Philips IntelliVue MP40, IntelliVue MP50, IntelliVue MP60, IntelliVue MP70, IntelliVue MP90 User manual
IntelliVue MP40/50 and MP60/70/90
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
IntelliVue Patient Monitor
MP40/50 and MP60/70/90
Release B.0 with Software Revision B.0x.xx
Patient Monitoring

Part Number M8000-9001D
Printed in Germany 11/03
Re-order Number: 453563499331
*M8000-9001D*

M8000-9001D
1Table Of Contents
1 Basic Operation 1
Introducing the IntelliVue Family 2
IntelliVue MP40/MP50 2
MP40/MP50 Major Parts and Keys 3
IntelliVue MP60/MP70 4
MP60/MP70 Major Parts and Keys 4
MP90 Major Parts and Keys 5
Remote Alarm Device 5
Related Products 6
Flexible Module Server (M8048A) 6
Measurement Modules 6
Multi-Measurement Server (M3001A) 8
M3015A and M3016A Measurement Server Extensions 9
M3012A Hemodynamic Measurement Server Extension 10
Anesthetic Gas Module (AGM) 10
Operating and Navigating 11
Using the Touchscreen 12
Using the MP60/MP70/MP90 SpeedPoint 12
Using the MP40/MP50 Navigation Point 13
Using a Mouse or Trackball 13
Using Keys 13
Permanent Keys 14
SmartKeys 14
Hardkeys 15
Pop-Up Keys 15
Using the On-Screen Keyboard 16
Using the On-Screen Calculator 16
Operating Modes 16
Disabling Touchscreen Operation 17
Using a Second Display 17
Tailoring Your Monitor 17
Understanding Screens 17
Switching to a Different Screen 18
Using the Visitor Screen 18
Changing a Screen’s Content 18
Understanding Profiles 18
Swapping a Complete Profile 20
Swapping a Settings Block 20
Default Profile 20
Locked Profiles 20
Changing Measurement Settings 20
Switching a Measurement On and Off 21
i

Switching Numerics On and Off 21
Adjusting a Measurement Wave 21
Changing a Wave Speed 21
Using Labels 21
Changing Measurement Labels (e.g. Pressure) 22
Resolving Label Conflicts 22
Changing Monitor Settings 23
Adjusting the Screen Brightness 23
Adjusting Touch Tone Volume 23
Setting the Date and Time 23
Checking Your Monitor Revision 23
Getting Started 24
Inspecting the Monitor 24
Switching On 24
Setting up the Measurement Modules 24
Starting Monitoring 24
Disconnecting from Power 25
Networked Monitoring 25
Using Remote Applications 25
2 What’s New? 27
What’s New in Release B.0? 27
What’s New in Release A.2? 28
3 Alarms 29
Visual Alarm Indicators 30
Audible Alarm Indicators 30
Alarm Tone Configuration 30
Traditional Audible Alarms (HP/Agilent/Philips/Carenet) 31
ISO/IEC Standard 9703-2 Audible Alarms 31
Changing the Alarm Tone Volume 31
Minimum Volume for No Central Monitoring INOP 31
Acknowledging Alarms 32
Acknowledging Disconnect INOPs 32
Alarm Reminder (ReAlarm) 32
Pausing or Switching Off Alarms 32
To Pause All Alarms 33
To Switch All Alarms Off 33
To Switch Individual Measurement Alarms On or Off 33
While Alarms are Paused or Off 33
Restarting Paused Alarms 33
Resetting Arrhythmia Alarm Timeouts 34
Extending the Alarm Pause Time 34
Alarm Limits 34
Viewing Individual Alarm Limits 34
Viewing All Alarm Limits 35
ii

Changing Alarm Limits 36
About Automatic Alarm Limits (AutoLimits) 37
Documenting Alarm Limits 37
Reviewing Alarms 38
Alarm Messages Window 38
Review Alarms Window 38
Understanding Alarm Messages 39
Latching Alarms 39
Viewing the Alarm Latching Settings 39
Alarm Latching Behavior 40
Silencing Latched Alarms from an Information Center 40
Testing Alarms 40
Alarm Behavior at On/Off 40
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs 41
Patient Alarm Messages 41
Technical Alarm Messages (INOPs) 47
5 Managing Patients 65
Admitting a Patient 65
Patient Category and Paced Status 66
Quick Admitting a Patient 66
Editing Patient Information 67
Discharging a Patient 67
Transferring a Patient 68
Transferring a Centrally Monitored Patient 68
Transferring a Patient with an MMS 69
Resolving Patient Information Mismatch 69
Manually Resolving Patient Mismatch 69
Patient Mismatch - If One Set of Patient Data is Correct 70
Patient Mismatch - If Neither Patient Data Set is Correct 70
Patient Mismatch - If Both Patient Data Sets Are Correct 71
Automatically Resolving Patient Mismatch 71
Care Groups 71
Understanding Care Group Symbols 72
Viewing the Care Group Overview Bar 73
Viewing the My Care Group Window 73
Viewing the Other Patient Window 74
Using Care Group Alarms 74
6 ECG, Arrhythmia, and ST Monitoring 75
Placing ECG Electrodes 75
Connecting ECG Cables 75
Selecting the Primary and Secondary ECG Leads 76
Checking Paced Status 76
Understanding the ECG Display 77
iii

Monitoring Paced Patients 77
Setting the Paced Status (Pace Pulse Rejection) 78
Avoiding Pace Pulse Repolarization Tails 78
Changing the Size of the ECG Wave 78
To Change the Size of an Individual ECG Wave 78
To Change the Size of all the ECG Waves 79
Changing the Volume of the QRS Tone 79
Changing the ECG Filter Settings 79
Choosing EASI or Standard Lead Placement 80
About ECG Leads 80
ECG Leads Monitored 80
Changing Lead Sets 80
ECG Lead Fallback 81
ECG Lead Placements 81
Standard 3-Lead Placement 81
Standard 5-Lead Placement 82
Chest Electrode Placement 83
10-Lead Placement 84
Conventional 12-Lead ECG 84
Modified 12-Lead ECG 85
Choosing Standard or Modified Electrode Placement 86
Labelling 12-Lead ECG Reports 86
Capture 12-Lead 86
EASI ECG Lead Placement 87
ECG, Arrhythmia, and ST Alarm Overview 88
Using ECG Alarms 89
Extreme Alarm Limits 89
ECG Alarms Off Disabled 89
HR Alarms When Arrhythmia Analysis is Switched Off 89
HR Alarms When Arrhythmia Analysis is Switched On 89
ECG Safety Information 89
About Arrhythmia Monitoring 91
Arrhythmia Options 91
Where can I find more information? 91
Switching Arrhythmia Analysis On and Off 92
Choosing an ECG Lead for Arrhythmia Monitoring 92
Aberrantly-Conducted Beats 92
Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter 92
Intermittent Bundle Branch Block 93
Understanding the Arrhythmia Display 93
Viewing Arrhythmia Waves 93
Arrhythmia Beat Labels 93
Arrhythmia Status Messages 94
Rhythm Status Messages 94
Ectopic Status Messages 95
iv

