Page 1

Cat. No.W457-E1-05
Cat. No. Z264-E2-04-X Smart Sensor ZFX-C USER´S MANUAL
CRT1 Series
CompoNet Slave Units
and Repeater Unit
OPERATION MANUAL
Page 2

CRT1 Series
CompoNet Slave Units
and Repeater Unit
Operation Manual
Revised October 2008
Page 3

iv
Page 4

v
Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use according to proper procedures by a qualified operator
and only for the purposes described in this manual.
The following conventions are used to indicate and classify precautions in this manual. Always heed
the information provided with them. Failure to heed precautions can result in injury to people or damage to property.
!DANGER Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
!WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
!Caution Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury, or property damage.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The word “Unit” is also capitalized when it refers to
an OMRON product, regardless of whether or not it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation “Ch,” which appears in some displays and on some OMRON products, often means
“word” and is abbreviated “Wd” in documentation in this sense.
The abbreviation “PLC” means Programmable Controller. “PC” is used, however, in some Programming Device displays to mean Programmable Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1,2,3... 1. Indicates lists of one sort or another, such as procedures, checklists, etc.
OMRON, 2006
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form, o
r
by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission o
f
OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless, OMRON assumes no responsibility
for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting from the use of the information contained in
this publication.
Page 5

vi
Page 6

vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
1 Intended Audience. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
2 General Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
5 Application Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xx
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxii
SECTION 1
Features and Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1-1 Features of CompoNet Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-2 Slave Unit Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
SECTION 2
Wiring Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2-1 CompoNet Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
2-2 Wiring Formations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2-3 Communications Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
2-4 Communications Cable Wiring Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
SECTION 3
Installation and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3-1 Installing Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-2 Connecting Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-3 Preparing Flat Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
3-4 Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3-5 Power Supply Wiring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3-6 Connecting External I/O for Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
SECTION 4
Basic Specifications of Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
4-1 Basic Specifications of Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
SECTION 5
Digital I/O Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
5-1 Status Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
5-2 Allocating I/O Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
5-3 Units with Screw Terminal Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
5-4 Units with Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
5-5 Units with Clamp Terminal Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Page 7

viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 6
Analog I/O Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
6-1 Overview of Analog I/O Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
6-2 Status Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
6-3 Maintenance Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
6-4 Analog Input Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
6-5 Analog Output Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .310
SECTION 7
Temperature Input Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
7-1 Temperature Input Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
7-2 Overview of Temperature Input Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
7-3 Status Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
7-4 Monitoring Temperature Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
7-5 Temperature Input Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
SECTION 8
Expansion Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
8-1 Expansion Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
8-2 Expansion Unit Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
SECTION 9
Bit Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
9-1 Status Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
9-2 Allocating I/O Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
9-3 Industry Standard Sensor Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
9-4 Clamp Terminal Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .384
SECTION 10
Repeater Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
10-1 Status Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
10-2 Repeater Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
SECTION 11
Smart Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 397
11-1 CX-Integrator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
11-2 Functions Common to All Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
11-3 Word Slave Unit and Bit Slave Unit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
11-4 Analog I/O Slave Unit Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
11-5 Temperature Input Unit Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
11-6 Functions Unique to Bit Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
Page 8

ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 12
Troubleshooting and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
12-1 Indicator Meanings and Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
12-2 Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
12-3 Device Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 501
Appendices
A CompoNet Explicit Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
B Object Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 527
C Connectable Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .543
D Current Consumption Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
E Precautions with Connecting Two-wire DC Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
Page 9

x
Page 10

xi
About this Manual:
This manual describes the installation and operation of the CompoNet Slave Units, and the Repeater
Unit and includes the sections described below.
Please read this manual carefully and be sure you understand the information provided before
attempting to install or operate a CompoNet Slave Unit or Repeater Unit. Be sure to read the precautions provided in the following section. Also be sure to read the CompoNet Master Unit Operation Man-
ual (see following table) together with this manual.
Precautions provide general precautions for using the CompoNet Slave Units, Repeater Units, Programmable Controller, and related devices.
Section 1 introduces the CompoNet Slave Units and the various models that are available.
Section 2 describes the configurations of CompoNet Networks.
Section 3 describes how to install and wire a CompoNet Network.
Section 4 provides the basic specifications of the Slave Units.
Section 5 describes the Digital I/O Slave Units.
Section 6 describes the Analog I/O Slave Units.
Section 7 describes the Temperature Input Units.
Section 8 describes the Expansion Units.
Section 9 describes the Bit Slave Units.
Section 10 describes the Repeater Unit.
Section 11 individually describes the functions provided by CompoNet Slave Unit. The functions are
divided into those supported by all CompoNet Slave Units and those supported only by specific CompoNet Slave Units.
Section 12 provides troubleshooting information that can be used in the event a problem occurs in
CompoNet Slave Unit operation. It also provides information on maintenance that should be performed
to ensure optimum application of the CompoNet Slave Units.
The Appendices provide specialized information, including information on CompoNet explicit messages, object mounting, connectable devices, current consumption, and precautions for connecting
two-wire DC sensors.
!WARNING Failure to read and understand the information provided in this manual may result in per-
sonal injury or death, damage to the product, or product failure. Please read each section
in its entirety and be sure you understand the information provided in the section and
related sections before attempting any of the procedures or operations given.
Page 11
xii
Related Manuals:
Cat. No. Models Name Description
W457
(this manual)
CRT1 Series CompoNet Slave Units and
Repeater Unit Operation
Manual
Provides the specifications of CompoNet
Slave Units and Repeater Unit.
W456 CS1W-CRM21 and CJ1W-
CRM21
CS/CJ-series CompoNet
Master Units Operation
Manual
Provides an overview of CompoNet Networks,
communications specifications, wring methods, and CompoNet Master Unit functions.
W342 CS1G/H-CPU@@H
CS1G/H-CPU@@-EV1
CS1D-CPU@@H
CS1D-CPU@@S
CS1W-SCB@@-V1
CS1W-SCU@@-V1
CJ1G/H-CPU@@H
CJ1G-CPU@@P
CJ1G-CPU@@
CJ1M-CPU@@
CJ1W-SCU@@-V1
CP1H-X@@@@-@
CP1H-XA@@@@-@
CP1H-Y@@@@-@
NSJ@-@@@@(B)-G5D
NSJ@-@@@@(B)-M3D
SYSMAC CS/CJ/CP Series
SYSMAC One NSJ Series
Communications Commands Reference Manual
Describes the communications commands
used with CS-series, CJ-series, and CPseries PLCs and NSJ Controllers.
W464 CXONE-AL@@C-EV@/
CXONE-AL@@D-EV@
SYSMAC CS/CJ/CP/NSJ
Series CX-Integrator Ver.
2.3 Operation Manual
Describes CX-Integrator operating methods,
e.g., for setting up and monitoring networks.
Page 12

xiii
Read and Understand this Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON
representative if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a
period of one year (or other period if specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF THE
PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS
DETERMINED THAT THE PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES,
LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS,
WHETHER SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE, OR STRICT
LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the individual price of the product on which
liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY, REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS
REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS
WERE PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND NOT SUBJECT TO
CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
Page 13

xiv
Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards, codes, or regulations that apply to the
combination of products in the customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party certification documents identifying
ratings and limitations of use that apply to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a
complete determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end product, machine,
system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular attention must be given. This is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses
listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or electrical interference, or conditions or
uses not described in this manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems, aviation systems, medical
equipment, amusement machines, vehicles, safety equipment, and installations subject to separate
industry or government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR
PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO
ADDRESS THE RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED AND INSTALLED
FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a programmable product, or any
consequence thereof.
Page 14

xv
Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time based on improvements and other
reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or features are changed, or when
significant construction changes are made. However, some specifications of the products may be changed
without any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix or establish key
specifications for your application on your request. Please consult with your OMRON representative at any
time to confirm actual specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for manufacturing purposes, even when
tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user in determining suitability and does
not constitute a warranty. It may represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users must
correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is subject to the OMRON Warranty and
Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed to be accurate; however, no
responsibility is assumed for clerical, typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
Page 15

xvi
Page 16

xvii
PRECAUTIONS
This section provides general precautions for using the CompoNet Slave Units, and the Repeater Unit.
The information contained in this section is important for the safe and reliable application of the CompoNet Slave
Units and Repeater Unit. You must read this section and understand the information contained before attempting
to set up or operate a CompoNet Network using CompoNet Slave Units or Repeater Units.
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
2 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
3 Safety Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
4 Operating Environment Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
5 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xx
6 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxii
6-1 Applicable Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxii
6-2 Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxii
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xxiii
Page 17

xviii
Intended Audience 1
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating the Unit. Be
sure to read this manual before attempting to use the Unit and keep this manual close at hand for reference during operation. Be sure this manual is delivered to the persons actually using the CompoNet Slave Units and Repeater
Units.
!WARNING It is extremely important that a PLC and all PLC Units be used for the speci-
fied purpose and under the specified conditions, especially in applications that
can directly or indirectly affect human life. You must consult with your OMRON
representative before applying a PLC System to the above-mentioned applications.
3 Safety Precautions
!WARNING Do not attempt to take any Unit apart and do not touch the interior of any Unit
while the power is being supplied. Also, do not turn ON the power supply
while the cover is open. Doing any of these may result in electric shock.
!WARNING Do not input voltages or currents exceeding the rated range to the Unit.
Exceeding the rated range may cause Unit failure or fire.
Page 18

xix
Operating Environment Precautions 4
!WARNING Provide safety measures in external circuits (i.e., not in the Slave Units),
including the following items, to ensure safety in the system if an abnormality
occurs due to malfunction of the PLC or another external factor affecting the
PLC operation. (“PLC” includes CPU Units, other Units mounted in the PLC,
and Remote I/O Terminals.) Not doing so may result in serious accidents.
• Emergency stop circuits, interlock circuits, limit circuits, and similar safety
measures must be provided in external control circuits.
• The PLC will turn OFF all outputs when its self-diagnosis function detects
any error or when a severe failure alarm (FALS) instruction is executed.
As a countermeasure for such errors, external safety measures must be
provided to ensure safety in the system.
• The PLC outputs may remain ON or OFF due to deposits on or burning of
the output relays, or destruction of the output transistors. As a countermeasure for such problems, external safety measures must be provided
to ensure safety in the system.
• When the 24-VDC output (service power supply) is overloaded or shortcircuited, the voltage may drop and result in the outputs being turned
OFF. As a countermeasure for such problems, external safety measures
must be provided to ensure safety in the system.
!WARNING The CPU Unit refreshes I/O even when the program is stopped (i.e., even in
PROGRAM mode). Confirm safety thoroughly in advance before changing the
status of any part of memory allocated to I/O Units, Special I/O Units, or CPU
Bus Units. Any changes to the data allocated to any Unit may result in unexpected operation of the loads connected to the Unit. Any of the following operation may result in changes to memory status.
• Transferring I/O memory data to the CPU Unit from a Programming
Device.
• Changing present values in memory from a Programming Device.
• Force-setting/-resetting bits from a Programming Device.
• Transferring I/O memory files from a Memory Card or EM file memory to
the CPU Unit.
• Transferring I/O memory from a host computer or from another PLC on a
network.
4 Operating Environment Precautions
!Caution Do not operate the control system in the following locations:
• Locations subject to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to temperatures or humidity outside the range specified
in the specifications.
• Locations subject to condensation as the result of severe changes in temperature.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to dust (especially iron dust) or salts.
• Locations subject to exposure to water, oil, or chemicals (including acids).
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
Page 19

xx
Application Precautions 5
!Caution The operating environment of the PLC System can have a large effect on the
longevity and reliability of the system. Improper operating environments can
lead to malfunction, failure, and other unforeseeable problems with the PLC
System. Make sure that the operating environment is within the specified conditions at installation and remains within the specified conditions during the
life of the system.
5 Application Precautions
Observe the following precautions when using a CompoNet Network.
• When transporting the Unit, use special packing boxes and protect it from
being exposed to excessive vibration or impact during transportation.
• Do not drop any Unit or subject any Unit to excessive shock or vibration.
Otherwise, Unit failure or malfunction may occur.
• Mount the Units securely using DIN Track, a Mounting Bracket, or screws.
• Make sure that all Slave Unit mounting screws and cable connector
screws are tightened to the torque specified in the relevant manuals.
Incorrect tightening torque may result in malfunction.
• Make sure that the terminal blocks, communications cables, and other
items with locking devices are properly locked into place. Improper locking
may result in malfunction.
• When installing the Units, ground to 100
Ω min.
• Wire all connections correctly according to instructions in the manual.
• Always separate Special Flat Cables (Standard and Sheathed) for different CompoNet systems by at least 5 mm to prevent unstable operation
due to interference. Do not bundle Special Flat Cables.
• Do not extend connection distances or the number of connected nodes
beyond the ranges given in the specifications.
• Do not allow foreign matter to enter the Units when wiring and installing
the Units.
• Use the correct wiring materials to wire the Units.
• Use the correct tools to wire the Units.
• Always use the specified communications cables and connectors.
• Confirm the polarity of all terminals before wiring them.
• Make sure that all terminal block screws are tightened to the torque specified in this manuals. Incorrect tightening torque may result in fire, malfunction, or failure.
• Always use the power supply voltage specified in this manual.
Page 20

xxi
Application Precautions 5
• Do not bend cables past their natural bending radius or pull on cables.
• Observe the following precautions when wiring the communications
cable.
• Separate the communications cables from the power lines or high-tension lines.
• Do not bend the communications cables past their natural bending radius.
• Do not pull on the communications cables.
• Do not place heavy objects on top of the communications cables.
• Always lay communications cable inside ducts.
• Take appropriate measures to ensure that the specified power with the
rated voltage and frequency is supplied. Be particularly careful in places
where the power supply is unstable. An incorrect power supply may result
in malfunction.
• Install external breakers and take other safety measures against short-circuiting in external wiring. Insufficient safety measures against short-circuiting may result in burning.
• Fail-safe measures must be taken by the customer to ensure safety in the
event of incorrect, missing, or abnormal signals caused by broken signal
lines, momentary power interruptions, or other causes.
• Confirm voltage specifications when wiring communications, the power
supply, and I/O crossovers. Incorrect wiring may result in malfunction.
• Do not apply voltages or connect loads to the Output Units in excess of
the maximum switching capacity. Excess voltage or loads may result in
burning.
• Do not apply voltages to the Input Units in excess of the rated input voltage. Excess voltages may result in burning.
• After replacing Units, resume operation only after transferring to the new
CPU Unit and/or Special I/O Units the contents of the DM Area, HR Area,
and other data required for resuming operation. Not doing so may result in
an unexpected operation.
• Check the user program for proper execution before actually running it on
the Unit. Not checking the program may result in unexpected operation.
• Check all wiring and switch settings to be sure they are correct.
• Always turn OFF the power supply to the PLC and Slave Units before
attempting any of the following. Not turning OFF the power supply may
result in malfunction or electric shock.
• Removing or attaching terminal blocks to Slave Units and Expansion
Units
• Connecting or removing terminal blocks
• Replacing parts
• Setting the DIP Switches and Rotary Switches
• Connecting cables or wiring the system.
• Confirm that no adverse effect will occur in the system before attempting
any of the following. Not doing so may result in an unexpected operation.
• Changing the operating mode of the PLC
• Force-setting/force-resetting any bit in memory
• Changing the present value of any word or any set value in memory
from the user program
Page 21

