Page 1

Reference Manual for the
NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless
Access Point 802.11g WG302
NETGEAR, Inc.
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
Phone 1-888-NETGEAR
202-10008-03
July 2005
July 2005 v3.0
Page 2

Technical Support
Please register to obtain technical support. Please retain your proof of purchase and warranty
information.
To register your product, get product support or obtain product information and product
documentation, go to http://www.NETGEAR.com
. If you do not have access to the World Wide
Web, you may register your product by filling out the registration card and mailing it to
NETGEAR customer service.
You will find technical support information at:
http://www.NETGEAR.com/
through the customer service area. If you want to contact technical
support by telephone, see the support information card for the correct telephone number for your
country.
© 2005 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
NETGEAR is a registered trademark of NETGEAR, INC. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft
Corporation. Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders. Information is subject to change without notice. All rights reserved.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the
right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not
assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit layout(s)
described herein.
Modifications made to the product, unless expressly approved by Netgear, could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to such condition.
ii
July 2005 v3.0
Page 3

Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Compliance Notice: Radio Frequency Notice
NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point
Tested to Comply
with FCC Standards
FCC ID: PY3WG302
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Placement and Range Guidelines
Indoors, computers can connect over 802.11 wireless networks at a maximum range of 500 feet (152.4 m)
for 802.11b devices. However, the operating distance or range of your wireless connection can vary
significantly, based on the physical placement of the wireless access point.
For best results, identify a location for your wireless access point according to these guidelines:
• Away from potential sources of interference , such as PCs, large metal surfaces, microwaves, and 2.4 GHz cordless
phones.
• In an elevated location such as a high shelf that is near the center of the wireless coverage area for all mobile
devices.
Failure to follow these guidelines can result in significant performance degradation or inability to wirelessly
connect to the wireless access point.
To meet FCC and other nat ional safety guideli nes for RF ex posure, the antennas fo r this device must be
installed to ensure a minimum separation distance of 20cm (7.9 in.) from persons. Further, the antennas shall
not be colocated with other transmitting structures.
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
July 2005 v3.0
iii
Page 4

FCC Statement
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
We Netgear,
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054, USA
Tel: +1 408 907 8000
declare under our sole responsibility that the product(s)
WG302 (Model Designation)
802.11g Pr oSafe Wireless Access Point (Product Name)
complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try and correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
iv
July 2005 v3.0
Page 5
• Reorient or locate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
RF Exposure Warning for North America, and Australia
Warning! To meet FCC and other national safety guidelines for RF exposure, the antennas for this device
(see below) must be installed to ensure a minimum separation distance of 20cm (7.9 in.) from persons.
Further, the antennas shall not be colocated with other antenna or radio transmitter.
Antenna Statement for North America and Australia
In addition to its own 2 antennas, the WG302 device has been approved for use with the following
detachable antennas and antenna cables:
Approved
Antennas
NETGEAR
ANT24D18
NETGEAR
ANT2409
NETGEAR
ANT24O5
Antenna Gain and
type
18 dBi, directional
outdoor/indoor
9 dBi, omnidirectional
outdoor/indoor
5 dBi, ceiling/wall
indoor
Approved Antenna
Cable
NETGEAR
ACC-10314-01 thru 05
NETGEAR
ACC-10314-01 thru 05
NETGEAR
ACC-10314-01 thru 05
Antenna Cable
Length
1.5 m to 30 m 19 dBm + 18 dBi ant.
1.5 m to 30 m 19 dBm + 9 dBi ant.
1.5 m to 30 m 19 dBm + 5 dBi ant.
Maximum
Transmit ted Power
* WG302 maximum radiated power in North America and Australia: 20 dBm – cable loss + antenna gain
Please go to www.netgear.com/go/wg302_fcc for an updated list of wireless accessories approved to be used
with the WG302 in North America and Australia.
Industry Canada Compliance Statement
This Class B Digital apparatus meets all the requirements of the Canadian Interference Causing Equipment
Regulations ICES 003.
Cet appareil numerique de classe B respecte les exigences du reglement du Canada sur le materiel brouilleur
NMB-003.
The device is certified to the requirements of RSS-210 for 2.4 GHz spread spectrum devices. The use of this
device in a system operating either partially or completely outdoors may require the user to obtain a license
July 2005 v3.0
v
Page 6

for the system according to the Canadian regulations. For further information, contact your local Industry
Canada office.
Product and Publication Details
Model Number: WG302
Publication Date: July 2005
Product Family: wireless access point
Product Name: NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Home or Business Product: Business
Language: English
Publication Part Number: 202-10008-03
vi
July 2005 v3.0
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1
About This Manual
Audience, Scope, Conventions, and Formats ................................................................1-1
How to Use This Manual ................................................................................................1-2
How to Print this Manual .................................................................................................1-3
Chapter 2
Introduction
About the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 ........................2-1
Key Features ..................................................................................................................2-2
AutoCell—The Self-Organizing Wireless Network ...................................................2-3
802.11g Standards-based Wireless Networking ......................................................2-4
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink ...............................................2-4
Compatible and Related NETGEAR Products ................................................................2-5
System Requirements ....................................................................................................2-5
What’s In the Box? .........................................................................................................2-6
Hardware Description .....................................................................................................2-6
Chapter 3
Basic Installation and Configuration
Observing Placement and Range Guidelines ..................... ................ ................ ............3-1
Cabling Requirements ..............................................................................................3-2
Default Factory Settings ...........................................................................................3-3
Understanding WG302 Wireless Security Options ................................. ........................ 3-4
Installing the WG302 Access Point ................................................................................3-5
How to Log In to the WG302 Using Its Default IP Address ..........................................3-11
Using the Basic IP Settings Options .............................................................................3-11
Understanding Basic Wireless Settings .............................. .......................... ................3-13
Understanding WEP/WPA Security Options .................................................................3-15
Before You Change the SSID and WEP Settings ..................................................3-18
How to Set Up and Test Basic Wireless Connectivity ............................................3-19
How to Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address ...............................................3-20
How to Configure WEP ..........................................................................................3-21
Contents iii
July 2005 v3.0
Page 8

How to Configure WPA with Radius .......................................................................3-22
How to Configure WPA-PSK ..................................................................................3-25
How to Configure WPA2 with Radius .....................................................................3-26
How to Configure WPA2-PSK ................................................................................3-28
How to Configure WPA and WPA2 with Radius .....................................................3-29
How to Configure WPA2-PSK and WPA2-PSK ......................................................3-32
Chapter 4
Management
Remote Management .....................................................................................................4-1
Using the Secure Telnet Interface ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..4-2
How to Use the CLI via the Console Port .................................................................4-2
CLI Commands ........................................................................................................4-3
Using Syslog and Activity Log Information .....................................................................4-4
Viewing General, Log, Station, and Statistical Information .............................................4-5
Statistics ................................................................. .................................................. 4-7
Viewing a List of Available Wireless Stations .................................................................4-8
Detecting a Rogue Access Point ....................................................................................4-9
Upgrading the Wireless Access Point Software ...........................................................4-10
Configuration File Management ...................................................................................4-11
Saving and Retrieving the Configuration ................................................................4-11
Restoring the WG302 to the Factory Default Settings ........................................... 4-12
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings .................................4-12
Changing the Administrator Password ......................... ....................................... ... 4-12
Chapter 5
Advanced Configuration
Understanding Advanced IP Settings for Wireless Clients ........... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..5-1
Understanding Advanced Wireless Settings ..................................................................5-2
AutoCell RF Management ..... .... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ........................5-2
Configuration .....................................................................................................5-3
AutoCell AP/Client Interaction ...................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..5-4
Additional AutoCell View Management Options ........................ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..5-5
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Setup ...............................................................................5-5
Configuring Wireless LAN Parameters ....................................................................5-6
Hotspot Settings .............................................................................................................5-7
Enabling Wireless Bridging and Repeating ....................................................................5-8
iv Contents
July 2005 v3.0
Page 9

How to Configure a WG302 as a Point-to-Point Bridge ...........................................5-9
How to Configure Multi-Point Wireless Bridging ....................................................5-10
How to Configure Wireless Repeating ...................................................................5-11
Chapter 6
Troubleshooting
No lights are lit on the access point. ...................................... ......................................... 6-1
The Wireless LAN activity light does not light up. ...........................................................6-2
The LAN light is not lit. ....................................................................................................6-2
I cannot access the Internet or the LAN with a wireless capable computer. .................6-2
I cannot connect to the WG302 to configure it. ......................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..6-3
When I enter a URL or IP address I get a timeout error. ................................................6-3
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings . .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..6-4
Appendix A
Specifications
Specifications for the WG302 ........................................................................................ A-1
Appendix B
Wireless Networking Basics
Wireless Networking Overview .............................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............................. B -1
Infrastructure Mode ................................................................................................. B-1
Ad Hoc Mode (Peer-to-Peer Workgroup) ............................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... . B-2
Network Name: Extended Service Set Identification (ESSID) ................................ B-2
Authentication and WEP Data Encryption .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... ........... B-2
802.11 Authentication .............................................................................................. B-3
Open System Authentication .............................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ....................... B-3
Shared Key Authentication ...................................................................................... B-4
Overview of WEP Parameters ................................................................................ B-5
Key Size .................................................................................................................. B-6
WEP Configuration Options ................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... .................................... B-7
Wireless Channels ....................... .... ... ... ... ..................................................................... B-7
WPA and WPA2 Wireless Security ................................................................................ B-8
How Does WPA Compare to WEP? ........................................................................ B-9
How Does WPA Compare to WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i)? ............................................ B-10
What are the Key Features of WPA and WPA2 Security? ........................ ... .... ... .. B-10
WPA/WPA2 Authentication: Enterprise-level User
Authentication via 802.1x/EAP and RADIUS .................................................. B-12
WPA/WPA2 Data Encryption Key Management ............................................. B-14
Contents v
July 2005 v3.0
Page 10

Is WPA/WPA2 Perfect? ................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............................ B-16
Product Support for WPA/WPA2 ........................................................................... B-16
Supporting a Mixture of WPA, WPA2, and WEP Wireless Clients is Discouraged B-16
Changes to Wireless Access Points ............................................................... B-17
Changes to Wireless Network Adapters ......................................................... B-17
Changes to Wireless Client Programs .......................... ......................... ......... B-18
Appendix C
Command Line Reference
Command Sets ..............................................................................................................C-1
Glossary
vi Contents
July 2005 v3.0
Page 11
Chapter 1
About This Manual
This chapter describes the intended audience, scope, conventions, and formats of this manual.
Audience, Scope, Conventions, and Formats
This reference manual assumes that the reader has basic to intermediate computer and Internet
skills. However, basic computer network, Internet, firewall, and VPN technologies tutorial
information is provided in the Appendices and on the Netgear website.
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
Table 1-1. Typographical Conventions
italics Emphasis, books, CDs, URL names
bold User input
fixed Screen text, file and server names, extensions, commands, IP addresses
This guide uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: This format is used to highlight information of importance or special interest.
This manual is written for the WG302 Access Point according to these specifications:
Table 1-2. Manual Scope
Product Version NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Manual Publication Date July 2005
Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR, Inc. Web site at
http://kbserver.netgear.com/products/WG302.asp.
About This Manual 1-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 12

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Use This Manual
The HTML version of this manual includes the following:
• Buttons, and , for browsing forwards or backwards through the manual one page
at a time
• A button that displays the table of contents and an button. Double-click on a
link in the table of contents or index to navigate directly to where the topic is described in the
manual.
• A button to access the full NETGEAR, Inc. online knowledge base for the
product model.
• Links to PDF versions of the full manual and individual chapters.
1-2 About This Manual
July 2005 v3.0
Page 13

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Print this Manual
To print this manual you can choose one of the following several options, according to your needs.
• Printing a Page in the HTML View.
Each page in the HTML version of the manual is dedicated to a major topic. Use the Print
button on the browser toolbar to print the page contents.
• Printing a Chapter.
Use the PDF of This Chapter link at the top left of any page.
– Click the PDF of This Chapter link at the top right of any page in the chapter you want to
print. The PDF version of the chapter you were viewing opens in a browser window.
Note: Your computer must have the free Adobe Acrobat reader installed in order to view
and print PDF files. The Acrobat reader is available on the Adobe Web site at
http://www.adobe.com.
– Click the print icon in the upper left of the window.
Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can save
paper and printer ink by selecting this feature.
• Printing the Full Manual.
Use the Complete PDF Manua l link at the top left of any page.
– Click the Complete PDF Manual link at the top left of any page in the manual. The PDF
version of the complete manual opens in a browser window.
– Click the print icon in the upper left of the window.
Tip: If your printer supports printing two pages on a single sheet of paper, you can save
paper and printer ink by selecting this feature.
About This Manual 1-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 14

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
1-4 About This Manual
July 2005 v3.0
Page 15

Chapter 2
Introduction
This chapter introduces the NETGEAR NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g
WG302. Minimal prerequisites for installation are presented in “System Requirements” on
page 2-5.
About the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.1 1g WG302
The NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 is the basic building block of a
wireless LAN infrastructure. It provides connectivity between Ethernet wired networks and
radio-equipped wireless notebook systems, desktop systems, print servers, and other devices.
The WG302 provides wireless connectivity to multiple wireless network devices within a fixed
range or area of coverage, interacting with a wireless network interface card (NIC) via an antenna.
T ypically, an individual in-building access point provides a maximum connectivity area with about
a 300 foot radius. The NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 can support a
small group of users in a range of several hundred feet. Most access points are rated between 30-70
users simultaneously.
The NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 acts as a bridge between the
wired LAN and wireless clients. Connecting multiple WG302 Access Points via a wired Ethernet
backbone can further lengthen the wireless network coverage. As a mobile computing device
moves out of the range of one access point, it moves into the range of another. As a result, wireless
clients can freely roam from one Access Point to another and still maintain seamless connection to
the network.
The auto-sensing capability of the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
allows packet transmission at up to 108 Mbps, or at reduced speeds to compensate for distance or
electromagnetic interference.
Introduction 2-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 16

