NEC Versa P Service Manual

PROPRIETARY NOTICE AND LIABILITY DISCLAIMER
The information disclosed in this document, including all designs and related materials, is
the valuable property of NEC Corporation (NEC) and/or its licensors. NEC and/or its licensors, as appropriate, reserve all patent, copyright and other proprietary rights to this document, including all design, manufacturing, reproduction, use, and sales rights thereto, except
to the extent said rights are expressly granted to others.
The NEC product(s) discussed in this document are warranted in accordance with the terms
of the Warranty Statement accompanying each product. However, actual performance of
each such product is dependent upon factors such as system configuration, customer data,
and operator control. Since implementation by customers of each product may vary, the
suitability of specific product configurations and applications must be determined by the
customer and is not warranted by NEC.
To allow for design and specification improvements, the information in this document is
subject to change at any time, without notice. Reproduction of this document or portions
thereof without prior written approval of NEC is prohibited.
FastFacts, and NEC SVGA, are U.S. trademarks of NEC Technologies, Inc.
All other product, brand, or trade names used in this publication are the trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective trademark owners.
First Printing — February 1995
Copyright 1995 Copyright 1995
NEC Technologies, Inc. NEC Corporation
1414 Massachusetts Avenue 7-1 Shiba 5-Chome, Minato-Ku
Boxborough, MA 01719 Tokyo 108-01, Japan
All Rights Reserved All Rights Reserved

xiii
Preface
This service and reference manual contains the technical information necessary to set up,
maintain, troubleshoot, and repair the NEC Versa™ P Series Notebook systems. It also
provides hardware and interface information for users who need an overview of the computer system design. The manual is written for NEC-trained customer engineers, system
analysts, service center personnel, and dealers.
The manual is organized as follows:
Section 1 Technical Information, provides an overview of the hardware and interface
components. System specifications are listed including computer dimensions, weight, environment, safety compliance, power consumption, and system memory specifications.
Section 2 Setup and Operation, takes the user from unpacking to setup and operation.
The section includes a description of operating controls, setting parameters and accessing
the NEC bulletin board system (BBS).
Section 3 Options, provides the user with installation procedures for the Versa P series
options.
Section 4 Troubleshooting and Repair, includes maintenance, troubleshooting, disas-
sembly and reassembly, and illustrated parts breakdown information. NEC service and spare
parts ordering information is also provided. Included is a list of NEC service and information telephone numbers that provide access to the NEC Bulletin Board System (BBS),
FASTFACTS, and Technical Information Bulletins.
Section 5 Troubleshooting and Options for the Docking Station II, includes mainte-
nance, troubleshooting, disassembly and reassembly, and illustrated parts breakdown information for the optional NEC Docking Station II.
Appendix A Connector Locations and Pin Assignments, provides a list of the main
board internal connector pin assignments and a list of external pin assignments.
An Index is included for convenience.

Abbreviations
xv
A ampere
AC alternating current
AT advanced technology
(IBM PC)
BBS Bulletin Board System
BCD binary-coded decimal
BCU BIOS Customized Utility
BIOS basic input/output system
bit binary digit
bpi bits per inch
bps bits per second
BUU BIOS Upgrade Utility
C centigrade
Cache high-speed buffer storage
CAM constantly addressable memory
CAS column address strobe
CD-ROM compact disk-ROM
CGA Color Graphics Adapter
CGB Color Graphics Board
CH channel
clk clock
cm centimeter
CMOS complementary metal oxide
semiconductor
COM communication
CONT contrast
CPGA ceramic pin grid array
CPU central processing unit
CRT cathode-ray tube
DAC digital-to-analog converter
DACK DMA acknowledge
DC direct current
DIP dual in-line package
DLAB Divisor Latch Address bit
DMA direct memory access
DMAC DMA controller
DOS disk operating system
DRAM dynamic RAM
DTE data terminal equipment
ECC error checking and correction
EDS error detecting system
EGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter
EMS Expanded Memory
Specification
EPP enhanced parallel port
EPROM erasable and programmable
ROM
EVGA Enhanced Video Graphics
Array
F Fahrenheit
FAX facsimile transmission
FCC Federal Communications
Commission
FG frame ground
FM frequency modulation
Fn Function
FRU field-replaceable unit
GB gigabyte
GND ground
HDD hard diskdrive
HEX hexadecimal
HGA Hercules Graphics Adapter
Hz hertz
IC integrated circuit
ID identification
IDE intelligent device electronics
IDTR interrupt descriptor table
register
IMR Interrupt Mask register
in. inch
INTA interrupt acknowledge
IPB illustrated parts breakdown

xvi Abbreviations
IRR Interrupt Request register
ISA Industry Standard Architecture
ISR In Service register
I/O input/output
IPC integrated peripheral controller
ips inches per second
IRQ interrupt request
K kilo (1024)
k kilo (1000)
KB kilobyte
kg kilogram
kHz kilohertz
kV kilovolt
lb pound
LDTR local descriptor table register
LED light-emitting diode
LSB least-significant bit
LSI large-scale integration
M mega
mA milliamps
max maximum
MB megabyte
MDA Monochrome Display Adapter
MFM modified frequency modulation
Mhz megahertz
mm millimeter
ms millisecond
MSB most-significant bit
NASC National Authorized Service
Center
NC not connected
NDP numeric data processor
NMI Non-maskable Interrupt
ns nanosecond
NSRC National Service Response
Center
PAL programmable array logic
PC personal computer
PCB printed circuit board
PFP plastic flat package
PIO parallel input/output
pixel picture element
PJQFP plastic J-lead quad flat pack
PLCC plastic lead chip carrier
PLL phase lock loop
p-p peak-to-peak
PPI programmable peripheral
interface
PROM programmable ROM
QFP quad flat pack
RAM random-access memory
RAMDAC RAM digital-to-analog
RAS row address strobe
RGB red green blue
RGBI red green blue intensity
ROM read-only memory
rpm revolutions per minute
R read
RTC real-time clock
R/W read/write
S slave
SCSI Small Computer System
Interface
SDLC Synchronous Data Link
Control
SG signal ground
SIMM single inline memory module
SQFP silver quad flat package
SVGA Super Video Graphics Array
SW switch
TAC Technical Assistance Center
TCP Thin chip package
TQFP Thin-quad flat package
TSC Technical Support Center
TTL transistor/transistor logic
tpi tracks per inch