xxii
Conformance to EC Directives 6
• Touch a grounded piece of metal to discharge static electricity from your
body before touching any Unit.
• When replacing relays or other parts, be sure to confirm that the ratings of
the new part are correct. Not doing so may result in malfunction or burning.
• Do not attempt to disassemble, repair, or modify any Units. Any attempt to
do so may result in malfunction, fire, or electric shock.
• On IP54 Bit Slaves, tighten the cover screws to the specified torque after
setting the rotary switches or performing wiring. The specified degree of
protection will not be achieved if the screws are not tightened sufficiently.
• Take appropriate and sufficient countermeasures when installing systems
in the following locations:
• Locations subject to static electricity or other forms of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible exposure to radioactivity.
• Locations close to power supplies.
6 Conformance to EC Directives
6-1 Applicable Directives
•EMC Directives
• Low Voltage Directive
6-2 Concepts
EMC Directives
The OMRON products described in this manual are designed so that they
individually comply with the related EMC Directives so that they can be more
easily built into other devices or the overall machine. The actual products have
been checked for conformity to EMC Directives (see note). Whether the products conform to the standards in the system used by the customer, however,
cannot be checked by OMRON and must be checked by the customer.
EMC-related performance of the OMRON devices that comply with EC Directives will vary depending on the configuration, wiring, and other conditions of
the equipment or control panel on which the OMRON devices are installed.
The customer must, therefore, perform the final check to confirm that devices
and the overall machine conform to EMC standards.
Note Applicable EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) standards are as follows:
EMS (Electromagnetic Susceptibility): EN 61131-2 and EN 61000-6-2
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference): EN 61131-2 and EN 61000-6-4
(Radiated emission: 10-m regulations)
Page 22

xxiii
Conformance to EC Directives 6
Low Voltage Directive
Always ensure that devices operating at voltages of 50 to 1,000 VAC and 75
to 1,500 VDC meet the required safety standards.
Applicable standard: EN 61131-2
6-3 Conformance to EC Directives
The OMRON products described in this manual comply with the related EMC
Directives. To ensure that the machine or device in which the products are
used complies with EC Directives, the products must be installed as follows:
1,2,3... 1. The products must be installed within a control panel.
2. A DC power supply with reinforced insulation or double insulation that can
maintain a stable output even if the input is interrupted for 10 ms must be
used for communications power, internal power, and I/O power. The
OMRON S82J-series Power Supply is recommended. (See note.)
3. Products complying with EC Directives also conform to the Emission Standards (EN 61131-2 and EN 61000-6-4). Radiated emission characteristics
(10-m regulations) may vary depending on the configuration of the control
panel used, other devices connected to the control panel, wiring, and other
conditions. You must therefore confirm that the overall machine or equipment complies with EC Directives.
4. Conformance with the EC Directives was confirmed with a system configuration using I/O wiring lengths of less than 30 m.
Note Conformance with the EMC Directive was confirmed when using
the recommended power supply.
Page 23

xxiv
Conformance to EC Directives 6
Page 24

1
SECTION 1
Features and Slave Units
This section introduces the CompoNet Slave Units and the various models that are available.
1-1 Features of CompoNet Slave Units. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-2 Features of CompoNet Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1-1-3 CompoNet Slave Unit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1-2 Slave Unit Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1-2-1 Word Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1-2-2 Bit Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1-2-3 Repeater Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1-2-4 Slave Unit Installation and Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Page 25

2
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
1-1 Features of CompoNet Slave Units
1-1-1 Overview
CompoNet Slave Units do not simply input and output ON/OFF signals, they
can also collect a variety of information that can improve equipment operating
rates.
They can also be used to build maintenance systems separate from control
systems. Coexisting control and maintenance systems can contribute to
reducing equipment startup time, recovery time after problems, and preventative maintenance of equipment.
■ Control System:
For remote I/O communications with the PLC, I/O is allocated for each node
address by default. In addition, Slave Unit status information other than I/O is
allocated in an input area in the Master Unit. The allocation can be set using
the CX-Integrator or explicit messages.
■ Maintenance System:
Slave Units can store several kinds of equipment data. This data can be read
from or written to the Slave Unit’s memory using the CX-Integrator or by sending explicit messages from the Master Unit (PLC) to the Slave Unit.
1-1-2 Features of CompoNet Slave Units
CompoNet Slave Units have the following features.
Main Features
The functions that can be used depend on the type of Slave Unit. For details,
refer to 1-1-3 CompoNet Slave Unit Functions.
Operation Time Monitor The Slave Unit can quickly measure the ON/OFF timing of input and output
contacts without relying on the ladder program. Contact types (IN - OUT, OUT
- IN, IN - IN, OUT - OUT) and trigger patterns (ON
→ OFF, OFF → ON, ON →
ON, OFF → OFF) can be freely combined for measurement. A time can be
set in the Slave Unit memory to enable notification of the status when the
measured time exceeds the set time.
This data can be set or read by using the CX-Integrator.
Contact Operation
Monitor
The number of times each input contact or output contact is turned ON can be
counted at a sampling frequency of 50 Hz maximum and stored. A value can
also be set in the Slave Unit to enable notification of the status if the number
of contact operations reaches the set value.
This data can be set or read by using the CX-Integrator.
Note The contact operation monitor and the total ON time monitor can-
not both be used for the same contact at the same time.
Total ON Time Monitor The total ON time of sensors, relays, and other devices are stored in the Slave
Unit memory. A value can also be set in the Slave Unit to enable notification of
the status if the total time reaches the set value.
These values can be set or read by using the CX-Integrator.
Note The total ON time monitor and the contact operation monitor can-
not be used at the same time for the same contact.
Automatic Baud Rate
Detection
The baud rate is automatically set to the same baud rate as the Master Unit;
therefore, there is no need to set the baud rate of the Slave Units.
Page 26

3
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Unit Conduction Time
Monitor
The total ON time of the Slave Unit's internal circuit power supply can be
stored. This value can be read using the CX-Integrator or explicit messages. A
value can also be set in the Slave Unit to enable obtaining notification of the
status if the total time reaches a set monitor value.
This data can be read or written by using the CX-Integrator.
Naming Units The user can set any name for each Unit as a comment. The names are
stored in Slave Unit memory.
This data can be read or written by using the CX-Integrator.
Naming Connected
Devices
Any name can be set for each I/O contact (e.g., sensor or valve) connected to
a Slave Unit. The names are stored in Slave Unit memory.
This data can be read or written by using the CX-Integrator.
Network Power Voltage
Monitoring
The network power supply voltage (present, maximum, and minimum values)
can be stored in the Slave Unit memory. A monitor voltage can also be set in
the Slave Unit to enable notification of the status if the voltage drops to the
preset value.
These values can be set or read by using the CX-Integrator.
I/O Power Status Monitor The I/O power status monitor function checks if the I/O power is ON or not,
and provides notification in a status area.
This data can be checked by using the CX-Integrator.
Communications Error
History Monitor
The previous four error records (communications error codes and the power
voltage when the error occurred) can be held in the Slave Unit memory.
This data can be read by using the CX-Integrator.
Input Filters The Slave Units read input values multiple times during the set period to elim-
inate the effect of switch chattering and data omissions caused by noise. An
ON delay or OFF delay can also be implemented by using this function.
These settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Communications Error
Output Setting
The output value when a communications error occurs can be set for each
word of an Output Unit.
These settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Preventing Malfunctions
Caused by Inrush Current
at Startup
This function holds inputs from when the power is turned ON until the Unit stabilizes, i.e., inputs are not received while the I/O power is OFF and for 100 ms
after the I/O power is turned ON. This contributes to eliminating input errors
caused by inrush current when the I/O power is turned ON.
These settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Power Short-circuit
Detection
The I/O power current is monitored. If an excessive current is detected, it is
assumed that a power short-circuit has occurred and the sensor power output
is turned OFF forcibly.
The status can be checked by using the LED indicators on the Slave Unit or
by using the CX-Integrator.
Load Short-circuit
Detection
The output load current is monitored. If an excessive current is detected, it is
assumed that an load short-circuit has occurred and the output is turned OFF
forcibly to prevent damage to the Unit's output circuit.
The status can be checked by using the LED indicators on the Slave Unit or
by using the CX-Integrator.
Removable Terminal Block The terminal block can be removed.
Page 27

4
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Expansion Using
Expansion Units
One Expansion Unit can be added to a Digital I/O Slave Unit (with 2-tier terminal block and 16 points). This extends the range of possible system configurations by making it possible to expand to a variety of I/O combinations, e.g., 16
inputs and 8 outputs or 24 inputs (16 inputs + 8 inputs).
Scaling Converted data can be scaled to any value by the user. Ladder program cal-
culations for the Master Unit are not required if the scaling function is used
with the Slave Unit. The offset compensation function can also be used to offset scaled values.
These settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Last Maintenance Date
(Maintenance Function)
The date that maintenance was performed can be written in the Slave Unit by
using the CX-Integrator.
Cumulative Counter The cumulative counter function calculates the integral time for input (or out-
put) analog values and reads the cumulative value. Monitor values can be set
in Units. If the cumulative counter value exceeds the set monitor value, the
Cumulative Counter Monitor Flag in general status turns ON.
These values can be set and read by using the CX-Integrator.
Moving Average An Analog Input Unit or Temperature Input Unit can calculate the moving aver-
age of the last eight inputs and use it as the converted data. Smooth input values can be obtained by averaging the inputs if there are rapid fluctuations in
the input.
Settings for averaging are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Setting the Number of AD
Conversion Points
The conversion cycle is 4 ms max. when using all 4 analog inputs. The AD
conversion cycle can be made faster if fewer AD conversion points are used.
Rate of Change
Calculations
You can find the rate of change during the set data sampling cycle for the
input value to an Analog Input Unit or Temperature Input Unit.
The rate of change settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Comparator The input to an Analog Input Unit or Temperature Input Unit or the calculated
data for a Unit can be compared with alarm settings (upper upper limit, upper
limit, lower limit, and lower lower limit) and the result stored in the Analog Status Flags. The Normal Flag (pass signal) turns ON for values that are in set
range.
The alarm settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Peak/Bottom Hold The peak/bottom hold function holds the maximum (peak) or the minimum
(bottom) input value to an Analog Input Unit or Temperature Input Unit. The
maximum (peak) or minimum (bottom) value can be compared with an alarm
set value and used to turn ON an alarm flag as status data. This is called the
comparator function.
The peak/bottom hold settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Top/Valley Hold The top/valley hold function holds the top or valley input value to an Analog
Input Unit or Temperature Input Unit. The Top/Valley Detection Timing Flag
can be used to check when top and valley values were detected. The top and
valley values can be compared with an alarm set value and used as status
data to turn ON alarm flags (comparator function).
The top/valley hold settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Page 28

5
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Disconnected Line
Detection
With Analog Input Units, the Disconnected Line Detection Flag for each input
can be used in the Master Unit to check whether the analog input lines (for
voltage inputs or current inputs) are disconnected for analog inputs that are
enabled under the setting of the number of AD conversion points.
This function is supported only when the input range is 1 to 5 V or 4 to 20 mA.
With Temperature Input Units, disconnections can be detected for each sensor input. The status can be checked at the Master Unit using the Disconnected Line Detection Flag.
User Adjustment The user adjustment function can be used to compensate offsets in input (or
output) values that occur due to the features of or connection method used for
input or output devices to adjust the input (or output). The conversion line is
adjusted at two points: 0% and 100%.
The adjustments can be made by using the CX-Integrator.
Top/Valley Count With Temperature Input Units, the maximum or minimum number of times the
top or valley value is reached can be counted for an application that has fixed
cycles of temperature changes. Explicit messages can be used to see if the
number of cycles has exceeded a monitoring set value.
The settings are made by using the CX-Integrator.
Temperature Range Total
Time Count
With Temperature Input Units, the length of time that the temperature input
value is within a user-set temperature range can be measured in seconds.
Explicit messages can be used to see if the measured time has exceeded a
monitoring set value.
The temperature range total time count settings are made by using the CXIntegrator.
Input Temperature
Variation Detection
With Temperature Input Units, the temperature difference between two inputs
for inputs 0 to 3 can be detected and compared with a monitoring set value.
Explicit messages can be used to see if the temperature difference has
exceeded the monitoring set value.
The input temperature variation detection settings are made by using the CXIntegrator.
Input Error Detection
Disable Function
With Temperature Input Units, if there is an unused input, detection of input
errors (including disconnection) can be disabled.
Input error detection is disabled by using the CX-Integrator.
Other Features
Rotary Switch Setting of
Node Addresses
Node addresses can now be set much more easily using rotary switches.
Bit-level Distribution (Bit
Slaves)
Slave Units are available with 2 inputs, 2 outputs, 4 inputs, or 2 inputs/2 outputs. These enable bit-level distribution of Slave Units. At the same time,
unused Slave Unit I/O can be suppressed.
IP54 Dust-tight, Splashproof Units (Bit Slaves)
The CRT1B-@D@@SP(-1) Units conform to the IEC IP54 dust-tight, splashproof degree of protection (see note).
Note For protection against human bodies and solid foreign objects,
IP54 requires that dust will not penetrate inside the device to a degree that would affecting operation. For protection against water ingress, water splashing from any direction must have no adverse
effect.
Page 29

