Motorola MC10H644FN, MC100H644FN Datasheet
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
The MC10H/100H644 generates the necessary clocks for the 68030,
68040 and similar microprocessors. The device is functionally equivalent
to the H640, but with fewer outputs in a smaller outline 20–lead PLCC
package. It is guaranteed to meet the clock specifications required by the
68030 and 68040 in terms of part–to–part skew, within–part skew and
also duty cycle skew.
68030/040
PECL–TTL CLOCK
DRIVER
• Generates Clocks for 68030/040
• Meets 68030/040 Skew Requirements
• TTL or PECL Input Clock
• Extra TTL and ECL Power/Ground Pins
• Within Device Skew on Similar Paths is 0.5 ns
• Asynchronous Reset
• Single +5.0V Supply
The user has a choice of using either TTL or PECL (ECL referenced to
+5.0V) for the input clock. TTL clocks are typically used in present MPU
systems. However, as clock speeds increase to 50MHz and beyond, the
inherent superiority of ECL (particularly differential ECL) as a means of
clock signal distribution becomes increasingly evident. The H644 also
uses differential ECL internally to achieve its superior skew characteristic.
The H644 includes divide–by–two and divide–by–four stages, both to
achieve the necessary duty cycle and skew to generate MPU clocks as required. A typical 50MHz processor application would
use an input clock running at 100MHz, thus obtaining output clocks at 50MHz and 25MHz (see Logic Symbol).
The 10H version is compatible with MECL 10H ECL logic levels, while the 100H version is compatible with 100K levels
(referenced to +5.0V).
FN SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 775–02
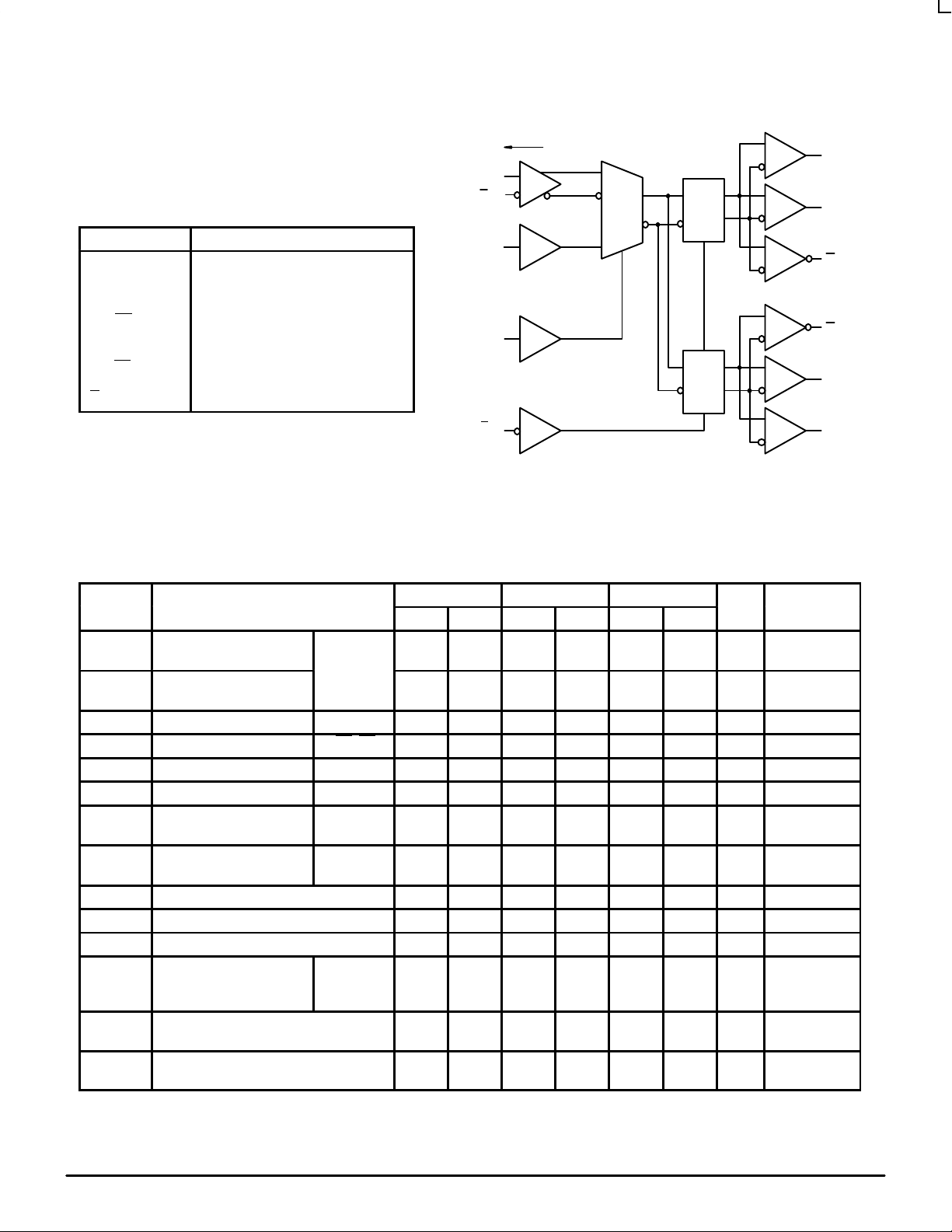
Function
Reset (R):
Synchronized Outputs:
Select (SEL):
The H644 also contains circuitry to force a stable state of the ECL input differential pair , should both sides be left open. In this
case, the DE side of the input is pulled LOW, and DE
MECL 10H is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
11/93
Motorola, Inc. 1995
LOW on RESET forces all Q outputs LOW and all Q outputs HIGH.
