Page 1

QTS-CLX-APACS
®
APACS
User Manual
IOBUS Module
Page 2

Page ii QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Because of the variety of uses for the products described in this publication, those
responsible for the application and use of these products must satisfy themselves that all
necessary steps have been taken to assure that each application and use meets all
performance and safety requirements, including any applicable laws, regulations, codes
and standards. In no event will Quest Technical Solutions be responsible or liable for
indirect or consequential damage resulting from the use or application of these products.
Any illustrations, charts, sample programs, and layout examples shown in this publication
are intended solely for purposes of example. Since there are many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Quest Technical Solutions does
not assume responsibility or liability (to include intellectual property liability) for actual
use based upon the examples shown in this publication.
Throughout this manual we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to
personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
These warnings help to:
WARNING!
IMPORTANT!
TIP
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Windows, Windows 95, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Vista are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
ControlLogix, RSLinx and RSLogix 5000 are tradema rk s of the Allen-Bradley Company, Inc.
APACS and 4-mation are trademarks of Siemens Moore Process Automation, Inc.
• identify a hazard
• avoid the hazard
• recognize the consequences
Identifies information that is especially important for successful
application and understanding of the product.
Identifies information that explains the best way to use the
QTS-CLX-APACS
Page 3

Page 4

QTS-CLX-APACS MODULE OVERVIEW 1
Part Number 2
Module Features 2
Power Requirements 3
Other Requirements 3
Package Contents 3
INSTALLATION 4
Prevent Electrostatic Discharge 4
Prepare the Chassis for Module Installation 4
Determine Module Slot Location 4
Insert the Module in the Chassis 5
Replacing a Module 6
Cabling and Termination 7
Software Installation 7
CONFIGURING THE MODULE IN RSLOGIX 5000 8
Module Configuration 8
Adding the Module 8
RSLINX 14
MONITOR MODE OPERATION 15
ClxApacsMonCfg Software 15
Exporting a 4-mation database file 16
Configuring the IOBUS 16
Assigning ControlLogix addresses 17
What gets mapped 18
Setting the Module Name 19
Page 5

QTS-CLX-APACS Page iii
Saving a Configuration File 21
Uploading and Downloading Configurations 21
Configuring the QTS-CLX-APACS Module in RSLogix 5000. 22
Aliases 22
Opening a Configuration File 24
Clearing the Configuration 24
Setting the RSLinx Path 24
Changing the Module Mode 24
USING MONITOR MODE FOR MIGRATION 25
MASTER MODE OPERATION 27
ClxApacsMasCfg Software 28
Configuring from an APACS IOBUS 28
Assigning ControlLogix addresses 30
What gets mapped 30
Setting the Module Name 32
Saving a Configuration File 33
Uploading and Downloading Configurations 33
Configuring the QTS-CLX-APACS Module in RSLogix 5000. 34
Aliases 35
Opening a Configuration File 37
Clearing the Configuration 37
Setting the RSLinx Path 37
Changing the Module Mode 37
ACCESSING DATA 38
Required Connections 38
I/O Data 38
Page 6

Page iv QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Program/Run 38
Diagnostic Data 38
TROUBLESHOOTING 40
ControlLogix Module LEDs 40
NET LED – IOBUS Status 40
CLX LED – ControlBus Status 40
OK LED – Module Health 41
All LEDs Red 41
QTS-CLX-APACS Module 4-Character Display 41
RSLogix 5000 41
The Debug Log 42
Diagnostic Counters 42
Slot Status Bits 42
Fatal Errors 43
UPDATING THE FIRMWARE 44
SPECIFICATIONS 45
QTS-CLX-APACS ControlLogix Module 45
SUPPORT 46
WARRANTY 47
Page 7

QTS-CLX-APACS Module Overview
The QTS-CLX-APACS connects a ControlLogix controller to an APACS
network.
Use the QTS-CLX-APACS to migrate APACS systems to ControlLogix controllers. You
can retain the APACS I/O as the first step in the migration.
The module acts as either a monitor or as a master on the APACS IOBUS. You select the
mode by downloading different firmware to the module, using the Windows configuration
programs provided.
In monitor mode, the QTS-CLX-APACS sends APACS I/O input and output data to input
data in the ControlLogix. It cannot transm it on the bus.
In master mode, the ControlLogix sends output data to the QTS-CLX-APACS, which then
transmits it as output data on the APACS IOBUS. The QTS-CLX-APACS sends APACS
input data to input data in the ControlLogix.
The QTS-CLX-APACS:
• supports IOBUS cable redundancy
• supports up to the maximum of 39 I/O cards allowed by the APACS IOBUS in a
maximum of 4 MODULRACS
®
IOBUS
The QTS-CLX-APACS communicates with the ControlLogix processor using scheduled
connections. You configure the module in RSLogix 5000 (v19 or greater) with up to:
• 10 I/O connections, 9 for data and 1 for status
Page 8

Page 2 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Each I/O connection supports:
• scheduled input data, 496 SINTs or 124 REALs
• scheduled output data, 496 SINTs or 124 REALs
The Windows configuration programs supplied with the module map IOBUS data to the
scheduled data. They also:
• upload and download configuration data
• map the IOBUS data to ControlLogix scheduled data
• save and open configuration files
• export aliases for use in your RSLogix 5000 application
• change the module mode, between monitor and master modes
Firmware Update
The module firmware can be updated using the Change Module Mode functions in the
Windows utilities supplied (see page 44).
Part Number
The part number of the module is QTS-CLX-APACS.
Module Features
The following figure shows the features of the module.
The module has:
• A label that ident if ies th e m o du le, te x t QTS
Universal Comm
• A 4-character scrolling display
• 3 LEDs, labelled NET, CLX, and OK, to indicate
the status of the I/O bus, the state of the connection
to the ControlLogix processor, and the internal state
of the module
• 2 5-pin Phoenix connectors to connect to the IOBUS
A and IOBUS B bus cables
The module supports insertion and removal under power.
The module is shipped in monitor mode, with a blank configuration.
Page 9