6
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Flat Cable Connected as a
Standard Feature (Bit
Slaves)
Bit Slave Units are sold with Standard or Sheathed Flat Cable already connected. Bit Slaves cannot be used, however, at a baud rate of 4 Mbps (no
branch lines).
No I/O Power Supply
Wiring Required (Bit
Slaves)
External I/O (sensors or actuators) connected to Bit Slaves using e-CON connectors or clamp terminals are supplied power through the Flat Cable. No
separate wiring is required for I/O power supply.
Industry Standard Sensor
e-CON Connectors
(CRT1-V@D08S(-1)/
CRT1-@D@@S(-1)/
CRT1-@D16SH(-1)/
CRT1B-@D02S(-1)/
CRT1B-@D0@SP(-1))
No special tools are required for connections because industry standard eCON connectors are used. Electrical cables do not need to be stripped and
are simply inserted with pliers. When using e-CON connectors, there is no
need to prepare special tools for wiring, and connectors from different makers
can be used interchangeably.
Units with MIL Connectors
(CRT1-V@D@@ML(-1))
MIL connectors, widely used in the electronic components and semiconductor
industries, help reduce wiring requirements.
Units with Clamp Terminal
Blocks (CRT1-@D@@SL(-
1)/CRT1B-MD04SLP(-1))
There is no need to tighten the screws because these Units use screw-less
clamp terminal blocks. Connections are made simply by inserting the pin terminals. Wiring can be completed in one step.
Page 30
7
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
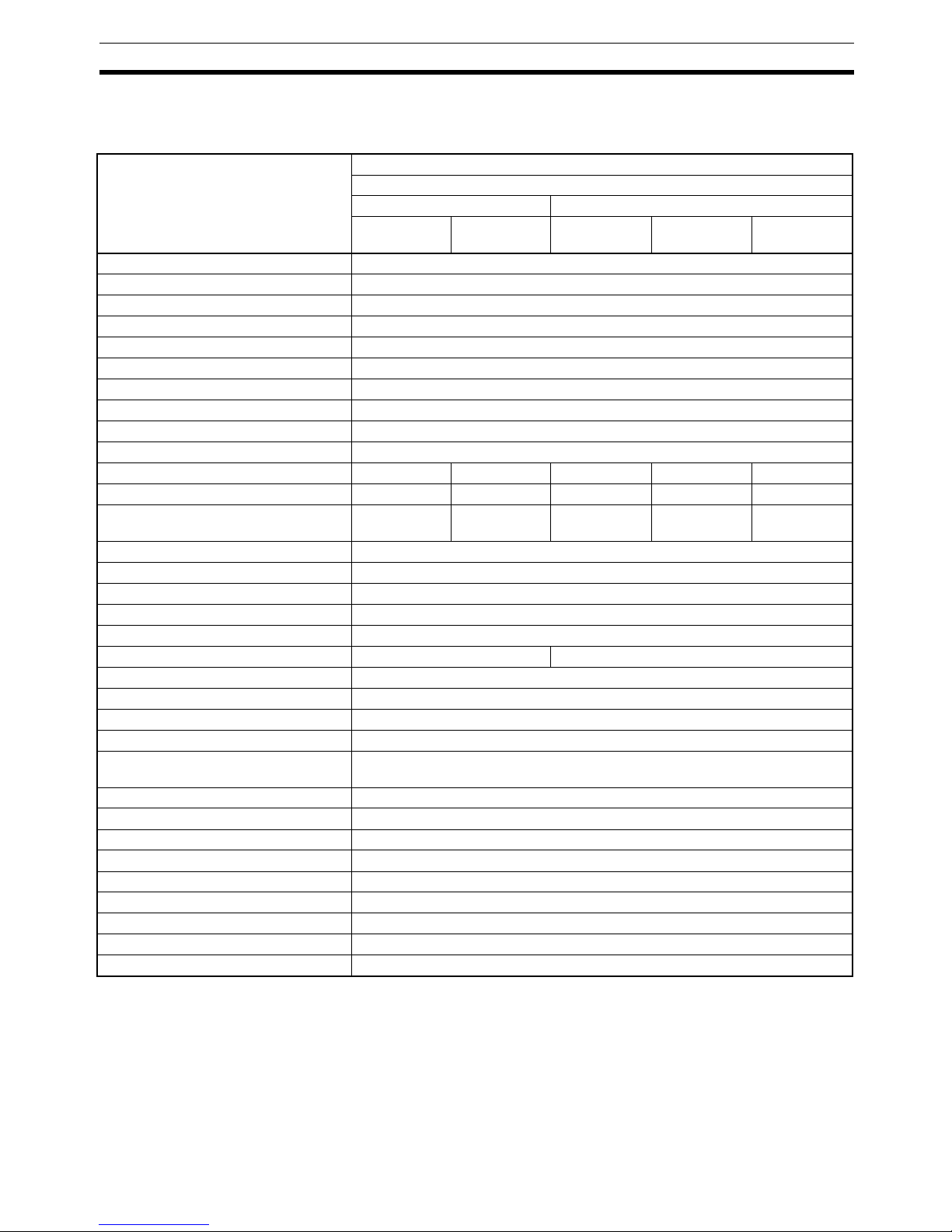
1-1-3 CompoNet Slave Unit Functions
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
2-tier Terminal block
CRT1-@D08(-1) CRT1-@D16(-1)
Function
Input Units Output Units Input Units Output Units I/O Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --Unconnected Line Detection --Load Short-circuit Detection --Disconnected Line Detection --Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --- Yes
Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 31

8
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
2-tier Terminal block
CRT1-ROS08 CRT1-ROS16 CRT1-ROF08 CRT1-ROF16
Function Output Units Output Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes Yes
Naming Units Yes Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- --Communications Error History
Monitor
Ye s Ye s
Input Filter --- --Communications Error Output Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
--- ---
Power Short-circuit Detection --- --Unconnected Line Detection --- --Load Short-circuit Detection --- --Disconnected Line Detection --- --Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --- Yes --- Yes
Scaling --- --Last Maintenance Date Yes Yes
Cumulative Counter --- --Moving Average --- --Setting the Number of AD
Conversion Points
--- ---
Rate of Change --- --Comparator --- --Peak/Bottom Hold --- --Top/Valley Hold --- --User Adjustment --- --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time
Count
---
Input Temperature Variation
Detection
---
Input Error Detection Disable
Function
---
Page 32

9
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
3-tier Terminal block
CRT1-@D08TA(-1)
(without Short-circuit and
Disconnected Line Detection)
CRT1-@D08TAH(-1)
(with Short-circuit and
Disconnected Line Detection)
Function Input Units Output Units Input Units Output Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes --Communications Error Output --- Yes --- Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes ---
Power Short-circuit Detection --- Yes --Unconnected Line Detection --- Yes --Load Short-circuit Detection --- --- Yes
Disconnected Line Detection --- --- Yes
Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 33

10
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
3-tier Terminal block
CRT1-@D16TA(-1)
(without Short-circuit and
Disconnected Line Detection)
CRT1-@D16TAH(-1)
(with Short-circuit and Disconnected
Line Detection)
Function Input Units Output
Units
I/O Units Input Units Output
Units
I/O units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Unconnected Line Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Load Short-circuit Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Disconnected Line Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 34

11
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
Units with e-CON Connectors
CRT1-V@D08S(-1)
Function Input Units Output Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --Communications Error Output --- Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by Inrush Current at
I/O Startup
Yes ---
Power Short-circuit Detection --Unconnected Line Detection --Load Short-circuit Detection --Disconnected Line Detection --Removable Terminal Block Structure --Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion Points --Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 35

12
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
Units with e-CON Connectors
CRT1-@D16S(-1)
(without Short-circuit and
Disconnected Line Detection)
CRT1-@D16SH(-1)
(with Short-circuit and Disconnected
Line Detection)
Function Input Units Output
Units
I/O Units Input Units Output
Units
I/O units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- Yes Yes --- Yes Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Unconnected Line Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Load Short-circuit Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Disconnected Line Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Removable Terminal Block Structure --Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 36

13
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
Units with e-CON Connectors
CRT1-@D32S(-1)
(without Short-circuit and
Disconnected Line Detection)
CRT1-@D32SH(-1)
(with Short-circuit and Disconnected
Line Detection)
Function Input Units Output
Units
I/O Units Input Units Output
Units
I/O units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- Yes Yes --- Yes Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Unconnected Line Detection --- Yes --- Yes
Load Short-circuit Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Disconnected Line Detection --- --- Yes Yes
Removable Terminal Block Structure --Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 37

14
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
Units with MIL Connectors
CRT1-V@D16ML(-1) CRT1-V@D32ML(-1)
Function
Input Units Output Units Input Units Output Units I/O Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --Unconnected Line Detection --Load Short-circuit Detection --Disconnected Line Detection --Removable Terminal Block Structure --Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 38

15
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Digital I/O Slave Units
Units with Screw-less Clamp Terminals
CRT1-@D08SL(-1) CRT1-@D16SL(-1)
Function
Input Units Output Units Input Units Output Units I/O Units
Operation Time Monitor Yes
Contact Operation Monitor Yes
Total ON Time Monitor Yes
Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes
Naming Units Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor Yes
Communications Error History Monitor Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Communications Error Output --- Yes --- Yes Yes
Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes --- Yes
Power Short-circuit Detection --Unconnected Line Detection --Load Short-circuit Detection --Disconnected Line Detection --Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --Scaling --Last Maintenance Date Yes
Cumulative Counter --Moving Average --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
---
Rate of Change --Comparator --Peak/Bottom Hold --Top/Valley Hold --User Adjustment --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 39

16
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Analog l I/O Slave Units Temperature Input Units
CRT1-AD04
CRT1-DA02
CRT1-TS04T
CRT1-TS04P
Function Input Units Output Units Input Units
Operation Time Monitor --- --Contact Operation Monitor --- --Total ON Time Monitor --- --Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes Yes
Naming Units Yes Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes Yes
Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- --Communications Error History Monitor Yes Yes
Input Filter --- --Communications Error Output --- Yes --Preventing Malfunctions Caused by Inrush
Current at I/O Startup
--- ---
Power Short-circuit Detection --- --Unconnected Line Detection --- --Load Short-circuit Detection --- --Disconnected Line Detection Yes --- Yes
Removable Terminal Block Structure Yes Yes
Expansion Using Expansion Units --- --Scaling Yes Yes
Last Maintenance Date Yes Yes
Cumulative Counter Yes Yes
Moving Average Yes --- Yes
Setting the Number of AD Conversion Points Yes --- --Rate of Change Yes --- Yes
Comparator Yes --- Yes
Peak/Bottom Hold Yes --- Yes
Top/Valley Hold Yes --- Yes
User Adjustment Yes Yes
Top/Valley Count --- Yes
Temperature Range Total Time Count --- Yes
Input Temperature Variation Detection --- Yes
Input Error Detection Disable Function --- Yes
Page 40

17
Features of CompoNet Slave Units Section 1-1
Yes: Supported, ---: Not supported
Note The Contact Operation Monitor and the Total ON Time Monitor cannot be
used at the same time for the same contact.
Unit Bit Slave Units Repeater Unit
CRT1B-@D02S(-1) CRT1B-@D0@SP(-1)
CRT1B-MD04SLP(-1)
CRS1-RPT01
Function Input Units Output
Units
Input
Units
Output
Units
I/O units
Operation Time Monitor Yes --Contact Operation Monitor Yes --Total ON Time Monitor Yes --Automatic Baud Rate Detection Yes Yes
Unit Conduction Time Monitor Yes Yes
Naming Units Yes Yes
Naming Connected Devices Yes --Network Power Voltage Monitor Yes Yes
I/O Power Status Monitor --- --Communications Error History Monitor Yes Yes
Input Filter Yes --- Yes --- Yes --Communications Error Output --- Yes --- Yes Yes --Preventing Malfunctions Caused by
Inrush Current at I/O Startup
Yes --- Yes --- Yes ---
Power Short-circuit Detection Yes --- Yes --- Yes --Unconnected Line Detection --- --Load Short-circuit Detection --- Yes --- Yes Yes --Disconnected Line Detection --- --Removable Terminal Block Structure --- --Expansion Using Expansion Units --- --Scaling --- --Last Maintenance Date Yes Yes
Cumulative Counter --- --Moving Average --- --Setting the Number of AD Conversion
Points
--- ---
Rate of Change --- --Comparator --- --Peak/Bottom Hold --- --Top/Valley Hold --- --User Adjustment --- --Top/Valley Count --Temperature Range Total Time Count --Input Temperature Variation Detection --Input Error Detection Disable Function ---
Page 41

18
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
1-2 Slave Unit Models
CompoNet Slave Units can be classified into the following groups.
Word Slave Units Word Slave Units are Slave Units that are allocated units of 16 bits (i.e.,
1 word) in I/O memory of the CPU Unit.
Digital I/O Slave Units: Slave Units with digital I/O
Analog I/O Slave Units: Slave Units with analog I/O
Temperature Input Units: Slave Units with temperature inputs
Expansion Units: Units that can be used to expand the number of I/O
points for Digital I/O Slave Units (with 2-tier terminal blocks and 16 points).
Bit Slave Units Bit Slave Units are Slave Units that are allocated units of 2 bits in I/O memory
of the CPU Unit. Bit Slave Units provide 2 or 4 digital contact I/O points and
have Standard or Sheathed Flat Cable already connected.
Repeater Units Units that can be used to expand the network by extending trunk lines or
branching.
1-2-1 Word Slave Units
Digital I/O Slave Units
Termina l Block wi th
Screws
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Digital I/O Slave Units
with 2-tier Terminal
Block
8 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID08 • Terminal blocks can be attached/
removed from the Unit.
• Expansion Units cannot be
added.
8 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID08-1
8 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD08
8 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD08-1
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16 • Terminal blocks can be attached/
removed from the Unit.
• Expansion Units can be added.
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16-1
8 inputs/8 outputs
(NPN)
CRT1-MD16 • Terminal blocks can be attached/
removed from the Unit.
• Expansion Units cannot be
added.
8 inputs/8 outputs
(PNP)
CRT1-MD16-1
8 outputs (relay
outputs)
CRT1-ROS08
8 outputs
(SSR outputs)
CRT1-ROF08
16 outputs
(relay outputs)
CRT1-ROS16 • Terminal blocks can be attached/
removed from the Unit.
• Expansion Units can be added.
16 outputs
(SSR outputs)
CRT1-ROF16
M
S
O
M
R
O
N
N
S
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
X
1
X
1
0
[0-6
3]
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
O
U
T
Page 42

19
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Digital I/O Slave
Units with 3-tier
Ter mi na l B l o c k
Without
Short-circuit and
Disconnected
Line
Detection
8 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID08TA • Terminal blocks can be
attached/removed from
the Unit.
• Expansion Units cannot
be added.
8 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID08TA-1
8 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD08TA
8 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD08TA-1
With
Short-circuit and
Disconnected
Line
Detection
8 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID08TAH
8 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID08TAH-1
8 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD08TAH
8 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD08TAH-1
Without
Short-circuit and
Disconnected
Line
Detection
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16TA
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16TA-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16TA
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16TA-1
8 inputs/8 outputs
(NPN)
CRT1-MD16TA
8 inputs/8 outputs
(PNP)
CRT1-MD16TA-1
With
Short-circuit and
Disconnected
Line
Detection
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16TAH
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16TAH-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16TAH
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16TAH-1
8 inputs/8 outputs
(NPN)
CRT1-MD16TAH
8 inputs/8 outputs
(PNP)
CRT1-MD16TAH-1
Page 43