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Key Features
The WG302 Access Point is easy-to-use and provides solid wireless and networking support.
Supported Standards and Conventions
The following standards and conventions are supported:
• Standards Compliant. The Wireless Access Point complies with the IEEE 802.11g for
Wireless LANs.
• WEP support. Support for WEP is included. 64-bit, 128-bit, and 152-bit keys are supported.
• Full WPA and WPA2 support. WPA and WPA2 enterprise class strong security with
RADIUS and certificate authentication as well as dynamic encryption key generation.
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK pre-shared key authentication without the overhead of RADIUS
servers but with all of the strong security of WPA.
• DHCP Client Support. DHCP provides a dynamic IP address to PCs and other devices upon
request. The WG302 can act as a client and obtain information from your DHPC server.
• SNMP Support. Support for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management
Information Base (MIB) management.
Key Features
The NETGEAR WG302 provides solid functionality, including these features:
• AutoCell RF Management. AutoCell provides advanced automated RF management that
improves performance and enhances security.
• Multiple Operating Modes
– Wireless Access Point. Operates as a standard 802.11g.
– Point-to-Point Bridge. In this mode, the WG302 only communicates with another
bridge-mode wireless station. You must enter the MAC address (physical address) of the
other bridge-mode wireless station in the field provided. WEP should be used to protect
this communication.
– Point-to-Multi-Point Bridge. Select this only if this WG302 is the “Master” for a group
of bridge-mode wireless stations. The other bridge-mode wireless stations must be set to
Point-to-Point Bridge mode, using this WG302's MAC address. They then send all traffic
to this “Master”, rather than communicate directly with each other . WEP should be used to
protect this traffic.
2-2 Introduction
July 2005 v3.0
Page 17

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
– Wireless Repeater. In this half-duplex mode, the WG302 only communicates with
another repeater-mode wireless station. You must enter the MAC address of both adjacent
repeater-mode wireless stations in the fields provided. WEP should be used to protect this
communication.
• Wireless Multimedia (WMM) support. WMM is a subset of the 802.11e standard. WMM
allows wireless traffic to have a range of priorities, depending on the kind of data.
Time-dependent information such as video or audio will have a higher priority than normal
traffic. For WMM to function correctly, wireless clients must also support WMM.
• Rogue Access Point detection. For enhanced security, you can scan the wireless network to
detect rogue access points.
• Hotspot settings. You can allow all HTTP (TCP, port 80) requests to be captured and
re-directed to the URL you specify.
• Upgradeable Firmware. Firmware is stored in a flash memory and can be upgraded easily,
using only your Web browser, and can be upgraded remotely.
• Access Control. The Access Control MAC address filtering feature can ensure that only
trusted wireless stations can use the WG302 to gain access to your LAN.
• Simple Configuration. If the default settings are unsuitable, they are easy to change.
• Hidden Mode. The SSID is not broadcast, assuring only clients configured with the correct
SSID can connect.
• Secure Telnet Command Line Interface. The Telnet command line interface enables direct
access over the serial port and easy scripting of configuration of multiple WG302 across an
extensive network via the Ethernet interface. An SSH client is required.
• Configuration Backup. Configuration settings can be backed up to a file and restored.
• Secure and Economical Operation. Adjustable power output allows more secure or
economical operation.
• Power over Ethernet. Power can be supplied to the WG302 over the Ethernet port from any
802.3af compliant mid-span or end-span source such as the NETGEAR FSM7326P Managed
Power over Ethernet Layer 3 managed switch.
• Autosensing Ethernet Connection with
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet networks.
• LED Indicators. Power, test, LAN speed, LAN activity, and wirele ss activity are easily
identified.
Auto Uplink Interface. Connects to 10/100 Mbps
AutoCell—The Self-Organizing Wireless Network
AutoCellTM, an embedded control system for 802.11 WLANs. AutoCell increases available
bandwidth and reduces WLAN installation and operating costs significantly.
Introduction 2-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 18

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
AutoCell is completely automatic: It is a continuous communication system that relies on a
lightweight protocol to monitor changes on the wireless domain while keeping overhead very low.
Among AutoCell's inherent advantages:
• Elimination of manual site surveys and channel maps
• Dynamic load balancing
• Plug-and-play-implementation
• Transparent fault recovery and failover
Since AutoCell is completely self-organizing, it holds human intervention to a minimum. That
reduces the people costs associated with deployment, management, and maintenance—making
802.11 WLANs practical, efficient, and cost-effective.
802.11g Standards-based Wireless Networking
The NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 provides a bridge between
Ethernet wired LANs and 802.11g compatible wireless LAN networks. It provides connectivity
between Ethernet wired networks and radio-equipped wireless notebook systems, desktop
systems, print servers, and other devices. Additionally , the WG302 supports the following wireless
features:
• Distributed coordinated function (CSMA/CA, Back off procedure, ACK procedure,
retransmission of unacknowledged frames)
• RTS/CTS handshake
• Beacon generation
• Packet fragmentation and reassembly
• Short or long preamble
• Roaming among access points on the same subnet
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
The WG302 can connect to a standard Ethernet network. The LAN interface is autosensing and
capable of full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
2-4 Introduction
July 2005 v3.0
Page 19

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
The wireless access point incorporates Auto UplinkTM technology. The Ethernet port will
automatically sense whether the Ethernet cable plugged into the port should have a ‘normal’
connection such as to a computer or an ‘uplink’ connection such as to a switch or hub. That port
will then configure itself to the correct configuration. This feature also eliminates any concerns
about crossover cables, as Auto Uplink will accommodate either type of cable to make the right
connection.
Compatible and Related NETGEAR Products
For a list of compatible products from other manufacturers, see the Wireless Ethernet
Compatibility Alliance Web site (WECA, see http://www.wi-fi.net).
The following NETGEAR products work with the WG302 Access Point:
• WAG511 ProSafe 108 Mbps Dual Band PC Card
• WAG311 ProSafe 108 Mbps Dual Band PCI Card
• WG311T 802.11g 108 Mbps Wireless PCI Card
• WG511T 802.11g 108 Mbps Wireless CardBus Adapter
• WG511 802.11g 54 Mbps Wireless CardBus Adapter
• WG111 801.11g 54 Mbps Wireless Bridge
System Requirements
Before installing the WG302, make sure your system meets these requirements:
• A 10/100 Mbps Local Area Network device such as a hub or switch
• The Category 5 UTP straight through Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connector included in the
package, or one like it
• A 100-240 V, 50-60 HZ AC power source
• A Web browser for configuration such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or above, or
Netscape Navigator 4.78 or above
• At least one computer with the TCP/IP protocol installed
• 802.11b or 802.11b-compliant devices, such as the NETGEAR WG511 Wireless Adapter
Introduction 2-5
July 2005 v3.0
Page 20

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
What’s In the Box?
The product package should contain the following items:
• NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Power adapter and cord (12 V dc, 1.2 A)
• Straight through Category 5 Ethernet cable
• WG302 802.11g ProSafe Wireless Access Point Installation Guide
• Resource CD for the NETGEAR WG302 ProSafe 802.11g Wireless Access Point which
includes this manual.
• Support Registration card
Contact your reseller or customer support in your area if there are any missing or damaged parts.
You can refer to the Support Information Card for the telephone number of customer support in
your area. You should keep the Support Information card, along with the original packing
materials, and use the packing materials to repack the WG302 if you need to return it for repair. T o
qualify for product updates and product warranty registrations, we encourage you to register on the
NETGEAR Web site at: http://www.NETGEAR.com.
Hardware Description
The WG302 front and rear hardware functions are described below.
Figure 2-1: WG302 front panel
2-6 Introduction
July 2005 v3.0
Page 21

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
The following table explains the LED indicators:
LED DESCRIPTION
PWR Power Indicator
Off No power.
On Power is on.
TEST Self Test Indicator
Blink Indicates self test, loading software, or system fault (if continues).
Note: This LED may blink for a minute before going off.
100 Ethernet LAN Speed Indicator
Off Indicates 10 Mbps Ethernet link detected
Green On 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet link detected.
LINK/ACT LAN Ethernet LAN Link Activity Indicator
Off Indicates no Ethernet link detected.
Green On 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet link detected, no activity.
Green Blink Indicates data traffic on the 100Mbps Ethernet LAN.
Amber 0n 10 Mbps Ethernet link detected, no activity.
Amber Blink Indicates data traffic on the 10Mbps Ethernet LAN.
802.11g WLAN Wireless LAN Link Activity Indicator
Off Indicates no wireless link activity.
Green Blink Wireless link activity.
Figure 2-2: WG302 rear panel
Introduction 2-7
July 2005 v3.0
Page 22

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Left and Right Detachable Antenna
The WG302 provides two detachable antenna.
• Restore to Factory Defaults Button
The restore to default button located between the Ethernet RJ-45 connector and the power
socket restores the WG302 to the factory default settings.
• Serial Console Port
Male DB-9 serial port for serial DTE connections.
• RJ-45 Ethernet Port
Use the WG302 Ethernet RJ-45 port to connect to an Ethernet LAN through a device such as a
hub, switch, router, or POE switch.
• Power Socket
This socket connects to the WG302 12V 1.2A power adapter.
2-8 Introduction
July 2005 v3.0
Page 23
Chapter 3
Basic Installation and Configuration
This chapter describes how to set up your NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g
WG302 for wireless connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration will enable computers
with 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapters to do such things as connect to the Internet, or access
printers and files on your LAN.
Note: Indoors, computers can connect over 802.11g wireless networks at ranges
of several hundred feet or more. This distance can allow for others outside your area
to access your network. It is important to take appropriate steps to secure your network
from unauthorized access. The WG302 Access Point provides highly effective security
features which are covered in detail in “Understanding WEP/WP A Security Options” on
page 3-15. Deploy the security features appropriate to your needs.
You need to prepare these three things before you can establish a connection through your wireless
access point:
• A location for the WG302 that conforms to the Observing Placement and Range Guidelines
below.
• The wireless access point connected to your LAN through a device such as a hub, switch,
router, or Cable/DSL gateway.
• One or more computers with properly configured 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapters.
Observing Placement and Range Guidelines
The operating distance or range of your wireless connection can vary significantly bas ed on the
physical placement of the wireless access point. The latency, data throughput performance, and
notebook power consumption of wireless adapters also vary depending on your configuration
choices.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 24
Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Note: Failure to follow these guidelines can result in significant performance
degradation or inability to wirelessly connect to the WG302. For complete performance
specifications, see Appendix A, “Specifications”.
For best results, place your wireless access point:
• Near the center of the area in which your PCs will operate.
• In an elevated location such as a high shelf where the wirelessly connected PCs have
line-of-sight access (even if through walls).
• Away from sources of interference, such as PCs, microwaves, and 2.4 GHz cordless phones.
• Away from large metal surfaces.
• Putting the antenna in a vertical position provides best side-to-side coverage. Putting the
antenna in a horizontal position provides best up-and-down coverage.
• If using multiple access points, it is better if adjacent access points use different
radio frequency
Channels to reduce interference. The recommended Channel spacing between adjacent access
points is 5 Channels (for example, use Channels 1 and 6, or 6 and 11).
The time it takes to establish a wireless connection can vary depending on both your security
settings and placement. WEP connections can take slightly longer to establish. Also, WEP
encryption can consume more battery power on a notebook computer.
Cabling Requirements
The WG302 Access Point connects to your LAN via twisted-pair Category 5 Ethernet cable with
RJ-45 connectors.
3-2 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 25

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Default Factory Settings
When you first receive your WG302, the default factory settings will be set as shown below. You
can restore these defaults with the Factory Default Restore switch on the rear panel — see
“WG302 front panel” on page 2-6.
FEATURE FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS
User Name (case sensitive) admin
Password (case sensitive) password
Operating Mode Access Point
Access Point Name netgearxxxxxx where xxxxxx are the last six
digits of the wireless access point's MAC address
Built-in DHCP client
Built-in DHCP server
IP Configuration
(if DHCP server is unavailable)
Network Name (SSID) NETGEAR
Broadcast Network Name (SSID) Enabled
802.11g Radio Frequency Channel 11
AutoCell RF Management
AutoCell Enhanced RF Security ‘stealth’ mode
WEP/WPA Disabled
Restricting connectivity based on MAC Access
Control List
Spanning Tree Protocol Enabled
Time Zone GMT
Time Zone Adjust for Daylight Saving TIme Disabled
SNMP Enabled but Trap forwarding is disabled
Secure Telnet Enabled
SugerG Mode Disabled
WMM Mode Disabled
DHCP client disabled
DHCP server disabled
IP Address: 192.168.0.228
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 26
Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Understanding WG302 Wireless Security Options
Your wireless data transmissions can be received well beyond your walls by anyone with a
compatible adapter. For this reason, use the security features of your wireless equipment. The
WG302 Access Point provides highly effective security features which are covered in detail in this
chapter. Deploy the security features appropriate to your needs.
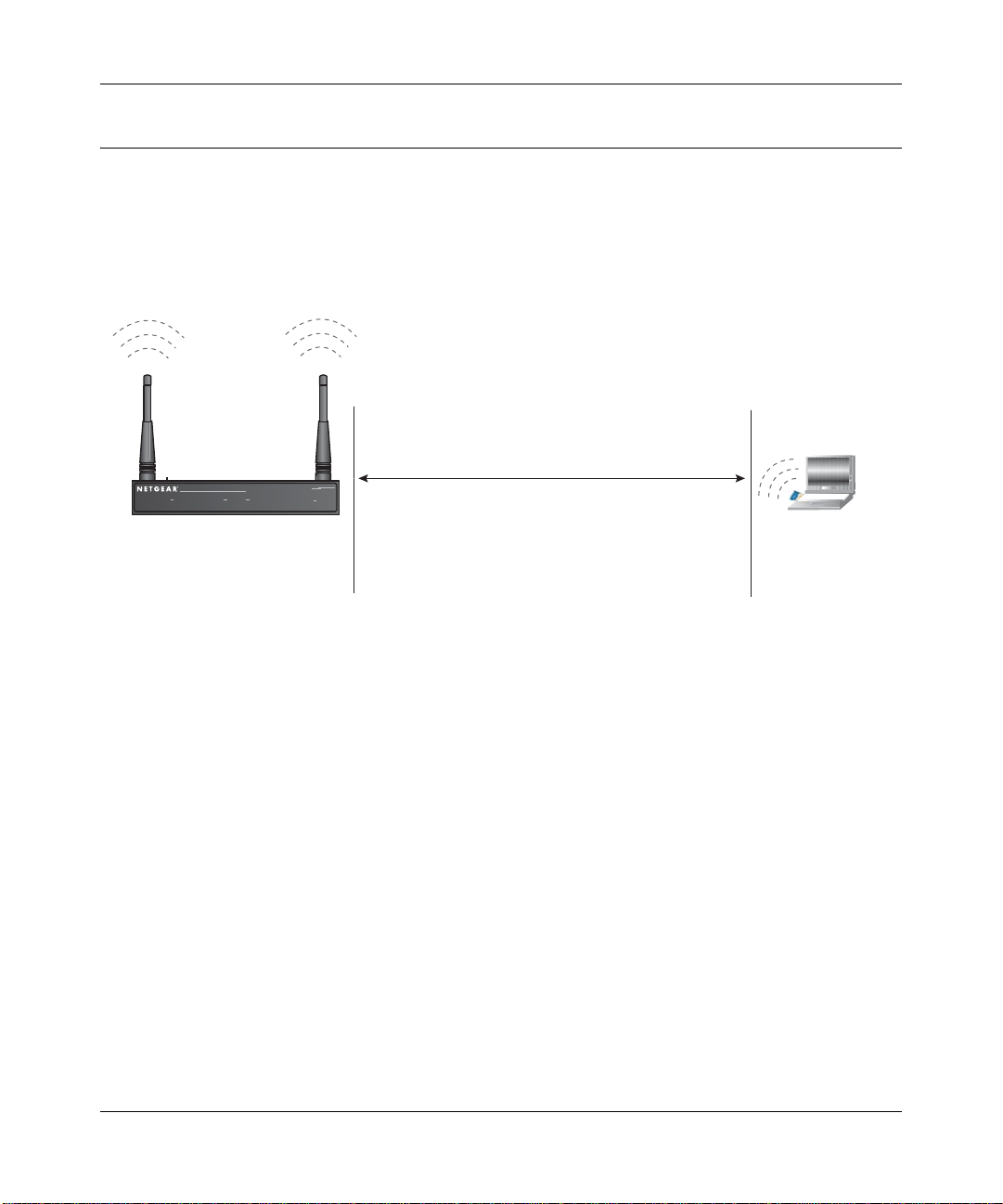
:LUHOHVV'DWD
6HFXULW\2SWLRQV
WG302
5DQJH8SWR)RRW5DGLXV
B
0RO3AFE7IRELESS!CCESS0OINT
072 ,!.
7IRELESS,!.
Figure 3-1: WG302 wireless data security options
There are several ways you can enhance the security of your wireless network:
• Restrict Access Based on MAC address. You can restrict access to only trusted PCs so that
unknown PCs cannot wirelessly connect to the WG302. MAC address filtering adds an
obstacle against unwanted access to your network, but the data broadcast over the wireless link
is fully exposed.
• Turn Off the Broadcast of the Wireless Network Name (SSID). If you disable broadcast of
the SSID, only devices that have the correct SSID can connect. This nullifies the wireless
network ‘discovery’ feature of some products such as Windows XP, but the data is still fully
exposed to a determined snoop using specialized test equipment like wireless sniffers.
• Use WEP. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) data encryption provides data security. WEP
Shared Key authentication and WEP data encryption will block all but the most determined
eavesdropper.
-/$%,
-%
.O3ECURITY%ASYBUTNOSECURITY
-!#!CCESS,IST.ODATASECURITY
7%03ECURITYBUTVULNERABLE
70!OR70!03+6ERYSTRONGSECURITY
!UTO#ELL2&@STEALTHMODE
3-4 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 27

