Page 1

Form 2844
Edition 11
© August 1993
Updated March 1997
MIC 2000
Installation, Wiring, Operation Manual
Brand
Page 2
PAGE 2
nformation in this installation, wiring, and operation
manual is subject to change without notice. One
I
manual is provided with each instrument at the time of
shipment. Extra copies are available at the price
published on the front cover.
Copyright © August 1993, all rights reserved. No part of
this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed or stored in aretrieval system, or translated into
any language in any form by any means without the written permission of the factory.
This is the Eleventh Edition of the 1/4 DIN Controller
manual. It was written and produced entirely on a desktop-publishing system. Disk versions are available by
written request to the factory - Advertising and Publications Department.
NOTE
We are glad you decided to open this manual. It is
written so that you can take full advantage of the features
of your new process controller.
It is strongly recommended that factory equipped applications incorporate a high or
low limit protective device which will shut down the equipment at a preset process
condition in order to preclude possible damage to property or products.
Page 3

Table of Contents
SECTION 1 - GENERAL Page Number
1.1 Product Description 5
SECTION 2 INSTALLATION & WIRING
2.1 Installation and Wiring 7
2.2 Preparation for Wiring 8
2.3 Input Connections 13
2.4 Output Connections 19
SECTION 3 CONFIGURATION & OPERATION
3.1 Configuration and Operation 22
3.2 Operation Summary 22
3.3 Configuration Summary 24
3.4 Tune Mode Operation 34
SECTION 4 - CONTROL CAPABILITY
4.1 Control Capability 37
4.2 Control Responses 37
4.3 Direct/Reverse Operation of Control Outputs 37
4.4 On-Off Control/Latched On-Off 38
4.5 Time Proportioning Control 38
4.6 Current Proportioning Control 38
4.7 Position Proportioning Control 38
4.8 Dual Output Control 40
4.9 Manual Operation of Proportional Outputs 41
4.10 Automatic Transfer Function 41
4.11 Setpoint Adjustments 42
PAGE 3
SECTION 5 - SERVICE
5.1 Service 44
5.2 Calibration 44
5.3 Test Mode 48
5.4 Troubleshooting and diagnostics 52
APPENDICES
A - Board Layout - Jumper Positioning
Figure A-1 Power Supply Board 59
Figure A-2 Processor Board 60
Figure A-3 Option Board 61, 62
B - Glossary of terms 63
C - Model Number Hardware Matrix Details 66
D - Specifications 67
E - Software Record/Reference Sheet 70
Warranty Inside back cover
Page 4

PAGE 4
FIGURES & TABLES
Figure 1-1 Controller Display Illustration 5
Figure 2-1 Panel Opening Sizes and Installation 7
Figure 2-2 Noise Suppression 9
Figure 2-3 Noise Suppression 10
Figure 2-4 Wiring Label 13
Figure 2-5 AC Power 13
Figure 2-6 Thermocouple Input 14
Figure 2-7 RTD Input 14
Figure 2-8 Volt, mV, mADC Input 15
Figure 2-9A 24VDC Transmitter Power Supply 16
Figure 2-9B 24VDC Power Supply 16
Figure 2-10 Remote Setpoint Input 17
Figure 2-11 Remote Digital Communications 18
Figure 2-12 Relay Output 19
Figure 2-13 SSR Driver Output 20
Figure 2-14 mADC Output 21
Figure 2-15 Position Proportioning Output 21
Figure 4-1 Proportional Bandwidth effect on Output 39
Figure 4-2 Dual Proportional Outputs 40
Figure 4-3 Setpoint Ramp Rate Example 42
Figure 4-4 Re-transmission Example 43
Figure 4-5 Setpoint Re-transmission Example 43
Table 3-1 Enable Mode Configuration Procedures 24
Table 3-2 Program Mode Configuration Procedures 28
Table 3-3 Tune Mode Configuration Procedures 33
Table 5-1 Calibration Procedures 45
Table 5-2 Test Procedures and Description 49
FLOW CHARTS
Flow - Calibration 44
Flow - Enable Mode 25
Flow - Program Mode 26
Flow - Setpoint 42
Flow - Standby Mode 41
Flow - Test Mode 48
Flow - Tune Mode 32
Page 5
Product Description 1.1
1.1.1 GENERAL
This instrument is a microprocessor based single loop controller capable of measuring,
displaying and controlling temperature, pressure, flow, and level from a variety of inputs.
Control functions, alarm settings and other parameters are easily entered through the front
keypad. All user's data can be protected from unauthorized changes with it’s ENABLE MODE
security system. Battery back-up protects against data loss during AC power outages.
The input is user configurable to directly connect to either thermocouple, RTD, mVDC, VDC
or mADC inputs. Thermocouple and RTD linearization, as well as thermocouple cold junction
compensation is performed automatically. The sensor input is isolated . The instrument can
operate on either 115VAC or 230VAC power at 50/60Hz. It is housed in an extruded aluminum enclosure suitable for panel mounting. It may be surface mounted using an optional
adaptor.
FIGURE 1-1
PAGE 5
MAN
S.P.
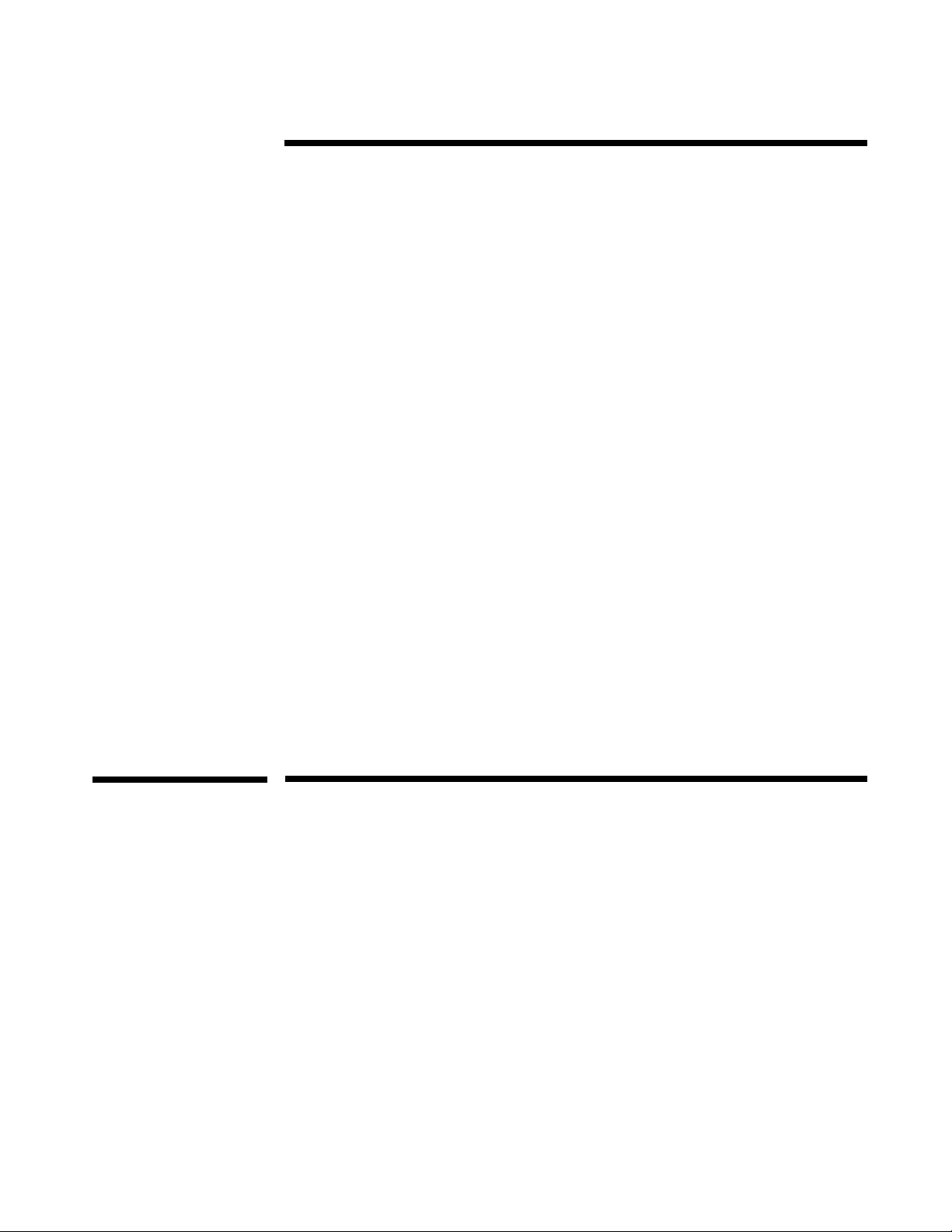
1.1.2 DISPLAYS
Each instrument is provided with a digital display and status indicators as shown in Figure
1-1. The digital display is programmable to show the process variable only, process variable
and setpoint, deviation from setpoint only, deviation and setpoint, or setpoint continuously.
Status indication is as shown (Figure 1-1). Display resolution is programmable for 0 to 3
decimal places depending upon the input type selected.
OUT1 OUT2
ALRM
°C
°F
U
Page 6

PAGE 6
1.1.3 CONTROL
The instrument can be programmed for on-off, time proportioning, current proportioning, or
position proportioning control implementations depending on the model number. A second
control output is an available option. Proportional control implementations are provided with
fully programmable separate PID parameters.
1.1.4 ALARM
Alarm indication is standard on all instruments. Alarm type may be set as PROCESS DIRECT
or REVERSE (High or Low), DEVIATION DIRECT or REVERSE (Above or Below setpoint), or
DEVIATION BAND TYPE (Closed or Open within the band). Alarm status is indicated by
LED. An alarm output can be provided by assigning any output(s) SPST relay(s) or SSR
Driver(s) to the alarm.
1.1.5 EXTENDED FEATURES SOFTWARE
EA Software Features
Fast Scan Provides an optional faster scan rate of 3 scans per second.
Normal scan is one scan per second.
Process Rounding Provides rounding of the process value displayed to reduce display
fluctuation. For example, the displayed value can be rounded to
the nearest 5 (display -5, 0, 5, 10, etc.). This is for display only and
does not affect the control action.
Extended Current The current outputs available can be extended to include 0-20mA
Output Ranges and 0-5VDC (with the appropriate shunt resistor), rather than the
standard 4-20mA and 1-5VDC outputs.
Process/Setpoint The process or setpoint value can be scaled over any desired
Value Retransmit range and retransmitted using one of the current outputs. (This
Capability precludes the use of the output for control).
Percent Output Provides a relay actuation based upon a proportional output being
Relay Actuation above or below a specified value.
Contact Closure Sensing This feature provides the following action: When a contact closure
for SP=PV is sensed, the setpoint will be set equal to the current process
value. This is only done on the transition from open to closed, and
not continuously while the switch is closed.
EB Software Features
Setpoint Ramp Provides a limitation on how fast the process value will ramp to setpoint by
Rate limiting the rate of change of an internal setpoint used for control versus
the setpoint the operator specifies.
Page 7
Installation and Wiring 2.1
w
Prior to proceeding with installation, verify the AC power input required by the instrument. AC
power input is either 115 VAC or 230 VAC and is specified in the model number and on the
wiring label affixed to the instrument housing. See Figure 2-4 (page 13) for a wiring label
description.
230 VAC models may be converted to 115 VAC operation by the user, by changing the
position of jumpers soldered on the Power Supply Board, see Appendix A-1 (page 59) for
details.
Electrical code requirements and safety standards should be observed and installation
performed by qualified personnel.
The electronic components of the instrument may be removed from the housing during
installation. To remove the components, loosen the locking screw located in the lower center
of the instrument’s front panel. Pull the entire instrument straight out of the
housing. During re-installation, the vertically mounted circuit boards should be properly
aligned in the housing. Be sure that the instrument is installed in the original housing. This
can be verified by matching the serial number on the unit to the serial number on the housing.
(Serial numbers are located on the inside of the housing enclosure and on the label on the
underside of the front panel)
specifications. The ambient compensator on the rear of the housing enclosure is calibrated to
the electronics of the instrument at the factory.
.
This will insure that each instrument is accurate to its published
PAGE 7
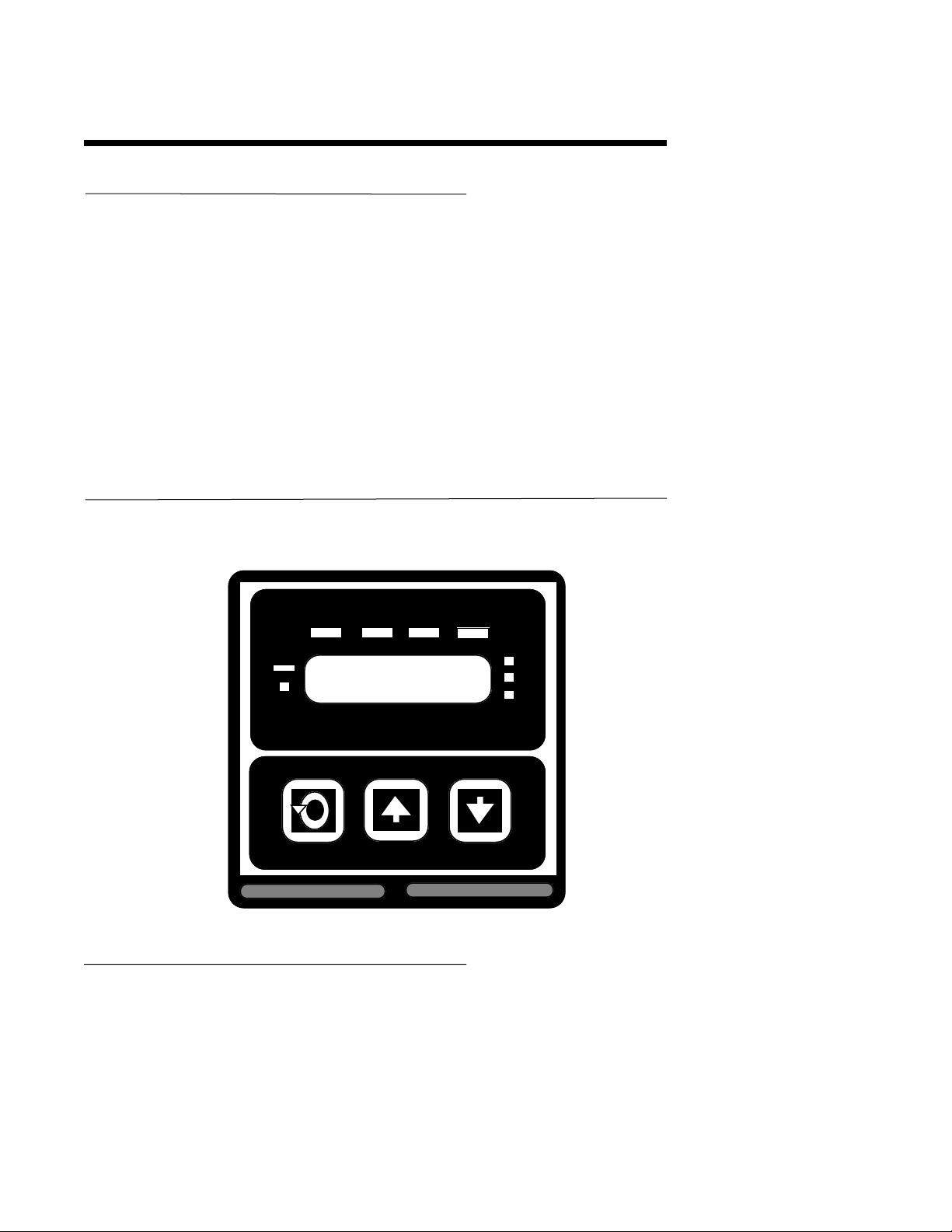
Recommended panel opening sizes are illustrated below (Figure 2-1). After the opening is
properly cut, insert the instrument housing into the panel opening. Insert the two panhead
screws provided, through the holes in the mounting bracket into the holes in the rear of the
instrument as shown in Figure 2-1. Firmly tighten the screws. Instruments are shipped
standard for panel mounting. To surface mount, an adaptor is required and should be
specified when ordering. For installation in wash-down areas, a watertight cover is available.
FIGURE 2-1 PANEL OPENING SIZES AND INSTALLATION
4.8 (.188) MAX PANEL THICKNESS
165.9 (6.53)
146.8 (5.78)
96.0
(3.78)
90.4
(3.560)
Side View
96.0 (3.78)
92 + or - 0.8
(3.622 + or - .031)
Panel
Mounting Bracket
PANEL
CUTOUT
SIZE
92+ or-.8
(3.622
+ or-.031)
90.4
(3.560)
Top View
All dimensions shown
in mm and inches. Inches
shown in ( ).
Mounting scre
Page 8

