NEC UPD75316GF-XXX-3B9, UPD75316GF-A-XXX-3B9, UPD75312GF-XXX-3B9, UPD75312GF-A-XXX-3B9 Datasheet
NEC Corporation 1991
Document No. IC-2825A
(O. D. No. IC-8270A)
Date Published December 1993 P
Printed in Japan
DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
The mark ★ shows major revised points.
DESCRIPTION
The µPD75316(A) is one of the 75X Series 4-bit single-chip microcomputer having a built-in LCD controller/
driver, and has a data processing capability comparable to that of an 8-bit microcomputer.
In addition to high-speed operation with 0.95 µs minimum instruction execution time for the CPU, the
µ
PD75316(A) can also process data in 1-, 4-, and 8-bit units. Therefore, as a 4-bit single-chip microcomputer
chip having a built-in LCD panel controller/driver, its data processing capability is the highest in its class in
the world.
Detailed functions are described in the following user's manual. Be sure to read it for designing.
µ
PD75308 User's Manual: IEM-5016
FEATURES
• Higher reliability than µPD75316
• Internal memory
• Program memory (ROM)
: 16256 × 8 bits (
µ
PD75316(A))
: 12160 × 8 bits (
µ
PD75312(A))
• Data memory
: 512 × 4 bits
• Capable of high-speed operation and variable instruction execution time to power save
• 0.95 µs, 1.91 µs, 15.3 µs (operating at 4.19 MHz)
• 122
µ
s (operating at 32.768 kHz)
• 75X architecture comparable to that for an 8-bit microcomputer is employed
• Built-in programmable LCD controller/driver
• Clock operation at reduced power dissipation: 5
µ
A TYP. (operating at 3 V)
• Enhanced timer function (3 channels)
• Interrupt functions especially enhanced for applications, such as remote control receiver
• Pull-up resistors can be provided for 31 I/O lines
• Built-in NEC standard serial bus interface (SBI)
• Upgraded model of
µ
PD7514 (µPD7500 Series)
• PROM version (
µ
PD75P316, µPD75P316A) available
APPLICATIONS
Suitable for controlling automotive and transportation equipment.
The
µ
PD75316(A) is treated as the representative model throughout this document,
unless there are differences between
µ
PD75312(A) and µPD75316(A) functions.
4-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
2
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package Quality Grade
µ
PD75312GF(A)-xxx-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14×20 mm) Special
µ
PD75316GF(A)-xxx-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14×20 mm) Special
Remarks: xxx is ROM code number.
Please refer to “Quality Grade on NEC Semiconductor Devices” (Document Number IEI-1209)
published by NEC Corporation to know the specification of quality grade on the devices and its
recommended applications.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN µPD75316(A) and µPD75316
Product
µ
PD75316(A)
µ
PD75316
Item
Quality Grade Special Standard
Directly Driving LED Not offered Offered
Absolute Maximum Ratings Differ in high-level output currrent and low-level output
current
DC Characteristics Differ in low-level output voltage
Electrical
Characteristics
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
3
FUNCTIONAL OUTLINE (1/2)
Item Function
Number of Basic 41
Instructions
Instruction Cycle • 0.95 µs, 1.91 µs, 15.3 µs (Main system clock: operating at 4.19 MHz)
• 122 µs (Subsystem clock: operating at 32.768 kHz)
ROM 16256 × 8-bit (µPD75316(A)), 12160 × 8-bit (µPD75312(A))
RAM 512 × 4 bits
General-Purpose • 4-bit manipulation: 8 (B, C, D, E, H, L, X, A)
Registers • 8-bit manipulation: 4 (BC, DE, HL, XA)
Accumulator • Bit accumulator (CY)
• 4-bit accumulator (A)
• 8-bit accumulator (XA)
Instruction Set • Abundant bit manipulation instructions
• Efficient 4-bit data manipulation instructions
• 8-bit data transfer instructions
• GETI instruction executing 2-/3-byte instruction with a single byte
I/O Line 40 8 CMOS input pins Pull-up by software is possible.
: 23
16 CMOS input/output pins
8 CMOS output pins Also serve as segment pins
8 N-ch open-drain input/output Withstand voltage: 10 V
Pull-up by mask option is possible.
: 8
LCD Controller/ • Segment number selection: 24/28/32 segments
Driver (4/8 pins can also be used as bit ports.)
• Display mode selection: Static, 1/2 duty, 1/3 duty (1/2 bias), 1/3 duty (1/3 bias), 1/4 duty
• Dividing resistor for LCD driving can be built-in by mask option.
Supply Voltage VDD = 2.7 to 6.0 V
Range
Internal
Memory
Timer 3 chs • 8-bit timer/event counter
• Clock source: 4 steps
• Event count is possible
• 8-bit basic interval timer
• Reference time generation: 1.95 ms, 7.82 ms, 31.3 ms, 250 ms
(operating at 4.19 MHz)
• Can be used as watchdog timer
• Watch timer
• Generates 0.5-second time intervals
• Count clock source: Main system clock or subsystem clock (selectable)
• Watch fast forward mode (generates 3.9-ms time intervals)
• Buzzer output (2 kHz)

µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
4
FUNCTIONAL OUTLINE (2/2)
Item Function
8-bit Serial Interface • Three modes:
• 3-line serial I/O mode
• 2-line serial I/O mode
• SBI mode
• LSB/MSB first selectable
Bit Sequential Special bit manipulation memory: 16 bits
Buffer • Ideal for remote controller
Clock Output Timer/event counter output (PTO0): Output of square wave at specified frequency
Function
Clock output (PCL): Φ, 524, 262, 65.5 kHz (operating at 4.19 MHz)
Buzzer output (BUZ): 2 kHz (operating at 4.19 MHz or 32.768 kHz)
Vector Interrupt • External: 3
• Internal: 3
Test Input • External: 1
• Internal: 1
System Clock • Ceramic/crystal oscillator circuit for main system clock oscillation: 4.194304 MHz
Oscillator Circuit • Crystal oscillator circuit for subsystem clock oscillation: 32.768 kHz
Standby STOP/HALT mode
Package 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm)

µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
5
CONTENTS
1. PIN CONFIGURATION (Top View) ................................................................................................ 7
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................................... 8