Arrhythmia Relearning 95
Initiating Arrhythmia Relearning Manually 95
Automatic Arrhythmia Relearn 96
Arrhythmia Relearn and Lead Fallback 96
Arrhythmia Alarms 96
Yellow Arrhythmia Alarms 97
Arrhythmia Alarms and Latching 97
Switching Individual Arrhythmia Alarms On and Off 97
Switching All Yellow Arrhythmia Alarms On or Off 97
Adjusting the Arrhythmia Alarm Limits 97
Arrhythmia Alarm Timeout Periods 97
Arrhythmia Alarm Chaining 99
Understanding PVC-Related Alarms 100
About ST Monitoring 101
Switching ST On and Off 101
Selecting ST Leads for Analysis 101
Understanding the ST Display 102
Updating ST Baseline Snippets 103
Recording ST Segments 103
Adjusting ST Measurement Points 104
ST Alarms 106
Single- or Multi-lead ST Alarming 106
Changing ST Alarm Limits 106
7 Monitoring Pulse Rate 107
Entering the Setup Pulse Menu 107
System Pulse Source 107
Switching Pulse On and Off 108
Using Pulse Alarms 108
Selecting the Active Alarm Source: HR or Pulse? 108
Alarm Source Selection Disabled 109
Changing HR/Pulse Alarm Limits 109
Extreme Alarm Limits 109
QRS Tone 109
8 Monitoring Respiration Rate (Resp) 111
Lead Placement for Monitoring Resp 111
Optimizing Lead Placement for Resp 111
Cardiac Overlay 111
Lateral Chest Expansion 112
Abdominal Breathing 112
Understanding the Resp Display 112
Changing Resp Detection Modes 112
Auto Detection Mode 112
Manual Detection Mode 113
Resp Detection Modes and Cardiac Overlay 113
v

Changing the Size of the Respiration Wave 113
Changing the Speed of the Respiration Wave 113
Using Resp Alarms 114
Changing the Apnea Alarm Delay 114
Resp Safety Information 114
9 Monitoring SpO
2
115
Selecting an SpO2 Sensor 116
Applying the Sensor 117
Connecting SpO2 Cables 117
Measuring SpO
2
118
Assessing a Suspicious SpO2 Reading 118
Understanding SpO2 Alarms 119
Adjusting the Alarm Limits 119
Adjusting the Desat Limit Alarm 119
Pleth Wave 119
Perfusion (Pleth) Indicator 120
Setting SpO2/Pleth as Pulse Source 120
Setting Up Tone Modulation 120
Setting the QRS Volume 120
Calculating SpO2 Difference 120
10 Monitoring NBP 121
Introducing the Oscillometric NBP Measurement 121
Measurement Limitations 122
Measurement Methods 122
Preparing to Measure NBP 122
Correcting the Measurement if Limb is not at Heart Level 123
Understanding the NBP Numerics 123
Starting and Stopping Measurements 124
Enabling Automatic Mode and Setting Repetition Time 124
Choosing NBP Alarm Source 125
Assisting Venous Puncture 125
Calibrating NBP 125
11 Monitoring Temperature 127
Making a Temp Measurement 127
Calculating Temp Difference 128
12 Monitoring Invasive Pressure 129
Setting up the Pressure Measurement 129
Selecting a Pressure for Monitoring 130
Zeroing the Pressure Transducer 130
Zeroing ICP 130
Determining a Pressure’s Most Recent Zero 131
Zeroing a Pressure Measurement 131
vi

Using the Zero Hardkey 131
Zeroing All Pressures Simultaneously 131
Troubleshooting the Zero 132
Adjusting the Calibration Factor 132
Displaying a Mean Pressure Value Only 132
Changing the Pressure Wave Scale 132
Optimizing the Waveform 133
Non-Physiological Artifact Suppression 133
Choosing the Pressure Alarm Source 133
Calibrating Reusable Transducer CPJ840J6 134
Making the Pressure Calibration 134
Troubleshooting the Pressure Calibration 135
Calculating Cerebral Perfusion 135
Measuring Pulmonary Artery Wedge Pressure 136
Editing the Wedge 137
Identifying the Pressure Analog Output Connector 137
13 Monitoring Cardiac Output 139
Hemodynamic Parameters 140
Using the C.O. Procedure Window 141
Accessing the Setup C.O. and Setup CCO Menus 142
Changing the C.O. Results Table Contents 142
Entering the HemoCalc Window 142
Viewing the Temperature Unit 142
Measuring C. O. Using the PiCCO Method 142
Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output 142
Setting Up the PiCCO C.O. Measurement 143
Performing PiCCO C.O. Measurements 144
Editing PiCCO C.O. Measurements 144
Saving and Calibrating PiCCO C.O. Measurements 145
CCO Calibration Status Indicators 145
Measuring C.O. Using the Right Heart Thermodilution Method 145
Setting up RH C.O. Measurements 146
Ice-Bath Setup for RH Thermodilution C.O. Measurements 146
Setting the Computation Constant 146
Performing RH C.O. Measurements 147
Editing and Saving RH C.O. Measurements 147
Documenting C.O. Measurements 147
C.O. Injectate Guidelines 148
Guidelines for Right Heart Thermodilution C.O. Injectate 148
Guidelines for PiCCO C.O. Injectate 148
Injectate for Patients with High ETVI Values (PiCCO Only) 149
C.O./CCO Curve Alert Messages 149
C.O./CCO Prompt Messages 150
C.O./CCO Warning Messages 151
C.O./CCO Safety Information 151
vii

14 Monitoring Carbon Dioxide 153
Using the Mainstream CO2 Extension (M3016A) 154
Preparing to Measure Mainstream CO
Checking Transducer Accuracy 154
Calibrating the Transducer 155
Attaching and Removing the CO2 Tra ns du cer 155
2
154
Using the Microstream CO2 Extension (M3015A) 156
Preparing to Measure Microstream CO2 156
Setting up Microstream CO2 Measurements 156
Using Microstream Accessories 156
Using the FilterLine and Airway Adapter 157
Removing Exhaust Gases from the System 157
Setting up Mainstream and Microstream 158
Adjusting the CO2 Wave Scale 158
Setting up CO2 Corrections 158
Changing CO2 Alarms 158
Changing the Apnea Alarm Delay 159
Deriving Alarms From awRR 159
Changing awRR Alarm Limits 159
15 Monitoring tcGas 161
Identifying tcGas Module Components 161
Setting the tcGas Sensor Temperature 162
Using the tcGas Site Timer 162
Setting the tcGas Site Timer 162
Restarting the tcGas SiteTimer 163
Disabling the tcGas Site Timer 163
Setting the tcGas Barometric Pressure 163
Remembraning the tcGas Transducer 163
New/Dried Out Transducers 164
Storing tcGas Transducers 164
Calibrating the tcGas Transducer 165
Calibration Failure 166
Troubleshooting tcGas Calibration 166
Applying the tcGas Transducer 167
Selecting the tcGas HeatPowerDisplay Mode 168
Zeroing the tcGas Relative Heat Power 168
Finishing tcGas Monitoring 168
TcGas Corrections 168
Temperature Correction for tcpCO
Metabolism Correction for tcpCO
2
2
168
168
16 Monitoring SvO
Preparing to Monitor SvO
2
2
169
170
Carrying out a Pre-insertion Calibration 170
viii

Inserting the Catheter 171
Performing a Light Intensity Calibration 171
Performing In-Vivo Calibration 172
Setting Up the In-Vivo Calibration 172
Making the In-Vivo Calibration 172
Calculating Oxygen Extraction 172
17 Using the AGM 173
Understanding the AGM Display 173
AGM Major Parts and Keys 174
Water tr ap 174
AGM Rear Panel 174
Understanding the Gas Measurement 175
Connecting AGM Accessories 175
Using the AGM Setup Menus 176
Choosing Numerics for Display 176
Humidity Correction for CO
Adjusting Wave Scales 176
2
Changing the Apnea Alarm Delay 177
Deriving Limit Alarms from awRR 177
Alarms and Zero Calibration 177
Automatic Alarm Suppression 177
Agent Identification 178
If Agent ID is Set to Manual 178
If Agent ID is Set to Auto 178
Exchanging Agents 178
Agent ID During Emergence from Anesthesia 178
Removing Gas from the Circuit 179
Returning the Gas Sample 179
Removing the Gas Sample 179
Entering AGM Standby Mode 179
Zero Calibration 180
Automatic Zero Calibration 180
Carrying Out Manual Zero Calibration 180
Suppressing Zero Calibration 180
Using the AGM During a Cardiopulmonary Bypass 180
AGM Safety Information 181
176
18 Monitoring EEG 183
EEG Monitoring Setup 184
Using the EEG Impedance/Montage Window 184
Choosing an EEG Electrode Montage 185
Changing the Impedance Limit 185
About Electrode-to-Skin Impedance 186
Impedance Indicators 186
About Compressed Spectral Arrays (CSA) 187
ix