Watchdog and Jabber Inhibit
A watchdog timer is implemented in the module’s hardware. If the firmware does not
kick the watchdog within the timeout period the watchdog times out and generates a fatal
error (see page 43) with error code D1. In master mode, the module stops scanning and
stops communicating with the ControlLogix.
A jabber inhibit timer is implemented in the module’s hardware. If the bus transmitter is
on longer than 150% of the longest frame time, the jabber inhibit forces the transmitter
off and generates a fatal error (see page 43) with error code D0. In master mode, the
module stops scanning and stops communicating with the ControlLogix.
Power Requirements
The QTS-CLX-APACS module requires 5 mA @ 24VDC and 475 mA @ 5.1VDC from
I/O chassis backplane.
Other Requirements
To use the Windows utility programs, you must have RSLinx software, version 2.54 or
later, with an activation. Use RSLinx Gateway or RSLinx Professional software. Do not
use RSLinx Lite.
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 3
Package Contents
• QTS-CLX-APACS module
• CD containing software and documentation
Page 10
Page 4 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Installation
Prevent Electrostatic Discharge
The module is sensitive to electrostatic discharge.
WARNING!
ATTENTION: Electrostatic discharge can damage integrated circuits
or semiconductors if you touch backplane connector pins. Follow these
guidelines when you handle the module:
• Touch a grounded object to discharge static potential
• Wear an approved wrist-strap grounding device
• Do not touch the backplane connector or connector pins
• Do not touch circuit components inside the module
• If available, use a static-safe work station
• When the module is not in use, keep it in its static-shield packaging
Prepare the Chassis for Module Installation
Before you install the ControlLogix module, you must install and connect a ControlLogix
chassis and power supply. To install these products, refer to the installation instructions
you received with them.
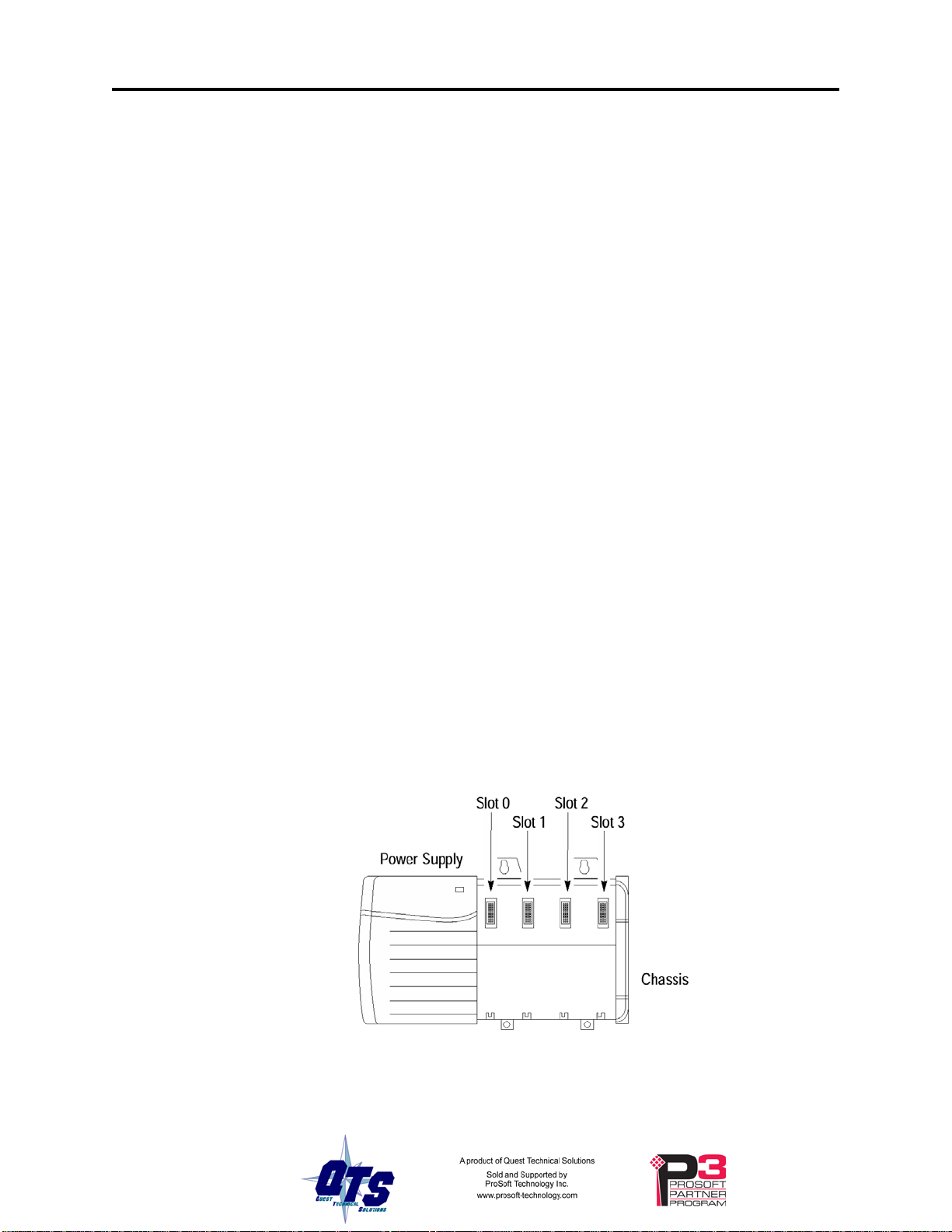
Determine Module Slot Location
This example shows chassis slot numbering in a 4-slot chassis. Slot 0 is the first slot and
is always located to the right of the power supply. You can use any size ControlLogix
chassis and install the module in any slot.
Figure 1 Chassis Slots
Page 11

You can install multiple QTS-CLX-APACS modules in the same chassis.
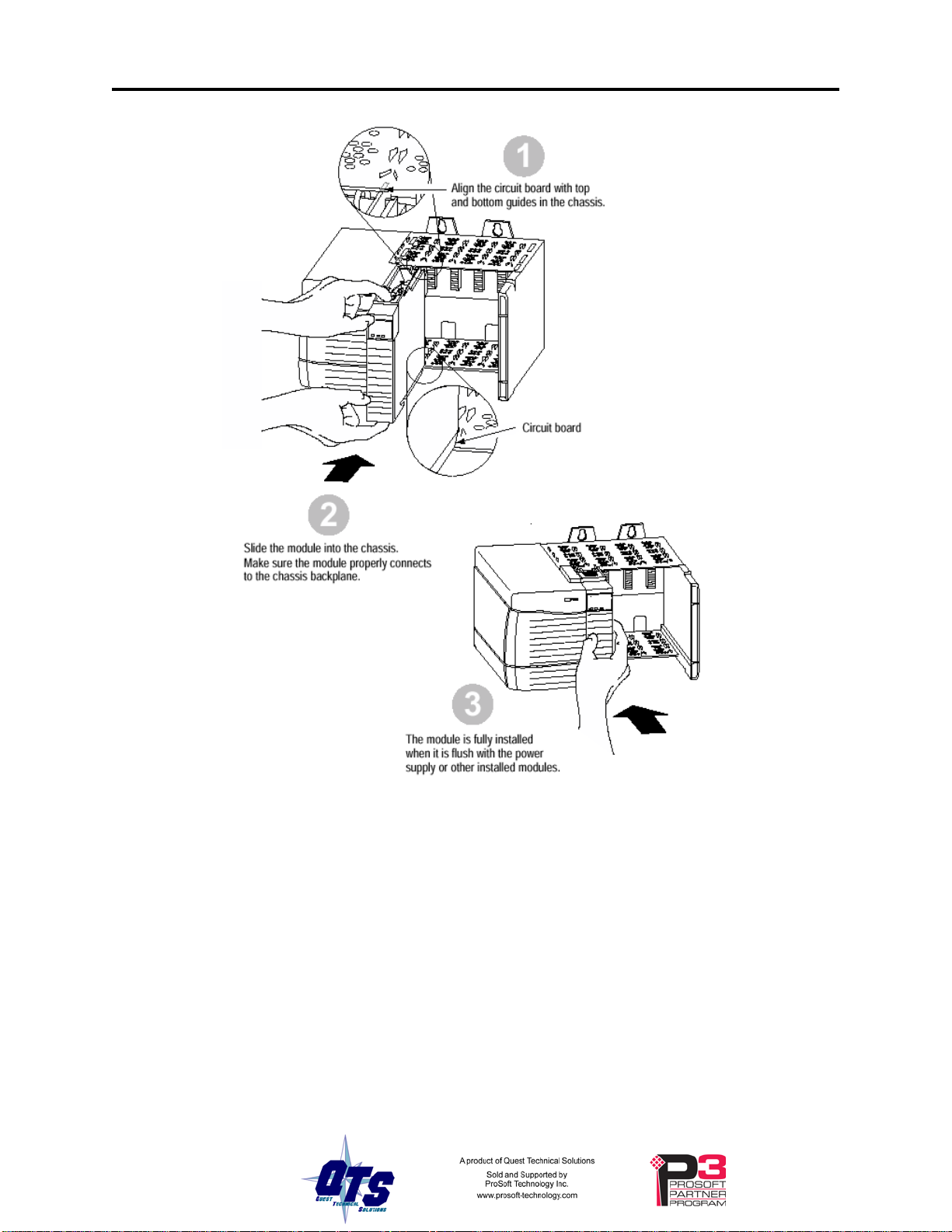
Insert the Module in the Chassis
The ControlLogix module is designed to be installed or removed while chassis power is
applied.
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 5
WARNING!
ATTENTION: When you insert or remove the module while
backplane power is on, an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an
explosion in hazardous location installations. Be sure that power is
removed or the area is nonhazardous before proceeding.
Repeated electrical arcing causes excessive wear to contacts on both the
module and its mating connector. Worn contacts may create electrical
resistance that can affect module operation.
Page 12
Page 6 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Replacing a Module
If you are replacing an existing module with an identical one, and you want to resume
identical system operation, you must:
• install the new module in the same slot.
• run the configuration program and download the appropriate con figura tion to the
module.
• check that it has the correct master or monitor firmware and the correct version.
• ensure that the data has been synchronized
Figure 2 Inserting the Module
Page 13