PAGE 8
Preparation for Wiring 2.2
2.2.1 WIRING GUIDELINES
Electrical noise is a phenomenon typical of industrial environments. The following are
guidelines that must be followed to minimize the effect of noise upon any instrumentation.
2.2.1.1 INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS
Listed below are some of the common sources of electrical noise in the industrial environment:
• Ignition Transformers
• Arc Welders
• Mechanical contact relay(s)
* Solenoids
Before using any instrument near the devices listed, the instructions below should be followed:
1. If the instrument is to be mounted in the same panel as any of the listed devices, separate
them by the largest distance possible. For maximum electrical noise reduction, the noise
generating devices should be mounted in a separate enclosure.
2. If possible, eliminate mechanical contact relay(s) and replace with solid state relays. If a
mechanical relay being powered by an instrument output device cannot be replaced, a
solid state relay can be used to isolate the instrument.
3. A separate isolation transformer to feed only instrumentation should be considered. The
transformer can isolate the instrument from noise found on the AC power input.
4. If the instrument is being installed on existing equipment, the wiring in the area should be
checked to insure that good wiring practices have been followed.
2.2.1.2 AC POWER WIRING
Earth Ground
The instrument includes noise suppression components that require an earth ground connection to function. To verify that a good earth ground is being attached, make a resistance
check from the instrument chassis to the nearest metal water pipe or proven earth ground.
This reading should not exceed 100 ohms. Use a 12 gauge (or heavier) insulated stranded
wire.
Neutral (For 115VAC)
It is good practice to assure that the AC neutral is at or near ground potential. To verify this, a
voltmeter check between neutral and ground should be done. On the AC range, the reading
should not be more than 50 millivolts. If it is greater than this amount, the secondary of this
AC transformer supplying the instrument should be checked by an electrician. A proper
neutral will help ensure maximum performance from the instrument.
2.2.1.3 WIRE ISOLATION
Four voltage levels of input and output wiring may be used with the unit:
• Analog input or output (i.e. thermocouple, RTD, VDC, mVDC or mADC)
• SPST Relays
• SSR driver outputs
• AC power
The only wires that should be run together are those of the same category. If they need to be
run parallel with any of the other lines, maintain a minimum 6 inch space between the wires.
If wires must cross each other, do so at 90 degrees. This will minimize the contact with each
other and reduces "cross talk" "Cross talk" is due to the EMF (electro Magnetic Flux) emitted
by a wire as current passes through it. This EMF can be picked up by other wires running in
the same bundle or conduit.
Page 9
In applications where a High Voltage Transformer is used, (i.e. ignition systems) the secondary of the transformer should be isolated from all other cables.
This instrument has been designed to operate in noisy environments, however, in some cases
even with proper wiring it may be necessary to suppress the noise at its source.
2.2.1.4 USE OF SHIELDED CABLE
Shielded cable helps eliminate electrical noise being induced on the wires. All analog signals
should be run with shielded cable. Connection lead length should be kept as short as
possible, keeping the wires protected by the shielding. The shield should be grounded at one
end only. The preferred grounding location is the sensor, transmitter or transducer.
2.2.1.5 NOISE SUPPRESSION AT THE SOURCE
Usually when good wiring practices are followed no further noise protection is necessary.
Sometimes in severe electrical environments, the amount of noise is so great that it has to be
suppressed at the source. Many manufacturers of relays, contactors, etc. supply "surge
suppressors" which mount on the noise source.
For those devices that do not have surge suppressors supplied, RC (resistance-capacitance)
networks and/or MOV (metal oxide varistors) may be added.
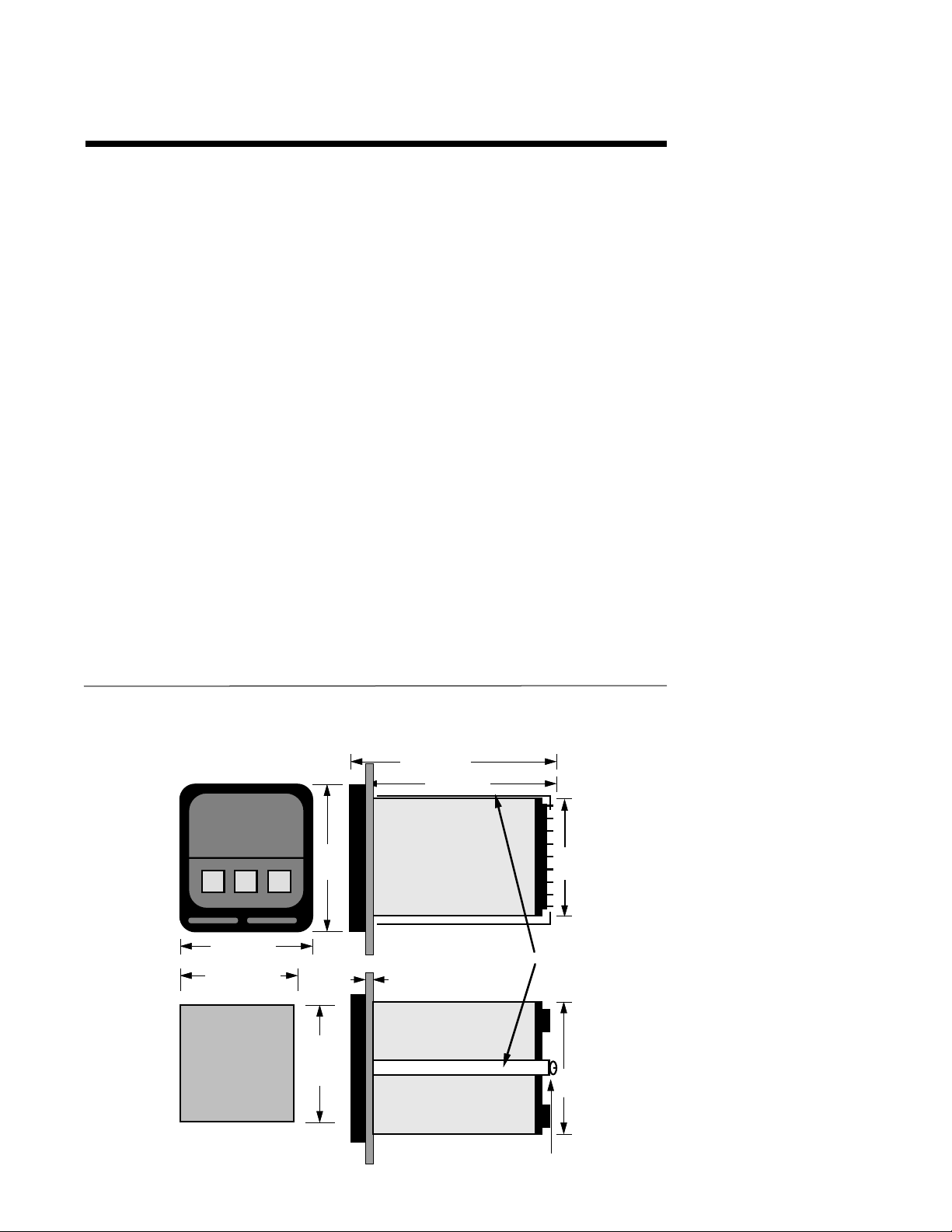
Inductive Coils - MOV's are recommended for transient suppression in inductive coils connected in parallel and as close a possible to the coil. See Figure 2-2. Additional protection
may be provided by adding an RC network across the MOV.
PAGE 9
FIGURE 2-2
A.C.
MOV
Inductive
Load
0.5
mfd
1000V
220
ohms
115V 1/4W
230V 1W
(Continued on next page)
Page 10
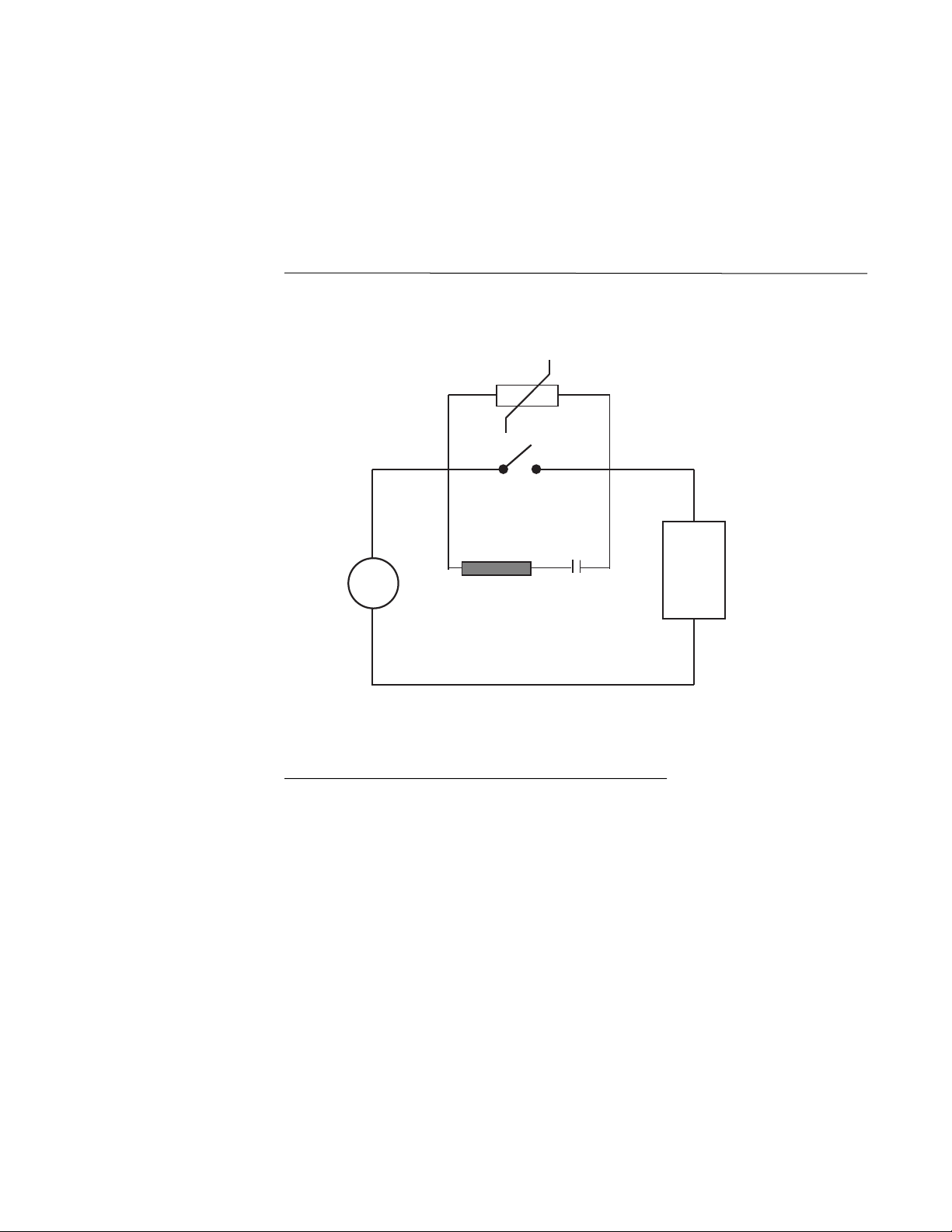
PAGE 10
Contacts - Arcing may occur across contacts when the contact opens and closes. This
results in electrical noise as well as damage to the contacts. Connecting a RC network
properly sized can eliminate this arc.
For circuits up to 3 amps, a combination of a 47 ohm resistor and 0.1 microfarad capacitor
(1000 volts) is recommended. For circuits from 3 to 5 amps, connect 2 of these in parallel.
See Figure 2-3.
FIGURE 2-3
MOV
Inductive
A.C.
2.2.2 SENSOR PLACEMENT (Thermocouple or RTD)
Two wire RTD's should be used only with lead lengths less than 10 feet.
If the temperature probe is to be subjected to corrosive or abrasive conditions, it should be
protected by the appropriate thermowell. The probe should be positioned to reflect true
process temperature:
In liquid media - the most agitated area.
In air - the best circulated area
R
C
Load
Page 11

