Page 1

O-Box
O-BoxB
O-Box
O-BoxB
0682
Operation instructions and warnings
Istruzioni ed avvertenze per l’uso
Instructions et avertissements
pour l’utilisation
Instrucciones y advertencias
para el uso
Anweisungen und Hinweise
zur Benutzung
Instrukcje i ostrzeżenia
dotyczące użytkowania
Aanwijzingen en aanbevelingen
voor het gebruik
Interface
Page 2

Page 3

English – 1
EN
ENGLISH
SOFTWARE USER’S LICENSE
The programs “O-Box Software Desktop” and “O-Box Software Mobile” are
protected by the laws of copyright and intellectual property; these software
applications are not sold, but are license-granted for non-exclusive use. Nice
s.p.a. remains proprietor of this program copy. The programs “O-Box Software
Desktop” and “O-Box Software Mobile” are license-granted as products combined with the product “O-Box”.
These software programs are supplied without guarantees regarding use and
safety. Furthermore, Nice s.p.a. shall not be held responsible for direct or indirect damages due to loss of profit, interruptions to work and similar, caused by
incorrect use of these software applications
TRADEMARK INFORMATION
The names AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, and MICROSOFT®are
registered trademarks of the respective owners; the products names stated in
this manual may also be registered by the respective owners.
GENERAL NOTES ON THE MANUAL
There are two programming unit models available: O-Box and
O-BoxB. These models are identical with the only difference on
the model O-BoxB, of a module for connection by Bluetooth
®
.
In this manual, the term “O-Box
” is used to refer to both
product models, unless otherwise specified.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION AND
INTENDED USE
1
The product O-Box (or O-BoxB, version with Bluetooth
®
module) comprises a
programming unit and dedicated software. The combination of these two elements is designed for the programming and maintenance of data and parameters of devices used for the automation of gates, garage doors, sun awnings,
shutters, road barriers with mobile arms and similar applications.
Any other use is to be considered improper! The manufacturer declines all
liability for damage resulting from improper use of the product and other
than as specified in this manual.
O-Box and the “NiceOpera” system
O-Box is a device that belongs to the system “NiceOpera”. This system has
been designed by Nice to simplify the phases of programming, use and maintenance of the devices in automation systems. The system is made up of various devices, both software and hardware, able to exchange data and information via radio, by means of an encoding system named “O-Code” or a physical
cable connection.
The main system devices are:
– NiceOne transmitters;
– NiceOne receivers (family OXI… ; family OX…);
– O-Box programming unit;
– control units and gearmotors with “Bus T4”;
– O-View programmer for devices with “Bus T4”.
IMPORTANT – For detailed information on all functionalities of the NiceOpera system and interdependency of the various system devices, refer
to the general manual “NiceOpera System Book”, also available on the
website www.niceforyou.com
Main operating characteristics of O-Box
Use of O-Box is especially recommended on automation systems with a high
technological content, as it enables the installer to perform many functions
directly from the office, without the need to visit the client’s premises; it also
enables configuration of a system directly on-site.
Page 4
2 – English
EN
The product incorporates a rechargeable 6 V battery, which enables operation
without a mains connection.
Note – the battery requires a complete recharging cycle of at least 10 hours.
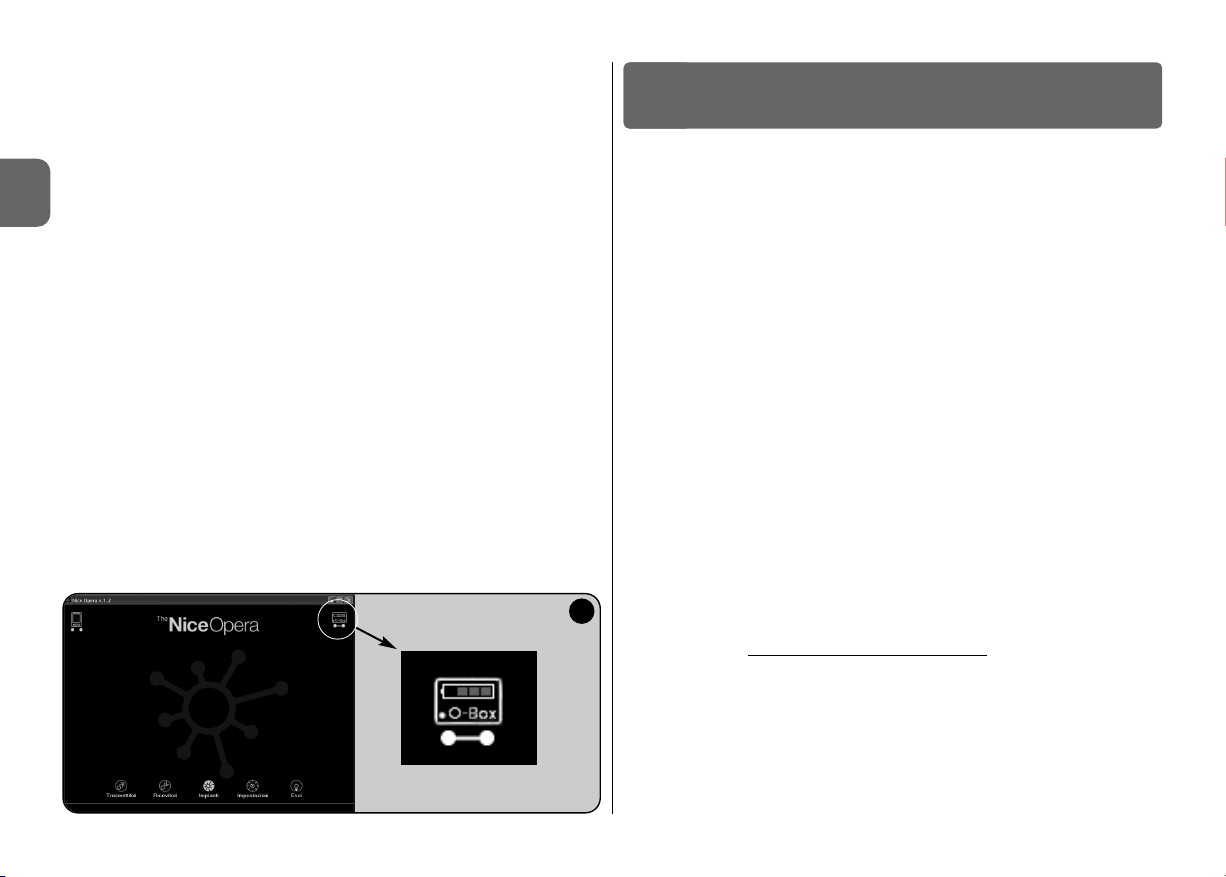
The charge level is indicated by the software (see fig. 1).
The battery recharges automatically each time O-Box is powered by an external power supply or by means of the USB cable.
2.1 – CONNECTIONS
• Connecting O-Box to the electrical mains
The product can be mains-powered using a 12 Vdc power supply unit (optional accessory) or via computer using a USB cable (supplied).
• Connecting O-Box to a personal computer
Use of O-Box (or O-BoxB) requires connection to a personal computer (PC)
equipped with a USB port, by means of the cable supplied, or via a serial port
by means of a RS232 cable (optional accessory).
Note – For this connection the USB socket is recommended (if present) as it
guarantees improved performance: it is more reliable, and ensures faster data
transmission, does not require configuration, and enables automatic recharging of the battery in O-Box.
• Connecting O-BoxB via Bluetooth
®
The model O-BoxB can also be connected via Bluetooth®to a computer or
palmtop (PDA) equipped with a
Bluetooth®interface.
This is a wireless connection: simply install the software on the computer or
palmtop and set the data according to the relative characteristics of the palmtop.
Note – Before activating the Bluetooth
®
connection, disconnect O-BoxB from
the USB port or serial port of the computer.
O-BoxB is designed to memorise up to 16 connections with different computers. To make the connection, switch on O-BoxB, set up the computer for connection via Bluetooth
®
and wait for the flashing light on the O-BoxB to become
permanently lit (confirming activation of the connection).
To delete the list of computer connections from the memory, proceed as follows:
This product enables administration and modification of systems using a database; this means rapid operations such as resetting and expanding existing
systems, replacement of transmitters etc...
In general O-Box can be used to:
• check, update, program or delete codes of transmitters “Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”,
“Plano”, and “NiceOne”;
• program the memories of receivers “Bio” and “FloR”;
• read and write transponder cards;
• program functions and parameters of transmitters “Bio”, “FloR”, and “Very”;
• optically read “Bio” transmitter codes;
• read and program parameters of receivers “SMX1” and “SMX2” via cable;
• receive data via radio from transmitters with SMILO, FLO, FLOR, O-CODE
encoding, to create user databases, program memories and receivers;
• program via radio transmitters in the series “NiceOne”;
• manage via radio all functions of receivers “NiceOne”
The software supplied with O-Box enables the configuration and programming
of all transmitters and receivers in the series “NiceOne”. It is also compatible
with all devices in the series “FloR”, “SMXI” and “Bio”.
HARDWARE: product description
and installation
2
1
Page 5
English – 3
EN
a) – on O-BoxB, press and hold the Activity key and wait for these phases to
be completed: O-BoxB emits a beep and the led turns off; the led lights up
again and O-BoxB emits a series of beeps.
b) – At this point the data stored in the O-BoxB memory have been deleted and
the Activity key can be released.
2.2 – ACCESSORIES (optional)
Note – O-Box is only supplied with the USB cable; all other cables are optional
and are not supplied in the pack. These cables are:
– Cable mod.
CABLA06 for connector D, in fig. 2: used to connect receivers in
the series “SMX” and “NiceOne”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA02 for connector M,infig. 2: used to receive codes of
transmitters in the series “Bio”.
– Serial 9-pin cable, RS232, mod.
CABLA01 for connector G,infig. 2: used to
connect O-Box to a computer.
– TTBUS Cable mod.
CABLA05 for connector H,in fig. 2: used to connect all
Nice tubular motors for sun awnings and shutters, equipped with TTBUS
port.
– Cable mod.
CABLA03 for connector I,infig. 2: used to connect transmitters
in the series “Very”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA02 for connector I, in fig. 2: used to connect transmitters
in the series “Bio” and “FloR”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA04 for connector I, in fig. 2: used to connect transmitters
in the series “Ergo” and “Plano”.
– Power supply unit mod.
ALA1, 12 V, 300 mA for connector E, in fig. 2: used
to connect O-Box to the electrical mains.
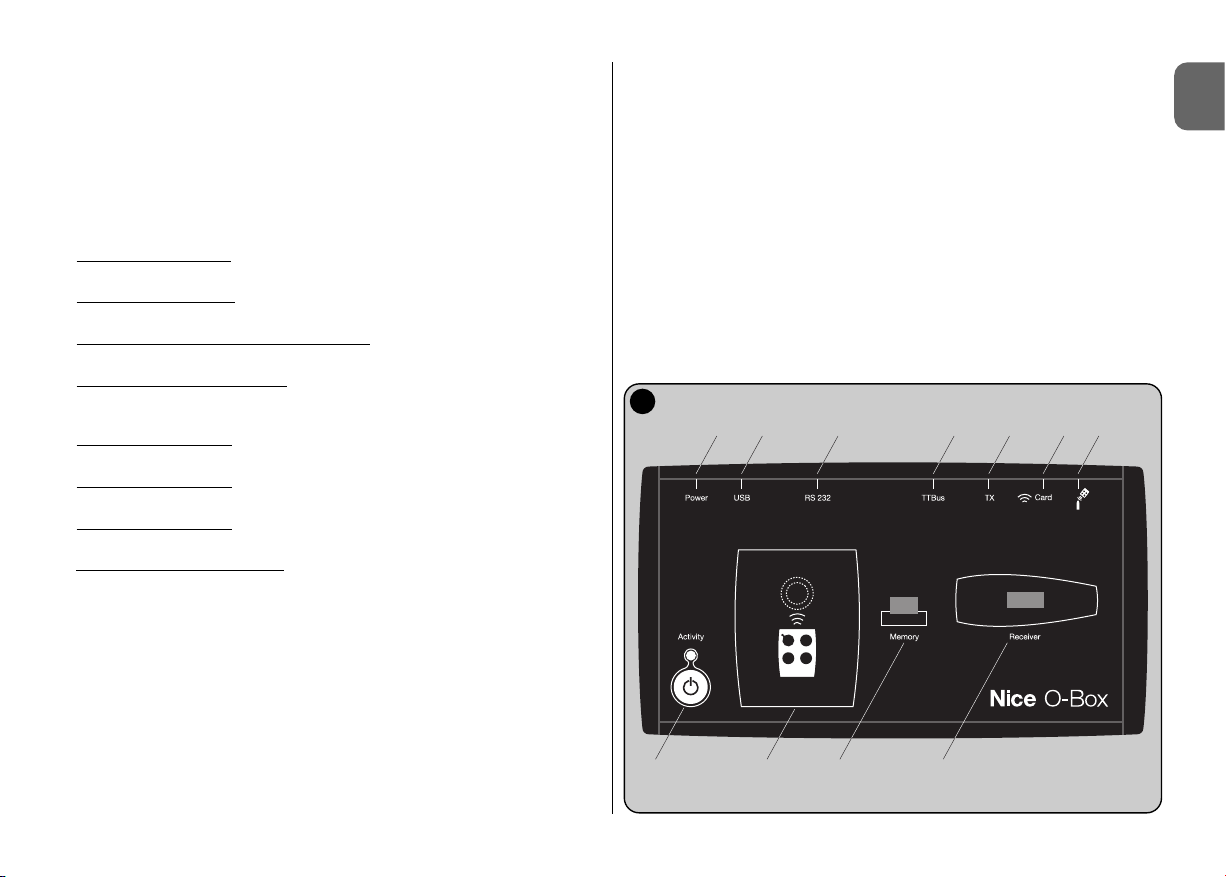
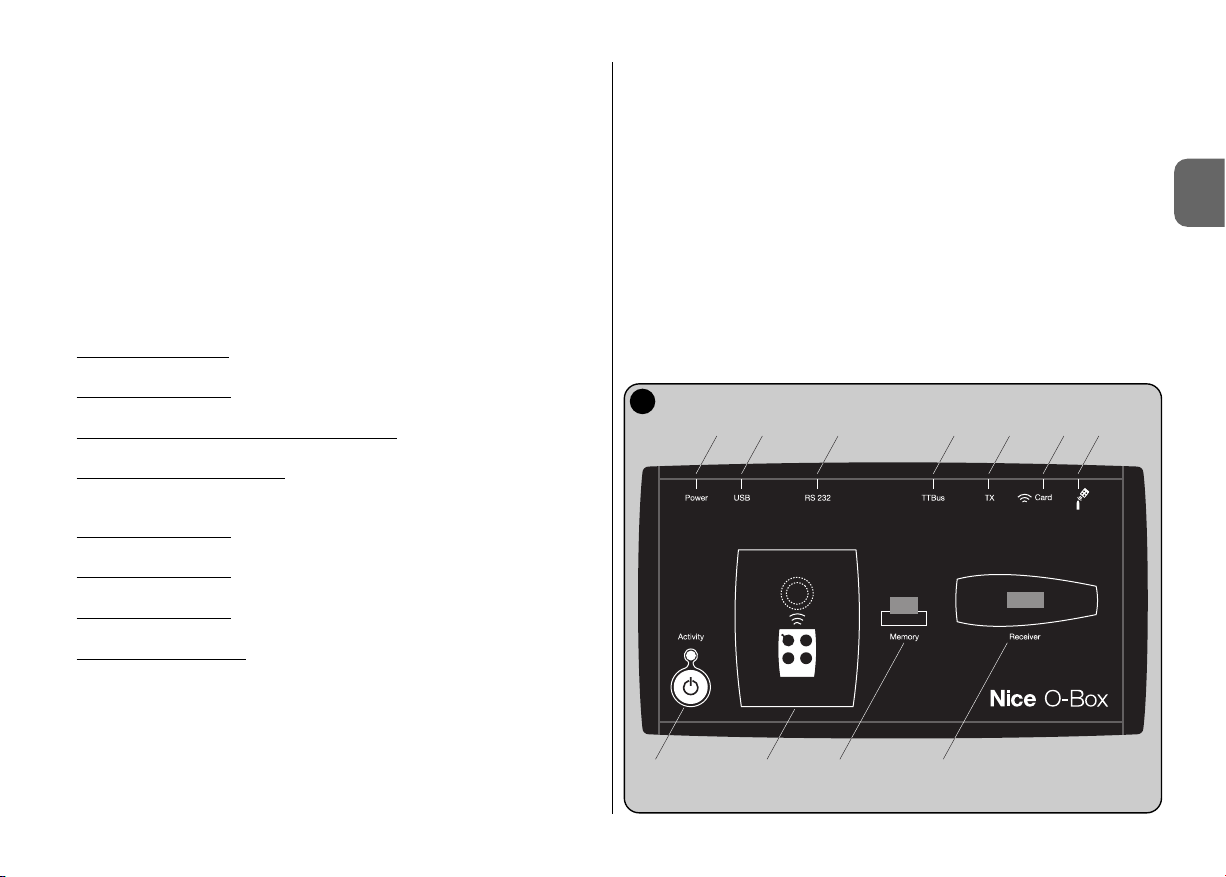
2.3 – CONNECTORS AND DEVICES COMPATIBLE WITH O-BOX
O-Box has various types of connectors (see fig. 2) to enable the connection of
a wide range of Nice devices. Note – Some of these connectors require a spe-
cific connection cable: for the model and characteristics of each cable, see
paragraph 2.2.
With reference to the letters in fig. 2 identifying the connectors and other
devices of O-Box, the following provides a detailed description of the relative
functions and use:
[A] – O-Box on/off key
To turn on O-Box press and hold the ON key for a few seconds until a brief
beep is emitted.
To turn off O-Box press and hold the ON key for a few seconds until a long
beep is emitted.
[B] – Area for connection via radio of transmitters in the series
“NiceOne”
This area enables programming via radio, i.e. without any physical connection,
of all transmitters in the Nice series “NiceOne”: transmitters are programmed by
placing them on the area outlined by the graphic sign.
During use of the software, the transmitter led emits a flash to indicate activation of communication via radio with the software. At this point the user can
start working with the software on the transmitter parameters (see chapter 3
paragraph 3.3).
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 6
4 – English
EN
[C] – Connector for “BM” memory boards
This connector enables connection of Nice BM memory boards to O-Box. To
connect a board, insert it directly in the connector and proceed with work using
the software (see chapter 3 paragraph 3.3).
[D] – “SM” type connector
The connector enables connection only of Nice receivers in the series “SM” and
“NiceOne” to O-Box. Some of these receivers can be inserted directly into the
connector, while others require cable mod. CABLA06. After connection, the
user can proceed with work using the software (see chapter 3 paragraph 3.3).
Note – The receivers in the series “NiceOne” (OXIT and OX2T) are also
designed to communicate with the software via radio. However, in this case
data transmission is slower than that via the SM connector.
[E] – Connector for external power supply, mod. ALA1
This connector enables connection of O-Box to the electrical mains by means
of an external 12 V dc power supply unit (optional accessory).
Note – Even if O-Box is turned off, the internal battery recharges each time the
power cable is connected to the mains.
[F] – Connector for “USB” cable
This connector enables connection of O-Box to the USB port of a computer by
means of a USB cable. After connection the software can be started up immediately for the relative work session.
Note– Even if O-Box is turned off, the internal battery recharges each time the
USB cable is connected to a powered computer.
[G] – “RS232” serial connector (cable mod. CABLA01)
This connector enables connection of O-Box to the RS232 serial port of a computer by means of a RS232 serial cable (optional accessory). After connection
the software can be started up immediately for the relative work session.
[H] – “TTBUS” connector (cable mod. CABLA05)
This connector enables the connection of Nice tubular motors for sun awnings
and shutters, equipped with TTBUS port to O-Box using the relative cable
(optional accessory).
[I] – Connector for transmitter cloning (cable mod. CABLA03 -
CABLA02 - CABLA04)
This connector enables the connection of Nice transmitters in the series “Bio”,
“FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano” and “Very” to O-Box using the relative cable (optional
accessory). To make the connection open the transmitter to insert the connection cable (*) and connect the other end of the connector to O-Box (I in fig. 2).
(*) Note:
– for transmitters in the series “Ergo” and “Plano” use cable mod. CABLA04
– for transmitters in the series “Bio” and “FloR” use cable mod. CABLA02
– for transmitters in the series “Very” use cable mod. CABLA03
[L] – Transponder card proximity reader
This proximity reader enables reading (blue cards and grey cards) or writing
(grey cards) of codes stored on the Nice transponder cards. To make the connection, place the card in front of the reader.
[M] – Optical reader connector for transmitters in the series “Bio”
This reader enables reading of the radio code of transmitters in the series “Bio”.
To make the connection, insert the optical reader (optional accessory, mod.
CABLA02) in the relative connector (M in fig. 2) and move the transmitter led
near to the head of the optical reader.
Page 7

English – 5
EN
There are two versions of the software provided on the installation CD “O-Box
Software Suite”:
• “O-Box Desktop” destined for installation on a personal computer (PC)
• “O-Box Mobile” destined for installation on a palmtop (PDA).
MINIMUM SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To use this software it must be installed on a computer or, if required, on a
palmtop of any brand and model, with the following minimum requirements:
VERSION FOR PC:
– Processor: type AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Recommended by Nice: Ty pe
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– RAM: 128 MB Recommended by Nice: 256 MB
– Free disk space: 30 MB Recommended by Nice: 100 MB
– Operating system: Windows
®
98 SE Recommended by Nice: Windows
®
2000 or later
– Video card: 800 x 600, with 256 colours
– Disk unit: CD-Rom (required for installation)
Note – Installation of the software requires installation of the program Microsoft
®
.NET
Framework Redistributable 2.0.
VERSION FOR PALMTOP:
– Processor: (300 MHz) Recommended by Nice:
(more than 300 MHz)
– RAM: 64 MB Recommended by Nice: 128 MB
– Storage memory: 5 MB Recommended by Nice: 100 MB
– Operating system: Windows
®
Mobile Recommended by Nice: Windows
®
2003 or 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE or later
– Connection: Bluetooth
®
– Resolution: 240 x 320, with 256 colours
– Pc with: CD-Rom (required for software installation on palmtop)
Note – Installation of the software requires installation of the program Microsoft
®
.NET
Framework Redistributable 2.0.
SOFTWARE: product description and use
3
3.1 – SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
Installation of the software is similar to any other type of computer program.
After inserting the installation CD, the installation software starts up automatically. If this does not happen, double click on the program icon “Setup.exe” and
follow the instructions on screen.
Note – Before starting software installation, disconnect O-Box from the computer.
BRIEF OVERVIEW OF SOFTWARE: Structure and subjects
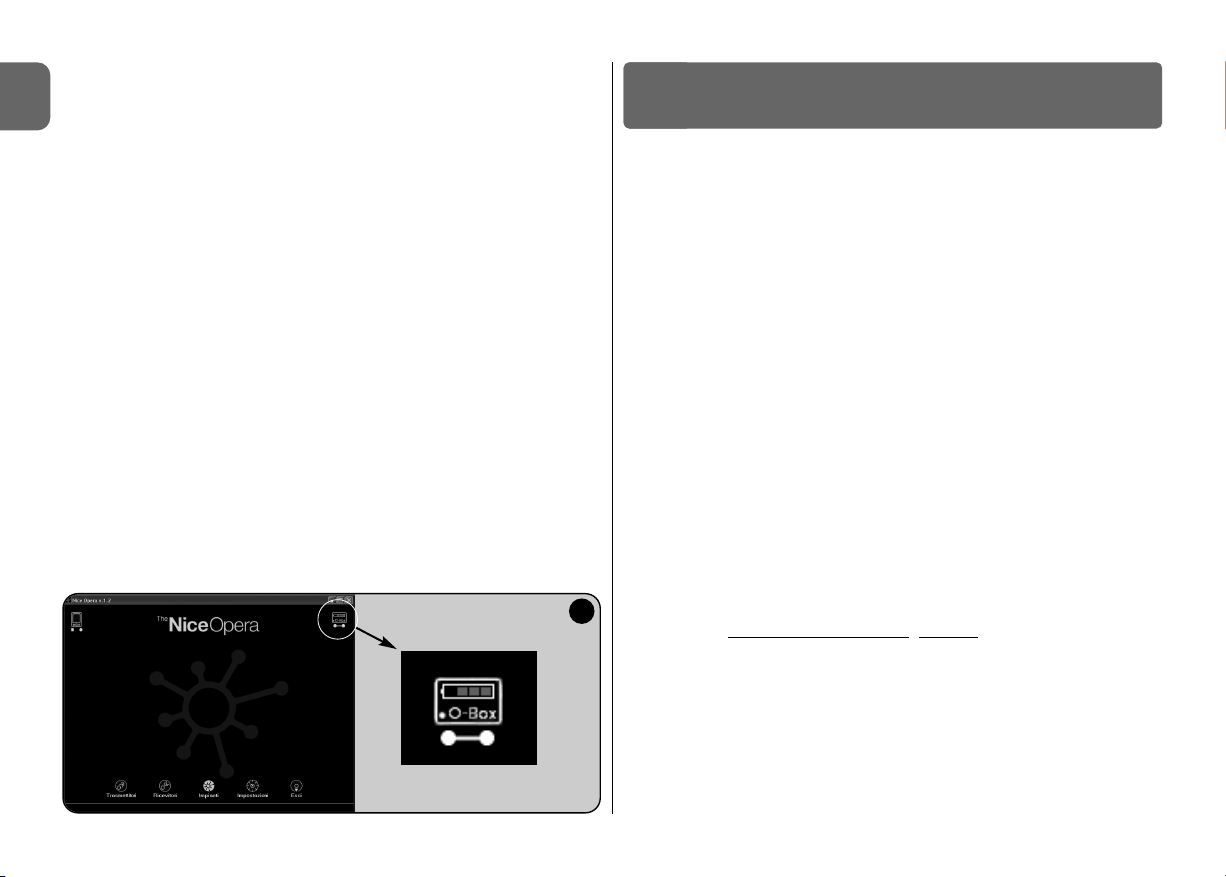
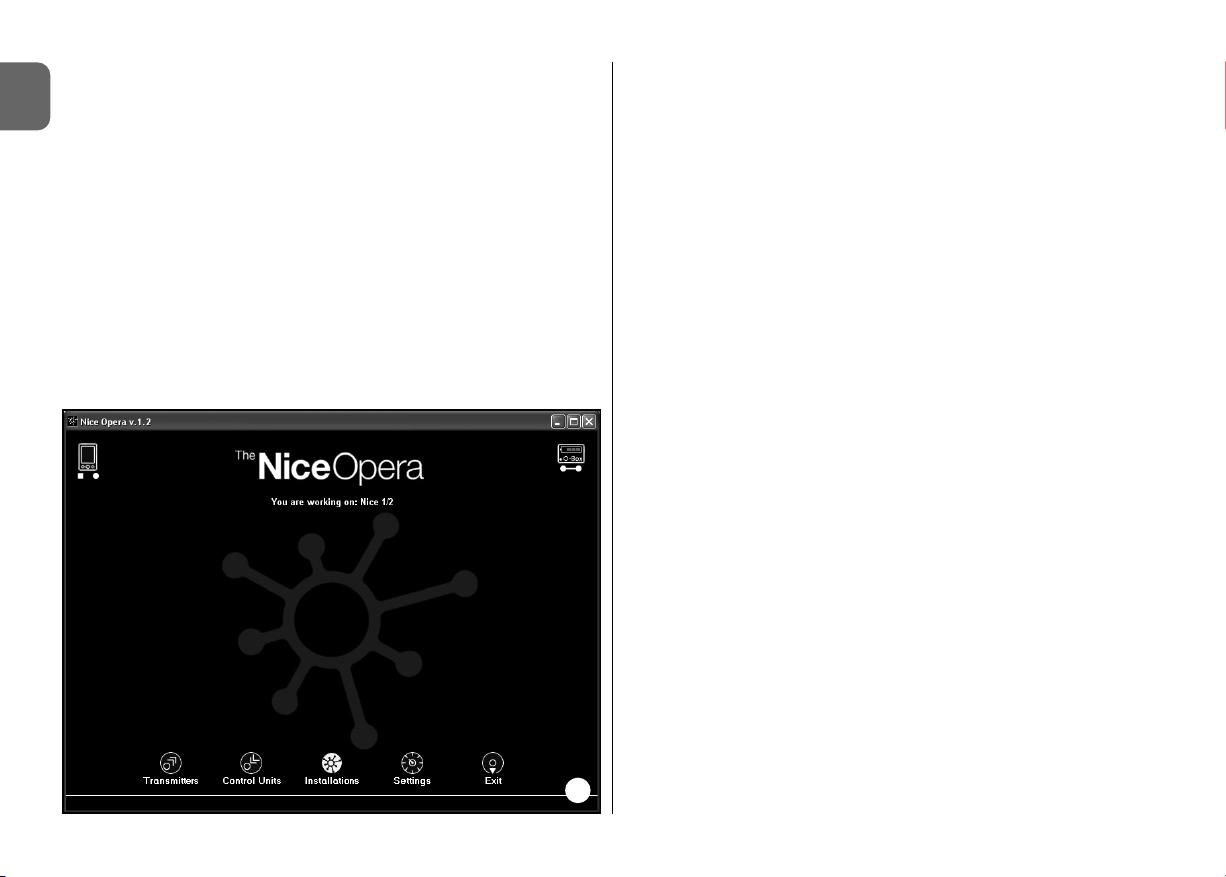
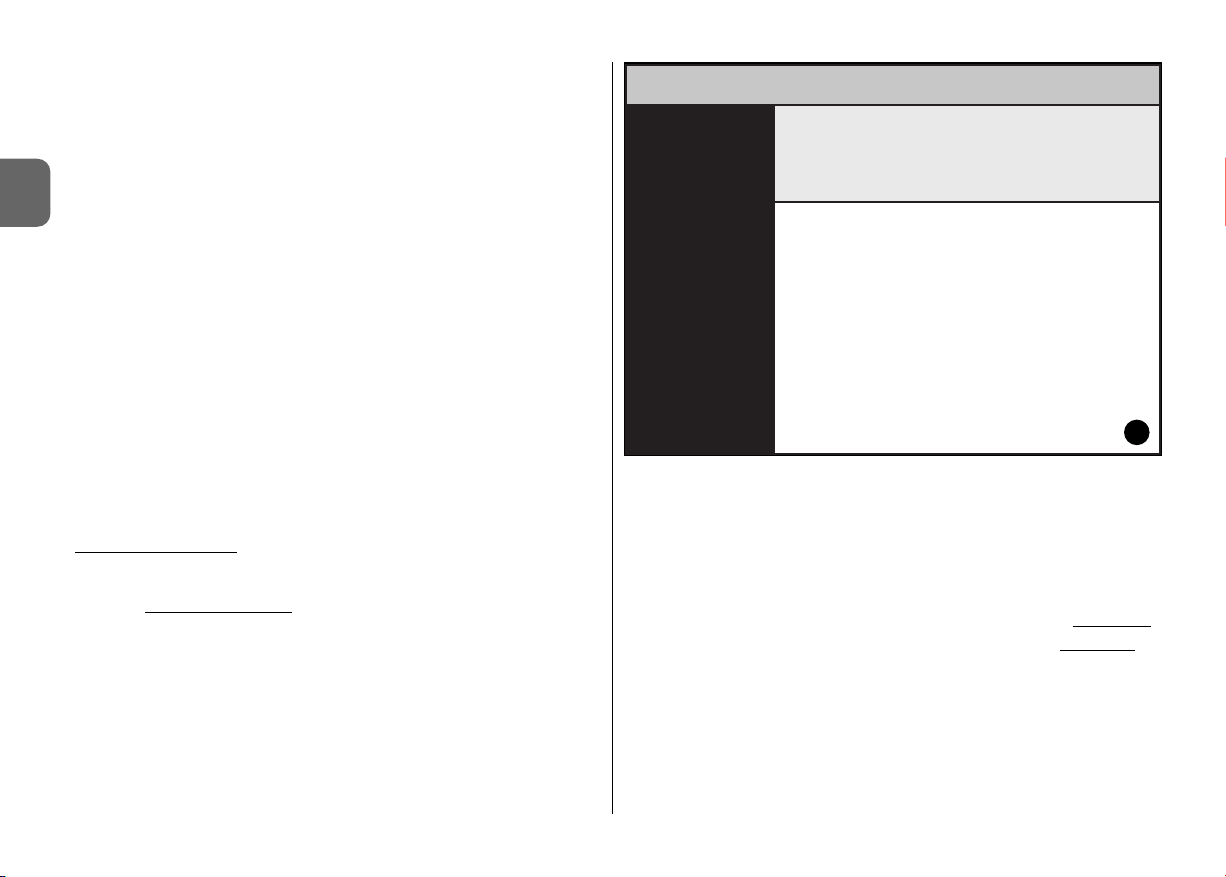
• Home page
After starting up the software, the “Home page” is displayed, i.e. the opening
screen (see fig. 3) containing the following subjects:
[1] – Indicates the palmtop computer connection status: click on this icon to
activate palmtop synchronisation.
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 8
6 – English
EN
[2] – Indicates the battery status and O-box connection status: in the event of a
connection error, click on this icon for the software to make a new connection to O-Box
[3] – “System selection” panel: on start-up of a work session, enables selec-
tion of the required work mode, to facilitate subsequent selections.
After programming a receiver, to save the configuration data only in its
memory or a file, select the option “Working without creating a system”.
Otherwise, after programming a receiver, to save the configuration data
both in its memory or a file, and also in a summarised datasheet of the
system in which the receiver is to be used, select the option “Work on the
last system” or “Select or create a system” (refer to paragraph 3.5.1).
[4] – Indicates access to the operative area for programming of Transmitters.
[5] – Indicates access to the operative area for programming of Receivers.
[6] – Indicates access to the operative area for management of Systems.
[7] – Indicates access to the operative area for software Settings.
[8] – Indicates the pushbutton used to exit the software.
[9] – Indicates the space for the display of data for software personalisation
(user name, etc.).
• Section windows
From the home page, select the section required (“Transmitters”, “Receivers”,
“Systems”, “Settings”) and, click on the relative icon to access the selected
section window, to run the required operations. (Note – each section option
can generate one or more windows). These windows normally comprise the
following elements (see fig. 4):
[a] – Browser bar
[b] – Function menu
[c] – Area with general data on device connected
[d] – Programming area
Browser bar items
The Browser bar displayed in each section window enables the user to move
from one window to another and the display of the specific area in which the
user is working.
The typical functions of the browser bar are:
– “Start” = click on this icon to return to the Home page
– “Back” = click on this icon to return to the previous
page
– “Next” = click on this icon to go to the next
page
– “Help” = click on this icon to display this instruction manual
– “Refresh” = in some windows, this icon can be used to refresh and update all
data.
IMPORTANT – In some windows, in addition to these” standard” functions,
other specific functions may be available regarding the device being programmed.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 9
English – 7
EN
3.2 – STARTING A WORK SESSION
To start a work session, proceed as follows:
– turn on O-Box;
– connect the device required to O-Box;
– start up the software (the home page is displayed);
– on the home page, press the button for the required section area;
– work in the subsequent section windows.
To access this area, first connect a transmitter to O-box and proceed as follows:
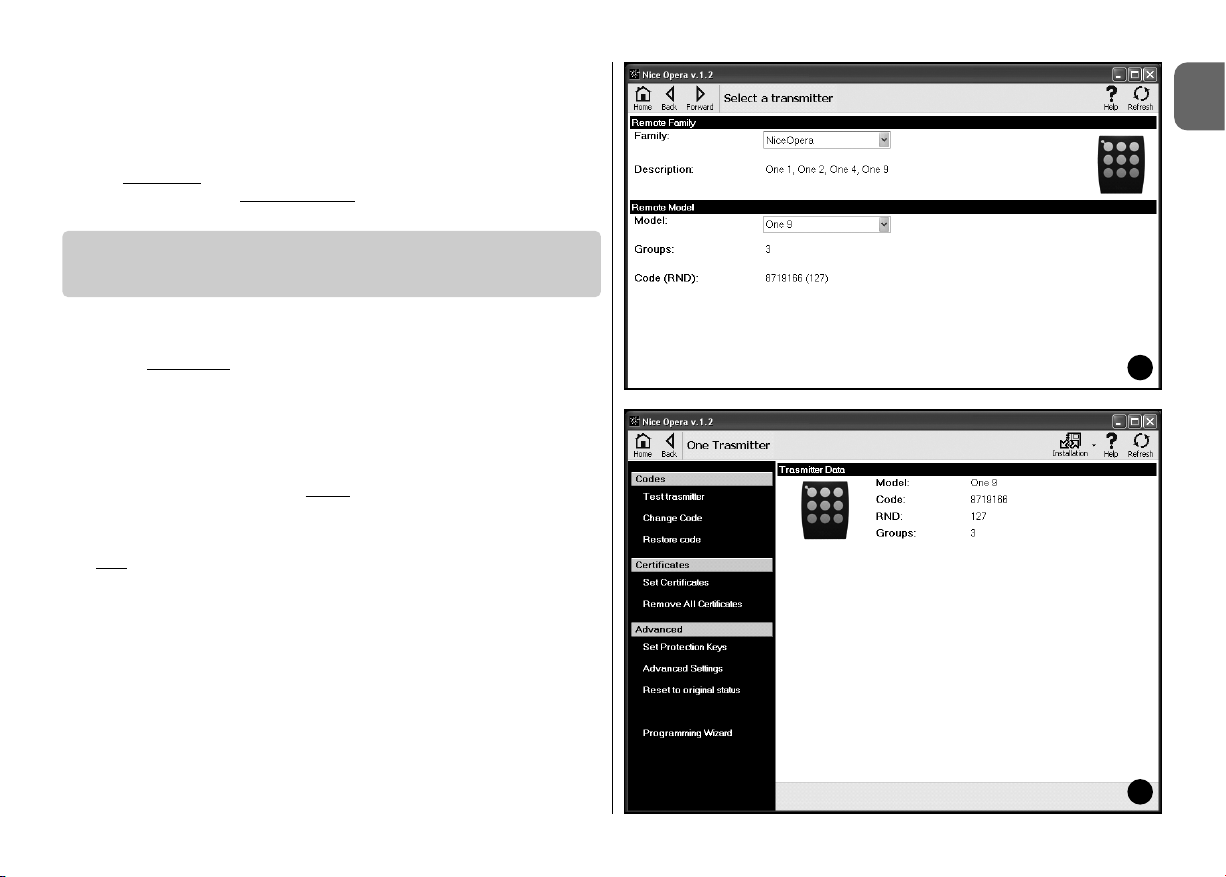
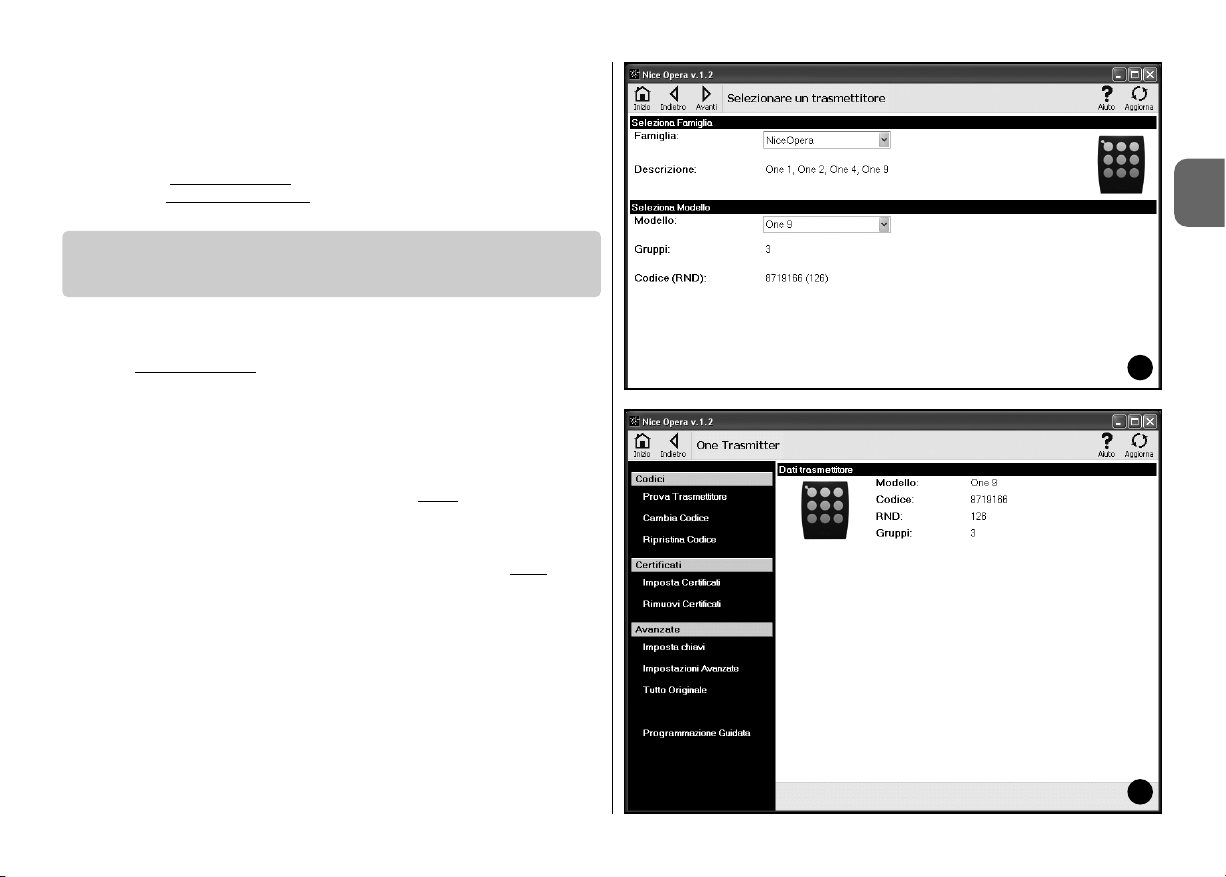
01. On the home page click on the icon “Transmitters” (fig. 3).
02. A main window is displayed for entry to the Transmitters section (fig. 5):
select the family and model of the transmitter to be programmed and click
on Next (on the browser bar) to move to the next page for programming
the transmitter.
Note – For NiceOne transmitters only: if the transmitter is positioned in
the O-box programming area before
accessing the Transmitters section,
the software automatically recognises the transmitter model and displays
the relative data, including the identity code and RND code.
Otherwise, if the transmitter is positioned in the O-box programming area
after accessing the Transmitters section, click on “Refresh” to ensure that
the software recognises the transmitter model and displays the relative
data.
03. A second Transmitter section window is displayed for programming (fig.
6): in the Functions menu, select the required item and work in the opera-
tive area for modifying and adding parameters as required.
IMPORTANT – Some functions offer the possibility of programming several transmitters in sequence, by simply connecting one transmitter after
another to O-Box. Confirmation of successful programming and the signal
to indicate that the next transmitter can be positioned in place of the previous one is given by two beeps.
3.3 – TRANSMITTERS SECTION
5
6
Page 10
8 – English
EN
The functions menu is divided into the three following sections: Codes; Certificates; Advanced (fig. 4). Important – The functions available in each sec-
tion vary according to the type of transmitter to be programmed.
–– CODES ––
This section enables entry of the codes of a transmitter, with the following functions:
– Transmitter test
: this function enables the user to test correct operation of
the transmitter and display the identity code and variable section of the RND
code.
– Change Code: this function enables the user to change the original identity
code of a transmitter.
IMPORTANT – To program several transmitters in sequence with progressive
codes, click on the icon “Program Sequence”; and compile two of the following
fields: “By code”, “Step” (i.e. the increment of the code between one transmitter and the other) and “N° codes”; then click on “Check”. At this point the software automatically complete the field left blank previously.
– Restore code: this function enables the user to restore the original (factory
set) identity code of a transmitter.
–– CERTIFICATES ––
This section enables entry of the certificates of a transmitter, with the following
functions:
– Set Certificates
: this function enables the user to enter the “Certificate” of a
receiver in a transmitter. For each certificate the user can set the memorisation
in the transmitter in “Mode I” or “Mode II”.
If memorisation is in mode “Mode II” (each key of the transmitter corresponds
to a specific function of the receiver) simply click on the item “Function” to
select the function number required and then select the key to be memorised
on the transmitter under “Buttons”.
Note – The variety of controls available for transmitter memorisation depends on
the type of transmitter and model of control unit to be used for this transmitter. A
detailed list of controls is provided in the instruction manual of the control unit.
– Remove Certificates
: this function enables the user to remove all certificates
of a transmitter.
–– ADVANCED ––
This section enables entry of the protection codes and operating parameters of a transmitter with the following functions:
– Set Codes
: this function enables the user to personalise a transmitter, i.e.
modify the protection codes of “Installer”, “Installation” and “Altera”. In particular, “Altera” is compatible with the previous systems “FloR”.
CAUTION! – Do not forget the new protection code otherwise the transmitter
will no longer be usable with this specific receiver.
– Advanced settings: This function enables entry of the following parameters:
Number of blocks: enables modification of the number of identity code
repetitions when this code is transmitted. It is useful to modify this parameter
for special automations requiring faster response times to a command sent
than the default values
Priority: enables replacement of an existing transmitter, maintaining the
same identity code. This is obtained by increasing the priority of the NEW
transmitter by one unit with respect to the OLD transmitter.
Enable RND: this function enables the user to enable or disable manage-
ment of the variable section of the RND code.
Enable code transfer: enables the option on the transmitter to transfer its
enable code to another transmitter.
Copy between different models: enables the user to enable or disable
copying of the “enable codes” between different models of transmitter.
Enable Repeater: enables the user to enable or disable management of
code repetition on receivers equipped with the “repeater” function.
Note – Click on “Factory settings” to set the default values of the parameters
listed above (“Advanced Settings”).
– All Original
: this function enables the user to restore all default settings on a
transmitter: this means that the original identity code is reset, all certificates are
removed and the default values of the various parameters are restored.
Important – For safety reasons, this function does not modify the value of the
protection codes, i.e. does not restore the factory settings.
– Guided Programming: this function enables the user to program a transmitter using all sections described above in sequence.
Page 11
English – 9
EN
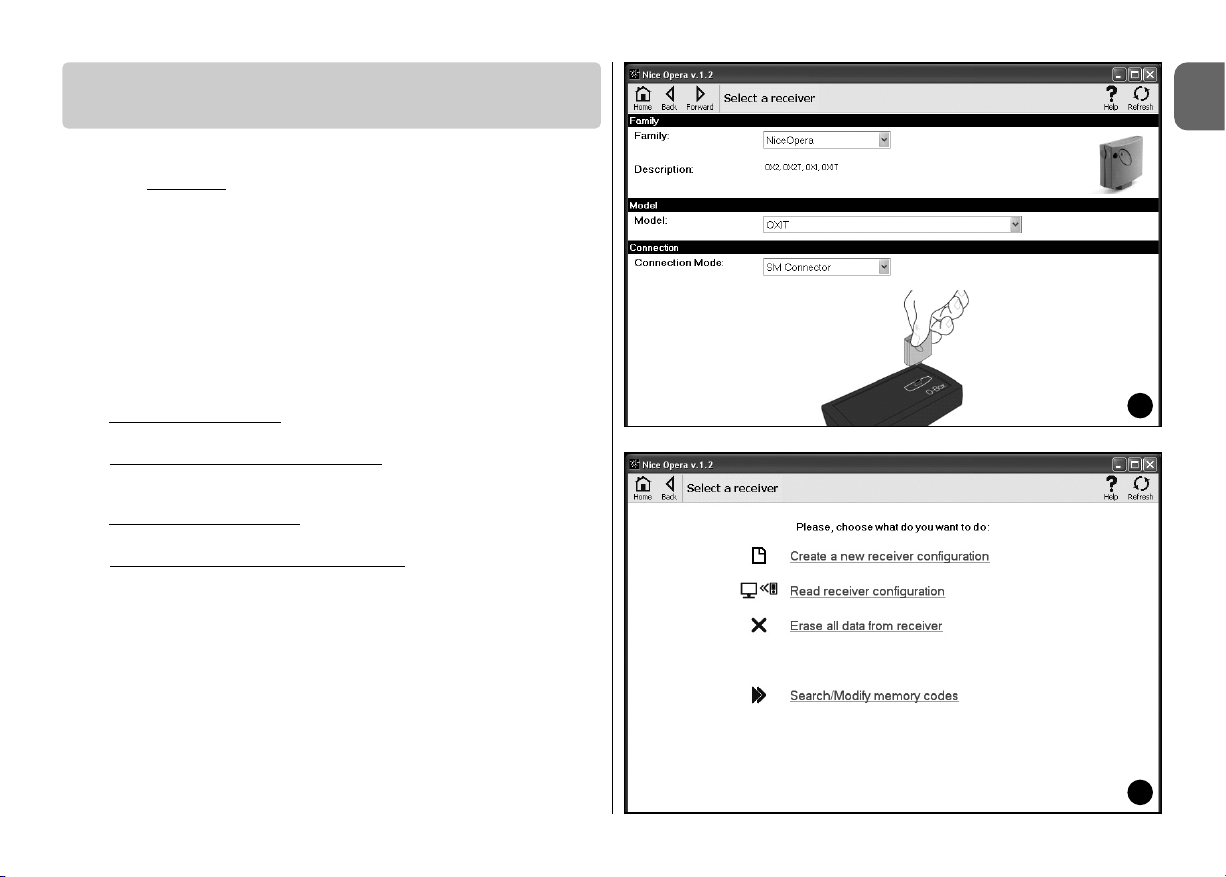
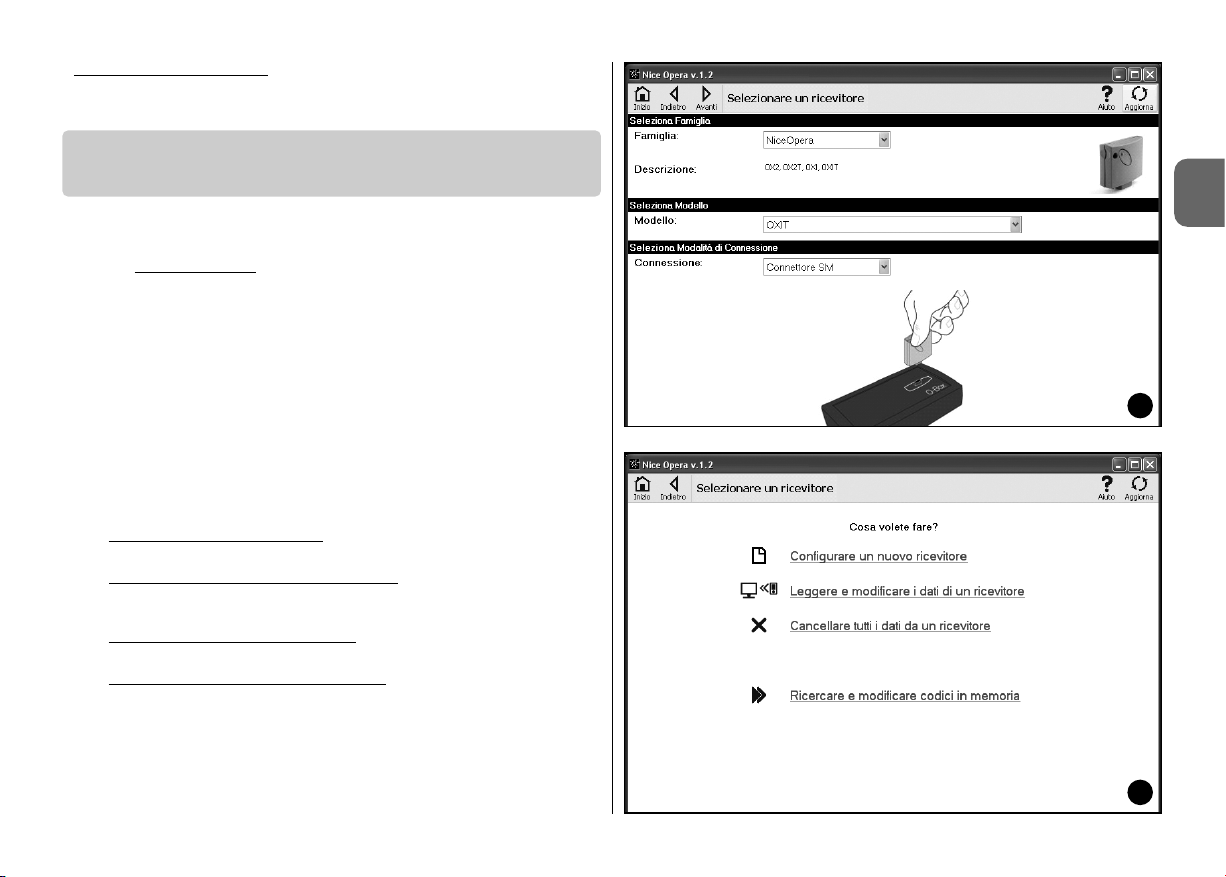
To access this area, first connect a receiver to O-box and proceed as follows.
01. On the home page
click on the icon “Receivers” (fig. 3).
02. A main window is displayed for entry to the Receivers section (fig. 7): select
the family and model of the receiver to be programmed (the system checks
whether there are receivers of this family connected to O-Box and automatically displays the model. However, the model can be selected manually).
Then on the browser bar, click on “next” to go to the next window.
Note – If programming a receiver in the series “NiceOpera” select the type
of connection used: wireless (in this case the receiver certificate must be
entered) or connector on O-Box (in this case use the SM connector).
03. After selecting the receiver family, a second window is displayed, entitled
“What do you want to do?”, requesting which operations to be per-
formed (fig. 8):
• Configure a new receiver
(this operation enables configuration of a new
receiver).
• Read and modify the data of a receiver
(this operation enables reading
and modification of the data of a receiver, saving each time the modifications applied).
• Cancel all data of a receiver
(this operation completely formats the data
of a receiver).
• Search and modify codes in the memory
(operation present only for
receivers of the family “NiceOne”. The operation enables direct operations
on the receiver memory).
04. A third window is then displayed for programming (fig. 9). In this window,
in the Functions menu select the required item and work in the operative
area for modifying and adding parameters as required.
The functions menu is divided into the three following sections: Codes in
memory; Settings; Import / Export.
–– CODES IN MEMORY ––
In this section the user can modify codes stored in the memory of all types of
receiver. To do this, click on the function “Modify Codes” to access the following options:
3.4 – RECEIVERS SECTION
7
8
Page 12

