
QC SERIES
IP CAMERAS
USER MANUAL
Thank You for Choosing a Q-See Product!
All of our products are backed by a conditional service warranty covering all hardware for 12
months from the date of purchase. Additionally, our products also come with a free exchange
policy that covers all manufacturing defects for one month from the date of purchase.
Permanent upgrading service is provided for the software and is available at www.Q-See.com.
Be certain to make the most of your warranty by completing the registration form online. In
addition to warranty and technical support benefits, you’ll receive notifications of product
updates along with free downloadable firmware updates for your NVR. Register today at
www.Q-See.com!
Please see the back of this manual for exclusions.
About this Manual
This manual is written for the Q-See’s QCN series of IP Cameras and was accurate at the time
it was completed. However, because of our ongoing effort to constantly improve our products,
and the different capabilities of the three models additional features and functions may have
been added since that time and on-screen displays may change. We encourage you to
visit our website at www.Q-see.com to check for the latest firmware updates and product
announcements.
This manual covers the setup and local operation of the IP cameras whether used in
conjunction with an NVR or as stand-alone devices. Instructions for use with an NVR is written
specifically with Q-See’s QC-Series NVRs. If you are using another brand, please consult your
system’s manual for configuration instructions. The QC-Series User Manual and Remote
Monitoring Guide will both be useful in configuring your system. Both are included on the
CD that accompanied your NVR and can likewise be found on www.Q-See.com/support.
Throughout the manual we have highlighted warnings and other important information that will
assist you in operating your new system in a safe and trouble-free manner. Please take the
time to read and follow all instructions and pay attention to alerts as shown below:
IMPORTANT! Red boxes with this icon indicate warnings. To prevent
possible injury or damage to the product, read all warnings before use.
NOTE! Text in blue boxes with the Information icon offer additional guidance
and explanations about how to make the most out of your system.
© 2011-2013 Q-See. Reproduction in whole or in part without written permission is
prohibited. All rights reserved. This manual and software and hardware described herein, in
whole or in part, may not be reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable
form without prior written approval.
Trademarks: All brand names and products are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
Q-See is a registered trademark of DPS, Inc.
Disclaimer: The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The
manufacturer makes no representations or warranties, either express or implied, of any kind
with respect to completeness of its contents.
Manufacturer shall not be liable for any damages whatsoever from misuse of this product.
Version 2.1 2/15/14
2 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CAMERA MOUNTING & SPECIFICATIONS 8
Additional Considerations 9
QCN7001B 10
QCN7002D 11
QCN8001D 12
Mounting and Adjusting Dome Cameras 13
Reset Button and SD Card 13
QCN8002B 14
Adjusting the lens 15
SD Card 15
QCN8004B 18
QCN8009D 19
QCN8010Z 20
Mounting Your Camera 21
Operation 23
Reset Button and SD Card 23
Specifications 23
QCN8014Z 26
Mounting Your Camera 27
Operation 29
Micro SD Card 29
Specifications 29
2. CONNECTING IP CAMERAS 32
2.1 What are IP Cameras? 32
2.2 Connecting an IP Camera 33
Locally connecting to an NVR 33
Cameras connected through a network 34
2.3 Adding and Removing Cameras in Your System 36
Local cameras 36
Cameras on the same network 36
QC NVR Remote Device menu 37
2.4 Connecting Your Camera to a Remote Network 40
Before you get started 40
Obtaining IP information using IPCONFIG in Windows 41
Testing the Connection 43
Opened ports and Internet IP address 45
2.5 Troubleshooting Network Connections 46
Opening Ports 46
Issues with DHCP 50
Multiple Routers on the Network 51
Configuring ActiveX 54
2.6 Additional Network services 59
Entering the DNS Information into the Camera 61
2.7 Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) 63
3. USING WEB SERVICE 64
3.1 Live View 64
Function Buttons (PC only) 65
3.2 Setup 66
Camera 66
Video 67
3.3 Network 68
TCP/IP 68
Static IP Address 68
PPPoE 69
DDNS 69
IP Filter 69
SMTP (E-Mail) 70
UPnP (Universal Plug ‘n’ Play) 70
Bonjour 70
3.4 Event 71
Motion Detection 71
Video Masking 72
Disconnection 72
IP Conflict 72
3.5 Record 73
Record Shedule 73
Snapshot Schedule 73
File Destination Path 74
Record Control 74
3.6 System 75
General 75
Date & Time 75
Account 76
Default 76
Import/Export 76
Auto Maintain 76
Upgrade 76
Information 77
Alarm 78
Logout 78
(Contents continued on next page)
5

4. PRO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE 79
4.1 Installing PRO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE (PSS) 79
System Requirements 79
Installing Smart PSS on a PC 79
Installing Smart PSS on a Macintosh 80
4.2 Using Smart PSS 80
Log In 80
Adding A System to PSS 81
Home Page 84
Preview 85
Video Search and Playback 87
Alarms 89
General 91
Device Setup 91
Tour 94
E-Map 95
TV Wall 96
PC-NVR 96
5. MOBILE SURVEILLANCE 97
5.1 iPhone and iPad 97
5.2 Android 102
5.3 BlackBerry 106
5.4 Symbian 109
5.5 Windows Mobile 112
Q-SEE PRODUCT WARRANTY 114
Questions or Comments? Contact Us 114
6 7

CAMERA MOUNTING &
CHAPTER 1
SPECIFICATIONS
When installing your camera, it is important to select a proper site not only for field of view, but
for other considerations as well:
Distance from viewing/recording device. The further the camera is from the NVR or power
source, the higher the chances of signal degradation. Typical 100Ω Ethernet Cable provides
acceptable signal at distances up to 330’ (100m). At greater distances, UL-Listed shielded
RG59 should be used. The camera’s power supply should be located as near to the camera
as possible when the distance exceeds 200’ as the power level will drop over extended
distances resulting in a decrease in video quality.
Do not place near high voltage wires or other sources of electrical interference. Electrical
interference will degrade the quality of the signal.
Place camera out of reach to avoid damage.
Avoid direct exposure to weather. Do not place the camera where rain or snow will hit the lens
directly nor should the camera be placed so that the sun or bright light shines directly into the
lens. Your camera is weatherproof, but it will not work when submerged in water. Ensure that
all power and video connections are not directly exposed to water and are protected from the
elements.
Do not place camera behind a window. If there is a light source behind the camera, it can cause
a reflection in the window that will obscure events on the other side of the glass. Likewise,
the camera’s infrared LEDs will reflect off the glass and shine into the lens, thus degrading the
image.
Light levels should be approximately the same between camera and target area. A camera in a
brightly-lit area looking into a shaded area, or vice versa, may produce inadequate results.
The above are guidelines and the optimal
location for your camera will depend on your
unique circumstances. As a general rule, the
locations highlighted in green in the picture to
the right indicate the best locations to mount
your camera. Both locations are sheltered
from rain or snow and offer good sight lines
to allow your camera to monitor a wide
area. Because your camera is weatherproof,
it requires less protection than weatherresistant cameras and it can be placed in
more exposed locations if needed. Keep in
mind that this camera is designed to operate
between 14°F to 122°F (-10°C to 50°) with a
relative humidity of up to 95%) and consider
wind chill and other environmental factors
when selecting your location.
Your camera comes with both a ceiling and
wall mount. Where you locate your camera
will determine which mount you will need to
use. The mounting surface must be sturdy
and able to hold at least five times the
camera’s total weight.
PICTURE 1-1
Because your camera is weatherproof, it requires less protection than weather-resistant cameras
and it can be placed in more exposed locations if needed. Keep in mind that most Q-See
cameras are designed to operate between 14°F to 122°F (-10°C to 50°) with a relative humidity of
up to 95%) and consider wind chill and other environmental factors when selecting your location.
Specialty cameras are also available from Q-See which are able to operate in more extreme
environments.
ADDITIONAL CONSIDERATIONS
Most users prefer to operate their systems with the DVRs recording only when motion is
detected. This provides the most efficient use of the hard drive’s capacity, plus making it easier
for a recording to be located. However, if the a camera’s location has a lot of “environmental”
motion, such as a fan, wind, or the like, you will receive a lot of “false alarms.” Usually, these
events can be avoided by simply adjusting the placement of the camera. Other situations may
require some fine-tuning of your settings. Chapter 8 Alarms, covers these settings in detail,
but some easily avoidable situations are presented below:
TV/Computer Screens. If the camera can see a video screen, it will trigger a motion alarm
any time the screen changes, whether there is a video or simply a screen saver. The screen can
be masked out as described in Section 4.2. You can also reduce the level of motion sensitivity
in specific areas of the screen by following the instructions in Section 8.3.
Fans/Machinery. Motion is motion and if machinery within the camera’s field of view starts
automatically, it will cause an alert. Similarly, if the camera is mounted on a wall with machinery on
the other side that causes it to vibrate, that can also cause it to detect motion. Moving machinery
within the camera’s field of view may be masked off as mentioned above, or motion detection may
be turned off for that channel. If there is another camera that covers access to the area where the
machinery is located, you can set it so that the first camera will only be recording when triggered
by a motion event detected by this second camera. See “Triggers” in described in Section 8.3.
Bugs. An occasional insect flying through the field of view is usually not enough to trigger an
alert. However, some flying insects are attracted to infrared light and will swarm the camera.
This is usually a temporary situation that occurs at only a certain time of the year. Lighting the
area with yellow “bug light” of sufficient brightness can keep the camera operating in daylight
mode and keep the infrared LEDs turned off. A second solution is to set the channel to record all
the time, and turn motion detection off at night until “bug season” is over. Reducing the motion
sensitivity (Section 8.3) can also reduce alerts as can using another camera to trigger recording
as described above.
Additionally, keep your cameras clear of spider webs as the movement of the webs due to wind
or critters in the web will cause an alert. The reflection of the infrared off the webs and back into
the camera will also reduce the night vision range.
Snow/Rain.
temporarily disabled to avoid false alarms. However, positioning the camera further under shelter,
such as closer to the wall and away from the edge of the eaves, can make the rain or snow too
small for the camera to notice. Adjusting motion sensitivity may also help in some situations.
As with bugs, this is usually a seaonal event and may require motion detection to be
8 9

QCN7001B
PICTURE 1-2
QCN7002D
PICTURE 1-3
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
System
remote operation
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
Image Sensor 1/3” 1.3 Megapixel Aptina CMOS
Lens 6mm
IR LEDs / Range 30 LED / 100’
Pixel 1280 x 960
Day/Night Mode Electrical Day/Night
Signal/Noise Ratio >50dB
Min. Illumination 0.1LUX/F1.2 (color) 0.05LUX/F1.2 (b/w)
Gain Control Manual/Auto
Video
White Balance Manual/Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/3-1/10000
Comp. Standard H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Image Resolution 1.3M (1280x960), 720p (1280x720), D1 (704x480)
Encoding Speed NTSC: 1.3M @15fps + D1@15fps,
720p @30fps + D1@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 128Kbps-8192Kbps
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG on computer
Ethernet RJ-45 (10/100Base-T)
Network
Network Functions HTTP, TCP/IP, IPv4/IPv6, ARP, IGMP, ICMP, RTSP, RTP, UDP,
SMTP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, PPPoE, UPNP, NTP, Bonjour,
SNMP, Onvif
Remote Operation Monitor, Playback, System setting, Log information,
Maintenance & Upgrade
Operation
Power Supply DC12V, PoE
Consumption Max.1.5W
Operating
15°F to +120°F (-10°C to+50°C) Humidity 10%-90%
Environment
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
remote operation
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
Image Sensor 1/3” 1.3 Megapixel Aptina CMOS
Lens 3.6mm
Pixel 1280 x 960
Day/Night Mode Electrical Day/Night
Signal/Noise Ratio >50dB
Min. Illumination 0.1LUX/F1.4 (color) 0.05LUX/F1.2 (b/w)
Gain Control Manual/Auto
Video
White Balance Manual/Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/3-1/10000
Comp. Standard H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Image Resolution 1.3M (1280x960), 720p (1280x720), D1 (704x480)
Encoding Speed NTSC: 1.3M @15fps + D1@15fps,
720p @30fps + D1@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 128Kbps-8192Kbps
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG on computer
Ethernet RJ-45 (10/100Base-T)
Network
Network Functions HTTP, TCP/IP, IPv4/IPv6, ARP, IGMP, ICMP, RTSP, RTP, UDP,
SMTP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, PPPoE, UPNP, NTP, Bonjour,
SNMP, Onvif
Remote Operation Monitor, Playback, System setting, Log information,
Maintenance & Upgrade
Operation
Power Supply DC12V, PoE
Consumption Max.1.5W
Operating
15°F to +120°F (-10°C to+50°C) Humidity 10%-90%
Environment
10 11