3. PIN FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................................................. 9
3.1 PORT PINS............................................................................................................................................. 9
3.2 NON PORT PINS ................................................................................................................................... 11
3.3 PIN INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS ........................................................................................................... 13
3.4 RECOMMENDED PROCESSING OF UNUSED PINS .......................................................................... 15
3.5 NOTES ON USING THE P00/INT4, AND RESET PINS ...................................................................... 16
4. MEMORY CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................... 16
5. PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTIONS........................................................................................ 20
5.1 PORTS .................................................................................................................................................... 20
5.2 CLOCK GENERATOR CIRCUIT ............................................................................................................ 21
5.3 CLOCK OUTPUT CIRCUIT .................................................................................................................... 22
5.4 BASIC INTERVAL TIMER ..................................................................................................................... 23
5.5 WATCH TIMER ...................................................................................................................................... 24
5.6 TIMER/EVENT COUNTER ..................................................................................................................... 25
5.7 SERIAL INTERFACE .............................................................................................................................. 27
5.8 LCD CONTROLLER/DRIVER.................................................................................................................. 29
5.9 BIT SEQUENTIAL BUFFER................................................................................................................... 31
6. INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS................................................................................................................ 31
7. STANDBY FUNCTIONS .................................................................................................................. 33
8. RESET FUNCTION........................................................................................................................... 34
9. INSTRUCTION SET ......................................................................................................................... 36
10. SELECTION OF MASK OPTION ..................................................................................................... 42
11. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................................................... 43
12. PACKAGE DRAWINGS ................................................................................................................... 55

µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
6
13. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ............................................................................... 57
APPENDIX A. COMPARISION OF FEATURES AMONG THIS SERIES PRODUCTS ..................... 58
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS .............................................................................................. 59
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS.............................................................................................. 60
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
7
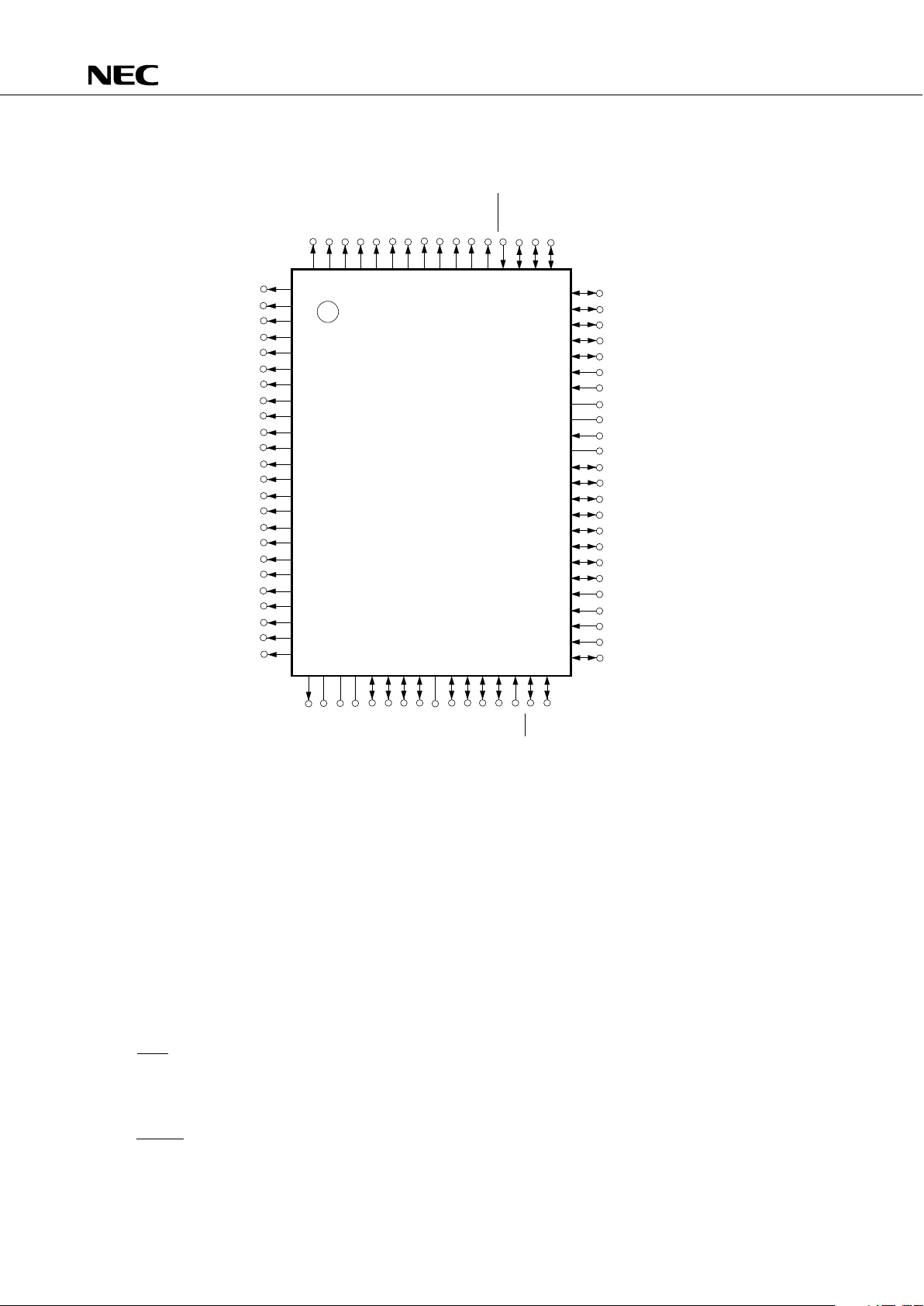
P00-P03 : Port 0 S0-S31 : Segment Output 0-31
P10-P13 : Port 1 COM0-COM3 : Common Output 0-3
P20-P23 : Port 2 VLC0-VLC2 : LCD Power Supply 0-2
P30-P33 : Port 3 BIAS : LCD Power Supply Bias Control
P40-P43 : Port 4 LCDCL : LCD Clock
P50-P53 : Port 5 SYNC : LCD Synchronization
P60-P63 : Port 6 TI0 : Timer Input 0
P70-P73 : Port 7 PTO0 : Programmable Timer Output 0
BP0-BP7 : Bit Port BUZ : Buzzer Clock
KR0-KR7 : Key Return PCL : Programmable Clock
SCK : Serial Clock
INT0, INT1, INT4: External Vectored Interrupt 0, 1, 4
SI : Serial Input INT2 : External Test Input 2
SO : Serial Output X1, X2 : Main System Clock Oscillation 1, 2
SB0, SB1 : Serial Bus 0,1 XT1, XT2 : Subsystem Clock Oscillation 1, 2
RESET : Reset Input NC : No Connection
1. PIN CONFIGURATION (Top View)
S12
PD75316GF(A)
– –3B9×××
µ
V
LC0
S11
1
80
2
P70/KR4
78
77 76 7574 73 72 71 69 68 67 66 65
S10S9S8S7S6S5S4S3S2S1S0
RESET
P73/KR7
P72/KR6
P71/KR5
S13
S14
S15
S16
S17
S18
S19
S20
S21
S22
S23
S24/BP0
S25/BP1
S26/BP2
S27/BP3
S28/BP4
S29/BP5
S30/BP6
S31/BP7
COM0
COM1
COM2
COM3
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
BIAS
V
LC1VLC2
P40
P41
P42
P43
V
SS
P50
P51
P52
P53
P00/INT4
P01/SCK
P02/SO/SB0
25
26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
P63/KR3
P62/KR2
P61/KR1
P60/KR0
X2
X1
NC
XT2
XT1
V
DD
P33
P32
P31/SYNC
P30/LCDCL
P23/BUZ
P22/PCL
P21
P20/PTO0
P13/TI0
P12/INT2
P11/INT1
P10/INT0
P03/SI/SB1
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
PD75312GF(A)
– –3B9×××
µ
79
70
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
8
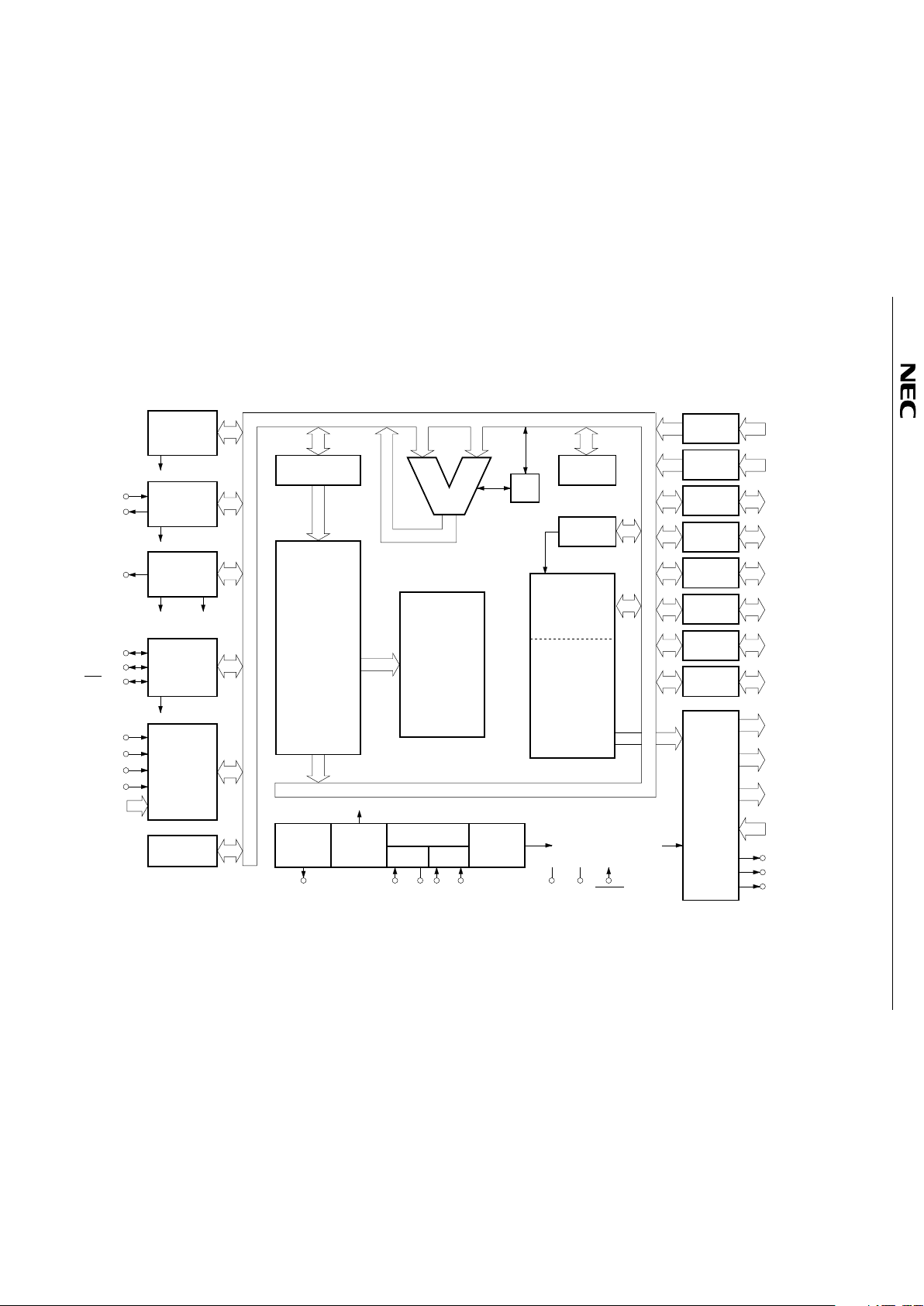
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
TI0/P13
BASIC
INTERVAL
TIMER
INTBT
TIMER/EVENT
COUNTER
#0
INTT0
PTO0/P20
BUZ/P23
WATCH
TIMER
INTW f
LCD
INTCSI
CLOCKED
SERIAL
INTERFACE
SI/SB1/P03
SO/SB0/P02
SCK/P01
PROGRAM
COUNTER (14)
ALU
CY
SP (8)
BANK
INT0/P10
INT1/P11
INT2/P12
INT4/P00
KR0/P60
–KR7/P73
8
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
BIT SEQ.