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Use WPA, WPA-PSK, WPA2, or WPA2-PSK. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2)
data encryption provides data security . The very strong authentication along with dyn amic per
frame rekeying of WPA make it virtually impossible to compromise. Because this is a new
standard, wireless device driver and software availability may be limited.
• Use AutoCell Enhanced RF Security ‘Stealth Mode.’ In addition to standard encryption and
security mechanisms such as WEP and WP A, the WG302 A utoCell feature provides
self-organizing micro cells for an additional level of privacy for enterprises. In this mode,
AutoCell shrinks the size of coverage to the minimum to reach clients but also shrinks the size
of the beacons that access points use to announce their presence. This mode makes an
enterprise wireless LAN nearly invisible to users outside an office building. AutoCell clients
such as the NETGEAR WAG511 are highly-recommended for Enhanced RF Security.
Installing the WG302 Access Point
Before installing the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302, you should
make sure that your Ethernet network is up and working. You will be connecting the access point
to the Ethernet network so that computers with 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapters will be able
to communicate with computers on the Ethernet network. In order for this to work correctly , verify
that you have met all of the system requirements, shown on page 2-5.
1SET UP THE WG302 ACCESS POINT
Tip: Before mounting the WG302 in a high location, first set up and test the WG302 to verify
wireless network connectivity.
a. Prepare a computer with an Ethernet adapter. If this computer is already part of your
network, record its TCP/IP configuration settings.
b. Configure the computer with a static IP address of 192.168.0.210 and 255.255.255.0 for
the Subnet Mask.
c. Connect an Ethernet cable from the WG302 to the computer.
d. Turn on your computer, connect the power adapter to the WG302 and verify the following:
– The PWR power light goes on.
– The LAN light of the wireless access point is lit when connected to a powered on
computer.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-5
July 2005 v3.0
Page 28
Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
2CONFIGURE LAN AND WIRELESS ACCESS
a. Configure the WG302 Ethernet port for LAN access.
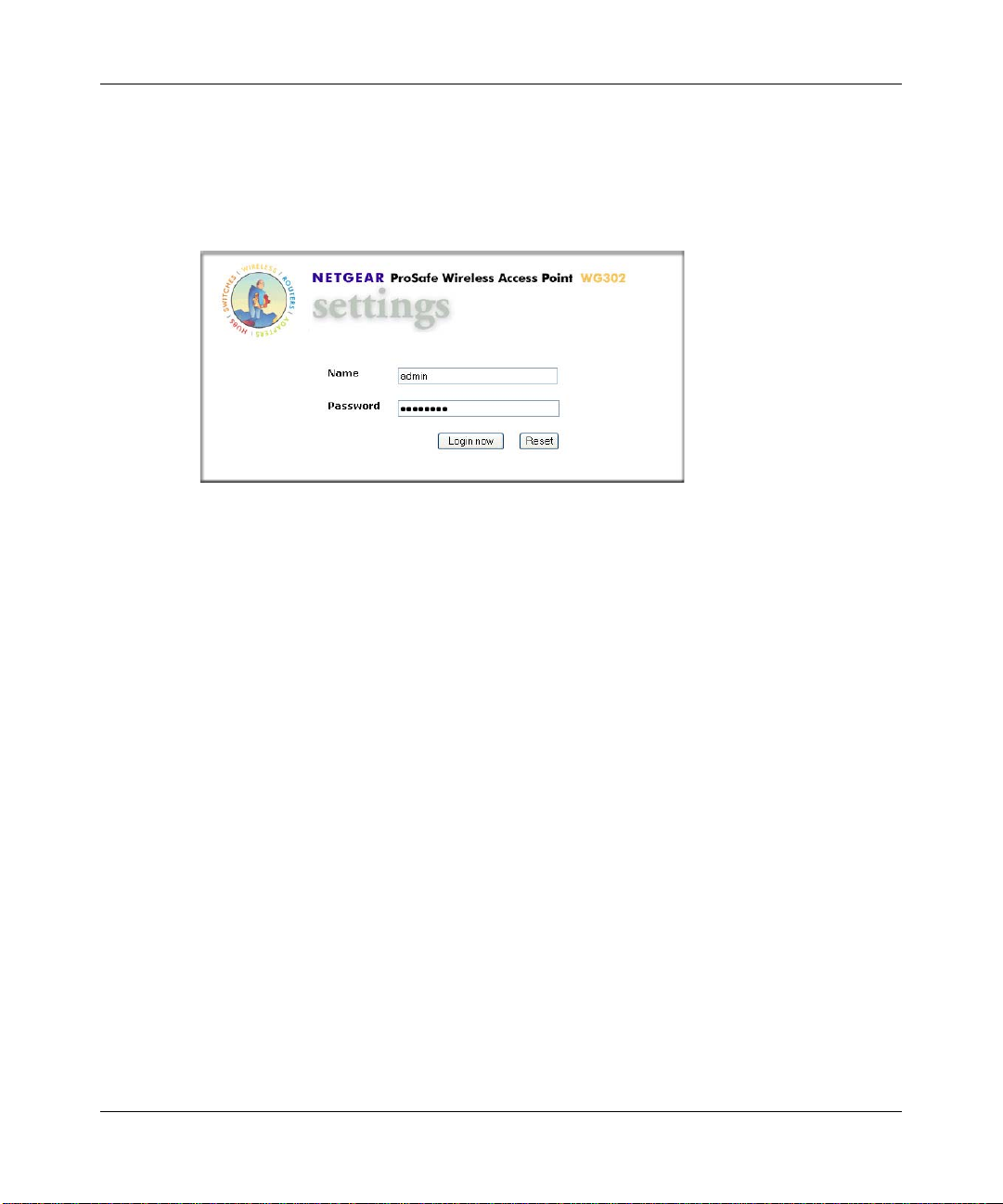
• Connect to the WG302 by opening your browser and en tering http://192.168.0.228 in
the address field. A login window like the one shown below opens:
Figure 3-2: Login window
• When prompted, enter admin for the user name and password for the password, both
in lower case letters.
3-6 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 29
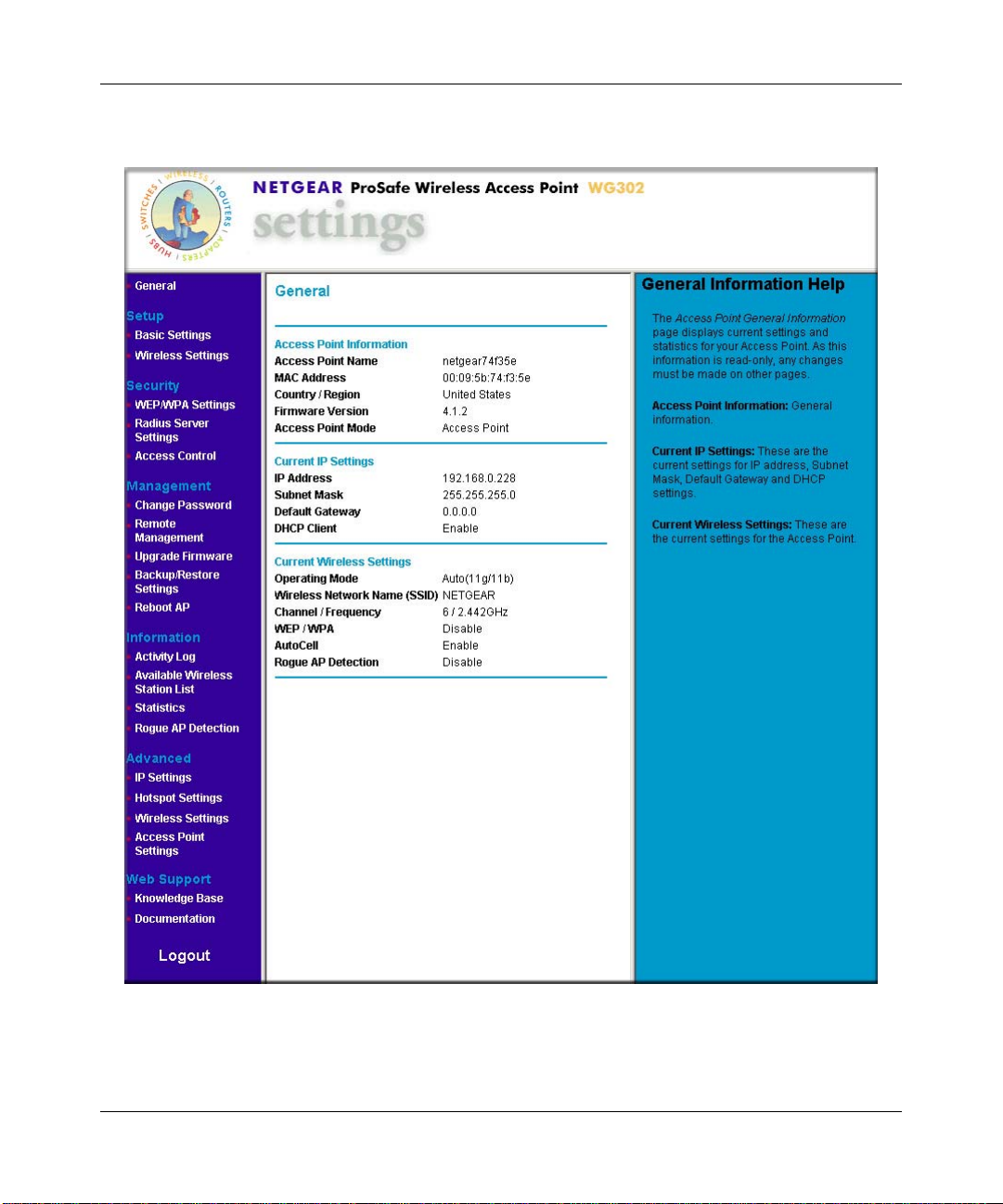
Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• The Web browser will then display the WG302 settings page.
Figure 3-3: Login result: WG302 home page
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-7
July 2005 v3.0
Page 30
Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
– When the wireless access point is connected to the Internet, click the Knowledge
Base or the Documentation link under the Web Support menu to view support
information or the documentation for the wireless access point.
– If you do not click Logout, the wireless access point will wait 5 minutes after
there is no activity before it automatically logs you out.
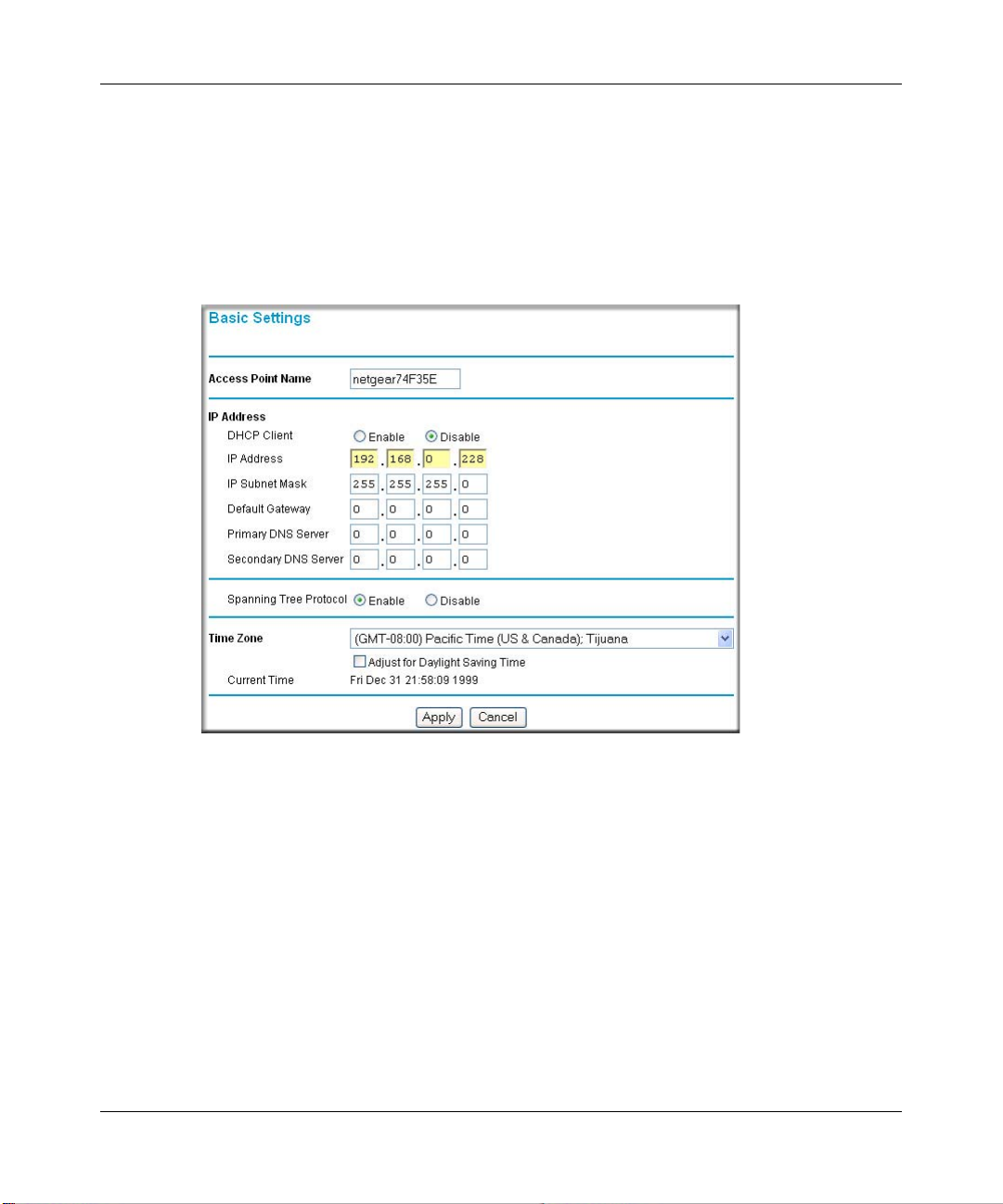
• Click the Basic Settings link to view the Basic Settings menu.
Figure 3-4: Basic Settings menu
• Configure the settings appropriate for your network.
3-8 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 31