QCN8001D
PICTURE 1-4
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
System
remote operation
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
System Status SD card status, bit stream stats, log, and software version.
Image Sensor 1/3” 2.0 Mp SONY progressive scan Exmor CMOS
Min. Illumination 0.2LUX/F1.6 (color), 0.01LUX/F1.6 (b/w)
Lens Auto-Iris 3.6@F1-6
Pixel 1920x1080 (1080p)
Day/Night Mode Automatic
Auto Aperture DC drive
Gain Control Fixed/Auto
White Balance Manual/Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/4-1/10000
Video
Video Comp.
Standard
H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Video Frame Rate NTSC: Main stream 1080P @30fps, 1.3M @30fps, 720P
@30fps; Substream 704x480@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 56Kbps-8192Kbps
MJPG is adjustable along with bit rate
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG
Privacy Mask Maximum 4 privacy zones supported
Video Adjustment Brightness, contrast, hue, saturation and gain
Video Info Channel title, time, motion detection, masking
Motion Detect 396 (18x22) zones. Six sensitivity levels. Motion detection
activation options: alarm, recording, snapshot, log and e-mail
Network 1-channel wire Ethernet port, 10/100 Base-T Ethernet
Network
Network Protocols Standard HTTP, TCP/IP, ARP, IGMP, ICMP, RTSP, RTP,UDP,
RTCP, SMTP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, PPPOE, UPNP, NTP,
Bonjour,SNMP.
Remote Operation Monitor, system setup, file download, log information,
maintenance and upgrade.
Recording
& Backup
Recording Priority Manual>External alarm >Video detect>Schedule
Local Storage 32GB internal
Backup Remote through PSS
Power
Power Through RJ45 connector when connected to POE or 12v .5A
through aux. power connector
Consumption <10W
Temperature 15F to 140F
Env.
IP Rating IP66
Humidity 10-90%
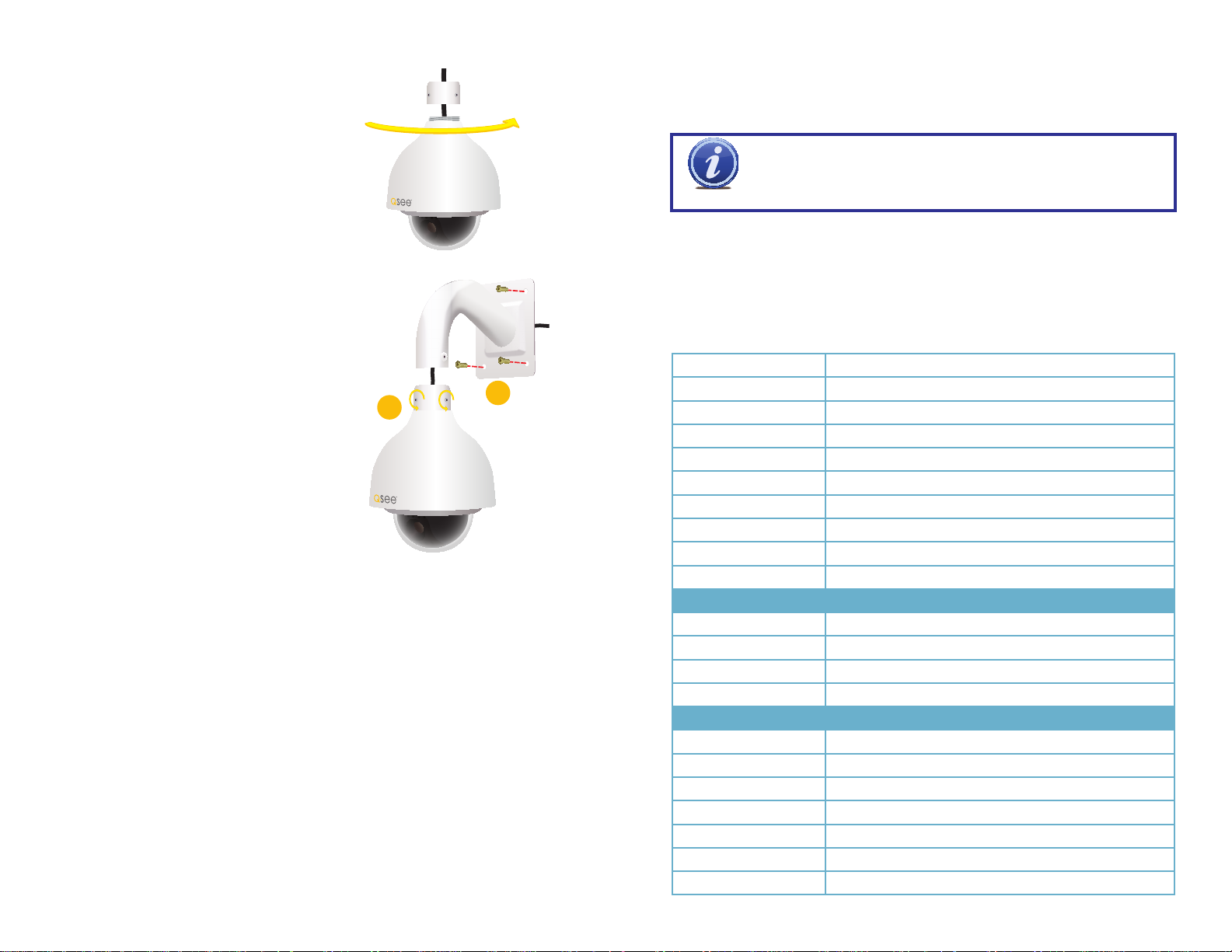
MOUNTING AND ADJUSTING DOME CAMERAS
Remove the camera cover using the included hex wrench to unscrew the three retaining bolts.
The camera’s lens can only be positioned
vertically (up and down) with the horizontal
direction being determined by how the
camera is positioned. Ideally, you should
temporarily connect the camera to the NVR
(or network) and use the QC View mobile
app to determine the best angle for your
camera.
Once you’ve determined the proper position
and location for the camera, use the included
mounting template to drill the holes for the
plastic anchors and cable (if needed).
insert the screws into the anchors through the camera base plate and tighten. If the camera is
connected, then make final adjustments to the lens position. Make sure that the clear dome is
free of dust, fingerprints and other contaminants before reattaching the cover.
RESET BUTTON AND SD CARD
Both the QCN7002D and QCN8001D have a Reset button accessible only when the camera
cover has been removed. This is only for use if the camera becomes inoperable.
The QCN8001D also has a slot for a Micro SD card which allows the camera to record images
and video when it is operating on its own network (ie; not directly connected to the NVR with
the Ethernet cable. Please see Section 3.5 for instructions on recording with an SD card.
PICTURE 1-5
12 13
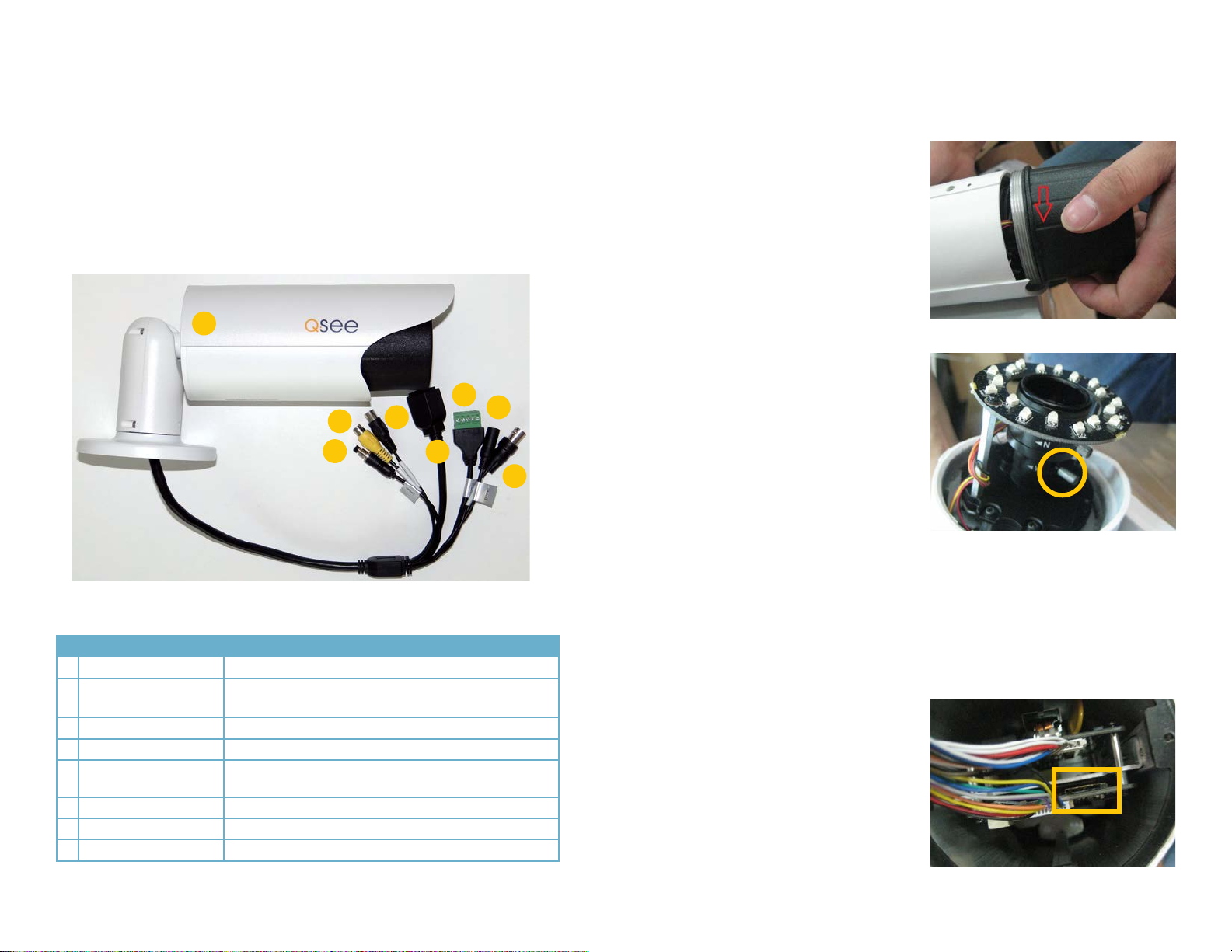
QCN8002B
In addition to its video surveillance functions, the QCN8001B is able to accept input from
other devices and either pass their signals back to an NVR, or utilize them to trigger recording
or alert actions when it is being used in a stand-alone role. The camera has 32GB of internal
memory allowing it to record video and still images without the need for an NVR.
By using the audio input and output to connect both a microphone and speaker - and with
similar audio equipment on the user’s end, two-way communication can take place. Two
alarm sensors can be connected to the alarm block with a single output to an audible alarm,
an external alarm input or to a DVR. When used with an NVR or on a network, the alarm signal
can trigger recording and its signal can be transmitted via the Cat 5 cable to an NVR.
ADJUSTING THE LENS
The QCN8001B has a lens that can be manually adjusted between 3.3mm and 12mm.
The 3.3mm setting provides a 67° field of view. The 12mm setting enlarges subjects by
approximately three times compared to the 3.3mm configuration, with the field of view
narrowing to 22°.
The camera is set at the factory to the 3.3mm
position. To adjust the lens, you will have to
first remove the black cover at the front of the
camera by twisting it counter-clockwise. Take
care not to damage the cover or the threads
during this step.
1
6
3
2
4
5
7
8
PICTURE 1-6
# Item Function
1 Storage Internal 32GB memory
2 Reset Resets camera if user is locked out.
3 Audio In Input for optional microphone
4 Audio Out Connect to speaker
5 RJ45 (Ethernet) Port For network connectivity, video output and power input (via
POE)
6 Alarm 2 Alarm inputs 1 Output
7 Power For use without POE
8 Video Out BNC video output (for testing
Once the cover has been removed, you can
adjust the zoom and focus using the two
knobs located on the lens body behind the
LED circuit board. You may need to loosen
them by twisting the knob counter-clockwise
before making the adjustments. Do not apply
excessive force to the knobs as they can
snap off, leaving your camera unable to be
adjusted.
It is recommended that you have some way to view the camera’s view while making the
adjustments to ensure that the image is properly in focus and includes the entire area that
you wish to monitor. This can be done using a camera tester connected to the BNC Video
Out plug or by connecting it to an NVR where you can monitor it using the video display. A
third method would be by connecting the camera to a network using the steps described
in Chapter 2 and then accessing it remotely using a mobile device with a sufficiently large
screen clarity. However, with this method it is important to keep in mind that mobile devices
use the lower-quality substream video so final adjustments may still need to be made.
SD CARD
The QCN8002B also has a slot for a Micro
SD card which allows the camera to record
images and video when it is operating on
its own network (ie; not directly connected
to the NVR with the Ethernet cable. To
access, remove the back of the camera by
loosening the four screws holding the stand
to the camera. Please see Section 3.5 for
instructions on recording with an SD card.
PICTURE 1-7
PICTURE 1-8
PICTURE 1-9
14 15

QCN8002B Specifications
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
remote operation
System
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
System Status SD card status, bit stream stats, log, and software version.
Image Sensor 1/3” 2.0 Mp SONY progressive scan Exmor CMOS
IR LEDs 18
Max IR range 65’
Min. Illumination 0.2LUX/F1.2 (color), 0.01LUX/F1.6 (b/w), 0.0 LUX/F1.2 (w/IR)
Lens Auto-Iris 3.3-12mm@F1-6
Pixel 1920x1080 (1080p)
Day/Night Mode Automatic
Auto Aperture DC drive
Gain Control Fixed/Auto
White Balance Manual/Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/4-1/10000
Video Comp.
H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Standard
Video
Video Frame Rate NTSC: Main stream 1080P @30fps, 1.3M @30fps, 720P
@30fps; Substream 704x480@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 56Kbps-8192Kbps
MJPG is adjustable along with bit rate
Video Flip Supported
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG
Privacy Mask Maximum 4 privacy zones supported
Video Adjustment Brightness, contrast, hue, saturation and gain
Video Info Channel title, time, motion detection, masking
Motion Detect 396 (18x22) zones. Six sensitivity levels. Motion detection
activation options: alarm, recording, snapshot, log and e-mail
Audio Ouput 1-channel RCA
Audio
Bidirectional Talk Reuses first audio input channel
Audio Bit Rate 128/64/10.2 Kbps
Audio Comp. G.711a/G.711u/PCM
Network 1-channel wire Ethernet port, 10/100 Base-T Ethernet
Network
Network Protocols Standard HTTP, TCP/IP, ARP, IGMP, ICMP, RTSP, RTP,UDP,
RTCP, SMTP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, PPPOE, UPNP, NTP,
Bonjour,SNMP.
Remote Operation Monitor, system setup, file download, log information,
maintenance and upgrade.
Recording
& Backup
Recording Priority Manual>External alarm >Video detect>Schedule
Local Storage 32GB internal
Backup Remote through PSS
Connectors
Video Output 1-channel BNC analog video out
Auxilliary
Audio Input 1-channel RCA
Audio Output 1-channel RCA
Alarm 2-channel input, 1-channel output
Power
Power Through RJ45 connector when connected to POE or 12v .5A
through aux. power connector
Consumption <10W
Temperature 15F to 140F
Env.
IP Rating IP66
Humidity 10-90%
16 17
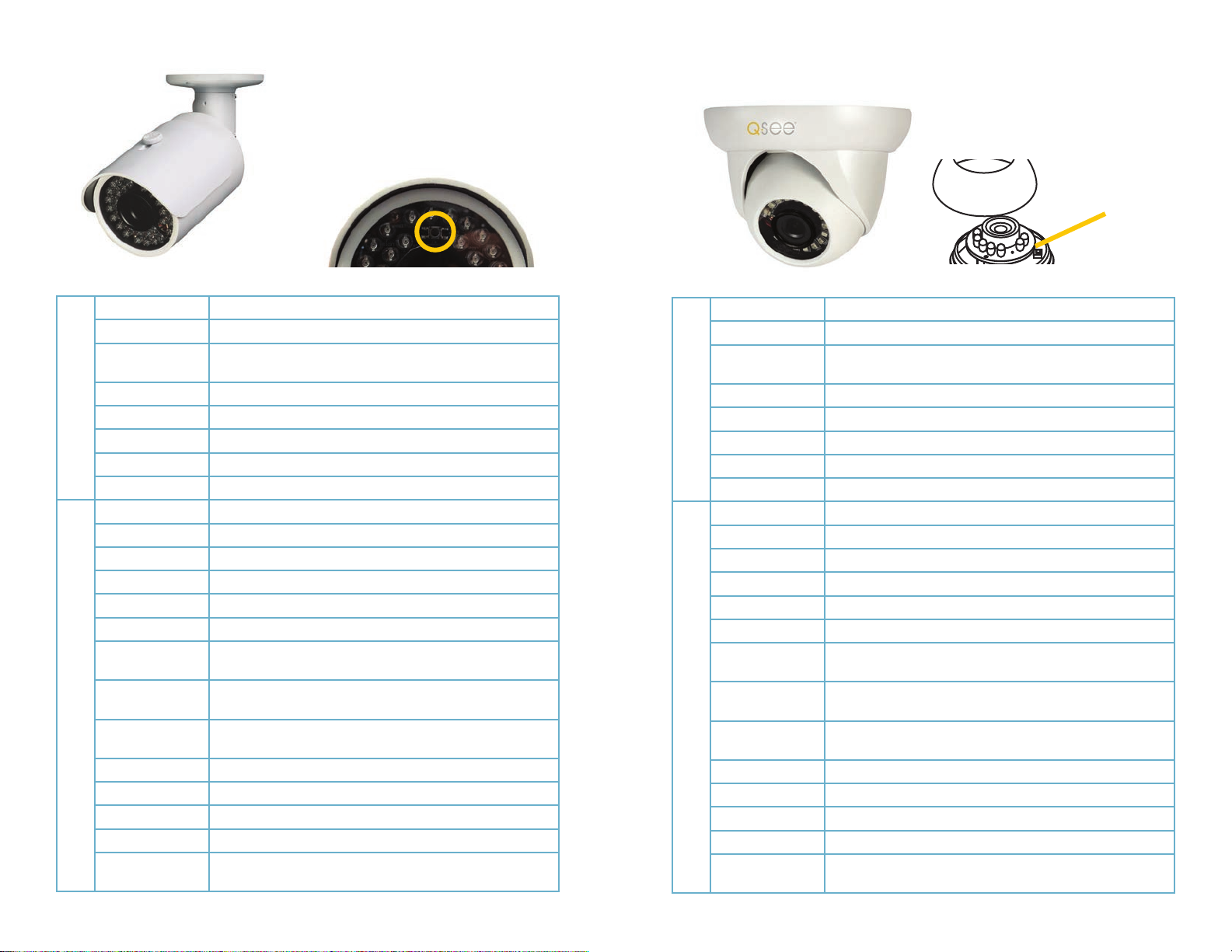
QCN8004B QCN8009D
In case of forgotten password, the camera’s
Reset button is located above the lens. To
access this button, remove the sun shade
and then unscrew the front of the camera
from the body. Be careful to not leave finger
prints or dust on the inside of the lens when
replacing.
In case of forgotten password, the camera’s
Reset button is located above the lens. To
access this button, unscrew the lens collar
from the camera body. Be careful to not leave
finger prints or dust on the inside of the lens
when replacing.
Reset Button
PICTURE 1-10
PICTURE 1-11 PICTURE 1-12 PICTURE 1-13
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
System
remote operation
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
System Status Bit stream stats, log, and software version.
Image Sensor 1/3” 2.0 Mp SONY progressive scan Exmor CMOS
Min. Illumination 0.1LUX/F1.2 (color), 0.01LUX/F1.2 (b/w)
Lens Auto-Iris 3.6@F1-6
Pixel 1920x1080 (1080p)
Day/Night Mode Automatic (ICR) Color/Black & White
Auto Aperture DC drive
Gain Control Manual/Auto
White Balance Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/4-1/10000
Video
Video Comp.
Standard
H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Video Frame Rate NTSC: Main stream 1080P @30fps, 1.3M @30fps, 720P
@30fps; Substream 704x480@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 32Kbps-8192Kbps
MJPG is adjustable along with bit rate 32-20480
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG
Privacy Mask Maximum 4 privacy zones supported
Video Adjustment Brightness, contrast, hue, saturation and gain
Video Info Channel title, time, motion detection, masking
Motion Detect 396 (18x22) zones. Six sensitivity levels. Motion detection
activation options: alarm, recording, snapshot, log and e-mail
Main Processor Texas Instruments DaVinci high-performance DSP
OS LINUX
System Resources Supports simultaneous real-time network, local record, and
System
remote operation
User Interface Remote operation through Web Service and PSS
System Status Bit stream stats, log, and software version.
Image Sensor 1/3” 2.0 Mp SONY progressive scan Exmor CMOS
Min. Illumination 0.1LUX/F1.2 (color), 0.01LUX/F1.2 (b/w)
Lens Auto-Iris 3.6@F1-6
Pixel 1920x1080 (1080p)
Day/Night Mode Automatic (ICR) Color/Black & White
Auto Aperture DC drive
Gain Control Manual/Auto
White Balance Auto
Exposure Mode Manual/Auto NTSC: 1/4-1/10000
Video
Video Comp.
Standard
H.264/JPEG/MJPG
Video Frame Rate NTSC: Main stream 1080P @30fps, 1.3M @30fps, 720P
@30fps; Substream 704x480@30fps
Video Bit Rate H.264 32Kbps-8192Kbps
MJPG is adjustable along with bit rate 32-20480
Snapshot 1f/s snapshot. Files saved as JPG
Privacy Mask Maximum 4 privacy zones supported
Video Adjustment Brightness, contrast, hue, saturation and gain
Video Info Channel title, time, motion detection, masking
Motion Detect 396 (18x22) zones. Six sensitivity levels. Motion detection
activation options: alarm, recording, snapshot, log and e-mail
18 19

