Page 1

PSG1006004CE
Home Theater Audio System
Model No. SU-HTB500PP
SC-HTB500PP
Product Color: (K)...Black Type
A6
Note: Please refer to the original service manual for:
O Wireless Subwoofer Unit SB-WA500PP-K, Order No. PSG1006031CE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAG E PAG E
1 Safety Precautions ----------------------------------------------- 3
1.1. General Guidelines---------------------------------------- 3
1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment ------------------------- 4
1.3. Caution For Fuse Replacement------------------------ 4
1.4. Protection Circuitry ----------------------------------------4
1.5. Safety Part Information -----------------------------------5
1.6. Safety Installation Instructions -------------------------6
2Warning--------------------------------------------------------------7
© Panasonic Corporation 2010. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of
law.
Page 2

2.1. Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD)
to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices ----------7
2.2. Service caution based on Legal restrictions---------8
3 Service Navigation------------------------------------------------9
3.1. Service Information ----------------------------------------9
4 Specifications ---------------------------------------------------- 10
5 Location of Controls and Components------------------ 11
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operations -------------------- 11
5.2. Remote Control Key Buttons Operation ------------ 12
5.3. Audio Information ---------------------------------------- 12
6 Self diagnostic and special mode setting -------------- 13
6.1. Automatically Displayed Error Codes --------------- 13
6.2. Service Mode---------------------------------------------- 14
7 Service Fixture & Tools --------------------------------------- 18
8 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions---------------19
8.1. Disassembly flow chart ---------------------------------20
8.2. Main Parts Location Diagram ------------------------- 20
8.3. Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly ----------21
8.4. Disassembly of Wireless Adapter P.C.B. ---------- 26
8.5. Disassembly of Front Speaker L (SP1) ------------ 28
8.6. Disassembly of Front Speaker R (SP2) ----------- 29
8.7. Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly ---------- 30
8.8. Disassembly of LED P.C.B. and Panel Tact
Switch P.C.B. --------------------------------------------- 33
8.9. Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B. ---------------------- 35
8.10. Disassembly of Main P.C.B. -------------------------- 37
8.11. Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B. ------------------------40
8.12. Replacement of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
----------------------------------------------------------------43
8.13. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5802) ---------- 45
8.14. Disassembly of HDMI P.C.B. ------------------------- 47
9 Service Position ------------------------------------------------- 50
9.1. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B. (Side
A) -------------------------------------------------------------50
9.2. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B. (Side
B) -------------------------------------------------------------51
9.3. Checking and Repairing of Wireless Adapter
P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------------- 52
9.4. Checking and Repairing of SMPS P.C.B. --------- 53
9.5. Checking and Repairing of HDMI P.C.B. (Side
A) ------------------------------------------------------------55
9.6. Checking and Repairing of HDMI P.C.B. (Side
B) ------------------------------------------------------------56
10 Voltage Measurement & Waveform Chart--------------- 57
10.1. HDMI P.C.B. (1/5) --------------------------------------- 57
10.2. HDMI P.C.B. (2/5) --------------------------------------- 58
10.3. HDMI P.C.B. (3/5) --------------------------------------- 59
10.4. HDMI P.C.B. (4/5) --------------------------------------- 60
10.5. HDMI P.C.B. (5/5) --------------------------------------- 61
10.6. MAIN P.C.B. (1/2) ----------------------------------------62
10.7. MAIN P.C.B. (2/2) ----------------------------------------63
10.8. LED P.C.B. ------------------------------------------------- 63
10.9. SMPS P.C.B. ----------------------------------------------64
10.10. WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B. ------------------------ 64
10.11. Waveform Chart (1/2) ----------------------------------- 65
10.12. Waveform Chart (2/2) ----------------------------------- 66
11 Illustration of IC’s, Transistors and Diodes ------------67
12 Overall Simplified Block -------------------------------------- 68
13 Block Diagram --------------------------------------------------- 69
13.1. SYSTEM CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM ---------- 69
13.2. HDMI BLOCK DIAGRAM ------------------------------ 70
13.3. AUDIO (1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM --------------------- 71
13.4. AUDIO (2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM --------------------- 72
13.5. IC TERMINAL CHART (HDMI/AUDIO) ------------ 73
13.6. POWER SUPPLY (1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM------- 74
13.7. POWER SUPPLY (2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM------- 75
14 Wiring Connection Diagram -------------------------------- 77
15 Schematic Diagram Notes ----------------------------------- 79
16 Schematic Diagram -------------------------------------------- 81
16.1. HDMI CIRCUIT (1/6)------------------------------------ 81
16.2. HDMI CIRCUIT (2/6)------------------------------------ 82
16.3. HDMI CIRCUIT (3/6)------------------------------------ 83
16.4. HDMI CIRCUIT (4/6)------------------------------------ 84
16.5. HDMI CIRCUIT (5/6)------------------------------------ 85
16.6. HDMI CIRCUIT (6/6)------------------------------------ 86
16.7. MAIN CIRCUIT (1/4) ------------------------------------ 87
16.8. MAIN CIRCUIT (2/4) ------------------------------------ 88
16.9. MAIN CIRCUIT (3/4) ------------------------------------ 89
16.10. MAIN CIRCUIT (4/4) ------------------------------------ 90
16.11. LED CIRCUIT, PANEL TACT SWITCH
CIRCUIT, AC INLET CIRCUIT ----------------------- 91
16.12. SMPS CIRCUIT (1/2) ----------------------------------- 92
16.13. SMPS CIRCUIT (2/2) ----------------------------------- 93
16.14. WIRELESS ADAPTER CIRCUIT -------------------- 94
17 Printed Circuit Board------------------------------------------ 95
17.1. HDMI P.C.B. (SIDE A) --------------------------------- 95
17.2. HDMI P.C.B. (SIDE B) --------------------------------- 96
17.3. MAIN P.C.B. (SIDE A) ---------------------------------- 97
17.4. MAIN P.C.B. (SIDE B) ---------------------------------- 98
17.5. LED P.C.B., PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B.------- 99
17.6. AC INLET P.C.B., SMPS P.C.B., WIRELESS
ADAPTER P.C.B. ---------------------------------------100
18 Terminal Function of IC’s ----------------------------------- 101
18.1. IC604 (RFKWMHTB500P) IC MICRO
PROCESSOR -------------------------------------------101
18.2. IC2002 (RFKWMHTB10PB) IC MICRO
PROCESSOR -------------------------------------------102
19 Exploded View and Replacement Parts List---------- 103
19.1. Exploded View and Mechanical replacement
Parts List--------------------------------------------------103
19.2. Electrical Replacement Parts List ------------------107
2
Page 3
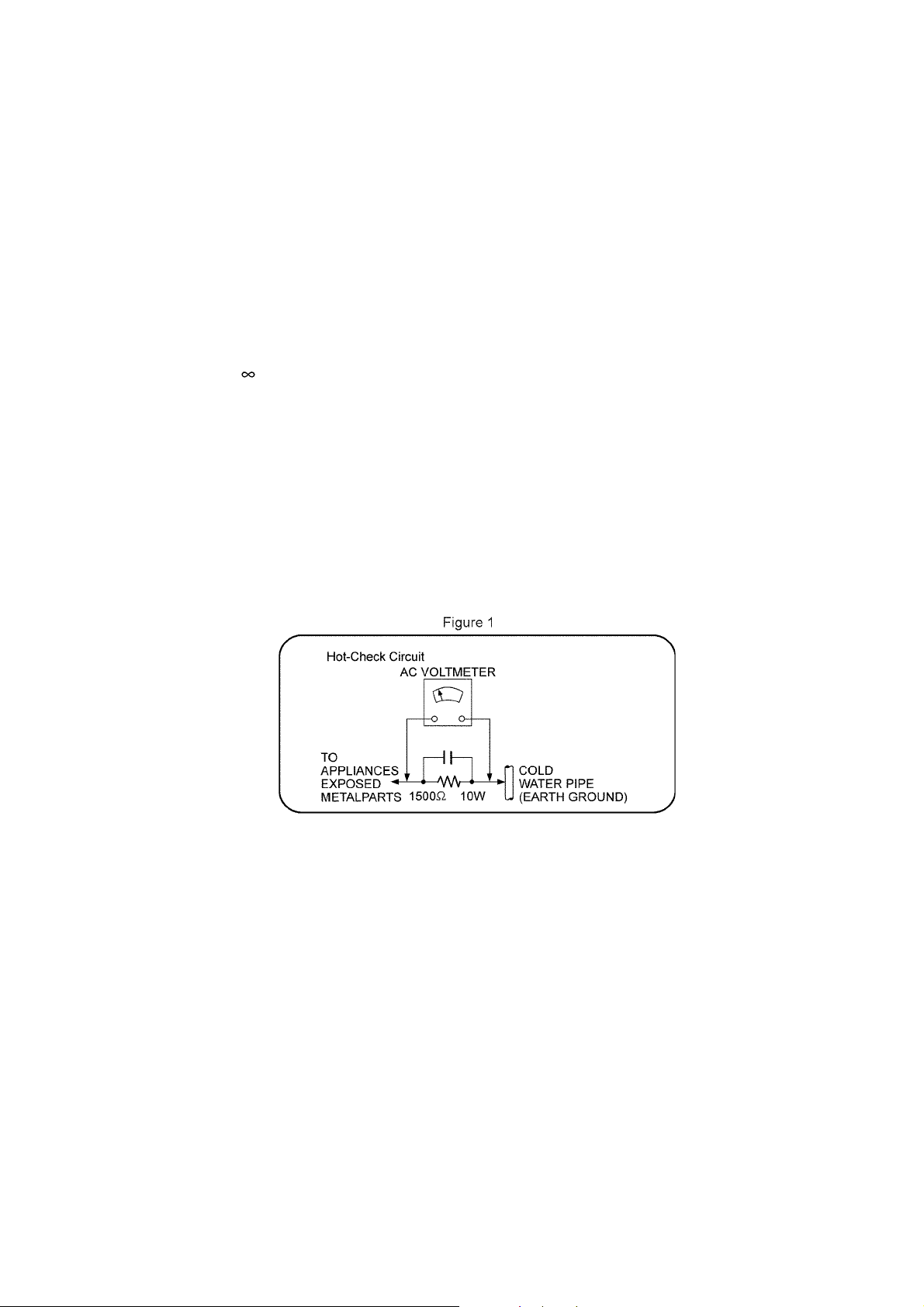
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, ensure that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, check for leakage current checks to prevent from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Using an ohmmeter measure the resistance value, between the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet part on
the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to the
chassis, the reading should be between 1MΩ and 5.2Ω. When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis,
the reading must be
1.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15μF capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set and a
good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or equivalent)
may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. should the measurement is outside of
the limits specified, there is a possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and re-checked before it is
returned to the customer.
3
Page 4

1.2. Before Repair and Adjustment
Disconnect AC power, discharge unit AC Capacitors for:
(C5700, C5701, C5702, C5703, C5704, C5706, C5708) through a 10Ω, 1W resistor to ground.
DO NOT SHORT-CIRCUIT DIRECTLY (with a screwdriver blade, for instance), as this may destroy solid state devices.
After repairs are completed, restore power gradually using a variac, to avoid overcurrent.
• Current consumption at AC 120 V, at 60 Hz in NO SIGNAL mode, at volume minimum, SEL: HDMI/D-IN should be ~200 mA.
1.3. Caution For Fuse Replacement
1.4. Protection Circuitry
The protection circuitry may have operated if either of the following conditions are noticed:
• No sound is heard when the power is turned on.
• Sound stops during a performance.
The function of this circuitry is to prevent circuitry damage if, for example, the positive and negative speaker connection wires are
"shorted", or if speaker systems with an impedance less than the indicated rated impedance of the amplifier are used.
If this occurs, follow the procedure outlines below:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Determine the cause of the problem and correct it.
3. Turn on the power once again after one minute.
Note:
When the protection circuitry functions, the unit will not operate unless the power is first turned off and then on again.
4
Page 5
1.5. Safety Part Information
Safety Parts List:
There are special components used in this equipment which are important for safety.
These parts are marked by in the Schematic Diagrams & Replacement Parts List. It is essential that these critical parts should
be replaced with manufacturer’s specified parts to prevent shock, fire or other hazards. Do not modify the original design without
permission of manufacturer.
Safety Ref. No. Part No. Part Name & Description Remarks
2 REXX1104 1P RED/BLACK WIRE (AC INLET-SMPS)
17 RGNX1156-K1 SPEC LABEL
A2 RFAX1027 AC CORD/W FERRITE CORE
A3 RQTX1179-2Y O/I BOOK (En/Cf)
PCB1 REPX0840D HDMI P.C.B. (RTL)
PCB2 REPX0839KA MAIN P.C.B. (RTL)
PCB5 REPX0841BA SMPS P.C.B. (RTL)
PCB6 REPX0841BA AC INLET P.C.B. (RTL)
DZ5701 ERZV10V511CS ZNR
L5701 ELF15N007A FILTER
L5702 ELF19H010A FILTER
T5703 ETS28BH1E5AC TRANSFORMER
T5751 ETS19AB2A6AG SUB TRANSFORMER
PC5720 B3PBA0000402 PHOTO COUPLER
PC5799 B3PBA0000402 PHOTO COUPLER
RY5701 K6B1AEA00003 RELAY
F1 K5D252APA008 FUSE
FP700 K5H302100004 FUSE PROTECTOR
TH5702 D4CAA5R10001 THERMISTOR
P5701 K2ABYA000001 AC INLET
C5700 F1BAF2220023 2200pF
C5701 F0CAF104A105 0.1uF
C5702 F0CAF104A105 0.1uF
C5703 F0CAF104A105 0.1uF
C5704 F1BAF1020020 1000pF
C5706 F1BAF1020020 1000pF
C5708 F1BAF1020020 1000pF
5
Page 6

1.6. Safety Installation Instructions
6
Page 7

2Warning
2.1. Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by electricity. Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and semiconductor “chip” components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by
electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equiped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equiped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as aluminium foil, to prevent electrostatic charge build up or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder remover device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static (ESD protected)” can
generate electrical charge to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminium foil or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient
to damage an ES device).
7
Page 8
2.2. Service caution based on Legal restrictions
2.2.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical components on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainly consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30 degrees C (86°F) more than that
of the normal solder.
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
The letter of “PbF” is printed either foil side or components side on the PCB using the lead free solder.
(See right figure)
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
• The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used.
(Definition: The letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
• To put lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
• Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
• Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt the
lead free solder.
• Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equipped with the temperature control after setting the temperature at 350±30 degrees
C (662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
• The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: Tin (Sn), 96.5%, Silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
8
Page 9

3 Service Navigation
3.1. Service Information
This service manual contains technical information which will allow service perssonnel’s to understand and service this model.
Please place orders using the parts list and not the drawing reference numbers.
If the circuit is changed or modified, this information will be followed by supplement service manual to be filed with original service
manual.
• Micro-processor :
1. The following components are supplied as an assembled part.
• Micro-processor IC, IC604 (RFKWMHTB500P).
• Micro-processor IC, IC2002 (RFKWMHTB10PB).
9
Page 10

4 Specifications
Q GENERAL
Power consumption: Main unit : 27 W
Digital transmitter : 1.2 W
Power consumption in standby mode: Main unit : Approx. 0.1 W
Power supply: AC 120 V, 60 Hz
Dimensions (W x H x D):
Main unit :
(Without wall mount bracket) 1029 mm x 108 mm x 58 mm (10 1/2” x 4 1/4” x 2 9/32”)
(With wall mount bracket) 1029 mm x 108 mm x 80 mm (10 1/2” x 4 1/4” x 3 5/32”)
Digital transmitter : 43.5 mm x 37.3 mm x 8.2 mm (1 23/32” x 1 15/32” x 5/16”)
Mass:
Main unit :
(Without wall mount bracket) Approx. 2.8 kg (6.2 lbs)
(With wall mount bracket) Approx. 2.9 kg (6.4 lbs)
Digital transmitter : Approx. 0.0095 kg (0.0209 lbs)
Operating temperature range: 0°C to +40°C (+32°F to +104°F)
Operating humidity range: 20% to 80% RH (no condensation)
Q AMPLIFIER SECTION
RMS Output Power
Front ch: 60 W per channel (4 Ω), 1 kHz, 10% THD
Total RMS Dolby Digital mode power: 240 W
FTC Output Power
Front ch: 25 W per channel (4 Ω), 120 Hz to 20 kHz, 1% THD
Total FTC Dolby Digital mode power: 87 W
Q SPEAKER SECTION
FRONT SPEAKERS (BUILT-IN)
Type: 1 way 1 speaker system (Bass Reflex)
Full range: 6.5 cm (2 1/2”) Cone type x 2
Output sound pressure: 78 dB/W(1m)
Frequency range: 35 Hz to 180 Hz (-16dB)
40 Hz to 160 Hz (-10dB)
Q TERMINAL SECTION
HDMI This unit supports “HDAVI Control 5” function.
HDMI input
Input Connector: Type A (19 pin)
HDMI AV output
Output Connector: Type A (19 pin)
Digital Audio Input (TV only)
Optical digital input: Optical terminal
Sampling frequency: 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz
Audio Format: LPCM, Dolby Digital
IR Blaster
Terminal 1: 3.5 mm (1/8”) jack
Q WIRELESS SECTION
Wireless module
Frequency range: 2.4 GHz to 2.4835 GHz
Number of channels: 3
Note:
1. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
2. Total harmonic distortion is measured by the digital spectrum analyzer.
10
Page 11
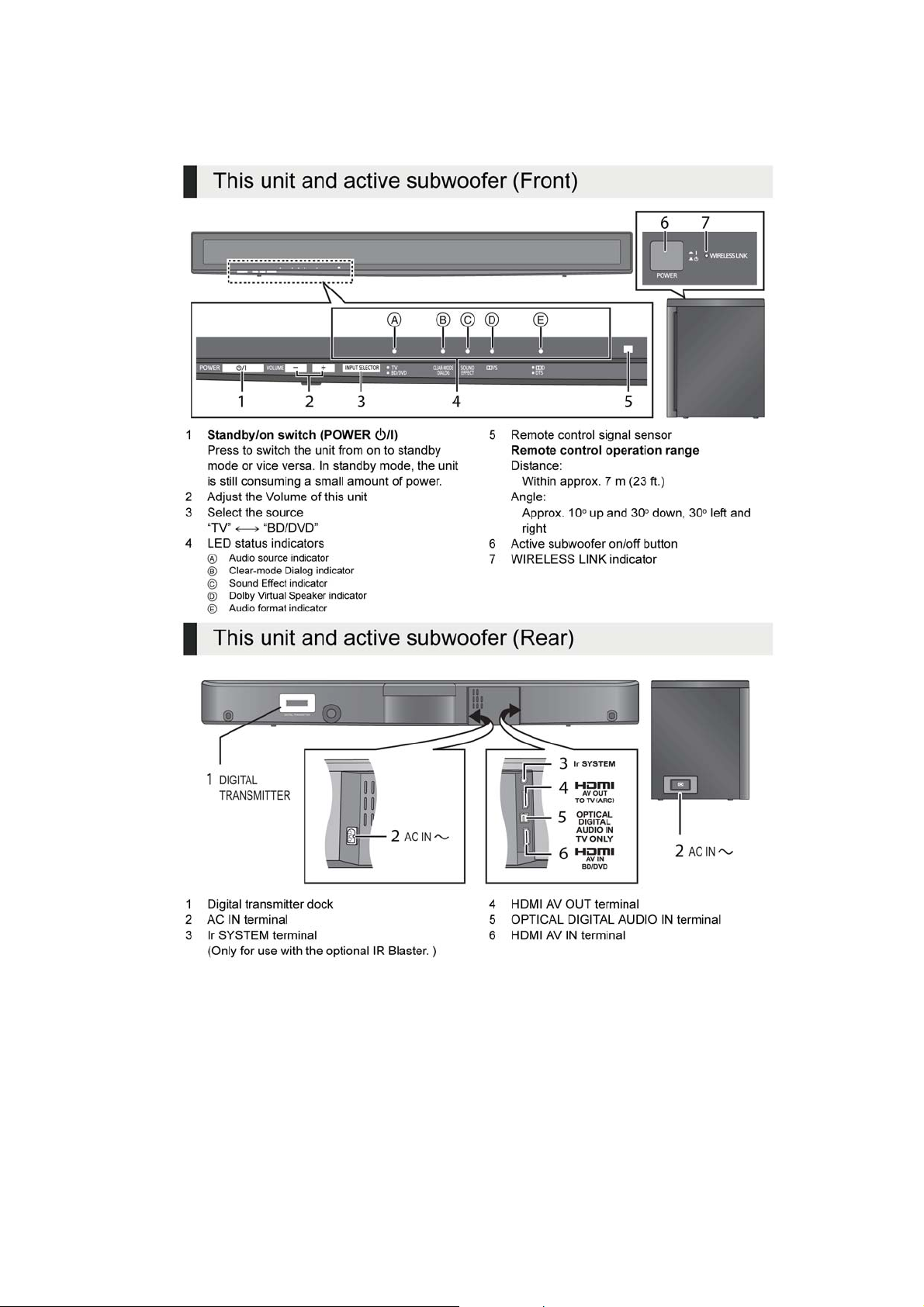
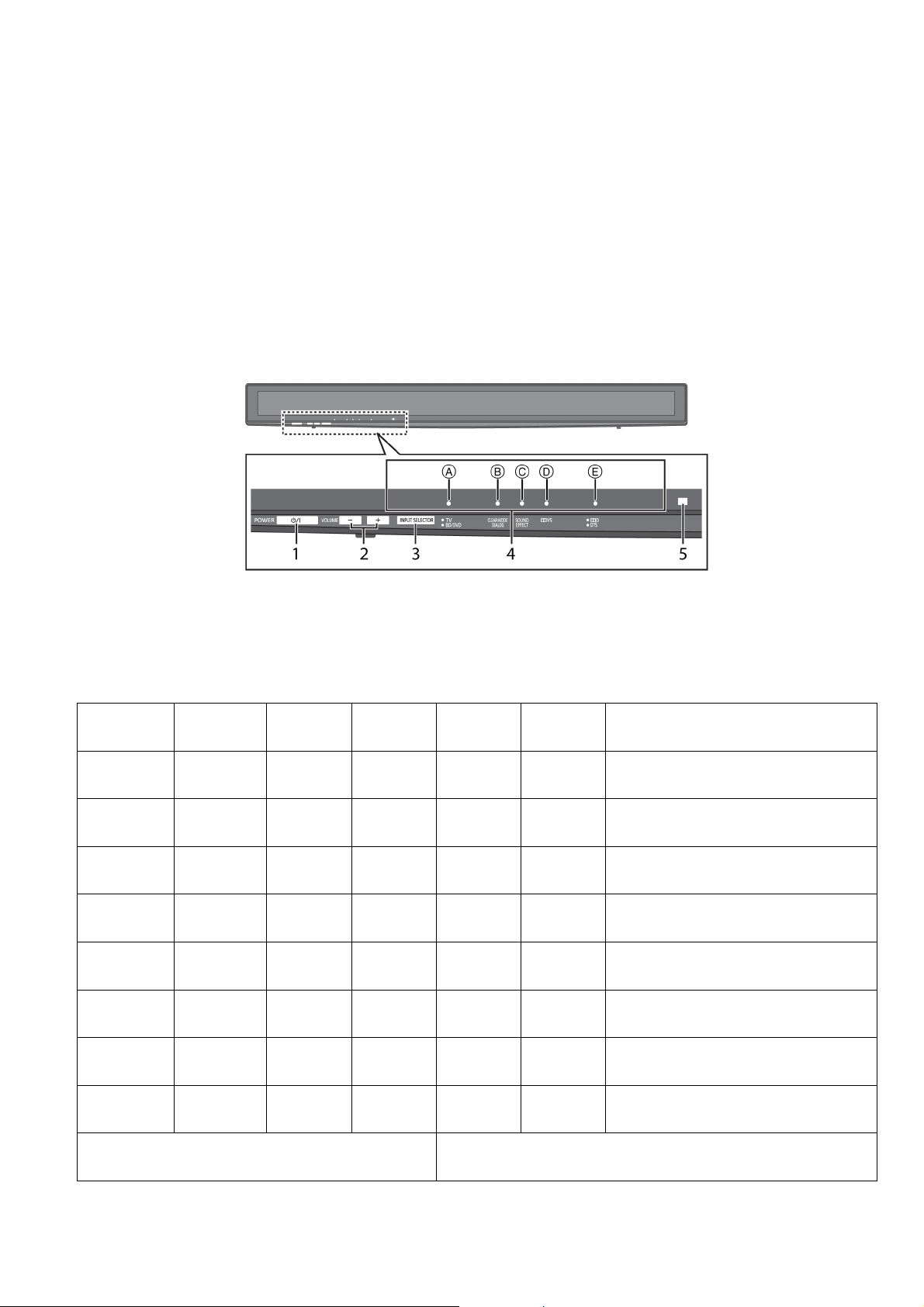
5 Location of Controls and Components
5.1. Main Unit Key Button Operations
11
Page 12