Cabling and Termination
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 7
WARNING!
Connect the QTS-CLX-APACS like any other IOBUS device.
Refer to the following Siemens document for details on cabling:
Refer to section 2.10.2 of the manual shown above.
Place the QTS-CLX-APA CS module at the beginning or end of the currently installed
MODULRAC racks:
Connecting the module disrupts bus traffic!
Connect the module at a time when it is safe to do so.
• "APACS+ / QUADLOG MODULRAC and Local Termination Panel
Installation and Service Instructions", SD39MODULRAC-1
1. Purchase a Siemens cable that fits the end of the MODULRAC rack that will
be used (left side of first rack or right side of last rack).
2. Cut off the end of the cable that will connect to the QTS-CLX-APACS
module and strip the cabling.
3. Wire the Bus A signals IOBUS (+) to I/O A+, IOBUS (-) to I/O A-, MRET
to MRET and MEN to MEN on the top Phoenix connector.
4. Set the shunt plug on the MODULRAC from terminate to the I/O bus
continue position and place a 120 ohm resistor between I/O A+ and I/O Asignals on the top Phoenix connector.
Repeat steps 1 through 4 for IOBUS B cabling on the bottom Phoenix connector of the
QTS-CLX-APACS module.
Terminate both ends of the IOBUS A and B using termination provided by the
MODULRAC racks or a 120 ohm resistor attached to the physical ends of the bus, if the
QTS-CLX-APACS module is placed at the beginning or end of the bus. There should be
two and only two terminators on each bus.
The cabling is the same for monitor and master modes of the QTS-CLX-APACS.
Software Installation
You must uninstall any previous version of the software before you can install a new
version. Use the Windows Control Panel Add and Remove Programs to remove the old
version.
Insert the CD supplied and run the program QtsApacs_vx.x.exe on the CD to install the
Windows software.
Page 14

Page 8 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Configuring the Module in RSLogix 5000
You configure the module in RSLogix 5000 to set how much scheduled data to transfer
and how often to transfer it.
The terms input and output are relative to the ControlLogix.
In monitor mode, the QTS-CLX-APACS sends APACS IOBUS input and output data to
input data in the ControlLogix. The QTS-CLX-APACS cannot transmit on the bus.
In master mode, the ControlLogix sends output data to the QTS-CLX-APACS, which
then transmits it as output data on the APACS IOBUS. The QTS-CLX-APACS sends
APACS input data to input data in the ControlLogix.
You should always access data using the aliases generated by the configuration programs.
Module Configuration
The ControlLogix configuration may be different for master and monitor modes of the
QTS-CLX-APACS.
The Windows configuration tools show the required connections and minimum
connection sizes.
The QTS-CLX-APACS module supports up to 10 scheduled connections. Connection 9
is reserved for diagnostics.
Discrete data is mapped from connection 0 upwards, analog data is mapped to connection
8 downwards.
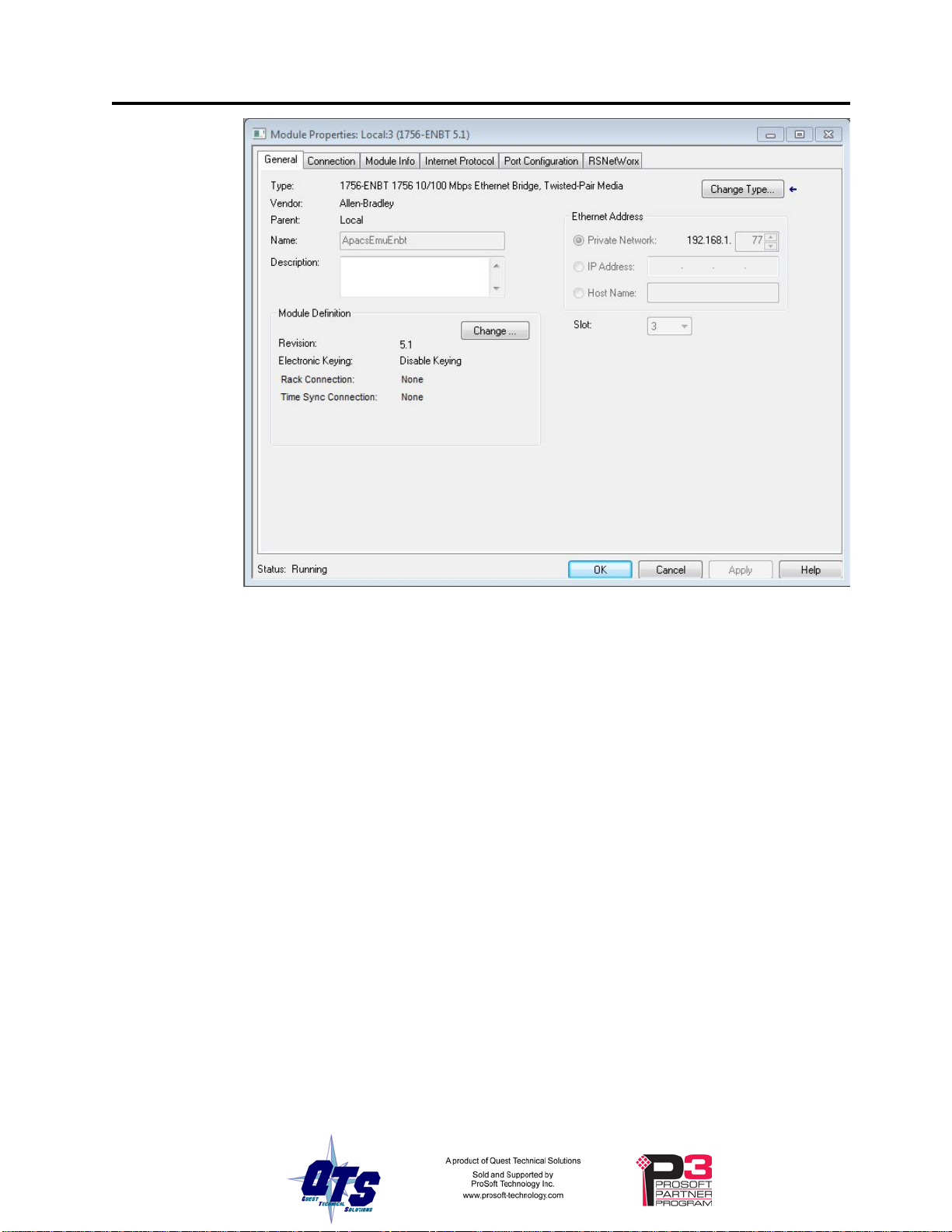
Adding the Module
1. Place an ENBT in the I/O tree.
Disable keying, set the Rack Connection to None, and set the slot to whatever slot the
QTS-CLX-APACS is in.
The IP address doesn't matter, e.g., use Private Network 192.168.1.77
The Name doesn't matter, e.g., use ApacsEmuEnbt
Page 15
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 9
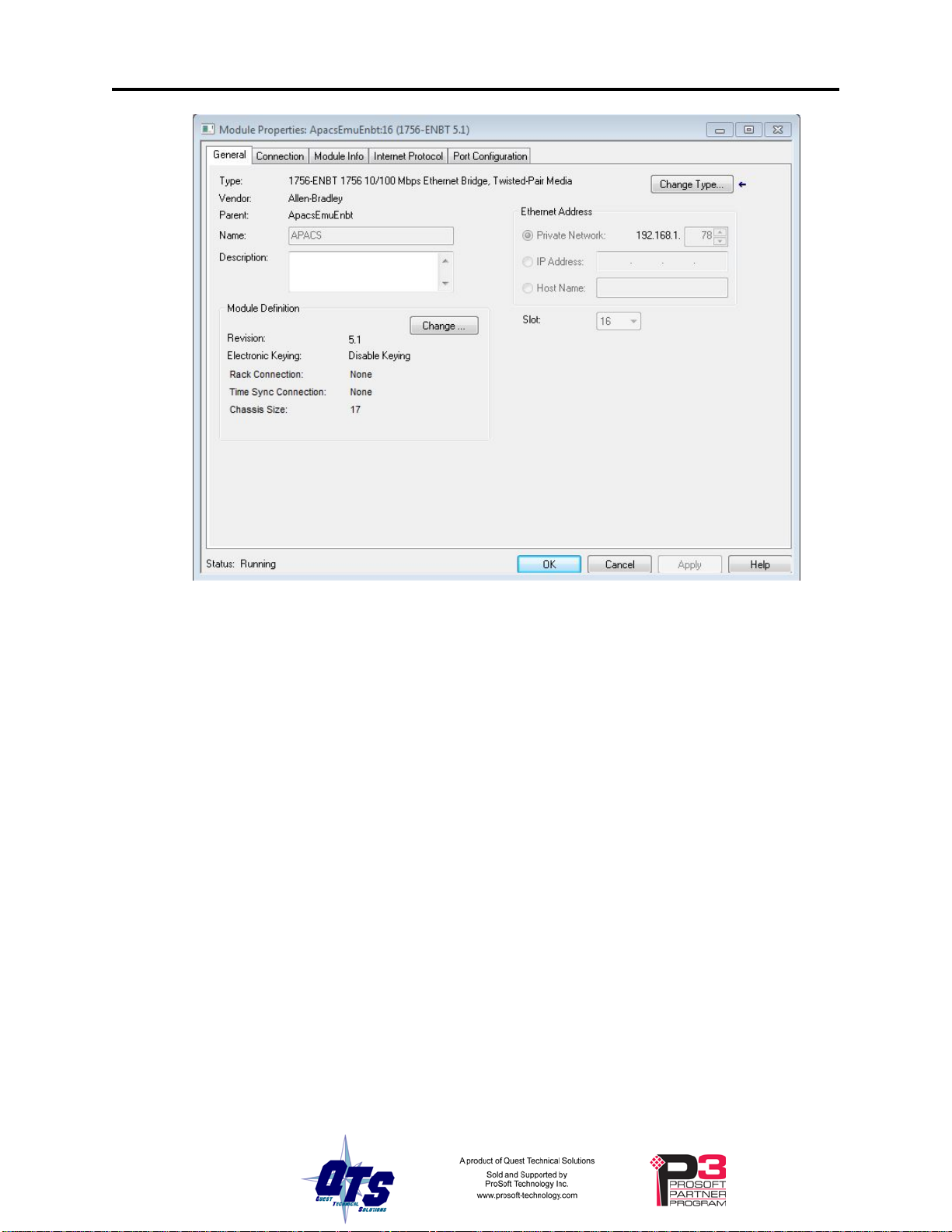
2. Place another ENBT on the Ethernet under the first ENBT.
Disable keying, set the Rack Connection to None, set the slot to 16.
The IP Address doesn't matter, e.g., Private Network 192.168.1.78
Name this ENBT what you want the Controller Tag Name to be, e.g., APACS.
Make this name the same as the name you give the module in the
configuration program (monitor or master).
This name will prefix all aliases.
TIP
This name will appear on the module’s 4-character scrolling display so
you can easily identify it if you have more that one QTS-CLX- APACS
module.
Page 16
Page 10 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
3. Place generic 1756-MODULEs in slots 0 to 9, as required.
The configuration programs assign IOBUS data to connections 0 to 8. Discrete inputs and
outputs and module status bytes are mapped to SINT data in connection 0 and up. That
is, if connection 0 is full, the configuration programs start mapping data to connection 1,
and so on.
Analog inputs and outputs are mapped to REAL data in connection 8 and down. That is,
if connection 8 is full, the configuration programs start mapping data to connection 7, and
so on
Diagnostic counters are mapped to INT data in connection 9.
Right click on the backplane associated with the second ENBT and select New Module.
Expand the Other tab, select a module of Type 1756-MODULE Generic 1756 Module
and click OK.
RSLogix 5000 displays the New Module dialog box.
Assign the module a Name and optionally a Description.
Set the Slot to match the connection number
Connection for SINT data
Set the Comm Format to Data – SINT
.
Set the Connection Parameters as shown. The sizes sh own are the maxim um values.
Page 17