UART universal asynchronous
receiver/transmitter
V volt
Vdc volts, direct current
VESA video electronics standards
association
VFO variable frequency oscillator
VGA Video Graphics Array
VLSI very large-scale integration
VRAM virtual RAM
W watt
W write
µf microfarad
µPD microprocessor
µs microsecond
Abbreviations xvii
Ω ohm

Contents
Preface........................................................................................................................ xiii
Abbreviations .............................................................................................................. xv
Section 1 Technical Information
Hardware Overview..................................................................................................... 1-2
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)............................................................................... 1-3
CPU Board ........................................................................................................... 1-4
System Board....................................................................................................... 1-4
Primary Battery .................................................................................................... 1-4
Secondary Battery ................................................................................................ 1-4
CMOS Battery...................................................................................................... 1-5
Bridge Battery...................................................................................................... 1-5
VersaBay PCMCIA Module Option...................................................................... 1-5
iii
Keyboard.............................................................................................................. 1-5
VersaTrack........................................................................................................... 1-5
System Memory........................................................................................................... 1-6
Memory Map........................................................................................................ 1-6
System Video.............................................................................................................. 1-7
Parallel Interface .......................................................................................................... 1-13
Serial Interface ............................................................................................................ 1-13
Versa P Series Chip Set............................................................................................... 1-13
System Logic ........................................................................................................ 1-14
Flash ROM........................................................................................................... 1-14
ROM BIOS .................................................................................................. 1-14
Peripheral Controller............................................................................................. 1-15
VGA Controller........................................................................................................... 1-15
Video Controller Architecture....................................................................... 1-15
Diskette Controller, Serial Interface, Parallel Interface.......................................... 1-16
Keyboard Controller............................................................................................. 1-16
PCMCIA Controller ............................................................................................. 1-16
Audio Controller................................................................................................... 1-17
I/O Addressing ..................................................................................................... 1-17
Interrupt Controllers............................................................................................. 1-18

iv Contents
Power Management Overview..................................................................................... 1-19
System Power Management.................................................................................. 1-19
Plug and Play ........................................................................................................ 1-20
Local Power Management .................................................................................... 1-20
Specifications .............................................................................................................. 1-21
Section 2 Setup and Operation
Unpacking the System ................................................................................................. 2-1
Setup........................................................................................................................... 2-1
Cable Connections................................................................................................ 2-2
Operating Controls...................................................................................................... 2-3
Power Management Status ................................................................................... 2-4
Battery Status............................................................................................... 2-6
Function Keys (Fn Keys) ...................................................................................... 2-6
Dip Switch............................................................................................................ 2-7
Power-on Self-Test (POST)......................................................................................... 2-8
POST Errors ........................................................................................................ 2-9
System Parameters....................................................................................................... 2-10
Auto Setup........................................................................................................... 2-10
Accessing Auto Setup........................................................................................... 2-10
Auto Setup Keys........................................................................................... 2-11
Auto Setup Parameter Options .................................................................................... 2-11
Parameter Descriptions......................................................................................... 2-12
Comms......................................................................................................... 2-12
Drives........................................................................................................... 2-13
Keyboard...................................................................................................... 2-13
Power........................................................................................................... 2-13
System.......................................................................................................... 2-14
Time/Date..................................................................................................... 2-14
Using Auto Setup to Select Parameters........................................................................ 2-15
Security Options.......................................................................................................... 2-16
System Password.................................................................................................. 2-16
Using the System Password .......................................................................... 2-16
Keyboard Lock Hotkey......................................................................................... 2-17
NEC Utilities............................................................................................................... 2-17
BACKLITE.EXE ................................................................................................. 2-17

Contents v
CMOSCOPY.EXE............................................................................................... 2-17
CMOSDUMP.EXE.............................................................................................. 2-18
ENABLACU Utility ............................................................................................. 2-18
HIGHLITE.EXE.................................................................................................. 2-18
VIDEOMOD.COM.............................................................................................. 2-18
WBATTERY.EXE............................................................................................... 2-18
BIOS UTILITIES........................................................................................................ 2-18
BIOS Customize Utility (BCU)............................................................................. 2-18
BIOS Update Utility (BUU) ................................................................................. 2-18
Precautions................................................................................................... 2-19
Downloading the Update Utility.................................................................... 2-19
Using the Update Utility ............................................................................... 2-20
Menu Functions............................................................................................ 2-21
Power Sources ............................................................................................................ 2-25
AC Adapter.......................................................................................................... 2-25
Battery Power ...................................................................................................... 2-26
Recharging the Battery Pack......................................................................... 2-26
Discharging the Battery Pack........................................................................ 2-27
Replacing the Primary Battery Pack............................................................................. 2-28
Saving Battery Power........................................................................................... 2-29
Automatic Power-Saving Features............................................................................... 2-30
Power Saving Levels ............................................................................................ 2-30
Active Mode ................................................................................................. 2-30
Local Stand-by Mode ................................................................................... 2-30
Suspend Mode.............................................................................................. 2-30
Using the Multimedia Features..................................................................................... 2-31
Audio................................................................................................................... 2-31
Line-In.......................................................................................................... 2-31
Microphone.................................................................................................. 2-31
CD-ROM Reader.......................................................................................... 2-31
Mixing.......................................................................................................... 2-32
Playing Back......................................................................................................... 2-32
Video ................................................................................................................... 2-32
Section 3 Options
Memory Cards............................................................................................................. 3-2
Secondary Battery Pack ............................................................................................... 3-4