5.2. Remote Control Key Buttons Operation
5.3. Audio Information
12
Page 13
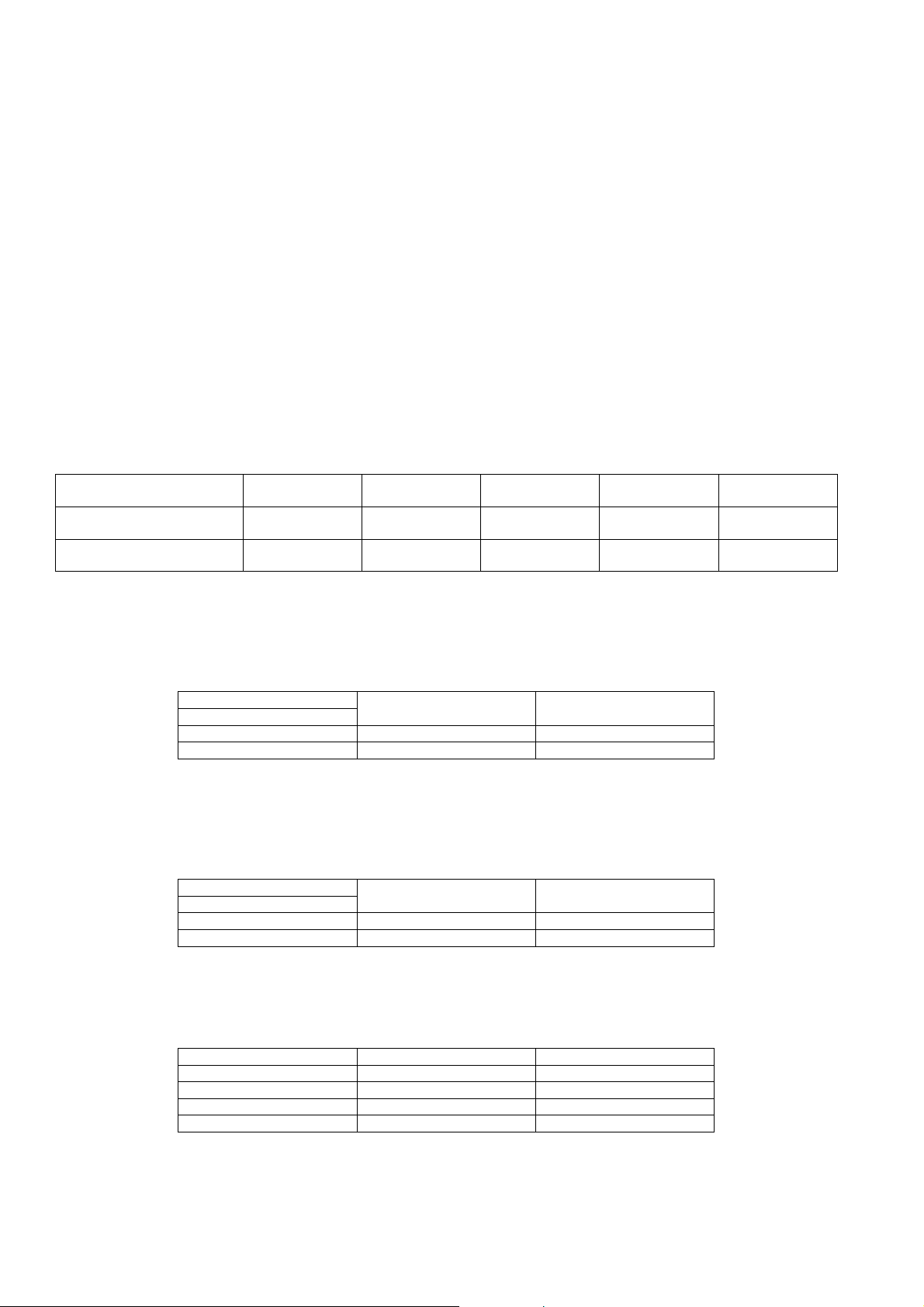
6 Self diagnostic and special mode setting
This unit is equipped with features of self-diagnostic & special mode setting for checking the functions & reliability.
Special Note : Checking of the reliability (ageing) & changer operation must be carry out to ensure good working condi-
tion in unit.
6.1. Automatically Displayed Error Codes
This model does not have a display unit hence error code (when a fault condition occurs) is represented by the LED status indicators. Refer to Fig 6.1
Here is the description of the LED status indicators:
LED 1 Audio source Indicator (TV, BD/DVD)
LED 2 Clear-mode Dialog indicator (Clear-Mode)
LED 3 Sound Effect Indicator (Sound-Effect)
LED 4 Dolby Virtual Sound Indicator (DVS)
LED 5 Audio Format Indicator (DD/DTS)
Fig 6.1
6.1.1. Error Code Display Details by LED Blinking Indicators
This section describes the LED status indicators by its blinking to represent the error codes.
Caution: The LED blinking process will stop only when the unit is power-off completely.
Error Code LED 1 (TV/BD/
DVD)
OVERLOAD
(F61) X XXX *
F76
* XXXX
F70 DSP
X XXX*2
F70 DAP
X XXX*3
F70 HDMI
X XXX*4
U701
*2 XXXX
U703
*3 XXXX
U704
*4 XXXX
“X” means LED off.
“*” means LED blink (RED) 1 time, then off.
“*2” means LED blink (RED) 2 times, then off.
LED 2
(CLEAR-
MODE)
LED 3
(SOUNDEFFECT)
LED 4 (DVS) LED 5 (DD/
DTS)
Speaker protection, D-AMP IC or Fan abnormality. Check for faulty parts and replace with
new parts if necessary.
DC Power/Voltage Supply abnormality. Check
for faulty parts and replace with new parts if
necessary.
DSP - Main Micro-p IC communication failure/
abnormality. Check for faulty parts and replace
with new parts if necessary.
DAP - Main Micro- P IC communication failure /
abnormality. Check for faulty parts and replace
with new parts if necessary.
HDMI to Main Micro-P IC communication error.
Check for faulty parts and replace with new
parts if necessary.
Connected devices error (HDCP non-compliance). Check for faulty parts and replace with
new parts if necessary.
HDMI connectionabnormality (cable damage,
HDCP non-complianceetc). Check for faulty
parts and replace with new parts if necessary.
HDMI image format incompatibility. Check for
faulty parts and replace with new parts if neces-
sary.
“*3” means LED blink (RED) 3 times, then off.
“*4” means LED blink (RED) 4 times, then off.
Table 6-1
Cause and Problem
13
Page 14
6.2. Service Mode
This mode can be used during servicing.
Here are the procedures to enter into service mode:
Step 1 : Power-up the main unit.
Step 2 : Press & hold [VOL+] button, [VOL-] button and [POWER] button on main unit.
This unit is equipped with service mode function for:
Step 1 : Checking the region/model and generation no.
Step 2 : Checking the Main micro-p & HDMI micro-p firmware version.
Legend:
“O” means LED ON
“X” means LED OFF
6.2.1. Checking of Main Micro-p Firmware version
Here are the procedures to check the region/model, generation no. and main firmware version:
Step 1 : Power-up the main unit.
Step 2 : Enter into service mode. (Refer to Section 6.2 for the procedures).
Step 3 : Press [VOL+] to check for the region/model & generation no. (Refer to table 6-2 for information on the LED indication).
Step 4 : Press [VOL+] to check for the main micro-p firmware version no. (Refer to table 6-2 for information on the LED indication).
Key Operation LED 1 (TV/BD/DVD) LED 2 (CLEAR-
Press [VOL+] button on main
unit for one time
Press [VOL+] button on main
unit for two times
Generation Bit No. Model Bit No. Region Bit 1 Region bit 0 O
Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
MODE)
LED 3 (SOUND-
EFFECT)
LED 4 (DVS) LED 5 (DD/DTS)
Table 6-2
6.2.1.1. Generation Bit No.
The generation bit no. is used for indication of the Model Year. (Refer to table 6-3 for more information).
Generation Bit Number Model By Year
(TV/BD/DVD) LED
X 0 2010
O 1 2011
Table 6-3
6.2.1.2. Model Bit No.
The model bit no. is to indicate the software for the specific model. (base on chip-select detection).
(Refer to table 6-4 for more information)
Model Bit Number Model No.
CLEAR-MODE LED
X 0 HTB500
O 1 HTB10/50
Table 6-4
(Green)
6.2.1.3. Region Bit No.
The region bit no. is to indicate the destination for model. (Refer to table 6-5 for more information).
Region Bit 1 Region Bit 0 Main Software
SOUND EFFECT DVS By Destination
X X 0 : Japan
X O 1 : US
O X 2 : Europe/Asia
Table 6-5
14
Page 15
6.2.1.4. Firmware version Bit No. (Bit 0~4)
It is to indicate the firmware version no. (Bit 0 ~4). (Refer to table 6-6 for more information).
Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Version No
DVS DPLII DOLBY DTS PCM/AAC
XXXXX 00
XXXXO 01
XXXOX 02
XXXOO 03
XXOXX 04
XXOXO 05
XXOOX 06
XXOOO 07
XOXXX 08
XOXXO 09
XOXOX 10
XOXOO 11
XOOXX 12
XOOXO 13
XOOOX 14
XOOOO 15
OXXXX 16
OXXXO 17
OXXOX 18
OXXOO 19
OXOXX 20
OXOXO 21
OXOOX 22
OXOOO 23
OOX X X 24
OOX XO 25
OOX OX 26
OOX OO 27
OOOX X 28
OOOX O 29
OOOOX 30
OOOOO 31
Table 6-6
15
Page 16
6.2.2. Checking of HDMI Micro-p Firmware version
Here are the procedures for checking the HDMI micro-p firmware version no:
Step 1 : Enter into service mode. (Refer to Section 6.2 for the procedures)
Step 2 : Press [VOL-] to check the region no. (Refer to table 6-7 for information).
Step 3 : Press [VOL-] to check the HDMI micro-p firmware version no. (Refer to table 6-7 for information).
Key Operation LED 1 (TV/BD/DVD) LED 2 (CLEAR-
Press [VOL-] button on main
unit
Press [VOL-] button on main
unit
Generation Bit No. Model Bit No. Region Bit 1 Region bit 0 O
Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
MODE)
LED 3 (SOUND-
EFFECT)
LED 4 (DVS) LED 5 (DD/DTS)
Table 6-7
6.2.2.1. Generation Bit No.
The generation bit no. is used for indication of the Model Year. (Refer to table 6-8 for more information).
Generation Bit Number Model By Year
(TV/BD/DVD) LED
X 0 2010
O 1 2011
Table 6-8
6.2.2.2. Model Bit No.
The model bit no. is to indicate the software for the specific model. (base on chip-select detection).
(Refer to table 6-9 for more information)
Model Bit Number Model No.
CLEAR-MODE LED
X 0 HTB500
O 1 HTB10/50
Table 6-9
(Green)
6.2.2.3. Region Bit No.
The region bit no. is to indicate the destination for model. (Refer to table 6-10 for more information).
Region Bit 1 Region Bit 0 HDMI Software
SOUND EFFECT DVS By last 2 digit
XX Invalid
XO For Japan
O X For Others
OO Invalid
Table 6-10
16
Page 17
6.2.2.4. Firmware version Bit No. (Bit 0~4)
It is to indicate the firmware version no. (Bit 0 ~4). (Refer to table 6-9 for more information).
Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Version No
DVS DPLII DOLBY DTS PCM/AAC
XXXXX 00
XXXXO 01
XXXOX 02
XXXOO 03
XXOXX 04
XXOXO 05
XXOOX 06
XXOOO 07
XOXXX 08
XOXXO 09
XOXOX 10
XOXOO 11
XOOXX 12
XOOXO 13
XOOOX 14
XOOOO 15
OXXXX 16
OXXXO 17
OXXOX 18
OXXOO 19
OXOXX 20
OXOXO 21
OXOOX 22
OXOOO 23
OOX X X 24
OOX XO 25
OOX OX 26
OOX OO 27
OOOX X 28
OOOX O 29
OOOOX 30
OOOOO 31
Table 6-11
6.2.3. Cold start
Here are the procedures to do a reset for the main unit.
Step 1 : Power-up the main unit.
Step 2 : Press & hold [POWER] button on main unit for 4s or more.
All LED will light-up and blink for 2 times (at frequency of 4Hz)
17
Page 18

7 Service Fixture & Tools
Prepare service tools before proccess service position.
Ref. No. Service Tools Remarks
SFT1 Main P.C.B. (CN700) - SMPS P.C.B. (H2016) REXX1103 (10P Cable Wire)
18
Page 19

