Page 1
查询UPD78P4038Y供应商
16/8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLER
The µPD78P4038Y, 78K/IV Series' product, is a one-time PROM or EPROM version of the µPD784035Y,
µ
PD784036Y, µPD784037Y, and µPD784038Y with internal masked ROM.
Since user programs can be written to PROM, this microcontroller is best suited for evaluation in system
development, manufacture of small quantities of multiple products, and fast start-up of applications.
For specific functions and other detailed information, consult the following user's manual.
This manual is required reading for design work.
µ
PD784038, 784038Y Sub-Series User's Manual, Hardware : U11316E
78K/IV Series User's Manual, Instruction : U10905E
DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD78P4038Y
FEATURES
• Compatible with the
µ
PD78P238, µPD78P4026, and µPD78P4038
• Internal PROM: 128 Kbytes
•
µ
PD78P4038YKK-T : EPROM (best suited for system evaluation)
•
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9 : PROM (best suited for manufacture of small quantities)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT: PROM (best suited for manufacture of small quantities)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9: PROM (best suited for manufacture of small quantities)
• Internal RAM: 4,352 bytes
• Supply voltage: VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V
• QTOP
ORDERING INFORMATION
TM
microcomputer
Remark The QTOP microcomputer is a microcomputer with a built-in one-time PROM that is totally supported
by NEC. The support includes writing application programs, marking, screening, and verification.
Part number Package Internal ROM
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm) One-time PROM
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm) One-time PROM
µ
PD78P4038YGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 mm) One-time PROM
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) One-time PROM
µ
PD78P4038YGK-×××-BE9 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) One-time PROM
µ
PD78P4038YKK-T 80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm) EPROM
(QTOP microcomputer)
(QTOP microcomputer)
In this reference, all ROM components that are common to one-time PROM and EPROM are referred to as
PROM.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Document No. U10742EJ2V0DS00 (2nd edition)
Date Published July 1998 J CP(K)
Printed in Japan
The mark shows major revised points.
©
1995
Page 2

µ
PD78P4038Y
QUALITY GRADE
Part number Package Quality grade
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm) Standard (for general electronic equipment)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm) Standard (for general electronic equipment)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-×××-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm) Standard (for general electronic equipment)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) Standard (for general electronic equipment)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-×××-BE9 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) Standard (for general electronic equipment)
µ
PD78P4038YKK-T 80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm) Not applied (for function evaluation)
Please refer to "Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Devices" (Document No. C11531E) published by NEC Corporation
to know the specification of quality grade on the devices and its recommended applications.
Caution The EPROM versions of the µPD78P4038Y are not intended for use in mass-produced products;
they do not have reliability high enough for such purposes. Their use should be restricted to
functional evaluation in experiment or trial manufacture.
Remark ××× is ROM code suffix.
2
Page 3
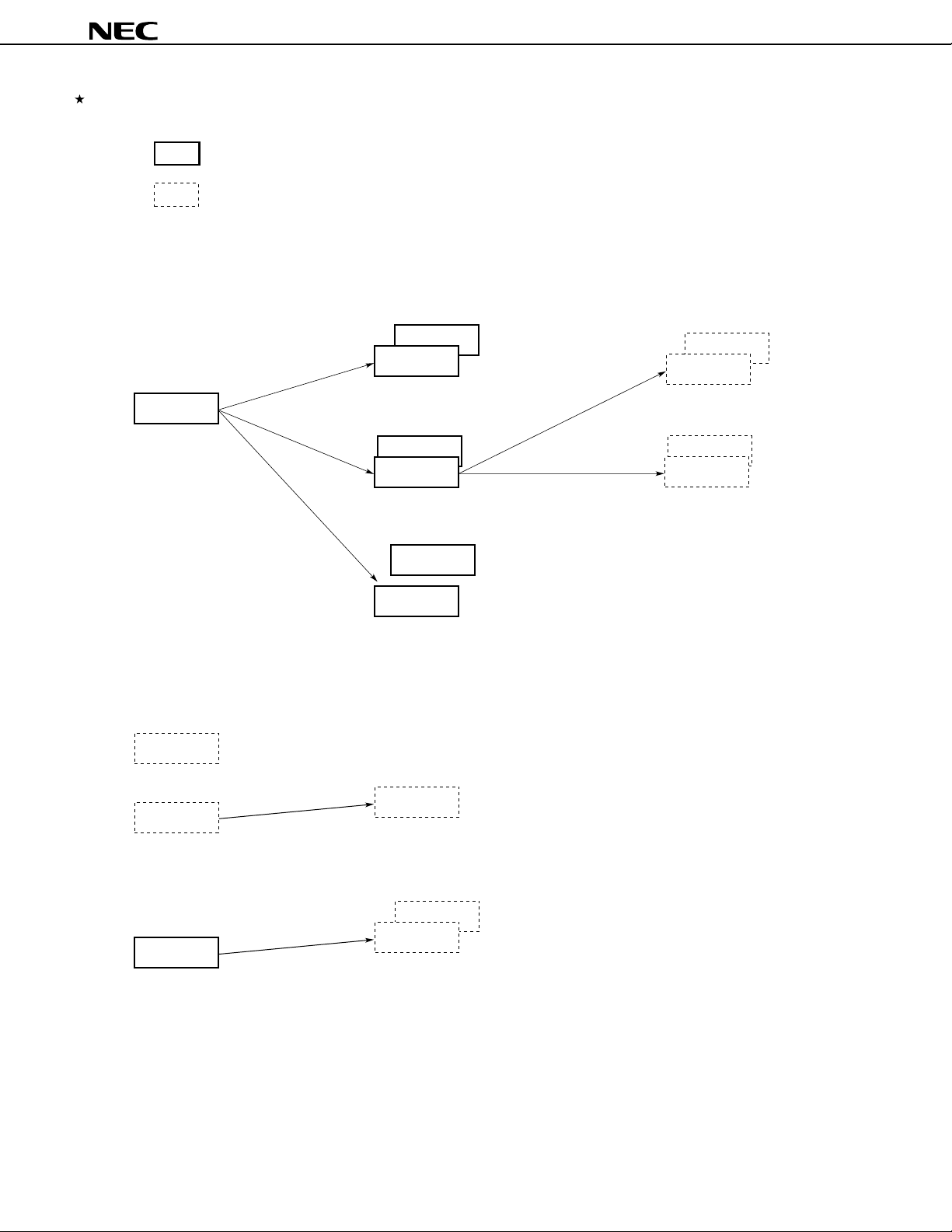
78K/IV SERIES PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT DIAGRAM
: Product under mass production
: Product under preparation
Standard Products Development
µ
PD78P4038Y
µ
PD784026
A/D converters,
16-bit timers, and
power management
functions have been
enhanced.
ASSP Development
µ
PD784955
DC inverter control
Connectable to the I
µ
PD784038Y
µ
PD784038
Internal memory has been expanded.
Pin-compatible with the PD784026
Connectable to the multimaster I
PD784216Y
µ
µ
PD784216
100 pins
I/O has been enhanced.
Internal memory has been expanded.
µ
PD784054
µ
PD784046
Built-in 10-bit A/D converter
2
C bus
µ
2
C bus
Connectable to the multimaster I
µ
PD784225Y
µ
PD784225
80 pins
ROM correction function has been added.
Connectable to the multimaster I
µ
PD784218Y
µ
PD784218
Internal memory has been expanded.
ROM correction function has been added.
2
C bus
2
C bus
µ
PD784908
Built-in IEBus
µ
PD784915
Software servo control
Built-in analog circuit for VCR
Timers have been enhanced.
TM
controller
µ
PD784937
Functions of the PD784908 have been enhanced.
Internal memory has been expanded.
ROM correction function has been added.
Connectable to the multimaster I
µ
PD784928Y
µ
PD784928
Functions of the PD784915 have been enhanced.
µ
2
C bus
µ
3
Page 4

FUNCTIONS
µ
PD78P4038Y
(1/2)
Item
Number of basic instructions
(mnemonics)
General-purpose register
Minimum instruction
execution time
Internal
memory
Memory space
I/O ports
Additional
function
Note
pins
Real-time output ports
Timer/counter
PWM outputs
Serial interface
A/D converter
D/A converter
PROM
RAM
Total
Input
Input/output
Pins with pull-
up resistor
LED direct
drive outputs
Transistor
direct drive
Functions
113
8 bits × 16 registers × 8 banks, or 16 bits × 8 registers × 8 banks (memory mapping)
125 ns/250 ns/500 ns/1,000 ns (at 32 MHz)
128 Kbytes (Can be changed to 48 K, 64 K, or 96 Kbytes by software)
4,352 bytes (Can be changed to 2,048 or 3,584 bytes by software)
Program and data: 1 Mbyte
64
8
56
54
24
8
4 bits × 2, or 8 bits × 1
Timer/counter 0: Timer register × 1 Pulse output capability
Capture register × 1 • Toggle output
Compare register × 2 • PWM/PPG output
• One-shot pulse output
Timer/counter 1: Timer register × 1 Pulse output capability
Capture register × 1 • Real-time output (4 bits × 2)
Capture/compare register × 1
Compare register × 1
Timer/counter 2: Timer register × 1 Pulse output capability
Capture register × 1 • Toggle output
Capture/compare register × 1 • PWM/PPG output
Compare register × 1
Timer 3 : Timer register × 1
Compare register × 1
12-bit resolution × 2 channels
UART/IOE (3-wire serial I/O): 2 channels (incorporating baud rate generator)
CSI (3-wire serial I/O, 2-wire serial I/O, I2C bus): 1 channel
8-bit resolution × 8 channels
8-bit resolution × 2 channels
Note Additional function pins are included in the I/O pins.
4
Page 5
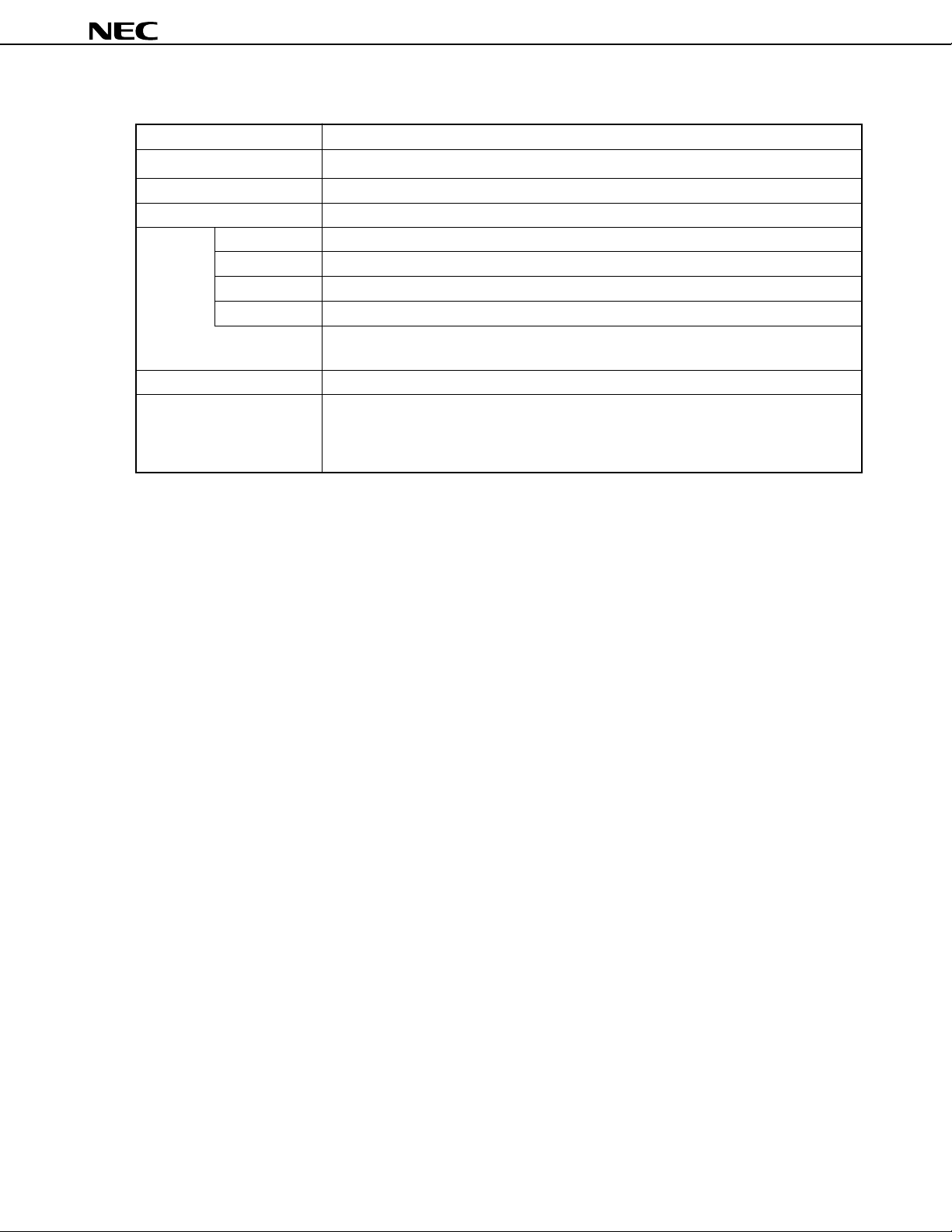
µ
PD78P4038Y
(2/2)
Item
Clock output
Watchdog timer
Standby
Interrupt
Supply voltage
Package
Hardware source
Software source
Nonmaskable
Maskable
Functions
Selected from fCLK, fCLK/2, fCLK/4, fCLK/8, or fCLK/16 (can be used as a 1-bit output port)
1 channel
HALT/STOP/IDLE mode
24 (17 internal, 7 external (sampling clock variable input: 1))
BRK instruction, BRKCS instruction, operand error
1 internal, 1 external
16 internal, 6 external
• 4-level programmable priority
• 3 operation statuses: vectored interrupt, macro service, context switching
VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V
80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm)
80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm)
80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm)
5
Page 6

