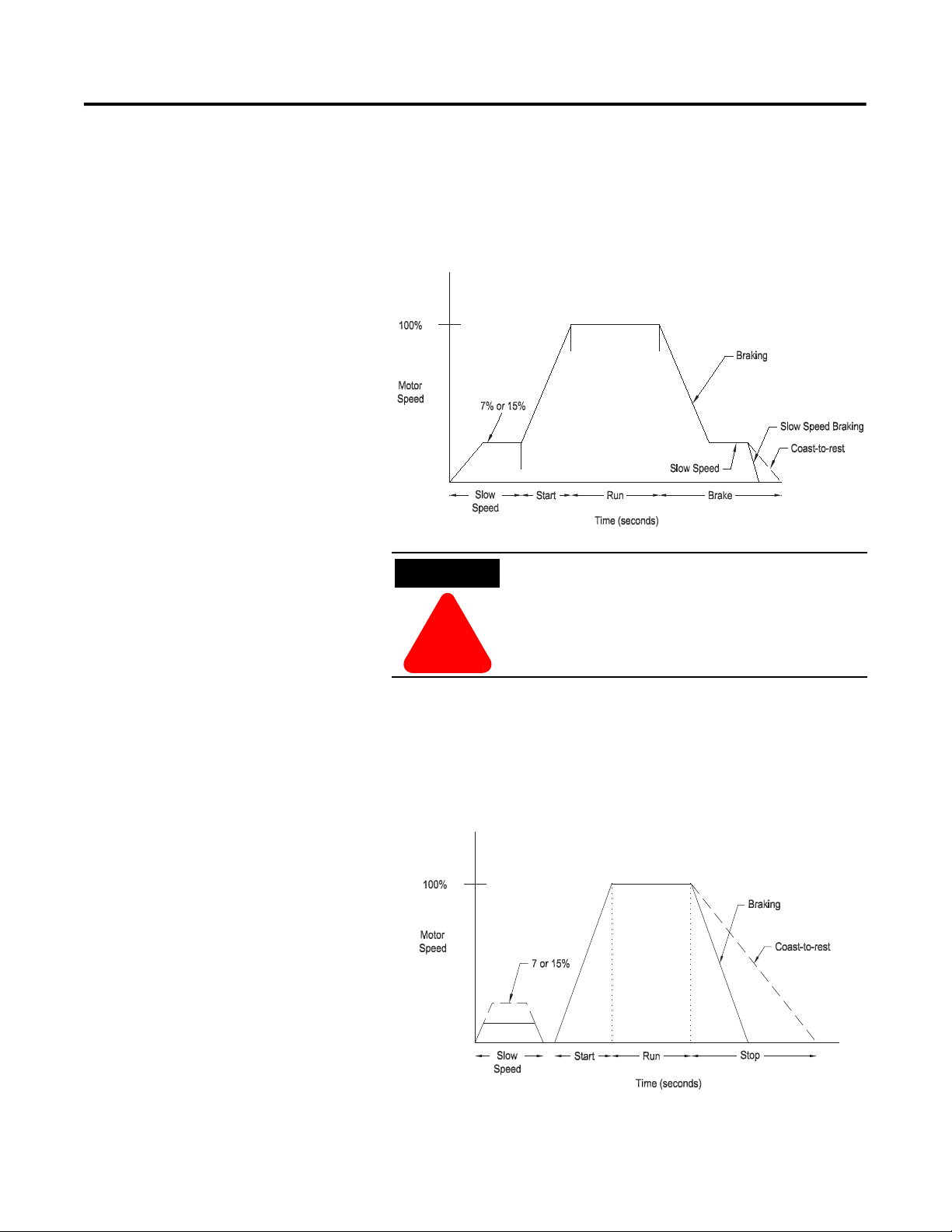
Accu-Stop™ Option
This option combines the benefits of the SMB Smart Motor Braking
and Preset Slow Speed options. For general purpose positioning, the
Accu-Stop option provides a brake from full speed to the preset slow
speed setting, then brakes to stop.
Figure 1.11 Accu-Stop Option
Accu-Stop and Slow Speed with Braking are not
intended to be used as an emergency stop. Refer to
applicable standards for emergency stop
requirements.
Slow Speed with Braking Option
The Slow Speed with Braking option provides a jog speed for process
set-up and braking-to-stop at the end of the cycle.
Figure 1.12 Slow Speed with Braking Option
Page 19

Product Overview 1-11
Protection and Diagnostics The SMC-Flex controller provides the protective and diagnostic
features described below.
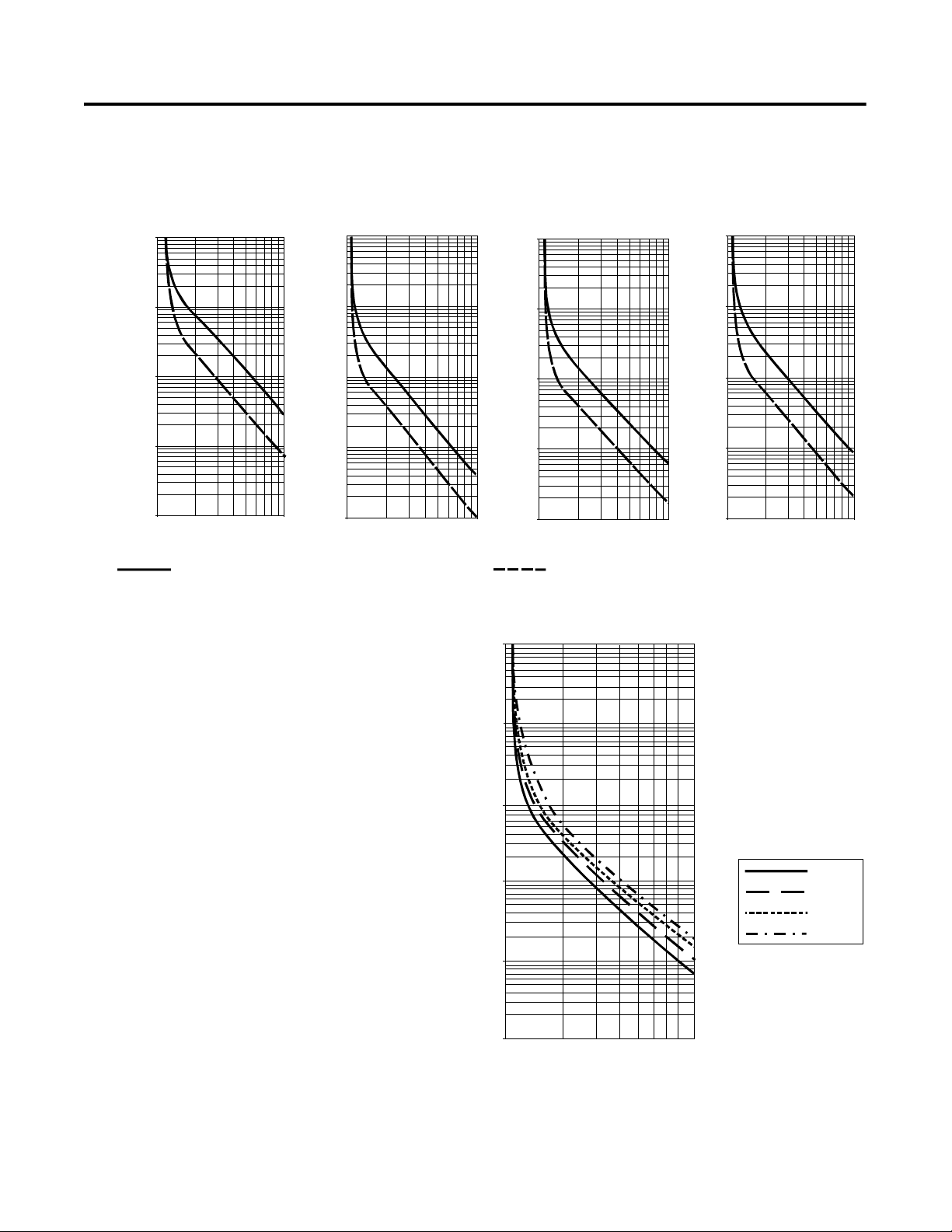
Overload
The SMC-Flex controller meets applicable requirements as a motor
overload protective device. Thermal memory provides added
protection and is maintained even when control power is removed.
The built-in overload controls the value stored in Parameter 12, Motor
Thermal Usage; an Overload Fault will occur when this value reaches
100%. The programming parameters below provide application
flexibility and easy setup.
Parameter Range
Overload Class Off, 10, 15, 20, 30
Overload Reset Manual – Auto
Motor FLC
Service Factor
Notes: (1) The factory default setting for Overload Class, which is
10, enables overload protection. The motor’s full load
current rating must be programmed to properly set
overload protection.
(2) Automatic reset of an overload fault requires the start
input to be cycled in a 2-wire control scheme.
1.0
…2200 A
0.01…1.99
The trip rating is 117% of the programmed FLC.
Figure 1.13 and Figure 1.14 provide the overload trip curves for the
available trip classes.
Underload
➀
Utilizing the underload protection of the SMC-Flex controller, motor
operation can be halted if a sudden drop in current is sensed.
The SMC-Flex controller provides an adjustable underload trip
setting from 0…99% of the programmed motor full load current
rating. Trip delay time can be adjusted from 0…99 seconds.
➀ Underload protection is disabled during slow speed and braking operations.
Page 20
1-12 Product Overview
Approximate trip time for 3-phase balanced
Approximate trip time for 3-phase balanced
1.0
10.0
100.0
1000.0
10000.0
1 10 2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4
0.1
1.0
10.0
100.0
1000.0
1 10 2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4
10.0
100.0
1000.0
10000.0
1
2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4
10.0
100.0
1000.0
10000.0
1 10 2 3 9 8 7 6 5 4
Approximate trip time for 3-phase balanced
condition from cold start.
Approximate trip time for 3-phase balanced
condition from hot start.
100%
0
1
10
100
1000
100000
Percent Full Load Current Setting
Class 10
Class 15
Class 20
Class 30
Auto Reset Times:
Class 10 = 90s
Class 15 = 135s
Class 20 = 180s
Class 30 = 270s
Class 10 Class 15 Class 20 Class 30
Figure 1.13 Overload Trip Curves
Approximate Trip Time (seconds)
Approximate Trip Time (seconds)
Approximate Trip Time (seconds)
1.0
Approximate Trip Time (seconds)
1.0
10
Multiples of FLC Multiples of FLC Multiples of FLC Multiples of FLC
condition from cold start.
condition from cold start.
Figure 1.14 Restart Trip Curves after Auto Reset
Seconds
1000%
Page 21