The device is designed to have the POS edges of the ÷2 and ÷4 outputs synchronized.
LOW selects the ECL input source (DE/DE). HIGH selects the TTL input source (DT).
goes HIGH.
Pinout: 20–Lead PLCC (Top View)
Q4 VT Q5 GT R
181317 16 15 14
19
2–1
GT
Q3
GT
Q2
GT
20
1
2
3
45678
Q1 VT Q0 SEL DT
12
10
VE
DE
V
11
BB
DE
GE
9
REV 3
MC10H644 MC100H644
PIN NAMES
PIN FUNCTION
GT
VT
VE
GE
DE, DE
V
BB
DT
Qn, Qn
SEL
R
TTL Ground (0V)
TTL VCC (+5.0V)
ECL VCC (+5.0V)
ECL Ground (0V)
ECL Signal Input (positive ECL)
VBB Reference Output
TTL Signal Input
Signal Outputs (TTL)
Input Select (TTL)
Reset (TTL)
VBB
DE
(ECL)
DE
(ECL)
DT
(TTL)
SEL
(TTL)
R
(TTL)
LOGIC DIAGRAM
2:1 MUX
÷2
÷4
TTL OUTPUTS
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
AC CHARACTERISTICS (VT = VE = 5.0 V ±5%)
0°C 25°C 85°C
Symbol Characteristic Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit Condition
t
PLH
t
PLH
t
skwd
t
skwd
t
skwd
t
skp–p
t
PD
t
R
t
F
f
max
TW Minimum Pulse Width Reset 1.5 – 1.5 – 1.5 – ns
t
rr
T
PW
TS Setup Time
TH Hold T ime
* Skews are specified for Identical Edges
Propagation Delay ECL
All Outputs 5.8 6.8 5.7 6.7 6.1 7.1 ns CL = 50pF
D to Output
Propagation Delay TTL
5.7 6.7 5.7 6.7 6.0 7.0 ns CL = 50pF
D to Output
* Within–Device Skew Q0, 1, 4, 5 – 0.5 – 0.5 – 0.5 ns CL = 50pF
* Within–Device Skew Q2, Q3 – 0.5 – 0.5 – 0.5 ns CL = 50pF
* Within–Device Skew All Outputs – 1.5 – 1.5 – 1.5 ns CL = 50pF
* Part–to–Part Skew Q0, 1, 4, 5 – 1.0 – 1.0 – 1.0 ns CL = 50pF
Propagation Delay
All Outputs 4.3 7.3 4.3 7.3 4.5 7.5 ns CL = 50pF
R to Output
Output Rise/Fall Time
All Outputs – 1.6 – 1.6 – 1.6 ns CL = 50pF
0.8V – 2.0V
Maximum Input Frequency 135 – 135 – 135 – MHz CL = 50pF
Reset Recovery Time 1.25 – 1.25 – 1.25 – ns
Pulse Width Out High or
Low @ fin = 100 MHz
Q0, 1 9.5 10.5 9.5 10.5 9.5 10.5 ns CL = 50pf
Relative 1.5V
and CL = 50 pf
ns
SEL to DE, DT
2.0 – 2.0 – 2.0 –
ns
SEL to DE, DT
2.0 – 2.0 – 2.0 –
MOTOROLA MECL Data
2–2
DL122 — Rev 6
 Loading...
Loading...