µ
PD78P4038Y
CONTENTS
1. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD78P4038Y AND MASKED ROM PRODUCTS .................... 7
2. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW) ......................................................................................... 8
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................................... 11
4. LIST OF PIN FUNCTIONS......................................................................................................... 12
4.1 Pins for Normal Operating Mode................................................................................................. 1 2
4.2 Pins for PROM Programming Mode (V
4.2.1 Pin functions .................................................................................................................. 15
4.2.2 Pin functions .................................................................................................................. 16
4.3 I/O Circuits for Pins and Handling of Unused Pins.................................................................. 17
PP ≥ +5 V or +12.5 V, RESET = L) .............................. 15
5. INTERNAL MEMORY SWITCHING (IMS) REGISTER ............................................................ 20
6. PROM PROGRAMMING ............................................................................................................ 21
6.1 Operation Mode .............................................................................................................................. 21
6.2 PROM Write Sequence.................................................................................................................. 23
6.3 PROM Read Sequence .................................................................................................................. 27
7. ERASURE CHARACTERISTICS (µPD78P4038YKK-T ONLY) ............................................... 28
8. PROTECTIVE FILM COVERING THE ERASURE WINDOW (µPD78P4038YKK-T ONLY) .. 28
9. QUALITY..................................................................................................................................... 28
10. SCREENING ONE-TIME PROM PRODUCTS .......................................................................... 28
11. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................................................... 29
12. PACKAGE DRAWINGS ............................................................................................................. 55
13. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ........................................................................ 59
APPENDIX A DEVELOPMENT TOOLS .......................................................................................... 61
APPENDIX B CONVERSION SOCKET (EV-9200GC-80) AND CONVERSION ADAPTER
(TGK-080SDW) .......................................................................................................... 64
APPENDIX C RELATED DOCUMENTS.......................................................................................... 67
6
Page 7
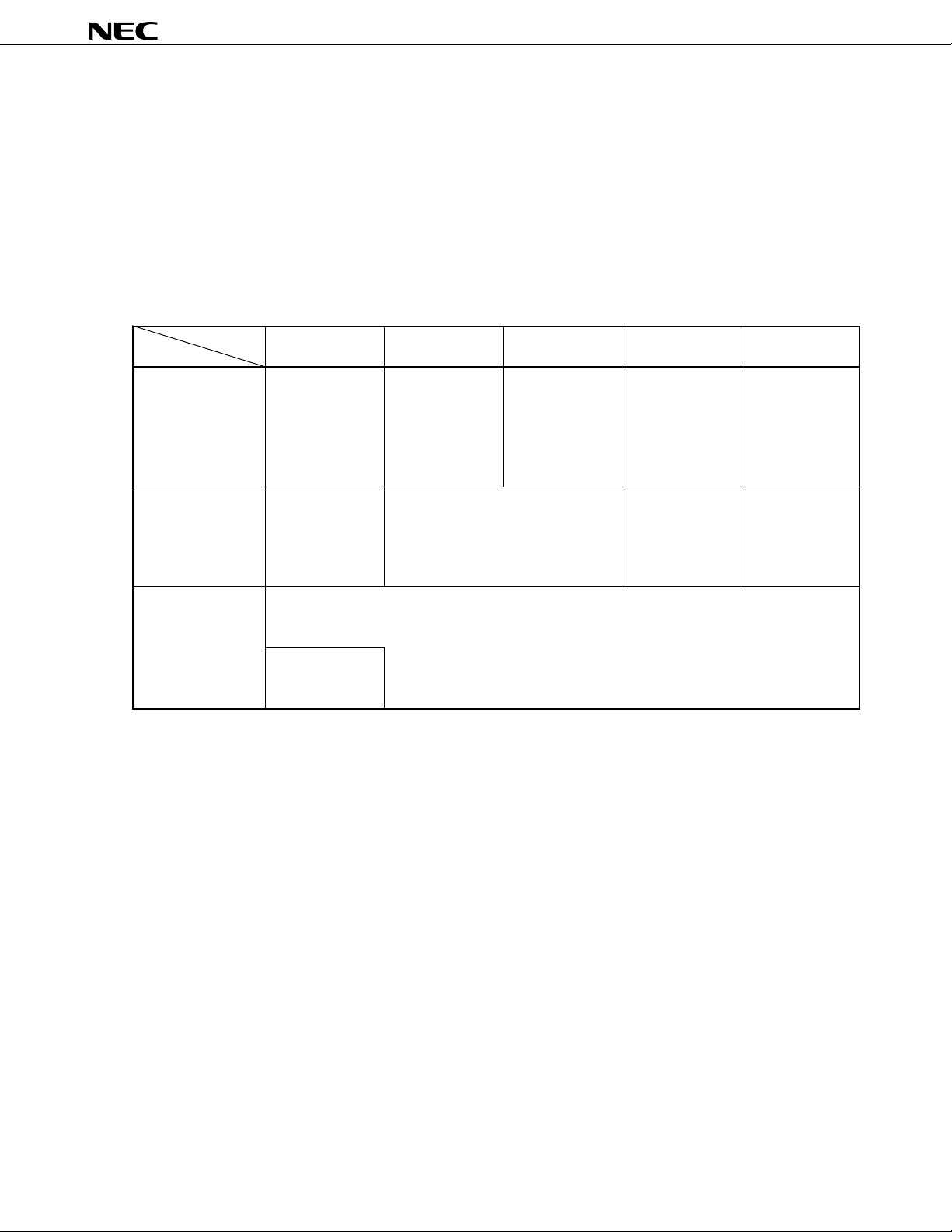
µ
PD78P4038Y
1. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD78P4038Y AND MASKED ROM PRODUCTS
The µPD78P4038Y is produced by replacing the masked ROM in the µPD784035Y, µPD784036Y, µPD784037Y,
or µPD784038Y with PROM to which data can be written. The functions of the µPD78P4038Y are the same as those
of the µPD784035Y, µPD784036Y, µPD784037Y, or µPD784038Y except for the PROM specification such as writing
and verification, except that the PROM size can be changed to 48 K, 64 K, or 96 Kbytes, and except that the internal
RAM size can be changed to 2,048 or 3,584 bytes.
Table 1-1 shows the differences between these products.
µ
Table 1-1. Differences between the
PD78P4038Y and Masked ROM Products
Product Name
Item
Internal program
memory
Internal RAM
Package
µ
PD78P4038Y
• 128-Kbyte
PROM
• Can be changed
to 48 K, 64 K, or
96 Kbytes by
IMS
• 4,352-byte
internal RAM
• Can be changed
to 2,048 or 3,584
bytes by IMS
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm)
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm)
• 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
80-pin ceramic
WQFN
(14 × 14 mm)
µ
PD784035Y
• 48-Kbyte
masked ROM
• 2,048-byte internal RAM
µ
• 64-Kbyte
masked ROM
PD784036Y
µ
PD784037Y
• 96-Kbyte
masked ROM
• 3,584-byte
internal RAM
µ
PD784038Y
• 128-Kbyte
masked ROM
• 4,352-byte
internal RAM
7
Page 8
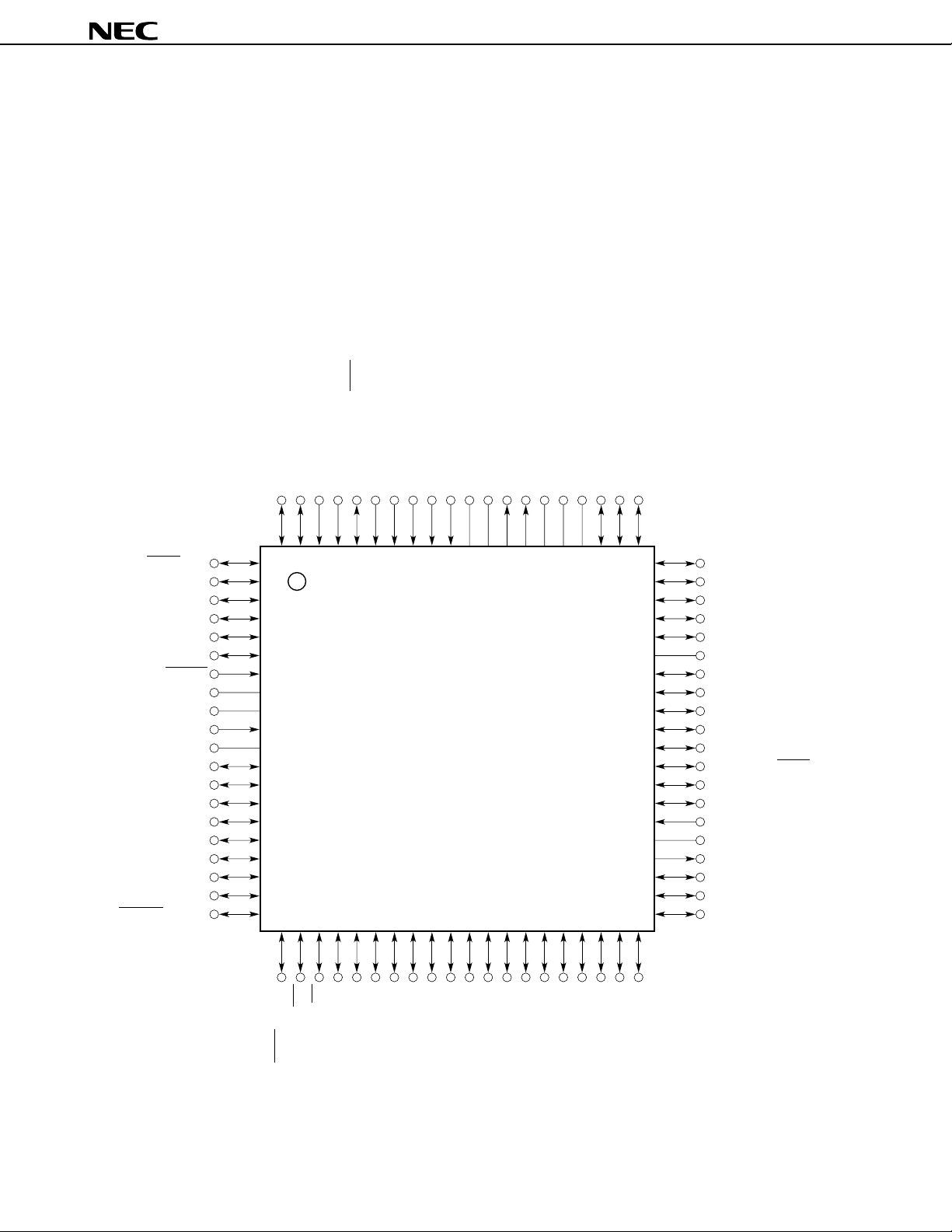
2. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
(1) Normal operating mode
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9, µPD78P4038YGC-×××-3B9
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT
• 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9, µPD78P4038YGK-×××-BE9
• 80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YKK-T
µ
PD78P4038Y
P32/SCK0/SCL
P33/SO0/SDA
P34/ TO0
P35/TO1
P36/TO2
P37/TO3
RESET
V
DD1
X2
X1
SS1
V
P00
P01
P02
P03
P04
P05
P06
P07
P67/REFRQ/HLDAK
REF3AVREF2
P31/ TxD/SO1
P30/RxD/SI1
P27/SI0
P26/INTP5
P25/INTP4/ASCK/SCK1
P24/INTP3
P23/INTP2/CI
P22/INTP1
P21/INTP0
P20/NMI
AV
ANO1
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
ANO0
AVSSAV
REF1AVDD
P77/ANI7
P76/ANI6
P75/ANI5
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
P74/ANI4
P73/ANI3
P72/ANI2
P71/ANI1
P70/ANI0
DD0
V
P17
P16
P15
X
D2/SO2
P14/T
X
D2/SI2
P13/R
P12/ASCK2/SCK2
P11/PWM1
P10/PWM0
Note
TEST
V
SS0
ASTB/CLKOUT
P40/AD0
P41/AD1
P42/AD2
P51/A9
P64/RD
P65/ WR
P63/A19
P66/ WAIT/HLDRQ
P62/A18
P61/A17
P60/A16
P57/A15
P56/A14
P55/A13
P54/A12
P53/A11
P52/A10
P50/A8
P47/AD7
P46/AD6
P45/AD5
P44/AD4
P43/AD3
Note Connect the TEST pin to VSS0 directly.
8
Page 9