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 11
Click OK
Connection for REAL data
Set the Comm Format to Data – REAL
Set the Connection Parameters as shown. The sizes show n are the maxim um values.
Click OK.
Page 18

Page 12 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Connection for Diagnostic Data
Diagnostics are always mapped to connection 9. Connection 9 is not required but we
strongly recommend that you create it.
Set the Comm Format to Data – INT
Set the Connection Parameters as shown.
Do not reduce the connection size for connection 9 from the values shown. In addition to
the diagnostic counters, other undocumented diagnostic information which may be useful
for technical support is also mapped to connection 9.
The sizes of connections 0 to 8 (as needed) can be smaller than the maximum to reduce
traffic in the ControlLogix backplane. Double click on the root of the network tree in the
APACS configuration programs to determine the minimum connection sizes.
RPI
Next, set the RPI for the connection.
Selecting an RPI.
The module supports RPIs from 2.0 to 750.0 ms. The default RPI is 5 ms.
Select an RPI appropriate to the I/O bus scan time and to your process. It makes no sense
to use an RPI that is much faster than the bus or process update time.
You can use different RPIs for each connection, depending on the requirements of your
application.
Page 19

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 13
For example, you can use a longer RPI for the diagnostic data in connection 9, for
example 500 milliseconds, since diagnostics do not need to be updated as frequently as
I/O data.
Remote Connections
If you are using the QTS-CLX-APACS in a remote chassis, for example a chassis
connected to the controlling ControlLogix processor over Ethernet or ControlNet, it may
be necessary to increase the RPI, as the intermediate network may not have sufficient
bandwidth to support faster updates (small RPIs).
Page 20

Page 14 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Parameter
Value
CLX-APACS-MAS (Master)
Vendor
832 (Quest Technical Solutions)
Product Type
12
1061 (Master)
Revision
depends on firmware
Serial Number
depends on module
RSLinx
When you right click on the module in RSLinx and select Properties, RSLinx displays the
following:
Device Name CLX-APACS-MON (Monitor)
Product Code 1062 (Monitor)
RSLinx Properties
To use the Windows utility programs, you must have RSLinx software, version 2.54 or
later, with an activation. Use RSLinx Gateway or RSLinx Professional software. Do not
use RSLinx Lite.
When you create a driver for the configuration programs to access the QTS-CLX-APACS
module, use the Remote Devices via Linx Gateway driver.
Page 21

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 15
Monitor Mode Operation
The following is a short summary of the steps typically followed. Refer to the
appropriate manual section for details.
Step Operation See page
Install the QTS-CLX-APACS module in the
ControlLogix chassis
Connect the module to the APACS IOBUS 7
Export the database from 4-mation software 16
Run the monitor configuration software 15
Import a 4-mation exported object file (obt) 16
Assign ControlLogix addresses to the IOBUS data 17
Set the module name 19
Save the configuration 21
Download the configuration to the module 21
Configure the module in RSLogix 5000 8
Create aliases for RSLogix 5000 22
Import the aliases into RSLogix 5000 23
Use the aliases to access the data 38
ClxApacsMonCfg Software
4
The QTS-CLX-APACS module is supplied with a Windows configuration tool,
ClxApacsMonCfg.exe for using the module as a monitor.
Use this configuration tool to:
• Configure the monitor from a 4-mation software object (obt) file
• Map I/O data to ControlLogix scheduled connections
• Save and load configuration files
• Set the RSLinx path to the QTS-CLX-APACS module
• Download and upload configurations
• Export aliases for I/O data for import into RSLogix 5000
• Switch between monitor and master modes
• Update the module firmware
Page 22

Page 16 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Exporting a 4-mation database fi le
The monitor configuration program uses a database file exported from the Siemens
4-mation Configuration Program.
To export a database file:
1. Go to the Module tree and put your cursor on the ACM
2. Select File/Export/Database…
3. In the Export Options box, check ASCII Format
4. Use the Directories: list to choose the destination
5. Click the Export button
Configuring the IOBUS
Run the monitor configuration tool, ClxApacsMonCfg.exe
Select Tools/Import APACS Configuration and select the 4-mation *.obt file to import.
When the file has been imported, check the module tree and confirm that the APACS
modules are all present and correct.
Page 23

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 17
Double click on each module and confirm that the channel types for that module are all
present and correct.
Assigning ControlLogix a ddresses
Select Tools/Auto-allocate CLX Addressing to map the APACS IOBUS data to
ControlLogix addresses.
The module tree now shows the CLX addresses associated with each APACS module.
Page 24