20
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Units with Connectors
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Digital I/O Slave
Units with e-CON
Connectors
Without
Shortcircuit
and Disconnected
Line
Detection
8 inputs (NPN) CRT1-VID08S • Equipped with e-CON
connectors.
• Expansion Units cannot
be added.
8 inputs (PNP) CRT1-VID08S-1
8 outputs (NPN) CRT1-VOD08S
8 outputs (PNP) CRT1-VOD08S-1
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16S
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16S-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16S
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16S-1
8 inputs and 8
outputs (NPN)
CRT1-MD16S
8 inputs and 8
outputs (PNP)
CRT1-MD16S-1
With
Shortcircuit
and Disconnected
Line
Detection
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16SH
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16SH-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16SH
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16SH-1
8 inputs and 8
outputs (NPN)
CRT1-MD16SH
8 inputs and 8
outputs (PNP)
CRT1-MD16SH-1
Without
Shortcircuit
and Disconnected
Line
Detection
32 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID32S
32 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID32S-1
32 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD32S
32 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD32S-1
16 inputs and 16
outputs (NPN)
CRT1-MD32S
16 inputs and 16
outputs (PNP)
CRT1-MD32S-1
With
Shortcircuit
and Disconnected
Line
Detection
32 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID32SH
32 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID32SH-1
32 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD32SH
32 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD32SH-1
16 inputs and 16
outputs (NPN)
CRT1-MD32H
16 inputs and 16
outputs (PNP)
CRT1-MD32H-1
Page 44

21
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Units with Clamp Terminal Blocks
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Digital I/O Slave Units
with MIL Connectors
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-VID16ML • Equipped with MIL connectors.
• Expansion Units cannot be
added.
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-VID16ML-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-VOD16ML
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-VOD16ML-1
32 inputs (NPN) CRT1-VID32ML
32 inputs (PNP) CRT1-VID32ML-1
32 outputs (NPN) CRT1-VOD32ML
32 outputs (PNP) CRT1-VOD32ML-1
16 inputs/16
outputs (NPN)
CRT1-VMD32ML
16 inputs/16
outputs (PNP)
CRT1-VMD32ML-1
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Digital I/O Slave
Units with Screwless Clamp Terminal Blocks
8 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID08SL • Equipped with screw-less clamp
terminals.
• Expansion Units cannot be
added.
8 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID08SL-1
8 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD08SL
8 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD08SL-1
16 inputs (NPN) CRT1-ID16SL
16 inputs (PNP) CRT1-ID16SL-1
16 outputs (NPN) CRT1-OD16SL
16 outputs (PNP) CRT1-OD16SL-1
8 inputs/8 outputs
(NPN)
CRT1-MD16SL
8 inputs/8 outputs
(PNP)
CRT1-MD16SL-1
Page 45

22
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Analog I/O Slave Units
Temperature Input Units
Expansion Units
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Analog I/O Slave
Units with 2-tier Terminal Block
4 inputs CRT1-AD04 I/O range:
0 to 5 V, 1 to 5 V,
0 to 10 V, −10 to 10 V, 0 to 20 mA,
4 to 20 mA
2 outputs CRT1-DA02
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Temperature Input
Units with 2-tier Terminal Block
4 inputs CRT1-TS04T Thermocouple input (Switchable
between R, S, K, J, T, E, B, N, L, U,
W, and PL2.)
CRT1-TS04P Platinum resistance thermometer
input (PT100 only)
M
S
O
M
R
O
N
A
N
A
L
O
G
T
E
R
M
I
N
A
L
C
R
T
1
-
A
D
0
4
N
S
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
X
1
X
1
0
[0
-6
3
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
/
D
S
W
O
N
IN
P
U
T
R
A
N
G
E
C
H
0,
1
I
N
P
U
T
R
A
N
G
E
C
H
2
,
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
M
S
O
M
RO
N
A
N
A
L
O
G
T
E
R
M
I
N
A
L
C
R
T1
-
AD
0
4
N
S
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
X
1
X
1
0
[
0
-
6
3
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
/D
SW
O
N
IN
P
U
T
R
A
N
G
E
C
H
0
,
1
I
N
P
U
T
R
A
N
G
E
C
H
2
,
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Expansion Units with
2-tier Terminal Block
8 inputs (NPN) XWT-ID08 • Expansion Units are used to add
points to Digital. I/O Slave Units
with 2-tier terminal blocks and 16
points.
• One Expansion Unit can be added
to one Slave Unit.
8 inputs (PNP) XWT-ID08-1
8 outputs (NPN) XWT-OD08
8 outputs (PNP) XWT-OD08-1
16 inputs (NPN) XWT-ID16
16 inputs (PNP) XWT-ID16-1
16 outputs (NPN) XWT-OD16
16 outputs (PNP) XWT-OD16-1
Page 46

23
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
1-2-2 Bit Slave Units
Slaves with Connectors
Slaves with Clamp Terminal Blocks
Note Bit Slaves have Standard or Sheathed Flat Cable connected as standard fea-
ture. They cannot be at a baud rate of 4 Mbps, for which branch lines are not
supported.
1-2-3 Repeater Units
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Bit Slave Units with eCON Connectors
2 inputs (NPN) CRT1B-ID02S • Standard Flat Cable connected as
standard feature.
2 inputs (PNP) CRT1B-ID02S-1
2 outputs (NPN) CRT1B-OD02S
2 outputs (PNP) CRT1B-OD02S-1
2 inputs (NPN) CRT1B-ID02SP • Sheathed Flat Cable connected
as standard feature.
• IP54 dust-tight and splash-proof
2 inputs (PNP) CRT1B-ID02SP-1
2 outputs (NPN) CRT1B-OD02SP
2 outputs (PNP) CRT1B-OD02SP-1
4 inputs (NPN) CRT1B-ID04SP
4 inputs (PNP) CRT1B-ID04SP-1
Type Appearance I/O capacity Model Features
Bit Slave Units with
Screw-less Clamp
Ter mi na l B l o c k s
2 inputs/2 outputs
(NPN)
CRT1B-MD04SLP • Sheathed Flat Cable connected
as standard feature.
• IP54 dust-tight and splash-proof
2 inputs/2 outputs
(PNP)
CRT1B-MD04SLP-1
Appearance Specification Model Features
Two communications connectors (Upstream port and downstream port)
One downstream port power
supply connector
Up to 64 Units can be connected for each Master Unit.
CRS1-RPT01 • For trunk line-branch line formations, sub-trunk
lines can be connected under a Repeater Unit
just like they can be under the Master Unit.
• For unrestricted branching formations, there are
no restrictions on the connections.
• Repeater Units enable branching the trunk line,
adding more nodes, increasing the connection
distance, and changing the type of cable
upstream and downstream of the Repeater Unit.
PORT2
PORT2
P
O
R
T
1
PORT1
P
R
T
PRT
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
NODE ADR
N
E
T
W
O
R
K
P
O
W
E
R
S
U
P
P
L
Y
NETWORK POWER SUPPLY
OMRON
OMRON
C
R
S
1
-P
R
T
0
1
CRS1-PRT01
R
P
T
RPT
X10
X10
[0-63]
[0-63]
X
1
X1
D
C
24V
DC24V
IN
PU
T
INPUT
S
M
S
MS
Page 47

24
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
1-2-4 Slave Unit Installation and Connection
Installing Slave Units Refer to the following table for the installation and wiring methods for the
Slave Units.
Slave Unit Installation and
Wiring Methods
Name Model Slave Unit
installation
I/O connection
method
Internal power External power
Digital
I/O
Slave
Units
With 2-tier Terminal Block
CRT1-ID08(-1) DIN Track Terminal block
with M3 screws
Supplied along
with communications power
An external I/O
power supply is
required for connected devices.
CRT1-OD08(-1)
CRT1-ID16(-1)
CRT1-OD16(-1)
CRT1-MD16(-1)
CRT1-ROS08
CRT1-ROF08
CRT1-ROS16
CRT1-ROF16
With 3-tier Terminal Block
CRT1-ID08TA(-1)
CRT1-OD08TA(-1)
CRT1-ID08TAH(-1)
CRT1-OD08TAH(-1)
CRT1-ID16TA(-1)
CRT1-OD16TA(-1)
CRT1-MD16TA(-1)
CRT1-ID16TAH(-1)
CRT1-OD16TAH(-1)
CRT1-MD16TAH(-1)
Page 48

25
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Digital
I/O
Slave
Units
With e-CON
Connectors
CRT1-VID08S(-1) DIN Track
or Mounting Bracket
e-CON connectors
Supplied along
with communications power
Shared with communications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-VOD08S(-1) I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-ID16S(-1) DIN Track Shared with com-
munications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-OD16S(-1) I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-MD16S(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply only for
inputs. (See note.)
CRT1-ID16SH(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-OD16SH(-1) I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-MD16SH(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply only for
inputs. (See note.)
CRT1-ID32S(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-OD32S(-1) I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-MD32S(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply only for
inputs. (See note.)
CRT1-ID32SH(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-OD32SH(-1) I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-MD32SH(-1) Shared with com-
munications power
supply only for
inputs. (See note.)
Name Model Slave Unit
installation
I/O connection
method
Internal power External power
Page 49

26
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Note For Bit Slave Units, the external I/O (sensor and actuator) power is also pro-
vided through the Flat Cable from the communications power supply connected to the Master Unit or the Repeater Unit. When calculating the output
current of the communications power supply, always include the external I/O
current consumption for Bit Slave Units.
Digital
I/O
Slave
Units
With MIL Connectors
CRT1-VID16ML(-1) DIN Track
or Mounting Bracket
MIL connectors Supplied along
with communications power
I/O power must be
supplied externally
for connected
devices.
CRT1-VOD16ML(-1)
CRT1-VID32ML(-1)
CRT1-VOD32ML(-1)
CRT1-VMD32ML(-1)
With Screw-less
Clamp Terminal
Blocks
CRT1-ID08SL(-1) DIN Track Screw-less
clamp terminal
block
CRT1-OD08SL(-1)
CRT1-ID16SL(-1)
CRT1-OD16SL(-1)
CRT1-MD16SL(-1)
Analog I/O Slave Units CRT1-AD04 Terminal block
with M3 screws
Separate power
supply required for
connected devices,
such as sensors
and actuators.
CRT1-DA02
Temperature Input Units CRT1-TS04T Shared with com-
munications power
supply. (See note.)
CRT1-TS04P
Digital I/O Slave Units
Expansion Units
XWT-ID08(-1) Refer to the follow-
ing section.
XWT-OD08(-1)
XWT-ID16(-1)
XWT-OD16(-1)
Bit
Slave
Units
With
e-CON
Connectors
CRT1B-ID02S(-1) M4 screw
installation
e-CON connectors
Supplied along
with communications power
Supplied along with
communications
power (See note.)
CRT1B-OD02S(-1)
IP54 CRT1B-ID02SP(-1)
CRT1B-OD02SP(-1)
CRT1B-ID04SP(-1)
With
Screwless
Clamp
Te r m i n a l
Blocks
IP54 CRT1B-MD04SLP(-1) Screw-less
clamp terminal
block
Repeater Units CRS1-RPT01 DIN Track
or M4
screw
installation
--- Communications
power for the downstream line must be
supplied from the
communications
power supply connector.
Name Model Slave Unit
installation
I/O connection
method
Internal power External power
Page 50

27
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Supplying I/O Power
to Expansion Units
Supply I/O power to Expansion Slave Units according to the following table.
Combination I/O power supply to
Expansion Slave Unit
Digital Input Slave Unit with Expansion Input Unit
Example: CRT1-ID16 + XWT-ID16 (or XWT-ID08)
Not required (The Expansion
Unit uses the same I/O power
supply as the Digital I/O Slave
Unit.)
Digital Input Slave Unit with Expansion Output Unit
Example: CRT1-ID16 + XWT-OD16 (or XWT-OD08)
Required (I/O power must be
supplied to both Units.)
Digital Output Slave Unit with Expansion Input Unit
Example: CRT1-OD16 + XWT-ID16 (or XWT-ID08)
Required (I/O power must be
supplied to both Units.)
Digital Output Slave Unit with Expansion Output
Unit
Example: CRT1-OD16 + XWT-OD16 (or XWTOD08)
Required (I/O power must be
supplied to both Units.)
Page 51

28
Slave Unit Models Section 1-2
Page 52

29
SECTION 2
Wiring Configurations
This section describes the configurations of CompoNet Networks.
2-1 CompoNet Networks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-1-1 Overall System Configuration and Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2-1-2 Segments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2-2 Wiring Formations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2-3 Communications Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-3-1 Cables That Can Be Used. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2-3-2 Criteria for Selecting Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2-3-3 Maximum Distance and Number of Connected Units for Types of
Communications Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2-4 Communications Cable Wiring Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2-4-1 Round Cable I. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2-4-2 Round Cable II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2-4-3 Flat Cable I/II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Page 53

30
CompoNet Networks Section 2-1
2-1 CompoNet Networks
2-1-1 Overall System Configuration and Elements
A CompoNet Network is a remote I/O system that consists of the following
elements.
System Configuration Example
Communications Cables CompoNet Networks use round cable I, round cable II, Flat Cable I (DCA4-
4F10 Standard Flat Cable), and Flat Cable II (DCA5-4F10 Sheathed Flat
Cable) for Communications Cables.
Master Unit The Master Unit manages the CompoNet Network and transfers I/O data
between the PLC and the Slave Units.
There is only one Master Unit per network. The Master Unit must be con-
nected to the trunk line.
Multidrop connection on branch line
CompoNet Master Unit
Branch
line
Slave Unit
Trunk line
Repeater Unit
Branch line
Branch
line
Branch line Branch line
Sub-branch
lines
Repeater Unit
Branch line Branch line
Repeater
Unit
Slave Unit
Repeater
Unit
Repeater
Unit
Sub-trunk line
: Repeater Unit
: T-branch
: Multidrop
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Sub-trunk
line
: Terminating Resistor
Sub-trunk
line
Sub-trunk line
Sub-trunk line
Page 54