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click the Wireless Settings link in the Setup section of the main menu to view the W ireless
b.
Settings menu.
Figure 3-5: Basic Wireless Settings menu
c.
Configure the wireless interface for wireless access. See the online help or the
Understanding Basic Wireless Settings topic of this Reference Manual for full
instructions.
Note: You must set the Regulatory Domain. It may not be legal to operate the wireless
access point in a region other than one of those identified in this field.
Now that you have finished the setup steps, you are ready to deploy the WG302 in your
network. If needed, you can now reconfigure the computer you used in step 1 back to its
original TCP/IP settings.
3DEPLOY THE WG302 ACCESS POINT
a. Disconnect the WG302 and position it where you will deploy it. The best location is
elevated, such as wall mounted or on the top of a cubicle, at the center of your wireless
coverage area, and within line of sight of all the mobile devices.
b. Lift the antenna on either side so that they are vertical.
Note: Consult the antenna positioning and wireless mode configuration information in the
Advanced Configuration chapter of the Reference Manual.
c. Connect an Ethernet cable from your WG302 Access Point to a LAN port on your router,
switch, or hub.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-9
July 2005 v3.0
Page 32

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Note: By default, WG302 is set to with the DHCP client disabled. If your network uses
dynamic IP addresses, you will need to change this setting.
d. Connect the power adapter to the wireless access point and plug the power adapter in to a
power outlet. The PWR, LAN, and Wireless LAN lights and should light up.
4VERIFY WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY
Using a computer with an 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapter with the correct wireless
settings needed to connect to the WG302 (SSID, WEP/WPA, MAC ACL, etc.), verify
connectivity by using a browser such as Netscape or Internet Explorer to browse the Internet,
or check for file and printer access on your network.
Note: If you are unable to connect, see Chapter 6, “Troubleshooting.”
3-10 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 33

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Log In to the WG302 Using Its Default IP Address
1. 192.168.0.228 is the default IP address of your access point. The WG302 is set by default with
the DHCP client disabled.
Note: The computer you are using to connect to the WG302 should be configured with an IP
address that starts with 192.168.0.x and a Subnet Mask of 255.25 5.255.0.
2. Open a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
3. Connect to the WG302 by entering its default address of http://192.168.0.228 into your
browser.
4. A login window like the one shown below opens:
Figure 3-6: Login window
Log in use the default user name of admin and default password of password.
Once you have entered your access point name, your Web browser should automatically find
the WG302 Access Point and display the home page, as shown i n “Login result: WG302 home
page” on page 3-7.
Using the Basic IP Settings Options
The Basic IP Settings menu is under the Basic heading of the main menu. Use this menu to
configure DHCP, static IP, and access point access point name settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-11
July 2005 v3.0
Page 34

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Figure 3-7: IP Settings menu
• Access Point Name (NetBIOS)
Enter a new name for the wireless access point and click Apply to save your changes.
• The IP Address
The wireless access point is shipped preconfigured with its DHCP client disabled and with the
following private static IP addresses:
– IP Address — 192.168.0.228
– IP Subnet Mask — 255.255.255.0
– Gateway — 0.0.0.0
– Primary and Secondary DNS Servers — 0.0.0.0
If your network has a requirement to use a different IP addressing scheme, you can make those
changes in this menu. These settings are only required if the “Use this IP address” radio button
is chosen. Remember to click Apply to save your changes.
3-12 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 35

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol in enabled by default for the wireless access point. This provides
network traffic optimization in settings with multiple WG302 Access Points.
•Time Zone
Select the time zone location for your setting.
Note: You must have an Internet connection to get the current time.
Understanding Basic Wireless Settings
To configure the wireless settings of your wireless access point, click the Wireless Settings link in
the Basic section of the main menu of the browser interface. The Basic Wireless Settings menu
will appear, as shown below.
Figure 3-8: Basic Wireless Settings menu
The Basic Wireless Settings menu options are discussed below:
• Country/Region. This field identifies the region where the WG302 can be used. It may not be
legal to operate the wireless features of the wireless access point in a region other than one of
those identified in this field. There is no default country domain, and the channel is set to 11.
Unless a country domain is selected, the channel cannot be changed.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-13
July 2005 v3.0
Page 36

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Turn Radio On. On by default, you can also turn off the radio to disable access through this
device. This can be helpful for configuration, network tuning, or troubleshooting activities.
• Wireless Network Name (SSID). The SSID is also known as the wireless network name.
Enter a value of up to 32 alphanumeric characters. In a setting where there is more than one
wireless network, different wireless network names provide a means for separating the traffic.
Any device you want to participate in a particular wireless network will need to use the SSID.
The WG302 default SSID is: NETGEAR.
– A group of Wireless Stations and a single access point, all using the same ID (SSID), form
a Basic Service Set (BSS).
– Using the same SSID is essential. Devices with different SSIDs are unable to
communicate with each other. However, some access points allow connections from
wireless stations which have their SSID set to “any” or whose SSID is blank (null).
– A group of wireless stations and multiple access points, all using the same ID (ESSID),
form an Extended Service Set (ESS).
– Different access points within an ESS can use different channels. T o reduce interference, it
is recommended that adjacent access points should use different channels.
– As wireless stations physically move through the area covered by an ESS, they will
automatically change to the access point which has the least interference or best
performance. This capability is called roaming.
Note: The AutoCell feature enhances the roaming, interference, and channel selection of
an extended wireless network.
• Broadcast Wireless Network Name (SSID). This field lets you turn off the SSID broadcast.
If you turn off the SSID broadcast, only stations that know the SSID will connect. Disabling
SSID broadcast somewhat hampers the wireless network ‘discovery’ feature of some products.
The default is to enable SSID broadcast.
Note: Broadcast Wireless Network Name (SSID) is automatically turned off when you
select the AutoCell Enhanced RF Security option in the advanced wireless settings page.
• Operating Mode. Select the desired wireless operating mode. The options are:
– Auto (11g/b) – Both 802.11g and 802.11b wireless stations can be used. This is the default.
– 11g Only - Only 802.11g wireless stations can be used. This is required for 108 Mbps data
rate operation.
3-14 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 37

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
– 11b Only - All 802.1 1b wireless stations can be used. 802.1 1g wireless stations can still be
used if they can operate in 802.11b mode.
• Channel. This field identifies which operating frequency will be used. It should not be
necessary to change the wireless channel unless you notice interference problems or setting up
the WG302 near another access point. See “Wireless Channels” on page B-7 for more
information on wireless channels.
Note: Channel selection is automatically adjusted by AutoCell when the Auto RF
Management option is enabled. The default setting is for the AutoCell Auto RF
Management option to be enabled.
– Access points use a fixed channel. You can select the channel used. This allows you to
choose a channel which provides the least interference and best performance. In the USA
and Canada, 11 channels are available.
Note: Channel 6 is required for 108 Mbps data rate.
– If using multiple access points, it is better if adjacent access points use different channels
to reduce interference. The recommended channel spacing between adjacent access points
is 5 channels (for example, use channels 1 and 6, or 6 and 11).
– In “Infrastructure” mode, wireless stations normally scan all channels, looking for an
access point. If more than one access point can be used, the one with the strongest signal is
used. This can only happen when the various access points are using the same SSID.
• Data Rate. Shows the available transmit data rate of the wireless network. 108 Mbps is only
available when the operating mode is 802.11g only and the channel is 6. The default is Best.
• Output Power. Set the transmit signal strength of the access point. The options are full, half,
quarter, eighth, and min. Decrease the transmit power if more than one AP is colocated using
the same channel frequency. The default is Full.
Note: Output power is automatically adjusted by AutoCell when the Auto RF
Management option is enabled. The default setting is for the AutoCell Auto RF
Management option to be enabled.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-15
July 2005 v3.0
Page 38

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Understanding WEP/WPA Security Options
The table below identifies the various WEP/WPA security options. A full explanation of these
standards is available in Appendix B, “Wireless Networking Basics”.
Figure 3-9: Wireless Security Settings
The WEP/WPA settings are explained as follows:
• Network Authentication: Specifies the Authentication type used. The default is Open
System. Select the desired option:
– Open System: If selected, you have the option of using WEP encryption, or no
encryption.
– Shared Key: If selected, you must use WEP; at least one shared key must be entered.
– Legacy 802.1x: If selected, you must configure the Radius Server Settings Screen.
– WPA-PSK: If selected, you must use TKIP encryption, and enter the WPA passphrase
(Network key).
– WPA with Radius: If selected, you must configure the Radius Server Settings Screen.
– WPA2-PSK: WPA2 is a later version of WPA. Only select this if all clients support
WPA2. If selected, you must use AES encryption, and enter the WPA passphrase
(Network key).
3-16 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 39

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
– WP A-PSK and WPA2-PSK: This selection allows clients to use either WPA (with TKIP)
or WPA2 (with AES). If selected, encryption must be TKIP + AES. The WPA passphrase
(Network key) must also be entered.
– WPA2 with Radius: WPA2 is a later version of WPA. Only select this if all clients
support WP A2. If selected, you must use AES encryption, and configure the Radius Server
Settings Screen.
– WPA and WPA2 with Radius: This selection allows clients to use either WPA (with
TKIP) or WPA2 (with AES). If selected, encryption must be TKIP + AES, and you must
also configure the Radius Server Settings Screen.
Note: All options are available if using Access Point mode. In other modes (e.g. Repeater or
Bridge) some options may be unavailable.
• Data Encryption: Select the desired option. The available options depend on the Network
Authentication setting above (otherwise, the default is None). The supported options are:
– None: No encryption is used.
– 64 bits WEP: Standard WEP encryption, using 40/64 bit encryption.
– 128 bits WEP: Standard WEP encryption, using 104/128 bit encryption.
– 152 bits WEP: Proprietary mode that will only work with other wireless devices that
support this mode.
– TKIP: This is the standard encryption method used with WPA.
– AES: This is the standard encryption method for WPA2. Some clients may support AES
with WPA, but this is not supported by this Access Point.
– TKIP + AES: This setting allows both WPA and WPA2 to be supported. Broadcast
packets use TKIP. For unicast (point-to-point) transmissions, WPA clients use TKIP, and
WPA2 clients use AES.
• Passphrase: To use the passphrase to generate the WEP keys, enter a passphrase and click
Generate Keys. You can also enter the keys directly. These keys must match the other
wireless stations.
• Key 1, Key 2, Key 3, Key 4: If using WEP, select the key to be used as the default key. Data
transmissions are always encrypted using the default key. The other keys can only be used to
decrypt received data.
• WP A Passphrase (Network Key): If using WPA-PSK, enter the passphrase here. All wireless
stations must use the same passphrase (network key). The network key must be from 8 to 63
characters in length.
• Wireless Client Security Separation: If enabled, the associated wireless clients will not be
able to communicate with each other. This feature is intended for hots pots and other public
access situations. The default is Disabled.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-17
July 2005 v3.0
Page 40

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Before You Change the SSID and WEP Settings
For a new wireless network, print this form and fill in the parameters. For an existing wireless
network, get the settings from the person who set up or is responsible for the network. Be sure to
set the Regulatory Domain correctly as the first step. Store this information in a safe place.
• SSID: The Service Set Identification (SSID) identifies the wireless local area network.
NETGEAR is the default WG302 SSID. However, you may customize it by using up to 32
alphanumeric characters. Write your customized SSID on the line below.
SSID: _________________________ __________
Note: The SSID in the wireless access point is the SSID you configure in the wireless adapter
card. All wireless nodes in the same network must be configured with the same SSID:
• Authentication
Circle one: Open System or Shared Key. Choose “Shared Key” for more security.
Note: If you select shared key, the other devices in the network will not connect unless they
are set to Shared Key and have the same keys in the same positions as those in the WG302.
• WEP Encryption Keys
For all four 802.11b keys, choose the Key Size. Circle one: 64, 128, or 152 bits
Key 1: ___________________________________
Key 2: ___________________________________
Key 3: ___________________________________
Key 4: ___________________________________
• WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
Record the WPA-PSK key: Record the WPA2-PSK key:
Key: ________________________________
• WPA RADIUS Settings
For WPA, record the following settings for the primary and secondary RADIUS servers:
Server Name/IP Address: Primary _________________
Port: ___________________________________
Shared Secret: ___________________________________
• WPA2 RADIUS Settings
For WPA2, record the following settings for the primary and secondary RADIUS servers:
Server Name/IP Address: Primary _________________
Port: ___________________________________
Shared Secret: ___________________________________
Key: _______________________________
Secondary __________________
Secondary __________________
Use the procedures described in the following sections to configure the WG302.
3-18 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 41