vi Contents
Hard Disk Drive .......................................................................................................... 3-6
PCMCIA Cards........................................................................................................... 3-8
Memory/Storage Card.......................................................................................... 3-11
Fax/Modem Card.................................................................................................. 3-11
Fax/Modem Card — Single Connection Installation.............................................. 3-11
Fax/Modem Card — Dual Connection Installation................................................ 3-14
VersaBay PCMCIA Module........................................................................................ 3-17
Parallel Printer............................................................................................................. 3-19
External Display .......................................................................................................... 3-20
External Keyboard Mouse ........................................................................................... 3-21
Docking Station II....................................................................................................... 3-22
Car DC Adapter .......................................................................................................... 3-24
NEC Versa Port Replicator.......................................................................................... 3-25
Section 4 Troubleshooting and Repair
Service ........................................................................................................................ 4-1
Technical Support................................................................................................. 4-2
Product Information ............................................................................................. 4-2
Ordering Information from FastFacts.................................................................... 4-3
Maintenance................................................................................................................ 4-4
Cleaning the System's Exterior.............................................................................. 4-4
Cleaning the System's Interior............................................................................... 4-4
Cleaning the VersaTrack....................................................................................... 4-5
Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................... 4-6
Diagnosing and Solving Problems......................................................................... 4-6
Remote Technical Support.................................................................................... 4-8
NEC Communications Assistant ........................................................................... 4-9
Diagnostic Output and Beep Codes....................................................................... 4-9
Disassembly and Reassembly ....................................................................................... 4-12
Primary Battery Pack (NiMH Battery).................................................................. 4-13
Memory Card....................................................................................................... 4-14
Hard Disk Drive ................................................................................................... 4-15
LCD..................................................................................................................... 4-17
Top Cover, Keyboard........................................................................................... 4-19
LCD Indicator Panel............................................................................................. 4-21
Diskette Drive ...................................................................................................... 4-22
CMOS Battery...................................................................................................... 4-24

Contents vii
CPU Board ........................................................................................................... 4-25
Bridge Battery...................................................................................................... 4-26
VersaTrack Assembly.................................................................................................. 4-27
System Board....................................................................................................... 4-28
Illustrated Parts Breakdown......................................................................................... 4-30
Section 5 Troubleshooting and Options for the Docking Station II
Disassembly and Reassembly ....................................................................................... 5-3
CRT Base/Top Cover Assembly ........................................................................... 5-4
Top Cover Mask Assembly................................................................................... 5-6
Blank Panels......................................................................................................... 5-6
Power Switch Assembly........................................................................................ 5-6
Interface Board..................................................................................................... 5-8
Backplane Board .................................................................................................. 5-10
LED Panel Board ................................................................................................. 5-12
Sound Board ........................................................................................................ 5-13
Drive Signal Cables............................................................................................... 5-13
Power Supply....................................................................................................... 5-15
Docking Station II Options.......................................................................................... 5-18
Expansion Board Installation ................................................................................ 5-18
Diskette/Tape Drive Installation............................................................................ 5-21
Hard Disk Drive Installation ................................................................................. 5-23
External CRT Monitor Installation........................................................................ 5-24
External Keyboard and Mouse Installation............................................................ 5-26
Headphones and Microphone Installation.............................................................. 5-27
Parallel Printer Installation.................................................................................... 5-28
RS-232C Device ................................................................................................... 5-29
Illustrated Parts Breakdown......................................................................................... 5-30
Appendix A Connector Locations and Pin Assignments
List of Figures
1-1 Versa P Series (Right Side View)................................................................... 1-1
1-2 Versa P Series (Left Side View)..................................................................... 1-2
1-3 Versa P Series (Rear View) ........................................................................... 1-3

viii Contents
2-1 Power and I/O Connector Locations.............................................................. 2-2
2-2 Control and Button Locations........................................................................ 2-3
2-3 Dip Switch Location...................................................................................... 2-7
2-4 Dip Switch Settings ....................................................................................... 2-8
2-5 Battery Release Latch Location ..................................................................... 2-28
2-6 Battery Pack Replacement ............................................................................. 2-29
3-1 Memory Compartment Cover Removal.......................................................... 3-2
3-2 Memory Card Upgrade.................................................................................. 3-3
3-3 Releasing the Diskette Drive.......................................................................... 3-4
3-4 Secondary Battery Installation ....................................................................... 3-5
3-5 Compartment Cover Removal........................................................................ 3-6
3-6 Hard Disk Drive Removal.............................................................................. 3-7
3-7 Hard Disk Drive Installation........................................................................... 3-8
3-8 Installing the PCMCIA Modem...................................................................... 3-12
3-9 Connecting the Adapter................................................................................. 3-12
3-10 Modem Connection ....................................................................................... 3-13
3-11 Installing a Dual Connection Fax/Modem Card.............................................. 3-14
3-12 Connecting the Adapter................................................................................. 3-15
3-13 Dual-RJ11 Connection ................................................................................... 3-16
3-14 Releasing the Diskette Drive.......................................................................... 3-17
3-15 VersaBay PCMCIA Module Installation ........................................................ 3-18
3-16 Printer Connection......................................................................................... 3-19
3-17 CRT Port Location........................................................................................ 3-20
3-18 External Keyboard/Mouse Connection........................................................... 3-21
3-19 Opening the Rear Cover.................................................................................3-22
3-20 Docking Station II Connection....................................................................... 3-23
3-21 Connecting the Car DC Adapter .................................................................... 3-24
3-22 Opening the Versa’s Right Rear Cover........................................................... 3-25
3-23 Attaching the Port Replicator......................................................................... 3-25
4-1 Locating the VersaTrack Ball......................................................................... 4-5
4-2 Release Latch Location .................................................................................. 4-13
4-3 Memory Compartment Cover ........................................................................ 4-14
4-4 Memory Card Removal .................................................................................. 4-15
4-5 Cover Removal.............................................................................................. 4-16
4-6 Hard Disk Drive Removal.............................................................................. 4-16