10 – English
EN
9
Add code: enables the user to add a code to the memory by manual entry
of the code.
Add Sequence
: enables the user to add a sequence of codes to the
memory of a receiver, compiling two of the following fields “start code”, “end
code” and “step between one code and next”, after which click on “Check”
for automatic compilation of the field previously left blank.
Add from TX
: enables the user to enter a transmitter code in the memory
of a receiver by simply pressing on a key of the transmitter.
Delete Code
: enables the user to delete one or more codes from the
memory of a receiver.
Find
: enables the user to find a transmitter code by simply entering the
code in the relative space or pressing any key of the transmitte
–– SETTINGS ––
In this section, using the functions present (“Certificates” - “Codes” “Advanced settings” - “Change Password”), the user can modify parameters
in a number of receiver families. The functions available in each section vary
according to the type of receiver or memory to be programmed: for more
details on these functions, divided by receiver family, refer to paragraph 3.4.1.
–– IMPORT / EXPORT––
In this section, the user can import, export, save and restore data on a receiver
using the functions present (“Read from file” - “Save to file” - “Copy”). The
functions available are:
Read from file
: enables the user to read a file (for example with extension
“.cor”) created with the programming unit management software BUPC or
created using the function “Save to file” in this section.
Save to file
: enables the user to write a file stored in the receiver memory
to enable subsequent reading using the function “Read from file” in this section. A file can also be saved in the previous format, for example with the
extension “.cor” (envisaged on the BUPC line) or in the new format (recom-
mended).
Copy
: enables the user to copy the contents of a receiver memory onto
the computer memory.
Paste
: enables the user to paste data from a computer memory into the
receiver memory, previously saved using the “Copy” function in this section.
3.4.1 – SETTINGS section: “BM” memories and Receivers
“NiceOne”
(family OXI...; family OX...)
The section “Settings” enables the user to enter operating parameters of a
receiver in the series “NiceOne” and a receiver with a “BM” memory, managing
all relative advanced functions.
BM MEMORIES
• Advanced settings: This function enables entry of the following parameters.
Memory lock
: this activates a lock on the memory board self-learning
operations when the board is inserted in its receiver. In other words, no new
codes can be entered on a receiver with a “locked” memory, and operation is
restricted exclusively to existing codes (refer also to the relative receiver
instructions).
Password
: enables entry of a password in the memory board; in other
words a numerical code accessible via software only by those in possession
of this specific code, used to control and restrict access to data stored on
the memory board. The password will be requested each time access is
required to memory contents, to read or modify data and codes present.
The password does NOT enable modifications to data stored on the memory board when the latter is inserted on a receiver: it locks all functions pro-
Page 13
English – 11
EN
grammable manually on the receiver that hosts this memory.
Timer: enables modifications to the timer time intervals. The time is dis-
played in hours minutes and seconds.
Altera
: this is a code that enables personalisation of a receiver; this code
is compatible with the previous systems “FloR”.
Caution! – Do not forget the new
protection code otherwise the receiver will
no longer be usable.
RND control
: enables the user to enable or disable control of the variable
section of the identity code (RND) of a receiver.
RND window
: enables modifications to the RND window of a receiver.
This window represents the portion of values within which the variable section of the identity (RND) code is accepted.
Note – Normally the window value is 100 and may have a value from 5 to
250.
Synchronism
: enables the user to activate or deactivate the receiver resynchronisation. If synchronism is deactivated, system safety is increased,
but if the transmitter exits the RND window, the identity code will have to be
memorised again in the receiver memory.
Native only
: enables the user to enable or disable the receiver for reception of commands sent by a transmitter with a code modified with respect to
factory settings.
NiceOne RECEIVERS
The functions available are:
• Certificates: this function enables reading and entry of receiver certificates
(up to a maximum of 4). In order, starting from the top, the receiver certificate
(present on the card in the pack) is listed, followed by 3 spaces usable to create groups of receivers.
Note – For more information on use of certificates, refer to the manual “Nice
Opera System Book”.
• Codes: this function enables the user to personalise a receiver, with the
option to modify the codes of “Installer”, “Installation” and “Altera”. In particular,
“Altera” is compatible with the previous systems “FloR”.
Caution! – Do not forget the new
protection code otherwise the receiver will no
longer be usable.
The codes are useful to personalise a system: in other words the original code
(factory setting) of a transmitter can be modified if required. For this reason the
codes must be the same on the transmitter and the receiver. In this case the OBox codes must also be modified to enable subsequent use.
• Advanced settings: This function enables entry of the following parameters.
Basic settings
- Enable original TX only: this function enables the user to enable or disable
operation of a receiver that receives the command from transmitters with a
modified code, i.e. with a code that is no longer the factory-set value.
- Disable RND: this function enables the user to enable or disable control of
the variable section of the identity code (RND) of a receiver.
Memorisation settings
- Memorisation lock by means of “Enable code”: this function enables the
user to lock memorisation of a new transmitter using the “Enable code” of an
old transmitter (already memorised). This procedure may be used only if two
transmitters with “O-Code” encoding are used.
- Memorisation lock by means of “Certificate”: this function enables the
user to lock memorisation of a new transmitter using the certificate of a
receiver.
- Remote memorisation lock: this function enables the user to lock memorisation of a new transmitter using an old transmitter with the procedure “in
the vicinity of transmitter”
BUS T4 settings
Note - The “Bus” is a system that enables connection of all automation system devices, using a single cable with several internal electrical wires. In this
type of connection, data communication between devices is via a specific
protocol, which in this case is the Nice “Bus T4”.
- Enable code repetition via bus: this function enables the user to enable
the option on a receiver to transfer the copy of a code received via radio from
a transmitter, to other connected devices, by means of the Bus T4 cable.
- Enable code reception via bus: this function enables the user to enable
the option on a receiver to receive a code transmitter via the Bus T4 cable by
another receiver (refer to the point above “Enable code repetition via bus”).
- Enable authorisation groups: This function enables the user to enable
management of radio codes in specific authorisation groups.
Page 14

12 – English
EN
Advanced settings
- Enable Repeater: this function enables code repetition. If there is the need
for remote control of an automation from a distance greater than that normally covered by the transmitter and receiver, a second receiver may be used
with the task of re-transmitting via radio the command to the end receiver (in
which the identity code is memorised of the transmitter that sent the command) to that the latter can execute the command.
- Enable key release management: during use of a transmitter, after sending a command, the manoeuvre does not stop precisely on release of the key
but proceeds briefly for a set time interval. If required, the manoeuvre can be
interrupted immediately on release of the transmitter key (e.g. during fine tuning operations) by enabling this function on the receiver.
- Disable priority management: this function enables the user to disable
reception on a receiver of commands sent by transmitters with priority
greater than 0.
Note – For more information on use of all functions described, refer to the manual “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Change Password: this function enables the entry of a password to restrict
access, also manual, to all functions of a receiver, by those not in possession of
this password.
The Systems section is a database that enables the creation and storage, for
each system, of an analytical datasheet summarising the client’s information
and settings of the receivers installed in the relative system. In particular there is
the option to modify systems, display codes, settings and save data of the
receivers installed, and in the event of malfunction enables restoral of automation operation.
This section is made up of two windows:
– a quick search function and selection of stored systems;
– another window containing a datasheet for collection of data related to a single system.
To access the Systems section, proceed as follows:
01. In the home page
(fig. 3) click on the icon “Systems”.
02. An initial window is displayed (fig. 10) for managing stored systems. This
comprises the following items:
• Browser bar with the following functions:
“Modify”
: enables modifications to system data.
“New system”: enables the creation of a new system.
“Copy”: enables copying of data from an existing system to create a
new identical version.
“Delete”: enables the user to delete one or more systems.
• The area “Filter on data” to enable simple and fast searches of stored
systems.
• The area “Systems List” showing the list of stored systems.
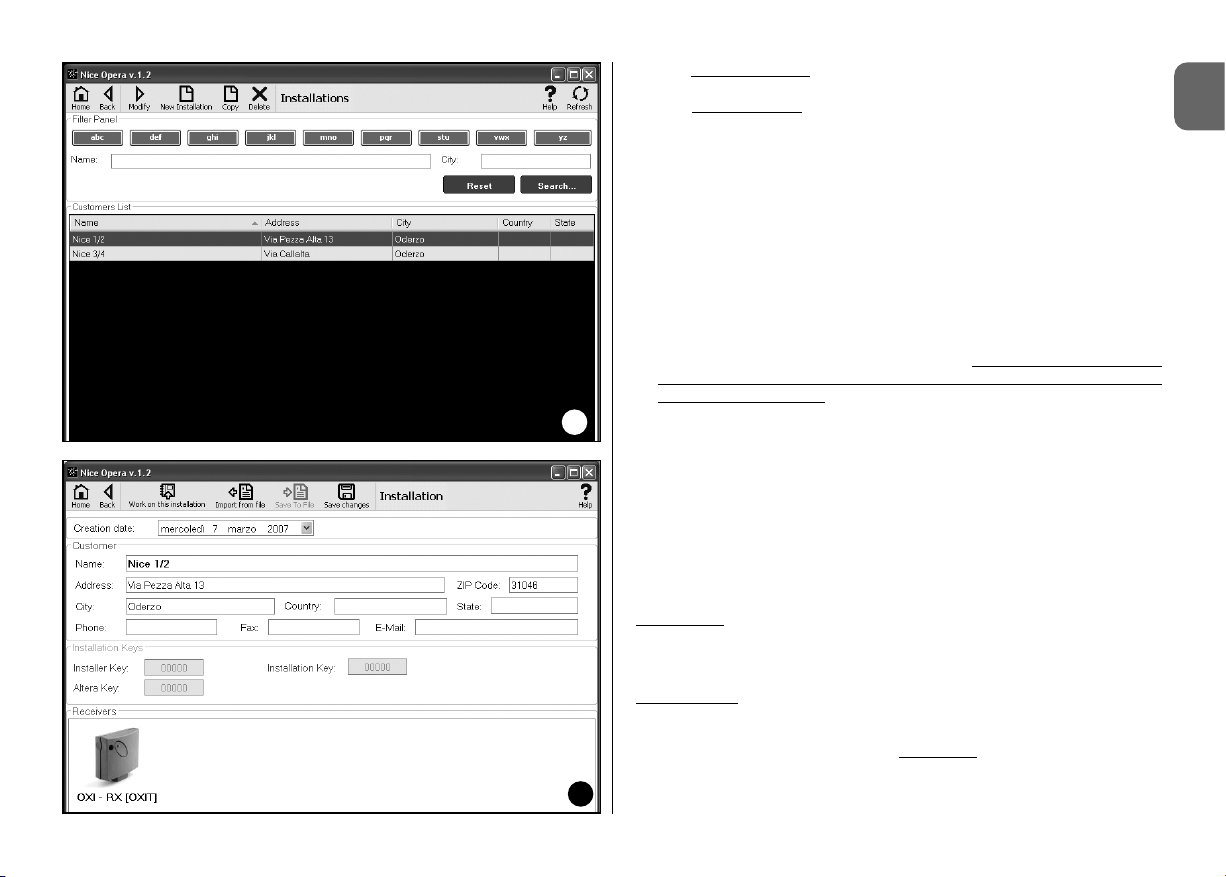
03. At this point, on selection of one of the following functions: “Modify”, “New
system” and “Copy”, a second window is displayed (fig. 11) with the
datasheet of the specific system. This comprises the following items.
• Browser bar with the following functions:
“Work on this system”
: enables work on a new or existing system
(refer to paragraph 3.5.1).
Save to file: enables the user to save data of receivers to be memorised on other files.
3.5 – SYSTEMS AREA
Page 15
English – 13
EN
10
11
“Import from File”: enables reading of receiver data from a file (refer to
paragraph 3.5.1).
“Save changes”
: enables the user to save modifications applied to a
system datasheet.
As well as the browser bar, this window displays 3 work sections: Client;
System codes; Receivers.
• Client: this enables entry of client data.
• System codes: this enables use of codes to personalise a system by
use of the fields “Installer Code”. “Installation Code” and “Altera”. These
codes are useful to restrict system management exclusively to those in
possession of the codes. The same code can be used on different systems or different codes for each system.
During programming of the transmitters and receivers in the series “Nice
Opera”, these are programmed automatically with the same codes as set
in the system board, if this board has previously been activated and
contains the set codes.
Note – For more information on use of codes, refer to the manual “Nice
Opera System Book”.
• Receivers: this section displays the receivers present in a system. To
add or delete receivers, refer to paragraph 3.5.1.
3.5.1 – Adding receivers on a system
In general, to add one or more receivers on a system board, there are two
optional procedures.
• direct mode
: this mode requires the condition that the data of the receiver to
be added to a system are already memorised on a file. Then, in the window displaying the system datasheet, click on the function “Import from file” (on the
browser bar) and select the required file.
• indirect mode
: This mode envisages the following operations:
- when the software is opened, in the panel “System selection”, select one of
the functions “Work on the last system” or “Select or create a system”; otherwise click on the icon “Systems” on the home page
.
– a window is displayed for management of stored systems (fig. 10) which
requires selection of the system on which the receiver is to be added (an existing system or a new version created at the time);
Page 16
14 – English
EN
– after confirming the selection, clicking on the icon “Work on this system”, the
software displays the initial window specifying the system on which the user is
working (fig. 12);
– then connect the relative receiver to O-Box and activate the section
“Receivers” to perform programming as required (refer to chapter 3.4);
- in the same window, click on the icon “System” and in the drop-down (*)
menu, select “Add to system”.
(*) Note – the menu associated with the icon “System” is dynamic as it displays
different items according to the relative circumstances. In general the items displayed are:
• first line: this states the name of the active system in italics, i.e. the system on
which the receiver being programmed can be saved.
• last line: this states the command “Add to system” to save the (new) receiver
programmed.
• other lines: these state the name of any receivers already present on the system. To modify one of these, select the name and modify the parameters as
required. To save the modifications applied, click on the icon “System” and in
12
the drop-down menu, select “Save changes...” (this item is only present if the
active system already has receivers present).
Page 17
English – 15
EN
This product constitutes an integral part of the automation system, therefore it must be disposed of along with it.
As in installation, also at the end of product lifetime, the disassembly and
scrapping operations must be performed by qualified personnel.
This product is made up of different types of material, some of which can be
recycled while others must be disposed of. Seek information on the recycling
and disposal systems envisaged by the local regulations in your area for this
product category.
Caution! – some parts of the product may contain pollutant or hazardous substances which, if disposed of into the environment, may cause serious damage
to the environment or physical health.
As indicated by the symbol on the left, disposal of this product
in domestic waste is strictly prohibited. Separate the waste into
categories for disposal, according to the methods envisaged
by current legislation in your area, or return the product to the
retailer when purchasing a new version.
Caution! – Local legislation may envisage serious fines in the event of abusive
disposal of this product.
Battery disposal
Even if discharged, the batteries can contain pollutant substances and therefore must NEVER be disposed of in common waste collection points. After removing the battery from the product, dispose of in accordance with local regulations governing classified waste disposal and collection.
Disposal of the product
Type: programming and code control unit for the following Nice products:
• receivers in the series NiceOne and SMX
• receiver-transmitter systems with “Bio”, “Flo”, “FloR”, “Smilo” and “O-Code” encoding;
• access control systems with “Morx” decoder; MOM transponder card readers or MOT
digital keypads
• devices using the TTBUS system;
Radio technology: radio receiver-transmitter at frequency of 433.92 MHz. Range up to
10 m.
Compatible connectors and devices:
• support area for transmitters in the series “NiceOne” (programming is via radio, without
contact);
• connector for memory boards “BM 60”, “BM 250”, “BM 1000”.
• connector for receivers in the series “SMX” and “NiceOne” (specific models, by means of
adaptor cable);
• connector for transmitters in the series Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo, Plano (by means of
adaptor cable);
• optical reader connector for transmitters in the series “Bio”.
• transponder card proximity reader;
• connector for TTBUS devices (by means of adaptor cable);
Connection to computer:
• Connector for USB cable
• Connector for RS232 serial cable
• Wireless connection with Bluetooth
®
technology (OboxB version only)
Power supply:
• Internal
: by means of rechargeable battery 6 V, 700 mAh.
• External
: via USB connection to computer or via power supply unit mod. ALA1, 12 Vdc,
Battery recharging time: approx. 15 hours.
Battery charge duration: approx. 10 hours of operation or 3 months on stand-by.
Battery lifetime: at least 100 complete discharge cycles.
Casing protection rating: IP 20 (use indoors or in protected environments only).
Operating temperature: from -20°C to +55°C
Dimensions (mm): 194 x 115 x H 40
Weight (g): 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Technical specifications of product
Page 18
16 – English
EN
CE DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Ce Declaration of conformity in accordance with Directive 1999/5/EC
Note – This Declaration of Conformity contains the individual declarations of conformity for the specified products; it was updated on the issue date of this manual
and the text herein has been drawn up for editorial purposes.
A copy of the original declaration for each product can be requested from Nice
S.p.a. (TV) I.
______________
The undersigned, Lauro Buoro, in the role of Managing Director, declares under his sole responsibility, that the product:
Manufacturer’s Name: NICE s.p.a.
Address: Via Pezza Alta 13, Z.I. Rustignè, 31046 Oder-
zo (TV) Italy
Type: OBOX programmer for radio controls with
radio receiver-transmitter 433,92 MHz and
transponder card reader.
OBOXB programmer for radio controls with
radio receiver-transmitter 433,92 MHz and
transponder card reader. Version with Blueto-
oth
®
technology
Models: OBOX, OBOXB
Accessories:
comply with the requirements of the following EC directive:
• 1999/5/EC; DIRECTIVE 1999/5/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
AND COUNCIL of 9 March 1999 regarding radio equipment and telecommunications terminal equipment and the mutual recognition of their
conformity, according to the following harmonised standards:
health protection standards: EN 50371:2002;
Electric safety: EN 60950-1:2001;
Electromagnetic compatibility : EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005; EN 301
489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002
Radio spectrum: EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2
V1.3.1:2006, EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004
The product complies with the requirements of the following EC directives, as amended by Directive 93/68/EEC of the European Council of 22
July 1993:
• 89/336/EEC DIRECTIVE 89/336/EEC OF THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL
of 3 May 1989 regarding the approximation of member state legislation related to electromagnetic compatibility, according to the following standards:
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Managing director)
Page 19

Italiano – 1
IT
ITALIANO
LICENZA D’USO DEL SOFTWARE
I programmi “O-Box Software Desktop” e “O-Box Software Mobile” sono protetti dalle leggi sul copyright e sulla proprietà intellettuale; questi software non
vengono venduti, ma vengono concessi in licenza d’uso non esclusiva. Nice
s.p.a. continua ad essere proprietaria di questa copia del programma. I programmi “O-Box Software Desktop” e “O-Box Software Mobile” sono concessi
in licenza, quale prodotti abbinati al prodotto “O-Box”.
Questi programmi software sono forniti senza garanzie riguardanti il modo di
utilizzo e la sicurezza. Inoltre Nice s.p.a. non è responsabile per danni diretti o
indiretti, inclusi i danni per perdita di profitto, interruzioni di lavoro e simili, derivanti dall’uso errato di questi software.
INFORMAZIONE SUI MARCHI
I marchi AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, MICROSOFT®sono marchi registrati dai rispettivi titolari; i nomi dei prodotti indicati nel presente manuale possono essere anche registrati dai rispettivi titolari.
NOTA GENERALE AL MANUALE
L’unità di programmazione è disponibile in due modelli: O-Box
e O-BoxB. Questi modelli sono simili tranne che per la presen-
za, nel modello O-BoxB, di un modulo per il collegamento Blue-
tooth
®
.
In questo manuale, il termine “O-Box
” è usato per identificare indistintamente i due prodotti, salvo dove è specificato diversamente.
DESCRIZIONE DEL PRODOTTO E
DESTINAZIONE D’USO
1
Il prodotto O-Box (o O-BoxB, versione con modulo Bluetooth®) è costituito da
un un’unità di programmazione e un software dedicato. L’insieme di questi due
elementi è destinato alla programmazione e alla manutenzione dei dati e dei
parametri contenuti nei dispositivi impiegati negli impianti di automatizzazione
di cancelli, portoni da garage, tende da sole, tapparelle, barriere stradali con
asta mobile e applicazioni similari.
Ogni altro uso è da considerarsi improprio! Il costruttore non risponde dei
danni risultanti da un uso improprio del prodotto, diverso da quanto previsto nel presente manuale.
L’O-Box e il sistema “NiceOpera”
L’O-Box è un dispositivo che fa parte del sistema “NiceOpera”. Questo sistema è stato progettato da Nice per semplificare le fasi di programmazione, di
uso e manutenzione dei dispositivi presenti negli impianti di automatizzazione. Il
sistema è formato da vari dispositivi, software e hardware, capaci di scambiarsi fra loro dati e informazioni via radio, attraverso un sistema di codifica chiamato “O-Code” o un collegamento ‘fisico’, tramite cavo.
I principali dispositivi che formano il sistema sono:
– trasmettitori NiceOne;
– ricevitori NiceOne (famiglia OXI… ; famiglia OX…);
– unità di programmazione O-Box;
– centrali e motoriduttori con “Bus T4”;
– programmatore O-View per dispositivi con “Bus T4”.
IMPORTANTE – Per approfondire in dettaglio tutte le funzionalità del
sistema NiceOpera e l’interdipendenza operativa che lega i vari dispositivi del sistema, consultare il manuale generale “NiceOpera System Book”,
disponibile anche nel sito internet www.niceforyou.com
Principali caratteristiche funzionali dell’O-Box
L’utilizzo dell’O-Box è particolarmente indicato negli impanti di automatizzazione ad elevato contenuto tecnologico, in quanto permette di svolgere molte funzioni direttamente nell’ufficio dell’installatore, senza la necessità di effettuare le
operazioni presso l’impianto del cliente; oppure, permette di configurare un
impianto direttamente presso il cliente.
Page 20
2 – Italiano
IT
Il prodotto integra una batteria ricaricabile da 6 V, che gli permette di funzionare senza il collegamento alla rete elettrica.
Nota – La batteria richiede un ciclo di ricarica completo di minimo 10 ore. Il
livello della carica è indicato all’interno del software (vedere fig. 1).
La batteria si ricarica automaticamente ogni volta che l’O-Box viene alimentato
con un alimentatore esterno o con il cavo USB.
2.1 – COLLEGAMENTI
• Collegare l’O-Box all’alimentazione elettrica
Il prodotto può essere alimentato dalla rete elettrica, utilizzando un alimentatore da 12 Vcc (accessorio opzionale) o da un computer, utilizzando il cavo USB
(in dotazione).
• Collegare l’O-Box ad un personal computer
Per utilizzare l’O-Box (o l’O-BoxB) è necessario collegarlo ad un personal
computer (PC) provvisto di una porta USB, tramite il cavo in dotazione, o provvisto di una porta seriale, tramite il cavo RS232 (accessorio opzionale).
Nota – Per questo collegamento è consigliabile usare la presa USB (se questa
è presente) in quanto offre migliori prestazioni: è più affidabile, più veloce nel
trasferimento dei dati, non necessita di nessuna configurazione e permette la
ricarica automatica della batterie interna all’O-Box.
• Collegare l’O-BoxB via Bluetooth
®
Il modello O-BoxB può essere collegato anche via Bluetooth®a un computer o
un palmare (PDA) provvisti di un’interfaccia
Bluetooth®.
Questo collegamento non necessita di cavi: è sufficiente installare il software
sul computer o sul palmare e impostare i dati in base alle caratteristiche del
proprio palmare.
Nota – Prima di attivare il collegamento Bluetooth
®
, scollegare l’O-BoxB dalla
porta USB o dalla porta seriale del computer.
L’O-BoxB è predisposto per memorizzare fino a 16 collegamenti con diversi
computer. Per stabilire il collegamento è necessario accendere l’O-BoxB, predisporre il computer al collegamento Bluetooth
®
e attendere che la luce lam-
Questo prodotto permette di amministrare e modificare gli impianti utilizzando
un archivio dati; si possono eseguire velocemente varie operazioni come il ripristino, l’ampliamento degli impianti esistenti, la sostituzione dei trasmettitori, ecc.
In generale l’O-Box può essere utilizzato per:
• controllare, aggiungere, programmare o cancellare i codici dei trasmettitori
“Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano”, “NiceOne”;
• programmare le memorie dei ricevitori “Bio” e “FloR”;
• leggere e scrivere card a transponder;
• programmare le funzioni e i parametri caratteristici dei trasmettitori “Bio”,
“FloR”, “Very”;
• leggere otticamente i codici dei trasmettitori “Bio”;
• leggere e programmare i parametri caratteristici dei ricevitori “SMX1” e
“SMX2” via cavo;
• ricevere dati via radio dai trasmettitori con codice SMILO, FLO, FLOR, OCODE, per creare archivi degli utenti, programmare le memorie e i ricevitori;
• programmare via radio i trasmettitori della serie “NiceOne”;
• gestire via radio tutte le funzioni dei ricevitori “NiceOne”.
Il software fornito con l’O-Box permette di configurare e programmare i Trasmettitori e i Ricevitori della serie “NiceOne”. Inoltre è compatibile anche con
tutti i dispositivi della serie “FloR”, “SMXI” e “Bio”.
HARDWARE: descrizione del prodotto
e sua installazione
2
1
Page 21
Italiano – 3
IT
peggiante del Led dell’O-BoxB diventi fissa (questo conferma che il collegamento è stato attivato).
Se c’è la necessità di cancellare dalla memoria la lista dei collegamenti ai computer, procedere nel modo seguente:
a) – mantenere premuto sull’O-BoxB il tasto di accensione Activity e attendere
la conclusione di queste fasi: l’O-BoxB emette un segnale acustico (beep) e il
Led si spegne; il Led si accende di nuovo e l’O-BoxB emette una sequenza di
segnali acustici (beep).
b) – A questo punto i dati presenti nella memoria dell’O-BoxB sono stati cancellati e si può quindi rilasciare il tasto di accensione.
2.2 – ACCESSORI (opzionali)
Nota – L’O-Box ha in dotazione solo il cavo USB; tutti gli altri cavi sono opzionali e non presenti nella confezione. Questi cavi sono:
– Cavo mod.
CABLA06 per il connettore D, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per collegare i
ricevitori della serie “SMX” e “NiceOne”.
– Cavo mod.
CABLA02 per il connettore M, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per ricevere i
codici dei trasmettitori della serie “Bio”.
– Cavo seriale a 9 poli, RS232, mod.
CABLA01 per il connettore G, di fig. 2:
utilizzarlo per collegare l’O-Box a un computer.
– Cavo TTBUS, mod.
CABLA05 per il connettore H, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per col-
legare tutti i motori tubolari per tende da sole e tapparelle di Nice, dotati di
porta TTBUS.
– Cavo mod.
CABLA03 per il connettore I, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per collegare i
trasmettitori della serie “Very”.
– Cavo mod.
CABLA02 per il connettore I, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per collegare i
trasmettitori della serie “Bio” e “FloR”.
– Cavo mod.
CABLA04 per il connettore I, di fig. 2: utilizzarlo per collegare i
trasmettitori della serie “Ergo” e “Plano”.
– Alimentatore mod.
ALA1 da 12 V, 300 mA per il connettore E, di fig. 2: utiliz-
zarlo per collegare l’O-Box alla rete elettrica.
2.3 – CONNETTORI E DISPOSITIVI COLLEGABILI ALL’O-BOX
L’O-Box dispone di vari tipi di connettori (vedere fig. 2) ai quali è possibile collegare molti dispositivi prodotti da Nice. Nota – Alcuni di questi connettori han-
no bisogno di un cavo di connessione specifico: per il modello e le caratteristiche di ciascun cavo, vedere il paragrafo 2.2.
Facendo riferimento alle lettere che identificano nella fig. 2 i connettori e gli altri
dispositivi dell’O-Box, ecco in dettaglio una panoramica sulla loro funzionalità e
utilizzo:
[A] – Tasto di accensione e spegnimento dell’O-Box
Per accendere l’O-Box tenere premuto il pulsante di accensione per alcuni
istanti fino ad udire un suono breve (beep).
Per spegnere l’O-Box tenere premuto il pulsante di accensione per alcuni istanti fino ad udire un suono lungo (beeeeeep).
[B] – Area per il collegamento via radio dei trasmettitori
della serie “NiceOne”
Questa area di appoggio permette di programmare via radio, cioè senza il collegamento fisico, i trasmettitori della serie “NiceOne” di Nice: la programmazione si effettua appoggiando il trasmettitore sulla zona di superficie delimitata dal
segno grafico.
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 22
4 – Italiano
IT
Durante l’utilizzo del software, il Led del trasmettitore emette un lampeggio che
indica l’attivazione della comunicazione via radio con il software stesso. A questo punto è possibile iniziare a lavorare con il software sui parametri del trasmettitore (vedere capitolo 3.3).
[C] – Connettore per le schede di Memoria “BM”
Questo connettore permette di collegare all’O-Box le schede di memoria “BM”
di Nice. Per connettere una scheda, innestarla direttamente sul connettore e
procedere poi a lavorare con il software (vedere capitolo 3.3).
[D] – Connettore di tipo “SM”
Questo connettore permette di collegare all’O-Box solo i ricevitori della serie
“SM” e “NiceOne” di Nice. Alcuni di questi ricevitori possono essere innestati
direttamente sul connettore, altri hanno bisogno del cavo mod. CABLA06. Dopo
l’innesto, si può procedere a lavorare con il software (vedere capitolo 3.3).
Nota – I ricevitori della serie “NiceOne” (OXIT e OX2T) sono predisposti per
comunicare con il software anche via radio. In questo caso, però, la trasmissione dati è più lenta di quella effettuata attraverso il connettore SM.
[E] – Connettore per l’alimentatore esterno, mod. ALA1
Questo connettore permette di collegare l’O-Box alla rete elettrica tramite un
alimentatore esterno da 12 Vcc (accessorio opzionale).
Nota – Anche se l’O-Box è spento, la batteria presente all’interno si ricarica
ogni volta che il cavo di alimentazione viene collegato alla rete elettrica.
[F] – Connettore per il cavo “USB”
Questo connettore permette di collegare l’O-Box alla porta USB di un computer, tramite il cavo USB. Subito dopo sarà possibile avviare il software per una
sessione di lavoro.
Nota – Anche se l’O-Box è spento, la batteria presente all’interno si ricarica
ogni volta che il cavo USB viene collegato a un computer acceso.
[G] – Connettore seriale “RS232” (cavo tipo mod. CABLA01)
Questo connettore permette di collegare l’O-Box alla porta seriale RS232 di un
computer, tramite il cavo seriale RS232 (accessorio opzionale). Subito dopo
sarà possibile avviare il software per una sessione di lavoro.
[H] – Connettore “TTBUS” (cavo tipo mod. CABLA05)
Questo connettore permette di collegare all’O-Box tutti i motori tubolari per tende da sole e tapparelle di Nice, dotati di porta TTBUS, tramite l’apposito cavo
(accessorio opzionale).
[I] – Connettore per clonazione trasmettitori (cavo tipo mod.
CABLA03 - CABLA02 - CABLA04)
Questo connettore permette di collegare all’O-Box i trasmettitori Nice della
serie “Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano” e “Very”, tramite il cavo dedicato (accessorio opzionale). Per effettuare il collegamento aprire il trasmettitore per
innestare il cavo di collegamento(*) e collegare l’altro capo al connettore
sull’O-Box (I in fig. 2).
(*) Nota:
– per i trasmettitori della serie “Ergo” e “Plano” usare il cavo mod. CABLA04
– per i trasmettitori della serie “Bio” e “FloR” usare il cavo mod. CABLA02
– per i trasmettitori della serie “Very” usare il cavo mod. CABLA03
[L] – Lettore di prossimità per card a transponder
Questo lettore di prossimità permette di leggere (card blu e card grigia) o di scrivere (card grigia) i codici contenuti nelle card a transponder di Nice. Per stabilire il collegamento è necessario posizionare la card davanti al lettore.
[M] – Connettore per lettore ottico per trasmettitori
della serie “Bio”
Questo lettore permette di leggere il codice radio dei trasmettitori della serie “Bio”.
Per stabilire il collegamento è necessario innestare il lettore ottico (accessorio
opzionale, mod. CABLA02) nell’apposito connettore (M in fig. 2) e avvicinare il
Led del trasmettitore alla testina del lettore ottico.
Page 23

