Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
Phili
MF RD700
Command Set
User & Reference Manual
User Manual
Revision 3.0
ps
Semiconductors
June 2005
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
CONTENTS
1 GENERAL INFORMATION 5
1.1 Scope 5
1.2 General description 5
2 MF RD700 COMMAND SET 7
2.1 General Description of serial communication 7
2.2 Overview of the delivered library stack 8
2.3 MfRC500 Interface wrappers 9
2.3.1 Mf500InterfaceOpen 9
2.3.2 Mf500InterfaceClose 10
3 MODULES 11
3.1 Administration Command Set 12
3.1.1 Included Functions 12
3.1.2 Function Desription 12
3.1.2.1 PcdGetRICVersion 12
3.1.2.2 PcdGetSnr 13
3.1.2.3 PcdReadE2 13
3.1.2.4 PcdReset 14
3.1.2.5 PcdRfReset 14
3.1.2.6 PcdSetTmo 15
3.1.2.7 PcdWriteE2 15
3.2 MIFARE® Classic Command Set 16
3.3 Handling the MIFARE Classic World 16
3.3.1 Included Functions 17
3.3.2 Function Description 18
3.3.2.1 Mf500PcdConfig 18
3.3.2.2 Mf500ActiveAntennaMasterConfig 18
3.3.2.3 Mf500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig 19
3.3.2.4 Mf500PiccAnticoll 19
3.3.2.5 Mf500PiccCommonRead 20
3.3.2.6 Mf500PiccCommonWrite 21
3.3.2.7 Mf500PiccHalt 22
3.3.2.8 Mf500PiccRead 22
3.3.2.9 Mf500PiccRequest 23
3.3.2.10 Mf500PiccSelect 24
2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.11 Mf500PiccValue 25
3.3.2.12 Mf500PiccValueDebit 26
3.3.2.13 Mf500PiccWrite 27
3.3.2.14 Mf500PiccWrite4 28
3.4 MIFARE® Authentication Procedures 29
3.4.1 Included Functions 29
3.4.2 Function Desription 30
3.4.2.1 Mf500PiccAuthE2 30
3.4.2.2 Mf500PiccAuthKey 31
3.5 MIFARE® Commands with calling compatible Interface 32
3.5.1 Inlcuded Functions 32
3.5.2 Function Description 32
3.5.2.1 Mf500PiccAuth 32
3.6 ISO 14443A Low Level Commands 33
3.6.1 Included Functions 33
3.6.2 Function Desription 34
3.6.2.1 Mf500PcdGetAttrib 34
3.6.2.2 Mf500PcdSetAttrib 35
3.6.2.3 Mf500PcdSetDefaultAttrib 36
3.6.2.4 Mf500PiccActivation 36
3.6.2.5 Mf500PiccActivateIdle 38
3.6.2.6 Mf500PiccActivateIdleLoop 39
3.6.2.7 Mf500PiccActivateWakeup 42
3.6.2.8 Mf500PiccCascAnticoll 43
3.6.2.9 Mf500PiccCascSelect 44
3.6.2.10 Mf500PiccCommonRequest 45
3.6.2.11 Mf500PiccExchangeBlock 46
3.7 Transparent Communication Channel between Host and Reader IC 47
3.7.1 Included Functions 47
3.7.2 Function Description 48
3.7.2.1 ExchangeByteStream 48
3.7.2.2 ReadRC 50
3.7.2.3 WriteRC 50
3.7.2.4 ReadMultiple 51
3.7.2.5 WriteMultiple 51
3.8 Utility Functions 52
3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.1
Included Functions 52
3.8.2 Function Desription 53
3.8.2.1 PcdEnableHighBaudRates 53
3.8.2.2 HostGetExecutionTime 53
3.8.2.3 HostTransTmrStart 54
3.8.2.4 HostTransTmrStop 54
3.8.2.5 Mf500HostCodeKey 55
3.8.2.6 Mf500PcdLoadKeyE2 55
3.8.2.7 PcdSetIdleMode 56
3.8.2.8 SwitchLED 56
3.8.2.9 DbgTrigger 57
3.8.2.10 StartDownload 57
3.8.2.11 PcdGetFwVersion 58
3.9 Self Test Functions 59
3.9.1 included Functions 59
3.9.2 Function Description 59
3.9.2.1 RicTestPcd 59
3.9.2.2 RicTestPicc 60
3.9.2.3 RicTestFlashNr 60
3.9.2.4 RicTestCommunication 61
4 RETURN VALUES OVERVIEW 62
4.1 Table of Return values 62
4.1.1 Common Communication Return Codes 62
4.1.2 Return Values’ Overview 63
5 REVISION HISTORY 68
Contact Information 70
4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
1 GENERAL INFORMATION
1.1 Scope
This document describes the functionality of the command set for MF RD700 ‘Pegoda’ reader. It include s the
functional description of the used commands and gives details, how to use or design-in this device from a
system and software viewpoint.
The default configuration for the MF RD700 uses the MF RC500 as the contactless reader IC.
In fact, the reader module can be used with all members of the new contactless reader IC family without any
additional hardware changes.
The command set defines all commands, which can be used by the different reader ICs as the MF RC530
and the MF RC531. These reader-ICs will be available soon to give the user the possibility to integrate these
ICs easy in the Pegoda environment. Consequently not all described commands are available in the
standard configuration of the Pegoda reader based on the MF RC500 reader IC.
These commands are marked in the description.
1.2 General description
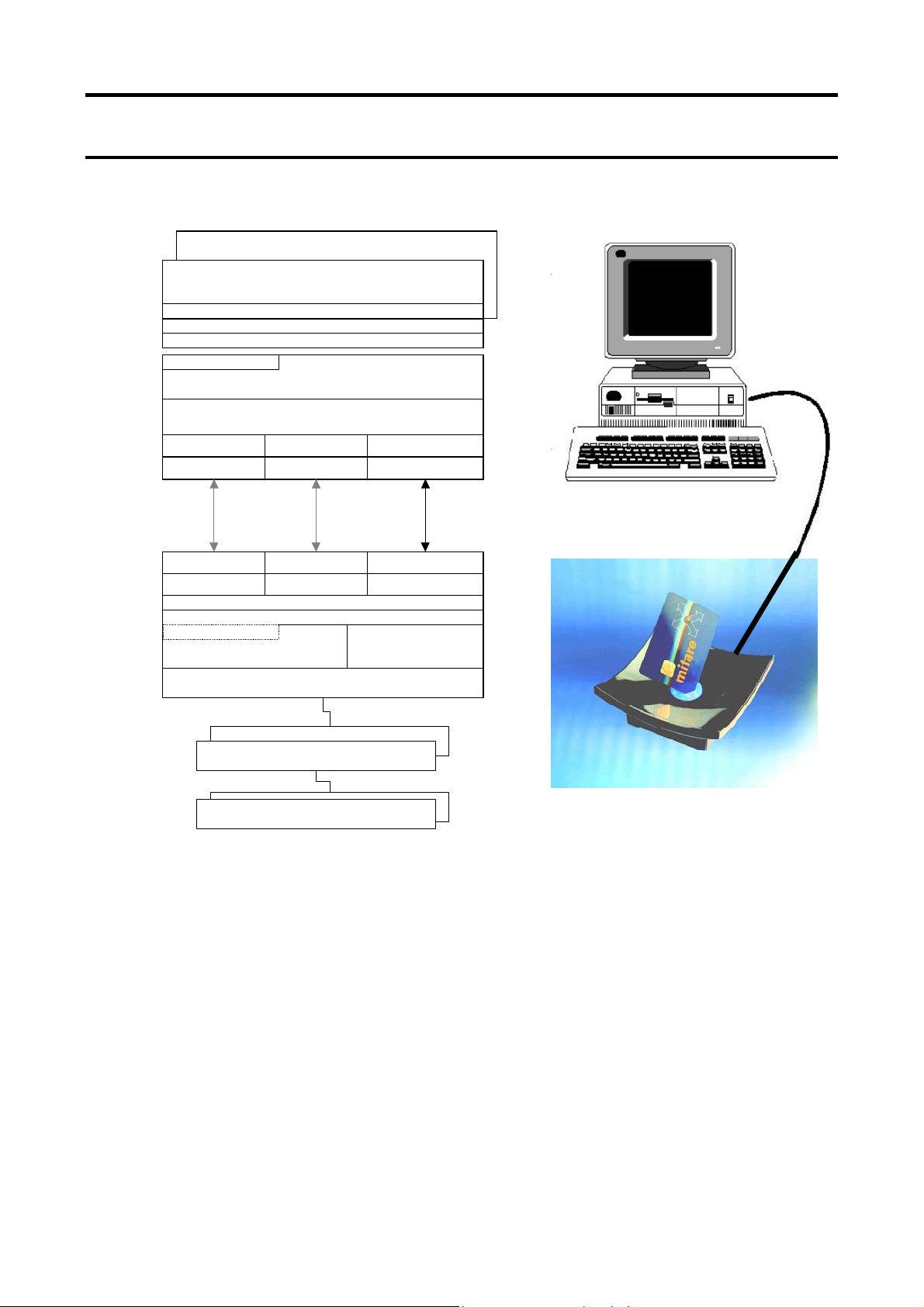
The MF RD700 Pegoda reader is ready to be connected to a PC.
Figure 1 shows the basic overview of the MF RD700’s software concept. Different levels of the PC libraries
can be identified:
Application Level
This level is user specific and might be used by the user to implement own applications and test
programs. The evaluation kit packages for the MF RC700 provide the MIFAREWND program and the
source code for the Rges program as example for small test programs on application level.
MF RD700 Command Set
This document describes the library giving the user the possibility to program an application to the
PEGODA reader. All necessary settings and command are explained in detail on the following pages.
HostRDCom
The library for the host to reader communication. This library establishes the communication between
the host and the reader. Default usage for the MF RD700 is the USB interface. Additionally RS232 and
IrDA are supported to give the user a large variety of interfaces. The description is included to that
package in the Application Note HostRDCom- User & Reference Manual.
The firmware of the MF RD700 covers the functionality of the basic function library of the MF RC 500.
This basic function library is described in the Application Note MIFARE® MF RC500 Basic F unction
Library.
The supported operating systems are limited to the Microsoft Windows Platform. Depending on the selected
connectivity type, Win98, Win2000 or Win NT 4.0 is supported. The content of this document should be
precise enough, to give the user the possibility writing own communication libraries for other operating
systems.
5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Application 2
Application 1
T= CL
MfG en eric
T=CL LL
RS232 API
RS232 Driver
RS232
MfRc500
RD700
Library Interface
HostRdCom
Sequenzer/Desequenzer
Generic Input/Output
IRDA API
IRDA Driver
IRDA
USB Protocol Driver
USB HW spec. Driver
USB
RS232 RX /T X
RS232 dep. access
T=CL
MIFARE LLL
IRDA RX/TX
IRDA dep. access
Read/W rite Memo ry
Sequenzer/Desequenzer
Shared Cmds
Read/W rite Memory
Reader IC
Antenna
Figure 1. General Software Overview
USB DMA
USB dep. access
6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
2 MF RD700 COMMAND SET
The following parts describe the MF RD700 command set in detail. The described functions are clustered in
different blocks as
general description of the serial interface
overview of the delivered library stack
MF Rc500 interface wrappers
General return values for the described functions are listed in chapter 4. Only relevant return values for the
explained commands are mentioned the description does not cover all communication-related errors.
