Panasonic DMRE-100 Service manual

Table Of Contents
COVER
1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1 .)
2 PREVENTION OF ELECTRO STATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) TO ELECTROSTATICALLY
SENSITIVE (ES) DEVICES
3 Precaution of Laser Diode
4 Handling the Lead-free Solder
4.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
5 Service Explorer
5.1 Service Explorer Express
5.2 Service Explorer in Detail
5.2.1 Does not operate
5.2.2 Poor Pictures
5.2.3 Other
5.2.4 Some defective functions
5.2.5 Caution when replacing the parts
6 Standard Inspection Specifications after Making Repairs

6.1 Standard Inspection Specification
6.2 Adjustment Procedures
6.2.1 Power Supply Adjustment
6.2.2 Audio Level Meter Adjustment (Automatically)
7 Assembling and Disassembling
7.1 Disassembly flow chart
7.2 P.C.B. Positions
7.3 The Top Cover
7.4 The Front panel
7.5 The Front (R) P.C.B.
7.6 The Front (L) and DV Jack P.C.B.
7.7 The SD & PC card P.C.B.
7.8 The ATAPI and DRIVE-ATAPI P.C.B.
7.9 The Digital P.C.B.
7.10 The DVD-RAM Drive
7.11 HDD
7.12 The Rear panel
7.12.1 In case of removing Fan motor from Rear panel
7.13 The Power Supply P.C.B. and Main P.C.B.
7.14 The Scart P.C.B. and SHIELD P.C.B.
7.15 The VIF Decoder P.C.B. and Nicam / Decoder P.C.B.

8 Service Positions
8.1 Checking procedure
8.2 Checking the Digital P.C.B.
8.3 Checking the Main P.C.B. and FRONT (L), (R) P.C.B.
8.4 Checking the Power Supply P.C.B.
8.5 Specifications for HDD Spin-up / Spin-down
9 List of Various Mode
9.1 List of Various Buttons
9.2 Special modes at a glance
9.2.1 Service modes
9.2.2 Other special modes
9.2.3 List of the U / H / F Error Displays
9.3 The information table of an error generating disk
9.3.1 Error generating disk type
9.3.2 Error generating disk state
9.3.3 Disk production maker ID
10 Abbreviations
11 Voltage and Waveform Chart
11.1 Power Supply P.C.B.
11.2 Main P.C.B.

11.3 Scart P.C.B.
11.4 Nicam / Decorder P.C.B.
11.5 Front (L) P.C.B.
11.6 Front (R) P.C.B.
11.7 PS9001, PS9002, PS9003 Connectors
11.8 PP9701, PP9702 Waveform
12 Block Diagram
12.1 Power Supply Block Diagram
12.1.1 Integrated Circuit Power Supply Chart ( PSC 1 - PSC 24 )
12.2 Analog Video Block Diagram
12.3 Analog Audio Block Diagram
12.4 Timer Block Diagram
12.5 Digital Section Block Diagram
12.5.1 Digital Video Section Block Diagram
12.5.2 Digital Audio Section Block Diagram
12.5.3 Digital Block IC Pin Terminal Chart (TC1-TC37)
13 Schematic Diagram
13.1 Interconnection Schematic Diagram
13.2 Main Power Supply Schematic Diagram
13.3 Sub Power Supply Schematic Diagram (P) ( Main P.C.B. 1 / 5 )
13.4 Main Net Schematic Diagram (M) ( Main P.C.B. 2 / 5 )

13.5 Video I / O Schematic Diagram (V) ( Main P.C.B. 3 / 5 )
13.6 Audio Schematic Diagram (A) ( Main P.C.B. 4 / 5 )
13.7 Timer Schematic Diagram (T) ( Main P.C.B. 5 / 5 )
13.8 Digital Net Schematic Diagram (DN) ( Digital P.C.B. 1 / 9 )
13.9 AV Input Schematic Diagram (AI) ( Digital P.C.B. 2 / 9 )
13.10 AV Encoder Schematic Diagram (EN) ( Digital P.C.B. 3 / 9 )
13.11 AV Decoder Schematic Diagram (AD) ( Digital P.C.B. 4 / 9 )
13.12 System Control Schematic Diagram (S) ( Digital P.C.B. 5 / 9 )
13.13 Glue Schematic Diagram (G) ( Digital P.C.B. 6 / 9 )
13.14 1394 DV Schematic Diagram (DV) (Digital P.C.B. 7 / 9)
13.15 Real Time Stream (RTSC) Schematic Diagram (DS) (Digital P.C.B. 8 / 9)
13.16 MPEG4 Schematic Diagram (MP) (Digital P.C.B. 9 / 9)
13.17 ATAPI Schematic Diagram
13.18 Drive ATAPI Schematic Diagram
13.19 Scart Schematic Diagram
13.20 VIF Decorder Schematic Diagram
13.21 Nicam / Decorder Schematic Diagram
13.22 SD & PC Card Schematic Diagram
13.23 Front (L) Schematic Diagram
13.24 Front (R) Schematic Diagram

14 Print Circuit Board
PV
14.1 Power Supply P.C.B.
14.2 Main P.C.B.
14.2.1 Main P.C.B. ( Section 1 / 4 )
14.2.2 Main P.C.B. ( Section 2 / 4 )
14.2.3 Main P.C.B. ( Section 3 / 4 )
14.2.4 Main P.C.B. ( Section 4 / 4 )
14.2.5 Main P.C.B. Address Information
14.3 Digital P.C.B.
14.3.1 Digital P.C.B. ( Section 1 / 2 )
14.3.2 Digital P.C.B. & DV Jack P.C.B. ( Section 2 / 2 )
14.3.3 Digital P.C.B. Address Information
14.4 Drive ATAPI & ATAPI P.C.B.
14.5 Scart P.C.B.
14.5.1 Scart P.C.B. (Section 1 / 2)
14.5.2 Scart P.C.B. (Section 2 / 2)
14.6 VIF Decorder P.C.B.
14.7 Nicam / Decorder P.C.B.
14.8 SD & PC Card P.C.B.
14.9 Front ( L ) & ( R ) P.C.B.
15 Exploded Views

15.1 Casing Parts & Mechanism Section 1
15.2 Casing Parts & Mechanism Section 2
15.3 Packing & Accessories Section
16 Replacement Parts List
17 Schematic Diagram for printing with A4 size

Service Manual
TOP NEXT
ORDER NO.DSD0309017C2
DVD Video Recorder
● DMR-E100HEE
Colour
(S).......................Silver Type
Specifications
Power supply: AC220-240 V, 50 Hz
Power consumption: 48 W
Recording system: DVD video recording standards (DVD-RAM),
Optical pick-up: System with 1 lens, 2 integration units (657 nm wavelength for DVDs, 785 nm wavelength for CDs)
Recordable discs: 12 cm 4.7 GB DVD-RAM discs
Recording time:
(with 4.7GB disc): Max. 6 hours
(with built-in 80GB HDD): Max. 106 hours
Region number: Region No.5
(Approx. 3W (Stand by mode))
DVD video standards (DVD-R)
12 cm 9.4 GB DVD-RAM discs
8 cm 2.8 GB DVD-RAM discs
12 cm 4.7 GB DVD-R discs
(for General Ver. 2.0/4X-SPEED DVD-R Revision 1.0)
8 cm 1.4 GB DVD-Rdiscs
(for General Ver. 2.0)
XP: 60 minutes
SP: 120 minutes
LP: 240 minutes
EP: 360 minutes
XP: 17 hours
SP: 34 hours
LP: 68 hours
EP: 106 hours

