Page 1

Perkins Phaser and 1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Models AA to AH and YA to YE
WORKSHOP MANUAL
Phaser 4 and 6 cylinder diesel engines for
automotive applications
1000 Series 4 and 6 cylinder diesel engines for
agricultural and industrial applications
Publication TPD 1312E, Issue 2.
© Proprietary information of Perkins Engines Company Limited, all rights reserved.
The information is correct at the time of print.
Published in February 2002 by Technical Publications.
Perkins Engines Company Limited, Peterborough PE1 5NA, England.
i
Page 2

This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
This publication is written in
Perkins Approved Clear English
Chapters
1 General information
2 Specifications
3 Cylinder head assembly
4 Piston and connecting rod assemblies
5 Crankshaft assembly
6 Timing case and drive assembly
7 Cylinder block assembly
8 Engine timing
9 Aspiration system
10 Lubrication system
11 Fuel system
12 C ooling system
13 Flywheel and housing
14 Electrical equipment
15 Auxiliary equipment
16 Sp ec ia l tools
The following pages contain a detailed table of contents
ii
Page 3

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Contents
1 General information
Introduction ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...1
Engine views . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...2
Engine identification . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...3
Safety precautions ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...5
Asbestos joints . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...6
Viton seals . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...7
Engine lift equipment ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...8
POWERPART consumable products .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...9
2 Specifications
Data and dimensions ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .28
Thread sealant ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .57
Recommended torque settings ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .58
Compression test data . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .61
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 i
Page 4

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3 Cylinder head assembly
General description ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 63
Rocker cover
Operation 3-1 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 64
Operation 3-2 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 65
Rocker ass embly
Operation 3-3 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 66
Operation 3-4 To dismantle and to assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 67
Operation 3-5 To inspect and to correct ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 68
Valve tip clearances
Operation 3-6 To check and to adjust (four cylinder engines) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 69
Operation 3-7 To check and to adjust (six cylinder engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 70
Valve springs
Operation 3-8 To change the valve springs (with cylinder head fitted) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... 71
Cylinder head assembly
Operation 3-9 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 73
Operation 3-10 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 75
Valves and valve springs
Operation 3-11 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 78
Operation 3-12 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 79
Operation 3-13 To inspect and to correct .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 80
Valve guides
Operation 3-14 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 81
Operation 3-15 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 82
Operation 3-16 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 83
Cylinder head
Operation 3-17 To inspect and to correct .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 84
Operation 3-18 To correct a valve seat with a valve seat cutter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 85
Operation 3-19 To fit valve seat inserts . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 86
ii Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 5

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4 Piston and connecting rod assemblies
General description .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .87
Big end bearing
Operation 4-1 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .89
Operation 4-2 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .90
Operation 4-3 To inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .90
Piston and connecting rod
Operation 4-4 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .91
Operation 4-5 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .92
Operation 4-6 To check the piston height above the cylinder block .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .94
Operation 4-7 To check piston height grade of a “Fastram” piston ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .95
Piston rings ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .96
Operation 4-8 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .97
Piston and connecting rod assembly
Operation 4-9 To dismantle and to assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .98
Piston and piston rings
Operation 4-10 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .99
Connecting rod
Operation 4-11 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...100
Small end bush
Operation 4-12 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...100
Piston cooling jets
Operation 4-13 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...101
Operation 4-14 To check the jet alignment ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...102
5 Crankshaft assembly
General description .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...103
Crankshaft pulley
Operation 5-1 To remove and to fit (four cylinder engines) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...105
Crankshaft pulley and damper
Operation 5-2 To remove (six cylinder engines) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...106
Operation 5-3 To fit (six cylinder engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...107
Operation 5-4 To inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...108
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 iii
Page 6

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Rear oil seal assembly .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 110
Operation 5-5 To remove and to fit (one-piece assembly) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 111
Operation 5-6 To remove and to fit (two-piece assembly) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 114
Operation 5-7 To renew the rear end oil seal (two-piece assembly) ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 116
Operation 5-8 To remove and to fit a wear sleeve . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 117
Rear oil seal assembly (engines with a flywheel housing that is oil filled)
Operation 5-9 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 118
Operation 5-10 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 119
Operation 5-11 To renew the rear oil seals ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 121
Operation 5-12 To fit and remove a "Wear-Sleeve" ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 123
Thrust washers
Operation 5-13 To check crankshaft end-float ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 124
Operation 5-14 To remove and to fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 125
Main bearings
Operation 5-15 To remove (with the crankshaft in position) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 126
Operation 5-16 To fit (with the crankshaft in position) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 127
Operation 5-17 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 127
Crankshaft
Operation 5-18 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 128
Operation 5-19 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 129
Operation 5-20 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 132
Balancer unit
Operation 5-21 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 133
Operation 5-22 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 134
Operation 5-23 To dismantle . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 135
Operation 5-24 To assemble . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 137
Operation 5-25 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 141
Operation 5-26 To remove and to fit the needle roller bearings ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 142
Operation 5-27 To remove and to fit the bushes for the balance weights . ... ... ... ... .. 143
6 Timing case and drive assembly
General description ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 145
Timing case cover
Operation 6-1 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 146
Operation 6-2 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 147
Front oil seal
Operation 6-3 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 148
Operation 6-4 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 149
Operation 6-5 To remove and to fit a wear sleeve . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 151
iv Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 7

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Idler gear and hub
Operation 6-6 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...152
Operation 6-7 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...154
Idler gear and hub for the Bendix or Knorr-Bremse compressor ... ... ... ... ... ... ...156
Operation 6-8 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...156
Operation 6-9 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...157
Fuel pump gear
Operation 6-10 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...158
Operation 6-11 To fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...159
Camshaft gear
Operation 6-12 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...160
Operation 6-13 To fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...161
Crankshaft gear
Operation 6-14 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...162
Timing case
Operation 6-15 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...163
Operation 6-16 To fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...164
Camshaft and tappets
Operation 6-17 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...166
Operation 6-18 To fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...167
7 Cylinder block assembly
General description .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...169
Cylinder block
Operation 7-1 To dismantle ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...170
Operation 7-2 To assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...171
Operation 7-3 To inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...173
Operation 7-4 To remove and to fit a new type ‘D’ plug to the tappet chamber ... ... ...174
Cylinder liner
Operation 7-5 To inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...176
Operation 7-6 To recover a glazed liner ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...177
Operation 7-7 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...178
Operation 7-8 To fit a service liner ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...180
Operation 7-9 To fit a partially finished liner .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...183
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 v
Page 8

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
8 Engine timing
Standard operations
Operation 8-1 To set number 1 piston to TDC on the compression stroke ... ... ... ... .. 187
Operation 8-2 Another method to set number 1 piston to TDC . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 188
Operation 8-3 To check the valve timing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 189
Engines fitted with Bosch EPVE fuel injection pumps .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 190
Operation 8-4 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump (10° or more, static) ... .. 191
Operation 8-5 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump (9° or less, static) ... ... .. 193
Operation 8-6 To check the timing mark of the fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 194
Operation 8-7 To check the engine timing mark ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 195
Operation 8-8 To check the timing of the pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... .. 196
Engines fitted with Bosch MW in-line fuel injection pumps .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 197
Operation 8-9 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 198
Engines fitted with Lucas/Delphi DPA and DPS fuel injection pumps . ... ... ... ... .. 200
Operation 8-10 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 201
Operation 8-11 To check the timing mark of the fuel injection pump . ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 202
Operation 8-12 To check the engine timing mark .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 203
Operation 8-13 To check the timing of the pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... .. 204
Engines fitted with a Lucas/Delphi DP200 Series fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... .. 205
Operation 8-14 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 207
Operation 8-15 To check the timing of the pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... .. 209
Engines fitted with Stanadyne fuel injection pumps . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 210
Operation 8-16 To check the timing of the fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 211
Operation 8-17 To check the timing mark of the fuel injection pump . ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 212
Operation 8-18 To check the engine timing mark .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 214
Operation 8-19 To check the timing of the pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... .. 215
9 Aspiration system
General description ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 217
Turbocharger
Operation 9-1 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 219
Operation 9-2 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 220
Operation 9-3 To clean the impeller and the compressor casing .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 222
Operation 9-4 To remove and to fit the actuator assembly of the waste-gate unit ... .. 223
Operation 9-5 To check and adjust the operation of the waste-gate . ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 224
Turbocharger faults ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 225
vi Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 9

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Open engine breather ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...227
Operation 9-6 To remove, to fit and to clean (early type) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...227
Operation 9-7 To clean and to renew (Later type) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...228
Operation 9-8 To renew (Latest type) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...229
Operation 9-9 To Inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...230
Closed breather system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...231
Operation 9-10 To clean the early closed breather system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...232
Operation 9-11 To renew latest closed breather system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...233
Operation 9-12 To repair the connection for the latest breather outlet elbow ... ... ... ...235
10 Lubrication system
General description (four cylinder engine lubrication system) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...237
General description (six cylinder engine lubrication system) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...238
Lubrication system flow diagram ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...239
Lubrication system flow diagram for the relief valve and balancer . ... ... ... ... ... ...240
Filter canister
Operation 10-1 To renew .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...241
Filter head
Operation 10-2 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...242
Sump
Operation 10-3 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...243
Oil strainer and suction pipe
Operation 10-4 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...244
Operation 10-5 To inspect and to correct .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...245
Lubricating oil pump
Operation 10-6 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...246
Operation 10-7 To fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...247
Operation 10-8 To inspect . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...248
Operation 10-9 To remove the idler shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...249
Operation 10-10 Alternative method to remove the idler shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...250
Operation 10-11 To fit the idler shaft (Six cylinder engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...251
Operation 10-12 To remove and to fit the idler shaft (four cylinder engines) ... ... ... ...252
Relief valve
Operation 10-13 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...253
Operation 10-14 To dismantle and to assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...254
Operation 10-15 To inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...254
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 vii
Page 10

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Flexible oil pipes
Operation 10-16 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 255
Operation 10-17 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 256
Operation 10-18 To Inspect ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..258
11 Fuel system
General description ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 259
Cold start advance unit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 262
Fuel filter elements
Operation 11-1 Fuel filter element types ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..264
Operation 11-2 To renew the filter element of the separate element type . ... ... ... ... .. 265
Operation 11-3 To renew the filter element of the canister type ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..266
Operation 11-4 To renew the filter element of the quick release canister type .. ... ... .. 267
Fuel filter canister (Bosch MW fuel injection pump)
Operation 11-5 To renew ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 268
Atomisers
Operation 11-6 Atomiser fault ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 269
Operation 11-7 To remove and to fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 269
Fuel lift pump
Operation 11-8 To remove and to fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 270
Operation 11-9 To dismantle . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..271
Operation 11-10 To assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..272
Operation 11-11 To test . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 273
Fuel lift pump (Bosch MW fuel injection pump)
Operation 11-12 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 274
Operation 11-13 To dismantle and assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 275
Bosch EPVE fuel injection pump (without a locking screw)
Operation 11-14 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 276
Operation 11-15 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 277
Bosch EPVE fuel injection pump (with a locking screw) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 278
Operation 11-16 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 279
Operation 11-17 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 281
Operation 11-18 To set .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 282
viii Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 11

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Bosch EPVE fuel injection pump
Operation 11-19 To set the injection advance device (KSB) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...285
Operation 11-20 To adjust . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...286
Operation 11-21 General description for pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ...287
Operation 11-22 To remove pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...289
Operation 11-23 To fit pin timed fuel injection pump . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...290
Operation 11-24 To adjust pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...292
Operation 11-25 To eliminate air from the fuel system . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...293
Operation 11-26 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...297
Operation 11-27 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...299
Operation 11-28 To adjust the fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...303
Operation 11-29 To remove and fit the adaptor plate for the fuel injection pump . ... ...304
Operation 11-30 To eliminate air from the fuel system . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...305
Lucas/Delphi DPA and DPS fuel injection pumps
Operation 11-31 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...306
Operation 11-32 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...307
Operation 11-33 To adjust . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...308
Operation 11-34 Electrical shut off solenoid (ESOS) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...309
Operation 11-35 To eliminate air from the fuel system . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...311
Operation 11-36 Standard method ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...312
Operation 11-37 Self-vent method ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...313
Lucas/Delphi DP 200 Series fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...314
Operation 11-38 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...315
Operation 11-39 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...317
Operation 11-40 To adjust . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...318
Operation 11-41 General description for pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ...319
Operation 11-42 To remove pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...321
Operation 11-43 To fit pin timed fuel injection pump . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...322
Operation 11-44 To adjust pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...324
Operation 11-45 Electrical shut off solenoid (ESOS) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...325
Operation 11-46 To eliminate air from the fuel system . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...327
Stanadyne fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...329
Operation 11-47 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...331
Operation 11-48 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...332
Operation 11-49 To adjust . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...333
Operation 11-50 General description for pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ...334
Operation 11-51 To remove pin timed fuel injection pump ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...335
Operation 11-52 To fit pin timed fuel injection pump . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...336
Operation 11-53 To adjust pin timed fuel injection pump .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...338
Operation 11-54 To eliminate air from the fuel system . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...341
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 ix
Page 12

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
12 Cooling system
General description ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 343
Thermostats
Operation 12-1 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 344
Operation 12-2 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 345
Operation 12-3 To test .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 346
Coolant pump (gear driven) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 347
Operation 12-4 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 347
Operation 12-5 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 348
Operation 12-6 To dismantle (early engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 349
Operation 12-7 To assemble (early engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 350
Operation 12-8 To dismantle (later engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 353
Operation 12-9 To assemble (later engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 354
Operation 12-10 To remove and fit pressed steel covers (latest engines) ... ... ... ... .. 358
Coolant pump (belt driven) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 360
Operation 12-11 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 360
Operation 12-12 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 362
Operation 12-13 To dismantle ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 363
Operation 12-14 To assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..364
Coolant pump (auxiliary) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 366
Operation 12-15 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 366
Operation 12-16 To dismantle ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 367
Operation 12-17 To assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..368
Fan
Operation 12-18 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 370
Fan drive
Operation 12-19 To remove and to fit the early pulley ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 370
Operation 12-20 To remove and to fit the latest pulley .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 371
Lubricating oil cooler
Operation 12-21 To remove and to fit (four cylinder turbocharged engines) . ... ... ... .. 372
Operation 12-22 To remove and to fit (six cylinder engines) . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 373
Operation 12-23 To remove (six cylinder turbocharged engines) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 374
Operation 12-24 To fit (six cylinder turbocharged engines) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 376
Operation 12-25 To dismantle and to assemble - six cylinder engines . ... ... ... ... ... .. 378
Operation 12-26 To dismantle and to assemble (six cylinder turbocharged engines) .. 380
Operation 12-27 To remove and to fit vertical canister type .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 381
Operation 12-28 To remove and to fit horizontal canister type .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 382
Cooler by-pass valve
Operation 12-29 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 383
x Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 13

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Intercooler . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...384
Operation 12-30 To remove .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...384
Operation 12-31 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...385
Operation 12-32 To clean and to inspect .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...386
13 Flywheel and housing
General description .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...387
Flywheel
Operation 13-1 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...388
Ring gear
Operation 13-2 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...390
Flywheel housing
Operation 13-3 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...391
14 Electrical equipment
Operation 14-1 To check the drive belts ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...394
Operation 14-2 To adjust belt tension ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...395
Operation 14-3 To remove and to fit the drive belts .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...396
Operation 14-4 To remove and to fit the alternator ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...397
Operation 14-5 To maintain the alternator ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...397
Alternator fault diagnosis ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...398
Operation 14-6 To remove and to fit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...400
Operation 14-7 To maintain the brush gear and the commutator . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...401
Operation 14-8 To test on the engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...402
Operation 14-9 To remove and to fit a fuelled starting aid ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...404
Operation 14-10 To remove and to fit a twin fuelled starting . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...405
Operation 14-11 How to check the fuelled starting aid .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...406
Operation 14-12 To remove and to fit a port heater .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...406
15 Auxiliary equipment
Wabco compressors
Operation 15-1 To remove the earliest compressor and drive assembly .. ... ... ... ... ...408
Operation 15-2 To fit the earliest compressor and drive assembly ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...409
Operation 15-3 To fit the early compressor and drive assembly ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...410
Operation 15-4 To fit the early compressor only ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...412
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2 xi
Page 14

Phaser/1000 Series
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Compressor drive for Wabco compressors
Operation 15-5 To remove and to fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 413
Operation 15-6 To dismantle . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..414
Operation 15-7 To assemble . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 416
Bendix compressors
Operation 15-8 To remove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 418
Operation 15-9 To fit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 419
Knorr-Bremse compressors
Operation 15-10 To remove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 421
Operation 15-11 To fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 422
Operation 15-12 To remove the reed valves . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 424
Operation 15-13 To fit the reed valves ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..425
Operation 15-14 To remove the top unloader valve .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 426
Operation 15-15 To fit the top unloader valve ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..426
Operation 15-16 To remove the crankshaft / connecting rod / piston / piston rings ... .. 427
Operation 15-17 To fit the crankshaft / connecting rod / piston / piston rings ... ... ... .. 428
Power steering pump
Operation 15-18 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 430
Adaptor for a hydraulic pump or a steering pump with a splined drive
Operation 15-19 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 431
Operation 15-20 To dismantle ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 432
Operation 15-21 To assemble ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..433
Exhauster
Operation 15-22 To remove and to fit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 434
16 Special tools
List of special tools .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 435
xii Workshop Manual, TPD 1312E, Issue 2
Page 15

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
1
General information 1
Introduction
This Workshop Manual has been written to provide assistance in the service and overhaul of Perkins Phaser
and 1000 Series engines. It should be used in conjunction with normal workshop practise and information
contained in current service bulletins. Mention of certain accepted practices therefore, has been purposely
omitted in order to avoid repetition. For overhaul procedures the assumption is made that the engine is
removed from the application.
Most of the general information which is included in the relevant User’s Handbook has not been repeated in
this workshop manual and the two publications should be used together.
Where the information applies only to certain engine types, this is indicated in the text.
The details of some operations will be different according to the type of fuel injection pump which is fitted. The
specific pump type used can be found by reference to the manufacturer’s identification plate on the pump body
but, generally, the type of pump fitted is as shown below:
l Lucas/Delphi - DPA, DPS and DP200 Series
l Bosch - EPVE and MW
l Stanadyne - DB2 and DB4.
When reference is made to the "left" or "right" side of the engine, this is as seen from the flywheel end of the
engine.
Special tools have been made available and a list of these is given in Chapter 16, Special tools. Reference to
the relevant special tools is also made at the beginning of each operation.
Data and dimensions are included in Chapter 2, Specifications.
Read and remember the "Safety precautions" on page 5. They are given for your protection and must be used
at all times.
Danger is indicated in the text by two methods:
Warning! This indicates that there is a possible danger to the person.
Caution: This indicates that there is a possible danger to the engine.
Note: Is used where the information is important, but there is not a danger.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 1
Page 16
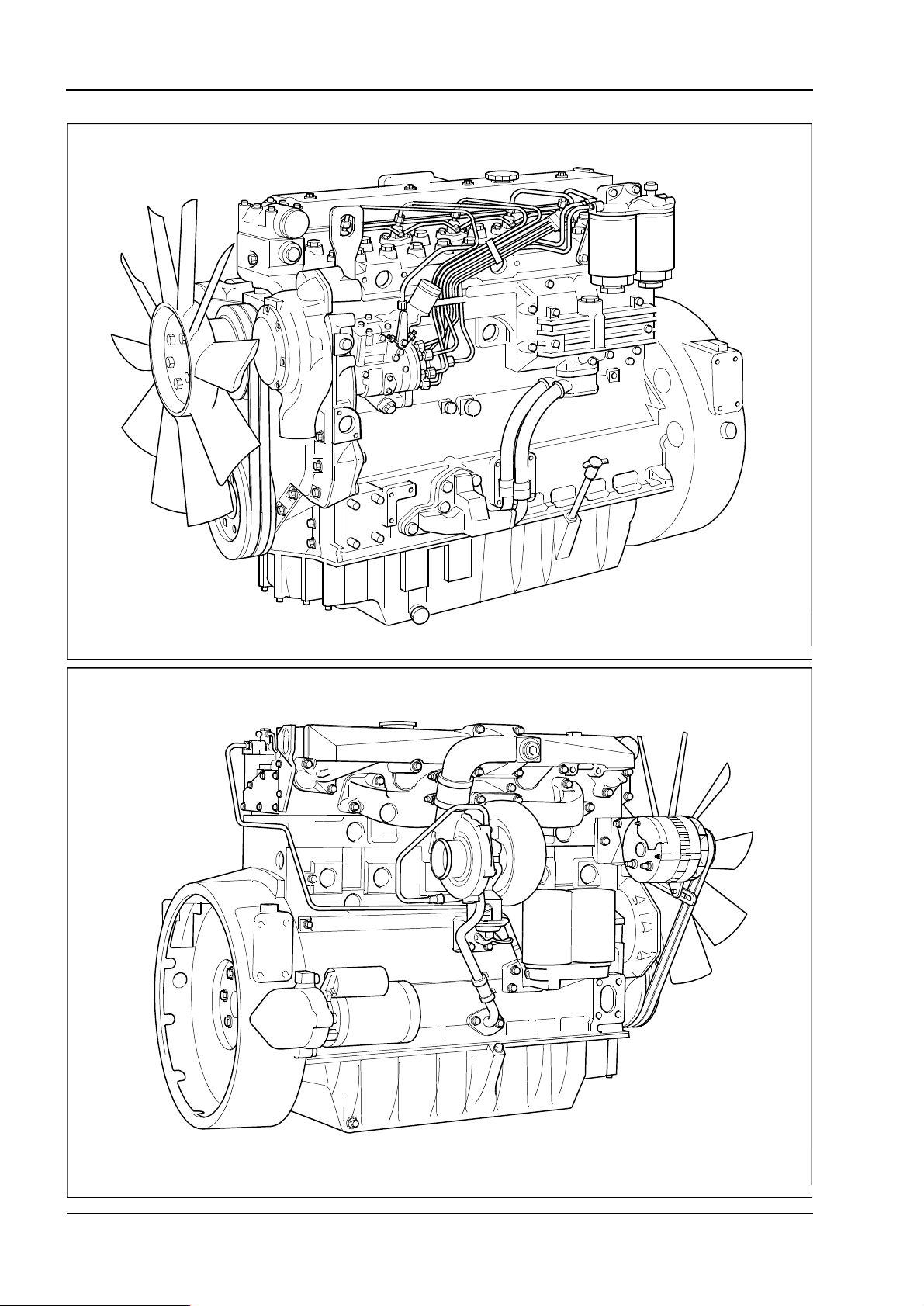
1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Engine views
Phaser/1000 Series
A0314N
A0315
2 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 17