2.1 General Description of serial communication
The MF RD700 reader can only be connected via serial data interfaces. The default configuration offers a
USB connection. Additionally, the command set includes additionally RS232 and IrDA interface to a host.
The serial data stream consists depend from the selected interface type frame- and transfer data.
Frame data depend on the selected interface
Transfer data depend only on the selected command
To explain this dependency, the expected serial transfer data stream is described at command level.
From a reader point of view the transfer data consists of an IN-transfer and an OUT-transfer.
IN-transfer data is sent from the host to the reader module.
OUT-transfer data is sent from the reader module to the host.
Additionally, the command code, which identifies the function at reader side is listed at each function.
Each function is described with the corresponding function prototype and stream data composition. The
number of bytes occupied by this parameter is written in brackets.
Multiple byte parameters are converted to the serial byte stream with the least significant byte first.
Example:
short value 0x0A05
is converted to
long value 0x04030201
is converted to
data[x] = 0x05
data[x+1] = 0x0A
data[x+3] = 0x04
7
data[x] = 0x01
data[x+1] = 0x02
data[x+2] = 0x03
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Note:
Pay attention, that the order of the parameter variables within the data stream may be different to the order in
the function prototype. The order of parameters in the function prototype is given by the logical matching of
the parameters. The data-stream’s order is given by data direction and data length. A word -aligned access
to multiple byte parameters is possible.
2.2 Overview of the delivered library stack
The RD700 command set and the HostRdCom libraries are necessary to access the reade r. All reader
commands are included in the RD700 command set. Therefore, the parameters of the functions are equal to
the parameters of the reader commands with the exception that the reader protocol has to be passed as first
parameter.
Example:
If the MF RC500’s basic function library command PcdWriteE2 to write data to the RC 500 EEPROM
signed char PcdWriteE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char length,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x24
IN startaddr (2) length (1) data (length)
OUT
Is called from the RD700 library, the corresponding interface looks like
signed short PcdWriteE2 (ProtocolBase* p_PB,
unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char length,
unsigned char * data)
Only the first parameter is additional and the return value range is extended to a short.
This conversion is done for any function in the Rd700 library.
The MFRC500 library encapsulates the interface handling to the application prog ramme r. At RC 500 level
the first parameter disappears and the interface changes to
signed short PcdWriteE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char length,
unsigned char * data)
which is similar to the reader command except the enlarged return value.
The MFRC500 library can only handle one reader for one application. Taking the advantage of the USB
interface offering the possibility to connect more than one reader to a PC, the user would probably like to
select one reader for his application. In this case the access to the HostRdCom interface is needed and the
additional first parameter is necessary.
If the MfRc500 library is used and more than one reader has to be connected to one PC, the first application
will select the first connected reader and second application the second one. You have no possibility to
change the order.
8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Note: In the following document the interface description for the Rd700 library has to be extended by the
interface handle and the enlarged return value. For the MfRc500 library the return value is extended
compared to the following description.
The MfRc500 library contains of two functions described in the chapter 2.3 covering the interface handling.
All other functions of this library and also of the Rd700 library are passed directly as reader commands to the
reader device.
2.3 MfRC500 Interface wrappers
As explained above, the MfRc500 library is a wrapper library over Rd700 and HostRdCom. In order to
provide a simpler (but less flexible) interface handling the library introduces two new functions.
Function name
Mf500InterfaceOpen
Mf500InterfaceClose
Table 2-1. MF RC500 Interface wrappers
2.3.1 MF500INTERFACEOPEN
signed char Mf500InterfaceOpen (unsigned long mode,
unsigned long options)
Parameters:
mode (IN) 4 bytes interface type description
0x00000030 USB
0x00000040 RS232
0x00000050 IrDA
signed char Mf500InterfaceOpen (unsigned long mode,
unsigned long options)
signed char Mf500InterfaceClose (void)
Function call
options (IN) 4 bytes interface options
Depending on the interface type, this parameter is used to specify additional parameters.
For USB and IrDA devices, this parameter is ignored.
For RS232 devices the COM-port can be specified e.g. 1 for COM1 or 2 for COM2.
Returns:
MI_OK
This function uses the HostRdCom interface to open a connection to the reader and use this handle for
following function calls of this library. Nearly all functions of the Rd700 library are equipped with a new
interface, where this handle is used.
9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
2.3.2 MF500INTERFACECLOSE
signed char Mf500InterfaceClose(void)
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK
This function corresponds to the Mf500InterfaceOpen function. Each time, the used interface should be
released; this function has to be called.
10
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3 MODULES
The MF RD700 command set contains of several modules covering different functionality:
Module Description
Administration Command set
Several Commands for reader IC administration and
configuration.
In order to support MIFARE
Command set, some of the Commands are split in a
MIFARE® Classics Command set
general interface and a special Mifare interface; both
have the same functionality with different parameter
settings.
MIFARE® Commands with calling compatible
Interface
ISO 14443A Low Level Commands
MIFARE® authentication procedure compatible to the
old reader devices
Specific ISO14443A commands not included in the
MIFARE
®
classic command set
Allows setting and resetting all registers and
Transparent Communication Channel between Ho st
exchanging a byte or bit stream with the tag.
and Reader IC
Utility Functions
Collection of utility functions for the microcontroller
environment
Self Test Functions MF RD700 Test Functions
Table 3-1. Modules
®
and ISO 14443-4
General return values for the described functions are listed in chapter 4. Only specific return values for the
explained functions are mentioned, the description does not cover all general communication related errors.
11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.1 Administration Command Set
The Administration Command Set covers several Commands for reader IC administration and configuration.
3.1.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name
PCDReset
PCDSetTmo
PCDGetSnr
PCDGetRICVersion signed char PcdGetRICVersion(unsigned char* version)
PCDReadE2
PCDWriteE2
PCDRFReset
Table 3-2. Administration Commands
Note: In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless, all received data are returned.
This feature helps to debug the errors. Even if all data seems to be received correctly (data is filled up with
reasonable values), a CRC, parity or other error could be reported.
signed char PcdReset (void)
signed char PcdSetTmo (unsigned long numberOfEtus)
signed char PcdGetSnr (unsigned char *snr)
signed char PcdReadE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char *data)
signed char PcdWriteE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char *data)
signed char PcdRfReset (unsigned short ms
Function call
unsigned char length,
unsigned char length,
3.1.2 FUNCTION DESRIPTION
3.1.2.1 PcdGetRICVersion
signed char PcdGetRICVersion (unsigned char * version)
Cmd-Code: 0x64
IN
OUT version (5)
Parameters:
snr (OUT) 5 bytes reader type ID
Returns:
MI_OK
The reader type ID depends on the current used reader IC. Please refer to the reader ICs data sheet.
12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.1.2.2 PcdGetSnr
signed char PcdGetSnr (unsigned char * snr)
Cmd-Code: 0x22
IN
OUT snr (4)
Parameters:
snr (OUT) 4 bytes serial number of the reader IC
Returns:
MI_OK
This function reads out 4 bytes serial number of the reader IC. The serial number is unique for all
delivered readers.
3.1.2.3 PcdReadE2
signed char PcdReadE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char length,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x23
IN startaddr (2) length (1)
OUT data (length)
Parameters:
startaddr (IN) EEPROM memory start address, Defines the start address for the read
operation
length (IN) number of data bytes to read
data (OUT) is a pointer to the length bytes long data buffer, to store the read data.
Returns:
CRRC
This function reads out data stored in the reader IC’s EERPOM beginning at the address ‘startaddr’. The
number of bytes to be read is given by the variable length and the read out data are stored in the
provided data buffer.
13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.1.2.4 PcdReset
signed char PcdReset (void)
Cmd-Code: 0x21
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK
MI_RESETERR error while resetting the reader IC
The MF RC500 reset pin is connected to the microcontroller and a reset can be performed. After each
reset, the automatic interface recognition of the reader IC is activated. Both, resetting the reader IC and
determining the interface is done by this function.
3.1.2.5 PcdRfReset
signed char PcdRfReset (unsigned short ms)
Cmd-Code: 0x20
IN ms (2)
OUT
Parameters:
ms (IN) time period in milliseconds. Defines the switch off time of the reader IC's RF-field in
milliseconds.
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function turns off the RF-field for a specified time in milliseconds by setting the variable ms.
Elapsing this time the RF-field is turned on approximately 1 millisecond later.
If the time variable ms is set to 0, the RF-field is turned off.
14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.1.2.6 PcdSetTmo
signed char PcdSetTmo (unsigned long numberOfEtus)
Cmd-Code: 0x27
IN numberOfEtus (4)
OUT
Parameters:
numberOfEtus (IN) Range [1..4294000] timeout period calculated in etu's of 9.44 us
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function sets a RF communication time out value. Every communication between the reader IC and
the card is controlled by a timeout value.
The timeout value is measured between the last bit sent to the tag and the first bit received from the tag.
3.1.2.7 PcdWriteE2
signed char PcdWriteE2 (unsigned short startaddr,
unsigned char length,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x24
IN startaddr (2) length (1) data (length)
OUT
Parameters:
startaddr (IN) EEPROM memory start address. Defines the start address for the write operation
length (IN) number of data bytes to write
data (IN) is a pointer to the length bytes long data buffer containing the data to be written to the
EEPROM.
Returns:
CRRC
This function writes a given length of data bytes stored in the data buffer to the reader IC's EEPROM
beginning at address startaddr.
15
Page 16
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.2 MIFARE
®
Classic Command Set
In order to support Mifare and ISO 14443-4 Command set, some of the Commands are split in a general
interface and a special Mifare interface; both have the same functionality with different parameter settings.
3.3 Handling the MIFARE
Cards of the MIFARE
instructions. The MF RC500 fully supports communication with these cards. Using the functions in this library
MIFARE
Classic instructions have to be sent to the card in correct sequences. To apply these sequences in
Classic World
Classic family (MIFARE Standard, MIFARE Light) support a defined set of
the appropriate way is the responsibility of the application software.
For further information on the cards command set please refer to the according product description of the
MIFARE Standard or the MIFARE Light IC.
The MIFARE
of the MIFARE
with a grey background in the following table. Having identified and selected the MIFARE
MIFARE
Classic command set can be divided in to 2 parts. The identification and selection procedure
protocol is implemented in an ISO14443A compliant way. These commands are marked
specific authentication procedure can be started. Finally, having passed the authentication
card the
procedure memory operations are allowed. In the following table the MIFARE® command set is named
according to the MIFARE® card IC specification.