8 Disassembly and Assembly Instructions
Caution Note:
• This section describes the disassembly and/or assembly procedures for all major printed circuit boards & main components for
the unit. (You may refer to the section of “Main components and P.C.B Locations” as described in the service manual)
• Before carrying out the disassembly process, please ensure all the safety precautions & procedures are followed.
• During the disassembly and/or assembly process, please handle with care as there may be chassis components with
sharp edges.
• Avoid touching heatsinks due to its high temperature after prolong use. (See caution as described below)
• During disassembly and assembly, please ensure proper service tools, equipments or jigs is being used.
• During replacement of component parts, please refer to the section of “Replacement Parts List” as described in the
service manual.
• Select items from the following indexes when disassembly or replacement are required.
• Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly
• Disassembly of Wireless Adapter P.C.B.
• Disassembly of Front Speaker L (SP1)
• Disassembly of Front Speaker R (SP2)
• Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly
• Disassembly of LED P.C.B. and Panel Tact Switch P.C.B.
• Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B.
• Disassembly of Main P.C.B.
• Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.
• Replacement of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
• Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5802)
• Disassembly of HDMI P.C.B.
19
Page 20
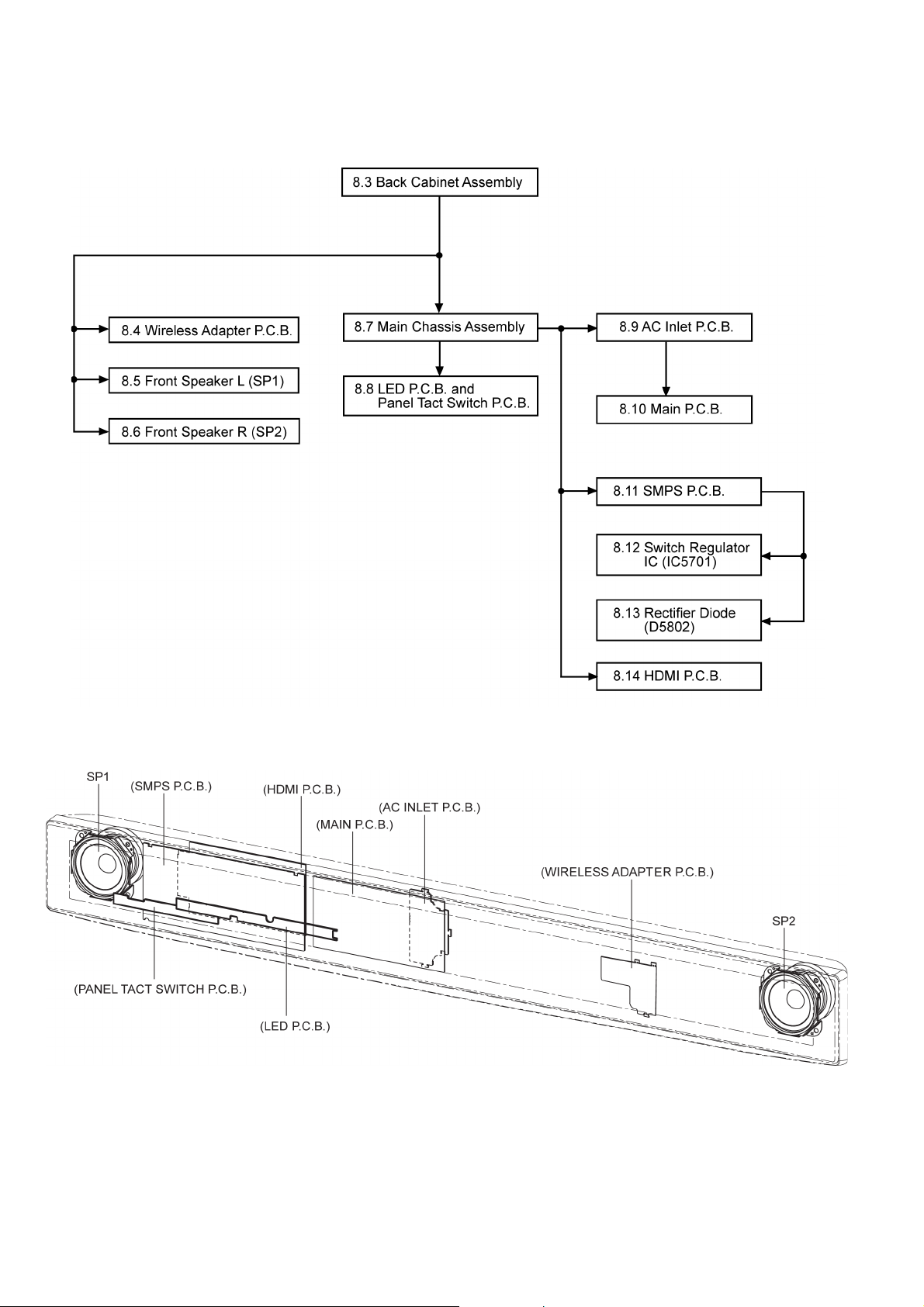
8.1. Disassembly flow chart
The following chart is the procedure for disassembling the casing and inside parts for internal inspection when carrying out the servicing.
To assemble the unit, reverse the steps shown in the chart below.
8.2. Main Parts Location Diagram
20
Page 21
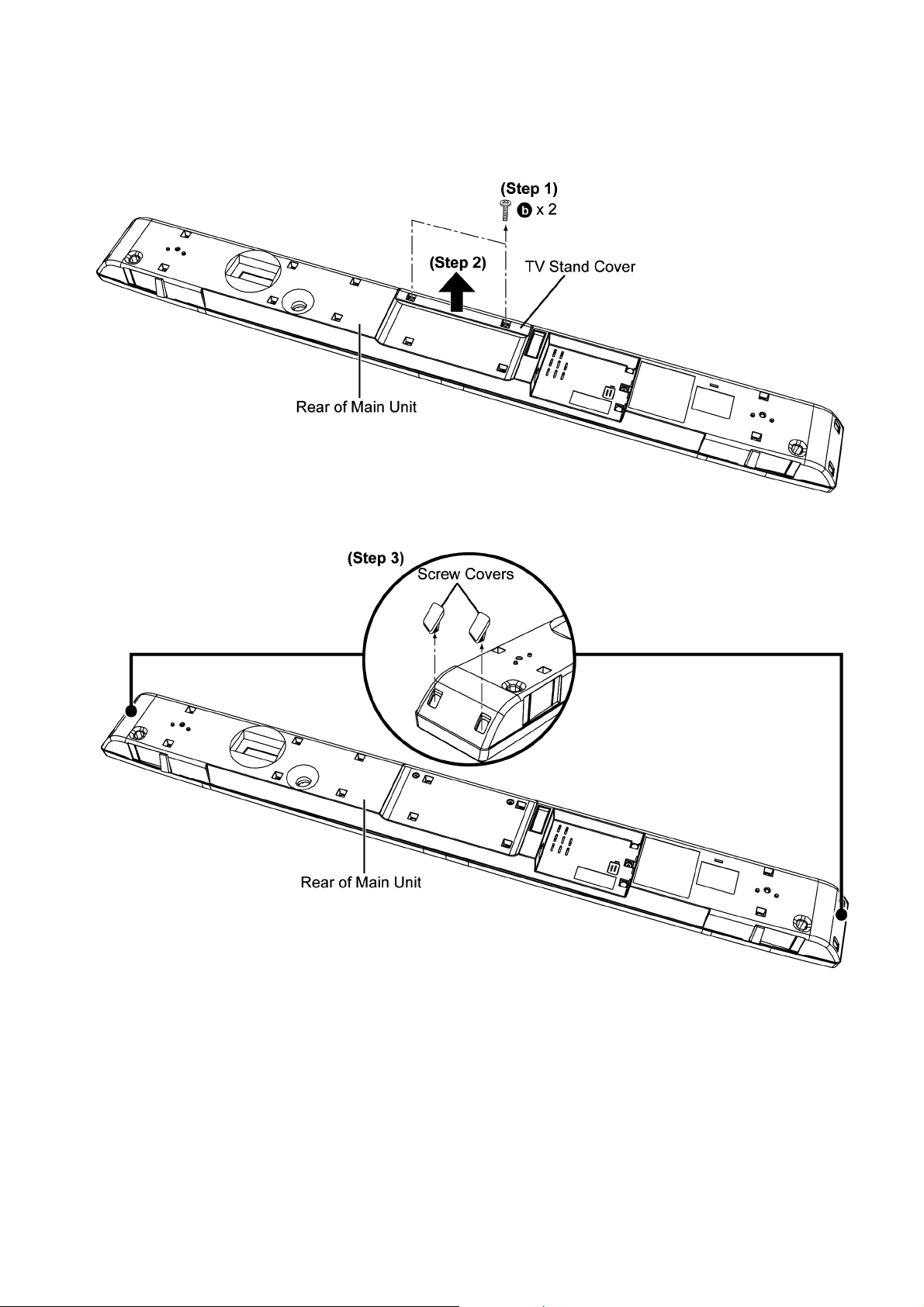
8.3. Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly
Step 1 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 2 : Remove the TV Stand Cover as arrow shown.
Step 3 : Remove 4 Screw Covers.
21
Page 22
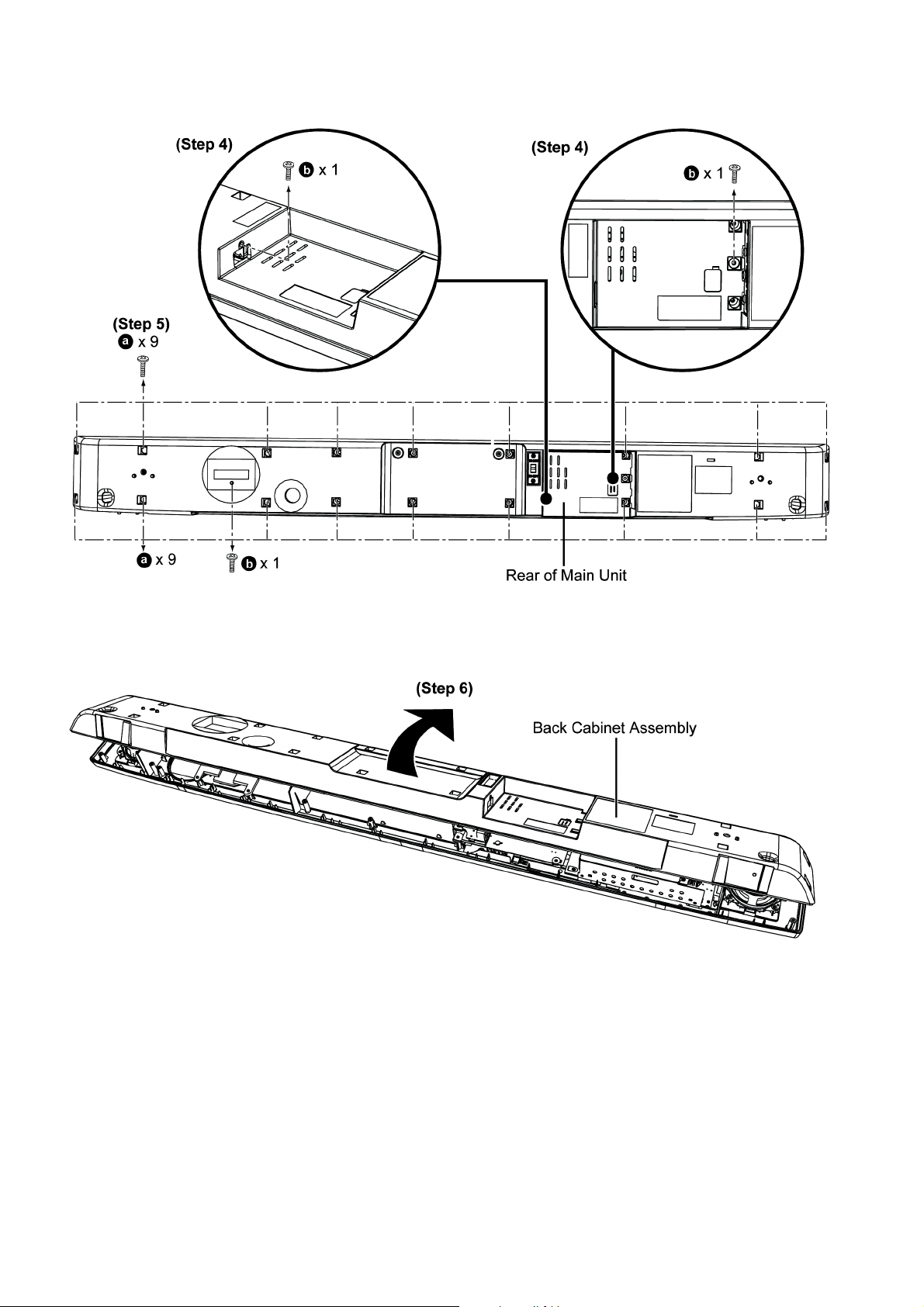
Step 4 : Remove 3 screws.
Step 5 : Remove 18 screws.
Step 6 : Lift up and flip over the Back Cabinet Assembly as arrow shown.
Caution : Do not exert too much force as it may damage the wiring within.
22
Page 23
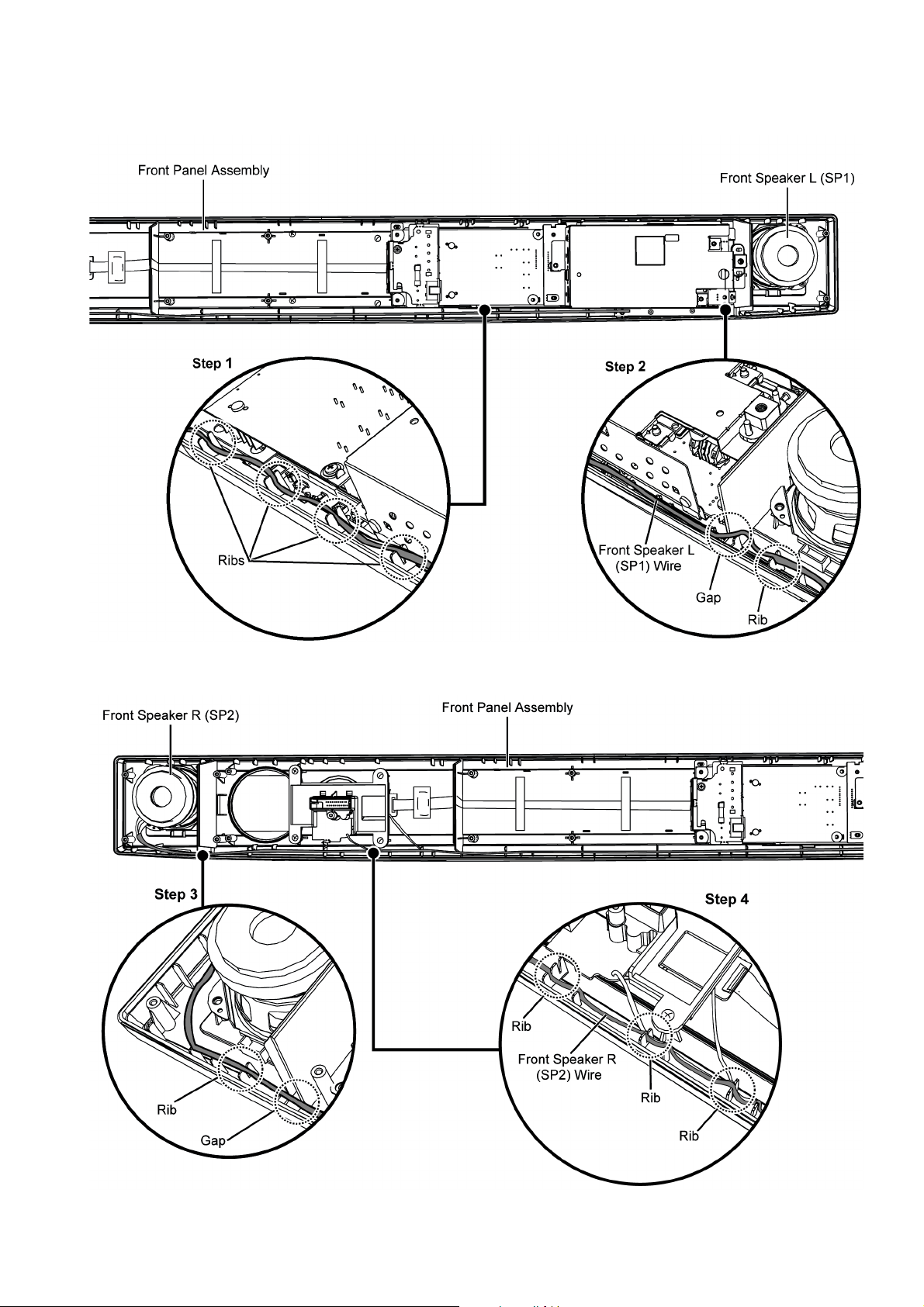
8.3.1. Wire Dressing for assembling
Step 1 : Ensure Front Speaker L (SP1) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly ribs.
Step 2 : Ensure Front Speaker L (SP1) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly gap and rib.
Step 3 : Ensure Front Speaker R (SP2) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly rib and gap.
Step 4 : Ensure Front Speaker R (SP2) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly ribs.
23
Page 24
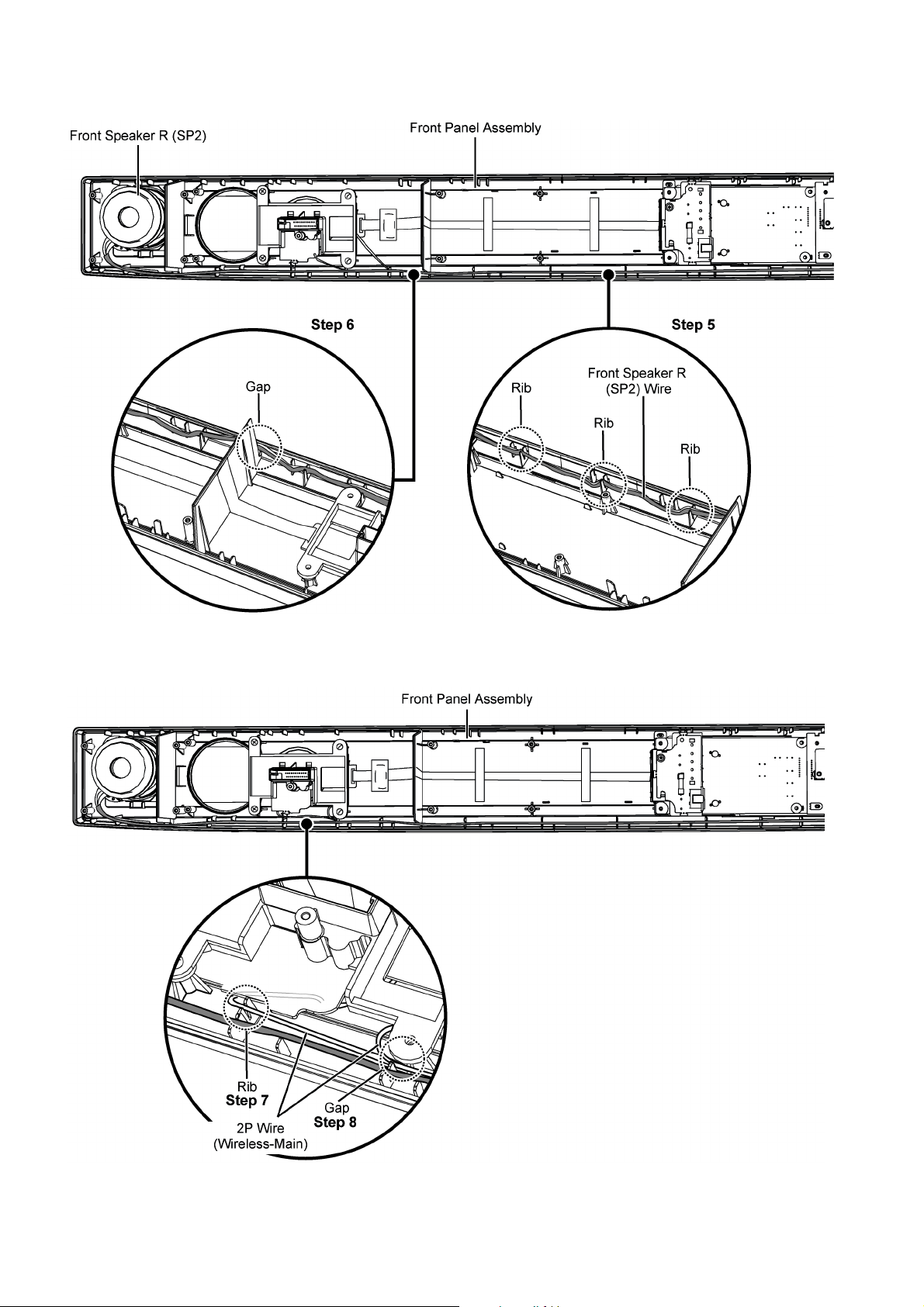
Step 5 : Ensure Front Speaker R (SP2) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly ribs.
Step 6 : Ensure Front Speaker R (SP2) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly gap.
Step 7 : Ensure 2P Wire (Wireless-Main) is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly rib.
Step 8 : Ensure 2P Wire (Wireless-Main) is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly gab.
24
Page 25
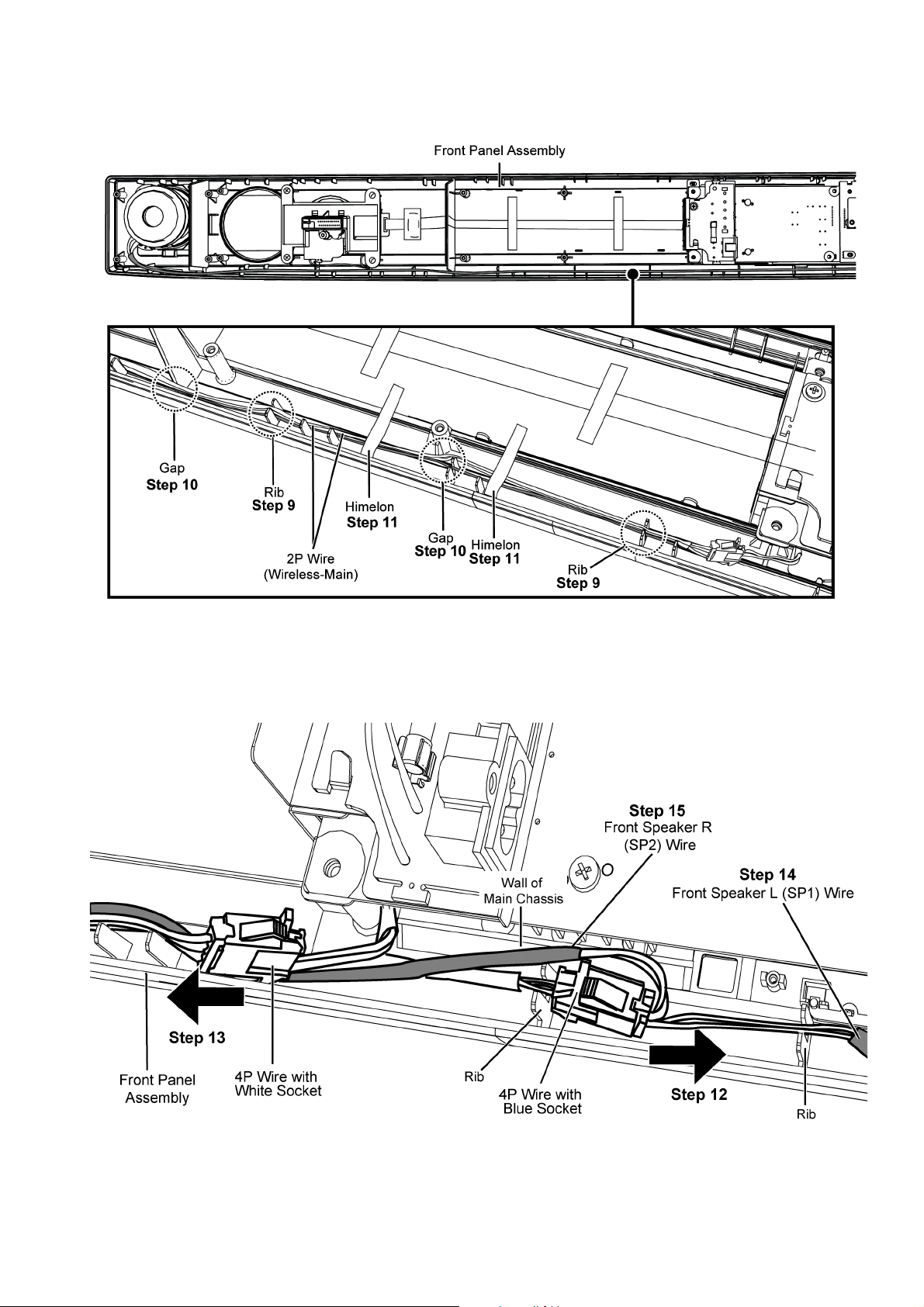
Step 9 : Ensure 2P Wire (Wireless-Main) is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly ribs.
Step 10 : Ensure 2P Wire (Wireless-Main) is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly gaps.
Step 11 : Paste 2 pieces of himelons over the wires.
Step 12 : Ensure 4P Wire Blue Socket must be dressed facing toward right direction as shown.
Step 13 : Ensure 4P Wire White Socket must be dressed facing toward left direction as shown.
Step 14 : Ensure Front Speaker L (SP1) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly rib.
Step 15 : Ensure Front Speaker R (SP2) wire is properly dressed into the Front Panel Assembly between rib and wall of Main Chas-
sis.
25
Page 26
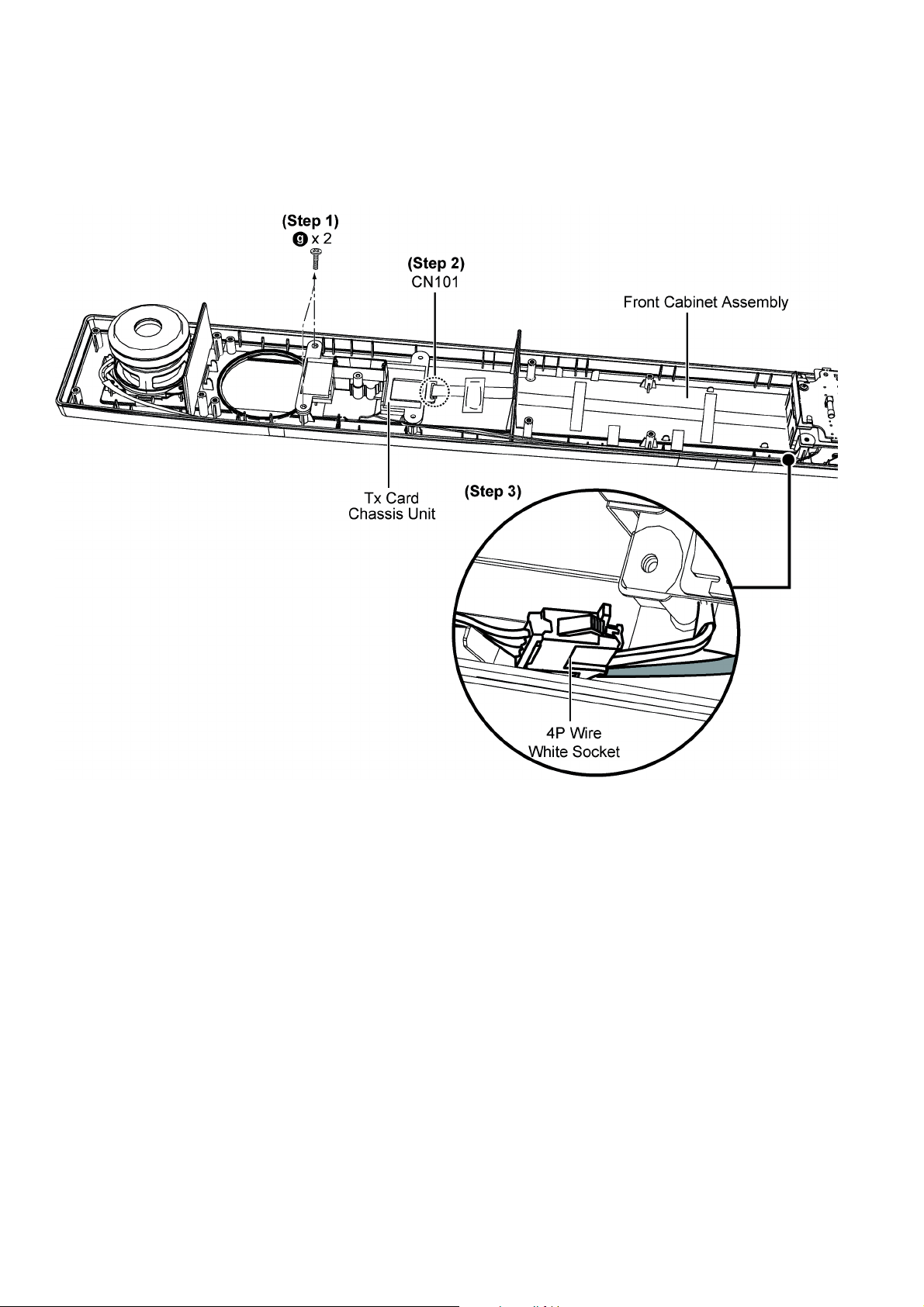
8.4. Disassembly of Wireless Adapter P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
Step 1 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 2 : Detach 14P FFC of connector (CN101) on Tx Card Chassis Unit.
Step 3 : Disconnect the 4P Wire White Socket.
26
Page 27
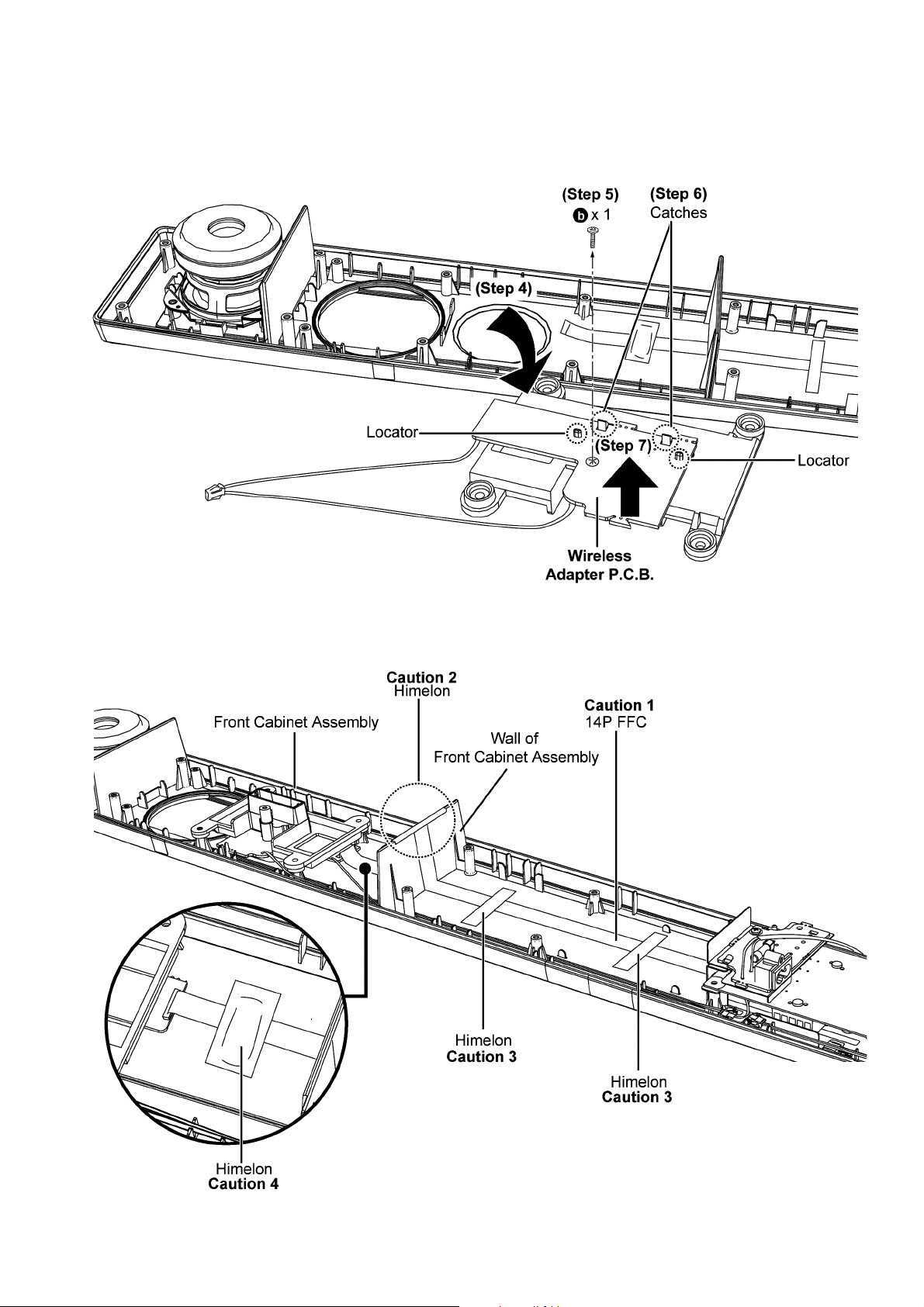
Step 4 : Flip over the Tx Card Chassis Unit as arrow shown.
Step 5 : Remove 1 screw.
Step 6 : Release the catches.
Step 7 : Remove the Wireless Adapter P.C.B. as arrow shown.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the Wireless Adapter P.C.B. is properly seated onto the locators.
Caution 1 : During assembling, ensure the 14P FFC must be dressed flatly onto the Front Cabinet Assembly.
Caution 2 : During assembling, ensure to paste the himelon over the 14P FFC onto wall of the Front Cabinet Assembly.
Caution 3 : During assembling, ensure to paste the himelon over the 14P FFC onto the Front Cabinet Assembly.
Caution 4 : During assembling, ensure to paste the himelon over ferrite core onto the Front Cabinet Assembly.
27
Page 28
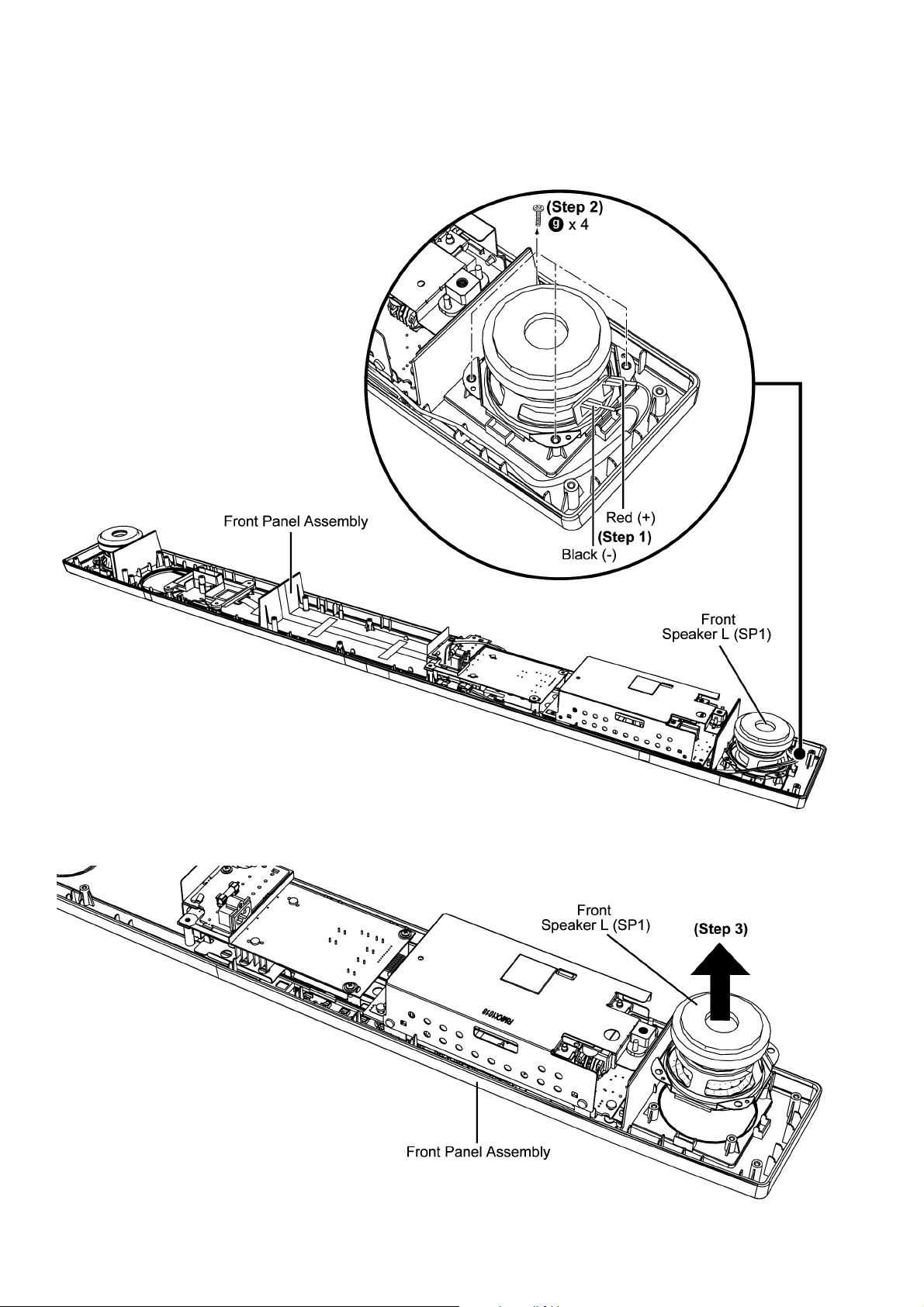
8.5. Disassembly of Front Speaker L (SP1)
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
Step 1 : Detach the Red (+) and Black (-) speaker wires.
Step 2 : Remove 4 screws.
Step 3 : Remove the Front Speaker L (SP1).
28
Page 29
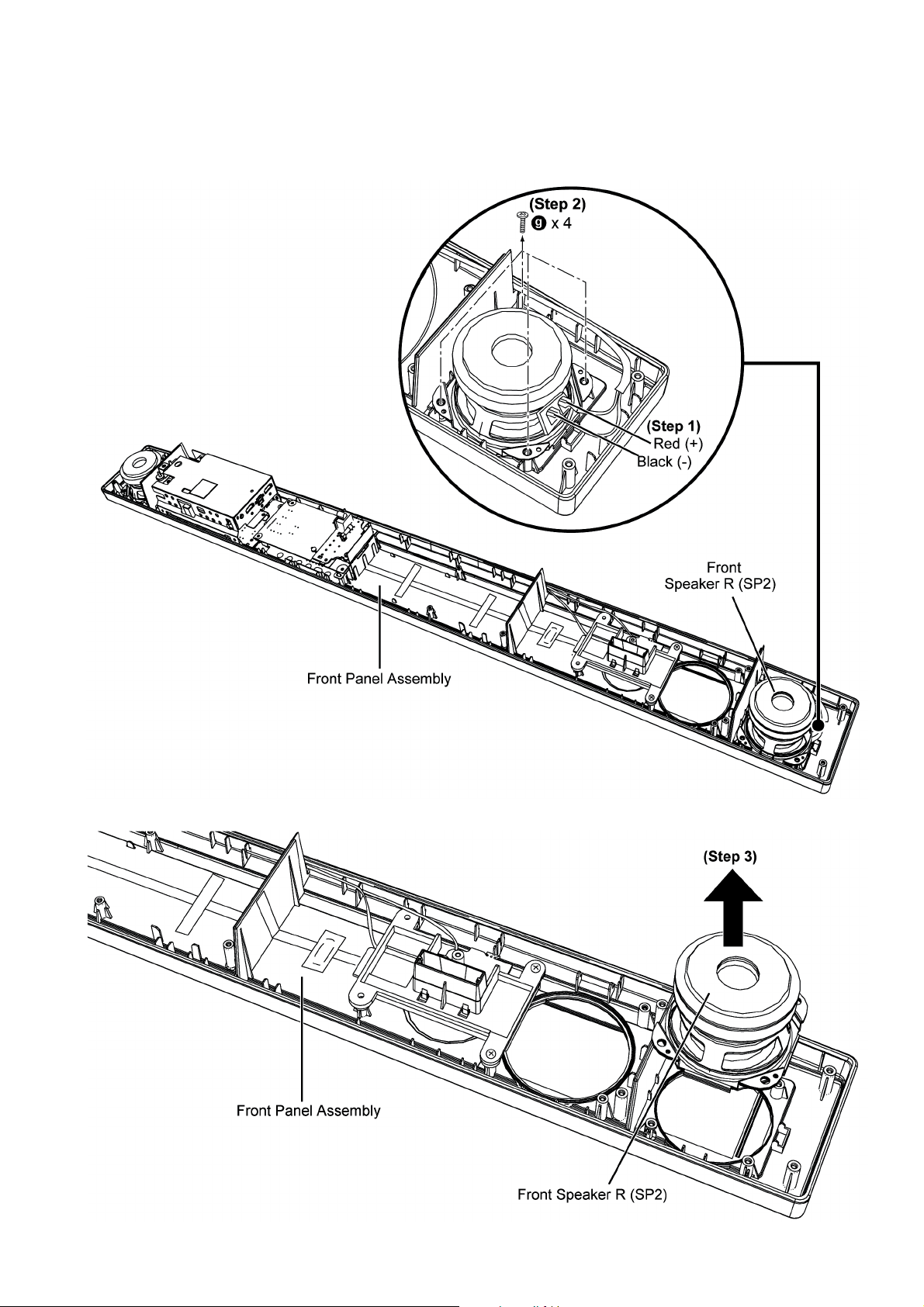
8.6. Disassembly of Front Speaker R (SP2)
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
Step 1 : Detach the Red (+) and Black (-) speaker wires.
Step 2 : Remove 4 screws.
Step 3 : Remove the Front Speaker R (SP2).
29
Page 30
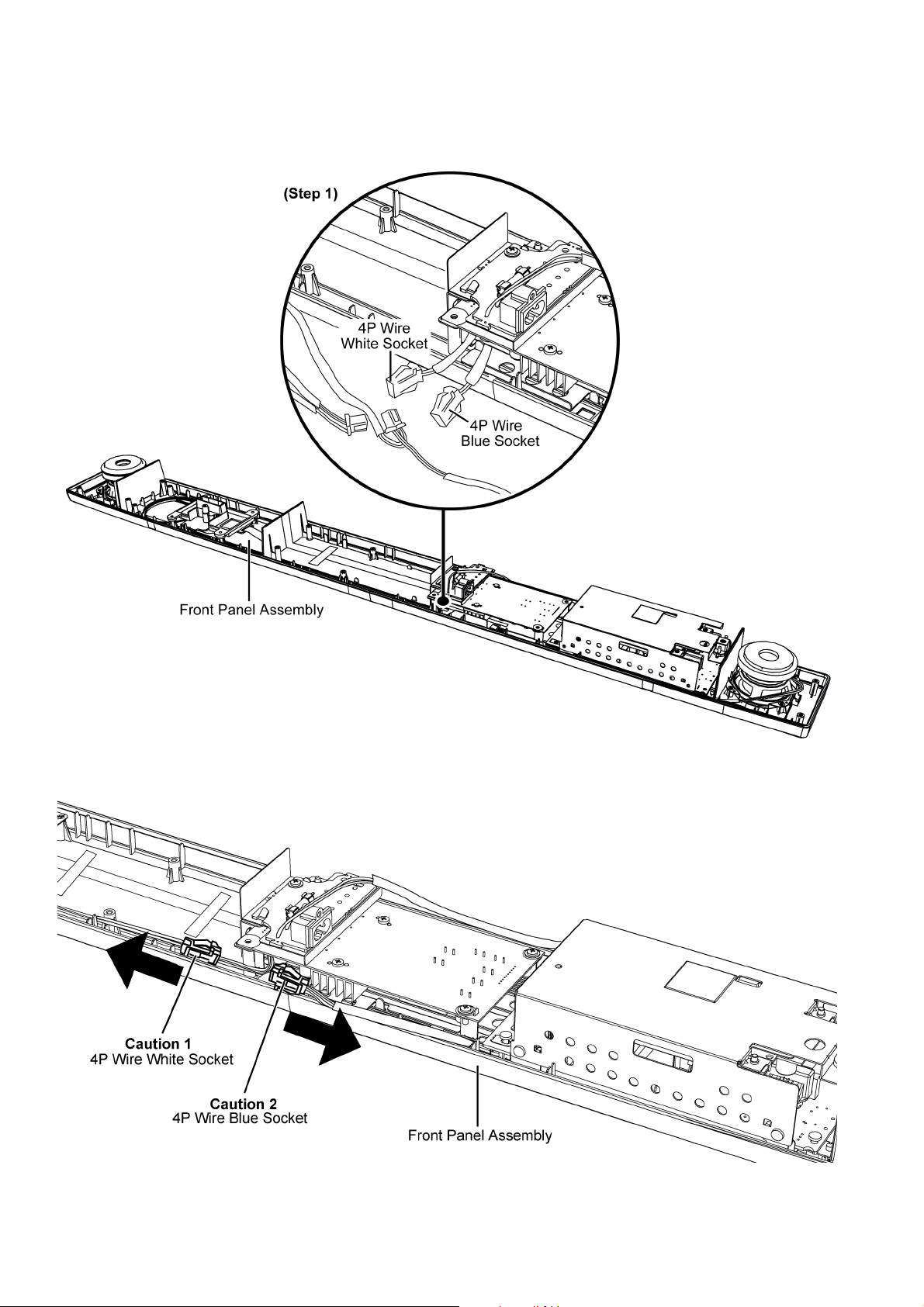
8.7. Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
Step 1 : Disconnect the 4P Wire Blue Socket and 4P Wire White Socket.
Caution 1 : During assembling, ensure 4P Wire White Socket must be dressed facing toward left direction as shown.
Caution 2 : During assembling, ensure 4P Wire Blue Socket must be dressed facing toward right direction as shown.
30
Page 31

Step 2 : Place the Main Chassis Assembly beside the Front Panel Assembly as arrow shown.
Step 3 : Detach 12P FFC of the connector (CN300) on Main P.C.B.
Step 4 : Detach 14P FFC of the connector (CN100) on Main P.C.B.
Step 5 : Remove Main Chassis Assembly.
31
Page 32

Caution 1 : Before assembling the Main Chassis Assembly, ensure the FFC of the connector (CN350) is properly bend at
supporting tape area.
Caution 2 : During assembling, ensure the Main Chassis Assembly is seated properly onto the locators.
32
Page 33

8.8. Disassembly of LED P.C.B. and Panel Tact Switch P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly”.
Step 1 : Remove 4 screws and detach Panel Tact Switch P.C.B..
Step 2 : Slightly detach the Panel Tact Switch P.C.B. from Front Panel Assembly.
Step 3 : Remove 3 screws.
Step 4 : Remove the PC Sheet.
Step 5 : Remove the LED P.C.B. together with Panel Tact Switch P.C.B. as arrow shown.
33
Page 34

Caution 1 : During assembling, ensure the LED P.C.B. is seated properly onto the locator.
Caution 2 : During assembling, ensure the 3P Cable Wire is properly dressed behind Front Panel Assembly rib.
34
Page 35

8.9. Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly”.
Step 1 : Cut off the Cable Tie.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the head of cable tie must be facing inward and tail of cable tie must be properly cut
with remaining 1mm away from the head.
Step 2 : Remove 1 screw.
Step 3 : Slightly lift up the AC Inlet P.C.B. as arrow shown.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the AC Inlet P.C.B. is properly seated onto the locators.
35
Page 36

Step 4 : Desolder the wires, black (TL20) and red (TL10).
Step 5 : Remove the AC Inlet P.C.B. as arrow shown.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the cable wire is properly seated onto the hook.
36
Page 37

8.10. Disassembly of Main P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly”.
• Refer to (Step 1) to (Step 3) of “Disassembly of AC Inlet P.C.B.”.
Step 1 : Remove the PC Sheet Assembly as arrow shown.
Step 2 : Remove 2 screws.
37
Page 38

Step 3 : Detach the 50P FFC of the connector (CN200) on Main P.C.B..
Step 4 : Detach the 12P FFC of the connector (CN300) on Main P.C.B..
Step 5 : Detach the 14P FFC of the connector (CN100) on Main P.C.B..
Step 6 : Slightly push forward the Main P.C.B. to avoid touching the Main Chassis Unit and lift it up as arrow shown.
Step 7 : Flip the Main P.C.B. to top of the Main Chassis Assembly.
38
Page 39