QCN8010Z
In addition to its video surveillance functions, the QCN8010Z is able to accept input from other
devices and utilize them to trigger recording or alert actions when it is being used in a standalone role. The camera also has a slot for a 32GB Micro SD Card to serve as internal memory
allowing it to record video and still images without the need for an NVR.
By using the audio input and output to connect both a microphone and speaker - and with
similar audio equipment on the user’s end, two-way communication can take place. Two
alarm sensors can be connected to the alarm block with a single output to an audible alarm,
an external alarm input or to a DVR. When used with an NVR or on a network, the alarm signal
can trigger recording and its signal can be transmitted via the Cat 5 cable to an NVR.
1
2
3
4
PICTURE 1-14
5
Protective Shipping Collar
Remove and discard.
Reset Button
Micro SD Card Slot
PICTURE 1-15
MOUNTING YOUR CAMERA
Your camera is designed to mount directly
to an overhead surface or to a wall using the
included bracket. The appropriate assembly
and mounting instructions are presented on
the next pages. Both methods will require
you to open the camera by loosening the
three housing bolts using included torx (star)
wrench. It is not recommended to remove
them from the camera cover.
Remove and discard the foam insert from around the camera head. This protective packaging
will interfere with camera movement.
x3
HD
PICTURE 1-16
We have also included fabric gloves with your camera to help you prevent getting fingerprints
# Item Function
1 RJ45 (Ethernet) Port For network connectivity, video output and power input (via
POE)
2 Alarm 2 Alarm inputs 1 Output
3 Audio In Input for optional microphone
4 Power For use without POE
5 Audio Out Connect to speaker
or scratches inside or outside of the clear glass dome or camera lens. Handle the camera with
care at all times - especially when the cover has been removed. Do not attempt to move the
camera lens by hand to avoid damaging the mechanism.
Once you’ve determined the proper position and location for the camera, use the included
mounting template to drill the holes for the plastic anchors and cable (if needed).
20 21

Ceiling Mount
Mounting the camera to an overhead surface will be by attaching the camera’s base directly to the
surface using screws and anchors as needed. We have included screws and plastic anchors suitable
to most situations, but you must use your judgement regarding whether they are suitable for your
specific situation and mounting surface. The mounting surface and hardware must be sturdy and able
to hold at least five times the camera’s total weight.
1. Use the included adhesive mounting template
to drill the mounting holes - and the hole for
the cable to pass through, if needed.
2. Insert anchors into the holes - if needed.
3. If you will be running the camera cable through
the mounting surface, make the connection
to the RG45 cable at this time. Feed the cable
into the hole, making certain that it does
not subject to pinching, tight bends or other
severe constrictions as this could damage the
cable and lead to loss of control and video.
4. Line up the mounting holes on the base of the
camera to the holes in your mounting surface
and secure the camera
5. Reattach the camera’s cover. Take care to
remove dust, debris or fingerprints from inside
clear dome beforehand.
Wall Mount
Mounting the camera to a wall or other vertical surface will utilize the included adaptor plate and
swan neck mounting bracket. You must purchase screws, bolts or anchors suitable for your specific
situation and mounting surface. The mounting surface and hardware must be sturdy and able to hold
at least five times the camera’s total weight.
1. Use the mounting plate as a template to locate
and drill the mounting holes. If the cables will
be running through the mounting surface, drill
a hole for them at this time as well.
2. Run the camera’s cables through the central
hole in the adapter plate.
3. Use the included bolts to attach the plate to
the base of the camera.
4. Reattach the camera’s cover. Take care to
remove dust, debris or fingerprints from inside
clear dome beforehand.
5. Feed the cables through the swan neck
mount.
6. Attach the camera/adapter assembly to the
mount by inserting the threaded collar into the
mount and rotating until it is tight.
7. Tighten the retaining screw on the mount.
8.
Connect camera to cable and feed cables into
hole in mounting surface, if needed.
9. Attach mount to surface.
PICTURE 1-17
PICTURE 1-18
HD
HD
OPERATION
The Quick Installation Poster that came with your camera provides basic instruction on
how to connect, program and operate your camera. Further detailed instruction is provided in
the User Manual included on the CD that also accompanied your NVR.
NOTE! Unlike an analog PTZ camera, an IP PTZ camera does not need a
RS485 connection to the recorder to control its movements. Control signals
will be sent to the camera via the attached Ethernet cable whether the camera
is directly connected to an NVR or remotely connected via the Internet.
RESET BUTTON AND SD CARD
The QCN8010Z has a Reset button accessible only when the camera cover has been
removed. This is only for use if the camera becomes inoperable.
The QCN8010Z also has a slot for a Micro SD card which allows the camera to record images
and video when it is operating on its own network (ie; not directly connected to the NVR with
the Ethernet cable. Please see Section 3.5 for instructions on recording with an SD card.
SPECIFICATIONS
Camera Type PTZ
Camera Technology IP
Image Sensor size 1/3 inch Sony Exmor
Image Sensor Type CMOS
Image Resolution 1920 x 1080
Megapixels (digital) 2
Effective Pixels 1944 x 1092
Lens Size 3mm to 9mm (3X Optical Zoom- 16X Digital Zoom)
Angle of View (horizontal) 31° to 93°
IR Cut Filter Yes
22 23
Night Vision
IR LEDS None
Infrared Wavelength Not Applicable
Min Lux Illumination Color 0.05/B&W 0.0005 F1.2 Auto ICR
Night Vision Range Not Applicable
Additional Image Features
Auto Iris Yes
On Screen Display Yes
Backlight Compensation Yes BLC/HLC
Electronic Shutter 1/1 – 1/30,000s
Gain Control Auto/Manual
Wide Dynamic Range DWDR
Noise Reduction 2D/3D
PTZ
Horizontal Rotation 0-355°
Vertical Tilt 2-90°
Preset and Cruise Patterns
Audio
Audio Microphone Supports external microphone
Audio Range Dependent on external microphone
Connectivity
Connector Types RJ45/POE
External Connections RJ45, Audio in/out, Alarm 2 in 1 out, RS485, SD memory
Wireless No
Remote Monitoring
Use as Standalone Yes
Compatible Mobile
Devices
Compatible Systems NVRs
Power
Power Supply POE or 12 V 1.5A
Power Consumption 15W
255 Pelco, (80 DH-SD), 5 Pattern, 8 Tour, 5 Auto Scan, Auto
Pan
iPhone/iPad, Android, Windows Phone 7.5/8
Physical
Weatherproof Yes
IP Rating 66
Body Construction Metal
Mounting Hardware Screws, wall mount, ceiling mount
Weight 3 lbs
Dimensions (WxH) 6.25 x 5.25
Operating Temperature 14°F – 131°F
24 25

QCN8014Z
The QCN8014Z is a pan-tilt-camera with 12x
optical and 16x digital zoom. The camera
also has a slot for a 64GB Micro SD Card to
serve as internal memory allowing it to record
video and still images without the need for
an NVR.
It also supports external alarm and audio
inputs. It is able to accept input from other
devices and utilize them to trigger recording
or alert actions when it is being used in a
stand-alone role. It is able to support up to
two external alarm inputs as well as a single
output. The audio input and output allows
the user to connect both a microphone and
speaker to the camera. When used along
with similar equipment on the users end including through a mobile device - two-way
communication can take place.
Due to customer feedback, the wire leads
are unfinished leaving it to the user to attach
connectors as needed. If the additional
functionality is not needed, the entire cable
is easier to pass through the mount. It is
recommended that unused wire leads be
wrapped in electrical tape. The wire leads are
identified below.
The camera’s cable also includes the POE socket and an additional power socket for use with
the included 24V power supply if the camera is not directly connected to the NVR via a POE
port. Most Q-See NVRs such as the QC828, QC838 and QC8116 can power the camera
through their built-in POE ports.
Wire Color Purpose
Red Alarm COM
Brown Alarm Out
White Alarm In 1
Blue Alarm In 2
Gray Audio Out
Black Ground
Green Audio Ground
Purple Audio In
PICTURE 1-19
Protective Shipping Collar
Remove and discard.
Micro SD Card Slot
PICTURE 1-20
MOUNTING YOUR CAMERA
Your camera is designed to mount to a
wall using the included bracket. Before
mounting, you will need to open the camera
by loosening the three housing bolts
using included torx (star) wrench. It is not
recommended to remove them from the
camera cover.
Remove and discard the foam shipping collar (See Picture 1-20) from around the camera
head. This protective packaging will interfere with camera movement. If you intend to use a
Micro SD card in your camera, you can insert it at this time. You can close the camera after
you are finished.
We have also included fabric gloves with your camera to help you prevent getting fingerprints
or scratches inside or outside of the clear glass dome or camera lens. Handle the camera with
care at all times - especially when the cover has been removed. Do not attempt to move the
camera lens by hand to avoid damaging the mechanism.
Once you’ve determined the proper position and location for the camera, use the included
mounting template to drill the holes for the plastic anchors and cable (if needed).
Instructions for mounting your camera are on the following page.
x3
PICTURE 1-21
26 27
Mounting Instructions
1. Run the included 100’ network cable from the
NVR to the camera’s location or a network port.
2. Use the mounting bracket to mark the position
for the mounting holes. Ensure that the camera
will be horizontal by using a spirit or bubble
level. Also mark location of hole for cables to
pass through the mounting surface.
3. Drill the mounting and cable holes.
4. Insert included mounting anchors into surface.
5. Screw mounting collar onto camera body.
6. Feed the cables through the mount and out the
hole in the back before securing the camera/
collar assembly to the mounting bracket.
7. Tighten the three retaining screws on the collar
so that the camera housing does not turn.
8 Connect the camera cables to the extension
cable.
9. Secure the camera and mount assembly to the
wall using the included screws.
7
PICTURE 1-22
9
OPERATION
The Quick Installation Poster that came with your camera provides basic instruction on
how to connect, program and operate your camera. Further detailed instruction is provided in
the User Manual included on the CD that also accompanied your NVR.
NOTE! Unlike an analog PTZ camera, an IP PTZ camera does not need a
RS485 connection to the recorder to control its movements. Control signals
will be sent to the camera via the attached Ethernet cable whether the camera
is directly connected to an NVR or remotely connected via the Internet.
MICRO SD CARD
The QCN8014Z also has a slot for a Micro SD card on the camera head, next to the lens (See
Picture 1-20) which allows the camera to record images and video when it is operating on
its own network (ie; not directly connected to the NVR with the Ethernet cable. Please see
Section 3.5 for instructions on recording with an SD card.
SPECIFICATIONS
Camera Type PTZ Extreme Weather
Camera Technology IP ONVIF Profile S
Image Sensor size 1/3 inch Sony Exmor
Image Sensor Type CMOS
Image Resolution 1920 x 1080
Megapixels (digital) 2
Effective Pixels 1944 x 1092
Lens Size 5.1mm to 61.2mm (12X Optical Zoom-16X Digital Zoom)
Angle of View (horizontal) 5° to 51°
IR Cut Filter Yes
Night Vision
IR LEDS None
Infrared Wavelength Not Applicable
Min Lux Illumination Color 0.05/B&W 0.005 F1.6 Auto ICR
Night Vision Range Not Applicable
Additional Image Features
Auto Iris None
On Screen Display No
Backlight Compensation Yes BLC/HLC
Electronic Shutter 1/3s – 1/30,000s
Gain Control Auto/Manual
Wide Dynamic Range DWDR
Noise Reduction 2D/3D
28 29
PTZ
Zoom 12x optical 16x digital
Horizontal Rotation 0-360°
Vertical Tilt 2-90°
Preset and Cruise
Patterns
Audio
Audio Microphone Supports external microphone
Audio Range Dependent on external microphone
Connectivity
Connector Types RJ45/POE+
External Connections RJ45, Audio in/out, Alarm 2 in 1 out,, SD memory (64GB)
Wireless No
Remote Monitoring
Use as Standalone Yes
Compatible Mobile
Devices
Compatible Systems NVRs
Power
Power Supply POE+ or 24 V 1.5A
Power Consumption 12W (22W Heater on)
Physical
Weatherproof Yes
IP Rating 66
Body Construction Metal
Mounting Hardware Screws, wall mount
Weight 5 lbs
Dimensions (WxH) 7.5 x 9.25
Operating Temperature -40°F – 140°F
255 Pelco, (80 DH-SD), 5 Pattern, 8 Tour, 5 Auto Scan, Auto
Pan
iPhone/iPad, Android, Windows Phone 7.5/8
30 31

CONNECTING IP CAMERAS
CHAPTER 2
2.1 WHAT ARE IP CAMERAS?
Internet Protocol (IP) or Network cameras differ from conventional video cameras in that each
is a stand-alone device with a built-in processor of its own. Rather than being processed and
encoded on the recorder, the video is instead processed and encoded on the camera itself
before being sent to the recorder. The onboard processor allows the camera to operate on its
own with the video being available directly from the camera itself. The video can be recorded
onto internal memory (depending on model), sent to an FTP drive, accessed by a computer
or be streamed directly to a Digital Network Video Recorder (NVR) using standard network
protocols.
When it is connected to the NVR - whether locally, through a network or over the Internet the
NVR treats an IP camera as a peripheral device with the NVR serving as the control interface
and recording system.
Q-See’s QC-series NVRs feature an industry-exclusive built-in Power Over Ethernet (POE)
block that allows you to connect up to four IP cameras directly to it up to 200 feet away using
RJ-45 (Ethernet) cables without the need to purchase a separate power block or to locate
the cameras near power outlets. The Ethernet cable will both power the camera and deliver
the video signal to your system. Cameras beyond the number of POE ports, or those located
away from the NVR will require a separate power source, such as from the powered port of a
POE hub, or from a power supply. This power source must be located between the camera
and the network. It is not possible to power a camera through a network or over the Internet
using a POE port.
2.2 CONNECTING AN IP CAMERA
LOCALLY CONNECTING TO AN NVR
Your IP camera delivers video through a standard Cat 5, 5A or 6 Ethernet cable connected
to the RJ-45 socket at the end of the cable leading from the camera. Under most conditions,
power is delivered to the camera through this cable when it is connected to a POE block.
Regardless of how it is connected to the NVR, it is best to use a continuous length of cable,
whenever possible, rather than multiple short segments as each intervening connection could
result in a small loss of power and signal.
The following directions are for connecting your IP camera(s) to one of Q-See’s QC-Series
NVRs with a built-in POE block of powered Ethernet ports. If you are using another brand of
NVR, please consult that system’s user manual.
STEP 1. Connect one of the long
Ethernet cables to the socket on the
wire leading from the camera.
Cameras connecting to your system over a network (local or Internet) will also ultimately
connect through your network’s router and their signal will be received by the NVR through its
Network port. Cameras located outside of the network, and those being used as stand-alone
devices, will be accessed by using their web address - whether by entering it into the NVR, a
web browser, or through a surveillance program.
STEP 2. Plug the other end of the
Ethernet cable into any of the Power
over Ethernet (PoE) ports on the back
of the NVR or into a stand-alone POE
block.
In the latter cases, the camera will
also need to be connected to a
network.
STEP 3. Repeat for additional cameras.
PICTURE 2-1
PICTURE 2-2
32 33

Using the Power Over Ethernet Block
NVR
POE
Block
POE
Block
Network
Network
Port
POE
Router
NVR
POE
Block
POE
Block
POE
Router/
Modem
POE
Router/
Modem
NetworkNetwork
Port
Internet
Internet
NVR
POE
Block
POE
Block
POE
Router/
Modem
POE
Router/
Modem
NetworkNetwork
Port
Internet
Internet
Your NVR’s POE block will power up to four cameras while receiving their video signals. This
is the primary and preferred method to connect cameras to your NVR. This feature cannot be
expanded through use of a network switch. These ports are also not to be used to connect
the NVR to a network router. When an IP camera is connected to the NVR through the POE
port, it will receive power immediately, but there may be a delay of up to a minute before the
camera’s signal appears on the screen as the system establishes connectivity.
If you are unsure, and if your camera has
infrared LEDs, you may cup your hand over
the lens area to activate the infrared night
vision mode. You will see a faint red glow
from the LEDs confirming that the camera
has power.
NVR
POE
POE
Block
Block
PICTURE 2-3
CAMERAS CONNECTED THROUGH A NETWORK
There are two types of networks – local (LAN or Intranet) and Internet (or WAN). Cameras can
be accessed by the NVR over both types.
Connections Over the Internet
A third connection option is via the Internet.
This method is more complicated, but it
allows the user to view cameras that are
located in a completely different building –
or region – from the NVR itself. In essence,
your NVR will be remotely monitoring those
cameras. As such, the user will need to
forward ports using the IP Tool software
included on the Manuals and Software
CD to obtain the IP address for any camera
that will be accessed over the Internet. Full
instructions are covered in Chapter 2.
NVR
Router/
NetworkNetwork
Modem
Port
POE
POE
Block
Block
PICTURE 2-5
Internet
Internet
Router/
Modem
POE
POE
Local Networks
For cameras positioned too far away to
reasonably run a network cable directly to the
NVR, you can connect it to the same network
as the NVR and the system will be able to
access and use them.
Ultimately, each camera will have to connect
to the same router that the NVR is connected
to. They will need to be connected to a
power source on their side of the network preferably a POE - as the POE block on the
NVR itself is unable to provide power through
the network.
Alternately, if your NVR was bundled with cameras, they may include a power input as
additional power option. You will need to acquire a power adapter that matches the ratings
listed on the camera itself if you are not connecting them to a POE.
The NVR will connect to these cameras through the same cable that it uses to communicate
with the network.
NVR
Network
Network
Port
POE
POE
Block
Block
PICTURE 2-4
Router
POE
34 35