Contents ix
4-7 LCD Locking Tabs........................................................................................ 4-17
4-8 LCD Removal................................................................................................ 4-18
4-9 Locating Screws............................................................................................ 4-19
4-10 Removing the Top Cover ............................................................................... 4-20
4-11 Keyboard Connectors .................................................................................... 4-21
4-12 Locking Tabs ................................................................................................. 4-22
4-13 Diskette Drive Release Latch Location .......................................................... 4-23
4-14 Diskette Drive Removal................................................................................. 4-23
4-15 Removing the CMOS Battery ........................................................................ 4-24
4-16 CPU Board Removal ..................................................................................... 4-27
4-17 Bridge Battery on Hard Disk Housing............................................................ 4-28
4-18 VersaTrack Assembly Screw.......................................................................... 4-29
4-19 VersaTrack Cable Connector......................................................................... 4-30
4-20 System Board Connectors.............................................................................. 4-31
4-21 Versa P Series Parts Breakdown — Upper Assembly..................................... 4-31
4-22 Versa P Series Breakdown — Lower Assembly............................................. 4-33
5-1 CRT Base Removal ....................................................................................... 5-4
5-2 Top Cover Screw .......................................................................................... 5-4
5-3 Two Screws................................................................................................... 5-5
5-4 Top Cover Removal....................................................................................... 5-5
5-5 Top Cover Mask Assembly Screws................................................................ 5-6
5-6 Blank Panel Removal/Power Switch Assembly Screws................................... 5-7
5-7 Power Switch Cable....................................................................................... 5-7
5-8 Cable Removal............................................................................................... 5-8
5-9 Interface Board Bracket Screws (Rear Panel)................................................. 5-9
5-10 Interface Board Bracket Screw (Backplane)................................................... 5-9
5-11 Interface Board Removal............................................................................... 5-10
5-12 Backplane Board Cable(s) Removal............................................................... 5-10
5-13 Backplane Board Screws ............................................................................... 5-11
5-14 LED Panel Board Screws .............................................................................. 5-12
5-15 Sound Board Connector and Screws.............................................................. 5-13
5-16 Signal Cable(s) Removal................................................................................ 5-14
5-17 Power Supply Screws (Rear Panel)................................................................ 5-15
5-18 Removing the Power Cable............................................................................ 5-16
5-19 Hard Disk Drive Guide Removal.................................................................... 5-16
5-20 Power Supply Removal.................................................................................. 5-17

x Contents
5-21 Expansion Slot Connector Locations ............................................................. 5-18
5-22 Expansion Slot Cover Removal...................................................................... 5-19
5-23 Board Alignment ........................................................................................... 5-19
5-24 Expansion Board Installation ......................................................................... 5-20
5-25 Diskette Drive Installation.............................................................................. 5-21
5-26 Diskette Drive Cable Connections .................................................................. 5-21
5-27 Drive A Selection Switch Location ................................................................ 5-22
5-28 Hard Disk Drive Guide.................................................................................. 5-23
5-29 Drive Guide Hole Locations........................................................................... 5-23
5-30 Hard Disk Drive Cable Connections ............................................................... 5-24
5-31 CRT Base Installation.................................................................................... 5-24
5-32 Monitor Cable Connection............................................................................. 5-25
5-33 Keyboard and Mouse Connection .................................................................. 5-26
5-34 Headphones and Microphone Installation....................................................... 5-27
5-35 Parallel Printer Connection............................................................................. 5-28
5-36 RS-232C Connection..................................................................................... 5-29
5-37 Versa Series Docking Station II IPB.............................................................. 5-32
A-1 System Board Connector Locations............................................................... A-1
A-2 CPU Board Connector Locations (Front)....................................................... A-2
A-3 CPU Board Connector Locations (Rear) ........................................................ A-3
List of Tables
1-1 Versa System Memory Map ........................................................................... 1-6
1-2 CRT Display Mode (CRT only)..................................................................... 1-7
1-3 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 TFT, Simultaneous CRT).............................. 1-9
1-4 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 STN-D/S, Simultaneous CRT Display).......... 1-10
1-5 LCD Display Mode (800x600 TFT, Simultaneous CRT Display) ................... 1-11
1-6 Versa P Series Chip Types and Technologies................................................. 1-13
1-7 Versa P I/O Address Map.............................................................................. 1-17
1-8 Versa P Series Interrupt Level Assignments................................................... 1-18
1-9 Specifications................................................................................................. 1-22
2-1 I/O Connector Descriptions ........................................................................... 2-2
2-2 Control and Button Functions........................................................................ 2-3
2-3 FnKey Operations.......................................................................................... 2-7
2-4 POST Error Messages................................................................................... 2-9

Contents xi
2-5 Auto Setup Key Functions............................................................................. 2-11
2-6 Auto Setup Parameter Options....................................................................... 2-11
2-7 Automatic Power-Saving Features................................................................. 2-30
3-1 PCMCIA Drivers and Utilities ....................................................................... 3-9
3-2 PCMCIA Drive Designations......................................................................... 3-11
4-1 NEC Service and Information Telephone Numbers ........................................ 4-1
4-2 Problems and Solutions.................................................................................. 4-6
4-3 Diagnostic Output and Beep Codes................................................................ 4-9
4-4 Diagnostic Output and Beep Codes Looped on POST ................................... 4-11
4-5 Versa P Series Disassembly Sequence............................................................ 4-12
4-6 Versa P Series Field-Replaceable Parts Upper Assembly ........................... 4-30
4-7 Versa P Series Field-Replaceable Parts Lower Assembly........................... 4-32
4-8 Option and Documentation Part Numbers...................................................... 4-34
5-1 Docking Station II Problems and Solutions.................................................... 5-1
5-2 Disassembly Parts Sequence........................................................................... 5-3
5-3 Power Supply Requirements.......................................................................... 5-15
5-4 Docking Station II Field-Replaceable Parts List ............................................. 5-30
A-1 System Board Connectors.............................................................................. A-1
A-2 CPU Board Connectors (Front)..................................................................... A-2
A-3 CPU Board Connector Descriptions (Rear).................................................... A-3
A-4 External Keyboard Connector Pin Assignments.............................................. A-3
A-5 Mouse Interface Connector Pin Assignments ................................................. A-4
A-6 Serial Port Connector Pin Assignments.......................................................... A-4
A-7 CRT Connector Pin Assignments................................................................... A-5
A-8 Parallel Printer Pin Assignments ..................................................................... A-5
A-9 Expansion Connector Pin Assignments........................................................... A-6
A-10 Power Connector ........................................................................................... A-11
A-11 Hard Disk Drive Connector ........................................................................... A-11
A-12 Internal Diskette Drive Connector..................................................................A-13

xii Contents

Section 1
Technical Information
The NEC Versa P series computers integrate Intel's Pentium® P54C-75 MHz microprocessor. The systems offer a unique transportable unit in the following configurations:
n Versa 75P 75-MHz CPU, Thin-film transistor (TFT), color LCD, 8-MB stan-
dard RAM, 16 KB cache RAM (internal), 256 KB cache RAM (external), 256KB ROM
n Versa 75P 75-MHz CPU, Super VGA (SVGA), color LCD, 8-MB standard
RAM, 16 KB cache RAM (internal), 256 KB cache RAM (external), 256-KB
ROM
Figure Section 1-1 and Figure Section 1-2 show system features.
Brightness
Control
Memory
Compartment
Hard Disk
Drive
Diskette Drive/
Secondary Battery
Figure Section 1-1 Versa P Series (Right Side View)