Displaying CSAs 188
Changing EEG Settings 188
Switching EEG Numerics On and Off 188
Changing the Scale of the EEG Waves for Display 188
Changing Filter Frequencies 189
Changing the Speed of the EEG Wave 189
EEG Reports 189
EEG Safety Information 190
EEG and Electrical Interference 190
19 Monitoring BIS 191
BIS Monitoring Setup 192
BIS Continuous Impedance Check 193
BIS Cyclic Impedance Check 193
Starting a Cyclic Impedance Check 193
Stopping a Cyclic Impedance Check 193
BIS Impedance Check Window 194
BIS Impedance Indicators 194
Changing the BIS Smoothing Rate 195
Switching BIS and Individual Numerics On and Off 195
Changing the Scale of the EEG Wave 195
Switching BIS Filters On or Off 195
BIS Safety Information 196
20 Trends 197
Viewing Trends 197
Viewing Graphic Trends 197
Viewing Vital Signs Trends 198
Tre nd s Po p- Up Ke ys 198
Setting Up Trends 199
Choosing Which Measurements are Trended 199
Choosing Trend Measurement Groups 199
Changing Parameter Scales 200
Choosing Trend Resolution 200
Documenting Trends 201
Screen Trends 202
Changing the Selection of Screen Trends Displayed 203
Changing the Screen Trend Time 203
21 Calculations 205
Viewing Calculations 205
Calculations Windows 206
Calculations Pop-Up Keys 206
Reviewing Calculations 207
Performing Calculations 207
Entering Values for Calculations 208
x

Automatic Value Substitution 208
Automatic Unit Conversion 208
BSA Formula 208
Documenting Calculations 209
22 Event Surveillance 211
Event Groups 211
Event Episode 212
Episode Types 212
Event Triggers 212
Viewing Events 213
Events Pop-Up Keys 213
Event Counter 214
Event Summary View 214
Event Review Window 215
Event Episode Window 216
The Event Counter 216
Counting Combi-Events 216
Counting Neonatal Event Review (NER) Events 217
Levels of Event Surveillance 217
Setting Up and Using Event Surveillance 217
Setting Up Events 218
Triggering Events Manually 218
Annotating Events 219
The Event Database 219
Documenting Events 219
Documenting Event Review 219
Documenting an Event Episode 219
Event Recordings 220
Event Review Recordings 220
Event Episode Recordings 221
Event Reports 221
Event Review Reports 222
Event Episode Reports 223
23 Recording 225
Starting and Stopping Recordings 226
Starting Recordings 226
Extending Recordings 226
Stopping Recordings 226
Quickstarting Realtime Recordings 226
Overview of Recording Types 227
ECG Capture Recordings 227
Creating and Changing Recordings Templates 228
Changing ECG Wave Gain 228
Recording Priorities 229
xi

Sample Recording Strip 229
Recording Strip Code 230
Recorded Waveforms 230
Maintaining Recording Strips 230
Reloading Paper 231
Recorder Status Messages 231
24 Printing Patient Reports 233
Starting Reports Printouts 233
Stopping Reports Printouts 234
Setting Up Reports 234
Setting Up ECG Reports 234
Setting Up Vital Signs and Graphic Trend Reports 235
Setting Up Auto Reports 236
Setting Up Individual Print Jobs 237
Checking Printer Settings 238
Switching Printers On Or Off for Reports 238
Dashed Lines on Reports 238
Unavailable Printer: Re-routing Reports 239
Printer Status Messages 239
Sample Report Printouts 239
Alarm Limits Report 240
Realtime Report 241
Cardiac Output Report 242
ECG Reports 243
Other Reports 243
25 Using the Drug Calculator 245
Performing Drug Calculations 246
Converting Units 246
Charting Drip Progress 247
Using the Titration Table 247
Documenting Drug Calculations 247
26 VueLink Modules 249
Connecting an External Device 250
Changing VueLink Waves and Numerics Displayed 250
Viewing the VueLink Device Data Window 250
Using VueLink Screens 251
Switching VueLink On and Off 251
Alarms/INOPs From External Devices 251
Language Conflict with External Device Drivers 252
27 Respiratory Loops 253
Using the Loops Window 254
xii

28 Care and Cleaning 255
General Points 255
AGM Accessories 256
Cleaning 256
Disinfecting 256
Cleaning Monitoring Accessories 257
Sterilizing 257
Cleaning the Recorder Printhead 257
Cleaning the Batteries and Battery Compartment 257
29 Using the Batteries 259
Battery Power Indicators 259
Battery LED 260
Battery Status on the Main Screen 260
Battery Status Window 261
Viewing Individual Battery Status 261
Documenting Battery Status 261
Replacing Batteries 262
Maintaining Batteries 262
Display Brightness Setting 262
Checking Battery Charge 263
Charging Batteries 263
Reconditioning Batteries 263
Unequally-Charged Batteries 263
Battery Safety Information 264
30 Maintenance and Troubleshooting 265
Inspecting the Equipment and Accessories 265
Inspecting the Cables and Cords 265
Service Task Schedule 266
Troubleshooting 267
Disposing of the Monitor 267
Disposing of Empty Calibration Gas Cylinders 267
31 Accessories 269
ECG/Resp Accessories 269
Trunk C ab le s 269
3-Electrode Cable Sets 269
5-Electrode Cable Sets 270
10-Electrode Cable Sets 270
3-Electrode One Piece Cables 270
5-Electrode One Piece Cables 270
Set Combiners and Organizers 271
NBP Accessories 271
Adult/Pediatric Multi-Patient Comfort Cuffs and Disposable Cuffs 271
xiii

Reusable Cuff Kits 271
Adult/Pediatric Antimicrobial Coated Reusable cuffs 272
Adult/Pediatric Soft Single Patient Single-Hose Disposable Cuffs 272
Neonatal/Infant Cuffs (Disposable, non-sterile) 272
Invasive Pressure Accessories 273
SpO2 Accessories 273
Temperature Accessories 276
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Accessories 276
Mainstream CO2 Accessories 277
Microstream CO2 Accessories 277
tcGas Accessories 279
EEG Accessories 279
BIS Accessories 279
BIS Sensors 279
Other BIS Accessories 280
AGM Accessories 280
SvO2 Accessories 280
Recorder Accessories 281
32 Installation and Specifications 283
Intended Use 283
Indication for Use 283
Manufacturer’s Information 284
Responsibility of the Manufacturer 284
Trademark Acknowledgement 284
Symbols 285
Installation Safety Information 286
Connectors 286
MP40/MP50 287
MP60/MP70 288
MP90 289
Altitude and Barometric Pressure 290
Monitor Safety Specifications 290
Physical Specifications 291
Environmental Specifications 292
M4605A Battery Specifications 294
Monitor Performance Specifications 294
Measurement Specifications 298
ECG/Arrhythmia/ST 298
Respiration 301
SpO
2
NBP 302
Invasive Pressure and Pulse 304
Te m p 305
CO
2
Cardiac Output / Continuous Cardiac Output 308
301
306
xiv