2.3 ADDING AND REMOVING CAMERAS IN YOUR SYSTEM
View 1
View 4
View 8
View 9
View 16
Pan/Tilt/Zoom
Auto Focus
LOCAL CAMERAS
Once you have connected your cameras, you will need to add them to your system’s
display. For cameras connecting to one of Q-See’s QC-Series NVRs, they will automatically
appear on-screen shortly after being plugged in. Cameras will be assigned to the first
available channel by the NVR in this case, regardless of which port in the block that they
were connected to. These cameras can only be removed from your display by physically
disconnecting the cameras from the NVR.
CAMERAS ON THE SAME NETWORK
Cameras sharing the network with the NVR will not automatically connect. There are three
ways to connect them on a QC-Series NVR. The first two methods are by either using the
Add Camera icon in the Live View window, or right-clicking within it. The third method uses
the Remote Device window located in the Main Menu.
Add Camera
Moving the cursor to the center of any empty
channel will reveal the Add Camera icon
shown in Picture 2-6. Clicking on this will
open a window listing available cameras.
QC NVR REMOTE DEVICE MENU
Use of remote IP cameras connected to a network - whether local or remote - requires
your NVR to be connected to a router. It also requires that the cameras are connected to a
router as well - even if it isn’t the same one as the NVR. If you intend to connect to devices
that are located outside of your local network, then this router must be able to access the
Internet. Instructions for connecting your system to the Internet are presented in the Remote
Monitoring Guide that also came on the CD with your system. It is also available from our
online resource at www.Q-See.com/Support.
Similarly, the remote devices must be able to communicate with the local network or Internet.
This will be covered in Section 2.4. You will need to follow the instructions in that chapter in
order to obtain an IP address for any cameras that will be accessed over the Internet. Once
you have connected your cameras to a router you can connect to them using the Remote
Device window.
MAIN MENU
This window can be reached by clicking on
the Remote Device icon in the Main menu...
SEARCH
INFO
RECORD SETTINGS
ADVANCED BACKUPREMOTE DEVICE
SHUTDOWN
SETTING
PICTURE 2-6
PICTURE 2-8
...or through the Shortcut menu by right-
Clicking on IP Search will refresh this list.
Simply click on the desired camera from the
list and it will become the camera for that
channel. Please note that it is possible to load
a camera which is already in use by another
channel. In which case, you will have two
identical channels.
REMOTE DEVICE
2 IP Address Port Device ID Manufacturer Type
1 10.1.1.65 1 YZC2OC061966 Private IPC-HFW210
2 10.1.1.67 2 YZCAU192012 Private IPC-HFW321
IP Search Manual Add
None
Filter
Add Cancel
PICTURE 2-7
clicking on the screen and selecting Remote
Device.
Color Setting
Search
Record Status
Tour Setup
Remote Device
Alarm Output
PICTURE 2-9
36 37

When the window opens, you will be presented with a list of all conneced devices in the
lower portion. This section, marked Device Added, indicates the status of each device along
with other information about it.
4 IP Address Port Device ID Manufacturer Type
1 10.1.1.65 Port 1 YZC2OC061966 Private IPC
2 10.1.1.67 Port 2 YZCAU192012 Private IPC
3 10.1.1.68 Port 4 TC2FW25600095 Private IPC
4 196.219.8.50 4000 Private
IP Search Add
Device Added
channel Edit Delete Status IP Address Port Device ID
1 196.610.6.46 37777
2 10.1.1.67 Port 2 YZCAU192012
3 10.1.1.68 Port 4 TC2FW25600095
4 10.1.1.65 Port 1 YZC2OC061966
Delete Manual Add
REMOTE DEVICE
None
Filter
OK Cancel
PICTURE 2-10
Icon Meaning Description
Editable
Cannot
Delete
Removable
Device
You may edit the settings on this device by double-clicking on it
This device is connected directly to the NVR and must be physically
unplugged to be removed from this list.
This device may be deleted from the list by checking the box next to
it and clicking on the Delete button below.
The connected device is operating normally.
Status OK
Device
Error
There is an issue with the connected device that is preventing it from operating
normally.
Clicking on IP Search under the upper portion of the window will generate a list of all devices
that the NVR was able to locate - both directly connected as well as connected to the same
network as your system. Items showing a short IP address beginning with “10” are cameras
directly connected to the NVR and who’s IP addresses were assigned by the NVR itself. Care
should be taken that you do not attempt to connect a device that is already connected to the
system as it will create a duplicate video feed and could cause connectivity issues.
Edit
Double-clicking on a device in the Device Added portion of the window will display
information regarding the connected remote device. Making any changes within this window
will not change anything on the camera or remote device itself. To make those changes, you
will need to access the camera or other remote device (such as a DVR) directly, or through
one of the remote methods described in the Remote Monitoring Guide.
Once you have made those changes, you will need to update the user name and password
within the Edit window. Failing to change these in this window will result in an on-screen
message about incorrect password and may lock you out of the IP camera for a period of 30
minutes in the case of QC-Series cameras - other brands may vary.
It is important that you do not remove the
device you are making the changes upon
from the list of connected devices before
editing the information in the Edit window. If
you later remove the device from the list and
wish to reconnect, you will need to do so
using the Manual Add feature as described
below.
Similarly, if you already know the IP address
and port of the camera, you can use the
Manual Add feature.
4 IP Address Port Device ID Manufacturer Type
1 10.1.1.65 Port 1 YZC2OC061966 Private IPC
2 10.1.1.67 Port 2 YZCAU192012 Private IPC
3 10.1.1.68 Port 4 TC2FW25600095 Private IPC
Channel
4 196.219.8.50 4000 Private
Manufacturer
IP Address
IP Search Add
TCP Port
Device Added
User
channel Edit Delete Status IP Address Port Device ID
Password
1 196.610.6.46 37777
Remote Channel
2 10.1.1.67 Port 2 YZCAU192012
Decoder Buffer
3 10.1.1.68 Port 4 TC2FW25600095
4 10.1.1.65 Port 1 YZC2OC061966
Delete Manual Add
REMOTE DEVICE
EDIT
1
Private
IPC.myq-see.com
32555
admin
1
280
Save Cancel
None
Filter
OK Cancel
PICTURE 2-11
IMPORTANT! To avoid connection issues, you should not change the
information within the Edit window unless you have first made those changes
to the remote device itself.
The lower portion of the window shows all devices currently connected to your NVR. If all of
your channels are occupied, you will need to delete one of the connected devices from this
list by selecting the check box next to it and clicking delete. Items with a gray “X” are directly
connected to your NVR and may only be removed by physically disconnecting them from your
system.
Clicking on the IP Search button will create a list of all remote devices that the NVR was able
to detect. You may limit this search to only IP cameras by selecting IPC in the Filter pulldown. Items being accessed by your NVR over the Internet will not appear in the list at the top
of the window. They must be added manually (see below).
If you have an available channel, you may add a device by selecting the check box next to it
and then clicking Add. Please note that if you changed the default user name and password
for your camera(s) in the Web Service application as described in Chapter 3, you will need to
use the the Manual Add feature instead.
38 39

2.4 CONNECTING YOUR CAMERA TO A REMOTE NETWORK
Shut Down
Devices and Printers
Default Programs
Help and Support
As was mentioned in the previous section, cameras connected to the same network router
as the NVR can be discovered by that system and added. Cameras on a different network
require additional steps to be connected to an NVR, and these same steps are needed if one
is going to be accessing the camera only using a computer or mobile device.
First and foremost, you will need to physically connect your camera to a router. This router can
be part of an existing network of computers, or it can be the router/modem supplied by your
Internet Service Provider (ISP) to connect you to the Internet. This connection will be made by
plugging the other end of the Ethernet cable that you connected to the camera into a router or
into an Ethernet port that connects to a router.
You cannot connect the camera to the Internet through a modem because there is no method
available to cause the modem to dial out to the ISP. Your camera will need to be directly
connected to its own power supply - whether it is a power adapter or a Power Over Ethernet
(POE) block. In the case of the latter, the POE block will then connect to the router or network.
Your camera is not designed to be connected wirelessly to a network. It is also recommended
that the router that the camera is connected to should be connected directly to the Internet
rather than to another router if Internet access is desired as multiple routers can create
problems with connectivity. You will also need to have a computer connected to the same
router - at least temporarily - to make certain settings. If, after following the instructions you
are still not able to access your NVR, please see Section 2.5 Troubleshooting Network
Connections later in this chapter.
In order to access your camera over the Internet, you will have to determine its IP address.
Each device on a network - both a LAN or the Internet - has a specific IP address. This
address is what allows different devices on the network to communicate with each other. You
will also need to confirm that two ports, or openings, have been permitted by your router to
allow communication to and from your camera.
BEFORE YOU GET STARTED
You will need to have:
• Your router’s brand, model number and manual. The manual is also usually available on
your router’s manufacturer’s website.
• The “Manuals and Software” CD that came with your camera. It contains necessary
software and links to other important programs which are mentioned in this guide.
• Your router’s password (the default password should be in your router’s manual).
• Your router’s Gateway address.
OBTAINING IP INFORMATION USING IPCONFIG IN WINDOWS
You will need to get your router settings to not only create an IP address, but for the Default
Gateway information as well.
To get the router settings:
STEP 1. To access the router’s settings you will need to enter the Command (CMD)
panel on a computer also connected to the same router.
A. WINDOWS XP – Select Run from
your Windows START menu (lower
left of screen) and type “cmd” after
the prompt.
B. WINDOWS VISTA and WINDOWS
7 – Click on the START menu
(Windows icon) in the lower left of
your screen. Type “cmd” into the field
that says, “Search programs and
files” and hit ENTER or click on the
magnifying glass icon.
STEP 2. Type “ipconfig” at the prompt
(Red arrow in Picture 2-14) to
access router settings.
STEP 3. Write down the Default Gateway
number (bottom green arrow).
Microso Internet Explorer
Microso Office Outlook 2007
iTunes
Adobe Acrobat
All Programs
start
start
Inbox Microsof... iTunes
PICTURE 2-12
Microso Office Outlook 2007
Scky Notes
iTunes
Adobe Acrobat
All Programs
cmd
PICTURE 2-13
Devices and Printers
Default Programs
Help and Support
Run
Log Off
Shut down
If your camera is able to automatically connect to your network, you will only need your
router’s Gateway address to connect to your camera from outside of the local network.
However, if your camera is unable to connect automatically, you will need this information in
order to make the connection.
40 41
PICTURE 2-14

OBTAINING IP INFORMATION USING A MAC
The easiest method for locating the router’s Gateway address for Macintosh is through the
computer’s Network window.
TESTING THE CONNECTION
Your camera features UPnP (Universal Plug ‘n Play) connectivity. This allows network devices
to be automatically added to the network and communicate with other devices within it
without additional setup. If your Network router has this feature - and it is turned on - your
camera may be accessible from the moment you connect it to the network.
STEP 1. Click on the System
Preferences icon at the bottom of
the Macintosh’s screen.
STEP 2. Click on the Network icon.
STEP 3. Make sure that your network
connection is highlighted in the list of
connections to the right of the main
part of the Network window and
that its status reads “Connected.”
The Router’s IP address will be
displayed.
PICTURE 2-15
PICTURE 2-16
To test this, once you have connected the
IP camera to a network, you will need to run
the ConfigTool software on a computer
connected to the same router.
This Windows software is located in the
Software folder on the CD that came with
your system. Macintosh computer users will
need to use the Search Device function
within the Device Manage window in PSS
to locate the camera. PSS is covered in
Chapter 4.
When ConfigTool launches, it will produce
a list of all QC-Series IP cameras that are
connected to the same network. This
will confirm that your camera has been
successfully added to your network.
To ensure that the camera and the
connection are operating properly, right click
on the camera’s name in the list.
A pop up window saying, “Open Device
Web” will open. Click on it to open a browser
window.
PICTURE 2-18
PICTURE 2-19
PICTURE 2-20
When the browser window has opened, you
will be presented with a login screen for the
Q-See Web Service. Since you’re on the
PICTURE 2-17
same network as the camera, you will want to
select LAN from the options at the bottom of
the screen.
PICTURE 2-21
42 43

The default username and password are admin and admin. It is recommended for security
Page Safety Tools
This page will serve as a free utility for remotely verifying a port is open or closed. It will
be useful for users who wish to check to see if a server or ISP is blocking certain ports.
reasons that you change the password before you add the device to your NVR. See Section
3.6 for instructions on modifying the password on your camera.
Internet Explorer users may be asked to download an ActiveX plug-in from Q-See
International, Ltd. Firefox and Chrome users may be asked to allow QuickTime to run. In these
cases, you should allow the required plugins to operate. In some cases, you will be returned
to the log in screen after the plugin has loaded. This is normal.
OPENED PORTS AND INTERNET IP ADDRESS
Just as with your NVR, you will need to confirm that your ports are open and that your camera
is accessible from the Internet. You will also need to get the Internet IP address which you will
use to connect to the camera outside of its local network.
Confirming that the ports have been opened
To confirm that your ports have been forwarded successfully, go to www.canyouseeme.org
using a computer connected to the same router as the camera.
Although ConfigTool is Windows only, the Web Service browser program will operate on
Macintosh computers as well. To access your camera without ConfigTool, simply enter the
camera’s local IP address into the browser window on a computer located on the same
network.
After you log in, you should see live video
from your camera. This confirms that your
connection and camera are operating
optimally. You may also use the Web Service
program to access your camera separately
from your NVR. The camera can also be
accessed through the PSS software included
on the CD. These are both covered in the
next chapters.
PICTURE 2-22
Once you have confirmed that you can access your camera on a local network - and if you
wish to access it from over the Internet - you will need to confirm that the camera’s ports have
been opened as well as obtain the camera’s Internet IP address
If you are unable to see video from your camera, you should check all connections and ensure
that your computer software is operating properly. You may also wish to try to connect using
a different browser or computer if the problem persists. Instructions for opening ports and
troubleshooting connection issues are provided in the next section.
STEP 1. Enter “85” into the box labeled
“What Port?”
STEP 2. Click on the Check button.
Browser - Windows Internet Explorer
hp://canyouseeme.org/
Open Port Check Tool
CanYouSeeMe.org - Open Port Check Tool
STEP 3. You should see a green
“Success” message. If not, return to
ConfigTool and double-click on the
camera in the list. Change port 85 to
81 or 83 and click Apply to save your
changes before checking using that
new number on CanYouSeeMe.
STEP 4. Repeat for port 37777. If there
Your IP: 81.919.622.24
What Port?
Check
Success: I can see your service on
81.919.622.24 on port (85)
Your ISP is not blocking port 85
PICTURE 2-23
is a problem with port 37777, then try
37000 in the same manner as above.
Obtaining Internet IP address
This website will also display your Public IP address near the top of the page above the box
where you entered your port number. This is the first part of the number which you will use to
access the IP camera using your NVR, the PSS software, the Web Service browser app or
your mobile device from outside of your local network (away from the building in which your
NVR is located). The second part is the first port number that you confirmed was open. Using
the number shown in the image above, you would enter http://81.919.622.24:85 with 85
being the opened port. If you used a number other than 85 for the first port, you will use that
instead, placing it after the colon (“:”) in the address.
Be sure to record this address for use at your NVR. If you had to use a different port than
37777 you will need to record that as well.
44 45

2.5 TROUBLESHOOTING NETWORK CONNECTIONS
OPENING PORTS
The most common factor causing network connection issues is for communication between
the device and a device outside the network to be blocked. The router’s built-in-firewall is
designed to keep malicious users and software out of the network. At times, this can also
block legitimate connections. To avoid this, routers can allow communication to pass through
specific ports within the firewall. These “virtual tunnels” only allow access to specific devices
within the network. Properly managed with passwords and other safeguards, these do not
pose a threat to the security of the network.
Option 2: Opening Ports Using DMZ
The exact location of DMZ within the router’s settings vary by manufacturer so please consult
your router’s manual for the location of this feature. The method for accessing your router’s
settings, however, is pretty standard.
NOTE! If you are an AT&T Internet or Uverse customer, you should follow the
instructions laid out in Option 3 as they specifically apply to the brand of router
used by AT&T.
If your network’s router has the UPnP feature turned on, it and the camera should “discover”
each other on the network in less than a minute. Ports 85 and 37777 will be “forwarded”
to the camera’s local network IP address, allowing it to communicate with the Internet. The
former allows you to control the camera, while the latter port is used by the camera for the
video stream.
However, some brands of routers, such as the 2Wire used by AT&T for it’s Uverse service
do not include this feature. In this case, the ports will need to be manually forwarded using
one of the methods described on the next few pages. You will only need to use one of these
methods - which are the same if you are using a Macintosh or Windows PC. If you are still
unable to connect your NVR to the Internet using any of these procedures, the likely cause
is the presence of multiple routers on your network. Solutions to overcome that situation are
presented at the end of this section.
Regardless of the method you use, you will need to get your router’s Public (Internet) IP and
Gateway addresses in order to log into the router, and eventually connect to the camera.
Option 1: UPnP
Check your router’s manual to confirm the presence of the UPnP feature. You may need to log
into your router to turn it on. There are legitimate reasons to disable UPnP, but you may wish
to enable it briefly in order to allow the camera to connect. Once you’ve confirmed that the
camera’s ports have been opened and you’ve set the camera to use a Static IP address as
described later in this section, you can disable UPnP.
The location of the UPnP settings within your router vary by brand and model. Consult your
router’s manual to locate and enable this feature before continuing.
STEP 1. On a computer connected to
the same router as your camera,
open a web browser and enter the
Gateway (Router’s IP address) into
the browser window’s address bar to
access your router.
STEP 2. Locate the DMZ settings in
your router. Each manufacturer is
different so please consult your
router’s manual for the location of this
setting. Two examples are shown at
right.
STEP 3. Enable DMZ.
STEP 4. Enter the NVR’s IP address.
STEP 5. Click on Apply or Save to
preserve your settings.
Leave your router control panel open as you
will need to obtain DNS information from
your router in Section 1.5 Domain Name
System (DNS). You should now proceed to
the section entitled Confirming that Ports
are Opened.
Browser - Windows Internet Explorer
hp://10.6.196.6
PICTURE 2-24
PICTURE 2-25
PICTURE 2-26
46 47