1-2 Technical Information
PCMCIA
Slot 1
PCMCIA
Slot 0
Figure Section 1-2 Versa P Series (Left Side View)
Battery
VersaTrack
HARDWARE OVERVIEW
The base unit includes a color LCD panel, a 2 1/2-inch 340-MB, 540-MB, or 810-MB hard
disk drive, a 3 1/2-inch, 1.44-MB diskette drive (VersaBay), a primary battery pack, and a
PS/2 compatible 83-key keyboard. A 79-key keyboard is used for U.K. and Germany.
One memory card slot is available for the addition of a 4-, 8-, 12-, 16-, or 32-MB capacity
memory card. Two Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA)
card slots, supported by the Cirrus Logic CL-PD6720-B PCMCIA controller, allow for the
addition of either two PCMCIA Type II cards or one PCMCIA Type III card. The
PCMCIA controller is compatible with the Intel 82365B chip set used in earlier Versa systems.
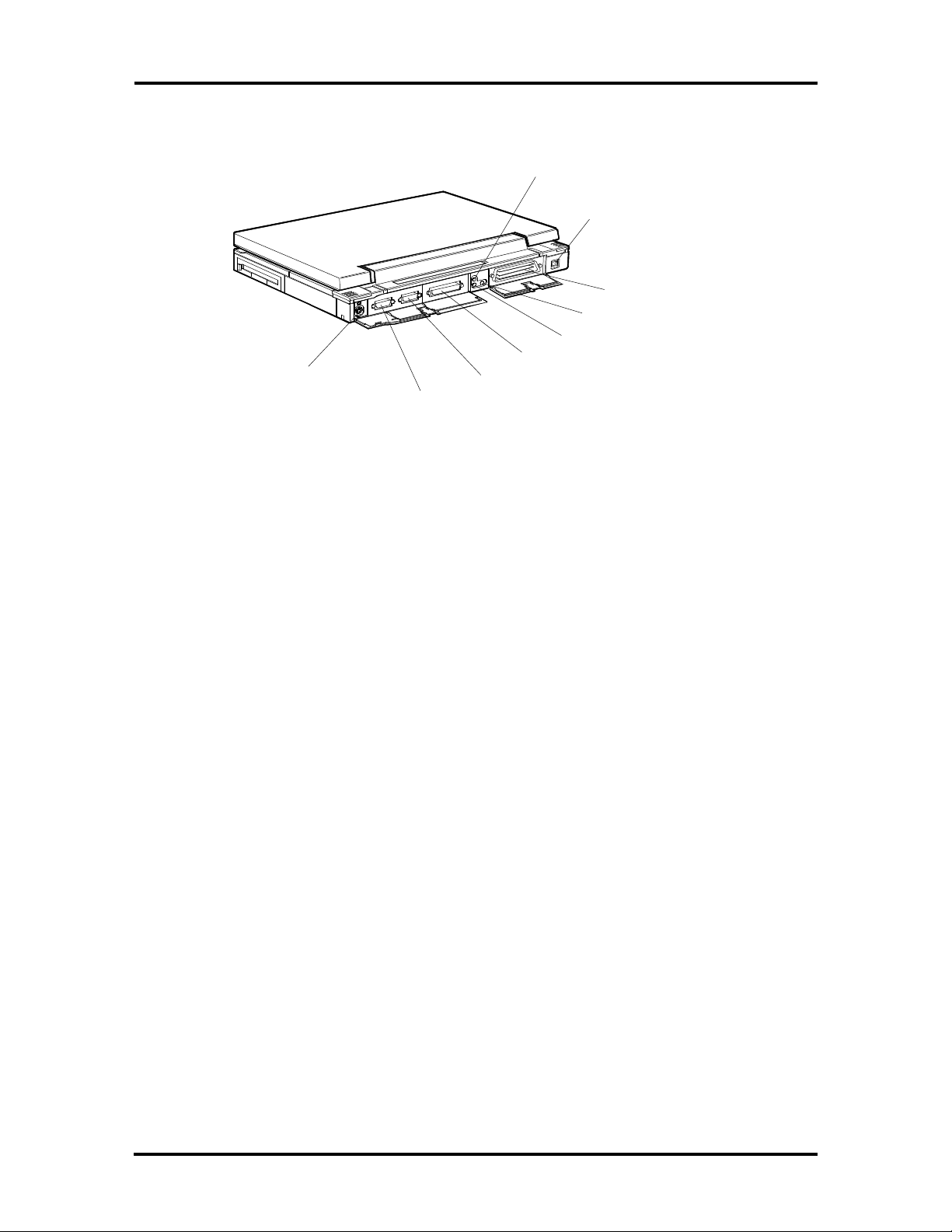
Figure Section 1-3 shows the standard I/O interface ports on the system's rear panel. These
include one 6-pin shared PS/23-style keyboard/mouse port, one 15-pin Super VGA CRT
port, one 9-pin (RS-232C) serial port, one 25-pin enhanced printer (parallel) port, one microphone port, one headphones port, one line-in port, one expansion port (for the optional
Docking Station II or port replicator), and one 4-pin power connector port.
Technical Information 1-3
Line-In
Keyboard/Mouse
Port
Port
Printer Port
Serial Port
CRT Port
Power
Connector
Port
Expansion Port
Headphones Port
Microphone Port
Figure Section 1-3 Versa P Series (Rear View)
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
The system integrates a built-in LCD. The LCD supports VESA Local (VL) bus video. The
LCD operates with the Chips & Technologies 65545A VGA controller. The controller supports Super VGA. For more information on the 65545A VGA controller, read the description provided in the Versa P Series Chip Set subsection.
The Versa P system features the following types of LCDs.
n TFT — thin-film transistor color LCD, 0.3mm dot pitch, 12-bit digital interface,
640 x 480 resolution, 64,000 colors.
n SVGA — TFT color LCD, 0.3mm dot pitch, 12-bit digital interface, 800 x 600
resolution, 256 out of 227,000 colors.
In addition, the CRT port on the system's rear panel allows the user to connect an optional
monochrome or color external display to the system. The computer supports the LCD and
external display simultaneously.
Power-saving features for controlling the LCD's backlighting include the ROM-based hot
key Fn F5, DOS BACKLITE.EXE utility, and Auto Setup power management settings. See
Section 2, Setup and Operation, for information on using these settings. In addition, the
automatic LCD status sense feature conserves the backlight. When the LCD is closed the
backlight shuts off, saving battery power.