tcGas 308
SvO
2
EEG 310
BIS 310
Anesthetic Gas Module 311
309
Safety and Performance Tests 313
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Specifications 313
Accessories Compliant with EMC Standards 313
Electromagnetic Emissions 314
Avoiding Electromagnetic Interference (Resp and BIS) 314
Electromagnetic Immunity 315
Recommended Separation Distance 315
Recommended separation distances from portable and mobile RF communication equipment316
Electrosurgery Interference/Defibrillation/Electrostatic Discharge 317
Fast Transients/Bursts 317
Restart time 317
33 Default Settings Appendix 319
Alarm Default Settings 320
ECG, Arrhythmia, and ST Default Settings 320
Pulse Default Settings 323
Respiration Default Settings 324
SpO2 Default Settings 324
NBP Default Settings 325
Temperature Default Settings 325
Invasive Pressure Default Settings 326
Cardiac Output Default Settings 326
CO2 Default Settings 327
tcGas Default Settings 328
SvO2 Default Settings 328
AGM Default Settings 328
EEG Default Settings 329
BIS Default Settings 329
VueLink Default Settings 330
xv

xvi

1
1Basic Operation
This Instructions for Use is for clinical professionals using the IntelliVue MP40/50 (M8003A/
M8004A) and MP60/70/90 (M8005A/M8007A/M8010A) patient monitors. Unless otherwise
specified, the information here is valid for all the IntelliVue patient monitors.
The basic operation section gives you an overview of the monitor and its functions. It tells you how to
perform tasks that are common to all measurements (such as entering data, switching a measurement
on and off, setting up and adjusting wave speeds, working with profiles). The alarms section gives an
overview of alarms. The remaining sections tell you how to perform individual measurements, and how
to care for and maintain the equipment.
Familiarize yourself with all instructions including warnings and cautions before starting to monitor
patients. Read and keep the Instructions for Use that come with any accessories, as these contain
important information about care and cleaning that is not repeated in this book.
This guide describes all features and options. Your monitor may not have all of them; they are not all
available in all geographies. Your monitor is highly configurable. What you see on the screen, how the
menus appear and so forth, depends on the way it has been tailored for your hospital may not be
exactly as shown here.
In this guide:
•A warning alerts you to a potential serious outcome, adverse event or safety hazard. Failure to
observe a warning may result in death or serious injury to the user or patient.
•A caution alerts you to where special care is necessary for the safe and effective use of the product.
Failure to observe a caution may result in minor or moderate personal injury or damage to the
product or other property, and possibly in a remote risk of more serious injury.
• Monitor refers to the entire patient monitor. Display refers to the physical display unit. Display
Screen and Screen refer to everything you see on monitor’s display, such as measurements, alarms,
patient data and so forth.
1

1 Basic Operation Introducing the IntelliVue Family
Introducing the IntelliVue Family
The Philips IntelliVue family of patient monitors offers a monitoring solution optimized for the
surgical, cardiac, medical and neonatal care environments. Combining patient surveillance and data
management, it allows multi-measurement monitoring by linking separate modules with “plug-andplay” convenience.
Your monitor stores data in trend, event, and calculation databases. You can see tabular trends (vital
signs) and document them on a local or remote printer. You can view measurement trend graphs, with
up to three measurements combined in each graph, to help you identify changes in the patient’s
physiological condition. You can view fast-changing measurement trends with beat to beat resolution
and see up to four high resolution trend segments. Event surveillance enhances documentation and
review of physiologically significant events by automatically detecting and storing up to 50 userdefined clinical events over a 24 hour period.
There is a choice of monitor configurations, as explained below. All models can also use computer
devices such as a mouse, a trackball and a keyboard.
IntelliVue MP40/MP50
The IntelliVue MP40/MP50 (M8003A/M8004A)
patient monitor has a 12-inch TFT LCD flat panel
SVGA display. The standard input devices for the MP50
are the Touchscreen and integrated navigation point; the
MP40 is supplied with an integrated navigation point
only. Up to six waves can be shown on MP40/MP50
Screens, as well as the 12-Lead ECG Screen.
The MP40/MP50 can be connected to one MultiMeasurement Server (MMS) and any one of the
measurement server extensions. The IntelliVue family
plug-in measurement modules can be connected to its
four integrated plug-in module slots with plug-and-play convenience (the only exception is the SvO
module, M1021A, which cannot be used with the MP40/MP50). The integrated module slots replace
the Flexible Module Server (M8048A), which cannot be used with the MP40/MP50.
2
2
Introducing the IntelliVue Family 1 Basic Operation
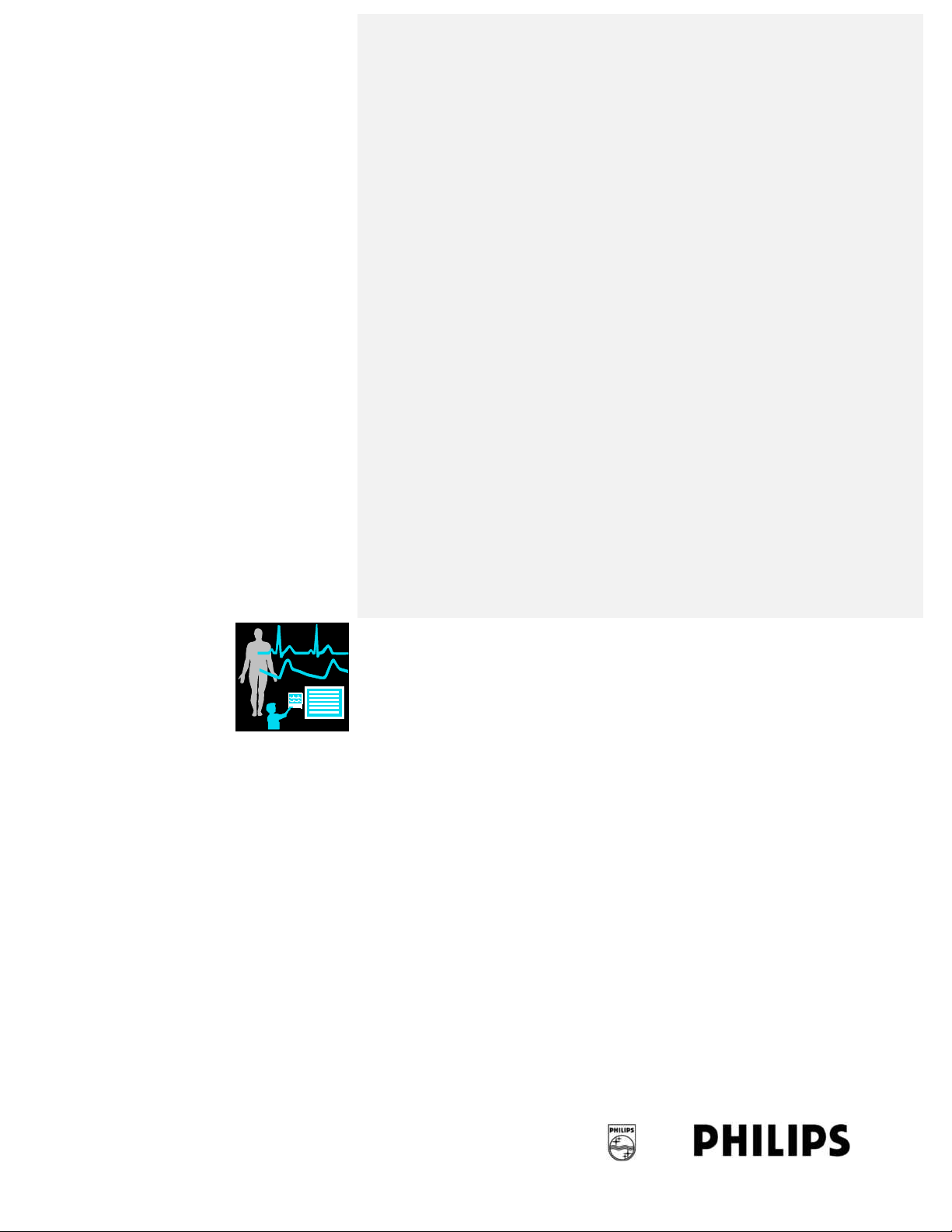
MP40/MP50 Major Parts and Keys
MP40/MP50 left side
1 Color-coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms off lamp
3 Model indicator
4 ECG out
5 Navigation Point
6 Part number and serial number
7 Quick-release mounting release
8 Plug-in module slots
MP40/MP50 front panel
MP40/MP50 LED Colors and their Meanings
On/Standby LED
Error LED
Battery LED
AC Power
Green when monitor is switched on
Red if there is a problem with the monitor
Green, yellow, and red.
See the “Battery LED” on page 260 for details
Green when monitor is connected to mains power
1
On/Standby switch
2
On/Standby LED
3
Error LED
4
Battery status LED
5
AC power operation LED
6 “read the documentation” symbol
7
Mounting quick- release lever
3