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
1
Engine identification
The Perkins Phaser and 1000 Series engines have been designed for specific applications, as shown below:
l Phaser for automotive applications
l 1000 Series for agricultural and industrial applications.
Each series consists of both four and six cylinder engines, each of which will have four basic engine types naturally aspirated, compensated, turbocharged and turbocharged/intercooled.
There are different models in each series.
Phaser engines are named according to their approximate power output, for example:
Phaser 110T - four cylinder engine rated at 106 bhp ("T" indicates that the engine is turbocharged).
Phaser 210Ti - six cylinder engine rated at 210 bhp ("Ti" indicates that the engine is turbocharged and
intercooled).
1000 Series engines are identified by a system of numbers and letters, for example:
1006-6TW - six cylinder engine of six litres ("TW" indicates that the engine is turbocharged and intercooled).
In this Workshop Manual, the different engine types are indicated by their code letters. These are the first two
letters of the engine number as indicated below:
Code letters Engine type
AA Four cylinder, naturally aspirated
AB Four cylinder, turbocharged
AC Four cylinder, compensated
AD Four cylinder, turbocharged and intercooled
AE Four cylinder, turboch arge d an d i ntercoo led designed to conform to th e USA em is s ion legislation
AG Four cylinder, naturally aspirated with belt driven coolant pump
AH Four cylinder, turbocharged with belt driven coolant pump
YA Six cylinder, naturally aspirated
YB Six cylinder, turbocharged
YC Six cylinder, compensated
YD Six cylinder, turbocharged and intercooled
YE Six cylinder, turbocharged and intercooled designed to conform to the USA emission legislation
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 3
Page 18
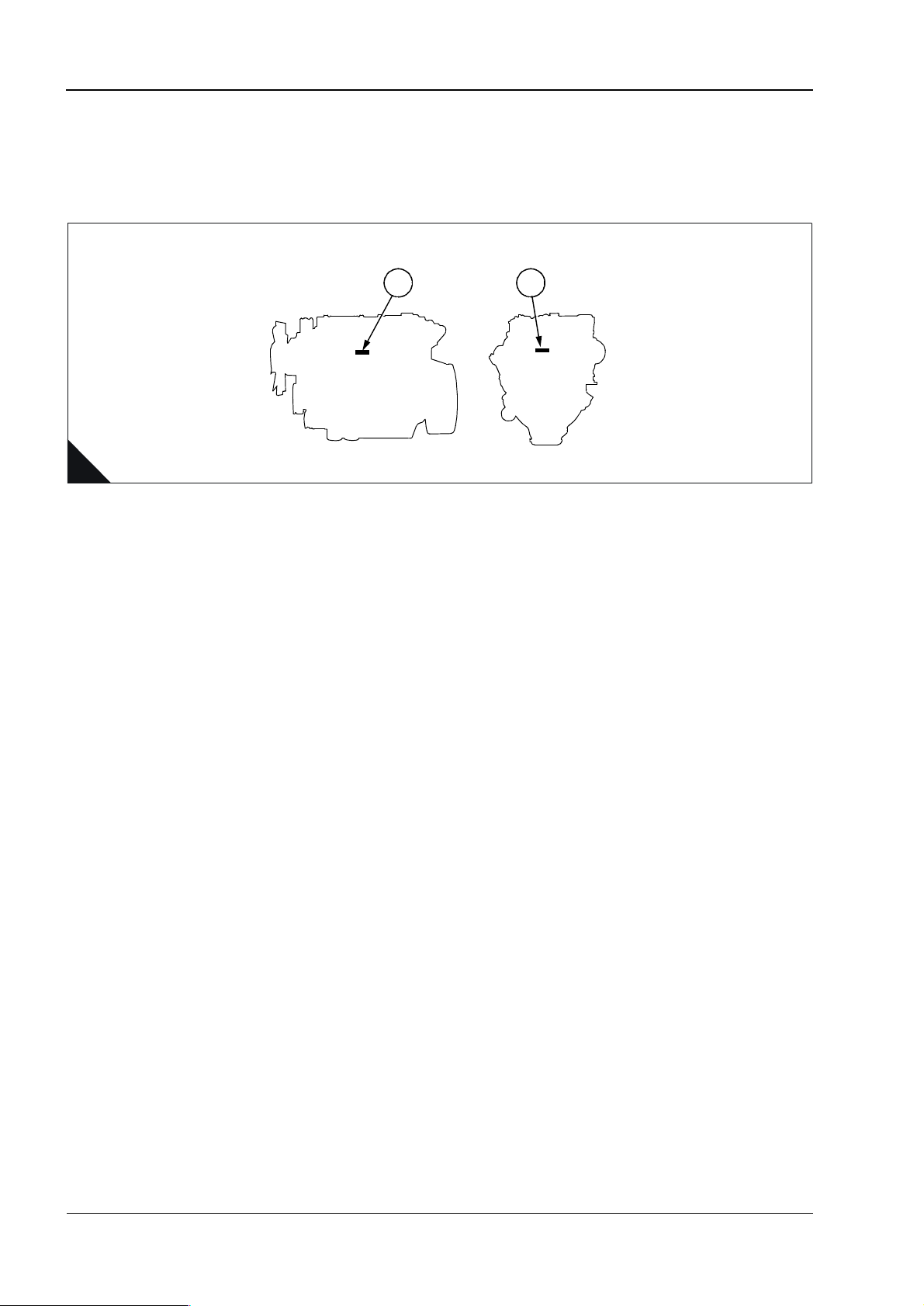
1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
The engine number is stamped on a label which is fastened to the left side (A1) or rear (A2) of the cylinder
block. An example of an engine number is AB30126U510256N.
Further information about the engine number system can be found in the relevant User’s Handbook.
Note: If you need parts, service or information for your engine, you must give the complete engine number to
your Perkins distributor.
1 2
Phaser/1000 Series
A
A0043
4 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 19

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
1
Safety precautions
These safety precautions are important . You must refer also to the local regulations in the country of use.
Some items only refer to specifi c appl ic ati on s.
l Only use these engines in the type of application for which they have been designed.
l Do not change the specification of the engine.
l Do not smoke when you put fuel in the tank.
l Clean away fuel which has been spilt. Material which has been contaminated by fuel must be moved to a
safe place.
l Do not put fuel in the tank while the engine runs (unless it is absolutely necessary).
l Do not clean, add lubricating oil, or adjust the engine while it runs (unless you have had the correct training;
even then extreme care must be used to prevent injury).
l Do not make adjustments that you do not understand.
l Ensure that the engine does not run in a location where it can cause a concentration of toxic emissions.
l Other persons must be kept at a safe distance while the engine or auxiliary equipment is in operation.
l Do not permit loose clothing or long hair near moving parts.
l Keep away from moving parts during engine operation.
Warning! Some moving parts cannot be seen clearly while the engine runs.
l Do not operate the engine if a safety guard has been removed.
l Do not remove the filler cap of the cooling system while the engine is hot and while the coolant is under
pressure, because dangerous hot coolant can be discharged.
l Do not use salt water or any other coolant which can cause corrosion in the closed circuit of the cooling
system.
l Do not allow sparks or fire near the batteries (especially when the batteries are on charge) because the
gases from the electrolyte are highly flammable. The battery fluid is dangerous to the skin and especially
to the eyes.
l Disconnect the battery terminals before a repair is made to the electrical system.
l Only one person must control the engine.
l Ensure that the engine is operated only from the control panel or from the operators position.
l If your skin comes into contact with high-pressure fuel, obtain medical assistance immediately.
l Diesel fuel and lubricating oil (especially used lubricating oil) can damage the skin of certain persons.
Protect your hands with gloves or a special solution to protect the skin.
l Do not wear clothing which is contaminated by lubricating oil. Do not put material which is contaminated
with oil into the pockets of clothing.
l Discard used lubricating oil in a safe place to prevent contamination.
l Ensure that the control lever of the transmission drive is in the "out-of-drive" position before the engine is
started.
l Use extreme care if emergency repairs must be made in adverse conditions.
l The combustible material of some components of the engine (for example certain seals) can become
extremely dangerous if it is burned. Never allow this burnt material to come into contact with the skin or with
the eyes. Refer to "Viton seals" on page 7.
l Read and use the instructions relevant to "Engine lift equipment" on page 8.
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 5
Page 20

1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
l Always use a safety cage to protect the operator when a component is to be pressure tested in a container
of water. Fit safety wires to secure the plugs which seal the hose connections of a component which is to
be pressure tested.
l Do not allow compressed air to contact your skin. If compressed air enters your skin, obtain medical help
immediately.
l Turbochargers operate at high speed and at high temperatures. Keep fingers, tools and debris away from
the inlet and outlet ports of the turbocharger and prevent contact with hot surfaces.
l Fit only genuine Perkins parts.
Phaser/1000 Series
Asbestos joints
Some joints and gaskets contain compressed asbestos fibres in a rubber compound or in a metal outer cover.
The "white" asbestos (Chrysotile) which is used is a safer type of asbestos and the risk of damage to health is
extremely small.
l The risk of asbestos from joints occurs at their edges or if a joint is damaged when a component is removed
or if a joint is removed by abrasive action.
l To ensure that the risk is kept to a minimum, the precautions given below must be applied when an engine
which has asbestos joints is dismantled or assembled.
l Work in an area with good ventilation.
l Do not smoke.
l Use a hand scraper to remove the joints - do not use a rotary wire brush.
l Ensure that the joint to be removed is wet with oil or water to contain loose particles.
l Spray all asbestos debris with water and put it in a closed container which can be sealed for safe disposal.
6 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 21

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
1
Viton seals
Some seals used in engines and in components fitted to engines are made of Viton.
Viton is used by many manufacturers and is a safe material under normal conditions of operation. If Viton is
burned, a product of this burnt material is an acid which is extremely dangerous. Never allow this burnt material
to come into contact with the skin or with the eyes.
If it is necessary to come into contact with components which have been burnt, ensure that the precautions
which follow are used:
l Ensure that the components have cooled.
l Use Neoprene gloves and discard the gloves safely after use.
l Wash the area with calcium hydroxide solution and then with clean water.
l Disposal of components and gloves which are contaminated must be in accordance with local regulations.
If there is contamination of the skin or eyes, wash the affected area with a continuous supply of clean water or
with calcium hydroxide solution for 15-60 minutes. Obtain immediate medical attention.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 7
Page 22
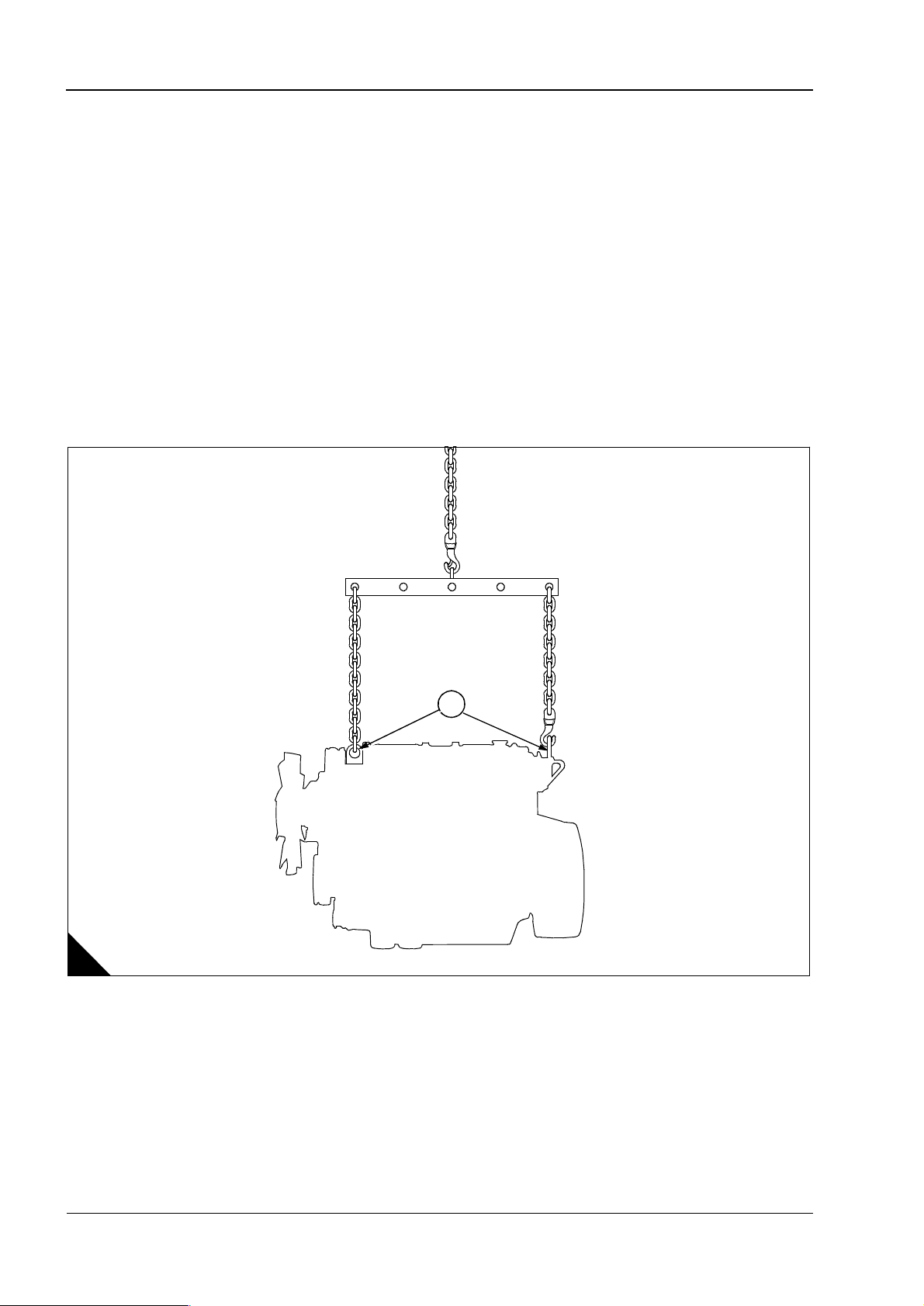
1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Engine lift equipment
The maximum weight of the engine without coolant, lubricant or a gearbox fitted will vary for different
applications. It is recommended that lift equipment of the minimum capacity listed below is used:
l Four cylinder engines: 500 kg (1100 lbs)
l Six cylinder engines: 600 kg (1320 lbs)
Before the engine is lifted
l Always use lift equipment of the approved type and of the correct capacity to lift the engine. It is
recommended that lift equipment of the type shown in (A) is used, to provide a vertical lift directly above
the engine lift brackets (A1). Never use a single lift bracket to raise an engine.
l Check the engine lift brackets for damage and that they are secure before the engine is lifted. The torque
for the setscrews for the engine lift brackets is 44 Nm (33 lbf ft) 4,5 kgf m.
l To Prevent damage to the rocker cover, ensure that there is clearance between the hooks and the rocker
cover.
l Use lift equipment or obtain assistance to lift heavy engine components such as the cylinder block, cylinder
head, balancer unit, flywheel housing, crankshaft and flywheel.
A
1
A0044
8 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 23

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
1
POWERPART consumable products
Perkins have made available the products recommended below in order to assist in the correct operation,
service and maintenance of your engine and your machine. The instructions for the use of each product are
given on the outside of each container. These products are available from your Perkins distributor.
POWERPART Antifreeze
Protects the cooling system against frost and corrosion. Part number 21825166.
POWERPART Easy Flush
Cleans the cooling system. Part number 21825001.
POWERPART Gasket and flange sealant
To seal flat faces of components where no joint is used. Especially for aluminium components. Part number
21820518.
POWERPART Gasket remover
An aerosol for removal of sealants and adhesives. Part number 21820116.
POWERPART Griptite
To improve the grip of worn tools and fasteners. Part number 21820129.
POWERPART Hydraulic threadlock
To retain and seal pipe connections with fine threads. Especially suitable for hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Part number 21820121.
POWERPART Industrial grade super glue
Instant adhesive designed for metals, plastics and rubbers. Part number 21820125.
POWERPART Lay-Up 1
A diesel fuel additive for protection against corrosion. Part number 1772204.
POWERPART Lay-Up 2
Protects the inside of the engine and of other closed systems. Part number 1762811.
POWERPART Lay-Up 3
Protects outside metal parts. Part number 1734115.
POWERPART Metal repair putty
Designed for external repair of metal and plastics. Part number 21820126.
POWERPART Pipe sealant and sealant primer
To retain and seal pipe connections with coarse threads. Pressure systems can be used immediately. Part
number 21820122.
POWERPART Radiator stop leak
For the repair of radiator leaks. Part number 21820127.
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 9
Page 24

1
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
POWERPART Retainer (high strength)
To retain components which have an interference fit. Part number 21820638.
POWERPART Retainer (oil tolerant)
To retain components which have a transition fit. Part number 21820603.
POWERPART Safety cleaner
General cleaner in an aerosol container. Part number 21820128.
POWERPART Silicone adhesive
An RTV silicone adhesive for applications where low pressure tests occur before the adhesive sets. Used for
sealing flange where oil resistance is needed and movement of the joint occurs. Part number 21826038.
POWERPART Silicone RTV sealing and jointing compound
Silicone rubber sealant which prevents leakage through gaps. Part number 1861108.
POWERPART Stud and bearing lock
To provide a heavy duty seal to components that have a light interference fit. Part number 21820119.
POWERPART Threadlock and nutlock
To retain small fasteners where easy removal is necessary. Currently Loctite 222e. Part number 21820119 or
21820120.
Phaser/1000 Series
POWERPART Universal jointing compound
Universal jointing compound which seals joints. Part number 1861117.
10 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 25

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Specifications 2
Basic engine data
Number of cylinders:
AA, AB, AC, AD, AE, AG, AH.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4
YA, YB, YC, YD, YE ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6
Cylinder arrangement.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... In-line
Cycle ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Four stroke
Direction of rotation . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Clockwise from the front
Induction system:
AA, AG, YA.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Naturally aspirated
AB, AH, YB.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Turbocharged
AC, YC. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... A ltitude compensated
AD, AE, YD, YE... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Turbocharged/intercooled
Combustion system. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Direct injection
Nominal bore ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .100 mm (3.937 in)
Stroke.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .127 mm (5.000 in)
Compression ratio:
AA, AG, YA.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 16.5:1
Certain YA engines.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 17.5:1
AB, AC, AD, AH, YB, YC, YD.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 16.0:1
AE, YE. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 17.5:1
Certain AD engines . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...17.25:1 or 17.5:1
Cubic capacity:
- Four cylinder engines ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .4 litres (243 in
- Six cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .6 litres (365 in
Firing o rder:
- Four cylinder engines ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1, 3, 4, 2
- Six cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4
Valve tip clearance (cold):
Inlet.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,20 mm (0.008 in)
Exhaust ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,45 mm (0.018 in)
Lubricating oil pressure (minimum at maximum engine speed and normal engine temperature):
Engines without piston cooling jets.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .207 kpa (30 lbf/in
Engines with piston cooling jets... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .280 kpa (40 lbf/in2) 2,8 kgf/cm
2
) 2,1 kgf/cm
3
)
3
)
2
2
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 27
Page 26
2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Data and dimensions
Note: T his information is given as a guide for personnel engaged on engine overhauls. The dimensions which
are shown are those which are mainly used in the factory. The information applies to all engines, unless an
engine type code is shown.
Cylinder head
Angle of valve seat:
Exhaust 46° ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... (88° included angle)
Inlet ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 46° (88° included angle) or 31° (118° included angle)
Diameter of parent bore for valve guide. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,87/15,89 mm (0.6247/0.6257 in)
2
Leak test pressure . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 200 kPa (29 lbf/in
Head thickness .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 102,79/103,59 mm (4.047/4.078 in)
Minimum permissible thickness after head face has been machined ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..102,48 mm (4.035 in)
AE, YE engines.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... See Operation 3-17
Maximum permissible distortion of cylinder head
Four cylinder engines
A1... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,08 mm (0.003 in)
A2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,15 mm (0.006 in)
A3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,15 mm (0.006 in)
Six cylinder engines
) 2,04 kgf/cm
2
A1... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,13 mm (0.005 in)
A2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,25 mm (0.010 in)
A3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,25 mm (0.010 in)
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3
2
2
3
A
A0067
28 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 27