Command Abbr. Code Argument Response Possible After
Request ALL ATR 52 None Tag Type (ATQ) card's POR, HALT,
communication failure
Request IDLE ATR 26 None Tag Type (ATQ) card's POR, communication
failure
Anticollision AC 93,95,
Select SEL 93,95,
Authentication AUT 60
(optional parts of the
97
card's serial number)
Card serial number Answer to select
97
(rest of) card's
serial number
(ATS)
ATR, AC
ATR, AC
Block address Acknowledge SEL, AUT, RD, WR, TRANS
61
Read RD 30 Block address 16 byte data
block
Write WR A0 Block address and
Acknowledge SEL*), AUT, RD, WR,
16 byte data block
Decrement DEC C0 Block address and
Acknowledge SEL*), AUT, RD, WR,
4 byte value
Increment INC C1 Block address and
Acknowledge SEL*), AUT, RD, WR,
4 byte value
Restore REST C2 Block address and
Acknowledge SEL*), AUT, RD, WR,
4 byte dummy value
SEL*), AUT, RD, WR,
TRANS
TRANS
TRANS
TRANS
TRANS
Transfer TRANS B0 Block address Acknowledge DEC, INC, REST
Halt HALT 50 Dummy address None SEL, AUT, RD, WR, TRANS
Table 3-3. MIFARE® Classic Command Set
16
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
A command can be executed successfully only if it is carried out after a function listed in the column
'Possible After'. Otherwise a failure is returned and the card falls back into the initial state.
*)
Although the command might be executed after a SEL command, it will fail since the card is not
authenticated.
3.3.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name
MfPcdConfig
Mf500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig
Mf500ActiveAntennaMasterConfig
Mf500PiccRequest
Mf500PiccAnticoll
Mf500PiccSelect
Mf500PiccRead
Mf500PiccCommonRead
Mf500PiccWrite
Mf500PiccWrite4
Mf500PiccCommonWrite
char Mf500PiccValue
Mf500PiccValueDebit
Mf500PiccHalt
Function call
signed char Mf500PcdConfig (void)
signed char Mf500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig (void)
signed char Mf500ActiveAntennaMasterConfig (void
signed char Mf500PiccRequest (unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char *atq)
signed char Mf500PiccAnticoll (unsigned char bcnt,
unsigned char *snr)
signed char Mf500PiccSelect (unsigned char *snr,
unsigned char *sak)
signed char Mf500PiccRead (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *data)
signed char Mf500PiccCommonRead (unsigned char cmd,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char datalen,
unsigned char *data)
signed char Mf500PiccWrite (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *data)
signed char Mf500PiccWrite4 (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *data)
signed char Mf500PiccCommonWrite (unsigned char cmd,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char datalen,
unsigned char *data)
signed char Mf500PiccValue (unsigned char dd_mode,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *value,
unsigned char trans_addr)
signed char Mf500PiccValueDebit (unsigned char dd_mode,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *value)
signed char Mf500PiccHalt (void)
Table 3-4, MIFARE® Commands
17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2 FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
3.3.2.1 Mf500PcdConfig
signed char Mf500PcdConfig (void)
Cmd-Code: 0x10
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK
MI_RESETERR
MI_INTERFACEERR
This function has to be called before the first data is written to the MF RC500 in order to perform the
internal configuration. A reset of the reader IC is done and several registers are set.
3.3.2.2 Mf500ActiveAntennaMasterConfig
signed char Mf500ActiveAntennaMasterConfig(void)
Cmd-Code: 0x2A
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function initializes the master reader IC to use it in an active antenna configuration.
This function is additional to the standard configuration Mf500PcdConfig.
The MF RC500 reader IC configured in the master configuration is able to communicate with another
MF RC500 configured in the slave configuration via the digital MFin and MFout pins. The
corresponding slave configuration routine for the slave MF RC 500 can be initialized by the function
MF500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig.
The active antenna configuration itself is described in the datasheet for the MF RC500.
18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.3 Mf500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig
signed char Mf500ActiveAntennaSlaveConfig(void)
Cmd-Code: 0x2B
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
CRRC
The MF RC500 reader IC configured in the slave configuration is able to communicate with another MF
RC500 configured in the master configuration via the digital MFIn and MFOut pins.
The master MF RC500 reader IC sends commands and data using the MFOut pin. The slave reader IC
receives the data via MFIn pin. Sending data back from the slave IC is done connecting the MFOut for
the slave IC and MFIn for the master MF RC500.
In this configuration the slave module can not be initialized by the microcontroller because only the MF
In/Out interface is connected between both MF RC500's. The slave module has to be initialized before
the connection is established. During this initialization the appropriate parameter settings are written to
the E2PROM. After POR (power on reset) the IC reads these settings and initializes itself automatically
as a slave IC.
Additionally, it is possible to connect the slave reader IC to the µC to have the possibility to change the
setting in the application later. ´
3.3.2.4 Mf500PiccAnticoll
signed char Mf500PiccAnticoll (unsigned char bcnt, unsigned char * snr)
Cmd-Code: 0x12
IN bcnt (1)
IN/OUT snr (4)
OUT
Parameters:
bcnt (IN) Range: [0..32] Number of SNR-bits that are known (default value is 0);
snr (IN/OUT) 4 bytes serial number (number of bits, which are known and indicated by bcnt
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_SERNRERR SNR Check byte does not correspond to SNR
19
Page 20
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
This function calls MF500PiccCascAnticoll with a select_code 0x93 to perform the anticollision for
MIFARE
3.3.2.5 Mf500PiccCommonRead
signed char Mf500PiccCommonRead (unsigned char cmd,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char datalen,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x28
IN cmd (1) addr (1) datalen (1)
OUT data (datalen)
Parameters:
cmd read command byte
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type]. Addresses the card's block address from which data shall be
®
Classic card ICs.
PICC_READ16
read. For MIFARE® Standard cards, addr can take a value from 0 to 63 (255 for Mifare Pro), for
other card types refer to the according product description.
datalen length of data bytes array
data (OUT) is a pointer to the datalen byte data block read from the card's memory
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
MI_BYTECOUNTERR wrong number of bytes received
This function directly reads out a datalen block from the specified card's blockaddress addr.
20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.6 Mf500PiccCommonWrite
signed char Mf500PiccCommonWrite (unsigned char cmd,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char datalen,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x1F
IN cmd (1) addr (1) datalen (1) data (datalen)
OUT
Parameters:
cmd write command byte
PICC_WRITE16
PICC_WRITE4
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] Addresses the card's block address to which data shall be
written. For MIFARE® Standard cards, addr can take values from 0 to 63 (255 for Mifare
Pro), for other card types please refer to the according product description.
datalen length of data bytes array
data (OUT) is a pointer to the datalen bytes data block, which should be written to the card
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_WRITEERR error while writing data
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
This function writes a datalen bytes block to the specified card's block address addr. Having sent the
command the card indicates with an ACK, that the direct memory access is possible. Having received
the ACK, the MF RC500 sends the datalen bytes data block and waits for an ACK again. In case of an
error a return code according to the MF RC500's error flags is generated.
Note:
The card type has to support the selected datalen e.g. Mifare® UltraLight for a 4 bytes write
21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.7 Mf500PiccHalt
signed char Mf500PiccHalt (void)
Cmd-Code: 0x1D
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
CRRC
This function sets a MIFARE® Classic compatible card into the halt state. Having send the command to
the card, the function does not expect a cards response. Only in case of any error the card sends ba ck
a NACK. If the command was successful, the card does not return with an ACK. Thus, the function is
successful, if a timeout in the MF RC500 is indicated.
3.3.2.8 Mf500PiccRead
signed char
Mf500PiccRead (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x19
IN addr (1)
OUT data (16)
Parameters:
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type]. Addresses the card's block address from which data shall be
read. For MIFARE® Standard cards, addr can take a value from 0 to 63 (255 for Mifare
Pro), for other card types, refer to the according product description.
data (OUT) is a pointer to the 16 byte data block read from the card's memory
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
MI_BYTECOUNTERR wrong number of bytes received
This function directly reads out a 16 long byte block from the specified card's blockaddress addr.
22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.9 Mf500PiccRequest
signed char Mf500PiccRequest (unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char * atq)
Cmd-Code: 0x11
IN req_code (1)
OUT atq (2)
Parameters:
rq_code (IN)
PICC_REQALL Request Code 52hex
PICC_REQIDL Request Code 26hex
atq (OUT) 16 bit ATQ (answer to request).
atq[0] .. LSByte;
atq[1] .. MSByte
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
This function accesses the reader module and activates sending the REQ code to the MIFARE® card.
Having sent the command to the card the function waits for the card's answer.
Note:
This function has an identical functionality to the Mf500PiccCommonRequest function, which is
described by ISO 14443A command set. Depending on the Request Code and the state of the cards in
the field all cards reply with their Tag-Type synchronously. The time between end of the Request
command and start of reply of the card is exactly 8 * 9.44 us long. The Tag-Type field is 16 bits long and
only one bit out of 16 is set.
When cards with different Tag-Types are in field, the MF RC500 is able to identify all types of cards in
the RF-field. Further more, the Tag-Type is used to identify a card with cascaded serial number. Double
and Triple serial numbers are possible.
Relevant bit positions LSByte:
[8..7] UID size
00 standard 32 bit long UID
01 UID size double (56 bit long)
10 UID size triple (80 bit long)
[5..1] if any bit is set, frame anticollision is supported; tag type recognition
The complete MSByte is RFU.
Note:
Future cards will work also with other request codes.
23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.10 Mf500PiccSelect
signed char Mf500PiccSelect (unsigned char * snr,
unsigned char * sak)
Cmd-Code: 0x13
IN snr (4)
OUT sak (1)
Parameters:
snr (IN) 4 bytes serial number
sak (OUT) 1 byte select acknowledge
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
This function selects a card by the specified serial number. All other cards in the field fall back into the
idle mode and they are not longer involved during the communication. The actua l select procedure is
done by the function Mf500PiccCascSelect, which is called with select_code 0x93.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.11 Mf500PiccValue
signed char Mf500PiccValue (unsigned char dd_mode,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char * value,
unsigned char trans_addr)
Cmd-Code: 0x1B
IN dd_mode (1) addr (1) value (4) trans_addr (1)
OUT
Parameters:
dd_mode (IN) selects the value format related operation
PICC_INCREMENT Increment
PICC_DECREMENT Decrement
PICC_RESTORE Restore
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] Addresses the card's data block address. The card IC internally
reads the stored value and takes it as initial value for the calculation. For MIFARE
standard cards, addr can take a value from 0 to 63, for MIFARE® Pro cards, addr can
take values from 0 to 255, for other card types please refer to the according product
description.
value (IN) is a pointer to a 4 byte positive value.
trans_addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] Addresses the card's block address to which the result of
the calculation shall be transferred. For MIFARE® standard cards, trans_addr can take
a value from 0 to 63 (255 for Mifare Pro), for other card types please refer to the
according product description.
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_VALERR wrong value format
MI_CODEERR
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
®
This function performs the INCREMENT, DECREMENT and RESTORE command. Precondition for
success is that the data block is formatted as value block.
For INCREMENT and DECREMENT, the command doesn't write back the value to the memory location
directly, but loads the transfer buffer with the increased value, which could be transferred to any
authenticated block by the TRANFER command.