1-4 Technical Information
CPU Board
The CPU board is a 75-MHz (model G8SBJ) board. It connects to the system board via
connectors P1 and P2. The system integrates the Intel’s Pentium P54C chip (75 Mhz internal, 25 Mhz external). The chip controls important functions including power management,
direct drive bus interface and memory management. The CPU operates at a default clock
speed of 75 MHz. It has a 32-bit internal data bus and requires an operating voltage of 3.3
volts.
The chip's floating point unit (FPU) provides an internal math coprocessor. In addition, the
microprocessor has an internal on-chip cache controller with 16 KB cache memory. (internal) and 256 KB cache memory (external).
CPU board connectors include the memory card connector (P1), the keyboard connectors
(P2 and P3), and the LCD indicator panel connector (P4). For a list of CPU board connector descriptions and an accompanying illustration, see Appendix A.
System Board
The system board (G8SBK) is inside the base unit, under the CPU board. It contains system
components including I/O subsystems. The battery charger board connects to the system
board via connector P10.
For a list of system board connector descriptions and an accompanying illustration, see Appendix A. System board specifications are listed in Table Section 1-9 at the end of this section.
Primary Battery
The system uses a nickel metal hydride (NiMH) battery (also called “smart” battery) as its
transient power source. The smart battery communicates battery status via the LCD indicator (or gas gauge). The battery pack installs in the compartment next to the PCMCIA assembly. The battery uses 7.2 volts with a 3800 mAH capacity and weighs 520 grams. The
primary battery pack lasts approximately two to three hours, depending on the LCD type.
The primary battery should be discharged every 30 to 45 days using the Discharge utility.
To discharge the battery means to drain all of the battery’s power. Sometimes a battery
does not last as long if not fully discharged between charges. The discharging process takes
several minutes depending on how fully charged the battery was. See Section 2, Setup and
Operation, for Discharge utility procedures.
Secondary Battery
An optional secondary battery (same battery type as the primary) can be added in place of
the diskette drive. See Section 3, Options, for installing the battery The battery uses 7.2
volts with a 3800 mAH capacity. The smart battery weighs 540 grams.