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Inlet and exhaust valves
Inlet valves
Diameter of valve stem ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..9,46/9,49 mm (0.3725/0.3735 in)
Clearance in valve guide ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,02/0,10 mm (0.0008/0.0039 in)
Maximum clearance in valve guide ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,13 mm (0.005 in)
Diameter of valve head ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..44,86/45,11 mm (1.766/1.776 in)
Angle of valve face . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..45° or 30°
Full length ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..122,66/123,07 mm (4.829/4.845 in)
Seal arrangement ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Rubber seal fitted to valve guide
Depth of valve head below the face of cylinder head AA, AB, AC, AD, AG, AH, YA, YB, YC:
Production limits . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,27/1,60 mm (0.050/0.063 in)
Service limit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,85 mm (0.073 in)
AD vehicle applications fitted with an intercooler ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,37/1,68 mm (0.054/0.066 in)
YA engines fitted with original valve seat inserts ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,37/1,68 mm (0.054/0.066 in)
Depth of valve head below the face of cylinder head YD:
Production limits . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,37/1,68 mm (0.054/0.066 in)
Engine build list YD 80571 . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,27/1,60 mm (0.050/0.063 in)
AE, YE engines:
Production limits (for 45° valves) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,37/1,62 mm (0.054/0.064 in)
Service limit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,85 mm (0.073 in)
Production limits (for 30° valves) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,27/1,76 mm (0.050/0.069 in)
Service limit (for 30° valves) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 2,01 mm (0.079 in)
Note: The inlet valve depth for certain engine types fitted with valve seat inserts can vary. The complete engine
number must be given to the distributor when parts are needed.
Exhaust valves
Diameter of valve stem ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..9,43/9,46 mm (0.371/0.372 in)
Clearance in valve guide . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,05/0,13 mm (0.002/0.005 in)
Maximum clearance in valve guide . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,15 mm (0.006 in)
Diameter of valve head ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..37,26/37,52 mm (1.467/1.477 in)
Angle of valve face .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .45°
Full length ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..123,07/123,57 mm (4.845/4.865 in)
Seal arrangement ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Rubber seal fitted to valve guide
Depth of valve head below face of cylinder head AA, AB, AC, AD, AG, AH, YA, YB, YC:
Production limits .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,28/1,60 mm (0.050/0.063 in)
Service limit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,85 mm (0.073 in)
AD vehicle applications fitted with an intercooler ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,47/1,79 mm (0.058/0.070 in)
YA engines fitted with original valve seat inserts ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,47/1,79 mm (0.058/0.070 in)
Depth of valve head below face of cylinder head AE, YD, YE:
Production limits . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,47/1,79 mm (0.058/0.070 in)
Service limit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,85 mm (0.073 in)
Engine build list YD 80571 . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,28/1,60 mm (0.050/0.063 in)
Note: The exhaust valve depth for certain engine types fitted with valve seat inserts can vary. The complete
engine number must be given to the distributor when parts are needed.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 29
Page 28
2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
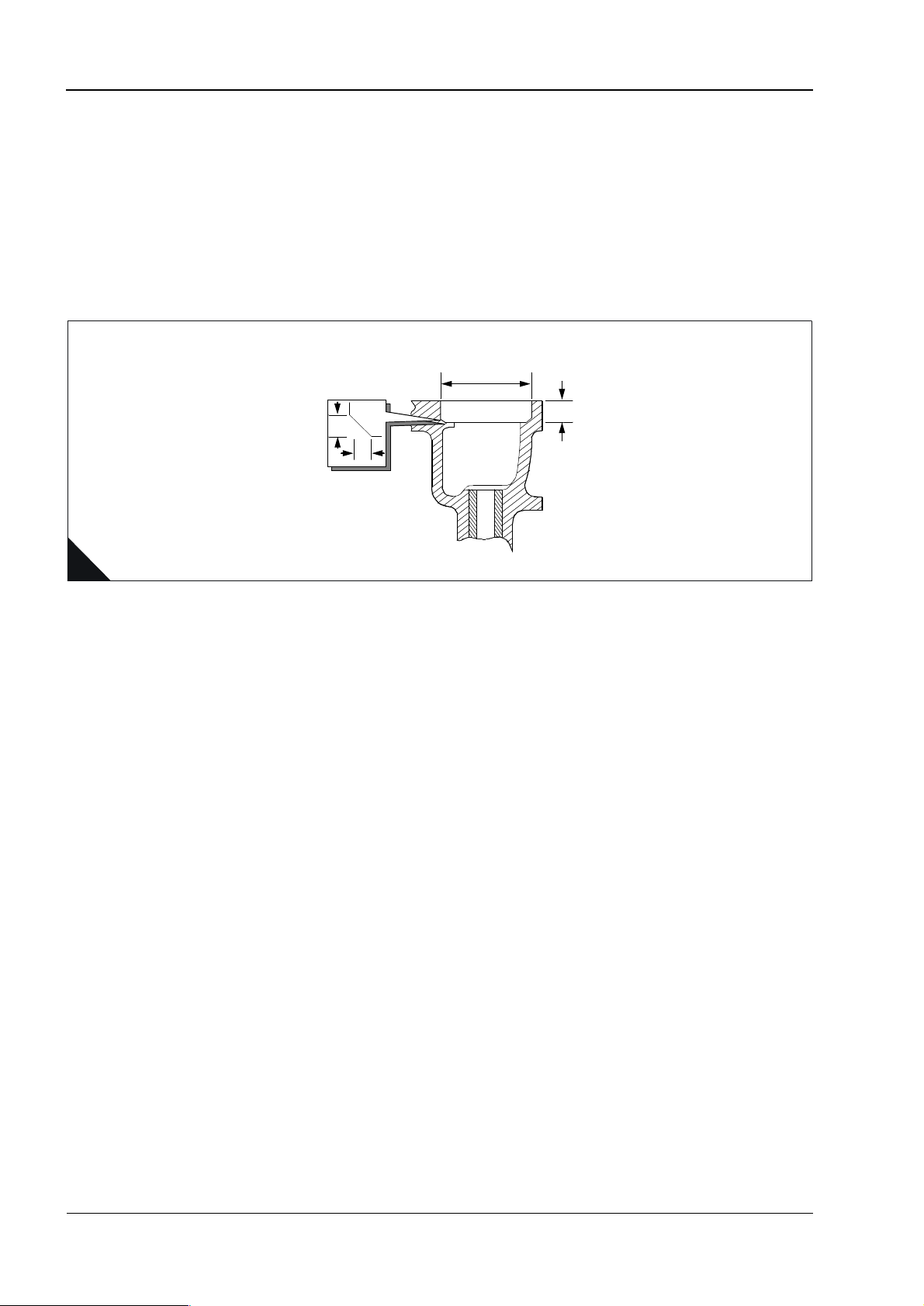
Dimensions of recesses for valve seat inserts
Inlet
A1... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7,19/7,32 mm (0.283/0.288 in)
A2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 51,22/51,24 mm (2.0165/2.0175 in)
A3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Radius 0,38 mm (0.015 in) maximum
Exhaust
A1... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 9,52/9,65 mm (0.375/0.380 in)
A2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 42,62/42,65 mm (1.6780/1.6790 in)
A3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Radius 0,38 mm (0.015 in) maximum
2
A
3
1
3
A0068
30 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 29
Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Valve seat insert tool
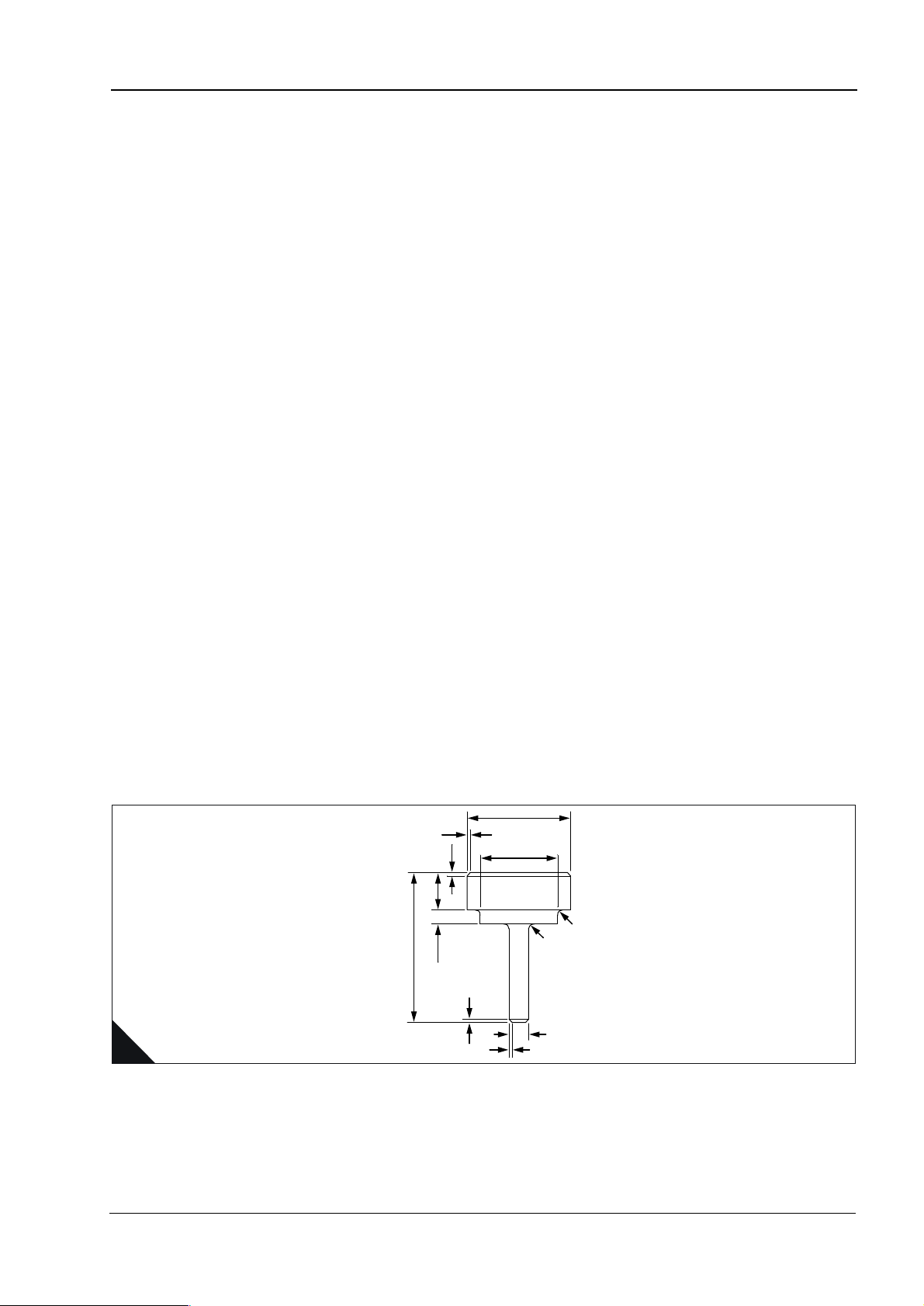
Inlet (for 45° valves)
A1 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A2 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..19,05 mm (0.750 in)
A3 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6,35 mm (0.250 in)
A4 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76,20 mm (3.00 in)
A5 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..37,26/37,28 mm (1.467/1.468 in)
A6 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..51,00/51,23 mm (2.008/2.017 in)
A7 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,79 mm (0.031 in)
A8 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A9 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A10.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..9,45/9,47 mm (0.372/0.373 in)
Inlet (for 31° valves)
A1 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A2 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..19,05 mm (0.750 in)
A3 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,00 mm (0.118 in)
A4 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76,20 mm (3.00 in)
A5 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..35,30/35,60 mm (1.390/1.402 in)
A6 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..43,94/43,99 mm (1.730/1.732 in)
A7 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,79 mm (0.031 in)
A8 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A9 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A10.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..9,45/9,47 mm (0.372/0.373 in)
Exhaust (for 45° valves)
A17.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A2 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..19,05 mm (0.750 in)
A3 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7,92 mm (0.312 in)
A4 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76,20 mm (3.00 in)
A5 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..32,58/32,84 mm (1.283/1.293 in)
A6 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..42,39/42,62 mm (1,669/1.678 in)
A7 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,79 mm (0.031 in)
A8 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A9 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1,59 mm (0.063 in)
A10.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..9,45/9,47 mm (0.372/0.373 in)
1
1
2
34
A
6
5
7
8
9
10
9
A0069
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 31
Page 30

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Valve guides and valve springs
Valve guides
Inside diameter .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 9,51/9,56 mm (0.3744/0.3764 in)
Outside diameter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,90/15,91 mm (0.6260/0.6265 in)
Interference fit of valve guide in cylinder head... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,03/0,07 mm (0.0012/0.0027 in)
Full length:
Inlet ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 57,94 mm (2.281 in)
Exhaust.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 61,10 mm (2.406 in)
Protrusion from bottom of recess for valve spring . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,10 mm (0.594 in)
Double valve springs (outer)
Fitted length... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 35,8 mm (1.41 in)
Load at fitted length ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 176/195 N (39.5/43.7 lbf) 18/20 kgf
Number of active coils ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...3.6
Number of damper coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1
Direction of coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Left hand - damper coil to cylinder head
Double valve springs (inner)
Fitted length... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 34,0 mm (1.34 in)
Load at fitted length ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 89/104 N (20/23 lbf) 9/11 kgf
Number of active coils ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...4.9
Number of damper coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1
Direction of coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Right hand - damper coil to cylinder head
Single valve springs
Fitted length... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 40,0 mm (1.57 in)
Load at fitted length ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 312/344 N (70.1/77.3 lbf) 31,8/35,1 kgf
Number of active coils ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...4.5
Number of damper coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0
Direction of coils. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Left hand
Tappets, rocker shaft, rocker levers and bushes
Tappets
Diameter of tappet stem. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 18,99/19,01 mm (0.7475/0.7485 in)
Diameter of tappet bore in cylinder block... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19,05/19,08 mm (0.7500/0.7512 in)
Clearance of tappet in cylinder block. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04/0,09 mm (0.0015/0.0037 in)
Rocker shaft
Outside diameter ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19,01/19,04 mm (0.7485/0.7495 in)
Rocker levers and bushes
Diameter of parent bore for bush... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,23/22,26 mm (0.8750/0.8762 in)
Outside diameter of bush... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,28/22,31 mm (0.8770/0.8785 in)
Interference fit of bush in rocker lever ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,020/0,089 mm (0.0008/0.0035 in)
Internal diameter of fitted bush when reamed ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19,06/19,10 mm (0.7505/0.7520 in)
Clearance between rocker lever bush and rocker shaft. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,03/0,09 mm (0.001/0.0035 in)
Maximum permissible clearance between rocker lever bush and rocker shaft.. ... ... ... ... ..0,13 mm (0.005 in)
32 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 31

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Pistons and piston cooling jets
Pistons (naturally aspirated engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ."Quadram" combustion bowl, controlled expansion,
. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... inserted top ring groove
Diameter of bore for gudgeon pin ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,928/34,934 mm (1.3751/1.3754 in)
Height of piston above top face of cylinder block ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,14/0,36 mm (0.005/0.014 in)
Width of groove for top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,57/2,59 mm (0.101/0.102 in)
Width of groove for second ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,55/2,57 mm (0.100/0.101 in)
Width of groove for third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..4,03/4,06 mm (0.1587/0.1598 in)
Pistons (turbocharged engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ."Quadram" combustion bowl, controlled expansion,
. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .inserted top ring groove, reduced diameter top land
Diameter of bore for gudgeon pin ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 38,103/38,109 mm (1.500/1.5004 in)
Height of piston above top face of cylinder block ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,14/0,36 mm (0.005/0.014 in)
Width of groove for top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Tapered
Width of groove for second ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,56/2,58 mm (0.1008/0.1016 in)
Width of groove for third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..4,04/4,06 mm (0.1591/0.1598 in)
Pistons (turbocharged AE, YE,Y D
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..."Fastram" combustion bowl, controlled expansion,
. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...inserted top ring groove, high top ring groove
Diameter of bore for gudgeon pin ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..39,7003/39,7009 mm (1.5355/1.5358 in)
Difference between height grades... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,046 mm (0.0018 in)
Height of piston above top face of cylinder block ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,38/0,50 mm (0.015/0.020 in)
Width of groove for top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Tapered
Width of groove for second ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,56/2,58 mm (0.1008/0.1016 in)
Width of groove for third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..4,04/4,06 mm (0.1591/0.1598 in)
(1) Some AD and YD lists are fitted with f astram pistons which are designed for use in emission controlled areas. Some of these pistons
are non-expansion controlled.
(1)
, AD
(1)
engines)
Piston cooling jets (turbocharged engines)
Valve open pressure ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. 178/250 kPa (26/36 lbf/in
2
) 1,8/2,6 kgf/cm
Piston rings
Early naturally aspirated engines
Top compression ring.. ... ... ... ... ... Barrel face, molybdenum insert, with chamfer at the top of the inner face
Second compression ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Taper face, cast iron
Oil scraper ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Coil spring loaded, chromium faced
Width of top ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,48/2,49 mm (0.097/0.098 in)
Width of second ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,48/2,49 mm (0.097/0.098 in)
Width of third ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..3,98/3,99 mm (0.1566/0.1571 in)
Clearance of top ring in groove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,08/0,11 mm (0.003/0.004 in)
Clearance of second ring in groove. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,06/0,09 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Clearance of third ring in groove . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,04/0,08 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Gap of top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,40/0,85 mm (0.016/0.033 in)
Gap of second ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,30/0,76 mm (0.012/0.030 in)
Gap of third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,38/0,84 mm (0.015/0.033 in)
2
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 33
Page 32

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Later naturally aspirated engines
Top compression ring ... ... ... ... ... .Barrel face, molybdenum insert, with chamfer at the top of the outer face
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... and a step on the inner face
Second compression ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Tapered outer face with a step, cast iron
Oil scraper ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Coil spring loaded, chromium faced
Width of top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 2,48/2,49 mm (0.097/0.098 in)
Width of second ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 2,48/2,49 mm (0.097/0.098 in)
Width of third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,98/3,99 mm (0.1566/0.1571 in)
Clearance of top ring in groove.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,08/0,11 mm (0.003/0.004 in)
Clearance of second ring in groove... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,06/0,09 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Clearance of third ring in groove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04/0,08 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Gap of top ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,28/0,63 mm (0.011/0.025 in)
Gap of second ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,40/0,65 mm (0.016/0.033 in)
Gap of third ring . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,38/0,84 mm (0.015/0.033 in)
Turbocharged engines
Top compression ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Barrel face, molybdenum insert, wedge
Second compression ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Taper face, cast iron
Oil scraper ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Coil spring loaded, chromium face
Width of top ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Wedge
Width of second ring .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 2,48/2,49 mm (0.097/0.098 in)
Width of third ring... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,98/3,99 mm (0.156/0.157 in)
Clearance of top ring in groove.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Wedge
Clearance of second ring in groove... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,07/0,11 mm (0.003/0.004 in)
Clearance of third ring in groove ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,05/0,08 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Gap of top ring ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,35/0,80 mm (0.014/0.031 in)
Gap of top ring with internal step... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,35/0,70 mm (0.014/0.028 in)
Gap of second ring. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,30/0,76 mm (0.012/0.030 in)
For second rings with outside step ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,40/0,85 mm (0.016/0.033 in)
Gap of third ring . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,38/0,84 mm (0.015/0.033 in)
Phaser/1000 Series
Connecting rods and bearings
Connecting rods (naturally aspirated engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ’H’ section, square shape small end
Location of cap to connecting rod.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Serrations
Diameter of parent bore for big end... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 67,21/67,22 mm (2.6460/2.6465 in)
Diameter of parent bore for small end ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 38,89/38,92 mm (1.531/1.532 in)
Length between centres. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 219,05/219,10 mm (8.624/8.626 in)
Connecting rods (turbocharged engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ’H’ section, wedge shape small end
Location of cap to connecting rod:
Vehicle applications ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Flat joint face with dowels
Non-vehicle applications ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Serrations
Diameter of parent bore for big end... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 67,21/67,22 mm (2.6460/2.6465 in)
Diameter of parent bore for small end ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 42,056/42,083 mm (1.655/1.656 in)
Length between centres. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 219,05/219,10 mm (8.624/8.626 in)
34 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 33