BUFFER (16)
PROGRAM
MEMORY
(ROM)
16256 8 BITS
: PD75316(A)
12160 8 BITS
: PD75312(A)
×
DECODE
AND
CONTROL
GENERAL REG.
DATA
MEMORY
(RAM)
512 4 BITS
×
f /2
X
N
VDDVSSRESET
PCL/P22 XT1 XT2 X1 X2
SUB MAIN
CLOCK
OUTPUT
CONTROL
CLOCK
DIVIDER
SYSTEM CLOCK
GENERATOR
STAND BY
CONTROL
CPU
CLOCK
f
LCD
SYNC/P31
LCDCL/P30
BIAS
V -V
LC0 LC2
3
LCD
CONTROLLER
/DRIVER
4
8
24
COM0-COM3
S24/BP0
-S31/BP7
S0-S23
PORT 7
P70-P734
PORT 6
P60-P634
PORT 5
P50-P534
PORT 4
P40-P434
PORT 3
P30-P334
PORT 2
P20-P234
PORT 1
P10-P134
PORT 0
P00-P034
×
µ
µ
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
9
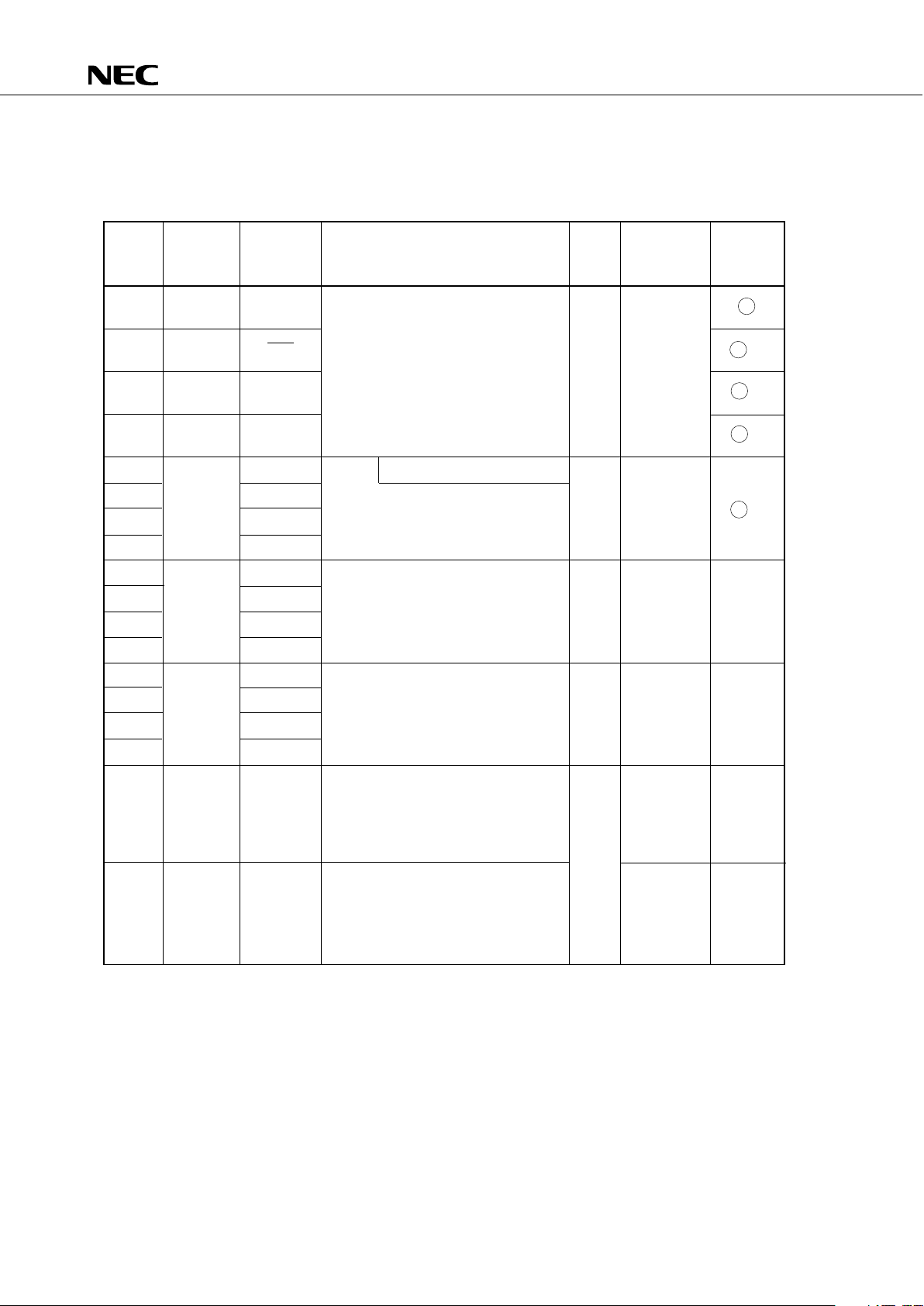
3. PIN FUNCTIONS
3.1 PORT PINS (1/2)
Input/
Output
Circuit
TYPE
P00
P01
P02
P03
P10
P11
P12
P13
P20
P21
P22
P23
P30
P31
P32
P33
P40-43
P50-53
Pin Name
Input/Output Function 8-Bit I/O When Reset
Also Served
As
INT4
SCK
SO/SB0
SI/SB1
INT0
INT1
INT2
TI0
PTO0
—
PCL
BUZ
LCDCL
SYNC
—
—
—
—
4-bit input port (PORT0)
Pull-up resistors can be specified in 3-bit
units for the P01 to P03 pins by software.
With noise elimination function
4-bit input port (PORT1)
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in 4-bit units by software.
4-bit input/output port (PORT2)
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in 4-bit units by software.
Programmable 4-bit input/output port
(PORT3)
This port can be specified for input/
output in bit units.
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in 4-bit units by software.
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output port
(PORT4)
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in bit units. (mask option)
Withstand voltage is 10 V in the opendrain mode.
N-ch open-drain 4-bit input/output port
(PORT5)
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in bit units. (mask option)
Withstand voltage is 10 V in the opendrain mode.
Input
Input
Input
Input
High level
(with internal
pull-up
resistor) or
high impedance
B
B -C
E-B
E-B
M
M
×
×
×
×
*: Circles indicate Schmitt trigger inputs.