25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
The RESTORE command loads the transfer buffer with the value stored at data block address, while
the given value is only a dummy value, which only have to be in valid range. With a subsequent
TRANSFER command a backup management for Value Blocks is established.
After sending the command to the card the function waits for the card's answer. In case of an error
Mf500PiccValue() generates a return code according to the MF RC500's error flags, otherwise the
value is sent to the card and then it waits for a NACK. As an exception in the protocol step in case of an
error only a NACK is sent back by the card. Thus, the function is successful, if a time out occurs.
After the calculation is done, a TRANSFER is automatically performed to the block address trans_addr.
After sending the command to the card the function waits for the card's answer and generates a return
code according to the MF RC500's error flags. A TRANSFER command is only possible directly after a
RESTORE, INCREMENT or DECREMENT command.
The value inside a Value Block is four bytes wide and stored tow times in normal and one time in bitinverted manner for data security issues. Additionally the initial address of the Value Block is stored two
times normal and two times bit-inverted. In case of a backup of a Value Block, this address contains the
original address of the Value Block.
Note: Only positive numbers are allowed for the parameter value.
3.3.2.12 Mf500PiccValueDebit
signed char Mf500PiccValueDebit (unsigned char dd_mode,
unsigned char addr,
unsigned char * value)
Cmd-Code: 0x1C
IN dd_mode (1) addr (1) value (4)
OUT
Parameters:
dd_mode (IN) PICC_DECREMENT only decrement operations are allowed
addr (IN) Range [card type dependent] address of the block on the card with which calculation sh all
be performed. A valid address range can be obtained from the card description.
value (IN) is a pointer to a 4 byte positive value.
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_VALERR wrong value format
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
This function executes calculations on value debit blocks with cards, that support automatic transfer
(MIFARE light, MIFARE PLUS, MIFARE PRO, MIFARE PROX, ..).
Having sent the command to the card the function waits for the card's answer. In case of an error, it
generates a return code according to the MF RC500's error flags.
3.3.2.13 Mf500PiccWrite
signed char Mf500PiccWrite (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x1A
IN addr (1) data (16)
OUT
Parameters:
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] Addresses the card's block address to which data shall be
written. For MIFARE® Standard cards, addr can take values from 0 to 63 (255 for Mifare
Pro), for other card types please refer to the according product description.
data (OUT) is a pointer to the 16 byte data block, which should be written to the card
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_WRITEERR error while writing data
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
This function writes a 16 byte long block to the specified card's block address addr. Having sent the
command the card indicates with an ACK, that the direct memory access is possible. Having received
the ACK, the MF RC500 sends the 16 bytes data block and waits for an ACK again. In case of an error
a return code according to the MF RC500's error flags is generated.
27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.3.2.14 Mf500PiccWrite4
signed char Mf500PiccWrite4 (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char * data)
Cmd-Code: 0x1E
IN addr (1) data (4)
OUT
Parameters:
addr (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] Addresses the card's block address to which data shall be
written.
data (OUT) is a pointer to the 4 byte data block, which should be written to the card
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_NOTAUTHERR not authenticated for this sector
MI_WRITEERR error while writing data
MI_CODINGERR wrong coding of 8 bit ack/nack
MI_CODEERR
This function writes a 4 byte block to the specified card's block address addr. Having sent the command
the card indicates with an ACK, that the direct memory access is possible. Having received the ACK,
the MF RC500 sends the 4 bytes data block and waits for an ACK again. In case of an error a return
code according to the MF RC500's error flags is generated.
Note:
The card type has to support the 4 bytes write e.g.. Future card ICs may support that command.
28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.4 MIFARE
The Crypto1 functionality is based on a stream cipher with a key length of 48 bits, called Master Keys. To
access data of a MIFARE® Classic card, passing the authentication is needed For a successful ca rd
authentication and access to the card's data, the correct Master Key has to be stored within the reader IC.
After the card's selection as defined in ISO14443A the user has the possibility to start the authentication
according to the MIFARE® Classic command set.
The Crypto1 authentication is a mutual 3-pass authentication. This procedure is done automatically by
executing the Authent1- and the Authent2-Commands. During the card authentication procedure, the stream
cipher generator is initialized. The communication with a MIFARE® Classic card following a successful
authentication is encrypted.
During the authentication command the reader IC reads the Master Key from the internal Master Key Buffer.
The Master Key is always taken from the Master Key Buffer. Therefore the commands for Crypto1
authentication do not require addressing of a Master Key. The user has to ensure that the correct Master
Key is prepared in the Master Key Buffer before the card authentication is triggered.
The Master Key Buffer can be loaded
from the E²PROM
directly from the µ-Processor via the FIFO-Buffer
The Master Keys have to be coded in a special way, therefore a convenience function is provided.
®
Authentication Procedures
3.4.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name
Mf500PiccAuthE2
Mf500PiccAuthKey
Table 3-5. MIFARE® authentication procedures
Function call
signed char Mf500PiccAuthE2 (unsigned char auth_mode,
unsigned char *snr,
unsigned char key_sector,
unsigned char block)
signed char Mf500PiccAuthKey (unsigned char auth_mode,
unsigned char *snr,
unsigned char *keys,
unsigned char sector)
29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.4.2 FUNCTION DESRIPTION
3.4.2.1 Mf500PiccAuthE2
signed char Mf500PiccAuthE2 (unsigned char auth_mode,
unsigned char * snr,
unsigned char key_sector,
unsigned char block)
Cmd-Code: 0x15
IN auth_mode (1) snr (4) key_sector (1) block(1)
OUT
Parameters:
auth_mode (IN) selects master key A or master key B
PICC_AUTHENT1A
PICC_AUTHENT1B
snr (IN) 4 byte serial number of the card, that should be authenticated
key_sector (IN) Range [0..15] specifies the EEPROM address where the keys are stored in the MF
RC 500
block (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] addresses the block address on the card, which shall be
authenticated. For MIFARE standard cards, addr can take a value from 0 to 63, for
other card types please refer to the according product description.
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_AUTHERR wrong keys for selected card
MI_KEYERR error while loading keys
This function authenticates one card's sector using the specified mode. After sending the command to
the card the function waits for the card's answer. The keys for authentication have to be stored at the
corresponding location in the E2PROM.
30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.4.2.2 Mf500PiccAuthKey
signed char Mf500PiccAuthKey (unsigned char auth_mode,
unsigned char * snr,
unsigned char * keys,
unsigned char sector)
Cmd-Code: 0x18
IN auth_mode (1) snr (4) keys (12) sector(1)
OUT
Parameters:
auth_mode (IN) selects master key A or master key B
PICC_AUTHENT1A
PICC_AUTHENT1B
snr (IN) 4 byte serial number of the card, which should be authenticated
keys (IN) 12 bytes coded master keys for card authentication
block (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] addresses the card's block address, which shall be
authenticated. For MIFARE® Standard cards, block can take a value from 0 to 63, for
other card types please refer to the according product description.
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR wrong number of bits received
MI_AUTHERR wrong keys for selected card
MI_KEYERR error while loading keys
This function authenticates one card's sector using keys stored in the µController. The keys are first
loaded to the reader module and used for authentication of the specified sector. In order to get the
required keys coded, the function Mf500HostCodeKey has to be used.
31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.5 MIFARE
®
Commands with calling compatible Interface
Former reader IC's had different programming interfaces especially concerning the authentication proce dure.
In order to provide a "soft" migration of existing sources to this reader IC, some functions included into the
programming interface.
3.5.1 INLCUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name Function call
signed char Mf500PiccAuth (unsigned char auth_mode,
Mf500PiccAuth
unsigned char key_sector,
unsigned char block)
Table 3-6. MIFARE® commands with calling compatible interface
3.5.2 FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
3.5.2.1 Mf500PiccAuth
signed char Mf500PiccAuth (unsigned char auth_mode,
unsigned char key_sector,
unsigned char block)
Cmd-Code: 0x14
IN auth_mode(1) key_sector(1) block(1)
OUT
Parameters:
auth_mode (IN) selects master key A or master key B
PICC_AUTHENT1A
PICC_AUTHENT1B
key_sector (IN) Range [0..15] specifies the key RAM address from which the data should be taken
block (IN) Range [0..dep.card type] addresses the card's block address on the card, which shall be
authenticated. For MIFARE® Standard cards, block addr can take a value from 0 to 63,
for other card types please refer to the according product description.
Returns:
CRRC
This function authenticates one card's sector (according to the block address) u s ing the specified
master key A or B, addressed with auth_mode. Having sent the command to the card the function waits
for the card's answer. This function is calling compatible with authentication fun ctions former reader
IC's. The keys are stored by the microcontroller, which should be capable for the key management.
32
Page 33
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6 ISO 14443A Low Level Commands
The ISO14443A defines several basic communication command s. Parts of the ISO14443A command set are
part of the MIFARE
®
classic command set described in the MIFARE® chapter and commands to establish an
open protocol based on the ISO14443 part 4. The T=CL implementation is based on a High Level
Programming Interface to the application and a Low Level Command Interface to the dedicated reader IC.
The implementation of these Low Level Commands is the only part, which depends on the reader IC
therefore these functions are treated in this document.
3.6.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name Function call
Mf500PcdGetAttrib
signed char Mf500PcdGetAttrib(
unsigned char *FSCImax,
unsigned char *FSDImax,
unsigned char *DSsupp,
unsigned char *DRsupp,
unsigned char *DREQDS)
Mf500PcdSetAttrib
signed char Mf500PcdSetAttrib (unsigned char DSI,
unsigned char DRI)
Mf500PcdSetDefaultAttrib
Mf500PiccCommonRequest
signed char Mf500PcdSetDefaultAttrib (void)
signed char Mf500PiccCommonRequest (
unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char *atq)
Mf500PiccCascAnticoll
signed char Mf500PiccCascAnticoll (
unsigned char select_code,
unsigned char bcnt,
unsigned char *snr)
Mf500PiccCascSelect
signed char Mf500PiccCascSelect (
unsigned char select_code,
unsigned char *snr,
unsigned char *sak)
Mf500PiccActivation
signed char Mf500PiccActivation(
unsigned char ctl_flag,
unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char *br,
unsigned char *atq,
unsigned char *sak,
unsigned char *uid,
unsigned char *uid_len,
unsigned char *script,
unsigned short script_len,
unsigned char *resp,
unsigned short *resp_len,
unsigned char sec)
signed char Mf500PiccActivateIdle (
Mf500PiccActivateIdle
*
unsigned char br,
unsigned char *atq,
unsigned char *sak,
unsigned char *uid,
unsigned char *uid_len)
*
Mf500PiccActivateIdleLoop
signed char Mf500PiccActivateIdleLoop (
unsigned char br,
33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
unsigned char *atq,
unsigned char *sak,
unsigned char *uid,
unsigned char *uid_len,
unsigned char sec)
signed char Mf500PiccActivateWakeup (
unsigned char br,
unsigned char *atq,
unsigned char *sak,
unsigned char *uid,
unsigned char uid_len)
signed char Mf500PiccExchangeBlock (
unsigned char *send_data,
unsigned short send_bytelen,
unsigned char *rec_data,
unsigned short *rec_bytelen,
unsigned char append_crc,
unsigned long timeout)
Mf500PiccActivateWakeup
Mf500PiccExchangeBlock
Note: All functions marked with an
*
Table 3-7. ISO14443A Command Set
*
are no longer available.