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Connecting rod bearings
Type:
- Naturally aspirated engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Steel back, aluminium/tin bearing material
- Turbocharged engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Steel back, lead bronze bearing material with lead finish
Width:
- Naturally aspirated engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..31,62/31,88 mm (1.245/1.255 in)
- Turbocharged engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..31,55/31,88 mm (1.240/1.255 in)
Thickness at centre of bearings:
- Naturally aspirated engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,835/1,842 mm (0.0723/0.0725 in)
- Turbocharged engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..1,835/1,844 mm (0.0723/0.0726 in)
Bearing clearance:
- Naturally aspirated engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,035/0,081 mm (0.0014/0.0032 in)
- Turbocharged engine ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,030/0,081 mm (0.0012/0.0032 in)
Available undersize bearings... ... ... ... ... ... -0,25 mm (-0.010 in); -0,51 mm (-0.020 in); -0,76 mm (-0.030 in)
2
Gudgeon pins and small end bushes
Gudgeon pins (naturally aspirated engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Fully floating
Outside diameter . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,920/34,925 mm (1.3748/1.3750 in)
Clearance fit in piston boss . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,003/0,014 mm (0.0001/0.0006 in)
Gudgeon pins (turbocharged engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Fully floating
Outside diameter . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..38,095/38,100 mm (1.4998/1.5000 in)
AE, YE and 110 Ti and 135 Ti AD lists ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..39,694/39,700 mm (1.5628/1.5630 in)
Clearance fit in piston boss . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,003/0,014 mm (0.0001/0.0006 in)
Small end bushes (naturally aspirated engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Steel back, lead-bronze or lead-bronze tin bearing material
Outside diameter . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..38,94/39,03 mm (1.535/1.536 in)
Inside diameter (reamed) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,94/34,96 mm (1.3758/1.3765 in)
Clearance between bush in small end and gudgeon pin. ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,020/0,043 mm (0.0008/0.0017 in)
Small end bushes (turbocharged engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Steel back, lead bronze bearing material
AE, YE, and certain AD lists
Outside diameter . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..42,16/42,19 mm (1.6600/1.6613 in)
Inside diameter (reamed) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..38,12/38,14 mm (1.5008/1.5015 in)
AE, YE and certain AD lists
Clearance between bush in small end and gudgeon pin. ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,020/0,043 mm (0.0008/0.0017 in)
AE, YE. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,010/0,035 mm (0.0004/0.0014 in)
(1)
Certain AD lists
(1) AD lists which are subject to emission legislation.
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,023/0,044 mm (0.0009/0.0017 in)
(1)
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Steel back, lead bronze tin bearing materials
(1)
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..39,719/39,738 mm (1.5637/1.5645 in)
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 35
Page 34

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Crankshaft
Diameter of main journals:
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76,16/76,18 mm (2.998/2.999 in)
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 76,159/76,190 mm (2.9984/2.9996 in)
Maximum wear and ovality on journals and crank pins . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04 mm (0.0016 in)
Width of front journal.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 36,93/37,69 mm (1.454/1.484 in)
Width of centre journal... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 44,15/44,22 mm (1.738/1.741 in)
Width of all other journals .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 39,24/39,35 mm (1.545/1.549 in)
Diameter of crank pins... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 63,47/63,49 mm (2.499/2.500 in)
Width of crank pins ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 40,35/40,42 mm (1.589/1.591 in)
Diameter of flange.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 133,27/133,37 mm (5.247/5.251 in)
Depth of recess for spigot bearing:
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 20,22/20,98 mm (0.796/0.826 in)
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 14,72/15,48 mm (0.579/0.609 in)
Bore of recess for spigot bearing:
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 46,96/46,99 mm (1.849/1.850 in)
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 51,97/51,99 mm (2.046/2.047 in)
Crankshaft end-float... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,05/0,38 mm (0.002/0.015 in)
Maximum permissible end-float. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,51 mm (0.020 in)
Fillet radii of journals and crank pins.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,68/3,96 mm (0.145/0.156 in)
Undersize journals and crank pins. ... ... ... .. -0,25 mm (-0.010 in); -0,51 mm (-0.020 in); -0,76 mm (-0.030 in)
Crankshaft heat treatment
Induction hardened ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Part numbers 31315662, 31315992, 31315993 and 3131H024
Nitrocarburised... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Part numbers 31315661, 31315991 and 3131H022
60 hour Nitride ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Part number 3131H021
Nitreg . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Part number 3131H031
Crankshaft overhaul
Cautions:
l The “Nitreg” process is a special factory process that needs specialist equipment and personnel with the
correct training. Do not use any other heat treatment process on these crankshafts.
l In service it is not possible to regrind the “Nitreg” crankshaft for overhaul purposes. A “new for old”
crankshaft is available.
Notes:
l Induction hardened crank shafts need not be hardened after they have been machined undersize.
l Nitrocarburised crankshafts must be hardened again each time they are machined. These crankshafts
must be nitrocarburised or, if this process is not available, they can be nitrided for 20 hours. If neither
process is available a new crankshaft, or Power Exchange crankshaft, must be fitted.
l Crankshafts which have been nitrided for 60 hours can be reground 0,25 mm (0.010 in) without the need
to harden them again.
l Check the crankshaft for cracks before and after it is ground. Demagnetise the crankshaft after it has been
checked for cracks.
l After the crankshaft has been machined remove any sharp corners from the lubricating oil holes.
l Surface finish and fillet radii must be maintained.
Continued
36 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 35
Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
The finished sizes for crankshaft journals (A) which have been ground undersize are given in the table below:
Item
1
2
0,25 mm
(0.010 in)
75,905/75,926 mm
(2.9884/2.9892 in)
63,216/63,236 mm
(2.4888/2.4896 in)
0,51 mm
(0.020 in)
75,651/75,672 mm
(2.9784/2.9792 in)
62,962/62,982 mm
(2.4788/2.4796 in)
75,397/75,418 mm
(2.9684/2.9692 in)
62,708/62,728 mm
(2.4688/2.4696 in)
3 39,47 mm (1.554 in) maximum - 4 37,82 mm (1.489 in) maximum - 5 44,68 mm (1.759 in) maximum - 6 40,55 mm (1.596 in) maximum - 7 133,17 mm (5.243 in) minimum - 8 Do not machine this diameter - 9 3,68/3,96 mm (0.145/0.156 in) - -
Surface finish for journals, crank pins and fillet radii must be 0,4 microns (16 micro inches).
Surface finish for seal area of crankshaft palm must be 0,4/1,1 microns (16/43 micro inches).
6666
9
2
9999
2
8
0,76 mm
(0.030 in)
A
9
111117
22
43533
666666
9
2
1111111
9
99999
2222
9999
9
9
4,8 mm
0.189 in
2
7
3333334
8
A0120
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 37
Page 36

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
With the crankshaft on mountings at the front and rear journals, the maximum run-out (total indicator reading)
at the journals must not be more than shown below:
Journal 4 cylinder crankshafts 6 cylinder crankshafts
1 Mounting Mounting
2 0,08 mm (0.003 in) 0,10 mm (0.004 in)
3 0,15 mm (0.006 in) 0,20 mm (0.008 in)
4 0,08 mm (0.003 in) 0,25 mm (0.010 in)
5 Mounting 0,20 mm (0.008 in)
6 - 0,10 mm (0.004 in)
7 - Mounting
Run-out must not be opposite. The difference in run-out between one journal and the next must not be more
than 0,10 mm (0.004 in).
Run-out on the crankshaft pulley diameter, rear oil seal diameter and the rear flange diameter must not be
more than 0,05 mm (0.002 in) total indicator reading.
Phaser/1000 Series
38 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 37

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Crankshaft bearings and thrust washers
Main bearings
Four cylinder engines:
Type (All bearings) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Steel back, 20% tin-aluminium bearing material
Six cylinder engine s:
Centre bearing and all Phaser 210Ti bearings ... ... .Steel back, lead bronze bearing material with lead finish
All other bearings. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Steel back, 20% tin-aluminium bearing material
Bearing width
Four cylinder engines:
Centre bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..36,32/36,70 mm (1.430/1.445 in)
All other bearings. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..31,62/31,88 mm (1.245/1.255 in)
Six cylinder engine s:
Centre bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..36,32/36,70 mm (1.430/1.445 in)
All other bearings. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..30,86/31,12 mm (1.215/1.225 in)
Bearing thickness at centre
Four cylinder engines:
All bearings.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,083/2,089 mm (0.0820/0.0823 in)
Six cylinder engine s:
Centre bearing and all Phaser 210Ti bearings ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,087/2,096 mm (0.0822/0.0825 in)
All other bearings. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,083/2,089 mm (0.0820/0.0823 in)
Bearing clearance
Four cylinder engines:
All bearings.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,057/0,117 mm (0.0022/0.0046 in)
Six cylinder engine s:
Centre bearing and all Phaser 210Ti bearings ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,035/0,110 mm (0.0014/0.0043 in)
All other bearings. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,047/0,117 mm (0.0018/0.0046 in)
Available undersize bearings... ... ... ... ... ... -0,25 mm (-0.010 in); -0,51 mm (-0.020 in); -0,76 mm (-0.030 in)
Crankshaft thrust washers
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Steel back, lead bronze bearing material
Position ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Each side of centre main bearing
Thickness:
Standard.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,26/2,31 mm (0.089/0.091 in)
Oversize .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..2,45/2,50 mm (0.096 /0.0 98 in)
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 39
Page 38

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Balancer unit
Diameter of drive shaft for front bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 28,562/28,575 mm (1.1245/1.1250 in)
Diameter of drive shaft for rear bearing . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23,787/23,800 mm (0.9365/0.9370 in)
Number of teeth on gear of drive shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21
Backlash from gear of drive shaft to idler gear .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,17/0,29 mm (0.007/0.011 in)
End-float of drive shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,13/0,30 mm (0.005/0.012 in)
Diameter of bore for front bearing of drive shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 34,912/34,937 mm (1.3745/1.3755 in)
Diameter of bore for rear bearing of drive shaft. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 29,972/29,993 mm (1.1800/1.1808 in)
Diameter of bore for idler gear... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 47,64/47,65 mm (1.8755/1.8760 in)
Diameter of hub of idler gear . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 38,09/38,10 mm (1.4996/1.5000 in)
End-float of idler gear. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,07/0,23 mm (0.003/0.009 in)
Thickness of thrust washer for idler gear... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 4,14/4,29 mm (0.163/0.169 in)
Number of teeth on idler gear ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 37
Inside diameter of bushes in balancer frame and end cover (fitted).. ... 38,133/38,174 mm (1.5013/1.5029 in)
Diameter of spigots for balance weights ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 38,054/38,069 mm (1.4982/1.4988 in)
Fit of spigot in bush ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,064/0,120 mm (0.0025/0.0047 in)
End-float of balance weights.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,19/0,40 mm (0.007/0.016 in)
Backlash of gears on balance weights... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,10/0,27 mm (0.004/0.011 in)
Backlash of drive gear to spline on balance weight... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,05/0,20 mm (0.002/0.008 in)
Number of teeth on drive gear... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24
Number of teeth on spline on balance weight ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 16
Timing case and drive assembly
Camshaft
Diameter of number 1 journal ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,71/50,74 mm (1.9965/1.9975 in)
Diameter of number 2 journal ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,46/50,48 mm (1.9865.1.9875 in)
Diameter of number 3 journal:
Four cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 49,95/49,98 mm (1.9665/1.9675 in)
Six cylinder engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,20/50,23 mm (1.9765/1.9775 in)
Diameter of number 4 journal:
Six cylinder. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 49,95/49,98 mm (1.9665/1.9675 in)
Clearance of all journals ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,06/0,14 mm (0.0025/0.0055 in)
Cam lift:
Inlet ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7,62/7,69 mm (0.2999/0.3029 in)
Exhaust.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7,71/7,79 mm (0.3036/0.3066 in)
Maximum permissible ovality and wear on journals... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,05 mm (0.021 in)
End-float:
Production limits. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,10/0,41 mm (0.004/0.016 in)
Service limit ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,53 mm (0.021 in)
Width of spigot for thrust washer ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5,64/5,89 mm (0.222/0.232 in)
Camshaft thrust washer
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 360°
Depth of recess in cylinder block for thrust washer ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5,46/5,54 mm (0.215/0.218 in)
Thickness of thrust washer ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5,49/5,54 mm (0.216/0.218 in)
Relationship of thrust washer to front face of cylinder block.. ... ... ... ... ... .-0,05/+0,08 mm (-0.002/+0.003 in)
40 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 39

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Camshaft gear
Number of teeth... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..56
Diameter of bore.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,93/34,95 mm (1.3750/1.3760 in)
Outside diameter of hub of camshaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,90/34,92 mm (1.3741/1.3747 in)
Clearance fit of gear on hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,008/0,048 mm (0.0003/0.0019 in)
Fuel pump gear
Number of teeth... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..56
Bore:
AE, YE. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..36,00/36,06 mm (1.417/1.419 in)
All other engine types.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Tapered
Clearance fit on hub:
AE, YE. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,003/0,075 mm (0.0001/0.0030 in)
Crankshaft gear
Number of teeth... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..28
Diameter of bore.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..47,625/47,650 mm (1.8750/1.8760 in)
Diameter of hub for gear on crankshaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..47,625/47,645 mm (1.8750/1.8758 in)
Transition fit of gear on crankshaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... -0,020/+0,048 mm (-0.0008/+0.0010 in)
Idler gear and hub
2
Number of teeth... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..63
Diameter of bore of gear.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..57,14/57,18 mm (2.2495/2.2512 in)
With needle roller bearings.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..69,01/69,03 mm (2.717/2.718 in)
Width of gear and split bush assembly (fitted in position) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..30,14/30,16 mm (1.186/1.187 in)
Inside diameter of flanged bushes (fitted in position).. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,78/50,80 mm (1.9999/2.000 in)
Outside diameter of hub .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..50,70/50,74 mm (1.9960/1.9975 in)
With needle roller bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..54,987/55,000 mm (2.1648/2.1654 in)
Clearance of bushes on hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,04/0,10 mm (0.0016/0.0039 in)
End float of gear:
Production limits .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,10/0,20 mm (0.004/0.008 in)
With needle roller bearings.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,24/0,33 mm (0.009/0.013 in)
Service limit . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,38 mm (0.015 in)
Backlash for all gears.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,08 mm (0.003 in) minimum
Idler gear and hub for the Bendix compressor
Number of teeth... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..32
Diameter of bore of gear.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..55,010/55,025 mm (2.1657/2.1663 in)
Outside diameter of hub .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..50,000/49,990 mm (1.9960/1.9975 in)
End float of gear with needle roller bearing fitted ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,12/0,16 mm (0.005/0.006 in)
Backlash gear.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,07 mm (0.003 in) mini mu m
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 41
Page 40

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Cylinder block assembly
Cylinder block
Height between top and bottom faces ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 441,12/441,33 mm (17.367/17.375 in)
Diameter of parent bore for cylinder liner... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 104,20/104,23 mm (4.103/4.104 in)
Depth of recess for flange of cylinder liner. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,81/3,91 mm (0.150/0.154 in)
Diameter of recess for flange of cylinder liner ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 107,82/107,95 mm (4.245/4.250 in)
Diameter of parent bore for main bearing.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 80,416/80,442 mm (3.1660/3.1670 in)
Camshaft bore diameter
Four cylinder engines:
Number 1 (for bush)... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 55,56/55,59 mm (2.188/2.189 in)
Number 2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,55/50,60 mm (1.990/1.992 in)
Number 3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,04/50,09 mm (1.970/1.972 in)
Six cylinder engines:
Number 1 (for bush)... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 55,56/55,59 mm (2.188/2.189 in)
Number 2... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,55/50,60 mm (1.990/1.992 in)
Number 3... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,29/50,34 mm (1.980.1.982 in)
Number 4... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,04/50,09 mm (1.970/1.972 in)
Bore of bush for number 1 camshaft journal.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 50,79/50,85 mm (2.000/2.002 in)
Cylinder liners
Type:
Production.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Dry, interference fit, flanged
Service... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Dry, transition fit, flanged
Service... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Dry, transition fit, flanged, with flame ring
Partially finished liner. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Dry, interference fit, flanged, with flame ring
AE, YE, 110Ti and 135Ti AD lists:
Production.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Dry, interference fit, flanged, with flame ring
Outside diameter of production liner.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 104,25/104,28 mm (4.105/4.106 in)
Interference fit of production liner .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,03/0,08 mm (0.001/0.003 in)
Inside diameter of production liner. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 100,00/100,03 mm (3.937/3.938 in)
Transition fit of service liner... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...+/- 0,03 mm (+/- 0.001 in)
Inside diameter of service liner (fitted) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..100,04/100,063 mm (3.9385/3.9395 in)
Inside diameter of service liner with a flame ring (fitted) ... ... ... ... ... ... ..100,00/100,063 mm (3.937/3.939 in)
Maximum permissible wear of liner bore ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 0,25 mm (0.010 in)
Thickness of flange ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,81/3,86 mm (0.150/0.152 in)
Relative position of top of liner flange to top face of cylinder block ... ... ... ... ... ... ...0,10 mm (0.004 in) above
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,10 mm (0.004 in) below
Partially finished liner
Inside diameter of partially finished liner ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 99,162/99,415 mm (3.9040/3.9139 in)
Interference fit of partially finished liner in parent bore .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,025/0,076 mm (0.003/0.001 in)
Hone angle (cross hatch)... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 30°/35°
Final finish grade, silicon carbide (Plateau hone) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,65/1,3 micrometers
Inside diameter of finished liner . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 100,00/100,03 mm (3.937/3.938 in)
42 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 41

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Engine timing (Bosch EPVE fuel injection pump)
Fuel injection pump
Type ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . Early EPVE without a locking screw
Direction of rotation from drive end ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Clockwise
Outlet for number 1 cylinder ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ."C"
Note: For details of the later model Bosch EPVE fuel injection pumps fitted with a locking screw, see "Bosch
EPVE fuel injection pump (with a locking screw)" on page 278.
Static timing
The engine check angle must be used with special tool 21825610 and with the engine set with number 1 piston
at top dead centre (TDC) on compression stroke. The pump mark angle and the piston displacement are
checked with the pump plunger set at 1,00 mm (0.039 in) plunger lift.
The code letters are included in the setting code stamped on the side of the fuel injection pump. Some fuel
pumps may have the setting code stamped on a modification plate which is fastened to the flange of the pump.
If a modification plate is fitted, use the code letters stamped on this plate.
A typical setting code is 2643J603DK/1/3020; in this example the code letters are "DK".
Fuel pump
code letters
BK 308 314 12 1,78 0.070
CK 308 314 12 1,78 0.070
DK 306 313 14 2,42 0.095
EK 308.5 315.5 14 2,42 0.095
(1)
EK
EL - - 9 - EM 288.5 295.5 14 2,42 0.095
FM 289 295 12.5 1,93 0.076
JM - - 6 - -
(3)
JM
(4)
JM
(2)
KC
(2)
KL
(2)
ML
PM - - 12 - -
SK - - 9 - -
(2)
TL
VM - - 2 ATDC - -
Engine check
angle
(degrees)
306.5 315.5 18 3,99 0.157
-- 2 --
-- TDC --
-- TDC --
-- TDC --
-- TDC --
-- TDC --
Pump mark
angle
(degrees)
Static timing position before
TDC
(degrees)
Piston displacement
mm in
(1) Engines to build list YA80433 with the data plate of the fuel injection pump stamped J609.
(2) The cold start device (KSB) must be energised before the timing is set, see Operation 11-19.
(3) Engines to build lists AD70229 and AD70230.
(4) Engines to build list AD80643
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 43
Page 42
2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Engine timing (Bosch in-line fuel injection pump)
Fuel injection pump
Fuel pump type .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . MW
Direction of rotation from drive end ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Clockwise
Outlet for number 1 cylinder... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Drive end of fuel pump
Static timing
The piston position probe 21825630 or 21825947 is used to set the engine check angle to 100° BTDC.
A locally made washer (A) must be fitted onto the piston position probe when the engine check angle is less
than 100° BTDC.
The thickness of the piston position probe washer, dimension A, for a particular engine is shown in the table
below. The general dimensions for the piston position probe washer are shown in (A).
A
Fuel pump code
WM 98 2,302
HL 100 LC 100 -
MC 100 -
VK 100 -
10,00-10,05 mm
21,1-21,2 mm
Engine check angle
(degrees)
A
Piston position probe washer
thickness
(mm)
44 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 43

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Engine timing (Lucas CAV/Delphi DPA and DPS) fuel injection pump
Fuel injection pump
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..DPA or DPS
Direction of rotation from drive end . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Clockwise
Outlet for number 1 cylinder:
- AA, AB, AC, AD. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Letter "W"
- YA, YB, YC, YD. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Letter "Y"
Static timing
The engine check angle must be used with special tool 21825610 and with the engine set with number 1 piston
at top dead centre (TDC) on the compression stroke. The pump is checked with the pump set at the start of
injection for number 1 cylinder.
The code letters are included in the setting code stamped on the data plate of the fuel injection pump. Some
fuel pumps may have the setting code stamped on a modification plate which is fastened to the flange of the
pump. If a modification plate is fitted, use the code letters stamped on this plate.
A typical setting code is 2643C601BM/4/2860; in this example the code letters are "BM".
Fuel pump code letters
AK 325.5 336
AM 282 290.5
BF 326 334
BM 281 291
CM 282.5 291.5
DM 282.25 290.5
FK 325.5 336
GK 325 336
GM 282 290.5
HK 326 336
HM 282 291
JK 325 334
KK 325 334
LK 327 337.5
(1)
LK
MK 326 336
(2)
MK
PK 326 334
RK 328 336
RM 282.5 290.5
TK 327 334
UK 326 334
XM 282 291
Engine check angle
(degrees)
328 337.5
325 336
Pump mark angle
(degrees)
(1) Effective from engine list YA 31257.
(2) Effective from engine list YA 50532.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 45
Page 44