Option 3: Opening Ports Using DMZ on 2Wire Routers
r
Page Safety Tools
This page will serve as a free utility for remotely verifying a port is open or closed. It will
be useful for users who wish to check to see if a server or ISP is blocking certain ports.
2Wire brand routers are currently the exclusive router used for AT&T’s Uverse and other
Internet servers. Their configuration protocols are different enough that you should follow
these instructions rather than the generic router instructions in Option 2 if you are an AT&T
customer.
STEP 1. On a computer connected to
the same router as the IP Camera,
open a web browser and enter the
Gateway (Router’s IP address) into
the browser window’s address bar to
access your router.
STEP 2. Click on the Settings tab and
then Firewall. Once in Firewall,
click on Applications, Pinholes and
DMZ.
STEP 3. In the Select Your Computer
area, locate your camera’s IP address
and click on it.
STEP 4. Scroll down to select User
Defined.
STEP 5. Click on Add a new user-
defined application.
STEP 6. In the box labeled Application
Profile Name, enter “IP Camera”.
STEP 7. Ensure that TCP is selected.
STEP 8. Enter 85 in the From and To
boxes for Port (or Range).
STEP 9. Leave the next two boxes blank
to use the default settings.
STEP 10. Click on Add to List. Your
router will require you to log in to
accept the settings. If you have not
created your own password for your
router, it is the 10-digit System Key
printed on the label on your router
between the square brackets “[ ]”.
STEP 11. Once your settings have been confirmed, repeat Steps 8-10, this time
entering 37777 for the From and To ports.
STEP 12. Click on Back and then select Ip Camera from the list of Applications. Clicking
on Add and then Save.
Leave your router control panel open as you will need to obtain DNS information from your
router in Section 2.6 Additional Network Services.
Browser - Windows Internet Explore
PICTURE 2-27
2
3
4
5
PICTURE 2-28
hp://10.6.196.6
6
7-8
10
Confirming That Ports are Opened
To confirm that your ports have been forwarded successfully, go to www.canyouseeme.org
using a computer connected to the same router as the camera.
STEP 1. Enter “85” into the box labeled
“What Port?”
STEP 2. Click on the Check button.
STEP 3. You should see a green
“Success” message. If not, return
to the NVR’s Network window and,
in the Network tab, change port 85
to 81 or 83 and click Apply to save
your changes before checking using
that new number on CanYouSeeMe.
Afterwards, you will need to forward
that new port using Option 2 or 3.
STEP 4. Repeat for port 37777. If there
is a problem with port 37777, then try
37000 in the same manner as above.
This website will also display your Public IP address near the top of the page above the box
where you entered your port number. This is the number which you will use to access the IP
camera using a web browser, the PSS program or your mobile device from outside of your
local network (away from the building in which your camera is located).
NOTE! If you are successful after changing from port 85, then you will need to
add that to the IP address when accessing the camera via the Internet. If, for
example, you changed to port 81, the address would now read 64.245.112.90:81
Browser - Windows Internet Explorer
hp://canyouseeme.org/
Open Port Check Tool
CanYouSeeMe.org - Open Port Check Tool
Your IP: 81.919.622.24
What Port?
Check
Success: I can see your service on
81.919.622.24 on port (85)
Your ISP is not blocking port 85
PICTURE 2-29
48 49

ISSUES WITH DHCP
As long as you are connecting your camera to a router with DHCP enabled, you should not
have an issue connecting to your camera. The majority of routers do have the DHCP feature,
but some users disable this feature and manually assign IP addresses to the devices on their
network. The first step in resolving a connectivity issue, is to ensure that DHCP is active on
your router. You will need to consult your router’s manual for information on where this feature
is located.
If you have disabled DHCP and prefer
to manually assign IP addresses to your
network devices, you may do so using the
ConfigTool software. If you do not know
the correct IP information, you can use
the Windows IPCONFIG command shown
in Section 2.3 to obtain the needed
information.
MULTIPLE ROUTERS ON THE NETWORK
If you have tried the previous methods and are still unable to connect to your camera from
outside of the local network, it is possible that there may be more than one router between
your camera and the Internet. Having more than one router between the camera and the
Internet will block communication to and from your device. The simplest remedy is to connect
the camera to the router that directly connects to the Internet.
To find out the number of routers on your network, you will need to download a FREE router
detection program.
STEP 1. Go to http://www.pcwintech.
com/shanes-toolbox
Double-click on the desired device to open
the camera’s Login window within Config
Tool to open the IP Address Modification
window.
Enter the IP address, default gateway and
subnet mask.
Click OK to save, and you will see the
information update in the Device List.
Right-click on the camera to open it in the
Web Service browser program and proceed
as described in Section 2.4, above.
Alternately, you may wish to turn on DHCP
in your router long enough to allow the
camera to obtain an IP address, which
you can then change to Static in the Web
Service’s Network TCP/IP window.
Enter the information into the proper fields
in ConfigTool’s IP Address Modification
window.
PICTURE 2-30
PICTURE 2-31
STEP 2. Click on Detect Multiple
Routers to begin the download.
STEP 3. Unzip the application to install it.
STEP 4. Click on the detect_routers
application to run it.
PICTURE 2-33
PICTURE 2-34
Click OK to save, and you will see the
information update in the Device List.
Right-click on the camera to open it in the Web Service browser program and proceed as
described in the next chapter.
PICTURE 2-32
50 51

STEP 5. Click on CHECK NOW to
detect how many Routers are in the
network.
PICTURE 2-35
STEP 6. If there is only one router detected, and you are using UPnP, then you will need
to turn off that setting and attempt to connect using DMZ as described in Section
1.2 Opening Ports.
If you are using DMZ, check to make sure that the UPnP option is turned off.
If Multiple Routers are Detected
If there are multiple routers, you will see a
display similar to Picture 2-36.
If so, it may be preferable to connect your
NVR and computer to the router that
connects directly to the Internet. However,
this is not always possible depending upon
your particular situation.
Setting Up DMZ in Router 2
STEP 1. Login into Router 1 by putting
the IP of Router 1 into the Internet
Explorer browser, as in the example
shown in Picture 2-37 where the IP
address of Router 1 is 192.168.0.1
STEP 2. Find the status page on the
router settings that shows the WAN/
Internet IP address and write it down
this WAN IP address.
STEP 3. Log into the Router 2 by putting
the IP of Router 2 into the Internet
Explorer browser, as in example
shown in Picture 2-37 where the IP
address of Router 2 is 192.168.1.1
STEP 4. Find the DMZ page in the
router settings.
STEP 5. Enter the WAN IP for Router 1
into the DMZ page and enable DMZ.
NOTE! If you do not have a DMZ setting in the router, check to see if there
is a Bridge setting. If so, then use the Bridge setting instead of DMZ.
STEP 6. Save your changes.
You have forwarded the ports on the router to which the NVR is connected, to the IP address
of the NVR, and set the second router to pass the connection to this router.
PICTURE 2-37
PICTURE 2-36
In this case, you will need to proceed with the next section and set up DMZ in the second
router to allow communications to pass through it from the first. If only one router is detected
you will need to consult your router’s manual.
52 53

CONFIGURING ACTIVEX
Accessing your NVR using Internet Explorer is generally as simple as using an interactive
website. Some users may need to configure Microsoft’s built-in ActiveX controls prior to
logging into their camera in order to ensure smooth operation. ActiveX is built into Internet
Explorer to enable it use multimedia content. Sometimes, this can cause conflicts with security
settings within the browser program itself.
Setting Up ActiveX Control
STEP 1. Open Internet Explorer
STEP 2. Click on Tools
STEP 3. Select Internet Options in the
pull-down menu
PICTURE 2-38
STEP 4. Click on the Security Tab
STEP 5. Select Trusted Sites
STEP 6. Click on the Sites button
STEP 7. Uncheck the “Require server
verification (https:) for all sites in
this zone” button.
STEP 8. Type the NVR’s IP address
(obtained during Network Setup)
or DDNS domain name into the “Add
this website to the zone:” box.
STEP 9. Click the Add button
STEP 10. Close the window.
PICTURE 2-40
STEP 11. Click the Custom level…
button.
PICTURE 2-39
PICTURE 2-41
54 55

STEP 12. Pull down the “Reset to:”
menu button and select Low
STEP 13. Click the Reset button
STEP 14. Click “Yes” when asked, “Are
you sure you want to change the
setting for this zone?”
Troubleshooting: User Account Control for Windows Vista and Windows 7
Some users of computers using Windows Vista or Windows 7 operating systems may receive
an error message informing of a codec that is missing or not installed. This conflict can be
resolved by turning off User Account Control (UAC).
Windows Vista
STEP 1. Open the Control Panel
(accessible by clicking on the
Windows icon in the lower left of your
screen.
PICTURE 2-45
STEP 2. Select User Accounts and
Family Safety.
PICTURE 2-42
PICTURE 2-46
STEP 3. Select “Add or Remove User
Account.”
STEP 15. Click OK
STEP 16. Click Apply
STEP 17. Click OK
STEP 18. Close Internet Explorer
PICTURE 2-43
Open a browser window in Internet Explorer and enter the IP address or DDNS name
(obtained in Section 1.1) into the address bar.
You will see a log in screen similar to that
shown in Picture 2-44 or yellow alert bar at
the top of the window asking for permission
to open an ActiveX application. Allow it to
install webrec.cab control to reach the
sign-in screen.
Proceed to Chapter 3 for instructions on
logging in and remote monitoring.
PICTURE 2-44
STEP 4. Select the desired user account.
STEP 5. Select Turn User Account
Control on or off
PICTURE 2-47
PICTURE 2-48
56 57

PICTURE 2-49
Page Safety Tools
ADVANCED
All of your Internet and network connecon details are displayed on this page.
2.6 ADDITIONAL NETWORK SERVICES
Once you have connected the IP camera to a network and are able to access it from another
network as well, you will need to obtain the Domain Name System (DNS) from your router and
enter it into your camera to enable the camera to send out e-mail alerts. Optionally, you will
also want to set up a Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) to creatr an easy-to-use web
address that you can use in place of the string of numbers making up the IP address when
logging into the camera.
STEP 6. Uncheck the box next to “Use
User Account Control (UAC) to help
protect your computer.”
STEP 7. You will then be asked to restart
your computer for the change to take
effect.
Windows 7
STEP 1. Open up the Start Menu
(accessible by clicking on the
Windows icon in the lower left of your
screen.
STEP 2. Type “uac” into the search bar
and hit ENTER. The User Account
Control will open or you will be offered
a link to click to open it.
STEP 3. Move slider to lowest setting
and press OK.
PICTURE 2-50
Microso Office Outlook 2007
Scky Notes
iTunes
Adobe Acrobat
All Programs
uac
PICTURE 2-51
Devices and Printers
Default Programs
Help and Support
Shut down
Entering these settings may be made within the Web Service or PSS software running on a
computer connected to the same router as the camera. The method for obtaining the DNS is
identical for either program. Both of these programs will be covered in full in their respective
chapters following this one. However, it is generally easier to make the settings in Web
Service, later accessing the camera using PSS since these settings must be made on a
computer connected to the same router as the camera.
OBTAINING DNS INFO - MACINTOSH AND PC USERS
STEP 1. On a computer connected to
the same router as your camera,
open a web browser and enter the
Gateway (Router’s IP address) into
the browser window’s address bar to
access your router.
STEP 2. Locate your router’s status
window (may also be named
“Information” or “Info”, it will list the
DNS number. You will only need to
use the primary set of numbers write it down for later use.
Browser - Windows Internet Explorer
hp://10.6.196.6
PICTURE 2-53
Browser - Windows Internet Explorer
hp://81.919.622.24
Router
DEVICE INFO
LOGS
STATISTICS
INTERNET SESSIONS
ROUTING
WIRELESS
SETTINGS
DEVICE INFORMATION
WAN
MAC Address :
Subnet Mask :
Default Gateway :
Primary DNS Server :
Secondary DNS Server :
Advanced DNS :
PICTURE 2-54
IP Address :
STATUS
00:24:01:77:f9:00
81.919.622.249
255.255.255.0
81.919.622.24
10.6.196.6
(null)
Disabled
PICTURE 2-52
58 59

MACINTOSH COMPUTERS
In addition to retrieving the DNS info from the router, Macintosh users can get it from the
computer’s Network window.
STEP 1. Click on the System
Preferences icon at the bottom of
the Macintosh’s screen.
PICTURE 2-55
STEP 2. Click on the Network icon.
ENTERING THE DNS INFORMATION INTO THE CAMERA
STEP 1. Open another browser window
and enter the camera’s Local IP
address which you obtained in
Section 2.4.
STEP 2. When the browser window has
opened, you will be presented with
a login screen for the Q-See Web
Service. Since you’re on the same
network as the camera, you will want
to select LAN from the options at the
bottom of the screen.
The default username and password are admin and admin. It is recommended for security
reasons that you change the password once you have finished making your settings.
Internet Explorer users may be asked to download an ActiveX plug-in from Q-See
International, Ltd. Firefox and Chrome users may be asked to allow QuickTime to run. In these
cases, you should allow the required plugins to operate. In some cases, you will be returned
to the log in screen after the plugin has loaded. This is normal.
PICTURE 2-58
PICTURE 2-56
STEP 3. Make sure that your network
connection is highlighted in the list of
connections to the right of the main
part of the Network window and that
its status reads “Connected.”
The DNS server information will be
shown. Write this down for use in the
next section.
PICTURE 2-57
If you are able to log in with Internet Explorer, but are unable to view the video from the
camera, please adjust the ActiveX settings as described at the end of Section 2.5.
60 61

STEP 3. Once the camera has opened. Click on the Network tab on the left and then on
the TCP/IP option.
STEP 4. Enter the DNS number
2.7 DYNAMIC DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DDNS)
This is an optional step which allows you to take advantage of Dynamic Domain Name
Service, or DDNS. Not to be confused with DNS above, DDNS allows you to enter a
conventional web address when remotely logging into your Camera from outside of your
network. It also allows you to avoid having to repeat Sections 2.3 when/if your ISP reassigns
IP addresses. Q-See offers DDNS service for free at www.MyQ-See.com and your IP camera
is configured to accept account information from that site.
STEP 5. Click Save.
PICTURE 2-59
STEP 1. Open a browser window and go
to www.MyQ-See.com
STEP 2. Register with the website and
follow the instructions for creating
a domain name. The website will
display your pubic IP address and
your domain name which will look like
this: http://example.myq-See.com
NEW USER REGISTRATION
EMAIL ADDRESS
PASSWORD
PASSWORD
CONFIRM
FIRST NAME
LAST NAME
SECURITY
QUESTION..
ANSWER
CONFRIM
YOU’RE HUMAN
My first phone number
New Captcha
Enter the text you see above
Submit
Reset
Submit
Reset
PICTURE 2-60
STEP 3. In your camera, click on the Network tab on the far left of the window.
STEP 4. Click on the DDNS option.
STEP 5. Check the Enable box and select MyQ-See.com in the DDNS server pull-down
menu.
STEP 6. Enter your account information – including the user name and password that
you used when creating your domain name .
PICTURE 2-61
STEP 7. Click the Save button to preserve your settings.
62 63

USING WEB SERVICE
The Web Service app allows you to access your camera with only a web browser. You
connect with the camera by entering its address into the browser just like any other web page.
As was explained in the previous chapter, if you are on the same network as the camera,
then enter the local IP address shown in ConfigTool into a browser address window. When
connecting to the camera from outside of its local network, you’ll either use the Internet IP
address obtained from CanYouSeeMe in Section 2.3 or the address you created using
DDNS in Section 2.6. No matter whether you’re accessing the camera locally or remotely, the
operation will remain the same. You will not be able to access a camera directly connected to
your NVR using the Web Service application.
Accessing the camera will bring up the login
screen for the program. If you are connecting
locally, the default video stream will be the
larger Main Stream. Selecting WAN from the
choices in the Login window will default to
the lower-bandwidth Sub Stream. You can
choose to switch between either stream
once you have connected using the tabs
above and to the left of the video display.
The amount of activity on the network(s) can
affect the streaming rate from the camera to
your computer or mobile device.
PICTURE 3-1
CHAPTER 3
3.1 LIVE VIEW
When you have logged in, you will see a live
view from that camera. Live View is the
default mode for the Web Service program.
TCP is the default protocol. Use of the
Multicast protocol for streaming requires it to
be set up in your router.
FUNCTION BUTTONS (PC ONLY)
PC users have three functions that can be
performed while in Live View and the buttons
for these are located immediately below the
tabs in the upper right:
Digital Zoom - After clicking this button, click
and drag on a section of the video image to
enlarge it.
Snapshot - Clicking this will take a still image of the current video feed.
Local Record - This will begin recording video to your computer’s hard drive.
You will be able to set the location where video and still images are saved onto your
computer’s hard drive in the Camera option under the Setup tab.
Digital
Zoom
Snapshot Local
Record
PICTURE 3-3
PICTURE 3-2
The main function of the Live View window is, of course, to display the video stream from the
camera. There are additional settings available from the tabs located to the upper right of the
video image. The operations of these will be covered on the following pages.
64 65