31
CompoNet Networks Section 2-1
Slave Units Some Slave Units receive output data from the Master Unit across the Com-
poNet Network and output it. Other Slave Units send data that has been input
across the network to the Master Unit. There are two types of Slave Unit
according to the I/O capacity of the Slave Unit.
• Word Slave Units: A Word Slave Unit is allocated 16 bits (i.e., 16 I/O
points) in the I/O memory of the CPU Unit.
• Bit Slave Units: A Bit Slave Unit is allocated 2 bits (i.e., 2 I/O points) in the
I/O memory of the CPU Unit.
Repeater Unit Using Repeater Units enables expanding network connections as follows:
• Extending the Communications Cable
• Increasing the number of nodes (Units)
• Creating long-distance T-branches from the trunk line and sub-trunk lines
(See note.)
• Converting between different types of cable (round cable I, round cable II,
Flat Cable I, and Flat Cable II)
A sub-trunk line downstream from a Repeater Unit can be connected with the
same communications specifications (i.e., distances and number of Slave
Units) as the trunk line.
Up to 64 Repeater Units can be connected per network (i.e., per Master Unit).
When Repeater Units are connected in series from the Master Unit, up to two
layers can be created.
Note The physical layer is not connected across a Repeater Unit. The
connection is thus different from a branch connection, which
branches the same physical layer.
Terminating Resistors With a CompoNet Network, the Master Unit is located at one end of the trunk
line and a Terminating Resistor is connected to the other end of the trunk line.
If Repeater Units are used, each Repeater Unit is treated like a Master Unit,
i.e., Terminating Resistor is connected to the most remote end of the subtrunk line downstream from the Repeater Unit.
Note A Terminating Resistor reduces signal bouncing to stabilize com-
munications and must always be connected to the most remote end
of the network lines below the Master Unit and each Repeater Unit.
Always connect a Terminating Resistor to ensure the quality of the
transmission path.
Trunk Lines and Branch
Lines
The trunk lines and branch lines in a CompoNet Network are defined as follows:
• Trunk line: The transmission path between the Master Unit and the Terminating Resistor.
• Sub-trunk line: The transmission path between the Repeater Unit and the
Terminating Resistor (when a Repeater Unit is used)
• Branch line: The transmission path created using a T-branch from the
trunk line or sub-trunk line.
• Sub-branch line: The transmission path created using a T-branch from a
branch line. (T-branching is not possible from sub-branch lines.)
Note Due to differences in functionality, the same type of cable must be
used between the trunk line and a branch line, a sub-trunk line and
a branch line, and a branch line and a sub-branch line. Different
types of cable can be used between the trunk line and a sub-trunk
line.
Branches There are two ways to create branch lines.
Page 55

32
CompoNet Networks Section 2-1
1) T-branch Connections
• T-branch connections using Flat Connectors (when Flat Cable I or Flat
Cable II is used)
• T-branch connections using commercially available relay terminals (when
round cable I or round cable II is used)
2) Multidrop Connections
• Multidrop connections using Flat Connectors and Multidrop Connectors
(when Flat Cable I or Flat Cable II is used)
• Multidrop connections using Open Type Connectors (when round cable I
or round cable II is used)
Note Flat Connectors can also be used to extend the Communications
Cable.
Communications Power
Supply
This is the power supply for communications and internal operations for each
Unit.
A commercially available 24-VDC power supply is used for communications
and internal operations in each Unit.
One communications power supply can be connected for a trunk line or a subtrunk line. Communications power is supplied to the trunk line from the Master
Unit and to a sub-trunk line from the Repeater Unit.
One power supply cannot be used to supply communications power to more
than one line (i.e., to the trunk line and sub-trunk line or to two sub-trunk
lines).
I/O Power Supply A commercially available 24-VDC power supply is used to power the I/O oper-
ations of the external I/O device connected to a Unit. It is connected to the I/O
power supply terminal of the Unit.
2-1-2 Segments
Segment Layers When Repeater Units are used, the CompoNet Network is divided into seg-
ments by the Repeater Units. Each segment is connected to the network, but
is isolated electrically. Three layers of these isolated segments can be configured, called segments 1, 2, and 3, counted in order from the Master Unit.
Repeater Units can be used to add a maximum of two extra segment layers.
Including Repeater Units connected using multidrop connections, a maximum
of 64 Repeater Units can be connected in a single network (i.e., to a single
Master Unit).
Master Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Repeater
Unit
Repeater
Unit
Second-layer Repeater Units
First-layer Repeater Units
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Terminating
Resistor
Segment 1
Segment 2
Segment 3
Page 56

33
Wiring Formations Section 2-2
Number of Units Per
Segment
A maximum of 32 Slave Units and Repeater Units can be connected in one
segment.
2-2 Wiring Formations
There are two possible wiring formations for a CompoNet Network.
Trunk Line-Branch
Line Formation
With this wiring formation, the trunk line is differentiated from branch lines and
there are restrictions on the number of branches and the number of connections.
Unrestricted Wiring
Formation
With this wiring formation, there is no distinction between the trunk line and
branch lines. There are no wiring restrictions as long as the total cable length
does not exceed 200 m. There is also no limit in the number of branches.
The formation to be used is determined automatically by the type of cable to
used and the required baud rate.
❍ : Trunk line - branch line wiring formation
: Unrestricted wiring formation
Note Lines cannot be branched from the trunk line when the baud rate is
4 Mbps. (Only multidrop connections can be used for branching
from the trunk line or sub-trunk lines.)
Master Unit
Trunk line
Branch line
Slave Unit
Terminating Resisto
r
Branch line
Branch line
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Master Unit
Slave Unit
Terminating Resistor
Repeater Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Terminating
Resistor
Cable type Baud rate
4 Mbps 3 Mbps 1.5 Mbps 93.75 kbps
Round cable I ❍ (See note.) ❍❍❍
Round cable II
Flat Cable I/II
❍ (See note.) ❍❍
Page 57

34
Communications Cable Section 2-3
The following table shows the conditions and restrictions for each formation.
2-3 Communications Cable
2-3-1 Cables That Can Be Used
The following four types of cable can be used in a CompoNet network.
Round cable I
Check with the manufacturer for applicable CompoNet products.
Use commercially available VCTF cable with two 0.75-mm
2
conductors (JIS
C3306) that meet CompoNet specifications.
Round cable II
Check with the manufacturer for applicable CompoNet products.
Use commercially available VCTF cable with four 0.75-mm
2
conductors (JIS
C3306) that meet CompoNet specifications.
Item Wiring formation
Trunk line-branch line formation Unrestricted wiring formation
Master Unit location End of network Anywhere in network (not necessarily at the
end)
Maximum number of Slave
Units connected to any one
branch line
1 or 3 depending on the cable type and
baud rate
No restrictions
Terminating Resistor location On the opposite ends of the trunk line and
all sub-trunk lines from the Master Unit and
each Repeater Unit
On the most remote ends from the Master
Unit and each Repeater Unit
Blue or black: BDL White: BDH
Red: BS+
White: BDH
Black: BS−
Green or Blue: BDL
Page 58

35
Communications Cable Section 2-3
Flat Cable I (DCA4-4F10 Standard Flat Cable)
CompoNet-compatible products other than DCA4-4F10 can be used. Confirm
applicability with the manufacturer.
Flat Cable II (DCA5-4F10 Sheathed Flat Cable)
CompoNet-compatible products other than DCA5-4F10 can be used. Confirm
applicability with the manufacturer.
Note (1) The characteristics of each conductor in Flat Cable I and Flat Cable II
have been adjusted to the application. Check the line insulator colors and
use each line only for the application given in the above table.
(2) For information on applicable CompoNet products and manufacturers, re-
fer to the ODVA home page.
Conduc-
tor No.
Insulation
color
Application Nominal
cross-sec-
tion
Allowable
current (A)
1 Red BS+ (communications power
supply positive side)
0.75 mm
2
5 max.
2 White BDH (signal high) 0.5 mm
2
---
3 Blue BDL (signal low) 0.5 mm
2
---
4BlackBS− (communications power
supply negative side)
0.75 mm
2
5 max.
Black: BS−
Red: BS+
White: BDH
Blue: BDL
Conduc-
tor No.
Insulation
color
Application Nominal
cross-sec-
tion
Allowable
current (A)
1 Red BS+ (communications power
supply positive side)
0.75 mm
2
5 max.
2 White BDH (signal high) 0.5 mm
2
---
3 Blue BDL (signal low) 0.5 mm
2
---
4BlackBS− (communications power
supply negative side)
0.75 mm
2
5 max.
Black: BS−
Red: BS+
White: BDH
Blue: BDL
Page 59

36
Communications Cable Section 2-3
2-3-2 Criteria for Selecting Cables
Selecting Cable Types Select the cable type using the following items as conditions.
Note Bit Slaves come with a Flat Cable already connected. If this cable is removed,
the Unit cannot be connected.
Using Different Cable
Types
The same type of cable must be used for all lines downstream from the Master Unit (i.e., the trunk line and branch lines, sub-trunk lines and their branch
lines, and branch lines and sub-branch lines must use the same type of
cable).
When Repeater Units are used, however, different cables can be used for the
trunk line and sub-trunk lines, and for sub-trunk lines and sub-trunk lines,
above and below a Repeater Unit.
Note Round cable I, round cable II, Flat Cable I (Standard) and Flat Cable II
(Sheathed) are treated as different types of cable.
Restrictions in
Distance between
Cables of Multiple
CompoNet Systems
When using more than one CompoNet System with Flat Cable I or II, operation may be unstable due to interference. To prevent this, the Flat Cables for
the different CompoNet Systems must be separated from each other by at
least 5 mm.
Item Cable type
Round cable I Round cable II Flat Cable I Flat Cable II
Application • When using com-
mercially available
cable is desirable.
• To provide communications power
separately.
• When using commercially available
cable is desirable.
• To supply communications power to all
Slave Units with the
communications
cable.
• To supply communications power to all
Slave Units with the
communications
cable.
• To supply communications power to all
Slave Units with the
communications
cable.
• Applications in environments that
required IP54 compliance (drip-proof,
splash-proof).
Slave
Unit
connections
Word Slave Units Supported
Bit Slave
Units
Not supported. (See
note.)
Not supported. (See
note.)
Supported Not supported.
IP54 Bit
Slave
Units
Not supported. Supported
Wiring method for communications power supply
Wired separately
from the Communications Cable.
Supplied via Communications Cable. (Power is supplied from the
Master Unit and Repeater Units.)
Master Unit location End of trunk line Baud rate other than 93.75 kbps: End of trunk line
93.75 kbps: Anywhere in network
Repeater Unit
Slave Unit
Cable (trunk line)
Slave Unit
Cable (sub-trunk line)
Different types of cable can be used.
The same type of cable must be used.
Master
Unit
The same type of cable must be used.
Page 60

37
Communications Cable Section 2-3
2-3-3 Maximum Distance and Number of Connected Units for Types of
Communications Cables
The maximum lengths for each cable are shown below, along with the maximum number of Slave Units that can be connected. Do not exceed these limits.
Baud Rate of 4 Mbps
(No Branching, See
note.)
Note Bit Slave Units come with Flat Cable and cannot be connected. The network
must consist of only Word Slave Units and multidrop connections. (Use
DCN4-MD4 Multidrop Connectors for Flat Cable.)
Baud Rate of 3 Mbps
Master Unit
Repeater
Unit
Trunk line length
Branch line length
Branch line length
Branch
line length
Branch
line length
Branch
line length
Branch line
length
Branch line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-trunk line length
Sub-branch
line length
Terminating
Resistor
Slave Units
Item Round cable I/II Flat Cable I/II
Length per trunk line or sub-trunk line
(maximum length with two Repeater Units)
30 m (90 m) 30 m (90 m)
Branch line length Lines cannot be branched from the
trunk line. (Only multidrop connections
are possible from the trunk line or subtrunk lines.)
Total branch line length
Restrictions on branch line locations
Number of Slave Units (including Repeater
Units) per trunk line or sub-trunk line
32 32
Item Round cable I/II Flat Cable I/II
Length per trunk line or sub-trunk line
(maximum length with two Repeater Units)
30 m (90 m) 30 m (90 m)
Branch line length 0.5 m 0.5 m
Total branch line length 8 m 8 m
Restrictions on branch line locations 3/m 3/m
Number of Units per branch (See note 1.) 1 1
Maximum sub-branch line length Not supported. Not supported.
Page 61

38
Communications Cable Section 2-3
Baud Rate of
1.5 Mbps
Note (1) The number of Units per branch is the maximum number of Slave Units
or Repeater Units that can be connected to one branch using multidrop
or T-branch connections (sub-branch lines).
(2) Lines cannot be branched from the trunk line. (Only multidrop connec-
tions are possible from the trunk line or sub-trunk lines.)
(3) Sub-branch lines can be branched from branch lines.
Baud Rate of
93.75 kbps
Note The number of Units per branch is the maximum number of Slave Units or
Repeater Units that can be connected to one branch using multidrop or Tbranch connections (sub-branch lines).
Total sub-branch line length Not supported. Not supported.
Number of Slave Units (including Repeater
Units) per trunk line or sub-trunk line
32 32
Item Round cable I/II Flat Cable I/II
Item Round cable I Round cable II
Flat Cable I/II
Without
branch-
ing
With
branch-
ing
Length per trunk line or sub-trunk line
(maximum length with two Repeater Units)
100 m
(300m)
30 m
(90m)
30 m (90 m)
Branch line length Not sup-
ported.
(See
note 2.)
2.5 m 2.5 m
Total branch line length Not sup-
ported.
(See
note 2.)
25 m 25 m
Restrictions on branch line locations --- 3/m 3/m
Number of Units per branch (See note 1.) 3 3
Maximum sub-branch line length Not sup-
ported.
0.1 m (See note 3.)
Total sub-branch line length Not sup-
ported.
2 m (See note 3.)
Number of Slave Units (including Repeater
Units) per trunk line or sub-trunk line
32 32 32
Item Round cable I Round cable II
Flat Cable I/II
Length per trunk line or sub-trunk line
(maximum length with two Repeater Units)
500 m (1,500 m) Unrestricted wiring
is enabled for a total
length of 200 m.
Branch line length 6 m
Total branch line length 120 m
Restrictions on branch line locations 3/m
Number of Units per branch (See note.) 1
Maximum sub-branch line length --Total sub-branch line length --Number of Slave Units (including Repeater
Units) per trunk line or sub-trunk line
32 32
Page 62