Playable discs: 12 cm 4.7 GB DVD-RAM discs
12 cm 9.4 GB DVD-RAM discs
8 cm 2.8 GB DVD-RAM discs
12 cm 4.7 GB DVD-R discs
(for General Ver. 2.0)
8 cm 1.4 GB DVD-R discs
(for General Ver. 2.0)
DVD-VIDEOdiscs
CD-Audio discs (CD-DA)
Video CD discs
DVD-Audio discs
CD-R/ CD-RW discs
(CD-DA, Video CD, MP3 formatted discs)
Built-in HDD Capacity: 80GB
Drive Unit: High Speed Drive (correspond to 4 times speed with DVD-R disc)
Television System
Tuner System: PAL-BGH, I, DK/ SECAM-BG, DK
Channel Coverage:
OIRT (DK) VHF: Ch R1-R12,
CCIR (BGH) VHF: Ch E2-E12,
UHF: Ch 21-69
CATV: Ch 44MHz-470MHz
UHF: Ch 21-69
CATV: Ch S01-S05, M1-M10, U1-U10, S21-S41
(PAL-I) UHF: Ch 21-69
RF Converter Output: Not provided
Video
Video System: SECAM (Only Input)/ PAL colour signal, 625 lines, 50 fields NTSC colour signal, 525 lines, 60 fields
Recording System: MEPG2 (Hybrid VBR), MPEG4 (VBR)
Video in: AV1/AV2 (21 pin), AV3/AV4 (pin jack)
S-Video in: AV2 (21 pin), AV3/AV4 (S terminal)
1Vp-p 75 ohm, terminated
1Vp-p 75 ohm, terminated
RGB In: AV2 (21 pin), 0.7Vp-p (PAL) 75 ohm, terminated
Video Out: AV1/AV2 (21 pin), Video Out (pin jack)
S-Video Out: AV1 (21 pin), S-Video Out(S terminal)
1Vp-p 75 ohm, terminated
1Vp-p 75 ohm, terminated
RGB Out: AV1 (21 pin) 0.7Vp-p (PAL) 75 ohm, terminated
DV Input: 4 pin
Audio
Recording system: Dolby Digital 2ch, Linear PCM
2ch (XP mode), G.726 (MPEG4)
Audio In: AV1/AV2 (21pin) AV3/AV4 (pin jack)
Input Level: Standard: 0.5 Vrms
Full scale: 2 Vrms at 1k Hz
Input Impedance: More than 10k ohm
Audio Out: AV1/AV2 (21 pin) Audio Out (pin jack)
Output Level: Standard: 0.5 Vrms
Full scale: 2 Vrms at 1k Hz
Output impedance: less than 1k ohm
Digital Audio Out: Optical terminal (PCM, Dolby Digital, DTS, MPEG)
SD/PC Card Slot
SD Memory Card Slot: 1 pc.
PC Card Slot (Type II): 1 pc.
Still Picture (JPEG, TIFF)
Compatible Media
(SD Card Slot):
SD Memory Card, MultiMediaCard

Compatible Media
(PC Card Slot):
Format: FAT12, FAT16
Image File Format: JPEG conforming to DCF (Design rule for Camera File system), (Sub sampling 4:2:2 or 4:2:0) TIFF (Uncompressed RGB chunky), DPOF Compatible
Number of pixels: 320×240 to 6144×4096
Thawing Time: Approx. 7 sec. (2 Mpixels)
SD Video (MPEG4,
MPEG2)
Compatible Media
(SD Card Slot):
Compatible Media
(PC Card Slot):
MPEG4
Codec: Video: MPEG4 conforming,
Number of pixels: super fine/fine: 320×240 (QVGA),
Recording rate (max): superfine: 1050 kbps,
File format: SD-Video format conforming (ASF)
MPEG2 *Recording coversion and transfer is possible from card to HDD or DVD-RAM disc.
Codec: MPEG2
File format: SD-Video format conforming
Dimensions: Approx.
Mass: Approx. 5.5 kg (12.13 lbs)
Operating temperature: 5°C-40°C (41°F-104°F)
Operating humidity range: 10%-80% RH (no condensation)
Clock unit: Quartz-controlled 12-hour digital display
A PC Card adaptor conforming to PC Card Standards, ATA Flash PC Card, PC Card Adaptor (SD Memory Card, xD-Picture Card, Microdrive, Multi MediaCard, CompactFlash, SmartMedia, Memory Stick), Mobile hard disc
SD Memory Card, MultiMediaCard (restricted to fine, normal, economy of MPEG4)
Mobile hard disk (Only read)
Audio: G.726 conforming
normal/economy: 176×144 (QCIF)
fine: 430 kbps,
normal: 300 kbps,
economy: 100 kbps
(include Audio transfer rate as 32 kbps)
*After Video Recording coversion and transfer to HDD or DVD-RAM disc, the playback is possible.
(SD-Video Entertainment Video Profile)
(VR conversion and transfer is possible from card to HDD or DVD-RAM disc)
430 (W)×79 (H)×296 (D) mm
[Approx. 1615/ 16“(W)×31/ 8” (H)×1111/ 16” (D)]
(excludingprotrusions)
LASER Specification
Class 1 LASER Product
Wave length: 779-791 nm 653-662 nm
Laser power: No hazardous radiation is emitted with the safety protection.
Solder:
This model uses lead free solder (PbF).
Notes:
Mass and dimensions are approximate.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Notes:
The part of DVD RAM Drive (VXY1789) is listed separately.
Please refer to ORDER NO. RAM0307003C0.
© 2003 Matsushita Electric Industrial CO., Ltd. All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law.

1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
TOP
1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1 .)

1.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts
which have been overheated or damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation
papers shields are properly installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from
being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See Figure 1 .)

1.1.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT COLD CHECK
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between the jumpered AC plug and each
exposed metallic cabinet part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors, control shafts,
etc. When the exposed metallic part has a return path to thechassis, the reading should be
between 1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the chassis, the reading must be
.
Figure 1

1.1.2 LEAKAGE CURRENT HOT CHECK (See
Figure 1 .)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an isolation transformer for this
check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15μF capacitors, between each
exposed metallic part on the set and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in
Figure 1 .
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity, to measure the potential across
the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. A leakage current tester
(Simpson Model 229 or equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage current must
not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a measurement is outsideof the limits specified, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be repaired and rechecked before it is
returned to the customer.