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Set Up and Test Basic Wireless Connectivity
Follow the instructions below to set up and test basic wireless connectivity. Once you have
established basic wireless connectivity , you can enable security settings appropriate to your needs.
1. Log in to the WG302 using its default address of http://192.168.0.228 or at whatever IP
address the unit is currently configured. Use the default user name of admin and default
password of password, or whatever password you set up.
2. Click the Wireless Settings link in the main menu of the WG302.
3. Choose a suitable descriptive name for the wireless network name (SSID). In the SSID box,
enter a value of up to 32 alphanumeric characters. The default SSID is NETGEAR.
Note: The SSID of any wireless access adapters must match the SSID you configure in the
NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302. If they do not match, you will
not get a wireless connection to the WG302.
4. Select the Country/Region in which the wireless interface will operate.
5. Set the Channel. It should not be necessary to change the wireless channel unless you notice
interference problems or are near another wireless access point. Select a channel that is not
being used by any other wireless networks within several hundred feet of your wireless access
point. For more information on the wireless channel frequencies see “Wireless Channels” on
page B-7.
6. For initial configuration and testing, leave the Wireless Card Access List set to “Everyone”
and the Encryption Strength set to “Disabled.”
7. Click Apply to save your changes.
Note: If you are configuring the WG302 from a wireless computer and you change the
SSID, channel, or security settings, you will lose your wireless connection when you
click Apply. You must then change the wireless settings of your computer to match the
new settings.
8. Configure and test your PCs for wireless connectivity.
Program the wireless adapter of your PCs to have the same SSID and channel that you
configured in the WG302. Check that they have a wireless link and are able to obtain an IP
address by DHCP from the WG302.
Once your PCs have basic wireless connectivity to the WG302, you can configure the advanced
wireless security functions.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-19
July 2005 v3.0
Page 42

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address
To restrict access based on MAC addresses, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the WG302 using its default address of http://192.168.0.228 or at whatever IP
address the unit is currently configured. Use the default user name of admin and default
password of password, or whatever LAN address and password you have set up.
Note: When configuring the WG302 from a wireless computer whose MAC address is
not in the access control list, if you select Turn Access Control On, you will lose your
wireless connection when you click Apply. You must then access the wireless access
point from a wired computer or from a wireless computer which is on the access control
list to make any further changes.
2. From the Security menu, click the Access Control link to display the Access Control List
menu shown below.
Figure 3-10: Access Control List menu
3.
Select the Turn Access Control On check box.
3-20 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 43

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Choose to use the local MAC address database stored on the access point, or use the RADIUS
4.
MAC address database stored on a RADIUS server. If you choose the RADIUS MAC Address
Database, you must configure the RADIUS Server Settings first.
5. Then, either select from the list of available w ireless ca rds the WG30 2 has foun d in your area,
or enter the MAC address and device name for a device you plan to use. You can usually find
the MAC address printed on the wireless adapter.
6. Click Add to add the wireless device to the access list. Repeat these steps for each additional
device you want to add to the list.
7. Be sure to click Apply to save your wireless access control list settings.
Now, only devices on this list will be allowed to wirelessly connect to the WG302.
How to Configure WEP
To configure WEP data encryption, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the WG302 using its default address of http://192.168.0.228 or at whatever IP
address the unit is currently configured Use the default user name of admin and default
password of password, or whatever LAN address and password you have set up.
2. Click the WEP/WPA Settings link in the main menu of the WG302.
Figure 3-11: Wireless Settings menu
3.
Choose Open System or Shared Key authentication.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-21
July 2005 v3.0
Page 44

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Select encryption strength.
4.
5. You can manually or automatically program the four data encryption keys. These values must
be identical on all PCs and Access Points in your network.
• Automatic - enter a word or group of printable characters in the Passphrase box and click
the Generate button. The four key boxes will be automatically populated with key values.
• Manual - enter ten hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-f, or A-F)
Select which of the four keys will be the default.
See “Overview of WEP Parameters” on page B-5 for a full explanation of each of these
options, as defined by the IEEE 802.11 wireless communication standard.
6. Click Apply to save your settings.
Note: If you use a wireless computer to configure WEP settings, you will be
disconnected when you click Apply. Reconfigure your wireless adapter to match the
new settings or access the wireless access point from a wired computer to make any
further changes.
How to Configure WPA with Radius
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Windows XP and Windows 2000 with Service Pack 3 do include the client software that
supports WPA. Nevertheless, the wireless adapter hardware and driver must also support WPA.
Consult the product document for your wireless adapter and WPA client software for instructions
on configuring WPA settings.
To configure WPA, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.228 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
3-22 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 45

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click Radius Server Settings in the Security menu.
2.
Figure 3-12: Radius Server Settings
3.
Enter the Radius settings.
• Authentication/Access Control Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is
required for authentication using Radius. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is
required for communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be
configured which is used on failure on Primary Radius Server
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1812.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-23
July 2005 v3.0
Page 46

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
• Re-authentication Time: The time interval in seconds after which the supplicant will be
authenticated again with the Radius Server. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Global-key Re-Key Time: Check on this option to enable Re-keying of Global Key. The
Global Key Re-Key can be done based on time interval in seconds or number of packets
exchanged using the global key. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Update if any station disassociates: Check on this option to refresh global key when any
stations disassociated with wireless Access Point.
• Accounting Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is required for accounting
using Radius Server. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is required for
communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be configured which
is used on failure on Primary Radius Server.
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1813.
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
5. Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu.
Figure 3-13: Wireless Settings menu
3-24 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 47

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Choose WPA with Radius from the list.
6.
7. Click Apply to save your settings.
How to Configure WPA-PSK
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Windows XP and Windows 2000 with Service Pack 3 do include the client software that
supports WPA. Nevertheless, the wireless adapter hardware and driver must also support WPA.
Consult the product document for your wireless adapter and WPA client software for instructions
on configuring WPA settings.
To configure WPA-PSK, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.228 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
2. Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu of the WG302.
Figure 3-14: WEP/WPA Settings menu
3.
Choose WPA-PSK from the list.
4. Enter the pre-shared key passphrase.
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-25
July 2005 v3.0
Page 48

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Configure WPA2 with Radius
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA2. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Make sure your client card supports WPA2. Consult the product document for your wireless
adapter and WPA2 client software for instructions on configuring WPA2 settings.
To configure WPA2, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.229 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
2. Click Radius Server Settings in the Security menu.
Figure 3-15: Radius Server Settings menu
3-26 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 49

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Enter the Radius settings.
3.
• Authentication/Access Control Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is
required for authentication using Radius. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is
required for communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be
configured which is used on failure on Primary Radius Server
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1812.
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
• Re-authentication Time: The time interval in seconds after which the supplicant will be
authenticated again with the Radius Server. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Global-key Re-Key Time: Check on this option to enable Re-keying of Global Key. The
Global Key Re-Key can be done based on time interval in seconds or number of packets
exchanged using the global key. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Update if any station disassociates: Check on this option to refresh global key when any
stations disassociated with wireless Access Point.
• Accounting Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is required for accounting
using Radius Server. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is required for
communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be configured which
is used on failure on Primary Radius Server.
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1813.
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-27
July 2005 v3.0
Page 50

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu.
5.
Figure 3-16: WEP/WPA Settings menu
6.
Choose WPA2 with Radius from the list.
7. Click Apply to save your settings.
How to Configure WPA2-PSK
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA2. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Make sure your client card supports WPA2. Consult the product document for your wireless
adapter and WPA2 client software for instructions on configuring WPA2 settings.
To configure WPA2-PSK, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.229 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
3-28 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 51

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu of the WG302.
2.
Figure 3-17: WEP/WPA Settings menu
3.
Choose WPA2-PSK from the list.
4. Enter the pre-shared key passphrase.
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
How to Configure WPA and WPA2 with Radius
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Windows XP and Windows 2000 with Service Pack 3 do include the client software that
supports WPA. Nevertheless, the wireless adapter hardware and driver must also support WPA.
Consult the product document for your wireless adapter and WPA client software for instructions
on configuring WPA settings.
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA2. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Make sure your client card supports WPA2. Consult the product document for your wireless
adapter and WPA2 client software for instructions on configuring WPA2 settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-29
July 2005 v3.0
Page 52

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
To configure WPA and WPA2, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.229 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
2. Click Radius Server Settings in the Security menu.
Figure 3-18: Radius Server Settings menu
3-30 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 53

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Enter the Radius settings.
3.
• Authentication/Access Control Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is
required for authentication using Radius. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is
required for communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be
configured which is used on failure on Primary Radius Server
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1812.
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
• Re-authentication Time: The time interval in seconds after which the supplicant will be
authenticated again with the Radius Server. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Global-key Re-Key Time: Check on this option to enable Re-keying of Global Key. The
Global Key Re-Key can be done based on time interval in seconds or number of packets
exchanged using the global key. The default is 3600 seconds.
• Update if any station disassociates: Check on this option to refresh global key when any
stations disassociated with wireless Access Point.
• Accounting Radius Server Configuration: This configuration is required for accounting
using Radius Server. IP Address, Port No. and Shared Secret is required for
communication with Radius Server. A Secondary Radius Server can be configured which
is used on failure on Primary Radius Server.
• IP Address: The IP address of the Radius Server. The default is 0.0.0.0.
• Port Number: Port number of the Radius Server. The default is 1813.
• Shared Secret: This is shared between the Wireless Access Point and the Radius Server
while authenticating the supplicant.
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-31
July 2005 v3.0
Page 54

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu.
5.
Figure 3-19: WEP/WPA Settings menu
6.
Choose WAP and WPA2 with Radius from the list.
7. Click Apply to save your settings.
How to Configure WPA2-PSK and WPA2-PSK
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Windows XP and Windows 2000 with Service Pack 3 do include the client software that
supports WPA. Nevertheless, the wireless adapter hardware and driver must also support WPA.
Consult the product document for your wireless adapter and WPA client software for instructions
on configuring WPA settings.
Note: Not all wireless adapters support WPA2. Furthermore, client software is required on the
client. Make sure your client card supports WPA2. Consult the product document for your wireless
adapter and WPA2 client software for instructions on configuring WPA2 settings.
To configure WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK, follow these steps:
1. Log in at the default LAN address of http://192.168.0.229 with the default user name of
admin and default password of password, or using whatever LAN address and password you
have set up.
3-32 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 55

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Click WEP/WPA Settings in the Security menu of the WG302.
2.
Figure 3-20: WEP/WPA Settings menu
3.
Choose WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK from the list.
4. Enter the pre-shared key passphrase.
5. Click Apply to save your settings.
Basic Installation and Configuration 3-33
July 2005 v3.0
Page 56

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
3-34 Basic Installation and Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 57

Chapter 4
Management
This chapter describes how to use the management features of your NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless
Access Point 802.11g WG302. These features can be found by clicking on the Maintenance
heading in the Main Menu of the browser interface.
Remote Management
Access the Remote Management screen by clicking on Remote Management under Management
on the main menu.
Figure 4-1: Remote Management screen
Enter the Remote Management information.
• Remote Console, Secure Shell (SSH): If set to Enable, the Wireless Access Point will only
allow remote access via Secure Shell and Secure Te lnet. The default is Enable.
• SNMP: Enable SNMP to allow the SNMP network management software, such as HP
OpenView, to manage the wireless access point via SNMPv1/v2 protocol.
• Public Community Name: The community string to allow the SNMP manager to read the
wireless access point's MIB objects. The default is public.
Management 4-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 58

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Private Community Name: The community string to allow the SNMP manager to read and
write the wireless access point's MIB objects. The default is private.
• IP address to Receive T raps: The IP address of the SNMP manager to receive traps sent from
the wireless access point. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Using the Secure Telnet Interface
The WG302 includes a secure Telnet command line interface (CLI). You can access the CLI from
a secure Telnet client over the Ethernet port or over the serial console port.
.
Note: You must use a secure Telnet client such as Absolute Telnet. Also, when you
configure the client, use the SSH1, 3DES option. If you use the Telnet client to connect
over the Ethernet port, use the IP address of the WG302 as the host name.
How to Use the CLI via the Console Port
1. Using the null-modem cable, connect a VT100/ANSI terminal or a workstation to the
port labeled Console.
If you attached a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation, start a secure
terminal-emulation program.
2. Configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following settings:
• Baud rate: 9,600 bps
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: none
• Stop bit: 1
• Flow control: none
These settings appear below the connector on the back panel.
4-2 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 59

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Press the return key, and the screen below should appear.
3.
Figure 4-2: Secure Telnet Client
The login name is admin and password is the default password.
After successful login, the screen should show the (Access Point Name)> prompt. In this
example, the prompt is netgear74F35E.
Enter help to display the CLI command help..
CLI Commands
The CLI commands are listed in Appendix C, “Command Line Reference.”
Management 4-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 60

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Using Syslog and Activity Log Information
The Information contains the activity log link you can use for setting up a syslog server and
viewing activity log information. From the main menu of the browser interface, under the
Information heading, click the Station List link to view the list, shown below:
Figure 4-3: Syslog and Activity Log information
Enable the SysLog option if you have a SysLog server on your LAN. If enabled, you must enter
the IP address of your SysLog server and the port number your SysLog server is configured to use.
• SysLog Server IP address: The access point will send all the SysLog to the specified IP
address if SysLog option is enabled. Default: 0.0.0.0
• Port: The port number configured in the SysLog server on your LAN. Default: 514
The Activity Log Window displays the Access Point system activity.
You may click Refresh to update the display or Click Save As. To save the log contents into a file
on your PC, click Save As and save the file to a disk drive.
4-4 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 61

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Viewing General, Log, Station, and Statistical Information
The General information screen provides a summary of the current WG302 configuration settings.
From the main Menu of the browser interface, click General to view the System Status screen,
shown below.
Figure 4-4: Wireless Access Point Status screen
Management 4-5
July 2005 v3.0
Page 62

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
This screen shows the following parameters:
Table 4-1. General Information Fields
Field Description
Access Point Information
Access Point Name (NetBIOS
name)
MAC Address Displays the Media Access Control address (MAC address) of the
Country/Region Displays the domain or region for which the wireless access point is
Firmware Version The version of the firmware currently installed.
Access Point Mode Identifies the operating mode of the WG302: Access Point,
Current IP Settings
IP Address The IP address of the wireless access point.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask for the wireless access point.
Default Gateway The default gateway for the wireless access point communication.
DHCP Client Enabled indicates that the current IP address was obtained from a
Current Wireless Settings
Operating Mode Identifies the 802.11 operating mode of the WG302.
Wireless Network Name (SSID) Displays the wireless network name (SSID) being used by the
Channel/Frequency Identifies the channel the wireless port is using. 11 is the default
WEP/WPA WEP/WPA setting.
AutoCell AutoCell setting.
Rogue AP Detection Rogue AP detection setting.
The default name may be changed if desired.
wireless access point’s Ethernet port.
licensed for use. It may not be legal to operate this wireless access
point in a region other than one of those identified in this field.
Point-to-point bridge, Multi-point bridge or Repeater.
DHCP server on your network. Disabled indicated a static IP
configuration.
wireless port of the wireless access point. The default is NETGEAR.
channel setting. See “Wireless Channels” on page B-7 for the
frequencies used on each channel.
4-6 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 63