Product Overview 1-13
Undervoltage
➀
Utilizing the undervoltage protection of the SMC-Flex, motor
operation can be halted if a sudden drop in voltage is detected.
The SMC-Flex controller provides an adjustable undervoltage trip
setting from 0…99% of the programmed motor voltage. Trip delay
time can be adjusted from 0…99 seconds.
An alarm (pre-fault) indication level can be programmed to indicate
the unit is getting close to faulting. The alarm modification
information is displayed through the LCD, HIM, Communication (if
applicable) and alarm contact closing.
Overvoltage
➀
Utilizing the overvoltage protection of the SMC-Flex, motor
operation can be halted if a sudden increase in voltage is detected.
The SMC-Flex controller provides an adjustable overvoltage trip
setting from 0…199% of the programmed motor voltage. Trip delay
time can be adjusted from 0…99 seconds.
An alarm (pre-fault) indication level can be programmed to indicate
the unit is getting close to faulting. The alarm modification
information is displayed through the LCD, HIM, Communication (if
applicable) and alarm contact closing.
Unbalance
➀
The SMC-Flex is able to detect an unbalance in line voltages. Motor
operation can be halted if the unbalance is greater than the desired
range.
The SMC-Flex controller provides an adjustable unbalance setting
from 0…25% of the line voltages. Trip delay time can be adjusted
from 0…99 seconds.
An alarm (pre-fault) indication level can be programmed to indicate
the unit is getting close to faulting. The alarm modification
information is displayed through the LCD, HIM, Communication (if
applicable) and alarm contact closing.
➀ Undervoltage, overvoltage, and voltage unbalance protection are disabled during braking operation.
Page 22
1-14 Product Overview
Stall
600%
Percent
Full
Load
Current
Time (seconds)
Programmed Start Time
100%
Running Jam
Percent
Full
Load
Current
Time (seconds)
User Programmed Trip Level
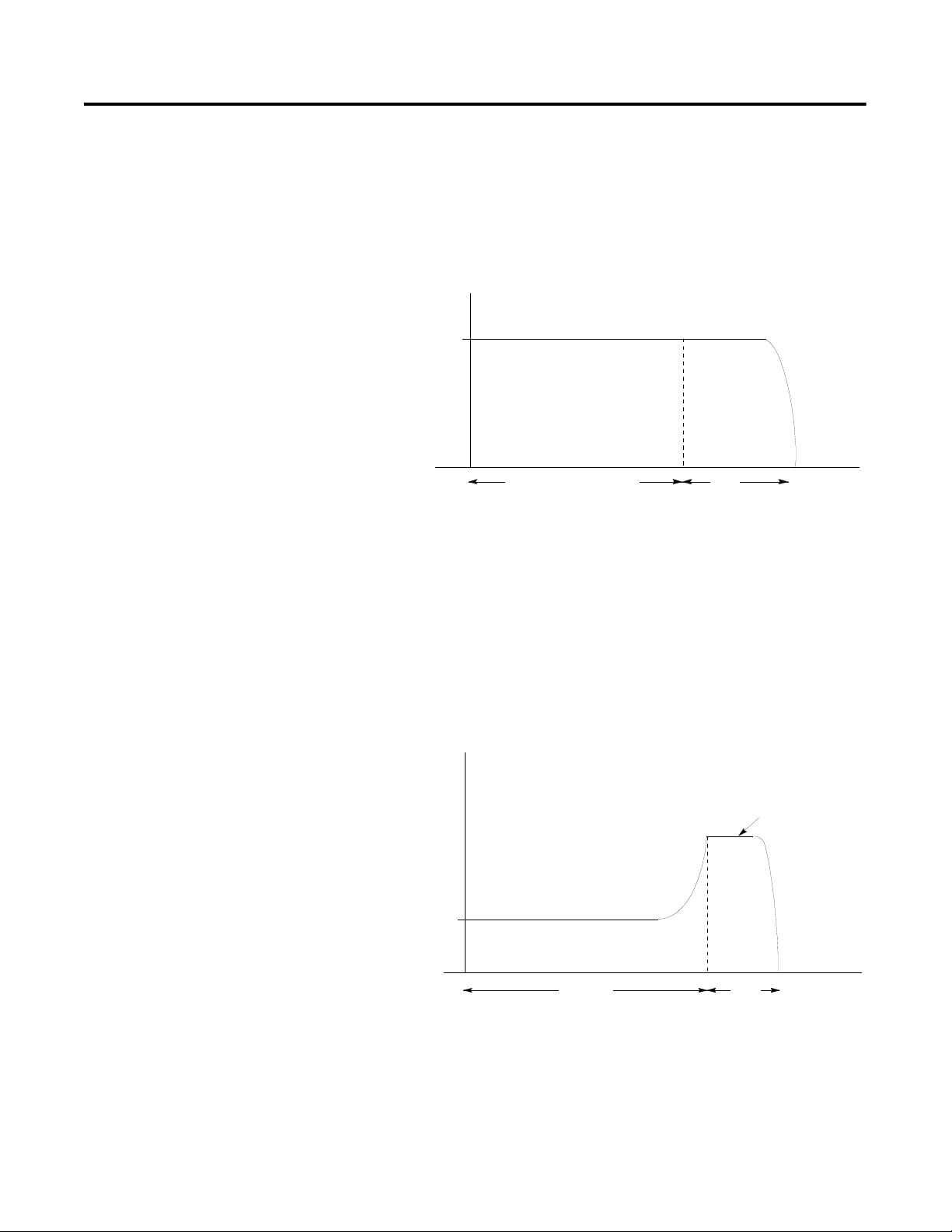
Stall Protection and Jam Detection
The SMC-Flex controller provides both stall protection and jam
detection for enhanced motor and system protection.
• Stall protection is user-adjustable from 0.0…10.0 seconds (in
addition to the ramp time programmed).
Figure 1.15 Stall Protection
• An alarm (pre-fault) indication level can be programmed to
indicate the unit is getting close to faulting. The alarm
modification information is displayed through the LCD, HIM,
Communication (if applicable) and alarm contact closing.
• Jam detection allows the user to determine the jam level (up to
1000% of the motor’s FLC rating) and the delay time (up to
99.0 seconds) for application flexibility.
Figure 1.16 Jam Detection
➀➁
➀ Jam detection is disabled during slow speed and braking operation.
➁ Unit will self-protect in a jam condition.
Page 23
Product Overview 1-15
Ground Fault
In isolated or high impedance-grounded systems, core-balanced
current sensors are typically used to detect low level ground faults
caused by insulation breakdowns or entry of foreign objects.
Detection of such ground faults can be used to interrupt the system to
prevent further damage, or to alert the appropriate personnel to
perform timely maintenance.
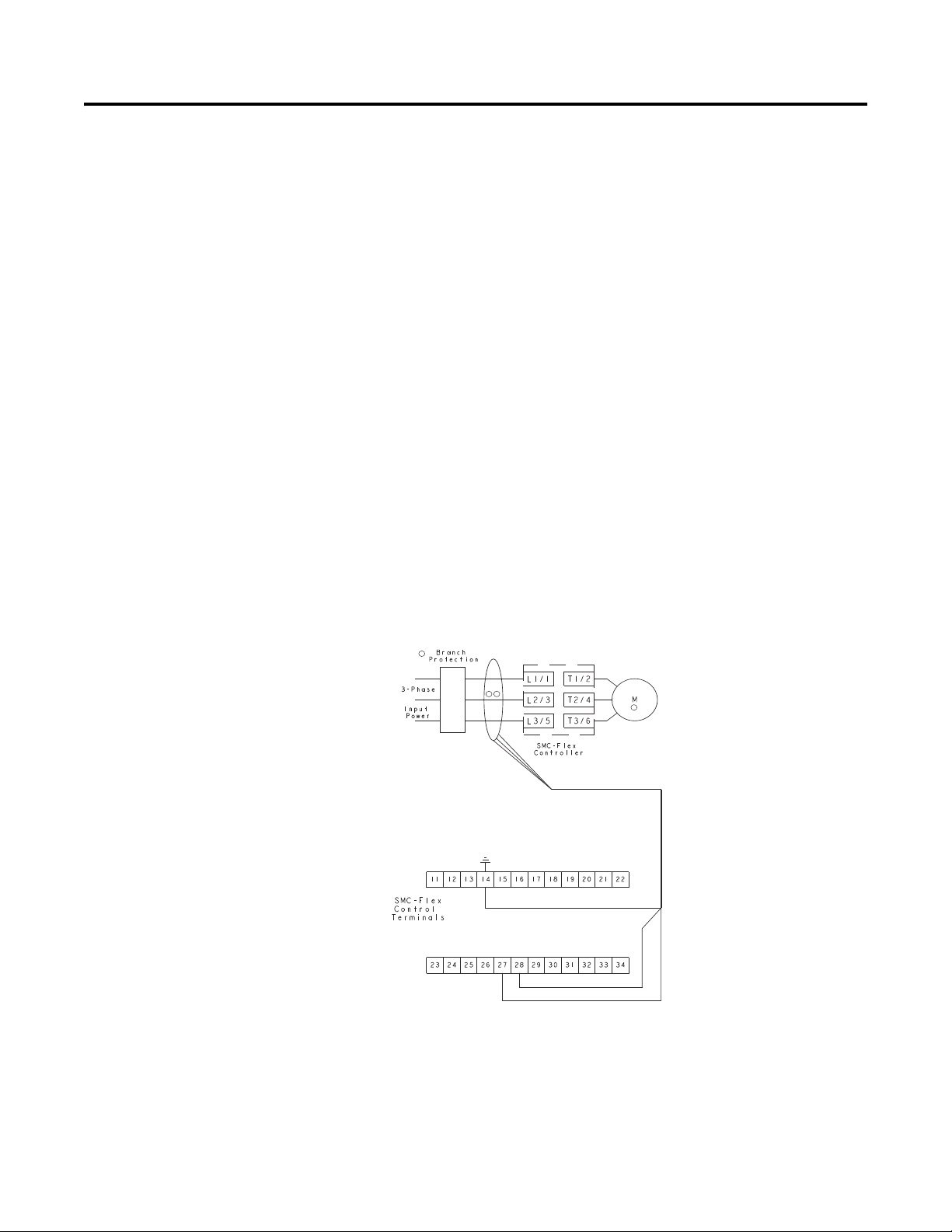
The SMC-Flex’s ground fault detection capabilities require the use of
external sensor. Installation of this sensor allows the option of
enabling Ground Fault Trip, Ground Fault Alarm, or both.
For the 5…480 Amp devices, the recommended sensor is a Cat. No.
825-CBCT core balance current transformer for 1…5 A corebalanced ground fault protection.
For the 625…1250 A devices, the recommended sensor is shown
below and provides 5…25 A core-balanced ground fault protection.
• Manufacturer: Allen-Bradley
• Description: 600 Volt-Rated Current Transformer
• Catalog Number: 1411-126-252
• Ratio: 2500:5
Figure 1.17
1
2
1
BLACK
WHITE
SHIELD
SHIELD
BLACK
WHITE
➀ Customer supplied.
➁ Cat. No. 825-CBCT or Flex-Core Cat. No. 126-252
1
Note: When connecting the ground fault sensors, the secondary of
the CT should be shorted until the connection to the Flex
control module is completed.
Page 24

1-16 Product Overview
Ground Fault Trip
The SMC-Flex will trip with a ground fault indication if:
• No other fault currently exists
• Ground fault protection is enabled
• GF Inhibit Time has expired
• GF Current is equal to or greater than the GF Trip Level for a
time period greater than the GF Trip Delay
Parameter 75, Gnd Flt Inh Time, allows the installer to inhibit a
ground fault trip from occurring during the motor starting sequence
and is adjustable from 0…250 seconds.
Parameter 74, Gnd Flt Delay, allows the installer to define the time
period a ground fault condition must be present before a trip occurs. It
is adjustable from 0.1…250 seconds.
Parameter 73, Gnd Flt Level, allows the installer to define the ground
fault current at which the SMC-Flex will trip. It is adjustable from
1.0…5.0 A or 5.0…25 A, depending on the service size.
Important: The ground fault inhibit timer starts after the maximum
phase of load current transitions from 0 A to 30% of the
device’s minimum FLA Setting or the GF Current is
greater than or equal to 0.5 A. The SMC-Flex does not
begin monitoring for a ground fault condition until the
Gnd Flt Inh Time expires.
Ground Fault Alarm
The SMC-Flex will indicate a Ground Fault Alarm if:
• No warning currently exists
• Ground fault alarm is enabled
• GF Inhibit Time has expired
• GF Current is equal to or greater than the Gnd Flt A Lvl
Parameter 77, Gnd Flt A Lvl, allows the installer to define the ground
fault current at which the SMC-Flex will indicate a warning. It is
adjustable from 1.0…5.0 A or 5.0…25 A, depending on the service
size.
Parameter 78, Gnd Flt A Dly, allows the installer to define the time
period a ground fault alarm condition must be present before a trip
occurs. It is adjustable from 0…250 seconds.
Page 25
Product Overview 1-17
10
20
100
250
550
1330
4000
-20°C TNF-20K
0°C TNF- 5K
TNF+15K
TNF+ 5K
TNF
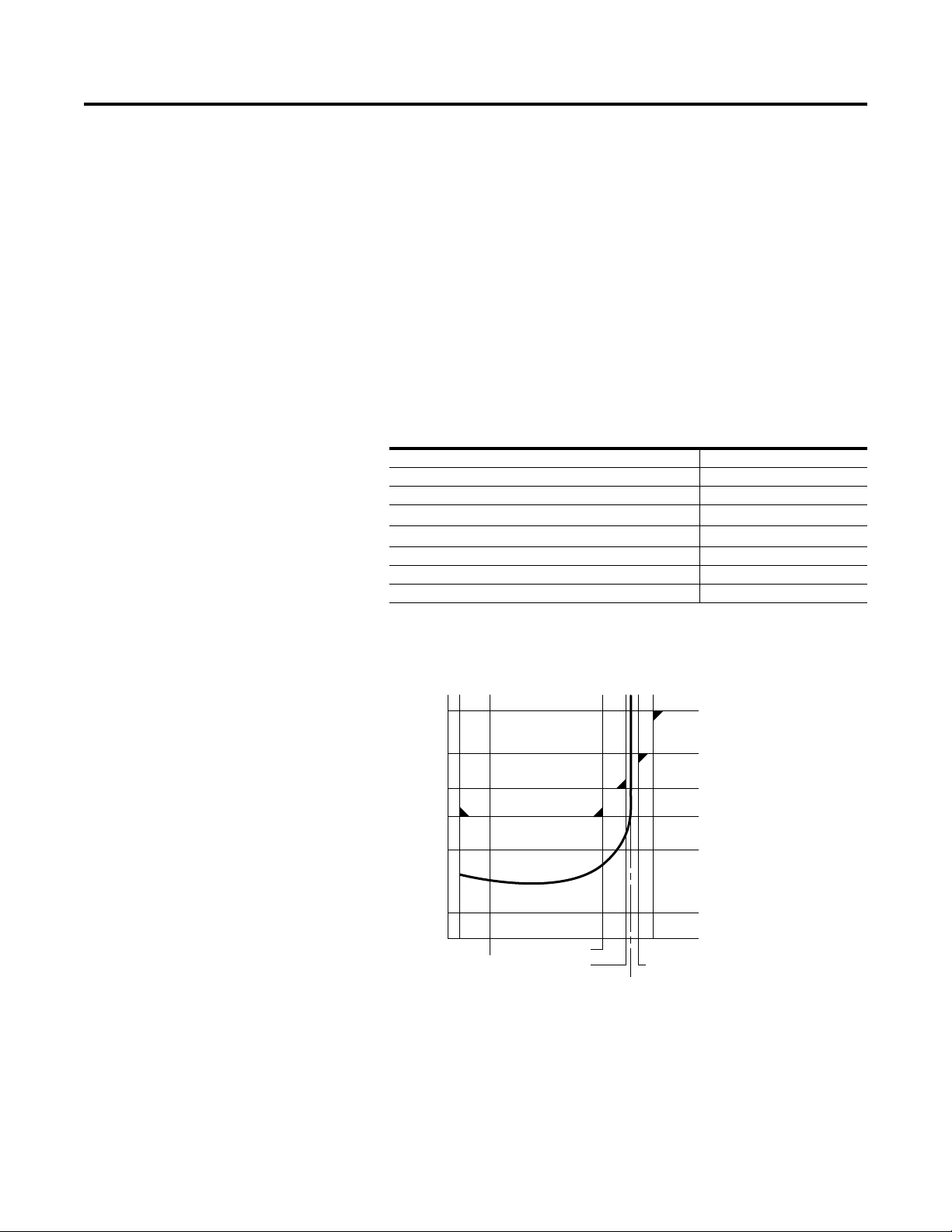
Thermistor/PTC Protection
The SMC-Flex provides terminals 23 and 24 for the connection of
positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistor sensors. PTC
sensors are commonly embedded in motor stator windings to monitor
the motor winding temperature. When the motor winding temperature
reaches the PTC sensor’s temperature rating, the PTC sensor’s
resistance transitions from a low to high value. Since PTC sensors
react to actual temperature, enhanced motor protection can be
provided to address such conditions as obstructed cooling and high
ambient temperatures.
The following table defines the SMC-Flex PTC thermistor input and
response ratings:
Table 1.A PTC Input Ratings
Response resistance 3400 Ω ±150 Ω
Reset resistance 1600 Ω ±100 Ω
Short-circuit Trip Resistance 25 Ω ±10 Ω
Maximum Voltage at PTC Terminals (R
Maximum Voltage at PTC Terminals (R
Maximum Number of Sensors 6
Maximum Cold Resistance of PTC Sensor Chain 1500 Ω
Response Time 800 ms
= 4kΩ) < 7.5V
PTC
= open) 30V
PTC
The following figure illustrates the required PTC sensor
characteristics, per IEC-34-11-2.
Figure 1.18 PTC Sensor Characteristics per IEC-34-11-2
PTC Trip
The SMC-Flex will trip with a PTC indication if:
• No other fault currently exists
• PTC protection is enabled
Page 26