THERMOCOUPLE LEAD RESISTANCE
Thermocouple lead length can affect instrument since the size (gauge) and the length of the
wire affect lead resistance.
To determine the temperature error resulting from the lead length resistance, use the following
equation:
Terr = TLe * L where; TLe = value from appropriate table below
L = length of leadwire in thousands of feet.
TABLE 1
Temperature error in °C per 1000 feet of Leadwire
AWG Thermocouple Type:
No. J K T R S E B N C
10 .34 .85 .38 1.02 1.06 .58 7.00 1.47 1.26
12 .54 1.34 .61 1.65 1.65 .91 11.00 2.34 2.03
14 .87 2.15 .97 2.67 2.65 1.46 17.50 3.72 3.19
16 1.37 3.38 1.54 4.15 4.18 2.30 27.75 5.91 5.05
18 2.22 5.50 2.50 6.76 6.82 3.73 44.25 9.40 8.13
20 3.57 8.62 3.92 10.80 10.88 5.89 70.50 14.94 12.91
24 8.78 21.91 9.91 27.16 27.29 14.83 178.25 37.80 32.64
PAGE 11
TABLE 2
Temperature Error in °F per 1000 feet of Leadwire
AWG Thermocouple Type:
No.JKTRSEBNC
10 .61 1.54 .69 1.84 1.91 1.04 12.60 2.65 2.27
12 .97 2.41 1.09 2.97 2.96 1.64 19.80 4.21 3.66
14 1.57 3.86 1.75 4.81 4.76 2.63 31.50 6.69 5.74
16 2.47 6.09 2.77 7.47 7.52 4.14 49.95 10.64 9.10
18 4.00 9.90 4.50 12.17 12.28 6.72 79.95 10.64 9.10
20 6.43 15.51 7.06 19.43 19.59 10.61 126.90 26.89 23.24
24 15.80 39.44 17.83 48.89 49.13 26.70 320.85 68.03 58.75
Example:
A 1/4 Din unit is to be located in a control room 660 feet away from the process. Using 16
AWG, type J thermocouple, how much error is induced?
Terr = TLe * L
TLe = 2.47 (°F/1000 ft) from Table 2
Terr = 2.47 (°F/1000 ft) * 660 ft
Terr = 1.6 °F
Page 12
PAGE 12
RTD LEAD RESISTANCE
RTD lead length can affect instrument accuracy, since the size (gauge) and length of the wire
affect lead resistance.
To determine the temperature error resulting from the lead length resistance, use the following
equation:
Terr = TLe * L where; TLe = value from Table 3 if 3 wire RTD or Table 4 is 2 wire RTD
L = length of lead wire in thousands of feet
TABLE 3 3 Wire RTD
AWG No. Error °C Error °F
10 ± 0.04 ± 0.07
12 ± 0.07 ± 0.11
14 ± 0.10 ± 0.18
16 ± 0.16 ± 0.29
18 ± 0.26 ± 0.46
20 ± 0.41 ± 0.73
24 ± 0.65 ± 1.17
TABLE 4 2 Wire RTD
AWG No. Error °C Error °F
10 ± 5.32 ± 9.31
12 ± 9.31 ± 14.6
14 ± 13.3 ± 23.9
16 ± 21.3 ± 38.6
18 ± 34.6 ± 61.2
20 ± 54.5 ± 97.1
24 ± 86.5 ± 155.6
Example:
An application uses 2000 feet of 18 AWG copper lead wire for a 3 wire RTD sensor. What is
the worst case error due to this leadwire length?
Terr = TLe * L
TLe = ± .46 (°F/1000 ft) from Table 3
Terr = ± .46 (°F/1000 ft) * 2000 ft
Terr = ± 0.92°F
Page 13
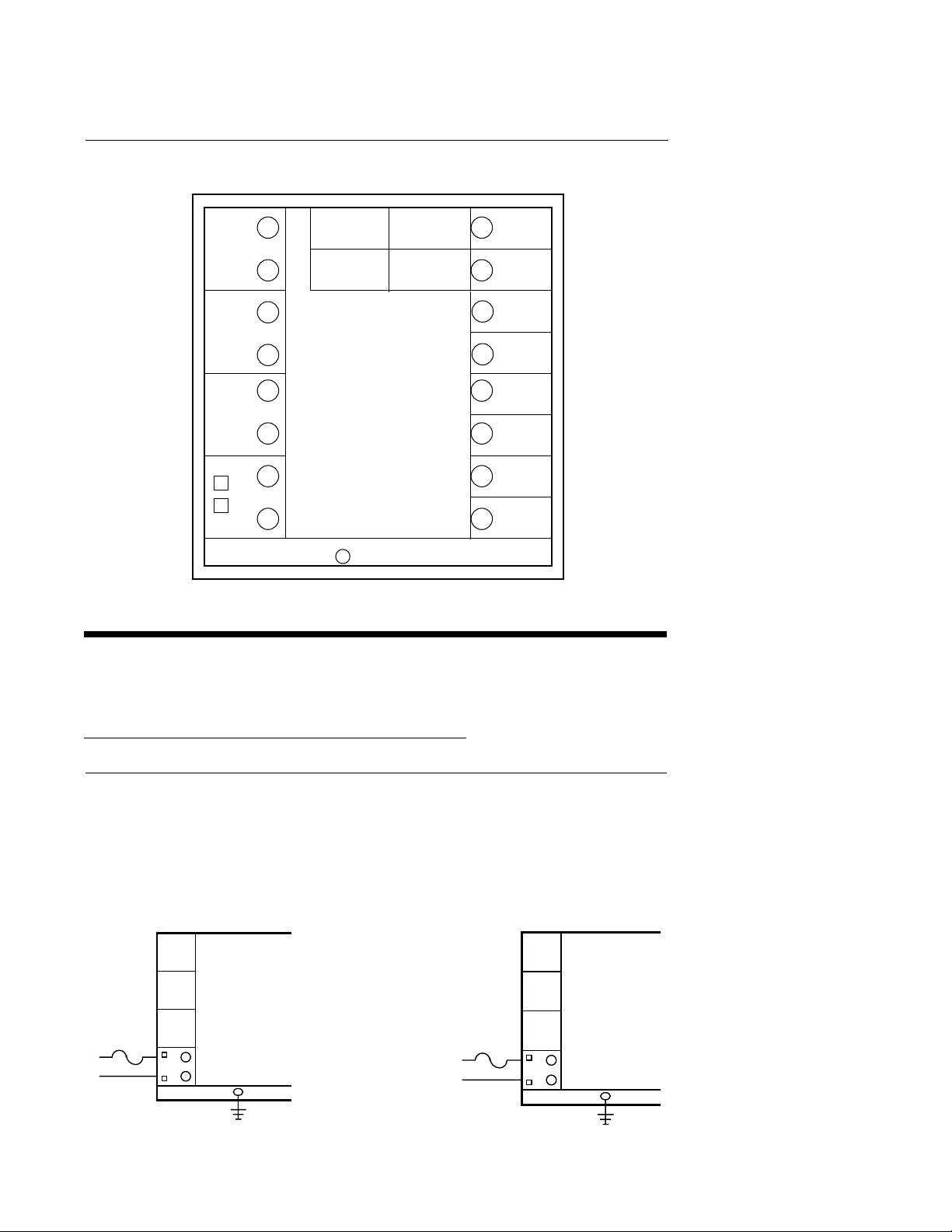
FIGURE 2-4 WIRING LABEL
PAGE 13
RELAY C
RELAY B
RELAY A
115
230
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
VAC
A
SERIAL A
SERIAL B
INPUT RATINGS:
115/230 VAC 50/60 HZ 15VA MAX
RELAY OUTPUT RATINGS:
115VAC 5.0A RESISTIVE
230VAC 2.5A RESISTIVE
230VAC 1/8 HP
115/230VAC 250VA
MAXIMUM AMBIENT : 55°C
POS.PROP.
WIPER
POS.PROP.
HIGH
REMOTE
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
MADE IN U.S.A.GROUND
SETPT
OUT2
4-20mA
OUT1
4-20mA
RETURN
SIGNAL +
CJC
SIGNAL -
+
+
+
Input Connections 2.3
In general, all wiring connections are made to the instrument after it is installed.
electrical shock. AC power wiring must not be connected to the source distribution
panel until all wiring connection procedures are completed.
Avoid
2.3.1 INPUT CONNECTIONS
FIGURE 2-5
AC Power
Connect 115 VAC hot and neutral to terminals B and A respectively as illustrated below.
Connect 230 VAC as described below. Connect Earth ground to the ground screw as shown.
115 VAC INSTRUMENT VOLTAGE
Rear View
.5 AMP*
FUSE
L1
L2
B
A
GROUND
*Supplied by customer
230 VAC INSTRUMENT VOLTAGE
Rear View
.25 AMP*
FUSE
L1
L2
B
A
GROUND
*Supplied by the customer
Page 14
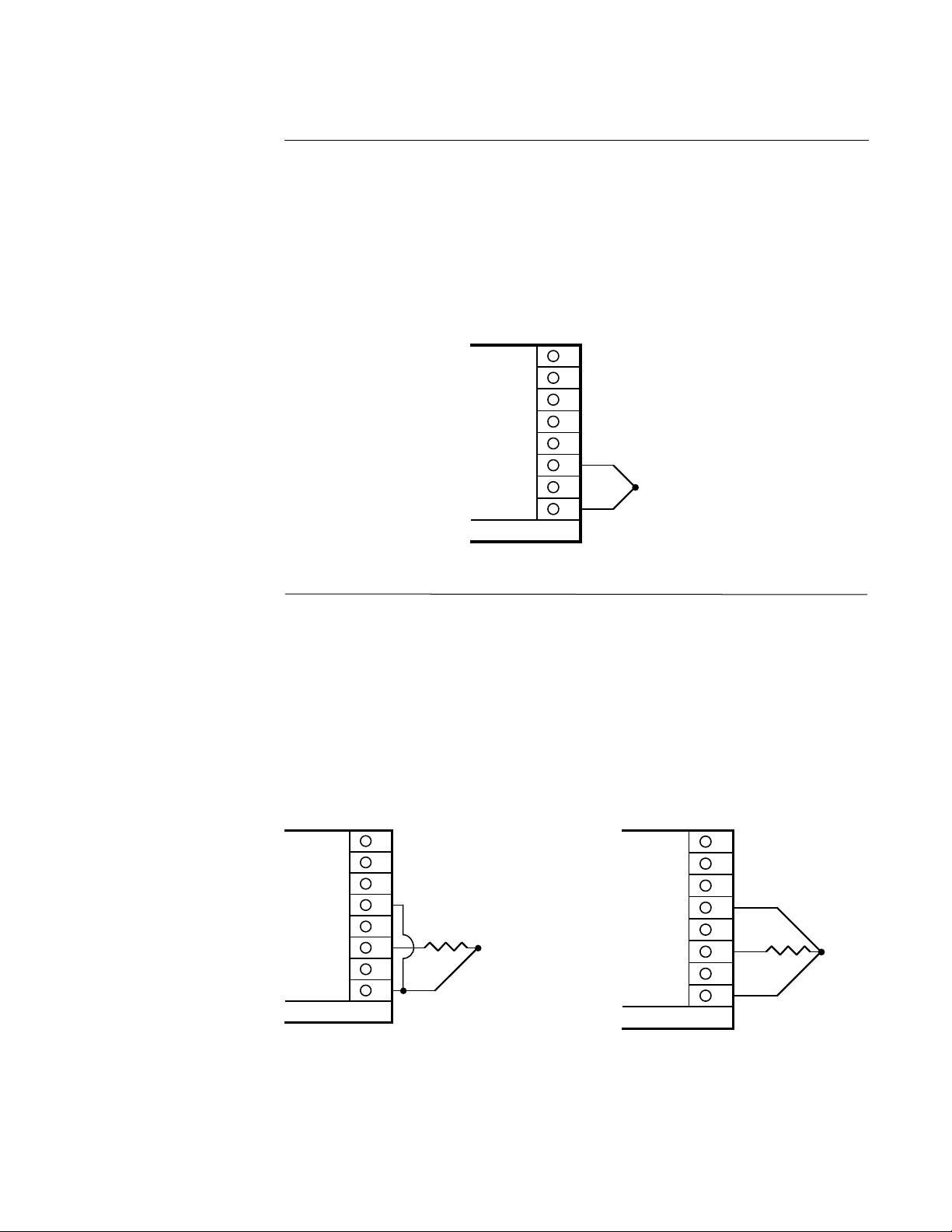
PAGE 14
FIGURE 2-6
Thermocouple (T/C) Input
Make thermocouple connections as illustrated below. Connect the positive leg of the thermocouple to terminal 3, and the negative to terminal 1. For industrial environments with comparatively high electrical noise levels, shielded thermocouples and extension wire are recommended. Be sure that the input conditioning jumpers are properly positioned for a thermocouple input. See Appendix A-2 (page 60) and A-3 (page 61, 62).
THERMOCOUPLE INPUT
Rear view
8
7
6
5
4
+
3
2
1
-
300 OHMS
MAXIMUM
LEAD
FIGURE 2-7
RTD Input
Make RTD connections as illustrated below. For a three wire RTD, connect the resistive leg
of the RTD to terminal 3, and the common legs to terminal 1 and 5. For a two wire RTD,
connect one wire to terminal 1 and the other wire to terminal 3 as shown below. A jumper
wire supplied by the customer must be installed between terminals 1 and 5. Be sure that the
input conditioning jumpers are properly positioned for an RTD input. See Appendix A-2 (page
60) and A-3 (page 61, 62).
2 WIRE RTD INPUT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
JUMPER*
4
3
2
1
100 OHM*
PLATINUM
3 WIRE RTD INPUT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
100 OHM*
PLATINUM
*Supplied by customer
*Supplied by the customer
Page 15
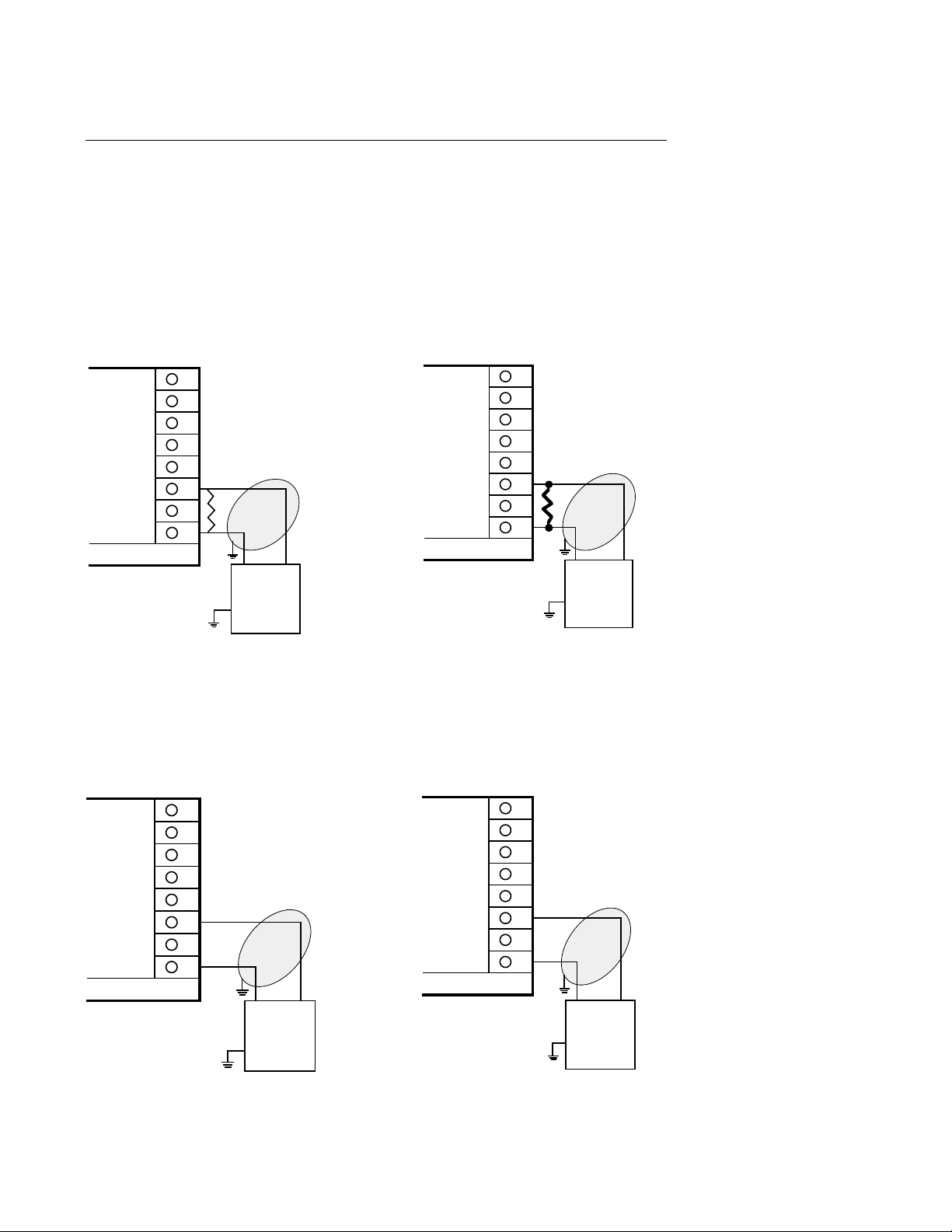
FIGURE 2-8
Volt, mV, mADC Input
Make volt, millivolt and milliamp connections as shown below. Terminal 3 is positive and
terminal 1 is negative. Milliamp input requires a 250 ohm shunt resistor (supplied with the
instrument) installed across the input terminals and by configuring the instrument for either 0
to 5 or 1 to 5 VDC input. If desired, milliamp DC input can be facilitated by installing an
optional 2.5 ohm resistor across the input terminals and configuring the instrument for either 0
to 50 or 10 to 50 mVDC. Be sure that the input conditioning jumpers are properly positioned
for the input type selected. See Appendix A-2 (page 60) and A-3 (page 61, 62).
PAGE 15
MILLIAMP DC INPUT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Shielded Twisted
Pair
+
-
MILLIAMP DC
SOURCE
250 OHM SHUNT
RESISTER
REQUIRED
MILLIAMP DC INPUT
NOTE: Fault detection is not functional for 0-20mA inputs.
MILLIVOLT DC INPUT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
+
3
2
1
-
Shielded Twisted
Pair
VOLT DC INPUT
Rear View
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Shielded Twisted
Pair
+
-
MILLIAMP DC
SOURCE
2.5 OHM SHUNT
RESISTER
REQUIRED
Shielded Twisted
Pair
+
-
MILLIVOLT DC
SOURCE
50 MILLIVOLT DC
MAXIMUM
NOTE: Fault detection is not functional for 0-20mA inputs.
VOLT DC
SOURCE
5 VOLT DC
MAXIMUM
Page 16
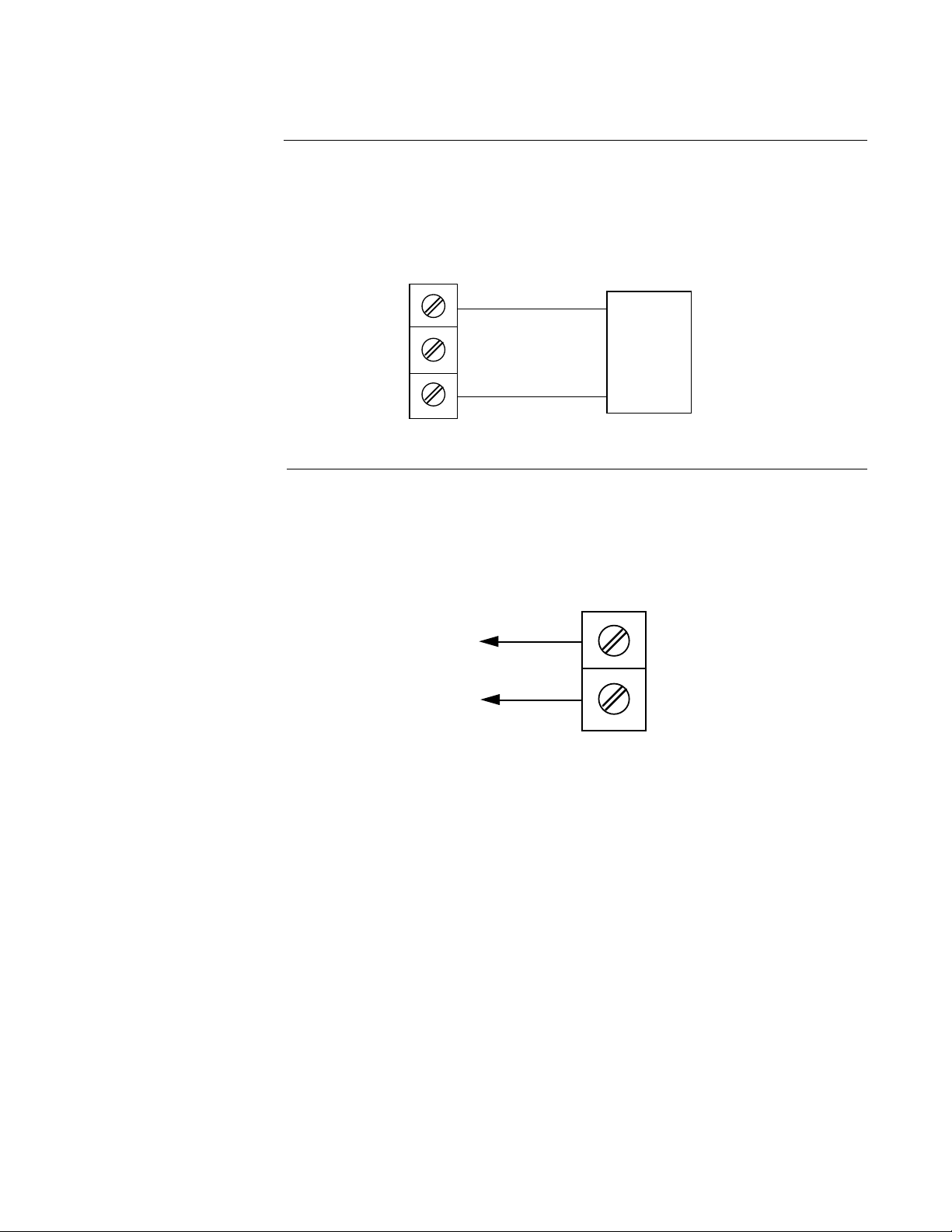
PAGE 16
FIGURE 2-9A
24 Volt Transmitter Power Supply (XP Option)
Make connections as shown below. Terminal 3 is positive (+) and terminal 1 is negative (-)/
Be sure the input conditioning jumpers are properly positioned for the input type selected.
See Figure A-2 Processor Board, page 60, and Figure A-3 Option Board, page 61 or 62. Note
the 250 ohm shunt resistor is not required.
+3
2
-1
FIGURE 2-9B
24 Volt Power Supply (XA Option)
Make connections as shown below. Terminal G is positive (+) and terminal H is negative (-).
Be sure the input conditioning jumpers are properly positioned. See Figure A-2 Processor
Board, page 60 and Figure A-3 Option Board, page 61 or 62.
+
Two Wire
Transmitter
-
H -
24VDC
G +
Page 17
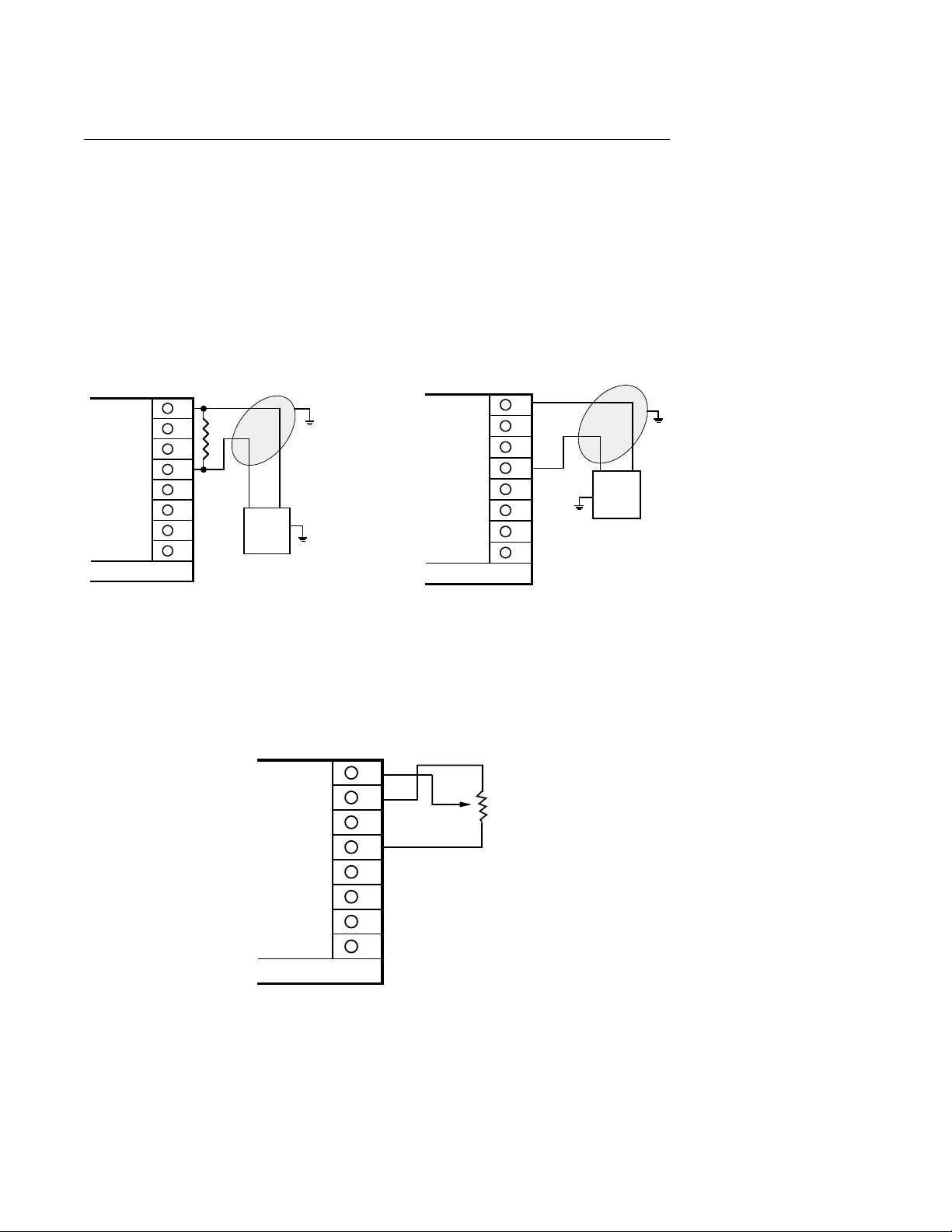
FIGURE 2-10
Remote Setpoint Input - VDC, mADC and Potentiometer
Input connections are illustrated below. Terminal 8 is positive and terminal 5 is negative.
The remote setpoint input can be configured for either 0 to 5VDC or 1 to 5 VDC input. Make
sure that the voltage input matches the voltage configuration selected in the Program mode.
For mA inputs, a 250 ohm shunt resistor must be installed between terminals 5 and 8. For
remote setpoint using a potentiometer, JU1 on options board must be in MM/PP (see page
61, 62).
PAGE 17
CURRENT DC REMOTE SETPOINT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Shielded Twisted Pair
+
-
MILLIAMP
SETPOINT
SIGNAL
250 OHM
SHUNT
RESISTER
NEEDED
POTENTIOMETER
Rear View
VOLT DC REMOTE SETPOINT
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
150 ohm to
10 K ohm
+
-
Shielded Twisted
Pair
VOLT DC
SETPOINT
SIGNAL
5VDC
MAXIMUM
Page 18
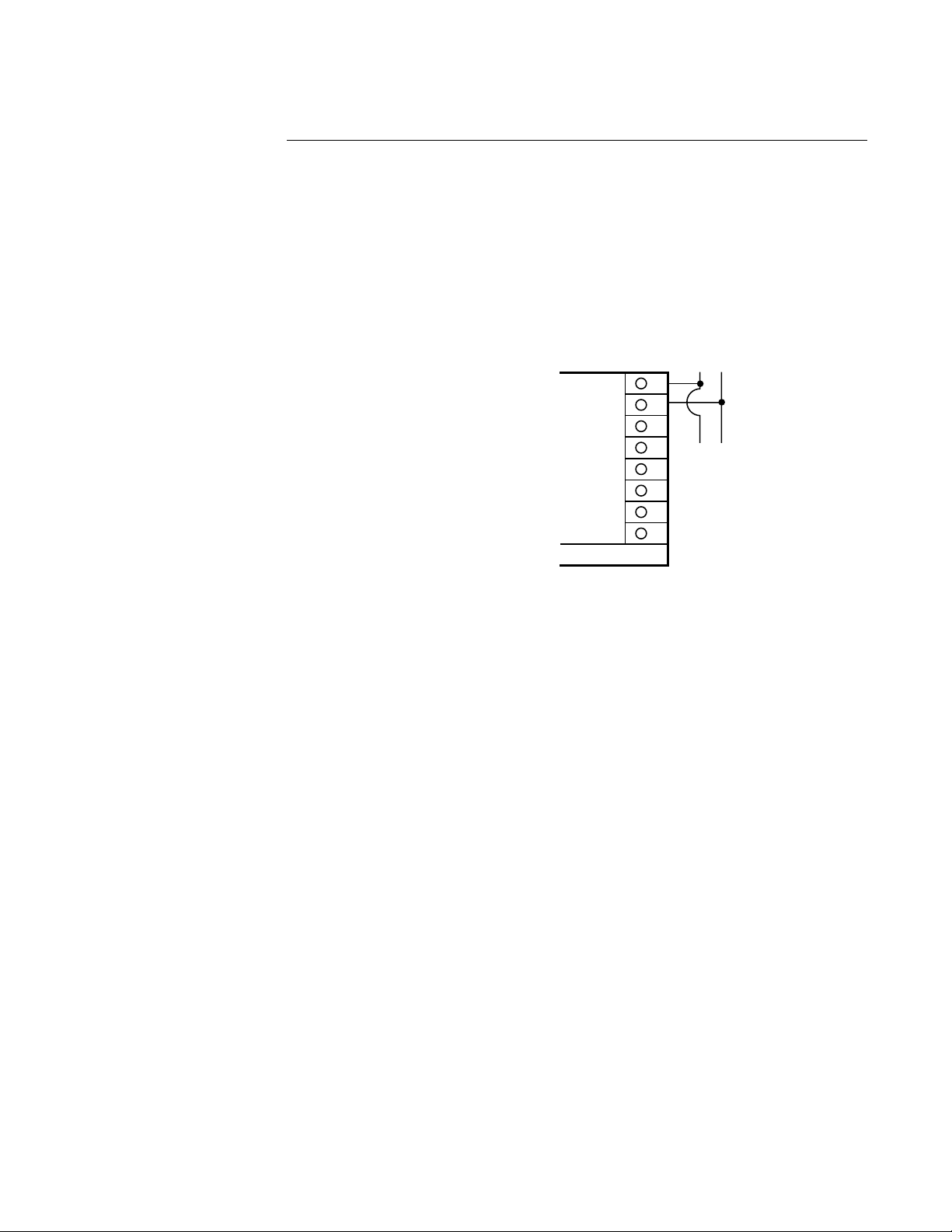
PAGE 18
FIGURE 2-11
Remote Digital Communications RS 485 Terminals 7 & 8
If the communications network continues on to other units, connect the shields together, but
not to the instrument. A terminating resistor should be installed at the terminals of the last
instrument in the loop. The shield should be grounded at the computer or the
convertor box, if used. See the Protocol Manual (Form 2878) for more details on the use of
the digital communications option.
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS
CONNECTIONS - TERMINALS 7 & 8
FROM HOST
Output 2 cannot be DC Current
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
COMPUTER
TO OTHER
INSTRUMENTS
Page 19
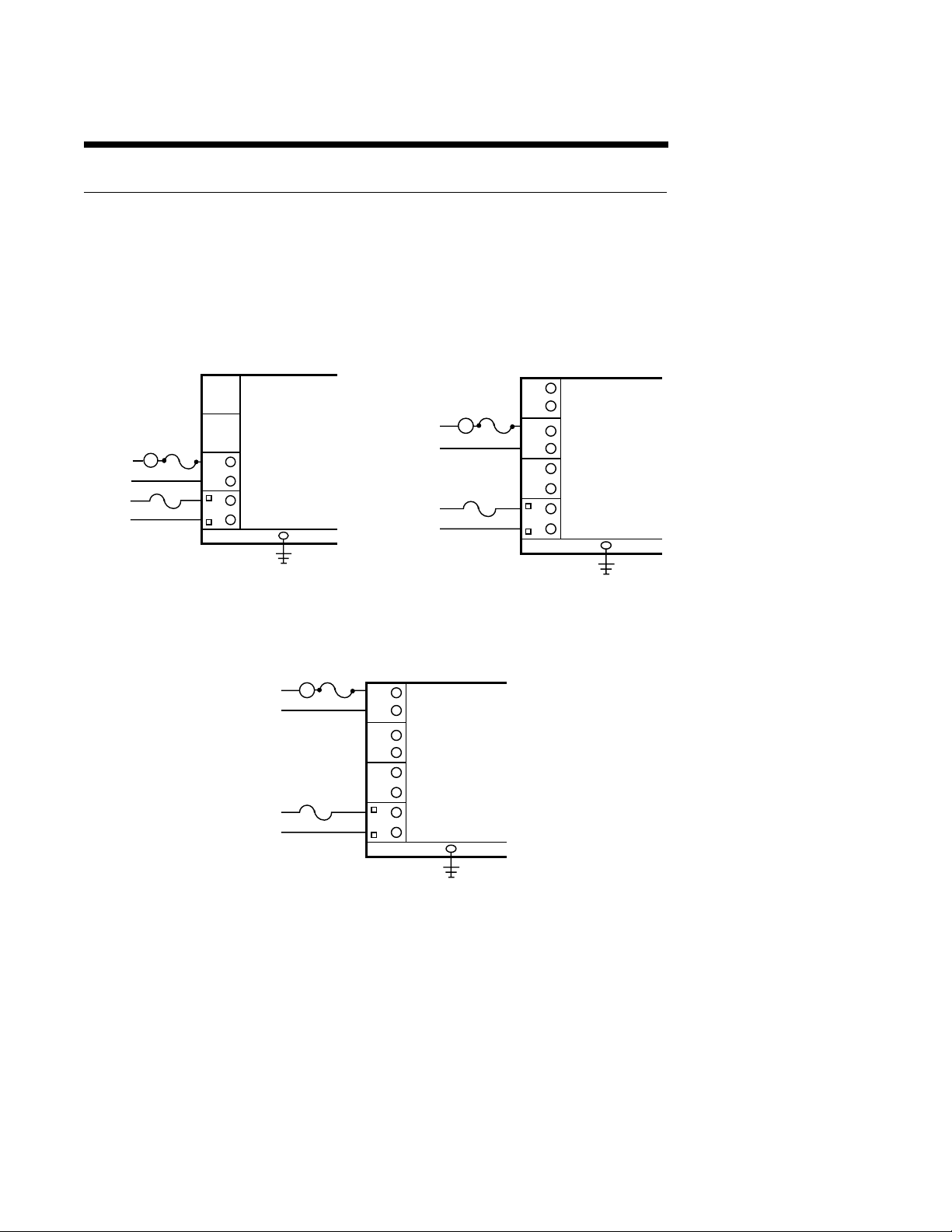
Output Connections 2.4
FIGURE 2-12
Relay Output
Connections are made to relay A as illustrated below. Connect relay(s) B & C (if present) in
the same manner. Relay contacts are rated at 5 amp Resistive load 115 VAC.
PAGE 19
INPUT
POWER
L2
L1
LOAD
RELAY A
D
C
B
A
Rear View
L2
L1
INPUT
POWER
GROUND
LOAD
INPUT
POWER
RELAY C
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
L2
L1
Rear View
LOAD
GROUND
RELAY B
Rear View
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
GROUND
Page 20
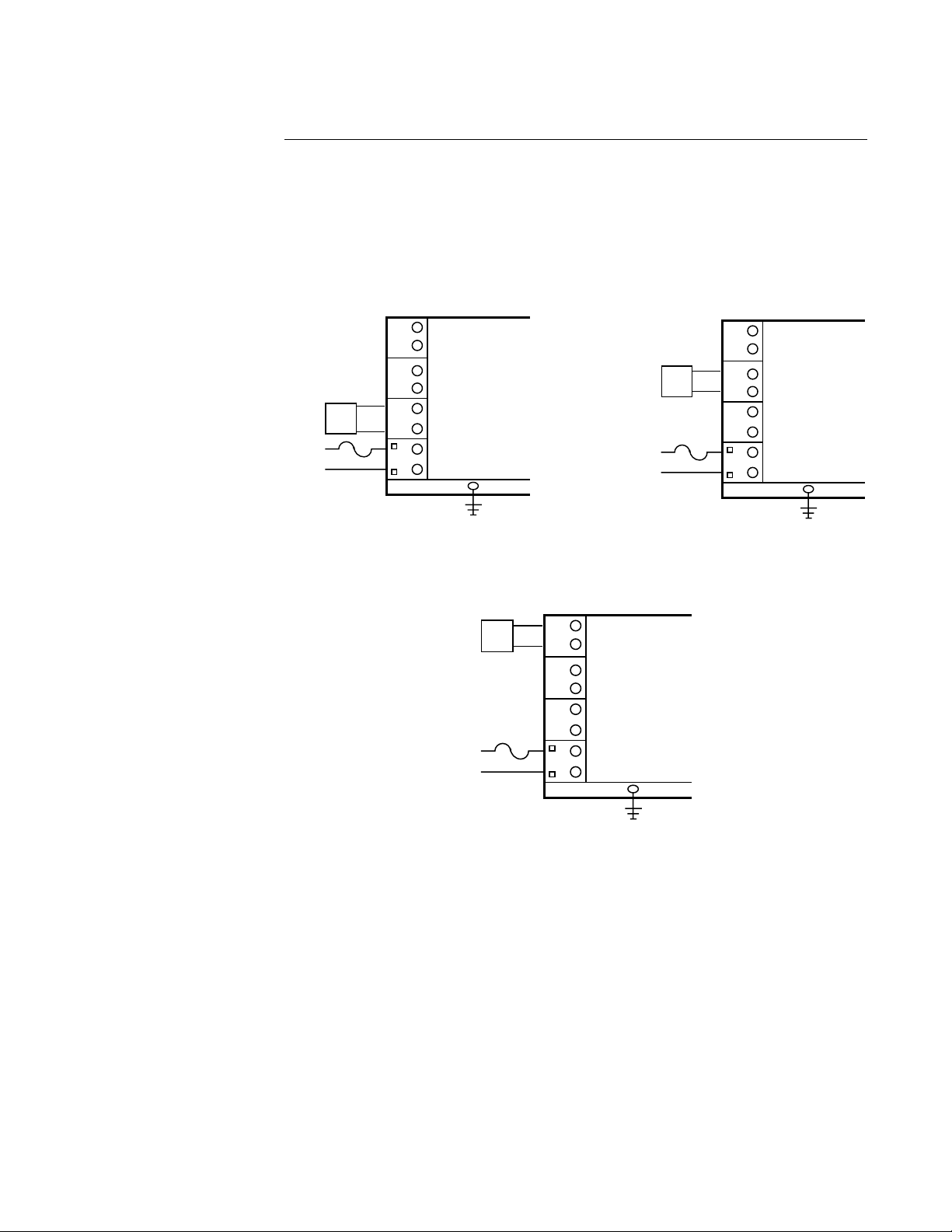
PAGE 20
FIGURE 2-13
SSR Driver Output
Connections are made to the solid state relay driver output located in the Relay A position as
shown. The solid state relay driver is a 5 VDC current sink output type. Connect the solid
state relay driver(s) in the Relay B and C position (if present) in the same manner.
INPUT
POWER
SOLID STATE
RELAY
SSR DRIVER (RELAY A)
Rear View
H
G
F
E
+
D
C
-
B
A
INPUT
POWER
GROUND
SOLID STATE
RELAY
SOLID STATE
RELAY
INPUT
POWER
SSR DRIVER (RELAY C)
Rear View
+
H
G
-
F
E
D
C
B
A
GROUND
SSR DRIVER (RELAY B)
Rear View
H
G
+
F
-
E
D
C
B
A
GROUND
Page 21
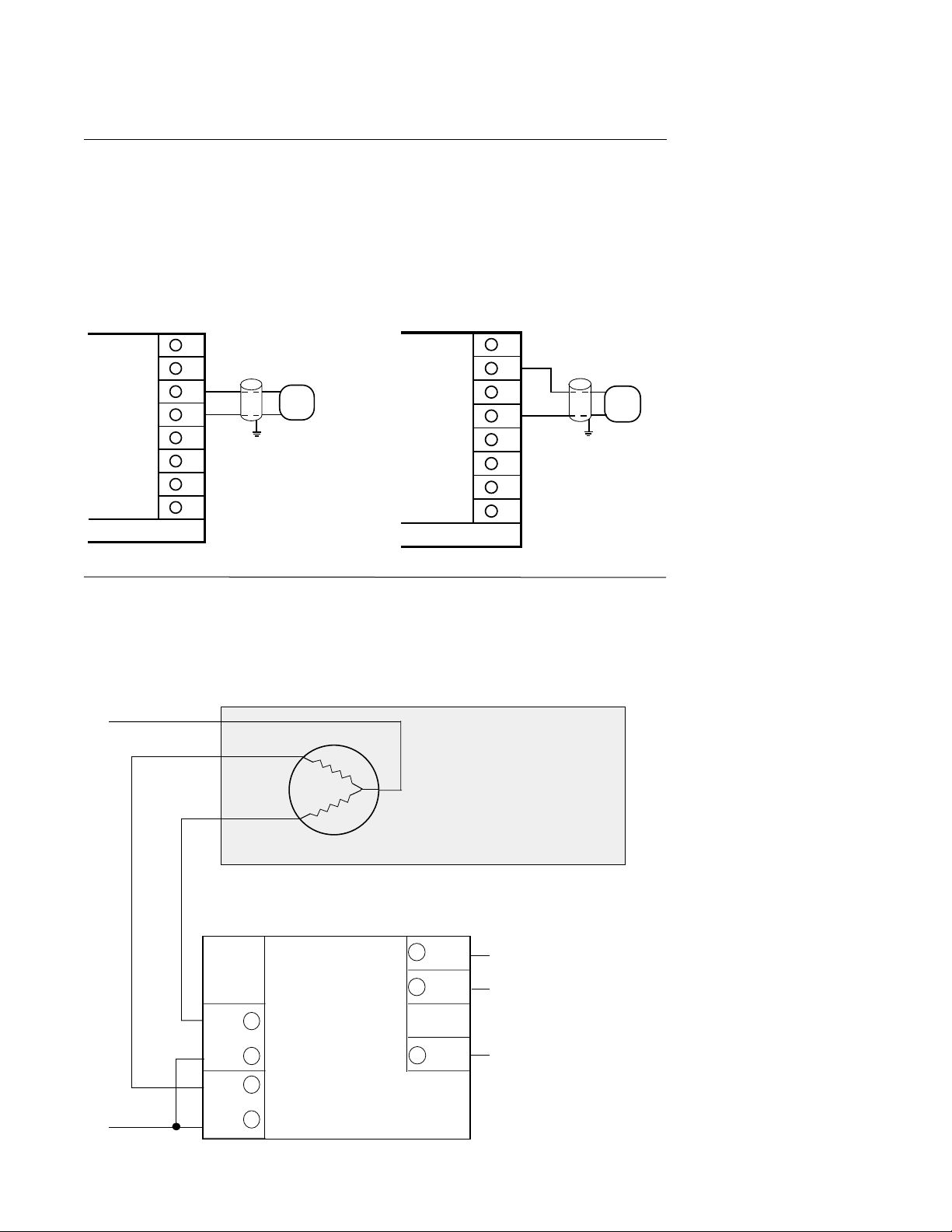
FIGURE 2-14
mADC Output
Connections are made for current outputs 1 or 2 as shown below. Connect the positive lead
to terminal 6 for Output 1 or terminal 7 for Output 2 , the negative leads connect to terminal 5.
Current outputs will operate up to 650 ohms maximum load. The current output(s) are
4 - 20 mADC. With the EA option, they can be selected for either 4-20 or 0-20 mADC.
PAGE 21
DC CURRENT OUTPUT 1
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
+
Shielded
Twisted
Pair
-
LOAD
650 OHMS
MAXIMUM
DC CURRENT OUTPUT 2
Rear View
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
+
Shielded
Twisted
Pair
-
LOAD
650 OHMS
MAXIMUM
FIGURE 2-15
Position Proportioning Output
The relay and slidewire feedback connections are made as illustrated below. The relay
assigned to Output 1 will be used to drive the motor in the open direction and the relay
assigned to Output 2 will be used to drive the motor in the closed direction. The minimum
slidewire feedback resistance is 135 ohms, the maximum resistance is 10K ohms.
L2
L1
RELAY B
RELAY A
OPEN
CLOSE
F
E
D
C
Modulating Motor
Rear View
POS.PROP.
8
WIPER
POS.PROP.
HIGH
7
5
+
RETURN
Page 22
PAGE 22
Configuration and Operation 3.1
3.1.1 POWER UP PROCEDURE
Verify all electrical connections have been properly made before applying power to the
instrument.
If the instrument is being configured (set up) for the first time, it may be desirable to disconnect the controller output connections. The instrument will go into the Control mode following
the power up sequence and the output(s) may turn on. During power up, the seven digit
model number will be displayed. Next, the software revision level will be displayed, followed
by the EPROM tab number. Instrument self test 1 through 3 will take place as they are
displayed. After completion of the tests Ctrl will be displayed for 3 seconds. At this time
another mode of operation may be selected by pressing the SCROLL key.
3.1.2 CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE
Parameter selections and data entry are made via the front keypad. To ease configuration
and operation, the user selectable features have been divided into several sections (modes).
Data and parameter entries are made by stepping through each mode and making an
appropriate response or entry to each step as necessary for the application.
Control
(CtrL)
Test
(tESt)
Calibrate
(CAL)
Program
(Prog)
Tune
(tunE)
Setpoint Select
(SPS)
Operation Summary 3.2
3.2.1 KEYPAD OPERATION
SCROLL KEY
This key is used to:
1. Display enabled modes of operation
2. Display a mode parameter value
3. Advance display from a parameter value to the next parameter code
4. Exit some calibration/test functions
5. Used with other keys:
A. With UP key to view output percentages of proportional output(s)
B. With DOWN key
1. On power up to alter model number
2. Enter calibration /test functions
Standby
(StbY)
Page 23