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Statistics
The Information - Statistics screen provides various LAN and WLAN statistics.
Figure 4-5: Wireless Access Point Status screen
Table 4-1. Statistics Fields
Field Description
Wired Ethernet Received/Transmitted
Packets The number of packets sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Bytes The number of bytes sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Wireless Received/Transmitted
Unicast Packets The Unicast packets sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Broadcast Packets The Broadcast packets sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Multicast Packets The Multicast packets sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Total Packets The Wireless packets sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Total Bytes The Wireless bytes sent since the WG302 was restarted.
Refresh button
Click the Refresh button to update the statistics on this screen.
Management 4-7
July 2005 v3.0
Page 64

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Viewing a List of Available Wireless Stations
The Available Wireless Station List contains a table of all IP devices associated with the wireless
access point in the wireless network defined by the Wireless Network Name (SSID). From the
main menu of the browser interface, under the Information heading, click the Available Wireless
Station List link to view the list, shown below.
For each device, the table shows the Station ID, MAC address, IP Address, and Status (whether the
device is allowed to communicate with the wireless access point or not).
Note that if the wireless access point is rebooted, the table data is lost until the wireless access
point rediscovers the devices. To force the wireless access point to look for associated devices,
click the Refresh button.
Note: A wireless network can include multiple wireless access points, all using the same network
name (SSID). This enables extending the reach of the wireless network and allows users to roam
from one access point to another, providing seamless network connectivity. Under these
circumstances, be aware that only the stations associated with this access point will be presented in
the Available Station List.
4-8 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 65

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Detecting a Rogue Access Point
For enhanced security, you can scan the wireless network to detect rogue a ccess points. Detecting
Rogue AP’s involves scanning the wireless environment on all available channels looking for
unidentified AP’s. In particular, unidentified AP’s that are using the SSID of a legitimate network
can present a serious security threat.
Figure 4-6: Rogue AP Detection menu
Once you turn on Rogue AP Detection in the WG302, the AutoCell Enabled AP continuously
scans the wireless network and collects information about all APs heard on their channel. The
information collected includes: SSID, MAC Address, Channel, and AutoCell Enabled.
The user can Grant authorization to an unidentified AP, Save the Authorized APs into a file,
Import the previous Authorized APs from a file.
Note: The AP will disconnect all the wireless connections if Rogue AP Detection is turned ON.
Management 4-9
July 2005 v3.0
Page 66

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Upgrading the Wireless Access Point Software
.
Note: When uploading software to the WG302 Access Point, it is important not to
interrupt the Web browser by closing the window , clicking a lin k, or loading a new page.
If the browser is interrupted, the upload may fail, corrupt the software, and render the
WG302 completely inoperable.
You cannot perform the firmware upgrade from a workstation connected to the WG302 via a
wireless link. The firmware upgrade must be performed via a workstation connected to the
WG302 via the Ethernet LAN interface.
The software of the WG302 Access Point is stored in FLASH memory, and can be upgraded as
new software is released by NETGEAR. Upgrade files can be downloaded from Neater’s Web site.
If the upgrade file is compressed (.ZIP file), you must first extract the image (.RMG) file before
sending it to the wireless access point. The upgrade file can be sent using your browser.
Note: The Web browser used to upload new firmware into the WG302 must support HTTP
uploads, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or above, or Netscape Navigator 4.78 or above.
1. Download the new software file from NETGEAR, save it to your hard disk, and unzip it.
2. From the main menu Management section, click the Upgrade Firmware link to display the
screen above.
3. In the Upgrade Firmware menu, click the Browse button and browse to the location of the
image (.RMG) upgrade file.
4. Click Upload.
When the upload completes, your wireless access point will automatically restart. The upgrade
process typically takes about one minute.
In some cases, you may need to reconfigure the wireless access point after upgrading.
4-10 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 67

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Configuration File Management
The WG302 Access Point settings are stored in the wireless access point in a configuration file.
This file can be saved (backed up) to a user’s computer, retrieved (restored) from the user’s
computer, or cleared to factory default settings.
From the main menu Management heading, click the Backup/Restore Settings link to bring up the
menu shown below.
Figure 4-7: Settings Backup menu
The three options displayed are described in the following sections:
Saving and Retrieving the Configuration
The Backup/Restore Settings menu allows you to save or retrieve a file containing your wireless
access point’s configuration settings.
To save your settings, click the Save button. Your browser will extract the configuration file from
the wireless access point and prompts you for a location on your computer to store the file. You
can give the file a meaningful name at this time, such as WG302.cfg.
Management 4-11
July 2005 v3.0
Page 68

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
To restore your settings from a saved configuration file, enter the full path to the file on your
computer or click the Browse button to locate the file. When you have located it, click the Retrieve
button to upload the file. After completing the upload, the WG302 will reboot automatically.
Restoring the WG302 to the Factory Default Settings
It is sometimes desirable to restore the wireless access point to the factory default settings. This
can be done by using the Restore function, which restores all factory settings. After a restore, the
wireless access point's password will be password, the WG302's DHCP client is enabled, the
default LAN IP address is 192.168.0.228, and the access point name is reset to the name printed on
the label on the bottom of the unit.
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings
To restore the factory default configuration settings without knowing the login password or IP
address, you must use the Default Reset button on the rear panel of the wireless access point (see
“WG302 rear panel” on page 2-7). The reset button has two functions:
• Reboot. When pressed and released, the Wireless Access Point will reboot (restart).
• Reset to Factory Defaults. This button can also be used to clear all da ta and restore all
settings to the factory default values.
To clear all data and restore the factory default values:
1. Power Off the WG302
2. Hold the Reset Button down while you Power On the WG302 for 5 seconds.
3. Continue holding the Reset Button until the LEDs blink twice.
4. Release the Reset Button.
The factory default configuration has now been restored, and the WG302 is ready for use.
Changing the Administrator Password
The default password is password. Change this password to a more secure password. You cannot
change the administrator login name.
4-12 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 69

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
From the main menu of the browser interface, under the Management heading, click Change
Password to bring up the menu shown below.
Figure 4-8: Set Password menu
T o change the password, first enter the old password, and then enter the new password twice. Click
Apply to save your change.
Management 4-13
July 2005 v3.0
Page 70

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
4-14 Management
July 2005 v3.0
Page 71

Chapter 5
Advanced Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the advanced features of your NETGEAR ProSafe
Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302:
• IP Settings: Use the AP as a DHCP server for wireless clients.
• Wireless Settings: Set up AutoCell and configure advanced wireless LAN parameters.
• Access Point Settings: Enable wireless bridging and repeating.
These features can be found under the Advanced heading in the main menu.
Understanding Advanced IP Settings for Wireless Clients
The default advanced IP wireless settings usually work well. If you want the AP to act as a DHCP
server gateway for wireless clients, use this feature. The AP can accept both static and DHCP
clients.
Figure 5-1: Advanced IP Settings for Wireless Clients screen
Advanced Configuration 5-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 72

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Understanding Advanced Wireless Settings
The advanced wireless settings menu enables configuration of the following:
• AutoCell RF management
• Wi-Fi multimedia (WMM) setup
• Hotspot settings
• Advanced wireless parameters
These options are discussed below.
AutoCell RF Management
AutoCell provides advanced RF wireless management features that improve performance and
enhance security.
Table 5-1. What does AutoCell do?
Problem AutoCell Settings
Erosion of privacy Optional setting allows Wi-Fi network to be nearly
undetectable by neighbors and hackers.
(Enhance RF Privacy -- Default: Disable)
Diminishing performance from
multiple APs installed in one
area.
Complexity of installation Customers can put APs anywhere they want and in any
Increasing interference Clients and APs avoid interference from neighbors and
APs and clients load-balance traffic across under utilized
APs. (Auto RF Management -- Default: Enable).
density APs. (Auto RF Management -- Default: Enable)
other unexpected sources.
(Auto RF Management -- Default: Enable).
AutoCell's self-organizing micro cells provide an additional level of privacy for enterprises.
AutoCell clients are highly-recommended for Enhanced RF Security.
5-2 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 73

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Configuration
Figure 5-2: Advanced Wireless Settings screen AutoCell Setup options
There are two AutoCell configuration setting choices:
• Enable/disable Auto RF Management: Enabled by defaul t
• Enable/disable Enhanced RF Security (‘Stealth Mode’): Disabled by default
Auto RF Management
Note: Channel selection and power management is automatically adjusted by AutoCell
when the Auto RF Management option is enabled.
In this mode, AutoCell APs and clients load-balance traffic across under utilized APs. This mode
avoids interference from neighbors clients and APs and other unexpected sources.
Enhanced RF Security ‘Stealth Mode’
Note: Broadcast Wireless Network Name (SSID) is automatically turned off when you
select the AutoCell Enhanced RF Security option.
In this mode, AutoCell shrinks the size of coverage to the minimum to reach clients but also
shrinks the size of the beacons that access points use to announce their presence. This mode makes
an enterprise wireless LAN nearly invisible to users outside an office building.
Advanced Configuration 5-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 74

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
AutoCell AP/Client Interaction
AutoCell's self-organizing micro cells provide performance benefits and an additional leve l of
privacy for enterprises.
• Automatic Transmit Power Control. An AutoCell-enabled client’s RF transmit power level
is automatically coordinated with an AutoCell-enabled AP. This creates client micro-cells and
reduces co-channel interference with other clients and APs on the same frequency and
improves overall throughput and performance. (Requires: AutoCell-enabled AP)
• Automatic Load-Balancing. An AutoCell-enabled client will seek out and associate to the
lightest loaded AutoCell-enabled AP available. (Requires: AutoCell-enabled AP)
• Rapid Roaming. An AutoCell-enabled client will accurately and rapidly detect movement as
distinguished from RF anomalies such as arbitrary and momentary changes in the surrounding
RF domain. When it detects true movement, the client immediately seeks the best available
AP at the highest data rate possible instead of waiting for the data rate to decline. (Does not
Require AutoCell-enabled APs)
5-4 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 75

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Additional AutoCell View Management Options
Figure 5-3: AutoCell View wireless network
AutoCell Vi ew is an available management tool that provides sophisticated views of your wireless
network and enables managing the wireless communications easily from a simple console.
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) Setup
WMM is a subset of the 802.11e standard. WMM allows wireless traffic to have a range of
priorities, depending on the kind of data. Time-dependent information, such as video or audio, will
have a higher priority than normal traffic. For WMM to function correctly, wireless clients must
also support WMM.
WMM Support: Select Yes or No as required on the Advanced Wireless Settings menu. The
default is No.
Advanced Configuration 5-5
July 2005 v3.0
Page 76

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Configuring Wireless LAN Parameters
The default advanced wireless LAN parameter settings usually work well. If you want the AP to
operate in Super-G mode, use this feature.
Figure 5-4: Advanced Wireless Settings screen
The table below describes the advanced wireless parameters.
Table 5-1. Advanced Wireless LAN Settings Fields
Field Description
Enable SuperG Mode Click Enable to enable SuperG Mode.
RTS Threshold The packet size used to determine whether it should use the CSMA/CD (Carrier
Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) or the CSMA/CA (Carrier
Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) mechanism for packet
transmission.
Fragmentation Length This is the maximum packet size used for fragmentation. Packets larger than
the size programmed in this field will be fragmented. The Fragment Threshold
value must be larger than the RTS Threshold value.
Beacon Interval Specifies the data beacon rate between 20 and 1004.
DTIM Interval The Delivery Traffic Indication Message specifies the data beacon rate between
1 and 255.
Preamble Type A long transmit preamble may provide a more reliable connection or slightly
longer range. A short transmit preamble gives better performance. Long is the
default
Antenna Select the desired antenna for transmitting and receiving. Auto is the default.
5-6 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 77

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Hotspot Settings
You can allow all HTTP (TCP, port 80) requests to be captured and re-directed to the URL you
specify.
Figure 5-5: Hotspot Settings screen
Enable HTTP Redirect: Enable this if you want all HTTP (TCP, port 80) requests to be captured
and re-directed to the URL you specify.
URL: Enter the URL of the Web Server you wish HTTP requests to be redirected to.
Advanced Configuration 5-7
July 2005 v3.0
Page 78

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Enabling Wireless Bridging and Repeating
The NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302 lets you build large bridged
wireless networks.
Figure 5-6: Advanced Wireless Settings Access Point Mode set tings
Examples of wireless bridged configurations are:
• Client Access Point to Access Point, the default
• Point-to-Point Bridge
• Multi-Point Bridge
• Repeater with Wireless Client Association
These features are discussed below.
5-8 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 79

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
LAN
Segment 1
Router
AP in
Point-to-Point
Bridge Mode
AP in
Point-to-Point
Bridge Mode
LAN
Segment 2
Hub or Switch
AP1
ETHERNET
RESET
5-12VDC
AP2
ETHERNET
RESET
5-12VDC
How to Configure a WG302 as a Point-to-Point Bridge
Figure 5-7: Point-to-Point Bridge
Configure the WG302 (AP1) on LAN Segment 1 in Point-to-Point Bridge mode.
1.
2. Configure the WG302 (AP2) on LAN Segment 2 in Point-to-Point Bridge mode.
AP1 must have AP2’s MAC address in its Remote MAC Address field and AP2 must have
AP1’s MAC address in its Remote MAC Address field.
3. Configure and verify the following parameters for both access points:
• Verify that the LAN network configuration of the WG302 Access Points both are
configured to operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices
• Both use the same ESSID, Channel, authentication mode, if any, and security settings if
security is in use.
4. Verify connectivity across the LAN 1 and LAN 2.
• A computer on either LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files
and printers of any other PCs or servers connected to LAN Seg ment 1 o r LAN Segmen t 2 .
Advanced Configuration 5-9
July 2005 v3.0
Page 80