Italiano – 5
IT
Il software presente nel CD di installazione “O-Box Software Suite” è fornito in
due versioni:
• “O-Box Desktop” destinato all’installazione in un personal computer (PC)
• “O-Box Mobile” destinato all’installazione in computer palmare (PDA).
REQUISITI MINIMI DEL SISTEMA
Per usare questo software è necessario installarlo su un computer e, se lo si
desidera, su un palmare di qualsiasi marca e modello, con i seguenti requisiti
minimi:
VERSIONE PER PC:
– Processore: tipo AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Consigliato da Nice: tipo
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– Memoria RAM: 128 MB Consigliato da Nice: 256 MB
– Spazio libero su disco: 30 MB Consigliato da Nice: 100 MB
– Sistema operativo: Windows
®
98 SE Consigliato da Nice: Windows
®
2000 o successivi
– Scheda video: 800 x 600, con 256 colori
– Unità disco: CD-Rom (necessaria per l’installazione)
Nota – L’installazione del software comprende l’installazione del programma
Microsoft
®
.NET Framework Redistributable 2.0.
VERSIONE PER PALMARE:
– Processore: (300 MHz) Consigliato da Nice:
(maggiore di 300 MHz)
– Memoria RAM: 64 MB Consigliato da Nice: 128 MB
– Memoria archiviazione: 5 MB Consigliato da Nice: 100 MB
– Sistema operativo: Windows
®
Mobile Consigliato da Nice: Windows
®
2003 o 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE o successivi
– Connessione: Bluetooth
®
– Risoluzione video: 240 x 320 con 256 colori
– Pc con: CD-Rom (necessario per l’installazione del software nel palmare)
Nota – L’installazione del software comprende l’installazione del programma
Microsoft
®
.NET Framework Redistributable 2.0.
SOFTWARE: descrizione e uso del prodotto
3
3.1 – INSTALLAZIONE DEL SOFTWARE
L’installazione del software è simile a quella di un qualsiasi altro programma per
computer.
Dopo aver inserito il CD di installazione, il software di installazione si avvia automaticamente. Se questo non avviene, fare doppio clic sull’icona del programma “Setup.exe” e seguire le istruzioni dell’installazione guidata.
Nota – Prima di iniziare l’installazione del software si consiglia scollegare l’OBox dal computer.
BREVE PANORAMICA SUL SOFTWARE: Struttura e argomenti
• Schermata iniziale (home page)
Dopo aver avviato il software, viene visualizzata la “Home page”, cioè la schermata iniziale (vedere fig. 3) che contiene i seguenti argomenti:
[1] – Indica lo stato del collegamento del computer palmare: cliccando su que-
sta icona si attiva la sincronizzazione del palmare.
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 24
6 – Italiano
IT
[2] – Indica lo stato della batteria e lo stato del collegamento con l’O-Box: in
caso di errore di connessione, cliccando su questa icona il software esegue una nuova connessione all’O-Box.
[3] – Pannello “Selezione impianto”: permette di scegliere all’avvio di una ses-
sione di lavoro la modalità operativa desiderata, agevolando le scelte successive.
Se dopo la programmazione di un ricevitore si desidera salvare i dati di
configurazione solo nella sua memoria o in un file, selezionare l’opzione
“Lavorare senza la creazione di un impianto”.
Se invece, dopo la programmazione di un ricevitore si desidera salvare i
dati di configurazione oltre che nella sua memoria e in un file, anche in una
scheda riassuntiva dell’impianto in cui il ricevitore verrà usato, selezionare
l’opzione “Lavorare sull’ultimo impianto” o “Selezionare o creare un
impianto” (fare riferimento al paragrafo 3.5.1).
[4] – Indica l’accesso all’area operativa dedicata alla programmazione dei Tra -
smettitori.
[5] – Indica l’accesso all’area operativa dedicata alla programmazione dei
Ricevitori.
[6] – Indica l’accesso all’area operativa dedicata alla gestione degli Impianti.
[7] – Indica l’accesso all’area operativa dedicata alle Impostazioni del software.
[8] – Indica il pulsante da premere per uscire dal software.
[9] – Indica lo spazio in cui appaiono i dati per personalizzare il software
(...nome dell’utente ecc.).
• Schermata tematica
Dalla schermata iniziale si sceglie l’area tematica che interessa (“Trasmettitori”,
“Ricevitori”, “Impianti”, “Impostazioni”) e, cliccando sulla relativa icona, si
accede alla schermata tematica dell’area scelta, in cui poter eseguire tutte le
operazioni desiderate. (Nota – ciascuna area tematica può sviluppare l’argo-
mento in una o più schermate successive). Queste schermate sono composte
tipicamente dai seguenti elementi (vedere fig. 4):
[a] – Barra di navigazione.
[b] – Menu delle funzioni
[c] – Area con i dati generali del dispositivo collegato
[d] – Area per la programmazione
Elementi presenti nella Barra di navigazione
La “Barra di navigazione” presente in ciascuna schermata tematica permette di
spostarsi da una schermata all’altra e permette di capire in ogni istante in quale area si sta operando.
Le funzioni tipiche della barra di navigazione sono:
–“Inizio” = cliccando su questa icona si ritorna alla Schermata iniziale
–“Indietro” = cliccando su questa icona si ritorna alla schermata precedente
–“Avanti” = cliccando su questa icona si passa alla schermata successiva
–“Aiuto” = cliccando su questa icona si visualizza il presente manuale
d’istruzioni
–“Ricarica” = in alcune schermate, ciccando su questa icona si ricaricano e si
aggiornano i dati.
IMPORTANTE – In alcune schermate, oltre a queste funzioni “standard”, possono essere presenti altre funzioni specifiche riguardanti il dispositivo che si sta
programmando.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 25
Italiano – 7
IT
3.2 – COME INIZIARE UNA SESSIONE DI LAVORO
Per iniziare una sessione di lavoro effettuare le seguenti operazioni:
– accendere l’O-Box;
– collegare all’O-Box un dispositivo sul quale si intende lavorare;
– avviare il software (si apre la schermata principale);
– premere sulla schermata iniziale
il pulsante dell’area tematica prescelta;
– operare sulle schermate tematiche
successive.
Per accedere a questa area tematica, collegare prima all’O-Box un trasmettitore sul quale si vuole operare e poi procedere nel modo seguente.
01. Nella schermata iniziale
cliccare sull’icona “Trasmettitori” (fig. 3).
02. Appare una prima schermata dell’area tematica “Trasmettitori” (fig. 5):
selezionare la famiglia e il modello del trasmettitore che si vuole program-
mare e cliccare su “Avanti” (nella barra di navigazione) per passare alla
schermata successiva in cui programmare il trasmettitore.
Nota – Solo per i trasmettitori NiceOne: se il trasmettitore viene posizio-
nato nell’area di programmazione dell’O-Box prima
di accedere all’area
tematica “Trasmettitori”, il software riconosce automaticamente il modello
del trasmettitore e ne visualizza i dati, compreso il codice d’identità e il
codice RND.
Se, invece, il trasmettitore viene posizionato sull’O-Box dopo
essere
entrati nell’area tematica “Trasmettitori”, occorre cliccare sull’icona “Ricarica” per far si che il software riconosca il modello del trasmettitore e ne
visualizzi i dati.
03. Appare una seconda schermata dell’area “Trasmettitori”, dedicata alla
programmazione (fig. 6): quindi, selezionare nel Menu delle Funzioni la
funzione desiderata e lavorare nell’area operativa dedicata a modificare,
aggiungere ecc. i parametri desiderati.
IMPORTANTE – Alcune funzioni offrono la possibilità di programmare in
sequenza diversi trasmettitori, semplicemente collegando all’O-Box un
trasmettitore di seguito all’altro. La conferma dell’avvenuta programmazione e il segnale che si può cambiare il trasmettitore con uno successivo
da programmare è dato da due suoni (beep).
3.3 – AREA TEMATICA “TRASMETTITORI”
5
6
Page 26

8 – Italiano
IT
Il menu delle funzioni è suddiviso in 3 sezioni che sono: Codici; Certificati;
Avanzate (fig. 4). Importante – Le funzioni disponibili in ciascuna sezione
variano in base al tipo di trasmettitore che si desidera programmare.
–– CODICI ––
Questa sezione permette di impostare i codici di un trasmettitore e presenta le
seguenti funzioni:
– Prova Trasmettitore
: questa funzione permette di verificare il corretto funzio-
namento del trasmettitore e di visualizzare il codice d’identità e la parte variabile del codice RND.
– Cambio Codice: questa funzione permette di cambiare il codice di identità
originale di un trasmettitore.
IMPORTANTE – Per programmare più trasmettitori in sequenza con codici in
progressione, occorre cliccare sull’icona “Programma Sequenza”; compilare
due dei seguenti campi: “A Codice”, “Step” (cioè l’incremento del codice tra un
trasmettitore ed un altro) e “N° codici”; infine, cliccare su “Verifica”. A questo
punto il software completa automaticamente il campo lasciato vuoto precedentemente.
– Ripristina Codice: questa funzione permette di ripristinare il codice originale
(di fabbrica) del trasmettitore.
–– CERTIFICATI ––
Questa sezione permette di impostare i certificati di un trasmettitore e presenta le seguenti funzioni:
– Imposta Certificati
: questa funzione permette di inserire il “Certificato” di un
ricevitore in un trasmettitore. Per ogni Certificato è possibile impostare la
memorizzazione nel tasmettitore in “Modo I” o in “Modo II”.
Nel caso della memorizzazione in “Modo II” (ogni tasto del trasmettitore corrisponde ad una funzione specifica del ricevitore) basta selezionare, con dei
semplici clic, alla voce “Funzione” il numero della funzione desiderata e di
seguito, selezionare alla voce “Pulsanti” il tasto che si desidera memorizzare sul
trasmettitore.
Nota – La varietà dei comandi a disposizione per la memorizzazione del trasmettitore dipende dal tipo di trasmettitore e dal modello di Centrale con la
quale si utilizzerà questo trasmettitore. La lista dettagliata dei comandi è riportata nel manuale istruzioni della stessa Centrale.
– Rimuovi Certificati
: questa funzione permette di rimuovere tutti i Certificati
dal trasmettitore.
–– AVANZATE ––
Questa sezione permette di impostare le chiavi di protezione ed i parametri
di funzionamento di un trasmettitore: presenta le seguenti funzioni:
– Imposta Chiavi
: questa funzione permette di personalizzare un trasmettitore;
cioè, di modificare le chiavi di protezione “Installatore”, “Installazione” e “Altera”.
In particolare, “Altera” è compatibile con i precedenti sistemi “FloR”.
Attenzione! – Non dimenticare la nuova chiave di protezione altrimenti il tra-
smettitore non è più utilizzabile con quel ricevitore.
– Impostazioni Avanzate: Questa funzione permette di impostare i seguenti
parametri:
Numero trame: permette di variare il numero di ripetizioni del codice
d’identità, quando questo viene trasmesso. È utile modificare questo parametro per particolari automazioni che richiedono tempi di risposta ad un
comando inviato, più veloci di quelli impostati in fabbrica.
Priorità: permette di sostituire un trasmettitore esistente, mantenendo il
suo codice d’identità. Questo si ottiene aumentando di una unità la priorità
del NUOVO trasmettitore, rispetto a quello VECCHIO.
Abilita RND: permette l’abilitazione o disabilitazione della gestione della
parte variabile del codice d’identità (RND).
Passaggio codice abilitazione: permette al trasmettitore la facoltà o
meno di trasferire in un altro trasmettitore il proprio Codice di abilitazione.
Copia tra modelli differenti: permette l’abilitazione o disabilitazione della
copia dei “codici di abilitazione” tra modelli di trasmettitori diversi tra loro.
Abilita Repeater: permette l’abilitazione o la disabilitazione della gestione
della ripetizione del codice nei ricevitori dotati della funzione “Repeater”.
Nota – Cliccando sul pulsante “Valori di fabbrica” è possibile impostare i valori
di fabbrica dei parametri sopra citati (“Impostazioni Avanzate”).
– Tutto Originale
: questa funzione permette di riportare un trasmettitore alla
configurazione impostata in fabbrica: cioè viene ripristinato il codice d’identità originale, vengono rimossi i certificati e vengono ripristinati i valori dei vari
parametri.
Importante – Per motivi di sicurezza, questa funzione non modifica il valore del-
le chiavi di protezione, cioè non riporta il valore a quello originale.
Page 27
Italiano – 9
IT
- Programmazione Guidata: questa funzione permette di programmare un
trasmettitore utilizzando in sequenza tutte le sezioni sopra descritte.
Per accedere a questa area tematica, collegare prima all’O-Box un ricevitore
sul quale si vuole operare e poi procedere nel modo seguente.
01. Nella schermata iniziale
cliccare sull’icona “Ricevitori” (fig. 3).
02. Appare una prima schermata dell’area “Ricevitori” (fig. 7): selezionare la
famiglia e il modello del ricevitore che si vuole programmare (il sistema
controlla se ci sono ricevitori di quella famiglia collegati all’O-Box e mostra
automaticamente il modello. È comunque possibile scegliere manualmente il modello). Quindi, sulla barra di navigazione, cliccare su “Avanti” per
passare alla schermata successiva.
Nota – Se si sta programmando un ricevitore della serie “NiceOpera” è
necessario selezionare il tipo di connessione adottata: wireless (in questo
caso è necessario digitare il certificato del ricevitore) o connettore su OBox (in questo caso utilizzare il connettore SM).
03. Dopo aver selezionato la famiglia del ricevitore appare una seconda scher-
mata dal titolo “Cosa volete fare?”, che chiede quale operazione si inten-
de svolgere (fig. 8):
• Configurare un nuovo ricevitore
(questa operazione permette di configu-
rare un nuovo ricevitore).
• Leggere e modificare i dati di un ricevitore
(questa operazione permette
di leggere e di modificare i dati di un ricevitore, salvando di volta in volta
solo le eventuali modifiche apportate).
• Cancellare tutti i dati da un ricevitore
(questa operazione formatta intera-
mente i dati di un ricevitore).
• Ricercare e modificare codici in memoria
(operazione presente solo per i
ricevitori della famiglia “NiceOne”. L’operazione permette di agire direttamente sulla memoria del ricevitore).
04. Infine, appare una terza schermata dedicata alla programmazione (fig. 9).
In questa, selezionare nel Menu delle Funzioni la funzione desiderata e
lavorare nell’area operativa dedicata a modificare, aggiungere, ecc. i parametri desiderati.
3.4 – AREA TEMATICA “RICEVITORI”
7
8
Page 28

10 – Italiano
IT
9
Il menu delle funzioni è suddiviso in 3 sezioni che sono: Codici in memoria; Impostazioni; Importa / Esporta.
–– CODICI IN MEMORIA ––
In questa sezione è possibile modificare, in tutti i tipi di ricevitore, i codici contenuti nella memoria. Per fare questo basta cliccare sulla funzione “Modifica
Codici” ed accedere alle seguenti opzioni:
Aggiungi codice
: permette di aggiungere un codice alla memoria digitan-
do manualmente questo codice.
Aggiungi Sequenza
: permette di aggiungere alla memoria di un ricevitore
una sequenza di codici, compilando due dei seguenti campi “codice di partenza”, “codice di arrivo” e “passo tra un codice e l’altro”, e infine, cliccare su
“Verifica”, automaticamente viene completato il campo lasciato vuoto precedentemente.
Aggiungi da TX
: permette di inserire nella memoria di un ricevitore il codi-
ce di un trasmettitore, semplicemente premendo un tasto di quest’ultimo.
Cancella Codice
: permette di eliminare dalla memoria di un ricevitore, uno
o più codici.
Cerca
: permette di trovare il codice di un trasmettitore, semplicemente
digitando il codice dentro l’apposito spazio, oppure premendo un tasto qualsiasi sul trasmettitore.
–– IMPOSTAZIONI ––
In questa sezione, utilizzando le funzioni presenti (“Certificati” - “Chiavi” “Impostazioni Avanzate” - “Cambio Password”), è possibile modificare i
parametri contenuti in alcune famiglie di ricevitori. Le funzioni disponibili variano
in base al tipo di ricevitore o di memoria che si desidera programmare: per
approfondire queste funzioni, suddivise per famiglia di ricevitori, fare riferimento
al paragrafo 3.4.1.
–– IMPORTA / ESPORTA ––
In questa sezione, utilizzando le funzioni presenti (“Leggi da file” - “Salva su
file” - “Copia”), è possibile importare, esportare, salvare e ripristinare i dati con-
tenuti in un ricevitore. Le funzioni disponibili sono:
Leggi da File
: permette di leggere un file (ad esempio con estensione
“.cor”) creato con il software di gestione dell’unità di programmazione BUPC
oppure creato con la funzione “Salva su File” presente in questa sezione.
Salva su File
: permette di scrivere su un file il contenuto della memoria di
un ricevitore, in modo da poterlo successivamente leggere con la funzione
“Leggi da File” presente in questa sezione. È anche possibile salvare un file in
un formato precedente, ad esempio con estensione “.cor” (previsto dalla
linea BUPC) oppure nel nuovo formato (operazione consigliata).
Copia
: permette di copiare il contenuto della memoria di un ricevitore nel-
la memoria del computer.
Incolla
: permette di incollare nella memoria di un ricevitore i dati contenuti
nella memoria del computer, salvati precedentemente con la funzione
“Copia”, presente in questa sezione.
3.4.1 – Sezione IMPOSTAZIONI: Memorie “BM” e Ricevitori
“NiceOne” (famiglia OXI... ; famiglia OX...)
La sezione “Impostazioni” permette di impostare i parametri di funzionamento
di un ricevitore della serie “NiceOne” e di un ricevitore con memoria “BM”,
gestendone le funzioni avanzate.
Page 29
Italiano – 11
IT
MEMORIE BM
• Impostazioni Avanzate: questa funzione permette di impostare i seguenti
parametri.
Blocco Memoria
: attiva il blocco delle operazioni di autoapprendimento
della scheda di memoria, quando questa verrà inserita nel proprio ricevitore.
Cioè, in un ricevitore nel quale è presente una memoria “Bloccata”, non si
possono inserire nuovi codici, e il funzionamento è limitato ai soli codici esistenti (fare riferimento anche alle istruzioni proprie del ricevitore).
Password
: permette di inserire nella scheda di memoria una “Password”
(parola d’ordine); cioè, un codice numerico accessibile via software solo dai
possessori di tale codice, con il quale controllare e limitare l’accesso ai dati
contenuti nella scheda di memoria. La password verrà richiesta ogni volta
che si vorrà accedere al contenuto della memoria, per leggere o modificare i
dati e i codici presenti.
La Password NON permette di apportare modifiche ai dati contenuti nella
scheda di memoria quando questa è inserita in un ricevitore: blocca tutte le
funzioni programmabili manualmente sul ricevitore che ospita questa memoria.
Timer
: permette di modificare il tempo del timer. Il tempo è visualizzato in
“ore”, “minuti” e “secondi”.
Altera
: è una chiave che permette di personalizzare un ricevitore; questa
chiave è compatibile con i precedenti sistemi “FloR”.
Attenzione! – Non dimenticare la nuova chiave di protezione altrimenti il ricevitore non è più utilizzabile.
Controllo RND
: permette di attivare o disattivare il controllo della parte
variabile del codice d’identità (RND) in un ricevitore.
Finestra RND
: permette di modificare la finestra RND di un ricevitore.
Questa finestra rappresenta la porzione di valori entro i quali viene accettata
la parte variabile del codice d’identità (RND).
Nota – Normalmente il valore della finestra è 100 e può avere un valore da
5 a 250.
Sincronismo
: permette di attivare o disattivare la ri-sincronizzazione in un
ricevitore. Se il sincronismo è disattivato la sicurezza dell’impianto è maggiore, ma se un trasmettitore dovesse uscire dalla finestra RND, sarà necessario memorizzare nuovamente il codice d’identità nella memoria del ricevitore.
Solo Nativi
: permette di abilitare o di disabilitare il ricevitore alla ricezione
dei comandi inviati da un trasmettitore con un codice modificato rispetto a
quello standard di fabbrica.
RICEVITORI “NiceOne”
Le funzioni disponibili sono le seguenti:
• Certificati: questa funzione permette di leggere ed impostare i certificati di un
ricevitore (fino a un massimo di 4). In ordine, partendo dall’alto, si trova il certificato del ricevitore (contenuto nella card presente nella confezione) e di seguito
altri 3 spazi utilizzabili per creare dei gruppi di ricevitori.
Nota – Per un approfondimento sull’utilizzo dei certificati, fare riferimento al
manuale “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Chiavi: questa funzione permette di personalizzare un ricevitore, con la pos-
sibilità di variare le chiavi “Installatore”, “Installazione” e “Altera”. In particolare,
“Altera” è compatibile con i precedenti sistemi “FloR”.
Attenzione! – Non dimenticare la nuova
chiave di protezione altrimenti il ricevi-
tore non è più utilizzabile.
Le chiavi sono utili per personalizzare un sistema: cioè, è possibile modificare il
codice originale (di fabbrica) di un trasmettitore. Per questo motivo le chiavi
devono essere le stesse sia sul trasmettitore sia sul ricevitore. In questo caso è
necessario variare anche le chiavi dell’OBox, questo per poterla utilizzare successivamente.
• Impostazioni Avanzate: questa funzione permette di impostare i seguenti
parametri.
Impostazioni di Base
- Abilita solo TX originali: questa funzione permette di abilitare o disabilitare il funzionamento di un ricevitore che riceve il comando da trasmettitori il
cui codice è stato cambiato, cioè, non è più quello di fabbrica.
- Disabilita RND: questa funzione permette di attivare o disattivare il controllo della parte variabile del codice d’identità (RND) presenti in un ricevitore.
Impostazioni di Memorizzazione
- Blocco memorizzazione tramite “Codice di abilitazione”: questa funzione permette di bloccare la memorizzazione di un nuovo trasmettitore utilizzando il “Codice di abilitazione” di un vecchio trasmettitore (già memorizzato). Questa procedura può essere utilizzata solo se si utilizzano due trasmettitori con codifica “O-Code”.
- Blocco memorizzazione tramite “Certificato”: questa funzione permette
di bloccare la memorizzazione di un nuovo trasmettitore utilizzando il certificato di un ricevitore.
Page 30
12 – Italiano
IT
- Blocco memorizzazione a distanza: questa funzione permette di bloccare la memorizzazione di un nuovo trasmettitore utilizzando un vecchio trasmettitore, con la procedura “in vicinanza del trasmettitore”.
Impostazioni BUS T4
Nota – Il “Bus” è un sistema che permette di collegare fra loro tutti i dispositivi presenti in un impianto di automazione, mediante un cavo unico con alcuni fili elettrici all’interno. In questo tipo di collegamento la comunicazione dei
dati fra i dispositivi avviene utilizzando un protocollo specifico che, nel nostro
caso, e il “Bus T4” di Nice.
- Abilita ripetizione del codice via bus: questa funzione permette di abilitare in un ricevitore la possibilità di trasferire ad altri dispositivi collegati, attraverso il cavo bus T4, la copia di un codice ricevuto da un trasmettitore tramite segnale radio.
- Abilita ricezione del codice via bus: questa funzione permette di abilitare
su un ricevitore la ricezione di un codice, trasmesso attraverso il cavo bus T4
da un altro ricevitore (fare riferimento al punto precedente “Abilita ripetizione
del codice via bus”).
- Abilita gruppi di autorizzazione: questa funzione permette di abilitare la
gestione, in gruppi di autorizzazione, dei codici radio.
Impostazioni Avanzate
- Attiva “Repeater”: questa funzione permette di abilitare la ripetizione di un
codice. Se c’è la necessità di comandare un’automazione da una distanza
superiore a quella normalmente coperta dal trasmettitore e dal ricevitore, è
possibile utilizzare un secondo ricevitore con il compito di ritrasmettere a sua
volta, via radio, il comando verso il ricevitore destinatario (in cui è memorizzato il codice di identità del trasmettitore da cui è partito il comando), in modo
che quest’ultimo possa eseguire il comando.
- Attiva gestione rilascio tasto: durante l’utilizzo di un trasmettitore, dopo
aver inviato un comando, al rilascio del tasto la manovra non si ferma in quel
preciso istante ma prosegue ancora per un tempo brevissimo prefissato. Se
c’è la necessità di far interrompere la manovra esattamente nell’istante in cui
si rilascia il tasto del comando sul trasmettitore (ad esempio, durante le regolazioni minimali), è necessario attivare nel ricevitore questa funzione.
- Disabilita gestione priorità: questa funzione permette di disabilitare in un
ricevitore la ricezione di comandi inviati da trasmettitori con priorità maggiore
di 0.
Nota – Per un approfondimento sull’utilizzo di tutte le funzioni descritte, fare
riferimento al manuale “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Cambio Password: questa funzione permette di immettere una password
che serve per bloccare l’accesso, anche manuale, a tutte le funzioni contenute
in un ricevitore, da parte di chi non possiede tale password.
L’area tematica “Impianti” è uno schedario che permette di creare e archiviare,
per ogni impianto, una scheda analitica che raccoglie i dati anagrafici del cliente e le configurazioni dei ricevitori installati presso il suo impianto. In particolare
è possibile modificare gli impianti, visualizzare i codici, le impostazioni e salvare
i dati dei ricevitori installati; in caso di malfunzionamento, è possibile ripristinare
il funzionamento di un’automazione.
Quest’area tematica è composta da due schermate:
– una destinata ricerca veloce e alla selezione degli impianti archiviati;
– l’altra contenente una scheda per la raccolta dei dati relativi a un singolo
impianto.
Per accedere all’area tematica “Impianti” procedere nel modo seguente:
01. Nella schermata iniziale
(fig. 3) cliccare sull’icona “Impianti”.
02. Appare una prima schermata (fig. 10) di gestione degli impianti archiviati.
Questa è composta dai seguenti elementi.
• La “Barra di navigazione” con le seguenti funzioni:
“Modifica”
: permette di modificare i dati di un’impianto.
“Nuovo impianto”: permette di creare un nuovo impianto.
“Copia”: permette di copiare i dati di un’impianto esistente per crear-
ne uno nuovo uguale.
“Elimina”: permette di eliminare uno o più impianti.
• L’area “Filtro su dati” che permette di ricercare in modo semplice e velo-
ce gli impianti registrati.
• L’area “Lista Impianti” che mostra la lista degli impianti registrati.
3.5 – AREA TEMATICA “IMPIANTI”
Page 31

Italiano – 13
IT
10
11
03. A questo punto, selezionando una fra le seguenti funzioni: “Modifica”, “Nuo-
vo impianto” e “Copia”, appare una seconda schermata (fig. 11) con la
scheda relativa a un impianto. Questa è composta dai seguenti elementi.
• La “Barra di navigazione” con le seguenti funzioni:
“Lavora su questo impianto”
: permette di lavorare su un impianto
nuovo o esistente (fare riferimento al paragrafo 3.5.1).
“Salva su File”
: permette di salvare su altri file i dati dei ricevitori da
memorizzare.
“Importa da File”
: permette di leggere da un file i dati di un ricevitore
(fare riferimento al paragrafo 3.5.1).
“Salva Modifiche”
: permette di salvare le modifiche effettuate in una
scheda di un impianto.
Oltre alla barra di navigazione, questa schermata presenta 3 aree operative: Cliente; Chiavi impianto; Ricevitori.
• Cliente: in questa area è possibile inserire i dati anagrafici di un cliente.
• Chiavi impianto: in questa area è possibile utilizzare delle chiavi per per-
sonalizzare un impianto sfruttando i campi “Chiave Installatore”, “Chiave
Installazione” e “Altera”. Queste chiavi sono utili per limitare la gestione
degli impianti unicamente ai possessori delle chiavi. È possibile utilizzare
una stessa chiave su diversi impianti o chiavi diverse per ciascun impianto.
Durante la programmazione dei trasmettitori e dei ricevitori della serie
“Nice Opera”, questi saranno programmati automaticamente con le stes
-
se chiavi impostate nella scheda dell’impianto,
se questa scheda è stata
attivata precedentemente e contiene le chiavi impostate,
Nota – Per un approfondimento sull’utilizzo delle chiavi, fare riferimento al
manuale “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Ricevitori: in questa area sono visualizzati i ricevitori presenti in un
impianto. Per aggiungere o cancellare dei ricevitori, fare riferimento al
paragrafo 3.5.1.
3.5.1 – Aggiungere i ricevitori a un impianto
In generale, per aggiungere uno o più ricevitori all’interno di una scheda di un
impianto è possibile operare in due modi diversi.
• modo diretto
: questa modalità prevede che i dati del ricevitore da aggiunge-
re a un impianto siano già memorizzati su un file. Quindi, nella schermata che
Page 32

14 – Italiano
IT
visualizza la scheda di un impianto, cliccare sulla funzione “Importa da file” (nella barra di navigazione) e selezionare il file che interessa.
• modo indiretto
: questa modalità prevede le seguenti operazioni:
– all’apertura del software si seleziona nel pannello “Selezione impianto” una
tra le funzioni “Lavorare sull’ultimo impianto” e “Selezionare o creare un impianto”; in alternativa, cliccare l’icona “Impianti” nella schermata iniziale.
– appare la schermata di gestione degli impianti archiviati (fig. 10) in cui occorre selezionare l’impianto dove si desidera aggiungere il ricevitore (un impianto
esistente o anche uno nuovo, creato al momento);
– dopo aver confermato la scelta cliccando sull’icona “Lavora su questo
impianto”, il software mostra la schermata iniziale con l’indicazione dell’impianto sul quale si sta lavorando (fig. 12);
– quindi, collegare all’O-Box il ricevitore interessato e attivare l’area tematica
“Ricevitori” per effettuare la programmazione desiderata (fare riferimento al
capitolo 3.4);
– infine, nella stessa schermata, cliccare l’icona “Impianto” e scegliere nel menu
a tendina(*) la voce “Aggiungi a impianto”.
12
(*) Nota – Il menu associato all’icona “Impianto” è dinamico in quanto riporta
voci differenti, secondo le circostanze. In generale le voci sono:
• prima riga: riporta in corsivo il nome dell’impianto attivo; cioè quello nel quale
si può salvare il ricevitore che si sta programmando.
• ultima riga: riportato il comando “Aggiungi a impianto” per salvare il ricevitore
(nuovo) appena programmato.
• altre righe: riportano il nome dei ricevitori eventualmente già presenti nell’im-
pianto. Per modificare uno di questi basta sceglierne il nome e modificarne i
parametri. Infine, per salvare le modifiche apportate, cliccare l’icona “Impianto”
e scegliere nel menu a tendina la voce “Salva modifiche ...” (questa voce è presente solo se nell’impianto attivo sono presenti già dei ricevitori).
Page 33

Italiano – 15
IT
Questo prodotto è parte integrante dell'automazione, e dunque, deve
essere smaltito insieme con essa.
Come per le operazioni d'installazione, anche al termine della vita di questo
prodotto, le operazioni di smantellamento devono essere eseguite da personale qualificato.
Questo prodotto è costituito da vari tipi di materiali: alcuni possono essere riciclati, altri devono essere smaltiti. Informatevi sui sistemi di riciclaggio o smaltimento previsti dai regolamenti vigenti sul vostro territorio, per questa categoria
di prodotto.
Attenzione! – alcune parti del prodotto possono contenere sostanze inquinanti o pericolose che, se disperse nell’ambiente, potrebbero provocare effetti dannosi sull'ambiente stesso e sulla salute umana.
Come indicato dal simbolo a lato, è vietato gettare questo prodotto nei rifiuti domestici. Eseguire quindi la “raccolta separata”
per lo smaltimento, secondo i metodi previsti dai regolamenti
vigenti sul vostro territorio, oppure riconsegnare il prodotto al
venditore nel momento dell'acquisto di un nuovo prodotto
equivalente.
Attenzione! – i regolamenti vigenti a livello locale possono prevedere pesanti
sanzioni in caso di smaltimento abusivo di questo prodotto.
Smaltimento della batteria
La batteria, anche se esaurita, può contenere sostanze inquinanti e quindi,
NON deve essere buttata nei rifiuti comuni. Dopo aver rimosso la batteria dal
prodotto occorre smaltirla secondo i metodi previsti dai regolamenti locali per la
“raccolta separata”.
Smaltimento del prodotto
Tipologia: unità di programmazione e controllo codici per i seguenti prodotti Nice:
• ricevitori della serie “NiceOne” e “SMX”;
• sistemi ricetrasmittenti con codifiche “Bio”, “Flo”, “FloR”, “Smilo”, “O-Code”;
• sistemi di controllo accessi con decoder “Morx”; lettori di card a trasponder “MOM” o
tastiere digitali “MOT”;
• dispositivi che utilizzano il sistema TTBUS.
Tecnologia radio: ricetrasmettitore radio alla frequenza di 433.92 MHz. Portata fino a 10 m.
Connettori e dispositivi collegabili:
• area di appoggio per i trasmettitori della serie “NiceOne” (la programmazione avviene
via radio, senza contatto);
• connettore per schede di memoria “BM 60”, “BM 250”, “BM 1000”;
• connettore per ricevitori della serie “SM” e “NiceOne” (alcuni modelli, tramite cavo adattatore);
• connettore per trasmettitori della serie Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo, Plano (tramite cavo
adattatore);
• connettore per lettore ottico, per trasmettitori della serie “Bio”;
• lettore di prossimità per card a trasponder;
• connettore per dispositivi TTBUS (tramite cavo adattatore).
Connessione al computer:
• connettore per cavo USB;
• connettore per cavo seriale: RS232;
• connessione wireless in tecnologia Bluetooth
®
(solo versione O-BoxB).
Alimentazione:
• Interna
: attraverso la batteria ricaricabile 6 V, 700 mAh.
•Esterna
: attraverso il collegamento USB al computer oppure attraverso l’alimentatore
mod. ALA1, 12 Vdc.
Tempo di ricarica della batteria: circa 15 ore.
Durata della carica della batteria: circa 10 ore di funzionamento oppure 3 mesi in
stand-by.
Vita della batteria: almeno 100 cicli completi di scarica.
Grado di protezione del contenitore: IP 20 (utilizzo solo in ambienti interni e protetti).
Temperatura di esercizio: da -20°C a +55°C
Dimensioni (mm): 194 x 115 x H 40
Peso (gr): 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Caratteristiche tecniche del prodotto
Page 34

16 – Italiano
IT
DICHIARAZIONE CE DI CONFORMITÀ
Dichiarazione CE di conformità secondo Direttiva 1999/5/CE
Nota – La presente Dichiarazione di Conformità raccoglie il contenuto delle singole dichiarazioni di conformità dei singoli prodotti citati; è aggiornata alla data di edizione del presente manuale ed è stata riadattata per motivi editoriali.
Copia della dichiarazione originale per ogni prodotto può essere richiesta a Nice
S.p.a. (TV) I.
______________
Il sottoscritto Lauro Buoro in qualità di Amministratore Delegato, dichiara sotto la propria responsabilità che il prodotto:
Nome produttore: NICE s.p.a.
Indirizzo: Via Pezza Alta, 13, Z.I. Rustignè, 31046 Oderzo
(TV) Italia
Tipo: Programmatore OBOX per radiocomandi con rice-
trasmettitore radio 433,92 MHz e lettore di card a
transponder.
Programmatore OBOXB per radiocomandi con
ricetrasmettitore radio a 433,92 MHz e lettore di
card a transponder. Versione con tecnologia Blue-
tooth
®
Modelli: OBOX, OBOXB
Accessori:
Risulta conforme a quanto previsto dalla seguente direttiva comunitaria:
• 1999/5/CE DIRETTIVA 1999/5/CE DEL PARLAMENTO EUROPEO E
DEL CONSIGLIO del 9 marzo 1999 riguardante le apparecchiature
radio e le apparecchiature terminali di telecomunicazione e il reciproco
riconoscimento della loro conformità, secondo le seguenti norme
armonizzate:
protezione della salute : EN 50371:2002;
sicurezza elettrica : EN 60950-1:2001;
compatibilità elettromagnetica : EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005; EN 301
489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002
spettro radio : EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2 V1.3.1:2006,
EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004
Inoltre, risulta conforme a quanto previsto dalle seguenti direttive comunitarie, così come modificate dalla Direttiva 93/68/CEE del consiglio del
22 Luglio 1993:
• 89/336/CEE; DIRETTIVA 89/336/CEE DEL CONSIGLIO del 3 maggio
1989, per il riavvicinamento delle legislazioni degli Stati membri relative alla compatibilità elettromagnetica, secondo le seguenti norme:
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Amministratore Delegato)
Page 35

Français – 1
FR
FRANÇAIS
LICENCE D’EXPLOITATION DU LOGICIEL
Les programmes « O-Box Software Desktop » et « O-Box Software Mobile »
sont protégés par des lois sur le copyright et sur la propriété intellectuelle ; ces
logiciels ne sont pas vendus mais concédés en licence d’exploitation non
exclusive. Nice s.p.a. continue à être propriétaire de cette copie du programme. Les programmes « O-Box Software Desktop » et « O-Box Software
Mobile » sont concédés en licence, comme produits associés au produit « OBox ».
Ces logiciels sont fournis sans garanties concernant le mode d’utilisation et la
sécurité. D’autre part, Nice s.p.a. n’est pas responsable des dommages
directs ou indirects, y compris des dommages pour manque à gagner, interruptions de travail et similaires, dérivant de l’utilisation erronée de ces logiciels.
INFORMATION SUR LES MARQUES
Les marques AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, MICROSOFT®sont
des marques enregistrées par leurs propriétaires respectifs ; les noms des produits indiqués dans le présent manuel peuvent être enregistrées également par
leurs propriétaires respectifs.
REMARQUE GÉNÉRALE
L’unité de programmation est disponible en deux modèles : OBox et O-BoxB. Ces modèles sont semblables à part la pré-
sence, dans le modèle O-BoxB, d’un module pour la connexion
avec technologie Bluetooth
®
.
Dans ce guide, le terme « O-Box
» est utilisé pour identifier
indistinctement les deux produits, sauf quand une précision différente est donnée.
DESCRIPTION DU PRODUIT ET
TYPE D’UTILISATION
1
Le produit O-Box (ou O-BoxB, version avec module Bluetooth®) est constitué
d’une unité de programmation et d’un logiciel dédié. L’ensemble de ces deux
éléments est destiné à la programmation et à la maintenance des données et
des paramètres contenus dans les dispositifs utilisés dans les installations
d’automatisation de portails, portes de garage, stores, volets roulants, barrières levantes avec lisse mobile et applications similaires.
Toute autre utilisation doit être considérée comme impropre ! Le
constructeur ne répond pas des dommages résultant d’une utilisation
impropre du produit, différente de ce qui est prévu dans cette notice.
L’O-Box et le système « NiceOpera »
L’O-Box est un dispositif qui fait partie du système « NiceOpera ». Ce système
a été conçu par Nice SpA pour simplifier les phases de programmation, d’utilisation et de maintenance des dispositifs présents dans les installations d’automatisation. Le système est constitué de différents dispositifs, logiciels et
matériels, capables d’échanger des données et des informations par radio à
travers un système de codage appelé « O-Code » ou une liaison filaire « phy-
sique ».
Les principaux dispositifs qui composent le système sont les suivants :
– émetteurs NiceOne ;
– récepteurs NiceOne (famille OXI… ; famille OX…) ;
– unité de programmation O-Box ;
– logiques de commande et opérateurs avec « Bus T4 » ;
– programmateur O-View pour dispositifs avec « Bus T4 ».
IMPORTANT – Pour approfondir en détail toutes les fonctions du système NiceOpera et l’interdépendance des différents dispositifs du système, consulter le manuel général « NiceOpera System Book », disponible également sur le site internet www.niceforyou.com
Principales caractéristiques fonctionnelles de l’O-Box
L’utilisation de l’O-Box est particulièrement indiquée dans les installations d’automatisation avec un contenu technologique élevé, car ce dispositif permet
d’effectuer de nombreuses fonctions directement dans le bureau de l’installa-
Page 36