1-18 Product Overview
• The resistance across terminals 23 and 24 is either greater than
the relay’s response resistance or less than the short-circuit trip
resistance.
Excessive Starts/Hour
The SMC-Flex controller allows the user to program the allowed
number of starts per hour (up to 99). This helps eliminate motor stress
caused by repeated starting over a short time period.
Overtemperature
The SMC-Flex controller monitors the temperature of the SCRs and
Bypass by using internal thermistors. When the power poles’
maximum rated temperature is reached, the unit will shut down and
restart is inhibited.
An overtemperature condition can indicate inadequate ventilation,
high ambient temperature, overloading, or excessive cycling. After
the temperature is reduced to allowable levels, the fault can be
cleared.
Open Gate
An open gate fault indicates that improper SCR firing, typically
caused by an open SCR gate, has been detected on one of the power
poles. Before the controller shuts down, it will attempt to start the
motor a total of three times.
Line Faults
The SMC-Flex controller continually monitors line conditions for
abnormal factors. Pre-start protection includes:
• Line Fault (with phase indication)
– Line voltage loss
– Missing load connection
– Shorted SCR
Running protection includes:
• Line Fault (no phase indication)
– Line voltage loss
– Missing load connection
Phase Reversal
➀
protection can be toggled either On or Off.
➀ Phase Reversal protection is functional only at pre-start.
Page 27

Metering Power monitoring parameters include:
• Three-phase current
• Three-phase voltage
•Power in kW
• Power usage in kWH
•Power factor
• Motor thermal capacity usage
• Elapsed time
Notes: (1) Voltage measurement is not available during the braking
operation of the SMB Smart Motor Braking, Accu-Stop,
and Slow Speed with Braking control options.
(2) The elapsed time and kWH values are automatically
saved to memory every 12 hours.
(3) Motor thermal capacity usage is determined by the built-
in electronic thermal overload. An overload fault occurs
when this value reaches 100%.
Product Overview 1-19
I/O The SMC-Flex has the ability to accept up to two (2) inputs and
four (4) outputs controlled over a network. The two inputs are
controlled at terminal 16 (Option Input #1), and terminal 15
(Option Input #2). For these two inputs, see Chapter 4 for the
parameter settings and see Chapter 7 for the bit identification.
By using these two terminals as inputs, the Stop Input will need to be
programmed to meet the desired stop functionality.
The four (4) outputs are Aux #1, Aux #2, Aux #3, and Aux #4. All
auxiliary contacts are programmable to the function found on
page 4-14. If programmed to Network or Network NC, they can be
controlled over a Network. Please see Table 7.H that defines the
Logic Command Word (Control).
Page 28
1-20 Product Overview
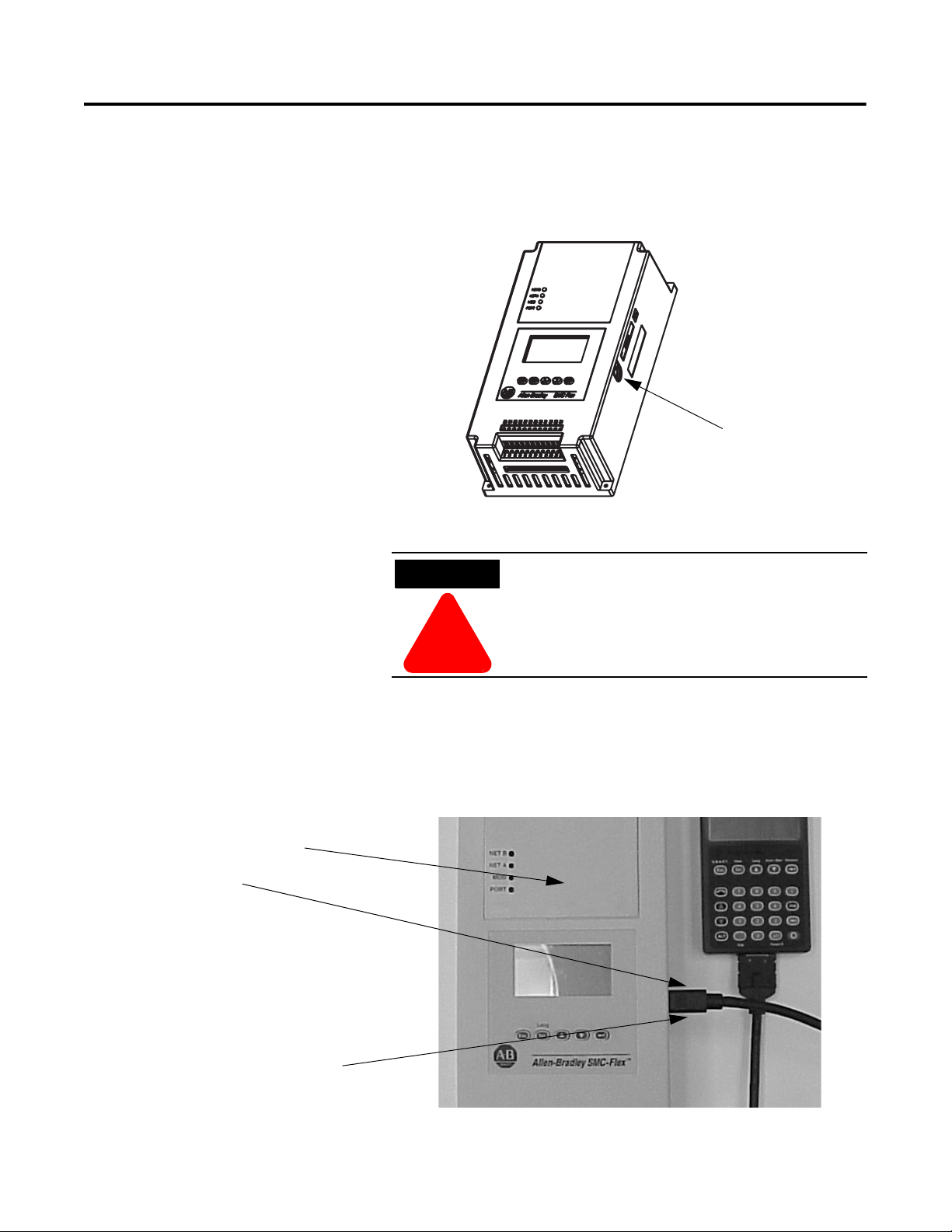
DPI
ATTENTION
!
Port 5 — DPI
Communications
Port 2
Ports 2 and 3 when two
HIMs are connected with
a splitter
Communication A serial interface port (DPI) is provided as standard, which allows
connection to the Bulletin 20-HIM LCD interface modules.
Figure 1.19 DPI Location
Two peripheral devices can be connected to the DPI.
The maximum output current through the DPI is
280 mA.
Programming Setup is easy with the built-in keypad and three-line, sixteen character
backlit LCD. Parameters are organized in a three-level menu
structure, using a text format for straightforward programming.
Figure 1.20 Built-in Keypad and LCD
Page 29
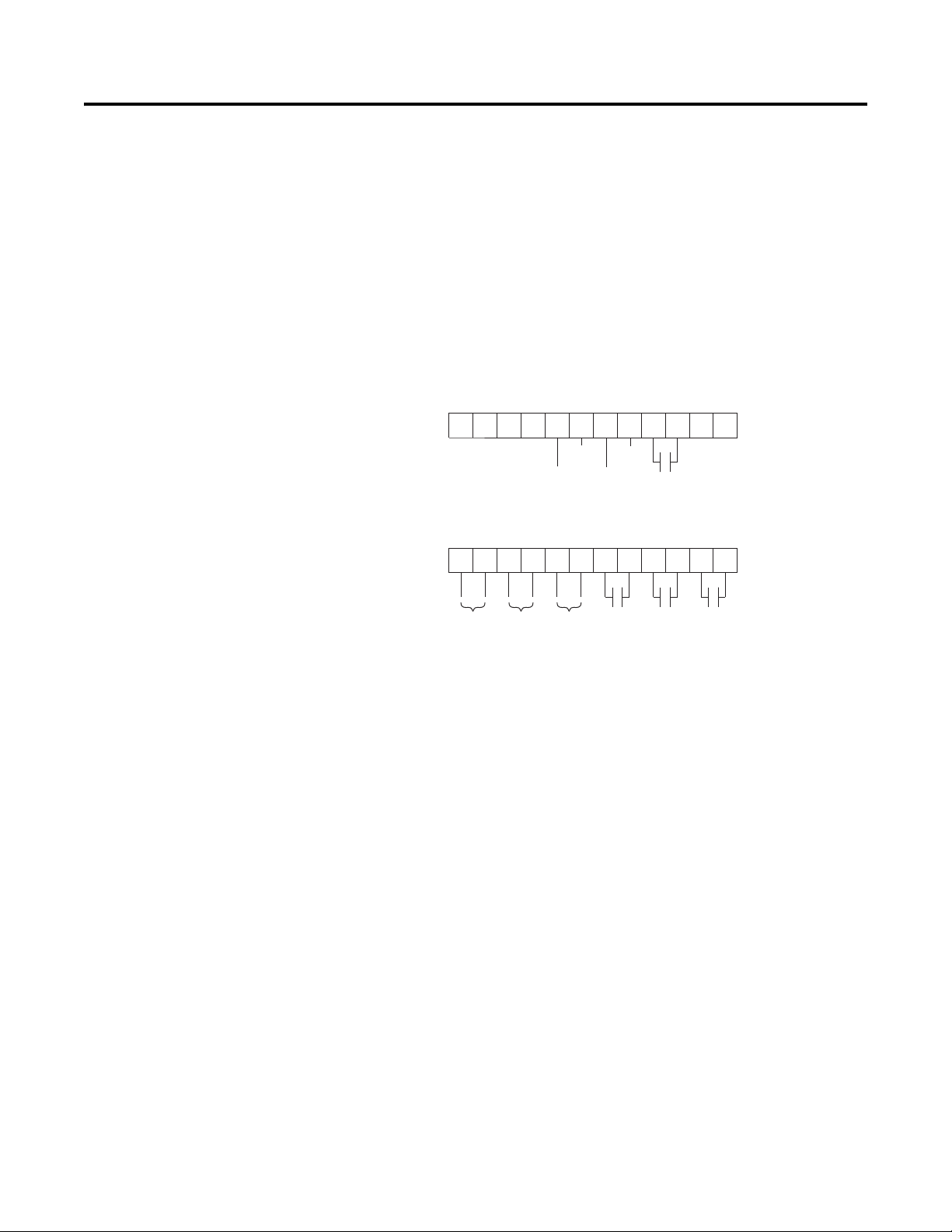
Product Overview 1-21
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3
Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
Stop
Input
Start
Input
Opt
Input #2
Opt
Input #1
Status Indication Four programmable hard contact outputs are provided as standard. All
auxiliary contacts are programmable for the following states:
• Normal (N.O./N.C.)
• Up-to-Speed (N.O./N.C.)
• Alarm (N.O./N.C.)
• Fault (N.O./N.C.)
• Network Control (N.O./N.C.)
• External Bypass (N.O.)
Figure 1.21 Control Terminals
Network inputs can be obtained through proper programming of
Option Input #1 and Option Input #2.
Page 30

1-22 Product Overview
Notes
Page 31

Chapter 2
Installation
Degree of Protection The SMC-Flex soft starters have an IP00 or IP2X protection rating,
depending on the size. Taking into account the ambient conditions,
the device must be installed in IP54 (Type 2) switchgear cabinets.
Make sure that no dust, liquids, or conductive parts can enter the soft
starter. Soft starter operation produces waste heat (heat loss). See
Table 2.A or Specifications on page A-9, for details.
Receiving It is the user’s responsibility to thoroughly inspect the equipment
before accepting the shipment from the freight company. Check the
item(s) received against the purchase order. If any items are damaged,
it is the responsibility of the user not to accept delivery until the
freight agent has noted the damage on the freight bill. Should any
concealed damage be found during unpacking, it is again the
responsibility of the user to notify the freight agent. The shipping
container must be left intact and the freight agent should be requested
to make a visual inspection of the equipment.
Unpacking Remove all packing material, wedges, or braces from within and
around the controller.
Inspecting After unpacking, check the item(s’) nameplate catalog number
against the purchase order.
Storing The controller should remain in its shipping container prior to
installation. If the equipment is not to be used for a period of time, it
must be stored according to the following instructions in order to
maintain warranty coverage.
• Store in a clean, dry location.
• Store within an ambient temperature range of –20°C to +75°C
(–4°F to +167°F).
• Store within a relative humidity range of 0% to 95%,
noncondensing.
• Do not store equipment where it could be exposed to a corrosive
atmosphere.
• Do not store equipment in a construction area.
Page 32

2-2 Installation
Lifting Points
Lifting For controllers rated 625…1250 A, the device should only be lifted
from designated lifting points. The lifting points are designed to
accept a ½ -13 threaded hoist ring capable of lifting 2500 pounds.
These points are identified in Figure 2.1.
Figure 2.1 Lifting Points
Page 33

Installation 2-3
ATTENTION
!
ATTENTION
!
ATTENTION
!
ATTENTION
!
General Precautions In addition to the precautions listed throughout this manual, the
following statements, which are general to the system, must be read
and understood.
The controller contains ESD- (electrostatic
discharge) sensitive parts and assemblies. Static
control precautions are required when installing,
testing, servicing, or repairing the assembly.
Component damage may result if ESD control
procedures are not followed. If you are not familiar
with static control procedures, refer to applicable
ESD protection handbooks.
An incorrectly applied or installed controller can
damage components or reduce product life. Wiring
or application errors, such as undersizing the motor,
incorrect or inadequate AC supply, or excessive
ambient temperatures, may result in malfunction of
the system.
Only personnel familiar with the controller and
associated machinery should plan or implement the
installation, start-up, and subsequent maintenance
of the system. Failure to do this may result in
personal injury and/or equipment damage.
Hazardous voltages that can cause shock, burn, or
death are present on L1, L2, L3, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5,
and T6.
Power terminal covers can be installed to prevent
inadvertent contact with terminals. Disconnect the
main power before servicing the motor controller or
associated wiring.
Heat Dissipation The following table provides the maximum heat dissipation at rated
current for the controllers. For currents lower than rated value, heat
dissipation will be reduced.
Table 2.A Maximum Heat Dissipation
SMC
Rating
5 A 25 A 43 A 60 A 85 A 108 A 135 A 201 A 251 A 317 A 361 A 480 A 625 A 700 A 970 A 1250 A
Max.
Watts
70 70 81 97 129 91 104 180 198 225 245 290 446 590 812 1222
Page 34