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Engine timing (Stanadyne fuel injection pump)
Fuel injection pump
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Stanadyne DB2 or DB4
Outlet for number 1 cylinder:
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 8 o’clock position as seen from the rear of the pump
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 9 o’clock position as seen from the rear of the pump
Direction of rotation from drive end ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Clockwise
Fuel system ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Self-vent
Static timing
The engine check angle must be used with special tool 21825610 and with the engine set with the piston of
the number 1 cylinder at top dead centre (TDC) on the compression stroke. The pump is checked with the
pump set at the start of injection for the number one cylinder.
Fuel pump code letters
AC 282 291
AL 326 336
BL 326 336
CL 327 333
(1)
CL
DL 332 338
FL 326 333
GL 326 332
HC 282 290.5
JL 325 334.5
KM 282 290
LM 282 287
(2)
LM
MM 282 287
(3)
MM
NC 282 294
SL 331.5 338
SM 282 291
TC 282 290
TM 282 290.5
UC 228.5 296
VL 326 389
XK 325 331.5
YK 325 334.5
YL 330 338
ZK 326 334
(4)
ZM
(5)
ZM
Engine check angle
(degrees)
- 247.5
288.5 295
288.5 295
282 287
282 289
Pump mark an gle
(degrees)
(1) Pin timed fuel injection pump.
(2) For engines fitted fuel injection pumps part numbers 2643U211 and 2643U213.
(3) For engines fitted fuel injection pump part number 2643U214.
(4) Effective from pump serial number 7665964.
(5) Effective from pump serial number 7665965.
46 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 45

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Aspiration system
Turbocharger
The make and type of turbocharger fitted is marked on the turbocharger identification plate; as a general guide
the make and type of turbocharger fitted are as follows:
AB ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Garrett T31 or Schwitzer S2A
AC ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Schwitzer S2A
AD ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Schwitzer S2A
AE ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Garrett T25
AH ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Garrett T25
YB ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Garrett T04B, TBP4 or Schwitzer S2B
YD ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Schwitzer S76
YE ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Garrett TBP4
Waste-gate test pressure for rod movement of 1,00 mm (0.039 in)
The turbocharger part number is on the turbocharger identification plate, which is fitted to the body of the
turbocharger.
Turbocharger
part number
2674A053 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,20-1,28 2674A081 88-98 12.8-14.2 0,90-1,00
2674A054 110-120 16.0-17.4 1,12-1,22 2674A082 88-92 12.8-13.3 0,90-0,93
2674A055 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32 2674A084 118-128 17.1-18.5 1,20-1,30
2674A056 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32 2674A085 88-98 12.8-14.2 0,90-1,00
2674A057 118-126 17.1-18.3 1,20-1,28 2674A086 118-128 17.1-18.6 1,20-1,30
2674A058 118-126 17.1-18.3 1,22-1,32 2674A087 101-109 14.7-15.6 1,03-1,11
2674A059 118-126 17.1-18.3 1,20-1,28 2674A128 101-109 14.6-15.8 1,02-1,11
2674A062 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22 2674A129 101-109 14.6-15.8 1,02-1,11
2674A063 92-98 13.3-14.2 0,93-0,99 2674A130 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22
2674A064 110-103 15.9-14.9 1,11-1,04 2674A131 101-109 14.6-15.8 1,02-1,11
2674A067 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32 2674A138 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22
2674A068 110-103 15.9-14.9 1,11-1,04 2674A139 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32
2674A072 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32 2674A144 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22
2674A075 118-126 17.1-18.3 1,20-1,28 2674A146 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22
2674A077 113-120 16.4-17.4 1,15-1,22 2674A149 133-143 19.3-20.7 1,35-1,45
2674A078 110-120 16.0-17.4 1,12-1,22 2674A150 145-155 21.0-22.5 1,47-1,58
2674A079 120-130 17.4-18.9 1,22-1,32 2674A306 143- 153 20.8- 22.2 1,46- 1,56
Waste-gate pressure
(kPa) (lbf/in
2
) (kgf/cm2) (kPa) (lbf/in2) (kgf/cm2)
Turbocharger
part number
Waste-gate pressure
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 47
Page 46

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Lubrication system
Lubricating oil pump (four cylinder engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Differential rotor, gear driven
Number of lobes. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Inner rotor 6, outer rotor 7
Clearance of outer rotor to body:
Without balancer unit. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,15/0,34 mm (0.006/0.013 in)
With balancer unit .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,31/0,45 mm (0.012/0.017 in)
Clearance of inner rotor to outer rotor ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04/0,13 mm (0.0015/0.0050 in)
End-float of rotor assembly ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,03/0,10 mm (0.001/0.004 in)
Lubricating oil pump (six cylinder engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Differential rotor, gear driven
Number of lobes:
Inner rotor .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..4
Outer rotor.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..5
Clearance of outer rotor to body ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,15/0,34 mm (0.006/0.013 in)
Clearance of inner rotor to outer rotor ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04/0,13 mm (0.0015/0.0050 in)
End clearance YA, YC:
Inner rotor .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,05/0,12 mm (0.002/0.005 in)
Outer rotor.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,04/0,11 mm (0.0015/0.0044 in)
End clearance (six cylinder turbocharged engines):
Inner rotor .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,043/0,118 mm (0.0017/0.0046 in)
Outer rotor.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,031/0,106 mm (0.0012/0.0042 in)
Idler gear for lubricating oil pump
End float. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,03/0,33 mm (0.001/0.013 in)
Inside diameter of bush (fitted) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,23/22,26 mm (0.875/0.866 in)
Outside diameter of idler shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,19/22,21 mm (0.873/0.874 in)
Clearance of bush of idler gear on shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,020/0,066 mm (0.0008/0.0026 in)
Oil pressure relief valve (standa rd)
Diameter of bore for plunger.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 18,24/18,27 mm (0.718/0.719 in)
Outside diameter of plunger... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 18,16/18,18 mm (0.715/0.716 in)
Clearance of plunger in bore.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,06/0,11 mm (0.002/0.004 in)
Length of spring (fitted):
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..59,8 mm (2.4 in)
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..55,6 mm (2.2 in)
Load on spring (fitted):
- Four cylinder engines .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,9/23,1 N (3.6/5.2 lbf) 1,6/2,4 kgf
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12,9/18,6 N (2.9/4.2 lbf) 1,3/1,9 kgf
Pressure to open valve (four cylinder engines):
- Without piston cooling jets... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 340/395 kPa (49/57 lbf/in
- With piston cooling jets ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 415/470 kPa (60/68 lbf/in2) 4,2/4,8 kgf/cm
- Six cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 345/414 kPa (50/60 lbf/in2) 3,5/4,2 kgf/cm
2
) 3,4/4,0 kgf/cm
2
2
2
48 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 47

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Oil pressure relief valve (with balancer)
Diameter of bore for plunger ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..16,00/16,03 mm (0.630/0.631 in)
Outside diameter of plunger ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,95/15,98 mm (0.628/0.629 in)
Clearance of plunger in bore... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,02/0,08 mm (0.0008/0.003 in)
Length of spring (fitted) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 42,7 mm (1.7 in)
Load on spring (fitted):
- Engines without piston cooling jets ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .24/30 N (5.4/6.7 lbf) 2,4/3,1 kgf
- Engines with piston cooling jets ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .34/38 N (7.6/8.5 lbf) 3,5/3,9 kgf
Pressure to open valve:
- Engines without piston cooling jets ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 414 kPa (60 lbf/in
2
) 4,2 kgf/cm
- Engines with piston cooling jets ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 523 kPa (76 lbf/in2) 5,3 kgf/cm
Oil filter
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Full flow, screw-on type canister
Pressure to open by-pass valve in filter... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 55/83 kPa (8/12 lbf/in
2
) 0,6/0,8 kgf/cm
Pressure to open by-pass valve in oil cooler... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 172 kPa (25 lbf/in2) 1,8 kgf/cm
2
2
2
2
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 49
Page 48

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Fuel system
Fuel lift pump (four cylinder engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .A.C.Delco, type XD
Method of drive .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Eccentric on camshaft of engine
2
Static pressure (no delivery).. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..42/70 kPa (6/10 lbf/in
Test pressure (75% of minimum static pressure) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .31 kPa (4.5 lbf/in2) 0,32 kgf/cm
Fuel lift pump (six cylinder engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . A.C.Delco, type LU
Method of drive .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Eccentric on camshaft of engine
Static pressure (no delivery).. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..34,5/55,2 kPa (5/8 lbf/in
Test pressure (75% of minimum static pressure) .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...26 kPa (3.75 lbf/in2) 0,26 kgf/cm
Fuel filter
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Twin parallel flow or single element
Fuel lift pump (AE, YE - four and six cylinder engines)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Bosch, FP/KG24MW304
Method of drive .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Eccentric on camshaft of engine or on camshaft of fuel injection pump
Fuel filter
) 0,4/0,7 kgf/cm
2
) 0,35/0,56 kgf/cm
2
2
2
2
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Twin parallel flow or single element
Fuel lift pump (engines with a Bosch in-line fuel injection pump)
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Bosch, FP/KG24MW304
Method of drive .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Eccentric on camshaft of engine or on camshaft of fuel injection pump
Fuel filter
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Twin parallel flow or single element
50 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 49

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Atomiser service settings
2
Code Holder Nozzle
HU 2645A302 2645A604 220 3233 22,3
HV 2645A302 2645A606 250 3674 25,3
HZ 2645A302 2645K603 220 3233 22,3
JA 2645A302 2645A607 250 3674 25,3
JB 2645A302 2645A608 250 3674 25,3
JE 2645A302 2645A608 220 3233 22,3
JF 2645A304 2645A606 250 3674 25,3
JG 2645A304 2645A607 230 3380 23,3
JH 2645A302 2645A612 250 3674 25,3
JJ 2645A302 2645A611 250 3674 25,3
JK 2645A302 2645A613 220 3233 22,3
JL 2645A304 2645A614 250 3674 25,3
JR 2645A304 2645A615 250 3674 25,3
JS 2645A304 2645A612 250 3674 25,3
JT 2645A304 2645A616 250 3674 25,3
JU 2645A302 2645A617 220 3233 22,3
JY 2645A302 2645A621 250 3674 25,3
KC 2645L309 2645A625 286 4203 29,0
KD 2645L310 2645A626 290 4262 29,4
KE 2645L311 2645A627 290 4262 29,4
KF 2645L311 2645A628 290 4262 29,4
KG 2645L314 2645A629 290 4262 29,4
KN 2645L315 2645A635 290 4262 29,4
KP 2645L318 2645A636 290 4262 29,4
KU 2645L317 2645A627 290 4262 29,4
KW 2645L311 2645K609 290 4262 29,4
NJ 2645L304 2645L607 220 3233 22,3
NK 2645L305 2645L609 225 3307 22,8
NL 2645L305 2645L608 225 3307 22,8
NM 2645L304 2645L611 230 3380 23,3
NN 2645L303 2645L612 230 3380 23,3
NP 2645L304 2645L613 220 3233 22,3
NR 2645L303 2645L614 230 3380 23,3
NS 2645L303 2645L612 250 3674 25,3
NT 2645L304 2645L615 230 3380 23,3
NU 2645L303 2645L605 220 3233 22,3
NV 2645L304 2645L616 220 3233 22,3
NW 2645L303 2645L613 220 3233 22,3
NX 2645L306 2645L617 290 4262 29,4
PC 2645L310 2645L622 290 4262 29,4
PD 2645L310 2645L622 275 4041 27,9
PE 2645L306 2645L617 280 4115 28,4
RD 2645F303 2645F603 247 3630 25,0
RE 2645F304 2645F604 247 3630 25,0
RF 2645F304 2645F605 247 3630 25,0
RH 2645F304 2645F608 247 3630 25,0
RK 2645F304 2645F610 266 3902 27,0
atm (lbf/in
Set and reset pressure
2
)MPa
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 51
Page 50

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Code Holder Nozzle
RM 2645F306 2645F611 247 3630 25,0
RN 2645F306 2645F612 247 3630 25,0
RP 2645F309 2645F611 247 3630 25,0
RR 2645F307 2645F614 247 3630 25,0
RS 2645F307 2645F615 247 3630 25,0
RT 2645F308 2645F616 247 3630 25,0
RU 2645F310 2645F617 247 3630 25,0
RV 2645F311 2645F610 247 3630 25,0
Note: The code letters are stamped on the side of the atomiser body just below the connection for the nut of
the high pressure pipe.
atm (lbf/in
Set and reset pressure
2
)MPa
52 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 51

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Cooling system
Coolant pump (four cylinder engines and early six cylinder engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Centrifugal, gear driven
Outside diameter of shaft for drive gear .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,91/15,92 mm (0.6262/0.6257 in)
Diameter of bore of drive gear. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,85/15,88 mm (0.6244/0.6252 in)
Interference fit of drive gear on shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,03/0,06 mm (0.0012/0.0024 in)
Diameter of bore of impeller ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,87/15,89 mm (0.6249/0.6257 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for impeller.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,91/15,92 mm (0.6264/0.6268 in)
Interference fit of impeller on shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,02/0,05 mm (0.0007/0.0020 in)
Diameter of bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..29,99/30,00 mm (1.1807/1.1811 in)
Diameter of bore for bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..29,96/29,98 mm (1.1795/1.1803 in)
Interference fit of bearing in pump body.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Dimension of impeller boss to front face of pump body (fitted) - early engines... .8,1/8,5 mm (0.319./0.335 in)
(1)
Dimension of impeller boss to front face of pump body (fitted) - latest engines
Dimension of gear from rear face of pump body (fitted).. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,6/2,6 mm (0.024/0.102 in)
(1) Impeller part number 3746X071.
Coolant pump (six cylinder engines and later four cylinder engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Centrifugal, gear driven
Outside diameter of shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..18,95/18,96 mm (0.7460/0.7465 in)
Diameter of bore of drive gear. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..18,90/18,92 mm (0.7441/0.7449 in)
Interference fit of drive gear on shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,03/0,06 mm (0.0012/0.0024 in)
Diameter of bore of impeller ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,87/15,89 mm (0.6249/0.6257 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for impeller.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,91/15,92 mm (0.6264/0.6268 in)
Interference fit of impeller on shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,02/0,05 mm (0.0007/0.0020 in)
Diameter of bore for bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..38,06/38,08 mm (1.4983/1.4993 in)
Diameter of bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..38,09/38,10 mm (1.4995/1.5000 in)
Interference fit of bearing in pump body.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Dimension of impeller boss to front face of pump body (fitted) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .7,7/8,0 mm (0.303./0.315 in)
Dimension of gear from rear flat face of pump body (fitted) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..21,0/21,5 mm (0.827/0.846 in)
Dimension of gear from rear face of bearing (fitted) ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,47/1,53 mm (0.018/0.060 in)
.. .7,1/7,5 mm (0.28./0.30 in)
Auxiliary coolant pump (fitted to certain intercooled engines)
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Centrifugal, belt driven
Outside diameter of shaft for pulley. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,001/15,009 mm (0.5906/0.5909 in)
Inside diameter of bore of pulley . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..14,935/14,956 mm (0.5879/0.5888 in)
Interference fit of pulley on shaft . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,05/0,07 mm (0.0019/0.0028 in)
Diameter of bore of impeller ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,875/15,893 mm (0.625/0.6257 in)
Outside diameter of shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,9055/15,9182 mm (0.6263/0.6267 in)
Interference fit of impeller on shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Impeller to body clearance .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,64/0,89 mm (0.025/0.035 in)
Coolant pump
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Centrifugal, belt driven
Outside diameter of shaft for pulley. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..24,587/24,600 mm (0.9679/0.9685 in)
Inside diameter of bore of pulley . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..24,628/24,648 mm (0.9696/0.9704 in)
Clearance fit of pulley on shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,03/0,06 mm (0.001/0.002 in)
Diameter of bore of impeller ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,872/15,893 mm (0.6248/0.6257 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for impeller.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..15,9055/15,9182 mm (0.6263/0.6267 in)
Interference fit of impeller on shaft .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Impeller to body clearance .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,69/0,89 mm (0.027/0.035 in)
Diameter of bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 62,000 mm (2.440 in)
Diameter of bore for bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 62,019/62,000 mm (2.441/24.000 in)
Interference fit of bearing in pump body.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 53
Page 52

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Thermostat
Type:
Four cylinder engines. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Single, wax element, by-pass blanking
Six cylinder engines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Twin, wax element, by-pass blanking
Nominal temperature stam ped on
thermostat by-pass valve
82 °C
(180 °F)
71 °C
(160 °F)
"Start to open"
temperature
77/85 °C
(170/185 °F)
67/75 °C
(153/167 °F)
"Fully open"
temperature
92/98 °C
(198/208 °F)
85/88 °C
(185/190 °F)
Minimum valve lift, fully
open
9 mm
(0.35 in)
9 mm
(0.35 in)
Fan drive housing
Early engines:
Bore of housing for bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41,98/41,99 mm (1.6527/1.6531 in)
Outside diameter of bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41,99/42,00 mm (1.6531/1.6535 in)
Interference fit of bearing in housing.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,00/0,02 mm (0.0000/0.0008 in)
Bore of hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21,946/21,958 mm (0.8640/0.8645 in)
Outside diameter of shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21,987/22,000 mm (0.8656/0.8661 in)
Interference fit of shaft in hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,029/0,054 mm (0.0011/0.0021 in)
Maximum permissible end-float of shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,25 mm (0.010 in)
Latest engines:
Bore of housing for bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41,97/41,98 mm (1.6524/1.6527 in)
Outside diameter of bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 41,99/42,00 mm (1.6531/1.6535 in)
Interference fit of bearing in housing.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,01/0,03 mm (0.0004/0.0012 in)
Bore of hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21,938/21,958 mm (0.8637/0.8645 in)
Outside diameter of shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 21,987/22,000 mm (0.8656/0.8661 in)
Interference fit of shaft in hub ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,029/0,062 mm (0.0011/0.0024 in)
Maximum permissible end-float of shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 0,25 mm (0.010 in)
Flywheel and flywheel housing
Limits for flywheel housing run-out and alignment (total indicator reading)
Diameter of housing flange bore Maximum limit (total indicator reading)
mm in mm in
362 14.25 0,23 0.009
410 16.14 0,25 0.010
448 17.63 0,28 0.011
511 20.11 0,30 0.012
584 22.99 0,36 0.014
648 25.51 0,41 0.016
787 30.98 0,48 0.019
54 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 53

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Electrical equipment
Note: The information which follows is general and can change with specific applications.
Alternators
Make and type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... Lucas, AC5RA, AC5RS, A127 and Butec 5524
Rating:
Lucas:
AC5RA and AC5RS. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 12V/60A or 24V/40A
A127 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 12V/55A or 12V/65A
Butec:
5524. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24V/55A
Rotation ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..Clockwise from drive end
Starter motors
Make and type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... CAV M45G, CAV S115 or Lucas M127
Voltage:
M45G and S115 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12V or 24V
M127 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12V
Number of teeth on pinion ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..10
Maximum starter cable resistance at 200 °C (680 °F):
12V.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 0.0017 ohms
24V.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . 0.0034 ohms
Starting aid
Type. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .Electrically operated heater, with a fuel supply
Voltage ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12V (dropping resistor used on 24V system)
Flow rate of fuel through starting aid ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3,5/5,9 ml/min
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 55
Page 54

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Auxiliary equipment
Wabco compressor
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .. Wabco 159 or 229
Number of teeth on compressor drive gear:
- Early compressor. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 26
- Latest compressor ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 42
Inside diameter of drive gear:
- Early compressors... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23,750/23,775 mm (0.9350/0.9360 in)
- Latest compressors . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23,773/23,790 mm (0.9359/0.9366 in)
Outside diameter of compressor drive shaft.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 23,753/23,765 mm (0.9352/0.9356 in)
Transition fit of gear on shaft of early compressors... ... ... ... ... ... ... - 0,015/+0,022 mm (-0.0006/+0.0009 in)
Clearance fit of gear on shaft of latest compressors.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,008/0,037 mm (0.0003/0.0014 in)
Bore for bush . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 19,000/19,030 mm (0.7480/0.7492 in)
Inside diameter of bush.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,875/15,900 mm (0.625/0.626 in)
Outside diameter of bush... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..19,050/19,075 mm (0.075/0.7510 in)
Interference fit of bush in compressor casing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,020/0,075 mm (0.0008/0.0030 in)
Compressor drive assembly for Wabco compressors
Early engines:
Number of teeth on idler gears .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 27
Inside diameter of idler gear .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,23/22,25 mm (0.875/0.876 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for idler gears ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,23/22,24 mm (0.8750/0.8756 in)
Transition fit of gears on shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... -0,01/+0,.02 mm (-0.0004/+0.0008 in)
Inside diameter of front bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24,987/25,003 mm (0.9837/0.9844 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for front bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 25,014/25,026 mm (0.9848/0.9853 in)
Interference fit of bearing on shaft. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,011/0,039 mm (0.0004/0.0015 in)
Housing bore for front bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 61,948/61,966 mm (2.4389/2.4396 in)
Outside diameter of front bearing .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 61,983.62,004 mm (2.4403/2.4411 in)
Interference fit of front bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,017/0,056 mm (0.0007/0.0022 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for rear bush . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,82/15,85 mm (0.6228/0.6240 in)
Clearance fit of shaft in bush . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ..0,025/0,08 mm (0.001/0.003 in)
Latest engines:
Number of teeth on front idler gear ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 26
Number of teeth on rear idler gear. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 39
Inside diameter of idler gears. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,25/22,27 mm (0.8760/0.8768 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for idler gears ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 22,23/22,24 mm (0.8750/0.8756 in)
Clearance fit of gears on shaft... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,01/0,04 mm (0.0004/0.0016 in)
Inside diameter of front bearing. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 24,987/25,003 mm (0.9837/0.9844 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for front bearing ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 25,002/25,011 mm (0.9843/0.9847 in)
Interference fit of bearing on shaft. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,002/0,021 mm (0.0001/0.0008 in)
Housing bore for front bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 61,912/61,931 mm (2.4375/2.4382 in)
Outside diameter of front bearing .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 61,987/62,000 mm (2.4404/2.4409 in)
Interference fit of front bearing... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,06/0,09 mm (0.002/0.003 in)
Outside diameter of shaft for rear bush . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 15,82/15,85 mm (0.623/0.624 in)
Clearance fit of shaft in bush . ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 0,025/0,080 mm (0.001/0.003 in)
Bendix compressor
Type... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...Bendix 1W150R or 1W250R
Number of teeth on compressor drive gear ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 28
Taper of compressor drive shaft ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...1 in 8
56 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 55