Page 18 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
What gets mapped
I/O Data
APACS IOBUS discrete inputs and outputs are mapped to the input data on ControlLogix
connections from 0 upwards, as required. Discrete input and output data points consist of
a byte of data and are mapped to SINT data in the ControlLogix. The low bit in each
SINT corresponds to the value of the point (0 or 1, False or True).
APACS IOBUS analog inputs and outputs are mapped to the input data on ControlLogix
connections from 8 downward, as required. Analog inputs and outputs are mapped to
REAL data in the ControlLogix.
In addition, each discrete output, analog input and analog output has an associated status
byte. These are also mapped to SINT input da ta in the ControlLogix, in connections 0
and up.
Diagnostic Counters
QTS-CLX-APACS diagnostic counters are integers are mapped to ControlLogix input
data of type INT on connection 9.
Alias Name Offset Description
StatRxGood 0 Good packets received from the network
StatAbortErr 1 Bad packets, abort errors
Page 25

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 19
Alias Name Offset Description
StatBusANoiseErr 2 Bad packets, network noise
StatFrameErr 3 Bad packets, framing errors
StatCrcErr 4 Bad packets, CRC errors
StatProtocolErr 5 Protocol errors
StatRxTimeOut 6 Bad packets, timeout errors
Each alias name is prefixed by the module name and an underscore.
In addition, bit 0 of the first word of output data on connection 9 is used for the command
to clear the diagnostic counters. The alias name is StatResetBit. The counters are cleared
when this bit changes from 0 to 1.
Slot Status Bits
The QTS-CLX-APACS maintains an array of bits that indicate the status of the APACS
modules.
In master mode, the bit is 0 if the module has good communication status and is 1 if the
associated module is in error or is not responding.
Use the slot status bits to determine when you can access data from a module in master
mode. Some APACS modules take several seconds to go online.
In monitor mode, the bits do not update and are always 0. Aliases to the bits are provided
by the configuration tool for compatibility with master mode.
Aliases for these bits have names like
APACS_SlotStatus_R01S04
for the bit associated with the module in rack 1 slot 4.
Use the aliases to access the status bits.
If the ControlLogix loses communication with the QTS-CLX-APACS, it
sets the first four bytes of connection 0 to FF hexadecimal (11111111
TIP
binary).
Monitor these four bytes to determine if there is a problem.
Setting the Module Name
To set the module name, right click on the QTS-CLX-APACS at the root of the tree and
select Edit Module Properties.
Page 26

Page 20 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
The QTS-CLX-APACS Module Properties dialog appears.
Enter the Module Name. It can be up to 15 characters long. It should follow the rules for
naming ControlLogix aliases; it should contain only alphanumeric characters and the
underscore. Click OK to accept the name.
The name is displayed on the 4-character disp lay and i s used by ClxApacsMonCfg to
build aliases for ControlLogix data.
The default name assigned when you create a monitor configuration is MonImport.
The name should be unique so that if you have more than one QTS-CLX-APACS
module, the aliases associated with each module are unique.
Page 27

Use the same name that you assign the second ENBT module associated
TIP
with the QTS-CLX-APACS in RSLogix 5000 to make it easy to
associate aliases with the module. See page 9.
Saving a Configuration Fil e
To save a configuration to disk, select File/Save or File/Save As.
Uploading and Downloading Conf igurations
To download a configuration to the QTS-CLX-APACS, select Tools/Download
Configuration or use the Download Configuration to Module button on the toolbar.
To upload a configuration from the QTS-CLX-APACS, select Tools/Upload
Configuration or use the Upload Configuration from Module bu tton on the toolbar. The
uploaded configuration will be given the default file name Untitled.
If the RSLinx path to the module has not been set when you upload or download, an
RSLinx Path Selection window opens.
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 21
Page 28

Page 22 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Configuring the QTS-CLX-APACS Module in RSLogix 5000.
Follow the procedure on page 8 to configure the QTS-CLX-APACS in RSLogix 5000.
To determine which connections you need to create, right click on the root of the tree and
select Edit Module Properties.
The QTS-CLX-APACS Module Properties dialog box appears. It shows the required
connections and the minimum connection sizes.
Aliases
In the example shown, the required connections are:
• connection 0 with type SINT, minimum input size 70 and minimum output size 1
• connection 8 with type REAL, minimum input size 39 and minimum output size 1
In addition, connection 9 is always shown, although it is not required. Connection 9 is
used for module diagnostics. It is recommended that you always create connection 9,
with the sizes shown.
In monitor mode, the QTS-CLX-APACS does not wait for all connections to be open.
The configuration tool creates aliases for I/O data that can be exported and imported into
RSLogix 5000.
Write programs using these aliases rather than using absolute addresses. If the mapping
of the I/O data changes, simply reimport the new aliases and the program will point to the
new data locations.
To export aliases, select Files/Export Alias File…
Page 29

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 23
Enter the RSLinx Path Specifier to set the location of the module. This will be the name
of the second ENBT module associated with the QTS-CLX-APACS modules (see page
8). In the example shown, the name is APACS.
Type the FileName or use the Select File Name button to enter the file location where the
exported aliases will be saved.
If you are using monitor mode to develop an application that will be used in master
mode, check the Create Temp Array Alias Tags checkbox. This creates aliases fo r the
internal arrays you will need. Refer to page 25 for details.
Click OK to create the alias file.
WARNING!
Importing Aliases in RSLogix 5000
To import the alias file into RSLogix 5000, you must be offline. Select Tools/Import…
and import the alia s file.
TIP
Alias Format
ClxApacsMonCfg builds each alias name from the Module Name and address
information (Rack, Slot and Channel) supplied by the configuration program
The ControlLogix data address is built from the RSLinx Path Specifier you enter and the
data mappings created by the configuration program.
If you change the I/O or ControlLogix configuration, re-import aliases so
that the ControlLogix processor uses th e corre ct addr es ses and clear the
ControlLogix output table so that values don’t get written to incorrect
addresses.
If you have changed mode on the QTS-CLX-APACS, delete any aliases
you previously imported into RSLogix 5000 before you import the new
aliases.
Example:
ALIAS,"","APACS_AI_R01S06C02","APACS_AI_R01S06C02","","APACS:8:I.Data[1]"
Page 30

Page 24 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
In this example, the module is in rack 1slot 6. The alias is for an analog input from
channel 2 on the module, which is mapped to ControlLogix address input data at offset 1
of connection 8.
To build the alias name, ClxApacsMonCfg prefixes the name with the module name and
an underscore. It prefixes the address with the RSLinx path specifier.
Opening a Configuration File
To open a configuration file, select File/Open..
This does not change the configuration in the module; the configuration in the module
changes only when you download.
Clearing the Configuration
To clear the configuration in the program, select File/New.
This does not change the configuration in the module; the configuration in the module
changes only when you download.
Setting the RSLinx Path
Select Tools/Set RSLinx Path… to assign or change the current RSLinx path.
This may be useful if, for example, you have more than one QTS-CLX- APACS module.
Changing the Module Mode
Select Tools/Change Module Mode… to switch a QTS-CLX-APACS module between
monitor and master modes, or to update the module firmware (see page 44)
Select the firmware to download and click Apply. When the download is complete,
ClxApacsMonCfg displays the version of the firmware downloaded.
Page 31

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 25
Using Monitor Mode for Migration
You can use monitor mode on the QTS-CLX-APACS to migrate existing APACS
applications to ControlLogix.
In monitor mode, the QTS-CLX-APAC S captures live inputs and outputs from the
APACS IOBUS.
You first create two arrays in the ControlLogix:
• [Module name]_TempApacsSintOutputArray[8,500] of type SINT
• [Module name]_TempApacsRealOutputArray[8,125] of type REAL
The configuration program creates aliases for IOBUS inputs and outputs and for dummy
outputs in the temporary arrays.
You import those aliases into RSLogix 5000, then create a new ControlLogix application
that reads live inputs from the APACS IOBUS and writes outputs to the temporary
arrays, always using the aliases from ClxApacsMonCfg.
You compare the outputs from the new ControlLogix application (in the temporary array)
with the live outputs fro m IOBUS.
When you are satisfied that the new application duplicates the behaviour of the existing
control application (state of outputs and timing), disconnect the APACS controller and
switch the QTS-CLX-APACS module to master mode.
Export aliases from ClxApacsMasCfg in master mode and import them into RSLogix
5000. The names for the output aliases will be the same as those that previously pointed
to the temporary array but now they will point to the corresponding IOBUS outputs.
Your new ControlLogix application will write to the real outputs instead of the temporary
array. Since you developed your application using these aliases, no further changes
should be necessary.
You will start up with a ControlLogix application that has been tested and proven to
duplicate the behaviour of the previous APACS control application.
Example:
This is the alias ClxApacsMonCfg generated in monitor mode for a monitored discrete
output
ALIAS,"","APACS_DO_R01S04C01","APACS_DO_R01S04C01","","APACS_TempApacsSintOutp
utArray[0,0]"
and this is the alias it generated for the same output in master mod e
ALIAS,"","APACS_DO_R01S04C01","APACS_DO_R01S04C01","","APACS:0:O.Data[0] "
The alias names are the same but in the first case the program wrote to the temporary
SINT array; in the second it wrote to a ControlLogix output.
Similarly for analog outputs, this is the alias ClxApacsMonCfg generated in monitor
mode for a monitored analog output
ALIAS,"","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","","APACS_TempApacsRealOutp
utArray[0,0]"
Page 32