2 – Français
FR
Le produit contient une batterie rechargeable de 6 V, qui lui permet de fonctionner sans être branché au secteur.
Note – La batterie demande un cycle de recharge complet de 10 heures minimum. Le niveau de la charge est indiqué à l’intérieur du logiciel (voir fig. 2).
La batterie se recharge automatiquement à chaque fois que l’O-Box est alimenté avec un bloc d’alimentation extérieur ou par le câble USB..
2.1 – CONNEXIONS
• Connecter l’O-box à l’alimentation électrique.
Le produit peut être alimenté par le secteur électrique, en utilisant un bloc d’ali-
mentation de 12 Vcc (accessoire en option) ou par un ordinateur, en utilisant le
câble USB (inclus dans la fourniture).
• Connecter l’O-Box ad un ordinateur
Pour utiliser l’O-Box (ou l’O-BoxB) il faut le connecter à un ordinateur (PC)
muni d’un port USB, à l’aide du câble fourni, ou muni d’un port série, à l’aide
du câble RS232 (accessoire en option).
Note – Pour cette connexion, il est conseillé d’utiliser la prise USB (si elle est
présente) car elle offre de meilleures performances : elle est plus fiable, plus
rapide dans le transfert des données, n’a besoin d’aucune configuration et permet la recharge automatique de la batterie interne de l’O-Box.
• Connecter l’O-BoxB par Bluetooth
®
Le modèle O-BoxB peut être connecté également par Bluetooth®à un ordinateur de bureau ou de poche (PDA) munis d’une interface
Bluetooth®.
Cette connexion n’a pas besoin de câbles : il suffit d’installer le logiciel sur l’ordinateur de bureau ou sur l’ordinateur de poche et de configurer les données
suivant les caractéristiques de son propre ordinateur de poche.
Note – Avant d’activer la connexion Bluetooth
®
, déconnecter l’O-BoxB du port
USB ou du port série de l’ordinateur.
L’O-BoxB est prévu pour mémoriser jusqu’à 16 connexions avec différents ordinateurs. Pour établir la connexion, il suffit d’allumer l’O-BoxB, de préparer l’ordinateur à la connexion Bluetooth
®
et attendre que la lumière clignotante de la
teur, sans avoir besoin de le faire directement sur l’installation du client ; ou
bien, il permet de configurer l’installation directement chez le client.
Ce produit permet d’administrer et de modifier les installations en utilisant une
archive des données ; on peut effectuer rapidement différentes opérations
comme la remise en service, l’extension des installations existantes, le remplacement des émetteurs, etc.
En général, l’O-Box peut être utilisé pour :
• contrôler, ajouter, programmer ou effacer les codes des émetteurs « Bio »,
« FloR », « Ergo », « Plano », « NiceOne » ;
• programmer les mémoires des récepteurs « Bio » et « FloR » ;
• lire et écrire des cartes à transpondeur ;
• programmer les fonctions et les paramètres caractéristiques des émetteurs
« Bio », « FloR », « Very » ;
• lire optiquement les codes des émetteurs « Bio » ;
• lire et programmer les paramètres caractéristiques des récepteurs « SMX1 »
et « SMX2 » par liaison filaire ;
• recevoir par radio des données de la part d’émetteurs avec code SMILO,
FLO, FLOR, O-CODE, pour créer des archives des utilisateurs, programmer
les mémoires et les récepteurs ;
• programmer par radio les émetteurs de la série « NiceOne » ;
• gérer par radio toutes les fonctions des récepteurs « NiceOne ».
Le logiciel fourni avec l’O-Box permet de configurer et de programmer les
émetteurs et les récepteurs de la série « NiceOne ». De plus, il est compatible
avec tous les dispositifs de la série « FloR », « SMXI » et « Bio ».
MATÉRIEL : description du produit et
de son installation
2
1
Page 37

Français – 3
FR
led de l’O-BoxB devienne fixe (ce qui confirme que la connexion a été activée).
S’il se révèle nécessaire d’effacer de la mémoire la liste des connexions aux
ordinateurs, procéder de la façon suivante :
a) – maintenir enfoncée sur l’O-BoxB la touche d’allumage Activity et attendre
la conclusion de ces phases : l’O-BoxB émet un signal sonore (bip) et la led
s’éteint ; la led se rallume puis l’O-BoxB émet une séquence de signaux
sonores (bips).
b) – Les données qui étaient présentes dans la mémoire de l’O-BoxB sont
maintenant effacées et on peut relâcher la touche d’allumage.
2.2 – ACCESSOIRES (en option)
Nota – L’O-Box est fourni uniquement avec le câble USB ; tous les autres
câbles sont en option et ne sont pas présents dans l’emballage. Ces câbles
sont :
– Câble mod.
CABLA06 pour le connecteur D,de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser pour
connecter les récepteurs de la série « SMX » et « NiceOne ».
– Câble mod.
CABLA02 pour le connecteur M, de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser pour rece-
voir les codes des émetteurs de la série « Bio ».
– Câble série à 9 pôles, RS232, mod.
CABLA01 pour le connecteur G, de la
fig. 1 : l’utiliser pour connecter l’O-Box à un ordinateur.
– Câble TTBUS, mod.
CABLA05 pour le connecteur H, de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser
pour connecter tous les moteurs tubulaires pour stores et volets roulants de
Nice, munis de port TTBUS.
– Câble mod. CABLA03 pour le connecteur I, de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser pour
connecter les émetteurs de la série « Very ».
– Câble mod.
CABLA02 pour le connecteur I, de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser pour
connecter les émetteurs de la série « Bio » et « FloR ».
– Câble mod.
CABLA04 pour le connecteur I, de la fig. 2 : l’utiliser pour
connecter les émetteurs de la série « Ergo » et « Plano ».
– Alimentation mod.
ALA1 de 12 V, 300 mA pour le connecteur E, de la fig. 2 :
l’utiliser pour connecter l’O-Box au secteur.
2.3 – CONNECTEURS ET DISPOSITIFS POUVANT TRE
CONNECTÉS À L’O-BOX
L’O-Box dispose de différents types de connecteurs (voir fig. 2) auxquels il est
possible de connecter de nombreux dispositifs produits par Nice. Note –
Certains de ces connecteurs ont besoin d’un câble de connexion spécifique :
pour le modèle et les caractéristiques de chaque câble, voir le paragraphe 2.2.
En se référant aux lettres qui identifient dans la fig. 2 les connecteurs et les
autres dispositifs de l’O-Box, voici en détail un panorama sur leur fonction et
leur utilisation :
[A] – Touche d’activation/désactivation de l’O-Box
Pour allumer l’O-Box maintenir la pression sur la touche d’activation pendant
quelques instants jusqu’à l’émission d’un bref bip sonore.
Pour éteindre l’O-Box maintenir la pression sur la touche d’activation pendant
quelques instants jusqu’à l’émission d’un long bip sonore.
[B] – Zone pour la connexion par radio des émetteurs de la série
« NiceOne »
Cette zone d’appui permet de programmer par radio, c’est-à-dire sans
connexion physique, les émetteurs de la série « NiceOne » de Nice : la programmation s’effectue en posant l’émetteur sur la surface délimitée par le signe
graphique.
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 38

4 – Français
FR
Durant l’utilisation du logiciel, la led de l’émetteur émet un clignotement qui
indique l’activation de la communication par radio avec le logiciel proprement
dit. On peut alors commencer à travailler avec le logiciel sur les paramètres de
l’émetteur (voir chapitre 3 paragraphe 3.3).
[C] – Connecteur pour les cartes de mémoire « BM »
Ce connecteur permet de connecter à l’O-Box les cartes de mémoire « BM »
de Nice. Pour connecter une carte, l’embrocher directement sur le connecteur
puis travailler avec le logiciel (voir chapitre 3, paragraphe 3.3).
[D] – Connecteur de type « SM »
Ce connecteur permet de connecter à l’O-Box uniquement les récepteurs de
la série « SM » et « NiceOne » de Nice. Certains de ces récepteurs peuvent être
embrochés directement sur le connecteur, d’autres ont besoin du câble mod.
CABLA06. Après l’avoir embroché on peut travailler directement avec le logiciel (voir chapitre 3, paragraphe 3.3).
Note – Les récepteurs de la série « NiceOne » (OXIT et OX2T) sont prévus pour
communiquer avec le logiciel également par radio. Dans ce cas, toutefois, la
transmission des données est plus lente que celle qui est effectuée à travers le
connecteur SM.
[E] – Connecteur pour l’alimentateur extérieur, mod. ALA1
Ce connecteur permet de connecter l’O-Box au port USB d’un ordinateur, à
l’aide d’un câble USB. Juste après, il sera possible de lancer le logiciel pour
une session de travail.
Note – Même si l’O-Box est éteint, la batterie présente à l’intérieur se recharge
à chaque fois que le câble d’alimentation est connecté au secteur électrique.
[F] – Connecteur pour le câble « USB »
Ce connecteur permet de connecter l’O-Box au port USB d’un ordinateur, à
l’aide d’un câble USB. Juste après, il sera possible de lancer le logiciel pour
une session de travail.
Note - Même si l’O-Box est éteint, la batterie présente à l’intérieur se recharge
à chaque fois que le câble USB est connecté à un ordinateur allumé.
[G] – Connecteur série « RS232 » (câble type mod. CABLA01)
Ce connecteur permet de connecter l’O-Box au port série RS232 d’un ordinateur, à l’aide d’un câble série RS232 (accessoire en option). Juste après, il sera
possible de lancer le logiciel pour une session de travail.
[H] – Connecteur « TTBUS » (câble type mod. CABLA05)
Ce connecteur permet de connecter à l’O-Box tous les moteurs tubulaires pour
stores et volets roulants de Nice, munis de port TTBUS, à l’aide du câble spécifique (accessoire en option).
[I] – Connecteur pour clonage émetteurs (câble type mod.
CABLA03 - CABLA02 - CABLA04)
Ce connecteur permet de connecter à l’O-Box les émetteurs Nice de la série
« Bio », « FloR », « Ergo », « Plano » et « Very », à l’aide du câble dédié (accessoire en option). Pour effectuer la connexion, ouvrir l’émetteur pour brancher le
câble de connexion(*) et connecter l’autre extrémité au connecteur sur l’O-Box
(I - fig. 2).
(*) Note:
– pour les émetteurs de la série « Ergo » et « Plano » utiliser le câble mod.
CABLA04
– pour les émetteurs de la série « Bio » et « FloR » utiliser le câble mod.
CABLA02
– pour les émetteurs de la série « Very » utiliser le câble mod. CABLA03
[L] – Lecteur de proximité pour carte à transpondeur
Ce lecteur de proximité permet de lire (carte bleue et carte grise) ou d’écrire
(carte grise) les codes contenus dans les cartes à transpondeur de Nice. Pour
établir la connexion, il faut positionner la carte devant le lecteur.
[M] – Connecteur pour lecteur optique pour émetteurs de
la série « Bio »
Ce lecteur permet de lire le code radio des émetteurs de la série « Bio ».
Pour établir la connexion, il faut embrocher le lecteur optique (accessoire en
option, mod. CABLA02) dans le connecteur (M dans la fig. 2) et approcher la
led de l’émetteur à la tête du lecteur optique.
Page 39

Français – 5
FR
Le logiciel se trouvant dans le CD d’installation « O-Box Software Suite » est
fourni en deux versions :
• « O-Box Desktop » destiné à l’installation sur un ordinateur de bureau (PC)
• « O-Box Mobile » destiné à l’installation sur un ordinateur de poche (PDA).
CONFIGURATION MINIMALE DU SYSTÈME
Pour utiliser ce logiciel, il faut l’installer sur un ordinateur normal ou, si on le souhaite, sur un ordinateur de poche de n’importe quelle marque et modèle, ayant
la configuration minimale suivante :
VERSION POUR PC:
– Processeur : type AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Conseillé par Nice : type
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– Mémoire RAM : 128 Mo Conseillé par Nice : 256 Mo
– Espace libre sur disque : 30 Mo Conseillé par Nice : 100 Mo
– Système d’exploitation : Windows
®
98 SE Conseillé par Nice : Windows
®
2000 ou versions successives
– Carte vidéo : 800 x 600, à 256 couleurs
– Unité disque : CD-Rom (nécessaire pour l’installation)
Note – L’installation du logiciel comprend l’installation du programme Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
VERSION POUR ORDINATEUR DE POCHE
– Processeur : (300 MHz) Conseillé par Nice :
(supérieur à 300 MHz)
– Mémoire RAM : 64 Mo Conseillé par Nice : 128 Mo
– Mémoire archivage : 5 Mo Conseillé par Nice : 100 Mo
– Système d’exploitation : Windows
®
Conseillé par Nice : Windows
®
Mobile 2003 ou 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE ou versions successives
– Connexion : Bluetooth
®
– Résolution moniteur : 240 x 320, à 256 couleurs
– PC avec : CD-Rom (nécessaire pour l’installation du logiciel dans l’ordinateur de poche)
Note – L’installation du logiciel comprend l’installation du programme Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
LOGICIEL : description et utilisation
du produit
3
3.1 – INSTALLATION DU LOGICIELE
L’installation du logiciel est similaire à celle de n’importe quel autre programme
pour ordinateur.
Après l’introduction du CD d’installation dans le lecteur, le logiciel d’installation
se lance automatiquement. Si ce n’est pas le cas, double-cliquer sur l’icône du
programme « Setup.exe » et suivre les instructions de l’installation guidée.
Note - Avant de commencer l’installation du logiciel il est conseillé de déconnecter l’O-Box de l’ordinateur.
BREF PANORAMA SUR LE LOGICIEL : Structure et contenu
• Page initiale (home page)
Après avoir lancé le logiciel, la « Home page » s’affiche, c’est-à-dire la page initiale (voir fig. 3) qui contient les informations suivantes :
[1] – Indique l’état de connexion de l’ordinateur de poche : en cliquant sur cette
icône la synchronisation de l’ordinateur de poche s’active.
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 40

6 – Français
FR
[2] – Indique l’état de la batterie et l’état de la connexion avec l’O-Box : en cas
d’erreur de connexion, en cliquant sur cette icône le logiciel effectue une
nouvelle connexion à l’O-Box.
[3] – Panneau « Sélection installation » : permet de choisir au démarrage
d’une session de travail la modalité voulue en facilitant les choix successifs.
i après la programmation d’un récepteur on désire sauvegarder les données de configuration uniquement dans sa mémoire ou dans un fichier,
sélectionner l’option « Travailler sans la création d’une installation ».
Si au contraire après la programmation d’un récepteur on désire sauvegarder les données de configuration dans sa mémoire, dans un fichier,
mais aussi dans une fiche récapitulative de l’installation dans laquelle le
récepteur sera utilisé, sélectionner l’option « Travailler sur la dernière installation » ou « Sélectionner ou créer une installation » (se référer au para-
graphe 3.5.1).
[4] – Indique l’accès à la zone dédiée à la programmation des Émetteurs.
[5] - Indique l’accès à la zone dédiée à la programmation des Récepteurs.
[6] - Indique l’accès à la zone dédiée à la gestion des Installations.
[7] - Indique l’accès à la zone dédiée aux Consignes du logiciel.
[8] - Indique la touche à presser pour quitter le logiciel.
[9] - Indique l’espace dans lequel apparaissent les paramètres pour personna-
liser le logiciel (...nom de l’utilisateur etc.)
• Page thématique
À partir de la page initiale on choisit la zone thématique désirée (« Émetteurs »,
« Récepteurs », « Installations », « Consignes ») et, en cliquant sur l’icône
correspondante, on accède à la page thématique de la zone choisie, dans
laquelle on peut effectuer toutes les opérations voulues. (Note – chaque zone
thématique peut développer le thème dans une ou plusieurs pages successives). Ces pages vidéo sont composées typiquement des éléments suivants
(voir fig. 4) :
[a] – Barre de navigation.
[b] – Menu des fonctions
[c] – Zone avec les données générales du dispositif connecté
[d] – Zone pour la programmation
Éléments présents dans la Barre de navigation
La « Barre de navigation » présente dans chaque page thématique permet de
se déplacer d’une page à l’autre et de comprendre à tout moment dans quelle
zone on est en train d’opérer.
Les fonctions typiques de la barre de navigation sont :
–« Début » = en cliquant sur cette icône on revient à la Page initiale
–« En arrière » = en cliquant sur cette icône on revient à la page précédente
–« En avant » = en cliquant sur cette icône on passe à la page successive
–« Aide » = en cliquant sur cette icône on affiche le présent guide d’instruc-
tions
–« Actualiser » = dans certaines pages, en cliquant sur cette icône les don-
nées se mettent à jour.
IMPORTANT – Dans certaines pages, en dehors de ces fonctions « standard »,
il peut y avoir d’autres fonctions spécifiques concernant le dispositif que l’on
est en train de programmer.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 41

Français – 7
FR
3.2 – COMMENT COMMENCER UNE SESSION DE TRAVAIL
Pour commencer une session de travail effectuer les opérations suivantes :
– allumer l’O-Box ;
– connecter à l’O-Box un dispositif sur lequel on veut intervenir ;
– lancer le logiciel (la page principale s’ouvre) ;
– presser dans la page initiale
la touche de la zone thématique choisie ;
– intervenir sur les pages thématiques
successives.
Pour accéder à cette zone thématique, connecter d’abord à l’O-Box un émetteur sur lequel on veut intervenir puis procéder de la façon suivante.
01. Dans la page initiale
cliquer sur l’icône « Émetteurs » (fig. 3).
02. Une première page s’affiche dans la zone thématique « Émetteurs » (fig. 5)
: sélectionner la famille et le modèle d’émetteur que l’on souhaite programmer et cliquer sur « En avant » (dans la barre de navigation) pour passer à la page successive dans laquelle programmer l’émetteur.
Note – Uniquement pour les émetteurs NiceOne : si l’ émetteur est
positionné dans la zone de programmation de l’O-Box avant
d’accéder à
la zone thématique « Émetteurs », le logiciel reconnaît automatiquement le
modèle d’ émetteur et en affiche les données, y compris le code d’identité
et le code RND.
Si au contraire, l’émetteur est positionné sur l’O-Box après
avoir accédé à
la zone thématique « Émetteurs », il faut cliquer sur l’icône « Actualiser »
pour que le logiciel reconnaisse le modèle d’émetteur et en affiche les
données.
03. Une deuxième page s’affiche dans la zone « Émetteurs », dédiée à la pro-
grammation (fig. 6) : sélectionner la fonction désirée dans le Menu des
Fonctions et intervenir dans la zone dédiée aux modifications, ajouts, etc.
des paramètres désirés.
IMPORTANT – Certaines fonctions offrent la possibilité de programmer à
la suite différents émetteurs, simplement en connectant à l’O-Box un
émetteur après l’autre. La confirmation de la programmation et le signal
avertissant que l’on peut passer à un autre émetteur à programmer est
donnée par deux bips sonores.
3.3 – ZONE THÉMATIQUE « ÉMETTEURS »
5
6
Page 42

8 – Français
FR
Le menu des fonctions est subdivisé en 3 sections qui sont : Codes ; Certificats ; Avancées (fig. 4). Important – Les fonctions disponibles dans chaque
section varient suivant le type d’émetteur que l’on souhaite programmer.
–– CODES ––
Cette section permet de configurer les codes d’un émetteur et présente les
fonctions suivantes :
– Essai Émetteur
: cette fonction permet de vérifier le fonctionnement correct
de l’émetteur et d’afficher le code d’identité et la partie variable du code RND.
– Changer le Code : cette fonction permet de changer le code d’identité original d’un émetteur.
IMPORTANT – Pour programmer plusieurs émetteurs à la suite avec des
codes progressifs
, il faut cliquer sur l’icône « Programme Séquence » ; remplir
deux des champs suivants : « Au Code », « Pas » (c’est-à-dire l’incrémentation
du code entre un émetteur et un autre) et « Nombre de codes » ; cliquer ensuite
sur « Vérifier ». Le logiciel complète alors automatiquement le champ laissé
préalablement vide.
– Rétablir le Code : cette fonction permet de rétablir le code d’identité original
(d’usine) de l’émetteur.
–– CERTIFICATS ––
Cette section permet de configurer les certificats d’un émetteur et présente
les fonctions suivantes :
– Configurer Certificats
: cette fonction permet de charger le « Certificat »
d’un récepteur dans un émetteur. Pour chaque certificat, il est possible de
sélectionner la mémorisation dans l’émetteur en « Mode I » ou en « Mode II ».
En cas de mémorisation en « Mode II » (chaque touche de l’émetteur correspond à une fonction spécifique du récepteur) il suffit de sélectionner, avec de
simples clics, dans la rubrique « Fonction » le numéro de la fonction désirée
puis, sélectionner à la rubrique « Touches » la touche que l’on souhaite mémoriser sur l’émetteur.
Note – La variété des commandes à disposition pour la mémorisation de
l’émetteur dépend du type d’émetteur et du modèle de logique de commande
avec laquelle on utilisera cet émetteur. La liste détaillée des commandes figure
dans la notice spécifique de la logique de commande.
– Éliminer les certificats
: cette fonction permet d’effacer tous les certificats
de l’émetteur.
–– AVANCÉES ––
Cette section permet de configurer les clés de protection et les paramètres
de fonctionnement d’un émetteur et présente les fonctions suivantes :
– Configurer les clés
: cette fonction permet de personnaliser un émetteur ;
c’est-à-dire, de modifier les clés de protection « Installateur », « Installation » et
« Altera ». En particulier, « Altera » est compatible avec les précédents systèmes
« FloR ».
Attention ! – Ne pas oublier la nouvelle
clé de protection autrement l’émetteur
n’est plus utilisable avec ce récepteur.
– Consignes avancées
: Cette fonction permet de configurer les paramètres
suivants.
Nombre de trames : permet de modifier le nombre de répétitions du code
d’identité, quand celui-ci est transmis. Il est utile de modifier ce paramètre
pour certains automatismes qui demandent des temps de réponse à une
commande envoyée plus rapides que ceux qui ont été programmés en usine.
Priorité : permet de remplacer un émetteur existant, en maintenant son
code d’identité. Cela s’obtient en augmentant d’une unité la priorité du
NOUVEL émetteur, par rapport à l’ANCIEN.
Activer RND : permet l’activation ou la désactivation de la gestion de la
partie variable du code d’identité (RND).
Passage code d’activation : donne à l’émetteur la faculté de transférer
ou pas dans un autre émetteur son Code d’activation.
Copier entre modèles différents : permet l’activation ou la désactivation
de la copie des « codes d’activation » entre modèles d’émetteurs différents.
Activer le répéteur : permet l’activation ou la désactivation de la gestion de
la répétition du code dans les récepteurs munis de la fonction « Répéteur ».
Note – En cliquant sur la touche « Valeurs d’usine » il est possible de sélectionner
les valeurs d’usine des paramètres susmentionnés («Consignes avancées »).
– Tout Original
: cette fonction permet de rétablir dans un émetteur toute la
configuration effectuée en usine : c’est-à-dire que le code d’identité original et les
valeurs des différents paramètres sont rétablis, et les certificats sont éliminés.
Important – Pour des raisons de sécurité, cette fonction ne modifie pas la valeur
des clés de protection, et ne rétablit donc pas dans ce cas la valeur originale.
Page 43

Français – 9
FR
- Programmation guidée : cette fonction permet de programmer un émetteur
en effectuant l’une après l’autre toutes les sections décrites plus haut.
Pour accéder à cette zone thématique, connecter d’abord à l’O-Box un récepteur sur lequel on veut intervenir puis procéder de la façon suivante.
01. Dans la page initiale
cliquer sur l’icône « Récepteurs » (fig. 3).
02. Une première page s’affiche dans la zone thématique « Récepteurs » (fig.
7): sélectionner la famille et le modèle de récepteur que l’on désire pro-
grammer (le système contrôle s’il y a des récepteurs de cette famille
connectés à l’O-Box et montre automatiquement le modèle. Il est possible
dans tous les cas de choisir manuellement le modèle). Puis, sur la barre de
navigation, cliquer sur « En avant » pour passer à la page successive.
Note – Si on est en train de programmer un récepteur de la série « NiceOpera » il faut sélectionner le type de connexion adoptée : sans fil (dans ce
cas il faut taper le certificat du récepteur) ou connecteur sur O-Box (dans
ce cas utiliser le connecteur SM).
03. Après avoir sélectionné la famille du récepteur une deuxième page s’af-
fiche intitulée « Que voulez-vous faire ? », qui demande quelle opération
on souhaite accomplir (fig. 8):
• Configurer un nouveau récepteur
(cette opération permet de configurer
un nouveau récepteur).
• Lire et modifier les données d’un récepteur
(cette opération permet de
lire et de modifier les données d’un récepteur, en enregistrant à chaque
fois les modifications apportées).
• Effacer toutes les données d’un récepteur
(cette opération formate
entièrement la mémoire d’un récepteur).
• Chercher et modifier les codes mémorisés
(opération présente unique-
ment pour les récepteurs de la famille « NiceOne ». L’opération permet
d’agir directement sur la mémoire du récepteur).
04. Enfin, une troisième page s’affiche, dédiée à la programmation (fig. 9).
Dans cette page, sélectionner la fonction désirée dans le Menu des Fonctions et intervenir dans la zone dédiée aux modifications, ajouts, etc. des
paramètres désirés.
3.4 – ZONE THÉMATIQUE « RÉCEPTEURS »
7
8
Page 44

10 – Français
FR
9
Le menu des fonctions est subdivisé en 3 sections qui sont : Codes
mémorisés ; Consignes ; Importer / Exporter.
–– CODES MÉMORISÉS ––
Dans cette section, il est possible de modifier, dans tous les types de récepteur,
les codes contenus dans la mémoire. Pour cela, il suffit de cliquer sur la fonction « Modifier Codes » et d’accéder aux options suivantes :
Ajouter code
: permet d’ajouter un code à la mémoire en tapant manuel-
lement ce code.
Ajouter Séquence
: permet d’ajouter à la mémoire d’un récepteur une
séquence de codes, en remplissant deux des champs « code de départ »,
« code d’arrivée » et « pas entre un code et l’autre », puis cliquer sur « Vérifier », automatiquement le champ qui était vide se remplit.
Ajouter depuis le TX
: permet d’enregistrer dans la mémoire d’un récepteur le code d’un émetteur, simplement en pressant une touche de ce dernier.
Effacer Code
: permet d’éliminer de la mémoire d’un récepteur, un ou plu-
sieurs codes.
Chercher
: permet de trouver le code d’un émetteur, simplement en
tapant le code dans l’espace prévu à cet effet, ou bien en pressant une
touche quelconque sur l’émetteur.
–– CONSIGNES ––
Dans cette section, en utilisant les fonctions présentes (« Certificats » « Clés » - « Consignes Avancées » - « Changer Mot De Passe »), il est pos-
sible de modifier les paramètres contenus dans certaines familles de récepteurs. Les fonctions disponibles varient suivant le type de récepteur ou de
mémoire que l’on désire programmer : pour approfondir ces fonctions, subdivisées par famille de récepteurs, se référer au paragraphe 3.4.1.
–– IMPORTER / EXPORTER ––
Dans cette section, en utilisant les fonctions présentes (« Lire depuis le
fichier » - « Enregistrer sur le fichier » - « Copier »), il est possible d’importer,
d’exporter, d’enregistrer et de rétablir les données contenues dans un récepteur. Les fonctions disponibles sont :
Lire depuis le fichier
: permet de lire un fichier (par exemple avec extension
« .cor ») créé avec le logiciel de gestion de l’unité de programmation BUPC ou
créé avec la fonction « Enregistrer sur le fichier » présente dans cette section.
Enregistrer sur le fichier
: permet d’écrire sur un fichier le contenu de la
mémoire d’un récepteur, de manière à pouvoir le lire ensuite avec la fonction
« Lire depuis le fichier » présente dans cette section. Il est aussi possible
d’enregistrer un fichier dans un format précédent, par exemple avec extension « .cor » (prévu par la ligne BUPC) ou bien dans le nouveau format (opé-
ration conseillée).
Copier
: permet de copier le contenu de la mémoire d’un récepteur dans
la mémoire de l’ordinateur.
Coller
: permet de coller dans la mémoire d’un récepteur les données
contenues dans la mémoire de l’ordinateur, sauvegardées précédemment
avec la fonction « Copier », présente dans cette section.
3.4.1 – Section CONSIGNES : Mémoires « BM » et Récepteurs
« NiceOne »
(famille OXI... ; famille OX…)
La section « Consignes » permet de configurer les paramètres de fonctionnement d’un récepteur de la série « NiceOne » et d’un récepteur avec mémoire
« BM », en en gérant les fonctions avancées.
Page 45

Français – 11
FR
MÉMOIRES BM
• Consignes avancées : Cette fonction permet de configurer les paramètres
suivants :
Blocage mémoire
: active le blocage des opérations d’auto-apprentissage
de la carte de mémoire, quand celle-ci sera insérée dans son récepteur.
C’est-à-dire que dans un récepteur contenant une mémoire « Bloquée », on
ne peut pas insérer de nouveaux codes, et le fonctionnement est limité uniquement aux codes existants (se référer également aux instructions propres
au récepteur).
Mot de passe
: permet d’insérer dans la carte de mémoire un « Mot De
Passe », c’est-à-dire un code numérique accessible par logiciel uniquement
pour les possesseurs de ce code, avec lequel contrôler et limiter l’accès aux
données contenues dans la carte de mémoire. Le mot de passe sera
demandé à chaque fois que l’on veut accéder au contenu de la mémoire,
pour lire ou modifier les données et les codes présents.
Le mot de passe NE PERMET PAS de modifier les données contenues dans
la carte de mémoire quand elle est insérée dans un récepteur : il bloque
toutes les fonctions programmables manuellement sur le récepteur dans
lequel cette mémoire est insérée.
Temporisateur
: permet de modifier le temps du temporisateur. Le temps
es affiché en « heures », « minutes » et « secondes ».
Altera
: c’est une clé qui permet de personnaliser un récepteur ; cette clé
est compatible avec les précédents systèmes « FloR ».
Attention ! – Ne pas oublier la nouvelle clé de protection autrement le récepteur n’est plus utilisable.
Contrôle RND
: permet d’activer ou de désactiver le contrôle de la partie
variable du code d’identité (RND) dans un récepteur.
Plage RND
: permet de modifier la plage RND d’un récepteur. Cette plage
représente la plage des valeurs à l’intérieur de laquelle la partie variable du
code d’identité (RND) est acceptée.
Note – Normalement la valeur est 100 et peut varier de 5 à 250.
Synchronisme
: permet d’activer ou de désactiver la resynchronisation
dans un récepteur. Si le synchronisme est désactivé la sécurité de l’installation est supérieure, mais si un émetteur devait sortir de la plage RND, il faudra mémoriser de nouveau le code d’identité dans la mémoire du récepteur.
Originaux uniquement
: permet d’activer ou de désactiver le récepteur à
la réception des commandes envoyées par un émetteur avec un code modifié par rapport au code standard d’usine.
RÉCEPTEURS NiceOne
Les fonctions disponibles sont les suivantes :
• Certificats : cette fonction permet de lire et de configurer les certificats d’un
récepteur (jusqu’à un maximum de 4). Dans l’ordre, en partant du haut, on
trouve le certificat du récepteur (contenu dans la carte présente dans l’emballage) puis 3 autres espaces utilisables pour créer des groupes de récepteurs.
Note – Pour un approfondissement sur l’utilisation des certificats, se référer au
« Nice Opera System Book ».
• Clés. cette fonction permet de personnaliser un émetteur, avec la possibilité
de modifier les clés « Installateur », « Installation » et « Altera ». En particulier,
« Altera » est compatible avec les précédents systèmes « FloR ».
Attention ! – Ne pas oublier la nouvelle
clé de protection autrement le récep-
teur n’est plus utilisable.
Les clés sont utiles pour personnaliser un système : c’est-à-dire qu’elles permettent de modifier le code original (d’usine) d’un émetteur. C’est la raison pour
laquelle les clés doivent être les mêmes tant sur l’émetteur que sur le récepteur.
Dans ce cas il faut modifier aussi les clés de l’O-box pour pouvoir l’utiliser par la
suite.
• Consignes avancées : Cette fonction permet de configurer les paramètres
suivants :
Consignes de base
- Activer uniquement TX d’origine : cette fonction permet d’activer ou de
désactiver le fonctionnement d’un récepteur qui reçoit la commande de la
part d’émetteurs dont le code a été modifié et n’est donc plus celui d’usine.
- Désactiver RND : cette fonction permet d’activer ou de désactiver le
contrôle de la partie variable du code d’identité (RND) présent dans un
récepteur.
Consignes de mémorisation
- Blocage mémorisation par « code d’activation » : cette fonction permet
de bloquer la mémorisation d’un nouvel émetteur en utilisant le « Code d’activation » d’un ancien émetteur (déjà mémorisé). Cette procédure ne peut
être utilisée que si l’on utilise deux émetteurs avec codage « O-Code ».
- Blocage mémorisation par « certificat » : cette fonction permet de bloquer la mémorisation d’un nouvel émetteur en utilisant le certificat d’un
récepteur.
Page 46

12 – Français
FR
- Blocage mémorisation à distance : cette fonction permet de bloquer la
mémorisation d’un nouvel émetteur en utilisant un ancien émetteur, avec la
procédure « à proximité de l’émetteur ».
Consignes BUS T4
Note – Le « Bus » est un système qui permet de connecter entre eux tous les
dispositifs présents dans une installation d’automatisation à l’aide d’un seul
câble contenant plusieurs conducteurs électriques. Dans ce type de
connexion, la communication des données entre les dispositifs utilise un protocole spécifique qui dans notre cas est le « Bus T4 » de Nice.
- Activer la répétition du code par bus : cette fonction permet d’activer
dans un récepteur la possibilité de transférer à d’autres dispositifs connectés, à travers le câble bus T4, la copie d’un code reçu par un émetteur à travers un signal radio.
- Activer la réception du code par bus : cette fonction permet d’activer sur
un récepteur la réception d’un code, transmis à travers le câble bus T4
depuis un autre récepteur (se référer au point précédent « Activer la répéti-
tion du code par bus »).
- Activer les groupes d’autorisation : cette fonction permet d’activer la
gestion des codes radio en groupes d’autorisation.
Consignes avancées
- Activer « Répéteur » : cette fonction permet d’activer la répétition d’un
code. S’il est nécessaire de commander un automatisme depuis une distance
supérieure à celle qui est normalement couverte par le rayon d’action de
l’émetteur et du récepteur, on peut utiliser un deuxième récepteur ayant pour
tâche de retransmettre à son tour, par radio, la commande vers le récepteur
destinataire (dans lequel est mémorisé le code d’identité de l’émetteur d’où
est partie la commande), de manière qu’il puisse exécuter la commande.
- Activer la gestion « relâchement touche » : durant l’utilisation d’un émetteur, après avoir envoyé une commande, quand on relâche la touche la
manœuvre ne s’arrête pas à cet instant précis mais continue encore pendant
un temps très court préétabli. S’il faut que la manœuvre s’arrête exactement
au moment où on relâche la touche du commande sur l’émetteur (par exemple, durant les réglages minimums), il faut activer cette fonction dans le
récepteur.
- Désactiver la gestion des priorités : cette fonction permet de désactiver
dans un récepteur la réception de commandes envoyées par des émetteurs
avec priorité supérieure à 0.
Note – Pour un approfondissement sur l’utilisation de toutes les fonctions
décrites, se référer au « Nice Opera System Book ».
• Changer mot de passe : cette fonction permet d’entrer un mot de passe qui
sert à bloquer l’accès, y compris manuel, à toutes les fonctions contenues
dans un récepteur, de la part de qui ne possède pas ce mot de passe.
La zone thématique « Installations » est un répertoire qui permet de créer et
d’archiver, pour chaque installation, une fiche analytique qui regroupe les coordonnées du client et les configurations des récepteurs installés dans son installation. En particulier, il est possible de modifier les installations, de visualiser les
codes et les consignes et d’enregistrer les données des récepteurs installés ;
en cas de problème de fonctionnement, il est possible de rétablir le fonctionnement de l’automatisme.
Cette zone thématique comprend deux pages vidéo :
– une destinée à la recherche rapide et à la sélection des installations archivées ;
– l’autre contenant une fiche pour la collecte des données relatives à une seule
installation.
Pour accéder à la zone thématique « Installations » procéder de la façon suivante :
01. Dans la page initiale
(fig. 3) cliquer sur l’icône « Installations ».
02. Une première page s’affiche (fig. 10) pour la gestion des installations
archivées. Elle est composée des éléments suivants.
• La « Barre de navigation » avec les fonctions suivantes :
« Modifier »
: permet de modifier les données d’une installation.
« Nouvelle installation » : permet de créer une nouvelle installation.
« Copier » : permet de copier les données d’une installation existante
pour en créer une nouvelle identique.
« Éliminer » : permet d’éliminer une ou plusieurs installations.
• La zone « Filtre sur données » qui permet de rechercher de façon simple
et rapide les installations enregistrées.
3.5 – ZONE THÉMATIQUE « INSTALLATIONS »
Page 47

Français – 13
FR
10
11
• La zone « Liste des Installations » qui affiche la liste des installations
enregistrées.
03. À ce point, en sélectionnant l’une des fonctions suivantes : « Modifier »,
« Nouvelle installation » et « Copier », une deuxième page s’affiche (fig. 11)
avec la fiche relative à une installation. Elle est composée des éléments
suivants.
• La « Barre de navigation » avec les fonctions suivantes :
«
Travailler sur cette installation » : permet de travailler sur une nouvelle
installation ou sur une installation existante (se référer au paragraphe
3.5.1).
« Enregistrer sur le fichier » : permet d’enregistrer sur d’autres fichiers
les données des récepteurs à mémoriser.
« Importer du fichier » : permet de lire dans un fichier les données d’un
récepteur (se référer au paragraphe 3.5.1).
« Enregistrer les modifications » : permet d’enregistrer les modifications
effectuées dans la fiche d’une installation.
En plus de la barre de navigation, cette page contient 3 zones d’intervention : Client ; Clés installation ; Récepteurs.
• Client : dans cette zone, il est possible de saisir les coordonnées d’un
client.
• Clés installation : dans cette zone il est possible d’utiliser des clés pour
personnaliser une installation en exploitant les champs « Clé Installateur »,
« Clé Installation » et « Altera ». Ces clés sont utiles pour limiter la gestion
des installations uniquement aux possesseurs des clés. Il est possible
d’utiliser la même clé sur différentes installations ou des clés différentes
pour chaque installation.
Durant la programmation des émetteurs et des récepteurs de la série
« Nice Opera », ceux-ci seront programmés automatiquement avec les
mêmes clés que celles qui figurent dans la fiche de l’installation, si cette
fiche a été activée précédemment et contient les clés paramétrées.
Note – Pour un approfondissement sur l’utilisation des clés, se référer au
« Nice Opera System Book ».
• Récepteurs : cette zone affiche les récepteurs présents dans une instal-
lation. Pour ajouter ou effacer des récepteurs, se référer au paragraphe
3.5.1.
Page 48

14 – Français
FR
3.5.1 – Ajouter les récepteurs à une installation
En général, pour ajouter un ou plusieurs récepteurs sur la fiche relative à une
installation il est possible d’opérer de deux manières différentes.
• mode direct
: cette modalité prévoit que les données du récepteur à ajouter
à une installation sont déjà mémorisées sur un fichier. Dans ce cas, dans la
page qui affiche la fiche d’une installation, cliquer sur la fonction « Importer du
fichier » (dans la barre de navigation) et sélectionner le fichier désiré.
• mode indirect
: cette modalité prévoit les opérations suivantes :
– à l’ouverture du logiciel on sélectionne dans le panneau « Sélection installation » l’une des fonctions « Travailler sur la dernière installation » ou « Sélection-
ner ou créer une installation » ; en alternative, cliquer sur l’icône « Installations »
dans la page initiale.
– la page de gestion des installations enregistrées (fig. 10) s’affiche et il faut y
sélectionner l’installation où l’on souhaite ajouter le récepteur (une installation
existante ou une nouvelle, créée sur l’instant) ;
– après avoir confirmé le choix en cliquant sur l’icône « Travailler sur cette ins-
12
tallation », le logiciel montre la page initiale avec l’indication de l’installation sur
laquelle on est en train de travailler (fig. 10) ;
- connecter ensuite à l’O-Box le récepteur concerné et activer la zone thématique « Récepteurs » pour effectuer la programmation désirée (se référer au
chapitre 3.4);
– pour finir, dans la même page, cliquer sur l’icône « Installation » et choisir
dans le menu déroulant(*) l’option « Ajouter à l’installation ».
(*) Note – Le menu associé à l’icône « Installation » est dynamique dans la
mesure où il contient des options différentes, selon les circonstances. En général les options sont :
• première ligne : indique en italique le nom de l’installation active ; c’est-à-dire
celle dans laquelle on peut enregistrer le récepteur que l’on est en train de programmer.
• dernière ligne : indique la commande « Ajouter à l’installation » pour enregis-
trer le récepteur (nouveau) que l’on vient de programmer.
• autres lignes : indiquent le nom des récepteurs éventuellement déjà présents
dans l’installation. Pour modifier l’un deux, choisir le nom et modifier les paramètres. Pour finir, pour enregistrer les modifications apportées, cliquer sur
l’icône « Installation » et choisir dans le menu déroulant l’option « Enregistrer les
modifications ... » (cette option n’est présente que si des récepteurs sont déjà
présents dans l’installation active).
Page 49

Français – 15
FR
Ce produit fait partie intégrante de l’automatisme et doit donc être mis au
rebut avec cette dernière.
Comme pour l’installation, à la fin de la durée de vie de ce produit, les opérations de démantèlement doivent être effectuées par du personnel qualifié.
Ce produit est constitué de différents types de matériaux : certains peuvent être
recyclés, d’autres doivent être mis au rebut. Informez-vous sur les systèmes de
recyclage ou de mise au rebut prévus par les normes en vigueur dans votre
région pour cette catégorie de produit.
Attention! – certains composants du produit peuvent contenir des substances
polluantes ou dangereuses qui pourraient avoir des effets nuisibles sur l’environnement et sur la santé des personnes s’ils n’étaient pas adéquatement éliminés.
Comme l’indique le symbole ci-contre, il est interdit de jeter ce
produit avec les ordures ménagères. Procéder à la « collecte
différenciée » des composants pour leur traitement conformément aux méthodes prescrites par les normes locales en
vigueur ou restituer le produit au vendeur lors de l’achat d’un
nouveau produit équivalent.
Attention! – les règlements locaux en vigueur peuvent prévoir de lourdes sanctions en cas d’élimination prohibée de ce produit.
Mise au rebut de la batterie
La batterie, même quand elle est usagée, peut contenir des substances polluantes et ne doit donc pas être jetée avec les ordures ménagères. Après avoir
retiré la batterie du produit, il faut la mettre au rebut suivant les méthodes prévues pour la collecte différenciée par les réglementations locales.
Mise au rebut du produit
Typologie unité de programmation et contrôle des codes pour les produits Nice suivants :
• récepteurs des séries NiceOne et SMX;
• systèmes récepteurs-émetteurs avec codages « Bio », « Flo », « FloR », « Smilo », « OCode » ;
• systèmes de contrôle d’accès avec décodeur « Morx » ; lecteurs de cartes à transpondeur MOM ou claviers numériques MOT
• dispositifs qui utilisent le système TTBUS ;
Technologie radio : récepteur-émetteur radio à la fréquence de 433,92 MHz. Portée
jusqu’à 10 m.
Connecteurs et dispositifs pouvant être connectés :
• zone d’appui pour les émetteurs de la série « NiceOne » (la programmation s’effectue
par radio, sans contact) ;
• connecteur pour cartes de mémoire « BM 60 », « BM 250 », « BM 1000 ».
• connecteur pour récepteurs de la série « SMX » et « NiceOne » (certains modèles, par
câble adaptateur) ;
• connecteur pour émetteurs de la série Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo, Plano (par câble adaptateur) ;
• connecteur pour lecteur optique, pour émetteurs de la série « Bio ».
• lecteur de proximité pour carte à transpondeur ;
• connecteur pour dispositifs TTBUS (par câble adaptateur) ;
Connexion à l’ordinateur :
• connecteur pour câble USB
• connecteur pour câble série RS232
• connexion wireless en technologie Bluetooth
®
(uniquement version O-boxB)
Alimentation :
• Interne
: à travers la batterie rechargeable 6 V, 700 mAh.
•Externe
: à travers la connexion USB à l’ordinateur ou à travers l’alimentateur mod.
ALA1, 12 Vcc,
Temps de recharge de la batterie : environ 15 heures
Durée de la charge de la batterie : environ 10 heures de fonctionnement ou 3 mois en
stand-by.
Vie de la batterie : au moins 100 cycles complets de décharge
Indice de protection du boîtier : IP 20 (utilisation exclusivement à l’intérieur ou dans des
locaux protégés).
Température de service : de -20°C à +55°C
Dimensions (mm) : 194 x 115 x h 40
Poids (g) : 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Caractéristiques techniques du produit
Page 50