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Thread sealant
When setscrews or studs are fitted into holes which are tapped through the cylinder block, a suitable sealant
must be used to prevent leakage.
Micro encapsulated anaerobic sealant (M.E.A.S) fasteners have been introduced instead of jointing
compounds or other sealants when the fasteners are fitted in through holes into oil or coolant passages. The
identification of these fasteners, as supplied, is by a red, blue, or other colour sealant around the fastener
threads.
With M.E.A.S. sealed studs, the sealed end must be fitted into the cylinder head / cylinder block etc. Ensure
that the threaded holes have a 1,59 mm (0.0625 in) 45° chamfer, to ensure that when the new fasteners are
fitted the M.E.A.S. sealant is not removed. If the fasteners have to be removed and fitted again, the threads
must be cleaned and a suitable sealant used.
Note: New setscrews have sealant applied by the manufacturer to the first 13,0 mm (0.50 in) of the threads.
If the setscrews are to be used again, clean the old sealant from the male and female threads and apply new
sealant, POWERPART Threadlock and Nutlock to the setscrews.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 57
Page 56

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Recommended torque settings
The torque tensions below apply to components lubricated lightly with clean engine oil before they are fitted.
Description
Cylinder head assembly
Setscrews, cylinder head
Fasteners, rocker shaft brac ke ts :
Aluminium brackets M12 40 30 4,1
Cast iron and sintered steel brackets M12 75 55 7,6
Cap nuts, rocker cover M12 20 15 2,1
Cap nuts, aluminium rocker cover (with shim washer) M12 30 22 3,0
Setscrews, inlet manifold to cylinder head M10 44 33 4,5
Nuts (plated), exhaust manifold to cylinder head M10 44 33 4,5
Nuts (non-plated), exhaust manifold to cylinder head M10 50 37 5,1
Setscrews, engine lift bracket M10 44 33 4,5
Piston and connecting rod assemblies
Nuts, connecting rods
Setscrews, connecting rods
Banjo bolts, piston cooling jets
Crankshaft assembly
Setscrews, main bearings
Setscrews, crankshaft pulley
Setscrews, viscous damper to crankshaft pulley M12 75 55 7,6
Cap screws, viscous damper to crankshaft pulley M8 35 26 3,6
Cap screws, rubber bonded damper to crankshaft pulley M8 35 26 3,6
Setscrews, rear oil seal housing to cylinder block M8 22 16 2,2
Torxscrew, rear oil seal housing to cylinder block M8 22 16 2,2
Cap screws, bridge piece to cylinder block M6 16 12 1,6
Cap screws, rear oil seal housing to bridge piece M8 18 13 1,9
Cap screws, rear oil seal housing to bridge piece M6 13 10 1,3
Torxscrew, rear oil seal housing to bridge piece M8 18 13 1,9
Setscrew, idler gear hub of balancer unit M12 93 68 9,5
Nut, drive gear of balance weight
Setscrews, rear cover of balancer frame M10 54 40 5,5
Setscrews, oil transfer plate (balancer unit) M10 30 22 3,1
Setscrews, oil pump to balancer frame M8 27 20 2,8
Setscrews, balancer to cylinder block M10 54 40 5,5
Timing case and drive assembly
Setscrews, timing case to cylinder block M8 22 16 2,2
Setscrews, timing case to cylinder block M10 44 33 4,5
Setscrews, hub of idler gear M10 44 33 4,5
Setscrew, camshaft gear M12 78 58 8,0
Setscrew, camshaft gear
(for engines, with 45 mm long setscrew)
Setscrews, timing ca se co ver to tim ing case M8 22 16 2,2
Nuts, timing case cover to timing case M8 22 16 2,2
Thread
size
1
/2 UNF See Operation 3-10
1
/2 UNF 125 92 12,7
1
/2 UNF 155 114 15,8
3
/8 UNF 20 15 2,0
5
/8 UNF 265 196 27,0
7
/16 UNF 115 85 11,8
1
/2 UNF 82 60 8,4
M12 100 74 10,0
Nm lbf ft kgf m
Torque
58 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 57

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
2
Description
Cylinder block
Setscrews, fitted instead of piston cooling jets
Aspiration system
Nuts, turbocharger to manifold M10 44 33 4,5
Setscrew, breather cover M6 9 7 0,9
Fuel system
Nuts, high-pressure fuel pipes M12 22 16 2,2
Setscrews, atomiser M8 12 9 1,2
Setscrews, fuel lift pump M8 22 16 2,2
Nut for gear of fuel injection pump M14 80 59 8,2
Cap screw for gear of in-line fuel injection pump
(AE, YE engines)
Nut for hub of in-line fuel injection pump
(AE, YE engines)
Nuts for adaptor plate of in-line fuel injection pump
(AE, YE engines)
Nuts for flange of fuel injection pump M8 22 16 2,2
Locking screw for Bosch VE fuel injection pump shaft M10 27 20 2,8
Locking screw for DP 200 fuel injection pump shaft 10 A/F 10 7 1,0
Lubrication system
Plug, lubricating oil sump
Setscrews, oil pump to front bearing cap M8 22 16 2,2
Setscrews, cover for oil pump M8 28 21 2,9
Fasteners, lubricating oil sump M8 22 16 2,2
Cooling system
Setscrews, fan drive housing to timing case M10 44 33 4,5
Setscrews, fan drive pulley to hub M8 22 16 2,2
Setscrews, fan drive pulley to hub M10 44 33 4,5
Setscrews, fan M8 22 16 2,2
Connector, oil cooler to oil filter head
Setscrews, coolant pump to timing case M8 22 16 2,2
Nut, auxiliary coolant pump pulley
Setscrew, intercooler flange to inlet manifold M6 7 5 0,7
Setscrew, intercooler body to inlet manifold M8 22 16 2,2
Temperature switch (plastic thermostat housing) - 4 3 0,4
Plug (plastic thermostat housing)
Plug (plastic thermostat housing)
Flywheel and housing
Setscrews, flywheel to crankshaft
Setscrews, cast iron flywheel housing to cylinder block M10 44 33 4,5
Stamped 8.8 M12 75 55 7,6
Stamped 10.9 M10 63 46 6,4
Stamped 10.9 M12 115 85 11,7
Setscrews, aluminium flywheel housing to cylinder block M10 70 52 7,1
Setscrews, flywheel housing to cylinder block (paper joint) M10 70 52 7,1
Thread
size
3
/8 UNF 27 20 2,8
M8 44 33 4,5
M18 115 84 11,8
M10 44 33 4,5
3
/4 UNF 34 25 3,5
3
/4 UNF 58 42 5,8
1
/2 UNF 70 52 7,1
1
/2 NPSI 4 3 0,4
3
/4 NPSI 4 3 0,4
1
/2 UNF 105 77 10,7
Nm lbf ft kgf m
Torque
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 59
Page 58

2
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Description
Electrical equipment
Nut, alternator pulley:
CAV AC5RA and AC5RS
Lucas A127, and motorola, 22mm A/F M17 80 59 8,2
Lucas A127, and motorola, 24mm A/F M17 80 59 8,2
Bosch 55A M14 50 37 5,1
Bosch 55A M16 50 37 5,1
Butec 5524
Setscrew, side bracket to front bracket M12 75 55 7,6
Setscrew adjusting lever to alternator M8 11 8 1,1
Setscrew adjusting lever to bracket M8 11 8 1,1
Fuelled start aid to induction manifold
Port heater aid to induction manifold M22 60 44 6,1
Auxiliary equipment
Nut, compressor drive gear:
6,4 mm (0.25 in) thick
10 mm (0.4 in) thick
Nuts for gears of auxiliary drive assembly:
6,4 mm (0.25 in) thick
10 mm (0.4 in) thick
Nut for gears of auxiliary drive assembly M20 130 95 13,3
Thread
size
5
/8 UNF 55 40 5,6
5
/8 UNF 55 40 5,6
7
/8 UNF 31 23 3,1
3
/4 UNF 80 59 8,2
3
/4 UNF 130 95 13,3
3
/4 UNF 80 59 8,2
3
/4 UNF 130 95 13,3
Nm lbf ft kgf m
Torque
60 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 59

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Compression test data
Tests have shown that many factors affect compression pressures. Battery and starter motor condition,
ambient conditions and the type of gauge used can give a wide variation of results for a given engine.
2
It is not possible to give accurate data for compression pressure, but tests have shown that the results should
be within 2000/3500 kPa (300/500 lbf/in
Compression tests should only be used to compare between the cylinders of an engine. If one or more
cylinders vary by more than 350 kPa (50 lbf/in
Compression tests should not be the only method used to show the condition of an engine, but they should be
used together with other symptoms and tests.
How to do a compression test
Caution: Before the compression test, ensure that the battery is in good condition and that it is fully charged.
Also ensure that the starter motor is in good condition.
1 Ensure that the valve tip clearances are set correctly, see Operation 3-6 for four cylinder engines or
Operation 3-7 for six cylinder engines.
2 Remove the atomisers.
3 Fit a suitable gauge into the atomiser hole of the cylinder to be tested.
Caution: Ensure that the engine cannot start:
4 Disconnect the stop solenoid or put the stop control in the no-fuel position.
5 Operate the starter motor and note the pressure indicated on the gauge.
6 Repeat for each cylinder.
2
) 21,0/35,0 kgf/cm2 for diesel engines.
2
) 3,5 kgf/cm2, then those cylinders may be faulty.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 61
Page 60

This page is intentionally blank
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Page 61

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
Cylinder head assembly 3
General description
In a diesel engine there is little carbon deposit and for this reason the number of hours run is no indication of
when to overhaul a cylinder head assembly. The factors which indicate when an overhaul is necessary are
how easily the engine starts and its general performance.
The cylinder head assembly has two valves fitted for each cylinder, each fitted with double or single valve
springs, according to the engine application. The double springs have damper coils which are fitted towards
the top face of the cylinder head.
In most engines the face angle of the valves is 45°, but some engines have inlet valves with a face angle of
30°. The angle of the valve seats in the cylinder head are either 46° or 31°.
The valves move in phosphated guides which can be renewed. The exhaust valve guide has a counterbore at
the bottom and is a little longer than the inlet valve guide.
Both valve stems are fitted with oil seals which fit over the top of the valve guides.
Turbocharged engines and some naturally aspirated engines have valve seat inserts fitted in the cylinder head
for both inlet and exhaust valves. Engines which do not have valve seat inserts fitted as standard, in
production, can have them fitted in service.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 63
Page 62

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Rocker cover
To remove Operation 3-1
Engines are supplied with either an aluminium rocker cover (A) or with rocker covers made of a composite
material (B). The aluminium cover on some engines, has a dust seal which is fitted between the rocker cover
and the induction manifold. The dust seal of the composite rocker cover is fitted permanently to the side of the
rocker cover with adhesive.
1 Disconnect the breather pipe.
2 Remove the cap nuts (A2/B2) together with the steel washers (B3) and the shim washers (B4) from the top
of the rocker cover.
3 Lift off the rocker cover and the joint (B6). For aluminium covers, remove the rocker cover dust seal (A1/B7).
Caution: When the rocker cover is fitted, the cap nuts are tightened onto the nuts of the rocker brackets.
During removal of the cap nuts, it is possible to loosen the nuts of the rocker brackets. The nuts of the rocker
brackets should be tightened to the correct torque every time the cover is removed.
A
1
2
A0045
1
7
6
B
2
3
4
5
A0046
64 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 63

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To fit Operation 3-2
1 Check the seal of the oil filler cap (A1), the sealing washers (A5), the steel washer (A3) and, if fitted, the
shim washer (A4) for the cap nuts (A2).
2 Check the condition of the rocker cover joint (A6) and of the dust seal (A7). If necessary, the joint and the
seal can be removed and renewed.
3 Clean the joint face of the cylinder head and fit the rocker cover together with the dust seal.
4 Fit the sealing washers, the steel washers, the shims (if fitted) and the cap nuts.
Caution: Damage to the sealing washer can occur if the cap nut is not tightened centrally through the sealing
washer and the rocker cover. If the sealing washer is damaged it must be renewed.
5 Tighten the cap nuts to 20 Nm (15 lbf ft) 2,1 kgf m.
Notes:
l The latest engines have an extra shim washer (A4) fitted between the cap nut sealing washer and the steel
washer for the cap nut. If shim washers are fitted to aluminium rocker covers, tighten the cap nuts to 30 Nm
(22 lbf ft) 3,0 kgf m. If shim washers are fitted to composite rocker covers, tighten the cap nuts to 20 Nm
(15 lbf ft) 2,1 kgf m.
l Some earlier 1000 Series engines have a rocker cover joint that has a ribbed bottom face. When this joint
is fitted, ensure that the flat face of the joint is towards the rocker cover.
A
1
7
6
2
3
4
5
A0046
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 65
Page 64

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Rocker ass embly
To remove and to fit Operation 3-3
To remove
1 Remove the rocker cover, see Operation 3-1.
2 Release evenly and gradually the fasteners of the rocker shaft brackets; begin with the end brackets and
move toward the centre. Remove the fasteners and the washers and lift off the rocker assembly.
Note: The washers between the fasteners and the rocker brackets have been removed on the latest engines
and new flange faced nuts and setscrews have been fitted.
3 Remove the rubber oil seal (A) from the oil supply connection or from the oil supply hole in the cylinder head.
To fit
1 Fit a new rubber oil seal in the oil supply hole in the cylinder head (A).
2 Check that the push rods fit correctly in the sockets of the tappets. Fit the rocker assembly; ensure that the
oil supply connection is fitted correctly into the oil seal. Check that the ends of the adjustment screws fit
correctly in the sockets of the push rods.
3 Fit the washers (if fitted) and fasteners of the rocker shaft brackets and tighten the fasteners evenly and
gradually; begin with the inner fasteners and work towards the end fasteners. Tighten the fasteners evenly to
the correct torque according to the material of the rocker shaft brackets:
l Aluminium: 40 Nm (30 lbf ft) 4,1 kgf m.
l Cast iron: 75 Nm (55 lbf ft) 7,6 kgf m.
l Sintered steel: 75 Nm (55 lbf ft) 7,6 kgf m.
A
66 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0047A
Page 65

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To dismantle and to assemble Operation 3-4
To dismantle
1 Remove the clips from both ends of the rocker shaft. Ensure that the ends of the rocker shaft are not
damaged. Release the location screw (A1) for the oil supply connection.
2 Dismantle the assembly and make a note of the position of each component to ensure that they can be
assembled more easily.
To assemble
1 Ensure that the oil holes in the rocker shaft and in the rocker levers are not restricted.
2 Lubricate the components with clean engine lubricating oil before assembly. Assemble the components in
the correct order (A) and ensure that the location screw (A1) for the oil supply connection is fitted correctly in
the hole (A2) in the rocker shaft. Fit the clips to the ends of the rocker shaft.
2
1
A
A0048
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 67
Page 66

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To inspect and to correct Operation 3-5
To inspect
1 Clean and inspect all the components for wear and any other damage. Check the clearance of the rocker
levers on the rocker shaft. If the clearance is larger than 0,13 mm (0.005 in), renew the rocker lever bush and/
or the rocker shaft.
To correct
1 To renew the rocker lever bush, press out the old bush with a suitable mandrel.
2 Align the lubrication hole of the new bush on the same side as the rocker lever lubrication hole and press
the bush into position.
3 Ream the bush in the rocker lever to give a clearance on the rocker shaft of 0,03/0,09 mm (0.001/0.004 in).
Clean thoroughly the bush and check that the oil hole is free from debris.
Note: The rocker levers used on some low rated engines do not have bushes.
68 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 67
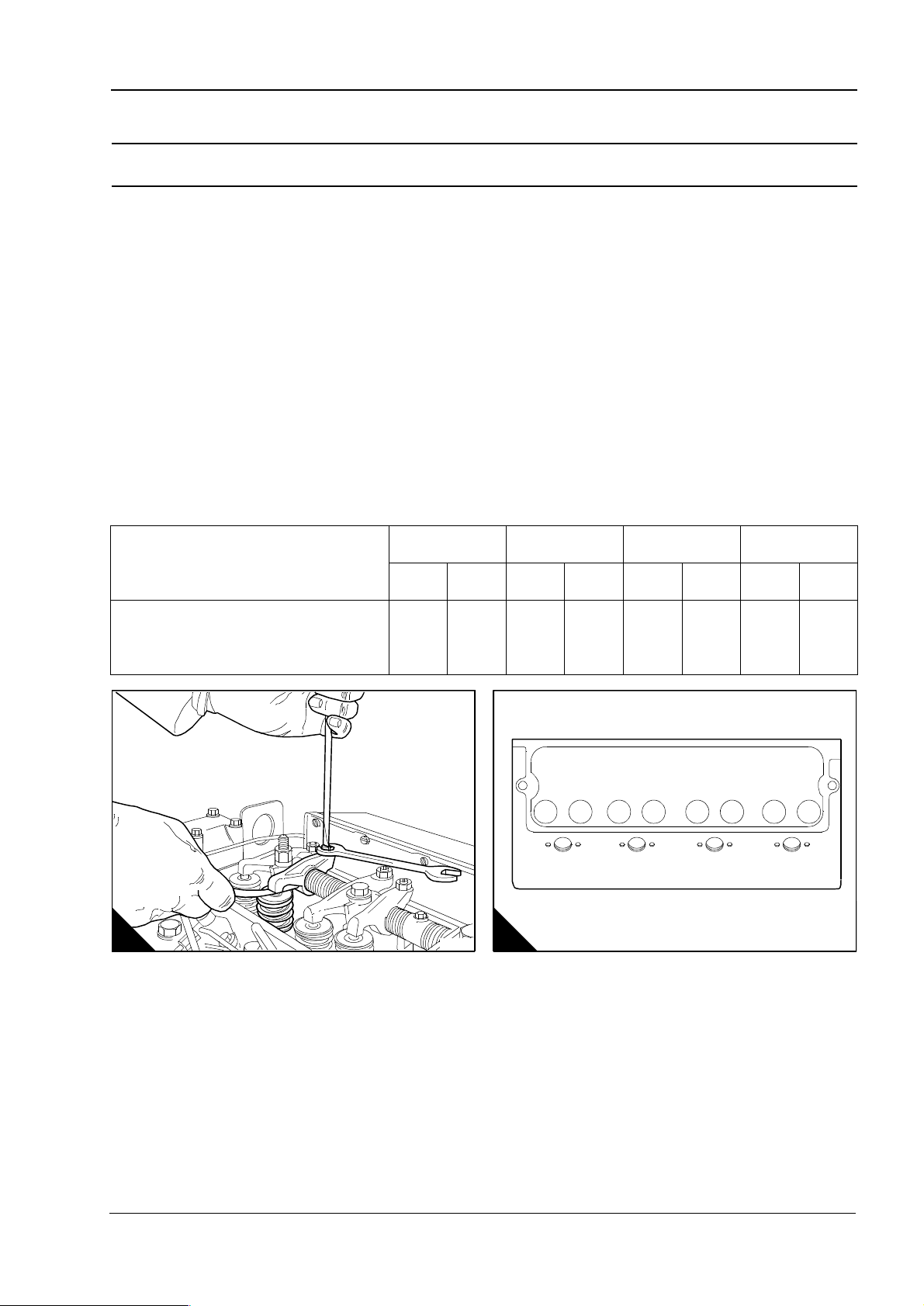
Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
Valve tip clearances
To check and to adjust (four cylinder engines) Operation 3-6
Notes:
l The valve tip clearance is measured between the top of the valve stem and the rocker lever (A). With the
engine hot or cold, the correct clearances are 0,20 mm (0.008 in) for the inlet valves and 0,45 mm (0.018 in)
for the exhaust valves. The valve positions are shown at (B).
l The sequence of valves from number 1 cylinder is shown in the table below. Number 1 cylinder is at the
front of the engine.
1 Rotate the crankshaft in the normal direction of rotation until the inlet valve (B8) of number 4 cylinder has
just opened and the exhaust valve (B7) of the same cylinder has not closed completely. Check the clearances
of the valves (B1 and B2) of number 1 cylinder and adjust them, if necessary.
2 Set the valves (B3 and B4) of number 2 cylinder as indicated above for number 4 cylinder. Then check /
adjust the clearances of the valves (B5 and B6) of number 3 cylinder.
3 Set the valves (B1 and B2) of number 1 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B7 and
B8) of number 4 cylinder.
4 Set the valves (B5 and B6) of number 3 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B3 and
B4) of number 2 cylinder.
Cylinder
and
Valve number
Valve
I = Inlet
E = Exhaust
A
1234
12345678
IEEI IEEI
12 34 56 78
A0049
B
A0050
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 69
Page 68