1 Basic Operation Introducing the IntelliVue Family
IntelliVue MP60/MP70
The IntelliVue MP60/MP70 (M8005A/M8007A) patient monitors integrate the display unit, with a
15” color LCD display, and the data processing unit into one. Up to eight waves can be shown on the
screens, as well as the 12-Lead ECG Screen. The MP60 uses the SpeedPoint as its primary input device
while the MP70 uses touch screen operation but may have an optional SpeedPoint.
The monitors can be connected to the Multi-Measurement Server (MMS) and any one of the
measurement server extensions, and to the Flexible Module Server (M8048A). The IntelliVue family
plug-in measurement modules can be connected to its FMS module slots with plug-and-play
convenience.
The MP60/MP70 has two integrated slots for plug-in modules. You can combine one each of the
following modules in these slots: Pressure, Temperature, C.O., and VueLink. You can also use the twoslot recorder module in the integrated slots.
MP60/MP70 Major Parts and Keys
1 Color coded alarm lamps
1
2
891011 7
3
6
4
5
2 Alarms Off lamp
3Display
4Model indicator
5 SpeedPoint (optional for MP70)
6 Part number and serial number
7 Mounting adapter release
8AC power LED
9Error LED
10 Power on/standby switch
11 Power on LED
4

Introducing the IntelliVue Family 1 Basic Operation
MP90 Major Parts and Keys
In the MP90, the display and the processing unit are separate components. It offers both touchscreen
and the Remote SpeedPoint as standard input devices.
AC Power LED
Power on LED
Display Unit
Remote Alarm Device
The Remote Alarm Device provides audio and visual indicators of alarms, in addition to those shown
on the display.
1
5
Error LED
Processing Unit
2
1 Two color coded alarm lamps (right-hand lamp flashes
red or yellow for patient alarms, left-hand lamp flashes
light blue for INOPs)
2 Alarms off lamp - when illuminated it indicates that all
patient alarms are deactivated.
3
4
3 Speaker - for alarm prompts, QRS tones and so forth
4 Monitor power on /standby switch. Press to switch
monitor on remotely. Press and hold for one second to
turn monitor off.
5 Power on LED - green when monitor is on
Power on Switch
5
1 Basic Operation Related Products
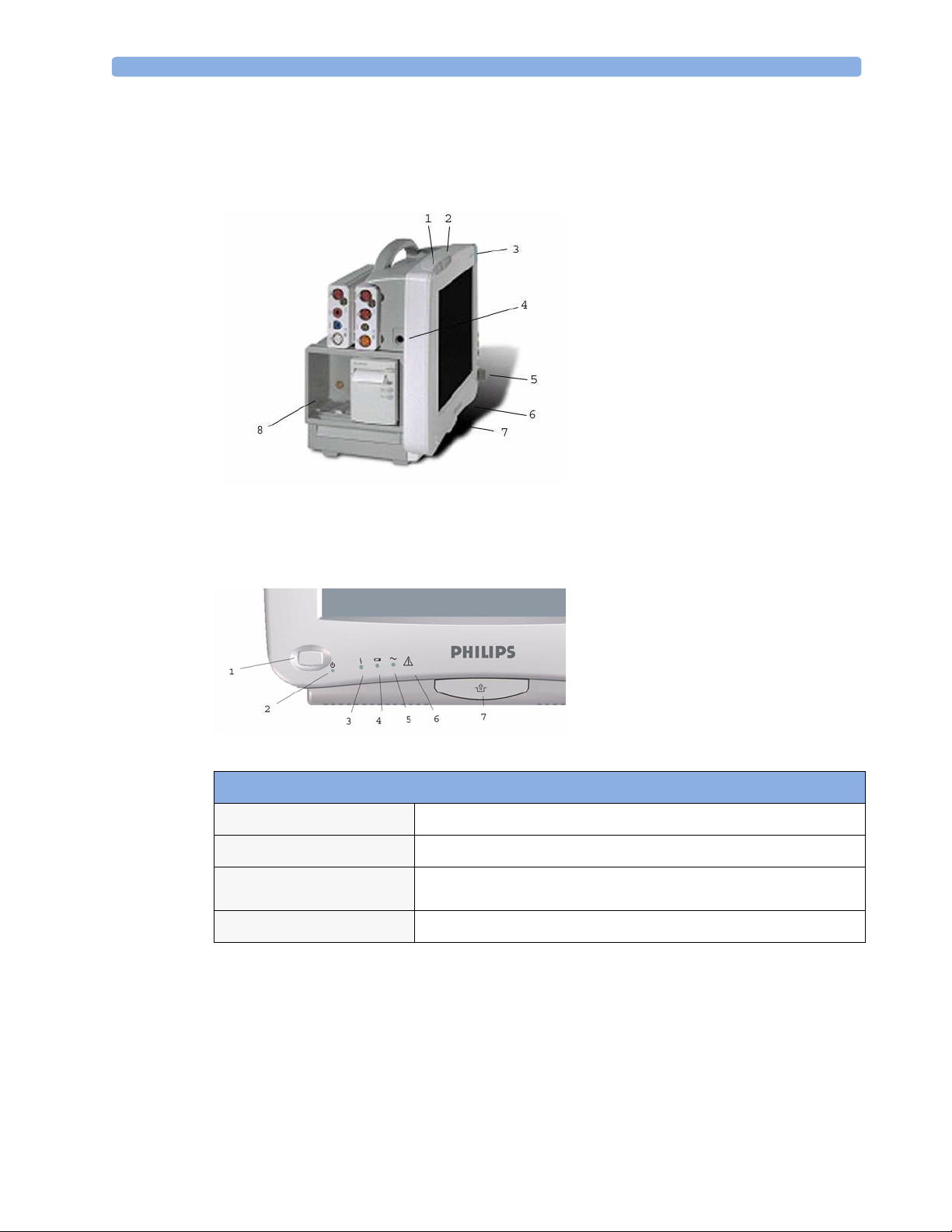
Related Products
Related products extend the measurement capabilities of your monitor. None of the related devices
have their own power on/standby switches. They take their power from the monitor, and switch on
automatically when you turn on the monitor. A green power-on LED indicates when they are drawing
power from the monitor. A permanently illuminated, or flashing, red LED indicates a problem with
the unit that requires the attention of qualified service personnel.
Flexible Module Server (M8048A)
MP60/70/90
The flexible module server (FMS) lets you use up to eight plug-in physiological measurement modules.
only
With the MP90 (M8010A) you can connect two FMSs to use up to 10 measurement modules.
Connect the FMS to the monitor via the measurement server link cable (MSL). Use the MSL
connector on the left-hand side to connect additional measurement servers. Use the connector on the
right to connect to the monitor.
Measurement Modules
You can use up to eight measurement modules with the Flexible Module Server (M8048A), two
additional modules in the integrated module slots in the MP60/MP70, and up to four in the integrated
slots in the MP40/MP50. Available modules are:
1
Multi-Measurement
Server
2
Measurement server
extension
3
Measurement server
mount
4
Flexible Module Server
5
BIS engine
6 Power on LED
7
Interruption indicator
• Invasive blood pressure, with up to five pressure modules simultaneously (M1006B)
• Temperature, with up to four temperature modules simultaneously (M1029A)
• Oxygen saturation of arterial blood (SpO
• Cardiac output (M1012A), and Continuous cardiac output with M1012A Option #C10
• Transcutaneous gas (M1018A)
• Mixed venous oxygen saturation - SvO
• Recorder (M1116B)
• VueLink device interface, with up to four VueLink modules simultaneously (M1032A)
• EEG (M1027A)
• Bispectral Index - BIS (M1034A)
6
) (M1020B)
2
(M1021A) MP60/70/90 monitor only
2
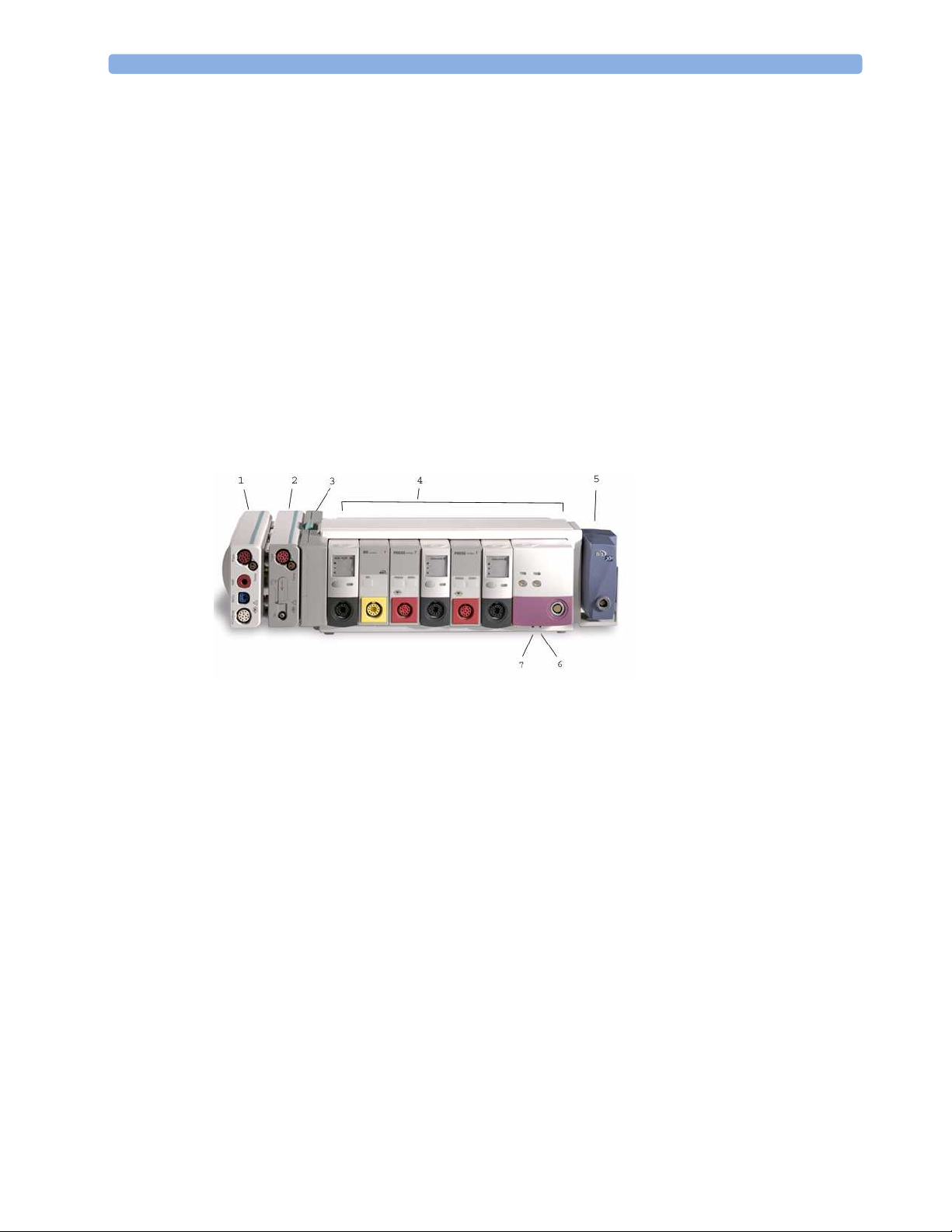
Related Products 1 Basic Operation
You can plug and unplug modules during monitoring. Insert the module until the lever on the module
clicks into place. Remove a module by pressing the lever upwards and pulling the module out.
Reconnecting a module to the same monitor restores its label and measurement settings, such as alarms
limits. If you connect it to a different monitor, the module remembers only its label.
The connector socket on the front of each module is the same color as the corresponding connector
plug on the transducer or patient cable.
Press the Setup key on the module’s front to display the measurement’s setup menu on the monitor
screen. When the setup menu is open, a light appears above the key. Some modules have a second key.
On the pressure module, for example, it initiates a zeroing procedure.
Example Module (Pressure)
1Module name
2Setup key LED
3 Setup key to enter setup menu of
measurement modules or VueLink
device data window
4 Connector socket for patient cable/
transducer
5 Second module-specific key, for
example Zero
1
2
3
80x80
4
PRESS
Press
5
7