Page 26 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
and the corresponding alias in master mode
ALIAS,"","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","","APACS:8:O.Data[0] "
The alias names are the same but in the first case the program wrote to the temporary
REAL array; in the second it wrote to a ControlLogix output.
Slot Status Bits
In monitor mode, the bits do not update and are always 0. Aliases to the bits are provided
by the configuration tool for compatibility with master mode.
When you develop your control application using monitor mode, include logic that
monitors the slot status bits to determine when you can access I/O data, so that the logic
will be in place when you switch to master mode.
Page 33

WARNING!
The following is a short summary of the steps typically followed. Refer to the
appropriate manual section for details.
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 27
Master Mode Operation
Never connect the APACS in master mode to the network while the
ACM is controlling I/O. It transmits even if there is no configuration
and will disrupt communication.
Step Operation See page
1 Install the QTS-CLX-APACS module in the
ControlLogix chassis
2 Power down all APACS racks.
3 Connect the module to the APACS IOBUS 7
4 Run the QTS-CLX-MAS master configuration
program, ClxApacsMasCfg.exe
5 Temporarily load the monitor firmware on the
QTS-CLX-APACS
6 Clear the stored ACM configuration on the
QTS-CLX-APACS
7 Power up the APACS racks and wait for the OK
LEDs on all modules to be green
8 Read the captured configuration data that the ACM
sent to the modules
9 Check that all modules and channels are correct 28
10 Assign ControlLogix addresses to the IOBUS data 30
11 Set the module name 32
4
28
28
28
28
12 Save the configuration 33
13 Remove the ACM
14 Change the QTS-CLX-APACS to master mode 37
15 Download the configuration to the module 33
16 Configure the module in RSLogix 5000 8
17 Create aliases for RSLogix 5000 35
18 Import the aliases into RSLogix 5000 36
19 Use the aliases to access the data 38
Page 34

Page 28 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
ClxApacsMasCfg Software
The QTS-CLX-APACS module is supplied with a Windows configuration tool,
ClxApacsMasCfg.exe for configuring the module as a master.
Use this configuration tool to:
• Switch between monitor and master mode
• Capture IOBUS configuration data from a running network
• Map I/O data to ControlLogix scheduled connections
• Save and load configuration files
• Set the RSLinx path to the QTS-CLX-APACS module
• Download and upload configurations
• Export aliases for I/O data for import into RSLogix 5000
• Update the module firmware
Configuring from an APACS IOBUS
The QTS-CLX-APACS master must be configured by capturing configuration
information sent by an APACS ACM master to a running APACS IOBUS system at
powerup. Power must be cycled to all APACS modules in all APACS racks in the
system. All APACS modules must be present and configured. Check that the OK LEDs
on all modules are green.
WARNING!
Wire the QTS-CLX-APACS as described on page 7. If you have been using monitor
mode, the wiring does not need to be changed.
Power down all APACS racks.
Run the master config tool, ClxApacs Ma sCfg .ex e.
Select Tools/Change Module Mode to temporarily load the monitor firmware.
Select Tools/Clear ACM Config to cl ear any previously stored configuration.
Power up the rack and wait for the OK LEDs on all APACS modules to go green.
Select Tools/ Read ACM Config to build the module tree from the configuration data the
QTS-CLX-APACS has captured..
Connecting the module to the IOBUS disrupts bus traffic!
Connect the module only at a time when it is safe to do so.
Check the module tree and confirm that the APACS modules are all present and correct.
Page 35

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 29
Double click on each module and confirm that the channel types for that module are all
present and correct.
Page 36

Page 30 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Assigning ControlLogix a ddresses
Select Tools/Auto-allocate CLX Addressing to map the APACS IOBUS data to
ControlLogix addresses.
The module tree shows the CLX addresses associated with each APACS module.
What gets mapped
APACS IOBUS discrete inputs are mapped to the input data on ControlLogix
connections from 0 upwards, as required. Discrete outputs are mapped to the output data
on ControlLogix connections from 0 upwards, as required
Discrete input and output data points consist of a byte of data and are mapped to SINT
data in the ControlLogix. The low bit in each SINT corresponds to the value of the point
(0 or 1, False or True).
APACS IOBUS analog inputs are mapped to the input data on ControlLogix connections
from 8 downward, as required. APACS IOBUS analog outputs are mapped to the output
data on ControlLogix connections from 8 downward, as required. Analog inputs and
outputs are mapped to REAL data in the ControlLogix.
In addition, each discrete output, analog input and analog output has an associated status
byte. These are also mapped to SINT input data in the ControlLogix, in connections 0
and up.
Page 37

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 31
Diagnostic Counters
QTS-CLX-APACS diagnostic counters are integers and are mapped to ControlLogix
input data of type INT on connection 9.
Alias Name Offset Description
StatTxGood 0 Good packets transmitted on both channels
StatBusARxGood 1 Good packets received on bus A
StatBusARxTimeOut 2 Receive timeouts on bus A
StatBusAAbortErr 3 Abort errors on bus A
StatBusANoiseErr 4 Noise errors on bus A
StatBusACrcErr 5 CRC errors on bus A
StatBusBRxGood 6 Good packets received on bus B
StatBusBRxTimeOut 7 Receive timeouts on bus B
StatBusBAbortErr 8 Abort errors on bus B
StatBusBNoiseErr 9 Noise errors on bus B
StatBusBCrcErr 10 CRC errors on bus B
StatProtocolErr 11 Protocol errors
The alias names are prefixed with the module name and an underscore.
In addition, bit 0 of the first word of output data on connection 9 is used for the command
to clear the diagnostic counters. The alias name is StatResetBit. The counters are cleared
when this bit changes from 0 to 1.
Slot Status Bits
The QTS-CLX-APACS maintains an array of bits that indicate the status of the APACS
modules.
Use the slot status bits to determine when you can access data from a module. Some
APACS modules take several seconds to go online.
In master mode, the bit is 0 if the module has good communication status and is 1 if the
associated module is in error or is not responding.
In monitor mode, the bits do not update and are always 0. Aliases to the bits are provided
by the configuration tool for compatibility with master mode.
Aliases for these bits have names like
APACS_SlotStatus_R01S04
for the bit associated with the module in rack 1 slot 4.
Use the aliases to access the status bits.
Page 38

Page 32 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
If the ControlLogix loses communication with the QTS-CLX-APACS, it
sets the first four bytes of connection 0 to FF hexadecimal (11111111
TIP
binary).
Monitor these four bytes to determine if there is a problem.
Setting the Module Name
To set the module name, right click on the QTS-CLX-APACS at the root of the tree and
select Edit Module Properties.
The QTS-CLX-APACS Module Properties dialog appears.
Page 39