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To check and to adjust (six cylinder engines) Operation 3-7
Notes:
l The valve tip clearance is measured between the top of the valve stem and the rocker lever (A). With the
engine hot or cold, the correct clearances are 0,20 mm (0.008 in) for the inlet valves and 0,45 mm (0.018 in)
for the exhaust valves. The valve positions are shown at (B).
l The sequence of valves from number 1 cylinder is shown in the table below. Number 1 cylinder is at the
front of the engine.
1 Rotate the crankshaft in the normal direction of rotation until the inlet valve (B12) of number 6 cylinder has
just opened and the exhaust valve (B11) of the same cylinder has not closed completely. Check the clearances
of the valves (B1 and B2) of number 1 cylinder and adjust them, if necessary.
2 Set the valves (B4 and B3) of number 2 cylinder as indicated above for number 6 cylinder. Then check /
adjust the clearances of the valves (B9 and B10) of number 5 cylinder.
3 Set the valves (B8 and B7) of number 4 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B5 and
B6) of number 3 cylinder.
4 Set the valves (B1 and B2) of number 1 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B11 and
B12) of number 6 cylinder.
5 Set the valves (B9 and B10) of number 5 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B3 and
B4) of number 2 cylinder.
6 Set the valves (B5 and B6) of number 3 cylinder. Then check / adjust the clearances of the valves (B7 and
B8) of number 4 cylinder.
Cylinder
and
Valve number
Valve
I = Inlet
E = Exhaust
A
123456
123456789101112
IEEIIEEIIEEI
12 34 56 78 9101112
A0049
B
A0028
70 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 69

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
Valve springs
To change the valve springs (with cylinder head fitted) Operation 3-8
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Valve spring compressor 21825932
Stud adaptor used with 21825666 21825672
Note: Steps 1 to 12 refer to a change of valve springs for a single cylinder.
Warning! Wear eye protection during this operation.
1 Remove the rocker cover, see Operation 3-1.
2 Rotate the crankshaft in the normal direction of rotation until the inlet valve of the relevant cylinder has just
opened and the exhaust valve has not fully closed. In this position the piston will be at approximately top dead
centre (TDC).
3 Remove the rocker assembly , see Oper ation 3- 3.
4 Fit the valve spring compressor (A1) and the relevant adaptor (A2 or A3).
5 Compress the valve spring(s) and remove the collets. Ensure that the valve springs are compressed
squarely or damage to the valve stem can occur.
Caution: Do not rotate the crankshaft while the valve springs are removed.
Setscrew adaptor used with 21825932 21825673
6 Release the valve spring compressor and remove the valve spring caps and valve spring(s).
7 Put the new valve springs in position. If double valve springs are fitted, ensure that the closed damper coils
are towards the cylinder head, see Operation 3-12.
1
A
3
2
A0051
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 71
Page 70

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
8 Fit the valve spring caps.
Caution: Ensure that the valve springs are compressed squarely or damage can occur to the valve stem.
9 Fit the valve spring compressor, compress the valve springs and fit the collets. Remove the valve spring
compressor.
10 Fit the rocker assembly, see Operation 3-3.
11 Check the valve tip clearances, see Operation 3-6 for four cylinder engines or Operation 3-7 for six cylinder
engines.
12 Fit the rocker cover, see Operation 3-2.
Note: If other or all of the valve springs are to be changed, they can be changed two cylinders at a time. The
sets of cylinders are:
l For 4 cylinder engines: 1 and 4, 2 and 3
l For 6 cylinder engines: 1 and 6, 2 and 5, 3 and 4
If the rocker assembly has been removed, piston TDC can be found as follows
1 Fit the valve spring compressor and compress the valve springs to open the valve.
2 Rotate the crankshaft, by hand, in the normal direction of rotation until the piston touches the valve.
3 Continue to rotate the crankshaft, and at the same time, release pressure on the valve spring compressor
until the piston is at TDC (B).
Phaser/1000 Series
B
72 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0052/1
Page 71

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
Cylinder head assembly
To remove Operation 3-9
1 Drain the cooling system.
2 Disconnect the battery terminals.
3 Remove the air filter/cleaner hose at the induction manifold.
4 For engines fitted with turbochargers, remove the air filter/cleaner hose at the compressor inlet of the
turbocharger.
5 Remove the pipe which is fitted between the fuelled starting aid in the induction manifold and the fuel filter.
Disconnect the electrical connection.
6 For engines fitted with a boost control device, remove the boost control pipe which is fitted between the
induction manifold and the top of the fuel injection pump.
7 Remove the induction mani fol d.
8 For engines fitted with turbochargers, disconnect all connections to the turbocharger and remove the
turbocharger, see Operation 9-1.
9 Remove the exhaust manifold.
10 Remove the low-pressure fuel pipes which are fitted between the fuel injection pump and the fuel filter.
Note: Where a Bosch fuel injection pump is fitted, keep the fuel outlet banjo bolt with the fuel injection pump.
11 Remove the fuel pipe fitted between the fuel lift pump and the fuel filter. Remove the fuel filter bracket
together with the fuel filter.
12 Remove the high-pressure fuel pipes.
Caution: Where access to the fuel injection pump outlet unions is possible, ensure that a separate spanner is
used to prevent movement of the fuel injection pump outlets when the connections of the high-pressure pipes
are released. Fit suitable covers to all open connections on the fuel injection pump.
13 Remove the atomiser leak-off pipe.
14 Remove the atomisers, see Operation 11-7. Fit suitable covers to the nozzles and the open connections.
15 If a compressor is fitted, remove the coolant pipe which is fitted between the cylinder head and the
compressor, then remove the coolant pipe which is fitted between the by-pass connection and the compressor.
16 Release the clip of the coolant by-pass hose at the cylinder head. Release the setscrews and remove the
coolant by-pass connection and the hose.
17 Disconnect the coolant temperature sender unit.
18 For turbocharged and some naturally aspirated four cylinder engines, remove the oil cooler, see Operation
12-21.
19 Remove the rocker cover, see Operation 3-1.
20 Remove the rocker assembly, see Operation 3-3.
21 Remove the push rods.
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 73
Page 72

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
22 Release the cylinder head setscrews evenly and gradually in the reverse sequence to that shown in (A) for
six cylinder engines or (B) for four cylinder engines.
M
L L
29 24
30
M
S S S S S S S S S S S S
31 32
M
M M M M M M
M
18 8 2 13 23 28
19 9 1 3 14
20
21 22 11 12 6 5 17 16 27 26
M
M
M
10 7 4 15 25
M
M
M
M
A
7
M
6 5
13
M
3
M
4 15
17
14
S
16
L
M
18 8 1 2
M
19
L
20
M
21
S
S S S S S S
22
M
9
M
10
M M M
11 12
M
M
A0055
B
A0053
23 Check the setscrews for distortion with a straight edge (C1) held along the setscrew (C2). If there is a visual
reduction in the diameter of the thread (C3) that has not been in engagement with the cylinder block, the
setscrew must be discarded.
Caution: Do not use a lever to separate the cylinder head from the cylinder block.
24 Remove the cylinder head and put it on a surface that will not damage the face of the cylinder head.
1
2
3
C
A0054
74 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 73

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To fit Operation 3-10
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number
Angle gauge (to tighten cylinder head
setscrews)
1 Clean the bottom face of the cylinder head and top face of the cylinder block. Ensure that there is no debris
in the cylinder bores.
Notes:
l Early engines have two 6 mm (0.236 in) location pins (A1), one at each end of the cylinder head, pressed
into the cylinder block to hold the cylinder head gasket in the correct position before the cylinder head is
fitted.
l Latest engines have two 8 mm (0.315 in) location pins (A1), one at each end of the cylinder head, pressed
into the cylinder block to hold the cylinder head gasket in the correct position before the cylinder head is
fitted.
Cautions:
l To prevent damage to the cylinder head gasket, ensure that the location pins are pressed in the cylinder
block before the cylinder head is fitted.
l The cylinder head gasket must be fitted without jointing compound.
2 Put the cylinder head gasket in position; It is stamped "FRONT TOP" for correct assembly (A).
3 To ensure the cylinder head is fitted into the correct position, fit two suitable
positions 15 and 20 (Operation 3-9/B) or positions 25 and 30 (Operation 3-9/A). Put the cylinder head in
position.
4 Lightly lubricate the threads of the cylinder head setscrews and the thrust faces of the setscrew heads.
Engage some of the setscrews in their correct positions and remove the guide studs. Engage the remainder
of the setscrews in their correct positions.
5 Gradually and evenly tighten the setscrews to 110 Nm (80 lbf ft) 11,1 kgf m in the sequence shown in
Operation 3-9 (A/B).
6 Repeat step 5 to ensure that all the setscrews are tightened to the correct torque.
21825607
1
/2 UNF guide studs (B1) in
1
FRONT TOP
1
A
A0056
B
A0057
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 75
Page 74

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
7 Tighten the setscrews, in the correct sequence, a further part of a turn according to the length of the
setscrews, see Operation 3-9 (A/B). Short setscrews (S) must be turned a further 150° (2.5 flats). Medium
length setscrews (M) must be turned a further 180° (3 flats). Long setscrews (L) must be turned a further 210°
(3.5 flats). A special tool (C) can be used for this operation.
Fit the tool between the socket and the handle. Position the stop (C1) against a suitable protrusion on the
cylinder head to prevent movement of the degree dial in a clockwise direction. Rotate the pointer to align with
the relevant angle on the degree dial for the length of setscrew. Tighten the setscrew until the pointer on the
tool is aligned with the zero position on the degree dial.
If no tool is available, make a suitable mark on the cylinder head in line with a corner of each setscrew (D).
Make another mark, at the correct angle (counter-clockwise), on the edge of the flange of each fastener
according to the length of the setscrew. Tighten each setscrew in the correct sequence until the marks on the
flange are next to, and in line with, the marks on the cylinder head.
Phaser/1000 Series
1
C
8 Put the push rods in position. Ensure that the end of each push rod fits correctly in the tappet socket.
9 Fit the rocker assembly, see Operation 3-3.
10 Set the valve tip clearances, see Operation 3-6 for four cylinder engines or Operation 3-7 for six cylinder
engines.
11 Fit the atomisers, see Operation 11-7.
12 Fit the high-pressure fuel pipes; tighten the connection nuts to 22 Nm (16 lbf ft) 2,2 kgf m.
Caution: Where access to the fuel injection pump outlet unions is possible, ensure that a separate spanner is
used to prevent movement of the fuel injection pump outlets when the connections of the high pressure pipes
are tightened.
13 Fit the fuel filter and the bracket. Fit the low-pressure fuel pipes between the fuel injection pump and the
fuel filter.
14 Fit the coolant by-pass connection; tighten the setscrews and hose clip.
15 If a compressor is fitted, fit the coolant pipe between the cylinder head and the compressor, then fit the
pipe between the coolant by-pass and compressor.
16 For turbocharged and some naturally aspirated four cylinder engines, fit the oil cooler, see Operation 12-21.
A0058
150° 180° 210°
D
SML
A0059
Continued
76 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 75

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Note: There are three types of joints for the exhaust and induction manifold: asbestos, asbestos free and
metal. The joints fitted to an engine must be of the same material and should be changed as a set.
If joints made from different materials are fitted to an engine, the manifolds may leak or break. This will cause
a loss of engine performance and could cause internal damage to the engine.
17 Fit the exhaust manifold. The manifold joints are fitted without jointing compound.
18 For engines fitted with turbochargers, fit the turbocharger, see Operation 9-2.
19 For four cylinder engines: Fit the induction manifold. Ensure that the manifold joints for the front and rear
positions are fitted with the notch at the top left when the manifold is fitted to the cylinder head (E). The manifold
joint for the centre position can be fitted either way. Fit the joints without jointing compound. The latest four
cylinder engines are fitted with a one piece induction manifold joint.
For six cylinder engines: Fit the induction manifold. Ensure that the joints are fitted with the notch at the top
and the straight edge towards the centre (F). Fit the joints without jointing compound. Some of the latest six
cylinder engines are fitted with a one piece induction manifold joint. The latest six cylinder engines are fitted
with a one piece induction manifold joint.
3
E
20 Fit the fuel pipe between the fuel filter and the fuel lift pump.
21 Fit the fuel pipe between the fuel filter and the fuelled starting aid in the induction manifold. Connect the
electrical connection to the cold start device.
22 For engines fitted with boost control devices, fit the boost control pipe between the induction manifold and
the top of the fuel injection pump.
23 Fit the electrical connection to the coolant temperature sender unit.
24 Connect the coolant outlet and the hoses for the cab heater. Tighten the clips.
25 Fill the cooling system.
26 Connect the air filter/cleaner.
27 Connect the battery.
28 Eliminate air from the fuel system:
l Bosch EPVE fuel injection pumps, see Operation 11-25.
l Bosch MW fuel injection pumps, see Operation 11-30.
l Lucas/Delphi DPA and DPS fuel injection pumps, see Operation 11-35
l Lucas/Delphi DP 200 fuel injection pumps, see Operation 11-46.
l Stanadyne fuel injection pumps, Operation 11-54.
29 Start the engine and run it at low speed. Check that oil flows from the holes in the rocker levers. If the oil
flow is correct, fit the rocker cover, see Operation 3-2.
Note: It is not necessary to tighten the cylinder head setscrews again with the engine hot or after a limited
period in service.
A0060
F
A0061
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 77
Page 76

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Valves and valve springs
To remove Operation 3-11
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Valve spring compressor 21825932
Stud adaptor 21825672
1 Remove the cylinder head, see Operation 3-9.
2 Clean the bottom face of the cylinder head and check the depth of the heads of the valves below the face
of the cylinder head, see Operation 3-13.
3 Make a suitable mark on the heads of the valves to ensure that the valves can be fitted in their original
positions, if they are to be used again.
Warning! Wear eye protection during this operation.
Caution: Ensure that the valve springs are compressed squarely or the valve stem can be damaged.
4 Use the valve spring compressor and the relevant adaptor to compress the valve spring(s) and remove the
collets (A1).
5 Release the valve spring compressor and remove the valve spring cap (A2), valve spring(s) (A3/A4), valve
stem seal (A5) and the valve seat washer (A6).
6 Repeat steps 4 and 5 for the other valves.
Setscrew adaptor 21825673
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
78 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0062
Page 77

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To fit Operation 3-12
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Valve spring compressor 21825666
Stud adaptor 21825672
Note: The components of the valve assembly are shown in (A). Certain engines are fitted with single valve
springs.
Warning! Wear eye protection during this operation.
1 Lubricate the valve stems (A7 and A8) with clean engine oil and fit the valves in their respective guides.
2 Fit the spring seat washers (A6). Fit new valve stem seals (A5) on the valve guides. If double valve springs
are used, fit the inner and outer valve springs (A3 and A4) on the spring seat washers with their damper coils
toward the cylinder head. If single valve springs are used, the spring does not have a damper coil and it can
be fitted with either end to the cylinder head. Fit the valve spring caps (A2).
Caution: Ensure that the valve springs are compressed squarely or damage can occur to the valve stem.
3 Use the valve spring compressor and the relevant adaptor to compress the valve spring(s) and fit the collets
(A1).
Setscrew adaptor 21825673
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 79
A0062
Page 78

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To inspect and to correct Operation 3-13
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Gauge, valve depth 21825496 Dial gauge for use with 21825496 21825617
1 Check the depth of the valves below the face of the cylinder head before the valve springs are removed.
2 Ensure that the heads of the valves and the bottom face of the cylinder head are clean.
3 Put the valve depth gauge on the face of the cylinder head and zero the dial gauge.
4 Carefully put the valve depth gauge in position over the head of each valve (A) and make a note of the
measurement. The maximum depth, in service, is given in the relevant Data and dimensions for "Inlet and
exhaust valves" on page 29.
5 If a valve is below the depth limit, check the valve depth with a new valve in position. If the valve depth is
still below the limit and a valve seat insert is fitted, the insert must be renewed.
6 Where a valve seat insert is not fitted, the bottom face of the cylinder head can be machined to reduce the
valve depth, or an insert can be fitted, see Operation 3-19.
Caution: If the bottom face of the cylinder head is to be machined, ensure that the thickness, of the cylinder
head will not be less than 102,48 mm (4.035 in) after the cylinder head has been machined.
Notes:
l On AE and YE engines the protrusion of the atomiser nozzle below the bottom face of the cylinder head
must not be more than 4,82 mm (0.190 in).
l The nozzle protrusion must be measured with the nozzle seat washer fitted.
7 Check the valves for cracks. Check the stems of the valves for wear and for correct fit in their valve guides.
8 Check that the seat faces of the valves are not badly burnt or damaged. Seat faces of valves which are
damaged can be ground on a special machine. Valves which have only a little damage can be lapped to their
valve seats. When new valves are fitted, the valve depths must be checked, see step 1.
9 Check that the load on the valve springs is correct at their fitted length, refer to the relevant Data and
dimensions for "Valve guides and valve springs" on page 32. Fit new valve springs at every complete engine
overhaul.
A
80 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0063
Page 79

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
Valve guides
To inspect Operation 3-14
The maximum clearance (A5), between the valve stem and the bore of the guide is 0,13 mm (0.005 in) for inlet
valves and 0,15 mm (0.006 in) for exhaust valves.
If the clearance, with a new valve fitted, is more than the limit, then a new valve guide (A4) must be fitted.
It is recommended that the procedure given below is used to check the valve guide clearance:
1 Put a new valve in the valve guide.
2 Put a dial test indicator with a magnetic base (A1) onto the face of the cylinder head.
3 With the valve lifted 15,0 mm (0.6 in) and the gauge (A2) in contact with the edge of the valve head (A3),
move the valve radially away from the gauge. With the valve held in this position, set the gauge zero.
4 Move the valve radially across the axis of the cylinder head towards the gauge. Make a note of the reading
on the gauge. If the reading is equal to or greater than the data given below, a new valve guide (A4) must be
fitted.
Maximum permissible clearance with a valve lift of 15,0 mm (0.6 in):
l Inlet guide: 0,24 mm (0.009 in)
l Exhaust guide: 0,32 mm (0.013 in)
4
1
2
5
A
3
A0298
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 81
Page 80

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To remove Operation 3-15
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Remover/replacer for valve guides 21825478 Adaptor used with 21825478 21825479
1 Fit the adaptor (A4), 21825479, into the remover/replacer tool (A3), 21825478.
2 With the adaptor fitted to the tool, put the spacer (A5) in position on the tool. Pass the adaptor through the
valve guide and put the spacer and tool in position on the valve seat.
3 Fit the attachment (A7) to secure the adaptor to the valve guide.
4 Hold the top handle (A1) and turn the bottom handle (A2) clockwise to pull the valve guide out of the cylinder
head.
1
A
2
3
4
5
6
7
A0064
82 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 81

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To fit Operation 3-16
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Remover/replacer for valve guides 21825478
Adaptor used with 21825478 21825479
1 Clean the parent bore in the cylinder head for the valve guide.
2 Lubricate the outer surface of the new valve guide (A6) with clean engine lubricating oil.
3 Fit the adaptor (A5), 21825479, into the remover/replacer tool (A3), 21825478
4 With the adaptor fitted to the tool, put the spacer (A4) in position on the tool. Pass the adaptor through the
cylinder head and put the spacer and tool assembly in position on the valve seat.
5 Put the valve guide in position on the adaptor and fit the distance piece (A7), 21825482. Fit the attachment
(A8) to secure the valve guide to the adaptor.
6 Hold the top handle (A1) and turn the bottom handle (A2) clockwise to pull the valve guide until the distance
piece contacts the cylinder head.
7 When the valve guide is fitted correctly, the top of the valve guide will have a protrusion of 15,10 mm
(0.594 in) above the valve spring seat.
Adaptor used with 21825478 and
21825479
21825482
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 83
A0065
Page 82

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Cylinder head
To inspect and to correct Operation 3-17
1 Remove the cylinder head assembly, see Operation 3-9.
2 Remove the thermostat housing.
3 Inspect the cylinder head for signs of gas or coolant leakage.
4 Remove the valve springs and the valves, see Operation 3-11.
5 Clean the face of the cylinder head and the passages for coolant and for lubricating oil. The water jacket can
be cleaned with a special solvent which must be used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
6 Test the cylinder head for leaks at the pressure given in the relevant Data and dimensions for the "Cylinder
head" on page 28.
7 When the cylinder head is thoroughly clean, check it for cracks. Inspect carefully the areas around the valve
seats and around the holes for the atomiser nozzles.
8 The bottom face of the cylinder head can be machined if: there is distortion, see step 9; there are deep
scratches; or, for engines without valve seat inserts, the valve depths are below the service limit.
9 Use a straight edge and feeler gauges to check the cylinder head for distortion across and along its bottom
face, see "Maximum permissible distortion of cylinder head" on page 28. If the distortion is more than the given
limit, the bottom face can be machined.
Caution: Remove only the minimum material and ensure that the thickness of the cylinder head will not be
less than 102,48 mm (4.035 in) after the cylinder head has been machined.
Notes:
l On AE and YE engines the protrusion of the atomiser nozzle below the bottom face of the cylinder head
must not be more than 4,82 mm (0.190 in).
l The nozzle protrusion must be measured with the nozzle seat washer fitted.
Caution: After the cylinder head has been machined the valve seats must be corrected to give the correct
valve head depth.Work to the minimum limit to allow for later wear.
10 Check the valve seats for wear and for damage.
11 Before any work is done on the valve seats, new valve guides must be fitted, see Operation 3-15 and
Operation 3-16.
12 Where there is little damage, the valve and valve seat can be lapped. When the valve seats are lapped
keep the seat as narrow as possible and ensure that all the compound used to lap the valve and the seat is
removed.
13 More badly damaged valve seats can be corrected by use of the cutter tool, see Operation 3-18, or new
inserts can be fitted, see Operation 3-19.
84 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 83