3.2 SETUP
The options available in this tab are divided into several sections dedicated to the camera
itself, the network connection, event monitoring, direct recording to an FTP server, system
maintenance and history. Each of these sections will incude one or more submenus to allow
you complete control of your camera.
CAMERA
This is divided into two sub-menus - Conditions and Video. In Conditions, you can adjust
the camera’s settings to adjust for any lighting or environmental factors specific to its location
for the best possible image.
VIDEO
The Video sub-menu contains four tabs controlling how video is streamed from the NVR, the
camera’s built-in snapshot feature, on-screen displays and, on PCs the file path to save locally
recorded video and snapshots.
PICTURE 3-5
The settings available within the Video tab are similar to the options available in the Record
Setting menu which was covered in Section 2.2. However, these settings only apply to the
camera and not the NVR. If the Internet connection is poor either at the camera’s location
or with the monitoring PC or device, then the settings can be lowered to improve the video
transfer. For example; a bitrate of 4096 requires an upload speed of 4mbps.
The Snapshot tab allows you to set the
resolution, quality and frequency of snapshots
PICTURE 3-4
The Brightness, Contrast, Hue and Saturation sliders can be moved to improve image
clarity.
Gain - For cameras located in darker areas, Gain allows the camera to electronically
compensate by making the image brighter. The trade off is a potential loss in image quality
due to increased “noise” in the picture. You can allow the camera to adjust automatically or
manually, with an adjustable upper limit to prevent the image from reaching a point where it is
unusable due to excessive noise.
Exposure - this controls the amount of light reaching the camera’s receptors. This allows the
user to compensate for areas that are excessively lit resulting in overexposed images that
have some detail areas “blown out.” On a traditional camera, this feature would be controlled
by opening or closing the camera’s iris. On an IP camera, this is controlled electronically. You
can “lock” the exposure level to a specific setting by selecting Manual and adjusting it from
the pull-down menu.
Scene Mode - This allows the camera to compensate for sunlight versus moon light. This
is done by adjusting the red and blue light levels. This can be done automatically, or is fully
customizable by the user. The mode can also be disabled or set to permanently utilize only a
single mode.
captured by the camera. These are separate
from the snapshots captured by the NVR
using this camera.
You can change the camera’s name, create
a privacy mask and enable/disable the
on-screen display of the camera’s name
and time in the Overlay tab. Your NVR is
configured not to display the channel title
info on its screen, but you may change that
setting in the Overlay setting within the
Record Setting menu (see Section 4.3 of
the User Manual).
You may set up to four masked areas in the
camera’s display. These are separate from
those made in your system and cannot be
overriden by the masks made in the NVR.
Path allows you to select the location on your PC’s hard drive where video and snapshots will
be saved when the appropriate icon is selected in Live View.
PICTURE 3-6
PICTURE 3-7
66 67

3.3 NETWORK
The settings available in this menu govern how the camera connects to the outside world.
Many of these features are exactly like the same functions on the NVR.
TCP/IP
Like your NVR - and every other divice connected to your network router - the IP camera has
an Internet Protocol, or IP address. As a general rule, this should not be changed in order to
avoid future connection problems. However, if you wish to establish a static IP address, it is
done here.
PICTURE 3-8
STATIC IP ADDRESS
All routers currently on the market have DHCP functionality. This means that the router will
assign a newly-connected network device a random IP address that is not currently in use
by another device on your internal network. If this feature is enabled in the router as well as
selected within this window, the camera will automatically receive an IP address.
CONNECTION
The fields in this window allow you to set the maximum number of simultaneous user
connections, as well as showing which TCP port was forwarded.
PICTURE 3-9
PPPOE
If you are going to attach the NVR directly to a DSL or cable modem instead of to a router
then select the PPPOE option in the Network options. Before you proceed, you will need to
contact your ISP to obtain your User Name and Password. You will not have to worry about
Static IP (previous section).
DDNS
This was covered in Section 2.6.
IP FILTER
Using this window, you can create a “white list” of trusted IP addresses for users who are
allowed access to this camera. Any IP address that is not listed will not be allowed to access
this camera. If you will only be accessing this camera through the NVR, then you should
enter the NVR’s IP address as an extra layer of security. However, it is important to add the
IP address that you are currently accessing the camera from to ensure that you are able to
continue to make your settings without getting “locked out” of the camera. This address can
be removed once you have completed configuring the camera.
The reason for converting to a static IP address is to ensure that the camera’s IP address
stays unchanged in case of a power loss by the router. With the exception of 2Wire brand
routers, when a router or networked device reboots due to a power loss or other issue, the
addresses will change and the port forwarding configuration will no longer work. For that
reason, unless you have a 2Wire router, we recommend changing your NVR’s network
setting to a fixed, or “static” IP address which will not change.
To convert to a Static IP address, all you need to do is check that option and then click Save.
68 69

SMTP (E-MAIL)
The camera can send out its own e-mail alerts - with snapshot attachments. If the camera is
connected remotely to an NVR, these e-mails will be in addition to those that the NVR creates.
The camera’s e-mail address should therefore be different than that used for the NVR to avoid
confusion.
NOTE! Depending upon your settings, the system can generate a lot of e-mail
alerts. For that reason, we recommend setting up a dedicated e-mail address
specifically for the system to send alert notices. If you do not have your own
e-mail system (such as a corporate mail server) you should consider using a
limited amount of e-mail traffic we specifically recommend using Google’s Gmail service with
its higher limit. Similarly, you will want the alert e-mails to go to a different account than the
one sending them. This will ease your management of these alerts.
SMTP Server – This the SMTP server IP
Port – This is the port your mail provider uses
User Name and Password – These are for
Title – This is the subject line of e-mails
Receiver – This is the recipient e-mail
Attachment – This allows the e-mail to
SSL Enable – The system supports SSL encryption when this is enabled.
Interval – This adjusts the amount of time that will pass before the NVR sends out another
free e-mail provider. However, because many free e-mail services allow only a
name
the sending e-mail address and were
set up when you created the e-mail
account.
generated by this NVR.
account.
include one or more snapshots as
attachments
e-mail. The interval can be set from 0 seconds to ten hours (3600 seconds). If you are
getting too many e-mails, you may wish to increase the length of the interval. Using
this feature also helps prevent overloading your outgoing e-mail server.
PICTURE 3-10
UPNP (UNIVERSAL PLUG ‘N’ PLAY)
As described in Section 2.4, UPnP allows networked devices to communicate with each
other. UPnP, like DHCP, allows the router to assign the camera an IP address on its network.
and will automatically forward the ports for outside communication. In addition to the HTTP
(port 85) and TCP (port 37777) communications protocols, UDP and RTSP allow the camera
to stream data and communicate with other devices.
BONJOUR
Bonjour is Apple Inc.’s version of UPnP to enable easy network connectivity.
3.4 EVENT
Like your NVR, your IP camera can detect motion events and when it is being blocked
or masked. You can configure these features on your camera in the same manner as on
your NVR and alerts can be e-mailed and/or alarms triggered. Using these features on the
IP Camera would not interfere with the operations on the NVR and some users prefer the
duplication of event detection as a backup in case the NVR is affected.
PICTURE 3-11
The operation and setup of these event monitoring is identical to that on the NVR itself. See
Section 3.7 of the User Manual for full explanations.
MOTION DETECTION
Clicking on Setup next to Working Period
will open up a schedule allowing you to set
the periods when the camera will actively
detect motion events. You can set six periods
each day for the camera to be “on alert” using
the start and stop times at the bottom. Click
Save to preserve your changes and they will
appear on the schedule when you next open
the window.
PICTURE 3-12
You can enable a motion alert to trigger several one or more events - video recording, e-mail
alerts and snapshot images. Videos and snapshots are sent to an FTP site - which must be
set up by the user. Some camera models allow the insertion of a Micro SD flash memory
chip which can be used to store these images “onboard” the camera for retrieval using the
PSS software. Video recording is controlled by the Recording Schedule (see following
pages) which overrides the settings here. If the camera is set to record on motion detection,
those recordings will only take place during the time period(s) configured in the Recording
Schedule.
70 71

Anti-Dither - is the amount of time that the camera will delay before beginning the alarm
response. If the motion isn’t detected again during the delay period, the camera will not treat
it as an event.
Sensitivity - You can adjust the camera’s sensitivity to motion to minimize false alarms caused
by environmental factors such as insects.
Record Delay - This is the amount of time beyond the event that the camera will continue to
record.
In addition to triggering recording, you can also have the camera take a snapshot and send
an alert e-mail.
Click on the Setup button next to Area to
turn off motion detection in certain areas,
such as roads, a flag or trees that move in
the wind to avoid false alarms. Clicking on a
square in the grid, or clicking and dragging
across multiple areas will remove the blue
mask and deactivate motion detection in that
area.
PICTURE 3-13
VIDEO MASKING
If the camera detects that it is being blocked or covered, it can be configured to record, send
an e-mail and/or take a snapshot of what it sees. You can also set up a schedule so that it
will not be active during a regularly scheduled period when it might be blocked by a door, for
example.
DISCONNECTION
If the IP Camera detects that it no longer has a network connection, and if it has an SD flash
memory chip installed, it can record video to the chip for later recovery through the PSS
software.
3.5 RECORD
If you have enabled the record function for this camera elsewhere in the Web Service
program, you will need to set when those recordings will occur using the Record Schedule
tab. In addition, you will need to configure the destination for those files along with the
duration and quality of the recorded files.
Videos will be recorded in the .dav format and will require the use of the included video player
software to review and convert to a different format.
RECORD SHEDULE
The camera is configured to allow event recording all day and every day. To change these
settings, click on the Setup button to the right of the date you wish to schedule.
PICTURE 3-14
The pop-up Setup window will open allowing
you to set up to six periods within a day
during which recording will be enabled.
PICTURE 3-15
SNAPSHOT SCHEDULE
This is exactly like the Recording Schedule.
IP CONFLICT
Whether in DHCP or UPnP, the router will automatically assign IP addresses to devices on its
network. If someone on the network manually changes the IP address of a connected device
to an address identical to that of the IP camera, this can cause difficulty in accessing the
camera remotely. You can enable the camera to begin recording if this occurs.
72 73

FILE DESTINATION PATH
Unlike an NVR, the camera does not contain a hard drive on which to record its files. The
default method is to use an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) site to store the recorded files for later
access. An FTP site is the equivalent of an Internet-accessible hard drive. There are both free
and commercial sources for FTP hosting available through the web.
Some camera models allow the installation of a Micro SD card within the camera. Due to the
nature of security cameras, these chips are not easily accessible once the camera has been
installed, but the files may be retrieved using the PSS software. If you are using a camera
with an installed Micro SD card, an extra tab (not shown) will appear allowing you to make
additional configurations.
PICTURE 3-16
Both recorded video and snapshots can be saved to the FTP site. You can allow all types of
events to be saved, or choose only Timer (scheduled recordings), Motion Detection or Alarm
events to be saved to the FTP.
Use the FTP tab to direct the camera
where to save the files. You will also need
to enter the user name and password that
you normally use when you log into the
site yourself, or you can create a specific
user account for this camera. The Remote
Directory is the folder into which the files will
be saved.
PICTURE 3-17
RECORD CONTROL
This tab allows you to set the maximum
length of the recorded video, along with
amount of pre-event video is added to the
file. Like the NVR, you can have the camera
overwrite old files when the storage area is
exceeded, or it can stop recording until the
files are manually deleted.
Additionally, you may choose to record larger
main stream of video, or the smaller - and
lower quality - sub stream.
PICTURE 3-18
3.6 SYSTEM
This submenu is where the user can make changes to the camera itself, including setting local
time, configuring user accounts, upgrade the firmware and reset all values to their default
settings.
GENERAL
You can change the camera’s device name here, which will make it easier to pick out in the
Remote Device menu when adding it to your NVR.
PICTURE 3-19
English is the only language currently available and you can choose the video standard NTSC (North America and most of South America) or PAL (Europe), but this won’t generally
make a difference when monitoring the camera through the Web Service program or the NVR.
Account Lock Enable is disabled by default. Enabling this feature will lock the camera from
remote access - either by the NVR or through the Web Service - app if the wrong user names
or passwords are entered the selected number of times. If the camera is locked out, it will
need to be physically reset using the Reset button on or in the camera (depending on model).
DATE & TIME
The date and time can be set locally for the
camera and it can synchronize with a time
server and keep track of Daylight Savings
Time just like the NVR.
The SyncPC button will set the time to that of
the computer which you are using to access
it. Keep in mind, that settings on the NVR
can override this and synchronize the time
with itself as described in Section 4.3 of the
User Manual.
PICTURE 3-20
74 75

ACCOUNT
This window shows all the available user accounts. There are three pre-configured accounts
available with different authority levels. The admin account has full privileges to view or
change the camera’s settings, while the 666666 user account can only view the camera’s
live feed. The Authority List at the bottom of the window shows what each account may do
with the camera.
PICTURE 3-21
INFORMATION
This window shows both the current version of the sofware along with the camera’s serial
number in addition to an event log that the camera maintains.
PICTURE 3-22
Clicking on an event will bring up detailed information in the bottom window, including the
nature of the event.
You may edit, add or delete accounts, with the exception of the admin account. It is strongly
recommended that you change the passwords from their default settings. A maliscious user
would have to discover the camera’s IP address in order to access it in the first place, but
changing the password prevents unauthorized tampering.
DEFAULT
Clicking this button will reset everything to the factory default settings.
IMPORT/EXPORT
You can back up your camera’s configuration settings onto a computer to later import back
into the camera if needed.
AUTO MAINTAIN
This allows you to have the camera reboot on schedule to improve performance - much like a
computer. You can set the time and day of the week when this reboot will take place.
UPGRADE
Q-See releases firmware updates from time to time to address known issues, to address
specific issues or to add functionality. You can download the firmware update file to the
computer you are using to access the camera and then use the Browse button to navigate to
the file before clicking on Upgrade.
You can back up the logs to your computer or clear the log file.
76 77

ALARM
The Alarm window contains a log of all events, which can be searched by selecting the Alarm
Type of interest.
PICTURE 3-23
You can also have the camera alert you of any events that occur while you’re monitoring it.
Select an audio file from your computer to serve as the alarm tone.
LOGOUT
Clicking this tab will log you out of the camera and return you to the Login window.
PRO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE
CHAPTER 4
4.1 INSTALLING PRO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE (PSS)
In addition to using the web-based Web Service method to monitor and control your system,
Q-See also offers, the Smart PSS (Pro Surveillance Software). This free software is included
on the CD packaged along with your DVR. The file is also available for free download on
Q-See.com/support.
Smart PSS differs from the browser-based Web Service in that you can monitor up to 36
cameras at one time. These cameras can be connected to a QC-Series DVR or NVR, or they
can be IP cameras operating in stand-alone mode. Smart PSS is compatible with Windows
XP, Vista, 7 and 8 or Mac OSX 10.7 and later. PC users also have the option of installing
PC-NVR which enables the computer to be used as a security recorder and server.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Windows Macintosh
OS Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8 OSX 10.7, 10.8
CPU 2.4GHz or Higher 2.7GHz or Higher
Display Card Supports DirectX 8.0c or later
Memory Minimum 1GB (WinXP)
Video Display Minimum 1024x768 Minimum 1024x768
INSTALLING SMART PSS ON A PC
To install Smart PSS from the included CD using the menu
Click on the Software button in the CD’s
menu. Next, click on the PSS button. The
installer will start and ask you to select a
language - currently English or Chinese. By
default, the installer will place the application
within the Programs folder on your computer’s
hard drive. You can change the install location
if desired. Once installed, Smart PSS can be
launched like any other program.
To install Smart PSS from a download or from the CD
The latest version of Smart PSS can be downloaded from our support site, Q-See.com/
support and it comes in a highly compressed “.rar” format for faster download. You will need
to download an extraction program to be able to install PSS. One extraction program can be
downloaded for free at at http://rarlabs.com/download.htm
You can also access the Smart PSS installer directly from the CD’s menu. It is located in the
following directory: Software
PSS - Viewer Program PSS for Windows
PICTURE 4-1
The installer will start and ask you to select a language currently English or Chinese. By default, the installer will
place the application within the Programs folder on your
computer’s hard drive. You can change the install location
if desired. Once installed, Smart PSS can be launched
like any other program.
PICTURE 4-2
7978

INSTALLING SMART PSS ON A MACINTOSH
Smart PSS can be either installed from the included CD or downloaded from our support
site, Q-See.com/support. The download will be in the form of a .zip file which your computer
should automatically decompress. On the CD, it will be located in the following directory:
Software PSS - Viewer Program PSS for Mac. Simply drag and drop the application into
your Applications folder - or any other desired location - on your hard drive. You may wish to
create an “Alias” or shortcut on your desktop from the computers File menu or drag and drop
the program’s icon to your Toolbar for easy access to the program.
4.2 USING SMART PSS
LOG IN
Upon launch, you will be asked to log in. Enter admin for both the user name and password.
You can (and should) change this to ensure your security. Instructions for changing your
password are included later in this section. The Admin account cannot be deleted.
IMPORTANT! Please keep in mind that this manual and other documentation
are freely available for download online. Therefore it is absolutely essential that
you should change the passwords on your system and any application used to
access it in order to maintain the integrity of your system.
Once you have logged in, you will see the
Device Management page. In the future,
once you have added systems to Smart
PSS, you’ll be able to use the Home page to
manage them.
ADDING A SYSTEM TO PSS
As was written earlier, when opening Smart PSS for the first time, the Device Management
page will be opened to the Add Device tab as well.
PICTURE 4-5
If you are adding systems that are located on the same network as the computer, click on
Auto Add. Smart PSS will then search the network for any DVRs, NVRs or IP cameras that
are connected. Those that are found will be added to the list of systems that are available to
be added to Smart PSS. Select which systems to add using the check box to the left of that
device’s name.
The Device Management page consists of
two tabs: Add Device and Group Manager.
The first is used to add DVRs, NVRs and IP
cameras to the Smart PSS program, while
the second tab allows you to organize them
into groups for your convenience.
You can switch between the two pages as
desired. The Device Management page
can be closed, and its icon removed from the
top of the Smart PSS program window by
clicking the ‘X’ in the upper right of the icon.
It can be re-opened by clicing on the Device
Management icon in the Home page.
PICTURE 4-3
PICTURE 4-4
PICTURE 4-6
Once you’ve selected the desired systems, click on Add to allow Smart PSS to manage it. If
you do not see a specific system, click Refresh to search the network again.
80 81