Step 8 : Detach the 10P Cable Wire of the connector (CN700) on Main P.C.B..
Step 9 : Remove the Main P.C.B..
Caution : During assembling, ensure the 10P wire must be properly dressing as diagram shown.
39
Page 40

8.11. Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly”.
Step 1 : Release the Wire from the hook.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the cable wire is properly slot into the hook.
Step 2 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 3 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 4 : Release the Himelon from Sub Chassis Assembly.
Step 5 : Slightly lift up the Sub Chassis Assembly and place at the side as arrow shown.
Caution : Do not exert too much force as it may damage the FFC.
40
Page 41

Step 6 : Remove 1 screw.
Step 7 : Detach the 10P Cable Wire of the connector (CN700) on Main P.C.B..
Step 8 : Lift up the SMPS P.C.B..
Caution : During assembling, ensure the SMPS P.C.B. is properly seated onto the locators.
41
Page 42
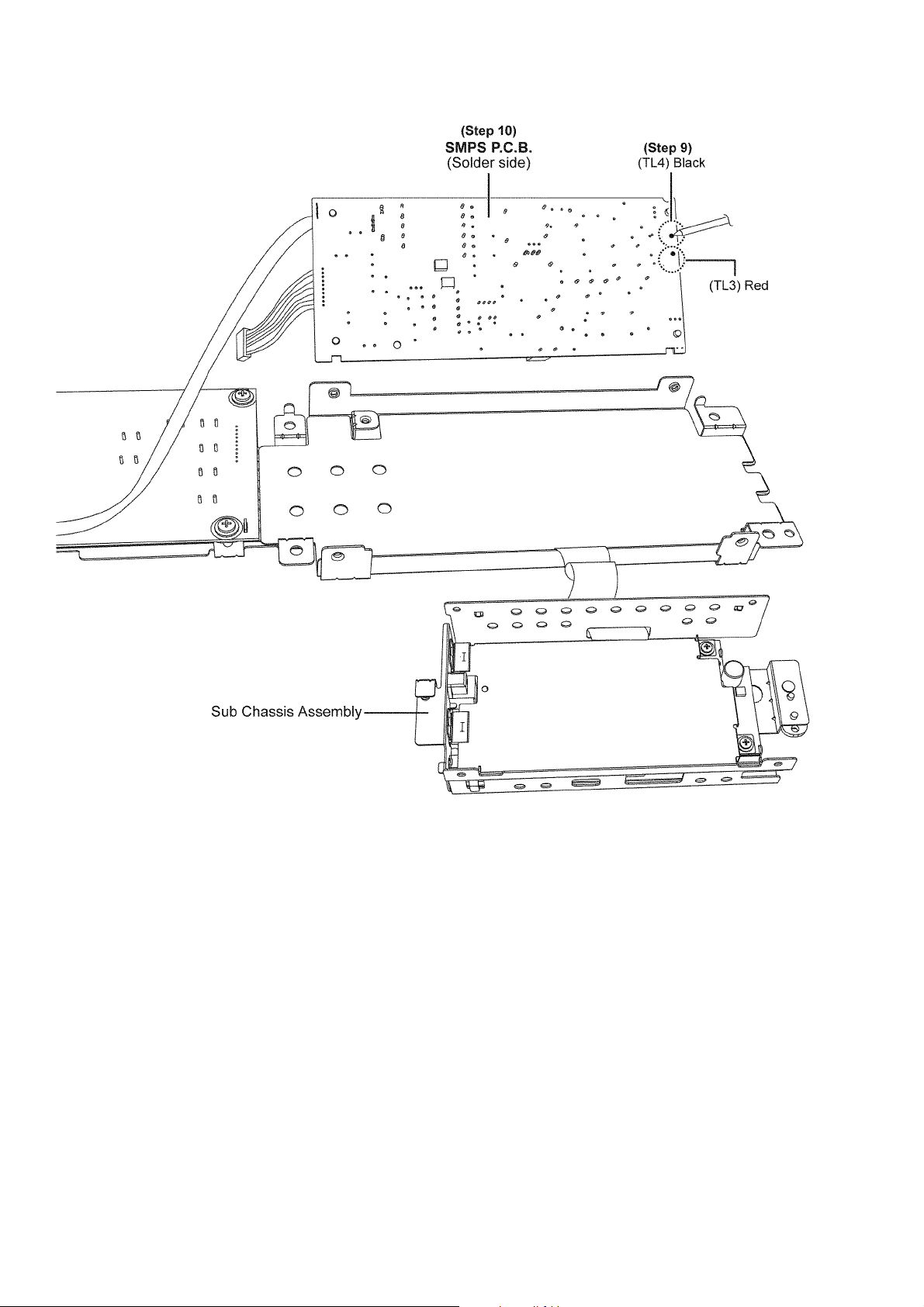
Step 9 : Desolder the wires, black (TL4) and red (TL3).
Step 10 : Remove the SMPS P.C.B..
42
Page 43

8.12. Replacement of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
• Refer to “Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.”.
8.12.1. Disassembly of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
Step 1 : Desolder pins of the Switch Regulator IC (IC5701) on
the solder side of SMPS P.C.B..
Step 2 : Remove 1 screw.
Caution : Avoid touching the Heatsink Unit B due to its
high temperature after prolonged use. Touching it may
lead to injuries.
Step 3 : Remove the Switch Regulator IC (IC5701).
43
Page 44
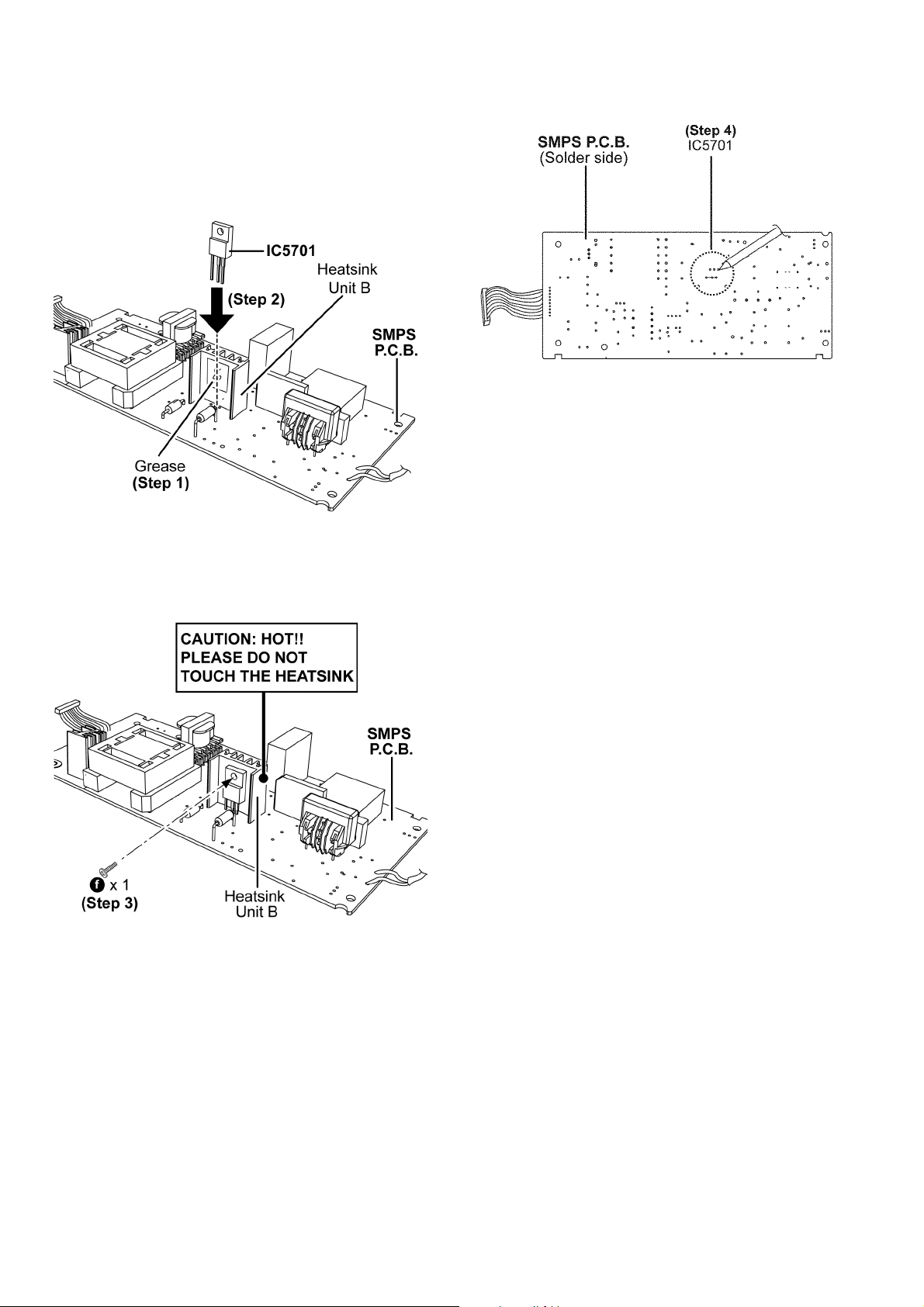
8.12.2. Assembly of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
Step 1 : Apply Grease on the Heatsink Unit B.
Step 2 : Mount the Switch Regulator IC (IC5701) onto the
SMPS P.C.B..
Caution : Ensure the pins of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701)
are properly seated on the SMPS P.C.B..
Step 4 : Solder pins of Switch Regulator IC (IC5701) on the sol-
der side of SMPS P.C.B..
Step 3 : Screw the Switch Regulator IC (IC5701) to the Heatsink Unit B.
Caution : Ensure the Switch Regulator IC (IC5701) is tightly
screwed to the Heatsink Unit B.
44
Page 45

8.13. Replacement of Rectifier Diode (D5802)
• Refer to “Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.”.
8.13.1. Disassembly of Rectifier Diode (D5802)
Step 1 : Desolder pins of the Rectifier Diode (D5802) on the
solder side of SMPS P.C.B..
Step 2 : Remove 1 screw.
Caution : Avoid touching the Heatsink Unit A due to its
high temperature after prolonged use. Touching it may
lead to injuries.
Step 3 : Remove the Rectifier Diode (D5802) from the Heatsink
Unit A.
45
Page 46

8.13.2. Assembly of Rectifier Diode (D5802)
Step 1 : Apply Grease on the Heatsink Unit A.
Step 2 : Mount the Rectifier Diode (D5802) onto the SMPS
P. C .B . .
Caution : Ensure the pins of Rectifier Diode (D5802) are
properly seated on the SMPS P.C.B..
Step 4 : Solder pins of the Rectifier Diode (D5802) on the sol-
der side of SMPS P.C.B..
Step 3 : Screw the Rectifier Diode (D5802) to the Heatsink Unit
A .
Caution : Ensure the Rectifier Diode (D5802) is tightly
screwed to the Heatsink Unit A.
46
Page 47
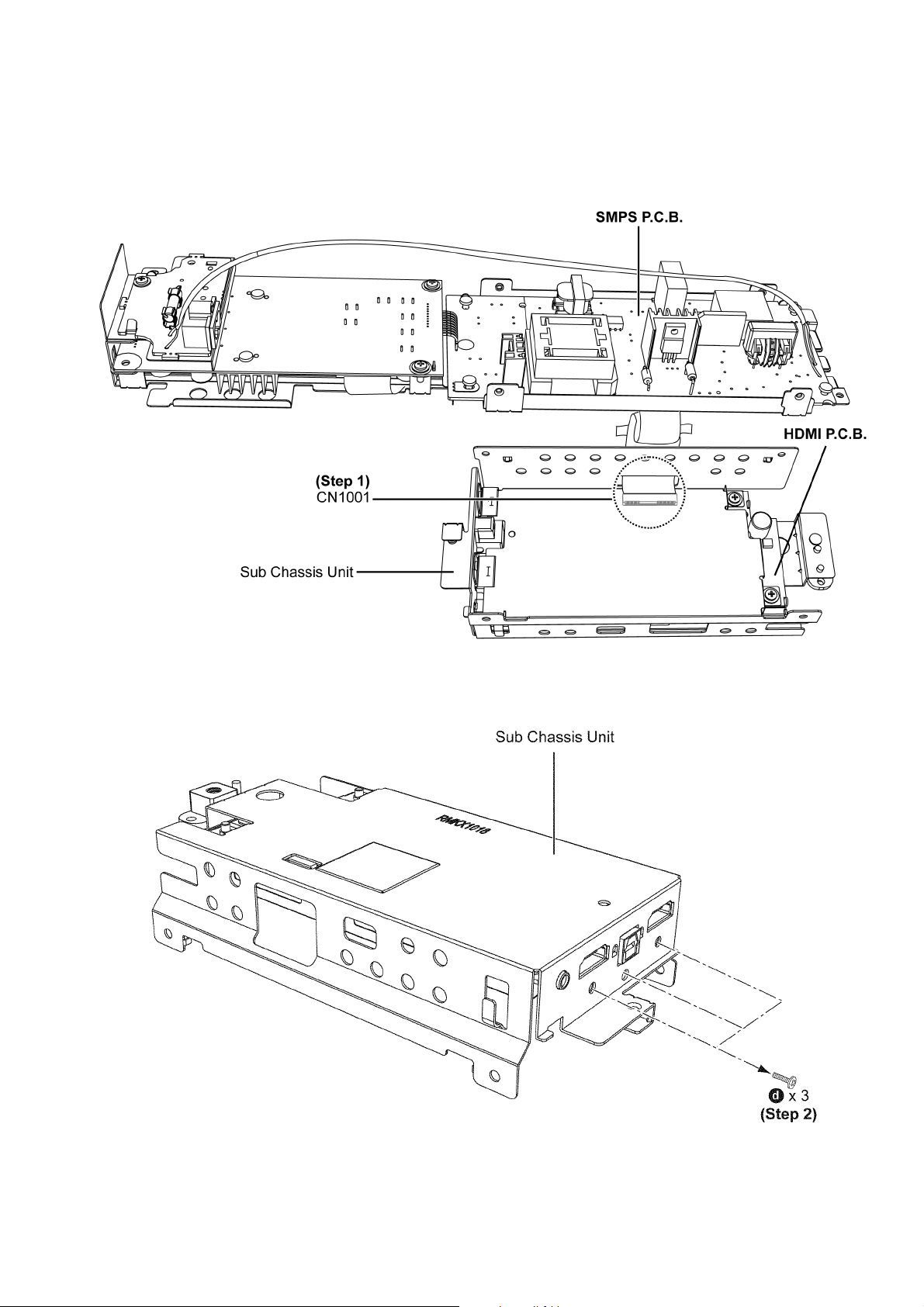
8.14. Disassembly of HDMI P.C.B.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Back Cabinet Assembly”.
• Refer to “Disassembly of Main Chassis Assembly”.
• Refer to (Step 1) - (Step 5) of “Disassembly of SMPS P.C.B.”.
Step 1 : Detach the 50P FFC of the connector (CN1001) on HDMI P.C.B..
Step 2 : Remove 3 screws.
47
Page 48

Step 3 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 4 : Lift up the HDMI P.C.B. Unit as arrow shown.
Caution : During assembling, ensure the HDMI P.C.B. Unit is properly seated onto the locators.
48
Page 49

Step 5 : Desolder the 2 legs of Shield Plate Unit.
Step 6 : Desolder the 2 legs of Shield Plate Unit.
Step 7 : Remove the HDMI P.C.B. Chassis as arrow shown.
49
Page 50

9 Service Position
Note: For description of the disassembly procedures, see the Section 8.
9.1. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B. (Side A)
Step 1 : Remove Back Cabinet Assembly.
Step 2 : Remove AC Inlet P.C.B..
Step 3 : Remove the PC Sheet Assembly.
Step 4 : Main P.C.B. (Side A) can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
50
Page 51

9.2. Checking and Repairing of Main P.C.B. (Side B)
Step 1 : Remove Back Cabinet Assembly.
Step 2 : Remove Main Chassis Assembly.
Step 3 : Remove AC Inlet P.C.B..
Step 4 : Remove the PC Sheet Assembly.
Step 5 : Remove Main P.C.B..
Step 6 : Connect 10P Cable Wire of connector (CN700) on Main P.C.B..
Step 7 : Connect 50P FFC of connector (CN200) on Main P.C.B..
Step 8 : Connect 14P FFC of connector (CN100) on Main P.C.B..
Step 9 : Connect 12P FFC of connector (CN300) on Main P.C.B..
Step 10 : Connect 4P Wire Blue Socket and 4P Wire Blue Socket.
Step 11 : Connect 4P Wire White Socket and 4P Wire White Socket.
Step 12 : Main P.C.B. (Side B) can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
51
Page 52

9.3. Checking and Repairing of Wireless Adapter P.C.B.
Step 1 : Remove Back Cabinet Assembly.
Step 2 : Remove 2 screws.
Step 3 : Flip over the Tx Card Chassis Unit as arrow shown.
Step 4 : Wireless Adapter P.C.B. can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
52
Page 53

9.4. Checking and Repairing of SMPS P.C.B.
Step 1 : Remove Back Cabinet Assembly.
Step 2 : Remove Main Chassis Assembly.
Step 3 : Remove SMPS P.C.B..
Step 4 : Connect 4P Wire Blue Socket.
Step 5 : Connect 4P Wire White Socket.
53
Page 54

Step 6 : Flip the SMPS P.C.B. as arrow shown.
Step 7 : Connect 10P Cable Wire to connector (CN700) with 10P Extension Cable Wire (SFT1).
Step 8 : SMPS P.C.B. can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
54
Page 55

9.5. Checking and Repairing of HDMI P.C.B. (Side A)
Step 1 : Remove Back Cabinet Assembly.
Step 2 : Remove Main Chassis Assembly.
Step 3 : Remove the HDMI P.C.B..
Step 4 : Attach the 50P FFC of the connector (CN1001) on HDMI P.C.B..
Step 5 : Connect 10P Cable Wire to connector (CN700) with 10P Extension Cable Wire (SFT1).
Step 6 : Connect 4P Wire Blue Socket.
Step 7 : Connect 4P Wire White Socket.
Step 8 : HDMI P.C.B. (Side A) can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
55
Page 56

9.6. Checking and Repairing of HDMI P.C.B. (Side B)
• Refer to (Step 1) to (Step 7) of “Checking and Repairing of HDMI P.C.B. (Side A)”.
Step 1 : Flip the HDMI P.C.B. as arrow shown.
Step 2 : HDMI P.C.B. (Side B) can be checked and repaired as diagram shown.
56
Page 57

10 Voltage Measurement & Waveform Chart
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 0 0 3.4 0 3.2 0 3.4 0 0 0 1.8 0 0 0 1.7 1.7 0.9 0 1.7
STANDBY 0 0 0 3.4 0 3.2 0 3.4 0 0 0 1.8 0 0 0 1.7 1.7 0.9 0 1.7
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 3.3 1.8 0.2 0.2 0 0.2 0.2 3.4 1.6 1.6 0 1.7 1.7 1.7 0 3.4 3.4 0 0 1.7
STANDBY 3.3 1.8 0.2 0.2 0 0.2 0.2 3.4 1.6 1.6 0 1.7 1.7 1.7 0 3.4 3.4 0 0 1.7
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 0 1.8 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 0.1 3.3 1.7 1.7 0 1.7 1.8 0 3.3 3.2 3.2 3.2
STANDBY 0 1.8 0 0 0 0 0.1 0 0.1 3.3 1.7 1.7 0 1.7 1.8 0 3.3 3.2 3.2 3.2
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.2 1.8 3.4 0 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.1 0 3.2 3.2 3.3 1.9
STANDBY 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.2 1.8 3.4 0 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.1 0 3.2 3.2 3.3 1.9
REF NO.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY1.93.41.8000003.4000001.800003.4
STANDBY1.93.41.8000003.4000001.800003.4
REF NO.
MODE 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120
CD PLAY0000003.43.43.43.401.800000003.3
STANDBY0000003.43.43.43.401.800000003.3
REF NO.
MODE 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128
CD PLAY 3.2 0 0.6 3.4 1.8 0.6 0 3.4
STANDBY 3.2 0 0.6 3.4 1.8 0.6 0 3.4
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 1.7 1.7 3.3 0 3.3 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 3.4 3.2 0 0 0 0 2.8 2.8 0 0
STANDBY 0 1.7 1.7 3.3 0 3.3 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 3.4 3.2 0 0 0 0 2.8 2.8 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY0005.0000000000000002.00
STANDBY0005.0000000000000002.00
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 5.0 1.0 0 2.5 0 1.0 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 3.3 0.2 1.7 0 0 0 1.7 1.6
STANDBY 5.0 1.5 0 2.5 0 1.4 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 1.7 0 0 0 1.7 1.7
IC1001
IC1002
SU-HTB500PP HDMI P.C.B.
IC1001
IC1002
IC1001
IC1001
IC1002
IC1001
IC1001
IC1001
Note:
• Indicated voltage values are the standard values for the unit measured by the DC electronic circuit tester (high-impedance) with
the chassis taken as standard.
Therefore, there may exist some errors in the voltage values, depending on the internal impedance of the DC circuit tester.
• Circuit voltage and waveform described herein shall be regarded as reference information when probing defect point because it
may differ from actual measuring value due to difference of Measuring instrument and its measuring condition and product itself.
10.1. HDMI P.C.B. (1/5)
57
Page 58

10.2. HDMI P.C.B. (2/5)
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64
CD PLAY 1.7 0.1 0 0.1
STANDBY 1.7 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 3.4 3.4 0 0 0
STANDBY 3.4 3.4 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 5.0 0 4.9 0 3.3
STANDBY 5.0 0 5.0 0 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 123456
CD PLAY 1.7 0 1.7 1.7 3.4 0
STANDBY 1.7 0 1.7 1.7 3.4 0
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 3.3 3.0 1.7 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.2 3.2 3.4 3.4 3.4 0 0
STANDBY 3.3 3.3 2.6 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.4 1.9 3.4 0 3.3 3.3 3.3
STANDBY 0 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.4 1.9 3.4 0 3.3 3.3 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
CD PLAY 0 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 0
STANDBY 0 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 0
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
STANDBY 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 1.2 1.2 0 2.1 3.4 3.3 0 0 0 1.1 1.5 3.2 1.6 0 1.4 3.2 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.3
STANDBY 1.2 1.2 0 2.1 3.4 3.3 0 0 0 1.1 1.5 3.2 1.6 0 1.3 3.2 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 3.2 3.2 0 0 0 3.2 3.2 0.7 0.2 0.6 3.2 3.2 0 0 3.1 3.1 0 3.2 3.2 0
STANDBY 3.2 3.2 0 0 0 3.2 3.2 0.7 0.2 0.6 3.2 3.2 0 0 3.1 3.1 0 3.2 3.2 0
IC1005
IC1006
IC2002
SU-HTB500PP HDMI P.C.B.
IC1002
IC2002
IC1006
IC1006
IC1008
IC1003
IC1004
58
Page 59

10.3. HDMI P.C.B. (3/5)
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY03.23.21.33.2000000000000000
STANDBY03.23.21.33.2000000000000000
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 0 3.2 0 0 0 0 3.0 2.9 3.3 3.3 3.4 0 0 3.3 0 0 3.2 3.3 0 0
STANDBY 0 3.2 0 0 0 0 3.0 2.9 3.3 3.3 3.4 0 0 3.3 0 0 3.2 3.3 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY000000003.43.40001.82.1003.23.20
STANDBY000000003.43.40001.82.1003.23.20
REF NO.
MODE 12345678
CD PLAY 0 0 3.2 0 3.2 3.2 0 3.2
STANDBY 0 0 3.2 0 3.2 3.2 0 3.2
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 3.9 3.2 3.3 0 0
STANDBY 3.9 3.2 3.3 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 0 1.7 1.7 1.6 0 1.7 0 0.2 0 0 0 0.2 0 1.7 0 1.6 1.6 1.7 0 3.3
STANDBY 0 1.7 1.7 1.6 0 1.7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1.7 0 1.6 1.6 1.7 0 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 123456
CD PLAY 1.6 0 1.6 1.6 3.3 1.6
STANDBY 1.6 0 1.6 1.6 3.3 1.6
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY1.100000000001.803.3000000
STANDBY1.200000000001.803.3000000
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 1.8 0 1.1 1.1 1.8 1.1 1.1 0 1.1 1.1 1.8 1.1 1.1
STANDBY 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 1.8 0 1.1 1.1 1.8 1.1 1.1 0 1.1 1.1 1.8 1.1 1.1
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 0 1.8 0 3.3 5 5 5 3.3 3.3 0.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5
STANDBY 0 1.8 0 3.3 5 5 5 3.3 3.3 0.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5
IC2003
IC2004
IC2101
SU-HTB500PP HDMI P.C.B.
IC2002
IC2101
IC2006
IC2081
IC2101
IC2002
IC2002
59
Page 60

10.4. HDMI P.C.B. (4/5)
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 2.6 2.6 2.6 1.8 0 3.3 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 1.8 2.4 1.2 1.3 1.3
STANDBY 2.6 2.6 2.6 1.8 0 3.3 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 1.8 2.4 1.2 1.3 1.3
REF NO.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY
1.2 1.3 1.3 1.3
1.3 1.2 0 0 3.3
1.3
1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.8 0
STANDBY
1.2 1.3 1.3 1.3
1.3 1.2 0 0 3.3
1.3
1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.8 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 2.5 3.2 1.8 0 0
STANDBY 2.5 3.2 1.8 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345678
CD PLAY 0 0 0 0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
STANDBY 0 0 0 0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
REF NO.
MODE 1234567891011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 1.3 1.2 1.3 0 0 3.3 1.3
1.3
1.3 1.3 0
1.8
1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 0 3.3 1.0 0.5
STANDBY 1.3 1.2 1.3 0 0 3.3 1.3
1.3
1.3 1.3 0
1.8
1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 0 3.3 1.0 0.5
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 0.5 0 0 1.8 1.8 0 0
0
000
3.3
3.3 3.3 0 0 1.8 3.3 0 0
STANDBY 0.5 0 0 1.8 1.8 0 0
0
000
3.3
3.3 3.3 0 0 1.8 3.3 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 0 3.3 0 0 0 3.3 0
0
03.30
0
0 1.8 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3
STANDBY 0 3.3 0 0 0 3.3 0
0
03.30
0
0 1.8 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 1.8
STANDBY 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.8 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 1.8
REF NO.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY00000003.33.301.81.801.61.63.33.3003.3
STANDBY00000003.33.301.81.801.61.63.33.3003.3
REF NO.
MODE 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120
CD PLAY 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 1.8 2.8 2.8 2.8 2.8 0 3.3 2.8 2.8 2.8 2.8 0 1.8 2.8
STANDBY 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 1.8 2.7 2.7 2.7 2.7 0 3.3 2.7 2.7 2.6 2.7 0 1.8 2.7
IC2232
IC2232
SU-HTB500PP HDMI P.C.B.
IC2101
IC2232
IC2232
IC2232
IC2232
IC2101
IC2102
IC2231
60
Page 61
10.5. HDMI P.C.B. (5/5)
REF NO.
MODE 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140
CD PLAY 2.8 2.8 2.8 0 3.3 2.8 2.8 2.8 2.8 0 1.8 2.8 2.8 1.2 1.3 0 3.3 1.3 1.2 1.3
STANDBY 2.7 2.7 2.7 0 3.3 2.7 2.7 2.7 2.7 0 1.8 2.8 2.7 2.7 1.3 0 3.3 1.3 1.2 1.3
REF NO.
MODE 141 142 143 144
CD PLAY 1.3 0 1.8 1.3
STANDBY 1.3 0 1.8 1.3
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 2.5 3.2 1.8 0 0
STANDBY 2.5 3.2 1.8 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 6.0 2.5 0 1.2 2.1
STANDBY 6.0 2.5 0 1.2 2.1
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 18.0 3.1 0 1.2 2.1
STANDBY 18.0 3.1 0 1.2 2.1
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 6.0 0 6.0 0 5.2
STANDBY 6.0 0 6.0 0 5.3
REF NO.
MODE ECB 12345 123456
CD PLAY 0 3.4 0 3.1 3.1 3.2
3.5
3.5 5.0 0 0 5.2 5.0 5.2
STANDBY 0 3.4 0 3.2 3.2 3.2
3.5
3.5 5.0 0 0 5.2 5.0 5.2
REF NO.
MODE 12345 123456 12345
CD PLAY
4.8 5.0 4.8 5.0
5.0 5.0 0 0
4.8
5.0 4.8 4.8 5.0 4.8 5.0 5.0
STANDBY
4.8 5.0 4.8 5.0
5.0 5.0 0 0
4.8
5.0 4.8 4.8 5.0 4.8 5.0 5.0
REF NO.
MODE 12345 12345 ECB ECB
CD PLAY 0 0.5 0 3.1 5.0 0 0.5 0 5.0 3.1 0 1.2 0 0 3.3 0
STANDBY 0 0.5 0 3.1 5.0 0 0.5 0 5.0 3.1 0 1.3 0 0 3.3 0
REF NO.
MODE ECB ECB ECB ECB ECB
CD PLAY
000
04.80 0
5.0
002.10
003.1
STANDBY
000
04.80 0
5.0
002.10
003.1
Q2231
Q2232
Q2233
Q2234
Q2103
Q2108
IC2232
IC4793
IC2232
IC2233
IC4722
IC4724
SU-HTB500PP HDMI P.C.B.
QR2001
QR2002
QR2004
QR2231
QR4704
Q2235
Q2236
QR2232
QR4703
61
Page 62