16 – Français
FR
DÉCLARATION CE DE CONFORMITÉ
Déclaration CE de conformité selon la directive 1999/5/CE.
Note – La présente Déclaration de conformité réunit le contenu des diverses
déclarations de conformité de chaque produit cité ; elle est muse à jour à la date
d’édition du présent manuel et a été réélaborée sur le pour des raisons d’édition.
Une copie de la déclaration originale pour chaque produit peut être demandée à
Nice S.p.a. (TV) I.
______________
Je soussigné Lauro Buoro en qualité d’Administrateur Délégué, déclare
sous mon entière responsabilité que le produit :
Nom du producteur : NICE s.p.a.
Adresse : Via Pezza Alta 13, 31046 Z.I. Rustignè, Oderzo
(TV) Italia
Type : Programmateur OBOX pour radiocommandes
avec récepteur-émetteur radio à 433,92 MHz
et lecteur de cartes à transpondeur.
Programmateur OBOXB pour radiocommandes avec récepteur-émetteur radio à
433,92 MHz et lecteur de cartes à transpondeur. Versione con tecnologia Bluetooth
®
Modèles : OBOX, OBOXB
Accessoires :
Est conforme à ce qui est prévu par la directive communautaire suivante :
• DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE DU PARLEMENT EUROPÉEN ET DU
CONSEIL du 9 mars 1999 concernant les équipements hertziens et
les équipements terminaux de télécommunication et la reconnaissance mutuelle de leur conformité, selon les normes harmonisées suivantes :
protection de la santé : EN 50371:2002 ;
sécurité électrique : EN 60950-1:2001 ;
compatibilité électromagnétique : EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005, EN 301
489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002 ;
spectre radio : EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2 V1.3.1:2006,
EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004 ;
Est conforme à ce qui est prévu par les directives communautaires suivantes, telles qu’elles sont modifiées par la directive 93/68/CEE du
conseil du 22 juillet 1993 :
• DIRECTIVE 89/336/CEE DU CONSEIL du 3 mai 1989 concernant le
rapprochement des législations des États membres relatives à la compatibilité électromagnétique, selon les normes harmonisées suivantes :
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Administrateur Délégué)
Page 51

Español – 1
ES
ESPAÑOL
LICENCIA DE USO DEL SOFTWARE
Los programas “O-Box Software Desktop” y “O-Box Software Mobile” están
protegidos por las leyes sobre el copyright y sobre la propiedad intelectual;
dichos programas no se venden, sino que se suministran bajo licencia de uso
no exclusiva. Nice s.p.a. es propietario de esta copia del programa. Los programas “O-Box Software Desktop” y “O-Box Software Mobile” se suministran
bajo licencia como productos combinados al producto “O-Box”.
Estos programas se suministran sin garantía sobre el modo de utilización y
sobre la seguridad. Además, Nice s.p.a. no se asume ninguna responsabilidad
por daños directos o indirectos, incluidos los daños por la pérdida de beneficio, interrupción de trabajo o demás, provocados por un uso incorrecto de
estos softwares.
INFORMACIÓN SOBRE LAS MARCAS
Las marcas AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®y MICROSOFT®son
marcas registradas por sus propios titulares; los nombres de los productos indicados en este manual pueden estar registrados por los titulares respectivos.
NOTA GENERAL DEL MANUAL
La unidad de programación está disponible en dos modelos:
O-Box y O-BoxB. Estos modelos son similares, salvo por la
presencia de un módulo para la conexión con tecnología
Bluetooth
®
en el modelo O-BoxB.
En este manual el término “O-Box
” se utiliza para identificar indistintamente los dos productos, salvo donde esté
especificado de otra manera.
DESCRIPCIÓN DEL PRODUCTO Y
USO PREVISTO
1
El producto O-Box (u O-BoxB, versión con módulo Bluetooth®) está formado
de una unidad de programación y de un software dedicado. El conjunto de
estos dos elementos está destinado a la programación y al mantenimiento de
los datos y de los parámetros contenidos en los dispositivos utilizados en las
instalaciones de automatización de cancelas, puertas de garaje, toldos, persianas, barreras de acceso con mástil móvil y aplicaciones similares.
¡Cualquier otro uso es considerado inadecuado! El fabricante no responde de los daños que pudieran surgir por un uso inadecuado del producto
y diferente de aquel previsto en este manual.
La O-Box y el sistema “NiceOpera”
La O-Box es un dispositivo que forma parte del sistema “NiceOpera”. Este sistema ha sido diseñado por Nice para simplificar las etapas de programación,
uso y mantenimiento de los dispositivos montados en las instalaciones de
automatización. El sistema está formado de varios dispositivos software y
hardware que intercambian entre sí los datos y las informaciones por radio,
mediante un sistema de codificación llamado “O-Code”, o de una conexión
“física” mediante un cable.
Los dispositivos principales que forman el sistema son:
– transmisores NiceOne;
– receptores NiceOne (familia OXI… ; familia OX…);
– unidades de programación O-Box;
– centrales y motorreductores con “Bus T4”;
– programador O-View para dispositivos con “Bus T4”.
IMPORTANTE – Para más detalles sobre todas las funciones del sistema
NiceOpera, sobre la interdependencia que asocia a los dispositivos del
sistema, consulte el manual general “NiceOpera System Book”, también
disponible en la página web www.niceforyou.com
Características funcionales principales de la O-Box
La O-Box es indicada en las instalaciones de automatización muy tecnológicas,
porque permite realizar muchas funciones directamente en la oficina del instalador, sin tener que llevar a cabo las operaciones en el lugar de la instalación del
cliente; o bien permite configurar una instalación directamente en lo del cliente.
Page 52

2 – Español
ES
El producto incorpora una batería recargable de 6 V, que permite el funcionamiento sin la conexión a la red eléctrica.
Nota – La batería requiere un ciclo de recarga completo de 10 horas como
mínimo. El nivel de la carga está indicado en el interior del software (véase la
fig. 1). La batería se recarga automáticamente cada vez que la O-Box es alimentada con un alimentador exterior o con el cable USB.
2.1 – CONEXIONES
• Conecte la O-Box a la alimentación eléctrica.
El producto puede ser alimentado desde la red eléctrica utilizando un alimentador de 12 Vcc (accesorio opcional), o desde un ordenador utilizando el cable
USB (suministrado de serie).
• Conecte la O-Box a un ordenador personal
Para utilizar la O-Box (o la O-BoxB) es necesario conectarla a un ordenador
personal (PC) dotado de un puerto USB, por medio del cable suministrado, o
dotado de un puerto serie, por medio del cable RS232 (accesorio opcional).
Nota – Para esta conexión se aconseja utilizar el puerto USB (en su caso) porque ofrece mejores prestaciones: es más confiable, más rápido para transferir
los datos, no requiere ninguna configuración y permite la recarga automática
de las baterías internas de la O-Box.
• Conecte la O-BoxB mediante Bluetooth
®
El modelo O-BoxB también puede ser conectado mediante Bluetooth® a un
ordenador o a un ordenador de bolsillo (PDA) que incorporen una interfaz
Blue-
tooth®.
Esta conexión no necesita cables: es suficiente instalar el software en el ordenador o en el ordenador de bolsillo y configurar los datos según las características del mismo ordenador.
Nota – Antes de activar la conexión Bluetooth
®
, desconecte la O-BoxB del
puerto USB o del puerto serie del ordenador.
La O-BoxB está preparada para memorizar hasta 16 conexiones con diferentes
ordenadores. Para establecer la conexión, encienda la O-BoxB, prepare el orde-
Este producto permite administrar y modificar las instalaciones utilizando un
archivo de datos; se pueden llevar a cabo rápidamente varias operaciones,
tales como el restablecimiento, la ampliación de las instalaciones existentes, la
sustitución de los transmisores, etc..
Por lo general, la O-Box puede ser utilizada para:
• controlar, añadir, programar o cancelar los códigos de los transmisores “Bio”,
“FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano” y “NiceOne”;
• programar las memorias de los receptores “Bio” y “FloR”;
• leer y escribir tarjetas por transponder;
• programar las funciones y los parámetros característicos de los transmisores
“Bio”, “FloR” y “Very”;
• leer de manera óptica los códigos de los transmisores “Bio”;
• leer y programar los parámetros característicos de los receptores “SMX1” y
“SMX2” por cable;
• recibir datos por radio de los transmisores con código SMILO, FLO, FLOR y
O-CODE, para crear archivos de los usuarios, programar las memorias y los
receptores;
• programar por radio los transmisores de la serie “NiceOne”;
• gestionar por radio todas las funciones de los receptores “NiceOne”.
El software entregado con la O-Box permite configurar y programar los Transmisores y los Receptores de la serie “NiceOne”. También es compatible con
todos los dispositivos de la serie “FloR”, “SMXI” y “Bio”.
HARDWARE: descripción del producto
y su instalación
2
1
Page 53

Español – 3
ES
nador para la conexión Bluetooth®y espere que la luz intermitente del Led de la
O-BoxB se encienda con luz fija (esto confirma que la conexión se ha activado).
Si tuviera que borrar de la memoria la lista de las conexiones a los ordenadores, proceda de la siguiente manera:
a) – mantenga pulsado en la O-BoxB el botón de encendido Activity y espere
que se concluyan estas etapas: la O-BoxB emitirá una señal acústica (tono de
aviso) y el Led se apagará; el Led se encenderá de nuevo y la O-BoxB emitirá
una secuencia de señales acústicas (tono de aviso).
b) – Entonces, los datos almacenados en la memoria de la O-BoxB se cancelarán y usted podrá soltar el botón de encendido.
2.2 – ACCESORIOS (opcionales)
Nota – La O-Box incorpora sólo el cable USB; todos los demás cables son
opcionales y no se suministran de serie. Dichos cables son:
– Cable mod.
CABLA06 para el conector D, de fig. 2: utilícelo para conectar
los receptores de la serie “SMX” y “NiceOne”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA02 para el conector M, de fig. 2: utilícelo para recibir los
códigos de los transmisores de la serie “Bio”.
– Cable serie de 9 polos, RS232, mod.
CABLA01 para el conector G, de fig.
1: utilícelo para conectar la O-Box a un ordenador.
– Cable TTBUS, mod.
CABLA05 para el conector H, de fig. 2: utilícelo para
conectar todos los motores tubulares para toldos y persianas de Nice, dotados de puerto TTBUS.
– Cable mod. CABLA03 para el conector I, de fig. 2: utilícelo para conectar los
transmisores de la serie “Very”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA02 para el conector I, de fig. 2: utilícelo para conectar los
transmisores de la serie “Bio” y “FloR”.
– Cable mod.
CABLA04 para el conector I, de fig. 2: utilícelo para conectar los
transmisores de la serie “Ergo” y “Plano”.
– Alimentador mod.
ALA1 de 12 V, 300 mA para el conector E, de fig. 2: utilí-
celo para conectar la O-Box a la red eléctrica.
2.3 – CONECTORES Y DISPOSITIVOS QUE PUEDEN CONECTARSE
A LA O-BOX
La O-Box incorpora varios tipos de conectores (véase la fig. 2) a los que es
posible conectar varios de los dispositivos fabricados por Nice. Nota – Algunos
de estos conectores necesitan un cable de conexión específico: para el mode-
lo y las características de cada cable, véase el párrafo 2.2.
Tomando como referencia las letras que en la fig. 2 identifican los conectores y
los demás dispositivos de la O-Box, a continuación se mencionan sus funciones y usos:
[A] – Botón de encendido y apagado de la O-Box
Para encender la O-Box, mantenga pulsado el botón de encendido durante
algunos segundos hasta oír un sonido breve (beep).
Para apagar la O-Box, mantenga pulsado el botón de encendido durante algunos segundos hasta oír un sonido largo (beeeeeep).
[B] – Área para la conexión por radio de los transmisores de la
serie “NiceOne”
Esta zona de apoyo permite programar por radio, es decir sin la conexión física,
los transmisores de la serie “NiceOne” de Nice: la programación se hace apoyando el transmisor en la zona de superficie delimitada por el signo gráfico.
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 54

4 – Español
ES
Durante el uso del software, el Led del transmisor emite un destello que indica
la activación de la comunicación por radio con el mismo programa. Entonces
es posible comenzar a trabajar con el software sobre los parámetros del transmisor (véase el capítulo 3, párrafo 3.3).
[C] – Conector para las tarjetas de Memoria “BM”
Este conector permite conectar las tarjetas de memoria “BM” de Nice a la OBox. Para conectar una tarjeta, insértela directamente en el conector y comience a trabajar con el software (véase el capítulo 3, párrafo 3.3).
[D] – Conector tipo “SM”
Este conector permite conectar a la O-Box únicamente los receptores de la
serie “SM” y “NiceOne” de Nice. Algunos de estos receptores pueden conectarse directamente en el conector, otros necesitan del cable mod. CABLA06.
Después de la conexión, se puede comenzar a trabajar con el programa (véase el capítulo 3, párrafo 3.3).
Nota – Los receptores de la serie “NiceOne” (OXIT y OX2T) están predispuestos
para comunicarse con el programa, incluso por radio. En este caso, la transmisión de los datos es más lenta que aquella que se hace con el conector SM.
[E] – Conector para el alimentador exterior, mod. ALA1
Este conector permite conectar la O-Box a la red eléctrica por medio de un alimentador exterior de 12 Vcc (accesorio opcional).
Nota – Aunque la O-Box esté apagada, la batería montada en el interior se
recargará cada vez que se conecte el cable de alimentación a la red eléctrica.
[F] – Conector para el cable “USB”
Este conector permite conectar la O-Box al puerto USB de un ordenador por
medio del cable USB. Inmediatamente después se podrá abrir el programar
para una sesión de trabajo.
Nota - Aunque la O-Box esté apagada, la batería montada en el interior se
recargará cada vez que se conecte el cable USB a un ordenador encendido.
[G] – Conector serie “RS232” (cable tipo mod. CABLA01)
Este conector permite conectar la O-Box al puerto serie RS232 de un ordenador por medio del cable serie RS232 (accesorio opcional). Inmediatamente
después se podrá abrir el programa para una sesión de trabajo.
[H] – Conector “TTBUS” (cable tipo mod. CABLA05)
Este conector permite conectar a la O-Box todos los motores tubulares para
toldos y persianas de Nice, dotados de puerto TTBUS, por medio del cable
respectivo (accesorio opcional).
[I] – Conector para la clonación de los transmisores (cables tipo
mod. CABLA03 - CABLA02 - CABLA04)
Este conector permite conectar a la O-Box los transmisores Nice de la serie
“Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano” y “Very”, por medio del cable respectivo (accesorio opcional). Para hacer la conexión, abra el transmisor para conectar el cable
de conexión (*) y conecte el otro extremo al conector en la O-Box (I en la fig. 2).
(*) Nota:
– para los transmisores de la serie “Ergo” y “Plano” utilice el cable mod.
CABLA04
– para los transmisores de la serie “Bio” y “FloR” utilice el cable mod. CABLA02
– para los transmisores de la serie “Very” utilice el cable mod. CABLA03
[L] – Lector de proximidad para tarjeta por transponder
Este lector de proximidad permite leer (tarjeta azul y tarjeta gris) o escribir (tarjeta gris) los códigos contenidos en las tarjetas por transponder de Nice. Para
establecer la conexión es necesario colocar la tarjeta delante del lector.
[M] – Conector para lector óptico para transmisores de la
serie “Bio”
Este lector permite leer el código radio de los transmisores de la serie “Bio”.
Para establecer la conexión hay que conectar el lector óptico (accesorio opcional, mod. CABLA02) en el conector (M de fig. 2) y acercar el Led del transmisor al cabezal del lector óptico.
Page 55

Español – 5
ES
El programa presente en el CD de instalación “O-Box Software Suite” se suministra en dos versiones:
• “O-Box Desktop” destinado a la instalación de un ordenador personal (PC)
• “O-Box Mobile” destinado a la instalación de un ordenador de bolsillo (PDA)
REQUERIMIENTOS MÍNIMOS DEL SISTEMA
Para utilizar este programa es necesario instalarlo en un ordenador y, si usted
lo deseara, en un ordenador de bolsillo de cualquier marca y modelo, con los
siguientes requerimientos mínimos:
VERSIÓN PARA PC:
– Procesador: tipo AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Aconsejado por Nice: tipo
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– Memoria RAM: 128 MB Aconsejado por Nice: 256 MB
– Espacio libre en el disco: 30 MB Aconsejado por Nice: 100 MB
– Sistema operativo: Windows
®
98 SE Aconsejado por Nice: Windows
®
2000 o superior
– Tarjeta de vídeo: 800 x 600, con 256 colores
- Unidad disco: CD-Rom (necesaria para la instalación)
Nota – La instalación del software incluye la instalación del programa Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
VERSIÓN PARA ORDENADOR DE BOLSILLO:
– Procesador: (300 MHz) Aconsejado por Nice:
(superior a 300 MHz)
– Memoria RAM: 64 MB Aconsejado por Nice: 128 MB
– Memoria almacenamiento: 5 MB Aconsejado por Nice: 100 MB
– Sistema operativo: Windows
®
Mobile Aconsejado por Nice: Windows
®
2003 ó 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE o superior
– Conexión: Bluetooth
®
– Resolución de vídeo: 240 x 320 con 256 colores
– PC con: CD-Rom (necesario para la instalación del programa en el ordenador de bolsillo)
Nota – La instalación del software incluye la instalación del programa Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
SOFTWARE: descripción y uso del producto
3
3.1 – INSTALACIÓN DEL SOFTWARE
La instalación del programa es similar a la instalación de cualquier otro programa para ordenador.
Después de haber insertado el CD de instalación, el software de instalación
arrancará automáticamente. Si así no fuera, haga doble clic sobre el icono del
programa “Setup.exe” y siga las instrucciones de la instalación guiada.
Nota – Antes de comenzar la instalación del software, se aconseja desconectar la O-Box del ordenador.
BREVE PANORÁMICA SOBRE EL SOFTWARE: estructura y argumentos
• Página principal (home page)
Después de haber abierto el programa, se visualizará la “Home page”, es decir
la página principal (véase la fig. 3) que contiene los siguientes argumentos:
[1] – Indica el estado de la conexión del ordenador de bolsillo: haciendo clic
sobre este icono se activará la sincronización del ordenador de bolsillo.
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 56

6 – Español
ES
[2] – ndica el estado de la batería y el estado de la conexión con la O-Box: en
el caso de error de conexión, haciendo clic sobre este icono, el programa
ejecutará una nueva conexión con la O-Box.
[3] – Panel “Selección instalación”: permite seleccionar, al abrirse una sec-
ción de trabajo, el modo de trabajo deseado, agilizando las selecciones
siguientes. Si después de la programación de un receptor se desean
almacenar los datos de configuración sólo en su memoria o en un fichero,
seleccione la opción “Trabajar sin crear ninguna instalación”.
Por el contrario, si después de la programación de un receptor se desean
almacenar los datos de configuración en su memoria y en un fichero,
incluso en una ficha recapitulativa de la instalación en que se utilizará el
receptor, seleccione la opción “Trabajar en la última instalación” o “Seleccionar o crear una instalación” (consulte el párrafo 3.5.1).
[4] – Indica el acceso a la zona operativa dedicada a la programación de los
Transmisores.
[5] – Indica el acceso a la zona operativa dedicada a la programación de los
Receptores.
[6] – Indica el acceso a la zona operativa dedicada a la gestión de las Instala-
ciones.
[7] – Indica el acceso a la zona operativa dedicada a las Configuraciones del
programa.
[8] – Indica el botón que hay que pulsar para salir del programa.
[9] – Indica el espacio en que aparecen los datos para personalizar el programa
(... nombre del usuario, etc.).
• Página temática
Desde la página principal seleccione el área temática de interés (“Transmisores”, “Receptores”, “Instalaciones”, “Configuraciones”) y, haciendo clic
sobre el icono correspondiente, se accede a la página temática del área
seleccionada donde se pueden ejecutar todas las operaciones deseadas.
(Nota – cada área temática puede desarrollar el argumento en una o varias
páginas sucesivas). Dichas páginas están formadas, típicamente, por los
siguientes elementos (véase la fig. 4):
[a] – Barra de navegación.
[b] – Menú de las funciones
[c] – Área con los datos generales del dispositivo conectado
[d] – Área para la programación
Elementos presentes en la Barra de navegación
La “Barra de navegación”, presente en cada página temática, permite desplazarse desde una página a otra e informa, en cada instante, en qué área se está
trabajando.
Las funciones típicas de la barra de navegación son:
–“Iniciar” = haciendo clic sobre este icono, se vuelve a la Página principal
–“Atrás” = haciendo clic sobre este icono, se vuelve a la página anterior
–“Siguiente” = haciendo clic sobre este icono, se pasa a la página siguiente
–“Ayuda” = haciendo clic sobre este icono, se visualiza este manual de ins-
trucciones
–“Recargar” = en algunas páginas, haciendo clic sobre este icono, ser recar-
gan y se actualizan los datos.
IMPORTANTE – En algunas páginas, además de estas funciones “estándares”, podrían estar presentes otras funciones específicas sobre el dispositivo
que se está programando.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 57

Español – 7
ES
3.2 – CÓMO COMENZAR UNA SESIÓN DE TRABAJO
Para comenzar una sesión de trabajo, siga estas operaciones:
– encienda la O-Box;
– conecte a la O-Box un dispositivo sobre el que se desea trabajar;
– arranque el programa (se abrirá la pantalla principal);
– pulse sobre la pantalla principal
el botón del área temática deseada;
– trabaje sobre las páginas temáticas
siguientes.
Para acceder a esta área temática, primero conecte a la O-Box un transmisor
sobre el que se desee trabajar y, posteriormente, proceda de la siguiente manera.
01. En la página principal
, haga clic sobre el icono “Transmisores” (fig. 3).
02. Se abrirá una primera página del área temática “Transmisores” (fig. 5):
seleccione la familia y el modelo del transmisor que desee programar y
haga clic sobre “Siguiente” (en la barra de navegación) para pasar a la
página siguiente donde programar el transmisor.
Nota – Sólo para los transmisores NiceOne: si se coloca el transmisor
en el área de programación de la O-Box antes
de acceder al área temática “Transmisores”, el programa reconocerá automáticamente el modelo
del transmisor y mostrará los datos, incluido el código de identidad y el
código RND.
Por el contrario, si se colocara el transmisor en la O-Box después
de
entrar en el área temática “Transmisores”, habrá que hacer clic sobre el
icono “Recargar” para que el programa reconozca el modelo del transmisor y muestre los datos.
03. Se abrirá una segunda página del área “Transmisores” dedicada a la pro-
gramación (fig. 6): seleccione en el Menú de las Funciones la función
deseada y trabaje en el área operativa dedicada a modificar, añadir, etc.
los parámetros deseados.
IMPORTANTE – Algunas funciones ofrecen la posibilidad de programar
en secuencia varios transmisores, simplemente conectando a la O-Box un
transmisor seguido del otro. La confirmación de que la programación se
ha ejecutado y la señal que indica que es posible cambiar el transmisor
con otro sucesivo a programar son dadas por dos tonos de aviso (beep).
3.3 – ÁREA TEMÁTICA “TRANSMISORES”
5
6
Page 58

8 – Español
ES
El menú de las funciones está subdividido en 3 secciones, a saber: Códigos;
Certificados; Avanzadas (fig. 4). Importante – Las funciones disponibles
en cada sección varían según el tipo de transmisor que se desee programar.
–– CÓDIGOS ––
Esta sección permite configurar los códigos de un transmisor y presenta las
siguientes funciones:
– Probar Transmisor
: esta función permite controlar el funcionamiento correc-
to del transmisor y permite visualizar el código de identidad y la parte variable
del código RND.
– Cambiar Código: esta función permite cambiar el código de identidad original de un transmisor.
IMPORTANTE – Para programar varios transmisores en secuencia con códi
gos en progresión, haga clic sobre el icono “Programar Secuencia”; cumplimente dos de los siguientes campos: “A Código”, “Step” (es decir el aumento
del código entre un transmisor y otro) y “Cantidad códigos”; por último, haga
clic sobre “Controlar”. Entonces, el programa completará automáticamente el
campo dejado en blanco anteriormente.
– Restablecer Código: esta función permite restablecer el código original (de
fábrica) del transmisor.
–– CERTIFICADOS ––
Esta sección permite configurar los certificados de un transmisor y presenta
las siguientes funciones:
– Configurar Certificados
: esta función permite insertar el “Certificado” de un
receptor en un transmisor. Para cada Certificado es posible configurar la
memorización en el transmisor en “Modo I” o en “Modo II”.
En el caso de la memorización en “Modo II” (cada botón del transmisor corresponde a una función específica del receptor) es suficiente seleccionar en el elemento “Función”, simplemente haciendo clic, el número de la función deseada
y, posteriormente, seleccionar en el elemento “Botones” el botón que se desea
memorizar en el transmisor.
Nota – La variedad de los mandos a disposición para la memorización del
transmisor depende del tipo de transmisor y del modelo de Central con que se
utilizará este transmisor. La lista detallada de los mandos está indicada en el
manual de instrucciones de la misma Central.
– Borrar Certificados
: esta función permite borrar todos los Certificados del
transmisor.
–– AVANZADAS ––
Esta sección permite configurar las claves de protección y los parámetros de
funcionamiento de un transmisor: presenta las siguientes funciones:
– Configurar Claves
: esta función permite personalizar un transmisor, es decir,
modificar las claves de protección “Instalador”, “Instalación” y “Altera”. En particular, “Altera” es compatible con los sistemas “FloR” anteriores.
¡Atención! – No se olvide la nueva
clave de protección porque si no el transmi-
sor no se podrá utilizar con ese receptor.
– Configuraciones Avanzadas
: esta función permite configurar los siguientes
parámetros:
Cantidad tramas: permite modificar el número de repeticiones del código
de identidad cuando éste es transmitido. Es útil modificar este parámetro
para automatizaciones específicas que requieren tiempos de respuesta con
un mando enviado más rápidos que aquellos configurados en fábrica.
Prioridad: permite sustituir un transmisor existente manteniendo su
código de identidad. Esto se obtiene aumentando una unidad la prioridad
del NUEVO transmisor respecto del VIEJO.
Habilitar RND: permite habilitar o deshabilitar la gestión de la parte varia-
ble del código de identidad (RND).
Paso Código Habilitación: permite que el transmisor tenga la facultad o
no la tenga de transmitir a otro transmisor su propio Código de habilitación.
Copiar entre modelos diferentes: permite la habilitación o deshabilita-
ción de la copia de los “códigos de habilitación” entre modelos de transmisores diferentes entre sí.
Activar “Repeater”: permite habilitar o deshabilitar la gestión de la repeti-
ción del código en los receptores que incorporan la función “Repeater”.
Nota – Haciendo clic sobre el botón “Valores de fábrica” se pueden configurar los
valores de fábrica de los parámetros antedichos (“Configuraciones Avanzadas”).
– Todo Original
: esta función permite colocar un transmisor en la configuración
hecha en fábrica, es decir que se restablece el código de identidad original, se
borran los certificados y se restablecen los valores de los diferentes parámetros.
Importante – Por motivos de seguridad, esta función no modifica el valor de
las claves de protección, es decir que el valor no vuelve a ser el original.
Page 59

Español – 9
ES
- Programación Guiada: esta función permite programar un transmisor utilizando en secuencia todas las secciones antedichas.
Para acceder a esta área temática, primero conecte a la O-Box un receptor
sobre el que se desee trabajar y, posteriormente, proceda de la siguiente
manera.
01. En la página principal
, haga clic sobre el icono “Receptores” (fig. 3).
02. Se abrirá una primera página del área “Receptores” (fig. 7): seleccione la
familia y el modelo del receptor que se desee programar (el sistema controlará si existen receptores de esa familia conectados a la O-Box y mostrará automáticamente el modelo. De todas maneras es posible seleccionar manualmente el modelo). Posteriormente, haga clic en la barra de
navegación sobre “Siguiente” para pasar a la página siguiente.
Nota – Si se está programando un receptor de la serie “NiceOpera” habrá
que seleccionar el tipo de conexión utilizada: wireless (en este caso habrá
que escribir el certificado del receptor) o conector en O-Box (en este caso
utilice el conector SM).
03. Después de haber seleccionado la familia del receptor, aparecerá una
segunda página con el título “¿Qué quiere usted hacer?”(fig. 8):
• Configurar un nuevo receptor
(esta operación permite configurar un
nuevo receptor).
• Leer y modificar los datos de un receptor
(esta operación permite leer y
modificar los datos de un receptor, memorizando de vez en vez sólo las
modificaciones hechas).
• Borrar todos los datos de un receptor (esta operación formatea los
datos de un receptor).
• Buscar y modificar códigos en la memoria
(esta operación está presen-
te sólo en los receptores de la familia “NiceOne”. La operación permite
actuar sobre la memoria del receptor).
04. Por último, aparece una tercera página dedicada a la programación (fig.
9). En dicha página, seleccione en el Menú de las Funciones la función
deseada y trabaje en el área operativa dedicada a modificar, añadir, etc.
los parámetros deseados.
3.4 – ÁREA TEMÁTICA “RECEPTORES”
7
8
Page 60

10 – Español
ES
9
El menú de las funciones está subdividido en 3 secciones, a saber: Códigos en la memoria; Configuraciones; Importar / Exportar.
–– CÓDIGOS EN LA MEMORIA ––
En esta sección es posible modificar, en todos los tipos de receptores, los
códigos que se encuentran en la memoria. A tal fin, es suficiente hacer clic
sobre la función “Modificar Códigos” y acceder a las siguientes opciones:
Añadir código
: permite añadir un código a la memoria escribiendo
manualmente este código.
Añadir Secuencia
: permite añadir en la memoria de un receptor una
secuencia de códigos, cumplimentando dos de los siguientes campos
“código inicial”, “código final” y “paso entre un código y el otro”, y por último,
haga clic sobre “Controlar”; el campo que había quedado en blanco se llenará automáticamente.
Añadir de TX
: permite insertar en la memoria de un receptor el código de
un transmisor, pulsando simplemente un botón de este último.
Borrar Código
: permite eliminar uno o varios códigos de la memoria de un
receptor.
Buscar
: permite buscar el código de un transmisor simplemente escribiendo el código dentro del espacio respectivo, o bien pulsando cualquier
botón del transmisor.
–– CONFIGURACIONES ––
En esta sección, utilizando las funciones presentes (“Certificados” - “Claves”
- “Configuraciones Avanzadas” - “Cambio Contraseña”), es posible modificar los parámetros contenidos en algunas familias de los receptores. Las funciones disponibles varían según el tipo de receptor o de memoria que se desea
programar: para más informaciones sobre estas funciones, subdivididas por
familia de receptores, consulte el párrafo 3.4.1.
–– IMPORTAR / EXPORTAR ––
En esta sección, utilizando las funciones presentes (“Leer de fichero” - “Guardar en fichero” - “Copiar”), es posible importar, exportar, guardar y restablecer
los datos contenidos en un receptor. Las funciones disponibles son:
Leer de Fichero
: permite leer un fichero (por ejemplo con extensión “.cor”)
creado con el programa de gestión de la unidad de programación BUPC, o
bien creado con la función “Guardar en fichero” presente en esta sección.
Guardar en Fichero
: permite escribir en un fichero el contenido de la
memoria de un receptor, a fin de poderlo leer sucesivamente con la función
“Leer de Fichero” presente en esta sección. También es posible guardar un
fichero en un formato anterior, por ejemplo con la extensión “.cor” (previsto
por la línea BUPC), o bien en el nuevo formato (operación aconsejada).
Copiar
: permite copiar el contenido de la memoria de un receptor en la
memoria del ordenador.
Pegar
: permite pegar en la memoria de un receptor los datos contenidos
en la memoria del ordenador, antes guardados con la función “Copiar”, presente en esta sección.
3.4.1 – Sección CONFIGURACIONES: Memorias “BM” y Receptores
“NiceOne”
(familia OXI... ; familia OX...)
La sección “Configuraciones” permite configurar los parámetros de funciona-
miento de un receptor de la serie “NiceOne” y de un receptor con memoria
“BM”, gestionando las funciones avanzadas.
Page 61

Español – 11
ES
MEMORIAS BM
• Configuraciones Avanzadas: esta función permite configurar los siguientes
parámetros:
Bloqueo Memoria
: activa el bloqueo de las operaciones de autoaprendizaje de la tarjeta de memoria cuando ésta es insertada en el receptor. Es
decir que en un receptor en el que hay una memoria “Bloqueada”, no se
pueden insertar nuevos códigos y el funcionamiento se limita sólo a los códigos existentes (consulte también las instrucciones del receptor).
Contraseña
: permite insertar en la tarjeta de memoria una “Contraseña”
(palabra clave), es decir, un código numérico al cual pueden acceder, por
medio del programa, sólo las personas que poseen dicho código, con el que
se puede controlar y limitar el acceso a los datos contenidos en la tarjeta de
memoria. La contraseña será pedida cada vez que se desee acceder al contenido de la memoria, para leer o modificar los datos y los códigos presentes.
La Contraseña NO permite realizar modificaciones a los datos contenidos en
la tarjeta de memoria cuando ésta esté insertada en un receptor: bloquea
todas las funciones programables manualmente en el receptor que aloja la
memoria.
Timer: permite modificar el tiempo del timer. El tiempo se visualiza en
“horas”, “minutos” y “segundos”.
Altera
: es una clave que permite personalizar un receptor; esta clave es
compatible con los sistemas “FloR” anteriores.
¡Atención! – No se olvide la nueva clave de protección porque si no el
receptor no se podrá utilizar.
Control RND
: permite activar o desactivar el control de la parte variable
del código de identidad (RND) en un receptor.
Ventana RND
: permite modificar la ventana RND de un receptor. Esta
ventana representa la porción de valores dentro de los cuales es aceptada la
parte variable del código de identidad (RND).
Nota – Normalmente el valor de la ventana es 100 y puede tener un valor de
5 a 250.
Sincronismo
: permite activar o desactivar la resincronización en un receptor. Si el sincronismo está desactivado, la seguridad de la instalación es
mayor, pero si un transmisor saliera de la ventana RND, habrá que memorizar nuevamente el código de identidad en la memoria del receptor.
Sólo Nativos
: permite habilitar o deshabilitar el receptor para que reciba
los mandos enviados por un transmisor con un código modificado respecto
de aquel estándar de fábrica.
RECEPTORES “NiceOne”
Las funciones disponibles son las siguientes:
• Certificados: esta función permite leer y configurar los certificados de un
receptor (hasta un máximo de 4). En orden, comenzando desde arriba, se
encuentra el certificado del receptor (contenido en la tarjeta presente en el
paquete) y, posteriormente, otros 3 espacios que se utilizan para crear grupos
de receptores.
Nota – Para más informaciones sobre el uso de los certificados, consulte el
manual “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Claves: esta función permite personalizar un receptor, con la posibilidad de
modificar las claves “Instalador”, “Instalación” y “Altera”. En particular, “Altera”
es compatible con los sistemas “FloR” anteriores.
¡Atención! – No se olvide la nueva
clave de protección porque si no el recep-
tor no se podrá utilizar.
Las claves son útiles para personalizar un sistema, por ejemplo, es posible
modificar el código original (de fábrica) de un transmisor. Por dicho motivo, las
claves deben ser las mismas, tanto en el transmisor como en el receptor. En
este caso, habrá que modificar también las claves de la O-Box para poderla
utilizar sucesivamente.
• Configuraciones Avanzadas: esta función permite configurar los siguientes
parámetros:
Configuraciones básicas
- Habilita sólo transmisores originales: esta función permite habilitar o deshabilitar el funcionamiento de un receptor que recibe el mando de transmisores cuyo código se ha cambiado, es decir, que no es más el de fábrica.
- Deshabilitar RND: esta función permite activar o desactivar el control de la
parte variable del código de identidad (RND) en un receptor.
Configuraciones de Memorización
- Bloqueo de la memorización mediante “Código de habilitación”: esta
función permite bloquear la memorización de un nuevo transmisor utilizando
el “Código de habilitación” de un transmisor viejo (ya memorizado). Este procedimiento puede utilizarse sólo si se utilizan dos transmisores con codificación “O-Code”.
- Bloqueo de la memorización mediante “Certificado”: esta función permite bloquear la memorización de un nuevo transmisor utilizando el certificado de un receptor.
Page 62

12 – Español
ES
- Bloqueo de la memorización a distancia: esta función permite bloquear
la memorización de un nuevo transmisor utilizando un viejo transmisor, con
el procedimiento “cercano del transmisor”.
Configuraciones BUS T4
Nota – El “Bus” es un sistema que permite conectar entre sí todos los dispositivos presentes en una instalación de automatización, por medio de un
cable único con algunos hilos eléctricos en su interior. En este tipo de conexión la comunicación de los datos entre los dispositivos se hace utilizando
un protocolo específico que, en este caso, es el “Bus T4” de Nice.
- Habilitar repetición del código mediante bus: esta función permite habilitar en un receptor la posibilidad de transferir a otros dispositivos conectados, por medio del cable bus T4, la copia de un código recibido desde un
transmisor por medio de la señal radio.
- Habilitar recepción del código mediante bus: esta función permite habilitar en un receptor la recepción de un código transmitido a través del cable
bus T4 desde otro receptor (consulte el punto anterior “Habilitar repetición
del código mediante bus”).
- Habilitar grupos de autorización: esta función permite habilitar la gestión,
en grupos de autorización, de los códigos de radio.
Configuraciones Avanzadas
- Activar “Repeater”: esta función permite habilitar la repetición de un código. Si fuera necesario accionar una automatización desde una distancia
superior a aquella cubierta normalmente por el transmisor y por el receptor,
es posible utilizar un segundo receptor con la función de retransmitir a su vez
por radio el mando hacia el receptor de destino (en el que está memorizado
el código de identidad del transmisor desde el que se ha dado el mando), a
fin de que este último pueda ejecutar el mando.
- Activar gestión soltar botón: durante el uso de un transmisor, después
de haber enviado un mando, al soltar el botón, el movimiento no se detiene
en ese preciso momento, sino que continúa durante un tiempo muy corto
predeterminado. Si fuera necesario que el movimiento se interrumpa exactamente en el momento en que se suelte el botón del mando en el transmisor
(por ejemplo durante las regulaciones precisas), habrá que activar esta función en el receptor.
- Deshabilitar gestión prioridad: esta función permite deshabilitar en un
receptor la recepción de mandos enviados desde transmisores con prioridades superiores a 0.
Nota – Para más informaciones sobre el uso de todas las funciones descritas,
consulte el manual “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Cambio Contraseña: esta función permite insertar una contraseña que sirva
para bloquear el acceso, incluso manual, a todas las funciones contenidas en
un receptor por alguien que no posea dicha contraseña.
El área temática “Instalaciones” es un fichero que permite crear y almacenar,
para cada instalación, una ficha analítica que recoja los datos personales del
cliente y las configuraciones de los receptores instalados en su instalación. En
particular, es posible modificar las instalaciones, visualizar los códigos, las configuraciones y guardar los datos de los receptores instalados; en el caso de un
funcionamiento incorrecto, es posible restablecer el funcionamiento de una
automatización.
Esta área temática está formada de dos páginas:
– una destinada a la búsqueda rápida y a la selección de las instalaciones
almacenadas;
– la otra que contiene una ficha para recoger los datos relativos a una instalación.
Para acceder al área temática “Instalaciones”, proceda de la siguiente manera:
01. En la página principal
(fig. 3), haga clic sobre el icono “Instalaciones”.
02. Se abrirá una primera página (fig. 10) de gestión de las instalaciones
almacenadas. Esta página está formada de los siguientes elementos.
• La “Barra de navegación” con las siguientes funciones:
“Modificar”
: permite modificar los datos de una instalación.
“Nueva instalación”
: permite crear una nueva instalación.
“Copiar”
: permite copiar los datos de una instalación existente para
crear una nueva igual.
“Eliminar”
: permite eliminar una o varias instalaciones.
• El área “Filtro en datos” que permite buscar de manera sencilla y rápida
las instalaciones memorizadas.
• El área “Lista Instalaciones” que muestra la lista de las instalaciones
memorizadas.
3.5 – ÁREA TEMÁTICA “INSTALACIONES”
Page 63