For systems that are not connected to the same network as the computer you are running
Smart PSS on, you must use the Manual Add button.
You’ll need to manually add the information
needed for the program to connect to the
item.
Title - Name the device to make it easy to
identify from the other systems you
may be controlling.
Group Name - Enter the name of an
established group. Or, if you’ve not
created one yet, enter the group
name and make sure that the Create
Group box at the bottom of the
window has been checked.
Type - Select whether the device is a DVR,
NVR or IP Camera (IPC).
IP/Domain Name - This should be the
public (Internet) address that you
obtained when setting up your DVR
(see Confirming That Ports are
Opened in Section 1.2 of this manual). It may also be the Dynamic Domain Name
Service (DDNS) address you created in Section 1.6.
Regardless of which you choose, you will not be able to connect to the camera using
its local network address because your computer and system are not on the same
network.
Port - The default for your device will be 3777, but if you’ve changed it during setup, then you
will need to enter the correct number in this field.
User Name & Password - Enter the User Name and Password that you use to log into your
system.
Get Info - Click on this to have Smart PSS query the device. Device Model and Serial
Number are read-only, but they and the other fields will be auto-filled.
PICTURE 4-7
Once you have finished adding systems to your Smart PSS program, you’ll return to the Add
Device tab and will see your devices listed.
PICTURE 4-8
Clicking on one will reveal three tools under the Operations heading at the far right.
Modify
Opens Manual Device
Addition window
You can also remove a device from Smart PSS by checking the box to the left of the device’s
name and clicking on Delete at the bottom of the window.
Clicking on the Next button on the bottom right of the window will take you to the Group
Manager tab. You can also switch between the two tabs simply by clicking on them.
Device Configuration
Opens Device
Configuration window
Delete
Remove device
PICTURE 4-9
Creating a Group
When you add an NVR or DVR, it will most likely be its own group. However, you can create a
new group using selected cameras from multiple systems up to 36 cameras.
1. Click on the New Group button on the left of the window and name your new group.
2. Choose a DVR, NVR or IP Camera from the Device List on the right. When selected,
all of that device’s channels will display in the middle.
3. Select the cameras that you wish to add to your new group and then click on the <<
button. They will appear in the group’s list of cameras.
4. To add cameras from another device to this group, repeat steps 1-3.
82 83

HOME PAGE
All of Smart PSS’ functions are accessed through its main window which is referred to as the
Home Page. The functions are divided into three areas; Basic, Extension and Setting.
PREVIEW
Viewing live video from your connected devices takes place in the Preview window.
1
PICTURE 4-10
The first area, Basic, is where you’ll find the live viewing, search and playback, and alarm
events functions which are the most commonly used. Extensions contains features and
operations not found on your system and Setting allows you to make changes to your DVR or
NVR as if you were at the machine. Clicking any one of the icons will open up a new window
within Smart PSS. You will be able to move between windows by clicking on its icon at the
top of the window. Hovering the mouse over the icon will reveal an X which can be clicked
upon to close that window. Only the Home Page window cannot be exited in that manner.
2 3
4
5
8
9
76
PICTURE 4-11
1 Icon Tab Switch between windows by clicking on icons in this area.
2 Viewing Area Shows video feed from camera
3 Active Screen Green outline indicates which channel is active for control
4 Device List/
PTZ Tabs
5 Information Bar Appears when mouse hovers over camera view. Contains
6 Tasks Allows quick access to saved tasks, such as tours, channel
7 Multi-Screen
Mode
8 Screen Aspect
Ratio/Full Screen
9 Shortcut Menu Gives access to additional controls and functions.
Shows available groups and cameras
PTZ Camera Controls
information about bit stream, and includes shortcut controls:
Turn audio on or off
Turn microphone on or off
Begin/end local record (saves to computer’s hard drive)
Take snapshot (saved to computer’s hard drive)
Closes channel
combinations, etc.
Slider adjusts between single-screen view and 36-screen view with
10 configurations possible.
Change the aspect ratio (height vs. width) of the on-screen view.
Click to bring window to full screen. Pressing ESC will return to
normal window view.
84 85

Cameras can be dragged from the Device List on the right of the window into a channel
space where the camera’s video will appear. If a camera is dragged onto a space where
another camera already is, the new video feed will replace the old one. You can close the
camera view by clicking on the X in the information bar that appears at the top of the video
image when you place the mouse cursor in that area.
Shortcut Menu
Right-clicking on any camera’s screen view
will open up the Shortcut Menu. This is
a different menu than that which appears
on screen in the DVR. This menu includes
the same controls that are available in the
Information Bar that appears above the
screen view along with addition of expanded
options and functions.
Adjust - This will open a new window with four sliders which allow you to adjust the
Brightness, Contrast, Color Saturation and Hue of that channel’s video. These settings will not
affect the recorded video.
Audio/Talk - If you have audio-equipped cameras, or a microphone co-located with a
camera, you can listen to the audio from that equipment. Similarly, if you have a microphone
connected to your computer and a speaker located near to the camera’s location, you can
use that to communicate. The system is not “duplex” like a telephone where you can talk and
hear at the same time, but rather it is like a CB radio or walky-talky where you will need to turn
off your microphone to hear any response. Depending upon network speeds, there may be a
lag, or delay between the time you say something and the person on the other end will here it.
Save as Video Task - You can save a camera as a “Video Task” that will create a shortcut
to that camera which can be accessed through the Tasks pulldown at the lower left of the
Preview window (Item 6 in Picture 4-11).
Close Video/Close All Video - Ends the
display of the live feed from the camera(s).
Does not close Smart PSS.
Start Record/Snapshot/Triple Snapshot
- Records video or still images directly to
the computer’s hard drive. The save paths
for these files can be set in Files are of the
General setting window which is located in
the bottom portion of the Home Page. Triple
Snapshot will, as the name suggests, save a
sequence of three images to your hard drive.
When Snapshot is selected - either through
the Shortcut Menu or the Information Bar
- a new window will open to allow you add
notes and classify the image before saving it.
StreamType, Quality/Fluency - These
settings allow you to adjust the video stream
to compensate for network and/or bandwidth
issues. Your system records both a Main
Stream - which is saved to the device’s
internal drive and an Extra Stream which
is lower quality, and therefore smaller to
better be sent out over a network. If you
are connecting through the same network as your security system, you should be able to use
the Main stream for the best quality. Likewise, if both your device and the computer are both
connected to networks with good Internet connections, the Main stream should also provide
best quality. However, if you regularly see breaks in on-screen movement, then switching
streams may improve the quality of the on-screen video. Also be aware that viewing multiple
screens at the same time can also affect the smoothness of the video they “overflow” the
available bandwidth of your connection. With Quality/Fluency, you can choose whether you
prefer higher quality images or whether smooth-flowing video is more important. None of the
changes made here will affect the quality of the video recorded onto your device’s hard drive.
PICTURE 4-12
PICTURE 4-13
Full Screen - This will bring the camera viewing windows to full screen by hiding the control
areas on the top, right and bottom. If you are viewing in a four-camera split screen, for
example, the four screens will occupy the available space on the computer monitor. Press
Esc on the keyboard to return to normal viewing mode.
VIDEO SEARCH AND PLAYBACK
Using Smart PSS to search for video recorded on your DVR functions in the same manner as
the search and playback function on the DVR itself.
STEP 1. Select the camera(s) you want
to search. The Calendar below the
camera list will highlight those dates
with recorded video in green. The
current date will be highlighted in
blue. Depending on network speeds,
it may take a few moments for the
Calendar to update.
STEP 2. Select the date to review and
press Search. The timeline at the
bottom of the window will show
colored blocks representing video
that has been recorded.
STEP 3. Click on a colored block to
begin playback. The playback
controls operate in the normal
manner. The slider is used to speed
up or slow down the playback rate.
As with Preview mode, the screen with the
green frame is considered the “active” screen
for purposes of using the controls.
PICTURE 4-14
86 87

ALARMS
This section will cover all of the areas of Smart PSS that deal with alarms as they are
interrelated. These alarms are in addition to those already set up in your system. You can
determine which of those pre-configured alerts will generate a notification in Smart PSS and
you can also create notifications and actions that will occur within the program itself. In this
1
2
3
765
9
PICTURE 4-15
1 Device List Choose which camera(s) you wish to search
2 Snapshot/
Record Bar
3 Calendar Shows which days have video records
4 Download
Manager
5 Playback
Controls
6 Volume Control Requires an microphone to be connected to that channel
7 Multi-Screen
Mode
8 Screen Aspect
Ratio/Full Screen
9 Timeline Shows videos recorded on that date.
Lists recorded files. Files can be downloaded to your computer
Take snapshot (saved to computer’s hard drive)
Closes channel
Opens list of videos saved to computer’s hard drive
Controls playback function in selected screen.
Starts playback of other channels with video recorded at the
same time.
Slider adjusts between single-screen view and 36-screen view with
10 configurations possible.
Change the aspect ratio (height vs. width) of the on-screen view.
Click to bring window to full screen. Pressing ESC will return to
normal window view.
Arrows to right of camera name filter results based on method of
recording.
Magnifying slider adjusts scale of timeline for precise selection of
video
4
8
manner, Smart PSS acts as a back up, or second layer of defense for your recorder and
property. If an intruder is able to get to your DVR, and the program is properly configured, you
will still retain evidence and be alerted - even if the phone cable at your system’s location is cut.
Alarm Setup
To begin, you will need to create the Alarm
Scheme using the Alarm Setting window.
Once the window has been opened, you will
need to create a name for this event, set the
time of day that it will be active and the nature
of the event. You can also have the computer
play an audible alert and, if the E-map
(described later) is configured, the camera’s
location will appear on screen. Click Loop
play to have the alarm play until silenced.
Setting the level is optional. You may decide,
for instance, that a motion detection event
in a certain area is less important (Level 5)
than a similar event in another (Level 1). This
will make it easier to filter alarm events when
searching for a specific event.
After you have created an event, move to
the next tab, Alarm Source, to select the
trigger for the event. Select the trigger(s) from
the list on the left of the window and click
on the >> button to add it to the right panel.
You can limit the type of alarm to just Motion
Detection, Camera Masking or Video Loss, or
you can have all three serve as triggers.
Lastly, in the LInk Video tab, select your
alarm from the Alarm Source list on the left
of the window and then choose which video
source(s) you will be using. Make sure that
your source is highlighted in blue or you will
get an alert asking you to select an alarm
source. Click OK to save your alarm. When
you return to the Alarm list, click on Close to
change it to Open in order to make it active.
If you have alarms attached to your system,
repeat these steps, using the Alarm Input
tab in the Alarm Source window for the
trigger.
PICTURE 4-16
PICTURE 4-17
PICTURE 4-18
88 89

Alarm Manager
This window contains the logs of alarm events that have occurred. They can be filtered by level
of severity if you included that when creating your alarm scheme. If events are happening at a
rapid pace, check the Stop Refresh box to “freeze” the list.
Clicking Display Overlay Window will leave
a small panel open on screen that will show
the number of alarms, CPU usage and a
volume control. It will appear above any other
applications you have running.
Use the Search tab to locate alarm events in the same manner as searching for video.
Alarm Link
This is a standalone window which, when activated by selecting it from the Home Page, will
pop up when an alarm is detected to show the linked video(s). It will run in the background
behind any other apps until an event occurs at which time it’ll pop up to appear on screen.
This allows you to have an instant video notification on your computer without having to run
the full Preview window at all times.
Alarm I/O
This allows you to group alarms together in the same manner as you can create groups of
cameras using Device Manager. When alarms in a group are activated, they can be used to
activate a siren, or other device connected to the system’s Alarm Out port.
PICTURE 4-19
GENERAL
While most of the controls in Smart PSS are for operating your system remotely, the General
Setting window is for controlling the program itself. There are two tabs in the General
settings window - General and File. The first tab, General, lets you perform some basic
housekeeping.
Network - Adjust this slider to reflect your network speed. It ranges from “WAN” to “1000M”
Log Save - This lets you set how long the activity logs are saved. Choose from 1 to 6 months.
Auto Login - When checked, Smart PSS will automatically log into your system when the
program is launched.
Auto Login Windows - If this is enabled and the computer restarts while Smart PSS is
running, then the computer will automatically log you back into Windows.
Auto Time Sync - If needed, you can instruct Smart PSS to sync to the computer’s internal
clock at a set time.
The File tab is where you set where recordings and snapshots will be saved on your
computer’s hard drive.
DEVICE SETUP
This window handles the functions found in the Alarm and Recording menus on your
system. Clicking on any of the five icons under the Device List on the left of the window will
open up the appropriate settings options.
PICTURE 4-20
When you have made a changes, click the OK button at the bottom right of the window to
save your new settings. You can also apply these settings to another camera by clicking on
the Use To... button and selecting the other camera.
90 91

Audio/Video
This window contains three tabs which allow you to control the settings for the video streams,
snapshot quality and quantity along with privacy masks and on-screen display.
Audio Video Stream - This tab allows you to make settings to optimize the video stream from
each camera. This is the same as found in the Camera Settings window of your system. You
can adjust the quality, frame rate, coding and other aspects of both the Main Stream, which is
recorded onto the DVR and sent through the local network as well as the Substream, which is
used by mobile devices and Internet access.
Pic Stream - You can set the quality and number of images taken when a snapshot is taken.
You can apply different settings depending on whether the image is captured manually, as a
result of motion detection or when triggered by an alarm.
Video Cover - This tab lets you mask up to four areas of the video as well as toggling the
display of the camera name, the date and the time.
To mask an area, select a camera and its
video will appear in the center left. Select
whether you wan the privacy mask to apply
to apply to just remote viewing, or on the
DVR itself and then click on the Edit (pencil)
button to the right to draw the privacy mask.
When managing multiple systems, it may
be easier to add an identifying name to a
particular channel to specify where a camera
is located. These overlays are separate from
those on the recorder itself. Click the Edit
button to position the overlay where desired.
The Date/Time overlay works in the same
manner.
Recording Settings
This window replicates the Schedule window on the DVR.
Recording Plan - This tab shows the current schedule for each camera. Click on Set and a
new window will open to allow you to set the recording mode and schedule.
Recording Control - Use this tab to adjust the pre-recording time (0 to 5 seconds) for this
camera when an event occurs.
Video Check
This window is identical to the Events menu on the recorder. You can set how the system
responds to Video Loss, Camera Masking and Motion Detection, including activating other
cameras, sending out alarm notices and etc.
Pic Property
These settings allow you to adjust the on-screen appearance of the video to compensate for
the lighting conditions where the camera is located. If the light changes during the day, you
can set two different lighting profiles.
PTZ Control
Make changes to the PTZ camera communication protocol, bit rate, and etc. if needed.
PICTURE 4-21
Account
Just as you can authorize others to use your system, you can also create user accounts for
others to use Smart PSS to observe and control any connected recorders. The process is
the same as on your DVR or NVR. And, you can grant users specific permissions or limit their
ability to make changes as needed.
STEP 1. Open the Account window and
select Add from the upper left.
STEP 2. The Add User window will
open. Enter the new user’s name and
password. You will also need to set
whether this user is a Manager or
Operator. Additionally, you may add
notes regarding this user.
STEP 3. Select which rights this user
is allowed from the User Authority
menu. You can also limit which
cameras and devices this user has
access to using the Device List on the
right of the window.
STEP 4. Click Add to save the new
account.
Select Add More to add additional users
without closing the window.
You can edit or remove a user account by
clicking on that user’s name in the Account
window and clicking on the Edit or Delete
button respectively.
Device Parameter Configuration
This button is located in the lower left of the
Device Setup menu and opens up the Device Configuration window. This window contains
menus granting access to more of your system’s functions . Detailed information on these
funtions is contained in respective parts of the User Manual. Included menus are: Network,
Event Manager, Storage Manager, System Configuration and System Info. Again, these
menus replicate those found on your recorder.
Network - The settings for your system’s connection to the network are located here.
Care should be given when altering these settings as changing them could result in loss of
connection to your recorder.
Event Manager - This contains the remaining settings that were not included in Video
Check, above. You can set responses for both the recorder itself and any other networked
systems. You are also able to configure the alarm responses for network conflicts, hard drive
failure or full disk among others.
Storage Manager - This shows the status of your recorder’s hard drive(s).
System Config - Many of these are found in your Settings menu on your system, including
the general settings, such as the system language, date format, daylight savings time, etc. You
PICTURE 4-22
PICTURE 4-23
92 93

can also add and manage users with access to that recorder. If you are connected to an NVR,
you may also add remote IP cameras to your system using the Remote Setting sub-menu.
Note that QC systems do not make use of the Serial Interface. The Auto Maintenance option
is to allow the NVR or DVR to reset on a schedule for optimal performance.
System Info - Use the Log Information submenu to search and download activity logs from
your system.
TOUR
Just as with your recorder, you can have Smart PSS cycle through your cameras. In this case,
those cameras can be connected to many different systems.
E-MAP
When systems and cameras are connected from multiple locations, it can sometimes be
difficult to keep track of where an event is occuring. Using the E-Map feature, you can import
a graphic map in .BMP, .JPG or .PNG format and place icons representing your cameras in
the appropriate location. Depending on where your cameras are located, the map can be the
floorplan of your building, or of a much larger area.
PICTURE 4-25
When you first select the E-Map icon, you will be asked to add a map. Once you have
imported the file, it will appear in the window. Select Edit and then drag a camera from the
PICTURE 4-24
STEP 1. Determine how many screens will be displayed at once and set the Windows
Number to the desired amount (up to 36).
STEP 2. Name your task and add a description if needed.
STEP 3. Drag cameras from the Device List on the right to the desired tab. A camera
can be placed in more than one tab. You can double-click on the Stay Time and
Stream Type to set the amount of time this channel will stay on screen and which
data stream will be used, respectively. Us the Up and Down buttons to organize the
order in which each channel will appear in a window.
STEP 4. Click OK to save your settings.
device list on the right to its location on the map. While in Edit mode, you may modify or add
to the map using the options in the Tool pulldown to the right.
If you selected Flash in E-Map option when
creating your Alarm Scheme, the icon for a
camera that is triggered will flash red to alert
you. You can double click on either icon, or
the camera’s name in the device list to see
its video.
PICTURE 4-26
94 95