10.6. MAIN P.C.B. (1/2)
REF NO.
MODE 1 2 3
CD PLAY
3.3 0 5.0
STANDBY
3.3 0 5.0
REF NO.
MODE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 1.8 0.1 0.8 0.9 0.1 0.1 2.0 0.1 3.3 1.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.9 0 0.5 0.8
STANDBY 1.8 0.1 0.8 0.9 0.1 0.1 1.9 0.1 3.3 1.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 0 1.9 0 0 0.9
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY0003.33.31.70000001.8003.33.2000
STANDBY 0 0 0 3.3 3.3 1.7 0 0 0 0 0 0 1.8 0 0 3.3 3.2 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY00000001.800003.33.300001.31.3
STANDBY00000001.800003.33.300001.31.4
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64
CD PLAY 1.3 1.3 1.6 0.1
STANDBY 1.3 1.3 1.6 0.1
REF NO.
MODE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
CD PLAY3.33.3003.303.30000000003.3000
STANDBY 3.3 3.3 0 0 3.3 0 3.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.3 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 3.3 3.3 3.3 10.1 0 20.3 20.3 10.1 0 0 10.2 20.3 10.2 10.2 20.3 10.2 0 0 10.2 20.3
STANDBY 3.3 3.3 3.3 10.1 0 20.3 20.3 10.1 0 0 10.2 20.3 10.2 10.2 20.3 10.2 0 0 10.2 20.3
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44
CD PLAY 20.3 0 10.2 3.3
STANDBY 20.3 0 10.2 3.3
REF NO.
MODE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011121314151617181920
CD PLAY 3.2 3.2 1.2 0.1 3.4 0.1 1.2 0 0 0 0 3.2 1.6 0 1.6 3.2 3.2 0 3.4 3.2
STANDBY 3.1 3.1 1.2 0.1 3.4 0.1 1.2 0 0 0 0 3.2 1.6 0 1.6 3.2 3.2 0 3.4 3.2
REF NO.
MODE 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
CD PLAY 0 3.4 3.2 3.4 0 3.2 0 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 0.4 0 0.2 0.6 0.7 0 0 0
STANDBY 3.2 3.4 0 3.4 0 3.2 0 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 0.4 0 0.2 0.6 0.7 0 0 0
IC401
IC401
IC604
SU-HTB500PP MAIN P.C.B.
IC107
IC604
IC405
IC405
IC405
IC401
IC401
62
Page 63

10.7. MAIN P.C.B. (2/2)
REF NO.
MODE 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
CD PLAY 0 0 3.2 2.1 0 0 0 0.8 2.0 0 0 0 0 3.2 0 0 0 0 0 0
STANDBY 0 0 3.2 2.1 0 0 0 1.2 2.0 0 0 0 0 3.2 0 0 0 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
CD PLAY 0 3.2 3.2 0 0 0 0 0 0.6 3.4 3.4 3.2 3.2 0 3.4 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.2 0
STANDBY 0 3.2 3.2 0 0 0 0 0 0.6 3.4 3.4 3.2 3.2 0 3.4 3.2 3.4 3.2 3.2 0
REF NO.
MODE 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100
CD PLAY 3.2 0 3.4 0.3 0 0 0 0 3.2 3.1 3.5 3.5 0 3.4 3.4 0 0 3.3 3.2 0
STANDBY 3.2 0 3.4 0.3 0 0 0 0 3.2 3.1 3.5 3.5 0 3.4 3.4 0 0 3.3 3.2 0
REF NO.
MODE 12345678
CD PLAY 3.0 3.0 0 0 3.2 3.2 0 3.2
STANDBY 3.1 3.0 0 0 3.1 3.1 0 3.1
REF NO.
MODE 1234
CD PLAY 4.0 6.0 0 0
STANDBY 3.9 6.0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 123
CD PLAY 3.3 0 6.0
STANDBY 3.3 0 6.0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 20.0 12.0 0 1.1 2.0
STANDBY 20.0 12.0 0 1.1 2.0
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 20.0 5.0 0 1.2 1.9
STANDBY 20.0 5.0 0 1.2 1.9
REF NO.
MODE ECB ECB ECB ECB ECB
CD PLAY
000
16 -0.1 0 10.0 0 10.0 10.0 0 10.0 0 0 0
STANDBY
000
16 -0.1 0 0.3 0 0.3 0.3 0 0.3 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE ECB ECB ECB
CD PLAY
000
3.2 0 3.2 0 0 0
STANDBY
000
3.2 0 3.2 0 0 0
QR600
QR601
QR602
Q500
Q501
Q704
IC606
SU-HTB500PP MAIN P.C.B.
IC604
IC700
IC701
IC702
IC604
IC604
IC605
Q114
Q116
REF NO.
MODE 123456789101112131415161718
CD PLAY
003.10
0.5 0.6 0.6 0.1 0.6
4.6
4.6 0.6 0.6 2.0 0 0 0 4.4
STANDBY
003.10
0.5 0.6 0.6 0.1 0.6
4.6
4.6 0.6 0.6 2.0 0 0 0 4.4
SU-HTB500PP LED P.C.B.
IC300
10.8. LED P.C.B.
63
Page 64

10.9. SMPS P.C.B.
REF NO.
MODE 1234567
CD PLAY 159.3 0 0 17.5 0.1 1.3 0.6
STANDBY 159.3 0 0 17.5 0.1 1.3 0.6
REF NO.
MODE 12345678
CD PLAY 6.0 0.8 2.4 12.3 165.0 0 0 0
STANDBY 6.0 0.8 2.4 12.3 165.0 0 0 0
REF NO.
MODE 123
CD PLAY 18.3 2.5 0
STANDBY 18.3 2.5 0
REF NO.
MODE 123
CD PLAY 4.8 2.5 0
STANDBY 4.8 2.5 0
REF NO.
MODE E C B E C B E C B
CD PLAY 6.9 7.8 6.9 0 3.3 0 0 0.1 0.7
STANDBY 6.9 7.8 6.9 0 3.3 0 0 0.1 0.7
SU-HTB500PP SMPS P.C.B.
Q5720
Q5841
Q5899
IC5701
IC5799
IC5801
IC5899
REF NO.
MODE 12345
CD PLAY 6.0 2.5 0 1.2 2.1
STANDBY 6.0 2.5 0 1.2 2.1
IC100
SU-HTB500PP WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
10.10. WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
64
Page 65

10.11. Waveform Chart (1/2)
WF No. IC401-19 (PLAY)
2Vp-p(20nsec/div)
WF No. IC401-20 (PLAY)
1Vp-p(20nsec/div)
WF No. IC401-42,43,44,45,46,
47 (PLAY)
6Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC401-29,31 (PLAY)
3.2Vp-p(500nsec/div)
WF No. IC401-40,41 (PLAY)
6Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC405-6,8,16,18 (PLAY)
6Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC405-28,31,36,39 (PLAY)
32Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC604-13 (PLAY)
2.6Vp-p(50nsec/div)
WF No. IC604-15 (PLAY)
2Vp-p(50nsec/div)
WF No. IC1001-17 (PLAY)
2Vp-p(20nsec/div)
WF No. IC1001-18 (PLAY)
1.7Vp-p(20nsec/div)
WF No. IC1001-23,24,26,27,
34 (PLAY)
3.4Vp-p(5usec/div)
WF No. IC1001-48 (PLAY)
3.6Vp-p(10usec/div)
WF No. IC1001-49 (PLAY)
6Vp-p(2usec/div)
WF No. IC1001-51 (PLAY)
6.4Vp-p(2usec/div)
WF No. IC1002-44 (PLAY)
8Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC1002-47 (PLAY)
0.2Vp-p(5msec/div)
WF No. IC1002-54 (PLAY)
6.4Vp-p(2usec/div)
WF No. IC1002-64 (PLAY)
4Vp-p(2nsec/div)
WF No. IC1008-4 (PLAY)
2.4Vp-p(200nsec/div)
65
Page 66

10.12. Waveform Chart (2/2)
WF No. IC2002-10 (PLAY)
0.5Vp-p(10usec/div)
WF No. IC2002-11 (PLAY)
3Vp-p(20usec/div)
WF No. IC2002-13 (PLAY)
3.8Vp-p(100nsec/div)
WF No. IC2002-15 (PLAY)
2.6Vp-p(100nsec/div)
WF No. IC1008-6 (PLAY)
3Vp-p(200nsec/div)
WF No. IC2101-4,6,7 (PLAY)
5.2Vp-p(500nsec/div)
WF No. IC2101-8 (PLAY)
3.6Vp-p(5usec/div)
WF No. IC2101-9 (PLAY)
5Vp-p(5usec/div)
WF No. IC2006-3 (PLAY)
6.8Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC2006-8,12 (PLAY)
3.4Vp-p(5usec/div)
WF No. IC2006-17 (PLAY)
5.2Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC2232-78 (PLAY)
6Vp-p(1usec/div)
WF No. IC2232-81,82,83,84
(PLAY)
3.4Vp-p(5usec/div)
WF No. IC2232-94 (PLAY)
3Vp-p(20nsec/div)
WF No. IC2232-95 (PLAY)
1Vp-p(20nsec/div)
66
Page 67

11 Illustration of IC’s, Transistors and Diodes
No.1
No.1
MIP2F20MSSCF
1
4
5
2
3
C0JBAQ000073 (18P)
C0JBAZ001466 (20P)
C1AB00003217 (44P)
C3ABMG000238 (50P)
C0FBZK000013 (64P)
C1AB00002975 (100P)
C1AB00003216 (64P)
C2HBCY000030 (128P)
C0CBCAG00015
C0CBCBG00013
C0DBAYH00005
C0CBABC00117
RFKWMHTB10PB
RFKWMHTB500P
C3EBEC000047
C3EBEC000060
C0DAEMZ00001
1
3
2
B1ABCF000011
B1ABCF000079
B1ABMF000020
B1ADBL000010
B1GBCFGG0030
B1GBCFJJ0007
B1GBCFNN0004
B1GDCFJJ0008
B0BC010A0007
B0BC012A0264
B0BC018A0267
B0BC030A0264
B0BC5R600003
B0BC6R2A0266
Cathode
Anode
A
Ca
A
Ca
Cathode
Anode
B0EAKT000061
B0EAKT000062
B0EAMM000057
B0HAMP000094
B0JAMF000011
B0HBSM000054
B0EDKT000009
B3AGB0000037
Ca
A
A
Ca
A
A
C0JBAR000396
C0JBAB000986
C0CBCBC00049
C0CBCDC00014
C0EBG0000107
B0JCME000012
B0JCPG000005
Cathode
Anode
A
Ca
2SC3940ARA
C0DAAMH00013
C2CBDD000001
B1CFGD000002
1
7
5
3
B0ACCK000005
B0JCAE000001
B0EBNR000015
A
Ca
Cathode
Anode
Anode
Anode
Anode
Cathode
C1AB00002989 (144P)
No.1
1
38
39
64
65
102
103
128
1
30
31
50
51
80
81
100
1
4
5
2
3
B1HBCFA00003
1
4
6
5
2
3
Cathode
Anode
A
Ca
1
10
11
20
MA2J1110GL
MAZ8300GML
8
4
67
Page 68

12 Overall Simplified Block
68
Page 69

13 Block Diagram
SU-HTB500PP SYSTEM CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM
D600
D602
D601
85
CN350CN300
6 SCL
5 SDA
MICRO PROCESSOR
RFKWMHTB500P
IC604
EEPROM
C3EBEC000060
X600
IC605
LED DI 80
LED DATA
76
CN350CN300
LED CLK 81
LED CLK
67
CN350CN300
LED CS 82
LED DRIVER
C0JBAQ000073
IC300
SCL 29
SDA 30
1 OUT
RESET
C0EBG0000107
IC606
AC SYNC 20
XIN 15
XOUT 13
LED LCK
LED DI
LED CLK
LED CS
94
CN350CN300
LED OE 85
LED OELED OE
KEY2 91
KEY2
INPUT SELECTOR
KEY2
S303
VOLUME-
S304
6V
11
CN352*CN351*
58
CN350CN300
KEY1 92
KEY1
POWER
KEY1
S300
VOLUME+
S301
22
CN352*CN351*
49
CN350CN300
REMOTE 19
REMOTE 5
REMOTE REMOCON
310
CN350CN300
83
CN700H2016*
VREF
5V
3.3V
REMOTE
CONTROL SENSOR
Z300
VDD 2
DAP SCL22
DAP SCL
DAP SCL
ECO DAMP93
ECO DAMP
ECO DAMP
DAP RESET26
DAP RESET
DAP RESET
DAP PDN63
DAP PDN
DAP PDN
DAP MUTE23
DAP MUTE
DAP MUTE
SD53
SD
DC DET94
DATA2
CLK3
LCK4
OE17
DCDET
DCDET
S DET95
SDET
PCONT90
PCONT
MUTE ALL21
MUTE ALL
DT OUT CODEC79
RESET CODEC78
CLK DSP69
MOSI DSP74
RESET DSP72
MISO DSP77
SDET
SD
DAP SDA24
DAP SDA
DAP SDA
VALID18
VALID
VALID
Q6 11
D305
Q5 10
D304
Q4 9
D303
Q2 7
Q1 6
D301
Q8 13
Q7 12
D307
LED P.C.B.
PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B.
MAIN P.C.B.
HDMI P.C.B.
SMPS P.C.B.
3912
CN200CN1001
465
CN200CN1001
3615
CN200CN1001
483
CN200CN1001
474
CN200CN1001
4110
CN200CN1001
RESET CODEC
M RESET43
2625
CN200CN1001
3417
CN200CN1001
2922
CN200CN1001
M RESET
REMOTE
H SO36
H SO
2724
CN200CN1001
M CLK37
M CLK
RESET DSP
MOSI DSP
MISO DSP
DT OUT CODEC
HDMI MUTE48
501
CN200CN1001
HDMI MUTE
M SI35
2823
CN200CN1001
M SI
PWR CTRL89
3219
CN200CN1001
PWR CTRL
CLK DSP
FROM/TO
AUDIO
FROM/TO
HDMI
TO
POWER SUPPLY
FROM/TO
AUDIO
FROM
POWER SUPPLY
QR600
MUTING
CONTROL
HDMIMUTE DIS27
HDMIMUTE DIS
QR602
MUTING
QR601
MUTING
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY
W-SDO
W-SDI
W-SCL
W SCL
W SDO
W SDI
DIGITAL
TRANSMITTER
WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
CN101
8
CN100 CN100
513
CN101
10
CN100 CN100
612
CN101
9
CN100 CN100
711
6
7
4
13.1. SYSTEM CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM
69
Page 70

13.2. HDMI BLOCK DIAGRAM
: HDMI AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
HDMI P.C.B.
JK2203
HDMI AV IN
(BD/DVD)
HOTPLUG
DDC SDA
DDC SCL
IC2003
C3EBEC000047
EEPROM
SCL 6
SDA 5
Q2108
LEVEL SHIFTER
IC2232
C1AB00002989
HDMI RECEIVER
X2002
RESET 100
SCDT 101
IC2231
TC - 2
C3EBEC000047
EEPROM
QR2231,QR2232
Q2231,Q2232
Q2233,Q2234
Q2235,Q2236
DSDA128
DSCL129
19
16
15
HDMI SWITCHING
CIRCUIT
R1X0- ~ R1X2R1X0+ ~ R1X2+
INT 102
XTALIN 95
XTALOUT 96
CSDA
CSCL
MUTEOUT
X2231 X2001
26
27
73
IC2002
RFKWMHTB10PB
MICRO PROCESSOR
IDROM CK22
IDROM DT21
CEC I/O17
RX1 HPD76
WRITESEL25
RX1 SCL26
RX1 SDA27
XCOUT
11
XCIN10
RX RESET39
RX SCDT74
RX INT20
XOUT13
XIN15
D0 ~ D35 TC - 1
HDMI POWER 42
MAIN POWER 43
I2C SCL
I2C SDA
36
35
DCDET 54
M RST 68
SO 30
CLK 28
REM 5
AMUTE 53
TX HPD 75
TX RESET 38
TX INT 19
SI 29
D2003
D2004
QR2001
MUTING
IC2101
C1AB00002975
HDMI TRANSMITTER
RESET25
INT24
HPD 51
CSDA49
CSCL48
47
DSDA
46 DDC SCL15
DSCL
Q2103
SWITCH
3.3V
X2003
25
P1 7
XCOUT4
XCIN6
IC1008
C2CBDD000001
MICRO CONTROLLER
TX0- ~
TX0+ ~
P1 3 17
TX2-
TC - 3
TX2+
QR2004
SWITCH
DCDET
HDMI POWER
H POWER
M SI
M RESET
H SO
M CLK
REMOTE
HDMI MUTE
3.3V
DCDET
HDMI POWER
CN200CN1001
3219
CN200CN1001
2823
CN200CN1001
2625
CN200CN1001
2922
CN200CN1001
2724
CN200CN1001
3417
CN200CN1001
501
JK4001
Ir SYSTEM
1
3
4
2
JK2101
HDMI AV OUT
(TO TV(ARC))
HOTPLUG19
DDC SDA16
TO
POWER SUPPLY
MAIN P.C.B.
FROM/TO
SYSTEM CONTROL
10
TMDS CLK+
TMDS CLK- 12 R1XC-57
13
CEC
MCLK
LRCK
IEC958
TMDS CLK+10
CEC13
HEAC+(ARC)14
ARC
ARC
MCLK
BCK
BCK
LRCK
I2S0
I2S0
I2S1
I2S1
I2S2
I2S2
I2S3
I2S3
TO AUDIO
IEC958
R1XC+58
ODCK 5 IDCK88
MCLK 89 MCLK5
SCK 86 SCK11
WS 85 WS10
SD0 81
SD1 82 SD18
SD2 83 SD27
SD3 84 SD36
SPDIF 78 SPDIF4
SD09
IC2006
C0JBAZ001466
LOGIC
1A12
1A24
1A36
1A48
2A111
2A213
2A315
2A417
31
TXC+
TXC- 30 TMDS CLK-12
IC2081
C0JBAB000986
INVERTER
3
2A
2Y4
1Y1 18
1Y2 16
14
1Y3
12
1Y4
2Y1 9
7
2Y2
2Y3 5
2Y4 3
SU-HTB500PP HDMI BLOCK DIAGRAM
70
Page 71

13.3. AUDIO (1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
TO AUDIO
SECTION (2/2)
SU-HTB500PP AUDIO(1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
1
2
3
4
5
CODEC
C0FBZK000013
IC1002
DSP
C2HBCY000030
IC1001
SDRAM
C3ABMG000238
IC1006
MULTIPLEXER
C0JBAR000396
IC1005
CDOUT 8
/RST 12
RESET
A6
ARC
MCLK
RXP7
JK4101
INPUT 3 42
RXP247
BCK
DAI SCLK129
LRCK
DAI LRCLK130
I2S2
DAI DATA224
I2S3
DAI DATA323
I2S0
DAI DATA027
IEC958
IEC 95844
XTAL OUT16
I2S1
DAI DATA126
DAO LRCLK1
54
DAO SCLK1
52
CX LRCLK
DAO MCLK
40
RMCK
355
CX SCLK
2
DAO DATA149DAO DATA2
48
CX SDIN2
DAO DATA0
51
64
DAI LRCLK2
32
DAI SCLK2
33
SAI LRCLK
DAI DATA4
34
SAI SDOUT
60
SCP1 CLK
126
121
SCP1 MISO 124
CCLK
7
SCP1 MOSI
123
CDIN
954
SAI SCCLK
61
CH11
COM 4CH03
RXP148
OMCK59
A0 - A10 TC - 4
DQ0 - DQ15 TC - 5
X1000
XTI17
XTO18
1932
CN200CN1001
3912
CN200CN1001
465
CN200CN1001
3615
CN200CN1001
483
CN200CN1001
474
CN200CN1001
4110
CN200CN1001
1833
CN200CN1001
DSP SD1
DSP SD3
DSP MCLK
DSP LRCLK
DSP SCLK
DSP SD1
DSP SD3
DSP MCLK
DSP LRCLK
DSP SCLK
1536
CN200CN1001
1635
CN200CN1001
1338
CN200CN1001
RESET CODEC
RESET DSP
MOSI DSP
MISO DSP
MCLK
ARC
IEC958
I2S0
I2S1
I2S2
I2S3
BCK
LRCK
DT OUT CODEC
CLK DSP
FROM/TO
SYSTEM CONTROL
FROM/TO
SYSTEM CONTROL
FROM HDMI
MAIN P.C.B.
OPTICAL
DIGITAL AUDIO IN
(TV)
: OPTICAL/HDMI AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
HDMI P.C.B.
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY
71
Page 72

13.4. AUDIO (2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
: OPTICAL/HDMI AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
2
5
4
3
1
DSP SD3
DSP MCLK
DSP LRCLK
DSP SCLK
DSP SD1
TO AUDIO
SECTION (1/2)
DAP SDA
DAP SCL
DAP RESET
DAP PDN
DAP MUTE
DAP SDA
DAP SCL
DAP RESET
DAP PDN
DAP MUTE
IC401
C1AB00003216
DIGITAL AUDIO PWM PROCESSOR
XTL OUT
19
X400
XTL IN
20
MCLK
63
LRCLK
26
SCLK
27
SDIN3
29
SDA
24
SCL
25
RESET
11
PDN
13
MUTE
14
CLOCK, PLL &
SERIAL DATAI/F
IIC SERIAL
CONTROL I/F
MAIN P.C.B.
DIGITAL AUDIO
PROCESSOR
DAP CONTROL PWM CONTROL
SYSTEM CONTROL
PWM SECTION
DEVICE CONTROL
VALID VALID
39
PWM P 4
47
PWM M 4
46
PWM P 3
45
PWM M 3
44
PWM FL+
PWM FL-
PWM FR+
PWM FR-
PWM FL+
PWM FL-
PWM FR+
PWM FR-
IC405
C1AB00003217
DIGITAL AMPLIFIER
5 SD(L)
6 PWM A
8 PWM B
16 PWM C
18 PWM D
7 RST AB(L)
17 RST CD(L)
BST A 43
OUT A
OUT B 36
BST B 34
BST C 33
OUT C 31
OUT D 28
BST D 24
WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
DIGITAL
TRANSMITTER
WCLK
BCLK
ADAT0
Q500,Q501
SWITCH
SP FL-
39
SP FL+
SP FR-
SP FR+
CN1019CN100CN100
114
CN1017CN100CN100
132
CN1015CN100CN100
141
CN401*
-
+
-
+
FRONT
(LEFT)
FRONT
(RIGHT)
4
CN401*
3
CN401*
2
CN401*
1
FROM/TO
SYSTEM CONTROL
SD
SD
VALID
VALID
ECO DAMP
ECO DAMP
DC DET
DC DET
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY
72
SD
VALID
ECO SUPLLY
CIRCUIT
Q114,Q116
DC DETECT
SP PROTCT
SU-HTB500PP AUDIO(2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 73

13.5. IC TERMINAL CHART (HDMI/AUDIO)
Q0 16 D0 98
Q1 15 D1 97
Q2 14 D2 96
Q3 13 D3 95
Q4 10 D4 94
Q5 9 D5 93
Q6 8 D6 92
Q7 7 D7 91
Q8 3 D8 90
Q9 2 D9 86
Q10 1 D10 85
Q11 144 D11 84
Q12 141 D12 83
Q13 140 D13 82
Q14 139 D14 81
Q15 138 D15 80
Q16 135 D16 79
Q17 134 D17 78
Q18 133 D18 77
Q19 132 D19 75
Q20 129 D20 74
Q21 128 D21 73
Q22 127 D22 72
Q23 126 D23 71
Q24 123 D24 70
Q25 122 D25 69
Q26 121 D26 68
Q27 120 D27 67
Q28 117 D28 63
Q29 116 D29 62
Q30 115 D30 61
Q31 114 D31 60
Q32 111 D32 59
Q33 110 D33 58
Q34 109 D34 57
Q35 108 D35
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
D17
D18
D19
D20
D21
D22
D23
D24
D25
D26
D27
D28
D29
D30
D31
D32
D33
D34
D3556
IC2101
HDMI TRANSMITTER
IC2232
HDMI RECEIVER
SIGNAL NAMETC
1
Pin NoPort Name Pin No Port Name
TX0- 33 9
TX0+ 34 7
TX1- 36 6
TX1+ 37 4
TX2- 39 3
TX2+
TX0-
TX0+
TX1-
TX1+
TX2-
TX2+40
TMDS D0-
TMDS D0+
TMDS D1-
TMDS D1+
TMDS D2-
TMDS D2+1
IC2101
HDMI TRANSMITTER
SIGNAL NAMETC
3
Pin NoPort Name Pin No Port Name
SU-HTB500PP IC TERMINAL CHART (HDMI/AUDIO)
JK2201
HDMI AV OUT (TO TV(ARC))
TMDS D0- 9 R1X0- 61
TMDS D0+ 7 R1X0+ 62
TMDS D1- 6 R1X1- 65
TMDS D1+ 4 R1X1+ 66
TMDS D2- 3 R1X2- 69
TMDS D2+ 1 R1X2+
R1X0-
R1X0+
R1X1-
R1X1+
R1X2-
R1X2+70
IC2232
HDMI RECEIVER
SIGNAL NAMETC
2
Pin NoPort Name Pin No Port Name
JK2203
HDMI AV IN (BD/DVD)
EXT A0 102 A0 21
EXT A1 101 A1 22
EXT A2 99 A2 23
EXT A3 97 A3 24
EXT A4 96 A4 27
EXT A5 93 A5 28
EXT A6 91 A6 29
EXT A7 90 A7 30
EXT A8 88 A8 31
EXT A9 87 A9 32
EXT A10 103 A10
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A1020
IC1006
SDRAM
IC1001
DSP
SIGNAL NAMETC
4
Pin NoPort Name Pin No Port Name
EXT DQ0 68 DQ0 2
EXT DQ1 65 DQ1 3
EXT DQ2 64 DQ2 5
EXT DQ3 63 DQ3 6
EXT DQ4 61 DQ4 8
EXT DQ5 60 DQ5 9
EXT DQ6 59 DQ6 11
EXT DQ7 58 DQ7 12
EXT DQ8 78 DQ8 39
EXT DQ9 77 DQ9 40
EXT DQ10 75 DQ10 42
EXT DQ11 74 DQ11 43
EXT DQ12 72 DQ12 45
EXT DQ13 71 DQ13 46
EXT DQ14 70 DQ14 48
EXT DQ15 69 DQ15
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ1549
IC1006
SDRAM
IC1001
DSP
SIGNAL NAMETC
5
Pin NoPort Name Pin No Port Name
73
Page 74