UP KEY
This key is used to:
1. Increase displayed parameter value
2. View setpoint (press and release)
3. Increase setpoint (press and hold)
4. With a parameter code displayed
A. Press once to exit mode
B. Press twice to enter Control mode
5. Used with other keys
A. In Control mode with SCROLL key to view output percentages of proportional
output(s).
B. With DOWN Key
1. On power up resets instrument
2. Lamp test (press and release)
3. Enter Enable Mode (press and hold)
DOWN KEY
This key is used to:
1. Decrease displayed parameter value
2. View setpoint (press and release)
3. Decrease setpoint (press and hold)
4. Enter modes
5. While in a mode, will sequence the parameter codes
6. Used with other keys
A. With SCROLL key
1. On power up to alter model number
2. Enter calibration/test functions
B. With UP key
1. On power up resets instrument
2. Lamp test (press and release)
3. Enter enable mode (press and hold)
PAGE 23
3.2.2 CONFIGURATION DISPLAYS
During configuration, the display shows the parameter codes and values. During operation,
the display is used to indicate process value, setpoint, deviation from setpoint, proportional
output percentage, etc.
3.2.3 MODE SELECTION
If the instrument is in the Control mode, repeated depressions of the SCROLL key will cause
the instrument to display the code corresponding to each mode that is enabled. To enter a
mode, with the mode displayed, depress the DOWN key. Entry into any mode except the
Control, Tune and Enable modes will cause the output(s) to turn off.
Note: If Display Select = 5 (Setpoint Continuously) it takes two depressions of the
SCROLL key to exit Control.
Page 24