2-4 Installation
Enclosures The open-style design of the SMC-Flex controller requires that it be
installed in an enclosure. The internal temperature of the enclosure
must be kept within the range of 0…50°C.
For Type 12 (IP54) enclosures, the following guidelines are
recommended to limit the maximum controller ambient temperature.
There should be a clearance of at least 15 cm (6 in.) above and below
the controller. This area allows air to flow through the heatsink.
Table 2.B Minimum Enclosure Size ➊
Controller
Rating (A)
5 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
25 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
43 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
60 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
85 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
108 762 (30) 610 (24) 305 (12)
135 762 (30) 610 (24) 305 (12)
201 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
251 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
317 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
361 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
480 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
625 2286 (90) 889 (35) 508 (20)
780 2286 (90) 889 (35) 508 (20)
5 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
25 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
43 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
60 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
85 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
108 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
135 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
201 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
251 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
317 1524 (60) 965 (38) 356 (14)
361 1524 (60) 965 (38) 356 (14)
480 ➊ 1524 (60) 965 (38) 356 (14)
480 ➋ 2286 (90) 889 (35) 508 (20)
625 2286 (90) 1397 (55) 508 (20)
780 2286 (90) 1397 (55) 508 (20)
5 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
25 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
43 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
60 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
85 610 (24) 406 (16) 254 (10)
108 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
135 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
201 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
251 965 (38) 762 (30) 356 (14)
317 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
361 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
480 1295 (51) 914 (36) 356 (14)
625 2286 (90) 1397 (55) 508 (20)
780 2286 (90) 1397 (55) 508 (20)
➊ Larger enclosure may be required based on options selected. Consult your local Rockwell
Automation Sales office or Allen-Bradley distributor.
➋ Use this row for 460V -58 and 575V -59.
➌ Use this row for 460V -59 and 575V -60 and -61.
B Height A Width C Depth
Non-Combination Controller [mm (in.)]
Combination Controllers with Fusible Disconnect
Combination Controllers with Circuit Breaker
IP65 (Type 4/12)
Page 35

Installation 2-5
Mounting All units are fan cooled. It is important to locate the controller in a
position that allows air to flow vertically through the power module.
The controller must be mounted in a vertical plane and have a
minimum of 15 cm (6 in.) free space above and below the
controller.
When drilling or installing near the softstarter, make sure that
adequate measures are taken to protect the device from dust and
debris. See Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2 SMC-Flex Mounting Protection
Page 36

2-6 Installation
C
F
B
E
A
D
H
Figure 2.3 Dimensions: 5…85 A Controllers
5…85 A
Controller
Unit
mm 150.1 307 203.1 120 291 119.8 14.1 5.7 kg
A
WidthBHeightCDepth
DEFH
in. 5.91 12.09 8.00 4.72 11.46 4.72 0.56 12.6 lb.
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
Approx.
Ship. Wt.
Page 37

Figure 2.4 Dimensions: 108…135 A Controllers
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Installation 2-7
Unit
108…135 A
Controller
mm 196.4 443.7 212.2 166.6 367 129.5 26 15 kg
in. 7.74 17.47 8.35 6.56 14.45 5.10 1.02 33 lb.
A
Width
B
Height
C
Depth
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
DEFG
Approx.
Ship. Wt.
Page 38

2-8 Installation
157.25
(6.2)
6.4
(.250)
253.8
(9.992)
40.9
(1.6)
C
1.000
13.5
(.531)
50.8
(2.0)
24.9
(.980)
25
(.984)
48
(1.890)
SCALE
#8-32 UNC-2B
M10 X 1.5
560
(22.047)
225
(8.858)
504.1
(19.847)
150
(5.906)
Ø
13
(.513)
Ø
11.5
(.453)
Ø
27.5
(1.083)
19.7
(.776)
91.189
(3.59)
164.126
(6.46)
152.749
(6.01)
44.311
(1.74)
79.811
(3.14)
245.689
(9.67)
80
(3.15)
SEE DETAIL AA
G
Figure 2.5 Dimensions: 201…251 A Controllers
201…251 A
Controller
Unit
A
WidthBHeightCDepth
DEFGHI
Approx.
Ship. Wt.
mm 225 560 253.8 150 504.1 157.25 91.189 44.311 79.811 30.4 kg
in. 8.858 22.047 9.992 5.906 19.847 6.2 3.59 1.74 3.14 67 lb.
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
Page 39

40.9
(1.6)
276.5
(10.89)
182.25
(7.18)
C
63.5
(2.50)
17
(.67)
22.5
(.89)
#8 - 32 UNC - 2B
12.522
(.49)
32.74
(1.29)
48
(1.89)
M12 x 1.75
30.5
(1.20)
Figure 2.6 Dimensions: 317…480 A Controllers
Installation 2-9
Unit
A
WidthBHeightCDepth
DEFGH I
Ship. Wt.
Approx.
317…480 A
Controller
mm 290 600 276.5 200 539.18 182.25 104.5 55.5 103.5 45.8 kg
in. 11.42 23.62 10.89 7.87 21.23 7.18 4.11 2.19 4.07 101 lb.
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
Page 40

2-10 Installation
23.5023.50
596,9596,9
[ ]
41.0041.00
1041,41041,4
[ ]
2.002.00
50,850,8
[ ]
4.004.00
101,6101,6
[ ]
1.201.20
30,530,5
[ ]
21.6921.69
550,9550,9
[ ]
1.641.64
41,641,6
[ ]
7.897.89
200,4200,4
[ ]
23.3923.39
594,1594,1
[ ]
38.4538.45
976,6976,6
[ ]
.90.90
2323
[ ]
13.6313.63
346,2346,2
[ ]
2X 2X .2525
6,46,4
[ ]
.
7878
19,819,8
[ ]
3.623.62
92,192,1
[ ]
8.468.46
214,9214,9
[ ]
3X 3X .2525
.05.05
[ ]
.39.39
1010
[ ]
13.8613.86
351,9351,9
[ ]
14.5414.54
369,4369,4
[ ]
19.5419.54
496,3496,3
[ ]
29.0229.02
737737
[ ]
Ø
.500.500
12,712,7
[ ]
Ø
.531.531
13,4913,49
[ ]
7.357.35
186,6186,6
[ ]
14.3514.35
364,4364,4
[ ]
8.258.25
209,5209,5
[ ]
7.007.00
177,8177,8
[ ]
4X 4X 2.752.75
69,869,8
[ ]
4X 4X 3.003.00
76,276,2
[ ]
Ø
.734.734
18,6418,64
[ ]
1.001.00
25,425,4
[ ]
SEE DETAIL ASEE DETAIL A
3X DETAIL A3X DETAIL A
#8-32 UNC-2B#8-32 UNC-2B
C
F
B
E
G
A
D
Figure 2.7 Dimensions: 625…780 A Controllers
625…780 A
Controller
A
Width
B
Height
C
Depth
DEFG
Approx.
Ship. Wt.
Unit
mm 596.9 1041.4 346.2 550.9 594.1 214.9 200.4 179 kg
in. 23.5 41.0 13.63 21.69 23.39 8.46 7.89 395 lb.
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
Page 41

41.0041.00
1041,41041,4[ ]
23.3923.39
594,1594,1[ ]
7.897.89
200,4200,4[ ]
1.641.64
41,641,6[ ]
.90.90
2323[ ]
21.6921.69
550,9550,9[ ]
23.5023.50
596,9596,9[ ]
3X 3X .15.15
3,83,8[ ]
13.8613.86
351,9351,9[ ]
14.5414.54
369,4369,4[ ]
19.5419.54
496,3496,3[ ]
29.0229.02
737737[ ]
4.574.57
116,2116,2[ ]
8.468.46
214,9214,9[ ]
2X 2X .25.25
6,46,4[ ]
13.6313.63
346,2346,2[ ]
Ø
.500.500
12,712,7[ ]
2.502.50
63,563,5[ ]
5.005.00
127127[ ]
.74.74
18,818,8[ ]
1.201.20
30,530,5[ ]
.28.28
7,27,2[ ]
Ø
.531.531
13,4913,49[ ]
38.4538.45
976,6976,6[ ]
4X 4X 2.252.25
57,157,1[ ]
4X 4X 2.002.00
50,850,8[ ]
Ø
.734.734
18,6418,64[ ]
8.258.25
209,5209,5[ ]
7.007.00
177,8177,8[ ]
7.357.35
186,6186,6[ ]
14.3514.35
364,4364,4[ ]
1.251.25
31,831,8[ ]
SEE DETAIL ASEE DETAIL A
3X DETAIL A3X DETAIL A
#8-32 UNC-2B#8-32 UNC-2B
C
F
B
E
G
A
D
Installation 2-11
Figure 2.8 Dimensions: 970…1250 A Controllers
970…1250 A
Controller
Unit
A
Width
B
Height
C
Depth
DEFG
Approx.
Ship. Wt.
mm 596.9 1041.4 346.2 550.9 594.1 214.9 200.4 224 kg
in. 23.5 41.0 13.63 21.69 23.39 8.46 7.89 495 lb.
All dimensions are approximate and are not intended for manufacturing purposes. Consult your
local Allen-Bradley distributor for complete dimension drawings.
Page 42

2-12 Installation
/1
3/5
/3
3/6
/4
/2
3
e
r
ec
n
SMC
C
r
r
s
➀
➀ Customer Supplied
➁
➀
➀
➁ Overload protection is included as a
standard feature of the SMC-Flex controller.
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
Power Factor
Correction Capacitors
➀
➀ Customer Supplied
➁
➀
➀
➁ Overload protection is included as a standard feature of the SMC-Flex controller.
➂ Energize 1/2 second before start command to SMC.
➂
➃ Open contactor after stopping method is complete.
➂ Energize contactor after up-to-speed.
➃ Open contactor before initiating a stop.
Alternate
➃
Power Factor
Correction Capacitors
The controller can be installed on a system with power factor
correction (PFC) capacitors. The capacitors must be located on the
line side of the controller. This must be done to prevent damage to the
SCRs in the SMC-Flex controller.
When discharged, a capacitor essentially has zero impedance. For
switching, sufficient impedance should be connected in series with
the capacitor bank to limit the inrush current. One method for limiting
the surge current is to add inductance in the capacitor’s conductors.
This can be accomplished by creating turns or coils in the power
connections to the capacitors.
• 250V — 15 cm (6 in.) diameter coil, 6 loops
• 480…690V — 15 cm (6 in.) diameter coil, 8 loops
Take care in mounting the coils so that they are not stacked directly
on top of each other; stacking will cause a cancelling effect. Also,
mount the coils on insulated supports away from metal parts so they
will not act as induction heaters. If an isolation contactor is used, put
capacitors in front of contactor.
Note: For further instructions, consult the PFC capacitor vendor.
Figure 2.9 Typical Wiring Diagram for Power Factor Correction Capacitors
-Phas
Input Powe
Prot
Branch
L1
L2
L
tio
Power Facto
Correction Capacitor
ontrolle
T1
T2
T
-Flex
Figure 2.10 Typical Wiring Diagram for Power Factor Correction Capacitors
and Contactor
Page 43

Installation 2-13
ATTENTION
!
ATTENTION
!
Protective Modules Protective modules containing metal oxide varistors (MOVs) can be
installed on controllers rated 5…1250 A and 200…600V, to protect
the power components from electrical transients. The protective
modules clip voltage transients generated on the lines to prevent such
surges from damaging the SCRs.
When installing or inspecting the protective module,
make sure that the controller has been disconnected
from the power source. The protective module
should be inspected periodically for damage or
discoloration. Replace if necessary.
Motor Overload
Protection
Thermal motor overload protection is provided as standard with the
SMC-Flex controller. If the overload trip class is less than the
acceleration time of the motor, nuisance tripping may occur.
Overload protection should be properly coordinated
with the motor.
Two applications require special consideration: two-speed motors,
and multi-motor protection.
Two-speed Motors
The SMC-Flex controller has overload protection available for single
speed motors. When the SMC-Flex controller is applied to a twospeed motor, the Overload Class parameter must be programmed to
OFF and separate overload relays must be provided for each speed.
Multi-motor Protection
If the SMC-Flex controller is controlling more than one motor,
individual overload protection is required for each motor.
Page 44

2-14 Installation
ATTENTION
!
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This product has been designed for Class A
equipment. Use of the product in domestic
environments may cause radio interference, in
which case, the installer may need to employ
additional mitigation methods.
The following guidelines are provided for EMC installation
compliance.
Enclosure
Install the product in a grounded metal enclosure.
Wiring
Wire in an industrial control application can be divided into three
groups: power, control, and signal. The following recommendations
for physical separation between these groups is provided to reduce the
coupling effect.
• Different wire groups should cross at 90° inside an enclosure.
• Minimum spacing between different wire groups in the same tray
should be 16 cm (6 in.).
• Wire runs outside an enclosure should be run in conduit or have
shielding/armor with equivalent attenuation.
• Different wire groups should be run in separate conduits.
• Minimum spacing between conduits containing different wire
groups should be 8 cm (3 in.).
• For additional guidelines, please refer to Wiring and Ground
guidelines, publication DRIVES-IN001A-EN-P.
Additional Requirements
• If linear acceleration is used, a separate conduit or wire way
should be used for the tachometer leads.
• Wire earth ground to control terminal 14.
• Use shielded wire for PTC, Tachometer, and ground fault input.
• Terminate shielded wires to terminal 14.
• Ground fault CT must be inside or within 3 m of metal enclosure.
To meet product susceptibility requirements, ferrite cores need to be
added to the communication lines. When using an external HIM (or
DPI interface), a core should be added to the HIM cable near the
SMC-Flex control module. The recommended core is Fair-Rite
no. 0431167281 or equivalent. When using a DeviceNet circuit, two
cores need to be added to the DeviceNet cable near the SMC-Flex
control module. The recommended cores are TDK ZCAT2023 0930H
and TDK ZCAT2035 0930 or equivalent. All cores specified are the
split type cores and can be added to existing connections.
Page 45

Chapter 3
4
1
5
3
2
3
3
➀
➀
Wiring
Terminal Locations The SMC-Flex controller wiring terminal locations are shown in
Figure 3.1 and Figure 3.2. Make wiring connections as indicated in
the typical connection diagrams. Incoming three-phase power
connections are made to terminals L1/1, L2/3, and L3/5. Load
connections to Line motors are made to T1/2, T2/4, and T3/6, while
load connections to Wye-Delta motors are made to T1/2, T2/4, T3/6,
T4/8, T5/10, and T6/12.
Figure 3.1 Wiring Terminal Locations (5…85 A)
Table 3.A Wiring Terminal Locations
1 Incoming Line Termination
2 Line Motor Connections
3 Delta Motor Connections
4 Control Terminations
5 Fan Terminations
IP20 protective covers on Delta termination must be removed when connecting in a Delta
➀
configuration.
Page 46

3-2 Wiring
4
1
5
3
2
3
3
Figure 3.2 Wiring Terminal Locations (108…480 A)
Table 3.A Wiring Terminal Locations
1 Incoming Line Termination
2 Line Motor Connections
3 Delta Motor Connections
4 Control Terminations
5 Fan Terminations
Page 47