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 33
Enter the Module Name. It can be up to 15 characters long. It should follow the rules for
naming ControlLogix aliases; it should contain only alphanumeric characters and the
underscore. Click OK to accept the name.
The name is displayed on the 4-character display and is used by ClxApacsMasCfg to
build aliases for ControlLogix data.
The default name assigned when you create a monitor configuration is HeardCfg.
The name should be unique so that if you have more than one QTS-CLX-APACS
module, the aliases associated with each module are unique.
Use the same name that you assign the second ENBT module associated
TIP
with the QTS-CLX-APACS in RSLogix 5000 to make it easy to
associate aliases with the module. See page 9.
Saving a Configuration Fil e
To save a configuration to disk, select File/Save or File/Save As.
Uploading and Downloading Conf igurations
To download a configuration to the QTS-CLX-APACS, select Tools/Download Config or
use the Download Config to Module button on the toolbar.
To upload a configuration from the QTS-CLX-APACS, select Tools/Upload Config or
use the Upload Config from Module button on the toolbar.
If the RSLinx path to the module has not been set when you upload or download, an
RSLinx Path Selection window opens.
Page 40
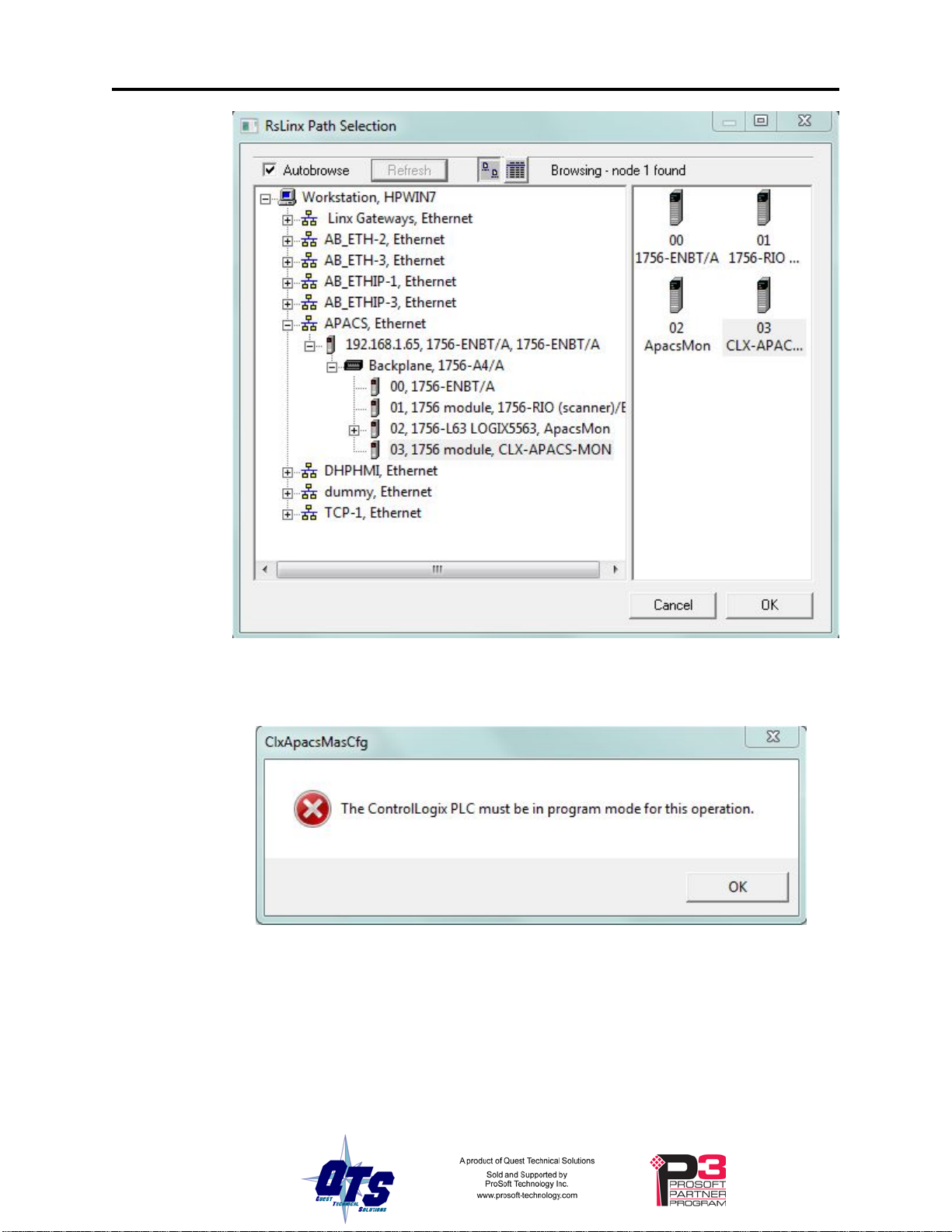
Page 34 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
If the ControlLogix processor with the connection to the QTS-CLX-APACS is in run
mode when you download, the following message is displayed.
Configuring the QTS-CLX-APACS Module in RSLogix 5000.
Follow the procedure on page 9 to configure the QTS-CLX-APACS in RSLogix 5000.
To determine which connections you need to create, right click on the root of the tree and
select Edit Module Properties.
Page 41

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 35
The QTS-CLX-APACS Module Properties dialog box appears. It shows the required
connections and the minimum connection sizes.
Aliases
In the example shown, the required connections are:
• connection 0 with type SINT, minimum input size 60 and minimum output size 9
• connection 8 with type REAL, minimum input size 37 and minimum output size 1
In addition, connection 9 is always shown, although it is not required. Connection 9 is
used for module diagnostics. It is recommended that you always create connection 9,
with the sizes shown.
The configuration tool creates aliases for I/O data that can be exported and imported into
RSLogix 5000.
Write programs using these aliases rather than using absolute addresses. If the mapping
of the I/O data changes, simply reimport the new aliases and the program will point to the
new data locations.
To export aliases, select Files/Export Alias File…
Page 42

Page 36 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Enter the RSLinx Path Specifier to set the location of the module. This will be the name
of the second ENBT module associated with the QTS-CLX-APACS modules (see page
9). In the example shown, the name is APACS.
Type the FileName or use the Select File Name button to enter the file location where the
exported aliases will be saved.
Click OK to create the alias file.
If you change the I/O or ControlLogix configuration, re-import aliases so
WARNING!
that the ControlLogix processor uses th e corre ct addr es ses and clear the
ControlLogix output table so that values don’t get written to incorrect
addresses.
Importing Aliases in RSLogix 5000
To import the alias file into RSLogix 5000, you must be offline. Select Tools/Import…
and import the alia s file.
If you have changed mode on the QTS-CLX-APACS, delete any aliases
TIP
you previously imported into RSLogix 5000 before you import the new
aliases.
Alias Format
ClxApacsMasCfg builds each alias name from the Module name and address information
(Rack, Slot and Channel) supplied by the configuration program
The ControlLogix data address is built from the RSLinx Path Specifier you enter and the
data mappings created by the configuration program.
To build the alias name, ClxApacsMasCfg prefixes the name with the module name and
an underscore. It prefixes the ControlLogix address with the RSLinx specifier you
supply.
Examples:
ALIAS,"","APACS_DO_R01S04C05","APACS_DO_R01S04C05","","APACS:0:O.Data[1] "
In this example, the alias is for a discrete output on channel 5 of the module in rack 1 slot
4, which is mapped to ControlLogix address output data at offset 1 of connection 0. The
module name is APACS, as is the RSLinx path.
ALIAS,"","APACS_DI_R01S05C01","APACS_DI_R01S05C01","","APACS:0:I.Data[18]"
In this example, the alias is for a discrete input on channel 1 of the module in rack 1 slot
5, which is mapped to ControlLogix address input data at offset 18 of connection 0.
ALIAS,"","APACS_AI_R01S06C03","APACS_AI_R01S06C03","","APACS:8:I.Data[2]"
In this example, the alias is for an analog input on channel 3 of the module in rack 1 slot
6, which is mapped to ControlLogix address input data at offset 2 of connection 8.
ALIAS,"","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","APACS_AO_R01S06C01","","APACS :8:O.Data[0] "
Page 43

In this example, the alias is for an analog output on channel 1 of the module in rack 1 slot
6, which is mapped to ControlLogix address output data at offset 0 of connection 8.
Opening a Configuration File
To open a configuration file, select File/Open..
This does not change the configuration in the module; the configuration in the module
changes only when you download.
Clearing the Configurat ion
To clear the configuration in the program, select File/New.
This does not change the configuration in the module; the configuration in the module
changes only when you download.
Setting the RSLinx Path
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 37
Select Tools/Set RSLinx Path… to assign or change the current RSLinx path.
This may be useful if, for example, you have more than one QTS-CLX- APACS module.
Changing the Module Mode
Select Tools/Change Module Mode… to switch a QTS-CLX-APACS module between
monitor and master modes, or to update the module firmware (see page 44).
Select the firmware to download and click Apply. When the download is complete,
ClxApacsMasCfg displays the version of the firmware downloaded.
Page 44