Español – 13
ES
10
11
03. Entonces, seleccionando una de las siguientes funciones: “Modificar”,
“Nueva instalación” y “Copiar”, se abrirá una segunda página (fig. 11) con
la ficha relativa a una instalación. Esta página está formada de los siguientes elementos.
• La “Barra de navegación” con las siguientes funciones:
“Trabajar en esta instalación
”: permite trabajar en una instalación nueva
o existente (consulte el párrafo 3.5.1).
“Guardar en fichero”
: permite guardar en otros ficheros los datos de los
receptores a memorizar.
“Importar de Fichero”
: permite leer desde un fichero los datos de un
receptor (consulte el párrafo 3.5.1).
“Guardar Modificaciones”
: permite guardar las modificaciones efectua-
das en una ficha de una instalación.
Además de la barra de navegación, esta página muestra 3 áreas operativas: Cliente; Claves instalación; Receptores.
• Cliente: en esta área es posible insertar los datos personales de un
cliente.
• Claves instalación: en esta área es posible utilizar algunas claves para
personalizar una instalación, aprovechando los campos “Clave Instalador”, “Clave Instalación” y “Altera”. Estas claves son útiles para limitar la
gestión de las instalaciones únicamente a las personas que poseen las
claves. Es posible utilizar una misma clave en varias instalaciones o claves
diferentes para cada instalación.
Durante la programación de los transmisores y de los receptores de la
serie “Nice Opera”, estos serán programados automáticamente con las
mismas claves configuradas en la tarjeta de la instalación, si dicha tarje-
ta ha sido antes activada y contiene las claves configuradas
,
Nota – Para más informaciones sobre el uso de las claves, consulte el
manual “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Receptores: en esta área se muestran los receptores presentes en una
instalación. Para añadir o cancelar receptores, consulte el párrafo 3.5.1.
3.5.1 – Añadir los receptores a una instalación
Por lo general, para añadir uno o varios receptores dentro de una tarjeta de una
instalación, es posible hacerlo de dos modos diferentes.
Page 64

14 – Español
ES
• modo directo: esta modalidad prevé que los datos del receptor que hay que
añadir a una instalación ya estén memorizados en un fichero. Posteriormente, en
la página que muestra la tarjeta de una instalación haga clic sobre la función
“Importar de fichero” (en la barra de navegación) y seleccione el fichero deseado.
• modo indirecto
: esta modalidad prevé las siguientes operaciones:
– al abrirse el programa, seleccione en el panel “Selección instalación” una de
las funciones “Trabajar en la última instalación” y “Seleccionar o crear una instalación”; como alternativa, haga clic sobre el icono “Instalaciones” en la página principal.
– aparecerá la página de gestión de las instalaciones almacenadas (fig. 10)
donde habrá que seleccionar la instalación donde se desea añadir el receptor
(una instalación existente o una nueva, creada en ese momento);
– después de haber confirmado la selección, haciendo clic sobre el icono “Trabajar en esta instalación”, el programa mostrará la página principal con la indicación de la instalación en la que se está trabajando (fig. 12);
- posteriormente, conecte a la O-Box el receptor y active el área temática
“Receptores” para hacer la programación deseada (consulte el capítulo 3.4);
12
– por último, en la misma página, haga clic sobre el icono “Instalación” y seleccione el elemento “Añadir a instalación” en el menú en cascada(*).
(*) Nota – El menú asociado al icono “Instalación” es dinámico porque muestra
diferentes elementos, según la circunstancia. Por lo general, los elementos son:
• primera línea: indica en cursivo el nombre de la instalación activa, es decir,
aquella en la que se puede memorizar el receptor que se está programando.
• última línea: indica el mando “Añadir a instalación” para memorizar el recep-
tor (nuevo) apenas programado.
• otras líneas: indican el nombre de los receptores que ya están presentes en la
instalación. Para modificar uno de estos, seleccione el nombre y modifique sus
parámetros. Por último, para memorizar las modificaciones hechas, haga clic
sobre el icono “Instalación” y seleccione en el menú en cascada el elemento
“Guardar modificaciones …”. (este elemento está presente únicamente si en la
instalación activa ya hay receptores).
Page 65

Español – 15
ES
Este producto forma parte integrante de la automatización y, por consiguiente, debe eliminarse junto con ésta.
Al igual que para las operaciones de instalación, también al final de la vida útil
de este producto, las operaciones de desguace deben ser efectuadas por personal experto.
Este producto está formado de varios tipos de materiales: algunos pueden
reciclarse y otros deben eliminarse. Infórmese sobre los sistemas de reciclaje o
de eliminación previstos por las normativas vigentes locales para esta categoría de producto.
¡Atención! – algunas piezas del producto pueden contener sustancias contaminantes o peligrosas que, si se las abandona en el medio ambiente, podrían
provocar efectos perjudiciales para el mismo medio ambiente y para la salud
humana.
Tal como indicado por el símbolo de aquí al lado, está prohibido arrojar este producto a los residuos urbanos. Realice la
“recogida selectiva” para la eliminación, según los métodos
previstos por las normativas vigentes locales, o bien entregue
el producto al vendedor cuando compre un nuevo producto
equivalente.
¡Atención! – las reglas locales pueden prever sanciones importantes en el
caso de eliminación abusiva de este producto.
Eliminación de la batería
La batería, aunque esté agotada, puede contener sustancias contaminantes y,
por dicho motivo, NO debe arrojarse en los residuos normales. Después de
haber quitado la batería del producto, elimínela según los métodos previstos
por las normas locales para la “recogida selectiva”.
Eliminación del producto
Tipología: unidad de programación y control de códigos para los siguientes productos
Nice:
• receptores de las series NiceOne y SMX
• sistemas de transreceptores con codificaciones “Bio”, “Flo”, “FloR”, “Smilo” y “O-Code”;
• sistemas de control de accesos con decodificador “Morx”; lectores de tarjeta por
transponder MOM o botoneras digitales MOT
• dispositivos que utilizan el sistema TTBUS;
Tecnología por radio: transreceptor por radio a la frecuencia de 433.92 MHz. Alcance
hasta 10 m.
Conectores y dispositivos que pueden conectarse:
• zona de apoyo para los transmisores de la serie “NiceOne” (la programación se hace
por radio, sin contacto);
• conector para las tarjetas de memoria “BM 60”, “BM 250”, “BM 1000”.
• conector para receptores de las series “SMX” y “NiceOne” (algunos modelos, por
medio de cable adaptador);
• conector para transmisores de las series Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo y Plano (por medio
de cable adaptador);
• conector para lector óptico para transmisores de la serie “Bio”.
• lector de proximidad para tarjeta por transponder;
• conector para dispositivos TTBUS (por medio de cable adaptador);
Conexión al ordenador:
• conector para cable USB
• conector para cable serie RS232
• Conexión wireless con tecnología Bluetooth
®
(sólo versión OboxB)
Alimentación:
• Interna
: por medio de la batería recargable 6 V, 700 mAh.
•Externa
: por medio de la conexión USB al ordenador o bien por medio del alimentador
mod. ALA1, 12 Vdc,
Tiempo de recarga de la batería: 15 horas aprox.
Duración de la carga de la batería: 10 horas de funcionamiento aprox., o bien 3 meses
en stand-by.
Vida útil de la batería: 100 ciclos completos de descarga como mínimo.
Grado de protección de la caja: IP 20 (uso únicamente en ambientes interiores y prote-
gidos).
Temperatura de trabajo: de -20°C a +55°C
Medidas (mm): 194 x 115 x H 40
Peso (gr): 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Características técnicas del producto
Page 66

16 – Español
ES
DECLARACIÓN DE CONFORMIDAD CE
Declaración de conformidad CE según la Directiva 1999/5/CE
Nota – La presente Declaración de Conformidad agrupa el contenido de cada
declaración de conformidad de cada uno de los productos citados; está actualizada a la fecha de edición de este manual y ha sido readaptada por motivos de
impresión.
Una copia de la declaración original de cada producto puede ser solicitada a Nice
S.p.a. (TV) I.
______________
El suscrito Lauro Buoro, en su carácter de Administrador Delegado,
declara bajo su responsabilidad que el producto:
Nombre del fabricante: NICE s.p.a.
Dirección: Via Pezza Alta 13, Z.I. Rustignè, 31046 Oder-
zo (TV) Italia
Tipo: Programador OBOX para radiomandos con
transreceptor radio 433,92 MHz y lector de
tarjetas por transponder.
Programador OBOXB para radiomandos con
transreceptor radio 433,92 MHz y lector de
tarjetas por transponder. Versión con tecnología Bluetooth
®
Modelos: OBOX, OBOXB
Accesorios:
Responde a las prescripciones de la siguiente directiva comunitaria:
• 1999/5/CE DIRECTIVA 1999/5/CE DEL PARLAMENTO EUROPEO Y
DEL CONSEJO del 9 de marzo de 1999 relativa a los equipos radioeléctricos y equipos terminales de telecomunicación y el recíproco
reconocimiento de su conformidad, según las siguientes normas
armonizadas:
protección de la salud: EN 50371:2002;
seguridad eléctrica: EN 60950-1:2001;
compatibilidad electromagnética: EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005; EN 301
489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002
espectro radioeléctrico: EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2
V1.3.1:2006, EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004
También satisface los requisitos previstos por las siguientes directivas
comunitarias, modificadas por la Directiva 93/68/CEE del consejo del
22 de julio de 1993:
• 89/336/CEE; DIRECTIVA 89/336/CEE DEL CONSEJO del 3 de mayo
de 1989 para la aproximación de las legislaciones de los Estados
miembros relativas a la compatibilidad electromagnética, según las
siguientes normas:
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Amministratore Delegato)
Page 67

Deutsch – 1
DE
DEUTSCH
DIE SOFTWARE-LIZENZ
Die Programme “O-Box Software Desktop” und “O-Box Software Mobile”
unterliegen dem Schutz von Copyright und geistigem Eigentum; die Software
wird nicht verkauft, sondern es werden lediglich einzelne Benutzerlizenzen vergeben. Die Fa. Nice s.p.a. bleibt Eigentümer der in Lizenz vergebenen Kopie
des Programms. Die Lizenz für die Programme “O-Box Software Desktop” und
“O-Box Software Mobile” gehören zum Produkt “O-Box”.
Diese Programme werden ohne Garantie für Benutzung und Sicherheit geliefert. Die Fa. Nice s.p.a. haftet nicht für direkte oder indirekte Schäden, einschließlich Gewinnverluste, Arbeitsunterbrechungen u. ä., die durch die nicht
sachgemäße Benutzung der Software verursacht wurden.
MARKENINFORMATIONEN
Die Marken AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, MICROSOFT®sind
geschützte Marken. Die im Handbuch angegebenen Produktbezeichnungen
können von den Produkteigentümern ebenfalls geschützt werden.
ALLGEMEINES ZUM HANDBUCH
Die Programmiereinheit ist in zwei Versionen verfügbar: O-Box
und O-BoxB. Die Modelle unterscheiden sich lediglich dadurch,
dass das Modell O-BoxB über ein Modul für den Bluetooth
®
Anschluss verfügt.
Der Begriff “O-Box
” wird in diesem Handbuch, wo nicht
ausdrücklich angegeben, für beide Modelle benutzt.
BESCHREIBUNG DES PRODUKTS UND
SEINES VERWENDUNGSZWECKS
1
Das Produkt O-Box (oder O-BoxB, Version mit Bluetooth® Modul) besteht aus
der Programmiereinheit und einer entsprechenden Softwareapplikation. Beide,
Programmiereinheit und Softwareapplikation, dienen der Programmierung und
Verwaltung von Daten und Parametern zur automatisierten Steuerung von
Toren, Garagentoren, Rollläden und Markisen, beweglichen Schranken und
ähnlichen Vorrichtungen.
Jedwede andere Benutzung ist als unsachgemäße Benutzung zu verstehen! Der Hersteller haftet nicht für aus der unsachgemäßen, nicht in diesem
Handbuch vorgesehenen Benutzung des Produkts, entstehende Schäden.
Die O-Box: Das System “NiceOpera”
Die O-Box ist Teil des Systems “NiceOpera”. Dieses System wurde von Nice
entwickelt, um die Programmierung, den Betrieb und die Wartung von Automatisierungsvorrichtungen zu vereinfachen. Das System besteht aus verschiedenen Vorrichtungen, Hard- und Software, die Informationen untereinander mittels eines Codierungssystems mit der Bezeichnung “O-Code” oder über eine
Kabelverbindung austauschen können.
Die Hauptelemente des Systems:
– Sender NiceOne;
– Empfänger NiceOne (Familie OXI… ; Familie OX…);
– Programmiereinheit O-Box;
– Steuerzentralen und Antriebsmotoren mit “Bus T4”;
– O-View Programmierung für Anlagen mit “Bus T4”.
WICHTIG – Um alle Funktionen des Systems NiceOpera und das Zusammenwirken der diversen Systemkomponenten im Detail zu verstehen, das
Systemhandbuch “NiceOpera System Book” einsehen. Das Handbuch ist
auch auf der Webseite www.niceforyou.com zu finden.
Die wesentlichen Funktionsmerkmale der O-Box
Die O-Box ist besonders für technologisch anspruchsvolle Automatisierungsanlagen geeignet. Mit der O-Box können zahlreiche Funktionen direkt im Büro
des Installateurs aufgerufen werden, ohne dass direkt an der Anlage des Kunden gearbeitet werden muss. Ebenso ist es möglich, eine Anlage direkt beim
Kunden zu konfigurieren.
Page 68

2 – Deutsch
DE
Mit einem 6V-Akku ist der Betrieb ohne Netzanschluss möglich.
Hinweis – Der Akku muss mindestens alle 10 Betriebsstunden aufgeladen werden. Die Software zeigt den Ladepegel an (siehe Abb. 1).
Wenn die O-Box extern stromversorgt oder ein USB-Kabel angeschlossen
wird, lädt sich der Akku automatisch auf.
2.1 – ANSCHLÜSSE
• O-Box an die Stromversorgung anschließen
Die O-Box kann an das Netz oder an einen 12V-Akku (optional) angeschlossen
werden, oder über ein USB-Kabel (wird mitgeliefert) vom Computer stromversorgt werden.
• O-Box an einen PC anschließen
Um die O-Box (oder die O-BoxB) betreiben zu können, ist der Anschluss an
einen PC mit USB-Eingang über das mitgelieferte Kabel erforderlich. Über ein
RS232-Kabel (optional) ist auch der Anschluss an den seriellen Port möglich.
Hinweis – Vorzuziehen ist dabei der USB-Port (insofern vorhanden), der mehr
Leistung bietet: Sichere, schnellere Datenübertragung, keine Konfiguration
erforderlich, automatisches Aufladen des internen Akkus der O-Box.
• Anschluss der O-BoxB über Bluetooth
®
Das Modell O-BoxB kann via Bluetooth®an einen Computer oder Handheld
(PDA) mit
Bluetooth®Interface angeschlossen werden.
Für diesen Anschluss sind keine Kabel erforderlich: Es reicht aus, die Software
im Computer oder Handheld zu installieren und die entsprechenden Daten des
Handheld einzugeben.
Hinweis – Vor der Aktivierung des Bluetooth
®
Anschlusses das USB-Kabel
bzw. das RS232-Kabel von der O-Box abziehen.
Die O-Box kann bis zu 16 Anschlüsse diverser Computer speichern. Um die
Verbindung herzustellen, die O-BoxB einschalten, Computer für den Bluetooth
®
Anschluss einstellen und warten bis die Led der O-BoxB aufhört zu blinken. In
diesem Moment ist die Verbindung aktiv. Wenn die Liste der Computeranschlüsse aus dem Speicher gelöscht werden soll, wie folgt vorgehen:
Mit der O-Box können Anlagen mittels eines Datenarchivs verwaltet und modifiziert werden. Verschiedene Operationen, wie die Zurücksetzung, die Erweiterung einer vorhandenen Anlage, Erneuerung von Sendern und Empfängern,
usw. können so bequem durchgeführt werden.
Im Allgemeinen kann die O-Box für folgende Anwendungen eingesetzt werden:
• Prüfen, Ergänzen, Programmieren oder Löschen der Sendercodierungen
“Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano”, “NiceOne”;
• Programmieren der Speicher der Empfänger “Bio” und “FloR”;
• Transponder Cards lesen und schreiben;
• Programmieren der Funktionen und Parameter der Sender “Bio”, “FloR”,
“Very”;
• Optisches Auslesen der Sendercodes “Bio”;
• Lesen und programmieren der Parameter der Sender “SMX1” und “SMX2”
über Kabel;
• Datenempfang über Funk von Sendern mit der Codierung SMILO, FLO,
FLOR, O-CODE, um Benutzerarchive zu erstellen, Speicher und Empfänger
zu programmieren;
• Über Funk die Sender der Reihe “Nice One” programmieren;
• Über Funk alle Funktionen der Empfänger “Nice One” programmieren.
Die mit der O-Box gelieferte Software ermöglicht das Konfigurieren und Programmieren der Sender und Empfänger der Reihe “Nice One”. Kompatibel mit
allen Geräten der Reihen “FloR”, “SMXI” und “Bio”.
HARDWARE: Beschreibung des Produkts,
Installation
2
1
Page 69

Deutsch – 3
DE
a) – Starttaste Activity der O-BoxB gedrückt halten und das Ende folgender
Phasen abwarten. Die O-BoxB gibt einen Signalton (Beep) aus, die Led schaltet sich aus und kurz darauf wieder ein, woraufhin die O-BoxB eine nun Reihe
von Signaltönen (Beeps) ausgibt.
b) – Die im O-BoxB-Speicher gespeicherten Daten wurden gelöscht, die Starttaste kann losgelassen werde.
2.2 – ZUBEHÖR (optional)
Hinweis – Mit der O-BoxB wird ein USB-Kabel geliefert; alle anderen Kabel
sind optional und nicht im Lieferumfang enthalten. Die betreffenden Kabel sind
folgende:
– Kabel, Mod.
CABLA06 für den Anschluss D, Abb. 2: Für den Anschluss von
Empfängern der Reihen “SMX” und “NiceOne”.
– Kabel, Mod.
CABLA02 für den Anschluss M, Abb. 2: Für den Empfang der
Sendercodes der reihe “Bio”
– Serielles Kabel, 9-polig, Mod.
CABLA01 für den Anschluss G, Abb. 2: Für
den Anschluss der O-Box an einen Computer.
– Kabel TTBUS, Mod.
CABLA05 für den Anschluss H, Abb. 2: Anschluss aller
für mit TTBUS ausgestattete Rohrmotoren für Rollläden und Markisen von
Nice.
– Kabel Mod.
CABLA03 für den Anschluss I, Abb. 2: Für den Anschluss von
Sendern der Reihe”Very”.
– Kabel Mod.
CABLA02 für den Anschluss I, Abb. 2: Für den Anschluss von
Sendern der Reihen “Bio” und “FloR”.
– Kabel Mod.
CABLA04 für den Anschluss I, Abb. 2: Für den Anschluss von
Sendern der Reihen “Ergo” und “Plano”.
– Netzteil, Mod.
ALA1,12 V, 300 mA für den Anschluss E, Abb. 2: Für den
Anschluss der O-Box an das Stromnetz.
2.3 – ANSCHLÜSSE UND AN DIE O-BOX ANSCHLIESSBARE GERÄTE
Die O-Box verfügt über verschiedene Anschlusstypen (siehe Abb. 2), über die
zahlreiche Nice-Geräte angeschlossen werden können. Hinweis – Für einige
dieser Anschlüsse ist ein besonderes Kabel erforderlich: Zu Kabeltypen und
deren Merkmalen siehe Abschnitt 2.2.
In der Abb. 2 werden Anschlüsse und andere Vorrichtungen der O-Box mit
Buchstaben bezeichnet. Hier eine detaillierte Übersicht über die Funktionen
und deren Benutzung:
[A] – Taste zum Ein- und Ausschalten der O-Box
Um die O-Box einzuschalten die Taste für einige Momente gedrückt halten bis
ein kurzer Ton (Beep) ausgegeben wird.
Um die O-Box auszuschalten die Taste für einige Momente gedrückt halten bis
ein langer Ton (Beeeeeeep) ausgegeben wird.
[B] – Bereich Funkanschluss von Sendern der Reihe “NiceOne”
Der markierte Bereich ermöglicht die Fernprogrammierung der Sender der Reihe “Nice One” über Funk (also ohne physische Verbindung). Die Programmierung erfolgt nach Aufsetzen des Sender auf die markierte Fläche.
Während des Programmieren blinkt die Led des Senders als Zeichen dafür,
dass die Funkkommunikation mit der Software hergestellt ist. An diesem Punkt
kann mit der Programmierung der einzelnen Senderparameter (siehe Kapitel 3
Abschnitt 3.3) begonnen werden.
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 70

4 – Deutsch
DE
[C] – Anschluss für “BM”-Speicherplatinen
Über diesen Anschluss kann eine “BM”-Speicherplatine von Nice an die O-Box
angeschlossen werden. Die Platine direkt auf dem Anschluss einsetzen und mit
dem Programmieren beginnen (siehe Kapitel 3 Abschnitt 3.3).
[D] – Anschluss vom Typ “SM”
Über diesen Anschluss werden ausschließlich Empfänger der Reihen “SM” und
“NiceOne” an die O-Box angeschlossen. Einige diese Empfänger können direkt
auf dem Anschluss eingesetzt werden, für andere ist ein Kabel Mod. CABLA06
erforderlich. Nach dem Einsetzen kann mit dem Programmieren begonnen
werden (siehe Kapitel 3 Abschnitt 3.3).
Hinweis – Die Sender der Reihe “NiceOne” (OXIT und OX2T) können auch über
Funk programmiert werden. Dabei ist die Datenübertragung allerdings langsamer, als bei über den SM-Anschluss.
[E] – Anschluss für externes Netzteil, mod. ALA1
Dieser Anschluss ist für den Anschluss der O-Box an das Stromnetz über ein
externes 12V-Netzteil (optionales Zubehör).
Hinweis – Auch bei abgeschalteter O-Box wird der interne Akku aufgeladen,
sobald das Netzkabel an die Stromversorgung angeschlossen wird.
[F] – Anschluss für “USB”-Kabel
Über diesen Anschluss kann die O-Box mittels eines USB-Kabels an den USBPort eines Computers angeschlossen werden. Sofort nach dem Anschließen
kann mit dem Programmieren begonnen werden.
Hinweis – Auch bei abgeschalteter O-Box wird der interne Akku aufgeladen,
sobald das USB-Kabel an einen eingeschalteten Computer angeschlossen
wird.
[G] – Serieller Anschluss “RS232” (Kabel vom Typ Mod. CABLA01)
Über diesen Anschluss kann die O-Box mittels eines seriellen RS232-Kabels
(optionales Zubehör) an den seriellen RS232-Port eines Computers angeschlossen werden. Sofort nach dem Anschließen kann mit dem Programmieren
begonnen werden.
[H] – Serieller Anschluss “TTBUS” (Kabel vom Typ Mod. CABLA05)
Über diesen Anschluss können alle Rohrmotoren für Markisen und Rollläden
von Nice mit TTBUS-Port über ein entsprechendes Kabel (optionales Zubehör)
an die O-Box angeschlossen werden.
[I] – Anschluss für das Klonen von Sendern (Kabeltyp, mod.
CABLA03 - CABLA02 - CABLA04)
Über diesen Anschluss können Nice-Sender der Reihen “Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”,
“Plano” und “Very” über das entsprechende Kabel (optionales Zubehör) an die
O-Box angeschlossen werden. Um die Verbindung herzustellen, den Sender
öffnen um das Anschlusskabel einzustecken (*). Das andere Kabelende an den
entsprechenden Anschluss der O-Box anschließen (I in Abb. 2).
(*) Hinweis:
- für Sender der Reihen “Ergo” und “Plano” ein Kabel Mod. CABLA04 verwenden.
- für Sender der Reihen “Bio” und “FloR” ein Kabel Mod. CABLA02 verwenden.
- für Sender der Reihe “Very” ein Kabel Mod. CABLA03 verwenden.
[L] – Proximity-Leser für Transponder Cards
Der Proximity-Leser ermöglicht das Lesen (blaue Karte, graue Karte) oder
Schreiben (graue Karte) der auf den Nice Transponder Cards enthaltenen
Codes. Um die Verbindung herzustellen die Card vor den Leser halten.
[M] – Anschluss für optische Leser für Sender der Reihe “Bio”
Dieser Leser liest den Funkcode der Sender der Reihe “Bio”.
Um die Verbindung herzustellen den optischen Leser in den entsprechenden
Anschluss (M in Abb. 2) einsetzen (optionales Zubehör, Mod CABLA02) und
die Led des Senders dem Lesekopf des optischen Lesers annähern.
Page 71

Deutsch – 5
DE
Il software presente nel CD di installazione “O-Box Software Suite” è fornito in
due versioni:
• “O-Box Desktop” destinato all’installazione in un personal computer (PC)
• “O-Box Mobile” destinato all’installazione in computer palmare (PDA).
SYSTEMANFORDERUNGEN
Die Software kann auf allen Computern oder Handheld-Geräten aller Marken,
die die folgenden Minimalerfordernisse erfüllen, installiert werden.
VERSION FÜR PC:
– Prozessor: Ty p AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Nice Empfehlung: Ty p;
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– RAM: 128 MB Nice Empfehlung: 256 MB
– Verfügbarer Festplattenplatz: 30 MB Nice Empfehlung: 100 MB
– Betriebssystem: Windows
®
98 SE Nice Empfehlung: Windows
®
2000 oder höher
– Videokarte: 800 x 600, 256 Farben
– Datenträger: CD-Rom (für die Installation erforderlich)
Hinweis – Zusammen mit der Software wird das Programm Microsoft
®
.NET Framework
Redistributable 2.0. installiert
VERSION FÜR HANDHELD-GERÄTE:
– Prozessor: (300 MHz) Nice Empfehlung:
(300 MHz oder höher)
– RAM: 64 MB Nice Empfehlung: 128 MB
– Speicher: 5 MB Nice Empfehlung: 100 MB
– Betreibssystem: Windows
®
Mobile Nice Empfehlung: Windows
®
2003 oder 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE oder neuer
– Anschluss: Bluetooth
®
– Bildschirmauflösung: 240 x 320 con 256 colori
– PC mit: CD-Rom (für die Installation erforderlich)
Hinweis – Zusammen mit der Software wird das Programm Microsoft
®
.NET Framework
Redistributable 2.0. installiert
SOFTWARE: Beschreibung des Produkts,
Benutzung
3
3.1 – INSTALLATION DER SOFTWARE
Die Softwareinstallation verläuft genauso, wie die Installation jeder anderen
Computeranwendung.
Nach dem Einlegen der Installations-CD startet der Installationsvorgang automatisch. Anderenfalls das Programm-Icon “Setup-exe” anklicken und den
Installationsanweisungen folgen.
Hinweis – Vor der Installation die O-Box vom Computer trennen.
KURZÜBERSICHT DER SOFTWAREFUNKTIONEN: Aufbau, Funktionen
• Startbildschirm (Homepage)
Nach Starten der Software wird die Homepage (das Startbildschirmfenster)
aufgerufen (siehe Abb. 3), die folgende Funktionen enthält:
[1] – Zeigt den Status der Verbindung des Handheld-Geräts an: Icon anklicken,
um die Synchronisierung des Handheld-Geräts zu starten.
[2] – Zeigt den Akkustand und den Status der Verbindung mit der O-Box an:
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 72

6 – Deutsch
DE
Wenn die Verbindung nicht zu Stande kommt, erneut auf das Icon klicken
und die Software startet einen neuen Verbindungsversuch.
[3] – “Anlage wählen”: Hier kann beim Start der gewünschte Betriebsmodus
eingestellt werden. Das vereinfacht die nachfolgend vorzunehmenden Einstellungen.
Wenn nach der Programmierung eines Empfängers die Konfigurationsdaten ausschließlich in dessen Speicher oder in einer Datei gespeichert werden sollen, Option “Arbeiten ohne Anlage zu erstellen” wählen.
Wenn nach der Programmierung eines Empfängers die Konfigurationsdaten nicht nur in dessen Speicher oder in einer Datei gespeichert werden
sollen, sondern auch auf eines Sammelplatine der Anlage, in der der Empfänger eingesetzt wird, Option “An der letzten Anlage arbeiten” oder “Anlage wählen oder Anlage erstellen” wählen (siehe Abschnitt 3.5.1).
[4] – Zeigt den erfolgten Zugang zum Programmierbereich für die Programmie-
rung der Sender an.
[5] – Zeigt den erfolgten Zugang zum Programmierbereich für die Programmie-
rung der Empfänger an.
[6] - Zeigt den erfolgten Zugang zum Programmierbereich Verwaltung der
Anlagen an.
[7] - Zeigt den erfolgten Zugang zum Programmierbereich für die Einstellun-
gen der Software an.
[8] - Zeigt die Taste für das Schließen der Softwareapplikation an.
[9] – Zeigt an, wo sich die Daten für die individuellen Einstellungen der Software
(...Benutzername, usw.) befinden.
• Themenbildschirmfenster
Im Startbildschirmfenster wird das gewünschte Thema (“Sender”, “Empfänger”, “Anlagen”, “Einstellungen”) gewählt. Anklicken des entsprechenden
Icons öffnet das Themen-Bildschirmfenster, in dem alle gewünschten Operationen durchgeführt werden können. (Hinweis – Aus jedem Themenbereich
heraus kann der spezielle Gegenstand in einem oder mehreren Folgebildschirmfenstern entwickelt werden). Diese Bildschirmfenster bestehen aus den
folgenden Elementen (siehe Abb. 4):
[a] – Navigationsmenü
[b] - Funktionsmenü
[c] - Bereich für allgemeine Daten des angeschlossenen Geräts
[d] - Programmierbereich
Elemente des Navigationsmenüs
Mittels des in jedem Themenfenster vorhandenen Navigationsmenüs kann man
sich von einem Bildschirmfenster zum nächsten bewegen und jederzeit ablesen, wo genau man sich befindet.
Im Navigationsmenü finden wir folgende Positionen:
–“Start” = Anklicken dieses Icons öffnet das Startbildschirmfenster
–“Zurück” = Anklicken dieses Icons kehrt zum vorherigen
Bildschirmfenster
zurück
–“Vor” = Anklicken dieses Icons öffnet das nächste
Bildschirmfenster
–“Hilfe” = Anklicken dieses Icons öffnet die Bedienungsanweisungen
–“Neu Laden” = in einigen Bildschirmfenstern können durch Anklicken dieses
Icons die Daten neu geladen und aktualisiert werden.
WICHTIG – In einigen Bildschirmfenstern gibt es außer diesen Standardpositio-
nen noch andere, speziell die Geräte, die gerade bearbeitet werden, betreffende Funktionen.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 73

Deutsch – 7
DE
3.2 – SITZUNG STARTEN
Um eine Sitzung zu starten, wie folgt vorgehen:
– O-Box einschalten;
– Gerät, an dem gearbeitet werden soll, an die O-Box anschließen;
– Software starten (Hauptfenster öffnet sich);
– Im Startbildschirmfenster auf den gewünschten Themenbereich klicken;
– Gewünschte Eingaben in den Themenbildschirmfenstern vornehmen.
Um diesen Themenbereich aufzurufen zuerst den Sender, an dem gearbeitet
werden soll, an die O-Box anschließen; danach wie folgt vorgehen:
01. Im Startbildschirmfenster
auf das Icon “Sender” (Abb. 3) klicken.
02. Danach erscheint das Themenfenster “Sender” (Abb. 5): Senderfamilie
und Modell auswählen und auf “Weiter” klicken (im Navigationsmenü), um
zum folgenden Bildschirmfenster, in dem die Programmierung des Sen-
ders vorgenommen werden kann, zu gehen.
Hinweis – Nur für NiceOne Sender: Wenn der Sender vor
dem Aufrufen
des Themenbereichs “Sender” in den Programmierbereich der O-Box
gesetzt wird, erkennt die Software das Sendermodell automatisch und
zeigt die entsprechenden Daten, einschließlich Code und RND-Code an.
Wenn der Sender nach dem Aufrufen des Themenbereichs “Sender“” in
den Programmierbereich der O-Box gesetzt wird, auf das Icon “Neu
laden” klicken, damit die Software das Modell erkennt und die entsprechenden Daten anzeigt.
03. Daraufhin erscheint ein zweites Fenster des Bereichs “Sender”, in dem
Programmierungen vorgenommen werden können (Abb. 6): Im Funktionsmenü die gewünschte Funktion anwählen; danach können in den entsprechenden Eingabereichen Parameterdaten geändert, hinzugefügt.
WICHTIG – Einige Funktionen ermöglichen das sequenzweise Bearbeiten
mehrerer Sender. Dazu einfach einen Sender nach dem anderen an die OBox anschließen. Als Zeichen dafür, dass der Programmiervorgang abgeschlossen ist und der nächste Sender bearbeitet werden kann gibt die OBox zwei Signaltöne (Beep) aus.
3.3 – THEMENBEREICH “SENDER”
5
6
Page 74

8 – Deutsch
DE
Das Funktionsmenü ist in drei Abschnitte unterteilt: Codes; Kennungen;
Details (Abb. 4). Wichtig – Die in den einzelnen Abschnitten verfügbaren
Funktionen variieren je nach Sendertyp.
–– CODES ––
In diesem Abschnitt werden die Codes eines Senders eingestellt. Folgende
Funktionen sind verfügbar:
– Test Sender
: Über diese Funktion kann das korrekte Arbeiten des Senders
getestet und die Kennung und der veränderbare Teil des RND-Codes angezeigt werden.
– Code ändern
: Über diese Funktion kann die Originalkennung eines Senders
geändert werde.
WICHTIG – Um mehrere Sender sequenzweise für fortlaufende Codes
zu programmieren auf das Icon “Programm Sequenz” klicken und die beiden folgenden Felder ausfüllen: “Codeweise”, “Step” (von einem Sender zum nachfolgenden ansteigender Code) und “Anzahl Codes”; danach auf “Testen” klicken. Die
Software ergänzt zuvor leer gelassene Felder automatisch.
– Code wiederherstellen
: Über diese Funktion kann der werkseitig voreinge-
stellte Sendercode wieder hergestellt werden.
–– ZERTIFIKATE ––
In diesem Abschnitt werden die Zertifikate eines Senders eingestellt. Folgende
Funktionen sind verfügbar:
– Zertifikate eingeben: Über diese Funktion kann das “Zertifikat” eines Empfängers im Sender eingegeben werden. Für jedes Zertifikat kann die Speicherung im “Modus I” oder im “Modus II” erfolgen.
Bei Speicherung im “Modus II” (jede Taste des Sender entspricht einer
bestimmten Funktion des Empfängers) reicht es aus, mit wenigen Klicks unter
der Menüposition “Funktion” die Nummer der gewünschten Funktionen einzugeben und danach unter der Position “Tasten” die Taste, die im Sender gespeichert werden soll, zu wählen.
Hinweis – Die für die Speicherung im Sender verfügbaren Befehle hängen vom
Sendertyp und vom Modell der Zentrale ab, mit der dieser Sender benutzt wird.
Die detaillierte Auflistung der einzelnen Befehle im Handbuch zur Zentrale.
– Zertifikate löschen
: Über diese Funktion können Zertifikate aus dem Sender
gelöscht werden.
–– DETAILS ––
Hier können Verschlüsselungen und Betriebsparameter eines Senders eingegeben werden: Folgende Funktionen sind verfügbar:
– Schlüssel eingeben
: Über diese Funktion kann ein Sender individuell einge-
stellt werden, d. h. die Verschlüsselungen für “Installateur”, “Installation” und “Altera”. Insbesondere “Altera” ist kompatibel zu den vorhewirigen “FloR”-Systemen”.
Achtung! – Den neuen
Zugangsschlüssel nicht vergessen. Andernfalls ist der
Sender mit diesem Empfänger nicht mehr zu benutzen.
– Fortgeschrittene Einstellungen
: Hier können folgende Parameter eingestellt
werden.
Anzahl Blöcke: Hier kann die Anzahl der Wiederholungen der gesendeten
Kennung geändert werden. Bei bestimmten Automatisierungen, die schnellere Ansprechzeiten als die werkseitig voreingestellten erfordern.
Priorität: Ersetzen eines Senders, wobei die Kennung beibehalten wird
.
Dies wird durch Erhöhen der Priorität des NEUEN Senders gegenüber dem
ALTEN erreicht.
Freigabe RND: Freischalten und Sperren der Verwaltung des veränderba-
ren Teils der Kennung (RND).
Übergabe Freigabecode: Übertragen der Freigabecodes in einen ande-
ren Sender.
Kopieren unter verschiedenen Modellen: Freigabe oder das Sperren
von Kopien des “Freigabecodes” unter unterschiedlichen Sendern.
Freigabe Repeater: Freigabe oder das Sperren der Verwaltung der Wie-
derholungen bei Empfängern mit Repeater-Funktion.
Hinweis – Durch Anklicken der Taste “Werkseitige Werte” können die werkseitigen Werte der o. g. Parameter eingestellt werden (Fortgeschrittene Einstellungen).
– Alle Originaleinstellungen
: Diese Funktion setzt alle Parameterwerte auf die
werkseitigen Voreinstellungen: Wiederherstellen des Original Kenncodes, Entfernen von Zertifikaten und Wiederherstellen der Werte der verschiedenen
Parameter.
Wichtig – Aus Sicherheitsgründen ändert diese Funktion die Werte des Passwortschutzes nicht. D. h.: Es erfolgt keine Rücksetzung auf die Originalwerte.
- Programmieranleitung
: Mittels dieser Funktion kann ein Sender durch das
schrittweise Befolgen aller oben beschriebenen Schritte programmiert werden.
Page 75

Deutsch – 9
DE
Um diesen Themenbereich aufzurufen zuerst den Empfänger, an dem gearbeitet werden soll, an die O-Box anschließen; danach wie folgt vorgehen:
01. Im Startbildschirmfenster
auf das Icon “Empfänger” (Abb. 3) klicken.
02. Danach erscheint das Themenfenster “Empfänger” (Abb. 7): Familie und
Modell des Empfängers, der programmiert werden soll wählen (das
System prüft, ob Empfänger dieser Familie an die O-Box angeschlossen
sind und zeigt automatisch das Modell an; trotzdem kann das Modell
auch manuell ausgewählt werden). Danach im Navigationsmenü auf “Weiter” klicken, um zum nächsten Bildschirmfenster zu gehen.
Hinweis – Zum Programmieren eines Empfängers der Reihe “NiceOpera”
muss der angewandte Anschlusstyp gewählt werden: Wireless (in diesem
Fall muss das Zertifikat des Empfängers eingegeben werden) oder
Anschluss an O-Box (in diesem Fall SM-Anschluss benutzen).
03. Nach der Wahl der Empfängerfamilie erscheint ein zweites Bildschirmfen-
ster mit dem Titel “Was möchten Sie als nächstes tun?”, in dem anzugeben ist, welcher Vorgang nun durchgeführt werden soll (Abb. 8):
• Neuen Empfänger konfigurieren
(mittels dieser Operation wird ein neuer
Empfänger konfiguriert).
• Daten eines Empfängers lesen und ändern
(diese Operation ermöglicht
das Lesen und Ändern der Daten eines Empfängers, Änderungen werden
sofort gespeichert).
• Alle Daten eines Empfängers löschen (dieser Vorgang löscht alle Daten
zu einem Empfänger).
• Codes im Speicher suchen und ändern (diese Operation ist nur bei Empfängern der Reihe “NiceOne” möglich und ermöglicht das direkte Arbeiten
im Speicher des Empfängers).
04. Schließlich öffnet sich ein drittes Bildschirmfenster für die Programmierung
(Abb. 9). Im Funktionsmenü die gewünschte Funktion anwählen; danach
können in den entsprechenden Eingabereiche Parameterdaten geändert,
hinzugefügt, usw. werden
Das Funktionsmenü ist in drei Abschnitte unterteilt: Gespeicherte
Codes, Einstellungen, Importieren / Exportieren.
3.4 – THEMENBEREICH “EMPFÄNGER
7
8
Page 76

10 – Deutsch
DE
9
–– GESPEICHERTE CODES ––
In diesem Abschnitt können die gespeicherten Kennungen aller Empfänger
geändert werden. Hierzu auf “Codes ändern” klicken, um folgende Optionen
aufzurufen:
Code hinzufügen
: Hinzufügen eines Codes durch dessen manuelle Eingabe.
Folge hinzufügen
: Hinzufügen einer Folge von Codes durch Ausfüllen folgender Felder: “Ausgangscode”, “Zielcode” und “Schritt von einem Code
zum nächsten”. Anschließend auf “Prüfen” klicken. Das vorher leer gelassene Feld wird automatisch vervollständigt.
Aus TX hinzufügen
: Speichern eines Sendercodes im Empfänger durch
einen einfachen Tastenbefehl am Sender.
Code löschen
: Löschen eines oder mehrerer Codes aus dem Speicher
des Empfängers.
Suchen
: Suchen des Sendercodes durch Eingabe des Codes im entspre-
chenden Feld oder Drücken eine beliebigen Taste am Sender.
–– EINSTELLUNGEN ––
In diesem Abschnitt können die Parameter einiger Empfängerfamilien über die
vorhandenen Funktionen (“Zertifikate” - “Passwörter - “Fortgeschrittene
Einstellungen” - “Passwort ändern”) geändert werden. Die verfügbaren Funk-
tionen variieren je nach Empfängertyp oder zu programmierendem Speicher.
Für weitere Details zu diesen Funktionen, nach Empfängerfamilie geordnet, siehe Abschnitt 3.4.1.
–– IMPORTIEREN / ESPORTIEREN ––
In diesem Abschnitt können in einem Empfänger gespeicherte Daten mittels
der dort verfügbaren Funktionen (“Lesen von File” – “Speichern in File” –
“Kopieren”) importiert, exportiert, gespeichert und wieder hergestellt werden.
Verfügbare Funktionen:
Lesen von File
: Auslesen eines mit der Verwaltungssoftware der Programmiereinheit BUPC oder der Funktion “Als File speichern” erstellten Files (z. B.
mit der Dateiextension “.cor”).
Als File speichern
: Abspeichern des Speicherinhalts eines Empfängers als
File, so dass dieses später mittels der in diesem Abschnitt verfügbaren Funktion “Lesen von File” ausgelesen werden kann. Ein File kann in einem früheren Format, z. B mit der Dateiextension “.cor” (der Reihe BUPC) oder einem
neuen Format (empfohlen) gespeichert werden.
Kopieren
: Kopieren des Speicherinhalts eines Empfängers in den Spei-
cher des Computers.
Einfügen
: Einfügen der vorher mit der Funktion “Kopieren” dieses
Abschnitts im Arbeitsspeicher des Computers gesicherten Daten.
3.4.1 – Abschnitt EINSTELLUNGEN: Speicher “BM” und Empfänger
“NiceOne”
(Familie OXI... ; Familie OX...)
Der Abschnitt “Einstellungen” ermöglicht das Einstellen der Funktionsparameter von Empfängern der Serie “NiceOne” und Empfängern mit “BM”-Speicher
(Feineinstellung).
Page 77