µ
PD78P4038Y
A8-A19 : Address bus
AD0-AD7 : Address/data bus
ANI0-ANI7 : Analog input
ANO0, ANO1 : Analog output
ASCK, ASCK2 : Asynchronous serial clock
ASTB : Address strobe
DD : Analog power supply
AV
AVREF1-AVREF3 : Reference voltage
SS : Analog ground
AV
CI : Clock input
CLKOUT : Clock output
HLDAK : Hold acknowledge
HLDRQ : Hold request
INTP0-INTP5 : Interrupt from peripherals
NMI : Non-maskable interrupt
P00-P07 : Port 0
P10-P17 : Port 1
P20-P27 : Port 2
P30-P37 : Port 3
P40-P47 : Port 4
P50-P57 : Port 5
P60-P67 : Port 6
P70-P77 : Port 7
PWM0, PWM1 : Pulse width modulation output
RD : Read strobe
REFRQ : Refresh request
RESET : Reset
RxD, RxD2 : Receive data
SCK0-SCK2 : Serial clock
SCL : Serial clock
SDA : Serial data
SI0-SI2 : Serial input
SO0-SO2 : Serial output
TEST : Test
TO0-TO3 : Timer output
TxD, TxD2 : Transmit data
DD0, VDD1 : Power supply
V
VSS0, VSS1 : Ground
WAIT : Wait
WR : Write strobe
X1, X2 : Crystal
9
Page 10
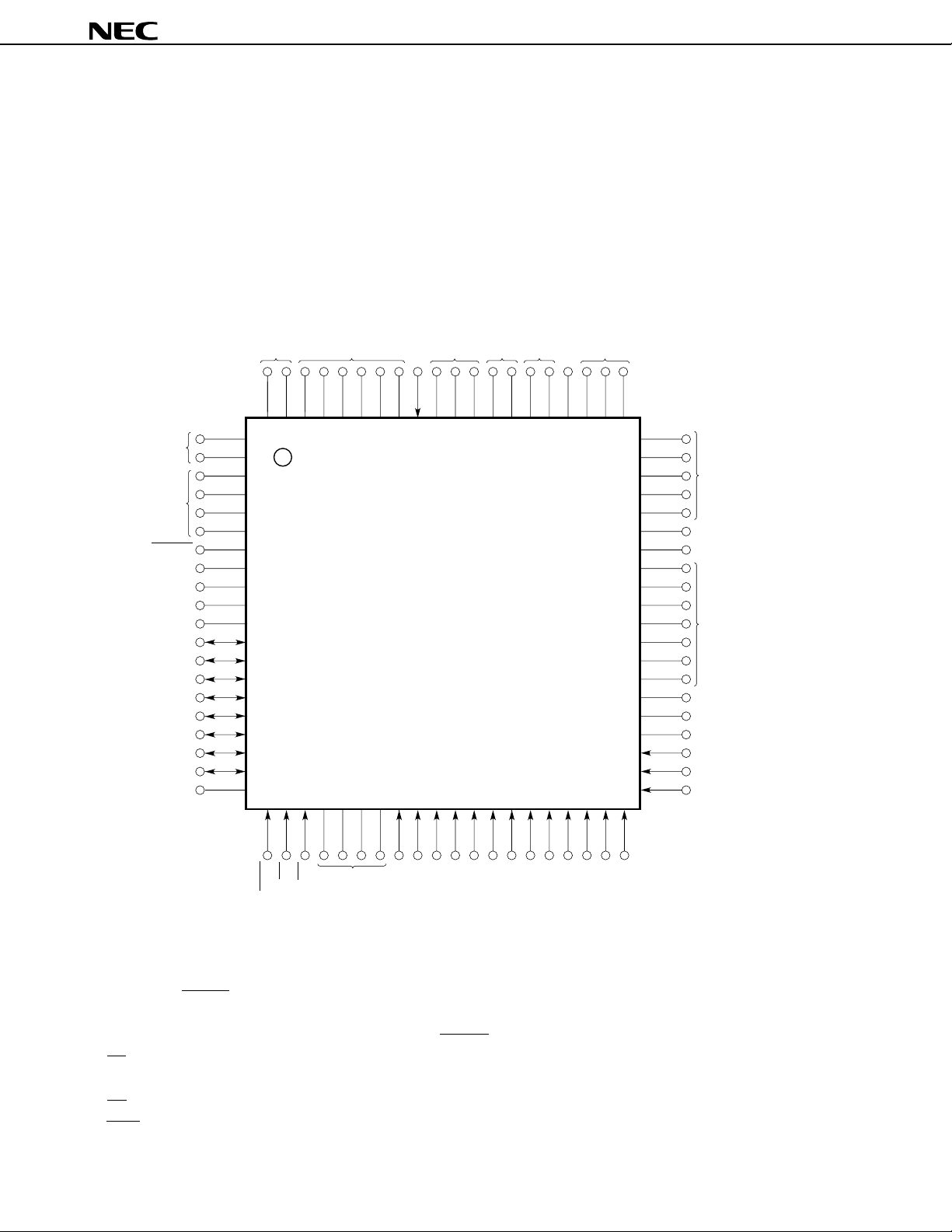
(2) PROM programming mode
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9, µPD78P4038YGC-×××-3B9
• 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT
• 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9, µPD78P4038YGK-×××-BE9
• 80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm)
µ
PD78P4038YKK-T
Open
VSS
A9
µ
PD78P4038Y
SS
V
Open
VSS
DD
Open
V
(L)
Open
RESET
V
Open
(L)
VSS
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
(L)
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DD
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
PGM
CE
OE
(L)
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A8A7A6A5A4
A10
A16
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
A3
Open
VDD
(L)
Open
PP
V
VSS
Open
A0
A1
A2
Caution L : Connect these pins separately to the V
SS pins through 10-kΩ pull-down resistors.
VSS : To be connected to the ground.
Open : Nothing should be connected on these pins.
RESET: Set a low-level input.
A0-A16 : Address bus RESET : Reset
CE : Chip enable V
DD : Power supply
D0-D7 : Data bus VPP : Programming power supply
OE : Output enable V
SS : Ground
PGM : Program
10
Page 11
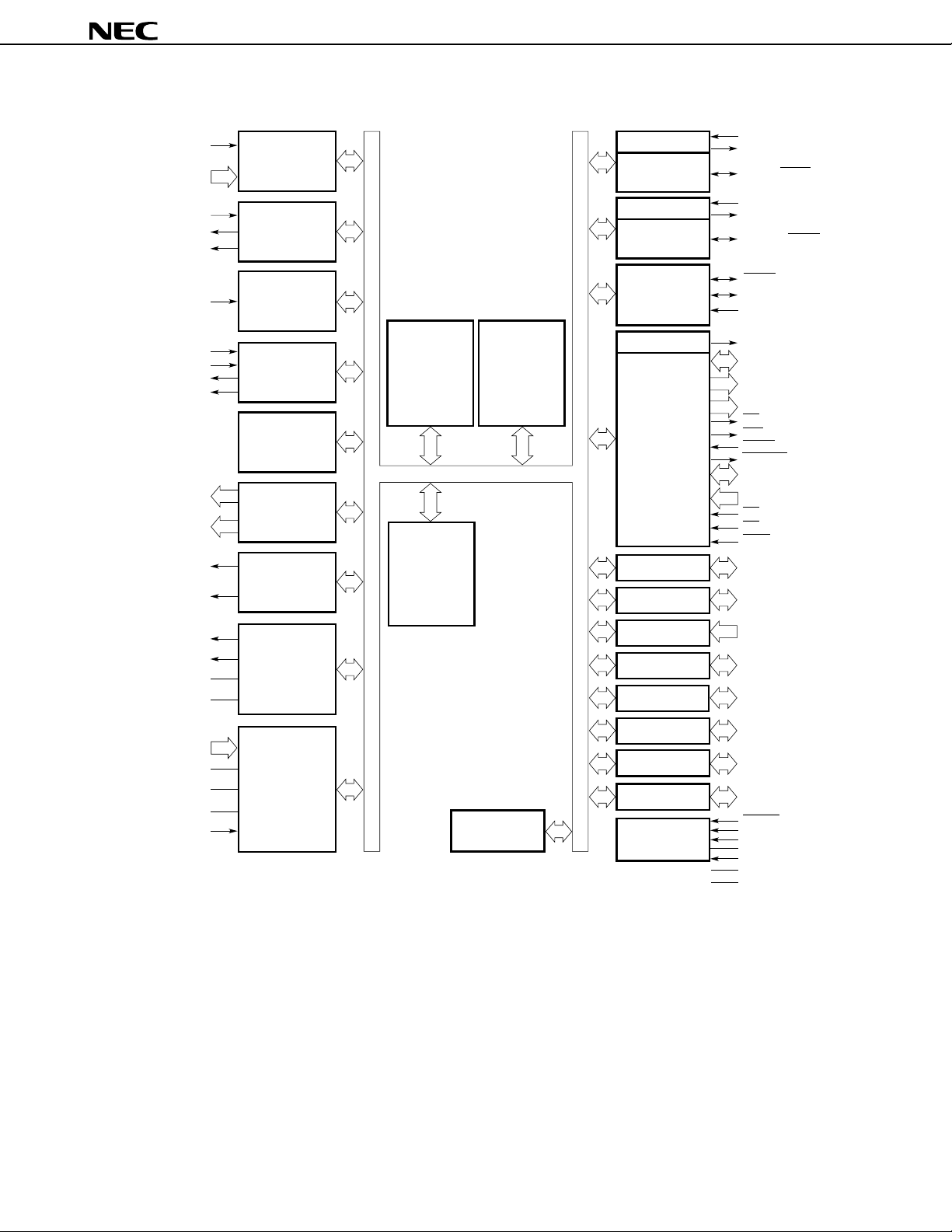
3. BLOCK DIAGRAM
NMI
INTP0-INTP5
INTP3
TO0
TO1
Programmable
interrupt
controller
Timer/counter 0
(16 bits)
UART/IOE2
Baud-rate
generator
UART/IOE1
Baud-rate
generator
µ
PD78P4038Y
X
D/SI1
R
T
X
D/SO1
ASCK/SCK1
X
D2/SI2
R
X
D2/SO2
T
ASCK2/SCK2
INTP0
INTP1
INTP2/CI
TO2
TO3
P00-P03
P04-P07
PWM0
PWM1
ANO0
ANO1
AV
REF2
AV
REF3
Timer/counter 1
(16 bits)
Timer/counter 2
(16 bits)
Timer 3
(16 bits)
Real-time
output port
PWM
D/A
converter
78 K/IV
CPU core
(RAM 512 bytes)
RAM
(3,840 bytes)
PROM
(128 Kbytes)
Clocked
serial
interface
Clock output
Bus
interface
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
SCK0/SCL
SO0/SDA
SI0
ASTB/CLKOUT
AD0-AD7
A8-A15
A16-A19
RD
WR
WAIT/HLDRQ
REFRQ/HLDAK
Note
D0-D7
Note
A0-A16
Note
CE
Note
OE
Note
PGM
P00-P07
P10-P17
P20-P27
P30-P37
P40-P47
ANI0-ANI7
AV
AV
REF1
AV
INTP5
Port 5
DD
Port 6
P50-P57
P60-P67
A/D
SS
converter
Watchdog
timer
Port 7
System
control
P70-P77
RESET
TEST
X1
X2
Note
PP
V
V
DD0
, V
DD1
V
SS0
, V
SS1
Note In the PROM programming mode.
11
Page 12
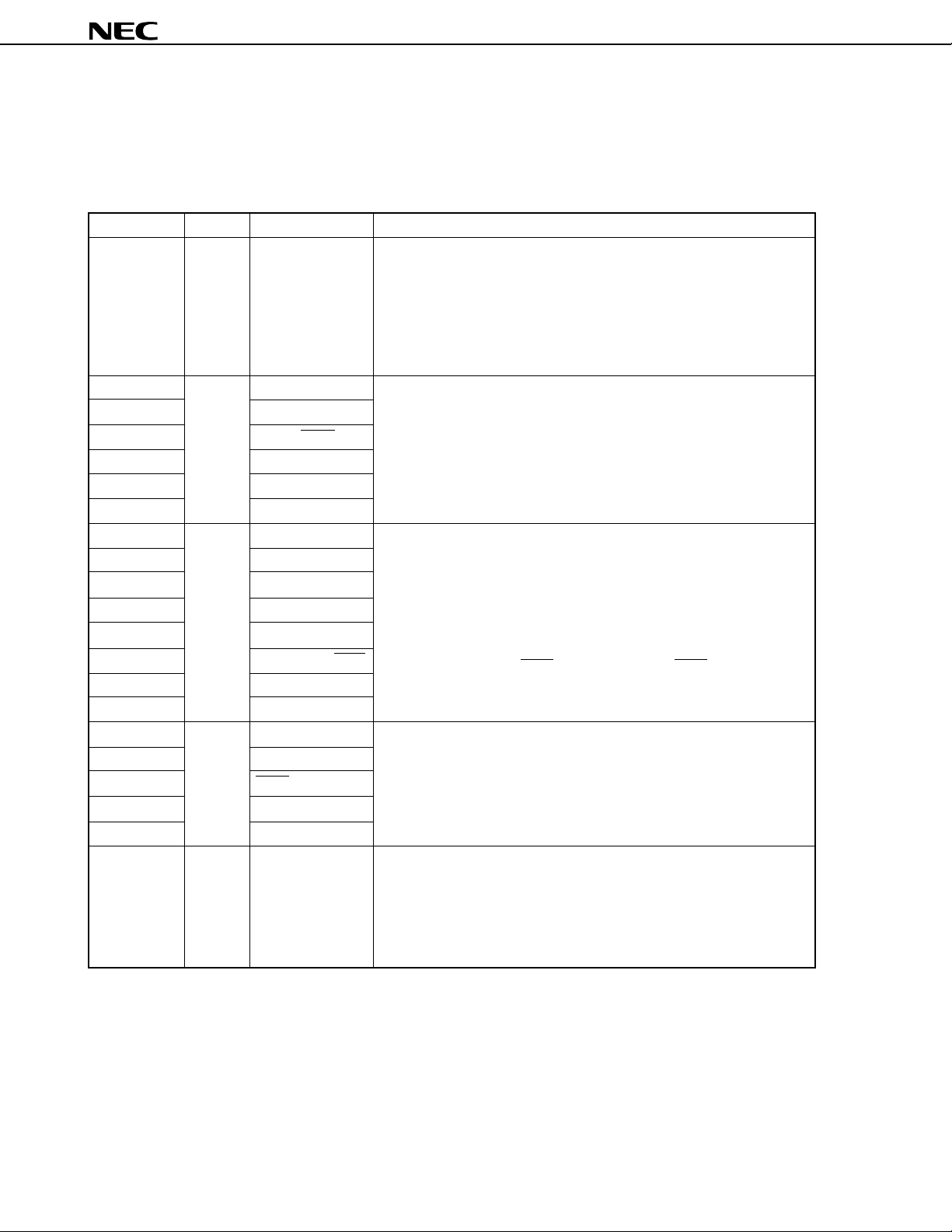
4. LIST OF PIN FUNCTIONS
4.1 Pins for Normal Operating Mode
(1) Port pins (1/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
P00-P07
P10
P11
P12
P13
P14
P15-P17
P20
P21
P22
P23
P24
P25
P26
P27
P30
P31
P32
P33
P34-P37
P40-P47
I/O
I/O
I/O
Input
I/O
I/O
Alternate-Function
–
PWM0
PWM1
ASCK2/SCK2
RXD2/SI2
TXD2/SO2
–
NMI
INTP0
INTP1
INTP2/CI
INTP3
INTP4/ASCK/SCK1
INTP5
SI0
RXD/SI1
TXD/SO1
SCK0/SCL
SO0/SDA
TO0-TO3
AD0-AD7
Function
Port 0 (P0):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Functions as a real-time output port (4 bits × 2).
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
• Can drive a transistor.
Port 1 (P1):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
• Can drive LED.
Port 2 (P2):
• 8-bit input-only port.
• P20 does not function as a general-purpose port (nonmaskable
interrupt). However, the input level can be checked by an interrupt
service routine.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for pins
P22 to P27 (in units of 6 bits).
• The P25/INTP4/ASCK/SCK1 pin functions as the SCK1 output pin by
CSIM1.
Port 3 (P3):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
Port 4 (P4):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
• Can drive LED.
12
Page 13
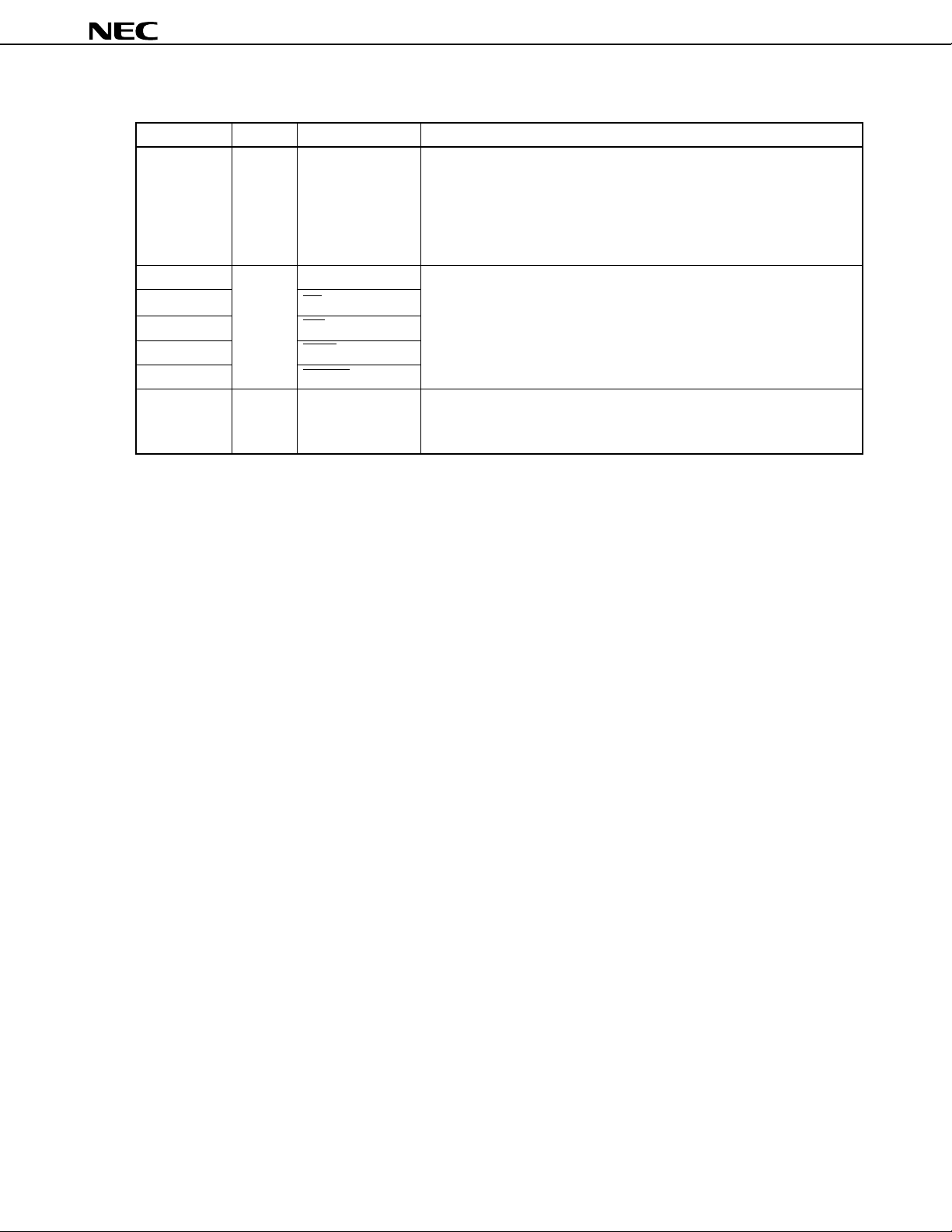
(1) Port pins (2/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
P50-P57
P60-P63
P64
P65
P66
P67
P70-P77
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Alternate-Function
A8-A15
A16-A19
RD
WR
WAIT/HLDRQ
REFRQ/HLDAK
ANI0-ANI7
Function
Port 5 (P5):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
• Can drive LED.
Port 6 (P6):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
• The use of the pull-up resistors can be specified by software for the pins
in the input mode together.
Port 7 (P7):
• 8-bit I/O port.
• Inputs and outputs can be specified bit by bit.
13
Page 14
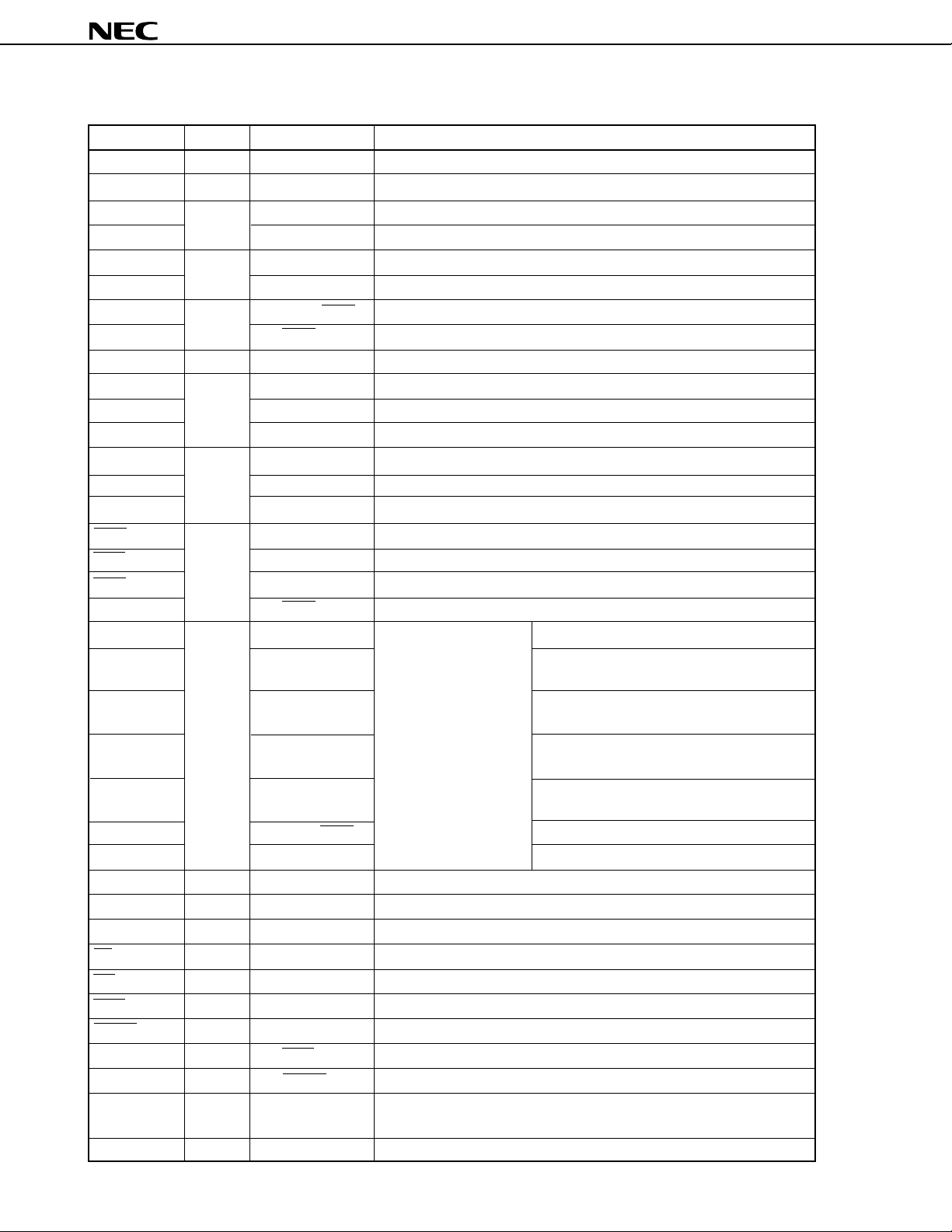
(2) Non-port pins (1/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
TO0-TO3
CI
RXD
RXD2
TXD
TXD2
ASCK
ASCK2
SDA
SI0
SI1
SI2
SO0
SO1
SO2
SCK0
SCK1
SCK2
SCL
NMI
INTP0
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
AD0-AD7
A8-A15
A16-A19
RD
WR
WAIT
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
ASTB
CLKOUT
I/O
Output
Input
Input
Output
Input
I/O
Input
Output
I/O
Input
I/O
Output
Output
Output
Output
Input
Output
Input
Output
Output
Output
Alternate-Function
P34-P37
P23/INTP2
P30/SI1
P13/SI2
P31/SO1
P14/SO2
P25/INTP4/SCK1
P12/SCK2
P33/SO0
P27
P30/RXD
P13/RXD2
P33/SDA
P31/TXD
P14/TXD2
P32/SCL
P25/INTP4/ASCK
P12/ASCK2
P32/SCK0
P20
P21
P22
P23/CI
P24
P25/ASCK/SCK1
P26
P40-P47
P50-P57
P60-P63
P64
P65
P66/HLDRQ
P67/HLDAK
P66/WAIT
P67/REFRQ
CLKOUT
ASTB
Function
Timer output
Input of a count clock for timer/counter 2
Serial data input (UART0)
Serial data input (UART2)
Serial data output (UART0)
Serial data output (UART2)
Baud rate clock input (UART0)
Baud rate clock input (UART2)
Serial data I/O (2-wire serial I/O, I2C bus)
Serial data input (3-wire serial I/O0)
Serial data input (3-wire serial I/O1)
Serial data input (3-wire serial I/O2)
Serial data output (3-wire serial I/O0)
Serial data output (3-wire serial I/O1)
Serial data output (3-wire serial I/O2)
Serial clock I/O (3-wire serial I/O0)
Serial clock I/O (3-wire serial I/O1)
Serial clock I/O (3-wire serial I/O2)
Serial clock I/O (2-wire serial I/O, I2C bus)
External interrupt request –
• Input of a count clock for timer/counter 1
• Capture/trigger signal for CR11 or CR12
• Input of a count clock for timer/counter 2
• Capture/trigger signal for CR22
• Input of a count clock for timer/counter 2
• Capture/trigger signal for CR21
• Input of a count clock for timer/counter 0
• Capture/trigger signal for CR02
–
Input of a conversion start trigger for A/D converter
Time multiplexing address/data bus (for connecting external memory)
High-order address bus (for connecting external memory)
High-order address bus during address expansion (for connecting external memory)
Strobe signal output for reading the contents of external memory
Strobe signal output for writing on external memory
Wait signal insertion
Refresh pulse output to external pseudo static memory
Input of bus hold request
Output of bus hold response
Latch timing output of time multiplexing address (A0-A7) (for connecting
external memory)
Clock output
14
Page 15
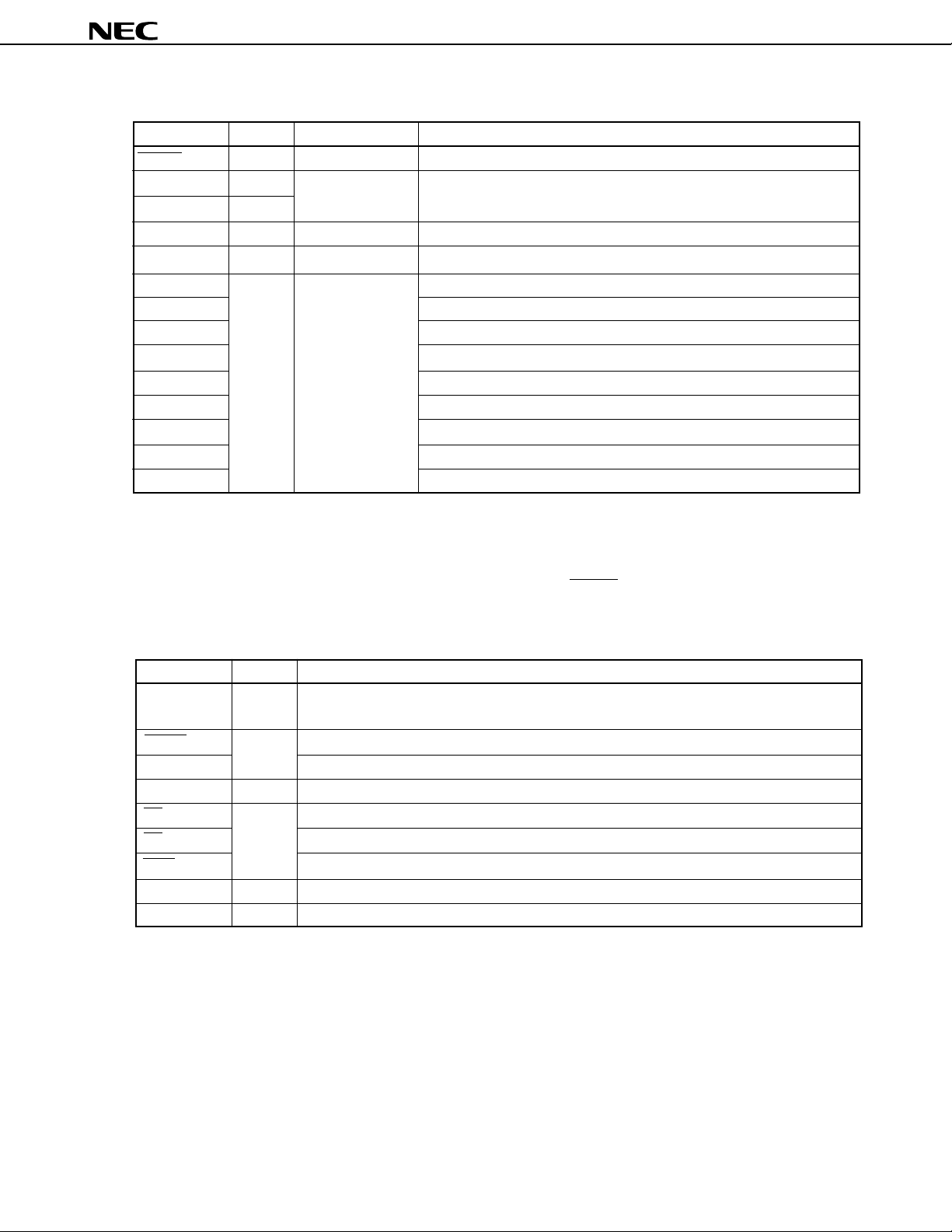
(2) Non-port pins (2/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
RESET
X1
X2
ANI0-ANI7
ANO0, ANO1
AVREF1
AVREF2, AVREF3
AVDD
AVSS
Note 1
VDD0
Note 1
VDD1
Note 2
VSS0
Note 2
VSS1
TEST
I/O
Input
Input
–
Input
Output
–
Alternate-Function
–
–
P70-P77
–
–
Chip reset
Crystal input for system clock oscillation (A clock pulse can also be input
to the X1 pin.)
Analog voltage inputs for the A/D converter
Analog voltage inputs for the D/A converter
Application of A/D converter reference voltage
Application of D/A converter reference voltage
Positive power supply for the A/D converter
Ground for the A/D converter
Positive power supply of the port part
Positive power supply except for the port part
Ground of the port part
Ground except for the port part
Directly connect to VSS0. (The TEST pin is for the IC test.)
Notes 1. The potential of the VDD0 pin must be equal to that of the VDD1 pin.
2. The potential of the VSS0 pin must be equal to that of the VSS1 pin.
Function
4.2 Pins for PROM Programming Mode (V
4.2.1 Pin functions
Pin Name
VPP
RESET
A0-A16
D0-D7
CE
OE
PGM
VDD
VSS
I/O
–
Input
I/O
Input
–
–
PROM programming mode selection
High voltage input during program write or verification
PROM programming mode selection
Address bus
Data bus
PROM enable input/program pulse input
Read strobe input to PROM
Program/program inhibit input during PROM programming mode
Positive power supply
GND
PP ≥ +5 V or +12.5 V, RESET = L)
Function
15
Page 16