Input
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
●●
F -A
M -C
F -B
High level
(with internal
pull-up
resistor) or
high impedance
*
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
3
P60
P61
P62
P63
P70
P71
P72
P73
BP0
BP1
BP2
BP3
BP4
BP5
BP6
BP7
KR0
KR1
KR2
KR3
KR4
KR5
KR6
KR7
S24
S25
S26
S27
S28
S29
S30
S31
●●
Also Served
As
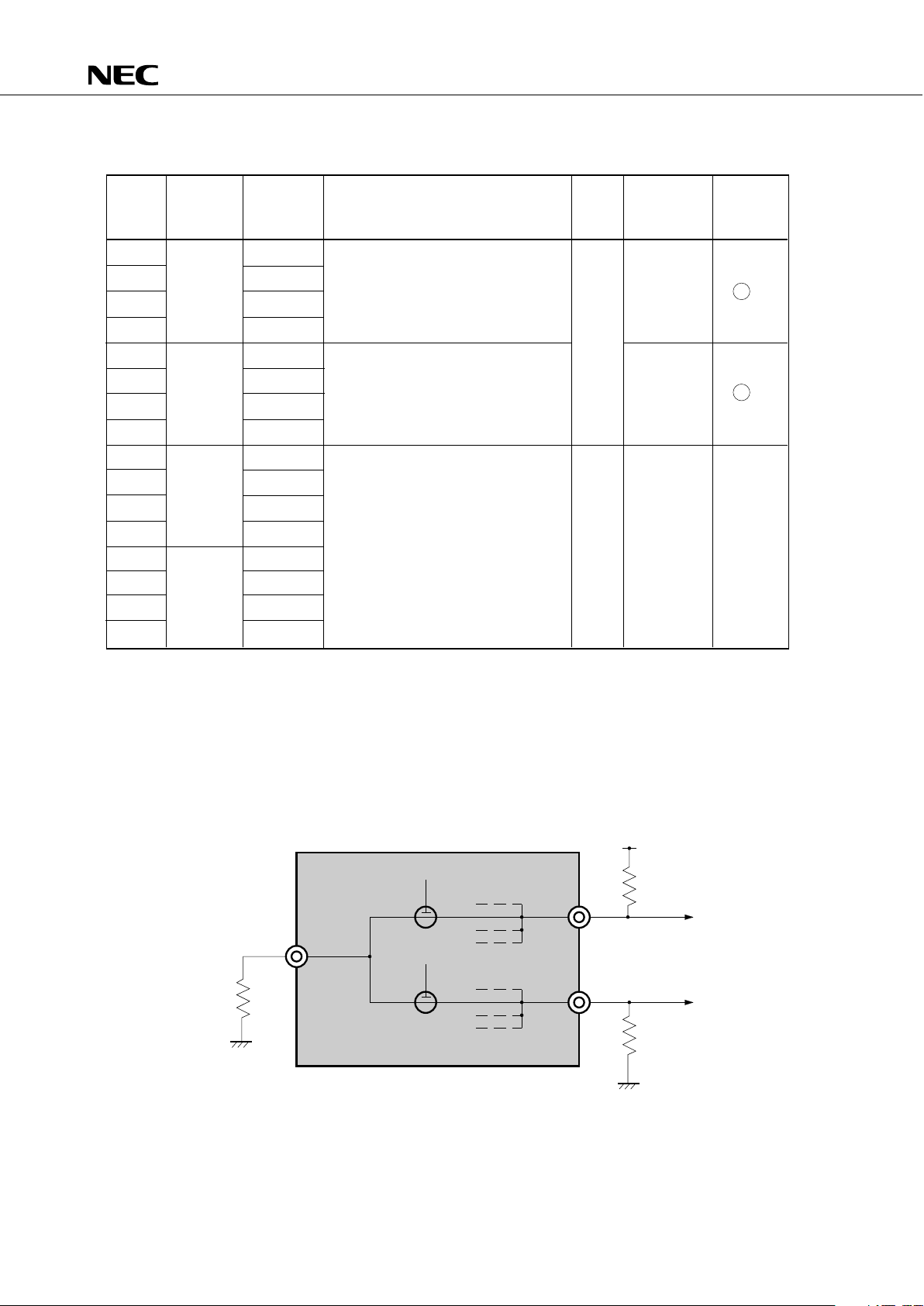
3.1 PORT PINS (2/2)
Input/
Output
Circuit
TYPE*
1
Programmable 4-bit input/output port
(PORT6)
This port can be specified for input/
output in bit units.
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in 4-bit units by software.
Input
F -A
4-bit input/output port (PORT7)
Internal pull-up resistors can be
specified in 4-bit units by software.
Input
F -A
Pin Name Input/Output Function 8-Bit I/O When Reset
1-bit output port (BIT PORT)
Shared with a segment output pin.
×
*2
G-C
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Output
Output
*1: Circles indicate Schmitt trigger inputs.
2: For BP0-7, V
LC1 indicated below are selected as the input source. However, the output level is
changed depending on BP0-7 and the V
LC1 external circuits.
Example: Since BP0-7 are connected to each other within the µPD75316(A) as shown in the diagram
below, the output level of BP0-7 depends on the sizes of R
1, R2 and R3.
PD75316(A)
µ
ON
ON
BP0
BP1
V
DD
R
2
R
3
V
LC1
R
1
10
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
11
TI0
PTO0
PCL
BUZ
SCK
SO/SB0
SI/SB1
INT4
INT0
INT1
INT2
KR0-KR3
KR4-KR7
S0-S23
S24-S31
COM0-
COM3
VLC0-VLC2
BIAS
LCDCL*
4
SYNC*
4
X1, X2
XT1
XT2
Input
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Output
Output
Output
—
Output
Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Input
Input
—
P13
P20
P22
P23
P01
P02
P03
P00
P10
P11
P12
P60-P63
P70-P73
—
BP0-7
—
—
—
P30
P31
—
—
—
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
*2
*2
*2
—
*3
Input
Input
—
—
B -C
E-B
E-B
E-B
F -A
F -B
M -C
B
B -C
B -C
F -A
F -A
G-A
G-C
G-B
—
—
E-B
E-B
—
—
Pin Name Input/Output
Also Served
As
Functon When Reset
Input/
Output
Circuit
TYPE*
1
3.2 NON PORT PINS
Timer/event counter external event pulse Input
Timer/event counter output
Clock output
Fixed frequency output (for buzzer or for trimming the system clock)
Serial clock input/output
Serial data output
Serial bus input/output
Serial data input
Serial bus input/output
Edge detection vector interrupt input (both
rising and falling edge detection are effective)
Edge detection vector
interrupt input (detection
edge can be selected)
Edge detection testable
input (rising edge detection)
Parallel falling edge detection testable input
Parallel falling edge detection testable input
Segment signal output
Segment signal output
Common signal output
LCD drive power
Internal dividing resistor (mask option)
Disconnect output for external expanded driver
Externally expanded driver clock output
Externally expanded driver sync clock output
To connect the crystal/ceramic oscillator to the
main system clock generator. When inputting the
external clock, input the external clock to pin X1,
and the reverse phase of the external clock to pin
X2.
To connect the crystal oscillator to the subsystem
clock generator.
When the external clock is used, pin XT1 inputs the
external clock. In this case, pin XT2 must be left
open.
Pin XT1 can be used as a 1-bit input (test) pin.
Clock synchronous
Asynchronous
Asynchronous
(to be cont'd)
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
12
Also Served
As
(cont'd)
Input/
Output
Circuit
TYPE*
1
Pin Name Input/Output Function When Reset
RESET
NC *
5
VDD
VSS
Input
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
System reset input
No connection
Positive power supply
GND
—
—
—
—
B
—
—
—
*1: Circles indicate Schmitt trigger inputs.
2: For these display output, V
LCX indicated below are selected as the input source.
S0 to S31: V
LC1, COM0 to COM2: VLC2, COM3: VLC0
However, display output level varies depending on the particular display output and VLCX
external circuit.
3: Internal dividing resistor provided : Low level
Internal dividing resistor not provided : High impedance
4: These pins are provided for future system expansion. At present, these pins are used only as
pins P30 and P31.
5: When sharing the printed circuit board with the
µ
PD75P316 and 75P316A, the NC pin must be
connected to V
DD.