Deutsch – 11
DE
BM-SPEICHER
• Fortgeschrittene Einstellungen: Hier können folgende Parameter eingestellt
werden:
Speicher sperren
: Sperrt die Selbstlernfunktion der Speicherplatine, wenn
diese in den Empfänger eingesetzt wird. Das heißt, in einen Empfänger mit
“gesperrtem” Speicher können keine neuen Codes eingegeben werden; die
Funktionen sind auf die vorhandenen Kennungen beschränkt (siehe auch die
Bedienungsweisungen des Empfängers selbst).
Passwort
: Eingeben eines Passworts, d. h. eines Nummerncodes, der
das Kontrollieren und Begrenzen des Zugangs zu den Daten der Speicherplatine sicherstellt. Das Passwort wird jedes mal dann abgefragt, wenn versucht wird, den Speicherinhalt aufzurufen und dessen Daten und die dort
gespeicherten Codes zu lesen oder zu verändern.
Das Ändern von auf der Speicherplatine enthaltenen Daten ist, insofern diese sich in einem Empfänger befindet, allein durch das Passwort noch NICHT
möglich: Sperrt alle manuell programmierbaren Funktionen des Empfängers,
in dem sich der Speicher befindet.
Timer
: Ändern der für den Timer eingestellten Zeit. Die Zeit wird in “Stun-
den”, “Minuten”, “Sekunden” angezeigt.
Wechseln
: Ein Passwortschutz, der das individuelle Einstellen eines Empfängers ermöglicht; kompatibel mit den vorausgehenden “FloR”-Systemen.
Achtung! – Den neuen Zugangsschlüssel nicht vergessen. Andernfalls ist
der Sender mit diesem Empfänger nicht mehr zu benutzen.
RND-Steuerung
: Aktivieren und Deaktivieren des veränderbaren Teils der
Kennung (RND) eines Empfängers.
RND-Fenster
: Ändern des RND-Fensters eines Empfängers. Das Fenster
zeigt die Werte innerhalb derer der veränderbare Teil der Kennung (RND)
anerkannt wird.
Hinweis – Normalerweise ist der Wert des Fensters 100. Er kann zwischen 5
und 250 liegen.
Synchronisierung
: Aktivieren und Deaktivieren der Neusynchronisierung
eines Empfängers. Wenn die Synchronisierungsfunktion aktviert ist, ist die
Anlage sicherer. Wenn sich der Sender allerdings außerhalb des RND-Fensters befindet, muss die Kennung neu im Empfänger gespeichert werden.
Nur Native
: Freischalten und Sperren des Empfängers für von einem Sender mit geändertem Code (nicht mehr der werkseitigen Originalkennung entsprechend) gesendete Steuerbefehle.
“NiceOne” EMPFÄNGER
Verfügbare Funktionen:
• Zertifikate: Lesen und eingeben der Zertifikate eines Empfängers (bis zu
max. 4). Von oben nach unten: Zertifikat des Empfängers (steht auf der in der
Verpackung beiliegenden Karte), in den drei nachfolgenden Feldern darunter
können Empfängergruppen eingegeben werden.
Hinweis – Für weitere Informationen zur Benutzung von Zertifikaten siehe “Nice
Opera System Book”.
• Schlüssel: Über diese Funktion kann ein Sender individuell eingestellt werden,
d. h. die Verschlüsselungen für “Installateur”, “Installation” und “Wechseln“. Die
Funktion “Altera” ist kompatibel mit den vorausgehenden “FloR”_Systemen.
Achtung! – Den neuen
Zugangsschlüssel nicht vergessen. Andernfalls ist der
Sender mit diesem Empfänger nicht mehr zu benutzen.
Dieser Schlüssel ermöglicht die individuelle Anpassung des Systems. D. h. die
werkseitige Originalkennung eines Senders kann hier geändert werden. Aus
diesem Grund müssen die Schlüssel von Sender und Empfänger übereinstimmen. Auch die Schlüssel der O-Box müssen geändert werden, damit diese
danach eingesetzt werden kann.
• Fortgeschrittene Einstellungen
: Hier können folgende Parameter eingestellt
werden:
Grundeinstellungen
- Nur Original TX: Freigeben und Sperren eines Empfängers für von einem
Sender mit geändertem Code (nicht mehr der werkseitigen Originalkennung
entsprechendem) gesendete Steuerbefehle.
- RND sperren: Aktivieren und Deaktivieren des veränderbaren Teils des
Codes (RND) eines Empfängers.
Speichereinstellungen
- Sperren des Speichers durch “Freigabecode”: Mittels dieser Funktion
kann die Speicherung eines neuen Senders durch Benutzung des “Freigabecodes” eines (bereits gespeicherten) vorhandenen Senders verhindert werden. Dieser Vorgang ist nur, wenn zwei Sender mit “O-Code”-Codierung
benutzt werden möglich.
- Speichersperrung mittels “Zertifikat”: Über diese Funktion kann die
Speicherung eines neuen Senders durch Benutzung des Zertifikats eines
Empfängers verhindert werden.
Page 78

12 – Deutsch
DE
- Sperren der Fernspeicherfunktion: Mittels dieser Funktion kann die Speicherung eines neuen Senders durch Benutzung eines vorhandenen Senders
für die Funktion “Sender in Proximity” ausgeschlossen werden.
BUS T4-Einstellungen
Hinweis – Der “Bus” ermöglicht die Verbindung aller in einer Automatisierungsanlage vorhandenen Geräte untereinander über ein einzelnes Kabel mit
diversen elektrischen Leitungen. Bei diesem Verbindungstyp erfolgt der
Datenaustausch zwischen den verschiedenen Geräten durch einspezielles
Protokoll, in unserem Fall der “T4 Bus” von Nice.
- Freigabe Codewiederholung über Bus: Freischalten eines Empfängers
für die Weitergabe der Kopie eines von einem Sender über Funk erhaltenen
Codes an andere Geräten über das Bus T4 Kabel.
- Freigabe Codeempfang über Bus: Freischalten eines Empfängers für den
Empfang eines über das BUS T4 Kabel von einem anderen Empfänger
gesendeten Codes (siehe “Freigabe Codewiederholung über Bus”).
- eigabe Autorisierungsgruppen: Freischalten der Verwaltung der Funkcodes über Autorisierungsgruppen.
Fortgeschrittene Einstellungen
- “Repeater” aktivieren: Freischalten der Wiederholung eines Codes. Wenn
eine Automatisierung aus einer über die normalerweise von Sender und
Empfänger abgedeckte Entfernung hinausgehende Distanz gesteuert werden soll, kann eine zweiter Empfänger eingesetzt werden, mit der Aufgabe,
den Befehl über Funk zum Zielempfänger (in dem die Kennung des Senders,
der den Befehl ausgibt gespeichert ist) weiter zu leiten, so dass der Zielempfänger den gesendeten Befehl ausführen kann.
- Verwaltung Tastenfreigabe einschalten: Wenn bei der Benutzung eines
Senders die Taste losgelassen wird, wird das Manöver nicht im selben
Moment gestoppt, sondern erst nach einer kurzen voreingestellten Verzögerungszeit. Wenn das Manöver exakt in dem Moment gestoppt werden soll, in
dem die Steuertaste des Senders losgelassen wird (z. B. während der Feineinstellung), muss diese Funktion am Empfänger eingestellt werden.
- Sperren der Steuerung von Prioritäten: Sperren eines Empfängers für
von Sendern gesendete Steuerbefehle mit Priorität > 0 gesendete Steuerbefehle.
Hinweis – Für weitere Informationen zur Benutzung aller hier beschriebenen
Funktionen siehe “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Passwort ändern: Über diese Funktion kann ein Passwort eingegeben werden, dass den Zugang (auch den manuellen Zugang) zu allen Funktionen eines
Empfängers, ohne dieses Passwort ausschließt.
Im Themenbereich “Anlagen” kann für jede Anlage eine Analysekarte mit den
Kundendaten und den Konfigurationsdaten zu in der Anlage dieses Kunden
installierten Empfängern erstellt und gespeichert werden. Im Einzelnen können
Anlagen modifiziert, Codes und Einstellungen angezeigt und die Daten der
installierten Empfänger gespeichert werden. Bei Störungen kann die Funktionstüchtigkeit einer Automatisierung wieder hergestellt werden.
Dieser Themenbereich besteht aus zwei Bildschirmfenstern:
– Eines für die schnelle Suche und Anwahl gespeicherter Anlagen;
– das zweite mit je einer Karte für die Daten einer einzelnen Anlage.
Um den Themenbereich “Anlagen” aufzurufen wie folgt vorgehen:
01. Im Startbildschirmfenster
(Abb. 3) auf das Icon “Anlagen” klicken.
02. Daraufhin öffnet sich ein erstes Bildschirmfenster (Abb. 10) für die Verwal-
tung der gespeicherten Anlagen. Dieses besteht aus folgenden Elementen.
• Navigationsmenü mit folgenden Funktionen:
“Ändern”
: Für die Änderung von Daten zu einer Anlagen
“Neue Anlage”: Erstellen einer neuen Anlage.
“Kopieren”
: Kopieren der Daten einer vorhandenen Anlage für die
Erstellung einer neuen Anlage mit denselben Daten.
“Löschen”
: Löschen einer oder mehrerer Anlagen.
• Im Bereich “Daten filtern” können gespeicherte Anlagen bequem und
schnell gesucht werden.
• Der Bereich “Anlagen auflisten” zeigt eine Liste der gespeicherten Anlagen.
03. Hier kann eine der folgenden Funktionen angewählt werden: “Ändern”,
“Neue Anlage” und “Kopieren”. Daraufhin erscheint ein zweites Bildschirmfenster (Abb. 11) mit der Datenkarte zu einer Anlage. Dieses
besteht aus folgenden Elementen.
3.5 – THEMENBEREICH “ANLAGEN”
Page 79

Deutsch – 13
DE
10
11
• Navigationsmenü mit folgenden Funktionen:
“Diese Anlage bearbeiten”
: Bearbeiten einer neuen oder bereits vorhandenen Anlage (siehe Abschnitt 3.5.1).
Als File speichern
: Speichern der Daten zu speichernder Empfänger in
anderen Files.
Importieren aus File
: Lesen der Daten eines Empfängers aus einem File
(siehe Abschnitt 3.5.1).
“Änderungen speichern”
: Speichern der vorgenommenen Änderungen
in der Karte einer Anlage.
Neben dem Navigationsmenü befinden sich auf dieser Karte 3 Bereiche:
Kunde, Schlüssel Anlage, Empfänger.
• Kunde: Hier können die Kundendaten eingegeben werden.
• Schlüssel Anlage: In diesem Bereich können Schlüssel für die individu-
elle Anpassung einer Anlage eingegeben werden: “Schlüssel Installateur”,
“Schlüssel Installation” und “Wechseln”. Mit dieser Funktion kann der
Zugang zur Verwaltung der Anlage auf die Personen, die im Besitz des
Schlüssels sind, beschränkt werden. Es kann ein einzelner Schlüssel für
verschiedene Anlagen benutzt werden oder es können mehrere Schlüssel
für eine Anlage vergeben werden.
Die Programmierung von Sendern und Empfängern der Reihe “NiceOpera” erfolgt automatisch mit den in der Karte der Anlage eingegeben
Schlüsseln, insofern die Karte vorher aktiviert wurde und die eingege-
benen Schlüssel enthält
.
Hinweis – Für weitere Informationen zur Benutzung von Zertifikaten siehe
“Nice Opera System Book”.
• Empfänger: In diesem Bereich werden die in einer Anlage vorhandenen
Empfänger angezeigt. Zum Hinzufügen und Löschen von Empfängern siehe Abschnitt 3.5.1.
3.5.1 – Empfänger zu einer Anlage hinzufügen
Um einen oder mehrere Empfänger zu einer Anlage zur Karte einer Anlage hinzuzufügen, gibt es einen direkten und einen indirekten Modus:
• Direktmodus
: Beim Direktmodus sind die Daten des der Karte der Anlage
hinzuzufügenden Empfängers bereits in einem File gespeichert. Danach in dem
Bildschirmfenster mit der Karte der Anlage auf “Aus File importieren” (im Navigationsmenü) klicken und das gewünschte File auswählen.
Page 80

14 – Deutsch
DE
• Indirektmodus: Diese Modus sieht folgende Operationen vor:
– Nach dem Aufrufen der Software unter “Anlage wählen” eine der Funktionen
“Letzte Anlage bearbeiten” oder “Neue Anlage bearbeiten oder erstellen” auswählen; alternativ dazu im Startfenster auf das Icon “Anlagen” klicken.
– Daraufhin erscheint das Fenster für die Verwaltung der gespeicherten Anlagen (Abb. 10), in dem die vorhandene oder gerade erstellte Anlage, der ein
Empfänger hinzugefügt werden soll, auszuwählen ist.
– Nach Bestätigung der Auswahl auf das Icon “Diese Anlage bearbeiten” klikken. Darauf wird das Startfenster mit Anzeige der gerade bearbeiteten Anlage
angezeigt (Abb. 12).
– Danach den Empfänger an die O-Box anschließen und den Themenbereich
“Empfänger” aktivieren, um die gewünschten Programmierungen vorzuneh-
men (siehe Kapitel 3.4):
– Anschließend im selben Fenster auf das Icon “Anlage” klicken und aus dem
Ausklappmenü (*) die Position “Anlage hinzufügen” wählen.
(*) Hinweis – Das dem Icon “Anlage“ zugeordnete Menü ist dynamisch und
enthält je nach Kontext unterschiedliche Menüpositionen. Im Allgemeinen sind
dies:
12
• Erste Zeile: Name der aktiven Anlage (kursiv); d. h. der Anlage, in der der
gerade programmierte Empfänger gespeichert wird.
• Letzte Zeile: Enthält den Befehl “Zur Anlage hinzufügen” für die Speicherung
des (neuen) Empfängers, sobald dieser programmiert ist.
• Weitere Zeilen: Enthalten die Namen in der Anlage bereits vorhandener Empfänger. Um diese zu ändern, den entsprechenden Namen auswählen und die
Parameter bearbeiten. Um die vorgenommenen Änderungen zu speichern auf
das Icon “Anlage” klicken und im Ausklappmenü die Menüposition “Änderungen speichern ...” wählen. (diese Menüposition ist nur dann vorhanden, wenn in
der aktiven Anlage bereits Empfänger vorhanden sind):
Page 81

Deutsch – 15
DE
Das vorliegende Produkt ist Teil der Automatisierung und muss daher
zusammen mit derselben entsorgt werden.
Wie die Installationsarbeiten muss auch die Abrüstung am Ende der Lebensdauer dieses Produktes von Fachpersonal ausgeführt werden.
Dieses Produkt besteht aus verschiedenen Stoffen, von denen einige recycled
werden können, andere müssen hingegen entsorgt werden. Informieren Sie
sich über die Recycling- oder Entsorgungssysteme für dieses Produkt, die von
den auf Ihrem Gebiet gültigen Verordnungen vorgesehen sind.
Achtung! – bestimmte Teile des Produktes können Schadstoffe oder gefährliche Substanzen enthalten, die, falls in die Umwelt gegeben, schädliche Wirkungen auf die Umwelt und die menschliche Gesundheit haben könnten.
Wie durch das Symbol seitlich angegeben, ist es verboten, dieses Produkt zum Haushaltmüll zu geben. Daher differenziert
nach den Methoden entsorgen, die von den auf Ihrem Gebiet
gültigen Verordnungen vorgesehen sind, oder das Produkt
dem Verkäufer beim Kauf eines neuen, gleichwertigen Produktes zurückgeben.
Achtung! – die örtlichen Verordnungen können schwere Strafen im Fall einer
widerrechtlichen Entsorgung dieses Produktes vorsehen.
Entsorgen des Akkus
Der Akku enthält auch, wenn er leer ist, die Umwelt verschmutzende Stoffe. Er
darf NICHT mit dem Hausmüll entsorgt werden. Akkus sind den örtlichen Vorschriften für die getrennte Müllentsorgung entsprechend zu entsorgen.
Entsorgung des produktes
Typ: Programmier- und Codesteuerungseinheit für die nachfolgend genannten NiceProdukte:
• Empfänger der Reihe NiceOne und SMX
Sende-und Empfangssysteme mit den Codierungen “Bio”, “Flo”, “FloR”, “Smilo”,
“O-Code”;
• Zugangskontrollsysteme mit “Morx”-Decoder, MOM Transponder-Card-Lesegerät oder
MOT Digitaltastatur
• Geräte mit TTBUS-System
Funktechnologie: Sende- und Empfangsgeräte für 433.92 MHz. Reichweite: Bis zu 10m
Anschlüsse und anschließbare Geräte:
• Auflagefläche für Sender der Reihe “NiceOne” (die Programmierung erfolgt über Funk,
ohne physischen Kontakt);
• Anschluss für die Speicherplatinen “BM 60”, “BM 250”, “BM 1000”.
• Anschluss für Empfänger der Reihen “SMX” und “NiceOne” (für einige Modelle, mit
Adapterkabel);
• Anschluss für Sender der Reihen Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo, Plano (über Adapterkabel);
• Anschluss für optische Leser für Sender der Reihe “Bio”
• Proximity-Kartenleser für Transponder Cards
• Anschluss für Geräte mit TTBUS (über Adapterkabel;
Anschluss an den Computer:
• Anschluss für USB-Kabel
• Anschluss für serielle RS232-Kabel
• Wireless Anschluss, Bluetooth
®
(nur Version O-BoxB)
Stromversorgung:
• Intern: Über wieder aufladbaren Akku 6V, 700 mAh.
• Extern: Über USB-Anschluss am Computer oder Netzteil, Mod. ALA1, 12 Vdc,
Aufladezeit Akku: ca.15 Minuten
Betriebsdauer mit Akku: Ca. 10 Stunden Betrieb = 3 Monate Stand-By-Betrieb.
Lebensdauer des Akkus: Mindestens 100 Aufladezyklen.
Schutzgrad des Gehäuses: IP 20 (bei Benutzung ausschließlich in geschützten
Innenräumen).
Betriebstemperatur: -20° bis +55°C.
Abmessungen in mm: 194 x 115 x H 40
Gewicht in g: 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Merkmale des Produkts
Page 82

16 – Deutsch
DE
KONFORMITÄTSERKLÄRUNG
EG-Konformitätserklärung in Übereinstimmung mit der
Richtlinie 1999/5/CE
Hinweis – Diese Konformitätserklärung vereinigt die Konformitätserklärungen zu
den genannten einzelnen Produkten; sie wurde zum Zeitpunkt der Herausgabe
des Handbuchs aktualisiert. Die Ausgabe wurde entsprechend angepasst.
Eine Kopie der Original-Konformitätserklärung für jedes Produkt kann bei der Nice
S,.p.a.(TV) I. angefordert werden.
______________
Der hier unterzeichnete Lauro Buoro erklärt in seiner Eigenschaft als
geschäftsführender Direktor eigenverantwortlich, dass die Produkte:
Hersteller: NICE s.p.a.
Adresse: Via Pezza Alta, 13, Z.I. Rustignè, 31046 Oderzo
(TV) Italien
Typ: O-BOX Funkprogrammiereinheit mit Sende- und
Empfangsanlage 433,92 MHz und Transponder
Card Leser.
O-BOXB Funkprogrammiereinheit mit Sende- und
Empfangsanlage 433,92 MHz und Transponder
Card Leser. Version mit Bluetooth
®
Technologie
Modelle: OBOX, OBOXB
Zubehör:
den Richtlinien der EG entsprechen:
• 1999/5/CE RICHTLINIE 1999/5/CE DES EUROPÄISCHEN RATS vom
9. März 1999 über Funkanlagen und Telekommunikationsendeinrichtungen und die gegenseitige Anerkennung ihrer Konformität in Übereinstimmung mit den im folgenden genannten harmonisierten Normen:
Schutz der Gesundheit: EN 50371:2002;
Elektrische Sicherheit: EN 60950-1:2001;
Elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit: EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005; EN
301 489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002
Funkfrequenzspektrum : EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2
V1.3.1:2006, EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004
Die Produkte entsprechen den Vorschriften der folgenden EG-Richtlinien in ihrer von der Richtlinie 93/68/EWG des Europäischen Rats vom 22
Juli 1993 geänderten Version:
• 89/336/EWG; RICHTLINIE 89/336/EWG DES RATES vom 3. Mai
1989 zur Angleichung der Rechtsvorschriften der Mitgliedstaaten über
die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit in Übereinstimmung mit den
folgenden Richtlinien:
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Amministratore Delegato)
Page 83

Polski – 1
PL
POLSKI
LICENCJA NA UŻYTKOWANIE OPROGRAMOWANIA
Programy “O-Box Software Desktop” i “O-Box Software Mobile” są chronione
prawem autorskim i prawem własności intelektualnej; programy te nie są sprzedawane, natomiast ich użytkowanie jest dozwolone na podstawie licencji niewyłącznej. Nice s.p.a. pozostaje nadal właścicielem niniejszej kopii programu.
Licencja jest udzielana na programy “O-Box Software Desktop” i “O-Box
Software Mobile”, jako produkty związane z produktem “O-Box”.
Niniejsze programy są dostarczane bez gwarancji dotyczącej sposobu użytkowania i bezpieczeństwa. Ponadto Nice s.p.a. nie ponosi żadnej odpowiedzialności z tytułu jakichkolwiek szkód bezpośrednich czy pośrednich, łącznie ze
szkodami z tytułu utraty zysku, przerw w pracy i podobnych, wynikających z
błędnego użycia niniejszych programów.
INFORMACJE ODNOŚNIE ZNAKÓW FIRMOWYCH
Znaki AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, MICROSOFT®są zarejestrowanymi przez odpowiednich właścicieli znakami firmowymi; nazwy produktów
używane w niniejszej instrukcji także mogą być zarejestrowane przez odpowiednich właścicieli.
UWAGA OGÓLNA DO INSTRUKCJI
Zespół programowania dostępny jest w dwóch modelach: OBox i O-BoxB. Modele te są podobne do siebie, oprócz tego,
że tylko w modelu O-BoxB zainstalowano moduł komunikacyjny w technologii Bluetooth
®
.
W tej instrukcji termin “O-Box” jest używany w celu określenia obydwu produktów bez ich rozróżniania, z wyjątkiem
przypadku, gdy wyraźnie to zaznaczono.
OPIS I PRZEZNACZENIE PRODUKTU
1
Produkt O-Box (lub O-BoxB, wersja z modułem Bluetooth®) składa się z zespołu programowania i dedykowanego oprogramowania. Zestaw tych elementów
jest przeznaczony do programowania i zachowania danych oraz parametrów
urządzeń stosowanych w układach automatyki bram, bram garażowych, markiz
przeciwsłonecznych, żaluzji, szlabanów oraz w podobnych zastosowaniach.
Jakiekolwiek inne użycie jest uważane za niewłaściwe! Konstruktor nie
ponosi żadnej odpowiedzialności za szkody wynikłe z niewłaściwego
użycia produktu, innego niż przewidziane w niniejszej instrukcji.
O-Box i system “NiceOpera”
O-Box jest urządzeniem, które stanowi część systemu ”NiceOpera”. System
ten został zaprojektowany przez Nice w celu uproszczenia etapów programowania, użytkowania i konserwacji urządzeń stosowanych w układach automatyki. System składa się z różnych urządzeń, software’u i hardware’u, zdolnych
do wymiany pomiędzy sobą danych oraz informacji drogą radiową, za pomocą
systemu kodowania, zwanego ”O-Code”, lub za pomocą ”fizycznego” połączenia kablowego.
Podstawowe urządzenia składające się na system, to:
– nadajniki NiceOne;
– odbiorniki NiceOne (typ OXI ... ; typ OX ...);
– zespół programowania O-Box;
– centralki i siłowniki z “Bus T4”;
– programator O-View do urządzeń z “Bus T4”.
WAŻNE – Aby szczegółowo poznać wszystkie funkcje systemu NiceOpe-
ra oraz współzależność operacyjną pomiędzy różnymi urządzeniami systemu, należy zapoznać się z ogólną instrukcją ”NiceOpera System Book”,
dostępną także na stronie internetowej www.niceforyou.com
Zasadnicze cechy funkcjonalne zespołu O-Box
Zastosowanie zespołu O-Box jest szczególnie zalecane w instalacjach automatyki o zaawansowanej technologii, co pozwala na zrealizowanie wielu funkcji
bezpośrednio w siedzibie instalatora, bez konieczności wykonywania tych
czynności na instalacji u klienta; ewentualnie pozwala na skonfigurowanie urządzenia bezpośrednio u klienta.
Page 84

2 – Polski
PL
Produkt zawiera ładowalny akumulator o napięciu 6 V, który pozwala na pracę
bez podłączenia do sieci elektrycznej.
Uwaga – Akumulator wymaga cyklu pełnego naładowania przez co najmniej 10
godzin. Poziom naładowania jest pokazywany przez program (zobacz rys. 1).
Akumulator doładowuje się automatycznie każdorazowo, gdy O-Box będzie
zasilany z zasilacza zewnętrznego lub poprzez kabel USB.
2.1 – POŁĄCZENIA
• Podłączyć O-Box do sieci elektrycznej
Produkt może być zasilany z sieci elektrycznej z wykorzystaniem zasilacza 12
Vcc (wyposażenie dodatkowe) lub przez komputer, wykorzystując kabel USB
(na wyposażeniu).
• Podłączyć O-Box do komputera
Aby korzystać z modułu O-Box (lub O-BoxB) jest niezbędne podłączenie go
do komputera (PC), wyposażonego w port USB za pomocą kabla będącego
na wyposażeniu, lub do komputera wyposażonego w port szeregowy - za
pomocą kabla RS232 (wyposażenie dodatkowe).
Uwaga – W celu uzyskania najlepszych efektów zalecane jest stosowanie do
tego połączenia gniazda USB (jeżeli jest dostępne); łącze to jest bardziej niezawodne, szybsze w transmisji danych, nie wymaga żadnej konfiguracji oraz
umożliwia automatyczne doładowywanie akumulatora wewnętrznego w zespole O-Box.
• Podłączyć O-BoxB za pomocą Bluetooth
®
Model O-BoxB może być połączony także poprzez Bluetooth®do komputera
lub do palmtopa (PDA), wyposażonego w interfejs Bluetooth
®
.
Takie połączenie nie wymaga przewodów: wystarcza zainstalowanie oprogramowania w komputerze lub w palmtopie i wprowadzenie danych, na podstawie danych technicznych palmtopa.
Uwaga – Zanim uaktywni się połączenie poprzez Bluetooth
®
należy odłączyć O-
BoxB od portu USB lub portu szeregowego komputera.
Za pomocą O-BoxB jest przewidziane zapamiętanie aż do 16 połączeń z róż-
Ten produkt umożliwia zarządzanie i modyfikowanie instalacji z wykorzystaniem
pliku danych; szybko mogą być wykonane różne czynności, jak np. powrót do
stanu początkowego, rozbudowa istniejących instalacji, wymiana nadajników, itp.
Ogólnie zespół O-Box może być stosowany w celu:
• sterowania, dodawania, programowania i usuwania kodów nadajników ”Bio”,
“FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano”, “NiceOne”;
• programowania pamięci odbiorników ”Bio” i ”FloR”;
• odczytywania i zapisywania kart z transponderem;
• programowania funkcji i charakterystycznych parametrów nadajników “Bio”,
“FloR”, “Very”;
• optycznego odczytywania kodów nadajników ”Bio”;
• odczytywania i programowania charakterystycznych parametrów odbiorni-
ków “SMX1” i “SMX2” za pomocą przewodu;
• uzyskiwania danych drogą radiową z nadajników, w których stosowane są
kody SMILO, FLO, FLOR, O-CODE, w celu tworzenia plików użytkowników
oraz programowania pamięci i odbiorników;
• programowania poprzez radio nadajników serii ”NiceOne”;
• zarządzania poprzez radio wszystkimi funkcjami odbiorników ”NiceOne”;
Oprogramowanie dostarczone wraz z zespołem O-Box umożliwia konfigurowanie i programowanie nadajników i odbiorników serii ”NiceOne”. Jest ponadto kompatybilne z wszystkimi urządzeniami serii “FloR”, “SMXI” i “Bio”.
HARDWARE: opis i montaż produktu
2
1
Page 85

Polski – 3
PL
nymi komputerami. Aby ustalić połączenie, należy włączyć zespół O-BoxB,
przygotować komputer do połączenia za pomocą Bluetooth® i zaczekać, gdy
dioda w zespole O-BoxB przejdzie z trybu świecenia przerywanego na ciągłe
(potwierdza to fakt uaktywnienia połączenia).
Jeżeli istnieje potrzeba skasowania z pamięci listy połączeń z komputerem,
należy postępować w sposób następujący:
a) – przytrzymać w zespole O-BoxB wciśnięty przycisk włączania Activity i
zaczekać na wykonanie następujących etapów: O-BoxB emituje sygnał akustyczny (bip) i dioda gaśnie; dioda ponownie zapala się a O-BoxB emituje ciąg
sygnałów akustycznych (bip).
b) – w tym momencie dane zapamiętane w pamięci zespołu O-BoxB zostały
usunięte, można zatem zwolnić przycisk włączania.
2.2 – AKCESORIA (opcjonalnie)
Uwaga – Zespół O-Box ma na wyposażeniu tylko kabel USB; inne kable są
opcjonalne i nie występują w opakowaniu. Są to następujące kable:
– Kabel
CABLA06 do złącza typu D, rys.2: stosuje się do połączenia odbiorni-
ków serii “SMX” i “NiceOne”.
– Kabel CABLA02 do złącza typu M, rys.2: stosuje się do odbierania kodów
nadajników serii “Bio“.
– Kabel szeregowy o 9 pinach, RS232,
- CABLA01 do złącza typu G, rys.2:
stosuje się do połączenia zespołu O-Box z komputerem.
– Kabel TTBUS
- CABLA05 do złącza typu H, rys.2: stosuje się do połączenia
wszystkich silników rurowych do markiz przeciwsłonecznych oraz żaluzji
Nice, wyposażonych w port TTBUS.
– Kabel
CABLA03 do złącza typu I, rys.2: stosuje się do połączenia nadajni-
ków serii “Very”.
– Kabel
CABLA02 do złącza typu I, rys.2: stosuje się do połączenia nadajni-
ków serii “Bio” i “FloR”.
– Kabel CABLA04 do złącza typu I, rys.2: stosuje się do połączenia nadajni-
ków serii “Ergo” i “Plano”.
– Zasilacz
ALA1 12V, 300mA do złącza typu E, rys.2: stosuje się do podłącze-
nia zespołu O-Box do sieci elektrycznej.
2.3 – ZŁĄCZA I URZĄDZENIA PODŁĄCZANE DO ZESPOŁU O-Box
Zespół O-Box dysponuje różnego typu złączami (zobacz rys.2), poprzez które
można podłączać wiele urządzeń, będących produktami Nice. Uwaga – nie-
które z tych złączy wymagają specjalnego kabla połączeniowego: odnośnie do
modeli i danych technicznych każdego z kabli – zobacz paragraf 2.2.
Odnośnie liter, które identyfikują na rys.2 złącza oraz inne urządzenia zespołu
O-Box, poniżej zamieszczono szczegółowy przegląd ich działania i zastosowań:
[A] – Przycisk włączania i wyłączania zespołu O-Box
Aby włączyć zespół O-Box, należy przytrzymać wciśnięty przycisk włączania
przez chwilę, aż do usłyszenia krótkiego dźwięku (bip).
Aby wyłączyć zespół O-Box, należy przytrzymać wciśnięty przycisk włączania
przez chwilę, aż do usłyszenia długiego dźwięku (biiip).
[B] – Strefa połączeń przez radio nadajników serii “NiceOne”
Ta strefa umożliwia programowanie przez radio, tzn. bez fizycznego połączenia,
nadajników serii „NiceOne” firmy Nice; programowanie realizuje się umieszczając nadajnik w strefie oznakowanej graficznie.
E
A B C D
F G H I L M
2
Page 86

4 – Polski
PL
Podczas użytkowania programu dioda nadajnika emituje błysk, który wskazuje
aktywny stan komunikacji przez radio z programem. W tym momencie możliwe
jest rozpoczęcie pracy z programem nad parametrami nadajnika (zobacz rozdział 3 paragraf 3.3).
[C] – Złącze dla kart pamięci “BM”
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie do zespołu O-Box kart pamięci “BM” firmy
Nice. Aby podłączyć kartę, należy połączyć ją bezpośrednio do złącza a
następnie przystąpić do pracy z programem (zobacz rozdział 3, paragraf 3.3).
[D] – Złącze typu “SM”
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie do zespołu O-Box wyłącznie odbiorników serii
“SM” i “NiceOne” firmy Nice. Niektóre z tych odbiorników mogą być połączone
bezpośrednio do złącza, inne wymagają kabla model CABLA06. Po połączeniu
można przystąpić do pracy z programem (zobacz rozdział 3, paragraf 3.3)
Uwaga – Odbiorniki serii “NiceOne” (OXIT i OX2T) są przystosowane do komu-
nikowania się z programem także przez radio. Jednak w tym przypadku transmisja danych jest wolniejsza niż realizowana za pomocą złącza “SM”.
[E] – Złącze do zasilacza zewnętrznego ALA1
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie zespołu O-Box do sieci elektrycznej za
pośrednictwem zasilacza zewnętrznego 12Vcc (wyposażenie dodatkowe).
Uwaga – Jeżeli nawet zespół O-Box jest wyłączony, a kabel zasilający jest podłączony do sieci elektrycznej, to akumulator wewnątrz zespołu jest doładowywany.
[F] – Złącze do kabla “USB”
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie zespołu O-Box do portu USB komputera za
pośrednictwem kabla USB. Bezpośrednio po podłączeniu możliwe jest uruchomienie programu i praca z nim.
Uwaga – Jeżeli nawet zespół O-Box jest wyłączony, a kabel USB jest podłączony do komputera, to akumulator wewnątrz zespołu jest doładowywany
[G] – Złącze szeregowe “RS232” (kabel typu CABLA01)
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie zespołu O-Box do portu szeregowego komputera za pośrednictwem kabla szeregowego RS232 (wyposażenie dodatkowe).
Bezpośrednio po podłączeniu możliwe jest uruchomienie programu i praca z nim.
[H] – Złącze “TTBUS” (kabel typu CABLA05)
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie do zespołu O-Box wszelkich silników rurowych do markiz przeciwsłonecznych i żaluzji firmy Nice, wyposażonych w port
TTBUS, za pośrednictwem odpowiedniego kabla (wyposażenie dodatkowe)
[I] – Złącze do połączenia nadajników (kabel typu CABLA03 -
CABLA02 - CABLA04)
To złącze umożliwia podłączenie do zespołu O-Box nadajników Nice serii “Bio”,
“FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano” i “Very”, za pośrednictwem specjalnego kabla (wyposażenie dodatkowe). W celu zrealizowania połączenia należy otworzyć nadajnik, aby
połączyć kabel (*) i drugi jego koniec do złącza w zespole O-Box (I na rys. 1).
(*) Uwaga:
– do nadajników serii “Ergo” i “Plano” stosować kabel CABLA04.
– do nadajników serii “Bio” i “FloR” stosować kabel CABLA02.
– do nadajników serii “Very” stosować kabel CABLA03.
[L] – Czytnik zbliżeniowy do kart z transponderem
Ten czytnik zbliżeniowy umożliwia odczyt (dla kart niebieskich i szarych) lub
zapis (dla kart szarych) kodów zapisanych na kartach z transponderem Nice. W
celu ustanowienia połączenia konieczne jest umieszczenie karty przed czytnikiem.
[M] – Złącze czytnika optycznego do nadajników serii “Bio”
Ten czytnik umożliwia odczyt kodu radiowego nadajników serii “Bio”.
W celu ustanowienia połączenia konieczne jest podłączenie czytnika optycznego (wyposażenie dodatkowe - CABLA02) do odpowiedniego złącza (M na rys.
2) i zbliżenie diody nadajnika do głowicy czytnika optycznego.
Page 87

Polski – 5
PL
Oprogramowanie na instalacyjnym CD “O-Box Software Suite” jest dostarczane w dwóch wersjach:
• “O-Box Desktop” przeznaczone do zainstalowania na komputerze typu PC
• “O-Box Mobile” przeznaczone do zainstalowania na komputerze typu palm-
top (PDA).
MINIMALNE WYMAGANIA SYSTEMOWE
W celu używania tego oprogramowania koniecznym jest zainstalowanie go w
komputerze oraz – jeżeli to jest pożądane – na komputerze typu palmtop jakiejkolwiek marki i modelu, zgodnie z następującymi wymaganiami minimalnymi:
WERSJA DLA PC:
– Procesor: typ AMD®/Intel®(500 MHz) Zalecany przez Nice: typ
AMD
®
/Intel®(1 GHz)
– Pamięć RAM: 128 MB Zalecane przez Nice: 256 MB
– Wolne miejsce na dysku: 30 MB Zalecane przez Nice: 100 MB
– System operacyjny: Windows
®
98 SE Zalecany przez Nice: Windows
®
2000 lub wyższy
– Karta graficzna: 800 x 600, z 256 kolorami
– Jednostka dyskowa: CD-ROM (niezbędna do instalacji)
Uwaga – Instalacja oprogramowania obejmuje instalację programu Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
WERSJA DLA PALMTOPA:
– Procesor: (300 MHz) Zalecany przez Nice:
(więcej niż 300 MHz)
– Pamięć RAM: 64MB Zalecane przez Nice: 128 MB
– Wolne miejsce na dysku: 5 MB Zalecane przez Nice: 100 MB
– System operacyjny: Windows
®
Mobile Zalecany przez Nice: Windows
®
2003 lub 2003 SE Mobile 2003 SE lub wyższy
– Połączenie: Bluetooth
®
– Rozdzielczość graficzna: 240 x 320 z 256 kolorami
– PC: CD-ROM (niezbędny do instalacji oprogramowania w palmtopie)
Uwaga – Instalacja oprogramowania obejmuje instalację programu Microsoft
®
.NET Fra-
mework Redistributable 2.0.
SOFTWARE: opis i użycie produktu
3
3.1 – INSTALACJA OPROGRAMOWANIA
Instalacja oprogramowania jest podobna do jakiejkolwiek innej instalacji programu komputerowego.
Po włożeniu płytki instalacyjnej (CD) automatycznie uruchamia się program
instalacyjny. Jeżeli to nie nastąpi, należy kliknąć dwukrotnie na ikonie programu
“Setup.exe” a następnie postępować zgodnie z instrukcjami procesu instalacji.
Uwaga – Przed rozpoczęciem instalacji programu zaleca się odłączyć zespół
O-Box od komputera.
KRÓTKI PRZEGLĄD OPROGRAMOWANIA: Struktura i zagadnienia
• Ekran początkowy
(home page)
Po uruchomieniu programu wyświetlany jest ekran początkowy (“Home
page”) (zobacz rys. 3), który zawiera następujące elementy:
[1] – Wskazuje stan połączenia palmtopa: klikając na tę ikonę uaktywnia się
synchronizację palmtopa.
1
9
4 5 6 7 8
2
3
3
Page 88

6 – Polski
PL
[2] – Wskazuje stan akumulatora oraz stan połączenia z zespołem O-Box: w
przypadku błędu połączenia, po kliknięciu na tę ikonę program wykona
nowe połączenie do zespołu O-Box.
[3] – Panel “Wybierz instalację”: umożliwia przy uruchomieniu sesji roboczej
wybór pożądanego sposobu działania, udostępniając kolejne wybory.
Jeżeli po zaprogramowaniu odbiornika chce się zachować dane konfiguracyjne tylko w jego pamięci lub w pliku, należy wybrać opcję: “Pracuj nie
tworząc instalacji”.
Jeżeli natomiast po zaprogramowaniu odbiornika chce się zachować
dane konfiguracyjne oprócz w jego pamięci lub w pliku także na karcie
zbiorczej instalacji, w której ten odbiornik będzie użyty, należy wybrać
opcję: “Wykonaj operacje na ostatniej instalacji” lub “Wybierz lub utwórz
instalację” (zobacz paragraf 3.5.1).
[4] – Wskazuje dostęp do strefy operacyjnej, przeznaczonej na programowanie
Nadajników.
[5] – Wskazuje dostęp do strefy operacyjnej, przeznaczonej na programowanie
Odbiorników.
[6] – Wskazuje dostęp do strefy operacyjnej, przeznaczonej na zarządzanie
Instalacjami.
[7] – Wskazuje dostęp do strefy operacyjnej, przeznaczonej na Ustawienia
programu.
[8] – Wskazuje przycisk do kliknięcia w celu wyjścia z programu.
[9] – Wskazuje pole, w którym pojawiają się dane dotyczące personalizacji pro-
gramu (... nazwisko użytkownika, itd.).
• Ekran tematyczny
Na ekranie początkowym wybiera się interesującą opcję tematyczną (“Nadajniki”, “Odbiorniki”, “Instalacje”, “Ustawienia”) i klikając na odpowiednią ikonę,
wchodzi się na ekran tematyczny wybranej opcji, na którym można wykonać
wszystkie pożądane operacje. (Uwaga – ka da opcja tematyczna może rozwijać zagadnienie na jednym lub kilku kolejnych ekranach). Ekrany te standardowo składają się z następujących elementów (zobacz rys. 4):
[a] – Pasek nawigacji
[b] – Menu funkcji
[c] – Pole z ogólnymi danymi podłączonego urządzenia
[d] – Pole do programowania
Elementy obecne w pasku nawigacji
“Pasek nawigacji” pojawiający się na każdym ekranie tematycznym umożliwia
przechodzenie z jednego ekranu na inny oraz uświadomienie użytkownikowi w
każdej chwili, w jakim polu aktualnie działa.
Typowe funkcje paska nawigacji to:
– “Początek” = klikając na tę ikonę powraca się do ekranu początkowego
– “Wstecz” = klikając na tę ikonę powraca się do ekranu poprzedniego
– “Do przodu” = klikając na tę ikonę przechodzi się do ekranu następnego
– “Pomoc” = klikając na tę ikonę uruchamia się wyświetlenie niniejszej instrukcji.
– “Odświeżanie” = na niektórych ekranach, klikając na tę ikonę, uruchamia się
odświeżenie ekranu i uaktualnienie danych
WAŻNE – Na niektórych ekranach oprócz tych “standardowych” funkcji, mogą
pojawiać się inne funkcje specyficzne dotyczące urządzenia aktualnie programowanego.
4
(a)
(c)
(b)
(d)
Page 89