µ
PD78P4038Y
4.2.2 Pin functions
PP (Programming power supply): Input
(1) V
Input pin for setting the µPD78P4038Y to the PROM programming mode. When the input voltage on this pin
is +5 V or more and when RESET input goes low, the µPD78P4038Y enters the PROM programming mode.
When CE is made low for V
PROM cell selected by A0 to A16.
(2) RESET (Reset): Input
Input pin for setting the
when the input voltage on the VPP pin goes +5 V or more, the µPD78P4038Y enters the PROM programming
mode.
(3) A0 to A16 (Address bus): Input
Address bus that selects an internal PROM address (0000H to 1FFFFH)
(4) D0 to D7 (Data bus): I/O
Data bus through which a program is written on or read from internal PROM
PP = +12.5 V and OE = high, program data on D0 to D7 can be written into the internal
µ
PD78P4038Y to the PROM programming mode. When input on this pin is low, and
(5) CE (Chip enable): Input
This pin inputs the enable signal from internal PROM. When this signal is active, a program can be written or
read.
(6) OE (Output enable): Input
This pin inputs the read strobe signal to internal PROM. When this signal is made active for CE = low, a onebyte program in the internal PROM cell selected by A0 to A16 can be read onto D0 to D7.
(7) PGM (Program): Input
The input pin for the operation mode control signal of the internal PROM.
Upon activation, writing to the internal PROM is enabled.
Upon inactivation, reading from the internal PROM is enabled.
DD
(8) V
Positive power supply pin
SS
(9) V
Ground potential pin
16
Page 17
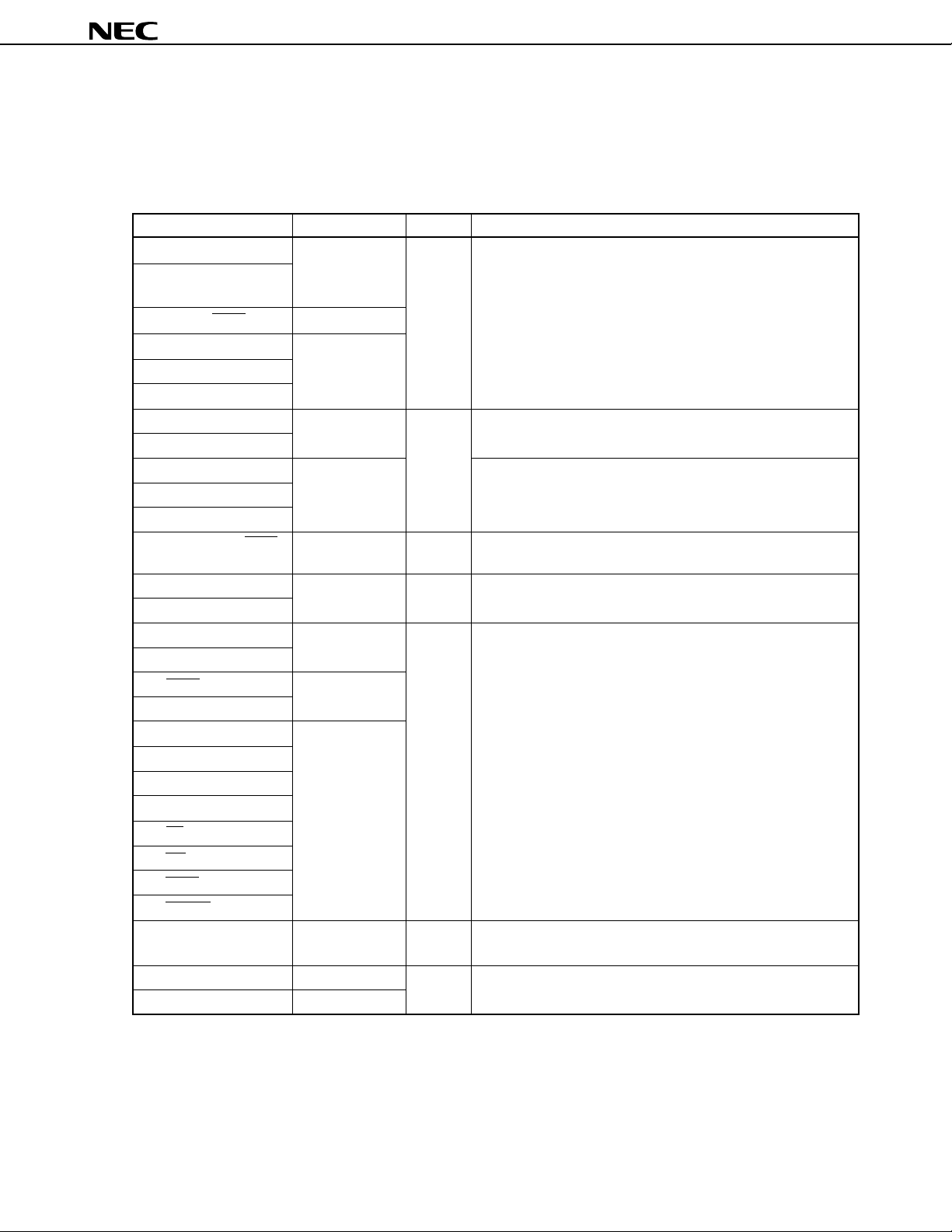
4.3 I/O Circuits for Pins and Handling of Unused Pins
Table 4-1 describes the types of I/O circuits for pins and the handling of unused pins.
Figure 4-1 shows the configuration of these various types of I/O circuits.
Table 4-1. Types of I/O Circuits for Pins and Handling of Unused Pins (1/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
P00-P07
P10/PWM0
P11/PWM1
P12/ASCK2/SCK2
P13/RXD2/SI2
P14/TXD2/SO2
P15-P17
P20/NMI
P21/INTP0
P22/INTP1
P23/INTP2/CI
P24/INTP3
P25/INTP4/ASCK/SCK1
P26/INTP5
P27/SI0
P30/RXD/SI1
P31/TXD/SO1
P32/SCK0/SCL
P33/SO0/SDA
P34/TO0-P37/TO3
P40/AD0-P47/AD7
P50/A8-P57/A15
P60/A16-P63/A19
P64/RD
P65/WR
P66/WAIT/HLDRQ
P67/REFRQ/HLDAK
P70/ANI0-P77/ANI7
ANO0, ANO1
ASTB/CLKOUT
I/O Circuit Type
5-H
8-C
5-H
2
2-C
8-C
2-C
5-H
10-B
5-H
20-A
12
4-B
I/O
I/O
Input
I/O
Input
I/O
I/O
Output
Recommended Connection Method for Unused Pins
Input state: To be connected to VDD0
Output state: To be left open
To be connected to VDD0 or VSS0
To be connected to VDD0
Input state: To be connected to VDD0
Output state: To be left open
To be connected to VDD0
Input state: To be connected to VDD0
Output state: To be left open
Input state: To be connected to VDD0 or VSS0
Output state: To be left open
To be left open
17
Page 18
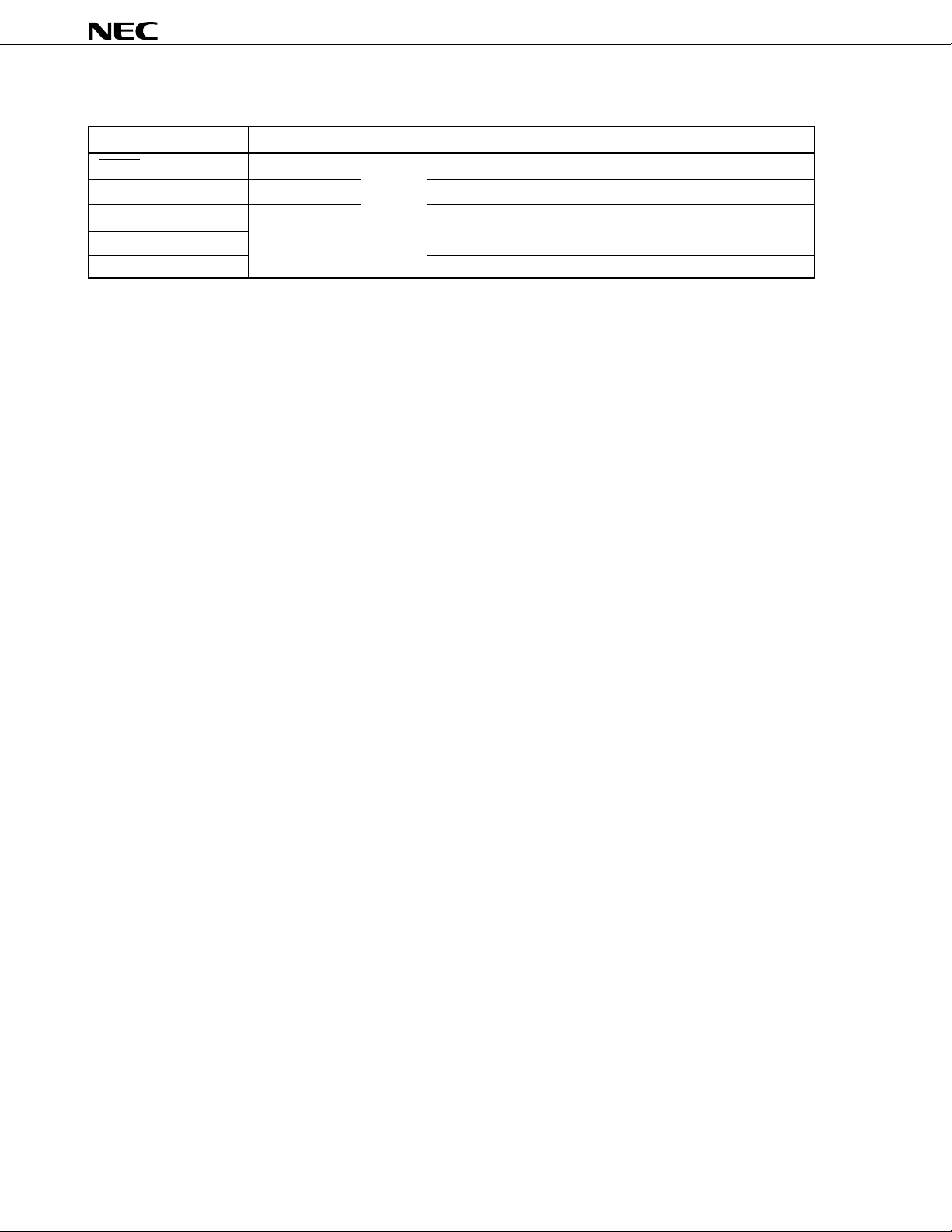
Table 4-1. Types of I/O Circuits for Pins and Handling of Unused Pins (2/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Pin
RESET
TEST
AVREF1-AVREF3
AVSS
AVDD
I/O Circuit Type
2
1-A
–
I/O
Input
Recommended Connection Method for Unused Pins
–
To be connected to VSS0 directly
To be connected to VSS0
To be connected to VDD0
Caution When the I/O mode of an I/O alternate-function pin is unpredictable, connect the pin to V
through a resistor of 10 to 100 kilohms (particularly when the voltage of the reset input pin
becomes higher than that of the low level input at power-on or when I/O is switched by software).
Remark Since type numbers are consistent in the 78K Series, those numbers are not always serial in each
product. (Some circuits are not included.)
DD0
18
Page 19
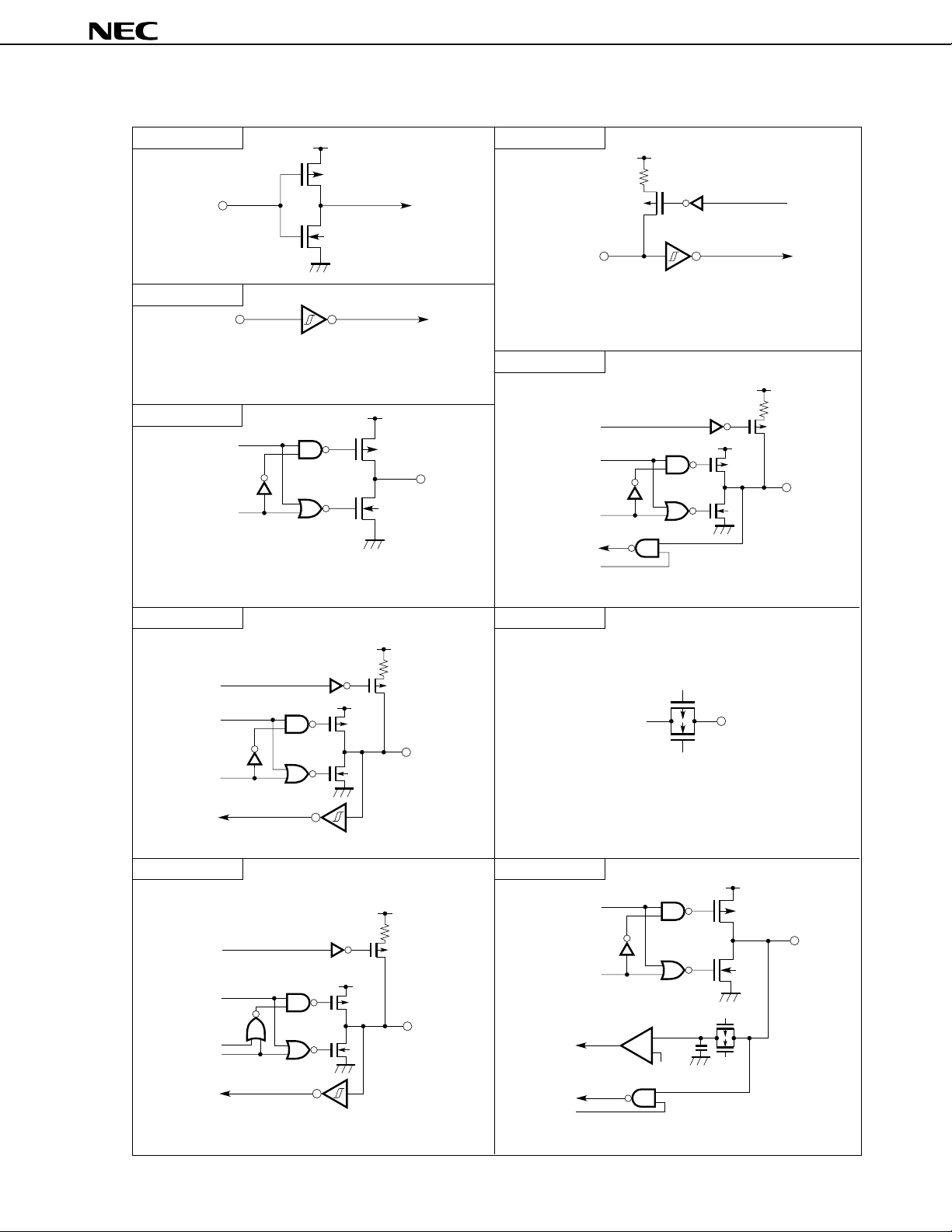
Figure 4-1. I/O Circuits for Pins
µ
PD78P4038Y
Type 1-A Type 2-C
V
DD0
P
IN
N
V
SS0
Type 2
IN
Schmitt trigger input with hysteresis characteristics
Type 5-H
Schmitt trigger input with hysteresis characteristics
Type 4-B
Data
DD0
V
P
OUT
Output
disable
N
V
SS0
Push-pull output which can output high impedance
(both the positive and negative channels are off.)
IN
Pull-up
enable
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
VDD0
V
DD0
Pull-up
enable
P
P
V
DD0
P
IN/OUT
N
V
SS0
Type 8-C
Pull-up
enable
Output
disable
Type 10-B
Pull-up
enable
Open
drain
Output
disable
Data
Data
Type 12
V
DD0
P
V
DD0
P
Analog output
voltage
IN/OUT
P
OUT
N
N
V
SS0
Type 20-A
V
DD0
V
DD0
Data
P
Output
V
DD0
disable
P
IN/OUT
N
V
SS0
Comparator
+
–
(Threshold voltage)
AV
AV
SS
REF
P
IN/OUT
N
V
SS0
P
N
Input
enable
19
Page 20
µ
PD78P4038Y
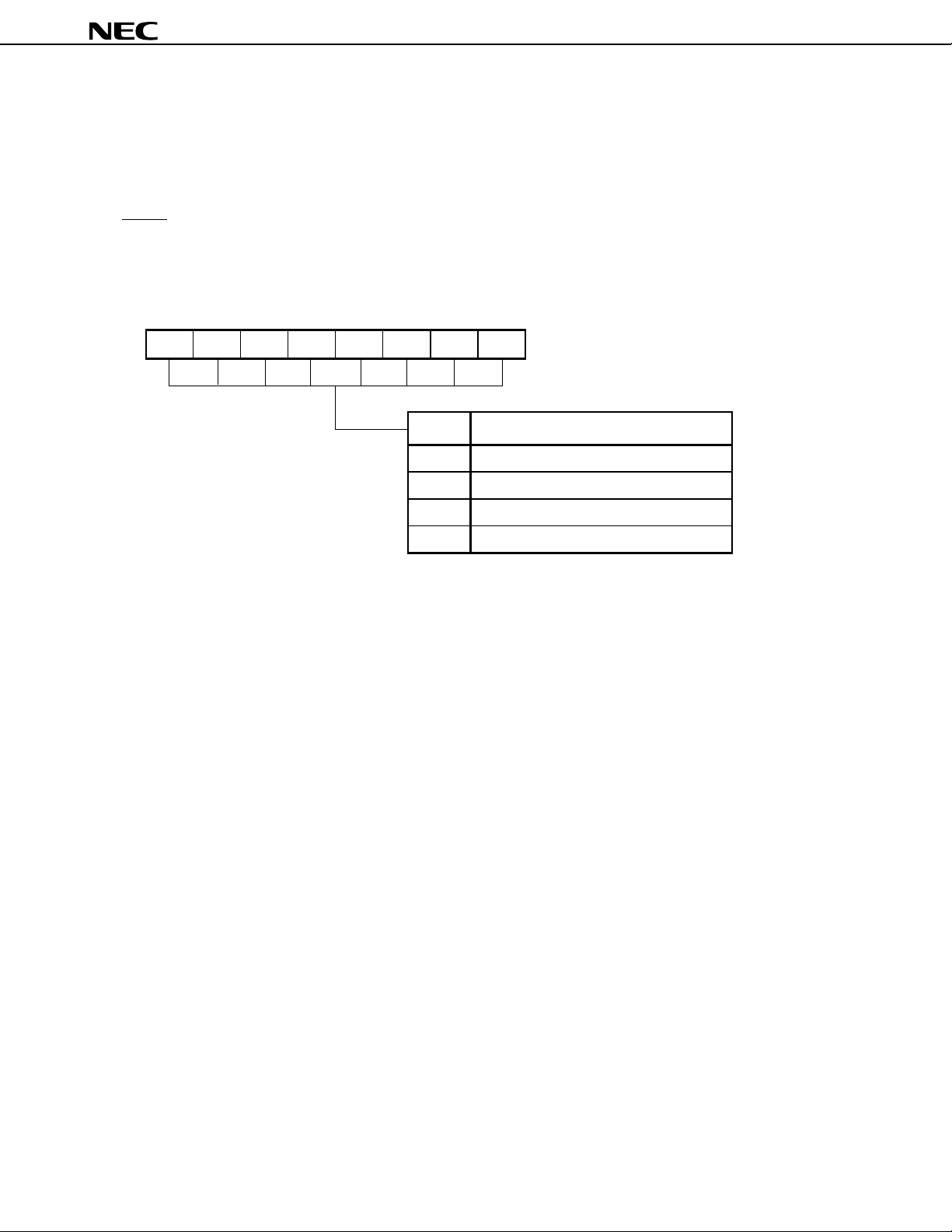
5. INTERNAL MEMORY SWITCHING (IMS) REGISTER
This register enables the software to avoid using part of the internal memory. The IMS register can be set to
establish the same memory mapping as used in ROM products that have different internal memory (ROM and RAM)
configurations.
The IMS register is set using 8-bit memory operation instructions.
A RESET input sets the IMS register to FFH.
Figure 5-1. Internal Memory Switching (IMS) Register
76543210
IMS IMS7 IMS6
IMS5
IMS4 IMS3 IMS2 IMS1 IMS0
The IMS is not contained in a mask ROM product (
IMS0-7
FFH
EEH
DCH
CCH
µ
PD784035Y, µPD784036Y, µPD784037Y, or µPD784038Y).
Same as the PD784038Y
Same as the PD784037Y
Same as the PD784036Y
Same as the PD784035Y
Address
0FFFCH
Memory Size
µ
µ
µ
µ
After Reset
FFH
R/W
But the action is not affected if the write command to the IMS is executed to the mask ROM product.
W
20
Page 21
µ
PD78P4038Y
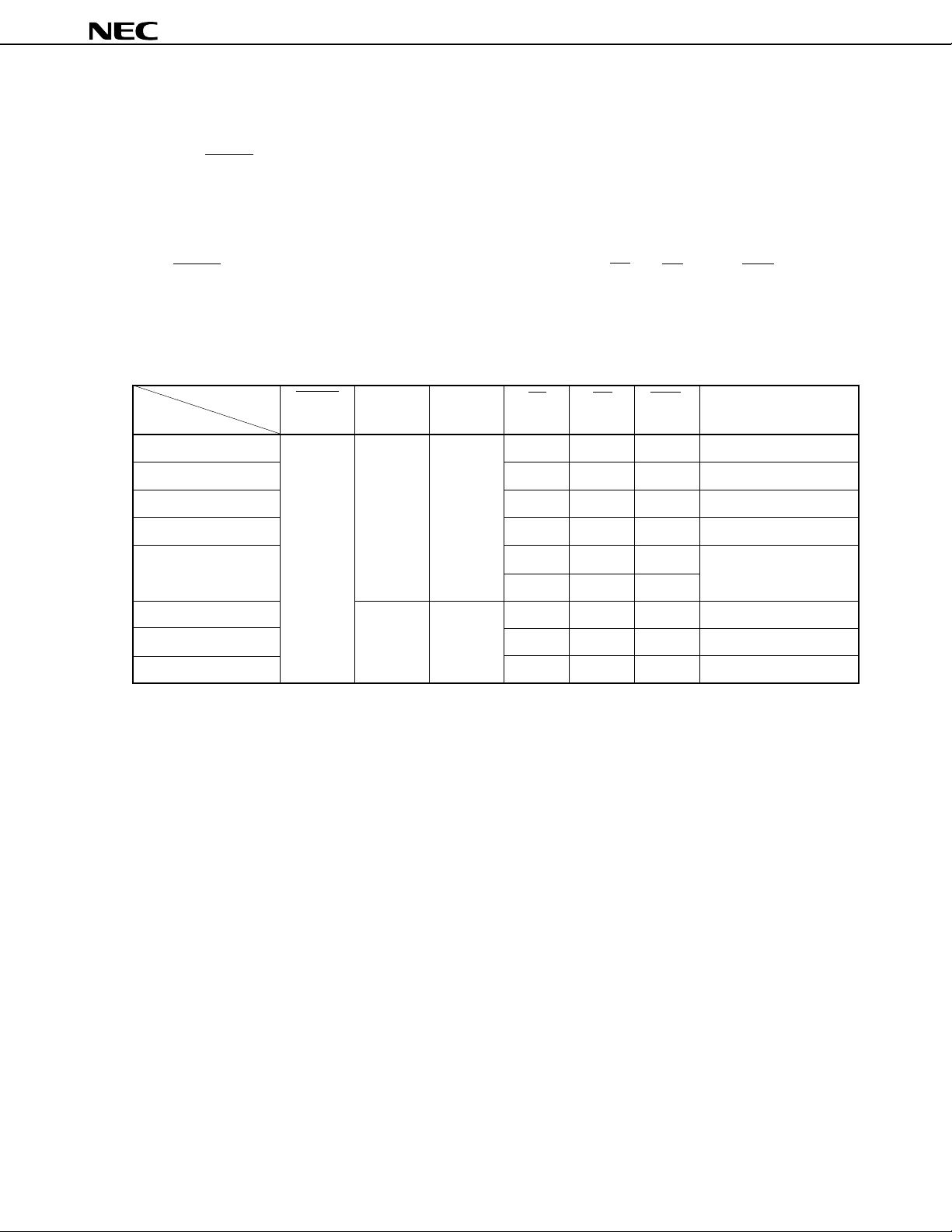
6. PROM PROGRAMMING
The µPD78P4038Y has an on-chip 128-KB PROM device for use as program memory. When programming, set
the VPP and RESET pins for PROM programming mode. See (2) in Chapter 2 with regard to handling of other, unused
pins.
6.1 Operation Mode
PROM programming mode is selected when +5 V or +12.5 V is added to the V
to the RESET pin. This mode can be set to operation mode by setting the CE pin, OE pin, and PGM pin as shown
in Table 6-1 below.
In addition, the PROM contents can be read by setting read mode.
Table 6-1. PROM Programming Operation Mode
Pin RESET VPP VDD CE OE PGM D0-D7
Operation Mode
Page data latch L +12.5 V +6.5 V H L H Data input
Page write H H L High impedance
PP pin or low-level input is added
Byte write L H L Data input
Program verify L L H Data output
Program inhibit × H H High impedance
× LL
Read +5 V +5 V L L H Data output
Output disable L H × High impedance
Standby H ××High impedance
Remark × = L or H
21
Page 22
µ
PD78P4038Y
(1) Read mode
Set CE to L and OE to L to set read mode.
(2) Output disable mode
Set OE to H to set high impedance for data output and output disable mode.
µ
Consequently, if several
select data output from any of the devices.
(3) Standby mode
Set CE to H to set standby mode.
In this mode, data output is set to high impedance regardless of the OE setting.
(4) Page data latch mode
At the beginning of page write mode, set CE to H, PGM to H, and OE to L to set page data latch mode.
In this mode, 1 page (4 bytes) of data are latched to the internal address/data latch circuit.
(5) Page write mode
After latching the address and data for one page (4 bytes) using page data latch mode, adding a 0.1 ms program
pulse (active, low) to the PGM pin with both CE and OE set to H causes page write to be executed. Later, setting
both CE and OE to L causes program verification to be executed.
If programming is not completed after one program pulse, the write and verify operations may be repeated X times
(where X ≤ 10).
PD78P4038Y devices are connected to a data bus, the OE pins can be controlled to
(6) Byte write mode
Adding a 0.1 ms program pulse (active, low) to the PGM pin with both CE and OE set to H causes byte write
to be executed. Later, setting OE to L causes program verification to be executed.
If programming is not completed after one program pulse, the write and verify operations may be repeated X times
(where X ≤ 10).
(7) Program verify mode
Set CE to L, PGM to H, and OE to L to set program verify mode. Use verify mode for verification following each
write operation.
(8) Program inhibit mode
µ
Program inhibit mode is used to write to a single device when several
parallel to OE , VPP, and D0 to D7 pins.
Use the page write mode or byte write mode described above for each write operation. Write operations cannot
be done for devices in which the PGM pin has been set to H.
PD78P4038Y devices are connected in
22
Page 23