2 PREVENTION OF ELECTRO STATIC
DISCHARGE (ESD) TO ELECTROSTATICALLY
SENSITIVE (ES) DEVICES
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such
components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES
devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistorsand semiconductor "chip" components.
The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused
by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped
assembly, drain off any ESD on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively,
obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap, whichshould be
removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a
conductive surface such as alminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure
of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as
"anti-static (ESD protected)" can generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to
damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before
you are ready to install it. (Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically
shorted together by conductive foam, alminum foil or comparableconductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES
device, touch the protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device
will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.

8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise
harmless motion such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot
from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD)sufficient to damage an ES device).
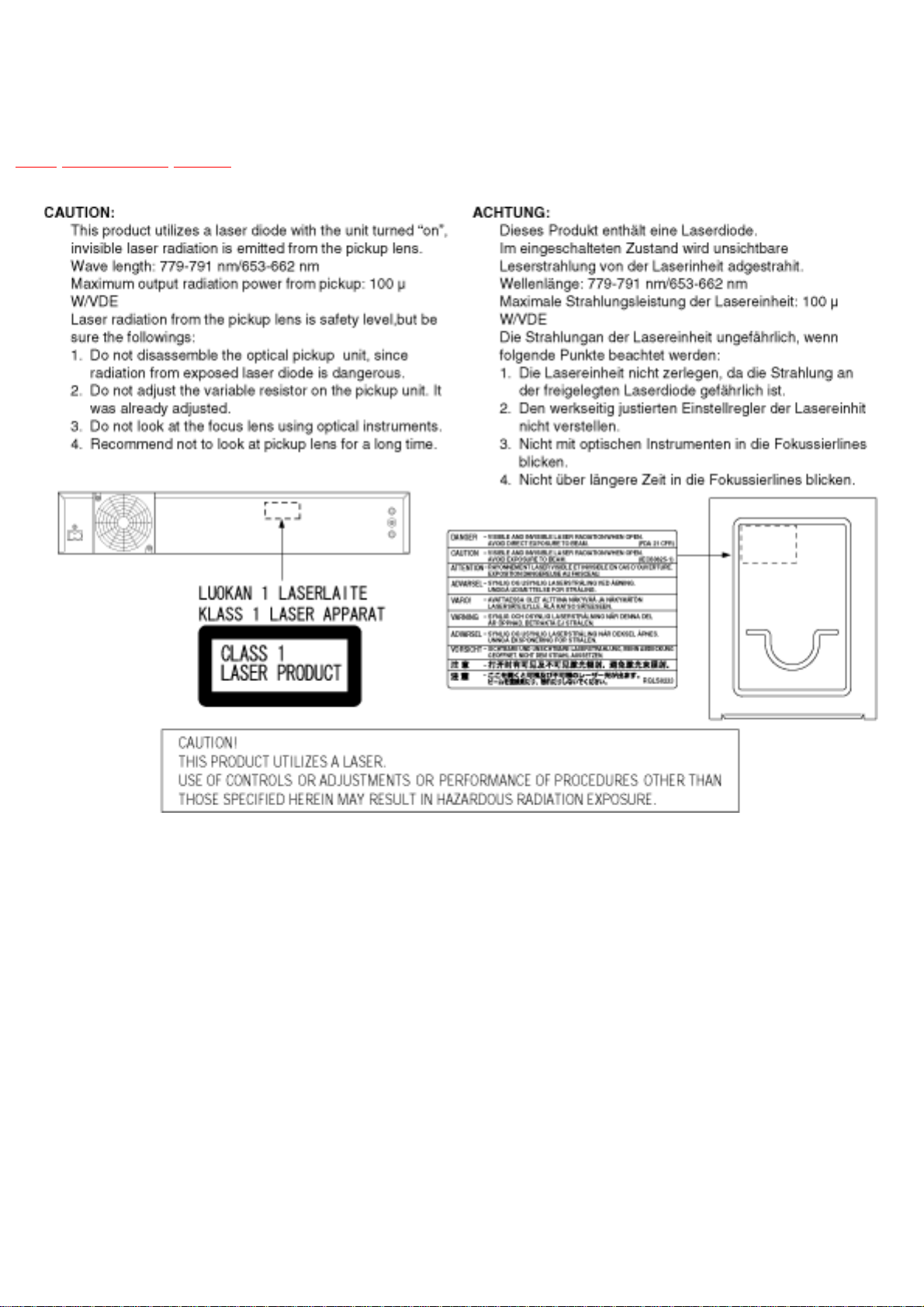
3 Precaution of Laser Diode
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT

4 Handling the Lead-free Solder
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
4.1 About lead free solder (PbF)

4.1 About lead free solder (PbF)
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Caution:
● Pb free solder has a higher melting point than standard solder; Typically the melting point is
50 - 70°F (30 - 40°C) higher. Please use a high temperature soldering iron. In case of the
soldering iron with temperature control,please set it to 700 ± 20°F (370 ± 10°C).
● Pb free solder will tend to splash when heated too high (about 1100°F/600°C).
● When soldering or unsoldering, please completely remove all of the solder on the pins or
solder area, and be sure to heat the soldering points with the Pb free solder until it melts
enough.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
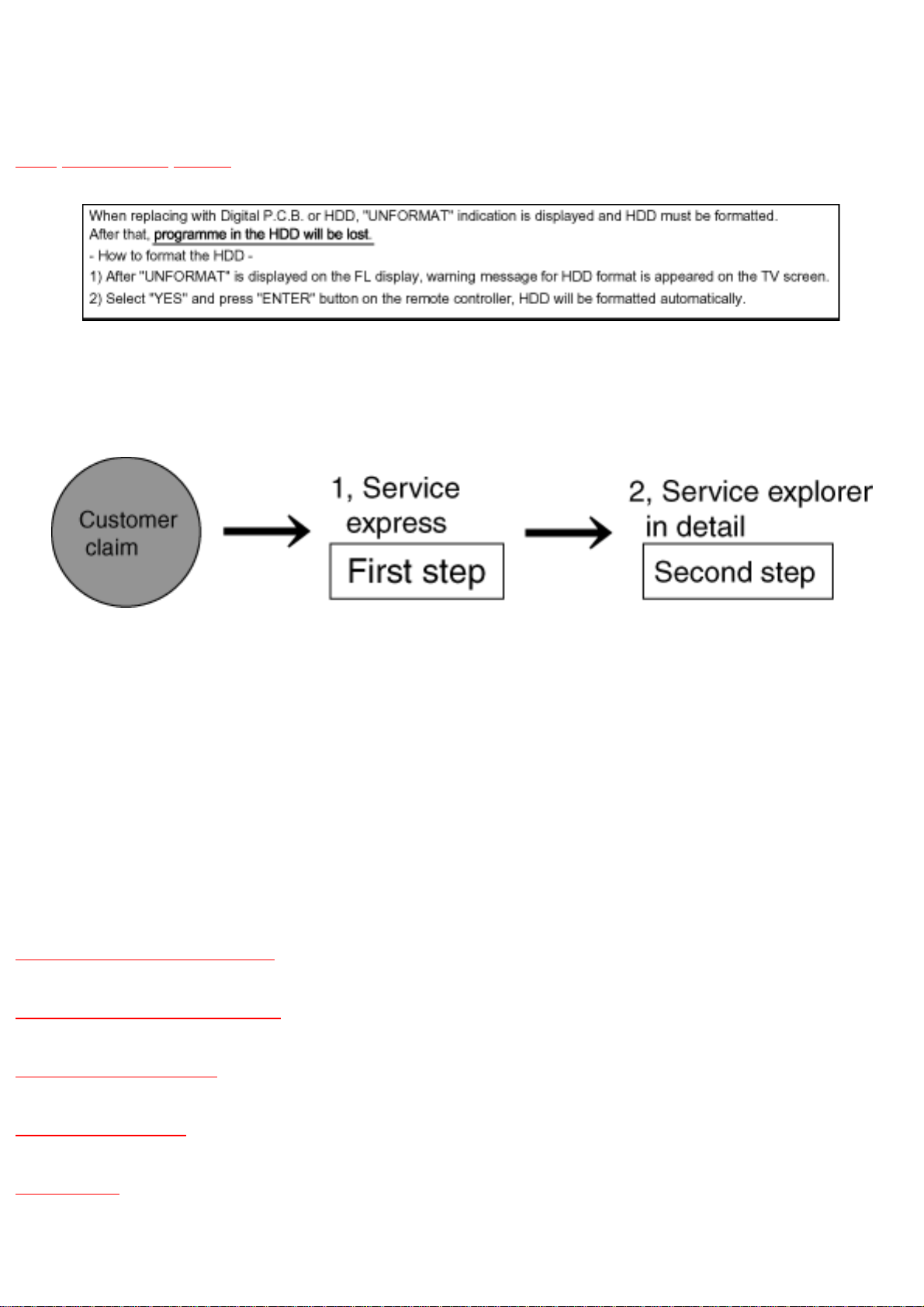
5 Service Explorer
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
The Service Explorer provides information about all possible causes based on the symptoms and
gives step by step instructions making parts. It consists of two parts, based on applications: the first is
the “Service Explorer Express” andthe second is “Service Explorer in Detail”.
1. For details about the service / test modesetting mentioned in the description, refer to the “List
of various modes”.
❍ Service mode setting: While the power is off, press TIME SLIP, STOP, and OPEN /
CLOSE simultaneously for five seconds.
❍ Process mode 1 setting: While the power is off, press SKIP(R), TIME SLIP, and
OPEN / CLOSE simultaneously for five seconds.
2. For disassembly and replacement procedures, refer to the “Assembling and Disassemling”.
5.1 Service Explorer Express
5.2 Service Explorer in Detail
5.2.1 Does not operate
5.2.2 Poor Pictures
5.2.3 Other

5.2.4 Some defective functions
5.2.5 Caution when replacing the parts
5.1 Service Explorer Express
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
The following steps allow you to check each block separately (HDD, Digital P.C.B., RAM drive,
Main / Power Supply / Front P.C.B.).
Items needed: RAM drive, Digital P.C.B., Digital extension cable, Remote control, HDD.
Conditions: Nothing special.
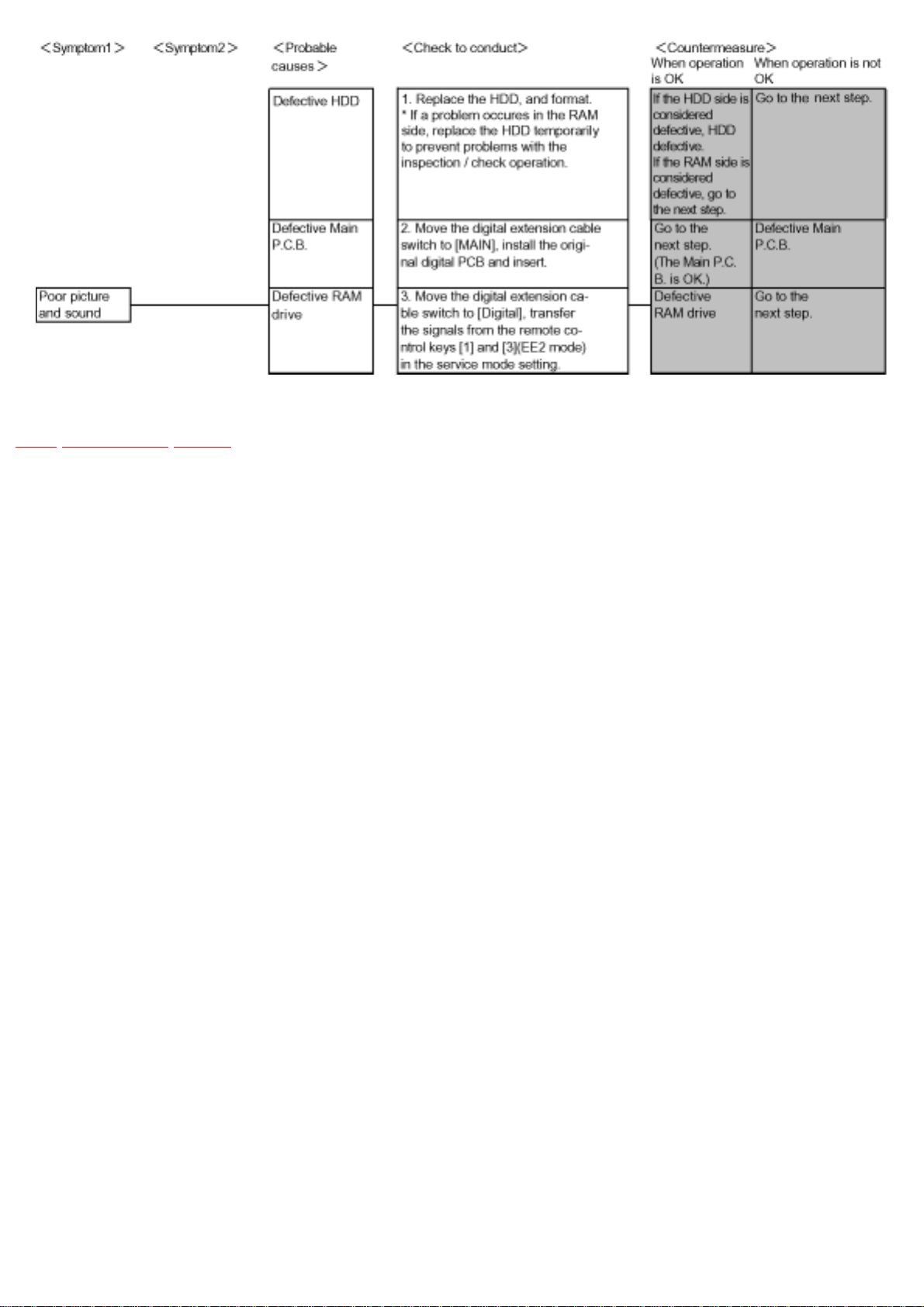
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT

5.2 Service Explorer in Detail
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
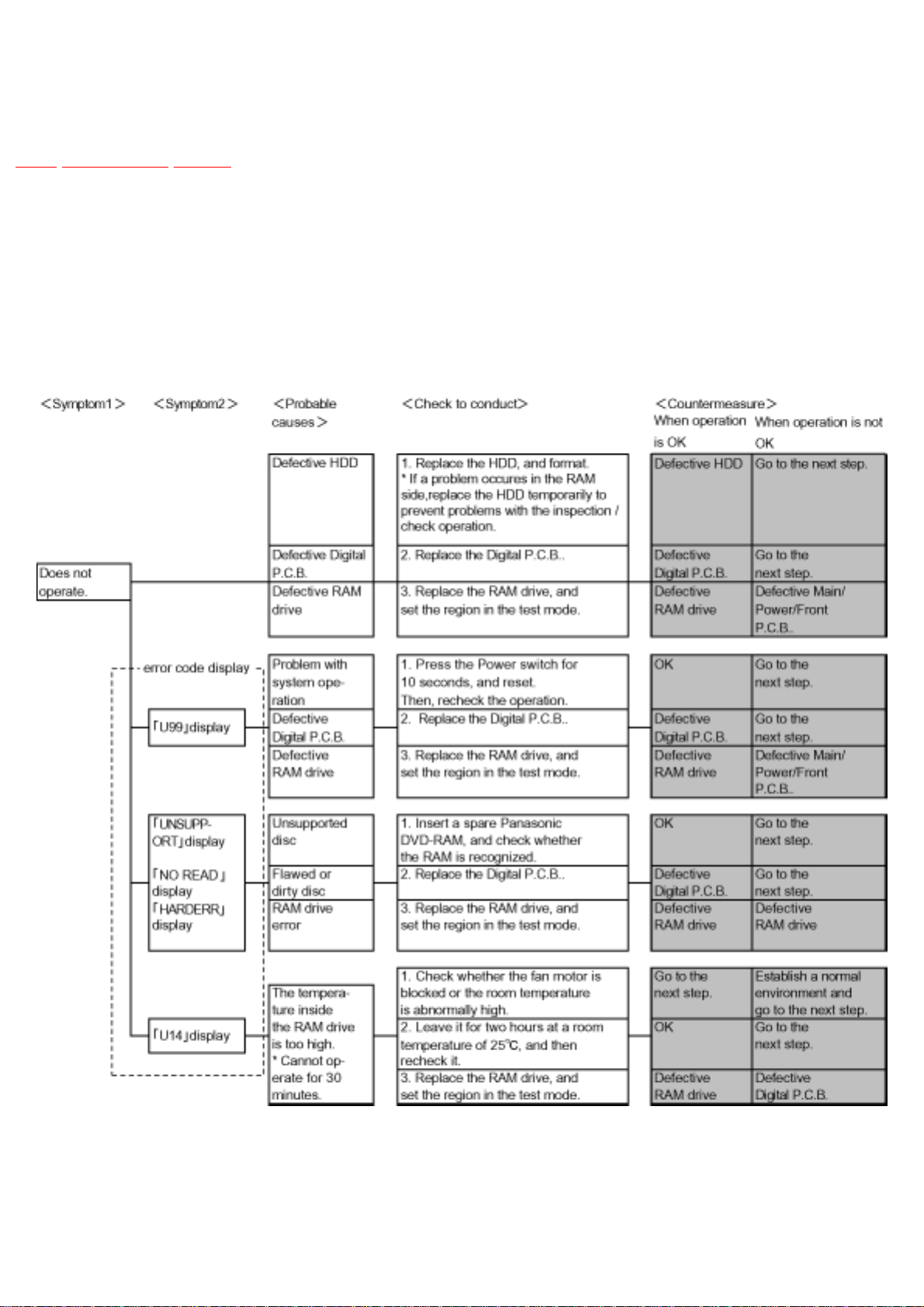
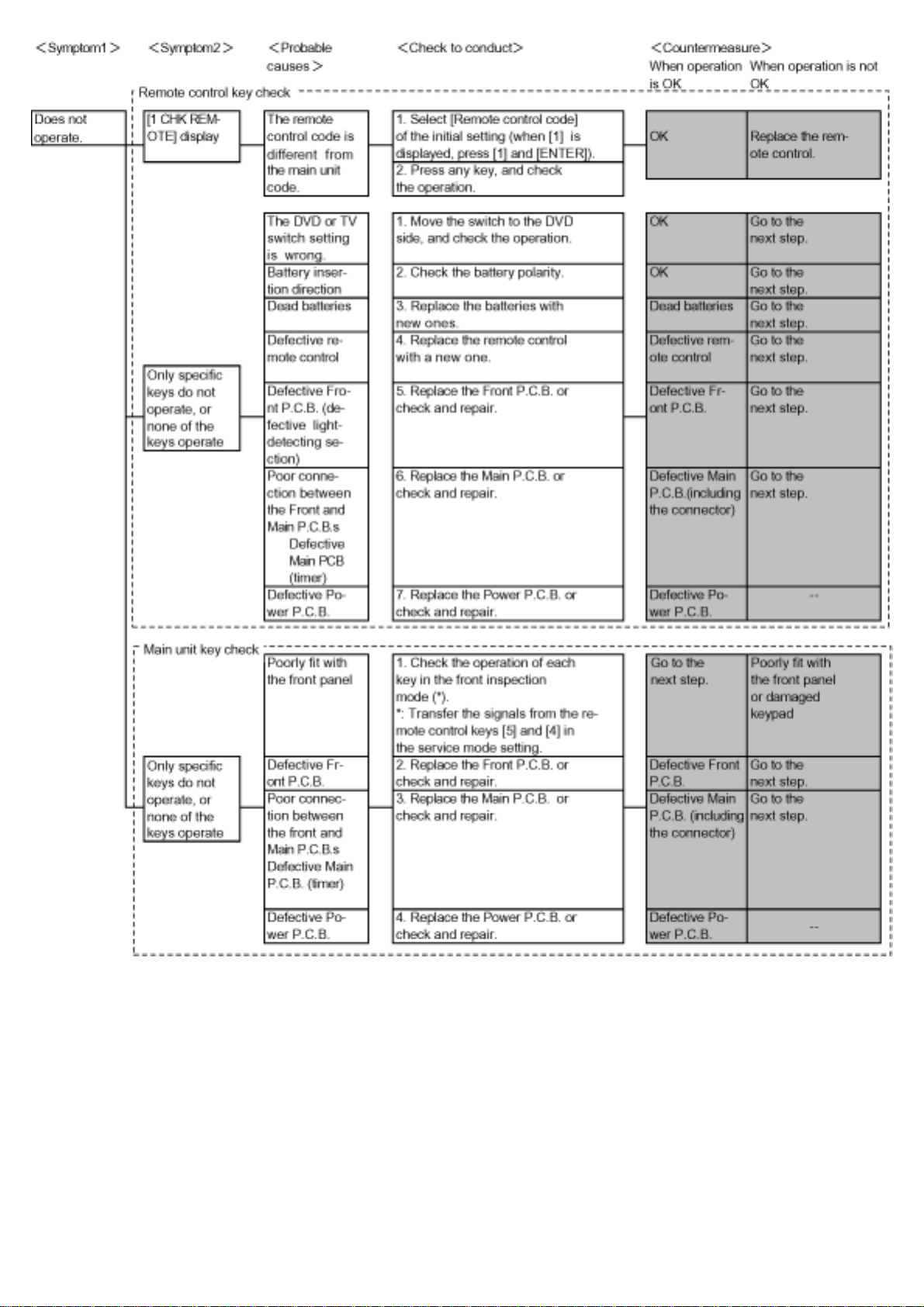
5.2.1 Does not operate
5.2.2 Poor Pictures
5.2.3 Other
5.2.4 Some defective functions
5.2.5 Caution when replacing the parts