Polski – 7
PL
3.2 – JAK ROZPOCZĄĆ SESJĘ ROBOCZĄ
Aby rozpocząć sesję roboczą, należy wykonać następujące czynności:
– włączyć zespół O-Box;
– podłączyć do zespołu O-Box urządzenie, na którym chce się pracować;
– uruchomić program (otwiera się ekran początkowy);
– kliknąć na ekranie początkowym na przycisku wybranej opcji tematycznej;
– działać na kolejnych ekranach tematycznych.
Aby wejść do tej opcji tematycznej, należy najpierw podłączyć do zespołu OBox nadajnik, z którym chce się pracować, a następnie postępować w następujący sposób.
01. Na ekranie początkowym
kliknąć na ikonie “Nadajniki” (rys. 3).
02. Pojawi się pierwszy ekran opcji tematycznej “Nadajniki” (rys. 5): wybrać
typ i model nadajnika, który chce się programować, oraz kliknąć (na pasku
nawigacyjnym) na przycisku “Do przodu”, aby przejść do kolejnego ekranu, w którym programuje się nadajnik.
Uwaga – Tylko dla nadajników NiceOne: jeżeli nadajnik zostanie usta-
wiony w strefie programowania zespołu O-Box zanim
nastąpi wejście do
opcji tematycznej “Nadajniki”, program rozpozna automatycznie model
nadajnika i wyświetli jego dane, łącznie z kodem identyfikacyjnym oraz
kodem RND.
Jeżeli natomiast nadajnik zostanie ustawiony w strefie zespołu O-Box po
wejściu do opcji tematycznej “Nadajniki”, należy kliknąć na ikonie
“Odśwież”, aby spowodować rozpoznanie przez program modelu nadajnika i wyświetlenie jego danych.
03. Pojawi się drugi ekran opcji “Nadajniki” przeznaczony na programowanie
(rys. 6): należy zatem wybrać z Menu funkcji pożądaną funkcję i działać w
strefie operacyjnej przeznaczonej do modyfikowania, dodawania, itd.
wybranych parametrów.
WAŻNE – Niektóre funkcje dają możliwość kolejnego programowania kilku
nadajników, podłączając po prostu do zespołu O-Box nadajniki jeden po
drugim. Potwierdzenie wykonania zaprogramowania oraz informacja o
gotowości do programowania kolejnego nadajnika są sygnalizowane dwoma dźwiękami (bip).
Fig. 3
3.3 – OPCJA TEMATYCZNA “NADAJNIKI”
5
6
Page 90

8 – Polski
PL
Menu funkcji jest podzielone na 3 sekcje: Kody, Certyfikaty, Ustawienia
zaawansowane (rys. 4). Ważne – Funkcje będące do dyspozycji w każdej
sekcji zmieniają się zależnie od typu nadajnika, jaki chce się zaprogramować.
–– KODY ––
Ta sekcja umożliwia wprowadzanie kodów nadajnika i obejmuje następujące
funkcje:
– Testuj nadajnik
: ta funkcja umożliwia sprawdzenie poprawnego działania
nadajnika, wyświetlenie kodu identyfikacyjnego oraz części zmiennej kodu
RND.
– Zmień kod: ta funkcja umożliwia zmianę początkowego kodu identyfikacyj-
nego odbiornika.
WAŻNE – Aby zaprogramować kolejno kilka nadajników z kodami progresywny
mi, należy kliknąć na ikonę “Program sekwencyjny”; wypełnić dwa z następujących pól: “Do kodu”, “Krok” (tj. zwiększanie kodu pomiędzy jednym nadajnikiem a
drugim) i “Liczba kodów”; w końcu należy kliknąć na “Weryfikuj”. W tym momencie program automatycznie wypełni pole, poprzednio pozostawione puste.
– Przywróć kod: ta funkcja umożliwia przywrócenie kodu początkowego
(ustawionego fabrycznie) nadajnika.
–– CERTYFIKATY ––
Ta sekcja umożliwia wprowadzenie certyfikatów nadajnika i obejmuje następujące funkcje:
– Ustaw certyfikaty
: ta funkcja umożliwia wprowadzenie “Certyfikatu” odbior-
nika w nadajniku. Dla każdego certyfikatu można ustalić zapamiętywanie w
nadajniku w jednym z trybów: “Tryb I” lub “Tryb II”.
W przypadku zapamiętywania w „Trybie II” (każdy przycisk nadajnika odpowiada specjalnej funkcji odbiornika) wystarczy wybrać prostymi kliknięciami na
zakładce „Funkcja” – numer żądanej funkcji, a następnie wybrać na zakładce
“Przyciski” – przycisk, jaki chce się zapamiętać w nadajniku.
Uwaga – Różnorodność komend będących do dyspozycji w procedurze zapamiętywania nadajnika zależy od typu nadajnika oraz od modelu centrali, z którą
współpracuje ten nadajnik. Lista szczegółowych komend jest zamieszczona w
instrukcji centrali.
– Usuń certyfikaty
: ta funkcja umożliwia usunięcie wszystkich certyfikatów z
nadajnika.
–– USTAWIENIA ZAAWANSOWAN ––
Ta sekcja umożliwia ustawienie kluczy zabezpieczających oraz parametrów
funkcjonowania nadajnika: obejmuje następujące funkcje:
– Ustaw klucze
: ta funkcja umożliwia personalizację nadajnika, czyli modyfika-
cję kluczy zabezpieczających “Instalator”, “Instalacja” i “Altera”. W szczególności klucz “Altera” jest kompatybilny z poprzednimi systemami “FloR”.
Uwaga! – Należy zapamiętać nowy klucz zabezpieczający, w przeciwnym razie
nadajnik nie będzie mógł być zdatny do użycia z tym odbiornikiem.
– Ustawienia zaawansowane: Ta funkcja umożliwia ustalenie następujących
parametrów:
Liczba ramek: umożliwia zmianę liczby powtórzeń kodu identyfikacyjnego
podczas jego przesyłania. Zmiana tego parametru jest korzystna dla szczególnych układów automatyki, które wymagają krótszych (niż ustawione
fabrycznie) czasów odpowiedzi na wysłaną komendę.
Priorytet: umożliwia zastąpienie istniejącego nadajnika, zachowując jego
kod identyfikacyjny. Uzyskuje się to poprzez zwiększenie o jednostkę prio-
rytetu NOWEGO nadajnika w stosunku do nadajnika STAREGO.
Uaktywnij RND: umożliwia aktywację lub dezaktywację zarządzania
zmienną częścią kodu identyfikacyjnego (RND).
Uaktywnij przejście kodu: umożliwia nadajnikowi nadanie uprawnienia
do przesłania własnego kodu uaktywniającego do innego nadajnika.
Kopiuj pomiędzy różnymi modelami: umożliwia aktywację lub dezakty-
wację kopii “kodów uaktywniających” pomiędzy modelami różniących się
między sobą nadajników.
Uaktywnij Repeater: umożliwia aktywację lub dezaktywację zarządzania
powtarzaniem kodu w odbiornikach wyposażonych w funkcję “Repeater”.
Uwaga – Klikając na przycisku “Ustawienia fabryczne” można ustalić fabryczne
wartości wyżej wymienionych parametrów (“Ustawienia zaawansowane”).
– Ustawienia fabryczne
: ta funkcja umożliwia przywrócenie ustawionej
fabrycznie konfiguracji nadajnika, tj. zostaje przywrócony początkowy kod
identyfikacyjny, zostają usunięte certyfikaty oraz zostają przywrócone wartości
różnych parametrów.
Ważne – Ze względów bezpieczeństwa funkcja ta nie zmienia wartości kluczy
zabezpieczających, tzn. nie przywraca początkowej wartości.
Page 91

Polski – 9
PL
- Programowanie kierowane: ta funkcja umożliwia programowanie nadajnika
z kolejnym wykorzystywaniem wszystkich wyżej opisanych sekcji.
Aby wejść do tej opcji tematycznej, należy najpierw podłączyć do zespołu OBox odbiornik, z którym chce się pracować, a następnie postępować w następujący sposób.
01. Na ekranie początkowym
kliknąć na ikonie “Odbiorniki” (rys. 3).
02. Pojawi się pierwszy ekran opcji tematycznej “Odbiorniki” (rys. 7): wybrać
typ i model odbiornika, który chce się programować (system sprawdza,
czy są podłączone do zespołu O-Box odbiorniki tego typu oraz automatycznie pokazuje model; jest jednak możliwy ręczny wybór modelu).
Następnie na pasku nawigacyjnym kliknąć na wyrazie “Do przodu”, aby
przejść do kolejnego ekranu.
Uwaga – Jeżeli programuje się odbiornik serii “NiceOpera” konieczny jest
wybór odpowiedniego typu połączenia: wireless [bezprzewodowe] (w tym
przypadku konieczne jest ręczne wprowadzenie certyfikatu odbiornika) lub
łącze do zespołu O-Box (w tym przypadku zastosować złącze SM).
03. Po dokonaniu wyboru typu odbiornika pojawi się drugi ekran z tytułem
“Co zamierzasz zrobić?”, tj. z zapytaniem o to, jakie czynności zamie-
rzasz podjąć. (rys. 8):
• Skonfiguruj nowy odbiornik
(ta czynność umożliwia skonfigurowanie
nowego odbiornika).
• Odczytaj i zmodyfikuj dane odbiornika
(ta czynność umożliwia odczytanie i modyfikację danych odbiornika, każdorazowo zapisując tylko ewentualne dokonane zmiany).
• Usuń wszystkie dane z odbiornika
(ta czynność całkowicie formatuje
pamięć odbiornika).
• Wyszukaj i zmień kody w pamięci
(czynność oferowana tylko do odbiorników typu “NiceOne”. Czynność umożliwia działanie bezpośrednio na
pamięci odbiornika).
04. W końcu pojawia się trzeci ekran przeznaczony na programowanie (rys.
9). Na tym ekranie należy wybrać z Menu funkcji pożądaną funkcję i dzia-
łać w strefie operacyjnej przeznaczonej do modyfikowania, dodawania,
itd. wybranych parametrów.
3.4 – OPCJA TEMATYCZNA “ODBIORNIKI”
Page 92

10 – Polski
PL
9
Menu funkcji jest podzielone na 3 sekcje: Kody w pamięci; Ustawienia; Importuj / Eksportuj.
–– KODY W PAMIĘCI ––
W tej sekcji możliwe jest modyfikowanie we wszystkich typach odbiorników
kodów zapamiętanych w pamięci. Aby to zrobić, wystarczy kliknąć na funkcji
“Zmień kody” i wejść do następujących opcji:
Dodaj kod
: umożliwia dodanie kodu do pamięci, wprowadzając go ręcz-
nie.
Dodaj sekwencję kodów
: umożliwia dodanie do pamięci odbiornika
sekwencję kodów, wypełniając dwa z następujących pól: “kod początkowy”,
“kod końcowy” i “krok pomiędzy kodami”, a następnie klikając wyraz “Weryfikacja”, automatycznie zostanie wypełnione pole, poprzednio pozostawione
puste.
Dodaj kod z TX
: umożliwia wprowadzenie do pamięci odbiornika kodu
nadajnika, po prostu naciskając przycisk tego ostatniego.
Usuń kody
: umożliwia usunięcie z pamięci odbiornika jednego lub więcej
kodów.
Szukaj
: umożliwia znalezienie kodu nadajnika, wpisując po prostu kod do
odpowiedniego pola, lub naciskając jakikolwiek przycisk na nadajniku.
–– USTAWIENIA ––
W tej sekcji stosując istniejące tu funkcje (“Certyfikaty” - “Klucze” - “Ustawienia zaawansowane” - “Zmiana hasła”), możliwa jest modyfikacja parame-
trów, występujących w niektórych typach odbiorników. Dostępne funkcje zmieniają się zależnie od typu odbiornika lub pamięci, którą chce się zaprogramować: aby poznać lepiej działanie tych funkcji, zależnie od typu odbiorników,
należy przejść do paragrafu 3.4.1.
–– IMPORTUJ / EKSPORTUJ ––
W tej sekcji stosując istniejące tu funkcje (“Czytaj z pliku” - “Zachowaj w pliku” - “Kopiuj”), możliwe jest importowanie, eksportowanie, zapamiętywanie i
odświeżanie danych, znajdujących się w odbiorniku. Dostępne funkcje to:
Czytaj z pliku
: umożliwia odczytanie pliku (np. z rozszerzeniem “.cor”),
utworzonego za pomocą programu zarządzającego zespołem programowania BUPC, lub utworzonego za pomocą funkcji “Zapisz do pliku”, występującej w tej sekcji.
Zachowaj w pliku
: umożliwia zapisanie w pliku zawartości pamięci odbiornika w taki sposób, aby możliwe było późniejsze jego czytanie za pomocą
funkcji “Czytaj z pliku”, występującej w tej sekcji. Jest także możliwe zachowanie pliku w formacie poprzednim, np. z rozszerzeniem “.cor” (przewidzianego dla linii BUPC) lub w nowym formacie (czynność zalecana).
Kopiuj
: umożliwia skopiowanie zawartości pamięci odbiornika do pamięci
komputera.
Wklej
: umożliwia wklejenie do pamięci odbiornika danych zapamiętanych
w pamięci komputera, zapamiętanych uprzednio za pomocą funkcji “Kopiuj”,
występującej w tej opcji.
3.4.1 – Sekcja USTAWIENIA: Pamięci “BM” i odbiorniki
“NiceOne” (typ OXI... ; typ OX...)
Sekcja “Ustawienia” umożliwia wprowadzanie parametrów działania odbiorni-
ka serii “NiceOne” oraz odbiornika z pamięcią “BM”, zarządzając funkcjami
zaawansowanymi.
Page 93

Polski – 11
PL
PAMIĘCI BM
• Ustawienia zaawansowane: ta funkcja umożliwia ustalenie następujących
parametrów.
Blokada pamięci
: uaktywnia blokadę czynności samouczących kartę
pamięci, gdy zostanie ona wstawiona do właściwego odbiornika; tj. w
odbiorniku, w którym pamięć jest zablokowana, nie można wprowadzać
nowych kodów, a działanie jest ograniczone tylko do kodów istniejących
(zapoznaj się także z odpowiednimi instrukcjami odbiornika).
Hasło
: umożliwia wprowadzenie w karcie pamięci hasła (“Password”); jest
to kod numeryczny dostępny za pomocą programu wyłącznie przez posiadaczy takiego kodu, za pomocą którego kontrolują i ograniczają dostęp do
danych na karcie pamięci. Żądanie podania hasła następuje każdorazowo,
gdy użytkownik domaga się dostępu do danych zawartych w pamięci, aby
odczytać lub zmodyfikować te dane lub pamiętane tam kody.
Hasło NIE umożliwia wprowadzenia zmian w danych zawartych na karcie
pamięci, gdy jest ona wstawiona w odbiornik: blokuje ono wszystkie funkcje
programowalne ręcznie w odbiorniku, który korzysta z tej pamięci.
Timer
: umożliwia zmianę czasu timera. Czas jest pokazywany w “godzi-
nach”, “minutach” i “sekundach”.
Altera
: jest to klucz, który umożliwia personalizację odbiornika; jest on
kompatybilny z poprzednimi systemami “FloR”.
Uwaga! – Należy zapamiętać nowy klucz zabezpieczający, w przeciwnym
razie odbiornik nie będzie mógł być dalej zdatny do użycia.
Kontrola RND: umożliwia aktywację lub dezaktywację kontroli części
zmiennej kodu identyfikowalnego (RND) w odbiorniku.
Okno RND
: umożliwia modyfikację okna RND odbiornika. Okno to przedstawia zakres wartości, spośród których jest przyjmowana część zmienna
kodu identyfikacyjnego (RND).
Uwaga – Standardowo wartość okna wynosi 100 i może przyjmować wartości z przedziału od 5 do 250.
Synchronizacja
: umożliwia aktywację i dezaktywację ponownej synchronizacji odbiornika. Jeżeli synchronizacja jest nieaktywna, bezpieczeństwo
instalacji jest większe, ale gdy nadajnik znajdzie się poza oknem RND,
koniecznym będzie ponowne zapamiętanie kodu identyfikacyjnego w pamięci odbiornika.
Tylko kody fabryczne
: umożliwia aktywację i dezaktywację odbiornika do
odbioru komend wysyłanych przez nadajnik z kodem zmienionym w stosunku do standardowego ustawienia fabrycznego.
ODBIORNIKI “NiceOne”
Są dostępne następujące funkcje:
• Certyfikaty: ta funkcja umożliwia odczyt i ustalenie certyfikatów odbiornika
(maksymalnie do 4). Kolejno, począwszy od góry, znajduje się certyfikat odbiornika (zapamiętany na karcie, znajdującej się w opakowaniu) i następne 3 inne
pola, nadające się do utworzenia grup odbiorników.
Uwaga – Aby dokładniej zapoznać się ze stosowaniem certyfikatów, zobacz
instrukcję “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Klucze: ta funkcja umożliwia personalizację odbiornika z możliwością zmiany
kluczy “Instalator”, “Instalacja” i “Altera”. W szczególności “Altera” jest kompatybilny z poprzednimi systemami “FloR”.
Uwaga! – Należy zapamiętać nowy klucz zabezpieczający, w przeciwnym razie
odbiornik nie będzie mógł być dalej zdatny do użycia.
Klucze są przydatne do personalizacji systemu: oznacza to możliwość zmiany
kodu początkowego (fabrycznego) nadajnika. Z tego powodu klucze powinny
być takie same w nadajniku jak i w odbiorniku. W takim przypadku konieczna
jest także zmiana kluczy zespołu O-Box, aby móc go następnie wykorzystać.
• Ustawienia zaawansowane: ta funkcja umożliwia ustalenie następujących
parametrów.
Ustawienia podstawowe
- Uaktywnij tylko TX oryginalne: ta funkcja umożliwia aktywację i dezakty-
wację działania odbiornika, który otrzymuje komendę z nadajnika, którego
kod został zmieniony, tzn. jest inny niż ustawiony fabrycznie.
- Dezaktywuj RND: ta funkcja umożliwia aktywację i dezaktywację kontroli
części zmiennej kodu identyfikacyjnego (RND) w odbiorniku.
Ustawienia zapamiętywania
- Blokada zapamiętywania za pomocą “Kodu uaktywnienia”: ta funkcja
umożliwia blokowanie zapamiętywania przez nowy nadajnik wykorzystując
“Kod uaktywnienia” starego nadajnika (już zapamiętanego). Ta procedura
może być stosowana tylko w przypadku, gdy używa się dwóch nadajników z
kodowaniem “O-Code”.
- Blokada zapamiętywania za pomocą “Certyfikatu”: ta funkcja umożli-
wia blokowanie zapamiętywania przez nowy nadajnik wykorzystując certyfikat odbiornika.
Page 94

12 – Polski
PL
- Blokada zapamiętywania na odległość: ta funkcja umożliwia blokowanie
zapamiętywania przez nowy nadajnik wykorzystując stary nadajnik z procedurą “w pobliżu nadajnika”.
Ustawienia BUS T4
Uwaga – “Bus”(magistrala) jest systemem, który umożliwia połączenie
pomiędzy wszystkimi urządzeniami danej instalacji automatyki, za pomocą
specjalnego kabla z kilkoma przewodami elektrycznymi wewnątrz. W tym
typie połączenia do przesyłania danych pomiędzy urządzeniami stosuje się
specyficzny protokół; w naszym przypadku jest to “Bus T4” firmy Nice.
- Uaktywnij powtarzanie kodu przez bus: ta funkcja umożliwia uaktywnienie w odbiorniku możliwości przesyłania do innych urządzeń, połączonych
poprzez kabel busT4, kopii kodu otrzymanego z nadajnika za pomocą
sygnału radiowego.
- Uaktywnij otrzymywanie kodu przez bus: ta funkcja umożliwia uaktywnienie w odbiorniku możliwości odbioru kodu, wysyłanego za pomocą kabla
bus T4 od innego odbiornika (zobacz poprzedni punkt “Uaktywnij powtarza-
nie kodu przez bus”).
- Uaktywnij grupy autoryzacji: ta funkcja umożliwia uaktywnienie zarządzania kodami radiowymi w grupach autoryzacji.
Ustawienia zaawansowane
- Uaktywnij “Repeater”: ta funkcja umożliwia aktywację powtarzania kodu.
Jeżeli istnieje potrzeba sterowania automatyką na odległość większą niż
zwykle pokrywa się z zakresem działania nadajnika i odbiornika, możliwe jest
stosowanie drugiego odbiornika z zadaniem retransmisji (tym razem drogą
radiową) komendy do odbiornika przeznaczenia (w którym został zapamiętany kod identyfikacyjny nadajnika, od którego przychodzi komenda), w taki
sposób, aby odbiornik mógł wykonać to polecenie.
- Uaktywnij zarządzanie zwalnianiem przycisku: podczas użytkowania
nadajnika po wysłaniu komendy i zwolnieniu przycisku manewr nie zatrzyma
się dokładnie w tym momencie, ale jest nadal wykonywany przez bardzo
krótki, ustalony z góry czas. Jeżeli zachodzi potrzeba przerwania manewru
dokładnie w chwili, w której następuje zwolnienie przycisku komendy w
nadajniku (na przykład podczas bardzo dokładnej regulacji), konieczne jest
uaktywnienie w odbiorniku tej funkcji.
- Dezaktywuj zarządzanie priorytetem: ta funkcja umożliwia dezaktywację
w odbiorniku odbioru komend wysyłanych przez nadajniki z priorytetem wyższym niż 0.
Nota – W celu dokładniejszego zapoznania się z wszystkimi wyżej opisanymi
funkcjami zobacz instrukcję “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Zmiana hasła: ta funkcja umożliwia wprowadzenie hasła, które służy do blokowania dostępu, także ręcznego, do wszystkich funkcji odbiornika, dla tego,
kto nie posiada hasła.
Opcja tematyczna “Instalacje” jest katalogiem, który umożliwia tworzenie i
archiwizowanie dla każdej instalacji karty analitycznej, w której zbierane są
dane rejestrowe klienta oraz dane o konfiguracji odbiorników zainstalowanych
w jego instalacji. W szczególności możliwe jest modyfikowanie instalacji,
wyświetlanie kodów oraz ustawianie i zachowywanie danych o zainstalowanych odbiornikach; w przypadku nieprawidłowego działania możliwe jest przywrócenie poprawnego działania automatyki.
Ta opcja tematyczna składa się z dwóch ekranów:
– jeden ekran przeznaczony do szybkiego szukania i wyboru zarchiwizowanych
instalacji;
– drugi zawierający kartę do pozyskiwania danych dotyczących pojedynczej
instalacji.
Aby wejść do opcji tematycznej “Instalacje”, należy postępować w sposób
następujący:
01. Na ekranie początkowym
(rys. 3) kliknąć na ikonę “Instalacje”.
02. Pojawi się pierwszy ekran (rys. 10) zarządzania instalacjami zarchiwizowa-
nymi. Zawiera on następujące elementy.
• “Pasek nawigacji” z następującymi funkcjami:
“Modyfikuj”
: umożliwia modyfikację danych instalacji.
“Nowa instalacja”: umożliwia utworzenie nowej instalacji.
“Kopiuj”: umożliwia skopiowanie danych istniejącej instalacji, aby
utworzyć nową instalację analogiczną.
“Usuń”: umożliwia usunięcie jednej lub więcej instalacji.
• Opcja “Filtruj dane”: umożliwia szukanie w prosty i szybki sposób zapa-
miętanych instalacji.
• Opcja “Lista instalacji”: wyświetla listę zapamiętanych instalacji.
3.5 – OPCJA TEMATYCZNA “INSTALACJE”
Page 95

Polski – 13
PL
10
11
03. W tym momencie, wybierając jedną z następujących funkcji: “Modyfikuj”,
“Nowa instalacja” i “Kopiuj”, pojawi się drugi ekran (rys. 11) z kartą dotyczącą danej instalacji. Składa się on z następujących elementów.
• “Pasek nawigacji” z następującymi funkcjami:
“Pracuj na tej instalacji”
: umożliwia pracę na nowej lub istniejącej
instalacji (zobacz paragraf 3.5.1).
“Zachowaj w pliku”: umożliwia zapamiętanie w innych plikach danych
odbiorników do zapamiętania.
“Importuj z pliku”: umożliwia odczytanie z pliku danych odbiornika
(zobacz paragraf 3.5.1).
“Zachowaj zmiany”: umożliwia zapamiętanie zmian wykonanych na
karcie instalacji.
Oprócz paska nawigacji ekran ten zawiera 3 pola operacyjne: Klient; Klu-
cze instalacji; Odbiorniki.
• Klient: w tej opcji możliwe jest wprowadzenie danych rejestrowych
klienta.
• Klucze instalacji: w tej opcji możliwe jest zastosowanie kluczy w celu per-
sonalizacji instalacji, wykorzystując pola „Klucze instalatora”, “Klucze instalacji” i “Altera”. Klucze te są przydatne w celu ograniczenia zarządzania instalacjami wyłącznie dla posiadaczy kluczy. Możliwe jest wykorzystanie tego
samego klucza do różnych instalacji lub różnych kluczy do każdej instalacji.
Podczas programowania nadajników i odbiorników serii “Nice Opera”,
będą one zaprogramowane automatycznie z tymi samymi kluczami wprowadzonymi do karty instalacji, jeśli ta karta została wcześniej uaktyw-
niona i zawiera wprowadzone klucze.
Uwaga – W celu dokładniejszego zapoznania się ze stosowaniem kluczy,
zobacz instrukcję “Nice Opera System Book”.
• Odbiorniki: w tej opcji są wyświetlane odbiorniki występujące w danej
instalacji. Aby dodać lub usunąć odbiornik, zobacz paragraf 3.5.1.
3.5.1 – Dodawanie odbiorników do instalacji
Na ogół, aby dodać jeden lub więcej odbiorników do karty instalacji, możliwe
jest postępowanie na dwa różne sposoby.
• sposób bezpośredni: ten sposób przewiduje, że dane odbiornika, który
dodajemy do instalacji, są już zapamiętane w pliku. Wówczas na ekranie, który
Page 96

14 – Polski
PL
wyświetla kartę instalacji, należy kliknąć na funkcji “Importuj z pliku” (na pasku
nawigacji) i wybrać odpowiedni plik.
• sposób pośredni
: ten sposób przewiduje następujące czynności:
– przy otwarciu programu wybiera się w panelu “Wybierz instalację” jedną z
funkcji “Pracuj z ostatnią instalacją” i “Wybierz lub utwórz instalację”; w przeciwnym razie kliknij ikonę “Instalacje” na ekranie początkowym.
– pojawi się ekran zarządzania instalacjami zarchiwizowanymi (rys. 10), na którym należy wybrać instalację, dla której chce się dodać odbiornik (instalację istniejącą lub nową, przed chwilą utworzoną);
– po potwierdzeniu wyboru, klikając na ikonę “Pracuj na tej instalacji”, program
pokaże ekran początkowy ze wskazaniem instalacji, na której się pracuje (rys. 12);
– wówczas podłączyć do zespołu O-Box dany odbiornik i uaktywnić opcję
tematyczną “Odbiorniki” w celu realizacji żądanego zaprogramowania (zobacz
rozdział 3.4);
– w końcu na tym samym ekranie kliknąć na ikonę “Instalacja” i wybrać w menu
rozwijanym (*) zakładkę “Dodaj instalację”.
12
(*) Uwaga – Menu skojarzone z ikoną “Instalacja” jest dynamiczne, o ile
wyświetla różne zakładki, zależnie od okoliczności. Na ogół są to następujące
zakładki:
• pierwszy wiersz: wyświetla kursywą nazwę aktywnej instalacji, tj. tej, dla któ-
rej można zapamiętać aktualnie programowany odbiornik.
• ostatni wiersz: wyświetla komendę “Dodaj do instalacji” w celu zapamiętania
odbiornika (nowego) właśnie zaprogramowanego.
• inne wiersze: wyświetla nazwę odbiorników ewentualnie istniejących w insta-
lacji. Aby dokonać modyfikacji jednego z nich, wystarczy wybrać nazwę i zmienić jego parametry. W końcu, aby zapamiętać dokonane zmiany, należy kliknąć
na ikonę “Instalacja” i wybrać w rozwijanym menu zakładkę “Zapamiętaj zmiany ...” (ta zakładka występuje tylko wtedy, gdy w aktywnej instalacji są już
odbiorniki).
Page 97

Polski – 15
PL
Produkt ten jest nierozłączną częścią automatyki, w związku z tym musi
być poddany utylizacji wraz nią.
Podobnie jak przy instalacji, także przy zakończeniu użytkowania niniejszego
produktu czynności utylizacji powinny być wykonane przez personel wykwalifikowany.
Niniejszy produkt składa się z różnego rodzaju materiałów, niektóre z nich
mogą być powtórnie użyte, inne muszą zostać poddane utylizacji. Należy
zasięgnąć informacji o systemach wtórnego przerobu i utylizacji, przewidzianych przez lokalne przepisy dla tej kategorii produktu.
Uwaga! – niektóre elementy produktu mogą zawierać substancje szkodliwe lub
niebezpieczne, które pozostawione w środowisku mogłyby zaszkodzić środowisku lub zdrowiu ludzkiemu.
Zgodnie ze wskazaniem symbolu na rysunku obok zabronione
jest wyrzucanie tego produktu razem z odpadami domowymi.
W celu utylizacji produktu należy przeprowadzić “segregację
odpadów” na potrzeby utylizacji, według metod przewidzianych lokalnymi przepisami, lub zwrócić produkt sprzedawcy
podczas zakupu nowego, równorzędnego produktu.
Uwaga! – lokalne przepisy mogą przewidywać poważne sankcje w przypadku
samodzielnej likwidacji tego produktu.
Utylizacja akumulatora
Akumulator, także zużyty, może zawierać substancje zanieczyszczające środowisko, zatem NIE może być wyrzucony wraz z odpadkami komunalnymi. Po
usunięciu akumulatora z produktu należy zutylizować go w sposób zgodny z
lokalnymi przepisami dotyczącymi “segregowania odpadów”.
Utylizacja produktu
Typologia: zespół programowania i kontroli kodów dla następujących produktów Nice:
• odbiorniki serii NiceOne i SMX;
• systemy nadajnik-odbiornik z kodowaniem “Bio”, “Flo”, “FloR”, “Smilo”, “O-Code”;
• systemy kontroli dostępu z dekoderem “Morx”; czytniki kart z transponderem MOM lub
klawiatura cyfrowa MOT;
• urządzenia stosujące system TTBUS;
Technologia radiowa: radionadajnik-odbiornik z częstotliwością 433.92 MHz. Zasięg do
10 m.
Złącza i urządzenia łączące:
• strefa do nadajników serii “NiceOne” (programowanie realizowane przez radio,
bezprzewodowe);
• złącze do kart pamięci “BM 60”, “BM 250”, “BM 1000”.
• złącze do odbiorników serii “SMX” i “NiceOne” (niektóre modele, poprzez kabel
dopasowujący);
• złącze do nadajników serii Bio, FloR, Very VR, Ergo, Plano
(poprzez kabel dopasowujący);
• złącze do czytnika optycznego do nadajników serii “Bio”;
• czytnik zbliżeniowy do kart z transponderem;
• złącze do urządzeń TTBUS (poprzez kabel dopasowujący);
Podłączenie do komputera:
• złącze przez kabel USB
• złącze przez kabel szeregowy RS232
• złącze bezprzewodowe w technologii Bluetooth
®
(tylko wersja OboxB)
Zasilanie:
• Wewnętrzne
: za pomocą akumulatora ładowalnego 6 V, 700 mAh.
• Zewnętrzne
: za pomocą połączenia USB do komputera lub poprzez zasilacz ALA1,
12Vdc,
Czas ponownego ładowania akumulatora: około 15 godzin
Okres utrzymywania naładowanego akumulatora: około10 godzin działania lub 3 mie-
siące w trybie oczekiwania (stand-by).
Żywotność akumulatora: co najmniej 100 cykli całkowitego rozładowania.
Stopień ochrony obudowy: IP 20 (użytkowanie tylko w pomieszczeniach wewnętrznych
i zabezpieczonych).
Temperatura pracy: od -20°C do +55°C
Wymiary (mm): 194 x 115 x H 40
Masa (gr): 410 (O-Box) - 460 (O-BoxB)
Dane techniczne produktu
Page 98

16 – Polski
PL
DEKLARACJA ZGODNOŚCI CE
Deklaracja zgodności CE zgodnie z dyrektywą 1999/5/WE
Uwaga – Niniejsza Deklaracja Zgodności stanowi zestawienie treści deklaracji
zgodności poszczególnych produktów, o których mowa w instrukcji. Treść deklaracji przedstawia stan według daty wydania niniejszej instrukcji, a forma jej tekstu
została dostosowana dla potrzeb druku.
Istnieje możliwość wystąpienia do Nice S.p.a. (TV) I o kopię oryginalnej deklaracji
poszczególnych produktów.
______________
Niżej podpisany Lauro Buoro, pełniący funkcję Prezesa Zarządu, deklaruje z pełną odpowiedzialnością, że produkt:
Nazwa producenta: NICE s.p.a.
Adres: Via Pezza Alta 13, 31046 Z.I. Rustignè, Oderzo
(TV) Włochy
Ty p: Programator OBOX do pilotów sterujących drogą
radiową 433,92 MHz i czytnik kart z transponderem.
Programator OBOX do pilotów sterujących drogą
radiową 433,92 MHz i czytnik kart z transponderem.. Wersja z technologią Bluetooth
®
Modele: OBOX, OBOXB
Akcesoria:
Spełnia wymagania dyrektywy unijnej:
• 1999/5/WE; DYREKTYWA PARLAMENTU EUROPEJSKIEGO I RADY
1999/5/WE z dnia 9 marca 1999 r. w sprawie urządzeń radiowych i
końcowych urządzeń telekomunikacyjnych oraz wzajemnego uznawania ich zgodności, zgodnie z następującymi zharmonizowanymi
normami:
ochrona zdrowia: EN 50371:2002;
bezpieczeństwo elektryczne: EN 60950-1:2001;
kompatybilność elektromagnetyczna: EN 301 489-1V1.6.1:2005;
EN 301 489-3V1.4.1:2002, EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1.:2002
widmo radiowe: EN 300220-2V2.1.1:2006, EN 300330-2
V1.3.1:2006, EN 300328 V1.7.1:2006, EN300440-2 V1.1.2:2004
Ponadto produkt spełnia wymagania następujących dyrektyw unijnych,
w treści zmodyfikowanej Dyrektywą Rady 93/68/EWG z dnia 22 lipca
1993:
• 89/336/EWG; DYREKTYWA RADY 89/336/EWG z dnia 3 maja 1989
roku, w sprawie zbliżenia ustawodawstw Państw Członkowskich
odnoszących się do kompatybilności elektromagnetycznej, zgodnie z
następującymi normami:
EN 55022:1998+A1:2000+A2:2003,
EN 55024:1998+A1:2001+A2:2003
Lauro Buoro
(Prezes Zarządu)
Page 99

Nederlands – 1
NL
NEDERLANDS
GEBRUIKSLICENTIE VAN DE SOFTWARE
De programma’s “O-Box-Software Desktop” en “O-Box Software Mobile” zijn
beschermd door het auteursrecht en het intellectueel eigendomsrecht; deze
software wordt niet verkocht, maar er worden niet-exclusieve gebruikslicenties
voor verleend. Nice s.p.a. blijft eigenaar van deze kopie van het programma. De
programma’s “O-Box Software Desktop” en “O-Box Software Mobile” zijn in
licentie gegeven, als producten die bij het product “O-Box” horen.
Deze softwareprogramma’s worden geleverd zonder garantie met betrekking
tot de gebruikswijze en de veiligheid. Bovendien is Nice s.p.a niet aansprakelijk
voor indirecte of directe schade, inclusief schade door winstverlies, werkonderbrekingen en dergelijke, veroorzaakt door onjuist gebruik van deze software.
INFORMATIE OVER DE MERKEN
De merken AMD
®
, INTEL®, BLUETOOTH®, WINDOWS®, MICROSOFT®zijn
merken die zijn geregistreerd door de respectievelijke eigenaren; de namen van
de in deze handleiding genoemde producten kunnen ook geregistreerd zijn
door de respectievelijke eigenaren.
ALGEMENE OPMERKING BIJ DE
HANDLEIDING
De programmeereenheid is leverbaar in twee modellen: O-Box
en O-BoxB. Deze modellen zijn vrijwel gelijk, alleen is het model
O-BoxB voorzien van een module voor de aansluiting via Blue-
tooth
®
technologie.
In deze handleiding wordt de term “O-Box
” gebruikt om de
twee producten zonder onderscheid aan te duiden, behalve waar anders gespecificeerd.
BESCHRIJVING VAN HET PRODUCT EN
GEBRUIKSBESTEMMING
1
Het product O-Box (of O-BoxB, uitvoering met Bluetooth®module) bestaat uit
een programmeereenheid en specifieke software. Deze twee elementen samen
zijn bestemd voor het programmeren en onderhouden van de gegevens en
parameters in apparatuur die gebruikt wordt in automatiseringsinstallaties van
poorten, garagedeuren, zonweringen, rolluiken, wegbarrières met slagbomen
en soortgelijke toepassingen.
Ieder ander gebruik wordt als oneigenlijk beschouwd! De fabrikant is niet
aansprakelijk voor schade veroorzaakt door oneigenlijk gebruik van het
product, anders dan het gebruik dat in deze handleiding beoogd wordt.
De O-Box en het systeem “NiceOpera”
De O-Box maakt deel uit van het systeem “NiceOpera”. Dit systeem is door
Nice ontworpen om het programmeren, gebruiken en onderhouden van de
apparatuur in automatiseringsinstallaties eenvoudiger te maken. Het systeem
bestaat uit meerdere elementen, software en hardware, die via radio onderling
gegevens en informatie kunnen uitwisselen met een codesysteem genaamd
“O-Code” of met een ‘fysieke’ aansluiting, via kabel.
De belangrijkste elementen van dit systeem zijn:
– NiceOne-zenders;
– NiceOne-ontvangers (familie OXI... ; familie OX...);
– Programmeereenheid O-Box;
– Besturingseenheden en reductiemotoren met “Bus T4”;
– Programmeereenheid O-View voor inrichtingen met “Bus T4”.
BELANGRIJK – Om alle functies van het systeem NiceOpera, alsmede de
onderlinge wisselwerking van de verschillende elementen van het systeem tot in detail te leren kennen, gelieve u de algemene handleiding
“NiceOpera System Book” te raadplegen; deze is ook beschikbaar op de
internetsite www.niceforyou.com
Belangrijkste functiekenmerken van de O-Box
Het gebruik van de O-Box is bijzonder geschikt voor hightech-automatiseringsinstallaties, omdat hiermee veel functies rechtstreeks op het kantoor van de
installateur kunnen worden uitgevoerd, zonder de noodzaak de werkzaamheden bij de installatie van de klant uit te voeren; of kan een installatie juist recht-
Page 100

2 – Nederlands
NL
Het product heeft een oplaadbare batterij van 6 V, waarmee het kan werken
zonder op het elektriciteitsnet te zijn aangesloten.
Opmerking – De batterij vergt minimaal 10 uur voor een oplaadcyclus. Het
oplaadniveau wordt aangegeven in de software (zie afb. 2)
De batterij wordt automatisch opgeladen wanneer de O-Box wordt gevoed
door een externe stroomvoorziening of door de USB-kabel.
2.1 – AANSLUITINGEN
• De O-Box aansluiten op de elektrische stroomvoorziening
Het product kan door het elektriciteitsnet worden gevoed via een adapter van
12 Vcc (apart leverbaar accessoire) of door een computer via de USB-kabel
(meegeleverd).
• De O-Box aansluiten op een personal computer
Om de O-Box (of O-BoxB) te gebruiken, moet deze worden aangesloten op
een personal computer (pc) met een USB-poort, door middel van de meegeleverde kabel, of een seriële poort, met de kabel RS232 (optioneel accessoire).
Opmerking – Voor deze aansluiting is het raadzaam de USB-connector te
gebruiken (indien aanwezig) omdat deze betere prestaties levert: hij is betrouwbaarder, sneller in het verzenden van data, heeft geen configuratie nodig en de
interne batterij van de O-Box kan hiermee automatisch worden opgeladen.
• De O-BoxB aansluiten via Bluetooth
®
Het model O-BoxB kan ook via Bluetooth®op een computer of een palmcomputer (PDA) voorzien van een
Bluetooth
®
interface worden aangesloten.
Voor deze aansluiting zijn geen kabels nodig: het is voldoende de software op
de computer of op de palmcomputer te installeren en de gegevens in te stellen
op grond van de kenmerken van de palmcomputer.
Opmerking – Alvorens de Bluetooth
®
-aansluiting te activeren, moet de O-BoxB
worden afgesloten van de USB-poort of van de seriële poort van de computer.
De O-BoxB kan tot 16 aansluitingen op verschillende computers in het geheugen opslaan. Om een aansluiting tot stand te brengen, moet de O-BoxB worden aangezet en moet de computer gereed worden gemaakt voor de Blue-
streeks bij de klant geconfigureerd worden.
Met dit product kunnen de installaties worden beheerd en gewijzigd met
gebruik van een gegevensarchief; er kunnen snel verschillende handelingen
mee worden verricht, zoals het heropstarten, het uitbreiden van bestaande
installaties, het vervangen van zenders, etc.
In het algemeen kan de O-Box gebruikt worden voor:
• het controleren, toevoegen, programmeren of verwijderen van codes van de
zenders “Bio”, “FloR”, “Ergo”, “Plano”, “NiceOne”;
• het programmeren van de geheugens van de ontvangers “Bio” en “FloR”;
• het lezen en beschrijven van transpondercards;
• het programmeren van de functies en karakteristieke parameters van de zenders “Bio”, “FloR” en “Very”;
• het optisch lezen van de codes van de zenders “Bio”;
• het via kabel lezen en programmeren van de karakteristieke parameters van
de ontvangers “SMX1” en “SMX2”;
• het via radio ontvangen van gegevens van de zenders met code SMILO,
FLO, FLOR, O-CODE, om gebruikersarchieven aan te maken en de geheugens en de ontvangers te programmeren;
• het via radio programmeren van de zenders van de serie “NiceOne”;
• het via radio besturen van alle functies van de ontvangers “NiceOne”.
Met de bij de O-Box geleverde software kunnen de zenders en ontvangers van
de serie “NiceOne” worden geconfigureerd en geprogrammeerd. Bovendien is de
software ook compatibel met alle apparaten uit de serie “FloR”, “SMXI” en “Bio”.
HARDWARE: beschrijving van het product en
het installeren ervan
2
1
 Loading...
Loading...