6.2 PROM Write Sequence
Figure 6-1. Page Program Mode Flowchart
Start
Address = G
V
DD
= +6.5 V, V
Address = Address + 1
Address = Address + 1
X = 0
Latch
Latch
PP
= +12.5 V
µ
PD78P4038Y
Address = Address + 1
Address = Address + 1
0.1 ms program pulse
No
DD
= 4.5-5.5 V, V
V
Pass
Latch
Latch
X = X + 1
Verify 4 bytes
Pass
Address = N ?
Yes
PP
Verify all bytes
All pass
= V
No
X = 10 ?
Fail
DD
Fail
Yes
Remark G = Start address
N = Program end address
Write end
Defective
23
Page 24

A2-A16
A0, A1
D0-D7
V
PP
V
DD
V
PP
V
DD
VDD+1.5
DD
V
Figure 6-2. Page Program Mode Timing
Page data latch Page program Program verify
Data input Data output
µ
PD78P4038Y
CE
PGM
OE
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
24
Page 25

Figure 6-3. Byte Program Mode Flowchart
Start
Address = G
DD
= +6.5 V, V
V
X
= 0
PP
= +12.5 V
µ
PD78P4038Y
Address = Address + 1
Remark G = Start address
N = Program end address
0.1 ms program pulse
No
Pass
Address = N ?
V
DD
= 4.5-5.5 V, V
Verify all bytes
= 10 ?
X
No
Yes
= X + 1
X
Verify
Fail
Pass
Yes
PP
= V
DD
Fail
All pass
Write end Defective
25
Page 26

A0-A16
Figure 6-4. Byte Program Mode Timing
Program Program verify
µ
PD78P4038Y
V
V
CE
PGM
OE
D0-D7
PP
DD
V
PP
V
DD
VDD+1.5
V
DD
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
Data input Data output
Cautions 1. Add V
2. Do not allow VPP to exceed +13.5 V including overshoot.
3. Reliability problems may result if the device is inserted or pulled out while +12.5 V is applied
26
DD before VPP, and turn off the VDD after VPP.
at VPP.
Page 27

6.3 PROM Read Sequence
Follow this sequence to read the PROM contents to an external data bus (D0 to D7).
µ
PD78P4038Y
(1) Set the RESET pin to low level and add +5 V to the V
other, unused pins.
(2) Add +5 V to the VDD and VPP pins.
(3) Input the data address to be read to pins A0 to A16.
(4) Set read mode.
(5) Output the data to pins D0 to D7.
Figure 6-5 shows the timing of steps (2) to (5) above.
Figure 6-5. PROM Read Timing
A0-A16
CE (input)
OE (input)
Address input
PP pin. See (2) in Chapter 2 with regard to handling of
D0-D7
Hi-Z Hi-Z
Data output
27
Page 28

µ
PD78P4038Y
7. ERASURE CHARACTERISTICS (µPD78P4038YKK-T ONLY)
Data written in the µPD78P4038YKK-T program memory can be erased (FFH); therefore users can write other
data in the memory.
To erase the written data, expose the erasure window to light with a wavelength shorter than approx. 400 nm. Normally,
ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 254 nm is employed. The amount of light required to completely erase the data
is as follows:
2
• Intensity of ultraviolet light × erasing time: 57.6 W•s/cm
• Erasing time: About 80 minutes (When using a 12,000 µW/cm2 ultraviolet lamp. It may, however, take more time
due to lamp deterioration, dirt on the erasure window, or the like.)
The ultraviolet lamp should be placed within 2.5 cm from the erasure window during erasure. In addition, if a filter
is attached to the ultraviolet lamp, remove the filter before erasure.
min.
8. PROTECTIVE FILM COVERING THE ERASURE WINDOW (µPD78P4038YKK-T ONLY)
To prevent EPROM from being erased inadvertently by light other than that from the lamp used for erasing EPROM,
or to prevent the internal circuits other than EPROM from malfunctioning by light, stick a protective film on the erasure
window except when EPROM is to be erased.
9. QUALITY
The µPD78P4038YKK-T is not intended for use in mass-produced products; they do not have reliability high enough
for such purposes. Their use should be restricted to functional evaluation in experiment or trial manufacture.
10. SCREENING ONE-TIME PROM PRODUCTS
NEC cannot execute a complete test of one-time PROM products (µPD78P4038YGC-3B9, µPD78P4038YGC8BT, and µPD78P4038YGK-BE9) due to their structure before shipment. It is recommended that you screen (verify)
PROM products after writing necessary data into them and storing them at 125°C for 24 hours.
28
Page 29

µ
PD78P4038Y
11. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Rating Unit
Supply voltage VDD –0.5 to +7.0 V
AVDD AVSS to VDD + 0.5 V
AVSS –0.5 to +0.5 V
Input voltage VI1 –0.5 to VDD + 0.5 V
VI2 TEST/VPP pin and –0.5 to +13.5 V
P21/INTP0/A9 pin in PROM
programming mode
Output voltage VO –0.5 to VDD + 0.5 V
Output low current IOL At one pin 15 mA
Total of all output pins 100 mA
Output high current IOH At one pin –10 mA
Total of all output pins –100 mA
A/D converter reference input AVREF1 –0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
voltage
D/A converter reference input
voltage
Operating ambient temperature TA –40 to +85 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –65 to +150 °C
AVREF2 –0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
AVREF3 –0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
Caution Absolute maximum ratings are rated values beyond which physical damage will be caused to the
product; if the rated value of any of the parameters in the above table is exceeded, even
momentarily, the quality of the product may deteriorate. Always use the product within its rated
values.
29
Page 30