39
Communications Cable Wiring Examples Section 2-4
2-4 Communications Cable Wiring Examples
The following wiring is required in a CompoNet Network.
• Two communications signal lines (communications data): BDH (communications data high) and BDL (communications data low)
• Two communications power supply lines (power for communications and
internal Slave Unit circuits): BS+ (communications power supply plus
side) and BS
− (communications power supply minus side)
The wiring method depends on the type of cable that is used.
2-4-1 Round Cable I
• Connect the two communications signal lines in parallel between the Master Unit or Repeater Unit and multiple Slave Units.
• Use Open Type Connectors (DCN4-TB4, for connecting Units) to connect
Communications Cables to Master Units, Repeater Units, and Slave
Units.
• To supply the communications power (24 VDC), connect the two communications power supply lines to each Slave Unit separately from the Communications Cables.
• Power is not supplied to the Master Unit or Repeater Units.
• A Terminating Resistor (DRS1-T) must be connected at the end of the
network.
Slave Units can also be connected in parallel using multidrop connections.
BDL
BDH
BDL
BDH
BDL
BDH
BS−BS+BS−BS+BS−
BS+
Terminating Resisto
r
(121 Ω)
Two communications
signal lines
Communications
Communications
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
24-VDC
communications
p
ower suppl
y
24-VDC
communications
power supply
24-VDC
communications
power supply
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Open Connector
Open Connector
Relay terminal block
Communications
BS+
BS−
BDL
BDH
Page 63

40
Communications Cable Wiring Examples Section 2-4
2-4-2 Round Cable II
• Connect the two communications signal lines and two communications
power lines in parallel between the Master Unit or Repeater Unit and multiple Slave Units.
• Use Open Type Connectors (DCN4-TB4, for connecting Units) to connect
Communications Cables to Master Units, Repeater Units, and Slave
Units.
• Connect the communications power supply (24 VDC) to the communications power supply connector for the Master Unit or Repeater Unit.
• Connect DCN4-TM4 Terminating Resistors and DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector Sockets at the ends of the network.
BDLBDH
BS−
BS+
BDLBDH
BS−
BS+
BDLBDH
BS−
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS−
BS+
Terminating Resistor
(121 Ω)
Communications Communications
Communications
Slave Unit Slave Unit Slave Unit
24-VDC
communications
p
ower suppl
y
24-VDC
communications
p
ower suppl
y
24-VDC
communications
p
ower suppl
y
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Open Connector
Open Connector
Page 64

41
Communications Cable Wiring Examples Section 2-4
Slave Units can also be connected in parallel using multidrop connections.
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Terminating Resistor
(121 Ω)
Two communications
signal lines
Two communications
power lines
Relay terminal block
Open Connector
Slave Unit
Slave Unit Slave Unit
O
p
en Connector
24-VDC
communications
power supply
Communications
power supply
connector
Communications
power
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
BDL
BDH
BS-
BS+
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Terminating Resisto
r
(121 Ω)
Two communications
signal lines
Two communications
power lines
Open Connector
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
O
p
en Connector
Communications
power
Page 65

42
Communications Cable Wiring Examples Section 2-4
2-4-3 Flat Cable I/II
• The two communications signal lines and the two communications power
supply lines are connected to the Master Unit, Repeater Units, and Slave
Units using Flat Cable.
• Connect the communications power supply (24 VDC) to the communications power supply connector for the Master Unit or Repeater Unit.
• A Terminating Resistor (DCN4-TM4 or DCN5-TM4) must be connected at
the end of the network.
Slave Units can also be connected in parallel by using multidrop connections.
A DCN4-MD4 Multidrop Connector is required for this.
Communications
connector
Flat Cable
• Communications signal lines: BS+ (red) and BS− (black)
• Communications power supply lines: BDH (white) and BDL (blue)
Terminating Resistor
(121 Ω)
Slave Unit
Communications
power supply,
24 VDC
Communications
power
Slave Unit
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Communications
power supply
connector
Communications
connector
Terminating Resisto
r
(121
Ω)
Slave Unit Slave Unit
Master Unit or
Repeater Unit
Flat Cable
Flat Connector
Plug
Multidrop
Connector
Page 66

43
SECTION 3
Installation and Wiring
This section describes how to install and wire a CompoNet Network.
3-1 Installing Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-1-1 Installation Method. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3-1-2 Installation Orientation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3-1-3 Mounting to a DIN Track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3-1-4 Mounting with a Mounting Bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3-1-5 Mounting with Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3-2 Connecting Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3-2-1 Round Cable I/II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-2-2 Flat Cable I/II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-3 Preparing Flat Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3-3-1 Round Cable II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3-3-2 Flat Cable I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3-3-3 Flat Cable II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3-4 Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3-4-1 Connecting Communications Cable to Slave Units and Repeater Units 64
3-4-2 Branching Communications Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3-4-3 Extending Communications Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3-4-4 Connection Locations for Terminating Resistor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3-5 Power Supply Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3-5-1 Power Supply Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
3-5-2 Connection Locations for Communications Power Supplies . . . . . . 76
3-5-3 Connecting the I/O Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3-5-4 Connecting the Communications and I/O Power Supplies. . . . . . . . 79
3-5-5 Precautions when Supplying Communications Power . . . . . . . . . . . 84
3-5-6 Precautions when Providing the I/O Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
3-5-7 Other Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3-6 Connecting External I/O for Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
3-6-1 Connecting to a Screw Terminal Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
3-6-2 Connecting to e-CON Connector Terminals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
3-6-3 Connecting to MIL Connector Terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
3-6-4 Connecting to Screw-less Clamp Terminal Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
3-6-5 Connecting External I/O to IP54 Bit Slave Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Page 67

44
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
3-1 Installing Slave Units
3-1-1 Installation Method
The installation method for Slave Units and Repeater Units depends on the
model.
Name Model Installation method
Digital I/O Slave
Units
With 2-tier Terminal Block CRT1-ID08(-1) DIN Track
CRT1-OD08(-1)
CRT1-ID16(-1)
CRT1-OD16(-1)
CRT1-MD16(-1)
CRT1-ROS08
CRT1-ROF08
CRT1-ROS16
CRT1-ROF16
With 3-tier Terminal Block CRT1-ID08TA(-1)
CRT1-OD08TA(-1)
CRT1-ID08TAH(-1)
CRT1-OD08TAH(-1)
CRT1-ID16TA(-1)
CRT1-OD16TA(-1)
CRT1-MD16TA(-1)
CRT1-ID16TAH(-1)
CRT1-OD16TAH(-1)
CRT1-MD16TAH(-1)
With e-CON Connectors CRT1-VID08S(-1) DIN Track or Mounting
Bracket
CRT1-VOD08S(-1)
CRT1-ID16S(-1) DIN Track
CRT1-OD16S(-1)
CRT1-MD16S(-1)
CRT1-ID16SH(-1)
CRT1-OD16SH(-1)
CRT1-MD16SH(-1)
CRT1-ID32S(-1)
CRT1-OD32S(-1)
CRT1-MD32S(-1)
CRT1-ID32SH(-1)
CRT1-OD32SH(-1)
CRT1-MD32SH(-1)
With MIL Connectors CRT1-VID16ML(-1) DIN Track or Mounting
Bracket
CRT1-VOD16ML(-1)
CRT1-VID32ML(-1)
CRT1-VOD32ML(-1)
CRT1-VMD32ML(-1)
With Screw-less Clamp Terminal
Blocks
CRT1-ID08SL(-1) DIN Track
CRT1-OD08SL(-1)
CRT1-ID16SL(-1)
CRT1-OD16SL(-1)
CRT1-MD16SL(-1)
Page 68

45
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
3-1-2 Installation Orientation
There are no restrictions in the orientation unless otherwise specified in the
instructions for the Unit. Installation is possible in any of the following six orientations.
3-1-3 Mounting to a DIN Track
Materials Required for
Installation
Installation
Orientation
1,2,3... 1. Hook the slot on the back of the Unit into the top of the DIN Track. Pull
down the DIN Track mounting pin and insert the Unit.
Analog I/O Slave Units CRT1-AD04 DIN Track
CRT1-DA02
Temperature Input Units CRT1-TS04T
CRT1-TS04P
Expansion Units XWT-ID08(-1)
XWT-OD08(-1)
XWT-ID16(-1)
XWT-OD16(-1)
Bit Slave Units With e-CON Connectors CRT1B-ID02S(-1) Screw installation (M4)
CRT1B-OD02S(-1)
IP54 CRT1B-ID02SP(-1)
CRT1B-OD02SP(-1)
CRT1B-ID04SP(-1)
With Screw-less Clamp Terminal Blocks
IP54 CRT1B-MD04SLP(-1)
Repeater Unit CRS1-RPT01 DIN Track or screw instal-
lation (M4)
Name Model Installation method
Vertical
MS NS
REMOTE
TERMINAL
WORD
NODE ADR
CRT1
CRT1
OD16
OD16
1
01234567 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
X10
[0-63]
X1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
NS
REMOTE
TERMINAL
WORD
NODE ADR
CRT1
CRT1
-
OD16
OD16
-
1
01234567 8
9
10 11
12
13
14
15
X10
[0
-
63]
X1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
NS
REMOTE
TERMINAL
WORD
NODE ADR
CRT1
CRT1
OD16
OD16
1
01234567 8
9
10 11
12
13
14
15
X10
[0
63]
X1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS NS
REMOTE
TERMINAL
WORD
NODE ADR
CRT1
CRT1
-
OD16
OD16
-
1
01234567 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
X10
[0-63]
X1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Name Model Remarks
35-mm DIN Track PFP-50N Length: 50 cm
PFP-100N Length: 100 cm
PFP-100N2 Length: 100 cm
End Plate PFP-M Two End Plates are required for each Slave Unit
and each Repeater Unit.
Page 69

46
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
2. Hook the bottom of the End Plate on the DIN Track first, and then the top.
Attach an End Plate on each side of the Unit, and tighten the screws to secure them. Check to make sure that the Unit is firmly secured.
3-1-4 Mounting with a Mounting Bracket
Slave Units with e-CON connectors (CRT1-V@D08S(-1)) or MIL connectors
(CRT1-V@D@@ML(-1)) can be panel-mounted or wall-mounted, either vertically or horizontally, using special Mounting Brackets.
Required Brackets
Dimensions CRT1-ATT01
DIN Track
DIN Track mounting pin
End Plate
Name Model Applicable Slave Unit
Mounting Bracket CRT1-ATT01 Units with MIL Connectors
CRT1-V@D16ML(-1)
CRT1-ATT02 Units with e-CON Connectors
CRT1-V@D08S(-1)
SRT2-ATT02 Units with MIL Connectors
CRT1-V@D32ML(-1)
18.7
35
(mm)
13
Mounting Hole Dimensions
Two, 3.2 dia. or M3
16±0.2
Page 70

47
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
CRT1-ATT02
SRT2-ATT02
Vertical Mounting Use a Mounting Bracket to vertically mount a Slave Unit to a panel or a wall.
Example: Mounting a CRT1-V@D32ML Slave Unit with MIL Connectors
Mounting Procedure 1. Attach the Mounting Bracket to the panel surface (or wall) with two Phillips
screws, as shown in the following diagram. For mounting hole dimensions,
refer to Dimensions above.
2. Mount the Slave Unit to the Mounting Bracket. The Mounting Bracket is the
same shape as a DIN Track, so use the same method as when mounting
to a DIN Track.
Horizontal Mounting Use a Mounting Bracket to horizontally mount (side mount) a Slave Unit to a
panel or a wall.
26.7
35
13
Mounting Hole Dimensions
Two, 3.2 dia. or M3
16±0.2
(mm)
32.5
35
7.3
Mounting Hole Dimensions
Two, 3.2 dia. or M3
16±0.2
(mm)
SRT2-ATT02
Mounting Bracket
Panel surface (wall)
Vertical on
panel surface
(wall)
Page 71

48
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
Example: Mounting a CRT1-V@D32ML Slave Unit with MIL Connectors
Mounting Procedure 1. Attach the Mounting Bracket to the panel surface (or wall) with two Phillips
screws, as shown in the following diagram. For mounting hole dimensions,
refer to Dimensions above.
2. Mount the Slave Unit to the Mounting Bracket. The Mounting Bracket is the
same shape as a DIN Track, so use the same method as when mounting
to a DIN Track.
Mounting Dimensions
Vertical Mounting to a Wall • Units with e-CON Connectors (CRT1-V@D08S(-1)) or MIL Connectors
(CRT1-V@D16ML(-1))
Horizontal (side)
mounting to panel
surface (or wall)
SRT2-ATT02
Mounting Bracket
Panel surface (wall)
6.0
45 45
Mounting Bracke
t
(mm)
(The Unit shown in the diagram is the CRT1-V@D08S(-1).)
Page 72

49
Installing Slave Units Section 3-1
• Units with MIL Connectors (CRT1-V@D32ML(-1))
Horizontal Mounting to a
Wall
• Units with e-CON Connectors (CRT1-V@D08S(-1)) or MIL Connectors
(CRT1-V@D16ML(-1))
• Units with MIL Connectors (CRT1-V@D32ML(-1))
3-1-5 Mounting with Screws
Refer to the dimensions for the particular Unit and prepare the mounting holes
in the panel. Tighten the M4 screws to a torque of 0.9 N·m, and check to be
sure that the Unit is securely mounted.
3.3
45 35
(mm)
Mounting Bracke
t
2.45
45 45
Mounting
Bracket
(mm)
(The Unit shown in the diagram is the CRT1-V@D08S(-1).)
0.1
45 35
Mounting
Bracket
(mm)
Page 73

50
Connecting Cables Section 3-2
Mounting Bit Slave
Units Using Screw
Brackets
The Bit Slave Units (CRT1B-ID02S(-1) and CRT1B-OD02S(-1)) are installed
using the enclosed screw bracket along with screw holes in one of the two orientations shown below.
Use the following procedure to mount the screw bracket.
1,2,3... 1. Insert the screw bracket into the back of the Bit Slave Unit along the
guides.
2. Press the screw bracket in until the hooks on the bracket are completely
locked into place.
3-2 Connecting Cables
In a CompoNet Network, Units can be connected and cables can be branched
and extended by using Communications Cable and mounting connectors to
Units. The methods for connecting Communications Cables and Units and for
branching depend on the cable type and branching formation used.
The differences are shown in the following table.
Screw brackets
Guides
Screw bracket
Screw bracket hoo
k
Page 74