3.6.2 FUNCTION DESRIPTION
3.6.2.1 Mf500PcdGetAttrib
signed char Mf500PcdGetAttrib (unsigned char *FSCImax,
unsigned char *FSDImax,
unsigned char *DSsupp,
unsigned char *DRsupp,
unsigned char *DREQDS)
Cmd-Code: 0x47
IN
OUT FSCImax (1) FSDImax (1) DSsupp (1) DRsupp (1) DREQDS (1)
Parameters:
FSCImax (OUT) Frame Size Integer PICC -> PCD max
0 ... 16 Bytes 5 ... 64 Bytes
1 ... 24 Bytes 6 ... 96 Bytes
2 ... 32 Bytes 7 ... 128 Bytes
3 ... 40 Bytes 8 ... 256 Bytes
4 ... 48 Bytes 9-F ... RFU > 256 Bytes
FSDImax (OUT) Frame Size Integer PCD -> PICC max
0 ... 16 Bytes 5 ... 64 Bytes
1 ... 24 Bytes 6 ... 96 Bytes
2 ... 32 Bytes 7 ... 128 Bytes
3 ... 40 Bytes 8 ... 256 Bytes
34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
4 ... 48 Bytes 9-F ... RFU > 256 Bytes
DSsupp (OUT) Supported Divide rs PICC -> PCD
0 ... 106 kBaud 2 ... 424 kBaud
1 ... 212 kBaud 3 ... 848 kBaud
DRsupp (OUT) Supported Dividers PCD -> PICC
0 ... 106 kBaud 2 ... 424 kBaud
1 ... 212 kBaud 3 ... 848 kBaud
DREQDS (OUT)
1 .. send and receive bauderates have to be equal
0 .. different send and recive baudrates are possible
Returns:
This function returns the device capabilities of the reader.
Note:
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda does not support the Higher
Baudrates.
For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
3.6.2.2 Mf500PcdSetAttrib
signed char Mf500PcdSetAttrib (unsigned char DSI,
unsigned char DRI)
Cmd-Code: 0x46
IN DSI (1) DRI (1)
OUT
Parameters:
DRI (IN) valid divider PC D -> PICC
0 ... 106 kBaud 2 ... 424 kBaud
1 ... 212 kBaud 3 ... 848 kBaud
DSI (IN) valid divider PICC -> PCD
0 ... 106 kBaud 2 ... 424 kBaud
1 ... 212 kBaud 3 ... 848 kBaud
Returns:
MI_OK attributes set
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED wrong or not supported baudrate ID
35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Set divider for communication baud rate on reader side.
Note:
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda does not support the Higher
Baudrates.
For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
3.6.2.3 Mf500PcdSetDefaultAttrib
signed char Mf500PcdSetDefaultAttrib (void)
Cmd-Code: 0x45
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK attributes set
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED wrong or not supported baudrate ID
Set MIFARE PCD (Proximity Coupling Device) with default values for the baud-rate divider (106 kBaud).
3.6.2.4 Mf500PiccActivation
signed char Mf500PiccActivation(unsigned char ctl_flag,
unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char *br,
unsigned char *atq,
unsigned char *sak,
unsigned char *uid,
unsigned char *uid_len,
unsigned char *script,
unsigned short script_len,
unsigned char *resp,
unsigned short *resp_len,
unsigned char sec)
Cmd-Code: 0x4A
IN br (1) ctl_flag (1) req_code (1) sec (1) uid_len (1) uid (10) script_len (2) script (script_len)
OUT br (1) atq (2) sak (1) uid_len(1) uid (10) resp_len (2) resp (resp_len)
Parameters:
ctl_flag (IN) should be 0x00 - RFU
req_code (IN)
PICC_REQALL Request Code 52hex
PICC_REQIDL Request Code 26hex
br (IN/OUT) Baudrate for MIFARE® Higher Baudrate communication
0 106 kBaud
36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
1 212 kBaud
2 424 kBaud
3 848 kBaud
The baudrate parameter defines the highest baudrate, which should be selected. In addition to
this parameter, the lower communication speed of both for send and receive of the reader and
the supported baudrates, which are indicated by the ATQ bytes are considered during baudrate
selection. The result of this selection is returned. That means, that the value passed to this
function only defines the highest selected baudrate. At the end, the selected baudrate is returned
by the function.
br DSI reader DRI reader ATQ bits selected baudrate
0 X X XXX 106 kBaud
X 0 X XXX 106 kBaud
X X 0 XXX 106 kBaud
X X X 000 106 kBaud
1 >= 1 >=1 XX1 212 kBaud
>= 1 1 >=1 XX1 212 kBaud
>=1 >=1 1 XX1 212 kBaud
>=1 >=1 >=1 001 212 kBaud
2 >= 2 >=2 X1X 424 kBaud
>= 2 2 >=2 X1X 424 kBaud
>=2 >=2 2 X1X 424 kBaud
>=2 >=2 >=2 01X 424 kBaud
3 3 3 1XX 848 kBaud
atq (OUT) Answer to Request
sak (OUT) Select acknowledge
uid (IN/OUT) up to 10 bytes UID. Please make sure, that the longest possible UID can be stored in
the array, that means the array should have at least 10 bytes storage. The UID can also
be provided to the the function, in this case the uid_len is 4, 7 or 10 and the uid
parameter stores all bytes of the uid. If the UID is passed to the function, no anticollision
will be performed. Only request and select are necessary.
uid_len (IN/OUT) range [0,4,7,10] no other values are permitted. Length of the UID
script (IN) data bytes, which should be sent to the PICC after selection
script_len (IN) number of data bytes, which should be sent. If 0 bytes are passed to the function, no
command will be transmitted to the PICC
resp (OUT) response from PICC after sending script data
resp_len (IN/OUT) number of bytes, which are received from the PICC. Before calling the function, this
parameter must be initialized to the maximum number of bytes expected from the
PICC. This is necessary, in order to prevent a buffer overflow.
37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
sec (IN) range [1..60] seconds, timeout value in seconds. If the value 0 is passed to the function, only
one request will be issued. If it fails, the function will return immediately, no retries will be
performed.
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_NOBITWISEANTICOLL non of the responding tags is supporting bitwise anticollision
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED br parameter receives a wrong value
MI_SERNRERR either wrong SNR Check byte or wrong cascading level
This function performs a request command according to the req_code, which is passed to the function.
In the case, that no card could be detected, the parameter sec controls further behavior. If sec is 0, the
function will return immediately. If sec is larger than 0, the function tries to detect a card for this period of
seconds.
Depending on the desired baudrate the anticollision and select supports cascad ed serial numbers. After
selection of the card, there is the possibility to issue an additional command. The response from the
card is returned to the calling function without interpretation.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda CL RD 700 does not support the
Higher Baudrates. Higher Baudrates are supported by MF RC 530, MF RC 531 and MF RC 632,
e.g. Pegoda CL RD 701. The command PcdEnableHighBaudRates has to be executed prior in order
to enable the higher baudrates.
For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
3.6.2.5 Mf500PiccActivateIdle
signed char Mf500PiccActivateIdle (unsigned char br,
unsigned char * atq,
unsigned char * sak,
unsigned char * uid,
unsigned char * uid_len)
Cmd-Code: 0x43
IN br (1)
OUT atq (2) sak (1) uid_len(1) uid (uid_len)
Parameters:
br (IN) Baudrate for MIFARE® Higher Baudrate communication
0 106 kBaud
38
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
1 212 kBaud
2 424 kBaud
3 848 kBaud
atq (OUT) Answer to Request
sak (OUT) Select acknowledge
uid (OUT) up to 10 bytes UID
uid_len (OUT) length of the UID
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_NOBITWISEANTICOLL non of the responding tags is supporting bitwise anticollision
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED br parameter receives a wrong value
MI_SERNRERR either wrong SNR Check byte or wrong cascading level
Attention: Beginning with release 1.12 of the reader firmware, this function is no longer valid. The
functionality is provided by the function Mf500PiccActivation. For compatibility purposes, this function is
redirected to the Mf500PiccActivation on Rd700 DLL level. That means, that all libraries build on the
Rd700 DLL will automatically use the new function.
This function performs a Request-Idle, Anticollision, Select sequence to activate the PICC and change
its state from IDLE to ACTIVE. Cascaded serial numbers are handled correctly.
According to the passed baud rate parameter, both PCD and PICC are switched to the new transfer rate
by this function.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda does not support the Higher
Baudrates.
For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
3.6.2.6 Mf500PiccActivateIdleLoop
signed char Mf500PiccActivateIdleLoop (unsigned char br,
unsigned char * atq,
unsigned char * sak,
unsigned char * uid,
unsigned char * uid_len,
unsigned char sec)
39
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Cmd-Code: 0x49
IN br (1) sec (1)
OUT atq (2) sak (1) uid_len(1) uid (uid_len)
Parameters:
br (IN) Baudrate for MIFARE® Higher Baudrate communication
0 106 kBaud
1 212 kBaud
2 424 kBaud
3 848 kBaud
atq (OUT) Answer to Request
sak (OUT) Select acknowledge
uid (OUT) up to 10 bytes UID
uid_len (OUT) length of the UID
sec (IN) range [1..60] seconds, timeout value in seconds
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_NOBITWISEANTICOLL non of the responding tags is supporting a bitwise anticollision
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED br parameter receives a wrong value
MI_SERNRERR Either wrong SNR Check byte or wrong cascading level
MI_WRONG_PARAMETER_VALUE wrong parameter passed to the function
Attention: Beginning with release 1.12 of the reader firmware, this function is no longer valid. The
functionality is provided by the function Mf500PiccActivation. For compatibility purposes, this function is
redirected to the Mf500PiccActivation on Rd700 DLL level. That means, that all libraries build on the
Rd700 DLL will automatically use the new function.
This function is similar to the function Mf500PiccActivateIdle, which is called internally within a loop.
This function returns with either a selected card, or a timeout.
If a timeout value of less than 1 seconds is passed to the function, one Mf500PiccActivateIdle statement
will be issued.
This function is very useful for very fast card transactions, because the card is selected without host
interaction and the application can proceed with either authentication for Mifare classic or ISO 14443-4
commands.
According to the passed baudrate parameter, both PCD and PICC are switched to the new transfer rate
by this function.
Please align the timeout value with the timeout for a single read-transaction on host side. If the timeout
value for the read transaction is less than the timeout of the ActivateIdleLoop, than the transaction will
be canceled without waiting for the response although the function is still in progress.
40
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda does not support the Higher
Baudrates.