Figure 3.3 Wiring Terminal Locations (625…1250 A)
3
1
2
Wiring 3-3
Table 3.B Wiring Terminal Locations
1 Incoming Line Terminations
2 Line Motor Connections
3 Terminal Block CP1 - Common Control Power Connections
(Fans, Contactors, and Control Modules)
Power Structure The SMC-Flex product has an integrated mechanical run contactor on
each phase of the motor to minimize heat generation during run time.
These contacts are pulled in sequentially in the 108…1250 A units. In
the 5…85 A units, these contacts are pulled in, all at once. The
SMC-Flex product also has a Current Transformer (CT), built in on
each phase of the motor to provide current readings.
Power Wiring
Refer to the product nameplate or User Manual for power lug
termination information including:
• Lug wire capacity
• Tightening torque requirements
• Lug kit catalog numbers (108…1250 A)
Page 48

3-4 Wiring
ATTENTION
!
Use of an isolation contactor or shunt trip type circuit breaker on the line side of the SMC. This
device should be capable of interrupting the motor’s lock rotor current.
Connection of this isolation device to an auxiliary contact on the SMC-Flex. The auxiliary contact
should be programmed for the “normal” condition. See Chapter 4 for additional information on
programming.
Failure of solid state power switching components can cause overheating due to a single-phase
condition in the motor. To prevent injury or equipment damage, the following is recommended:
Line Connected
The SMC-Flex by default is programmed to be connected to a line
controlled motor as shown in Figure 3.4. These motors typically have
3 leads and must be rated between 1…1250 amps. An optional
isolation contactor can be added to the circuit to provide galvanic
isolation of the motor and final electro-mechanical removal of power.
Figure 3.4
SMC-Flex
IC
5/L3
6/T3
10/T5
IC
3/L2
IC
1/L1
4/T2
8/T4
2/T1
12/T6
M
3~
Delta Connected
The SMC Flex can be programmed and connected to a delta
controlled motor as shown in Figure 3.5. These motors typically have
6 or 12 leads and must be rated between 1.8…1600 amps. It is
recommended that an isolation contactor be added to the circuit to
provide galvanic isolation of the motor and final electro-mechanical
removal of power.
Figure 3.5
Page 49

Wiring 3-5
2/T1
4/T2
6/T3
12/T6
8/T4
10/T5
M
3~
1/L1
5/L3
3/L2
IC
IC
IC
SMC-Flex
ATTENTION
!
Power Lugs Power lugs are required for devices rated 108..1250 A. In some cases
these lugs are sold in kits. Each kit contains three lugs. The number
and type of lugs required is listed in the following tables.
Table 3.C lists the recommended lugs for the SMC when configured
as a line connection. Table 3.D lists the recommended lugs when
using the SMC Flex with a delta connection. Note that devices rated
625…1250 A require the use of a power distribution block when used
with a delta connection.
Terminal covers are available for units rated
108…480 A which can make the product deadfront
(IP2X) safe. See Appendix D for the appropriate
catalog numbers for ordering.
Page 50

3-6 Wiring
Table 3.C SMC-Flex 5…1250 A, Line Connection Lug Information
SMC
Rating
Lug Kit
Cat. No.
Wire Strip
Length
5…85 A — 18…20 mm
108…135 A 199-LF1 18…20 mm
201…251 A 199-LF1 18…20 mm
317…480 A 199-LG1 18…25 mm
625…780 A 100-DL630 32 mm / 64 mm
970 A 100-DL860 26 mm / 48 mm
100-DL630 32 mm / 64 mm
1250 A
➀
100-DL860 26 mm / 48 mm
Conductor
Range
2.5…85 mm
(#14…3/0 AWG)
16…120 mm
(#6…250 MCM)
16…120 mm
(#6…250 MCM)
25…240 mm
(#4…500 MCM)
70…240 mm
(2/0…500 MCM)
120…240 mm
(4/0…500 MCM)
70…240 mm
(2/0…500 MCM)
120…240 mm
(4/0…500 MCM)
The 1250 A device requires one (1) each of the 100-DL630 and 100-DL860.
➀
Max. No. Lugs/Pole Tightening Torque
Line Side Load Side Wire — Lug Lug — Busbar
2
— — 11.3 N•m
(100 lb.-in.)
2
11 31 N•m
(275 lb.-in.)
2
22 31 N•m
(275 lb.-in.)
2
22 42 N•m
(375 lb.-in.)
2
22 45 N•m
(400 lb.-in.)
2
11 45 N•m
(400 lb.-in.)
2
11
45 N•m
2
11
(400 lb.-in.)
—
23 N•m
(200 lb.-in.)
23 N•m
(200 lb.-in.)
28 N•m
(250 lb.-in.)
68 N•m
(600 lb.-in.)
68 N•m
(600 lb.-in.)
68 N•m
(600 lb.-in.)
SMC
Rating
Suggested Lug
Cat. No.
108…135 A 1494R-N15
201…251 A 1494R-N14
317…480 A 150-LG5MC
625…780 A
970…1250 A
➀
➀
—
—
Table 3.D SMC-Flex 108…1250 A, Delta Connection Lug Information (for
Inside-the-Delta applications)
Conductor
Pole
Range
Line Side ➁ Wire — Lug Lug — Busbar
Max. No. Lugs/
25…240 mm
2
1 42 N•m
(#4…500 MCM)
50…120 mm
2
2 31 N•m
(1/0…250 MCM)
95…240 mm
2
1 33.9 N•m
(3/0…500 MCM)
25…240 mm
2
2 42 N•m
(#4…500 MCM)
25…240 mm
2
4 42 N•m
(#4…500 MCM)
For 625
➀
➁ Load side lug information for inside-the-delta applications is contained in Table 3.C.
…1250 A inside-the-delta connections, terminal blocks are required for line side
connections. Required terminal blocks are as follows:
- Allen-Bradley Part# 1492-BG (625…780 A: 2 per phase, 970…1250 A: 4 per phase). Short-Circuit
Protection = Fuses
- Cooper Bussmann Part# 16504-2 (625…780 A: 1 per phase, 970…1250 A: 2 per phase). ShortCircuit Protection = Circuit breaker
Tightening Torque
(375 lb.-in.)
(275 lb.-in.)
(300 lb.-in.)
(375 lb.-in.)
(375 lb.-in.)
23 N•m
(200 lb.-in.)
23 N•m
(200 lb.-in.)
28 N•m
(250 lb.-in.)
N/A
N/A
Page 51

Control Power Control Wiring
Refer to the product nameplate for control terminal wire capacity and
tightening torque requirements. Each control terminal will accept a
maximum of two wires. Refer to the product nameplate prior to
applying control power. Depending on the specific application,
additional control circuit transformer VA capacity may be required.
Controllers rated 5…480 A
The SMC-Flex controllers rated 5…480 A accept control power input
of 100…240V AC or 24V AC/DC, (+10/–15%) single-phase, 50/
60 Hz. A control power source of 125 VA is required. The control
power requirement for the control module is 75 VA. The control
power requirement for the fans is 20 or 50 VA. The control module
and fans are separately wired. The control module requirements are
shown in Table 3.E. The fans require additional power as defined in
Table 3.G.
Table 3.E Control Module Requirements
120…240V AC Transformer 75 VA
24V AC Transformer 130 VA
24V DC
Wiring 3-7
Inrush Current 5 A
Inrush Time 250 ms
Transient Watts 60 W
Transient Time 500 ms
Steady State Watts 24 W
Minimum Allen-Bradley Power Supply 1606-XLP50E
Controllers rated 625…1250 A
For controllers rated 625…1250 A, common control is required for
proper operation. Control power is connected to the product through
terminal block CP1, at terminals 1 and 4. This single connection point
feeds the control module, contactors, and fans. Control power must be
supplied as 110/120 VAC or 230/240 VAC, 50/60 Hz only. A control
power source of at least 800 VA is required. The control power
requirements include the control module (75 VA), bypass contactors
(526 VA max), and fan power (150 VA).
Depending on the specific application, additional control circuit
transformer VA capacity may be required.
Page 52

3-8 Wiring
Figure 3.6 230V Control Undervoltage Relay Settings for 625…1250 A
Devices
SEE NAMEPLATE FOR STATUS
LED
TIME DELAY
PICK-UP
TIME DELAY
DROP-OUT
10
SEC.
0.1
220
10
SEC.
0.1
115%
PICK-UP
% NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
85%
240
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
208
95%
DROP OUT
% PICK-UP
0%
GENERAL NOTES:
1. SET ALL RELAY POTENTIOMETERS PER ILLUSTRATION.
Page 53

178 2
4
6
5
3
CP1
14
13
22
21
A2
C
A1
CONTACTO R
A
UV. RELAY
SM C FLEX
CONTROL
MODULE
141322
21
A2
C
A1
CONTACTO R
B
141322
21
A2
C
A1
CONTACTO R
C
11
12
13
14
15 16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
262728
29
303132
33
34
243 1
F A N A
FN
GND
FL
F A N B FAN C
CONTACTO R/ FAN
IN P U T 230 V AC
7
FN
GND
FL
FN
GND
FL
See Figure 3.6 for setting information.
Wiring 3-9
Figure 3.7 Internal Wiring and 230V Control Undervoltage Relay Connection
Diagram for 625…1250 A Devices
Page 54

3-10 Wiring
CP1
CONTACTOR
A
SM C FLEX
CONTROL
MODULE
CONTACTOR
B
CONTACTOR
C
F A N A F A N B FAN C
CONTACTOR/ FAN
IN P U T 120 V AC
11
12
13
14
15 16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
262728
29
303132
33
34
243 1
FN
GND
FL
FN
GND
FL
FN
GND
FL
141322
21
141322
21
141322
21
A2
C
A1
A2
C
A1
A2
C
A1
Figure 3.8 Internal Wiring and 120V Control Connection Diagram for
625…1250 A Devices
Page 55

Wiring 3-11
ATTENTION
!
110/120 VAC
Jumpers
To
Supply
Jumper
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
Factory Set
110/120 VAC
Jumpers
To
Supply
1
2
3
4
5…480 A
625…1250 A
Fan Terminations
Fan Terminations
Control Power/
CP1
110/120 VAC
50/60 Hz ONLY
230/240 VAC
or
Control Wire Specifications
Table 3.F provides the control terminal wire capacity, the tightening
torque requirements, and the wire strip length. Each control terminal
will accept a maximum of two wires.
Table 3.F Control Wiring and Tightening Torque
Wire Size Torque Wire Strip Length
0.75…2.5 mm
2
(#18…14 AWG)
0.6 N•m (5 lb.-in.) 5.6…8.6 mm (0.22…0.34 in.)
Fan Power Controllers rated 5…1250 A have heatsink fan(s). Refer to Table 3.G
for the control power VA requirements of the heatsink fans.
Fan Terminations
See Figure 3.1, Figure 3.2, and Figure 3.3 for fan power connection
locations.
The fan jumpers have been factory installed for
110/120V AC input. Refer to Figure 3.9 for
220/240V AC fan wiring (5
…480A devices only).
Figure 3.9 Power Terminations
Factory Set
Optional
220/240 VAC
To
Supply
Table 3.G Heatsink Fan Control Power
SMC Rating Heatsink Fan VA
➀
5…135 A 20
201…251 A 40
317…480 A 60
625…780 A 150
970…1250 A 150
Internally wired.
➀
➀
Page 56

3-12 Wiring
Control Terminal Designations As shown in Figure 3.10, the SMC-Flex controller contains 24 control
terminals on the front of the controller.
Figure 3.10 SMC-Flex Controller Control Terminals
Terminal
Number
Description
Ter mi na l
Number
Description
11 Control Power Input ➀➃ 23 PTC Input ➁
12 Control Power Common ➀➃ 24 PTC Input ➁
13 Controller Enable Input ➁ 25 Tach Input
14 Control Module Ground 26 Tach Input
15 Option Input #2
➀➁ 27 Ground Fault Transformer Input ➁
16 Option Input #1 ➀➁ 28 Ground Fault Transformer Input ➁
17 Start Input ➀➁ 29 Aux. Contact #2➀➂
18 Stop Input ➀➁ 30 Aux. Contact #2➀➂
19 Aux. Contact #1➀➂ 31 Aux. Contact #3➀➂
20 Aux. Contact #1➀➂ 32 Aux. Contact #3➀➂
21 Not Used 33 Aux. Contact #4➀➂
22 Not Used 34 Aux. Contact #4➀➂
RC Snubbers are required on loads connected to auxiliary.
➀
➁ Do not connect any additional loads to these terminals. These “parasitic” loads may cause problems
with operation, which may result in false starting and stopping.
➂ External Bypass operates an external contactor and overload relay once the motor reaches full
speed. The SMC-FLEX overload functionality, diagnostics and metering are disabled when the
external bypass is activated. Proper sizing of the contactor and overload is required.
➃ Control power on units rated 625…1250 A is pre-wired internally, from terminal block CP1.
Page 57

Wiring 3-13
Standard Controller Wiring
Diagrams
3-Phase
Input Power
➀
Branch
Protection
Figure 3.11 through Figure 3.22 show typical wiring for the
SMC-Flex controller.
Figure 3.11 Typical Wiring Diagram for Standard Controller
L1/1
L2/3
L3/5
➀
➀
➀
SMC-Flex
Controller
Stop
Start
T1/2
T2/4
T3/6
M
➀
➀
➀
➁
11 12
13
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
25 26
TACH
Input
14
15 16
27
Ground
Fault
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
17
28 29
18 19 20
Aux #1
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
21
Aux #4
Page 58

3-14 Wiring
3-Phase
Input Power
Figure 3.12 Typical Wiring Diagram for Two-Wire Control with Stopping
Control (No DPI Control)
T1/2L1/1
L2/3
T2/4
M
➀
L3/5
T3/6
Branch
➀
Protection
➁
11 12
13
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
➀
➀
Two-Wire
Device
14
➀
➀
15 16
SMC-Flex
Controller
17
18 19 20
21
Aux #1
23
PTC
Input
24
25 26
TACH
Input
27
28 29
Ground
Fault
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
Notes: (1) Programmable controller interfacing in this diagram refers to hard-wiring between the
(2) The OFF state leakage current for a solid-state device must be less than 6 mA.
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
PLC’s output contacts and the SMC-Flex controller’s control terminals.
Aux #4
Page 59

Wiring 3-15
Figure 3.13 Typical Wiring Diagram for Dual Ramp Applications
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
➀
Protection
➀
➀
Ramp 1 Ramp 2
➀
➀
L1/1
L2/3
L3/5
SMC-Flex
Controller
Stop
Start
T1/2
T2/4
T3/6
M
➀
➀
➀
➁
11 12
13
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
25 26
TACH
Input
14
15 16
27
Ground
Fault
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
Note: The Dual Ramp feature is available only with the standard control version.
17
28 29
18 19 20
Aux #1
30 31 32 33
Aux #3Aux #2
21
22
34
Aux #4
Page 60