TV WALL
If you have a multi-screen video, or other large format display connected to your computer,
you can export your camera views instead of being contrained to a single computer monitor.
The operation of your video wall will follow
the same process used to set up your
Preview screen. You can splice the video
from two or more adjacent screens by
selecting them (hold Ctrl while clicking on the
screen(s)) You will need to “bind” your display
to a format by first using TV Wall setup. If
you do not see your video device shown
on the left part of the screen while in the
Screen Input Binding window, check your
connections and video drivers.
You can create multiple combinations of
screens. Each will be saved as a Task,
much as with the Preview window. You can
switch through Tasks from within the TV Wall
extension.
PICTURE 4-27
PICTURE 4-28
PC-NVR
This is an optional program that lets you use a computer as a Network Video Recorder and
server. This will allow you to take advantage of some broadband connections. You will need to
have installed the PC-NVR software on the computer that will be used for this purpose. Click
Add to get started. You will be entering the Name, IP address and network port information for
the computer that will be used, along with the user name and password needed to log into the
computer.
Once you have added your computer, you
can add cameras by dragging and dropping
them into the available screens. Set up a
recording schedule for each channel using
the Record Plan button. Click the Copy
button to apply your schedule to another
channel.
You may adjust the file packet size, network
settings, user access and manage the hard
drives through the Setup tab.
PICTURE 4-29
MOBILE SURVEILLANCE
In addition to remotely monitoring your phone over the Internet or a local network, you can
view live feeds and recorded events on your iPhone, iPad, Android mobile device, Symbian,
Windows Mobile or BlackBerry smartphone using free software.
Before you can access your DVR via a smartphone, you must have completed Port
Forwarding for ports 80 and 37777 as discussed in Section 2.3.
NOTE! As of this writing, the Symbian operating system was no longer being
supported by its manufacturer. The apps for Symbian, the older BlackBerry
operating system and Windows Mobile are provided by a third party and
instructions for use are provided as a courtesy.
These mobile applications are designed to work with DVRs and NVRs as well as IP cameras
operating in a stand-alone role. Therefore, there will be certain features and functions which
are not available for use with your camera, simply because your camera does not have the
same features found on a complete system. The primary purpose of accessing your camera
using a mobile device is to view the live video. You will not be able to access the camera’s
internal memory (if available) but some of the programs, including the QC View app, will allow
you to record video directly to your mobile device.
CHAPTER 5
5.1 IPHONE AND IPAD
In order to monitor your camera using your iPhone or iPad, you will need to install either the
Q-See QC View app for smartphones or Q-See QC View HD app if you’re using a tablet.
These are available for free through the Apple AppStore by searching for “Q-See.” Install either
one as you would any other AppStore application.
Both versions have identical functionality. The HD version for the iPad differs in that you can
view 16 cameras simultaneously and the viewing resolution is greater to take advantage of the
tablet’s higher resolution screen.
Q-See QC View
For smartphones:
Utilities
Released Apr 28, 2012
INSTALL
Q-See QC View HD
For tablets:
Utilities
Released May 2, 2012
INSTALL
PICTURE 5-1
PICTURE 4-30
9796

STEP 1. To launch QC View, simply tap
on its icon in your app menu.
STEP 2. Upon launch, the program will
display its main menu. To view your
camera, you will need to add it using
the Device Manager option.
STEP 5. You will need to enter certain
details in order to access your
camera. You will most likely want to
set up two methods to connect to
your system - one for when you’re on
the same network (ie; within the same
building as the camera and able to
connect wirelessly to your network)
as well as one for times when you’re
away and will be accessing using the
Internet IP address.
DVR Title: This should be a
descriptive name, such as “Camera
Local” or “Camera Internet” to help
you utilize the proper connection
method.
PICTURE 5-4
STEP 3. A connection to our
Demonstration system is already preloaded on the application. You can
remove this from your list at any time,
but it offers an easy option to get the
feel of how to use the program.
STEP 4. Click on Add to begin the
process of configuring QC View to
access your camera.
PICTURE 5-2
PICTURE 5-3
Server: Enter the LAN or Internet IP address as appropriate. If you set up a domain
name with MyQ-see.com, then you can enter that name for Internet connections.
Port: 37777.
User Name: admin (by default or use whatever user ID that you set in the camera)
Password: admin (by default or whatever password you set in the camera)
Channel amount: Since your camera offers only a single view, there will only be a
single channel available.
98 99

OPERATION
Once you have selected the device you wish to monitor, you are able to view the live feed
from your camera. You may capture still images from the video by pushing the Snapshot
button. These images will be found in your device’s Photos menu.
The Main menu gives you access to all of the functions of QC View. Touching the device’s
Return button - whether on screen, or on a keypad - while in one window will return you back
to this menu.
Initially, you will need to turn on your camera’s
display individually from the Device List. You
can bring up the device list by tapping on its
icon on the righ of the screen, or by doubletapping in an empty video display. Even
though the application will show multiple
channels available, there is only one channel
from the camera. A green surround around
your camera’s video shows that this is the
“active” channel and any actions performed
using the buttons on the left of the screen will
affect that channel.
Real-time Monitor: This window is where you will view the feed from your camera.
PICTURE 5-5
Audio (requires audioenabled camera)
Snapshot (saves to
Local Files)
Playback: This is not available when monitoring a camera.
Event List: When you set up Push Config (below) to notify you of events such as motion
detection, camera masking (video blind) or a local alarm triggered at the DVR itself, QC View
will keep a log of these events which can be reviewed in this list.
Channel Config: You are able to adjust
the configuration of each video channel to
optimize the performance on your iPad or
iPhone. These settings will not change those
set on your DVR, but instead allow you to
compensate for being in areas where with
poor connectivity, for example.
PICTURE 5-7
Push Config: This window provides you
a check list allowing you to indicate which
cameras will alert you based on motion
detection, camera masking, or a local alarm
triggered at the DVR itself. When Push is
activated, you will receive alerts on your
mobile device even when you’re not currently
in the program. You can click on an alert and
it will take you directly to video playback of
the incident that triggered the alert.
Favorites (groups of
channels)
Close Channel
Device list
PTZ Controls
PICTURE 5-6
Favorites: This is not applicable for the
camera as it only has a single channel.
Local Config: This is not applicable to your
camera.
PICTURE 5-8
Help: Opens the internal help documentation.
NOTE! If you like this application, please leave positive feedback in the App
Store.
100 101

5.2 ANDROID
In order to monitor your camera using your Android smartphone or tablet, you will need to
install either the Q-See QC View app for smartphones or Q-See QC View HD app if you’re
using a tablet. These are available for free through the Android market by searching for
“Q-See.” Install either one as you would any other Android application.
Both versions have identical functionality. The HD version for the Android tablet differs in
that you can view 16 cameras simultaneously and the viewing resolution is greater to take
advantage of the tablet’s higher resolution screen.
Q-See QC View
For smartphones:
For tablets:
PICTURE 5-9
STEP 1. To launch QC View, simply tap on its icon in your app menu.
DPSI
Free
Q-See QC View HD
DPSI
Free
STEP 3. A connection to our
Demonstration system is already preloaded on the application. You can
remove this from your list at any time,
but it offers an easy option to get the
feel of how to use the program.
STEP 4. Click on Add to begin the
process of configuring QC View to
access your camera.
PICTURE 5-11
STEP 5. You will need to enter certain
details in order to access your
camera. You will most likely want to
set up two methods to connect to
your system - one for when you’re on
the same network (ie; within the same
building as the camera and able to
connect wirelessly to your network)
as well as one for times when you’re
away and will be accessing using the
Internet IP address.
DVR Title: This should be a
STEP 2. Upon launch, the program will
display its main menu. To view your
DVR, you will need to add it using the
Device Manager option.
PICTURE 5-10
descriptive name, such as “Camera
Local” or “Camera Internet” to help
you utilize the proper connection
method.
Server: Enter the LAN or Internet IP
address as appropriate. If you set up
a domain name with MyQ-see.com,
then you can enter that name for
Internet connections.
Port: 37777.
User ID: admin (by default or use whatever user ID that you set in the camera)
Password: admin (by default or whatever password you set in the camera)
Max Channel: This will be 1.
PICTURE 5-12
102 103

OPERATION
Once you have selected the device you wish to monitor, you will be able to observe live video
from the camera. You may capture still images from the video by pushing the Snapshot
button.
Alarm Push: This window provides you a check list allowing you to indicate which cameras
will alert you based on motion detection, camera masking, or a local alarm triggered at the
DVR itself. When Alarm Push is activated, you will receive alerts on your mobile device even
when you’re not currently in the program. You can click on an alert and it will take you directly
to video playback of the incident that triggered the alert.
The Main menu gives you access to all of the functions of QC View. Touching the device’s
Return button - whether on screen, or on a keypad - while in one window will return you back
to this menu.
Initially, you will need to turn on your camera’s display individually from the Device List. You
can bring up the device list by tapping on its icon on the righ of the screen, or by doubletapping in an empty video display. Even though a multi-channel display will have more than
one space for video available, the camera can only provide one video stream.
The green surround around your camera’s view indicates that it is the “active” channel and any
actions performed using the buttons on the left of the screen will affect that channel.
Real-time Monitor: This window is where you will view the feeds from your cameras.
Play Back: You cannot use this function with a camera.
Snapshot (saves to
Local Files)
Device list
Favorites (groups of
channels)
Close Channel
Audio (requires audio-
enabled camera)
PTZ Controls
Favorites: This feature isn’t applicable as there is only one possible channel configuration
from your camera.
Local Files: Snapshots captured from the Real-time Monitor are stored here.
Config: This operation does not work while monitoring stand-alone cameras.
Help: Opens the internal help documentation.
PICTURE 5-13
104 105

5.3 BLACKBERRY
The QC-Series IP cameras support phones running Blackberry Version 5.0. You will need
to install a program called DMSS in order to monitor your camera using your BlackBerry
smartphone. This software is available both on the CD that accompanied your camera as well
as via download from www.Q-See.com/Support. If you are downloading the software, begin
with Step 1, below. Otherwise, copy the software from the CD to your computer’s desktop
and begin with Step 3.
STEP 1. Download the phone software
from Q-See.com/Support by looking
up your camera’s model number and
then selecting BlackBerry OS Smart
Phone Software.
STEP 2. Extract the files from the
software download. You will have two
files; dmss.alx and dmss.cod. Save
these files to your desktop.
STEP 8. Click on the DMSS icon to
launch the program. If this is your first
time using this application on your
phone, you will be presented with the
login screen shown in Picture 5-16.
STEP 9. Enter the following details:
Address: Enter the Server IP (your
public IP )
Port: 37777.
User ID: admin (by default or use
whatever user ID that you set in the
camera)
Password: admin (by default or
whatever password you set in the
camera)
PICTURE 5-15
PICTURE 5-16
PICTURE 5-14
NOTE! The file you download will be a .rar formatted archive. We use this
format to compress the file to the smallest possible size to speed up your
downloading. If you need an extraction utility to open it, you can find free
software at http://rarlabs.com/download.htm (PC) or http://www.unrarx.
com (Mac)
STEP 3. Connect your Phone to the PC using a USB cable.
STEP 4. Run BlackBerry Desktop Manager and make sure it detects the application.
STEP 5. Click on Application Loader.
STEP 6. On Add/Remove Application, click on Start. Then click on Browse and Go to
the Location where you have the dmss.alx file.
STEP 7. Once you finish uploading, you will see DMSS application in your blackberry (in
the Download folder).
After you log in, you will be able to see your
camera listed as a channel available to
monitor.
PICTURE 5-17
106 107

Once you’ve selected your camera, it will
display along with a list of selections.
Camera - Go back to the camera
selection window. You only have one
camera to choose from.
PTZ - Display/Hide PTZ controls. This is
not functional with your camera.
Full - Switch to full-screen display (no
controls). Clicking on the phone’s
scroll ball will return the display to
normal.
Set - Go to Video Monitor Interface
Exit - Exit the software.
Set
This returns you to the Login window where you can enter the information to connect to
another DVR, NVR or camera or exit DMSS. You can also use the Exit button at the
bottom of the screen.
PICTURE 5-18
5.4 SYMBIAN
QC-Series IP cameras can be configured to be remotely monitered by a phone running the 3rd
and 5th editions of the Symbian OS through the use of the DMSS software included on the
disk that came with your camera or available via download from www.Q-See.com/Support
If you are downloading the software, begin with Step 1, below. Otherwise, copy the software
from the CD to your computer’s desktop and begin with Step 3.
STEP 1. Download the phone software
from Q-See.com/Support by looking
up your camera’s model number and
then selecting Symbian OS Smart
Phone Software.
STEP 2. Extract the DMSS.sis
application from the archive and save
it to your desktop.
PICTURE 5-20
NOTE! The file you download will be a .rar formatted archive. We use this
format to compress the file to the smallest possible size to speed up your
downloading. If you need an extraction utility to open it, you can find free
software at http://rarlabs.com/download.htm (PC) or http://www.unrarx.
com (Mac)
PICTURE 5-19
STEP 3. Connect your phone to the
computer using a wireless or infrared
connection to send the software to
your phone as a message. Or, you
can use the Nokia PCSuite software
with a local connection to transfer
DMSS to your phone.
STEP 4. Double-click on the DMSS icon
to launch it.
PICTURE 5-21
108 109

STEP 5. Enter the following details:
Address: Enter the Server IP (your
public IP )
Port: 37777.
User ID: admin (by default or use
whatever user ID that you set in the
camera)
Password: admin (by default or
whatever password you set in the
camera)
STEP 7. Once you’ve selected your
camera, it will display along with a list
of selections.
Camera - Go back to the camera
selection window.
PTZ - Display/Hide PTZ controls. This is
not functional with your camera.
Full - Switch to full-screen display (no
controls). Clicking on the phone’s
scroll ball will return the display to
normal.
Video - Go to Video Monitor Interface
STEP 6. Once you’ve entered the
information and then the Login
button, you’ll be connected to your
camera and can chose which channel
to view. Your camera will only display
one channel as available.
PICTURE 5-22
PICTURE 5-23
PICTURE 5-24
110 111

5.5 WINDOWS MOBILE
Your QC-Series IP camera can be configured to be remotely monitered by a phone running the
Windows Mobile operating system through the use of the DMSS software included on the disk
that came with your camera or available via download from www.Q-See.com/Support
If you are downloading the software, begin with Step 1, below. Otherwise, copy the software
from the CD to your computer’s desktop and begin with Step 3.
STEP 1. Download the phone software
from Q-See.com/Support by looking
up your DVR’s model number and
then selecting Windows Mobile Pro
Smart Phone Software.
STEP 2. Extract the DMSS.cab file
from the archive and save it to your
desktop.
PICTURE 5-25
NOTE! The file you download will be a .rar formatted archive. We use this
format to compress the file to the smallest possible size to speed up your
downloading. If you need an extraction utility to open it, you can find free
software at http://rarlabs.com/download.htm (PC) or http://www.unrarx.
com (Mac)
STEP 4. After the program is installed,
you can launch it from the Programs
menu.
PICTURE 5-27
STEP 5. Upon launch, you will be
presented with a login window. Enter
the following details:
Address: Enter the Server IP (your
public IP )
Port: 37777.
User ID: admin (by default or use
whatever user ID that you set in the
camera)
Password: admin (by default or
whatever password you set in the
camera)
PICTURE 5-28
STEP 3. Connect your phone to the
computer and transfer the software to
your phone in the usual manner.
You will be asked whether you wish
to install the software to your device
or storage card.
PICTURE 5-26
STEP 7. Once you’ve logged in, select
your camera by double-clicking on
its name or by clicking on it once and
then selecting the Video button. You
will now be in the Video Monitor
interface.
Camera - Go back to the camera
selection window.
PTZ - Not functional with this camera.
Full - Switch to full-screen display (no
controls). You can also click on the
video itself, or use the maximize icon
in the upper right of the screen.
Video - Go to Video Monitor Interface.
To exit DMSS, click the X at the top right corner of the screen.
PICTURE 5-29
112 113

Q-SEE PRODUCT WARRANTY
Q-See is proud to back all of our products with a conditional service warranty covering all
hardware for 12 months from the date of purchase. Additionally, our products also come with
a free exchange policy that covers all manufacturing defects for one month from the date of
purchase. Permanent upgrading service is provided for the software.
Liability Exclusions:
Any product malfunction or abnormalities in operation or damage caused by the following
reasons are not within the free service scope of our company:
1. Equipment damage caused by improper operation.
2. Improper equipment operation environment and conditions (e.g., improper power,
extreme environmental temperatures, humidity, lightning and sudden surges of
electricity).
3. Damage caused by acts of nature (e.g., earthquake, fire, etc).
4. Equipment damage caused by the maintenance of personnel not authorized by Q-See.
5. Product sold over 12 months ago.
In order to fulfill the terms of your warranty, you must complete the registration process after
purchasing our product. To do this, simply fill out the User’s Information Card on our website
at www.Q-See.com
QUESTIONS OR COMMENTS? CONTACT US
PRODUCT SUPPORT, DOWNLOADS,
FIRMWARE UPDATES & MANUALS
24/7 Technical Resources
Live Chat (M-F, 9-5 PST)
www.Q-See.com/Support
114
Digital Peripheral Solutions, Inc.
8015 E. Crystal Drive
Anaheim, CA 92807
 Loading...
Loading...