PAGE 24
Configuration Summary 3.3
All configurable parameters are provided in Tables 3-1 thru 3-3 on the following pages. These
tables illustrate the display sequence, parameter adjustment and factory setting for each step.
The instrument is provided with a “time-out” feature. If the instrument is in any mode, other
than the Control mode, and no keypad activity takes place for 30 seconds, the mode will be
exited automatically. The instrument will then display the code for the respective mode. If a
mode code is displayed for five seconds with no key stroke activity the “time-out” will cause
the instrument to return to the Control mode of operation.
3.3.1 ENABLE MODE CONFIGURATION
The Enable Mode provides a means of enabling or disabling access to setpoint changes and
each of the non-control modes. In the Enable mode, each mode except Control, will be
displayed. Either “on” (enabled) or “oFF” (disabled) may be selected. See Table 3-1 (below)
for the Enable mode procedure. For additional security, the Enable mode may be locked out
by using a hardware jumper, JU 2, located on the Processor board. See Appendix A-2
(page 59).
3.3.2 PROGRAM MODE CONFIGURATION
The Program mode is used to configure or re-configure the instrument. All possible
parameters are illustrated in Table 3-2 (page 28) for illustrative purposes. Only those parameters that are applicable to the hardware options chosen or to previous parameter selections
will be displayed.
3.3.3 TUNE MODE CONFIGURATION
The Tune mode is used to adjust the tuning parameters and the alarm setting needed for
operation of the instrument.
TABLE 3-1 ENABLE MODE CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE
To enter the Enable mode depress and hold the UP and DOWN keys. All display lamps will
light, after ten seconds the display will read EnAb. If EnAb does not appear, check the
position of the Enable mode jumper, JU 2, located on the Processor board (See Appendix A2, page 60). Release the keys and the display will then change to EtSt.
Depress the SCROLL key to review the state (on or off) of the mode. Use the UP key to
enable a mode that is off. Use the DOWN key to disable a mode that is on. When all
selections have been made, to exit the Enable mode depress the UP key with a mode code
displayed EtSt, ECAL, etc.
STEP DESCRIPTION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
1 Test Mode EtSt on or oFF oFF
2 Calibration Mode ECAL on or oFF oFF
3 Program Mode EPro on or oFF on
4 Tune Mode Etun on or oFF on
5 Standby Mode ESby on or oFF on
6 Setpoint Select ESPS on or oFF oFF
7 Setpoint Changes ESPC on or oFF on
Page 25

ENABLE MODE FLOW CHART
PAGE 25
EnAb
EtSt
ECAL
EPro
Etun
ESbY
ESPS
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ESPC
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
Page 26

PAGE 26
PROGRAM MODE
Prog
A
inPS
iCor
out1
o1PL
out2
o2PL
rLyC
diSP
dPoS
Euu
EuL
HySt
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
out3
rLyA
rLyb
A
rSP
rSPu
rSPL
B
Page 27

PAGE 27
B
SPL
SPLL
(EA
Option)
AtFr
PFF
dFF
FSCn
C
Pout
(SPuL EA Option)
Pou
PoL
PorA
EA Option
PoAP
EB Option
SPrr
Prnd
Co1r
Co2r
C
Com Option
CCon
CbS
CAd
Page 28

PAGE 28
TABLE 3-2 PROGRAM MODE CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE
Press and release the SCROLL key until Prog is displayed. Use the DOWN key to enter the
Program mode. Depress and release the SCROLL key to advance the display through the
parameters and their values. Use the UP and DOWN keys to adjust the parameter values.
After adjusting a parameter, depress the SCROLL key to proceed to the next parameter.
After all selections have been made, depress the UP key with a parameter code in the display
(not a setting) to exit the mode.
Note that parameter values are referred to in Degrees (°) and Engineering Units in the
following tables. The input selection determines what the parameter values will be.
STEP DESCRIPTION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
1 Input Select inPS 0 = J °C Thermocouples
NOTE: Fault detection is not
functional for 0-20mA inputs.
2 Input Correction iCor -300° to 300°/Units
3 Output 1 out1 1 = On-Off Direct (Cooling)
1 = J °F
2 = K °C
3 = K °F
4 = T °C
5 = T ° F
6 = R °C
7 = R °F
8 = S °C
9 = S °F
10 = E °C
11 = E °F
12 = B °C
13 = B °F
14 = N °C
15 = N °F
16 = C °C
17 = C °F
20 = RTD °C
21 = RTD °F
30 = 0 to 5VDC / 0 to 20mA
31 = 1 to 5VDC / 4 to 20mA
32 = 0 to 50mVDC
33 = 10 to 50mVDC
34 = 0 to 25mVDC
2 = On-Off Reverse (Heating)
3 = Time Proportioning -
Direct (Cooling)
4 = Time Proportioning -
Reverse (Heating)
5 = Current Proportioning -
Direct (Cooling)
6 = Current proportioning -
Reverse (Heating)
7 = Position Proportioning
Reverse (Open)
8 = On-Off Latched * Direct
9 = On-Off Latched * Reverse
* Relays latch in the open position
1
0
2
4 Output 1 o1PL 0 to 100%
Percent Limit
100
Page 29

STEP DESCRIPION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
PAGE 29
5 Output 2 out2 0 = None Position
Proportioning Direct (Close)
1 = On-Off Direct (Cooling)
2 = On-Off Reverse (Heating)
3 = Time Proportioning-
Direct (Cooling)
4 = Time Proportioning-Reverse
(Heating)
5 = Current Proportioning-
Direct (Cooling)
6 = Current Proportioning-
Reverse (Heating)
7 = Position Proportioning
Reverse (Close)
6 Output 2 o2PL 0 to 100%
Percent Limit
7 Output 3 out3 0 = None
1 = Process Alarm-Direct
2 = Process Alarm-Reverse
3 = Deviation Alarm-Direct
4 = Deviation Alarm-Reverse
5 = Deviation Band Alarm-
Open within band
6 = Deviation Band Alarm-
Closed within band
8 Relay A rLyA 0 = Not assigned
Assignment 1 = Assigned to Output 1
2 = Assigned to Output 2
3 = Assigned to Output 3
4 = % Output Relay Actuation
(EA Option)
0
100
0
1
9 Relay B rLyb Same selection as Relay A
Assignment
10 Relay C rLyC Same selection as Relay A
Assignment
11 Display Select diSP 1 = Process Value (PV)
2 = PV and Setpoint
3 = Deviation
4 = Deviation and Setpoint
5 = Setpoint
12 Decimal Position dPoS 0 or 1 for T/C and RTD Input
0 to 3 for volt/mV Input
13 Engineering units Euu -9999 to 9999
Upper Value
14 Engineering units EuL -9999 to 9999
Lower Value
15 Hysteresis for HySt 0 to 300°/Units
On/Off Outputs (width of hysteresis band)
16 Remote Setpoint rSP 0 = None
1 = 1 to 5 Volts DC
2 = 0 to 5 Volts DC
3 = Contact Closure Sensing
for SP=PV (EA Option)
2
3
1
0
1000
0
3
0
Page 30

PAGE 30
STEP DESCRIPTION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
17 Remote Setpoint rSPu -9999 to 9999°/Units
Upper Value
18 Remote Setpoint rSPL -9999 to 9999°/Units
Lower Value
19 Setpoint SPL -9999 to 9999°/Units
Upper Limit (SPuL - EA Option)
20 Setpoint SPLL (EA Option) ± 9999 0
Lower Limit
21 Automatic Transfer AtFr 0 = No automatic transfer
1 = Transfer when PV
goes below setpoint
2 = Transfer when PV
goes above setpoint
22 Process PFF 1 to 20 (# of scans averaged)
Filter Factor 1 = no filtering
23 Display dFF 1 to 20 (# of scans averaged)
Filter Factor 1 = No Filtering
* Whenever inPS is changed, the parameter is set to the upper limit of advertised span.
1400*
0
1400*
0
1
1
Extended Features Software Options (EA)
24 Fast Scan FSCn 0 = Standard Scan -
1 scans/second
1= Fast Scan 3 scans/second
25 Process Rounding Prnd 1 to 100 degrees/units
1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001 = no
rounding depending on dPoS
26 Current Output 1 Co1r 0 = 0 to 20mADC
1 = 4 to 20mADC
27 Current Output 2 Co2r 0 = 0 to 20mADC
1 = 4 to 20mADC
28 Process Output Pout 0 = Not selected
1 = Process Assigned to
Current Output 1
2 = Process Assigned to
Current Output 2
3 = Setpoint Assigned to
Current Output 1
4 = Setpoint Assigned to
Current Output 2
29 Process/Setpoint Pou -9999 to 9999 degrees/units
Output Upper Value
30 Process/Setpoint PoL -9999 to 9999 degrees/units
Output Lower Value
0
1
1
1
0
2000
0
Page 31

STEP DESCRIPTION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
PAGE 31
31 Percent Output PorA 0 = None
Relay Actuation 1 = Based upon
proportional Output 1
On when process is
above PoAP
2 = Based upon proportional
Output 1
On when process is
below PoAP
3 = Based upon proportional
Output 2
On when process is
above PoAP
4 = Based upon proportional
Output 2
On when prcess is
below PoAP
32 Percent Output PoAP 0 to 100 percent
Actuation Point The relay assigned to
"Special Actuation 1"
will activate per PorA
at the percentage output
specified by PoAP.
Extended Features Software Options (EB)
0
95
33 Setpoint SPrr 0 to 100°/Units per minute
Ramp Rate 0 = not used
Communication Parameters 33-35 are optional
34 Communications CCon 0 = Off
Configuration 1 = Monitor Mode (Read Only)
2 = Normal Mode (Read & Write)
3 = Total Access with Limit Checking
4 = Total Access without
Limit Checking
35 Communications CbS 1 = 300 bit rate
Bit Rate 2 = 600 bit rate
3 = 1200 bit rate
4 = 2400 bit rate
5 = 4800 bit rate
6 = 9600 bit rate
36 Communications CAd 0 to 99
0.0
0
6
0
Page 32

PAGE 32
Address
TUNE MODE FLOW CHART
tunE
A
SPrd
PAL
dAL
dbAL
Pb1
Pb2
Ct1
Ct2
SEnS
FoP
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
rSEt
ArSt
rAtE
A
Page 33

TABLE 3-3 TUNE MODE CONFIGURATION PROCEDURE
Depress the SCROLL key until tunE is displayed. Use the DOWN key to enter the Tune
mode. Depress and release the SCROLL key to sequence through the parameters and their
values. Use the UP and DOWN keys to adjust the values. After adjusting a
parameter, depress the SCROLL key to proceed to the next parameter. After all
selections have been made, depress the UP key with a parameter code displayed (not a
setting) to exit the mode.
STEP DESCRIPTION DISPLAY AVAILABLE FACTORY YOUR
CODE SETTINGS SETTING SETTING
PAGE 33
1 Spread (Second SPrd -1000 to 1000 °/units
Output Position)
2 Process Alarm PAL -9999 to 9999 °/units
3 Deviation Alarm dAL -3000 to 3000 °/units
4 Deviation Band dbAL 1 to 3000 °/units
Alarm
5 1st Output Pb1 1 to 3000 °/units
Proportional
Band Width
6 2nd Output Pb2 1 to 3000 °/units
Proportional
Band Width
7 Manual Reset rSEt -1500 to 1500 °/units
8 Automatic Reset ArSt 0.0 to 100.0 repeats
(Integral) per minute
9 Rate ( Derivative) rAtE 0.0 to 10.0 minutes
10 Cycle Time Ct1 1 to 240 seconds
Output 1
0
0
0
1
100
100
0
0.0
0.0
30
11 Cycle Time Ct2 1 to 240 seconds
Output 2
12 Position Prop. SEnS 0.0 to 50.0 %
Sensitivity
13 First Output FoP -1000 to 1000 °/units
Position
Note: The Program, Tune and Enable Mode selections can be conveniently recorded on
the Software Reference Sheet located in Appendix E (page 70).
30
1.0
0
Page 34

PAGE 34
Tune Mode Operation 3.4
Proportional output control may require the adjustment (tuning) of the PID and other related
parameters. This provides a means for the instrument's control algorithm to be adjusted to
meet specific application requirements.
3.4.1 SYSTEMATIC TUNING METHOD
1. Changes in tuning parameters should be made one at a time.
2. After making any changes in tuning parameters, a disturbance should be introduced into
the process so that the process reaction may be observed. This process reaction, or
recovery, will tell whether the tuning parameters provide the desired control. It is usually
easiest to make a step change in setpoint to introduce this disturbance.
3. The change in setpoint, or disturbance, referenced above should be large enough to cause
an observable deviation of process from setpoint. However, this change should not be so
large that it will cause the controller output to proceed to either extreme limit.
4. Controller tuning for optimal control is not hard and fast, BE PATIENT. The process will
take a certian amount of time to react to the setpoint changes during tuning. The amount
of time depends upon the specific process, however, a period of 8 to 12 minutes should be
allowed between changes. The important point to remember is to allow the process to
react completely, do not rush through tuning of the controller. If the complete process
reaction is not observed, optimum control may never be achieved.
5. Time Proportioning control output(s) require(s) the cycle time to be adjusted for the
application. Short cycle times typically result in the most accurate process control, but will
cause the quickest wear out of any mechanical components.
6. Leave all other tuning parameters (except for the alarm settings, if used) at the factory
default settings. Obtain the best possible process reaction by adjusting the Proportional
Bandwidth parameter. The setting that achieves the best response for the process should
be left in the controller programming, and should be noted on the Software Reference
Sheet in Appendix E (page 70).
7. If there are to be no setpoint or load changes in the process, the Proportional Band
adjustment may be all that is necessary for proper control. If an offset still exists (the
process does not settle out at setpoint with the best possible proportional band adjustment)
Manual Reset may be added to eliminate this offset.
8. Auto Reset may be added to eliminate offsets and improve response to setpoint and load
changes. Increase Auto Reset from 0 to 0.2 increments. Start with a small amount.
Increase this increment if there is no apparent reaction. Remember to allow the process 8
to 12 minutes to react.
9. If necessary, Rate may be added. Rate is a dynamic tuning parameter. Rate may be
required to compensate for process lags or to help inhibit reset windup when a large
amount of Auto Reset (4 or 5 repeats per minute) is being used.
10. Controller tuning is not hard and fast. It may be necessary to adjust the tuning
parameters over a period of time to obtain optimal control of the process.
Page 35

3.4.2 ZIEGLER NICHOLS TUNING METHOD
This procedure has been determined empirically to yield 1/4 amptitude decay tuning parameters that are determined by watching the system in a sustained oscillation (curve C, page 36,
the ultimate proportional band and ultimate time period) and then using these values from this
sustained oscillation to calculate ideal parameters.
Determining Ultimate Proportional Band and Ultimate Time Period
1. Set Manual Reset rSet to 0.0, set ArSt to 0.0 and set rAtE to 0.0
2. Enter the Control mode of operation, observe the process reaction.
3. Set the Proportional Band (PB) at 100 and upset the process and observe the
response. One easy method for imposing the upset is to move the setpoint for a
few seconds and then return it to its original value.
4. Achieve a response curve similair to the sustained oscilaltion (curve C), this is the
Ultimate Proportional Band (UPB) and Ultimate Time Period (UTP).
a) If the response curve from step 3 does not damp out, as in Curve A from
the drawing, the PB is too low. The PB should be increased and step 3
repeated.
b) If the response in step 3 damps out, the PB is too high. The PB should
be decreased and step 3 repeated.
PAGE 35
These values obtained for Ultimate Proportional Band (UPB) and Ultimate Time Period (UTP)
are used to calculate ideal P, PI, PD, PID tuning parameters using the following ZieglerNichols equations:
Proporational only control (P) -
P (Pb) = 2 x UPB (degrees or units)
Proportional plus automatic reset (PI)
P (Pb) = 2.2 x UPB (degrees or units)
I (ArSt) = 1.2 / UTP (repeats per minute)
Proportional plus derivative (or rate) (PD) -
P (Pb) = 1.7 x UPB (degrees or units)
D (rAtE) = UTP / 8 (minutes)
Proportional plus automatic reset plus derivative (PID)
P (Pb) = 1.7 x UPB (degrees or units)
I (ArSt) = 2 / UTP (repeats per minute)
D (rAtE) = UTP / 8 (minutes)
If an overdamped response is desired, multiply the proportional band by two.
Page 36

PAGE 36
Period
C
A
B
Curve A : unstable
Curve B : stable
Curve C : continuously cycling,
ultimate PB and period
Page 37

Control Capability 4.1
A variety of user programmable control features and capabilities are available including:
• On-Off Control • Time Proportioning Control
• Current Proportioning • Position Proportioning Control
• Alarm Functions • Dual Output Control
• Auto/Manual Switching • Automatic Transfer
• Setpoint Adjustment • Process Re-transmission
The capabilities available in a specific unit are dependent upon the hardware options specified
when the instrument is ordered. Refer to Appendix C (page 61) for the decoding of the
instrument model number. Current proportioning control cannot be implemented if a current
output was not ordered. Position proportioning cannot be implemented if two relays (Outputs
1 and 2) and the option have not been ordered. The available output types and quantity of
each are as follows:
Type of Output Quantity Available
* SPST mechanical relay output Up to three
* SSR Driver Up to three
* mADC current output Up to two
The maximum number of SPST relay and/or SSR driver outputs available on a single instrument is three. Relay and SSR drivers may be assigned as either control or alarm outputs.
The mADC current output(s) may be assigned control or process value retransmission
output functions.
PAGE 37
Control Responses 4.2
Each instrument may be configured to provide 3 mode proportional control. Proportional
control is provided with Proportional Band, Integration, and Derivative responses.
Manual Reset is provided for use in lieu of, or in conjunction with automatic reset. A cycle
time adjustment parameter is provided for use with each time proportioning control output.
Direct/Reverse
Operation of Outputs 4.3
Direct operation is typically used with cooling applications. On-Off direct output(s) will turn on
when the process variable exceeds setpoint. Proportional direct output(s) will increase the
percentage of output as the process value increases within the proportional band.
Reverse operation is typically used with heating applications. On-Off reverse output(s) will
turn off when the process variable exceeds setpoint. Proportional reverse output(s) will
decrease the percentage of output as the process value increases within the proportional
band.
Page 38