3-16 Wiring
Figure 3.14 Typical Wiring Diagram for Start-Stop Control via DPI
Communications
Note: Use this wiring diagram when start-stop will come from
either a Bulletin 20-HIM LCD interface module or a
Bulletin 20-COMM communication module connected to the
SMC-Flex.
Note: Logic mask must be properly configured, see Chapter 8.
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
➀
Protection
➁
11 12
13
➀
14
➀
15 16
➀
L1/1
L2/3
L3/5
17
T1/2
T2/4
T3/6
SMC-Flex
Controller
18 19 20
M
➀
21
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
25 26
TACH
Input
Aux #1
27
28 29
Ground
Fault
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Page 61

11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
Start
M
OL
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
Stop
M
Branch
Protection
L2/3
L3/5
Input Power
3-Phase
SMC-Flex
Controller
T1/2L1/1
T2/4
T3/6
M
Existing Motor
Starter
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
➀
➀
➀➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➃
➂
➀➁
➀
Wiring 3-17
Figure 3.15 Typical Wiring Diagram for Retrofit Applications
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Overload protection should be disabled in the SMC-Flex controller.
➂ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➃ Aux #4 should be set for normal operation
Page 62

3-18 Wiring
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
Isolation
Contactor
(IC)
Aux #3
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
IC
Stop
Start
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➂
➁
➀
➀
➀
➀
Figure 3.16 Typical Wiring Diagram for Isolation Applications (DPI also)
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ Aux #4 should be set for normal operation.
Page 63

Wiring 3-19
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
Start
Stop
ST
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➂
➁
Figure 3.17 Typical Wiring Diagram for Shunt Trip Applications
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ Aux #2 should be set to fault operation.
Page 64

3-20 Wiring
Figure 3.18 Typical Wiring Diagram for Single-Speed Reversing Applications
3-Phase
Input Power
➀
Branch
Protection
E-Stop
➃
➀
➀➀
OFF
FOR REV
Reversing Contactors
➀
F
➀
R
F
L1/1
L2/3
T1/2
T2/4
M
➀
L3/5
R
SMC-Flex
Controller
T3/6
➀
R
➀
F
➀
R
➀
F
➀
➁
11 12
24
23
PTC
Input
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input rating.
14
13
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
25 26
TACH
Input
15 16
27
Ground
Fault
28 29
17
18 19 20
Aux #1
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
21
Aux #4
Customer supplied.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ No braking manuever allowed in wiring diagram.
➃ Maintained pushbutton.
Notes: (1) Minimum transition time for reversing direction is 1/2 second.
(2) Phase Reversal protection must be disabled in reversing applications.
Page 65

Wiring 3-21
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 33
22
34
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
Two-Speed Motor Starter
High
Low
L
H
L
H
H
L
Stop
HOL
LOL
H
H
1 sec.
1 sec.
H
L
Aux #3
PTC
Input
TAC H
Input
Ground
Fault
Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
H
L
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➁
➁
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➂
➃
Figure 3.19 Typical Wiring Diagram for Two-speed Applications
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Two-speed, consequent pole installations.
➂ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➃ Overload must be disabled in SMC-Flex.
Page 66

3-22 Wiring
Figure 3.20 Typical Wiring Diagram for SMC-Off-Bypass Control
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
➀
Protection
L1/1
L2/3
T1/2
T2/4
M
➀
L3/5
➀
➀
➀
T3/6
SMC-Flex
Controller
BC
Bypass
OffSMC
➀
X
X
Stop
Start
Bypass
OL
➀
➀
➀
Bypass
Connector (BC)
➀
➁
11 12
13
14
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
25 26
TAC H
Input
15 16
27
28 29
Ground
Fault
17
18 19 20
Aux #1
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
21
Aux #4
Page 67

Wiring 3-23
Figure 3.21 Typical Wiring Diagram for Hand-Off-Auto Control with Stop
Option and Start/Stop Push Buttons
Control Power
➁
C
➀
Start
➀
➀
C
H A
C
➀
➀
Auto
Device
➀
Stop
➀
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
25 26
TACH
Input
27
Ground
Fault
28 29
30 31 32 332234
Aux #1
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Page 68

3-24 Wiring
Soft Stop, Pump Control, and
SMB Smart Motor Braking
Figure 3.22 through Figure 3.25 show the different wiring for the Soft
Stop, Pump Control, and SMB Smart Motor Braking options.
Figure 3.22 Typical Wiring Diagram
Control Power
➂
Stop
➀
Start
➀
18 19 20
21
11 12
Option Stop
14
13
➀➁
15 16
17
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
PTC
Input
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Soft Stop, Pump Stop, or Brake.
➂ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
Note: Refer to Chapter 3 for typical power circuits.
25 26
TACH
Input
27
Ground
Fault
28 29
Aux #1
30 31 32 332234
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Page 69

Figure 3.23 Typical Retrofit Wiring Diagram
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
Option Stop
Start
M
OL
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
Control Power
Stop
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
➀
➄
➀
➀
➂
➀➃
➀➁
Wiring 3-25
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Overload protection should be disabled in the SMC-Flex controller.
➂ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➃ Soft Stop, Pump Stop, or Brake.
➄ Aux #4 should be set to normal operation.
Note: Refer to Chapter 3 for typical power circuits.
Page 70

3-26 Wiring
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
Option Stop
IC
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
Control Power
Start
Stop
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
➀
➀
➁
➀
➃
➀➂
Figure 3.24 Typical Wiring Diagram for Applications Requiring an Isolation
Contactor
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ Soft Stop, Pump Stop, or Brake.
➃ Aux #4 should be set to normal operation.
Note: Refer to Chapter 3 for typical power circuits.
Page 71

Wiring 3-27
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
H A
Control Power
100-240 VAC
Aux #3Aux #2
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
X00
X00
00X
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
Figure 3.25 Typical Wiring Diagram for Hand-Off-Auto (DPI) Control (Soft
Stop, Braking, and Pump Control Only)
Customer supplied.
➀
Page 72

3-28 Wiring
Preset Slow Speed Figure 3.26 and Figure 3.27 show the different wiring for the Preset
Slow Speed.
Figure 3.26 Typical Wiring Diagram for the Preset Slow Speed
Control Power
➁
Stop
➀
Option Command
11 12
13
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
24
23
25 26
14
➀➂
15 16
27
17
28 29
Start
➀
18 19 20
Aux #1
30 31 32 332234
21
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Fault
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ Slow Speed.
Note: Refer to Chapter 3 for typical power circuits.
Page 73

Wiring 3-29
11 12
13
14
15 16
17
18 19 20
21
23
24
25 26
27
28 29
30 31 32 332234
L1/1
L3/5
L2/3
T3/6
T2/4
T1/2
M
3-Phase
Input Power
Branch
Protection
SMC-Flex
Controller
H A
Aux #3Aux #2
Aux #4
Aux #1
SMC-Flex
Control Terminals
Option Command
Hand Start
Hand Stop
PTC
Input
TACH
Input
Ground
Fault
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀➁
➂
➀
➀
➃
Figure 3.27 Typical Slow Speed Wiring Diagram for Hand-Off-Auto (DPI)
Control
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Slow Speed.
➂ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➃ Aux #4 should be set to normal operation.
Page 74

3-30 Wiring
3LOW3PEED
3TOP
3TART
#ONTROL0OWER
"RAKE
!UX!UX
!UX
!UX
3-#&LEX
#ONTROL4ERMINALS
)#
04#
)NPUT
4!#(
)NPUT
'ROUND
&AULT
➂
Slow Speed with Braking Figure 3.28 shows the wiring for the Slow Speed with Braking option.
Figure 3.28 Typical Wiring Diagram for the Slow Speed with Braking with an
Isolation Contactor
Customer supplied.
➀
➁ Refer to the controller nameplate to verify the rating of the control power input voltage.
For units rated 625…1250 A, terminals 11 & 12 are factory pre-wired from terminal block
CP1 - terminals 1 & 4.
➂ Aux #4 should be set to normal operation.
Note: Refer to Chapter 3 for typical power circuits.
Page 75

Wiring 3-31
S
t
00%
p
(
)
p
C
t
p
s
S
t
p
p
s
al
C
d
n
n
C
d
n
C
d
n
C
d
d
ATTENTION
!
Sequence of Operation Figure 3.29 through Figure 3.34 show the different operation
sequences for the Soft Stop, Preset Slow Speed, Pump Control, SMB
Smart Motor Braking, Accu-Stop, and Slow Speed with Braking
options.
Figure 3.29 Soft Stop Sequence of Operation
1
oast-to-res
Soft Sto
Motor
eed
S
Push Button
tar
Sto
Soft Sto
Auxiliary Contact
Norm
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
Soft Sto
If Soft Stop Selecte
Time
Run
seconds
tar
The user is responsible for determining which
stopping mode is best suited to the application and
will meet applicable standards for operator safety on
a particular machine.
Page 76

3-32 Wiring
S
t
un
00%
or
d
)
d
s
s
al
d
p
S
t
C
d
C
d
n
C
d
n
C
d
n
n
C
d
n
5%
C
t
d
C
t
p
1
Mot
Spee
Figure 3.30 Preset Slow Speed Sequence of Operation
oast-to-res
Soft Sto
7 or 1
Push Button
tar
Sto
Slow Spee
Auxiliary Contact
Norm
Up-to-spee
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
lose
Ope
Slow Spee
tar
R
Time (seconds
oas
Page 77

Figure 3.31 Pump Control Sequence of Operation
Coast-to-Rest
100%
Up-to-Speed
Normal
Pump Stop
(Stop Option)
Stop
Motor Speed
Push Buttons
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Start
Auxillary Contacts
Time in Seconds
If the Pump Stop is Selected
If the Coast-to-Rest is Selected
Pump Stop
Run
Pump Start
1
ATTENTION
!
Wiring 3-33
The user is responsible for determining which
stopping mode is best suited to the application and
will meet applicable standards for operator safety on
a particular machine.
Page 78

3-34 Wiring
100%
Up-to-Speed
Normal
Smart Motor Braking
Stop
Motor Speed
Push Buttons
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Start
Auxillary Contacts
Time in Seconds
Run
Coast-to-Rest
Smart Motor Braking
Start
Start
Automatic Zero
Speed Shut-Off
If Brake
Selected
If Coast-to-Rest
Selected
(Stop Option )
1
ATTENTION
!
Figure 3.32 SMB Smart Motor Braking Sequence of Operation
The user is responsible for determining which
stopping mode is best suited to the application and
will meet applicable standards for operator safety on
a particular machine.
Page 79

Figure 3.33 Accu-Stop Sequence of Operation
Start Run
100 %
Motor
Speed
Time (seconds)
Accu-Stop
Braking
Slow Speed
Slow Speed
Braking
Accu-Stop
Push Buttons
Auxiliary Contacts
Up-to-speed
Normal
Stop
Start
Closed
Open
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
If Coast-to-rest
Selected
Slow
Speed
Braking
Slow
Speed
Coast-to-rest
➀
ATTENTION
!
Wiring 3-35
When Accu-Stop push button is closed, start/stop function is disabled.
➀
The user is responsible for determining which
stopping mode is best suited to the application and
will meet applicable standards for operator safety on
a particular machine.
Page 80

3-36 Wiring
ATTENTION
!
Motor Speed
Push Buttons
Slow Speed
(Stop Option )
Auxillary Contacts
Up-to-Speed
Start
Stop
Normal
SMB
3
100%
Closed
Closed
Closed
Closed
Closed
Closed
Figure 3.34 Slow Speed with Braking Sequence of Operation
1
Coast
2
Brake
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Open
Slow Speed
Start
Run
Time in Seconds
Coast-to-Stop
Braking
Brake
Coast
Brake
If the Coast-to-Rest
is Selected
Special Application Considerations Use of Protective Modules
The user is responsible for determining which
stopping mode is best suited to the application and
will meet applicable standards for operator safety
on a particular machine.
A protective module (see Figure 3.35) containing metal oxide
varistors (MOVs) can be installed to protect the power components
from electrical transients and/or electrical noise. The protective
modules clip transients generated on the lines and prevent such surges
from damaging the SCRs.
Page 81

Wiring 3-37
MADE IN U.S.A
PROTECTIVE MODULE
MAX. LINE VOLTAGE
Figure 3.35 Protective Module
There are two general situations that may occur which would indicate
the need for using the protective modules.
1. Transient spikes may occur on the lines feeding the SMC-Flex
controller (or feeding the load from the SMC-Flex controller).
Spikes are created on the line when devices are attached with
current-carrying inductances that are open-circuited. The energy
stored in the magnetic field is released when the contacts open the
circuit. Examples of these are lightly loaded motors,
transformers, solenoids, and electromechanical brakes. Lightning
can also cause spikes.
2. The second situation arises when the SMC-Flex controller is
installed on a system that has fast-rising wavefronts present,
although not necessarily high peak voltages. Lightning strikes can
cause this type of response. Additionally, if the SMC-Flex controller is on the same bus as other SCR devices, (AC/DC drives,
induction heating equipment, or welding equipment) the firing of
the SCRs in those devices can cause noise.
Note: protective modules may be placed on the line, load, or both
sides of the SMC. However, protective modules must NOT be
placed on the load side of the SMC when using inside-thedelta motor connections or with pump, linear speed, or
braking control.
Page 82

3-38 Wiring
/1
/5
/3
/6
/4
/2
3
e
r
Branc
otection
SMC
C
r
O
y (
)
O
y (
)
or
2
or
1
➀ Customer Supplied
➀
➀
➀
➀
➀
Multi-motor Applications The SMC-Flex controller will operate with more than one motor
connected to it. To size the controller, add the total nameplate
amperes of all of the connected loads. The stall and jam features
should be turned off. Separate overloads are still required to meet the
National Electric Code (NEC) requirements.
Note: The SMC-Flex controller’s built-in overload protection
cannot be used in multi-motor applications.
Figure 3.36 Multi-Motor Application
-Phas
Input Powe
Pr
L1
L2
T2
T1
Mot
No.
L3
h
-Flex
ontrolle
T3
Rela
verload
O.L.
Mot
No.
verload
Rela
O.L
Page 83