OPERATING CONDITIONS
• Operating ambient temperature (TA) : –40 to +85°C
• Rise time and fall time (t
r, tf) (at pins which are not specified) : 0 to 200
• Power supply voltage and clock cycle time : See Figure 11-1.
Figure 11-1. Power Supply Voltage and Clock Cycle Time
10,000
4,000
1,000
[ns]
CYK
125
100
Clock cycle time t
62.5
Guaranteed
operating
range
µ
PD78P4038Y
µ
s
CAPACITANCE (T
Parameter
Input capacitance
Output capacitance
I/O capacitance
10
01234567
A = 25°C, VDD = VSS = 0 V)
Symbol
CI
CO
CIO
f = 1 MHz
0 V on pins other than measured pins
Power supply voltage [V]
Conditions
MIN. TYP. MAX.
10
10
10
Unit
pF
pF
pF
30
Page 31

OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = +4.5 to 5.5 V, VSS = 0 V)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Resonator
Ceramic resonator
or crystal
External clock
Recommended Circuit Parameter
Oscillator frequency (fXX)
VSS1 X1 X2
C2C1
X1 input frequency (fX)
X1 X2
HCMOS
inverter
X1 input rise and fall times
(tXR, tXF)
X1 input high-level and lowlevel widths (tWXH, tWXL)
MIN.
4
4
0
10
MAX.
32
32
10
125
Unit
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
Caution When using the system clock generator, run wires in the portion surrounded by broken lines
according to the following rules to avoid effects such as stray capacitance:
• Minimize the wiring.
• Never cause the wires to cross other signal lines.
• Never cause the wires to run near a line carrying a large varying current.
• Cause the grounding point of the capacitor of the oscillator circuit to have the same potential
SS1. Never connect the capacitor to a ground pattern carrying a large current.
as V
• Never extract a signal from the oscillator.
31
Page 32

OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = 0 V)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Resonator
Ceramic resonator
or crystal
External clock
Recommended Circuit Parameter
Oscillator frequency (fXX)
VSS1 X1 X2
C2C1
X1 input frequency (fX)
X1 X2
HCMOS
inverter
X1 input rise and fall times
(tXR, tXF)
X1 input high-level and lowlevel widths (tWXH, tWXL)
MIN.
4
4
0
10
MAX.
16
16
10
125
Unit
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
Caution When using the system clock generator, run wires in the portion surrounded by broken lines
according to the following rules to avoid effects such as stray capacitance:
• Minimize the wiring.
• Never cause the wires to cross other signal lines.
• Never cause the wires to run near a line carrying a large varying current.
• Cause the grounding point of the capacitor of the oscillator circuit to have the same potential
SS1. Never connect the capacitor to a ground pattern carrying a large current.
as V
• Never extract a signal from the oscillator.
32
Page 33

µ
PD78P4038Y
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = AVSS = 0 V) (1/2)
Parameter
Input low voltage
Input high voltage
Output low voltage
Output high voltage
X1 input low current
X1 input high current
Symbol
VIL1
VIL2
VIL3
VIH1
VIH2
VIH3
VOL1
VOL2
VOL3
VOH1
VOH2
IIL
IIH
Conditions
For pins other than those described in
Notes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6
For pins described in Notes 1, 2, 3, 4,
and 6
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
For pins described in Notes 2, 3, and 4
For pins other than those described in
Notes 1 and 6
For pins described in Notes 1 and 6
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
For pins described in Notes 2, 3, and 4
IOL = 2 mA
For pins other than those described in
Note 6
IOL = 3 mA
For pins described in Note 6
IOL = 6 mA
For pins described in Note 6
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
IOL = 8 mA
For pins described in Notes 2 and 5
IOH = –2 mA
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
IOH = –5 mA
For pins described in Note 4
EXTC = 0
0 V ≤ VI ≤ VIL2
EXTC = 0
VIH2 ≤ VI ≤ VDD
MIN.
–0.3
–0.3
–0.3
0.7VDD
0.8VDD
2.2
VDD – 1.0
VDD – 1.4
TYP. MAX.
0.3VDD
0.2VDD
+0.8
VDD + 0.3
VDD + 0.3
VDD + 0.3
0.4
0.4
0.6
1.0
–30
+30
Unit
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
µ
µ
A
A
Notes 1. X1, X2, RESET, P12/ASCK2/SCK2, P20/NMI, P21/INTP0, P22/INTP1, P23/INTP2/CI, P24/INTP3,
P25/INTP4/ASCK/SCK1, P26/INTP5, P27/SI0, TEST
2. P40/AD0 to P47/AD7, P50/A8 to P57/A15
3. P60/A16 to P63/A19, P64/RD, P65/WR, P66/WAIT/HLDRQ, P67/REFRQ/HLDAK
4. P00 to P07
5. P10 to P17
6. P32/SCK0/SCL, P33/SO0/SDA
33
Page 34

µ
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = AVSS = 0 V) (2/2)
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Input leakage current
Output leakage current
VDD supply current
Pull-up resistor
Symbol
IL|
ILO
IDD1
IDD2
IDD3
RL
Conditions
0 V ≤ VI ≤ VDD
For pins other than X1 when EXTC = 0
0 V ≤ VO ≤ VDD
Operation mode fXX = 32 MHz
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
fXX = 16 MHz
VDD = +2.7 to 3.3 V
HALT mode fXX = 32 MHz
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
fXX = 16 MHz
VDD = +2.7 to 3.3 V
IDLE mode fXX = 32 MHz
(EXTC = 0) VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
fXX = 16 MHz
VDD = +2.7 to 3.3 V
VI = 0 V
MIN.
15
TYP.
25
12
13
8
MAX.
±10
±10
45
25
26
12
12
8
80
Unit
µ
µ
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
kΩ
A
A
34
Page 35

µ
PD78P4038Y
AC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = AVSS = 0 V)
(1) Read/write operation (1/2)
Parameter
Address setup time
ASTB high-level width
Address hold time (to ASTB↓)
Address hold time (to RD↑)
Delay from address to RD↓
Address float time (to RD↓)
Delay from address to data input
Delay from ASTB↓ to data input
Delay from RD↓ to data input
Delay from ASTB↓ to RD↓
Data hold time (to RD↑)
Delay from RD↑ to address active
Delay from RD↑ to ASTB↑
RD low-level width
Address hold time (to WR↑)
Delay from address to WR↓
Delay from ASTB↓ to data output
Delay from WR↓ to data output
Delay from ASTB↓ to WR↓
Symbol
tSAST
tWSTH
tHSTLA
tHRA
tDAR
tFRA
tDAID
tDSTID
tDRID
tDSTR
tHRID
tDRA
tDRST
tWRL
tHWA
tDAW
tDSTOD
tDWOD
tDSTW
Conditions
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
After program
is read
After data is
read
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
MIN.
(0.5 + a) T – 15
(0.5 + a) T – 31
(0.5 + a) T – 17
(0.5 + a) T – 40
0.5T – 24
0.5T – 34
0.5T – 14
(1 + a) T – 9
(1 + a) T – 15
0.5T – 9
0
0.5T – 8
0.5T – 12
1.5T – 8
1.5T – 12
0.5T – 17
(1.5 + n) T – 30
(1.5 + n) T – 40
0.5T – 14
(1 + a) T – 5
(1 + a) T – 15
0.5T – 9
MAX.
0
(2.5 + a + n) T – 37
(2.5 + a + n) T – 52
(2 + n) T – 40
(2 + n) T – 60
(1.5 + n) T – 50
(1.5 + n) T – 70
0.5T + 19
0.5T + 35
0.5T – 11
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Remarks T: t
a: 1 (during address wait), otherwise, 0
n: Number of wait states (n ≥ 0)
CYK (system clock cycle time)
35
Page 36

(1) Read/write operation (2/2)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Data setup time (to WR↑)
Data hold time (to WR↑)
Delay from WR↑ to ASTB↑
WR low-level width
Note
Symbol
tSODW
tHWOD
tDWST
tWWL
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
Note The hold time includes the time during which V
CL = 50 pF and RL = 4.7 kΩ.
Remarks T: t
CYK (system clock cycle time)
n: Number of wait states (n ≥ 0)
(2) Bus hold timing
Parameter
Delay from HLDRQ↑ to float
Delay from HLDRQ↑ to HLDAK↑
Delay from float to HLDAK↑
Delay from HLDRQ↓ to HLDAK↓
Delay from HLDAK↓ to active
Symbol
tFHQC
tDHQHHAH
tDCFHA
tDHQLHAL
tDHAC
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
Conditions
MIN.
(1.5 + n) T – 30
(1.5 + n) T – 40
0.5T – 5
0.5T – 25
0.5T – 12
(1.5 + n) T – 30
(1.5 + n) T – 40
OH1 and VOL1 are held under the load conditions of
MIN.
1T – 20
1T – 30
MAX.Conditions
MAX.
(6 + a + n) T + 50
(7 + a + n) T + 30
(7 + a + n) T + 40
1T + 30
2T + 40
2T + 60
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Remarks T: t
36
CYK (system clock cycle time)
a: 1 (during address wait), otherwise, 0
n: Number of wait states (n ≥ 0)
Page 37

(3) External wait timing
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Delay from address to WAIT↓ input
Delay from ASTB↓ to WAIT↓ input
Hold time from ASTB↓ to WAIT
Delay from ASTB↓ to WAIT↑
Delay from RD↓ to WAIT↓ input
Hold time from RD↓ to WAIT↓
Delay from RD↓ to WAIT↑
Delay from WAIT↑ to data input
Delay from WAIT↑ to WR↑
Delay from WAIT↑ to RD↑
Delay from WR↓ to WAIT↓ input
Hold time from WR↓ to WAIT
Delay from WR↓ to WAIT↑
Symbol
tDAWT
tDSTWT
tHSTWTH
tDSTWTH
tDRWTL
tHRWT
tDRWTH
tDWTID
tDWTW
tDWTR
tDWWTL
tHWWT
tDWWTH
Conditions
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
MIN.
(0.5 + n) T + 5
(0.5 + n) T +10
nT + 5
nT + 10
0.5T
0.5T
nT + 5
nT + 10
MAX.
(2 + a) T – 40
(2 + a) T – 60
1.5T – 40
1.5T – 60
(1.5 + n) T – 40
(1.5 + n) T – 60
T – 50
T – 70
(1 + n) T – 40
(1 + n) T – 60
0.5T – 5
0.5T – 10
T – 50
T – 75
(1 + n) T – 40
(1 + n) T – 70
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Remarks T: t
CYK (system clock cycle time)
a: 1 (during address wait), otherwise, 0
n: Number of wait states (n ≥ 0)
(4) Refresh timing
Parameter
Random read/write cycle time
REFRQ low-level pulse width
Delay from ASTB↓ to REFRQ
Delay from RD↑ to REFRQ
Delay from WR↑ to REFRQ
Delay from REFRQ↑ to ASTB
REFRQ high-level pulse width
Symbol
tRC
tWRFQL
tDSTRFQ
tDRRFQ
tDWRFQ
tDRFQST
tWRFQH
Remark T: tCYK (system clock cycle time)
Conditions
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
3T
1.5T – 25
1.5T – 30
0.5T – 9
1.5T – 9
1.5T – 9
0.5T – 15
1.5T – 25
1.5T – 30
MAX.MIN.
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
37
Page 38

SERIAL OPERATION (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, AVSS = VSS = 0 V)
(1) CSI
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Serial clock cycle time (SCK0)
Serial clock low-level width
(SCK0)
Serial clock high-level width
(SCK0)
SI0 setup time (to SCK0↑)
SI0 hold time (to SCK0↑)
SO0 output delay time
(to SCK0↓)
Symbol
tCYSK0
tWSKL0
tWSKH0
tSSSK0
tHSSK0
tDSBSK1
tDSBSK2
Input External clock
Output
Input External clock
Output
Input External clock
Output
CMOS push-pull output
(3-wire serial I/O mode)
Open-drain output
(2-wire serial I/O mode), RL = 1 kΩ
Conditions
When SCK0 and SO0 are CMOS I/O
When SCK0 and SO0 are CMOS I/O
When SCK0 and SO0 are CMOS I/O
Remarks 1. The values in this table are those when CL is 100 pF.
2. T : Serial clock cycle set by software. The minimum value is 16/f
3. fXX : Oscillator frequency
MIN.
10/fXX + 380
T
5/fXX + 150
0.5T – 40
5/fXX + 150
0.5T – 40
40
5/fXX + 40
0
0
XX.
MAX.
5/fXX + 150
5/fXX + 400
Unit
ns
µ
ns
µ
ns
µ
ns
ns
ns
ns
s
s
s
2
C
(2) I
Parameter
SCL clock frequency
Time to hold low SCL clock
Time to hold high SCL clock
Data hold time
Data setup time
Rise time of SDA or SCL
signal
Fall time of SDA or SCL signal
Load capacitance of each bus
line
Symbol
fSCL
tLOW
tHIGH
tHD; DAT
tSU; DAT
tR
tF
Cb
I2C Bus in Standard Mode
fXX = 4 to 32 MHz
MIN. MAX.
0 100
4.7
4.0
300
250
1,000
300
400
I2C Bus in Standard Mode
fXX = 8 to 32 MHz
MIN. MAX.
0 400
1.3
0.6
300 900
100
20 + 0.1Cb 300
20 + 0.1Cb 300
400
Unit
kHz
µ
µ
ns
ns
ns
ns
pF
s
s
38
Page 39

(3) IOE1, IOE2
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Serial clock cycle time
(SCK1, SCK2)
Serial clock low-level width
(SCK1, SCK2)
Serial clock high-level width
(SCK1, SCK2)
Setup time for SI1 and SI2
(to SCK1, SCK2↑)
Hold time for SI1 and SI2
(to SCK1, SCK2↑)
Output delay time for SO1 and
SO2 (to SCK1, SCK2↓)
Output hold time for SO1 and
SO2 (to SCK1, SCK2↑)
Symbol
tCYSK1
tWSKL1
tWSKH1
tSSSK1
tHSSK1
tDSOSK
tHSOSK
Conditions
Input VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
Output Internal, divided by 16
Input VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
Output Internal, divided by 16
Input VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
Output Internal, divided by 16
When data is transferred
Remarks 1. The values in this table are those when CL is 100 pF.
2. T: Serial clock cycle set by software. The minimum value is 16/fXX.
MIN.
250
500
T
85
210
0.5T – 40
85
210
0.5T – 40
40
40
0
0.5tCYSK1 – 40
MAX.
50
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
(4) UART, UART2
Parameter
ASCK clock input cycle time
ASCK clock low-level width
ASCK clock high-level width
Symbol
tCYASK
tWASKL
tWASKH
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
MIN.
125
250
52.5
85
52.5
85
MAX.Conditions
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
39
Page 40

CLOCK OUTPUT OPERATION
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
CLKOUT cycle time
CLKOUT low-level width
CLKOUT high-level width
CLKOUT rise time
CLKOUT fall time
Symbol
tCYCL
tCLL
tCLH
tCLR
tCLF
Conditions
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
MIN.
0.5tCYCL – 10
0.5tCYCL – 20
0.5tCYCL – 10
0.5tCYCL – 20
Remarks n: Divided frequency ratio set by software in the CPU (n = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16)
T: tCYK (system clock cycle time)
OTHER OPERATIONS
Parameter
NMI low-level width
NMI high-level width
INTP0 low-level width
INTP0 high-level width
Low-level width for INTP1-
INTP3 and CI
High-level width for INTP1-
INTP3 and CI
Low-level width for INTP4 and
INTP5
High-level width for INTP4 and
INTP5
RESET low-level width
RESET high-level width
Symbol
tWNIL
tWNIH
tWIT0L
tWIT0H
tWIT1L
tWIT1H
tWIT2L
tWIT2H
tWRSL
tWRSH
MIN.
4tCYSMP
4tCYSMP
4tCYCPU
4tCYCPU
nT
10
10
10
10
10
10
MAX.
10
20
10
20
MAX.Conditions
Unit
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
Unit
µ
µ
ns
ns
ns
ns
µ
µ
µ
µ
s
s
s
s
s
s
Remarks t
40
CYSMP: Sampling clock set by software
tCYCPU: CPU operation clock set by software in the CPU
Page 41

A/D CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS
A = –40 to +85°C, VDD = AVDD = AVREF1 = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = AVSS = 0 V)
(T
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Resolution
Total error
Linearity calibration
Quantization error
Conversion time
Sampling time
Analog input voltage
Analog input impedance
AVREF1 current
AVDD supply current
Note
Note
Symbol
tCONV
tSAMP
VIAN
RAN
AIREF1
AIDD1
AIDD2
Conditions
VDD = AVDD = +5.0 V ± 10%
VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 4.5 V
TA = -10 to +85°C
FR = 1
FR = 0
FR = 1
FR = 0
fXX = 32 MHz, CS = 1
STOP mode, CS = 0
MIN.
8
120
180
24
36
–0.3
TYP.
1,000
0.5
2.0
1.0
AV
MAX.
1.0
1.0
0.8
±1/2
REF1
+ 0.3
1.5
5.0
20
Note Quantization error is not included. This parameter is indicated as the ratio to the full-scale value.
Unit
bit
%
%
%
LSB
tCYK
tCYK
tCYK
tCYK
V
MΩ
mA
mA
µ
A
Remark t
CYK: System clock cycle time
41
Page 42

µ
PD78P4038Y
D/A CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V, VSS = AVSS = 0 V)
Parameter
Resolution
Total error
Settling time
Output resistance
Analog reference voltage
Resistance of AVREF2 and
AVREF3
Reference power supply
input current
Symbol
RO
AVREF2
AVREF3
RAIREF
AIREF2
AIREF3
Conditions
Load conditions: VDD = AVDD = AVREF2
4 MΩ, 30 pF = +2.7 to 5.5 V
AVREF3 = 0 V
VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V
AVREF2 = 0.75V
AVREF3 = 0.25V
Load conditions: VDD = AVDD = AVREF2
2 MΩ, 30 pF = +2.7 to 5.5 V
AVREF3 = 0 V
VDD = AVDD = +2.7 to 5.5 V
AVREF2 = 0.75V
AVREF3 = 0.25V
Load conditions: 2 MΩ, 30 pF
DACS0, 1 = 55 H
DACS0, 1 = 55 H
DD
DD
DD
DD
MIN.
8
0.75VDD
0
4
0
–5
TYP.
10
8
MAX.
0.6
0.8
0.8
1.0
10
VDD
0.25VDD
5
0
Unit
bit
%
%
%
%
µ
kΩ
V
V
kΩ
mA
mA
s
42
Page 43