Page 38 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Accessing Data
Required Connections
In master mode, the QTS-CLX-APACS does not begin scanning the I/O bus until all
ControlLogix connections to the module are present.
In monitor mode, the module does not wait for the ControlLogix connections.
I/O Data
Use the aliases created by ClxApacsMonCfg or ClxApacsMasCfg to access data to
ensure that you are using the correct address.
Each discrete point is mapped to a SINT in the ControlLogix. The data value is the low
bit in the SINT. Use the low bit of the Alias to read or change the data value.
Each analog point is mapped to a REAL in the ControlLogix.
Program/Run
In master mode, the QTS-CLX-APACS does not scan I/O in program mode.
Diagnostic Data
The QTS-CLX-APACS maintains diagnostic counters and other diagnostic status
information.
SlotStatus Bits
The QTS-CLX-APACS maintains an array of bits that indicate the status of the APACS
modules.
Use the slot status bits to determine when you can access data from a module. Some
APACS modules take several seconds to go online.
In master mode, the bit is 0 if the module has good communication status and is 1 if the
associated module is in error or is not responding.
Page 45

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 39
In monitor mode, the bits do not update and are always 0. Aliases to the bits are provided
by the configuration tool for compatibility with master mode.
Aliases for these bits have names like
APACS_SlotStatus_R01S04
for the bit associated with the module in rack 1 slot 4.
Use the aliases to access the status bits.
If the ControlLogix loses communication with the QTS-CLX-APACS, it
sets the first four bytes of connection 0 to FF hexadecimal (11111111
TIP
binary).
Monitor these four bytes to determine if there is a problem.
Diagnostic Counters
Refer to page 18 for details about monitor mode diagnostic counters.
Refer to page 31 for details about master mode diagnostic counters.
Page 46

Page 40 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Troubleshooting
ControlLogix Module LEDs
The module has three status LEDs to indicate the state of inte rn a l ope rations. The LED s
are labeled NET, CLX and OK.
NET LED – IOBUS Status
The NET LED shows the status of I/O communication.
Monitor Mode
Color Meaning
Red Bad frame received
Green Receiving good frames
Off Idle
Master Mode
Color Meaning
Red Cable A error
Yellow Cable B error
Green Receiving good frames
Flashing One or more APACS modules offline
Off Idle, not trying to talk to APACS modules
CLX LED – ControlBus Status
The CLX LED indicates the status of communication with the ControlLogix processor.
Color Meaning
Green All required connections are open
Flashing
Green/Off
Not all required connections are open (master mode)
Yellow Connection 0 not open (master mode)
Page 47

OK LED – Module Health
The OK LED indicates module health. A red LED indicates that module startup
diagnostics have failed or a major module fault has occurred. Green indicates that the
module has passed all power-up diagnostics and is functioning normally.
All LEDs Red
If all three LEDs are solid red and the 4-character display shows something like M#66,
this indicates that a fatal error has occurred. Refer to page 43 for information on clearing
fatal errors. If a fatal error occurs, clear the fatal error, save the file and contact
Technical Support.
QTS-CLX-APACS Module 4-Character Display
The 4-character display shows the firmware in the module, either APACS-MON or
APACS-MAS, followed by the firmware version number, and the Module Name you
entered in the module configuration.
If there is no configuration in the module, the display shows <NoConfig> instead of the
module name.
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 41
RSLogix 5000
If there is a problem with the connection to the module, the connections are shown with
yellow triangles in the I/O Configuration tree
The Connection tab for each connection to the QTS-CLX-APACS module displays an
error message if there is a problem with the connection to the module.
Page 48

Page 42 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
If the module has no configuration, it refuses connection requests from the ControlLogix
processor and returns an error.
The Debug Log
The firmware on the module maintains a log of informational and diagnostic messages
that can be useful in determining the cause of configuration and I/O bus problems.
To view the log, run the program LogMon from the Start Menu.
Diagnostic Counters
Refer to page 18 for details about monitor mode diagnostic counters.
Refer to page 31 for details about master mode diagnostic counters.
Slot Status Bits
The QTS-CLX-APACS maintains an array of bits that indicate the status of the APACS
modules.
Use the slot status bits to determine when you can access data from a module. Some
APACS modules take several seconds to go online.
In master mode, the bit is 0 if the module has good communication status and is 1 if the
associated module is in error or is not responding.
In monitor mode, the bits do not update and are always 0. Aliases to the bits are provided
by the configuration tool for compatibility with master mode.
Aliases for these bits have names like
APACS_SlotStatus_R01S04
Page 49

for the bit associated with the module in rack 1 slot 4.
Use the aliases to access the status bits.
TIP
Fatal Errors
Fatal errors occur when the firmware on the module encounters an unexpected condition.
The module stops running, turns all three LEDs red, and displays the fatal error number
on the 4-character display. The module also records its state at the time the fatal error
occurred in a log.
To clear the fatal error and capture the fatal error log:
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 43
If the ControlLogix loses communication with the QTS-CLX-APACS, it
sets the first four bytes of connection 0 to FF hexadecimal (11111111
binary).
Monitor these four bytes to determine if there is a problem.
1. Cycle power on the module. The 4-character display should show
“FatalErrorCapture requi re d”.
2. Run the utility FatalCapt.exe from the subdirectory Tools where you installed
the configuration tool.
3. Store the fatal error log to a file. This also clears the fatal error on the
module.
Contact technical support. Provide them with the fatal error log, which will help
diagnose the cause of the problem.
Page 50

Page 44 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Updating the Firmware
The module firmware is updated using either of the two configura tion program s.
Copy the new firmware file to the same directory as ClxApacsMonCfg.exe or
ClxApacsMasCfg.exe.
Select Tools/Set Module Mode.
To update the firmware, set the mode to match the firmware already loaded in the
module.
The configuration program displays the version after the firmware has been downloaded.
The QTS-CLX-APACS module displays the firmware and version currently loaded on
the 4-character display.
Page 51

QTS-CLX-APACS ControlLogix Module
Parameter Specification
Module Location ControlLogix chassis
Function ControlLogix module for APACS IOBUS
QTS-CLX-APACS Page 45
Specifications
Maximum Backplane
Current Load
Power dissipation 2.5W maximum
Environmental
Conditions:
Operational
Temperature
Storage Temperature –40 to 85°C (–40 to 185°F)
Relative Humidity 5-95% without condensation
5 mA @ 24VDC and 475 mA @ 5.1VDC
from I/O chassis backplane
0-60°C (32-140°F)
Page 52

Page 46 QTS-CLX-APACS March 2015
Support
How to Contact Us: Sales and Support
Sales and Technical Support for this product are provided by ProSoft Technology.
Contact our worldwide Sales or Technical Support teams directly by phone or email:
Asia Pacific
+603.7724.2080, asiapc@prosoft-technology.com
Europe – Middle East – Africa
+33 (0) 5.34.36.87.20, Europe@prosoft-technology.com
North America
+1.661.716.5100, support@prosoft-technology.com
Latin America (Sales only)
+1.281.298.9109, latinam@prosoft-technology.com
.
Page 53

QTS-CLX-APACS Page 47
Warranty
Quest Technical Solutions warrants its products to be free from defects in workmanship
or material under normal use and service for three years after date of shipment. Quest
Technical Solutions will repair or replace without charge any equipment found to be
defective during the warranty period. Final determination of the nature and responsibility
for defective or damaged equipment will be made by Quest Technical Solutions
personnel.
All warranties hereunder are contingent upon proper use in the application for which the
product was intended and do not cover products which have been modified or repaired
without Quest Technical Solutions approval or which have been subjected to accident,
improper maintenance, installation or application, or on which original identification
marks have been removed or altered. This Limited Warranty also will not apply to
interconnecting cables or wires, consumables nor to any damage resulting from battery
leakage.
In all cases Quest Technical Solutions’ responsibility and liability under this warranty
shall be limited to the cost of the equipment. The purchaser must obtain shipping
instructions for the prepaid return of any item under this Warranty provision and
compliance with such instruction shall be a condition of this warranty.
Except for the express warranty stated above Quest Technical Solutions disclaims all
warranties with regard to the products sold hereunder including all implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness and the express warranties stated herein are in lieu of all
obligations or liabilities on the part of Quest Technical Solutions for damages including,
but not limited to, consequential damages arising out of/or in connection with the use or
performance of the Product.
 Loading...
Loading...