Wiring 3-39
3
e
r
ec
n
/1
3/5
/3
/2
3/6
/4
SMC
C
r
C
C
O.L.
➁➁➁
➁
➃
➁
➁
➂
g
SMC-Flex Controller as a Bypass to
an AC Drive
-Phas
Input Powe
VFD Branch
Prot
tio
By using the controller as shown in Figure 3.37, a soft start
characteristic can be provided in the event that an AC drive is nonoperational.
Note: A controlled acceleration can be achieved with this scheme,
but speed control is not available in the bypass mode.
Figure 3.37 Typical Application Diagram of a Bypass Contactor for an AC
Drive
➀➀
L1
T1
L2
L
I
➀ Mechanical interlock required
➁ Customer supplied
➂ Many VF drives are rated 150% FLA. Because the SMC-Flex controller can be used for 600% FLA startin
separate branch circuit protection may be required.
➃ Overload protection is included as a standard feature of the SMC-Flex controller.
T2
T
I
-Flex
ontrolle
,
Page 84

3-40 Wiring
3
e
r
/1
3/5
/3
/2
3/6
/4
SMC
r
C
O.L.
C
H
➀
➀
➀
➀
➁
➀
SMC-Flex Controller with a Bulletin
1410 Motor Winding Heater
-Phas
Input Powe
H
Figure 3.38 Typical Application Diagram of SMC-Flex Controller with a
Bulletin 1410 Motor Winding Heater
I
L1
L2
L
Bulletin 1410 MW
T1
T2
T
-Flex Controlle
➀ Customer supplied.
➁ Overload protection is included as a
standard feature of the SMC-Flex controller.
Page 85

Chapter 4
Lang
Programming
Overview This chapter provides a basic understanding of the programming
keypad built into the SMC-Flex controller. This chapter also describes
programming the controller by modifying the parameters.
Keypad Description The keys found on the front of the SMC-Flex controller are described
below.
Esc
Sel
Escape Exit a menu, cancel a change to a parameter value, or
acknowledge a fault/alarm.
Select Select a digit, select a bit, or enter edit mode in a
parameter screen.
Will get to menu to change the language being displayed.
Up/Down
Arrows
Enter Enter a menu, enter edit mode in a parameter screen, or
Scroll through options increase/decrease a value, or
toggle a bit.
save a change to a parameter value.
Note: For ease of programming values, after using the Enter key to
edit, use the Sel key to jump to the digit that needs to be
modified, then use the arrow keys to scroll through the digits.
Programming Menu Parameters are organized in a three-level menu structure for
straightforward programming. Figure 4.1 details the programming
menu structure and the three-level hierarchy.
In order to change parameters, the controller must be in the STOP
mode, and the control voltage must be present.
Page 86

4-2 Programming
Device
Power-up and
Status Display
Parameter
Memory
Storage
Preferences
Diagnostics
Select
0
Monitoring
Set Up
Motor Protection
Communications
Utility
Linear LIst
0
SMC-FLEX
0
Reset to Defaults
0
Change Password
User Dspl Line
User Dspl Time
User Dspl Video
Reset User Display
0
Alarms
Faults
Device Revision
Choose Mode
OPERATION LEVEL
MAIN MENU
➀
➁
➁
Parameter menu
continued in Figure 4.2
GROUP MENU
or oror or
Esc
or
Esc
0
Select language
being displayed
Lang
Log-In
0
Enter Password
➂
Figure 4.1 Menu Structure Hierarchy
Sel
Esc
The SMC-Flex controller does not support EEPROM, Link, Process, or Start-up modes.
➀
➁ Steps back one level.
➂ Only displayed if a password other than “0” is entered.
Page 87

Figure 4.2 Parameter Menu Structure
Parameter
0
Metering Basic Overload Jam Comm Masks Language Linear List
Volts Phase A-B SMC Option Overload Class Jam F Lvl Logic Mask Language All parameters
Volts Phase B-C Motor Connection Service Factor Jam F Dly
Parameter Mgt
➃ Parameter Mgt ➃ Parameter Mgt ➃
Volts Phase C-A Line Voltage Motor FLC Jam A Lvl
Current Phase A Starting Mode Overload Reset Jam A Dly
DataLinks Motor Data
Current Phase B Ramp Time Overload A Lvl
Parameter Mgt
➃
Current Phase C Initial Torque
Parameter Mgt
➃
Data In A1 MotorFLC
Watt Meter Cur Limit Lvl
Stall
Data In A2 Motor ID
Kilowatt Hours Kickstart Time
Underload
Data In B1
Parameter Mgt
➃
Elapsed Time Kickstart Lvl Stall Dly Data In B2
Meter Reset Stop Input Underload F Lvl
Parameter Mgt
➃
Data In C1
Power Factor Option 1 Input Underload F Dly Data In C2
Mtr Therm Usage Option 2 Input Underload A Lvl
Ground Fault
Data In D1
Motor Speed Stop Mode Underload A Dly Data In D2
Stop Time
Parameter Mgt
➃
Gnd Flt Enable Data Out A1
Braking Current Gnd Flt Lvl Data Out A2
Overload Class
Undervoltage
Gnd Flt Dly Data Out B1
Service Factor Gnd Flt Inh Time Data Out B2
Motor FLC Undervolt F Lvl Gnd Flt A Enable Data Out C1
Overload Reset Undervolt F Dly Gnd Flt A Lvl Data Out C2
Aux1 Config Undervolt A Lvl Gnd Flt A Dly Data Out D1
Aux2 Config Undervolt A Dly
Parameter Mgt
➃
Data Out D2
Aux3 Config
Parameter Mgt
➃ Parameter Mgt ➃
Aux4 Config
PTC
Backspin Timer
Overvoltage
Parameter Mgt
➃
PTC Enable
Overvolt F Lvl
Parameter Mgt ➃
Dual Ramp (Option
2 Input = Dual
Ramp)
Overvolt F Dly
Overvolt A Lvl
Phase Reversal
Overvolt A Dly
Starting Mode 2
Parameter Mgt
➃
Phase Reversal
Ramp Time 2
Parameter Mtg
➃
Initial Torque 2
Unbalance
Cur Limit Lvl 2
Restart
Kickstart Time 2 Unbalance F Lvl
Kickstart Lvl 2 Unbalance F Dly Starts Per Hour
Parameter Mgt
➃
Unbalance A Lvl Restart Attempts
Unbalance A Dly Restart Dly
Preset SS (Option 2
Input = Preset SS)
Parameter Mgt
➃ Parameter Mtg ➃
Slow Speed Sel
Slow Speed Dir
Slow Accel Cur
Slow Running Cur
Parameter Mgt
➃
(Option 2 Input =
Accu-Stop)
Slow Speed Sel
Slow Accel Cur
Slow Running Cur
Braking Current
Stopping Current
Parameter Mgt
➃
Motor
Set Up
Utility Linear List⑤
Protection
Parameter
Monitoring
Communications
➀➂
➁
Esc
Programming 4-3
➀ Depending upon SMC option selected, some parameters may not appear in product display.
➁ Steps back one level.
➂ For further information on parameters, see Appendix B.
➃ For further information on parameter management, see page 4-6.
⑤ See page 4-4 for all SMC-Flex parameters available by the Linear List.
Page 88

4-4 Programming
Parameter No. Description Parameter No. Description Parameter No. Description
Table 4.A Parameter Linear List
1 Volts Phase A-B 49 OL Trip Enable/Disable 97 Data Out A2
2 Volts Phase B-C 50 Overload A Lvl 98 Data Out B1
3 Volts Phase C-A 51 Underload F Lvl 99 Data Out B2
4 Current Phase A 52 Underload F Dly 100 Data Out C1
5 Current Phase B 53 Underload A Lvl 101 Data Out C2
6 Current Phase C 54 Underload A Dly 102 Data Out D1
7 Watt Meter 55 Undervolt F Lvl 103 Data Out D2
8 Kilowatt Hours 56 Undervolt F Dly 104 Motor ID
9 Elapsed Time 57 Undervolt A Lvl 105 CT Ratio
10 Meter Reset 58 Undervolt A Dly 106 MV Ratio
11 Power Factor 59 Overvolt F Lvl 107 Aux1 Config
12 Mtr Therm Usage 60 Overvolt F Dly 108 Aux3 Config
13 Motor Speed 61 Overvolt A Lvl 109 Aux4 Config
14 SMC Option 62 Overvolt A Dly 110 Aux2 Config
15 Motor Connection 63 Unbalance F Lvl 111 Language
16 Line Voltage 64 Unbalance F Dly 112 Timed Start
17 Starting Mode 65 Unbalance A Lvl 113 I Shut Off Level
18 Ramp Time 66 Unbalance A Dly 114 UTS Level
19 Initial Torque 67 Jam F Lvl 115 Parameter Mgmt
20 Cur Limit Start 68 Jam F Dly 116 Backspin Timer
21 Reserved 69 Jam A Lvl 117 VShut Off Level
22 Kickstart Time 70 Jam A Dly 118 OL Reset Level
23 Kickstart Level 71 Stall Delay 119 Ambient Temp
24 Option Input 2 72 Gnd Flt Enable 120 Notch Position
25 Starting Mode 2 73 Gnd Flt Level 121 Notch Maximum
26 Ramp Time 2 74 Gnd Flt Delay 122 Start Delay
27 Initial Torque 2 75 Gnd Flt Inh time 123 By-pass Delay
28 Cur Limit Level 2 76 Gnd Flt A Enable 124 Fault 1
29 Reserved 77 Gnd Flt A Level 125 Fault 2
30 Kickstart Time 2 78 Gnd Flt A Delay 126 Fault 3
31 Kickstart Level 2 79 PTC Enable 127 Fault 4
32 Stop Mode 80 Phase Reversal 128 Fault 5
33 Stop Time 81 Start Per Hour 129 Ramp Time E
34 Pump Pedestal 82 Restart Attempts 130 Ramp Time 2E
35 Braking Current 83 Restart Delay 131 Stop Time E
36 Braking Time 84 Line Fault Disable 132 Option Input 1
37 Load Type 85 Emergency Run 133 Stop Input
38 High Eff Brake 86 Current Loss 134 Elapsed Time 2
39 Slow Speed Sel 87 Logic Mask
40 Slow Speed Dir 88 Data In A1
41 Slow Accel Cur 89 Data In A2
42 Slow Running Cur 90 Data In B1
43 Stopping Current 91 Data In B2
44 Overload Class 92 Data In C1
45 Service Factor 93 Data In C2
46 Motor FLC 94 Data In D1
47 Overload Reset 95 Data In D2
48 OL Shunt Time 96 Data Out A1
Page 89

Programming 4-5
Esc
Password The SMC-Flex controller allows the user to limit access to the
programming system through password protection. This feature is
disabled with a factory-set default of 0. To modify the password,
complete the procedure below.
Description Action Display
——
1. Press the ESC key to go from the
status display to the Main menu.
2. Scroll with the Up/Down keys until the
Preferences option is highlighted.
3. Press the Enter key to access the
Preferences menu.
4. Scroll with the Up/Down keys until the
Change Password option is
highlighted.
0.0 Amps
0 Volt
0 %MTU
Main Menu
in
Preferences
Diagnostics
Main Menu
Main Menu
Preferences
Preferences
Diagnostics
Diagnostics
Preferences:
Change Passwor
User Dspy lines
Preferences:
Change Password
User Dspy lines
d
5. Press the Enter key.
6. Press the Up/Down keys to enter the
desired number. If you are modifying
the password, make a note of it as
Prefs: Password
New Code:
Verify: 83
83
displayed. Use the Sel key to highlight
a single digit.
7. Verification of the new password is
required. Press the Enter key.
8. Press the Enter key after you have
completed modifying the password.
To complete the programming process, re-enter the Main Menu mode to log out. This will eliminate
➀
unauthorized access to the programming system.
➀
Preferences:
Change Password
User Dspy lines
Note: If you lose or forget the password, contact your local
Allen-Bradley distributor.
Page 90

4-6 Programming
EEPROM RAM ROM
Esc
Parameter Management Before you begin programming, it’s important to understand how the
controller memory is:
• structured within the SMC-Flex controller
• used on power-up and during normal operation
Refer to Figure 4.3 and the explanations below.
Figure 4.3 Memory Block Diagram
Sel
Random Access Memory (RAM)
This is the work area of the controller after it is powered up. The
SMC-Flex uses an Auto Store feature when programming parameters.
When parameters are modified in the program mode, the new values
are stored immediately in RAM and then in EEPROM, once the enter
key has been pressed. If control power is lost prior to the enter key
being pressed, these values will be lost. When the device first powers
up, the values from the EEPROM area of memory are copied into
RAM.
Read-only Memory (ROM)
The SMC-Flex controller comes with factory default parameter
values. These settings are stored in non-volatile ROM and are
displayed the first time you enter the Program mode. At any time you
can restore defaults by accessing the memory storage menu.
Description Action Display
Recalling Defaults
After parameter values have been modified,
factory default settings can still be re-initialized.
Memory Storage:
Reset to Defaults
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-only Memory
(EEPROM)
The SMC-Flex controller provides a non-volatile area for storing
user-modified parameter values in the EEPROM.
Page 91

Programming 4-7
0.0 Amps
0 Volt
0 %MTU
Esc
Main Menu
Parameter
Memory Storage
GP : File
Monitoring
Set Up
F
GP : File
Set Up
Motor Protection
F
F P: Group
Basic Set Up
G
FG : Parameter
Starting Mode
Ramp Time
P
FG :P#17
Starting M
ode
Current Lim
P
FG :P#18
Ramp Ti
me
10 Secs
P
Parameter Modification All parameters are modified using the same method. The basic steps
to performing parameter modification are described below.
Notes: (1) Parameter values modified while the motor is operating
are not valid until the next time that operation occurs.
(2) If the password is set, parameters cannot be adjusted
without logging in.
(3) Use the Sel key to highlight a single digit.
Description Action Display ➁
——
1. Press the ESC key to go from the
—
status display to the Main menu.
2. Scroll with the Up/Down keys
until the Parameter option is
highlighted.
3. Press the Enter key to access the
Parameter menu.
4. Scroll with the Up/Down keys
until the option you want to use
(Monitoring, Motor Protection,
etc.) is highlighted. For this
example, Set Up will be used.
5. Press Enter to select the Set Up
—
group.
6. Scroll to Basic Set Up and press
➀
Enter.
7. Scroll to the Starting Mode
parameter by using the Up/Down
keys, and press Enter.
8. Press Enter to select the option.
Scroll to the option of your
choice by using the Up/Down
keys. For this example, we will
choose Current Limit.
9. Press the Enter key to accept the
—
new setting.
10. Scroll to the next parameter by
using the Down key. Continue
the process until all desired
settings are entered.
The SMC Option advises the user if any control option (i.e., Pump Control) is resident. This parame ter
➀
is factory set and cannot be modified by the user.
➁ The display will indicate that the second line is now active by highlighting the first character. If the
LCD display does not provide a highlighted cursor, then the controller is in the Display mode.
Page 92