51
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
3-2-1 Round Cable I/II
3-2-2 Flat Cable I/II
3-3 Preparing Flat Connectors
To connect a Terminating Resistor to round cable II, to connect Flat Cable I or
II to Units and to branch or extend the wiring, Flat Connectors must be prepared and attached to the cables.
Note (1) Flat Connectors cannot be reused once they have been attached. Per-
form the procedure with care.
(2) Always hold on to the Flat Connector when connecting or disconnecting
it.
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
connections
Cable branches
T-branch connections Multidrop connections
Open Type Connector
Note Open Type Connectors
cannot be used for Bit
Slaves.
Commercially available relay terminal
block
Open Type Connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
connections
Cable branches
T-branch connections Multidrop connections
Flat Connector Plug
• Word Slaves and Repeater Units
•Bit Slaves
Note Bit Slave Units come with Flat
Cable already connected.
Flat Connector Socket + Flat Connector
Plug
Multidrop Connector
Note Multidrop connections using Mul-
tidrop Connectors are not possible using Flat Cable II
(Sheathed).
Branch line or
sub-branch line
Open Type Connecto
r
Slave/Repeater Unit
Trunk line,
sub-trunk line,
or branch line
Slave/Re
p
eater Unit
Relay terminal block
Open Type Connector
Trunk line,
sub-trunk line,
or branch line
Open Type Connector
Slave/Repeater Unit
Branch line or
sub-branch line
Flat Connector Plug
Slave/Re
p
eater Unit
Flat Connector Plug
Flat Cable (included)
Bit Slave Unit
Trunk line, sub-trunk line,
or branch line
Branch line or
sub-branch line
Flat Connector
Plug
Flat Connector Plug
(or connector provided with cable)
Slave/Repeater Unit
Flat Connector
Socket
Trunk line,
sub-trunk line,
or branch line
Multidrop Connectors
Slave/Repeater Unit
Flat Connector
Plug
Flat Connector
Plug
Cable Extension
Flat Connector Socket + Flat Connector Plug
Flat Connector Socket Flat Connector Socket
Flat Connector Plug
Flat Connector Plug
Trunk line and sub-trunk line
Trunk line and sub-trunk line
Page 75

52
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
(3) When connecting a Flat Connector, press it all the way in and then pull on
it to be sure it is locked into place.
Connectors Used
Tools Required
Name Appearance Model Application
Flat Connector I Socket DCN4-TR4 Used as a set with the DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector
Plug in the following applications:
• Extending the trunk line or sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching branch lines from the trunk line or
sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching sub-branch lines from a branch line.
Used independently when connecting a DCN4TM4 Terminating Resistor to the end of the trunk
line or a sub-trunk line.
Flat Connector I Plug DCN4-BR4 Used as a set with the DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket in the following applications:
• Extending the trunk line or sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching branch lines from the trunk line or
sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching sub-branch lines from a branch line.
Used independently in the following applications:
• Connecting Communications Cable to a Unit.
• Connecting Communications Cable to a DCN4MD4 Multidrop Connector (when a multidrop connection is used).
Flat Connector II Socket DCN5-TR4 Used as a set with the DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector
Plug in the following applications:
• Extending the trunk line or sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching branch lines from the trunk line or
sub-trunk lines.
• T-branching sub-branch lines from a branch line.
Used independently when connecting a DCN5TM4 Terminating Resistor to the end of the trunk
line or a sub-trunk line.
Flat Connector II Plug DCN5-BR4 Used as a set with the DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket in the following applications:
• Extending the trunk line or sub-trunk lines
• T-branching branch lines from the trunk line or
sub-trunk lines
• T-branching sub-branch lines from a branch line
Used independently to connect Communications
Cable to a Unit.
Name Appearance Model Application
Pliers DWT-A01 Crimping tool for DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket or DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plug
Pliers DWT-A02 Crimping tool for DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket or DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector Plug
Page 76

53
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
3-3-1 Round Cable II
This procedure is only required to connect a Terminating Resistor.
Preparing DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector Sockets
Component Names
■ Preparing the Cable
Cut the cable perpendicular to the length, and strip the sheath as shown in the
following diagram.
■ Setting the Cable Stopper
Set the Cable Stopper.
Close the cover, secure the hooks, and then press down on the cable stopper
until it clicks into place.
Cover Housing
Cable confirmation slot
Black
Cable labels
(Black, blue/green, white, and red)
Black
Green or blue
Red
Whit
e
Cable stopper
Page 77

54
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
■ Attaching the Cable
Confirm that the cable colors match the cable labels, and then insert the cable
end all the way to the back of the cover in which the cable stopper has already
been set.
■ Attaching the Housing
Confirm that the cable labels match the cable colors, and then temporarily
secure the housing to the cover.
Note The housing cannot be removed from the cover once it has been attached.
The connector may be damaged if the housing is forcefully removed.
■ Pressure-welding the Connector
The connector is pressure-welded using the DWT-A01 Pliers.
1,2,3... 1. As shown below, align the center (see arrows) of the connector cover with
the center of the pressure-welding block on the Pliers.
2. Squeeze firmly on the Pliers until the lock on the connector clicks into
place.
Note (1) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the edges.
(2) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the back of the pressure-
welding block.
Location of cable stopper
Housin
g
Pliers
Connector cover
Page 78

55
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
(3) Set the connector in the correct orientation.
3. After attaching the cable, confirm that it is properly pressure-welded as
shown below.
3-3-2 Flat Cable I
Preparing DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector Sockets
Component Names
■ Cutting the Cable (when Extending Cable or Connecting a Terminating
Resistor)
Cut the cable perpendicular to the length.
To prevent short-circuits, cut the cable with a sharp blade, such as wire cut-
ters, and be sure that there are no whiskers on the wires.
OK
NG
NG
Be sure the connector is locked
on both the left and right sides.
Be sure there are no
g
aps here.
Cover Housing
Cable confirmation slot
Cable labels
(Flat cable: black, blue, white, and red)
Black
Page 79

56
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
■ Setting the Cable Stopper (when Extending Cable or Connecting a
Terminating Resistor)
A stopper must be set in advance when extending a line or connecting a Terminating Resistor.
Close the cover, secure the hooks, and then press down on the cable stopper
until it clicks into place.
■ Attaching the Cable
■ T-branch Connections
1,2,3... 1. Align the cable labels and cable colors and insert the cable into the cover.
2. Hold the cable and secure it with the hooks.
■ Line Extensions and Terminating Resistors
Insert the cable end all the way into a cover with the cable stopper already set.
Cable stopper
Location of cable stoppe
r
Page 80

57
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
■ Attaching the Housing
Confirm that the cable labels and cable colors match and then temporarily
secure the housing to the cover.
Note The housing cannot be removed from the cover once it has been
attached. The connector may be damaged if the housing is forcefully removed.
■ Pressure-welding the Connector
The connector is pressure-welded using the DWT-A01 Pliers.
1,2,3... 1. As shown below, align the center (see arrows) of the connector cover with
the center of the pressure-welding block on the Pliers.
2. Squeeze firmly on the Pliers until the lock on the connector clicks into
place.
Note (1) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the edges.
(2) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the back of the pressure-
welding block.
(3) Set the connector in the correct orientation.
3. After attaching the cable, confirm that it is properly pressure-welded as
shown below.
Housing
Connector cover
Pliers
OK NG
NG
Page 81

58
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
Preparing DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plugs
Component Names
■ Cutting the Cable
Cut the cable perpendicular to the length.
To prevent short-circuits, cut the cable with a sharp blade, such as wire cut-
ters, and be sure that there are no whiskers on the wires.
■ Attaching the Cable
Align the cable labels and cable colors and insert the cable.
Confirm that the cable is inserted all the way to the back. (The cover is semi-
transparent.)
■ Pressure-welding the Connector
The connector is pressure-welded by using the DWT-A01 Pliers.
1,2,3... 1. As shown below, align the center (see arrows) of the connector cover with
the center of the pressure-welding block on the DWT-A01 Pliers.
Be sure the connector is locked on bot
h
the left and right sides.
Be sure there are no
g
aps here.
Cable labels
(Flat cable: black, blue, white, and red)
Lock lever
Black
Insert the cable to this point.
Page 82

59
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
2. Squeeze firmly on the Pliers until the lock on the connector clicks into
place.
Note (1) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the edges.
(2) Do not pressure-weld the connector cover at the back of the pressure-
welding block.
(3) Set the connector in the correct orientation.
3. After attaching the cable, confirm that it is properly pressure-welded as
shown below.
3-3-3 Flat Cable II
Preparing DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector Sockets
Component Names
■ Cutting the Cable
Cut the cable perpendicular to the length.
Pliers
Connector cover
OK
NG
NG
NG
Be sure there are no gaps here.
Cover
Page 83

60
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
To prevent short-circuits, cut the cable with a sharp blade, such as wire cutters, and be sure that there are no whiskers on the wires.
■ Setting the Cable Stopper (when Extending Cable or Connecting a
Terminating Resistor)
A stopper must be set in advance when extending a line or connecting a Terminating Resistor.
Set the cable into the cover and position it so that the cable end strikes the
cable stopper.
■ Attaching the Cable
1,2,3... 1. As shown in the diagram below, place the cable so that the white line is in
the direction of the side with the open cover, with the white line on the cable
facing upward.
T-branch Connections
Cable stopper
Middle of connecto
r
(Side with cover open)
(Top View)
White line
Connector
Cable
White line
Page 84

61
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
Line Extensions and Terminating Resistor Connections
2. Hold the cable so that it does not move and close the cover.
Note When extending the cable or connecting it to a Terminating Resis-
tor, make sure that the end of the cable is inserted all the way to the
cable stopper so that it will not be pulled out.
■ Pressure-welding the Connector
Use the DWT-A02 Pliers to pressure-weld the connector.
1,2,3... 1. Set the connector on the pressure-welding block of the crimping tool.
As shown below, align the center (see arrows) of the connector cover with
the center of the pressure-welding block on the Pliers.
2. Squeeze firmly on the Pliers until the lock on the connector clicks into
place.
Connector position reference surfaces
Pliers
Connector cover
Page 85

62
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
3. After attaching the cable, confirm that it is properly pressure-welded as
shown below.
Preparing DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector Plugs
Component Names
■ Cutting the Cable
Cut the cable perpendicular to the length.
To prevent short-circuits, cut the cable with a sharp blade, such as wire cutters, and be sure that there are no whiskers on the wires.
■ Attaching the Cable
1,2,3... 1. As shown in the diagram below, place the cable so that the white line is in
the direction of the side with the open cover, with the white line on the cable
facing upward.
Be sure there are no gaps here.
Be sure that the connector is locked.
Cover
White line
(Side with cover open)
From the left: red, white, blue, and blac
k
Page 86

63
Preparing Flat Connectors Section 3-3
2. Hold the cable so that it does not move and close the cover.
■ Pressure-welding the Connector
Use the DWT-A02 Pliers to pressure-weld the connector.
1,2,3... 1. As shown below, align the center (see arrows) of the connector cover with
the center of the pressure-welding block on the Pliers.
2. Squeeze firmly on the Pliers until the lock on the connector clicks into
place.
3. After attaching the cable, confirm that it is properly pressure-welded as
shown below.
Connector position reference surfaces
Pliers
Connector cover
Be sure there are no gaps here.
Be sure that the connector is locked.
Page 87

64
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
3-4 Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor
This section describes how to connect Flat Cable I/II or round cable I/II to
Slave Units, Repeater Units, and Terminating Resistors, and how to extend or
branch the cables.
Peripheral Devices Used
Terminating Resistor Specifications
3-4-1 Connecting Communications Cable to Slave Units and Repeater
Units
Connecting Round
Cable I/II
The DCN4-TB4 Open Type Connector is used to convert the communications
connector on the Slave Unit or Repeater Unit to a terminal block (M3) for connecting the cable wires.
Name Appearance Model Application
Open Type Connector (for
connecting Units)
DCN4-TB4 Converts the Unit's communications con-
nector into a screw terminal block to enable
connecting round cable I or round cable II to
a Slave Unit or Repeater Unit.
Relay terminal block --- Commercially available Used for T-branching round cable I or round
cable II.
Multidrop Connector DCN4-MD4 Used to connect Slave Units or Repeater
Units to trunk lines, sub-trunk lines, or
branch lines by using multidrop connections.
Terminating Resistor DCN4-TM4 This is a Connector-type Terminating Resis-
tor for Flat Cable I and round cable II.
It is connected to a DCN4-TR4 Flat Connec-
tor Socket at the end of a trunk line or subtrunk line.
Terminating Resistor DCN5-TM4 This is a Connector-type Terminating Resis-
tor for Flat Cable II.
It is connected to a DCN5-TR4 Flat Connec-
tor Socket at the end of a trunk line or subtrunk line.
Terminating Resistor DRS1-T This is a Terminal Block-type Terminating
Resistor for round cable I.
It is connected to the end of a trunk line or
sub-trunk line round cable I.
Type Connector Terminal block
Model DCN4-TM4 DCN5-TM4 DRS1-T
Resistance 121 Ω 121 Ω 121 Ω
Rated power 1/4 W 1/4 W 1/4 W
Accuracy 1% max. 1% max. --Capacity between power supply lines 0.01 µF0.01 µF ---
Page 88

65
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Installation Method
1,2,3... 1. Attach the Open Type Connector to the communications connector of the
Slave Unit or Repeater Unit.
Orient the Open Type Connector so that the side with the open terminals
is facing to the left and press in the Open Type Connector until it clicks into
place.
Note To remove the Open Type Connector once it has been attached,
firmly press in on the latches on both sides and pull out the Open
Type Connector.
2. Open the terminal cover of the Open Type Connector and connect the cable wires to BDH (communications data high) and BDL (communications
data low) in the terminal block. For round cable II, connect the cable wires
to BS+ (communications power supply plus) and BS- (communications
power supply minus).
Note Before connecting the cable wires to the terminal block, first attach the M3
crimp terminals shown below to the wires.
Connecting Flat
Cable I
A DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plug attached to a Communications Cable is
connected to the communications connector of a Slave Unit or Repeater Unit.
Installation Method Be sure the face of the Connector on which line colors are indicated (red,
white, black, and blue) is facing to the left and press in the Connector until it
clicks into place.
Open Connector
M3 terminal block
Communications
connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
MS
N
S
R
E
M
O
TE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
REM
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6.0 mm max.
6.0 mm max.
Communications
connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
Flat Connector Plug
Page 89