PAGE 38
On-Off Control / Latched On-Off 4.4
On-Off control can be implemented with SPST relay or SSR driver output(s) . On-Off
operation can be assigned to either or both Output 1 and 2. A hysteresis adjustment is
provided for On-Off Outputs. This adjustment is in terms of degrees/engineering units and
defines the bandwidth of the hysteresis. The hysteresis value straddles the setpoint. Relay
chatter can be eliminated by proper adjustment of this parameter. When operating in On-Off
control, the output(s) will turn on or off depending upon the setpoint, the process value, Tune
mode selections, and the hysteresis adjustment.
Resetting of an On-Off latched output (out1 = 8 or 9) is accomplished by pressing the UP
arrow. The relay will stay reset only if the condition is cleared.
Time Proportioning Control 4.5
Time Proportioning control can be implemented with a SPST relay or SSR driver. Time
Proportioning control can be selected for Output 1 and/or Output 2, depending on hardware
configuration. Time Proportioning control is accomplished by cycling the output on and off
during a prescribed period of time when the process variable is within the
proportional band.
Ex: Calculated output % = 40%; Cycle time adjustment = 20 seconds
Output on time = .4 x 20 = 8 seconds
Output off time = .6 x 20 = 12 seconds
When the unit is operating in the Control mode, the control algorithm determines the output %
required to correct for any difference between the process value and the
setpoint. The output calculation is affected by Tune mode parameter adjustments.
See Figure 4-1 (page 39) for proportional bandwidth effect on the output.
Current Proportioning Control 4.6
Current Proportioning control can be implemented on units provided with mADC current
output(s). Current Proportioning control provides a 4 to 20mADC or 0 to 20mADC output in
response to process value and setpoint. As with Time proportioning, the calculated output %
for Current proportioning control is affected by the Tune mode parameter adjustments.
See Figure 4-1 (page 39) for proportional bandwidth effect on the output.
Position Proportioning Control 4.7
Position Proportioning Control can be implemented on those units provided with two SPST
relay or two SSR driver outputs and the Position Proportioning (slidewire feedback) option.
Position Proportioning control permits the use of PID control when the final control element is
a modulating device such as a motorized valve. Two outputs are required to control the
valve. One output opens the valve, the second output closes the valve. The slidewire
feedback is used to indicate the valve position to the instrument. The valve position will be
dependant upon the process value, the setpoint and Tune mode
parameters.
Page 39

A Position Proportioning sensitivity adjustment is provided, which specifies a deadband
t
around the setpoint to prevent the valve from oscillating. The valve rotation time must be
entered, for proper operation, into the Tune mode paramter Ct1.
See Figure 4-1 for proportional bandwidth effect on the output.
FIGURE 4-1
Proportional Bandwidth Effect On Outpu
PAGE 39
100%
Output
Action
100%
Output
Action
0%
0%
PB=100
100 200
125 175
150
Setpoint
PB=50
150
Setpoint
Process
Variable
The Proportional Bandwidth is the area where the output is a percentage of the full output. The
size of the proportional band determines what change in the output will result from a change in the
process variable. In the upper figure when the process variable is at 125 the output will be at 75%
of full output. In the lower figure the proportional bandwidth is smaller. When the process variable
is at 125 the output is now at 100%. The larger the proportional band the smaller the "gain" and
vice versa.
Page 40

PAGE 40
g
g
Dual Output Control 4.8
Dual output control can be performed when two outputs are specified. The outputs may be
programmed for On-Off, Time Proportioning, or Current Proportioning, as applicable.
The output action is dependent upon the setpoint, the process value, and Tune mode parameters. If two proportional outputs are selected, both output proportional bands will be biased so
that 0 % of output is seen when the process value equals setpoint. The output(s) can be
biased by the use of the Tune mode parameters FOP and SPrd as shown below.
FIGURE 4-2
100%
Proportional
Output 1
First
Output
Position = X
The first output is programmed as a proportional reverse output and the second as a proportional direct output. (See Glossary, page 63, for definitions of these terms). Dual proportioning outputs are provided with separate proportional band and cycle time adjustments for
each output.
Reverse
Output
Actin
Control
Setpoint
-X
Direct
Actin
+Y
Output
Spread = Y
100%
Proportional
Output 2
Process
Value
Page 41

Manual Operation of Proportional Outputs 4.9
The Auto/Manual switching function applies to proportional control outputs only.
Switching between the automatic and manual control modes is accomplished by scrolling to
the Standby mode and pressing the DOWN key to enter the mode. Switching from automatic
to manual is always bumpless.
CAUTION: If the unit is in the Manual mode, be careful not to leave the process unwatched. Since the
unit is intentionally ignoring the setpoint, it is possible to unintentionally let the process exceed safe
limits. Limit devices must be used to guarantee the process does not get out of control.
The proportional output values initially displayed upon entry into the Standby mode will be the
last output values calculated by the control algorithm. Changes made to output values are
made "on-line".
When the unit is placed in manual, Po1 and/or Po2, as approporiate, will appear in the
display. If the keys are depressed within 5 second intervals, the units will respond as follows:
If a code is displayed:
SCROLL - The corresponding value will be displayed
DOWN - The next code will be displayed
If a value is displayed:
SCROLL - The next code will be displayed
UP - The value will increment
DOWN - The value will decrement
PAGE 41
To exit from the Standby mode (manual operation), depress the UP key twice. (Pressing the
UP key once stops the cyclic display and leaves the controller in Standby) The controller will
be in automatic control with Stby displayed. After a time-out period, the unit will display Crtl.
To get directly to the Ctrl display, press the UP key three times instead of twice. Shifting to
the Control mode is balanceless.
STANDBY MODE FLOW CHART
StbY
Po1
Po2
Automatic Transfer Function 4.10
Automatic transfer provides automatic switching from the Manual mode to the Control mode of
operation when the process value reaches setpoint. This feature is selectable in the Program
mode.
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
NOTE: If an error condition occurs while in the Manual mode and Automatic Transfer
Function is selected, the output will go to a Failsafe condition.
Page 42

PAGE 42
g
Setpoint Adjustments 4.11
Local
Local setpoint adjustment is accomplished by using the keypad. Press the UP key to
increase the setpoint value. Press the DOWN key to decrease the setpoint value. Holding
the key pressed will cause the value to change slowly at first then increasingly faster. The
range of the setpoint value can be limited by selecting the setpoint upper limit SPL in the
Program mode. The setpoint value can be protected from inadvertent changes by
disabling the Setpoint Change, ESPC, in the Enable mode.
Ramp Rate - EB Option Only
A selectable Ramp Rate function can be used to limit the rate at which the setpoint used
by the control algorithm will change. This feature will also establish a soft startup. Upon
power up, the instrument will take the initial process value as the setpoint. A setpoint ramp
will be calculated to increase the setpoint from the initial process value to the setpoint
that was seen prior to the power outage.
Sudden changes in the setpoint value entered via the keypad can be inhibited from
effecting the control outputs by use of this feature. The internal setpoint used to control
the process will ramp to the setpoint value entered at the rate of change selected.
FIGURE 4-3
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Setpoint Ramp
05
Time in Minutes
10
Setpoint
in
De
rees
205
204
203
202
201
200
Remote Setpoint
Remote Setpoint adjustment is an optional feature. The instrument setpoint can be
adjusted by supplying a signal to the remote setpoint terminals as indicated in the
installation section. Local or Remote setpoint operation is selected by pressing and
releasing the SCROLL key until the display reads setpoint select SPS. Press the DOWN
key to enter the Setpoint Select mode. The display will change to show the current
setpoint mode, either local loc or remote rSP. To change the setpoint mode press the
SCROLL key. To exit the setpoint mode press the UP key. To prevent unwanted setpoint
mode changes, the Setpoint Select mode can be disabled in the Enable mode. The
setpoint value can be adjusted by using the Digital Communcations Option. Refer to the
Protocol Manual (Form 2878) for more details about this option.
SETPOINT FLOW CHART
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
SPS
LOC
rSP
CtrL
Page 43

Process Re-transmission Output - EA Option Only
T
F
F
If the instrument is provided with a current output not used for process control, this output may
be assigned to provide a linear re-transmission of the process value. This output can be used
to provide a process signal to remotely installed recorders, panel meters, or data loggers.
The process output is scaled for the application by using the Program mode parameters
process/setpoint output value upper Pou and process/setpoint output value lower PoL. The
current output resolution is @ 200 steps, so for the best re-transmission accuracy, the span
between Pou and PoL should be as small as possible. If a current output is used for retransmission, the corresponding control output, out1 or out2, cannot be assigned to it.
The example illustrated in Figure 4-4 (below) shows a process re-transmission application for
0 to 200 degrees F.
FIGURE 4-4
PROCESS OUTPUT / RETRANSMISSION VALUES
EXAMPLE
100 %
OUTPU
PAGE 43
0%
0°
Setpoint Re-transmission Output - EA Option only
If the instrument is provided with a current output not used for process control, this output may
be assigned to provide a linear re-transmission of the setpoint value. The setpoint output is
scaled for the application by using the Program mode parameters process/setpoint output
value upper Pou and process/setpoint output value lower PoL. The current output resolution
is @ 200 steps, so for the best re-transmisstion accuracy, the span between Pou and PoL
should be as small as possible. If a current output is used for re-transmission, the corresponding control output, out1 or out2, cannot be assigned to it.
The example illustrated in Figure 4-5 (below) shows a setpoint re-transmission application for
0 to 400 degrees F.
INPUT
200°
FIGURE 4-5
SETPOINT OUTPUT / RETRANSMISSION
VALUES
EXAMPLE
100 %
OUTPUT
0%
0° F 400° F
SETPOINT
Page 44

PAGE 44
Service 5.1
This section contains Calibration , Test and Trouble-shooting procedures that can be performed by the user. Instruments are calibrated to its input type at the factory prior to shipment. Re-calibration should not be necessary under normal operating conditions.
Calibration 5.2
Caution: Do not attempt any of these calibrations without the proper test equipment with specifications
equal to or better than those listed.
Press and release the SCROLL key to sequence the display until CAL appears. If CAL does
not appear, refer to Section 3 for instructions on how to enable the Calibration mode. When
CAL appears on the display, press the DOWN key. The display will read CAL 1. CAL 1 can
be initiated at this time or press the SCROLL key to advance the display to the other calibrations available.
CALIBRATION FLOW CHART
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
CAL
CAL1
CAL2
CAL3
CAL4
CAL5
Prog
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
CAL6
CAL7
Page 45

TABLE 5-1 CALIBRATION PROCEDURES
Calibration
Procedure Description
CAL 1 Re-initialization of Program and Tune Mode values.
CAL 2 Main Calibration used by all inputs. This is the only calibration required
for voltage and millivolt inputs.
CAL 3 Cold Junction Compensation calibration used to correct for component
variation in CJC circuit.
CAL 4 Cold Junction utility. The temperature of the cold junction is displayed.
No adjustment is made with this procedure.
CAL 5 RTD input calibration used to correct for component differences in the
RTD input circuit.
CAL 6 CJC turn on/off
CAL 7 Factory Use Only
PAGE 45
5.2.1 CAL 1 PARAMETER INITIALIZATION
This procedure is performed to erase the information that was entered in the Program and
Tune modes . All parameters will be reset to default values. Prior to beginning this procedure
record the Program and Tune mode parameters so that they can be
re-entered. No special test equipment is required.
With CAL1 displayed, depress and hold the DOWN key, then press the SCROLL key. The
display will momentarily go blank. Release the keys. CAL1 will reappear on the display. This
calibration can be done again or another may be selected.
5.2.2 CAL2 MAIN CALIBRATION
This procedure determines and saves calibration values which correct for component variations relating to the input measuring function of the instrument. This is the only calibration
required for the volt and millivolt inputs. Additional calibration procedures are required for
thermocouple and RTD inputs.
A 50.00 ± .01mVDC source is required for calibrating. In addition make sure that JU1 on the
Processor board is in the “non volt” position. See Appendix A-2 (page 60).
Make sure all input wiring is disconnected. Short the input terminals 1 and 3 or apply 0.00
mV to the input. With CAL2 displayed, press and hold the DOWN key, then press the
SCROLL key. Release both keys and the instrument will display hLd1. Depress the DOWN
key; dELy will appear for up to ten seconds, then SCAn will appear for up to ten seconds. If
the calibration reference number which appears is not between -50 and +50, proceed per
note below. Otherwise, connect a 50.00 ± .01mV source to the input terminals. Press the
DOWN key and deLy will be displayed for ten seconds and then SCAn for ten seconds. Then
CAL2 will reappear. If there is a problem, the appropriate error code will be displayed.
Restore JU1 to the position necessary for the input type.
NOTE: If the calibration reference number falls outside the -50 to +50 range, depress
the SCROLL key and CAL2 will be displayed. Depress the DOWN key and perform the
calibration once more. Repeat the calibration until the number falls within the tolerance limits. If the calibration number remains outside these limits, check the connections to the test equipment and try the calibration again. If the number still does not
approach the tolerance limits contact an Applications Service Engineer at the factory
or a local representative.
Page 46

PAGE 46
Error Recovery - see 5.4 (page 52) for details. However, be sure that the millivolt source is
securely connected, functioning properly and the polarity is correct. Press the DOWN key to
bring the instrument back to dELy and try the calibration again. The calibration can be exited
at anytime hLd1 or the reference number is displayed by pressing the SCROLL key.
CAL 2 QUICK CALIBRATION
This routine wil allow the operator to execute a rough calibration on their unit via the keypad
with no other equipment or disturbance to established wiring. It is intended to provide a partial
recovery from a calibration corruption where the necessary equipment indicated in Cal 2-5
may not be available. It should be noted that this is not intended as a substitution to the main
calibration procedure described earlier and may considerably deter from the accuracy of the
instrument.
With CAL2 displayed, press and hold the DOWN ARROW key, then press the SCROLL key.
Release both keys and the instrument will display hLd1. Press and hold the UP ARROW key,
then press the SCROLL key. The display will momentarily blank and then CAL1 will be
displayed. Release both keys and depress the UP ARROW key. CAL will be displayed.
5.2.3 CAL 3 COLD JUNCTION COMPENSATION
This procedure determines and saves calibration values which correct component variations
relating to the cold junction compensation. This calibration must be preceeded by CAL2, the
main calibration, to properly calibrate the instrument. These two calibrations are the only
ones needed for proper operation with a thermocouple input.
Test equipment: one type J thermocouple and one mercury thermometer, accurate to ± .25
degrees C or equivalent are required.
Make sure all input wiring is disconnected and connect the J thermocouple to the input. Place
the thermometer next to the thermocouple and allow the controller to warm up for 30 minutes,
before proceeding with the calibration.
With CAL3 displayed, depress and hold the DOWN key. Then press the SCROLL key and
the unit will display hoLd. Release both keys. Press the DOWN key and deLy will be
displayed for ten seconds, then SCAn for ten seconds. If SCAn remains in the display for
much longer than ten seconds, refer to the note below. The instrument will compute and
display the cold junction temperature to the nearest tenth of a degree C. Compare reading
with thermometer and use the UP and DOWN keys to correct the reading, if necessary. To
end the procedure press the SCROLL key and CAL3 will be displayed again.
NOTE: If the instrument continues to display in SCAn, proceed as follows. With SCAn
displayed, press the SCROLL key. CAL3 should be displayed. With CAL3 displayed, while
pressing the DOWN key, press and release the SCROLL key. The instrument will display
hoLd. Press the UP key. The instrument will begin the calibration procedure with a default
value and proceed to deLy. Complete calibration as described above.
Error Recovery - see 5.4 ( page 52) for details on specific errors. The calibration can be
exited at any time hoLd is displayed by pressing the SCROLL key.
5.2.4 CAL 4 COLD JUNCTION TEMPERATURE UTILITY
This procedure displays the temperature sensed by the cold junction compensator (CJC).
No special test equipment is required.
With CAL4 displayed, press and hold the DOWN key then press the SCROLL key and
release both keys. SCAn will be displayed for ten seconds while the instrument
computes the CJC temperature. The result will then be displayed to a tenth of a degree C.
The input terminals must be shorted with a jumper wire. Remember, the temperature
displayed is that of the CJC terminals not the ambient temperature. To exit, press the
SCROLL key and CAL4 will be displayed.
Page 47

5.2.5 CAL 5 RTD INPUT
This procedure determines and saves calibration values which correct for component variations relating to RTD inputs. This calibration must be preceded by CAL2 to properly
calibrate the unit.
Test equipment needed will include a Decade Box (Resistance Substitution ) with .01%
resolution or equivalent. Make sure the jumpers JU1 (Processor Board), JU2 and JU3
(Options boards) are in the proper positions for RTD input. See Appendix A-2 (page 60) and
A-3 (page 61, 62).
With CAL5 displayed press and hold the DOWN key, then press the SCROLL key and
release both keys. hLd1 will then be displayed. Connect the Decade Box at 100 ohm setting
across the input terminals 1 and 3 and Jumper terminals 1 and 5. Press the DOWN key and
dELy will be displayed for up to ten seconds, then SCAn for ten seconds. When hLd2 is
displayed, connect 277 ohms to the input and press the DOWN key. Again dELy will display
for up to ten seconds, followed by SCAn for ten more seconds. CAL5 will be displayed after
the calibration is completed.
Error Recovery - See section 5.4 (page 51) for details about specific errors.
The Calibration mode can be exited any time the unit displays hLd1 or hLd2 by pressing the
SCROLL key.
5.2.6 CAL 6 COLD JUNCTION ON/OFF
With CAL 6 displayed, while pressing the DOWN ARROW key, press the SCROLL key. The
instrument will display C6 and the number of the mode in effect. Mode 0 is the normal
operating mode. The cold junction compensation is on. Mode 1 is the cold junction compensation disabled (off). Pressing the UP ARROW or DOWN ARROW will change the mode
selection. The Mode 1 functions to facilitate input testing with a non-temperature compensated millivolt source used to simulate thermocouple input.
PAGE 47
Page 48

PAGE 48
Test Mode 5.3
The Test mode can be entered, if enabled, by pressing and releasing the SCROLL key until
tESt is displayed. Press the DOWN key and tSt1 will be displayed. This test can be initiated
at this time or press the SCROLL key to advance to the desired test. Test 1, 2 and 3 are
performed as a block so the display will advance from tSt1 to tSt4.
All available test procedures are listed in TABLE 5-2 (page 49). Test 1, 2, and 3 are performed on start up, periodically during Control, and on entry into the Test mode. Test 4 is
executed on entry into and periodically during the Control mode. These tests can be used as
trouble-shooting aids.
TEST MODE FLOW CHART
tESt
tSt1
ON
OFF
Key
Actual Display
On/Off Display Use arrow keys
to turn on or off
Scroll Key
Numeric Display Use arrow keys
to change value
tSt4
tSt5
tSt6
tSt7
tSt8
tSt9
Up Arrow Key
Down Arrow
tStA
Page 49