DATA RETENTION CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85°C)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
Data retention voltage
Data retention current
VDD rise time
VDD fall time
VDD hold time
(to STOP mode setting)
STOP clear signal input time
Oscillation settling time
Input low voltage
Input high voltage
Symbol
VDDDR
IDDDR
tRVD
tFVD
tHVD
tDREL
tWAIT
VIL
VIH
Conditions
STOP mode
VDDDR = +2.7 to 5.5 V
VDDDR = +2.5 V
Crystal
Ceramic resonator
Specific pins
Note
MIN.
2.5
200
200
0
0
30
5
0
0.9VDDDR
TYP.
30
10
MAX.
5.5
50
40
0.1VDDDR
VDDDR
Note RESET, P20/NMI, P21/INTP0, P22/INTP1, P23/INTP2/CI, P24/INTP3, P25/INTP4/ASCK/SCK1,
P26/INTP5, P27/SI0, P32/SCK0/SCL, and P33/SO0/SDA pins
AC TIMING TEST POINTS
V
DD
- 1 V
0.45 V
0.8VDD or 2.2 V
0.8 V
0.8VDD or 2.2 V
Test points
0.8 V
Unit
V
µ
µ
µ
µ
ms
ms
ms
ms
V
V
A
A
s
s
43
Page 44

TIMING WAVEFORM
(1) Read operation
ASTB
A8-A19
AD0-AD7
RD
t
WSTH
t
SAST
µ
PD78P4038Y
t
t
DSTID
t
HSTLA
t
DAID
t
t
DSTR
t
DAR
FRA
t
DRID
DRST
t
HRA
t
t
HRID
DRA
(2) Write operation
ASTB
A8-A19
AD0-AD7
WR
t
WSTH
t
SAST
t
DAW
t
DSTW
t
HSTLA
t
DSTOD
t
DWOD
t
t
WRL
WWL
t
SODW
t
DWST
t
HWA
t
HWOD
44
Page 45

HOLD TIMING
ADTB, A8-A19,
AD0-AD7, RD, WR
t
FHQC
t
DCFHA
HLDRQ
t
DHQHHAH
HLDAK
EXTERNAL WAIT SIGNAL INPUT TIMING
(1) Read operation
ASTB
t
DSTWT
t
DSTWTH
t
HSTWTH
t
DHQLHAL
t
DHAC
µ
PD78P4038Y
A8-A19
AD0-AD7
RD
WAIT
(2) Write operation
ASTB
A8-A19
t
DAWT
t
DSTWT
t
DRWTL
t
DSTWTH
t
HSTWTH
t
HRWT
t
DRWTH
t
DWTID
t
DWTR
AD0-AD7
WR
WAIT
t
DAWT
t
DWWTL
t
HWWT
t
DWWTH
t
DWTW
45
Page 46

REFRESH TIMING WAVEFORM
(1) Random read/write cycle
t
RC
ASTB
WR
t
RC
t
RC
t
RC
RD
(2) When refresh memory is accessed for a read and write at the same time
ASTB
RD, WR
µ
PD78P4038Y
t
RC
REFRQ
(3) Refresh after a read
ASTB
RD
REFRQ
(4) Refresh after a write
ASTB
tDSTRFQ tDRFQST
tWRFQH
tWRFQL
t
DRRFQ
t
WRFQL
t
DRFQST
46
tDRFQST
WR
tDWRFQ
REFRQ
tWRFQL
Page 47

SERIAL OPERATION
(1) CSI
SCK
t
WSKL0
t
CYSK0
t
WSKH0
SSSK0tHSSK0
t
µ
PD78P4038Y
SI
SO
2
C
(2) I
SCL
SDA
(3) IOE1, IOE2
SCK
Input data
t
DSBSK1
Output data
t
t
WSKL1
HIGH
t
CYSK1
t
LOW
t
WSKH1
t
SU;DAT
SSSK1tHSSK1
t
t
R
t
F
t
HD;DAT
SI
SO
(4) UART, UART2
ASCK,
ASCK2
t
WASKH
t
CYASK
t
DSOSK
Output data
t
WASKL
t
HSOSK
Input data
47
Page 48

CLOCK OUTPUT TIMING
CLKOUT
INTERRUPT INPUT TIMING
NMI
µ
PD78P4038Y
t
CLH
t
CLR
t
CYCL
t
WNIH
t
CLL
t
CLF
t
WNIL
INTP0
CI,
INTP1-INTP3
INTP4, INTP5
RESET INPUT TIMING
t
WIT0H
t
WIT1H
t
WIT2H
t
WIT0L
t
WIT1L
t
WIT2L
tWRSH tWRSL
48
RESET
Page 49

EXTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
tWXH tWXL
X1
DATA RETENTION CHARACTERISTICS
STOP mode setting
tCYX
µ
PD78P4038Y
tXFtXR
VDD
tHVD tFVD tRVD
RESET
NMI
(Clearing by falling edge)
NMI
(Clearing by rising edge)
V
DDDR
tDREL
tWAIT
49
Page 50

DC PROGRAMMING CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25 ± 5°C, VSS = 0 V)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Parameter
High-level input
voltage
Low-level input
voltage
Input leakage current
High-level output
voltage
Low-level output
voltage
Output leakage
current
VDDP supply voltage
VPP supply voltage
VDDP supply current
VPP supply current
Symbol
VIH
VIL
ILIP
VOH
VOL
ILO
VDDP
VPP
IDD
IPP
Symbol
VIH
VIL
ILI
VOH
VOL
–
VCC
VPP
IDD
IPP
Note 1
Conditions
0 ≤ VI ≤ VDDP
IOH = –400 µA
IOL = 2.1 mA
0 ≤ VO ≤ VDDP, OE = VIH
Program memory write mode
Program memory read mode
Program memory write mode
Program memory read mode
Program memory write mode
Program memory read mode
Program memory write mode
Program memory read mode
Note 2
MIN.
2.2
-0.3
2.4
6.25
4.5
12.2
TYP.
6.5
5.0
12.5
VPP = VDDP
10
10
5
1.0
MAX.
VDDP + 0.3
0.8
±10
0.45
±10
6.75
5.5
12.8
40
40
50
100
Unit
V
V
µ
A
V
V
µ
A
V
V
V
V
mA
mA
mA
µ
A
Notes 1. Symbols for the corresponding µPD27C1001A
2. The V
DDP represents the VDD pin as viewed in the programming mode.
50
Page 51

µ
PD78P4038Y
AC PROGRAMMING CHARACTERISTICS (T
PROM Write Mode (Page Program Mode)
Note 1
Parameter
Address setup time
CE set time
Input data setup time
Address hold time
Input data hold time
Output data hold time
VPP setup time
VDDP setup time
Initial program pulse width
OE set time
Valid data delay time from OE
OE pulse width in the data latch
PGM setup time
CE hold time
OE hold time
Symbol
tVDS
tPGMS
tAS
tCES
tDS
tAH
tAHL
tAHV
tDH
tDF
tVPS
Note 2
tPW
tOES
tOE
tLW
tCEH
tOEH
A = 25 ± 5°C, VSS = 0 V)
Conditions
MIN.
0.095
TYP.
2
2
2
2
2
0
2
0
2
2
0.1
2
1
1
2
2
2
MAX.
130
0.105
2
Unit
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
ns
µ
µ
ms
µ
ns
µ
µ
µ
µ
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
Notes 1. These symbols (except tVDS) correspond to those of the corresponding µPD27C1001A.
µ
2. For
PD27C1001A, read tVDS as tVCS.
51
Page 52

PROM Write Mode (Byte Program Mode)
Note 1
Parameter
Address setup time
CE set time
Input data setup time
Address hold time
Input data hold time
Output data hold time
VPP setup time
VDDP setup time
Initial program pulse width
OE set time
Valid data delay time from OE
Symbol
tVDS
tAS
tCES
tDS
tAH
tDH
tDF
tVPS
Note 2
tPW
tOES
tOE
Conditions MAX.
MIN.
2
2
2
2
2
0
2
2
0.095
2
TYP.
0.1
1
Notes 1. These symbols (except tVDS) correspond to those of the corresponding µPD27C1001A.
2. For µPD27C1001A, read tVDS as tVCS.
µ
PD78P4038Y
Unit
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
130
0.105
2
ns
µ
µ
ms
µ
ns
s
s
s
PROM Read Mode
Parameter
Data output time from address
Delay from CE ↓ to data output
Delay from OE ↓ to data output
Data hold time to OE↑ or CE ↑
Data hold time to address
Note 2
Symbol
tACC
tCE
tOE
tDF
tOH
Conditions
CE = OE = VIL
OE = VIL
CE = VIL
CE = VIL or OE = VIL
CE = OE = VIL
Note 1
Notes 1. These symbols correspond to those of the corresponding
2. tDF is the time measured from when either OE or CE reaches VIH, whichever is faster.
MIN.
0
0
µ
PD27C1001A.
TYP.
1
1
MAX.
200
2
2
60
Unit
ns
µ
µ
ns
ns
s
s
52
Page 53

PROM Write Mode Timing (Page Program Mode)
Page data latch Page program Program verify
A2-A16
t
V
V
DDP
CE
PGM
OE
AS
A0, A1
t
DS
D0-D7
PP
V
V
DDP
+ 1.5
V
Hi-Z Hi-ZHi-Z
t
VPS
V
PP
DDP
t
VDS
DDP
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
t
LW
t
AHL
t
DH
Data input
t
PGMS
µ
PD78P4038Y
t
AHV
t
DF
Data
t
OE
output
t
CES
t
CEH
t
PW
t
OES
t
AH
t
OEH
53
Page 54

PROM Write Mode Timing (Byte Program Mode)
Program Program verify
A0-A16
t
AS
µ
PD78P4038Y
t
DF
D0-D7
V
PP
V
V
DDP
+ 1.5
V
DDP
V
CE
PGM
OE
Cautions 1. V
2. VPP including overshoot must not exceed +13.5 V.
3. Plugging in or out the board with the V
reliability.
Hi-Z Hi-ZHi-Z
t
DS
PP
V
DDP
DDP
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
DDP must be applied before VPP, and must be cut after VPP.
t
t
t
t
VPS
VDS
CES
DS
Data input
t
PW
t
DH
t
OES
PP pin supplied with 12.5 V may adversely affect its
t
OE
Data output
t
AH
PROM Read Mode Timing
A0-A16
CE
OE
D0-D7
Notes 1. For reading within t
DF is the time measured from when either OE or CE reaches VIH, whichever is faster.
2. t
54
Valid address
t
CE
Note 2
t
Note 1
t
ACC
Hi-Z Hi-Z
ACC, the delay of the OE input from falling edge of CE must be within tACC-tOE.
Note 1
t
OE
t
OH
Data output
DF
Page 55

12. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
80 PIN PLASTIC QFP (14x14)
µ
PD78P4038Y
A
B
61
60
41
40
CD
80
1
20
21
F
G
M
H
I
P
J
K
N
L
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.13 mm (0.005 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
detail of lead end
S
Q
R
M
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 17.2±0.4 0.677±0.016
B 14.0±0.2 0.551
C 14.0±0.2 0.551
D 17.2±0.4 0.677±0.016
F 0.825 0.032
G 0.825 0.032
H 0.30±0.10 0.012
I 0.13 0.005
J 0.65 (T.P.) 0.026 (T.P.)
K 1.6±0.2 0.063±0.008
L 0.8±0.2 0.031
M 0.15 0.006
N 0.10 0.004
P
Q 0.1±0.1 0.004±0.004
R5°±5° 5°±5°
S 3.0 MAX. 0.119 MAX.
+0.10
–0.05
2.7±0.1 0.106
+0.009
–0.008
+0.009
–0.008
+0.004
–0.005
+0.009
–0.008
+0.004
–0.003
+0.005
–0.004
S80GC-65-3B9-5
55
Page 56

80 PIN PLASTIC QFP (14×14)
µ
PD78P4038Y
A
B
4160
4061
detail of lead end
2180
201
F
G
H
M
I
P
N
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.13 mm (0.005 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
C D
S
R
Q
J
K
M
L
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 17.20±0.20 0.677±0.008
+0.009
B 14.00±0.20 0.551
C 14.00±0.20 0.551
D 17.20±0.20 0.677±0.008
F 0.825 0.032
G 0.825 0.032
H 0.32±0.06 0.013
I 0.13 0.005
J 0.65 (T.P.) 0.026 (T.P.)
K 1.60±0.20 0.063±0.008
L 0.80±0.20 0.031
+7°
–3°
+0.03
–0.07
M 0.17 0.007
N 0.10 0.004
P 1.40±0.10 0.055±0.004
Q 0.125±0.075 0.005±0.003
R3° 3°
S 1.70 MAX. 0.067 MAX.
+0.009
–0.008
–0.008
+0.009
–0.008
+0.002
–0.003
+0.009
–0.008
+0.001
–0.003
+7°
–3°
P80GC-65-8BT
56
Page 57

80 PIN PLASTIC TQFP (FINE PITCH) (12×12)
A
B
µ
PD78P4038Y
60
61
80
1
41
40
21
20
F
G
HI
M
J
P
N
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.10 mm (0.004 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
C D S
K
M
L
detail of lead end
QR
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 14.00±0.20 0.551±0.008
B 12.00±0.20 0.472
C 12.00±0.20 0.472
D 14.00±0.20 0.551±0.008
F
1.25 0.049
G 1.25
0.10
+0.05
–0.04
+0.055
–0.045
H 0.22 0.009±0.002
I
J 0.50 (T.P.)
K 1.00±0.20 0.039
L 0.50±0.20 0.020
M 0.145 0.006±0.002
N 0.10 0.004
P 1.05 0.041
Q 0.10±0.05
R5°±5° 5°±5°
S 1.27 MAX. 0.050 MAX.
+0.009
–0.008
+0.009
–0.008
0.049
0.004
0.020 (T.P.)
+0.009
–0.008
+0.008
–0.009
0.004±0.002
P80GK-50-BE9-5
57
Page 58

80 PIN CERAMIC WQFN
µ
PD78P4038Y
A
B
T
U1
U
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.06
mm (0.003 inch) of its true position (T.P.) at
maximum material condition.
K
C
D
W
G
F
Z
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
B
C
D
F
G
H
I
J
K
Q
R
S
T R 2.0 R 0.079
U
U1 2.1 0.083
W
Z 0.10 0.004
14.0±0.2
13.6
13.6
14.0±0.2
1.84
3.6 MAX.
0.45±0.10
0.06
0.65 (T.P.)
1.0±0.15
C 0.3
0.825
0.825
9.0
0.75±0.15
M
IH
J
X80KW-65A-1
0.551±0.008
0.535
0.535
0.551±0.008
0.072
0.142 MAX.
+0.004
0.018
–0.005
0.003
0.024 (T.P.)
+0.007
0.039
–0.006
C 0.012
0.032
0.032
0.354
+0.006
0.030
–0.007
Q
80
1
S
R
58
Page 59

µ
PD78P4038Y
13. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
The conditions listed below shall be met when soldering the µPD78P4038Y.
For details of the recommended soldering conditions, refer to our document Semiconductor Device Mounting
Technology Manual (C10535E).
Please consult with our sales offices in case any other soldering process is used, or in case soldering is done under
different conditions.
Table 13-1. Soldering Conditions for Surface-Mount Devices (1/2)
µ
PD78P4038YGC-3B9: 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 2.7 mm)
(1)
Soldering Process Soldering Conditions Symbol
Infrared ray reflow Peak package's surface temperature: 235°C IR35-00-3
Reflow time: 30 seconds or less (210°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 3
VPS Peak package's surface temperature: 215°C VP15-00-3
Wave soldering Solder temperature: 260°C or less WS60-00-1
Partial heating method Terminal temperature: 300°C or less –
Reflow time: 40 seconds or less (200°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 3
Flow time: 10 seconds or less
Number of flow processes: 1
Preheating temperature :
Heat time: 3 seconds or less (for one side of a device)
120°C max.
(measured on the package surface)
Caution Do not apply two or more different soldering methods to one chip (except for partial heating
method for terminal sections).
(2)µPD78P4038YGC-8BT: 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14 × 1.4 mm)
Soldering Process Soldering Conditions Symbol
Infrared ray reflow Peak package's surface temperature: 235°C IR35-00-2
Reflow time: 30 seconds or less (210°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 2
VPS Peak package's surface temperature: 215°C VP15-00-2
Wave soldering Solder temperature: 260°C or less WS60-00-1
Partial heating method Terminal temperature: 300°C or less –
Reflow time: 40 seconds or less (200°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 2
Flow time: 10 seconds or less
Number of flow processes: 1
Preheating temperature :
Heat time: 3 seconds or less (for one side of a device)
120°C max.
(measured on the package surface)
Caution Do not apply two or more different soldering methods to one chip (except for partial heating
method for terminal sections).
59
Page 60

Table 13-1. Soldering Conditions for Surface-Mount Devices (2/2)
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9: 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
(3)
µ
PD78P4038Y
Soldering Process
Infrared ray reflow
VPS
Partial heating method
Soldering Conditions
Peak package’s surface temperature: 235°C
Reflow time: 30 seconds or less (210°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 2
Exposure limit: 7 days
afterward)
<Caution>
Non-heat-resistant trays, such as magazine and taping trays, cannot be
baked before unpacking.
Peak package’s surface temperature: 215°C
Reflow time: 40 seconds or less (200°C or more)
Maximum allowable number of reflow processes: 2
Exposure limit: 7 days
afterward)
<Caution>
Non-heat-resistant trays, such as magazine and taping trays, cannot be
baked before unpacking.
Terminal temperature: 300°C or less
Heat time: 3 seconds or less (for one side of a device)
Note
(10 hours of pre-baking is required at 125°C
Note
(10 hours of pre-baking is required at 125°C
Symbol
IR35-107-2
VP15-107-2
–
Note Maximum number of days during which the product can be stored at a temperature of 25°C and a relative
humidity of 65% or less after dry-pack package is opened.
Caution Do not apply two or more different soldering methods to one chip (except for partial heating
method for terminal sections).
60
Page 61