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
13
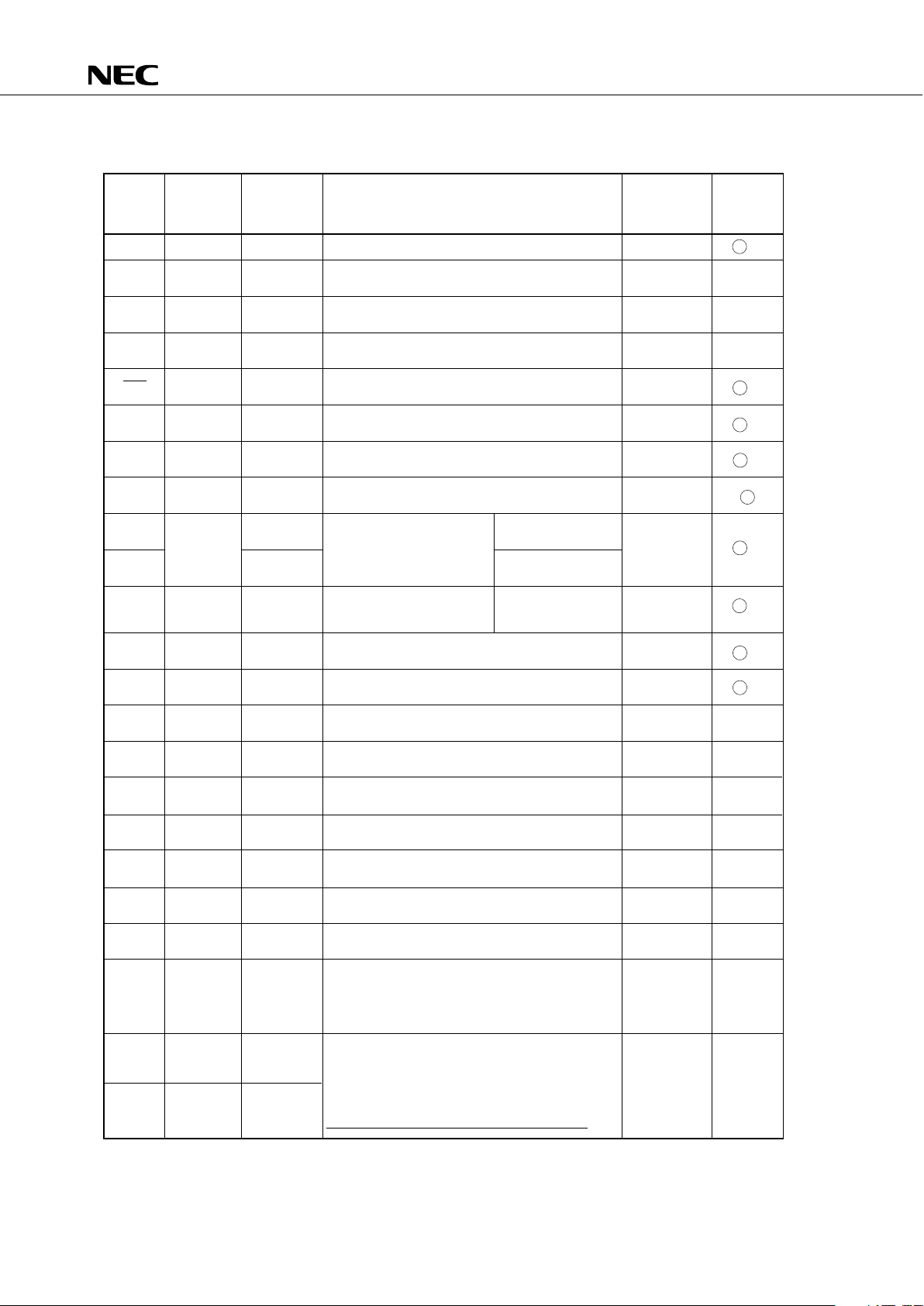
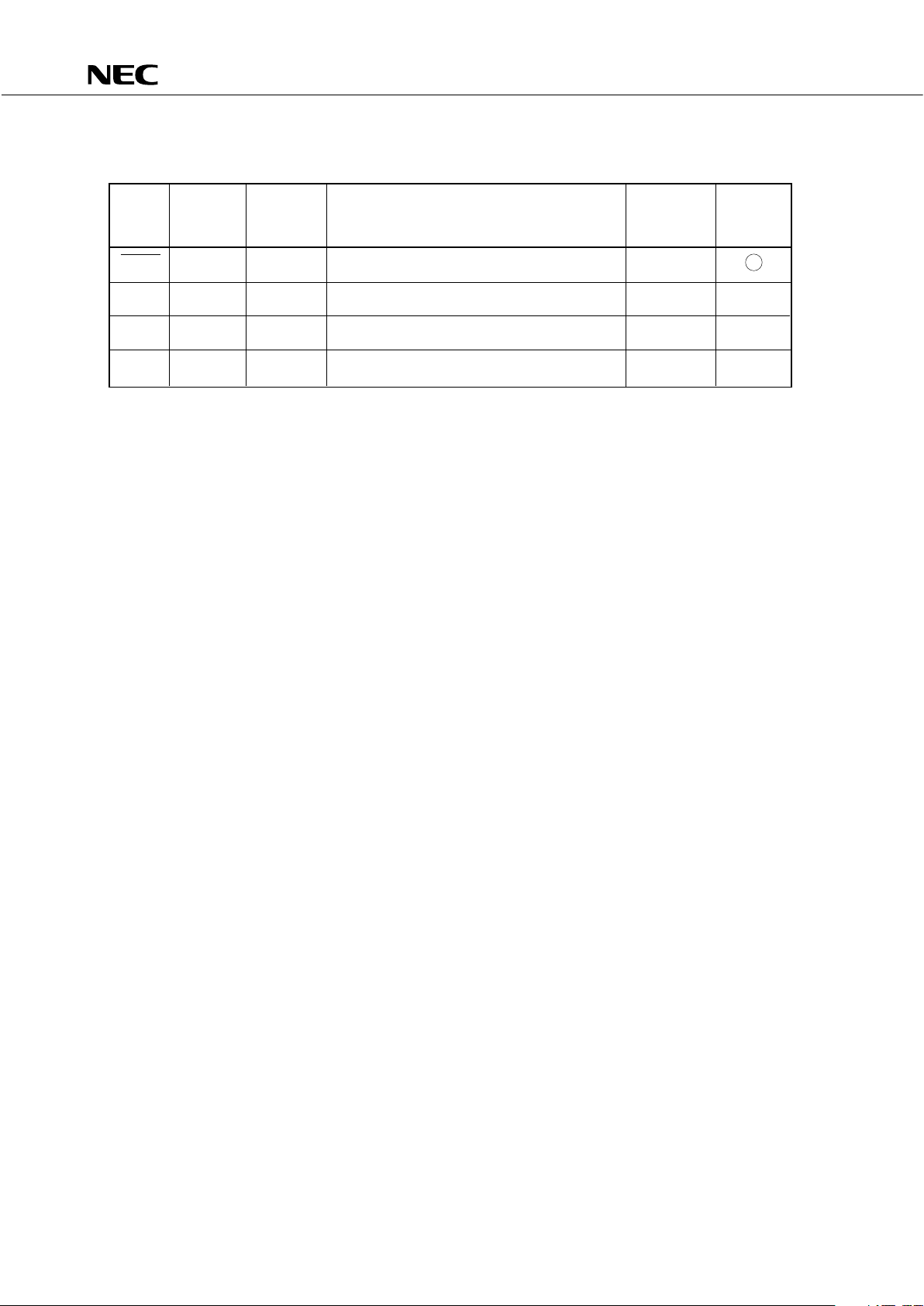
3.3 PIN INPUT/OUTPUT CIRCUITS
The following shows a simplified input/output circuit diagram for each pin of the
µ
PD75316(A).