66
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in on the
latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
Connecting Flat
Cable II
A DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector Plug attached to a Communications Cable is
connected to the communications connector of a Slave Unit or Repeater Unit.
Installation Method Orient the Connector so that the white line on the cable is facing to the left and
press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in on the
latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
3-4-2 Branching Communications Cables
There are two methods that can be used to branch the trunk line, sub-trunk
lines, and branch lines: T-branches and multidrop connections.
T-branches
Using Round Cable I/II Connect the cable wires by using a commercially available relay terminal
block.
Example: Round cable I
Note Before connecting the cable wires to the terminal block, first attach the M3
crimp terminals shown below to the wires.
MS
N
S
RE
M
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
RE
M
OT
E
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
RT1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Communications
connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Uni
t
Flat Connector Plug
MS
N
S
R
EM
O
TE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
R
EM
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Relay terminal bloc
k
Slave Unit
Page 90

67
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Using Flat Cable I Attach a DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plug to the DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
■ Installation Method
Be sure the surface of the Flat Connector Plug on which line colors are indicated (red, white, black, and blue) is facing downward and press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in on the
latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
Using Flat Cable II Attach a DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector Plug to the DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
■ Installation Method
Place the Flat Connector Plug so that the white line on the cable is facing
downward and press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in firmly
on the latches on both sides of the front of the Connector and pull
it out.
6.0 mm max.
6.0 mm max.
Flat Connector Socket
Flat Connector Plug
Slave Unit
Flat Connector Socket
Flat Connector Plug
Slave Unit
Page 91

68
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Multidrop Connections
Using Round Cable I/II The DCN4-TB4 Open Type Connector is used to convert the communications
connector on the Slave Unit or Repeater Unit to a terminal block (M3) for connecting the cable wires.
Example: Round cable I
■ Connection Method
1,2,3... 1. Orient the Open Type Connector so that surface with the open terminals is
facing to the left and press in the Open Type Connector until it clicks into
place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in firmly
on the latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
2. Open the terminal cover of the Open Type Connector and connect the cable wires to BDH (communications data high) and BDL (communications
data low) in the terminal block. For round cable II, connect the cable wires
to BS+ (communications power supply plus) and BS- (communications
power supply minus).
Note Before connecting the cable wires to the terminal block, first attach the M3
crimp terminals shown below to the wires.
Using Flat Cable I Attach a DCN4-MD4 Multidrop Connector to the communications connector of
the Slave Unit or Repeater Unit, and then attach two DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plugs that are already connected to Communications Cables.
M3 terminal block
Open Connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
Communications connecto
r
MS
N
S
R
E
M
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
M
S
N
S
RE
M
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6.0 mm max.
6.0 mm max.
Page 92

69
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
■ Installation Method
1,2,3... 1. Place the Multidrop Connector so that the surface with the printed number
is facing to the left and press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
2. Be sure the surfaces of the two Flat Connector Plugs on which line colors
are indicated (red, white, black, and blue) are facing to the left and press
in the Connectors until they click into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in on the latches on
both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
Using Flat Cable II Branching is not possible using multidrop connections.
3-4-3 Extending Communications Cables
The cable length for the trunk line, sub-trunk lines, branch lines, and subbranch lines can be extended by up to 10 levels by using Flat Connectors. The
maximum extendable length, however, is the maximum trunk line length.
(Refer to 2-3-3 Maximum Distance and Number of Connected Units for Types
of Communications Cables.)
Flat Connector Plug
Multidrop Connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
Communications connecto
r
M
S
N
S
R
E
M
O
T
E
TER
M
IN
AL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
CR
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
REM
OTE
TER
M
IN
AL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
CRT1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
R
EM
OTE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MS
N
S
R
EM
O
TE
TERMINAL
W
O
R
D
N
O
D
E
A
D
R
C
R
T1
CRT1
-
O
D
1
6
OD16
-
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
5
X
1
0
[0
-
63]
X
1
OUT
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Page 93

70
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Flat Cable I Attach a DCN4-BR4 Flat Connector Plug to a DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
Installation Method Be sure the surface of the Flat Connector Plug on which line colors are indi-
cated (red, white, black, and blue) is facing downward and press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in on the
latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
Flat Cable II Attach a DCN5-BR4 Flat Connector Plug to a DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
Installation Method Orient the Flat Connector Plug so that the white line on the cable is facing
downward and press in the Connector until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Connector once it has been attached, press in firmly
on the latches on both sides of the Connector and pull it out.
Flat Connector Socket
Trunk line or sub-trunk line
Flat Connector Plug
Flat Connector Socket
Up to 10 sets of
Connectors can be used.
Terminating Resistor
Flat Connector Plug
Trunk Line or
Sub-trunk Line
Flat Connector Plug
Flat Connector Socket
Flat Connector Socket
Flat Connector Plug
Page 94

71
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
3-4-4 Connection Locations for Terminating Resistor
A Terminating Resistor must always be connected to the trunk line and each
sub-trunk line on the opposite end from the Master Unit or Repeater Unit.
Note (1) Do not connect the Terminating Resistor at the same end of the cable as
the Master Unit or Repeater Unit.
(2) When the cable is branched at the locations shown in the figure below,
connect the Terminating Resistor at the end of the line so that the length
of a is greater than b.
Round Cable I Connect the cable wires to a DRS1-T Terminating Resistor.
Connection Method Connect the cable wires to the Terminating Resistor and tighten the screws.
The Terminating Resistor has no polarity, so either wire can be connected to
either terminal regardless of the color.
Master Unit
Trunk line
Connect the Terminating
Resistor on the opposite
end of the trunk line from
the Master Unit.
Terminating Resistor
Repeater
Unit
Sub-trunk line
Slave Unit
Connect the Terminating
Resistor on the opposite
end of the sub-trunk line
from the Repeater Unit.
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Terminating
Resistor
a
b
Cable length: a > b
Master Unit
Trunk line
Terminating Resisto
r
Repeater
Unit
Sub-trunk line
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Round cable I
Terminating Resistor
Page 95

72
Connecting Cables and Terminating Resistor Section 3-4
Note Before connecting the cable wires to the Terminating Resistor, first attach the
M3 crimp terminals shown below to the wires.
Round Cable II Attach a DCN4-TM4 Terminating Resistor to the DCN4-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to the cable.
Connection Method Push in the Terminating Resistor until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Terminating Resistor once it has been connected, press in on the
latches on both sides and pull it out.
Flat Cable I Attach a DCN5-TM4 Terminating Resistor to the DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
Installation Method Push in the Terminating Resistor until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Terminating Resistor once it has been connected,
press in on the latches on both sides and pull it out.
BDL (white) or BDH (black)
BDH (black) or BDL (white)
Round cable I
Terminating Resisto
r
6.0 mm max. 6.0 mm max.
Flat Connector Socket
Round cable II
Terminating Resistor
Flat Connector Socket
Terminating
Resistor
Page 96

73
Power Supply Wiring Section 3-5
When using a multidrop connection for branching a Slave Unit or Repeater
Unit, the Terminating Resistor can be directly connected to the Multidrop Connector that is connected to the Unit. (This is only possible when Flat Cable I is
used.)
Flat Cable II Attach a DCN5-TM4 Terminating Resistor to the DCN5-TR4 Flat Connector
Socket connected to Communications Cable.
Installation Method Push in the Terminating Resistor until it clicks into place.
Note To remove a Terminating Resistor once it has been connected,
press in on the latches on both sides and pull it out.
3-5 Power Supply Wiring
The following power supplies are required to operate the CompoNet Network.
Terminating Resistor
Flat Connector
Multidrop Connector
Slave Unit/Repeater Unit
Flat Connector
Socket
Terminating
Resistor
• Communications power supply: Used for communications with individual Units
and for internal circuit operations of Units.
• I/O power supply: Used for I/O operations for Units with external I/O.
Page 97

74
Power Supply Wiring Section 3-5
The method for supplying communications power and I/O power depends on
the types of cable and Slave Unit that are used. The differences are shown in
the following table.
Multi-power Supply
Slave Units
Using Round Cable I • Communications Power Supply
Supply power to the power supply terminals of the communications connectors of individual Units (or to the PORT1 connector for Repeater Units).
• I/O Power Supply
Supply I/O power to the I/O power supply terminals of individual Units, separately from the communications power supply. To prevent noise, be sure
to use separate power supplies for I/O and communications.
Using Round Cable II or
Flat Cable I/II
• Communications Power Supply
Supply communications power to the Master Unit's communications power
supply connector (or to the downstream port communications power supply connectors on Repeater Units).
• I/O Power Supply
Supply I/O power to the I/O power supply terminals of individual Units, separately from the communications power supply.
Slave Unit classifica-
tion according to
power supply method
Cable type Communications
power supply
I/O power supply
Multi-power supply Round cable I Supplied to Units
individually.
Supplied to individual Units separately from the
communications
power supply.
Round cable II
Flat Cable I/II
Supplied through
the Communications
Cable by supplying
power to the Master
Unit.
Network power supply Round cable I Cannot be used.
Round cable II
Flat Cable I/II
The communications power supply and
the I/O power supply are provided
together through Communications Cable.
BDH BDLBS+BS −V G
Communications power
supply
terminals
I/O power
supply
terminals
24-VDC communications
power supply
24-VDC
I/O power
supply
Round cable I
Master Unit
BS+
BDH
BDL
BS−
BS+
BS−
Overcurrent
protection
(current limit: 4 A)
When complying with UL standards,
install a device to limit the current
between the external power supply
and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
Page 98

75
Power Supply Wiring Section 3-5
Network Power
Supply Slave Units
These Units use the same set of power supply terminals for both communications and I/O power, so there is no need to provide separate power supplies.
(Bit Slave Units are sold with a Flat Cable already attached.) The common
communications and I/O power supply is provided to the Master Unit's communications power supply connector (or to the downstream port communications power supply connectors on Repeater Units).
3-5-1 Power Supply Specifications
Use a communications power supply that meets the following specifications.
BS+
BDH
BDL
BS−
BS+
BS−
BD H BD L BS +BS −V G
24-VDC communications
power supply
Master Unit
(or Repeater Unit)
Communications power
supply
terminals
I/O
power
supply
terminals
24-VDC
I/O power
supply
Round cable II or
Flat Cable I/II
Communications power supply connector on Master Unit
(or downstream port communications power supply connector
on Repeater Unit)
Overcurrent
protection
(current limit: 4 A)
When complying with UL standards,
install a device to limit the current
between the external power supply
and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
BS +
BDH
BDL
BS −
BS +
BS −
BDH BD L BS+BS
−
24-VDC communications
power supply
Master Unit
(or Repeater Unit)
Round cable II o
r
Flat Cable I/II
Communications power supply connector on Master Unit
(or downstream port communications power supply connector
on Repeater Unit)
Overcurrent
protection
(current limit: 4 A)
When complying with UL standards,
install a device to limit the current
between the external power supply
and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
Item Specification
Output voltage 24 VDC ±10%
Output ripple 600 mVp-p
Page 99

76
Power Supply Wiring Section 3-5
An OMRON S82-series Power Supply for the communications power supply
for CompoNet Slave Units is recommended.
Note For network power supply Slave Units, the external I/O power supply is also
provided through the Flat Cable from the communications power supply connected to the Master Unit or the Repeater Unit.
When calculating the output current of the communications power supply,
always include the external I/O current consumption and actual load current
for network power supply Slave Units.
For example, the power supply current consumption for Bit Slave Unit is
expressed by the following formula.
• Input Bit Slave Units:
Communications power supply current consumption = Bit Slave Unit communications current consumption + (Bit Slave Unit input current
× number
of inputs used) + (sensor current consumption
× number of sensors used)
• Output Bit Slave Units:
Communications power supply current consumption = Bit Slave Unit communications current consumption + (actual load current
× number of actu-
ators used)
• I/O Bit Slave Units:
Communications power supply current consumption = Bit Slave Unit communications current consumption + (Bit Slave Unit input current
× number
of inputs used) + (sensor current consumption
× number of sensors used)
+ (actual load current
× number of actuators used)
For details on current consumption for each Unit, refer to Appendix D Current
Consumption Summary.
3-5-2 Connection Locations for Communications Power Supplies
Round Cable I A 24-VDC power supply is connected individually to each Slave Unit. Power
does not need to be supplied to the Master Unit.
Output current Use a power supply that equals or exceeds the following total
current consumption:
• The current consumption of all Word Slave Units and
Repeater Units
• The current consumption of all Bit Slave Units and the current
consumption of their external I/O
Insulation Between output and AC power and between output and chas-
sis ground
Item Specification
+−
Master Unit
Open Type Connector
Round cable I
Communications
connector
24-VDC communications
power supply
Supply communications power directly to each Slave Unit.
Word Slave Unit
Terminating Resistor
Open Type Connector
Open Type Connector
Open Type Connector
Word Slave Unit
Word Slave Unit
Overcurrent
protection (See note.)
(current limit: 4 A)
Note:
When complying with UL standards, install a
device to limit the current between the external
power supply and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
Page 100

77
Power Supply Wiring Section 3-5
Before connecting the power supply, first connect a DCN4-TB4 Open Type
Connector to the communications connector to convert it to a screw terminal
block.
When using a Repeater Unit, supply power through the BS+ and BS
− termi-
nals of the Repeater Unit's PORT1 connector.
Round Cable II or Flat
Cable I/II
Connect a 24-VDC power supply to the Master Unit's communications power
supply connector (BS+ and BS
−). This provides communications power to
each Slave Unit and Repeater Unit connected by round cable II or Flat Cable
I/II. Connect only one communications power supply for the trunk line. The
cable between the communications power supply and the communications
power supply connector must be no longer than 3 m.
When Repeater Units are used, communications power to sub-trunk lines is
supplied by the downstream port communications power supply connectors
(BS+ and BS
−) of the Repeater Units. The cable between the communica-
tions power supply and the communications power supply connector must be
no longer than 3 m.
+
−
BS+
BS-
Connect an Open Type
Connector here.
24-VDC
communications power
supply
Overcurrent
protection (See note.)
(current limit: 4 A)
Note:
When complying with UL standards, install a
device to limit the current between the
external power supply and the Unit to 4 A or
less for the communications power supply.
Connect an Open Type Connector here.
24-VDC
communications power
supply
BS
BS
PORT1
PORT2
Overcurrent
protection (See note.)
(current limit: 4 A)
Note:
When complying with UL standards, install a device
to limit the current between the external power
supply and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
Communications
power supply
connector
3 m max.
Master Unit
Communications
power
supply
Communications
power supply,
24 VDC
Communications
connector
Round cable II or
Flat Cable I/II
Slave Unit
Terminating Resisto
r
Slave Unit
Slave Unit
Overcurrent
protection (See note.)
(current limit: 4 A)
Note:
When complying with UL standards, install a
device to limit the current between the external
power supply and the Unit to 4 A or less for the
communications power supply.
 Loading...
Loading...