TABLE 5-2 TEST PROCEDURES AND DESCRIPTION
TEST DESCRIPTION
Test 1 Microprocessor internal RAM test.; used to verify that the processor RAM is
functioning correctly.
Test 2 External RAM test; used to test the instrument’s RAM for proper
function.
Test 3 EPROM checksum test; used to check program for correct data.
Test 4 External RAM checksum test; displays the number of times Error 16
and 17 have occurred.
Test 5 Verifies that all keys are functional and all LED displays are working.
Test 6 Used to verify that all relays and/or solid state relay driver outputs are working.
Test 7 Used to check the operation of Output 1, mA current output.
Test 8 Used to check the operation of Output 2, mA current output.
Test 9 Auxiliary input test; used to test position proportioning (slidewire
feedback or remote setpoint voltage levels).
PAGE 49
Test A Communications hardware test; tests the send and receive functions.
5.3.1 TEST 1 - INTERNAL RAM TEST
Checks the Random Access Memory in the microprocessor. No special test equipment is
required for this test. With Test 1 displayed tSt1 press and hold the DOWN key then press
the SCROLL key. tSt1 will be displayed momentarily while the test is in progress. Upon
successful completion the instrument will initiate Test 2 automatically.
5.3.2 TEST 2 - EXTERNAL RAM TEST
Checks the operation of the RAM external to the microprocessor. No special test equipment
is required. After completion of Test1, tSt2 will be displayed momentarily while the test is in
progress. Upon successful completion of Test 2, Test 3 will be initiated.
5.5.3 TEST 3 PROGRAM - EPROM TEST
This is a checksum test to verify data integrity of the stored program. No special test equipment is required for this test. After completion of Test 2, tSt3 will be displayed momentarily
while the test is in progress. Upon successful completion the instrument will display tSt1.
5.3.4 TEST 4 - EXTERNAL RAM CHECKSUM TEST
This is a checksum test to verify the integrity of data stored in RAM and indicate the number
of times the instrument has had an Error 16 or 17. No special test equipment is required for
this test. With tSt4 displayed, press and hold the DOWN key then press the SCROLL key.
The display will go blank momentarily, then briefly display two numbers and then tSt4 will be
displayed. These numbers indicate the number of times Error 16 and 17 have occurred
respectively. Test 4 can be executed again, or another test may be selected. Test 4 occurs
when the instrument enters the Control mode and periodically during Control mode operation.
Page 50

PAGE 50
5.3.5 TEST 5 - KEYPAD/DISPLAY TEST
This test allows the operator to verify that the keys work and that all display elements can be
lighted. No special test equipment is required for this test. With tSt5 displayed press and
hold the DOWN key then press the SCROLL key. The display will go blank. Release both
keys, then press each key to be tested.
KEY DISPLAY
SCROLL SCRL
UP KEY uAro
DOWN KEY dAro
UP AND DOWN KEYS ALL LED’s AND SEGMENTS LIGHTED
To exit Test 5, press the SCROLL and UP key simultaneously. tSt5 will be displayed.
5.3.6 TEST 6 RELAY/SSR DRIVER OUTPUT TEST
Verifies that the Relay/SSR Driver output(s) are working. A volt/ohm meter will be useful to
verify the output opertion. With tSt6 displayed press and hold the DOWN key then press the
SCROLL key. oFF will be displayed. For SPST relay outputs, connect the
volt/ohm meter, set to ohms, across the relay outputs. For SSR driver outputs, connect the
volt/ohm meter across the output terminals in the volt/DC mode. Depress the DOWN key
repeatedly to advance through the following sequence:
DISPLAY RELAY ON
rLYA A Only
rLYb B Only
rLYC C Only
oFF None
The relays should be checked for continuity when on and high impedance when off. SSR
drivers will output 5 VDC when on and 0 VDC when off. This sequence may be repeated by
using the DOWN key. To exit press the SCROLL key and tSt6 will be displayed. The
existence of relay SSR outputs is dependent upon the hardware configuration.
5.3.7 TEST 7 - CURRENT OUTPUT 1 TEST
This test allows the user to verify that current Output 1 is functioning properly and will allow
the adjustment of the current output value for testing of associated equipment. A volt meter
with an appropriate shunt resistor or milliamp meter will be needed to execute this test. With
tSt7 displayed, depress and hold the DOWN key, then press the SCROLL key. Connect the
DVM or milliamp meter across the output terminals 5 and 6. The display will indicate 4
milliamps output. Use the UP and DOWN keys to vary the output in 1mA steps. The current
output reading should be ± 0.5mA at any output value. To exit the test, press the SCROLL
key and “tSt7” will be displayed. The existence of the mADC current output is dependent
upon the hardware configuration as indicated by the model number.
5.3.8 TEST 8 - CURRENT OUTPUT 2 TEST
This test is the same as Test 7 except for Output 2. Check the output at terminals 7 and 5.
Page 51

5.3.9 TEST 9 - AUXILIARY INPUT TEST
This test allows the operator to verify that the auxiliary inputs used for position
proportioning (slidewire) feedback or remote setpoint is functioning properly. A variable
voltage source, 5 VDC will be required to execute this test. With tSt9 displayed, press and
hold the DOWN key then press the SCROLL key. The Auxiliary input voltage will be displayed to the nearest hundredth of a volt. Connect the +5V source across the Auxiliary input
terminals (terminals 8 and 5) and adjust the voltage. Verify that the voltage
displayed changes accordingly. The displayed voltage should be typically 0 - 5VDC ± 0.3
volts. To terminate the test, press the SCROLL key. The display will show tSt9.
The existence of the auxiliary input tested in Test 9 depends upon the hardware
configuration as indicated by the model number.
5.3.10 TEST A - COMMUNCATIONS HARDWARE TEST
(Communications Option only)
This test allows the operator to verify that the communications hardware is functioning
properly. With tStA displayed, press and hold the DOWN key then press the SCROLL key.
The display will indicate SEnd. Each time the DOWN key is depressed, the unit will toggle
between SEnd and rEC (receive). With the desired function selected, depress the SCROLL
key.
In the SEnd (send or transmit) mode, the instrument will repeat the following sequence.
First, the transmitter will go logic 1 for one second. Next, the transmitter will change the
logic level to 0 for one second. Then, the transmitter will be disabled for one second. In the
rEC mode, the transmitter will be disabled. In either mode, the instrument will monitor the
line logic level. The display will be rEC0 when a logic 0 is on the line . The display will be
rEC1 when logic 1 is on the line. In the SEnd mode, the unit will display rEC when the
transmitter is disabled.
PAGE 51
To perform an internal test to verify the operation of the hardware, place the instrument in
the Send mode. Verify that the display cycles through rEC1, rEC0, and rEC. To verify that
the transmitter functions properly, two LED’s, each with a current limiting resistor, can be
connected to the communications terminals, with their polarities connected opposite of each
other. The following three states will be produced: one LED on, then the other LED on, then
both off. Alternately, a load resistor can be placed on the terminals, the voltage generated
across the load resistor is as follows: > +3 VDC then > -3VDC and then 0 VDC. The terminals
used are 7 & 8.
Another test method, would be to connect one or more instruments in the Receive mode to an
instrument in the Send mode. The instruments in the Receive mode should have their display
alternating in sync with the instrument that is in the Send mode. When the sending unit
displays rEC, the receiving units should display rE1.
To terminate the test, press the SCROLL key for one second. Upon exit, tStA will be displayed.
Page 52

PAGE 52
Trouble-shooting
and Diagnostics 5.4
This section consists of two columns. The first column is a list of some possible instrument
conditions. The second column is a list of steps that should improve the condition. The steps
should be performed in order until the condition improves or all the steps have been tried. If
the instrument condition has not improved, contact the nearest representative or the factory
for assistance.
Trouble-shooting should be performed by qualified personnel using the proper equipment and
following all safety precautions. Whenever possible, the trouble-shooting should be accomplished with the electrical power disconnected. The instrument contains static sensitive
components so care should be taken to observe anti-static procedures.
Condition Correction Steps
Display is blank (dark) 1. Verify that the correct instrument power, as
indicated on the wiring label on the housing, is
supplied to terminals A & B. If the voltage is not
correct, check the power source.
2. Turn off the instrument power. Wait about 5
seconds, then turn the power on again.
3. Turn off the instrument power, loosen the front
panel screw, and remove the instrument from the
housing. Inspect the instrument for poor
connections.
a. The white ribbon cable that connects the
Processor board (Appendix A-2, page 60)
to the Power Supply Board (Appendix A 1, page 59) must be properly aligned
and seated.
b. The Front Display board pins should be
properly aligned and seated in the
sockets on the Processor board
(Appendix A-2, page 60) and the
Power Supply board (Appendix A-1,
page 59).
c. The Display Driver (U-1), located on the
Display board, must be free of corrosion
and firmly seated in the socket. Reinsert
the instrument in the housing, tighten the
panel screw, and turn on the power.
4. Turn off the instrument power. Press and hold the
UP and DOWN keys. Turn on the power. Hold
the keys depressed for about 10 seconds. If the
display lights the model number, Program and
Tune mode parameters will need to be re-entered
(page 28 & 33 or the Software Ref. Sheet, page
70, if already filled out).
Model Number Displayed 1. Turn off the instrument power, wait 5 seconds then
is incorrect reapply the power. Verify that the number dis-
played during the power up sequence is the same
as indicated on the label affixed to the lower front
of the display bezel.
Page 53

2. Turn off the power to the instrument. Press and
hold the UP and DOWN keys and turn on the
Note: To re-initialize, follow
steps 2 & 3.
Relay/SSR Driver Output(s) 1. Verify that the Program and Tune mode
Malfunction parameters are correctly set (pages 28 & 33 or the
power. Keep the keys depressed until the model
number resets to 2100-000. Release the keys
and turn off the power.
3. To enter the correct model number, press and hold
the SCROLL and DOWN keys and turn on the
instrument power, 2100 should be displayed.
Wait about 5 seconds and release the keys. The
display should remain 2100. Use the UP/DOWN
keys as necessary to change the displayed
number to match the first 4 digits of the model
number. After adjusting the first 4 digits to the
proper values, press the SCROLL key and the
display will change to 000-. Use the UP/DOWN
keys to set the last 3 digits of the model number to
the correct values. Press the SCROLL key and
the power up sequence will complete. The
Program and Tune mode parameters will need to
be re-entered (page 28 & 33 or the Software Ref.
Sheet, page 70, if already filled out).
Software Ref. Sheet, page 70, if already filled out).
2. Turn off the power to the instrument. Wait about 5
seconds and turn the power on again. Confirm
that the model number displayed during the power
up sequence indicates that the output(s) is/are
present in the instrument. This number should
match the number on the label affixed to the lower
front of the display bezel. If model # is incorrect,
follow steps for "Model # displayed is incorrect".
3. Turn off the power to the instrument. Loosen the
front panel screw and remove the unit from the
housing. Inspect the Power Supply board
(Appendix A-1, page 59) for the presence of the
output device(s). Relay A is located at K1, Relay
B at K2, and Relay C at K3. A relay output will
appear to be a cube. The SSR Driver will appear
as a resistor and a jumper wire. The output will
not work if the hardware is not present.
4. Check the output operation by performing Test 6
as described in the Test section (page 48). If the
output(s) function(s) in the Test Mode re-examine
the Program and Tune Mode Parameters settings
(page 28 & 33, or the Software Ref. Sheet, page
68, if already filled out).
5. If the output appears not to turn off, remove the
power to the instrument. Loosen the front panel
screw and take the unit out of the housing. Clip
the resistor located on the Power Supply
(Appendix A-1, page 59) for the output(s) that
seem to stay on. A .01 microfarrad, 1 KV capacitor
should be connected from the terminal listed below, to
the AC ground for the output where the resistor
indicated was removed.
Relay A R12 Terminal C
Relay B R13 Terminal E
Relay C R14 Terminal G
(Continued on next page)
PAGE 53
Page 54

PAGE 54
(Continued from page 53)
Return the instrument to the case and tighten the
front panel screw. Turn the power on to the
instrument and check the operation of the
output(s).
mADC Output(s) 1. Verify that the Program and Tune mode
Malfunction parameters are correctly set (page 28 & 33 or the
Software Ref. Sheet, page 70, if already filled out).
2. Turn off the power to the instrument . Wait about 5
seconds and turn the power on again. Confirm
that the model number displayed during the power
up sequence indicates that the output is present in
the instrument. The number should match the
model number on the label located on the lower
front of the display bezel. If model # is incorrect,
follow steps for "Model # displayed is incorrect"
(page 52).
3. Turn off the power to the instrument. Loosen the
front panel screw and remove the unit from the
housing. Inspect the Option board (Appendix A-3,
page 61, 62) for the presence of the Current Output
Driver IC. Current 1 output is U-1 and Current 2
output is U-5. The current output cannot function
without the hardware being present . Return the
instrument to the housing and tighten the front
panel screw.
4. Refer to the Test section (page 48) and carry out
the procedure for the output(s) that is/are not
working. Test 7 operates current Output 1 and
Test 8 for current Output 2. If the current output
operates properly in the Test mode re-check the
Program and Tune mode parameters (page 28 &
33 or the Software Ref. Sheet, page 70, if already
filled out).
Error Code Displayed - The
display of error codes
will cause on/off outputs
and proportional outputs
to turn off.
SnSr 1. Inspect the sensor for proper operation and
Sensor Break or out of range connection to the instrument. Acceptable sensor
ranges for the instrument are listed in the
Specifications section of Appendix D (page 67).
2. Verify that the Program Mode input selection
matches the sensor input connected.
3. Check that the input conditioning jumpers on the
Processor board (Appendix A-2, page 60) and the
Option Board (Appendix A -3, page 61, 62) are in the
proper position for the sensor input.
4. Perform the calibration procedure(s), as described
in the Calibration section (page 44) , for the sensor
input type.
Page 55

rSEr 1. Check that the Remote Setpoint signal is present
Remote Setpoint Error and of the correct polarity between terminals 8 (+)
and 5 (-).
2. Perform the Auxiliary Input Test, Test 9 as
described in the Test section (page 51), the
voltage indicated during the test should be the
same as measured in the preceeding step.
3. Verify that the Remote Setpoint input voltage range
selected in the Program Mode (page 28) is the
same as the voltage that is present as the Remote
Setpoint input terminals.
FbEr 1. Inspect the Slidewire Feedback connections at
Slidewire Feedback Error terminals 8, 7, and 5. Be sure that the
connections are the same as shown in the position
proportioning illustration (page 21).
2. Measure the resistance of the Slidewire segment.
The minimum resistance must be 135 ohms, the
maximum 10 K ohms.
3. Perform the Auxiliary Input Test. Test 9 as
described in the Test section, the voltage indicated
should be between 0 and 5 VDC.
4. Turn off the power to the instrument. Loosen the
front panel screw and take the instrument out of
the housing. Verify that the jumper JU-1 on the
Option Board (Appendix A-3, page 61, 62) is in the
Motor Modulation position.
PAGE 55
Hi - Input more than 10% 1. Perform the steps listed for the SnSr error
Over Span condition (page 54).
Lo - Input more than 10% 1. Perform the steps listed for the SnSr error
Under Span condition (page 54).
o - display overrange 1. If this error code is displayed as a Program or Tune
(the “broken 6” appears mode parameter value , perform the CAL 1
on the left side of the display) procedure as described in the Calibration
section (page 45).
2. If this error code appears as part of the model
number during the power up sequence, follow the
steps listed for the Model number incorrect
condition (page 52).
Er 1 - Microprocessor RAM 1. Turn off the power to the instrument.
Failure 2. Loosen the front panel screw and remove the
instrument from the housing. Inspect that the
microprocessor (U1) is properly seated in the
socket located on the Processor board (Appendix
A-2, page 60). Return the instrument to the
housing and tighten the front panel screw. Turn
on the power.
Er 2 - External RAM Failure 1. Turn off the power to the instrument. Wait 5
seconds, and turn the power on.
Er 3 - EPROM Checksum 1. Perform the steps listed for Er 1 except that the
Failure EPROM (U2) on the Processor board should be
inspected.
Page 56

PAGE 56
Er 4 - RTD Mismatch Error 1. Check the connections to the instrument for the
RTD Input Calibration CAL5 as described in the
Calibration section (page 47). Repeat the RTD
Input Calibration.
Er 5 - No Zero Crossings 1. Turn off the power to the instrument. Wait 5
Detected seconds and turn the power on.
2. Turn off the instrument power. Loosen the front
panel screw and remove the instrument from the
housing. Inspect the white ribbon cable that
connects the Processor board to the Power
Supply board. Be sure that the cable is properly
aligned and seated in the socket on the Power
Supply board. Return the instrument to the
housing and tighten the front panel screw. Turn
on the power to the instrument.
3. Connect the instrument to another AC power
source.
Er 6 - AC line below 45 HZ 1. Turn off the power to the instrument. Wait 5
seconds and turn the power on.
2. Turn off the instrument power. Loosen the front
panel screw and remove the instrument from the
housing. Inspect the white ribbon cable that
connects the Processor board to the Power
Supply board. Be sure that the cable is properly
aligned and seated in the socket on the Power
Supply board. Return the instrument to the
housing and tighten the front panel screw. Turn
on the power to the instrument.
3. Connect the instrument to another AC power
source.
Er 7 - AC line over 65 HZ 1. Turn off the power to the instrument. Wait 5
seconds and turn the power on.
2. Turn off the instrument power. Loosen the front
panel screw and remove the instrument from the
housing. Inspect the white ribbon cable that
connects the Processor board to the Power
Supply board. Be sure that the cable is properly
aligned and seated in the socket on the Power
Supply board.
Er 8 - Cal 2 Volt Input Error 1. Check that 50 mVDC is properly connected to the
instrument and is within the tolerance limits as
indicated in the CAL 2 procedure of the Calibration
section (page 45).
2. Loosen the front panel screw and remove the
instrument from the housing. Inspect the
Processor board (Appendix A-2, page 60) to
insure that the input conditioning jumper JU 1 is in
the non-volt position.
3. Perform the CAL 2 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 45).
Er 9 - ADC Reference Number 1. Perform the CAL 2 procedure as described in the
Error Calibration section (page 45).
Page 57

Er10 - ADC Reference Voltage 1. Perform the CAL2 procedure as described in the
Error Calibration section (page 45).
Er 11 - Cold Junction 1. Be sure the Cold Junction Sensor is firmly
Compensation Error attached to terminals 2 and 4.
2. Perform the CAL 3 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 46).
Er 12 - CAL 2 Voltage Error 1. Check that 50 mVDC is properly connected to the
instrument and is within the tolerance limits as
indicated in the CAL 2 procedure of the Calibration
section (page 45).
2. Loosen the front panel screw and remove the
instrument from the housing. Inspect the
Processor board (Appendix A-2, page 60) to
insure that the input conditioning jumper JU1 is in
the non-volt position.
3. Perform the CAL 2 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 45).
Er 13 - RTD CAL 5 Input Error 1. Check that the resistance device is of the correct
value and properly connected to the instrument
and is within the tolerance limits as indicated in the
CAL 5 procedure of the Calibration section (page
47).
2. Loosen the front panel screw and remove the
instrument from the housing. Inspect the
Processor board (Appendix A-2, page 60) to
insure that the input conditioning jumper JU1 is in
the non-volt position and that the Option board
jumpers JU2 and JU3 are in the RTD position.
3. Perform the CAL 5 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 47).
PAGE 57
Er 14 - Cold Junction 1. Be sure the Cold Junction Sensor is firmly
Compensation Error attached to terminals 2 and 4.
2. Perform the CAL 3 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 46).
Er 15 - Ground Reference 1. Perform the CAL 2 procedure as described in the
Tolerance Error Calibration section(page 45).
Er 16 - Program/Tune Mode 1. Record all Program and Tune mode Parameters.
Checksum Error Perform the CAL 1 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 45). Re-enter the
Program and Tune mode Parameters (page 28 &
33 or the Software Ref. Sheet, page 70, if already
filled out).
Er 17 - Calibration Checksum 1. Perform the calibration procedures that are needed
Error for the input sensor that will be used.
Er 20 - Setpoint Validation 1. Use the UP or DOWN key to change the setpoint
Error value.
2. Record all Program and Tune mode Parameters.
Perform the CAL 1 procedure as described in the
Calibration section (page 45). Re-enter the
Program and Tune mode Parameters.
Page 58