4-8 Programming
Soft Start The following parameters are specifically used to adjust the voltage
ramp supplied to the motor.
Parameter Option
Starting Mode
This must be programmed for Soft Start.
Ramp Time
This programs the time period that the controller will
ramp the output voltage up to full voltage from the
Initial Torque level programmed.
Initial Torque
The initial reduced output voltage level for the
voltage ramp to the motor is established and
adjusted with this parameter.
Kickstart Time
A boost of current is provided to the motor for the
programmed time period.
Kickstart Level
Adjusts the amount of current applied to the motor
during the kickstart time.
➀
➀
If the controller senses that the motor has reached full speed before completing the Soft Start, it
will automatically switch to providing full voltage to the motor.
Soft Start
0…30 s
0…90% locked rotor torque
0.0…2.0 s
0…90% locked rotor torque
Current Limit Start To apply a current limit start to the motor, the following parameters
are provided for user adjustment:
Parameter Option
Starting Mode
This must be programmed for Current Limit.
Ramp Time
This programs the time period that the controller will
hold the fixed, reduced output voltage before
switching to full voltage.
Current Limit Level
This parameter provides adjustability for the reduced
output voltage level provided to the motor.
Kickstart Time
A boost of current is provided to the motor for the
programmed time period.
Kickstart Level
Adjusts the amount of current applied to the motor
during the kickstart time.
➀
➀
If the controller senses that the motor has reached full speed before completing the current limit
start, it will automatically switch to providing full voltage to the motor.
Current Limit
0…30 s
50…600% full load current
0.0…2.0 s
0…90% locked rotor torque
Page 93

Programming 4-9
Dual Ramp Start The SMC-Flex controller provides the user with the ability to select
between two Start settings. The parameters below are available in the
Set Up programming mode. To obtain Dual Ramp control, Ramp #1
is located in the Basic Set Up and Ramp #2 is located in the Option 2
Input (Dual Ramp).
Parameter Option
Set Up
The user must select the Set Up programming mode to obtain
access to the Dual Ramp parameters.
Basic Set Up/Starting Mode
Set Up as stated in previous pages.
Option 2 Input (Dual Ramp)
This allows the user the option to choose between two Soft Start
profiles defined by:
1. Start Mode/Ramp Time/Initial Torque and
2. Start Mode 2/Ramp Time 2/Initial Torque 2.
When this feature is turned on, the ramp time/initial torque
combination is determined by a hard contact input to terminal 15.
When this input signal is low, ramp time/initial torque are selected.
When this input is high, ramp time 2/initial torque 2 are selected.
Once the Option 2 Input has been set to Dual Ramp, you must ESC
back to the Parameter (File) menu. Re-enter into the Set Up menu to
show both Basic Set Up and Dual Ramp.
Basic Set Up/Start Mode
This selects the start mode for option #1.
Basic Set Up/Ramp Time
This programs the time period during which the controller will ramp
the output voltage up to full voltage for the first Start setup.
Basic Set Up/Initial Torque
This parameter establishes and adjusts the initial reduced output
voltage level for the first Soft Start setup.
Dual Ramp/Start Mode 2
This selects the start mode for option #2.
Dual Ramp/Ramp Time 2
This programs the time period during which the controller will ramp
the output voltage up to full voltage for the second Start setup.
Dual Ramp/Initial Torque 2
The initial reduced output voltage level for the second Start setup is
established and adjusted with this parameter.
➀
➁
➁
—
—
—
—
0…30 s
0…90%
locked rotor
torque
—
0…30 s
0…90%
locked rotor
torque
➀ The Dual Ramp feaure is available on the standard controller.
➁ Kickstart can be programmed for both start modes.
Page 94

4-10 Programming
Full Voltage Start The SMC-Flex controller may be programmed to provide a full
voltage start (output voltage to the motor reaches full voltage within
1/4 second) with the following programming:
Parameter Option
Starting Mode
This must be programmed for Full Voltage.
Full Voltage
Linear Speed The SMC-Flex provides the user the ability to control the motor speed
during starting and stopping maneuvers. A tach input is required as
specified in Linear Speed Acceleration on page 1-6
Parameter Option
Starting Mode
This must be programmed for Linear Speed.
Ramp Time
This programs the time period that the controller will
ramp from 0 speed to full speed.
Kickstart Time
A boost of current is provided to the motor for the
programmed time period.
Kickstart Level
Adjusts the amount of current applied to the motor
during the kickstart time.
.
Linear Speed
0…30 s
0.0…2.2 s
0…90% locked rotor
torque
Page 95

Programming 4-11
Programming Parameters The following table provides the option-specific parameters that are
provided with each control option. These parameters are in addition
to those already discussed in the Basic Set Up and Metering groups.
Diagrams supporting the options described below are shown later in
this chapter.
Option Parameter Range
Standard
Soft Stop SMC Option
This parameter identifies the type of
control present and is not user
programmable.
Soft Stop Time
Allows the user to set the time
period for the soft stopping function.
Preset Slow
Speed
SMC Option
This parameter identifies the type of
control present and is not user
programmable.
Slow Speed Select
Allows the user to program the slow
speed that best fits the application.
Slow Speed Direction
This parameter programs the slow
speed motor rotational direction.
Slow Accel Current
Allows the user to program the
required current to accelerate the
motor to slow speed operation.
Standard
0…120 s
Standard
Low: 7% – forward,
10% – reverse
High: 15% – forward,
20% – reverse
Forward, Reverse
0…450% of full load
current
Slow Running Current
Allows the user to program the
required current to operate the
motor at the slow speed setting.
0…450% of full load
current
Page 96

4-12 Programming
Option Parameter Range
Pump Control
Pump Control SMC Option
This parameter identifies the type of
control present and is not user
programmable.
Pump Stop Time
Allows the user to set the time
period for the pump stopping
function.
Starting Mode
Allows the user to program the
SMC-Flex controller for the type of
starting that best fits the application.
Braking Control
SMB Smart
Motor Braking
Accu-Stop SMC Option
SMC Option
This parameter identifies the type of
control present and is not user
programmable.
Braking Current
Allows the user to program the
intensity of the braking current
applied to the motor.
This parameter identifies the type of
control present and is not user
programmable.
Pump Control
0…120 s
Pump Start, Soft Start,
Current Limit Start
Braking Control
➀
0…400% of full load
current
Braking Control
Slow Speed Select
Allows the user to program the slow
speed that best fits the application.
Slow Accel Current
Allows the user to program the
required current to accelerate the
motor to slow speed operation.
Slow Running Current
Allows the user to program the
required current to operate the
motor at the slow speed setting.
Braking Current
Allows the user to program the
intensity of the braking current
applied to the motor.
Stopping Current
Allows the user to program the
intensity of the braking current
applied to the motor from slow
speed operation.
➀
➀
Low:7%
High:15%
0…450% of full load
current
0…450% of full load
current
0…400% of full load
current
0…400% of full load
current
Page 97

Programming 4-13
Option Parameter Range
Slow Speed
with Braking
SMC Option
This parameter identifies the type of
Braking Control
control present and is not user
programmable.
Slow Speed Select
Allows the user to program the slow
Low:7%
High:15%
speed that best fits the application.
Slow Accel Current
Allows the user to program the
0…450% of full load
current
required current to accelerate the
motor to slow speed operation.
Slow Running Current
Allows the user to program the
0…450% of full load
current
required current to operate the
motor at the slow speed setting.
Braking Current
➀
Allows the user to program the
0…400% of full load
current
intensity of the braking current
applied to the motor.
All braking/stopping current settings in the range of 1…100% will provide 100% braking current
➀
to the motor.
Page 98

4-14 Programming
Basic Set Up The Basic Set Up programming group provides a limited parameter
set, allowing quick start-up with minimal adjustment. If the user is
planning to implement some of the advanced features (e.g., Dual
Ramp, or Preset Slow Speed), then the Setup programming group
should be selected. It provides all the Basic Set Up parameter set plus
the advanced set.
Parameter Option
SMC Option
Displays the type of controller. This is factory set and not adjustable.
Motor Connection
Displays the motor type to which the device is being connected.
Line Voltage
Displays the system line voltage to which the unit is connected.
Starting Mode
Allows the user to program the SMC-Flex controller for the type of starting that best fits the application.
Ramp Time
This sets the time period during which the controller will ramp the output voltage.
Initial Torque
The initial reduced voltage output level for the voltage ramp is established and adjusted with this parameter.
Current Limit Level
The current limit level that is applied for the Ramp Time selected.
Kickstart Time
A boost current is provided to the motor for the programmed time period.
Kickstart Level
Adjusts the amount of current applied to the motor during kickstart.
Stop Input
Allows the user to select the operation of terminal 18, Stop Input.
Option 1 Input
Allows the user to select the operation of terminal 16, Option Input #1.
Option 2 Input
Allows the user to select the operation of terminal 15, Option Input #2.
Stop Mode
Allows the user to program the SMC-Flex controller for the type of stopping that best fits the application.
Stop Time
This sets the time period which the controller will ramp the voltage during a stopping maneuver.
Overload Class Disable, 10, 15, 20, 30
Service Factor 0.01…1.99
Motor FLC 1.0…2200
OL Reset Auto, Manual
Aux1 Config
Contact is provided as standard with the SMC-Flex controller. This contact is located at terminals 19 and 20.
Aux Contacts 1 allows the user to configure the operation of the contacts.
Aux2 Config
Contact is provided as standard with the SMC-Flex controller. This contact is located at terminals 29 and 30.
Aux Contacts 2 allows the user to configure the operation of the contacts.
Aux3 Config
Contact is provided as standard with the SMC-Flex controller. This contact is located at terminals 31 and 32.
Aux Contacts 3 allows the user to configure the operation of the contacts.
Aux4 Config
Contact is provided as standard with the SMC-Flex controller. This contact is located at terminals 33 and 34.
Aux Contacts 4 allows the user to configure the operation of the contacts.
Parameter Mgmt
Recall of factory default parameter values.
➀
➁
Starting Mode must be programmed to Soft Start to obtain access to the Initial Torque parameter.
➀
➁ Starting Mode must be programmed to Current Limit to obtain access to the Current Limit Level
parameter.
Standard
Line or Delta
Soft Start, Current Limit, Full Voltage, Linear
Speed
0…30 s
0…90% of locked rotor torque
50…600% FLC
0.0…2.0 s
0…90% of locked rotor torque
Coast, Stop Option
Disable, Coast, Stop Option, Fault, Fault NC,
Network
Disable, Slow Speed, Dual Ramp, Fault, Fault
NC, Network, Clear Fault
Disable, Soft Stop, Linear Speed
0.0…120 s
Normal, Up-to-speed, Fault, Alarm, Network
Control, External Bypass: (N.O./N.C.)
Normal, Up-to-speed, Fault, Alarm, Network
Control, External Bypass: (N.O./N.C.)
Normal, Up-to-speed, Fault, Alarm, Network
Control, External Bypass: (N.O./N.C.)
Normal, Up-to-speed, Fault, Alarm, Network
Control, External Bypass: (N.O./N.C.)
Ready, Load Default
Page 99

Programming 4-15
ATTENTION
!
For overload protection, it is critical that the data be
entered as it appears on the motor nameplate.
Motor Protection While the Basic Set Up group allows the user to get started with a
minimum number of parameters to modify, the Motor Protection
group allows full access to the SMC-Flex controller’s powerful
parameter set. Following is a listing of the additional setup parameters
provided.
Note: The majority of parameters have a Fault and an Alarm
setting.
Parameter Option
Overload
Allows the user to select the operation of the overload:
Underload
Undervoltage ➀
Overvoltage
Unbalance
Jam
Determines the trip level as a percentage of motor full load current and delay period.
Stall
Ground Fault
Motor PTC
Phase Reversal
Restarts
➁
Determines the trip level as a percentage of the motor’s FLA, and the delay
period.
Determines the trip level as a percentage of the line voltage and the delay period.
➀
Determines the trip level as a percentage of line voltage and delay period.
➀
Allows the user to set the current unbalance trip level and delay period.
➁
Allows the user to set the stall delay time.
➂
Allows the user to enable the ground fault level in amps, delay time, and inhibit
time.
➃
Allows the user to connect a PTC to the SMC and enable a fault when it becomes
active.
Determines the proper orientation of line connections to the SMC. If Enabled and
phases are out of sequence, a fault will be indicated.
Allows the user to determine the maximum number of restarts per hour the unit
can experience, and delay time between consecutive starts.
Trip Class, Service Factor, Motor FLC, Overload Reset,
Overload Alarm Level
Underload Fault Level, Underload Fault Delay, Underload
Alarm Level, Underload Alarm Delay
Undervoltage Fault Level, Undervoltage Fault Delay,
Undervoltage Alarm Level, Undervoltage Alarm Delay
Overvoltage Fault Level, Overvoltage Fault Delay,
Overvoltage Alarm Level, Overvoltage Alarm Delay
Unbalance Fault Level, Unbalance Fault Delay, Unbalance
Alarm Level, Unbalance Alarm Delay
Jam Fault Level, Jam Fault Delay, Jam Alarm Level, Jam
Alarm Delay
Stall Delay
Ground Fault Enable, Ground Fault Level, Ground Fault Delay,
Ground Fault Inhibit Time, Ground Fault Alarm Enable,
Ground Fault Alarm Level, Ground Fault Alarm Delay
PTC Enable
Phase Reversal
Restarts Per Hour, Restart Attempts, Restart Delay
➀ The delay time must be set to a value greater than zero when Undervoltage, Overvoltage, and
Unbalance are enabled.
➁ For Jam and Underload detection to function, the Motor FLC must be programmed in the Motor
Protection group. See Chapter 5 for instructions.
➂ See details in Ground Fault on page 1-15.
➃ See details in Thermistor/PTC Protection on page 1-17.
Page 100

4-16 Programming
Example Settings Undervoltage ➀
With Line Voltage programmed for 480V and the Undervoltage level
programmed for 80%, the trip value is 384V.
Overvoltage ➀
With Line Voltage programmed for 240V and the Overvoltage level
programmed for 115%, the trip value is 276V.
Jam ➁➂
With Motor FLC programmed for 150 A and the Jam level
programmed for 400%, the trip value is 600 A.
Underload ➁
With Motor FLC programmed for 90 A and the Underload level
programmed for 60%, the trip value is 54 A.
The average value of the three phase-to-phase voltages is utilized.
➀
➁ The largest value of the three phase currents is utilized.
➂ The SMC-Flex will self-protect.
 Loading...
Loading...