TYPE A (for TYPE E–B)
TYPE D (for TYPE E –
B, F
TYPE B
TYPE E–B
IN
V
DD
Input buffer of CMOS standard
data
output
disable
OUT
P–ch
N–ch
Push–pull output that can be set in a output
high–impedance state (both P–ch and N–ch are off)
IN
Schmitt trigger input with hysteresis characteristics
data
output
disable
Type D
Type A
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
P.U.R. : Pull–Up Resistor
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
TYPE B–C
TYPE F–A
IN
data
output
disable
Type D
Type B
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
IN/OUT
P.U.R. : Pull–Up ResistorP.U.R. : Pull
–Up Resistor
A)
–
V
DD
P–ch
N–ch
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
14
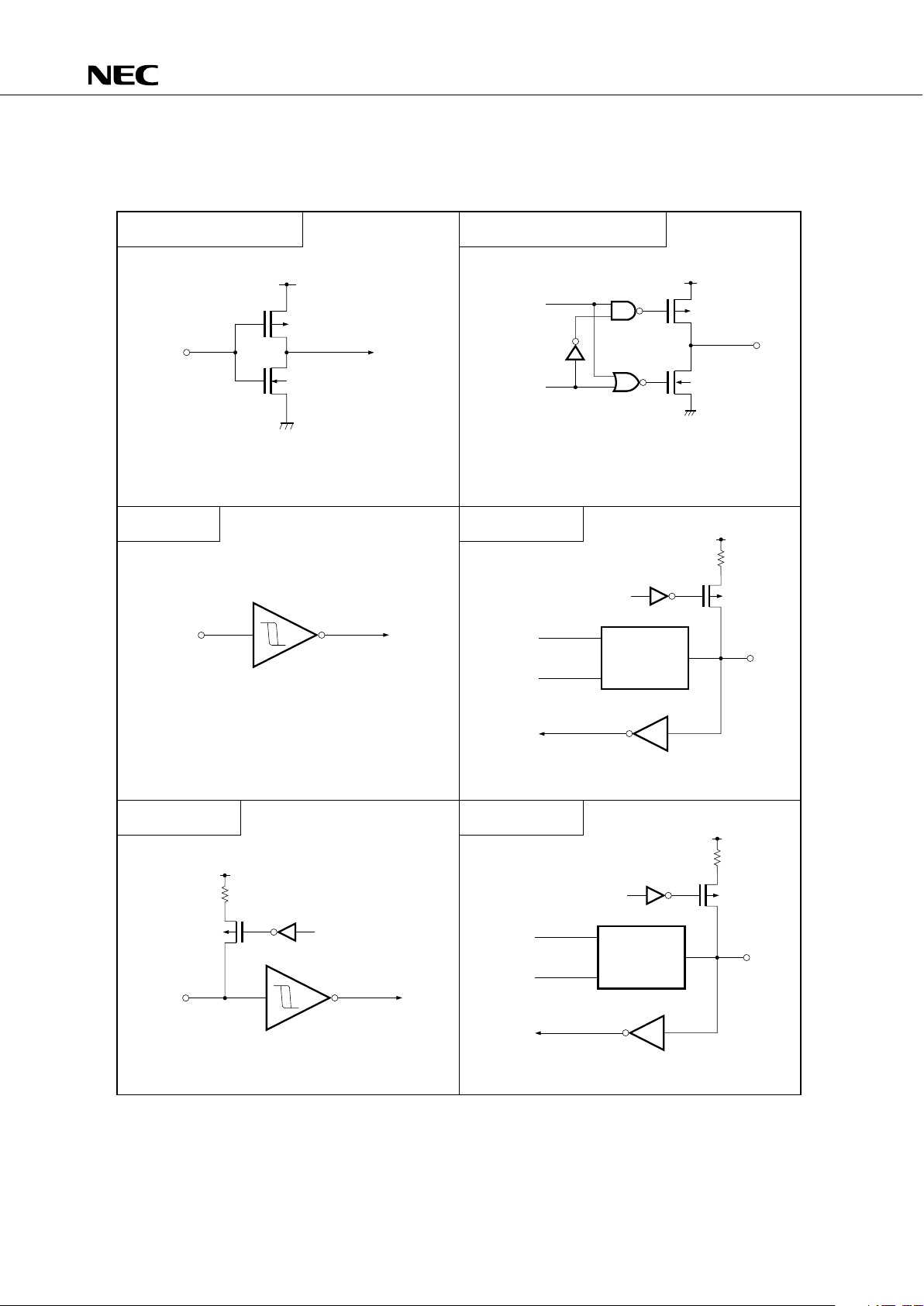
P-ch
TYPE M–C
data
output
disable
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
IN/OUT
P–ch
N-ch
TYPE F–B
TYPE M
data
output
disable
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
IN/OUT
Middle voltage input buffer
(withstand voltage: +10 V)
P.U.R. : Pull–Up Resistor
data
output
disable
P.U.R.
enable
V
DD
P.U.R.
P–ch
N-ch
P-ch
output
disable
(P)
output
disable
(N)
VDD
(Mask option)
P.U.R. : Pull–Up Resistor
IN/OUT
TYPE G–C
TYPE G–A
P.U.R. : Pull–Up Resistor
TYPE G–B
VDD
VLC0
VLC0
VLC1
VLC2
SEG
data/Bit Port data
P-ch
N-ch
OUT
N-ch
V
LC1
VLC2
P-ch
P-ch
N-ch
OUT
N-ch
VLC0
VLC1
VLC2
P-ch
N-ch
SEG
data
COM
data
OUT
P-ch N-ch
N-ch P-ch
N-ch

µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
15
3.4 RECOMMENDED PROCESSING OF UNUSED PINS
Connect to VSS
Table 3-1 Unused Pins Processing
Pin Recommended Connections
P00/INT4 Connect to VSS
P01/SCK
P02/SO/SB0 Connect to VSS or VDD
P03/SI/SB1
P10/INT0-P12/INT2
P13/TI0
P20/PTO0
P21
P22/PCL
P23/BUZ
P30/LCDCL
P31/SYNC Input : Connect to VSS or VDD
P32
Output: Open
P33
P40-P43
P50-P53
P60/KR0-P63/KR3
P70/KR4-P73/KR7
S0-S23
S24/BP0-S31/BP7 Open
COM0-COM3
VLC0-VLC2 Connect to VSS
BIAS Connect to VSS only when all of the VLC0-VLC2
pins are unused, otherwise, open.
XT1 Connect to VSS or VDD
XT2 Open
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
16
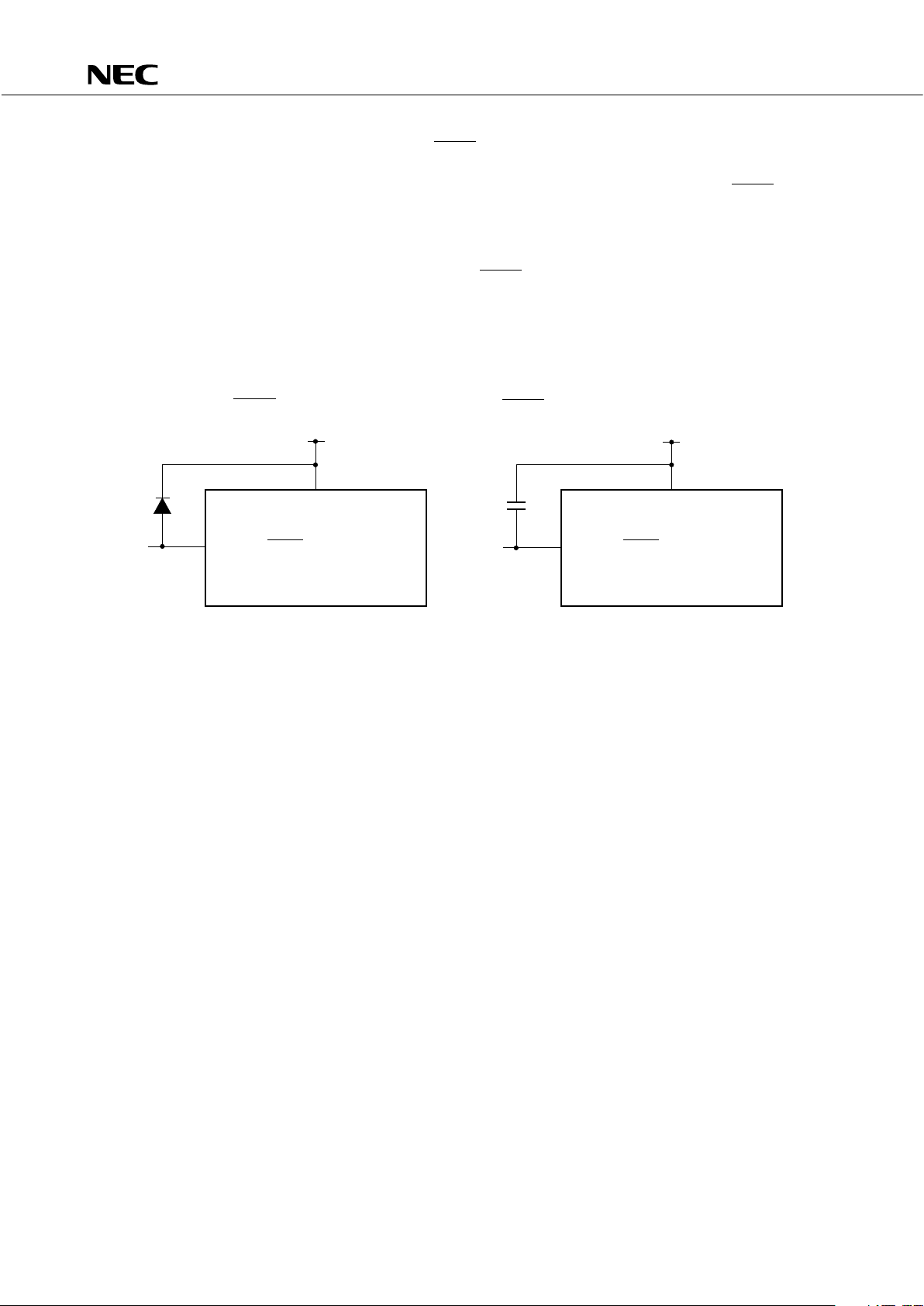
3.5 NOTES ON USING THE P00/INT4, AND RESET PINS
In addition to the functions described in Sections 3.1 and 3.2, an exclusive function for setting the test mode,
in which the internal fuctions of the
µ
PD75316(A) are tested, is provided to the P00/INT4 and RESET pins.