For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
41
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6.2.7 Mf500PiccActivateWakeup
signed char Mf500PiccActivateWakeup (unsigned char br,
unsigned char * atq,
unsigned char * sak,
unsigned char * uid,
unsigned char uid_len)
Cmd-Code: 0x44
IN br (1) sec (1) uid_len(1) uid (uid_len)
OUT atq (2) sak (1)
Parameters:
br (IN) Baudrate for MIFARE® Higher Baudrate communication
0 106 kBaud
1 212 kBaud
2 424 kBaud
3 848 kBaud
atq (OUT) Answer to Request
sak (OUT) Select acknowledge
uid (IN) up to 10 bytes UID
uid_len (IN) length of the UID
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_NOBITWISEANTICOLL non of the responding tags is supporting bitwise anticollision
MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED br parameter receives a wrong value
MI_SERNRERR either wrong SNR Check byte or wrong cascading level
Attention: Beginning with release 1.12 of the reader firmware, this function is no longer valid. The
functionality is provided by the function Mf500PiccActivation. For compatibility purposes, this function is
redirected to the Mf500PiccActivation on Rd700 DLL level. That means, that all libraries build on the
Rd700 DLL will automatically use the new function.
This function performs a Request-All, Anticollision, Select sequence to activate the PICC and change its
state from IDLE to ACTIVE state. Cascaded serial-numbers are handled correctly.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
The default configuration using the MF RC 500 for the Pegoda does not support the Higher
Baudrates. For the RC 500 the parameter br should be set to 0.
42
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6.2.8 Mf500PiccCascAnticoll
signed char Mf500PiccCascAnticoll(unsigned char select_code,
unsigned char bcnt,
unsigned char * snr)
Cmd-Code: 0x41
IN select_code (1) bcnt(1)
IN/OUT snr(4)
OUT
Parameters:
select_code (IN)
0x93 standard select code
0x95 cascaded level 1
0x97 cascaded level 2
bcnt (IN) Range: [0..32] Number of SNR-bits that are known (default value is 0);
snr (IN/OUT) 4 bytes serial number (number of bits, which are known and indicated by bcnt
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
MI_SERNRERR SNR Check byte does not correspond to SNR
Corresponding to the specification in ISO 14443A, this function handles extended serial numbers.
Therefore more than one select_code is possible.
The function transmits a select code and all ready tags are responding. The return value of this function
will be the serial number of one PICC.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
43
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6.2.9 Mf500PiccCascSelect
signed char Mf500PiccCascSelect (unsigned char select_code,
unsigned char * snr,
unsigned char * sak)
Cmd-Code: 0x42
IN select_code (1) snr(4)
OUT sak (1)
Parameters:
select_code (IN)
0x93 standard select code
0x95 cascaded level 1
0x97 cascaded level 2
snr (IN) 4 bytes serial number
sak (OUT) 1 byte select acknowledge
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
This functions selects a UID level, depending on select code and returns a Select Acknowledge byte.
Corresponding to the specification in ISO 14443 A, this function is able to handle extended serial
numbers. So that more than one select_codes are possible.
Relevant bit positions in SAK are 6 and 1. All other bit positions are RFU.
Valid combinations are:
XX1XX0XX UID complete, ATS available
XX0XX0XX UID complete, ATS not available
XXXXX1XX UID not complete
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
44
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6.2.10 Mf500PiccCommonRequest
signed char Mf500PiccCommonRequest (unsigned char req_code,
unsigned char * atq)
Cmd-Code: 0x40
IN req_code (1)
OUT atq (2)
Parameters:
rq_code (IN)
PICC_REQALL Request Code 52hex
PICC_REQIDL Request Code 26hex
atq (OUT) 16 bit ATQ (answer to request). atq[0] .. LSByte; atq[1] .. MSByte
Returns:
CRRC
MI_BITCOUNTERR 16 bits expected, wrong number received
Note:
This function has an identical functionality to function Mf500PiccRequest.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
45
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.6.2.11 Mf500PiccExchangeBlock
signed char Mf500PiccExchangeBlock(unsigned char* send_data,
unsigned short send_len,
unsigned char * rec_data,
unsigned short * rec_len,
unsigned char append_crc,
unsigned long timeout)
Cmd-Code: 0x48
IN send_len(2) send_data(send_len)
append_crc(1) timeout(4)
OUT rec_len(2) rec_data(rec_len)
Parameters:
send_data (IN)
send_len (IN)
rec_data (OUT)
rec_len (IN/OUT) The maximum length of data reserved with rec_data should be passed to the
function. The function will check this length against the received number of bytes.
append_crc (IN) CRC should be calculated by the reader IC
timeout (IN) Range [1..4255000] Unit [1 etu] e.g. 9.4 microseconds
Returns:
CRRC
This function exchanges data blocks between the PCD and PICC.
Note:
If append_crc is enabled, two CRC bytes are included in send_bytelen and rec_bytelen. The
received CRC bytes in the receive buffer are always set to zero.In case of an error, the appropriate
error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RF-Communication is returned. This is
done for debugging reasons.
46
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.7 Transparent Communication Channel between Host and Reader IC
In order to provide a flexible interface for future needs, every PCD should implement a transparent
communication channel between host and reader IC. This channel should make it possible to set and reset
all registers and exchange a byte or bit stream with the tag.
3.7.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name Function call
signed char ExchangeByteStream (unsigned char Cmd,
unsigned char *send_data,
ExchangeByteStream
ReadRC
WriteRC
ReadMultiple
WriteMultiple
unsigned short *rec_bytelen)
signed char ReadRC (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *value)
signed char WriteRC (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char value)
signed char ReadMultiple (unsigned char *addr_value,
unsigned short len
signed char WriteMultiple (unsigned char *a ddr_value,
unsigned short len
unsigned short send_bytelen,
unsigned char *rec_data,
)
)
Table 3-8. Transparent Communication between Host and Reader IC
47
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.7.2 FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
3.7.2.1 ExchangeByteStream
signed char ExchangeByteStream (unsigned char Cmd,
unsigned char * send_data,
unsigned short send_len,
unsigned char * rec_data,
unsigned short* rec_len)
Cmd-Code: 0x03
IN cmd(1) send_len(2) send_data(send_len) OUT rec_len(2) rec_data(rec_len)
Parameters:
Cmd (IN) reader IC command byte
PCD_IDLE 0x00 No action: cancel current command or home state
PCD_WRITEE2 0x01 Get data from FIFO and write it to the E2PROM
PCD_READE2 0x03 Read data from E2PROM and put it into the FIFO
PCD_LOADCONFIG 0x07 Read data from E2PROM and initialise the registers
PCD_LOADKEYE2 0x0B Read a master key from the E2PROM and put it into
the master key buffer
PCD_AUTHENT1 0x0C Perform the first part of the card authentication using
the Crypto1 algorithm.
Remark: The master key is automatically taken from the
master key buffer. this implies, that the command
LoadKeyE2 has to be executed before using a certain key
for card authentication
PCD_CALCCRC 0x12 Activate the CRC-Coprocessor
Remark: The result of the CRC calculation can be read from
the register CRCResultXXX
PCD_AUTHENT2 0x14 Perform the second part of the card authentication
using the Crypto1 algorithm.
PCD_RECEIVE 0x16 Activate Receiver Circuitry. Before the receiver
actually starts, the state machine waits until the time
configured in the register RxWait has passed.
Remark: It is possible to read any received data from the
FIFO while the Receive command is active. Thus it is
possible to receive an unlimited number of bytes by reading
them from the FIFO in timer.
PCD_LOADKEY 0x19 Read a master key from the FIFO and put it into the
master key buffer
Remark: The master key has to be prepared in a certain
format. Thus, 12 byte have to be passed to load a 6 byte
master key
48
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
PCD_TRANSMIT 0x1A Transmit data from FIFO to the card
Remark: If data is already in the FIFO when the command is
activated, this data is transmitted immediately. It is possible
to write data to the FIFO while the Transmit command is
active. Thus it is possible to transmit an unlimited number of
bytes in one stream by writting them to the FIFO in time.
PCD_TRANSCEIVE 0x1E Transmits data from FIFO to the card and after that
automatically activates the receiver. Before the receiver
actually starts,the state machine waits until the time
configured in the register RxWait has passed.
Remark: This command is the combination of Transmit and
Receive.
PCD_RESETPHASE 0x3F Runs the Reset- and Initialisation Phase
Remark: This command can not be activated by software,
but only by a Power-On or Hard Reset
send_data (IN) data to send, max. 270 bytes.
send_len (IN) number of bytes to send
rec_data (OUT) Received data from communication
rec_len (OUT) The maximum length of data reserved with rec_data should be passed to the
function. The function will check this length against the received number of bytes.
Returns:
CRRC
MI_WRONG_PARAMETER_VALUE
send_bytelen is equal or less than zero
Exchanges Transports data blocks between PCD <--> host.
In combination with a transparent register read and write command set, this functi on enables a
completely transparent communication between the Reader IC and the host. Every command can be
coded either on PC or on microcontroller side. Neither timeout values nor CRC and parity generation are
modified by this function. These parameters should be set in advance.
Note:
In case of an error, the appropriate error code is set. Nevertheless all received data during the RFCommunication is returned. This is done for debugging reason s.
49
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.7.2.2 ReadRC
signed char ReadRC (unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *value)
Cmd-Code: 0x02
IN addr(1)
OUT value(1)
Parameters:
addr (IN) register address of the reader IC
value (OUT) register value, which is read from the specified address.
Returns:
This function provides a transparent interface to the reader IC’s registers. Independent from the memory
location and reader IC connectivity, this function reads back the selected register’s value.
3.7.2.3 WriteRC
signed char WriteRC(unsigned char addr,
unsigned char *value)
Cmd-Code: 0x01
IN addr(1) value(1)
OUT
Parameters:
addr (IN) register address of the reader IC
value (IN) register value, which should be written to the specified address.
Returns:
This function provides a transparent interface to the reader IC’s registers. Independent from the memory
location and reader IC connectivity, this function writes a given value to the selected register address.
50
Page 51

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.7.2.4 ReadMultiple
signed char ReadMultiple (unsigned char *addr_value,
unsigned short len)
Cmd-Code: 0x05
IN addr_value
IN len
OUT addr_value
Parameters:
addr_value (IN) array with all register addresses of the reader IC
len (IN) number of entries in addr_value array
addr_value (OUT) register values, which were read from the specified addresses.
Returns:
This function provides a transparent interface to the reader IC’s registers. Independent from the memory
location and reader IC connectivity, this function reads back the selected register values.
3.7.2.5 WriteMultiple
signed char WriteMultiple (unsigned char *addr_value,
unsigned short len)
Cmd-Code: 0x04
IN addr_value
IN len
OUT
Parameters:
addr_value (IN) array with all register addresses and values to write alternately
len (IN) number of address and value pairs in addr_value array
Returns:
This function provides a transparent interface to the reader IC’s registers. Independent from the memory
location and reader IC connectivity, this function writes the given values to the selected register values.
51
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8 Utility Functions
Utility functions for the microcontroller environment.