PAGE 58
Er 36 - Incorrect Crystal 1. Turn off the power to the instrument, wait 5 seconds,
For Digital Comm. then turn the power on.
2. Check crystal, Y1, for 11 MHZ (see Appendix A-2,
Page 60).
Er 37 - Incorrect Micro. 1. Turn off the power to the instrument, wait 5 seconds,
For Digital Comm. then turn the power on.
2. Check to see if U1 is marked "8032" (see Appendix
A-2, Page 60).
Momentary Er 70 - 1. Tried to communicate while unit was in a non-control
Controller unable to respond mode.
within 250 milliseconds.
Momentary Er 71 - 1. The unit received a request before proper amount of
Byte received before the time has elapsed since last request.
response was transmitted.
Momentary Er 72 - 1. Data received not valid, possible corruption on the
Incorrect Block check comm link. Possible noise.
character was received.
Momentary Er 73 - 1. Improper parity selection on the transmitting terminal.
Byte received with incorrect 2. Incorrect baud rate.
parity. 3. Noise
Page 59

Appendix A
Board Layout - Jumper Positioning
FIGURE A-1 - Power Supply Board
TOP
R14
RELAY C
R13
RELAY B
R12
RELAY A
115 VAC JUMPER POSITION
JU6
JU5
JU4
PAGE 59
FRONT
OF UNIT
COMPONENT SIDE
230 VAC UNITS MAY BE
FIELD CONVERTED
TO 115 VAC BY MOVING
JUMPERS AS SHOWN
ABOVE .
115 VAC UNITS CANNOT
BE FIELD CONVERTED
TO 230 VAC!
JU6
JU5
JU4
230 VAC JUMPER POSITION
Page 60

PAGE 60
FIGURE A-2 - Processor Board
Revision L, M and M2
FRONT
OF UNIT
JU1
MICRO U1
BATTERY
T/C,mV,RTD,CAL2
VOLT
TOP
JU2
Y1
REV
EPROM U2
RAM U3
COMPONENT SIDE
JU2
ENABLE MODE
LOCKED
ENABLE MODE
UNLOCKED
Note: Locked and unlocked
positions differ from Rev J and
below and M3 and above.
Located on solder side
J12
JU1
J12
IF NO
OPTION
BOARD
FRONT
OF UNIT
JU1
Revision J and below AND M3 and above
MICRO U1
BATTERY
T/C,mV,RTD,CAL2
VOLT
TOP
EPROM U2
RAM U3
COMPONENT SIDE
JU2
JU2
Y1
REV
ENABLE MODE
UNLOCKED
ENABLE MODE
LOCKED
Located on solder side
J12
Rev. M2 and
above only
JU1
J12
IF NO
OPTION
BOARD
Page 61

FIGURE A-3 - Option Board, Revision E and above (For Rev. D and below, see next page)
PAGE 61
2nd 4-20
*Position
Prop.
Com
RS-485
Com &
2nd 4-20
*Pos. Prop . &
Alt. Com
JU1
JU3
JU2
T/C, mV, V
RTD
XPS
JU2
J15
J16
JU3
JU1
JU13
T/C, mV, V
RTD
XPS
REV
JU14
RSP &
Com
RRH &
Com
Alt.
Com
* Potentiometer Remote Setpoint
JU13
XPS
J15 - AC Input XPS cable from transformer
J16 - XPS to Relay C
JU14
XPSNo XPS No XPS
Page 62

PAGE 62
FIGURE A-3 - Option Board, Revision D and below
REV
FRONT
OF UNIT
For 2nd 4-20mA,
U5 is populated
TOP
JU1
U5
U1
For 1st 4-20mA,
U1 is populated
JU1
2ND 4-20 mADC
MOTOR MODULATION/
POSITION PROPORTIONING
POTENTIOMETER REMOTE
SETPOINT
DIGITAL
COMMUNICATIONS
422/485
COMPONENT SIDE
JU2
JU3
JU2
RTD
T/C, mV, VOLT
JU3
(NON-RTD)
RTD
T/C , mV , VOLT
(NON-RTD)
Page 63

Appendix B
Glossary of Terms
Automatic Reset (Integration)
Automatic reset is a Tune mode parameter that will bias the proportional output(s) to compensate for process load variations. This parameter is adjustable from 0.0 to 100.0 repeats per
minute. Factory default is 0.0. The display codes is ArSt.
Automatic Transfer
Automatic transfer is a Program mode parameter that will allow the instrument to switch from
the Manual to the Control mode of operation automatically when the process value reaches
setpoint.
Balanceless Transfer
This feature prevents changes in proportional output when changing from the Manual to
Control mode of operation. When transferring from the manual mode to the control mode, the
proportional outputs will be "balanceless" regardless of whether the unit is inside or outside
the proportional band. This only holds true if the Auto Reset (ArSt) value is greater than 0.
Bumpless Transfer
This feature prevents changes in proportional outputs when changing from the Control to the
Manual mode of operation only.
PAGE 63
Control Algorithm
A pre-programmed series of instructions that are used by the instrument when
determining the status of the output(s).
Cycle Time
This Tune mode parameter is used to select the on/off cycle time for time proportioning
outputs (Ct1 for Output 1 and/or Ct2 for Output 2). (See page 29, section 4.5)
When using the Position Proportioning option, Ct1 must be selected for the stroke time of the
motor.
Display Filter Factor
This Program mode parameter is used to dampen the process value displayed. The selections range from 1 through 20, the value represents the number of process scans that will be
averaged for the display value. Factory default is 1, no filtering.
Engineering Units Upper and
Engineering Units Lower
These Program mode parameters are used with volt, millivolt, and milliamp inputs. The
Engineering Units Upper Euu should be selected as the value to be displayed when the input
is at maximum. The Engineering Units Lower EuL should be selected as the value to be
displayed when the input is at minimum.
First Output Position
This parameter is adjustable from -1000 to 1000 units and represents a shift or offset of the
on-off actuation points or proportional band for the first output relative to the normal position.
For example, a negative value could be used to offset an expected overshoot. First Output
Position also shifts the proportional band with respect to the process value range outside of
which integral action is inhibited. Factory default is 0. Display code FoP.
Page 64

PAGE 64
Hysteresis
This parameter is adjustable from 0 to 300 units representing the width of the band (half
above and half below setpoint). Used with On-Off or Alarm outputs to reduce cycling. For
instance, with a value of 4 and a setpoint of 70, the output will turn On when the process
variable drops to 68 and stays On until 72 is reached, then turns Off the output. Factory
default is 3. Display code is HySt.
Input Correction
This parameter is used to adjust the process variable value to compensate for sensor errors.
This Program mode parameter is selectable from -300 to + 300 degrees/units. The factory
default is 0.
Manual Reset
This parameter is adjustable from -1500 to 1500 units representing a manual shift of proportional band(s) relative to the normal position. Manual reset is intended to be used when
automatic reset is not used to allow compensation for deviations from setpoint which remain
after the process has stabilized. Factory default is 0. Increasing the value increases the
process variable, i.e. if the process variable stabilized too low, increase the manual set.
Integral action, and conversely reset-windup inhibit apply over the same process value range
regardless of the manuals reset value. Display code rSEt.
Position Proportioning Sensitivity
A percentage of the first output proportional band width (Pb1).
Process Filter Factor
This Program mode parameter is used to dampen the process value used to calculate output
action. The process value is averaged to dampen the control outputs. This parameter is
adjustable from 1 to 20 . Factory default is 1.
Process Retransmission Output (EA Software Option)
This parameter allows for a linear milliamp proportional output relative to the process value.
The current output may be scaled over a range selectable by the user. This output can be
used to supply the process variable signal to remote chart recorders, panel meters, and data
logger instruments.
Process Output Upper and Lower Values (Used in conjunction with process or setpoint
retransmission output)
These parameters specify the process or setpoint value range over which the assigned
current output will vary in a linear manner from 100% to 0%. If the process or setpoint value
is greater than Pou, the output will be 100%. If the process or setpoint value is less than PoL,
the output will be 0%. Factory default values are 2000 for the upper value and 0 for the lower
value. Display codes Pou (upper) and PoL (lower).
Process Rounding
This Program mode parameter is used to determine the step size of the process value that
will be seen on the display. This feature can be used to reduce display fluctuation. This
parameter is adjusted from 1 to 100 degrees/units. The factory default is 1, no rounding (e.g.
Process rounding = 2, Process Value Display - 4, -2, 0, 2, 4, etc.).
Process Variable
The process variable refers to the condition of the process being measured (sensed). The
instrument will accept process inputs other than temperature (pressure, level, flow, etc.).
Proportional Band
This Tune mode parameter selects the span of the proportional output range. This parameter
is adjustable from 1 to 3000 degrees/units. Factory default is 100. If Output 1 is selected as a
proportional output, a display code of Pb1 will be seen. If Output 2 is selected as a proportional output, the display code will be Pb2.
Page 65

Rate (Derivative)
This parameter is adjustable from 0.0 to 10.0 minutes and specifies how the control action
responds to the rate of change in the process variable. For example, if the process variable is
rising rapidly to setpoint, power is turned off sooner than it would be if the rise were slow. In
effect, derivative action anticipates lags within the system and shifts the proportioning band by
an amount determined by the rate of change of the input sensor. Magnitude of the shift is
determined by a derivative time constant. If the time constant is, say, .1 minute (6 seconds),
for every unit per second rate of change of the process variable at the sensor, the proportioning band is moved 7 units in the direction that helps control. Likewise, if the time constant is 1
minute (60 seconds), for every unit per second rate of change of the process variable at the
sensor, the proportioning band is moved 60 units in the direction that helps control. Factory
default is 0.0. Display code rAtE.
Setpoint Re-transmission Output (EA Software Option)
This parameter allows for a linear milliamp output relative to the setpoint value. The current
output may be scaled over a range selectable by the user. This output can be used as a
manual setting station.
Spread (Second Output Position)
This parameter is adjustable from -1000 to 1000 units and represents a shift or offset of the
on-off actuation points or proportional band for the second output relative to the normal
position. A positive value creates a gap where no control outputs are on, a negative value
creates an overlap of control outputs (if the first output position is at the normal position).
Second Output Position also shifts the proportional band with respect to the process value
range outside of which integral action is highlighted (reset-windup inhibit). Factory default is
0. Display code SPrd.
PAGE 65
Setpoint Ramp Rate
This Program mode parameter provides a rate of change control of the instrument setpoint
value. This parameter is used to inhibit sudden upsets in the instrument control caused by
large setpoint changes. This feature also creates a soft start when the instrument power is
turned on. The instrument will read the process value at the time the power was turned on as
the setpoint value. A rate of change ramp will change the internal setpoint to the setpoint
seen by the instrument at the time the power was turned off.
Page 66

PAGE 66
Appendix C - Order Matrix
2
Input
1 T/C or MV
2 Volts/MA
3 RTD
4 All Inputs
Output 1
1 Relay
2 SSR Driver
3 4-20mA
Output 2
0 None
1 Relay
2 SSR Driver
3 4-20mA
Alarm
0 None
1 Relay
2 SSR Driver
Remote
0 None
1 Position Prop. *
2 Remote Setpoint
3 RS-485 Standard Com. **
5 RS-485 Total Access Com. **
Voltage
1 115VAC Input & Relays
2 230VAC Input & Relays
3 115VAC Input, 230VAC Relays
Option Suffix
None (blank)
EA Extended Features Software
EB Extended Features Software***
XP 24VDC Transmitter Power Supply
XA 24VDC Power Supply
BA Remote Keypad
* Limited to Model 2X11X1X or 2X22X1X
** Cannot be included when Output 2 selection is 3.
*** Suffix Option EB includes the EA features.
Page 67

Appendix D - Specifications
Input Specifications
THERMOCOUPLE
TYPE RANGE TYPE RANGE
J -130 TO 760C E 0 TO 750C
-200 TO 1400F 0 TO 1400F
K -130 TO 1370C B 200 TO 1800C
-200 TO 2500F 400 TO 3300F
T -200 TO 400C N 0 TO 1300C
-330 TO 750F 0 TO 2370F
R 200 TO 1650C C 200 TO 2300C
400 TO 3000F 390 TO 4170F
S 200 TO 1650C
400 TO 3000F
PAGE 67
RTD VOLTS MILLIVOLTS
100 ohm 0 to 5 VDC 0 to 25 mVDC
(.00385 OHM/OHM/C) 1 to 5 VDC 0 to 50 mVDC
-140 to 400C 10 to 50 mVDC
-220 to 750F
MILLIAMPS REMOTE SETPOINT
* 0 to 20 mADC 0 to 5 VDC
1 to 5 VDC
* 4 to 20 mADC is accommodated via the 1-5 VDC with the
addition of a shunt resistor.
SENSOR FAULT DETECTION
Displays Hi or Lo process input for thermocouple or RTD inputs (10% above or below range)
and sensor break, SnSr. On/Off outputs and proportional outputs go off. Sensor fault
detection is not functional for 0 to 5 VDC.
Page 68

PAGE 68
Output Specifications
CONTROL OUTPUT 1 AND 2
Relay Output SPST
115 VAC: 5.0 A Resistive; 1/8HP or 250 VA
230 VAC: 2.5 A Resistive; 1/8HP or 250 VA
SSR Driver Open collector output
Short circuit protected at 100 mA maximum
Provides 4 VDC at 20 mA or 3 VDC at 40 mA
Current Output 0-20mADC or 4-20 mADC into 650 ohms maximum.
ALARM OUTPUT
Relay Output SPST
115 VAC: 5.0 A Resistive; 1/8HP or 250 VA
230 VAC: 2.5 A Resistive; 1/8HP or 250 VA
SSR Driver Open collector output
Short circuit protected at 100 mA maximum
Provides 4 VDC at 20 mA or 3 VDC at 40 mA
Display Specifications
Digital Display Four (4) 7 segment LED’s each; .56 inches high
Status Indicators Individual LED indicators for Setpoint, Out 1, Out 2, Manual,
Alarm, Degrees F, Degrees C, or Engineering Units, minus sign for negative values
Alarm Adjustment Specifications
Process Alarm -9999 to 9999 units
Deviation Alarm -3000 to 3000 units
Deviation Band Alarm 1 to 3000 units
Control Adjustments Specifications
On/Off Hysteresis 0 to 300 units
Proportional Band 1 to 3000 units
Manual Reset -1500 to 1500 units
Auto Reset 0.0 to 100.0 repeats/minute
Rate 0.0 to 10.0 minutes
Cycle Time 1 to 240 seconds
Position Proportioning Sensitivity 0.0 to 50.0 %
First Output Position -1000 to 1000 units
Spread -1000 to 1000 units
Page 69

Performance Specifications
Measurement Error Limit • Type J,K,T,E,N, & C thermocouples and RTD
± 0.25% of reading plus 1 degree at 25 degree C
• Type R,S, & B thermocouple ± 0.25% of span at 25C
• mVDC, mADC and VDC ± 0.25% of scaled span plus
1 least significant digit at 25 degrees C
Ambient Temp. Error 0.01% of span per degree C deviation from 25
degrees C
Scan Rate 1 scan per second
3 scans per second with EA Option
Display Resolution 0 to 3 decimal places (depending upon input type
selected)
Auto Reset Windup Inhibit Auto reset is disabled when the process is outside of
the proportional band
Cold Junction Self compensation for ambient temperature. All
Compensation calibration values are stored in memory
PAGE 69
Noise Rejection Normal mode, 85dB minimum at 60 Hz or greater.
Common mode, 90dB minimum ± 8VDC maximum
peak for RTD input, 115 VAC maximum for other inputs
Line Voltage 115/230 VAC ± 10% 50/60 Hz
Power Consumption 15VA maximum
Operating Temperature 0 to 55 degrees C
32 to 131 degrees F
Storage Temperature -40 to 65 degrees C
-40 to 149 degrees F
Humidity 0 to 90% RH, noncondensing
Dimensions 1/4 DIN front panel (96mm X 96mm) 5.8 inches deep
Weight 3 pounds maximum
Vibration 0.5 to 100 Hz at 0.5g
Agency Approvals UL and CSA
Warranty 3 years, see inside back page for more details
Page 70

PAGE 70
Appendix E
Software Record/Reference Sheet
InPs
ICor
out1
o1PL
out2
o2PL
out3
rLyA
rLyb
rLyC
diSP
dPoS
Euu
EuL
HySt
rSP
rSPu
rSPL
SPL
SPuL
EA
SPLL
AtFr
PFF
dFF
FScn
Prnd
Co1r
Co2r
Pout
EA
Pou
PoL
PorA
POAP
EB
SPrr
CCon
CbS
CAd
Comm
SPrd
PAL
dAL
dbAL
Pb1
Pb2
rSEt
ArSt
rAtE
Ct1
Ct2
SEnS
FoP
Program Mode
Continued
Tune Mode
Enable ModeProgram Mode
ENAB ON OFF
EtSt
ECAL
EPro
Etun
ESby
ESPS
ESPC
Page 71

Warranty and Return Statement
These products are sold by the factory under the warranties set forth in the following paragraphs. Such warranties are extended only with respect to a purchase of these products, as
new merchandise, directly from the factory or from a factory distributor, representative or
reseller, and are extended only to the first buyer thereof who purchases them other than for
the purpose of resale.
Warranty
These products are warranted to be free from functional defects in materials and workmanship at the time the products leave the factory and to conform at that time to the specifications
set forth in the relevant instruction manual or manuals, sheet or sheets, for such products for
a period of three years.
THERE ARE NO EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES WHICH EXTEND BEYOND
THE WARRANTIES HEREIN AND ABOVE SET FORTH. THE FACTORY MAKES NO
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCTS.
Limitations
PAGE 71
The factory shall not be liable for any incidental damages, consequential damages, special
damages, or any other damages, costs or expenses excepting only the cost or expense of
repair or replacement as described above.
Products must be installed and maintained in accordance with factory instructions. Users are
responsible for the suitability of the products to their application. There is no warranty against
damage resulting from corrosion, misapplication, improper specifications or other operating
condition beyond our control. Claims against carriers for damage in transit must be filed by
the buyer.
This warranty is void if the purchaser uses non-factory approved replacement parts and
supplies or if the purchaser attempts to repair the product themselves or through a third party
without factory authorization.
Returns
The factory’s sole and exclusive obligation and buyer’s sole and exclusive remedy under the
above warranty is limited to repairing or replacing (at factory’s option), free of charge, the
products which are reported in writing to the factory at its main office indicated below.
The factory is to be advised of return requests during normal business hours and such returns
are to include a statement of the observed deficiency. The buyer shall pre-pay shipping
charges for products returned and the factory or its representative shall pay for the return of
the products to the buyer.
Approved returns should be sent to: 2 CAMPION ROAD
NEW HARTFORD, NY 13413 USA
Page 72

THE PARTLOW-WEST COMPANY
2 CAMPION ROAD • NEW HARTFORD, NY 13413 USA
1-800-866-6659 • 315-797-2222 • FAX 315-797-0403
 Loading...
Loading...