Technical Information 1-5
CMOS Battery
The lithium battery provides battery backup (3.0 Volts, 280 mAh) to prevent data loss in
the system’s complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) RAM. This memory area
contains information on the system’s configuration like date, time, drives, and memory. The
CMOS battery lasts approximately two years.
Bridge Battery
The bridge battery saves the memory contents and system status for up to 5 minutes while
in Suspend mode. It is situated next to the hard disk drive housing. The AC adapter maintains voltage in the bridge battery when the system is powered on or off. The bridge battery
provides 6 Volts, 50 mAH.
VersaBay PCMCIA Module Option
The VersaBay PCMCIA module adds two more PCMCIA card slots to the system when
the user is not using the diskette drive or secondary battery. The module installs in the system’s diskette drive slot.
Keyboard
The built-in, 83-key keyboard (U.S) or 79-key keyboard (UK and Germany) uses the standard QWERTY format. The keyboard provides 12 function keys and 8 cursor control keys,
with an Fn key for ROM-based key functions. The numeric keypad is embedded in the standard key layout.
VersaTrack
The built-in mouse makes it easy to use mouse-driven software such as Windows 3.1. The
buttons on either side of the mouse allow the user to select or deselect menu items.
The VersaTrack is the system's default pointing device unless a PS/2 mouse is installed. If
an external mouse is installed, then the VersaTrack is deactivated.
1-6 Technical Information
SYSTEM MEMORY
The system board provides 8 MB of standard random access memory (RAM) with 16 KB
internal cache, and 256 KB external cache. Base memory is 640 KB and extended memory
is 7168 KB (interleaved). The system does not support memory remap.
Optional memory cards with a value of 4-, 8-, 12-, 16-MB or 32-MB can be added to increase system memory. Additionally, 256 KB of read-only memory (ROM), 1 x 28F020,
enables the system BIOS to be flashed.
The system supports the following RAM configurations using optional memory cards:
n standard RAM plus an optional 4-MB memory card for a total of 12-MB RAM
n standard RAM plus an optional 8-MB memory card for a total of 16-MB RAM
n standard RAM plus an optional 12-MB memory card for a total of 20-MB RAM
n standard RAM plus an optional 16-MB memory card for a total of 24-MB RAM
n standard RAM plus an optional 32-MB memory card for a total of 40-MB RAM.
Memory Map
The system supports system and video shadowing, both controlled through complementary
metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS). The system supports BIOS as a cacheable area with
write protection. Table Section 1-1 lists the system's memory map.
Table Section 1-1 Versa System Memory Map
Memory Space Size Function
000000-09FFFF 640 KB Reserved for System Base Memory
0C0000-0C7FFF
0C8000-0CFFFF
0D0000-0DFFFF
0E0000-0FFFFF
E8000h-EFFFFFh
100000h-On-Board
32 KB
32 KB
64 KB
128 KB
64KB
Mapped to ISA BIOS
Mapped to ISA Bus
Mapped to PCMCIA Bus
Reserved for System BIOS
Reserved for System BIOS
Reserved for Extended and/or Expanded system
memory
Technical Information 1-7
SYSTEM VIDEO
The system's LCD operates using the Chips and Technologies 65545 VGA Controller.
Video signals travel from the controller through the system's 15-pin D-SUB connector using 5 volts.
System video integrates a 32-bit VL-bus interface using local bus video. The system ships
with 1 MB Video RAM (VRAM). It also supports video modes up to 1024 x 768 with 256
colors in CRT mode.
Table Section 1-2 lists display modes for both P53S and P53H models.
NOTE: Interlaced video modes are represented
with the letter I in the table below.
Table Section 1-2 CRT Display Mode (CRT only)
Mode
(Hex)
0, 1 Text 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 70
2, 3 Text 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 70
0*,1* Text 16 40x25 320x350 8x14 70
2, 3 Text 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 70
0**, 1** Text 16 40x25 360x400 9x16 70
2**, 3** Text 16 80x25 720x400 9x16 70
4, 5 Graph 4 40x25 320x200 8x8 70
6 Graph 2 80x25 640x200 8x8 70
7* Text Mono 80x25 720x350 9x14 70
7** Text Mono 80x25 720x400 9x16 70
D Planar 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 70
E Planar 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 70
F Planar Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 70
Display
Mode Colors
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate
10 Planar 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 70
11 Planar 2 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
12*** Planar 16 80x30 640x480 8x16 74
13 Packed
Pixel
20 4-bit 16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 40x25 320x200 8x8 70
1-8 Technical Information
Table Section 1-2 CRT Display Mode (CRT only)
Mode
(Hex)
22 4-bit
24 4-bit
24I 4-bit
30 8-bit
30*** 8-bit
32 8-bit
32# 8-bit
34 8-bit
Display
Mode Colors
Linear
Linear
Linear
Linear
Linear
Linear
Linear
Linear
Text
Display Resolution Font
16 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
16 128x48 1024x768 8x16 60
16 128x48 1024x768 8x16 43
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 74
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 74
256 128x48 1024x768 8x16 60
Refresh
Rate
34I 8-bit
Linear
40 15-bit
Linear
41 16-bit
Linear
60 Text 16 132x25 1056x400 8x16 68
61 Text 16 132x50 1056x400 8x16 68
6A, 70 Planar 16 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
6A***
70***
72, 75 Planar 16 128x48 1024x768 8x16 60
72I, 75I Planar 16 128x48 1024x768 8x16 43
78 Packed
79 Packed
79*** Packed
Planar 16 100x37 800x600 8x16 74
Pixel
Pixel
Pixel
256 128x48 1024x768 8x16 43
32K 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
64K 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 80x25 640x400 8x16 70
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 74
Technical Information 1-9
Table Section 1-2 CRT Display Mode (CRT only)
Mode
(Hex)
7C Packed
7C*** Packed
7EI Packed
7E Packed
*EGA Extension
**VGA Extension
***High Refresh Modes
Display
Mode Colors
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
Pixel
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 74
Pixel
256 128x48 1024x768 8x16 43
Pixel
256 128x48 1024x768 8x16 60
Pixel
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate
Table Section 1-3 lists display modes for the P53S model only.
Table Section 1-3 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 TFT, Simultaneous CRT)
Mode
(Hex)
0,1 Text 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
2,3 Text 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
0*, 1* Text 16 40x25 320x350 8x14 60
2*, 3* Text 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
0**, 1** Text 16 40x25 320.x4000 8x16 60
2**, 3** Text 16 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
4, 5 Graph 4 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
6 Graph 2 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
7* Text Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
7** Text Mono 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
D Planar 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
E Planar 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
F Planar Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
10 Planar 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
Display
Mode Colors
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate

1-10 Technical Information
Table Section 1-3 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 TFT, Simultaneous CRT)
Mode
(Hex)
11 Planar 2 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
12 Planar 16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
13 Packed
20 4-bit
30 8-bit
40 15-bit
41 16-bit
78 Packed
79 Packed
Display
Mode Colors
256 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
Pixel
16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Linear
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Linear
32K 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Linear
64K 80x30 540x480 8x16 60
Linear
256 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
Pixel
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Pixel
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate
*EGA Extension
**VGA Extension
Table Section 1-4 lists display modes for the P53H model only.
Table Section 1-4 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 STN-D/S, Simultaneous CRT
Display)
Mode
(Hex)
0, 1 Text 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
2, 3 Text 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
0*, 1* Text 16 40x25 320x350 8x14 60
2*, 3* Text 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
0**, 1** Text 16 40x25 320x400 8x16 60
2**, 3** Text 16 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
4,5 Graph 4 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
Display
Mode Colors
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refesh
Rate
6 Graph 2 80x25 640x200 8x8 60

Technical Information 1-11
Table Section 1-4 LCD Display Mode (640 x 480 STN-D/S, Simultaneous CRT
Display)
Mode
(Hex)
7* Text Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
7** Text Mono 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
D Planar 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
E Planar 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
F Planar Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
10 Planar 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
11 Planar 2 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
12 Planar 16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
13 Packed
20 4-bit
30 8-bit
78 Packed
Display
Mode Colors
256 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
Pixel
16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Linear
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Linear
256 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
Pixel
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refesh
Rate
79 Packed
Pixel
*EGA Extension
**VGA Extension
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Table Section 1-5 lists display modes for the P53H model only.
Table Section 1-5 LCD Display Mode (800x600 TFT, Simultaneous CRT Display)
Mode
(Hex)
0,1 Text 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
2,3 Text 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
0*, 1* Text 16 40x25 320x350 8x14 60
2*, 3* Text 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
0**, 1** Text 16 40x25 360x400 9x16 60
Display
Mode
Color
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate
(Hz)
1-12 Technical Information
Table Section 1-5 LCD Display Mode (800x600 TFT, Simultaneous CRT Display)
Mode
(Hex)
2**,3** Text 16 80x25 720x400 9x16 60
4,5 Graph 4 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
6 Graph 2 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
7* Text Mono 80x25 720x350 9x14 60
7** Text Mono 80x25 720x400 9x16 60
D Planar 16 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
E Planar 16 80x25 640x200 8x8 60
F Planar Mono 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
10 Planar 16 80x25 640x350 8x14 60
11 Planar 2 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
12 Planar 16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
13 Packed
20 4-bit
Display
Mode
Pixel
Linear
Color
256 40x25 320x200 8x8 60
16 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
Text
Display Resolution Font
Refresh
Rate
(Hz)
22 4-bit
Linear
30 8-bit
Linear
32 8-bit
Linear
6A, 70 Planar 16 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
78 Packed
Pixel
79 Packed
Pixel
7C Packed
Pixel
*EGA Extension
**VGA Extension
16 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 60
256 80x25 640x400 8x16 60
256 80x30 640x480 8x16 60
256 100x37 800x600 8x16 60