1 Basic Operation Related Products
Multi-Measurement Server (M3001A)
The Multi-Measurement Server (MMS) can simultaneously monitor 3-, 5- or 10-lead ECG (including
arrhythmia and ST monitoring), respiration, SpO
Depending on the monitor model, you can connect it to the monitor via a cable or mount it either on
the left side of the FMS or on the back of the monitor, as shown here.
, NBP and either invasive pressure or temperature.
2
MMS mounted on rear of MP40/MP50
(left) and MP60/MP70
8
Related Products 1 Basic Operation
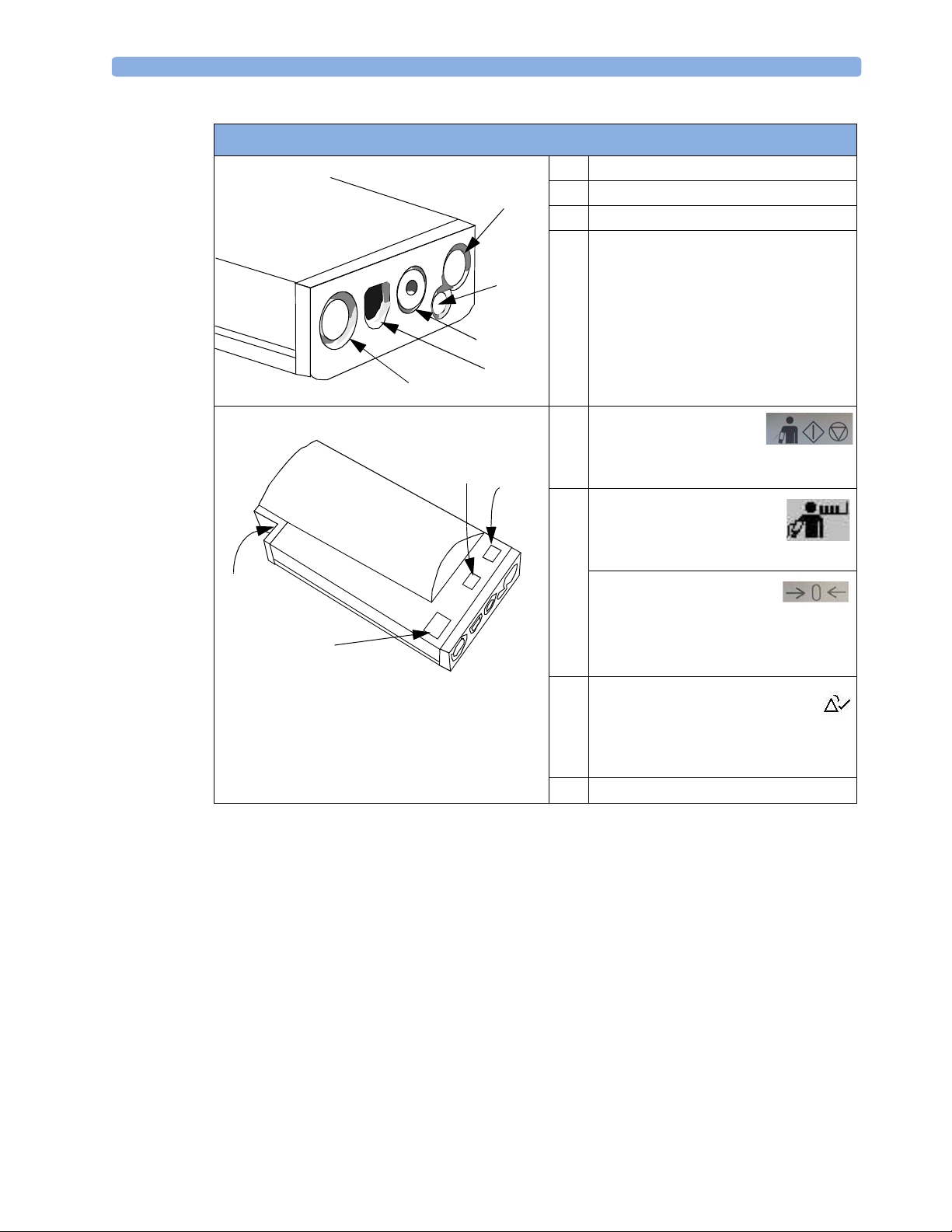
M3001A Connectors and Symbols
1 White ECG/Resp connector
2 Blue SpO
5
3 Red NBP connector
4 & 5Combined pressure (red) and temperature
(brown) connector - connect either invasive
4
3
pressure transducer or temperature probe.
You might have a version of the MMS that
does not have this connector.
connector
2
2
1
6
NBP Start/Stop key -
6
7
starts or stops NBP
measurements
7
NBP STAT key - starts NBP
STAT series of
measurements
9
OR
Zero key - initiates a zero procedure for the
8
connected pressure transducer when
pressed and held for a second
8
Silence: acknowledges all active
alarms by switching off audible
alarm indicators and lamps. Takes behavior
from SmartKey configuration
9
MSL cable connector to the monitor
M3015A and M3016A Measurement Server Extensions
The optional M3015A Microstream CO2 Extension adds microstream capnography and either
pressure or temperature to the MMS. The optional M3016A Mainstream CO
mainstream capnography and either pressure or temperature to the MMS. The measurement server
extensions connect to the MMS and use the MMS settings and power.
The measurement server extensions must not be disconnected during monitoring. When the
connection to the measurement server is broken, settings revert to default and any stored trend
information is lost.
Extension adds
2
9
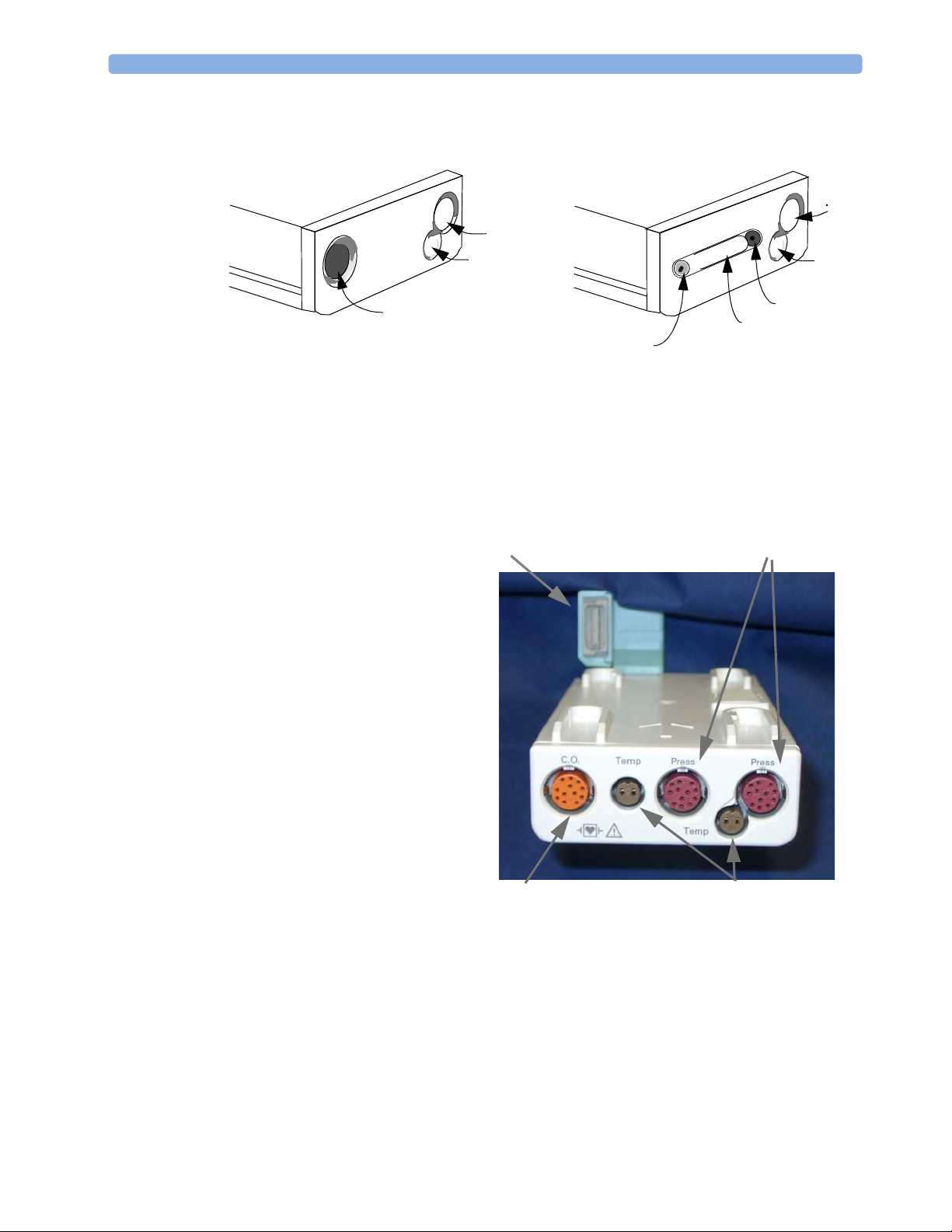
1 Basic Operation Related Products
M3015A Microstream
M3016A Mainstream
1
1
2
3
6
Pressure connector (red)
1
Temperature connector (brown)
2
Mainstream connector CO2 (optional)
3
Inlet
4
Microstream
5
Gas sample outlet
6
connector CO
M3012A Hemodynamic Measurement Server Extension
The M3012A Hemodynamic