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How to Configure Multi-Point Wireless Bridging
AP3
ETHERNET
RESET
Hub or Switch
LAN
Segment 3
5-12VDC
Router
192.168.0.1
LAN
AP in
Point-to-Point
Bridge Mode
RESET
AP1
ETHERNET
5-12VDC
'Master' AP in
Point-to-Multi-Point
Bridge Mode
AP2
ETHERNET
RESET
Hub or Switch
AP in
Point-to-Point
Bridge Mode
5-12VDC
Segment 1
LAN
Segment 2
Figure 5-8: Multi-Point bridging
Configure the Operating Mode of the WG302 Access Points.
1.
– WG302 (AP1) on LAN Segment 1 in Point-to-Point Bridge mode with the Remote MAC
Address of AP2.
– Because it is in the central location, configure WG302 (AP2) on LAN Segment 2 in
Point-to-Multi-Point Bridge mode. The MAC addresses of the adjacent APs are required
in AP2.
– Configure the WG302 (AP3) on LAN 3 in Point-to-Point Bridge mode with the Remote
MAC Address of AP2.
2. Verify the following parameters for all access points:
• Verify that the LAN network configuration the WG302 Access Points are configured to
operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices
• Only one AP is configured in Point-to-Multi-Point Bridge mode, and all the others are in
Point-to-Point Bridge mode.
• All APs must be on the same LAN. That is, all the APs LAN IP address must be in the
same network.
• If using DHCP, all WG302 Access Points should be set to “Obtain an IP address
automatically (DHCP Client)” in the IP Address Source portion of the Basic IP Settings
menu.
5-10 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 81

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• All WG302 Access Points use the same SSID, Channel, authentication mode, if any, and
encryption in use.
• All Point-to-Point APs must have AP2’s MAC address in its Remote AP MAC address
field.
3. Verify connectivity across the LANs.
• A computer on any LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files
and printers with any other PCs or servers connected to any of the three LAN segments.
• Wireless stations will not be able to connect to the WG302 Access Points in the
illustration above. If you require wireless stations to access any lan segment, you can
additional WG302 Access Points configured in Wireless Access Point mode to any LAN
segment.
Note: You can extend this multi-point bridging by adding additional WG302s configured in
Point-to-Point mode for each additional LAN segment. Furthermore, you can extend the range of
the wireless network with NETGEAR wireless antenna accessories.
How to Configure Wireless Repeating
AP3
ETHERNET
5-12VDC
RESET
AP in Repeater Mode
with client associations
Wireless PC
Associated with AP1
AP1
ETHERNET
5-12VDC
RESET
AP in Repeater Mode
with client associations
AP2
ETHERNET
5-12VDC
Router
192.168.0.1
RESET
AP in Repeater Mode
with client associations
Wireless PC
Associated with AP3
LAN
Segment 1
Wireless PC
Associated with AP2
Figure 5-9: Multi-Point bridging
Configure the Operating Mode of the WG302 Access Points.
1.
– WG302 (AP1) on LAN Segment 1 in Repeater mode with the Remote MAC Address of
AP2.
– Configure WG302 (AP2) in Repeater mode with MAC addresses of AP1 and AP3.
Advanced Configuration 5-11
July 2005 v3.0
Page 82

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
– Configure the WG302 (AP3) in Repeater mode with the Remote MAC Address of AP2.
2. Verify the following parameters for all access points:
• Verify that the LAN network configuration the WG302 Access Points are configured to
operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices
• All APs must be on the same LAN. That is, all the APs LAN IP address must be in the
same network.
• If using DHCP, all WG302 Access Points should be set to “Obtain an IP address
automatically (DHCP Client)” in the IP Address Source portion of the Basic IP Settings
menu.
• All WG302 Access Points use the same SSID, Channel, authentication mode, if any, and
encryption in use.
3. Verify connectivity across the LANs.
• A computer on any LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files
and printers with any other PCs or servers connected to any of the three WLAN segments.
Note: You can extend this repeating by adding up to 2 additional WG302s configured in repeater
mode. However, since Repeater configurations communicate in half-duplex mode, the bandwidth
decreases as you add Repeaters to the network. Also, you can extend the range of the wireless
network with NETGEAR wireless antenna accessories.
5-12 Advanced Configuration
July 2005 v3.0
Page 83

Chapter 6
Troubleshooting
This chapter provides information about troubleshooting your NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless
Access Point 802.11g WG302. After each problem description, instructions are given to help you
diagnose and solve the problem. For the common problems listed, go to the section indicated.
• Is the WG302 on?
• Have I connected the wireless access point correctly?
Go to “Installing the WG302 Access Point” on page 3-5.
• I cannot remember the wireless access point’s configuration password.
Go to “Changing the Administrator Password” on page 4-12.
Note: For up-to-date WG302 installation details and troubleshooting guidance visit
http://kbserver.netgear.com/products/WG302.asp.
If you have trouble setting up your WG302, check the tips below.
No lights are lit on the access point.
It takes a few seconds for the power indicator to light up. Wait a minute and check the
power light status on the access point.
If the access point has no power.
• Make sure the power cord is connected to the access point.
• Make sure the power adapter is connected to a functioning power outlet. If it is in a power
strip, make sure the power strip is turned on. If it is plugged directly into the wall, verify that it
is not a switched outlet.
• Make sure you are using the correct NETGEAR power adapter supplied with your access
point.
Troubleshooting 6-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 84

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
The Wireless LAN activity light does not light up.
The access point’s antennae are not working.
• If the Wireless LAN activity light stays off, disconnect the adapter from its power source and
then plug it in again.
• Make sure the antennas are tightly connected to the WG302.
• Contact NETGEAR technical support if the Wireless LAN activity light remains off.
The LAN light is not lit.
There is a hardware connection problem.Check these items:
• Make sure the cable connectors are securely plugged in at the access point and the network
device (hub, switch, or router). A switch, hub, or router must be installed between the access
point and the Ethernet LAN or broadband modem.
• Make sure the connected device is turned on.
• Be sure the correct cable is used. Use a standard Category 5 Ethernet patch cable. If the
network device has Auto Uplink™ (MDI/MDIX) ports, you can use either a crossover cable or
a normal patch cable.
I cannot access the Internet or the LAN with a wireless capable computer.
There is a configuration problem. Check these items:
• You may not have restarted the computer with the wireless adapter to have TCP/IP changes
take effect. Restart the computer.
• The computer with the wireless adapter may not have the correct TCP/IP settings to
communicate with the network. Restart the computer and check that TCP/IP is set up properly
for that network. The usual setting for Windows the Network Properties is set to “Obtain an IP
address automatically.”
• The access point’s default values may not work with your network. Check the access point
default configuration against the configuration of other devices in your network.
6-2 Troubleshooting
July 2005 v3.0
Page 85

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
I cannot connect to the WG302 to configure it.
Check these items:
• The WG302 is properly installed, LAN connections are OK, and it is powered on. Check that
the LAN port LED is green to verify that the Ethernet connection is OK.
• The default configuration of the WG302 is for a static IP address of 192. 168.0.228 and a Mask
of 255.255.255.0 with DHCP disabled. Make sure your network configuration settings are
correct.
• If you are using the NetBIOS name of the WG302 to connect, ensure that your computer and
the WG302 are on the same network segment or that there is a WINS server on your network.
• If your computer is set to “Obtain an IP Address automatically” (DHCP client), restart it.
• If your computer uses a Fixed (Static) IP address, ensure that it is using an IP Address in the
range of the WG302. The WG302 default IP Address is 192.168.0.228 and the default Subnet
Mask is 255.255.255.0. If you are not sure about these settings, follow the instructions for
“Installing the WG302 Access Point” on page 3-5.
When I enter a URL or IP address I get a timeout error.
A number of things could be causing this. Try the following troubleshooting steps.
• Check whether other PCs work. If they do, ensure that your PCs TCP/IP settings are correct. If
using a Fixed (Static) IP Address, check the Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS, and IP
Addresses.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, ensure that the WG302 is connected
and turned on. Connect to it and check its settings. If you cannot connect to it, check the LAN
and power connections.
• If the WG302 is configured correctly, check your Internet connection (DSL/Cable modem
etc.) to make sure that it is working correctly.
•Try again.
Troubleshooting 6-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 86

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings
The Reset button (see “WG302 rear panel” on page 2-7) has two functions:
• Reboot. When pressed and released quickly, the WG302 will reboot (restart).
• Reset to Factory Defaults. This button can also be used to clear ALL data and restore ALL
settings to the factory default values.
To clear all data and restore the factory default values:
1. Power off the WG302 and power it back on.
2. Use something with a small point, such as a pen, to press the Reset button in and hold it in for
at least 5 seconds.
3. Release the Reset button.
The factory default configuration has now been restored, and the WG302 is ready for use.
6-4 Troubleshooting
July 2005 v3.0
Page 87

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Appendix A
Specifications
This appendix provides technical specifications for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point
802.11g WG302.
Specifications for the WG302
Parameter NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
802.11g Data Rates 1, 2, 5.5, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 38, 54, & 108 Mbps (Auto-rate capable)
802.11g
Operating Frequencies
802.11g Encryption 40-bits (also called 64-bits), 128- and 152-bits WEP data encryption
Network Management Web-based configuration and status monitoring
Maximum Clients Limited by the amount of wireless network traffic generated by each node;
Status LEDs Power/Ethernet LAN/Wireless LAN/Test
Power Adapter 12V DC, 1.2 A
Electromagnetic
Compliance
Environmental
Specifications
2.412 ~ 2.462 GHz (US) 2.457 ~ 2.462 GHz (Spain)
2.412 ~ 2.484 GHz (Japan) 2.457 ~ 2.472 GHz (France)
2.412 ~ 2.472 GHz (Europe ETSI)
typically 15 to 20 nodes.
FCC Part 15 Class B and Class E
Operating temperature: 0 to 50° C
Operating humidity: 5-95%, non-condensing
Specifications A-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 88

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
A-2 Specifications
July 2005 v3.0
Page 89

Appendix B
Wireless Networking Basics
This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking.
Wireless Networking Overview
The WG302 Access Point conforms to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
802.11b and 802.11g standards for wireless LANs (WLANs). On an 802.11b or g wireles s link,
data is encoded using direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology and is transmitted in
the unlicensed radio spectrum at 2.5GHz. The maximum data rate for the 802.11b wireless link is
11 Mbps, but it will automatically back down from 11 Mbps to 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps when the radio
signal is weak or when interference is detected. The 802.11g auto rate sensing rates are 1, 2, 5.5, 6,
9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps.
The 802.11 standard is also called Wireless Ethernet or Wi-Fi by the Wireless Ethernet
Compatibility Alliance (WECA, see http://www.wi-fi.net), an industry standard group promoting
interoperability among 802.11 devices. The 802.11 standard offers two methods for configuring a
wireless network - ad hoc and infrastructure.
Infrastructure Mode
With a wireless Access Point, you can operate the wireless LAN in the infrastructure mode. This
mode provides wireless connectivity to multiple wireless network devices within a fixed range or
area of coverage, interacting with wireless nodes via an antenna.
In the infrastructure mode, the wireless access point converts airwave data into wired Ethernet
data, acting as a bridge between the wired LAN and wireless clients. Connecting multiple Access
Points via a wired Ethernet backbone can further extend the wireless network coverage. As a
mobile computing device moves out of the range of one access point, it moves into the range of
another. As a result, wireless clients can freely roam from one Access Point domain to another and
still maintain seamless network connection.
Wireless Networking Basics B-1
July 2005 v3.0
Page 90

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Ad Hoc Mode (Peer-to-Peer Workgroup)
In an ad hoc network, computers are brought together as needed; thus, there is no structure or fixed
points to the network - each node can generally communicate with any other node. There is no
Access Point involved in this configuration. This mode enables you to quickly set up a small
wireless workgroup and allows workgroup members to exchange data or share printers as
supported by Microsoft networking in the various W indows operating systems. Some vendors also
refer to ad hoc networking as peer-to-peer group networking.
In this configuration, network packets are directly sent and received by the intended transmitting
and receiving stations. As long as the stations are within range of one another, this is the easiest
and least expensive way to set up a wireless network.
Network Name: Extended Service Set Identification (ESSID)
The Extended Service Set Identification (ESSID) is one of two types of Service Set Identification
(SSID). In an ad hoc wireless network with no access points, the Basic Service Set Identification
(BSSID) is used. In an infrastructure wireless network that includes an access point, the ESSID is
used, but may still be referred to as SSID.
An SSID is a thirty-two character (maximum) alphanumeric key identifying the name of the
wireless local area network. Some vendors refer to the SSID as network name. For the wireless
devices in a network to communicate with each other, all devices must be configured with the
same SSID.
The ESSID is usually broadcast in the air from an access point. The wireless station sometimes can
be configured with the ESSID ANY. This means the wireless station will try to associate with
whichever access point has the stronger radio frequency (RF) signal, providing that both the access
point and wireless station use Open System authentication.
Authentication and WEP Data Encryption
The absence of a physical connection between nodes makes the wireless links vulnerable to
eavesdropping and information theft. To provide a certain level of security, the IEEE 802.11
standard has defined these two types of authentication methods:
• Open System. With Open System authentication, a wireless computer can join any network
and receive any messages that are not encrypted.
B-2 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
Page 91

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
• Shared Key. With Shared Key authentication, only those PCs that possess the correct
authentication key can join the network. By default, IEEE 802.11 wireless devices operate in
an Open System network.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) data encryption is used when the wireless devices are configured
to operate in Shared Key authentication mode.
802.11 Authentication
The 802.11 standard defines several services that govern how two 802.11 devices communicate.
The following events must occur before an 802.11 Station can communicate with an Ethernet
network through an access point, such as the one built in to the WG302:
1. Turn on the wireless station.
2. The station listens for messages from any access points that are in range.
3. The station finds a message from an access point that has a matching SSID.
4. The station sends an authentication request to the access point.
5. The access point authenticates the station.
6. The station sends an association request to the access point.
7. The access point associates with the station.
8. The station can now communicate with the Ethernet network through the access point.
An access point must authenticate a station before the station can associate with the access point or
communicate with the network. The IEEE 802.11 standard defines two types of authentication:
Open System and Shared Key.
• Open System Authentication allows any device to join the network, assuming that the device
SSID matches the access point SSID. Alternatively, the device can use the “ANY” SSID
option to associate with any available Access Point within range, regardless of its SSID.
• Shared Key Authentication requires that the station and the access point have the same WEP
Key to authenticate. These two authentication procedures are described below.
Open System Authentication
The following steps occur when two devices use Open System Authentication:
1. The station sends an authentication request to the access point.
Wireless Networking Basics B-3
July 2005 v3.0
Page 92

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
The access point authenticates the station.
2.
3. The station associates with the access point and joins the network.
This process is illustrated below.
802.11b Authentication
Open System Steps
1) Authentication request sent to AP
Access Point
Client
2) AP authenticates
3) Client connects to network
INTERNET LOCAL
WLAN
ProSafeWirelessVPNSecurityFirewall
Cable/DSL
LNK
PWR TEST
ACT
Enable
12345678
100
LNK/ACT
MODEL
FVM318
Cable or
DLS modem
attempting
to connect
Figure B-1: Open system authentication
Shared Key Authentication
The following steps occur when two devices use Shared Key Authentication:
1. The station sends an authentication request to the access point.
2. The access point sends challenge text to the station.
3. The station uses its configured 64-bit or 128-bit default key to encrypt the challenge text, and
sends the encrypted text to the access point.
4. The access point decrypts the encrypted text using its configured WEP Key that corresponds
to the station’s default key. The access point compares the decrypted text with the original
challenge text. If the decrypted text matches the original challenge text, then the access point
and the station share the same WEP Key and the access point authenticates the station.
5. The station connects to the network.
If the decrypted text does not match the original challenge text (the access point and station do not
share the same WEP Key), then the access point will refuse to authenticate the station and the
station will be unable to communicate with either the 802.11 network or Ethernet network.
B-4 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
Page 93