13.6. POWER SUPPLY (1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
IC5799
MIP2F20MSSCF
SWITCHING POWER
SUPPLY CONTROL
TR 3
VCC 4
S7
S8
D5
FB 2
VDD 1
AC INLET P.C.B.
P5701
AC INLET
F1
4132413
DZ5701
L5701
L5702
D5798
TH5702
2
D5799
T5751
SUB
TRANSFORMER
6
5
2
1
3
3
4
PC5799
FEED BACK
RY5701
214
SMPS P.C.B. MAIN P.C.B.
D5896
7
10
IC5899
C0DAEMZ00001
SHUNT
REGULATOR
2
1
1C
SYS5V
R2
SYS6V
CN700H2016*
101
IC700
C0CBABC00117
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
3IN
OUT 1
SYS3.3V
SYS6V
SYS3.3V
3.3V
6V
BK3.3V
1
SYS6V
2
SDET
3
TO POWER SUPPLY
SECTION (2/2)
IC5701
C0DAAMH00013
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
D1
VCC 4
OCP/BD 7
FB 6
GND 3
D5727
D5724
D5729
D5701
Q5720
REGULATOR
3
T5703
MAIN
TRANSFORMER
4
5
6
D5731
2
1
PC5720
FEED BACK
4
3
HOT COLD
D703
Q5899
SWITCH
8
11
D5802
10
9
DC DETECT
1
2
FEED BACK
CIRCUIT
IC5801
C0DAEMZ00001
SHUNT
REGULATOR
PCONT
Q5841
DCDET
VDD(+20V) +20V
CN700H2016*
83
CN700H2016*
56
CN700H2016*
1,29,10
FROM
SYSTEM CONTROL
S DET
FP700
21
D704
IC702
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
1 VIN
VOUT 2
DC DETECT
Q704
IC701
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
VOUT 2
1 VIN
D5V
+12V +12V
D700
SYS3.3V
VREF VREF
CN350CN300
D5V
211
D5V D5V
CN350CN300
11,121,2
VREF
5V
LED P.C.B.
D5V
5V
D706D701
3.3V
VDD
12V
5V
TO
SYSTEM CONTROL
D5V
4
SDET
SDET
IC107
C0CBABC00117
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
OUT 1
3IN
IC100
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
+12V
+12V
CN101CN100
1 VIN
1,213,14
VOUT 2
DAP3.3V
VDD
5V
WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY
74
SU-HTB500PP POWER SUPPLY(1/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 75
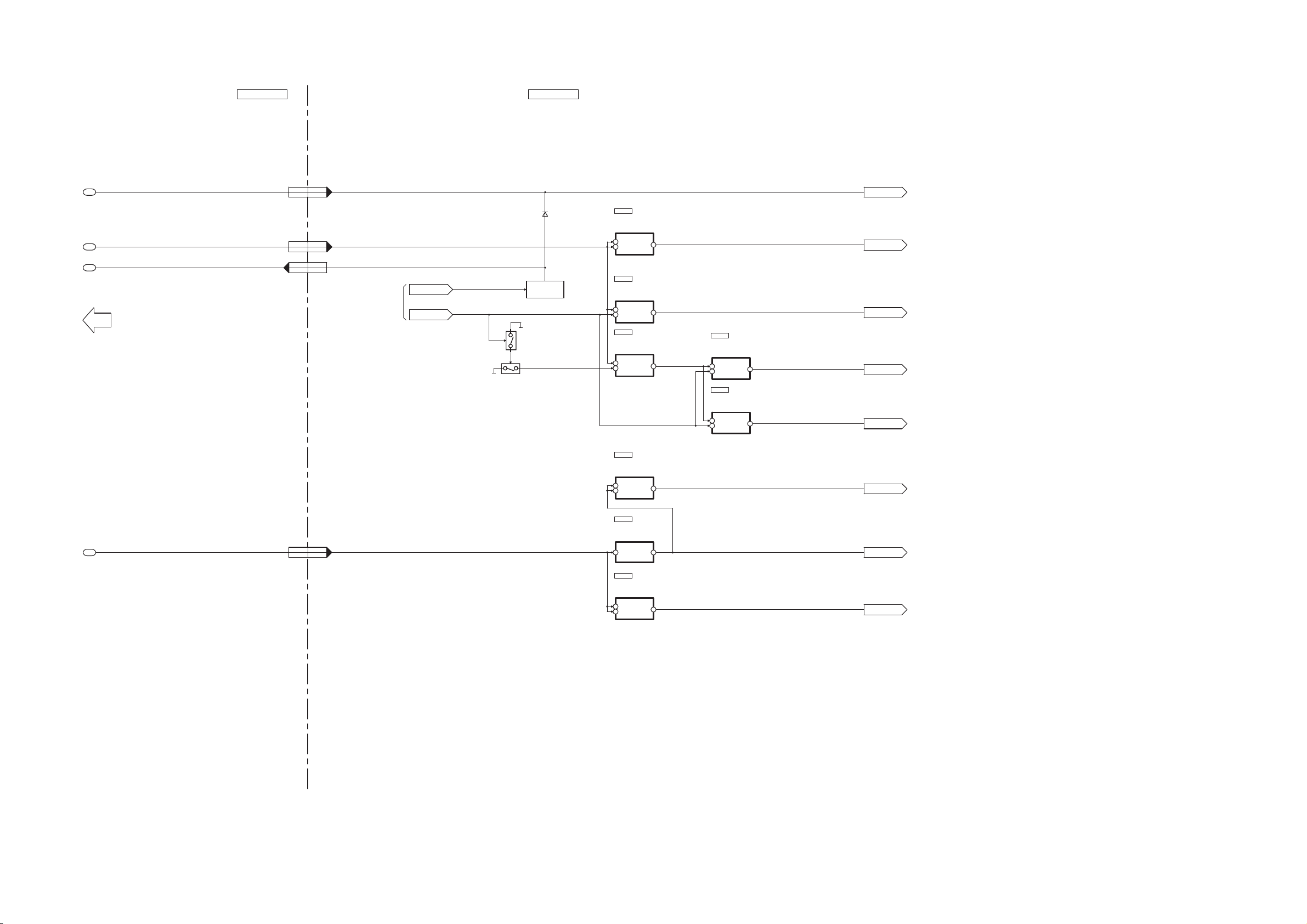
13.7. POWER SUPPLY (2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
TO POWER SUPPLY
SECTION (1/2)
1
2
3
4
D2006
IC1004
D3.3V
1 VIN
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
C0DBAYH00005
IC4724
VOUT 2
1IN
3 ON/OFF
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCBC00049
VOUT 2
VDDA(3.3V)
3.3V
D3.3V
3.3V
BK3.3V
3.3V
DCDET
FROM HDMI
HDMI POWER
MAIN P.C.B. HDMI P.C.B.
SU-HTB500PP POWER SUPPLY(2/2) BLOCK DIAGRAM
QR2002
DC DETECT
BK3.3V
30,3120,21
CN1001CN200
DCDET
1635
CN1001CN200
SYS6V
48,59,501,2,3
CN1001CN200
5V
VDDA(3.3V)
IC2004
1IN
2 ON/OFF
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCBG00013
OUT 3
SW3.3V
1.8V
SYS1.8V
IC4722
1 VIN
5 ON/OFF
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
C0DBAYH00005
VOUT 2
IC2102
1IN
2 ON/OFF
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCAG00015
OUT 3
IC2233
1IN
2 ON/OFF
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCAG00015
OUT 3
TO IC1001
TO IC1001
IC1003
1IN
2 ON/OFF
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCAG00015
OUT 3
VDD
VDD
TO IC2101
1.8V
1.8V
TO IC2232
SYS1.8V
1.8V
BK5V
5V
SW3.3V
5V
VDD
IC4793
1 VIN
3VC
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
C0CBCDC00014
VOUT 5
BK5V
D5V
42,43,447,8,9
CN1001CN200
QR4704
SWITCH
QR4703
SWITCH
BK3.3V
SYS6V
SDET
D5V
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY
75
Page 76

76
Page 77

14 Wiring Connection Diagram
NOTE: “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY.
SU-HTB500PP
WIRING CONNECTION DIAGRAM
CN401*
CN402*
TO
SPEAKERS
(FRONT)
(FOR ON BOARD
PROGRAMMING)
CN700
CN600
CN200
CN300
CN100
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
1
5
6
2
10
9
10
1
150
112
PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B. (SIDE B)
MAIN P.C.B. (SIDE B)
HDMI P.C.B. (SIDE B)
F
SMPS P.C.B.
E
AC INLET P.C.B.
G
WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
JK4101
OPTICAL DIGITAL
AUDIO IN (TV)
HDMI AV OUT
(TO TV (ARC))
JK2101
JK4001
JK2203
CN1001
1
2
3
19
15
10
5
1
21
4
3
19
15
10
5
1
150
HDMI AV IN
(BD/DVD)
Ir SYSTEM
CN351*
Z300
CN350
123
3
2
1
112
LED P.C.B. (SIDE B)
CN352*
1
2
3
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
AC VOLTAGE LINE.
PLEASE DO NOT TOUCH THIS P.C.B
(MAIN TRANSFORMER)
T5751
T5703
TL3*
RED
BLK
TL4*
H2016*
(SUB TRANSFORMER)
PRISEC
PRI
SEC
10
7
8
9
6
1
2
3
4
5
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
2
1
4
1
10
SOLDER SIDE
SOLDER SIDE
SOLDER SIDE
SOLDER SIDE
SOLDER SIDE
SENSOR
TL20*
TL10*
BLK
RED
P5701
120V 60Hz
AC IN
SOLDER SIDE
114
CN100
CN101
DIGITAL
TRANSMITTER
22
21
2
1
2
1
13
14
SOLDER SIDE
TL101*
TL102*
77
Page 78

78
Page 79

15 Schematic Diagram Notes
(All schematic diagrams may be modified at any time with
the development of new technology)
Notes:
S300:
S301: VOLUME UP switch (VOLUME +).
S303: SELECTOR switch (INPUT SELECTOR).
S304: VOLUME DOWN switch (VOLUME -).
POWER switch ( ).
• Voltage and Signal lines:
: +B signal line
: -B signal line
: Audio Output signal line
: Video Output signal line
• “ * ” REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY.
• Importance safety notice :
Components identified by ( ) mark have special characteristics important for safety.
Furthermore, special parts which have purposes of fire-retardant (resistors), high-quality sound (capacitors), low-noise
(resistors), etc. are used.
When replacing any of components, be sure to use only
manufacturer's specified parts shown in the parts list.
• Capacitor values are in microfarad(μF) unless specified
otherwise, F=Farad, pF=Pico-Farad
Resistance values are in ohm(Ω), unless specified otherwise, 1K=1,000Ω, 1M=1,000KΩ
: HDMI Video Input signal line
: Optical/HDMI Audio Input signal line
79
Page 80

80
Page 81

16 Schematic Diagram
A
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
A
HDMI CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 1
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
2/6 3/6
5/6
1/6
4/6 6/6
TO HDMI
SECTION (2/6)
TO HDMI
SECTION (4/6)
P1
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
: HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
: AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
: +B SIGNAL LINE
DQ1
DQ2
DQ0
0
R1025
DSP_SD3
DSP_SD1
3.3KR1029
R1028
3.3K
3.3KR1030
CX_SDIN2
C1071
0.1
33
33
33
33
33
33
R1023
R1038
R1037
R1045
R1039
R1031
0.1
C1072
0.1
C1075
C1049
10
C1081 10
C1080 10
DQ6
J0JHC0000021
LB1000
J0JHC0000021
LB1001
DQ7
4
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
2135
IC1003
C0CBCAG00015
0.1
C1059
DQ4
DQ5
865742
13
DQ3
LB1003
J0JHC0000021
MULTIPLEXER
33
R1024
C1035
0.1
C1045
10
C1037
1
J0JHC0000021
LB1006
R1015 82
CX_SCLK
CX_LRCLK
LDQM
RMCK
3
1
2
4
5
C0CBCBC00049
IC1004
IC1005
C0JBAR000396
A4A6A5
A3
A9A7A8
865742
13
A0
A1
BA0
A10
865742
13
RX1002
D1H83304A024
RX1003
D1H83304A024
RX1004
D1H83304A024
RX1008
D1H83304A024
RX1007
D1H83304A024
RX1006
D1H83304A024
RX1005
D1H83304A024
A2
865742
13
DQ9
DQ11
DQ10
DQ8
UDQM
DQ12
DQ14
DQ15
865742
13
DQ13
865742
13
865742
13
SD_CLK
SD_CKE
R1007
R1009
R1008
333333
DQ0
DQ15
LB1008
J0JHC0000021
1
C1038
DQ1
DQ14
C1039
0.1
DQ2
DQ13
DQ3
DQ12
C1070 0.1
SCP1_IRQ#
C1041
0.1
C1040
0.1
1000P
C1028
0.1
C1069
SD_WE
CAS
0.1
C1062
C1077
10
C1076
10
SD_CS
8657
132
4
D1H83304A024
RX1001
RAS
CS_CODEC
SCP1_MOSI
SCP1_MOSI
SCP1_MISO
DSP_RESET
CLK
CLK
INTREQ_CODEC
C1068
0.1
C1009 100P
C1007 100P
C1008 100P
C1006 100P
RESET_CODEC
L1000 J0JBC0000014
J0JBC0000014
J0JBC0000014
J0JBC0000014
J0JBC0000014
L1001
L1002
L1003
L1004
DT_OUT_CODEC
C1010 100P
A0
A10
A7
A8
R1021
82
1M
R1019
A5
A4
GND
A2
A3
A6
A1
0.1
C1044
C1032 9P
C1031 9P
X1000
H0J245500068
DQ5
DQ6
DQ4
LDQM
CAS
SD_WE
DQ7
C1043
0.1
UDQM
SD_CLK
DQ9
DQ11
DQ10
C1057
10
C1056
10
DQ8
C1042
0.1
RAS
SD_CKE
A9
BA0
SD_CS
C1029
0.1
C1030
0.1
R1020
10C1058
C1033 0.1
5.1K
J0JHC0000021
LB1002
R1014
3.3K
R1013
3.3K
SAI_LRCLK
SAI_SCLK
LRCLK
SAI_SDOUT
C1074
0.1
I2S3
I2S1
I2S0
I2S2
C1067
0.1
DAI_SCLK1
SCP1_MISO
SCP1_BSY
SCP1_BSY
2
1
49
12
10
9
11
40
39
41
13 38
6
4
5
45
47
46
8
7
43
42
44
27
26
24
25
22
20
18
16
14
15
17
19
21 30
29
34
33
36
37
35
31
32
23 28
3
48
50
IC1006
C3ABMG000238
R1012
3.3K
R1018
3.3K
SCP1_CS
0.1
C1063
C1064
0.1
C1065
0.1
C1073
0.1
0.1
C1066
5V
103
107
106
110
113
119
118
124
127
128
125
126
121
120
123
122
115
114
117
116
111
112
108
109
104
105
61
62
1211 14 1513 18 1916 17
957631 24 8
10
57
26 28 29272221 24 2523
45
47
46
42
43
40
39
41
44
37 383433 353130 32 36
55
56
51
52
49
48
50
54
53
20
60
59
58
95 94
10099102101
9698 97
64
63
85 8487 86 83 8081 76 6869 6567 667375 74 7072 7178 7779829193 92 89 8890
IC1001
C2HBCY000030
GND3
EXT_D2
IN
GND
NC
ON/OFF
OUT
VDD3
EXT_A12
PLL_REF_RES
XTAL_OUT
XTO
XTI
VSSVDD
A5
A4
A2
A3
GNDA
EXT_A9
EXT_A11
EXT_A8
EXT_D9
GNDIO3
EXT_D8
EXT_D3
GNDIO2
EXT_D0
VDDIO3
DAI_DATA0
DAI_DATA1
DAI_SCLK1
VDDIO8
VDD8
DAI_DATA3
GND8
DAI_DATA2
EXT_D10
EXT_D11
SD_CLKOUT
SD_DQM1#
SD_CLKIN
EXT_D6
EXT_D7
EXT_D4
EXT_D5
VDD2
HS3
EE_CS
GND1
INOUT
NC
ON/OFF
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
GND
6A
4
52
1
3 COMCH0
CH1
V+
GND
[39] HS4
TEST
VDD1
VDDIO1
GNDIO1
DBCK
RXP1
GND2
DAO_SCLK1
DAO_LRCKL1
SD_DQM0#
DBDA
DAI_SCLK2
DAI_DATA4
UART_TX_EN
DAI_LRCLK1
DAI_LRCLK2
GNDIO8
[40] DAO_MCLK
DAO_DATA0
DAO2_SCLK
DAO2_LRCLK
DAO_DATA1
DAO_DATA2
DAO1_DATA3
[65] EXT_D1
VDDIO2
EXT_D13
EXT_D12
EXT_D15
EXT_D14
[66] EXT_WE
SD_CLKEN
DSP
VDDA(3.3V)
EXT_CS2#
[103] EXT_A10
GNDIO5
SD_RAS#
SD_WE#
SD_CAS#
[104] BA0/EXT_A13
BA1/EXT_A14
EXT_A7
VDD4
EXT_A4
EXT_A5
EXT_A0
GND4
EXT_A2
EXT_A3
VDDIO5
EXT_A1
EXT_A6
GNDIO4
VDDIO4
VDDQ
DQ15
VSSQ
DQ14
VSS
DQ12
DQ13
NC
CKE
NC
DQ9
DQ8
CLK
VDDQ
VSSQ
UDQM
A8
A7
A9
DQ11
DQ10
DQ2
DQ3
VDD
DQ1
DQ0
VSSQ
VDDQ
SDRAM
BA
CS
A0
WE
CAS
DQ6
DQ7
LDQM
VSSQ
VDDQ
A10
RAS
DQ4
DQ5
UART_RXD
UART_CLK
VDD7
SCP2_CS#
GND6
VDD6
SCPY_IRQ#
SCP1_MISO
SCP1_CLK
SCP1_MOSI
SCP1_BSY
[1] SCP2_CLK
[2] SCP2_MISO
[3] SCP2_MOSI
VDD5
EXT_A15
SD_CS#
RESET
SCP1_CS
DSP_RESET
GND5
GNDIO6
EXT_A17
VDDIO6
EXT_OE#
EXT_CS1#
EXT_A18
EXT_A19
EXT_A16
UART_TXD
GNDIO7
VDDIO7
SCP1_IRQ#
SCP1_CS
SCP2_IRQ#
DDAC
A6A1
GND7
OMCK
33R1053
33R1055
CS_CODEC_M
RESET_CODEC_M
INTREQ_CODEC_M
R4368 1K
R4366 1K
R4367 1K
MOSI_DSP
MISO_DSP
C4452
4V330
R4370 1K
R4369 1K
R4371 100
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
DSP_GND
R4365
100
RESET_DSP
CS_DSP
CLK_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
C4369 22P
C4367 22P
C4368 22P
C4371 22P
C4370 22P
C4365 22P
C4366 22P
C4363 22P
C4364 22P
C4361 22P
C4362 22P
BUSY_DSP
R4364 1K
R4361 100
R4363 1K
R4362 1K
D3.3V
LB4108
J0JYC0000096
MCLK_D
J0JBC0000072
LB2001R2046
100
R2076 0
R2092 0
R2093 0
0R2075
R2074 0
BCK_D
LRCK_D
100R2047
R2049 100
100R2051
100R2052
100R2050
R2048 100
J0JBC0000072
LB2002
I2S_2_D
I2S_0_D
I2S_1_D
I2S_3_D
I2S1
I2S2
I2S3
DAI_SCLK1
I2S0
LRCLK
16.1. HDMI CIRCUIT (1/6)
81
Page 82

16.2. HDMI CIRCUIT (2/6)
A
B
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 2
HDMI CIRCUIT
TO HDMI
SECTION (1/6)
D3.3V
RXP1
IEC958_D
SAI_SDOUT
RMCK
DSP_MCLK
OMCK
SAI_LRCLK
SAI_SCLK
CX_SDIN2
DSP_SCLK
CX_SCLK
CX_LRCLK
DSP_LRCLK
: +B SIGNAL LINE
J0JHC0000021
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
LB1004LB1007
J0JHC0000021
LB2003
J0JBC0000072
C1027
C1055
0.1
10
33R1035
33R1010
82R1056
33R1051
33R1052
0.1C1036
82R1033
82R1036
82R1011
33R1042
33R1016
33R1017
R1046 0
R1032
0
C1083
0.01
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
C1012 1000P
C1013
C1014
C1015
C1016
R1022
4748 4445 4041 36 3335 343839 3743 4246
RXP2
RXP1
VD
DGND
VLS
SAI_SDOUT
RMCK
CX_SDOUT
ADCIN2
ADCIN1
OMCK
SAI_LRCLK
SAI_SCCLK
CX_SDIN4
CX_SDIN3
CX_SDIN2
1
23
100P
100P
100P
100P
100K
: HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
C1085
C1087
C1084
C1023 2200P
R1005
R1044
C1024
0.01
C1086
0.047
2.4K
150
10
C1054
RXP6
VLC
RXP7
VARX
IC1002
CODEC
CCLK
CDOUT
879465
0.1
C1025
AGND
LPFLT
MUTEC
[33] AOUTA2[34] AOUTB1[35] AOUTB1+
[17] VQ
[18] FILT+
CS
INT
CDIN
AOUTA1-
RST
0.01
C1026
RXP3
RXP4
IEC 958
[49] RXP0
[50] TXR
C0FBZK000013
[1] CX_SDIN1
[2] CX_SCLK
[3] CX_LRCLK
VD
DGND
C1011
0.1
C1050
10
AOUTA2+
AOUTB2+
AOUTA1+
AOUTB2-
AOUTA3-
AOUTA3+
AOUTB3+
AOUTB3-
AOUTA4-
AOUTA4+
AOUTB4+
AOUTB4-
REFGND
AINR-
AINR+
0.01
0.01
0.01
AGND
AINL+
VA
AINL-
1612 1310 11 1514
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
R1004 1K
R1003 1K
R1000
: AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
LB4101
J0JBC0000014
C4104
C4103
0.1
6.3V100
R2040 100
R2039 100
R2038 100
R2053 100
R2037 100
C2015
LB2004
J0JCC0000119
LB1005
J0JHC0000021
C1060 10
1KR1002
1KR1001
100
0R1026
16V10C1053
0.1C1022
6.3V100C1052
0.1C1021
0.1C1020
50V4.7C1051
ARC
RESET_CODEC
INTREQ_CODEC
CS_CODEC
SCP1_MOSI
DT_OUT_CODEC
HDMI_MUTE
RESET_DSP
MOSI_DSP
MISO_DSP
BUSY_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
CS_DSP
CLK_DSP
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
CS_CODEC_M
INTREQ_CODEC_M
RESET_CODEC_M
DCDET
REMOTE
H_POWER
H_REQ
5V
M_CS
H_SO
M_SI
MCLK
M_RST
HDMI_POWER_M
DSP_GND
BK3.3V
DSP_SD1
DSP_SD3
DSP_SCLK
DSP_LRCLK
DSP_MCLK
GND
SYS6V
CLK
R4102
R4101
0
0
C4101
0.01
LB2242
J0JHC0000021
J0JHC0000021
R2041 10K
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
LB4107
LB2010 J0JHC0000021
LB4106 J0JYC0000339
LB4105
LB4104
LB4103
LB4102
1
R2090
R2094
R4375
P1P1
JK4101
1
VCC
GND
2
3
INPUT
0
0
0
CN1001
1
HDMI_MUTE
2
DSP_GND
3
RESET_DSP
4
MOSI_DSP
5
MISO_DSP
6
BUSY_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
7
8
CS_DSP
9
DSP_GND
10
CLK_DSP
11
DSP_GND
12
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
13
CS_CODEC_M
14
INTREQ_CODEC_M
15
RESET_CODEC_M
16
DC_DET
17
REMOTE
18
KEY1
19
MAIN_POWER
20
H_REQ
21
M_CS
22
H_SO
23
M_SI
24
M_CLK
25
M_RST
26
HDMI_GND
27
HDMI_POWER
28
DSP_GND
29
DSP_GND
30
BK3.3V
31
BK3.3V
32
DSP_SD1
33
DSP_SD3
34
DSP_GND
35
DSP_SCLK
36
DSP_LRCLK
37
DSP_GND
38
DSP_MCLK
39
DSP_GND
40
DSP_GND
41
DSP_GND
42
+5V
43
+5V
44
+5V
45
HDMI_GND
46
HDMI_GND
47
HDMI_GND
48
SYS6V
49
SYS6V
50
SYS6V
OPTICAL
DIGITAL AUDIO IN
(TV)
50
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN200)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 9
1
TO HDMI
SECTION (3/6)
TO HDMI
SECTION (5/6)
82
2/6 3/6
1/6
5/6
4/6 6/6
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
Page 83

16.3. HDMI CIRCUIT (3/6)
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
A
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
A
HDMI CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 3
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
2/6 3/6
5/6
1/6
4/6 6/6
TO HDMI
SECTION (2/6)
TO HDMI
SECTION (6/6)
P1
P1
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
: HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE
: AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
: +B SIGNAL LINE
LB2011
J0JHC0000021
LB4201
J0JCC0000308
LB4200
J0JCC0000308
C4771
0.1
FOR ON BOARD
PROGRAMMING
1K
R2005
H0J327200172
X2002
47PC2004
0.1C2003
47P
C2005
H_POWER
HDMI_POWER
RX1_5V
R2066 82
R2068
100
R2067 82
100
R2069
4.7K
R2209
TX_DDC_SDA
TX_DDC_SCL
TX_HPD
RX1_HPD
RX_SCDT
QR2002
B1GBCFJJ0007
B0JCAE000001
D2001
B0JCAE000001
D2002
B0ACCK000005
D2009
C2007
0.1
M_RST
HDMI_MUTE
D2006
B0ACCK000005
DC DETECT
R2019 100
B0ACCK000005
D2003
QR2001
B1GBCFJJ0007
100R2011
100R2013
100R2012
100R2010
100KR2006
150KR2002
R2044
150
R2045
150
C2011
6.3V100
C2009
0.1
M_CS
TX_INT
RX_INT
H_SO
BK3.3V
RX_RST
I2C_CK
I2C_DT
R2022 10K
TX_RST
D2004
B0ACCK000005
R2021 100
MCLK
R2027 1.8K
M_SI
100R2033
R2026 100
4.7KR2032
R2031 4.7K
100R2034
1
C2006
R2023 47
C2001
0.1
R2024 47
R2025 100
3425
98
94
95
92
91
93
97
96
1
100
99
80 78 767779
87
86
88
89
82
84
83
81
85
90
1614 15 1711 1 312
69 67 65 64666870 51
49
45
47
46
41
44
42
43
48
50
30
39
37
35
32
31
34
33
36
38
40
22 2320 21 26 282724 2518 19
53555762 60 596163 58 56 54295275 73 717274
976810
IC2002
RFKWMHTB10PB
R2018 4.7K
C2013
1
7
8
54
3
2
1
6
C3EBEC000047
IC2003
R2028 1.8K
C2012 1000P
R2017 4.7K
R2016 4.7K
1000PC2010
B0ACCK000005
D2005
R2043
4.7K
R2042
4.7K
1KR2007
1.8KR2001
0R2055
100KR2008
100KR2009
C2002
1000P
VSYNC_M
CEC_IO
REMOTE
H_REQ
HDMI_LEDNC
NCNCNC
NC
NC
DCDET
NC
TX_HPD
STBY_H
STBY_H
5V_DET
NC
TX_DDC_CK
NC
KEY1
TX_DDC_DA
VCC2
VSS
NC
NC
NC
NC
AMUTE
DCDET
NC
SW_INT
M_RST
RX_SCDT
RX0_HPD
RX1_HPD
RX1_5V_DET
RX0_5V_DET
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
[50] NC
[49] CEC_OUT
NCIN2_5V
RX0_5V_DET
REQ
IN1_5V
AVSS
AVCC
NC
NC
NC
RX1_5V_DET
NC
Flash_CE
RX_RESET
NC
MAIN_POWER
Flash_EPM
HDMI_POWER
UPCON_SCL
UPCON_SDA
I2C SCL
GND
VREF
V_CHECK
I2C SDA
NC
NC
NC
Flash_BUSY
Flash_SCLK
TX_RESET
SI
XCOUT
NC
M_CSNCVSYNC_COUNT
XCIN
NC
CLK
CEC I/O
VCC1
VSS
BYTE
XIN
XOUT
RX_INT
CNVSS
RESET
TX_INT
SW_RST
RX1_SDA
RX1_SCL
IN1_5V
IN2_5V
IDROM_DT
IDROM_CK
WRITESEL
SO
REM
VSYNC_MONI
GND SDA
SCLA2
VCCA0
WPA1
SW_3.3V
V_CHECK
GND
MUTING
EEPROM
MICRO PROCESSOR
R2014 47K
R2015 47K
31
2
H2D400400018
X2001
100K
R2071
RX0_5V
WRITESEL_0
RX_EDID_CK
RX_EDID_DT
AMUTE
1KR2030
6
5
8
9
10
12
11
7
2
1
4
3
14
13
16
15
CN2001
+3.3V
IDROM_CK
IDROM_DT
TXD
GND
RXD
VCC
MODE
MODE
BUSY
SLCK
RESET
RESET1
RESET2
RESET2
CNVSS
CNVSS
CNVSS
GND
RESET
PIN46 (CE)
PIN41 (EPM)
100
R1058
C1018
0.1
7
8
9
6
1
2
5
3
4
12
14
16
18
19
20
17
15
13
10 11
IC1008
C2CBDD000001
MICRO CONTROLLER
R1062
4.7K
0
R1060
R1059
4.7K
C4785
10V470
R4374
1K
QR2004
B1ABMF000020
SWITCH
15
R4372
15
R4373
2
1
3
4
JK4001
Ir SYSTEM
3
1
2
X2003
H2D100500004
REMOTE
MODE
RESET1
AVCC
AVSS
XCIN
XCOUT
P3_5
P3_7
MODE
/RESET
P4_2/VREF
P1_7
P1_6
P4_5
P1_3
P1_1
P1_0
P1_4
P1_2
P1_5
P3_4
SYS6V
P3_3
100R2003
83
Page 84