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
3
To correct a valve seat with a valve seat cutter Operation 3-18
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Cutter for 46° inlet valve seats
Cutter for 31° inlet valve seats 21825642
Cutter for exhaust valve seats
(1) Included in set of adjustable cutters for valve seats under part number 21825518.
(1)
(1)
21825632 Pilot for use with valve seat cutters
Handle set for use with valve seat
(1)
21825631
cutters
1 Before any work is done on the valve seats, new valve guides must be fitted, see Operation 3-15 and
Operation 3-16.
2 Fit the pilot in the valve guide and tighten the pilot.
3 Select the relevant cutter. Set the blades of the cutters to the diameter of the valve seat to be cut. Fit the
cutter on the pilot and fit the handle (A). Ensure that the cutter is not allowed to fall on to the seat as this can
damage the blades.
4 Carefully turn the cutter in a clockwise direction. Remove only the minimum material to ensure a good seat.
Keep the seat as narrow as possible.
5 When the seat is cut, remove the cutter and the pilot. Remove any debris from the area of the valve seat
and the port.
6 Fit the valve and lightly lap the valve and the seat.
7 Check that the valve depth is within limits, refer to the relevant Data and dimensions for "Inlet and exhaust
valves" on page 29.
Note: If a valve seat has become too damaged or too worn to correct, a valve seat insert can be fitted, see
Operation 3-19. Turbocharged engines and some naturally aspirated engines have valve seat inserts fitted as
standard and these inserts can be renewed.
(1)
21825555
21825610
A
A0066
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 85
Page 84

3
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To fit valve seat inserts Operation 3-19
1 Remove the valve guide and clean the bore into which the guide is to be fitted.
2 Fit new valve guides, see Operation 3-15 and Operation 3-16.
3 With the bore of the new valve guide used as a pilot, machine the recess in the cylinder head to the
dimensions given in "Dimensions of recesses for valve seat inserts" on page 30, or machine out the old insert.
Remove all debris and clean the insert recess.
4 If the bottom face of the cylinder head has been machined, the insert will have to be surface ground on the
back face to ensure that there is no protrusion of the insert above the bottom face of the cylinder head. After
the back of the insert has been ground, ensure that the outer edge of the back face has a 0,9/1,3 mm (0.035/
0.051 in) chamfer at 30° to the vertical.
5 With the bore of the valve guide used as a pilot, and with the rear face of the insert towards the cylinder
head, press in the insert with the valve seat insert tool, see "Valve seat insert tool" on page 31. Do not use a
hammer on the insert and do not use lubrication. Use a hydraulic press or a hand press in one continuous
movement. Ensure that the bottom of the insert is in contact with the bottom of the recess.
6 Cut the valve seat at an included angle of 88° for 46° valve seats or 118° for 31° valve seats, see Operation
3-18, and lap the valve on to the valve seat. Ensure that the depth of the valve head below the face of the
cylinder head is within the production limits, refer to the relevant Data and dimensions for "Inlet and exhaust
valves" on page 29.
Note: Work as near as possible to the minimum figure to allow for future wear on the valve seat.
86 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 85

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
Piston and connecting rod assemblies 4
General description
The pistons used in Phaser and 1000 Series engines have either a "Quadram" (A) or a "Fastram" (B)
combustion chamber in the top of the piston. These combustion chambers are designed to give an efficient
mix of fuel and air.
The latest engines have pistons, with a "Fastram" combustion chamber and are available with different height
grades.
The pistons have two compression rings and an oil control ring. The groove for the top ring has a hard metal
insert to reduce wear of the groove. Axial location of the fully floating gudgeon pin is by circlips.
Controlled expansion pistons have a steel insert in the piston skirt.
Note: Controlled expansion piston are fitted on all naturally aspirated four cylinder engines (type AA).
Caution: The latest controlled expansion pistons must not be mixed in the engine with the early pistons.
Turbocharged engines which are rated higher than 2300 rev/min have an anodised area on the top face of the
piston.
Turbocharged engines have cooling jets fitted in the cylinder block to spray lubricating oil onto the inner surface
of the pistons.
FRONT
L
A
A0070
B
A0071
Continued
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 87
Page 86

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
The connecting rods are machined from "H" section forgings of molybdenum steel. The connecting rods of
turbocharged engines have wedge shaped small ends. Generally, the location of the bearing caps to the
connecting rods is made by serrations (C1) and the cap is retained by two nuts and bolts (C).
On some turbocharged engines, used in vehicle applications, the location of the bearing cap to the connecting
rod is made by dowels (D1) fitted in the bearing cap (D). The faces of these connecting rods and caps are flat
and the caps are retained by two setscrews.
Note: Always use the engine identification number to order new parts.
1
Phaser/1000 Series
1
C
A0073
D
A0072
88 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 87

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
Big end bearing
To remove Operation 4-1
1 Drain the engine lubricating oil .
2 Remove the lubricating oil sump, see Operation 10-3.
3 Remove the lubricating oil strainer and suction pipe, see Operation 10-4, or remove the balancer unit, see
Operation 5-21.
4 Rotate the crankshaft until the relevant connecting rod is at its lowest position.
5 Release the nuts and remove the bearing cap. Remove the bolts from the connecting rod. If the bearing cap
is retained by setscrews, the location of the bearing cap will be by two dowels. To remove these bearing caps,
release the setscrews by approximately four threads. Lightly hit the heads of the setscrews with a soft face
hammer to separate the connecting rod from the bearing cap. Remove the setscrews and the bearing cap.
6 Remove the lower half of the shell bearing from the cap, but keep it with its relevant cap.
7 Carefully push the connecting rod up the cylinder bore just enough to allow access to the upper half of the
shell bearing. Remove the bearing from the connecting rod. Keep the bearings from the connecting rod and
cap together.
Caution: Do not allow the connecting rods to hit the piston cooling jets, if fitted. If a cooling jet is hit, check its
alignment, see Operation 4-14, and renew it, if necessary.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 89
Page 88

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To fit Operation 4-2
1 Clean the bearing faces of the connecting rod and the crank pin.
2 If the cap has dowels for location on the connecting rod, ensure that the dowel protrusion is 3,0/4,5 mm
(0.12/0.18 in) above the cap faces. Clean the complete bearing and lubricate the bearing surface and the crank
pin with clean engine lubricating oil. Fit the upper half of the shell bearing to the connecting rod; ensure that
the location tag is fitted correctly in its recess (A1). Fit the connecting rod to the crank pin; ensure that the
assembly number on the connecting rod is on the same side as the other connecting rods.
3 Clean, lubricate and fit the lower half of the shell bearings into the cap; ensure that the location tag is fitted
correctly in its recess (A1). Fit the connecting rod bolts with the flat side of the head of the bolts towards the
connecting rod. Fit the cap to the connecting rod. Ensure that the assembly number on the cap is the same as
that on the connecting rod and that both of the assembly numbers are on the same side (B).
Note: When the fasteners are nuts, new nuts must be fitted.
4 Tighten the fasteners gradually and evenly to the recommended torque of 155 Nm (114 lbf ft) 15,8 kgf m for
setscrews, or 125 Nm (92 lbf ft) 12,7 kgf m for nuts.
5 Ensure that the crankshaft rotates freely.
6 Fit the lubricating oil strainer and suction pipe, see Operation 10 -4 , or fit the balancer unit, see Operati on
5-22.
7 Fit the lubricating oil sump, see Operation 10-3, and fill the sump to the correct level with lubricating oil of
an approved grade.
1
1
1
1
A
A0074
B
A0075
To inspect Operation 4-3
1 Check the bearings and the crank pin for wear or other damage, renew if necessary.
90 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 89

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
Piston and connecting rod
To remove Operation 4-4
1 Drain the lubricating oil and the cooli ng sys tem.
2 Remove the cylinder head assembly, see Operation 3-9.
3 Remove all carbon from the top of the bores of the cylinder liners.
4 Remove the lubricating oil sump, see Operation 10-3.
5 Remove the lubricating oil strainer and suction pipe, see Operation 10-4, or remove the balancer unit, see
Operation 5-21.
6 Remove the big end caps and the big end bearings from the connecting rods, see Operation 4-1.
Caution: Do not allow the connecting rods to hit the piston cooling jets, if fitted. If a cooling jet is hit, check its
alignment, see Operation 4-14, and renew it, if necessary.
7 Turn the connecting rods 90° to prevent contact with the piston cooling jets. Push the pistons and the
connecting rods out through the top of the cylinder liners. Keep the bearings and caps together to ensure that
they can be fitted in their original positions.
8 Inspect the crank pins for damage.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 91
Page 90

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To fit Operation 4-5
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number
Piston replacer tool 21825615
1 Ensure that the piston, the cylinder bore, the crank pin and the big end of the connecting rod are clean.
Lubricate the piston and the cylinder liner with clean engine lubricating oil.
2 Rotate the crankshaft until the relevant crank pin is at its lowest position. Lubricate the crank pin with clean
engine lubricating oil.
3 Fit the upper half of the shell bearings to the connecting rod. Ensure that the location tag is fitted correctly
in its recess. Lubricate the bearing with clean engine lubricating oil.
4 Put the piston replacer tool in position at the top of the relevant cylinder. The tool has a tapered bore to
compress the piston rings when the piston and connecting rod assembly is fitted. Ensure that the smaller end
of the tapered bore is towards the face of the cylinder block.
5 Put the piston ring gaps 120° apart. Pass the connecting rod through the piston replacer tool and allow the
piston to enter the tool. The arrow or "FRONT" mark on the top of the piston must be towards the front of the
engine. In this position the combustion bowl in the top of the piston will be towards the fuel injection pump side
of the engine.
6 Push the piston and connecting rod assembly through the piston replacer tool (A) and onto the crank pin. If
piston cooling jets are fitted, the piston and connecting rod assembly must be rotated to ensure that the
connecting rod will not hit the piston cooling jet as the assembly is fitted. When the connecting rod has passed
the piston cooling jet, rotate the connecting rod until the arrow or "FRONT" mark on top of the piston is towards
the front of the engine (B).
FRONT
A
92 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0076
B
A0077
Continued
Page 91

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
7 Clean the connecting rod cap and the lower half of the shell bearings. Fit the bearing to the cap; ensure that
the location tag is fitted correctly in its recess. Lubricate the bearing with clean engine lubricating oil. Fit the
cap and ensure that the assembly number is the same as that on the connecting rod and that the numbers are
on the same side.
8 Fit the fasteners; ensure that the flat side of the head of the bolts is towards the connecting rod. When the
fasteners are nuts, new nuts must be fitted. Tighten the fasteners gradually and evenly to the recommended
torque of 155 Nm (114 lbf ft) 15,8 kgf m for setscrews, or 125 Nm (92 lbf ft) 12,7 kgf m for nuts.
9 Check that the crankshaft will rotate freely.
10 Check the piston height above the top face of the cylinder block, see Operation 4-6.
11 Fit the lubricating oil strainer and suction pipe, see Operat ion 10-4, or fit the balancer unit, see Operati on
5-22.
12 Fit the lubricating oil sump, see Operation 10-3.
13 Fit the cylinder head assembly, see Operation 3-10.
14 Fill the sump to the correct level with lubricating oil of an approved grade.
15 Fill the cooling system.
4
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 93
Page 92

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To check the pis ton height above the cylinder block Operation 4-6
Special requirements
Special tools
Description Part number Description Part number
Piston height tool 21825496 Dial gauge for use with 21825496 21825617
1 Put the piston height tool on the face of the cylinder block and rotate the gauge dial to the zero position.
2 Rotate the crankshaft until the piston is approximately at top dead centre (TDC). Carefully put the tool over
the top of the piston with the plunger of the gauge in contact with the piston above the axis of the gudgeon pin
(A).
3 Rotate the crankshaft to ensure that the piston is at the highest position and make a note of the gauge
indication.
For engines fitted with "Quadram" pistons, the piston height above the face of the cylinder block should be
0,14/0,36 mm (0.005/0.014 in).
For engines fitted with "Fastram" pistons, grades A to L, the piston height above the top face of the cylinder
block should be 0,38/0,50 mm (0.015/0.020 in)
Notes:
l Two "Quadram" piston heights can be used in the factory: "H" - high, "L" - low. In service only "L" pistons
are supplied. If an "L" piston is used instead of an "H" piston, the height may be up to 0,19 mm (0.0075 in)
below the bottom limit.
l The top of the piston should not be machined.
l If the original piston is used, ensure that it is assembled to the correct connecting rod and is used in the
original cylinder.
A
94 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
A0077
Page 93

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
To check piston height grade of a “Fastram” piston Operation 4-7
For engines fitted with earlier "Fastram "pistons there are five height grades (A to E) of piston in production
and in service.
The latest "Fastram" pistons are supplied in six height grades (F to L) in production and in service. Identification
of the height grade is by the letter for each piston which is stamped on the top of the piston (A). The letter A or
F is the highest grade and letter E or L is the lowest grade. The difference between the grades is 0,045 mm
(0.0018 in).
A
B
C
D
A
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
1
A
A0079
B
A0080
If a new piston is fitted, ensure that it is of the correct height grade. The height grade can be checked by
measurement, from the centre of the gudgeon pin to the top of the piston (B1). The dimensions for each grade
are listed in the table below:
Piston grade letter
(1) Earlier engines
(1)
A
(1)
B
(1)
C
(1)
D
(1)
E
F 70,391
G 70,345
H 70,299
J 70,253
K 70,207
L 70,161
Piston height dimension
(mm)
70,334 G
70,289 H
70,244 J
70,199 K
70,154 L
Latest equivalent grade
Notes:
l The earlier piston grades A to E are now not supplied as a part. The latest equivalent grades G to L shown
in the table above are to be used instead.
l The top of the piston must not be machined.
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 95
Page 94

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Piston rings
The piston used in the Phaser and 1000 Series engines have two compression rings and an oil control ring.
All the piston rings are above the gudgeon pin. Piston rings have different design features. To ensure that the
correct type is obtained always use the engine identification number to order new parts.
Caution: Only expand the ring gaps enough to ensure that the ends of the rings do not damage the piston
when the ring is removed or put into position.
Phaser/1000 Series
96 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 95

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
To remove and to fit Operation 4-8
To remove
Remove the piston rings with a suitable ring expander. Keep the rings with their relevant piston.
To fit
Use a suitable piston ring expander to fit the piston rings.
1 Fit the spring of the oil control ring in the bottom groove with the latch pin inside both ends of the spring (A).
Fit the oil control ring over the spring (B2, C2 or D3). Ensure that the ring gap is at 180° to the latch pin.
2 Fit the cast iron ring with the taper face (B1 or C1) to the second groove with the word "TOP", or the
manufacturer's symbol, towards the top of the piston.
1
2
A
A0081 A0082
B
New second rings have a green identification mark which must be on the left of the ring gap when the ring is
fitted and the piston is upright.
The second ring on some engines has an outside step (D2) at the bottom of the tapered face.
3 Fit the chromium plated top ring, the manufacturer's symbol or the word 'TOP' must be towards the top of
the piston.
New top rings have a red or blue identification mark which must be on the left of the ring gap when the ring is
fitted and the piston is upright.
The top ring on some engines has an internal step (D1) on the top face.
4 Ensure that the ring gaps are 120° apart.
1
1
2
C
A0083
D
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 97
2
3
A0084
Page 96

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Piston and connecting rod assembly
To dismantle and to assemble Operation 4-9
To dismantle
1 Remove the piston rings, see Operation 4-8.
2 Remove the circlips which retain the gudgeon pin.
3 Put a mark on the piston to indicate the cylinder number as shown on the connecting rod. Put the mark on
the piston on the same side as the mark on the big end to ensure that they are assembled correctly (A).
Caution: Do not scratch or stamp the top of the piston, use a permanent ink marker to make a mark on the
piston.
4 Push the gudgeon pin out by hand. If the gudgeon pin is tight, heat the piston to 40/50 °C (100/120 °F) for
easy removal of the gudgeon pin.
To assemble
1 Clean the bore of the small end bush and lubricate it with clean engine lubricating oil.
2 Fit a new circlip in the circlip groove of one of the gudgeon pin bosses. Ensure that it fits correctly in the
groove.
3 With the piston upside down, put the connecting rod in position with the recess for the location of the big end
bearing (B1) on the same side as the lug on the gudgeon pin boss (B2). If the original piston is used, ensure
that it is assembled to the correct connecting rod and is used in the original cylinder. Engines with "Fastram"
pistons have six piston height grades, if a new piston is fitted, ensure that it is of the correct height grade, see
Operation 4-7.
4 Lubricate the gudgeon pin bosses with clean engine lubricating oil and push in the gudgeon pin towards the
circlip. If the gudgeon pin is a tight fit in the piston, heat the piston to 40/50 °C (100/120 °F) before the gudgeon
pin is fitted.
5 Fit a new circlip in the groove in the other gudgeon pin boss. Ensure that it fits correctly in the groove.
6 Fit the piston rings, see Operation 4-8.
4
A
98 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
4
A0085
1
2
B
A0086
Page 97

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
Piston and piston rings
To inspect Operation 4-10
1 Check the piston for wear and other damage.
2 Check that the piston rings are free to move in their grooves and that the rings are not broken.
3 Remove the piston rings, see Operation 4-8, and clean the piston ring grooves and the piston rings.
4 Fit new piston rings in the grooves and check for wear of the grooves with feeler gauges (A). Compare the
piston ring clearance in the groove to that given for new components in the relevant Data and dimensions for
"Pistons and piston cooling jets" on page 33, and renew the piston if necessary.
Note: Some pistons have a tapered top groove and the piston ring is wedge shaped, see Operation 4-8 (C/D).
When this occurs the top piston ring clearance cannot be checked by this method.
5 Clean all carbon from the top of the cylinder liners. Fit the piston rings in the top part of the cylinder liner and
measure the ring gap with feeler gauges (B). The coil spring must be fitted to the oil control ring when the gap
of this piston ring is measured.
The piston ring gaps for new components are given in the relevant Data and dimensions for "Pistons and piston
cooling jets" on page 33.
A
A0087
B
A0088
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 99
Page 98

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
Connecting rod
To inspect Operation 4-11
1 Check the connecting rod for distortion (A).
Note: The large and small end bores must be square and parallel with each other within the limits of
+/- 0,25 mm (0.010 in) measured 127 mm (5.0 in) each side of the connecting rod axis on a test mandrel. With
the small end bush fitted, the limits are reduced to +/- 0,06 mm (0.0025 in).
2 Check the small end bush for wear or for other damage and renew it, if necessary.
3 Check the fit of the gudgeon pin in the small end bush and check the gudgeon pin for wear. Refer to the
relevant Data and dimensions for "Gudgeon pins and small end bushes" on page 35.
A
L ±0,25mm
(0.010in)
127mm
(5in)
127mm
(5in)
L ±0,25mm
(0.010in)
P0009
Small end bush
To remove and to fit Operation 4-12
1 Press out the old bush with a suitable adaptor.
2 Clean the connecting rod bore and remove any sharp edges.
3 Press in the new bush. Ensure that the lubrication hole in the bush is on the same side as, and is aligned
with, the hole in the top of the connecting rod.
4 Ream the bush to get the correct clearance between the gudgeon pin and the bush. Refer to the relevant
Data and dimensions for "Gudgeon pins and small end bushes" on page 35.
Note: On turbocharged engines the small end is wedge shaped. After the small end bush has been fitted,
machine the bush to the shape of the small end and remove any sharp edges.
100 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
Page 99

Phaser/1000 S eries
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
4
Piston cooling jets
To remove and to fit Operation 4-13
To remove
1 Release the valve assembly and remove the piston cooling jet assembly (A).
Note: The crankshaft is removed in A to show clearly the piston cooling jet.
To fit
1 Check that the ball moves freely against spring pressure in the valve assembly and that the jet tube is not
damaged. Renew the valve assembly and/or the body as necessary.
2 Fit the piston cooling jet; ensure that the assembly is fitted correctly on the dowel in the cylinder block.
Tighten the valve assembly to 20 Nm (15 lbf ft) 2,0 kgf m.
Note: Latest engines have the dowel fitted in the cooling jet instead of the cylinder block.
1
A
A0089
Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2 101
Page 100

4
This document has been printed from SPI². Not for Resale
Phaser/1000 Series
To check the jet alignment Operation 4-14
1 Insert a 1,70 mm (0.067 in) diameter rod, of suitable length, into the jet. If a suitable rod is not available,
reduce the end of a thicker rod to 1,70 mm (0.067 in) diameter for a length of 16,00 mm (0.630 in).
2 When the rod is inserted into the jet it must extend out of the top of the cylinder within the area shown in (A).
33mm
(1.3in)
21mm
14mm
(0.5in)
(0.8in)
A
A0090
102 Workshop Manual, TPD 1312, issue 2
 Loading...
Loading...