Technical Information 1-13
PARALLEL INTERFACE
The system's parallel interface integrates National’s PC87332VLJ chip. It uses a 25-pin Dsubconnector that is Enhanced Capabilities Port (ECP) equipped. The port is located on the
system's rear panel.
The user selects between three parallel interface modes using Auto Setup. These include
unidirectional, bidirectional or enhanced. Unidirectional mode sends data output from the
standard ISA port only. Bidirectional mode sends data using the standard ISA port or PS/2
technology. Enhanced mode enables high speed data transmission to occur using either the
unidirectional or bidirectional modes.
The parallel port address is 378h and the interrupt level is IRQ07. Pin locations for the parallel interface are listed in Appendix A.
SERIAL INTERFACE
The RS-232C serial port is a 9-pin connector on the system’s rear panel. The serial port
consists of a 16550 compatible serial port controller with a programmable baud rate within
50/56000 bps. The serial port connects an RS-232C device or an external modem. The serial port address is 3F8h and the interrupt level is IRQ04.
VERSA P SERIES CHIP SET
Refer to Table Section 1-6 for a quick summary of the chip types used in the system. See
the Abbreviations section at the beginning of this manual for a translation of chip technologies.
Table Section 1-6 Versa P Series Chip Types and Technologies
Chip Manufacturer Description Technology
P54C Intel 75 MHz CPU 320-pin TCP
PT86C868/
PT86C718
N28F020-150 Intel 256k x 8 Flash ROM 32-pin PLCC
PT86C718 Pico Power IDE Interface, Peripheral
C&T65545 Chips &
PC87334VJG National
Pico Power System Logic 144-pin TQFP/
176-pin TQFP
176-pin TQFP
Controller, Interrupt
Multiplexer
VGA Controller 208-pin QFP
Technologies
Semiconductor
Diskette Controller, IDE,
Parallel Interface
100-pin TQFP
M38802M2-001HP Mitsubishi Keyboard Controller
CL-PD6720-B-2 Cirrus Logic PCMCIA Controller 208-pin QFP
64-pin TQFP
1-14 Technical Information
ES688S ESS Technology Audio Controller 100-pin SQFP
System Logic
The PT86C868/PT86C718 Pico Power chips each consist of a 144-pin plastic quad flatpackage. This two-chip controller supports fast graphics and I/O processing. The system
logic controller adds the following features:
n built-in level 2 cache controller
n integrated active power management
n integrated battery management
n high performance DRAM controller.
Flash ROM
The N28F020 flash ROM is a 32-pin, plastic lead chip carrier (PLCC). The chip allows easy
updates to the system's BIOS if needed. More specifically, the ROM is flashed electronically, installing the latest BIOS revisions to the system. It is possible to reprogram the BIOS
up to 100,000 times. See Section 2, Setup and Operation, for BIOS update procedures.
The N28F020 provides the system upgrade capability as well as the following:
n 2048-kilobit (kb) memory
n Quick-Pulse Programming Algorithm
n 150 nanoseconds (ns) maximum access time
n ETOX Nonvolatile flash technology
n CMOS low power consumption
n low noise feature.
ROM BIOS
The system uses a Flash ROM known as the system's ROM BIOS to store machine language programs. The BIOS size is 256 KB, which consists of 96 KB system utility
(PCMCIA, Auto Setup), 64 KB system BIOS, 32 KB video BIOS, 32 KB power management and 32 KB reserved.
The BIOS programs execute the power-on self-test (POST), initialize CPU controllers, and
interact with the LCD indicator panel, diskette drive, hard drive, communication devices
and peripherals. The system BIOS also contains Auto Setup and provides VGA controller
support. The ROM BIOS is copied into RAM (shadowing) for optimum performance.
The ROM BIOS contains both the system and video BIOS. The system BIOS is located in
the upper portion of the device, video BIOS is located in the lower portion. System BIOS is
located between F000h-FFFFh.

Technical Information 1-15
The BIOS often changes after the product release to provide enhanced features or bug
fixes. To acquire the latest BIOS release, the ROM is flashed electronically allowing the
BIOS update to occur without removing the ROM. See Section 2, Setup and Operation, for
BIOS upgrade procedures.
Peripheral Controller
The PT86C718A chip controls the Peripheral Controller, IDE Interface, and Interrupt Multiplexer. The chip integrates performance and power-saving features while providing the
following:
n 8-level 64-bit write buffer to VL bus
n interrupt multiplexing logic
n reset logic.
VGA Controller
The video architecture is maintained using the C&T65545 Controller and support logic. The
controller supports video standards including EGA and CGA.
This powerful circuitry provides the following features for the system via the controller and
LCD:
n 1-MB VRAM
n true-color and high-color display capability with 640 x 480 or 800 x 600 resolu-
tion
n supports LCD resolutions up to 1024 x 768
n hardware Bit Block Transfers (BITBLT)
n programmable power management
n simultaneous LCD/CRT display in 640 x 480 VGA display mode
n 256 color display
n power management support.
Video Controller Architecture
The video controller architecture is broken down into several modules. The five significant
modules include the sequencer, CRT controller, graphics controller, attribute controller and
dithering engine.
For example, the sequencer manages CPU and display memory timing. The CRT controller
controls sync and timing signals. The graphics controller permits the flow of communication
between the CPU data bus and the 32-bit internal data bus. The attribute controller produces a 4-bit wide video data stream that refreshes the display.
 Loading...
Loading...