16.4. HDMI CIRCUIT (4/6)
A
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 4
HDMI CIRCUIT
C2083
1
R2084
51
R2081
100
C2082
0.1
C2081
1
LB2081
J0JCC0000119
JK2101
HDMI AV OUT
(TO TV(ARC))
G1G2
HOT PLUG
+5V POWER
DDC/CEC GND
DDC_SDA
DDC_SCL
HEAC+(ARC)
CEC
TMDS CLK-
CLK GND
TMDS CLK+
TMDS D0-
D0 GND
TMDS D0+
TMDS D1-
D1 GND
TMDS D1+
TMDS D2-
D2 GND
TMDS D2+
G3 G4
VA2109
EZJZ0V80008B
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Q2108
B1CFGD000002
LEVEL SHIFTER
2DS2G
3
4
2
1
5
1D 1G
IC2081
C0JBAB000986
INVERTER
1
2
3
R2083 10K
R2082 100
R2101 47K
C2277
0
LB2102 J0JCC0000119
R2073
0
C2280
0
R2142 1K
R2141 27K
0.1C2142
330PC2141
R2085
10K
1Y
6
1A
5
GND
VCC
2Y
4
2A
J0JCC0000119LB2101
J0JCC0000119LB2103
J0JCC0000119LB2104
VA2101
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2102
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2103
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2104
EZAEG2A50AX
C2085
10
VA2105
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2106
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2107
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2108
EZAEG2A50AX
R2143 220
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE: +B SIGNAL LINE
D2101
B0JCAE000001
Q2103
B1ABCF000079
SWITCH
R2102
10K
VA2111
VA2110
R2107
5
6
7
8
5
6
7
8
EZJZ0V80008B
EZJZ0V80008B
1.8K
1.8K
R2106
VA2112
4
3
J0MAB0000235
2
1
4
3
J0MAB0000235
2
1
TO HDMI
SECTION (1/6)
R2103
10K
VA2113
EZJZ0V80008B
EZJZ0V80008B
L2101
L2102
R2105
47K
R2104
100
LB2082
J0JHC0000021
C2084
0.1
HPD
DSDA
DSCL
TXC-
TXC+
TX0-
TX0+
TX1-
TX1+
TX2-
TX2+
R2120
6.8K
R2121
6.8K
SW_3.3V
ARC
TX_DDC_SDA
TX_DDC_SCL
TX_HPD
BK5V
GND
CEC
BK3.3V
CEC_IO
TX_RST
TX_INT
I2C_CK
I2C_DT
1.8V
SW_3.3V
TXC-
TXC+
TX0-
TX0+
TX1-
TX1+
TX2-
TX2+
DSCL
DSDA
HPD
LB2105
LB2106
J0JHC0000021
LB2107
J0JHC0000021
J0JHC0000021
R2124
R2144
680
18
C2108 10
C2107 0.1
1000PC2109
C2110 1000P
C2111 1000P
1000PC2112
1000PC2113
C2114
10
LB2108
J0JHC0000021
47R2122
47R2123
10C2104
10C2105
10C2106
LB2109
J0JHC0000021
LB2110
J0JHC0000021
R2128
R2125
4.7K
1K
26
27
PVCC1
28
29
AGND
30
TXC-
31
TXC+
32
AVCC18
33
TX0-
34
TX0+
35
AGND
36
TX1-
37
TX1+
38
AVCC18
39
TX2-
40
TX2+
AGND
42
PVCC2
43
AGND
44
AVCC33
45
DDCPWR5V
46
DSCL
47
DSDA
CSCL
48
CSDA
49
50
R2126
4.7K
25
RESET
HPD
23 21 20224124
INT
RSVDL
C2115 0.1
DL3
IOVCC33
0.1C2116
R2129
47K
C2117
1000P
19 17 15 141618
DL2
DL1
DR2
DR3
[26] AGND
[27] EXT_SWING
[50] CI2CA
D35
GND
CVCC18
D34
D34
D33
D35
C2118
1000P
DL0
DR1
DR0
DCLK
C1AB00002975
HDMI TRANSMITTER
D30
D31
D32
D33
D30
D32
D31
D29
1000PC2119
13
GND
IOVCC33
IC2101
D28
D29
D28
BCK_TX
47R2130
SCK
CVCC18
GND
CVCC18
1000PC2120
I2S_0_TX
LRCK_TX
13
47R2131
10 8 7912 11
WS
SD0
D27
IOVCC33
D27
I2S_1_H
I2S_2_H
SD1
D26
D25
D26
I2S_3_H
MCLK_TX
865742
SD2
SD3
MCLK
[100] GND
[99] CVCC18
[76] CVCC18
D24
D23
D25
D23
D24
IEC958
RX2101
D1H83304A024
47R2132
R2133 47
465 213
SPDIF
VSYNC
HSYNC
IOVCC33
D21
D22
D20
7471 7267 685655 58575251 5453 65 6661 6259 60 6463 7069 73 75
D21
D20
D22
IDCK
GND
P1
P3
VSYNC
HSYNC
DE
C2125 0.1
DE
100
99
D0
98
97
D1
96
D2
95
D3
94
D4
93
D5
92
D6
91
D7
90
D8
89
88
87
86
D9
85
D10
84
D11
83
D12
82
D13
81
D14
80
D15
79
D16
78
D17
D18
77
76
D19
D19
0.1C2126
0.1C2122
10C2123
10C2124
1000PC2121
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
DCLK
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
D17
D18
2/6 3/6
1/6
5/6
4/6 6/6
TO HDMI
SECTION (5/6)
P2
R9000
0.1
R2284
R2285
00
HDMI
HDMI
GND
GND
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
84
Page 85

16.5. HDMI CIRCUIT (5/6)
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
A
HDMI CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 5
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
2/6 3/6
5/6
1/6
4/6 6/6
TO HDMI
SECTION (4/6)
TO HDMI
SECTION (2/6)
TO HDMI
SECTION (6/6)
P1
P2
P3
P1
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE: +B SIGNAL LINE
R2154
47
VSYNC_M
VSYNC
BCK_H
I2S_2_H
I2S_3_H
I2S_1_H
I2C_DT
I2C_CK
LRCK_H
82R2260
0.1
C2250
R2257
1.8K
R2258
1.8K
82R2259
LB2236
J0JHC0000021
D30
D28
I2S_1_D
I2S_1_H
D26
D24
D25
D27
I2S_0_D
D29
D1H83304A024
RX2240
D34
D32
D31
D33
D1H83304A024
RX2241
D35
C2266 1
C2267 1
4.7KR2267
C2264 0.1
0.1C2262
R2266 1K
R2264
4.7K
C2257
18P
82
R2261
MCLK_H
820
R2262
18P
C2256
X2231
H0J283500018
C2251 0.1
C2253 1
R2263
1M
0.1C2252
C2255
0.1
LB2237
J0JHC0000021
LB2238
J0JHC0000021
1000P
C2261
C2258
1
C2259
1
C2272 1
RX_RST
AMUTE
RX_INT
RX_SCDT
0.1C2271
I2S_0_H
D23
D21
D19
D17
D15
D13
D11
D9
D8
D10
D12
D14
D16
D18
D20
MCLK_H
MCLK_TX
R2153
47
BCK_TX
R2152
47
LRCK_TX
R2151
47
I2S_0_TX
IEC958_D
R2063
1K
LRCK_H
I2S_3_D
BCK_H
D22
I2S_2_D
J0JHC0000021
LB2009
C2019
1
IEC958
BCK_D
MCLK_D
I2S_3_H
LRCK_D
0.01
C2018
8
9
7
6
1
2
5
3
4
12
14
16
18
19
20
17
15
13
10
11
IC2006
C0JBAZ001466
I2S_2_H
DCLK
R2265
47
D5D4D7
D6
865742
13
D1H83304A024
RX2234
C2265
6.3V100
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
8657
4
12
3
D1H83304A024
RX2235
D1H83304A024
RX2239
D1H83304A024
RX2237
D1H83304A024
RX2236
D1H83304A024
RX2238
C2273 0.1
C2274 0.1
C2275 0.1
C2270 0.1
DE
HSYNC
865742
13
RX2232
D1H83304A024
0.1C2254
0.1C2260
0.1C2263
D2D3D0
D1
865742
13
D1H83304A024
RX2233
C2247
1
G1CR82KA0010
L2231
J0JHC0000021
LB2235
LB2243
0
LB2239
J0JCC0000308
C2246
0.1
C2236 0.1
C2233 10
C2235 1
C2234 10
C2244
C2243
C2245
C2239
C2237
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
C2238
1C2241
C2242
C2240
I2S_0_H
865742
13
D1H83304A024
RX2231
IEC958
47R2256
47R2255
C2249 0.1
R2278 82
0.1C2248
82
R2252
C2279 0
R2091 0
R2072 0
C2276
0
C2278
0
STBY_H
CVCC18
REGVCC
1Y3
2OE
1Y1
VCC
1Y2
2A3
2A4
2A1
2A2
1Y4
2Y2
1A1
2Y4
1OE
2Y3
1A3
1A2
GND
1A4
2Y1
Q28
CGND
CVCC18
Q29
Q22
Q21
Q23
Q16
Q17
Q14
Q13
Q15
Q19
Q18
IOGND
IOGND
ODCK
Q11
CVCC18
Q9
Q8
Q12
CGND
Q4
Q5
IOVCC33
Q7
Q6
CGND
CGND
CVCC18
IOVCC33
Q20
Q24
Q26
Q27
IOGND
Q25
IOVCC33
Q31
CVCC18
CGND
Q33
Q32
RSVDL
RSVDNC
INT
SCDT
[109] Q34
[1] Q10
IOGND
CI2CA
IOVCC33
RESET
IOGND
IOVCC33
Q35
Q30
RSVDNC
SPDIF
[71] AGND
MUTEOUT
RSVDNC
DSDA0
DSCL0
R0XC-
IOGND
IOVCC33
R0XC+
R1X2+
CGND
CVCC18WSSD3
SCK
IOVCC33
IOGND
SD0
SD2
SD1
[72] AVCC18
R1PWR5V
R1PWR5V
DSDA1
DSDA1
DSCL1
DSCL1
GND
CVCC18
VSYNC
CGND
CVCC18
EVNODD
CSCL
CSDA
R1X2-
[37] AVCC18
[38] AVCC33
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99
100101 102103104105 106107108
117
116
115
114
113
122
121
120
119
118
127
126
125
124
123
132
131
130
135
134
133
138
137
136
141
140
143
142
144
139
129
128
112
111
110
109
36 35 34 33 3132 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
R1XC+
R0X0-
AVCC33
R0X1-
AGND
AVCC33
R0X0+
R0PWR5V
AGND
AGND
AVCC33
RSVDNC
R1XC-
AGND
R0X1+
AVCC18
AGND
AVCC33
R0X2-
R0X2+
R1X1+
AGND
AVCC33
IOVCC33
IOGND
AGND
R1X0+
R1X1-
AVCC33
AVCC33
AGND
R1X0-
IOGND
Q0Q3Q2
Q1
IOVCC33
DE
IC2232
C1AB00002989
DVCC18
DGND
CVCC18
CGND
XTALIN
XTALVCC
XTALOUT
MCLK
HSYNC
SYS1.8V
SW_3.3V
RX0_5V
SW_3.3V
HDMI RECEIVER
LOGIC
47K
R2269
THERMAL PAD
T1
R1X1-
R1X1+
R1XC-
R1X0-
VA2235
R1XC+
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2236
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2237
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2238
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2231
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2232
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2233
EZAEG2A50AX
VA2234
EZAEG2A50AX
R1X0+
R1X2-
R1X2+
R2233
100K
J0JCC0000119LB2231
J0JCC0000119LB2232
J0JCC0000119LB2233
J0JCC0000119LB2234
47K
R2232
G3 G4
G1G2
5
3
4
7
9
8
6
1
2
10
13
15
17
19
18
16
14
11
12
JK2203
HDMI AV IN
(BD/DVD)
VA2240
EZJZ0V80008B
VA2241
EZJZ0V80008B
VA2239
EZJZ0V80008B
VA2242
EZJZ0V80008B
C2231
0.1
DDC_SDA
CEC
CLK GND
TMDS CLK-
D1 GND
D2 GND
TMDS D1+
TMDS D1-
TMDS D2+
TMDS D2-
D0 GND
TMDS D0-
TMDS D0+
TMDS CLK+
DDC_SCL
N.C.
DDC/CEC GND
HOT PLUG
HOTPLUG
+5V POWER
CEC
R2283
511
C2283
82R2254
82R2253
R2272 4.7
R2273 4.7
R2274 4.7
R2275 4.7
R2276 4.7
R2277 4.7
R2270 4.7
R2271 4.7
R1XC+
R1X0+
R1X1+
R1X2+
R1X2-
R1X1-
R1X0-
R1XC-
85
Page 86

16.6. HDMI CIRCUIT (6/6)
A
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 6
HDMI CIRCUIT
BK5V
HDMI_POWER_M
GND
TO HDMI
SECTION (5/6)
1.8V
P1
RX1_HPD
R1PWR5V
HOTPLUG
RX1_5V
DSDA1
DSCL1
QR2231
B1GBCFJJ0007
SWITCH
R2234
100
R2235
I
: HDMI/OPTICAL AUDIO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : HDMI VIDEO INPUT SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE : VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE: +B SIGNAL LINE
SYS6V
SYS1.8V
V_CHECK
P1
SW_3.3V
HDMI_POWER
IC2004
C0CBCBG00013
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
OUT
GND
NCINON/OFF
43215
C2014
C2016
6.3V100
C0CBCAG00015
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
GND
C2268
0.1
C2269
4V330
IC2233
NC
43215
OUT
1
ON/OFF
IN
LB2008
J0JHC0000021
D3.3V
5V
DSP_GND
LB2240
J0JHC0000021
LB2241
J0JHC0000021
R4774
15K
L4774
G1C330MA0291
C4769C4768
4V330
2/6 3/6
1/6
5/6
4/6 6/6
R4775
2.7K
IC4724
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING REGULATOR
GND
VOUT
1000PC4773
ADJ
ON/OFF
42135
C4770
1
R4776 10K
0.1
VIN
D4774
B0JCPG000005
SU-HTB500PP HDMI CIRCUIT
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
TO HDMI
SECTION (3/6)
LB2005
J0JHC0000021
IC4793
C0CBCDC00014
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
3
4
NC
VC
GND
LB2007
J0JHC0000021
D4726
B0JCME000012
C4781
0.1
C4784
6.3V100
B1GBCFNN0004
Q2231
B1HBCFA00003
R2238
22K
22K
R2239
15K
B1CFGD000002
LEVEL SHIFTER
82K
SWITCHING
1
2
3
Q2232
1K
R2236
R2237
2
VOUT
1
5
VIN
QR4704
SWITCH
R2240
10K
6
5
4
312
2G
2D
45
S
C4793
R2241
1
22K
22K
R2242
1G
1D
R4763
47K
Q2233
B1HBCFA00003
SWITCHING
1
2
3
2G
2D
B1CFGD000002
R4765 10K R4766 330
L4727
G1C330MA0291
C4767
4V330
10K
R2243
6
5
4
312
S
1G
1D
45
Q2234
LEVEL SHIFTER
B1GBCFJJ0007
IC4722
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING REGULATOR
GND
VIN
VOUT
1000PC4772
D4727
B0JCPG000005
IC2102
C0CBCAG00015
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
OUT
NC
GND
43215
C2127
4V330
R2035
100
1D
1G
S
47KR2244
312
2G
R2247 47K
2D
45
R2248
47K
R2245
47
R2246
47
QR2232
SWITCH
ADJ
ON/OFF
42135
1
10K
R4767
C4782
IN
ON/OFF
C2128
0.1
45
2D
B1CFGD000002
2G
312
S
1G
B1CFGD000002
1D
C3EBEC000047
C2232
QR4703
B1GBCFNN0004
SWITCH
Q2235
LEVEL SHIFTER
R2249
1K
Q2236
LEVEL SHIFTER
IC2231
EEPROM
SDA
GND
5
SCL
A2
6
WP
A1
7
VCC
A0
8
1
15KR2061
15KR2059
15KR2060
R2062
18K
RX_EDID_DT
WRITESEL_0
RX_EDID_CK
4
3
2
1
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
86
Page 87

16.7. MAIN CIRCUIT (1/4)
A
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
B
MAIN CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 7
SU-HTB500PP MAIN CIRCUIT
2/4
4/4
1/4
3/4
TO MAIN
SECTION (2/4)
TO MAIN
SECTION (3/4)
P1
FOR ON BOARD PROGRAMMING
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
R663
680
C605
0.01
142
3
IC606
C0EBG0000107
RESET
DAP_SDA
100R614
DAP_SCL
100R612
100R613
DAP_MUTE
R610
100K
REMOTE
VALID
100R657
100R611
C607
0.01
3
1
2
X600
H2B100500007
100R689
HDMIMUTE_DIS
DAP_RESET
10K
R609
0
R679
BK3.3V
4.7K
R653
10KR655
10KR654
47K
R656
C608
6.3V100
6
7
5
2
4
3
81
IC605
C3EBEC000060
EEPROM
0.01
C609
6
8
9
7
2
1
4
5
3
10
CN600
DGND
47K
R685
DAP_3.3V
47K
R686
MUTE_ALL
R605 150K
10KR604
C606 0.01
R616
10K
R607
1K
100R688
C602
0.1
C600
6.3V1000
R606
100K
R644
10K
LED_OE
LED_DI
R682 100
R683 100
RESET_CODEC_M
R666 100
R668 100
R670 100
R672 100
R673 100
R671 100
R669 100
R667 100
R665 100
CS_CODEC_M
MOSI_DSP
RESET_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
CLK_DSP
BUSY_DSP
CS_DSP
INTREQ_CODEC_M
MISO_DSP
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
R675 100
R674 100
SD
1000P
C612
100R636
DAP_PDN
R681 100
PCONT
100R632
PVCONT_ON
1KR629
1KR630
HDMI_MUTE
H_REQ
R661
10K
1KR659
600
M_RESET
LED_CS
M_CS
LED_CLK
M_SI
H_SO
R651
10K
R652
6.8K
C603
6.3V100
1KR650
C604
0.1
R649 10K
100R618
100R617
100R619
1KR621
100R620
KEY2
100R664
15KR646
1KR625
ECO_DAMP
1KR648
M_CLK
1KR622
220KR647
R624 10K
1KR623
100R658
15KR645
KEY1
10KR627
1KR626
100R684
DCDET
S_DET
PWR_CTRL
3425
98
94
95
92
91
93
97
96
1
100
99
80 78 767779
87
86
88
89
82
84
83
81
85
90
1614 15 1711 1312
69 67 65 64666870 51
49
45
47
46
41
44
42
43
48
50
30
39
37
35
32
31
34
33
36
38
40
22 2320 21 26 282724 2518 19
53555762 60 596163 58 56 54295275 73 717274
9768
10
IC604
RFKWMHTB500P
MICRO PROCESSOR
SYS6V
SYS3.3V
M_SI
AVSS
RXD
SCLK
SDA
[31] CE
DAP_SCL
DAP_SDA
DAP_MUTE
XIN
NM1
VCC
AVCC
NC
BYTE
CNVSS
VSS
XOUT
RESETNCNC
NC
REMOTE
REMOTE
VALID
AC_SYNC
[2] W_DET
W_INT
W-SDI
W_CL
W-SDO
[1] W_SSB
MUTE_ALL
DAP_RESET
VREF
SCL
VSS NC
AMP_POWER
BUSYFILTER
HDMIMUTE_DIS
VDDOUT
A1
A0
A2
VSS SDA
WP
SCL
VCC
GND
RESET
PIN46 (CE)
RXD
VCC
BUSY
SLCK
PIN41 (EPM)
TXD
CNVSS
PCONT
PIN 41
KEY1
KEY2
FL_CS
M_RESET
PWR CTRL
ECO_DAMP
DC_DET
M_CLK
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
REG2
RESET_CODEC
REG1
LED_CS
LED_CLK
[79] DT_OUT_CODEC
[80] LED_DI
BUSY_DSP
CS_DSP
RESET_DSP
CLK_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
CS_CODEC
MISO_DSP
MOSI_DSP
INTREQ_CODEC
PWR_CONTROL
PVCONT_ON
SD
VSS
VCC2
DAP_PDN
RC_LED
NCNCNC
NC
NCNCNC
NCNCNC
NC
H_REQ
OTW
[50] HDMI_CTRL
HDMI_MUTE
M_CS
PIN 46
FL_DI
LED_OE
FL_CLK
H_SOS_DET
TL
R643 10K
W_SDI
W_SCL
W_SDO
W_SSB
W_INT
47K
R615
R633 100
R634 100
R635 100
R601 100
R602 100
R600 100
R640 10K
87
Page 88

16.8. MAIN CIRCUIT (2/4)
B
G
G
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 8
MAIN CIRCUIT
TO MAIN
SECTION (1/4)
R446 10
R447 10
SD
PWM_FL+
PWM_FL-
PWM_FR+
VALID
PWM_FR-
L400
G0A200D00002
+12V
DGND
C441
16V33
C512
0.1
P1
P1
R448 100
R449 100
R451 100
R452 10
R453 10
C433
16V10
A
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
B
SP_FL+
C467
25V470
SP_FL-
C505
25V470
VDD
SP_FL-
SP_FL+
SP_FR-
SP_FR+
SP_FR+
SP_FR-
R528 100K
R527 100K
R520
100K
C548
50V10
R526 100K
100KR525
R502
5.6K
R503
5.6K
L414
G0B9R5K00007
1
L415
G0B9R5K00007
1
SP_PROTCT
43
2
43
2
R521
100K
C802
C803
0
0
HEATSINK
IC405
C1AB00003217
C429
0.1
R450
22K
C430
0.1
C431
C432
0.1
0.1
10R454
DIGITAL AMPLIFIER
GVDD_B
GVDD_A
1
2
OTW(L)
BST_A
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 33
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 24
NC
NC
SD(L)
PWM_A
RST_AB(L)
PWM_B
OC_ADJ
GND
AGND
VREG
M3
M2
M1
PWM_C
RST_CD(L)
PWM_D
NC
NC
VDD
GVDD_C
PVDD_A
PVDD_A
OUT_A
GND_A
GND_B
OUT_B
PVDD_B
BST_B
BST_C
PVDD_C
OUT_C
GND_C
GND_D
OUT_D
PVDD_D
PVDD_D
BST_D
GVDD_D
NC
NC
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
2322
C481
0.1
C492 0.033
C493
0.1
C497
0.1
C498 0.033
C507 0.033
C508
0.1
C509
0.1
0.033C510
C514
0.1
C494
C491
C515
C516
L406
G0A100H00018
C496
25V470
1
1
1
C519
1
25V470
L407
G0A100H00018
L408
G0A100H00018
L409
G0A100H00018
Q501
B1ABCF000011
SWITCH
Q500
B1ABCF000011
SWITCH
C501
C806
0.47
C807
0.47
C502
C522
C523
0.1
0.1
0.1
0.1
R522
33K
TO MAIN
SECTION (4/4)
R469
C447
0.01
C446
0.01
R468
R465
C443
0.01
C442
0.01
R464
3.3
C166
1000P
C165
1000P
3.3
3.3
C162
1000P
C161
1000P
3.3
C192
C191
C181
C186
1000P
1000P
1000P
1000P
TL
TL
402
CHASSIS
3
ZJ402
2
1
C187 0
C188 0
GND
1
GND2
GND
3
GND
4
FRONT_R+
1
FRONT_R-2
FRONT_L+
3
FRONT_L-
4
CN402*
CN401*
3
ZJ403
2
1
403
2/4
1/4
4/4
3/4
SU-HTB500PP MAIN CIRCUIT
TO
WIRELESS ADAPTER
CIRCUIT (TL102*)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 14
TO
WIRELESS ADAPTER
CIRCUIT (TL101*)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 14
TO SPEAKERS
(FRONT)
C
D
E
F
G
H
88
Page 89

16.9. MAIN CIRCUIT (3/4)
I
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
K
L
J
M
O
P
N
B
MAIN CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 9
SU-HTB500PP MAIN CIRCUIT
2/4
4/4
1/4
3/4
TO MAIN
SECTION (4/4)
TO MAIN
SECTION (1/4)
P1
C
TO
LED CIRCUIT
(CN350)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 11
A
TO
HDMI CIRCUIT
(CN1001)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 2
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
G
TO
WIRELESS ADAPTER
CIRCUIT (CN101)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 14
14
1
303
TL
1
12
50
1
D5V_1
R202
DSP_SD3
DSP_LRCLK
DSP_SCLK
R205
DSP_SD1
R206
R204
R203
J0JBC0000072
J0JBC0000072
J0JBC0000072
J0JBC0000072
J0JBC0000072
LB303 0
LB305 0
LB306 0
0LB304
LB302 0
C303
16V10
LB312 0
LB308 0
LB307 0
LB300 0
LB301 0
7
9
10
8
4
5
1
3
2
6
12
11
CN300
R201
0
R200
0
SYS6V_GND
SYS6V
LED_OE
REMOTE
KEY2
LED_CLK
D5V_2
LED_DI
LED_CS
KEY1
CS_DSP
CLK_DSP
INTREQ_DSP
INTREQ_CODEC_M
RESET_CODEC_M
CS_CODEC_M
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
HDMI_MUTE
MISO_DSP
BUSY_DSP
RESET_DSP
MOSI_DSP
REMOTE
S_DET
M_CLK
M_RESET
BK3.3V
G0A200D00002
L200
0.1
C200
0.1
C202
0.1
C201
R495
100
H_REQ
PWR_CTRL
M_SI
H_SO
M_CS
0.1
C407
6
7
5
9
47
44
39
40
35
31
27
24
21
20
22
16
15
18
17
11
13
12
10
14
19
23
26
25
30
28
29
34
32
33
38
36
37
43
41
42
46
45
49
48
8
1
3
4
2
50
CN200
16V10
C406
1MR404
X400
H0J135000003
10PC413
B0ACCK000005
D602
DAP_RESET
DAP_PDN
R435 100
1KR436
0.01
C453
16V10C410
220
R400
0.1
C401
C403 0.1
220
R401
0.1
C402
0.1
C400
0.01
C414
3.3R402
C409
1000P
0.1C404
0.1C405
C451
15P
15P
C452
C408 16V10
DGND
MUTE_ALL
0.1
C411
D600
B0ACCK000005
QR600
B1GBCFJJ0007
R4231
100K
D601
B0ACCK000005
B1GDCFJJ0008
QR601
B1GDCFJJ0008
MUTING
MUTING
MUTING CONTROL
QR602
SYS3.3V
HDMIMUTE_DIS
HDMI_MUTE
DAP_MUTE
DAP_3.3V
10PC415
C412
0.1
R407 47
R406 47
R414
10K
R409 82
R408 82
R413 47
0.1
C417
0.1
C416
PWM_FL+
PWM_FR+
PWM_FR-
R424 47
47R423
PWM_FL-
R418 47
R417 47
C421
0.1
C420
16V10
VALID
DAP_SDA
DSP_LRCLK
DSP_SD1
DSP_SCLK
DAP_SCL
4748 4445 4041 36 3335 343839 3743 4246
1
62
63
58
57
60
61
59
64
53
50
49
52
51
55
56
54
879465
23
24
21
18
19
17
20
22
1612 1310 11 151423
31
29
30
32
27
28
25
26
IC401
C1AB00003216
DIGITAL AUDIO PWM PROCESSOR
PLL_FLTM
[64] RESERVED
M_RESET
MCLK
[1] VRA_PLL
DSP_GND
DSP_GND
BK_3.3V
BK_3.3V
SDIN3 (FL/FR)
DSP_SCLK
DSP_GND
SDIN4 (C/SW)
HDMI_POWER
HDMI_GND
KEY2
D5V
DGND
D5V
KEY1
REMOTE
LED_OE
LED_CLK
LED_CS
LED_DATA
VREF(3.3V)
VREFGND
SYS6V
D5V_1
HDMI_GND
HDMI_GND
HDMI_GND
SYS6V
SYS6V
DSP_GND
DSP_MCLK
DSP_GND
D5V_1
D5V_1
DSP_GND
DSP_GND
DSP_LRCLK
[2] PLL_FLT_RET
PWM_M_6
PWM_P_6
MAIN_POWER
M_CS
H_REQ
PWM_M_5
PWM_P_5
REMOTE
KEY1(NC)
PWM_HPML
M_SI
H_SO
PWM_HPMR
PWM_HPPL
[47] PWM_P_4
CS_CODEC_M
CS_DSP
DSP_GND
INTREQ_DSP
MISO_DSP
DSP_GND
HDMI_MUTE
MOSI_DSP
BUSY_DSP
RESET_DSP
DT_OUT_CODEC_M
DSP_GND
CLK_DSP
PWM_M_8
[48] VR_PWM
PWM_M_7
PWM_P_7
PWM_P_8
RESET_CODEC_M
DCDET
INTREQ_CODEC_M
DVDD_PWM
DVSS_PWM
PWM_M_4
M_CLK
PWM_HPPR
MUTE
DVSS
DVDD
PDN
AVSS
AVSS
RESET
VBGAP
AVSS_PLL
PWM_P_1
PWM_P_2
PWM_M_2
[17] VRD_DPLL
HP_SEL
DVSS
DVSS
PSVC
DVDD
DVSS
[33] VR_DIG
BKND_ERR
XTL_IN
XTL_OUT
OSC_CAP
RESERVED
SDIN2
SDIN1
SCLK
SDIN4
SDA
SCL
LRCLK
SDIN3
RESERVED
RESERVED
PWM_M_1
VALID
AVDD_PLL
VRD_PLL
PWM_P_3
PWM_M_3
PLL_FLTP
J0JHC0000021
LB101
W_SDI
+12V
W_SCL
W_SDO
PGND
W_SSB
DSP_SD3
W_INT
CN100
8
9
11
12
10
2
5
6
3
4
1
7
14
13
GND
+12V
+12V
SDI
SCL
WCLK
DGND
BCLK
DGND
SSB
INT
ADAT0 (C/SW)
SDO
GND
0.1
C101
R100
R103
R105
R104
R101
R102
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
J0JYC0000339
C422
15P
89
Page 90