µ
APPENDIX A DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
The following development tools are available for system development using the µPD78P4038Y.
See also (5).
(1) Language processing software
RA78K4 Assembler package for all 78K/IV Series models
CC78K4 C compiler package for all 78K/IV Series models
DF784038 Device file for µPD784038Y Subseries models
CC78K4-L C compiler library source file for all 78K/IV Series models
(2) PROM write tools
PG-1500 PROM programmer
PA-78P4026GC Programmer adaptor, connects to PG-1500
PA-78P4038GK
PA-78P4026KK
PG-1500 controller Control program for PG-1500
PD78P4038Y
(3) Debugging tools
• When using the in-circuit emulator IE-78K4-NS
IE-78K4-NS In-circuit emulator for all 78K/IV Series models
IE-70000-MC-PS-B Power supply unit for IE-78K4-NS
IE-70000-98-IF-C Interface adapter when the PC-9800 series computer (other than a notebook)
is used as the host machine
IE-70000-CD-IF PC card and interface cable when a PC-9800 series notebook is used as the
host machine
IE-70000-PC-IF-C Interface adapter when the IBM PC/ATTM or compatible is used as the host
machine
IE-784038-NS-EM1
NP-80GC Emulation probe for 80-pin plastic QFP (GC-3B9 and GC-8BT types)
NP-80GK
EV-9200GC-80 Socket for mounting on target system board made for 80-pin plastic QFP
TGK-080SDW Adapter for mounting on target system board made for 80-pin plastic TQFP
EV-9900 Tool used to remove the µPD78P4038YKK-T from the EV-9200GC-80
ID78K4-NS Integrated debugger for IE-78K4-NS
SM78K4-NS System simulator for all 78K/IV Series models
DF784038 Device file for µPD784038Y Subseries models
Note
Note
Emulation board for evaluating µPD784038Y Subseries models
Emulation probe for 80-pin plastic TQFP (GK-BE9 type)
(GC-3B9 and GC-8BT types)
(fine pitch) (GK-BE9 type)
Note Under development
61
Page 62

µ
PD78P4038Y
• When using the in-circuit emulator IE-784000-R
IE-784000-R In-circuit emulator for all 78K/IV Series models
IE-70000-98-IF-B Interface adapter when the PC-9800 series computer (other than a notebook)
IE-70000-98-IF-C is used as the host machine
IE-70000-98N-IF Interface adapter and cable when a PC-9800 series notebook is used as the
host machine
IE-70000-PC-IF-B Interface adapter when the IBM PC/AT or compatible is used as the host
IE-70000-PC-IF-C machine
IE-78000-R-SV3 Interface adapter and cable when the EWS is used as the host machine
Note
Note
Emulation board for evaluating µPD784038Y Subseries models
Conversion board for 80 pins to use the IE-784038-NS-EM1 on the
IE-784000-R. The board is not needed when the conventional product
IE-784038-R-EM1 is used.
µ
PD784038Y Subseries
(GC-3B9 and GC-8BT types)
(fine pitch) (GK-BE9 type)
IE-784038-NS-EM1
IE-784038-R-EM1
IE-78400-R-EM Emulation board for all 78K/IV Series models
IE-78K4-R-EX2
EP-78230GC-R Emulation probe for 80-pin plastic QFP (GC-3B9 and GC-8BT types)
EP-78054GK-R Emulation probe for 80-pin plastic TQFP (fine pitch) (GK-BE9 type) for all
EV-9200GC-80 Socket for mounting on target system board made for 80-pin plastic QFP
TGK-080SDW Adapter for mounting on target system board made for 80-pin plastic TQFP
EV-9900 Tool used to remove the µPD78P4038YKK-T from the EV-9200GC-80
ID78K4 Integrated debugger for IE-784000-R
SM78K4 System simulator for all 78K/IV Series models
DF784038 Device file for µPD784038Y Subseries models
Note Under development
(4) Real-time OS
RX78K/IV Real-time OS for 78K/IV Series models
MX78K4 OS for 78K/IV Series models
62
Page 63

µ
PD78P4038Y
(5) Notes when using development tools
• The ID78K-NS, ID78K4, and SM78K4 can be used in combination with the DF784038.
• The CC78K4 and RX78K/IV can be used in combination with the RA78K4 and DF784038.
• The NP-80GC is a product from Naito Densei Machida Mfg. Co., Ltd. (044-822-3813). Consult the NEC sales
representative for purchasing.
• The TGK-080SDW is a product from TOKYO ELETECH CORPORATION.
Refer to: Daimaru Kogyo, Ltd.
Tokyo Electronic Components Division (03-3820-7112)
Osaka Electronic Components Division (06-244-6672)
• The host machines and operating systems corresponding to each software are shown below.
Host Machine PC EWS
[OS]
Software NEWSTM (RISC) [NEWS-OSTM]
RA78K4
CC78K4
PG-1500 controller
ID78K4-NS –
ID78K4
SM78K4 –
RX78K/IV
MX78K4
PC-9800 Series [WindowsTM] HP9000 Series 700TM [HP-UXTM]
IBM PC/AT and Compatibles [Windows]
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
SPARCstationTM [SunOSTM]
–
Note Software under MS-DOS
63
Page 64

µ
PD78P4038Y
APPENDIX B
CONVERSION SOCKET (EV-9200GC-80) AND CONVERSION ADAPTER (TGK-080SDW)
(1) Conversion socket (EV-9200GC-80) package drawings and recommended pattern to mount the socket
Connect the µPD78P4038YKK-T (80-pin ceramic WQFN (14 × 14 mm)) and EP-78230GC-R to the circuit board
in combination with the EV-9200GC-80.
Figure B-1. Package Drawings of EV-9200GC-80 (Reference) (unit: mm)
Based on EV-9200GC-80
(1) Package drawing (in mm)
E
D
C
No.1 pin index
A
B
EV-9200GC-80
1
F
M
N O
R
J
S
L
K
Q
P
64
G
H
I
EV-9200GC-80-G0E
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
O
N
P
Q
R
S
18.0
14.4
14.4
18.0
4-C 2.0
0.8
6.0
16.0
18.7
6.0
16.0
18.7
8.2
8.0
2.5
2.0
0.35
φ
2.3
1.5
0.709
0.567
0.567
0.709
4-C 0.079
0.031
0.236
0.63
0.736
0.236
0.63
0.736
0.323
0.315
0.098
0.079
0.014
φ
0.091
0.059
Page 65

µ
PD78P4038Y
Figure B-2. Recommended Pattern to Mount EV-9200GC-80 on a Substrate (Reference) (unit: mm)
Based on EV-9200GC-80
(2) Pad drawing (in mm)
G
J
K
F
E
D
L
C
B
A
HI
EV-9200GC-80-P1E
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
+0.001
–0.002
+0.001
–0.002
0.776
0.591
0.591
0.776
0.236
0.236
0.014
φ
0.093
φ
0.091
φ
0.062
+0.003
–0.002
+0.003
–0.002
+0.001
–0.001
+0.001
–0.002
+0.001
–0.002
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
Caution
19.7
15.0
0.65±0.02 × 19=12.35±0.05
0.65±0.02 × 19=12.35±0.05
15.0
19.7
6.0±0.05
6.0±0.05
0.35±0.02
φ
2.36±0.03
φ
2.3
φ
1.57±0.03
Dimensions of mount pad for EV-9200 and that for target
0.026 × 0.748=0.486
0.026 0.748=0.486
device (QFP) may be different in some parts. For the
recommended mount pad dimensions for QFP, refer to
"SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE MOUNTING
TECHNOLOGY MANUAL" (C10535E).
+0.003
–0.002
+0.003
–0.002
65
Page 66

(2) Conversion adapter (TGK-080SDW) package drawings
Connect the EP-78054GK-R to the circuit board in combination with the TGK-080SDW.
Figure B-3. Package Drawings of TGK-080SDW (Reference) (unit: mm)
TGK-080SDW (TQPACK080SD + TQSOCKET080SDW)
Package dimension (unit: mm)
A
B
T
H
EFG P
C
D
M2 screw
S
IJJJ LLLM
k
K
f
j
i
h
l
Protrusion : 4 places
n o
m
R
Q
Q
Q
O
O
O
N
g
v
u
r
t
s
q
p
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 18.0 0.709
B
11.77
C
0.5x19=9.5 0.020x0.748=0.374
D
0.5
E
0.5x19=9.5 0.020x0.748=0.374
F 11.77 0.463
G 18.0 0.709
H
0.5
I 1.58 0.062
J 1.2 0.047
K 7.64 0.301
L 1.2 0.047
M
1.58
N 1.58 0.062
O 1.2
P 7.64 0.301
Q 1.2 0.047
R 1.58 0.062
φ
S 3.55 0.140
T C 2.0 C 0.079
U 12.31
V 10.17 0.400
W 6.8 0.268
X 8.24 0.324
Y 14.8 0.583
Z 1.4±0.2 0.055±0.008
0.463
0.020
0.020
0.062
0.047
φ
0.485
U
V
c
d
W
X
Y
µ
PD78P4038Y
e
b
a
Z
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
a
0.5x19=9.5±0.10
b 0.25 0.010
φ
c 5.3 0.209
φ
d 5.3 0.209
φ
e 1.3 0.051
φ
f 3.55
φ
g 0.3 0.012
h 1.85±0.2 0.073±0.008
i 3.5 0.138
j 2.0 0.079
k 3.0 0.118
l 0.25
m 14.0 0.551
n 1.4±0.2 0.055±0.008
o 1.4±0.2 0.055±0.008
p
h=1.8 1.3 h=0.071 0.051
q 0~5° 0.000~0.197°
r 5.9
s 0.8 0.031
t 2.4 0.094
u 2.7 0.106
v 3.9 0.154
φ
TGK-080SDW-G1E
0.020x0.748=0.374±0.004
φ
φ
φ
φ
0.140
φ
0.010
φ
0.232
note: Product by TOKYO ELETECH CORPORATION.
66
Page 67

µ
PD78P4038Y
APPENDIX C RELATED DOCUMENTS
Documents Related to Devices
Document Name Document No.
English Japanese
µ
PD784031Y Data Sheet U11504E U11504J
µ
PD784035Y, 784036Y, 784037Y, 784038Y Data Sheet U10741E U10741J
µ
PD78P4038Y Data Sheet This manual U10742J
µ
PD784038, 784038Y Sub-Series User's Manual, Hardware U11316E U11316J
µ
PD784038Y Sub-Series Special Function Registers – U11090J
78K/IV Series User's Manual, Instruction U10905E U10905J
78K/IV Series Instruction Summary Sheet – U10594J
78K/IV Series Instruction Set – U10595J
78K/IV Series Application Note, Software Basic – U10095J
Documents Related to Development Tools (User's Manual)
Document Name Document No.
English Japanese
RA78K4 Assembler Package Operation U11334E U11334J
Language U11162E U11162J
RA78K Series Structured Assembler Preprocessor U11743E U11743J
CC78K4 Series Operation U11572E U11572J
Language U11571E U11571J
CC78K Series Library Source File U12322E U12322J
PG-1500 PROM Programmer U11940E U11940J
PG-1500 Controller PC-9800 Series (MS-DOSTM) Base EEU-1291 EEU-704
PG-1500 Controller IBM PC Series (PC DOSTM) Base U10540E EEU-5008
IE-78K4-NS To be released U13356J
soon
IE-784000-R EEU-1534 U12903J
IE-784038-NS-EM1 Planned Planned
IE-784038-R-EM1 U11383E U11383J
EP-78230 EEU-1515 EEU-985
EP-78054GK-R EEU-1468 EEU-932
SM78K4 System Simulator Windows Base Reference U10093E U10093J
SM78K Series System Simulator
ID78K4-NS Integrated Debugger Reference U12796E U12796J
ID78K4 Integrated Debugger Windows Base Reference U10440E U10440J
ID78K4 Integrated Debugger HP-UX, SunOS, NEWS-OS Base
External Parts User Open
Interface Specifications
Reference U11960E U11960J
U10092E U10092J
Caution The above documents may be revised without notice. Use the latest versions when you design
application systems.
67
Page 68

µ
PD78P4038Y
Documents Related to Software to Be Incorporated into the Product (User’s Manual)
Document Name Document No.
English Japanese
78K/IV Series Real-Time OS Basic U10603E U10603J
Installation U10604E U10604J
Debugger – U10364J
OS for 78K/IV Series MX78K4 Basic – U11779J
Other Documents
Document Name Document No.
English Japanese
IC PACKAGE MANUAL C10943X
Semiconductor Device Mounting Technology Manual C10535E C10535J
Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Device C11531E C11531J
NEC Semiconductor Device Reliability/Quality Control System C10983E C10983J
Guide to Prevent Damage for Semiconductor Devices by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Semiconductor Device Quality Control/Reliability Handbook – C12769J
Guide for Products Related to Microcomputer: Other Companies – U11416J
C11892E C11892J
Caution The above documents may be revised without notice. Use the latest versions when you design
application systems.
68
Page 69

µ
PD78P4038Y
NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1 PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS
Note: Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of
the gate oxide and ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken
to stop generation of static electricity as much as possible, and quickly dissipate
it once, when it has occurred. Environmental control must be adequate. When
it is dry, humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using insulators
that easily build static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and
transported in an anti-static container, static shielding bag or conductive
material. All test and measurement tools including work bench and floor should
be grounded. The operator should be grounded using wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need to
be taken for PW boards with semiconductor devices on it.
2 HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS
Note: No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If no
connection is provided to the input pins, it is possible that an internal input level
may be generated due to noise, etc., hence causing malfunction. CMOS device
behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices
must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused
pin should be connected to VDD or GND with a resistor, if it is considered to have
a possibility of being an output pin. All handling related to the unused pins must
be judged device by device and related specifications governing the devices.
3 STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION OF MOS DEVICES
Note: Power-on does not necessarily define initial status of MOS device. Production
process of MOS does not define the initial operation status of the device.
Immediately after the power source is turned ON, the devices with reset function
have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does not guarantee out-pin
levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. Device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. Reset operation must be executed immediately after
power-on for devices having reset function.
69
Page 70

µ
PD78P4038Y
Caution This product contains an I2C bus interface circuit.
When using the I
2
C bus interface, notify its use to NEC when ordering custom code. NEC can
guarantee the following only when the customer informs NEC of the use of the interface:
Purchase of NEC I
these components in an I
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips I2C Patent Rights to use
2
C system, provided that the system conforms to the I2C Standard
Specification as defined by Philips.
IEBus and QTOP are trademarks of NEC Corporation.
MS-DOS and Windows are registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries.
PC/AT and PC DOS are trademarks of IBM Corporation.
HP9000 series 700 and HP-UX are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
SPARCstation is a trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
SunOS is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
NEWS and NEWS-OS are trademarks of SONY Corporation.
70
Page 71

Regional Information
Some information contained in this document may vary from country to country. Before using any NEC
product in your application, pIease contact the NEC office in your country to obtain a list of authorized
representatives and distributors. They will verify:
•
Device availability
•
Ordering information
•
Product release schedule
•
Availability of related technical literature
•
Development environment specifications (for example, specifications for third-party tools and
components, host computers, power plugs, AC supply voltages, and so forth)
•
Network requirements
In addition, trademarks, registered trademarks, export restrictions, and other legal issues may also vary
from country to country.
NEC Electronics Inc. (U.S.)
Santa Clara, California
Tel: 408-588-6000
800-366-9782
Fax: 408-588-6130
800-729-9288
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: 0211-65 03 02
Fax: 0211-65 03 490
NEC Electronics (UK) Ltd.
Milton Keynes, UK
Tel: 01908-691-133
Fax: 01908-670-290
NEC Electronics Italiana s.r.1.
Milano, Italy
Tel: 02-66 75 41
Fax: 02-66 75 42 99
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Benelux Office
Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Tel: 040-2445845
Fax: 040-2444580
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Velizy-Villacoublay, France
Tel: 01-30-67 58 00
Fax: 01-30-67 58 99
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Spain Office
Madrid, Spain
Tel: 01-504-2787
Fax: 01-504-2860
NEC Electronics (Germany) GmbH
Scandinavia Office
Taeby, Sweden
Tel: 08-63 80 820
Fax: 08-63 80 388
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Hong Kong
Tel: 2886-9318
Fax: 2886-9022/9044
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Seoul Branch
Seoul, Korea
Tel: 02-528-0303
Fax: 02-528-4411
NEC Electronics Singapore Pte. Ltd.
United Square, Singapore 1130
Tel: 65-253-8311
Fax: 65-250-3583
NEC Electronics Taiwan Ltd.
Taipei, Taiwan
Tel: 02-719-2377
Fax: 02-719-5951
NEC do Brasil S.A.
Cumbica-Guarulhos-SP, Brasil
Tel: 011-6465-6810
Fax: 011-6465-6829
J98. 2
µ
PD78P4038Y
71
Page 72

µ
PD78P4038Y
Some related documents may be preliminary versions. Note that, however, what documents are preliminary is not indicated
in this document.
The export of these products from Japan is regulated by the Japanese government. The export of some or all of these
products may be prohibited without governmental license. To export or re-export some or all of these products from a
country other than Japan may also be prohibited without a license from that country. Please call an NEC sales
representative.
License not needed :µPD78P4038YKK-T
The customer must judge the need for license :µPD78P4038YGC-3B9, µPD78P4038YGC-×××-3B9,
µ
PD78P4038YGC-8BT
µ
PD78P4038YGK-BE9, µPD78P4038YGK-×××-BE9
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of NEC Corporation. NEC Corporation assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this
document.
NEC Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual
property rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein or any other liability arising
from use of such device. No license, either express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents,
copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Corporation or others.
While NEC Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its semiconductor devices,
the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks of damage or injury to persons or
property arising from a defect in an NEC semiconductor device, customers must incorporate sufficient safety
measures in its design, such as redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
NEC devices are classified into the following three quality grades:
"Standard", "Special", and "Specific". The Specific quality grade applies only to devices developed based on
a customer designated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The recommended applications
of a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of each
device before using it in a particular application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment,
audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic
equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
Specific: Aircrafts, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC devices is "Standard" unless otherwise specified in NEC's Data Sheets or Data Books.
If customers intend to use NEC devices for applications other than those specified for Standard quality grade,
they should contact an NEC sales representative in advance.
Anti-radioactive design is not implemented in this product.
M4 96. 5
 Loading...
Loading...