If a voltage exceeding V
DD is applied to either of these pins, the
µ
PD75316(A) is put into test mode. Therefore,
even when the
µ
PD75316(A) is in normal operation, if noise exceeding the VDD is input into any of these pins,
the
µ
PD75316(A) will enter the test mode, and this will cause problems for normal operation.
As an example, if the wiring to the P00/INT4 pin or the RESET pin is long, stray noise may be picked up and
the above montioned problem may occur.
Therefore, all wiring to these pins must be made short enough to not pick up stray noise. If noise cannot
be avoided, suppress the noise using a capacitor or diode as shown in the figure below.
• Connect a diode having a low VF across
P00/INT4 and RESET, and V
DD.
• Connect a capacitor across P00/INT4 and
RESET, and VDD.
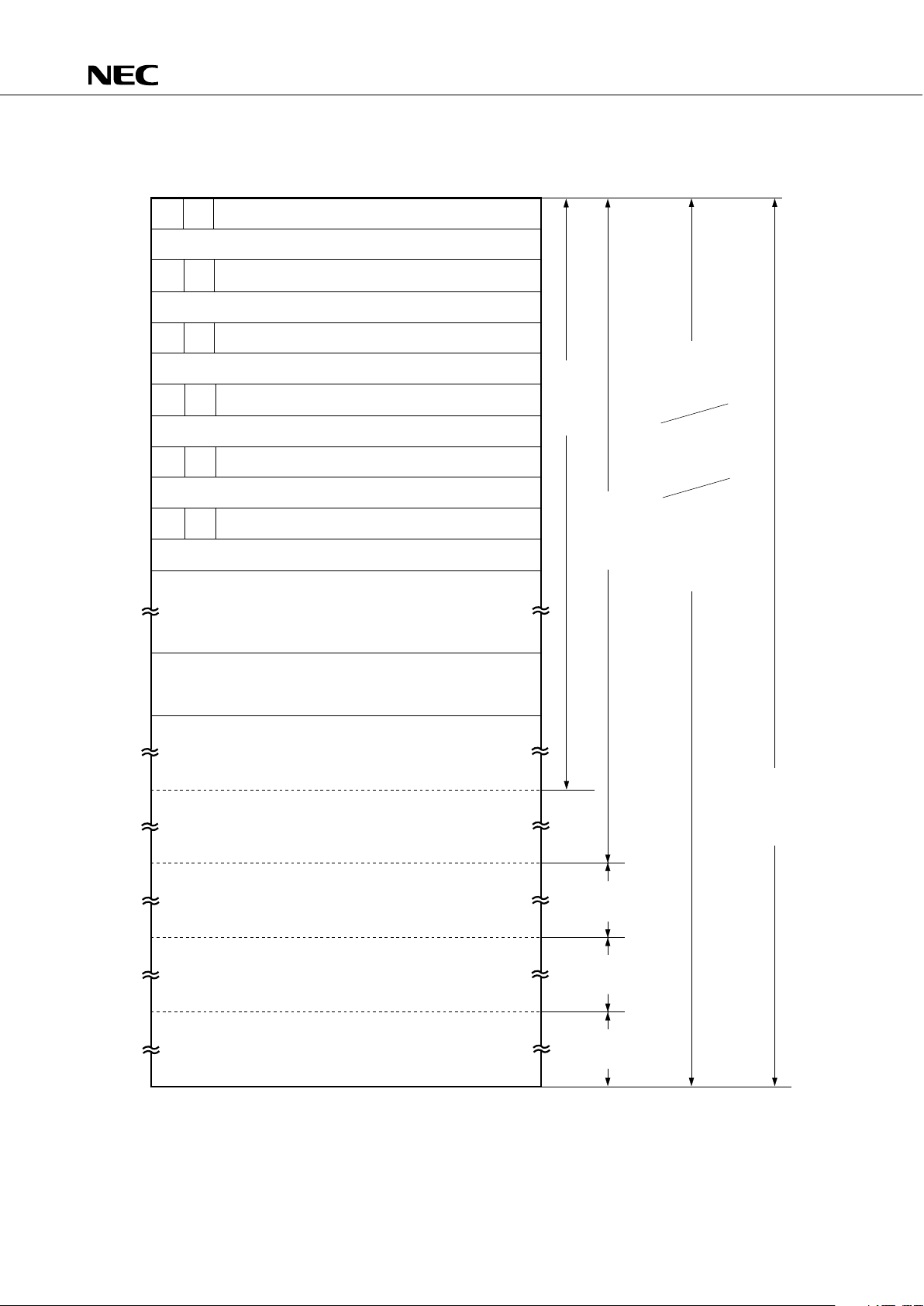
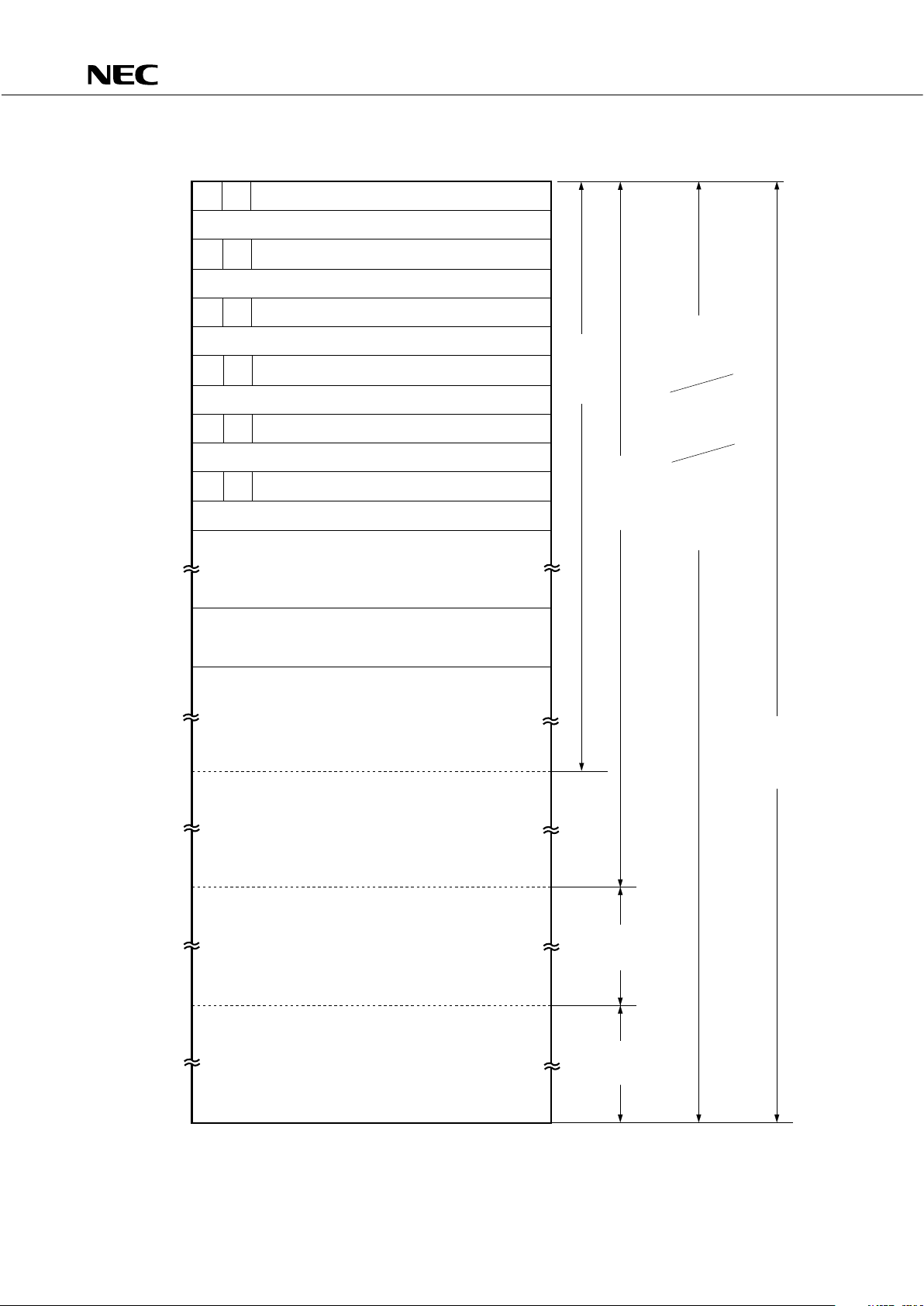
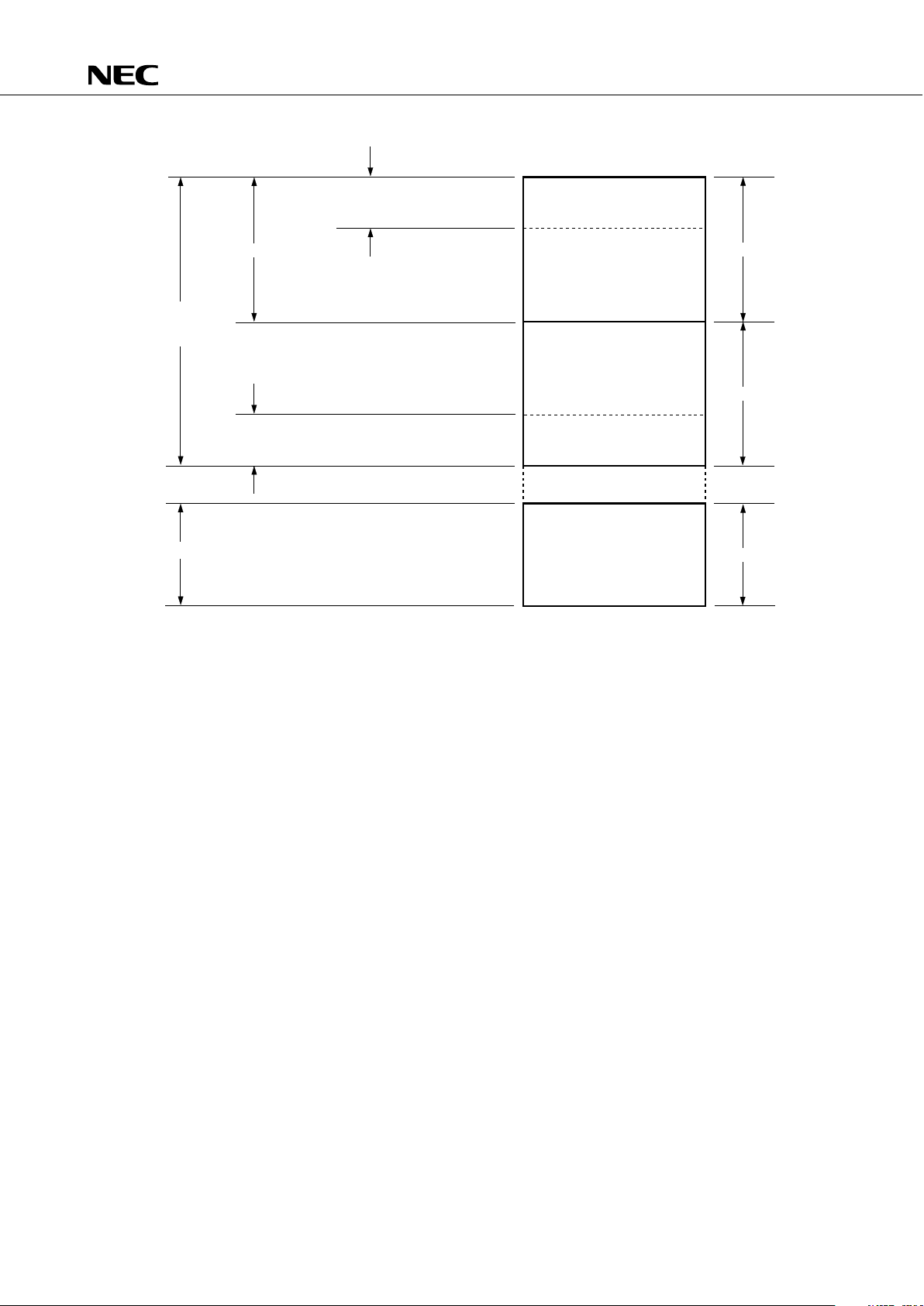
4. MEMORY CONFIGURATION
• Program memory (ROM) ...16256 × 8 bits (0000H-3F7FH): µPD75316(A)
...12160 × 8 bits (0000H-2F7FH):
µ
PD75312(A)
• 0000H, 0001H : Vector table to which address from which program is started is written after
reset
• 0002H-000BH: Vector table to which address from which program is started is written after
interrupt
• 0020H-007FH: Table area referenced by GETI instruction
• Data memory
• Data area .... 512 × 4 bits (000H–1FFH)
• Peripheral hardware area .... 128 × 4 bits (F80H–FFFH)
VDD
VDD
P00/INT4, RESET
VDD
VDD
P00/INT4, RESET
Low VF
diode
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
17
(a) µPD75316(A)
Address
7
6
5
0
0000H
MBE
0
0002H
MBE
0
0004H
MBE
0
0006H
MBE
0
0008H
MBE
0
000AH
MBE
0
0020H
007FH
0080H
07FFH
0800H
0FFFH
1000H
1FFFH
2000H
2FFFH
3000H
3F7FH
Internal reset start address (upper 6 bits)
Internal reset start address (lower 8 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT1 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT1 start address (lower 8 bits)
INTCSI start address (upper 6 bits)