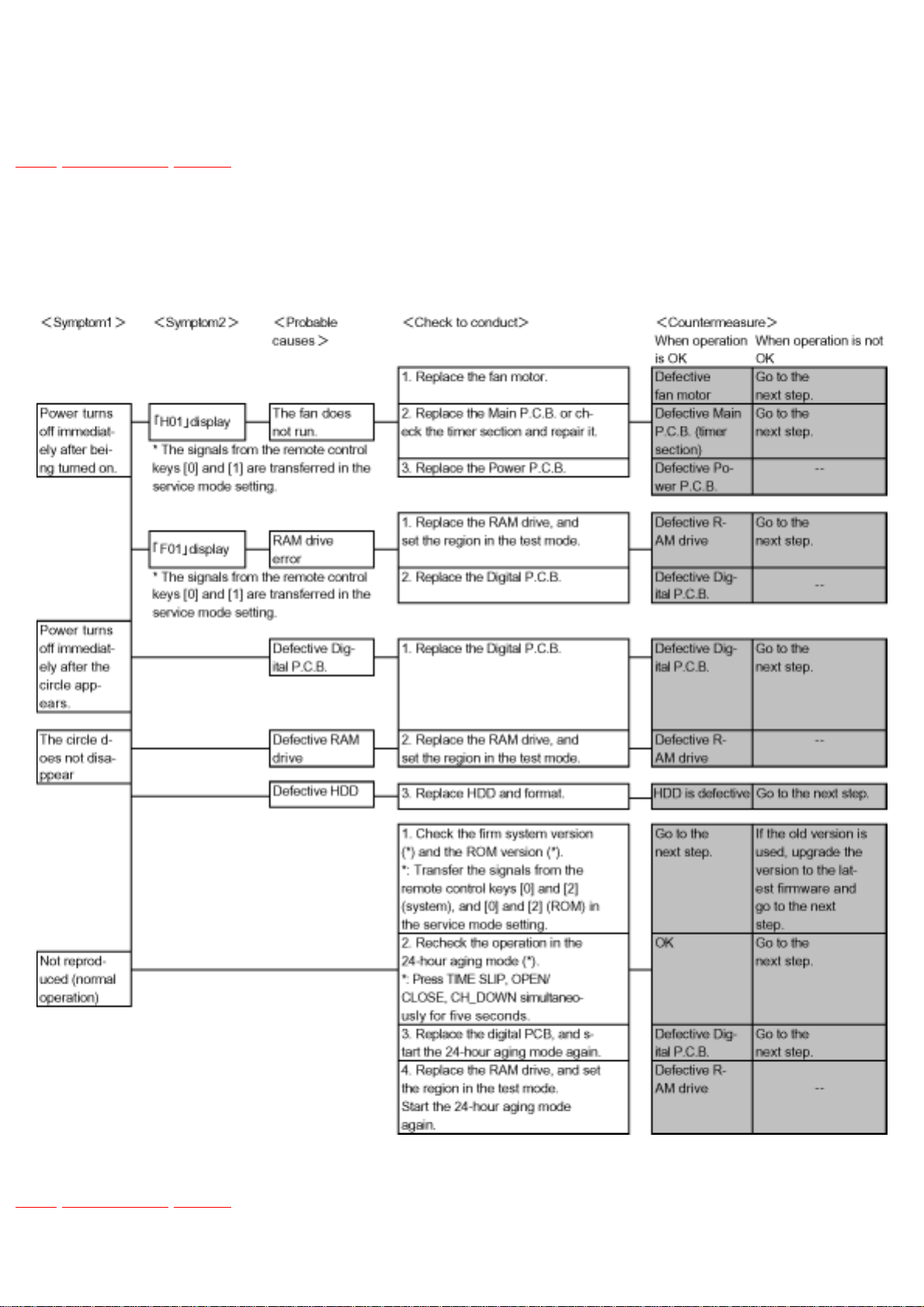
5.2.1 Does not operate
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
items needed: RAM drive, digital P.C.B., remote control.
Conditions: Nothing special.
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