Measurement Server Extension
(HMSE) can be connected to the
M3001A Multi-Measurement Server to
provide the following additional
measurements: Temperature, Pressure,
an additional Pressure or Temperature,
and C.O. and CCO measurements.
Connection to MMS
2
4
5
2
Pressure connectors
(red)
Anesthetic Gas Module (AGM)
See the AGM section of this Instructions for Use.
10
Cardiac Output connector
(orange; optional)
Temperature connectors (brown)
Operating and Navigating 1 Basic Operation
Operating and Navigating
Everything you need to operate the monitor is contained on its screen. Almost every element on the
screen is interactive. Screen elements include measurement numerics, waveforms, screen keys,
information fields, alarms fields and menus.
The configurability of the monitor means that often you can access the same element in different ways.
For example, you might be able to access an item through its on-screen setup menu, via a hard key, or
via a SmartKey. This Instructions for Use always describes how to access items via an on-screen menu.
You may use which ever way you find most convenient.
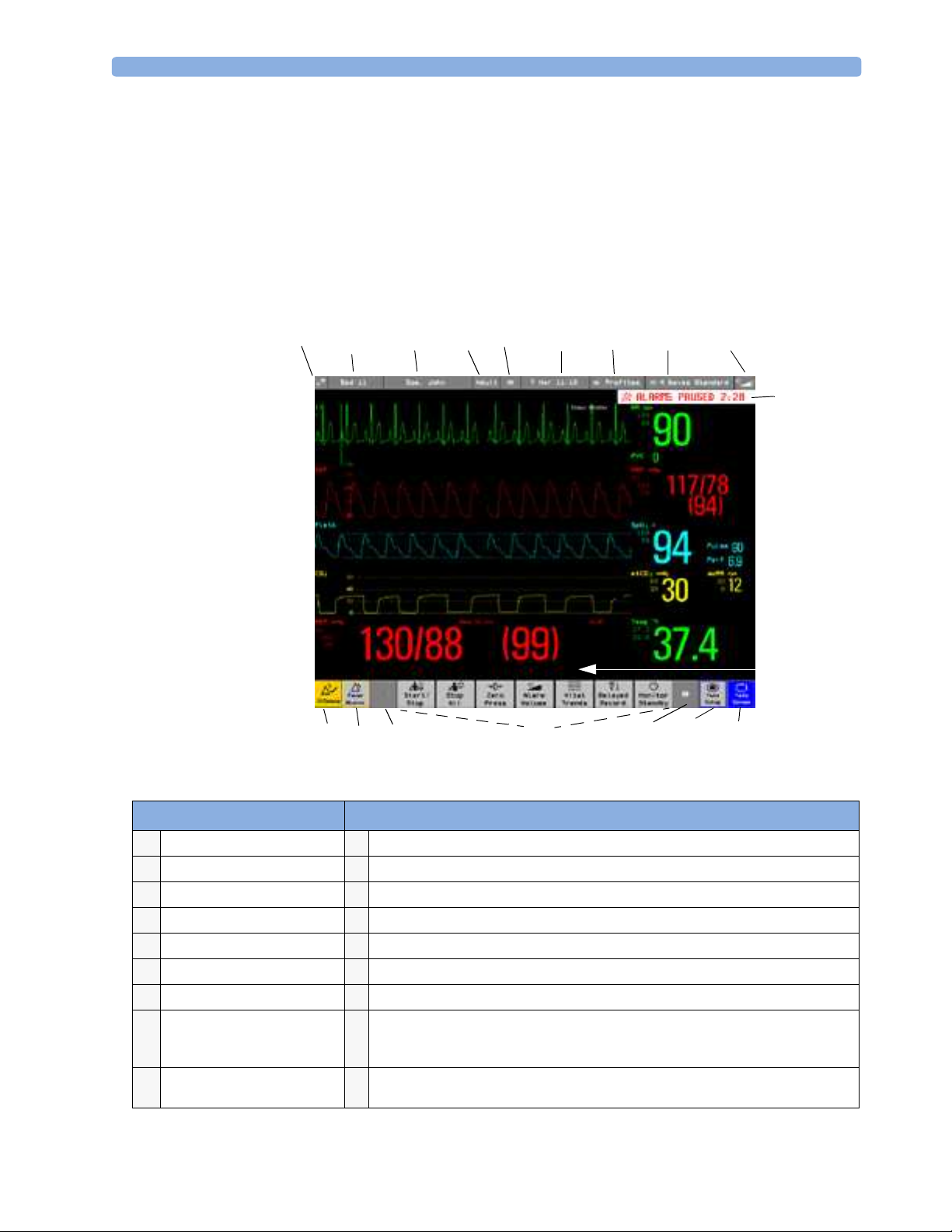
12 3
4
56 7 8 9
ABP Zero done at 11 Nov 02 7:31 am
18 1617
15
14
13
10
11
12
Monitor information line Other screen elements
network connection indicator
1
bed label
2
patient identification
3
patient category
4
paced status
5
date and time
6
access the profiles menu
7
current screen name/enter
8
change screen menu
adjust volume/level indicator
9
alarm status area - shows active alarm messages
10
status line - shows information messages and prompting you for action
11
close all open menus and windows and return to main screen
12
enter Main Setup menu
13
scroll right to display more SmartKeys
14
SmartKeys - these change according to your monitor’s configuration
15
scroll left to display more SmartKeys
16
Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Pause duration depends on monitor
17
configuration. If pause duration is infinite, this key is labeled Alarms Off. Select again to
immediately re-enable alarm indicators.
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and
18
lamps permanently or temporarily, if alarm reminder (ReAlarm) is configured on.
11