3.8.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
Function name
PcdEnableHighBaudRates
HostGetExecutionTime
HostTransTmrStart
HostTransTmrStop
Mf500HostCodeKey
Mf500PcdLoadKeyE2
PcdSetIdleMode
PcdGetFwVersion
StartDownload
ScriptCmds
Function call
signed char PcdEnableHighBaudRates(unsigned char *cryptogram)
signed char HostGetExecutionTime (unsigned long *us)
signed char HostTransTmrStart (void)
signed char HostTransTmrStop (unsigned long *us)
signed char Mf500HostCodeKey (unsigned char *uncoded,
unsigned char *coded)
signed char Mf500PcdLoadKeyE2(unsigned char key_type,
unsigned char sector,
unsigned char *uncoded_keys)
signed char PcdSetIdleMode (void)
signed char PcdGetFwVersion(unsigned char* version,
unsigned short *len)
signed char StartDownload (void)
signed char ScriptCmds(unsigned char* script,
unsigned short script_len,
unsigned char* resp,
unsigned short *resp_len)
SwitchLED
DbgTrigger
52
void SwitchLED (unsigned char on_off)
void DbgTrigger(unsigned char enableTrigger)
Table 3-9. Utility Functions
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.2 FUNCTION DESRIPTION
3.8.2.1 PcdEnableHighBaudRates
signed char PcdEnableHighBaudRates (unsigned char *cryptogram)
Cmd-Code: 0x4B
IN cryptogram(4bytes)
OUT
Parameters:
cryptogram (IN) 4 bytes serial number of reader IC as returned by PcdGetSnr
Returns:
MI_OK if succeeded
MI_WRONG_PARAMETER_VALUE if serial number incorrect
This function enables baud rates of more than 106kbit/s to be used from PCD to PICC.
3.8.2.2 HostGetExecutionTime
signed char HostGetExecutionTime (unsigned long *us)
Cmd-Code: 0x32
IN
OUT us(4)
Parameters:
us (OUT) elapsed time in microseconds
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function returns the elapsed time for the last command executed. The units are microsecond s. The
periode includes the command launching, execution and data receiving phase.
53
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.2.3 HostTransTmrStart
signed char HostTransTmrStart(void)
Cmd-Code: 0x30
IN
OUT
Parameters:
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function starts an internal adder for command execution periods. The added time units correspond
to the returned value of function HostGetExecutionTime().
3.8.2.4 HostTransTmrStop
signed char HostTransTmrStop(unsigned long *us)
Cmd-Code: 0x31
IN
OUT ms(4)
Parameters:
us (OUT) elapsed time in microseconds
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function returns the elapsed time in microseconds since HostTransTmrStart() was called. The
period is an accumulation of multiple command launching, execution and data receiving phases.
54
Page 55

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.2.5 Mf500HostCodeKey
signed char Mf500HostCodeKey (unsigned char * uncoded,
unsigned char * coded)
Cmd-Code: 0x16
IN uncoded(6)
OUT coded(12)
Parameters:
uncoded (IN) 6 bytes master key for card authentication
coded (OUT) 12 bytes coded master keys for card authentication
Returns:
MI_OK always
To pass the authentication procedure a coded master key is needed and this key has to be stored in the
MF RC500's internal key buffer. The coding of the 6 byte long uncoded master key to a 12 byte long
coded master key is performed using this function.
3.8.2.6 Mf500PcdLoadKeyE2
signed char Mf500PcdLoadKeyE2 (unsigned char key_type,
unsigned char sector,
unsigned char *uncoded_keys)
Cmd-Code: 0x17
IN key_type(1) sector(1) uncoded_keys(6)
OUT
Parameters:
key_type (IN) selects master key A or mast er key B
PICC_AUTHENT1A
PICC_AUTHENT1B
sector (IN) Range: [0..15] key sector number uncoded_keys (IN) 6 bytes key values
Returns:
MI_OK
CRRC
MI_KEYERR error while loading keys
55
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
This function stores the keys in the reader internal E2PROM. After successful loading, these keys are
available for the use by function Mf500PiccAuthE2.
3.8.2.7 PcdSetIdleMode
signed char PcdSetIdleMode (void)
Cmd-Code: 0x25
IN
OUT
Parameters:
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function puts the reader IC and controller in IDLE state, where the power consumption is reduced
to about 65 mA. Any other command will awake the reader module to normal operating mode.
3.8.2.8 SwitchLED
void SwitchLED (unsigned char on_off)
Cmd-Code: 0x60
IN on_off(1)
OUT
Parameters:
on_off (IN) switch the signal LED’s to state ON(1) or OFF(0) or AUTO(0xFF).
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function switches the signal LED’s of the reader module either to state ON (1 to 254 is passed),
OFF (0 is passed) or AUTO (0xFF is passed). The mode AUTO means, that the reader firm ware
controls the switching.
56
Page 57

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.2.9 DbgTrigger
void DbgTrigger (unsigned char enableTrigger)
Cmd-Code: 0x65
IN enableTrigger(1)
OUT
Parameters:
enableTrigger (IN) state ON(1) or OFF(0)
Returns:
MI_OK always
This function enables some trigger output pins for debugging with an oscilloscope. Port pin P2.1 and
port pin P6.3 are used for this purpuse.
Port P6.3 is high during communication with the reader IC (all card and administration commands).
Port P2.1 is high during processing of the interrupt service routine. The combination of these two
signals shows the communication handshake between reader IC and firmware.
3.8.2.10 StartDownload
signed char StartDownload(void)
Cmd-Code: 0x62
IN
OUT
Parameters: none
Returns:
MI_OK download mode could be entered
Other values means error codes
Put the hardware to the download mode to load a new firmware. There will no timeout be handled and
no break condition of this mode exists. Only the end of a download or a hardware reset could exit this
mode.
The reader device waits for a correct application firmware download.
57
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.8.2.11 PcdGetFwVersion
signed char PcdGetFwVersion(unsigned char* version,
unsigned short *len)
Cmd-Code: 0x63
IN
OUT len(2) version(len)
Parameters:
len (OUT) length of the version string (max. 128 bytes)
version (OUT) version string
Returns:
MI_OK always
The memory allocation for the version string has to be done by the calling function. The maximum
length of the version string is limited to 128 characters.
The returned string has following format: “Philips Semiconductors Gratkorn\r\nV1.3”
58
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.9 Self Test Functions
3.9.1 INCLUDED FUNCTIONS
This group of functions makes it possible to test all important parts of the MF RD700, as there are:
communication with a MIFARE® card, communication with PC or 'writing to the 'flash' memory.
Function name
RicTestPcd signed char RicTestPcd(unsigned char *errorNumber) RicTestPicc signed char RicTestPicc(unsigned char *errorNumber) RicTestFlashNr signed char RicTestFlashNr(unsigned char *errorNumber) RicTestCommunication
3.9.2 FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
3.9.2.1 RicTestPcd
signed char RicTestPcd (unsigned char *errorNumber)
Cmd-Code: 0x70
IN
OUT errorNumber (1)
Parameters:
errorNumber (OUT) specifies the error number (no MIFARE
signed char RicTestCommunication(unsigned char errorNumber)
Table 3-10. Self Test Functions
Function call
®
error number)
Returns:
MI_OK test okay
MI_TEST_FAILED test failed
MI_UNKNOWN_COMMAND command not found
An extensive test of the reader IC will be executed. The test includes all read/write registers, the FIFO
functionality (check over run etc.), interrupt requests, and the writing to the EEPROM.
This function writes 16 times to the EEPROM therefore make sure that this command is not included in a
loop.
59
Page 60

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
3.9.2.2 RicTestPicc
signed char RicTestPicc (unsigned char *errorNumber)
Cmd-Code: 0x71
IN
OUT errorNumber (1)
Parameters:
errorNumber (OUT) specifies the error number (no MIFARE
Returns:
MI_OK card read
MI_TEST_FAILED test failed
MI_UNKNOWN_COMMAND command not found
This function tries to read a MIFARE
®
card up to 100 times. After the first valid read operation, the function
returns with MI_OK.
®
error number)
If all 100 read operations failed, the return value is MI_TEST_FAILED.
3.9.2.3 RicTestFlashNr
signed char RicTestFlashNr (unsigned char *errorNumber)
Cmd-Code: 0x61
IN
OUT errorNumber (1)
Parameters:
errorNumber (OUT) specifies the error number (no MIFARE
®
error number)
Returns:
MI_OK card read
MI_TEST_FAILED test failed
MI_UNKNOWN_COMMAND command not found
The reader IC holds a unique serial number. To distinguish between several MF RD700 connected to USB
bus, this serial number is used to identify the different MF RD700. To have the possibility to read out the
serial number by an IO-Subsystem, it is recommended to write this number into the program memory
(FLASH).
60
Page 61

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Note:
A time out error happens if the serial number was not written to the Flash memory before this function is
called. This is correct, because the MF RD700 must do a reset sequence after the writing to the FLASH.
If the number was written already to the Flash, a second call will not perform a write again but the return
value is MI_OK.
3.9.2.4 RicTestCommunication
signed char RicTestCommunication (unsigned char *errorNumber)
Cmd-Code: 0x72
IN
OUT errorNumber (1)
Parameters:
errorNumber (OUT) specifies the error number (no MIFARE
®
error number)
Returns:
MI_OK communication okay
MI_TEST_FAILED test failed
MI_UNKNOWN_COMMAND command not found
This function performs a communication test between the MF RD700 and a host PC sending a dummy
command, which allows the MF RD700 to answers without any other internal operations. The host expects
an answer 18 times. If 11 ore more right answers are received, MI_OK will be returned otherwise
MI_TEST_FAILED is returned.