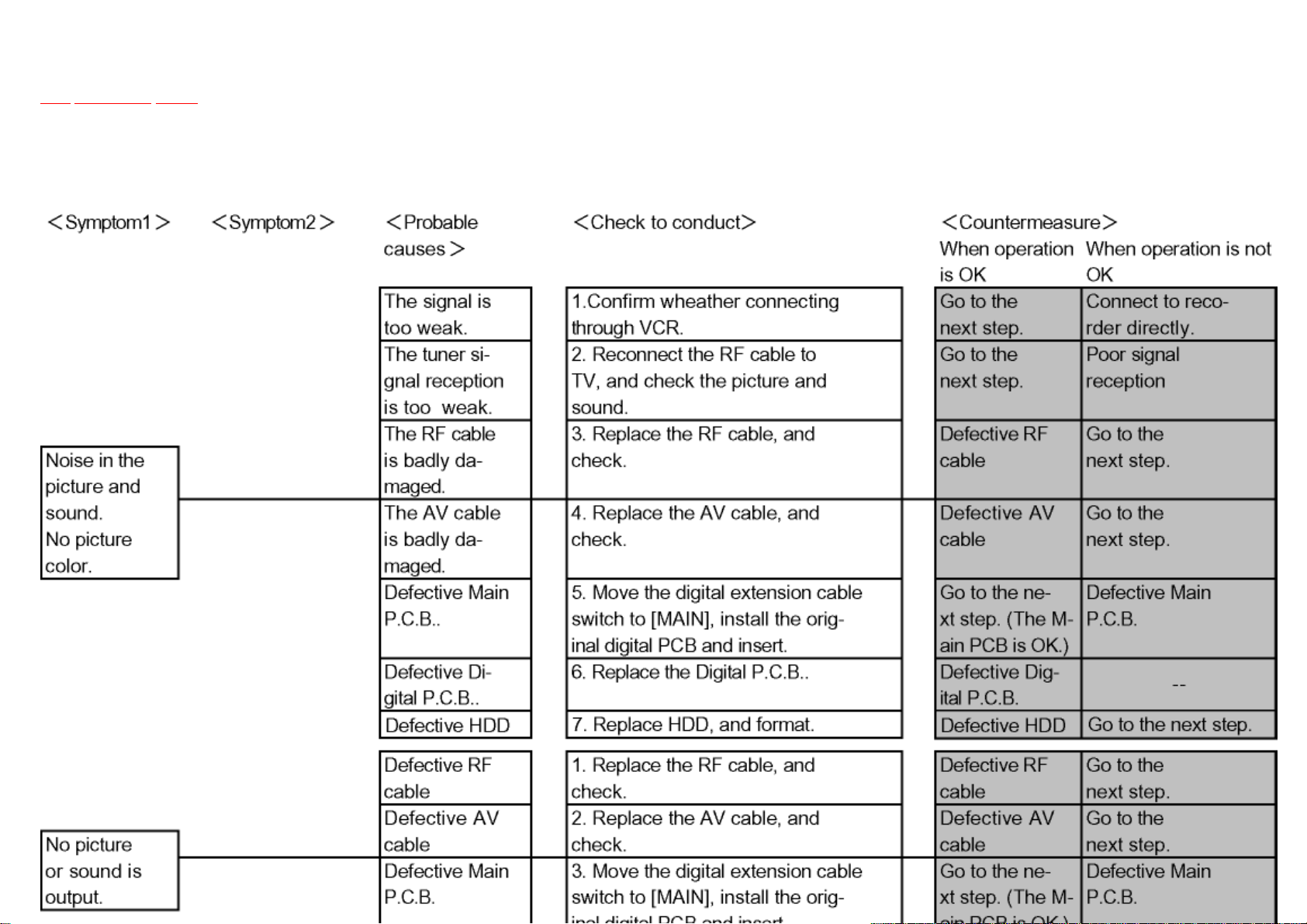
5.2.2 Poor Pictures
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Items needed: RAM drive, Digital P.C.B., RF cable, AV cable.
Conditions: Check with TU IN-AV OUT(EE). When recording or playback is partially needed, follow the instructions.