1 Basic Operation Operating and Navigating
Select a screen element to tell the monitor to carry out the actions linked to the element. For example,
select the Patient Identification element to call up the Patient Demographics window, or select
the HR numeric to call up the Setup ECG menu. Select the ECG wave segment to call up the ECG
lead menu. The network indicator and bed label elements show menus whose function is documented
in the Information Center Instructions for Use.
Using the Touchscreen
Select screen elements by pressing them directly on the monitor’s screen.
Using the MP60/MP70/MP90 SpeedPoint
MP60/70/90
Only
1
2
3
4
5
SpeedPoint (MP60/MP70
only)
1 Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and lamps. Behavior
follows the Silence permanent key configuration.
2 Alarms Off/Pause Alarms- pauses alarm indicators. Behavior follows the Pause Alarms permanent key
configuration.
3 Main Screen - close all open menus and windows and return to the main screen.
4 Back - go back one step to the previous menu.
5 SpeedPoint knob - rotate and tilt to highlight elements. Press to select.
6 Function keys on remote SpeedPoint - function identical to the first five SmartKeys configured for a
screen.
7 On/standby key
Rotate the SpeedPoint knob left or right. With each click, the highlight jumps to the neighboring
screen element. Alternatively, tilt the knob to move it in the direction of a screen element. A cursor
moves across the screen, following the direction of the knob. Any screen element under the cursor is
highlighted. When you reach the screen element you want, press the knob to select the element.
6
Remote SpeedPoint
7
12
Using the remote SpeedPoint, you can operate the monitor from a distant location such as at the foot
of the bed. The remote SpeedPoint can also be used with the MP40/MP50.
 Loading...
Loading...