61
Page 62

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
4 RETURN VALUES OVERVIEW
The naming of the return values allows differing between reader and communication retu rns:
MI_
Reader errors
COM_
Communication errors (generally)
COM_IRDA
Communication errors from the IRDA interface
COM_RS232
Communication errors from the RS232 Interface
COM_USB
Communication errors from the USB interface
4.1 Table of Return values
4.1.1 COMMON COMMUNICATION RETURN CODES
For communication commands with PICC's and special commands for the reader IC, there is a set of
messages, which can always occur and therefore they are not described explicitly at function level. These error messages are noted as Common Communication Return Codes CCRC :
Value Name
0 MI_OK
-1 MI_NOTAGERR
-2 MI_CRCERR CRC
-5 MI_PARITYERR
-19 MI_OVFLERR FIFO
-21 MI_FRAMINGERR
-22 MI_ACCESSTIMEOUT
-24 MI_COLLERR
-100 MI_NY_IMPLEMENTED
Table 4-1. CRRC Return values
62
Page 63

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
4.1.2 RETURN VALUES’ OVERVIEW
Value Name of the constant Short description
0 COM_SUCCESS Operation successful
0 MI_CHK_OK Operation successful
0 MI_CRC_ZERO Operation successful
0 MI_OK Operation successful
-1 MI_CHK_FAILED Reader: CRC Error
-1 MI_NOTAGERR Reader: No Card in RF-Field
-2 MI_CHK_COMPERR Reader: Check Compare Error
-2 MI_CRCERR Reader: CRC Error
-3 MI_EMPTY Reader: Value Overflow
-4 MI_AUTHERR Reader: Authentication failed
-5 MI_PARITYERR Reader: Parity error
-6 MI_CODEERR Reader: Code Error
-8 MI_SERNRERR Reader: Serial Number Error
-9 MI_KEYERR Reader: Key Error
-10 MI_NOTAUTHERR Reader: Not authenticated
-11 MI_BITCOUNTERR Reader: Bit count error
-12 MI_BYTECOUNTERR Reader: Byte count error
-13 MI_IDLE Reader: Idle
-14 MI_TRANSERR Reader: Transfer Error
-15 MI_WRITEERR Reader: Write error
-16 MI_INCRERR Reader: Increment error
-17 MI_DECRERR Reader: Decrement error
-18 MI_READERR Reader: Read error
-19 MI_OVFLERR Reader: Overflow error
-20 MI_POLLING Reader: Polling
-21 MI_FRAMINGERR Reader: Framing error
-22 MI_ACCESSERR Reader: Access error
-23 MI_UNKNOWN_COMMAND Reader: Unknown Command
-24 MI_COLLERR Reader: Reset error
63
Page 64
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Value Name of the constant Short description
-25 MI_INITERR Reader: Initialization failed
-25 MI_RESETERR Reader: Reset Error
-26 MI_INTERFACEERR Reader: Interface error
-27 MI_ACCESSTIMEOUT Reader: Access timeout
-28 MI_NOBITWISEANTICOLL Reader: Tag supports no bitwise anticollision
-30 MI_QUIT Reader: Quit error
-31 MI_CODINGERR Reader: Code Error
-51 MI_SENDBYTENR Reader: Wrong Number of Bytes to send
-53 MI_SENDBUF_OVERFLOW Reader: Send buffer overflow
-54 MI_BAUDRATE_NOT_SUPPORTED Reader: Baudrate not supported
-55 MI_SAME_BAUDRATE_REQUIRED Reader: Same baudrate required
-60 MI_WRONG_PARAMETER_VALUE Reader: Wrong parameter value
-100 MI_NY_IMPLEMENTED Reader: Not yet implemented
-101 MI_NO_MFRC Reader: No MFRC
-102 MI_MFRC_NOTAUTH Reader: MFRC_NOTAUTH
-103 MI_WRONG_DES_MODE Reader: Wrong DES Mode
-104 MI_HOST_AUTH_FAILED Reader: Host Authentication failed
-106 MI_WRONG_LOAD_MODE Reader: Wrong load mode
-107 MI_WRONG_DESKEY Reader: Wrong DES Key
-108 MI_MKLOAD_FAILED Reader: Master Key load failed
-109 MI_FIFOERR Reader: FIFO Error
-110 MI_WRONG_ADDR Reader: Wrong address
-111 MI_DESKEYLOAD_FAILED Reader: DES Key load failed
-112 MI_RECBUF_OVERFLOW Reader: Overflow of the receive buffer
-114 MI_WRONG_SEL_CNT Reader: Wrong Selection count
-117 MI_WRONG_TEST_MODE Reader: Wrong Test mode
-118 MI_TEST_FAILED Reader: Test failed
-119 MI_TOC_ERROR Reader: TOC Error
-120 MI_COMM_ABORT Reader: COMM Abort
-121 MI_INVALID_BASE Reader: Invalid base
-122 MI_MFRC_RESET Reader: MFRC Reset
64
Page 65

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Value Name of the constant Short description
-123 MI_WRONG_VALUE Reader: Wrong value
-124 MI_VALERR Reader: Value Error
-149 MI_WRONG_MAC_TOKEN Reader: Wrong MAC token
-150 MI_WRONG_TOKEN Reader: Wrong token
-151 MI_NO_VALUE Reader: No Value
-152 MI_MFRC150 Reader: MI_MFRC150
-153 MI_MFRC170 Reader: MI_MFRC170
-180 MI_WRONG_BASEADDR Reader: Wrong base address
-199 MI_NO_ERROR_TEXT_AVAIL Reader: No Error Text available
-254 MI_DRIVER_FAILURE Reader: Driver failure
-255 MI_INTERFACE_FAILURE Reader: Interface failure
-260 MI_SERERR Reader: Serial Number Error
-261 MI_CALLOPEN MfRd260 MfRc500: Call open!
-262 MI_RESERVED_BUFFER_OVERFLOW Reader: Overflow of the receive buffer
-1001 COM_ERROR HostRdCom: No overloaded function found
-1002 COM_NO_INTERFACE_HANDLE HostRdCom: No valid interface handle
-1003 COM_INTERFACE_OPEN HostRdCom: Interface is already opened
-1004 COM_INTERFACE_NOT_OPEN HostRdCom: Interface is not opened
-1005 COM_CREATE_FILE_FAILED HostRdCom: Comm and CreateFile() fail ed
-1006 COM_PURGE_COMM_FAILED HostRdCom: Command PurgeComm() failed
-1007 COM_GET_COMM_STATE_FAILED HostRdCom: Command GetCommState() failed
-1008 COM_SETUP_COMM_FAILED HostRdCom: Command SetupComm() failed
-1009 COM_SET_COMM_STATE_FAILED HostRdCom: Command SetCommState() failed
-1010 COM_SET_COMM_MASK_FAILED HostRdCom: Command SetMask() failed
-1011 COM_SET_COMM_TIMEOUTS_FAILED HostRdCom: Command SetCommTimeouts failed
-1012 COM_WRONG_VALUE HostRdCom: Passed parameter - wrong value
-1013 COM_WSASTARTUP_FAILED HostRdCom: Command WSAStartUp() failed
-1014 COM_WSA_SOCKET_FAILED HostRdCom: Command WSASocket() failed
-1015 COM_GETSOCKOPT_FAILED HostRdCom: Command GetSockOpt() failed
-1016 COM_READER_NOT_IN_RANGE HostRdCom: Discovery failed - Reader not in range
-1017 COM_CONNECT_FAILED HostRdCom: Connecting to reader failed
65
Page 66
Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Value Name of the constant Short description
-1018 COM_NEW_FAILED HostRdCom: New() failed - insufficient memory
-1019 COM_INVALID_WT_HANDLE HostRdCom: Invalid worker thread handle
-1020 COM_START_WT_FAILED HostRdCom: Starting worker thread failed
-1021 COM_INVALID_CB_HANDLE HostRdCom: Passed callback handle is invalid
-1022 COM_LEN_OVERFLOW HostRdCom: Buffer length overflow
-1023 COM_RS232_SERCOM_ERR HostRdCom: Error on RS232 interface
-1024 COM_RS232_SEND_CMD_NO_DLE_ERR HostRdCom: No DLE received from reader error
-1025 COM_RS232_SEND_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Error sending data to reader via RS232
-1026 COM_RS232_RESP_CMD_NAK_ERR HostRdCom: Reader response: NAK
-1027 COM_TIMEOUT HostRdCom: Timeout occurred
-1028 COM_RS232_RESP_TO_ERR HostRdCom: First received character from reader not
STX (RS232)
-1029 COM_RS232_RESP_OVERFLOW_ERR HostRdCom: Response buffer overflow (RS232)
-1030 COM_RS232_RECV_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Error receiving data from reader via RS232
-1031 COM_RS232_RESP_UNDERFLOW_ERR HostRdCom: To less bytes received from reader
(RS232)
-1032 COM_RS232_DATALENGTH_ERR HostRdCom: Wrong number of bytes received from
reader (RS232)
-1033 COM_RS232_CHECKSUM_ERR HostRdCom: Checksum error (RS232)
-1034 COM_RS232_TX_RX_SEQ_ERR HostRdCom: Sequence numbers not equal (RS232)
-1035 COM_RS232_COPY_DATA_ERR HostRdCom: Error copying data to command object
(RS232)
-1036 COM_IRDA_SELECT_FAILED HostRdCom: Command Select() failed (IrDA)
-1037 COM_IRDA_SEND_TIMEOUT HostRdCom: Send timeout error (IrDA)
-1038 COM_IRDA_SOCKET_NOT_READY HostRdCom: Socket not ready for transmitting data
(IrDA)
-1039 COM_IRDA_SEND_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Error sending data to reader via IrDA
-1040 COM_IRDA_RECV_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Erro r receiving data from reader via IrDA
-1041 COM_IRDA_RECV_TIMEOUT HostRdCom: Receive timeout error (IrDA)
-1042 COM_IRDA_TX_RX_SEQ_ERR HostRdCom: Sequence numbers not equal (IrDA)
-1043 COM_IRDA_COPY_DATA_ERR HostRdCom: Error copying data to command object
(IrDA)
-1044 COM_IRDA_LEN_ERR HostRdCom: Wrong number of bytes received from
reader (IrDA)
66
Page 67

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
Command Set MF RD 700
Value Name of the constant Short description
-1045 COM_NO_PROTOCOL_SET HostRdCom: No protocol set
-1046 COM_USB_DLL_LOAD_ERR HostRdCom: Error loading USB Dll
-1047 COM_USB_MISSING_FCT_ADDR HostRdCom: Error loading function addresses (UBS)
-1048 COM_USB_SEND_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Error sending data to reader (USB)
-1049 COM_USB_RECV_DEVICE_ERR HostRdCom: Error receiving data from reader (USB)
-1050 COM_USB_TX_RX_SEQ_ERR HostRdCom: Sequence numbers not equal (USB)
-1051 COM_USB_LEN_ERR HostRdCom: Wrong number of bytes received from
reader (USB)
-1052 COM_USB_COPY_DATA_ERR HostRdCom: Error copying data to command object
(IrDA)
-1053 COM_USB_NO_DEVICE_FOUND HostRdCom: No device found (USB)
-1054 COM_USB_SEND_TIMEOUT HostRdCom: Timeout period exceeded while writing to a
device (USB)
-1055 COM_USB_RECV_TIMEOUT HostRdCom: Timeout period exceeded while reading
from a device USB)
-1056 COM_USB_FILE_NOT_FOUND HostRdCom: File descriptor not longer valid (USB)
-1057 COM_USB_ACCESS_DENIED HostRdCom: Device could not be accessed (USB)
-1058 COM_RS232_ETX_DLE_EXPECTED HostRdCom: Receive error at ISO3964 protocol (RS232)
Table 4-2. Return Values’ Overview
67
Page 68

Philips Semiconductors User Manual Rev. 3.0 June 2005
5 REVISION HISTORY
REVISION DATE CPCN PAGE DESCRIPTION
Add point 3.8.2.1 PcdEnableHighBaudRates
3.0 June 2005 -
2.0 July 2002 - 68 revised version
Add point 3.7.2.4 ReadMultiple
Add point 3.7.2.5 WriteMultiple
1.1
0.1 - Internal Version
October
2001
- First Published Version
Table 5-1: Document Revision History
68
Page 69

Definitions
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Prel im i n ar y s p ec i f ic at i o n This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be
published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress
above one or more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress
ratings only and operation of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the
Characteristics section of the specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
Life support applications
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of
these products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling
these products for use in such applications do so on their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for
any damages resulting from such improper use or sale.
Page 70

Philips Semiconductors - a worldwide company
Contact Information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2002 SCA74
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without any notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
P h i l i
p i s
S e m
c o n d u c t
o r s
 Loading...
Loading...