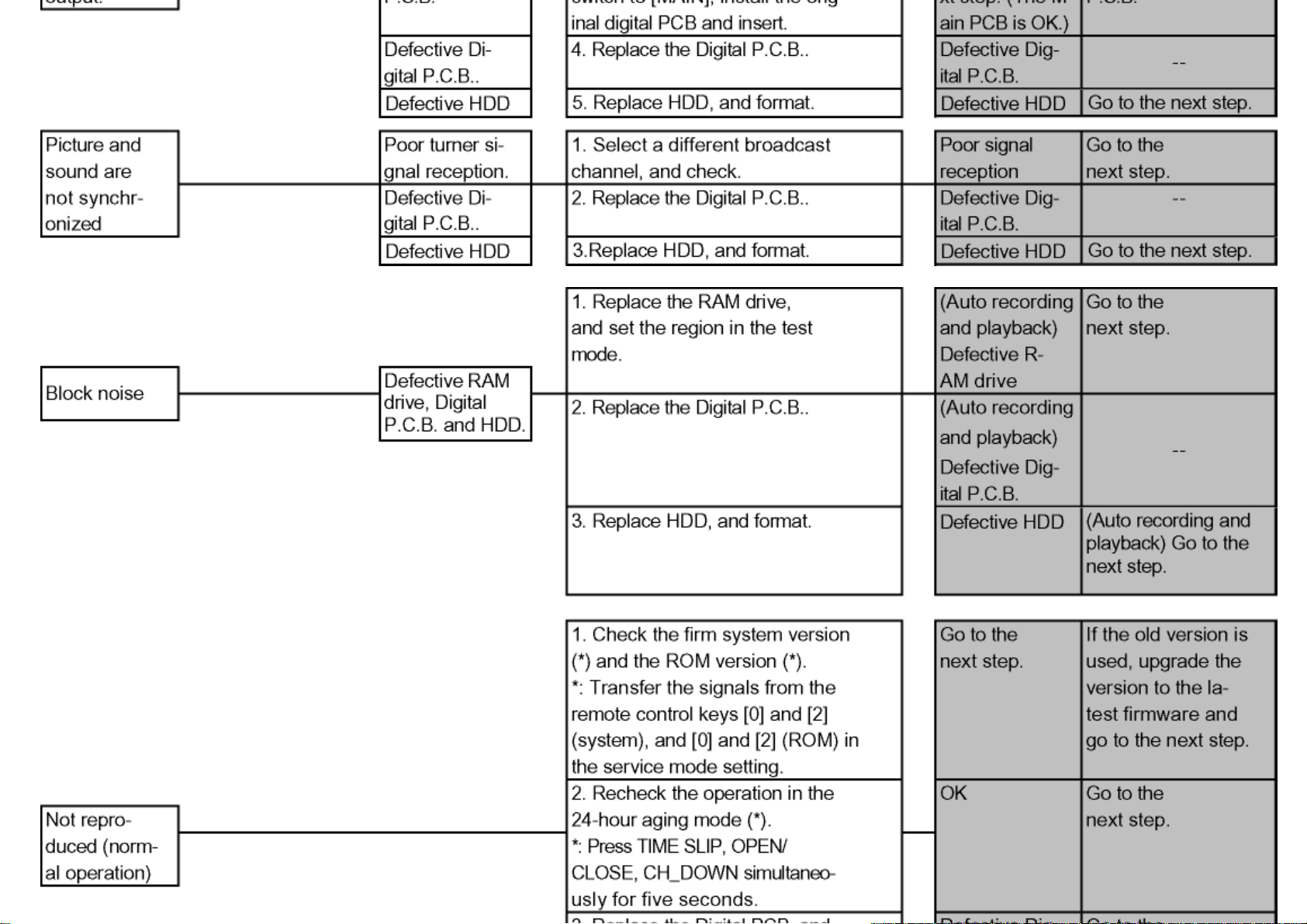
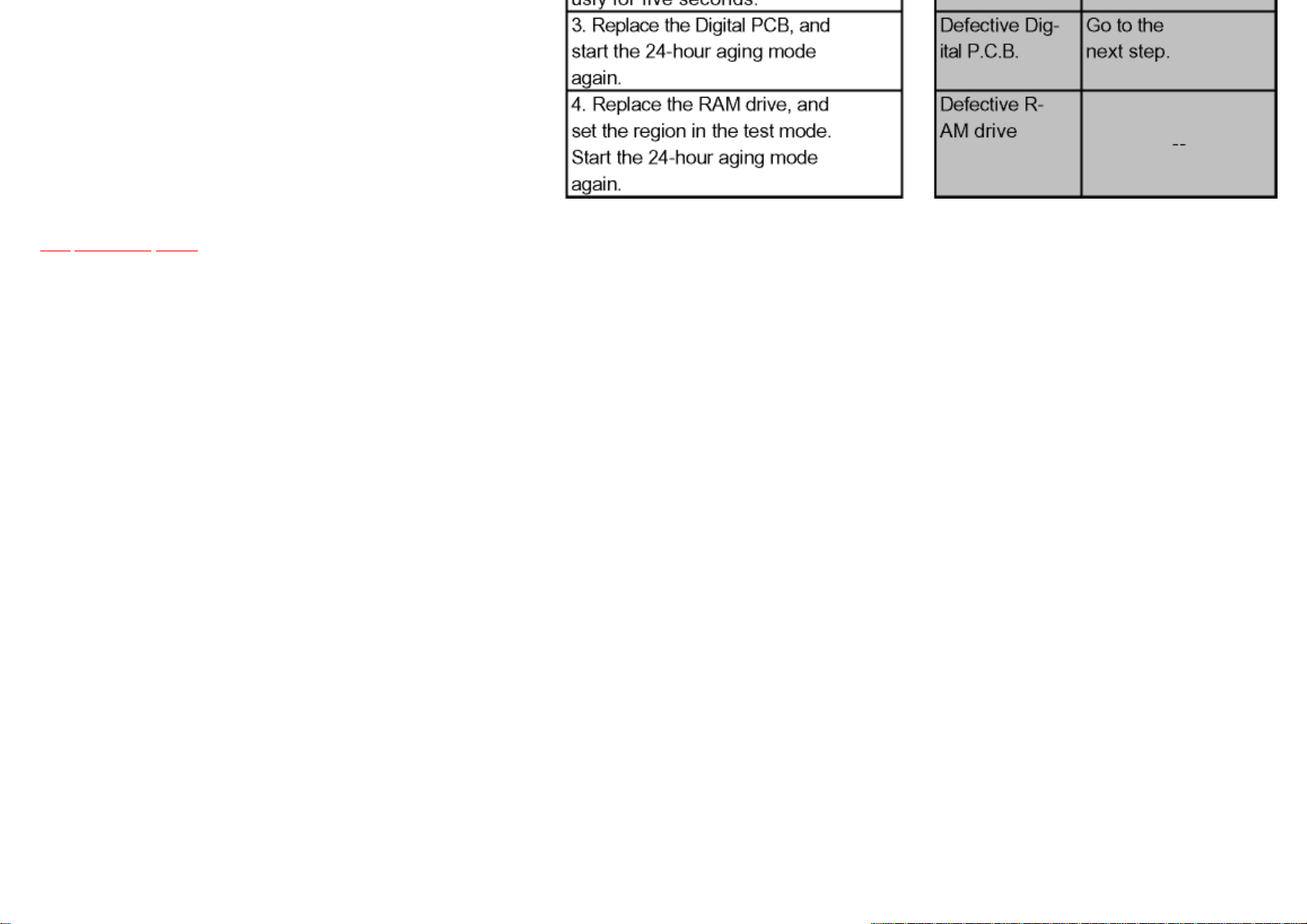
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
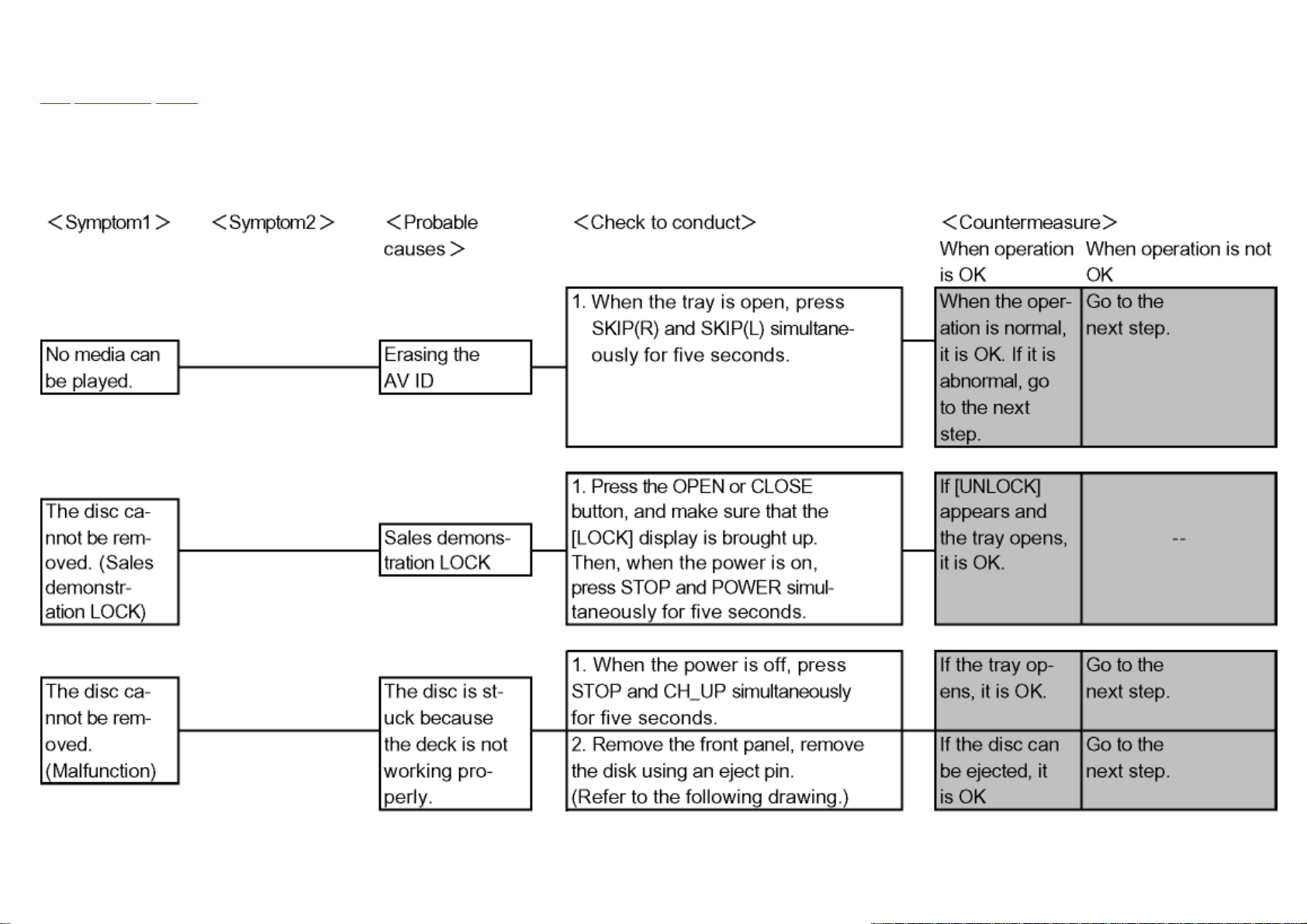
5.2.3 Other
TOP PREVIOUS NEXT
Items needed: Digital P.C.B., HDD.
Conditions: Nothing special.
 Loading...
Loading...