INTCSI start address (lower 8 bits)
INTT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
GETI instruction reference table
CALLF
! faddr
instruction
entry
address
BRCB
! caddr
instruction
branch
address
CALL ! addr
instruction
subroutine
entry address
BR ! addr
instruction
branch address
BR $addr
instruction
relational
branch address
(-15 to -1,
+2 to +16)
Branch destination
address and
subroutine entry
address for
GETI instruction
BRCB ! caddr
instruction branch
address
BRCB ! caddr
instruction branch
address
BRCB ! caddr
instruction branch
address
Fig. 4-1 Program Memory Map (1/2)
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
18
(b) µPD75312(A)
Address
7
6
5
0
0000H
MBE
0
0002H
MBE
0
0004H
MBE
0
0006H
MBE
0
0008H
MBE
0
000AH
MBE
0
0020H
007FH
0080H
07FFH
0800H
0FFFH
1000H
1FFFH
2000H
2F7FH
Internal reset start address (upper 6 bits)
Internal reset start address (lower 8 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
INT1 start address (upper 6 bits)
INT1 start address (lower 8 bits)
INTCSI start address (upper 6 bits)
INTCSI start address (lower 8 bits)
INTT0 start address (upper 6 bits)
INTT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
GETI instruction reference table
CALLF
! faddr
instruction
entry
address
BRCB
! caddr
instruction
branch
address
CALL ! addr
instruction
subroutine
entry address
BR ! addr
instruction
branch address
BR $addr
instruction
relational
branch address
(-15 to -1,
+2 to +16)
Branch destination
address and
subroutine entry
address for
GETI instruction
BRCB ! caddr
instruction branch
address
BRCB ! caddr
instruction branch
address
Fig. 4-1 Program Memory Map (2/2)
µ
PD75312(A), 75316(A)
19
000H
007H
008H
0FFH
100H
1DFH
1E0H
1FFH
F80H
FFFH
Data memory
Memory bank
(8 × 4)
256× 4
(248× 4)
256× 4
(224× 4)
Unmapped
(32 × 4)
128× 4
0
1
15
General-purpose
register area
Stack area
Display data memory area
Data area
Static RAM
(512× 4)
Peripheral hardware area
Fig. 4-2 Data Memory Map
 Loading...
Loading...