16.10. MAIN CIRCUIT (4/4)
B
F
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 10
MAIN CIRCUIT
P1
TO MAIN
SECTION (3/4)
DCDET
ECO_DAMP
GND
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
R236
4.7K
C158
R179
0.1220K
B0ACCK000005
C153
B0ACCK000005
0.1100K
K102
K103
R180
220K
D118
D119
0
0
B1ADBL000010
DC DETECT
Q114
B1ABCF000011
DC DETECT
Q116
R178
47K
R587
56K
R168
C151
50V1
R184 5.6K
R176 5.6K
SP_PROTCT
SP_FR+
SP_FL+
L706
G1A330ZA0007
C708
16V10
L707
G1A330ZA0007
TO MAIN
SECTION (2/4)
C0CBABC00117
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
LB700
0
C700
R705 56K
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING REGULATOR
VIN
C710 25V33
R714
R709 27K
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING REGULATOR
VIN
1
VOUT
1000PC715
VOUT
IC700
OUT
IC701
00R713
IC702
IN
GND
231
C701
1
R706 27K
ADJ
GND
42135
D705
R707 10K
B0JCPG000005
R708 3.9K
GND ADJ
42135
LB701
0
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
C709
0.47
SYS3.3V
+12V
D5V_1
P1
VDD
GND
SYS6V
SYS6V_GND
PCONT
PVCONT_ON
S_DET
PGND
DGND
D5V_2
BK3.3V
C150
25V470
B0ACCK000005D700
B0ACCK000005D706
B0ACCK000005D701
D703
B0BC012A0264
D704
B0BC030A0264
Q704
B1GBCFGG0030
DC DETECT
L421
J0JKB0000020
L422
J0JKB0000020
R712 0
R704 1K
R700
R701
0
0
12
FP700
3A
10
SYS6V
SYS6VGND
9
8
PCONT
SYNC (HDMI_CTRL)
7
ECO_CTRL
6
5
DC_DET
4
PGND
3
PGND
2
+20V
1
+20V
CN700
1
TO
SMPS CIRCUIT
(H2016*)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 12
10
I
J
K
L
M
N
C711
6.3V470
1000P
C713 25V33
C714
IC107
C0CBABC00117
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
L427
0
C418
1
D707
B0JCPG000005
OUT
231
GND
R710
10K
C712
0.47
DAP_3.3V
IN
C419
1
L426
J0JBC000072
2/4
1/4
4/4
3/4
SU-HTB500PP MAIN CIRCUIT
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
90
O
P
Page 91

16.11. LED CIRCUIT, PANEL TACT SWITCH CIRCUIT, AC INLET CIRCUIT
A
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
A
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
C
LED CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 11
D
PANEL TACT SWITCH CIRCUIT
E
AC INLET CIRCUIT
SU-HTB500PP LED / PANEL TACT SWITCH / AC INLET CIRCUIT
: +B SIGNAL LINE
B
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN300)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 9
TO
SMPS CIRCUIT
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 12
F
C357
0.1
1C356
10KR381
100PC354
100R351
100R352
D320
B0ACCK000005
D321
B0ACCK000005
R385
0
2
17
5
15
14
10
11
8
9
6
13
7
12
3
4
1
16
18
C0JBAQ000073
LED DRIVER
IC300
100PC351
100R354
100R353
100PC350
100PC352
100PC353
1
C355
R355 47
100P
C358
100P
C359
R356
3.3K
R357
R370
R371
100
100
56K
0R384
1
3
2
CN351*
R382 0
R383 0
1
3
2
CN352*
132
Z300
B3RAC0000019
REMOTE CONTROL SENSOR
43
21
S301
43
21
S304
43
21
S303
43
21
S300
7
9
10
8
4
5
1
1
12
3
2
6
12
11
CN350
D5V
D5V
Q2
Q1
Q4
Q3
CLK
DATA
VSS
Q0
LCK
Q7
Q8
Q5
Q6
OE
Q9
VDD
Q10
Q11
POWER INPUT SELECTOR VOLUME -VOLUME +
GND
RE
VREFGND
VDD
VREFGND
VREFGND
REMOCON
VREF
KEY1
KEY2
KEY1
KEY2
LED_LCK
LED_OE
LED_CLK
VREFGND
LED_DATA
KEY1
KEY2
P5701
TL10*
TL20*
(RED)
(BLK)
120V 60Hz
AC IN
ZA5701ZA5702
2.5A 125V
F1
D400
B0BC5R600003
D401
B0BC5R600003
R372
200
R369
1K
R367
200
R365
200
R363
200
R361
200
R360
1K
13
24
D304
B3AGB0000037
13
24
D305
B3AGB0000037
13
24
D301
B3AGB0000037
13
24
D303
B3AGB0000037
13
24
D307
B3AGB0000037
91
Page 92

16.12. SMPS CIRCUIT (1/2)
F
B
E
1
A
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 12
SMPS CIRCUIT
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
: +B SIGNAL LINE
P1
B
PC5799
B3PBA0000402
FEED BACK
R5894
R5890
2.2K
330
4
1
3
2
C
D5798
R5798
B0EAMM000057
100
D5896
B0JAMF000011
R5893
R5895
C
1
C5898
3
A
2
D
H2016*
10
TO
E
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN700)
IN SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAM - 10
1
SYS5V
SYS5VGND
PCONT
SYNC
ECO CTL
DCDET
GND
GND
VDD (+20V)
VDD (+20V)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
L5800
J0JKB0000020
L5801
G0A101ZA0045
DCDET
GND
VDD
R
IC5899
C0DAEMZ00001
SHUNT REGULATOR
R5898
4.7K
39K
15K
R5892
C5899
1000
4.7K
0.1
R5891
33K
D5899
B0ACCK000005
7
8
9
10
T5751
ETS19AB2A6AG
SUB TRANSFORMER
RY5701
K6B1AEA00003
4
31
6
5
4
3
R5786
200K
2
1
C5790
2200P
2
D5793
B0HAMP000094
C5706
F1BAF1020020
1000P
C5798
100V10
MIP2F20MSSCF
SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY CONTROL
D VCC
5
7
S FB
S VDD
8
C5799
400V6.8
IC5799
2
1
4
TR
3
2
1
3
D5799
B0EDKT000009
4
1000P
R5795C5795
R5797
C5796
0.1
330K
15K
C5797
470P
TO SMPS
SECTION (2/2)
Q5899
F
R5899
47K
B1ABCF000011
SWITCH
(RED)
TO
AC INLET
CIRCUIT IN
SCHEMATIC
G
DIAGRAM - 11
TL3*
TL4*
(BLK)
DZ5701
ERZV10V511CS
R5701
3.9M
C5701
F0CAF104A105
0.1
L5701
ELF15N007A
4
1
F0CAF104A105
3
2
F1BAF1020020
C5702
TL
0.1
C5704
1000P
14
H
GND
L5702
ELF19H010A
4
1
C5708
F1BAF1020020
1000P
3
2
TH5702
D4CAA5R10001
C5703
F0CAF104A105
0.1
2/21/2
SU-HTB500PP SMPS CIRCUIT
2
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
92
Page 93

16.13. SMPS CIRCUIT (2/2)
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
A
C
D
B
E
G
H
F
F
SMPS CIRCUIT
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 13
SU-HTB500PP SMPS CIRCUIT
2/21/2
TO SMPS
SECTION (1/2)
P1
2
1
: +B SIGNAL LINE
R5806
15K
A
R
3
2
C
1
IC5801
C0DAEMZ00001
SHUNT REGULATOR
C5818
0.1
C5810
0.1
0
0
6
3
ZJ5803
7
21
C5800
0
2
1
11
10
12
6
5
4
8
7
9
T5703
ETS28BH1E5AC
MAIN TRANSFORMER
R5801
2.7K
R5817
0
R5803
2.2K
R5802
18K
R5804
2.2K
C5808
25V470
C5839
0.01
C5801
0.01
312
B0HBSM000054
D5802
R5843
2.2K
C5845
25V470 25V470
R5842
1.5K
R5834
2.2K
C5844
K5721
0
R5726
0.27
C5747
560P
C5730
1
D5723
MA2J1110GL
D5732
MAZ8300GML
R5808
2.2K
D5725
B0BC6R2A0266
R5730
1K
R5809
330
R5807
330
4
3
1
2
PC5720
B3PBA0000402
FEED BACK
R5732
100
C5723
470P
R5733
47K
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
IC5701
C0DAAMH00013
SWITCHING REGULATOR
D5729
B0EAMM000057
C5727
2200P
R5725
R5721
10K
C5720
100P
200V100
C5711
~-~
3
2
4
+
1
D5701
B0EBNR000015
D5727
MA2J1110GL
R5722
2K
2K
MA2J1110GL
D5724
R5702
100K
100K
B0EAKT000062
D5703
D5700
B0EAKT000061
R5703
C5713
0.01
B0BC010A0007
D5721
R572022D5731
B0EAMM000057
Q5720
C5700
F1BAF2220023
2200P
R5724
R5723
33K
33K
C5722
2200P
C5721
220P
D5726
MA2J1110GL
C5726
50V10
D5722
B0BC018A0267
C5725
0.1
DCDET
GND
11
K3
K2
VDD
1
C5843
Q5841
B1GBCFGG0030
DC DETECT
V1
GND
V2
+25V
GND
GND
VCC
OLP/SS
S
D
FB
OCP/BD
2SC3940ARA
REGULATOR
TL
TL
13
TL
TL
GND
HEATSINK*
G2G1
HEATSINK*
G2G1
93
Page 94

16.14. WIRELESS ADAPTER CIRCUIT
G
B
B
B
1
A
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - 14
WIRELESS ADAPTER CIRCUIT
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
A
: +B SIGNAL LINE : AUDIO OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
TO DIGITAL TRANSMITTER
RESERVED
RF_GND
ADAT3 (NO USE)
221
ADAT2 (NO USE)
B
CN101
1
TO
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN100)
IN SCHEMATIC
C
DIAGRAM - 9
14
D
C105
0.1
E
ADAT0 (C/SW)
BCLK
DGND
WCLK
DGND
SSB
SCL
SDO
PGND
PGND
+12V
+12V
R101
1.8
C103
10V1000
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
INT
7
6
5
SDI
4
3
2
1
G0A330ZA0045
C100
16V470
LB105 0
J0JBC0000015
R102
L100
LB106
R103
3.9K27K
IC100
C0DBAYH00005
SWITCHING REGULATOR
ADJGND ON/OFFVIN
VOUT
B0JCPG000005
C101
10
D100
42135
R104
10K
C102
0.1
R130 100
LB101 0
R129 100
LB102 0
R128 100
R127 100
R126 100
R123 100
R124 100
R125 100
R122 1
LB104 0
C104
0.1
TL101*
320
ADAT1 (NO USE)
ADAT0 (C/SW)
DGND
BCLK
DGND
815
WCLK
9
SSB
10
SCL
11
TO
3
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN402*)
IN SCHEMATIC
4
DIAGRAM - 8
CN100
RESERVED
RESERVED
RESERVED
5V GND
WM_DET
SM0
SDO
221
194
185
176
5V
167
INT
14
13
SDI
12
J0JBC0000015
R120
10K
LB103
R121
18K
B
C
C106
6.3V220
C107
TL102*
0
TO
1
MAIN CIRCUIT
(CN402*)
IN SCHEMATIC
2
DIAGRAM - 8
D
E
F
F
G
H
SU-HTB500PP WIRELESS ADAPTER CIRCUIT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
G
H
94
Page 95

1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
10 1 12 13
A
HDMI P.C.B. (REPX0840D)
SU-HTB500PP
HDMI P.C.B.
(SIDE A)
0687A
0687A
R2254
R1025
R2248
R1035
RX1002
C2109
R1028
R2045
C2005
L1003
C1073
LB1000
IC1001
D2005
R4363
LB2231
R1008
IC4722
R2232
R1044
C1071
R1053
R2019
R4366
C2142
R2082
C1076
C1006
C1020
C1007
VA2111
R1021
R2144
R2239
R1042
R2040
C1055
C1021
R1036
LB1001
C4782
C1072
C1029
R1005
R2241
R2062
VA2240
Q2231
C2116
C2013
C2248
R1009
C2118
R2005
RX1004
C2082
R1056
R2283
C1059
C1080
R1023
D2004
R2243
QR2002
R2067
R2013
R2240
R2028
R2039
C2084
C1081
LB2004
C1030
R2044
R2234
C1069
R2001
R2142
C2126
R2066
C1023
R2055
R2085
LB2105
R1015
C1037
C2283
R2042
R1052
LB2081
C1084
Q2232
R4767
R2081
R2236
R1013
C2012
C2105
C1013
R1003
R2247
R2249
R4367
R2030
RX1008
R2021
R1020
R2037
C2115
C2108
C2004
R1029
R1051
C1063
R2014
VA2241
LB1003
R1007
QR4703
C1060
C2120
C1056
R2141
C1087
R2242
RX1003
(FOR ON BOARD PROGRAMMIG)
C2083
R4766
LB1004
C1036
LB2005
C1068
C2010
RX1007
QR2232
R2041
R1030
R2278
Q2233
R1001
Q2108
C1083
LB2233
R2237
C4371
RX1006
C2231
IC1002
C2128
LB2104
R2253
IC2102
C1022
C2081
C1028
R1010
IC1004
C2113
Q2236
R2043
C2119
C1045
C1015
QR2001
D2003
C2232
R1022
VA2242
R2083
C2104
R2022
VA2112
R1033
QR4704
IC1005
IC2002
LB2108
R4364
C1066
Q2235
R2023
R2038
VA2113
C2111
C2121
LB1007
C1049
R2060
C2016
VA2109
IC2004
R2233
RX1005
C2114
C2015
LB1002
LB2232
R1011
R2069
C1062
LB1006
R2124
X2002
C2125
C1064
D2006
C1035
R2235
R2143
R2018
C2085
C2124
R1002
LB2103
R2059
QR2231
R2126
R2035
LB2110
R1017
R1055
C2002
VA2110
C1024
R2130
R1018
R1012
C1057
C1075
C2122
C2141
C1027
R1059
R2061
C1026
R1026
R2131
C1058
C1014
C4368
LB2109
R4765
LB2107
VA2239
R1000
C4370
LB2102
LB2234
R2084
R1024
R2012
C1074
R2125
R2027
LB2101
C1016
C2110
C1070
C1033
IC1003
C1085
C1067
R1014
C1065
R2244
C2112
R2003
C1086
C2107
L1004
RX1001
R2024
IC2003
C2106
R2238
C1012
C4369
R1004
R1016
LB2082
Q2234
C1077
C2123
LB2106
IC2081
X2001
R1062
R1060
R4375
R2209
R1046
R4372
R4373
C1018
R4102
C2278
C2279
C2280
C2264
C2249
R2267
C2251
C2252
C2255
C2258
C2270
C2273
C2275
C2274
C2272
C2271
C2263
C2260
R2258
R2257
R2256
R2255
C2234
C2254
C2250
C2246
LB2235
LB2236
C2236
C2237
C2238
C2239
C2240
C2242
C2241
C2243
C2244
LB2237
LB2238
C2247
C2267
C2253
C2235
C2245
C2259
C2233
L2231
C2262
C2266
RX2232
RX2233
RX2234
RX2235
CN2001
LB2008
R2091
R2090
C4772
R2076
54321
123
4
5
32415
32415
LB4102
R2284
R2285
R9000
PbF
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
1
45
8
1515
16 10 2
123
65
4
54
12
3
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
34
5
1
2
3
6
5
4
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
6
5
4
1
2
3
6
5
4
3
2
4
1
5
15
10152025303538
39
40
45
50
55
60
64
65 70 75 80 85 90 95
100 102
103
105
110
116
120
125
128
1
5
10
15
20
25
30
51
55
60
65
70
75
80
31 35 40
45 50
81859095
100
1
5
10
15
16
17
20 25 30 32
33
35
40
45
48
4950556064
17 Printed Circuit Board
17.1. HDMI P.C.B. (SIDE A)
95
Page 96

17.2. HDMI P.C.B. (SIDE B)
A
HDMI P.C.B. (REPX0840D)
H
G
F
E
D
C
HDMI AV IN
(BD/DVD)
OPTICAL
DIGITAL
AUDIO IN (TV)
HDMI AV OUT
(TO TV (ARC))
Ir SYSTEM
JK4101
JK2203
1
2
3
JK2101
R2072
19
15
10
5
1
C2277
R2101
19
15
VA2101
10
5
VA2103
1
R2073
VA2102
VA2104
C2276
C4101
R4101
VA2105
VA2232
R2102
R2104
C4104
R2107
R2106
VA2236
VA2238
LB4101
VA2106
VA2107
VA2108
VA2235
Q2103
BCE
R2105
1
4
VA2234
C4103
JK4001
12
34
LB4201
LB4200
C4771
QR2004
B
R4374
C
E
IC2231
VA2231
VA2237
VA2233
D2101
R2121
R2103
R2129
C2117
26
L2101
30
35
L2102
40
45
50
51 55 60 65 70 75
R2123
R2122
8
5
R2128
C2265
R2246
R2245
R2120
R2270
R2271
R2272
R2273
R2274
R2275
R2276
R2277
37
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
72
IC2101
C2127
R2252
RX2231
RX2101
30
35
36
25
20
IC2232
73 75 80 85 90 95
R2133
R2261
LB2239
R2262
C2256
R2263
X2231
R2260
R2259
R2132
1510152025
100
95
90
85
80
76
C2268
15
10
100 105 108
C2257
C2269
IC2233
34251
11
15
20
LB2243
5
IC1008
R2265
1
R2269
R2266
C2261
R2264
10
CN1001
R2094
144
140
RX2236
135
RX2237
130
RX2238
125
RX2239
119
RX2240
113
109
RX2241
5
X2003
1
R1032
D2002
1 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 5045
R4365
C4363
C4361
C4364
C4362
LB4108
C4365
C4366
C4367
R4362
C1053
D2001
R1058
R2154
R2153
R2152
R2151
C1025
R4361
R2068
R2071
C2007
R4371
R4368
C1054
R2015
C1052
LB2003
R2052
R2051
R2050
R2016
R2017
L1002
D2009
C1009
L1001
LB1005
1
5
10
R4369
L1000
R2008
C1008
C1010
C1050
C1051
IC2006
R2009
R2011
C2019
R2025
R4370
C2001
C1011
R2026
20
15
11
R2006
C2009
R2010
R2031
R2034
R2063
C2018
LB2001
LB2002
R2048
R2049
C2003
C2006
R2032
R2033
R2053
R2002
R2007
LB4107
R2046
R2047
C2011
LB2010
LB4106
LB4105
C4452
C1040
LB2240
C4768
LB1008
C1031
LB2242
X1000
R1019
LB4104
LB4103
C1038
IC1006
R2074
26 30 35 40 45 50
LB2011
C1032
C1039
C1044
R2092
LB2241
L4774
C1042
R1031
C1043
C4769
R1039
R1038
C1041
R1045
D4727
1510152025
IC4724
C4773
D4774
R1037
R2093
R4774
54321
C4770
R4776
R2075
L4727
LB2007
PbF
C2014
R4763
LB2009
D4726
C4784
0687A
0687A
C4793
IC4793
C4781
C4785
123
54
R4775
C4767
B
A
(SIDE B)
1
SU-HTB500PP
HDMI P.C.B.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 1 12 13
1
96
Page 97

1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
10 1 12 13
B
MAIN P.C.B. (REPX0839KA)
SU-HTB500PP
MAIN P.C.B.
(SIDE A)
0686CA
0686CA
C803
R502
R503
C502
C501C522
C523
R528
R527
R526
R525
R184
R176
C802
C186
C191
C192
C181
C806
C807
C443
R465
C162
C161
R464
C442
R469
C166
C447
C165
R468
C446
R521
R520
C418
L427
L426
C419
IC107
R623
R622
R621
R672
R671
R670
R669
R665
R668
C701
LB701
C700
IC700
LB700
R712
R654
R656
IC701
C709
R706
R707
R705
R713
R714
IC702
C712
R709
R708
R710
R655
IC605
C609
R653
R679
R610
R701
R704
C512
R661
R686
R685
R200
C201
R201
R689
R688
QR600
D600
D601
QR602
D602
QR601
R4231
TL402
TL403
C714
C715
5
3
1
K102
K103
C187
C188
PbF
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
1
2
3
5
3
1
1
2
3
1
4
5
8
17.3. MAIN P.C.B. (SIDE A)
97
Page 98

17.4. MAIN P.C.B. (SIDE B)
B
MAIN P.C.B. (REPX0839KA)
H
G
F
E
D
C
PbF
CN700
R617
1
5
9
CN600
(FOR ON BOARD
PROGRAMMING)
0686CA
0686CA
FP700
3A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
R627
2
6
10
Q704
L421
L422
C711
R700
C600
R616
R614
51 55
R659
R657
R613
R612
60
C612
R636
C607
4
1
2
3
IC606
C605
R618
31
R619
R620
35
40
R624
45
R625
R626
50
TL600
R630
R629
R632
CN200
CN300
LB300
TL303
C303
L707
C608
X600
1
3
2
R609
C602
R663
1015202530
IC604
65 70 75 80
R673
10 5 112
LB307
LB305
LB303
LB308
LB312
C713
D707
C603
C606
R607
R606
R605
R604
R667
R666
R633
15
R652
R651
100
95
90
85
81
R681
R675
R674
C200
LB306
C604
R682
CN100
LB302
LB101
LB304
LB301
R634
R611
R635
R658
R649
R650
R648
R644
R664
R684
R643
R683
C202
1098765432111121314
C101
R100
L706
D705
R602
C409
R600
R601
R647
R640
R645
R646
L200
151015202530354050 45
C708
C710
R402
R615
R400
C401
C414
R401
C402
C403
1
C405
5
C404
C408
10
15
16
R436
R435
C451
C411
C452
C453
C410
R203
C412
X400
C415
R204
R202
R104
R102
R101
R495
C422
C400
IC401
17 20 25 30 32
C413
R404
R406
R407
R408
C441
R103
R105
D704
C
D706
D700
L400
C433
C406
C407
4950556064
R418
C421
48
45
40
35
C416
33
C417
R414
R413
C420
R409
R206
R205
C153
E
B
R168
D703
D119
D118
D701
R446
R448
R449
R450
C430
R451
R424
R417
R452
R453
R423
R454
R587
B
E
C151
C
Q114
C429
R447
1
5
10
IC405
15
C432
20
C431
Q116
Q501
R179
R236
C
C158
B
E
Q500
R178
C
C
R180
C481
44
C492
40
C493
35
C497
30
C508
C509
25
2322
C510
C514
E
B
E
B
C494
C491
C515
C516
C498
C507
HEATSINK
C548
C150
L414
R522
C496
C519
C467
C505
3
1
L406
L408
ZJ402
4
2
11
2
3
CN401*
4-FL-
3-FL+
2-FR-
1-FR+
R
L407
L409
L415
4
3
CN402*
4-GND
3-GND
2-GND
1-GND
2
1
B
TO
SPEAKERS
(FRONT)
ZJ403
11
2
3
B
A
(SIDE B)
NOTE: " * " REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY.
1
2
3
SU-HTB500PP
MAIN P.C.B.
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 1 12 13
1
98
Page 99

1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
10 1 12 13
C
LED P.C.B. (REPX0839KB)
D
PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B. (REPX0839KB)
SU-HTB500PP
LED / PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B.
NOTE: " * " REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY.
(SIDE A)
(SIDE A)
(SIDE B)
(SIDE B)
0686CB
0686CB
0686CB
0686CB
0686CC
0686CC
0686CC
0686CC
S304
S303
S301
S300
CN352*
R357
R356
(POWER)
(VOLUME -)
(VOLUME +)
(INPUT SELECTOR)
IC300
C356
R385
C357
C353
R363
R361
R360
R384
C359
C358
R367
D301
D303
D304
D305
D307
R351
R352
R353 R354
C350
Z300
SENSOR
C354
R381
CN350
C351
C352
R382
R383
C355
D320
D321
R355
R369
R365
123
CN351*
D400
D401
R370
R371
R372
PbF
PbF
PbF
PbF
1
2
34
1
2
34
1
2
3
4
1
2
34
18 1015
9
15
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
123
4
123
4
123
4
123
4
3
2
1
10
5
1
12
17.5. LED P.C.B., PANEL TACT SWITCH P.C.B.
99
Page 100

17.6. AC INLET P.C.B., SMPS P.C.B., WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
H
G
F
E
E
AC INLET P.C.B. (REPX0841BA)
AC IN
120V 60Hz
P5701
RED
BLK
TL10*
TL20*
ZA5702
PbF
F
SMPS P.C.B. (REPX0841BA)
F1
2.5A 125V
0691BB-4
0691BB-4
ZA5701
G
WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B. (REPX0841BC)
PbF
0691BC-4
0691BC-4
TL102*
C103
R122
R128
LB101
R129
DIGITAL
R101
LB102
C100
W105
LB103
R121
R120
D100
TL101*
531
IC100
C102
C101
R104
W103
R102
R103
R126
R124
R127
R125
R123
L100
W102
2221201918171615141312111098765432
LB106
LB105
W101
CN101
C104
10
12
14
LB104
C107
C106
CN100
1
R130
TRANSMITTER
C105
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
13
D
C
B
A
(MAIN TRANSFORMER)
C5800
H2016*
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C5845
C5844
TL11
L5800
W5
W3
W4
L5801
Q5841
BCE
R5842
C5843
W1
TL8
K3
D5802
TL6
R5843
C5810
R5802
K2
HEATSINK
C5808
W6
R5806
C5818
R5804R5803
R5801
R5817
3
2
1
R5834
W10
IC5801
1
3
2
ZJ5803
C5801
C5839
IC5899
T5703
12
11
10
9
8
7
R5894
R5890
R5895
R5893
C5898
R5892
231
R5891
D5896
C5899
T5751
TRANSFORMER)
W9
R5898
(SUB
R5899
NOTE: " * " REF IS FOR INDICATION ONLY.
SEC
R5807
R5809
PC5799
1
10
9
8
7
Q5899
R5808
BCE
Q5720
PRI
1
1
2
R5720
4
5
6
4
32
PC5720
4
32
PRISEC
W12
1
2
3
4
5
6
R5798
C5798
IC5799
R5795
C5795
C5797
D5798
D5793
C5706
E
C
D5723
D5721
C5720
R5721
B
D5722
D5726
D5731
R5703R5702
C5713
R5786
C5799
C5790
R5797
C5796
D5799
+1
14
-4
58
D5703
D5700
~2
IC5701
~3
1
C5747
D5725
W11
RY5701
1
4
76543
R5730
D5899
R5722
C5721
R5726
C5723
C5730
R5733
K5721
C5725
HEATSINK
2
3
D5729
C5722
R5725
D5732
R5724
D5701
+1
C5727
C5726
W15
D5727
C5703
W13
C5708
D5724
R5732
R5723
~2
C5711
W14
TH5702
K5712
~3
L5701
1
2
-4
2
3
C5700
L5702
C5702
1
4
TL13
DZ5701
4
3
W16
PbF
R5701
C5704
0691BA-4
0691BA-4
C5701
TL14
BLK
TL4*
RED
TL3*
CAUTION
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
AGE LINE.
AC VOL
T
PLEASE DO NOT T
OUCH THIS P
.C.B
SU-HTB500PP
AC INLET / SMPS / WIRELESS ADAPTER P.C.B.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 1 12 13
1
100
 Loading...
Loading...