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
This process is illustrated below.
802.11b Authentication
Shared Key Steps
request sent to AP
2) AP sends challenge text
Client
attempting
to connect
Figure B-2: Shared key authentication
3) Client encrypts
challenge text and
sends it back to AP
4) AP decrypts, and if correct,
authenticates client
5) Client connects to network
Cable/DSL
ProSafeWirelessVPNSecurityFirewall
PWR TEST
Access Point1) Authentication
INTERNET LOCAL
WLAN
LNK
ACT
Enable
12345678
100
LNK/ACT
MODEL
FVM318
Cable or
DLS modem
Overview of WEP Parameters
Before enabling WEP on an 802.11 network, you must first consider what type of encryption you
require and the key size you want to use. Typically, there are three WEP Encryption options
available for 802.11 products:
1. Do Not Use WEP: The 802.11 network does not encrypt data. For authentication purposes, the
network uses Open System Authentication.
2. Use WEP for Encryption: A transmitting 802.11 device encrypts the data portion of every
packet it sends using a configured WEP Key. The receiving device decrypts the data using the
same WEP Key. For authentication purposes, the network uses Open System Authentication.
3. Use WEP for Authentication and Encryption: A transmitting 802.11 device encrypts the data
portion of every packet it sends using a configured WEP Key. The receiving de vice decrypts the
data using the same WEP Key . For authentication purposes, the wireless network uses Shared Key
Authentication.
Note: Some 802.11 access points also support Use WEP for Authentication Only (Shared Key
Authentication without data encryption).
Wireless Networking Basics B-5
July 2005 v3.0
Page 94

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Key Size
The IEEE 802.11 standard supports two types of WEP encryption: 40-bit and 128-bit.
The 64-bit WEP data encryption method allows for a five-character (40-bit) input. Additionally , 24
factory-set bits are added to the forty-bit input to generate a 64-bit encryption key. The 24
factory-set bits are not user-configurable). This encryption key will be used to encrypt/decrypt all
data transmitted via the wireless interface. Some vendors refer to the 64-bit WEP data encryption
as 40-bit WEP data encryption since the user-configurable portion of the encryption key is 40 bits
wide.
The 128-bit WEP data encryption method consists of 104 user-configurable bits. Similar to the
forty-bit WEP data encryption method, the remaining 24 bits are factory set and not user
configurable. Some vendors allow passphrases to be entered instead of the cryptic hexadecimal
characters to ease encryption key entry.
128-bit encryption is stronger than 40-bit encryption, but 128-bit encryption may not be available
outside of the United States due to U.S. export regulations.
When configured for 40-bit encryption, 802.11 products typically support up to four WEP Keys.
Each 40-bit WEP Key is expressed as 5 sets of two hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F). For
example, “12 34 56 78 90” is a 40-bit WEP Key.
When configured for 128-bit encryption, 802.11 products typically support four WEP Keys but
some manufacturers support only one 128-bit key . The 128-bit WEP Key is expressed as 13 sets of
two hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F). For example, “12 34 56 78 90 AB CD EF 12 34 56 78 90”
is a 128-bit WEP Key.
Table B-1: Encryption Key Sizes
Encryption Key Size # of Hexadecimal Digits Example of Hexadecimal Key Content
64-bit (24+40) 10 4C72F08AE1
128-bit (24+104) 26 4C72F08AE19D57A3FF6B260037
Note: Typically, 802.11 access points can store up to four 128-bit WEP Keys but some 802.11
client adapters can only store one. Therefore, make sure that your 802.11 access and client
adapters’ configurations match.
B-6 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
Page 95

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
WEP Configuration Options
The WEP settings must match on all 802.11 devices that are within the same wireless network as
identified by the SSID. In general, if your mobile clients will roam between access points, then all
of the 802.11 access points and all of the 802.11 client adapters on the network must have the same
WEP settings.
Note: Whatever keys you enter for an AP, you must also enter the same keys for the client adapter
in the same order. In other words, WEP key 1 on the AP must match WEP key 1 on the client
adapter, WEP key 2 on the AP must match WEP key 2 on the client adapter, and so on.
Note: The AP and the client adapters can have different default WEP Keys as long as the keys are
in the same order. In other words, the AP can use WEP key 2 as its default key to transmit while a
client adapter can use WEP key 3 as its default key to transmit. The two devices will communicate
as long as the AP’s WEP key 2 is the same as the client’s WEP key 2 and the AP’s WEP key 3 is
the same as the client’s WEP key 3.
Wireless Channels
The wireless frequencies used by 802.11b/g networks are discussed below.
IEEE 802.11b/g wireless nodes communicate with each other using radio frequency signals in the
ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band between 2.4 GHz and 2.5 GHz. Neighboring
channels are 5 MHz apart. However, due to spread spectrum effect of the signals, a node sending
signals using a particular channel will utilize frequency spectrum 12.5 MHz above and below the
center channel frequency. As a result, two separate wireless networks using neighboring channels
(for example, channel 1 and channel 2) in the same general vicinity will interfere with each other.
Applying two channels that allow the maximum channel separation will decrease the amount of
channel cross-talk, and provide a noticeable performance increase over networks with minimal
channel separation.
The radio frequency channels used in 802.11b/g networks are listed in Table B-2:
Table B-2: 802.11b/g Ra dio Frequency Channels
Channel Center Frequency Frequency Spread
1 2412 MHz 2399.5 MHz - 2424.5 MHz
2 2417 MHz 2404.5 MHz - 2429.5 MHz
3 2422 MHz 2409.5 MHz - 2434.5 MHz
Wireless Networking Basics B-7
July 2005 v3.0
Page 96

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
Table B-2: 802.11b/g Ra dio Frequency Channels
Channel Center Frequency Frequency Spread
4 2427 MHz 2414.5 MHz - 2439.5 MHz
5 2432 MHz 2419.5 MHz - 2444.5 MHz
6 2437 MHz 2424.5 MHz - 2449.5 MHz
7 2442 MHz 2429.5 MHz - 2454.5 MHz
8 2447 MHz 2434.5 MHz - 2459.5 MHz
9 2452 MHz 2439.5 MHz - 2464.5 MHz
10 2457 MHz 2444.5 MHz - 2469.5 MHz
11 2462 MHz 2449.5 MHz - 2474.5 MHz
12 2467 MHz 2454.5 MHz - 2479.5 MHz
13 2472 MHz 2459.5 MHz - 2484.5 MHz
Note: The available cha nnels supported by the wireless products in various countries are dif ferent.
For example, Channels 1 to 11 are supported in the U.S. and Canada, and Channels 1 to 13 are
supported in Europe and Australia.
The preferred channel separation between the channels in neighboring wireless networks is 25
MHz (5 channels). This means that you can apply up to three different channels within your
wireless network. There are only 11 usable wireless channels in the United States. It is
recommended that you start using channel 1 and grow to use channel 6, and 11 when necessary, as
these three channels do not overlap.
WPA and WPA2 Wireless Security
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2) is a specification of standards-based, interoperable
security enhancements that increase the level of data protection and access control for existing and
future wireless LAN systems.
The IEEE introduced the WEP as an optional security measure to secure 802.11b (W i-Fi) WLANs,
but inherent weaknesses in the standard soon became obvious. In response to this situation, the
Wi-Fi Alliance announced a new security architecture in October 2002 that remedies the
shortcomings of WEP. This standard, formerly known as Safe Secure Network (SSN), is designed
to work with existing 802.11 products and offers forward compatibility with 802.11i, the new
wireless security architecture that has been defined by the IEEE.
B-8 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
Page 97

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
WPA and WPA2 offer the following benefits:
• Enhanced data privacy
• Robust key management
• Data origin authentication
• Data integrity protection
The Wi-Fi Alliance is now performing interoperability certification testing on Wi-Fi Protected
Access products. Starting August of 2003, all new Wi-Fi certified products have to support WPA.
NETGEAR is implementing WPA and WPA2 on client and access point products. The 802.11i
standard was ratified in 2004.
How Does WPA Compare to WEP?
WEP is a data encryption method and is not intended as a user authentication mechanism. WPA
user authentication is implemented using 802.1x and the Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP). Support for 802.1x authentication is required in WPA. In the 802.11 standard, 802.1x
authentication was optional. For details on EAP specifically, refer to IETF's RFC 2284.
With 802.1 1 WEP, all access points and client wireless adapters on a particular wireless LAN must
use the same encryption key. A major problem with the 802.11 standard is that the keys are
cumbersome to change. If you do not update the WEP keys often, an unauthorized person with a
sniffing tool can monitor your network for less than a day and decode the encrypted messages.
Products based on the 802.11 standard alone offer system administrators no effective method to
update the keys.
For 802.11, WEP encryption is optional. For WPA, encryption using Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol (TKIP) is required. TKIP replaces WEP with a new encryption algorithm that is stronger
than the WEP algorithm, but that uses the calculation facilities present on existing wireless devices
to perform encryption operations. TKIP provides important data encryption enhancements
including a per-packet key mixing function, a message integrity check (MIC) named Michael, an
extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism. Through
these enhancements, TKIP addresses all of known WEP vulnerabilities.
Wireless Networking Basics B-9
July 2005 v3.0
Page 98

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
How Does WPA Compare to WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i)?
WPA is forward compatible with the WPA2 security specification. WPA is a subset of WPA2 and
used certain pieces of the early 802.11i draft, such as 802.1x and TKIP. The main pieces of WPA2
that are not included in WPA are secure IBSS (Ad-Hoc mode), secure fast handoff (for specialized
802.11 VoIP phones), as well as enhanced encryption protocols, such as AES-CCMP. These
features were either not yet ready for market or required hardware upgrades to implement.
What are the Key Features of WPA and WPA2 Security?
The following security features are included in the WPA and WPA2 standard:
• WPA and WPA2 Authentication
• WPA and WPA2 Encryption Key Management
– Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
– Michael message integrity code (MIC)
– AES support (WPA2, requires hardware support)
• Support for a mixture of WP A, WPA2, and WEP wireless clients to allow a migration strategy ,
but mixing WEP and WPA/WPA2 is discouraged
These features are discussed below.
WPA/WPA2 addresses most of the known WEP vulnerabilities and is primarily intended for
wireless infrastructure networks as found in the enterprise. This infrastructure includes stations,
access points, and authentication servers (typically RADIUS servers). The RADIUS server holds
(or has access to) user credentials (for example, user names and passwords) and authenticates
wireless users before they gain access to the network.
The strength of WPA/WPA2 comes from an integrated sequence of operations that encompass
802.1X/EAP authentication and sophisticated key management and encryption techniques. Its
major operations include:
• Network security capability determination. This occurs at the 802.11 level and is
communicated through WPA information elements in Beacon, Probe Response, and (Re)
Association Requests. Information in these elements includes the authentication method
(802.1X or Pre-shared key) and the preferred cipher suite (WEP, TKIP, or AES).
B-10 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
Page 99

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
The primary information conveyed in the Beacon frames is the authentication method and the
cipher suite. Possible authentication methods include 802.1X and Pre-shared key. Pre-shared
key is an authentication method that uses a statically configured pass phrase on both the
stations and the access point. This obviates the need for an authentication server, which in
many home and small office environments will not be available nor desirable. Possible cipher
suites include: WEP, TKIP, and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). We talk more about
TKIP and AES when addressing data privacy below.
• Authentication. EAP over 802.1X is used for authentication. Mutual authentication is gained
by choosing an EAP type supporting this feature and is required by WPA. 802.1X port access
control prevents full access to the network until authentication completes. 802.1X
EAPOL-Key packets are used by WPA to distribute per-session keys to those stations
successfully authenticated.
The supplicant in the station uses the authentication and cipher suite information contained in
the information elements to decide which authentication method and cipher suite to use. For
example, if the access point is using the pre-shared key method then the supplicant need not
authenticate using full-blown 802.1X. Rather, the supplicant must simply prove to the access
point that it is in possession of the pre-shared key. If the supplicant detects that the service set
does not contain a WPA information element then it knows it must use pre-WPA 802.1X
authentication and key management in order to access the network.
• Key management. WPA/WPA2 features a robust key generation/management system that
integrates the authentication and data privacy functions. Keys are generated after successful
authentication and through a subsequent 4-way handshake between the station and Access
Point (AP).
• Data Privacy (Encryption). Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is used to wrap WEP in
sophisticated cryptographic and security techniques to overcome most of its weaknesses.
• Data integrity. TKIP includes a message integrity code (MIC) at the end of each plaintext
message to ensure messages are not being spoofed.
Wireless Networking Basics B-11
July 2005 v3.0
Page 100

Reference Manual for the NETGEAR ProSafe Wireless Access Point 802.11g WG302
WPA/WPA2 Authentication: Enterprise-level User Authentication via 802.1x/EAP and RADIUS
Wired Network with Optional
Wireless LAN
802.1x Port Based Network
Access Control
TCP/IP
WPA/W PA2
enabled
wireless
client with
“supplicant”
Figure B-3: WPA/WPA2 Overview
WPA/WPA2
enabled
Access Point
using
pre-shared key
or 802.1x
IEEE 802.1x offers an effective framework for authenticating and controlling user traffic to a
protected network, as well as providing a vehicle for dynamically varying data encry ption keys via
EAP from a RADIUS server, for example. This framework enables using a central authentication
server, which employs mutual authentication so that a rogue wireless user does not join the
network.
Ports Closed
Until
Authenticated
TCP/IP
Ports Opened
After
Authenticated
RADIUS Server
Login
Authentication
Certificate
Authority
(for
example
Win Server,
VeriSign)
It is important to note that 802.1x does not provide the actual authentication mechanisms. When
using 802.1x, the EAP type, such as Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS), or EAP Tunneled
Transport Layer Security (EAP-TTLS), defines how the authenticati on takes place.
Note: For environments with a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
infrastructure, WPA supports Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). For environments
without a RADIUS infrastructure, WPA supports the use of a pre-shared key.
Together, these technologies provide a framework for strong user authentication.
Windows XP implements 802.1x natively, and several NETGEAR switch and wireless access
point products support 802.1x.
B-12 Wireless Networking Basics
July 2005 v3.0
 Loading...
Loading...