Page 1

A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
Phone Adapter
with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
VoIP
VoIP
Installation and Troubleshooting Guide
®
Model No.
PAP2-VU
Page 2

Page 3

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Copyright and Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems,
Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
reserved. Other brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
How to Use this Guide
Your guide to the Phone Adapter has been designed to make understanding networking with the Phone Adapter
easier than ever. Look for the following items when reading this User Guide:
This exclamation point means there is a caution or warning and is
something that could damage your property or Phone Adapter.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about something you
might need to do while using the Phone Adapter.
This checkmark means there is a note of interest and is something you
should pay special attention to while using the Phone Adapter.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
word: definition.
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like
this:
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section.
PAP2-VD-UK-UG-41217NC BW
Page 4

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this Guide? 1
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter 3
Back Panel Ports 3
The Front Panel 4
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter 5
Overview 5
Instructions for Connecting the Phone Adapter 5
Placement Options 7
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu 9
Overview 9
Accessing the Interactive Voice Response Menu 9
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu 9
Configuring the Settings for Your Internet Phone Service 14
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 15
Common Problems and Solutions 15
Frequently Asked Questions 23
Appendix B: Windows Help 25
Appendix C: Glossary 27
Appendix D: Specifications 33
Appendix E: Warranty Information 35
Appendix F: Regulatory Information 37
Appendix G: Contact Information 39
Page 5

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
List of Figures
Figure 2-1: Back Panel 3
Figure 2-2: Front Panel 4
Figure 3-1: Connect the Phone Adapter to Your Network and Telephone 5
Figure 3-2: Connect the Telephone Cable 6
Figure 3-3: Connect the Ethernet Network Cable 6
Figure 3-4: Connect the Power 6
Figure 3-5: Attaching the Phone Adapter’s Base 7
Figure 3-6: Phone Adapter Standing on Base 7
Figure 3-7: Measurement between Wall-Mount Slots 8
Page 6

Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Linksys Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP. This Phone Adapter will allow
you to make phone or fax calls using the your broadband connection.
How does the Phone Adapter do this? The Phone Adapter connects your phones or fax machines to your network
router or gateway, so telephone service is delivered through your cable or DSL Internet connection. Each of the
Phone Adapter’s two telephone jacks operates independently, with separate phone service and phone numbers,
so you can have up to two phone lines per Adapter.
But what does all of this mean? Networks are useful tools for sharing Internet access and computer resources.
With the Phone Adapter, your phones or fax machines can share your high-speed Internet connection and take
advantage of it. You will be able to make phone calls using the account you set up with your Internet phone
service provider, even while you’re surfing the Internet. So, networks not only are useful in homes and offices,
but also can be fun.
Use the instructions in the Quick Installation or this Installation and Troubleshooting Guide to help you connect
the Phone Adapter after you have set up an account with your Internet phone service provider. These instructions
should be all you need to get the most out of the Phone Adapter.
What’s in this Guide?
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
This guide covers the steps for installing the Phone Adapter.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
1
Page 7

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Phone Adapter’s applications and this Installation and Troubleshooting Guide.
• Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter
This chapter describes the physical features of the Phone Adapter.
• Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
This chapter explains how to connect the Phone Adapter to your network and phones (or fax machines).
• Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
This chapter explains how to configure the Phone Adapter’s network settings.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some potential problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions,
regarding use of the Phone Adapter.
• Appendix B: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as
installing the TCP/IP protocol.
• Appendix C: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
• Appendix D: Specifications
This appendix provides the technical specifications for the Phone Adapter.
• Appendix E: Warranty Information
This appendix supplies the warranty information for the Phone Adapter.
• Appendix F: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the regulatory information regarding the Phone Adapter.
• Appendix G: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
2
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
Page 8

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter
Back Panel Ports
The Phone Adapter’s ports are located on the back panel.
Figure 2-1: Back Panel
PHONE 1 Port For your primary Internet phone line, the PHONE 1 port allows you to connect your
telephone to the Phone Adapter using the included telephone jack adapter (if necessary).
PHONE 2 Port If you add a second Internet phone service provider line, then use the PHONE 2 port. It
allows you to connect a second telephone (or fax machine) to the Phone Adapter using the
included telephone jack adapter (if necessary).
ETHERNET Port The ETHERNET port allows you to connect the Phone Adapter to your router or gateway
using a Category 5 (or better) Ethernet network cable.
POWER Port The POWER port is where you will connect the included power adapter.
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter
Back Panel Ports
NOTE: These Phone ports do
not carry any voltage.
3
Page 9

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
The Front Panel
The Phone Adapter’s LEDs are located on the front panel.
Figure 2-2: Front Panel
PHONE 1 LED Blue. The PHONE 1 LED is solidly lit when a telephone or fax machine has a registered
connection to your Internet phone service provider through the PHONE 1 port. (The
connection is registered if your Internet phone service account is active.) It flashes when
the phone is being used or an incoming call has been detected.
PHONE 2 LED Blue. The PHONE 2 LED is solidly lit when a telephone or fax machine has a registered
connection to your Internet phone service provider through the PHONE 2 port. It flashes
when the phone is being used or an incoming call has been detected.
ETHERNET LED Blue. The ETHERNET LED lights up when the Phone Adapter is connected to your network
through the Ethernet port. It flashes when there is data being sent or received.
Power LED Blue/Red. The Power LED lights up when the Phone Adapter is powered on and ready. It
flashes when the Phone Adapter is booting up, undergoing a self-test, or performing a
firmware upgrade. The LED lights up red when the Phone Adapter has failed its self-test or
is malfunctioning. Refer to “Appendix A: Troubleshooting” for more information.
4
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Phone Adapter
The Front Panel
Page 10
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
Overview
This chapter gives instructions on how to connect the Phone Adapter to your network and telephones or fax
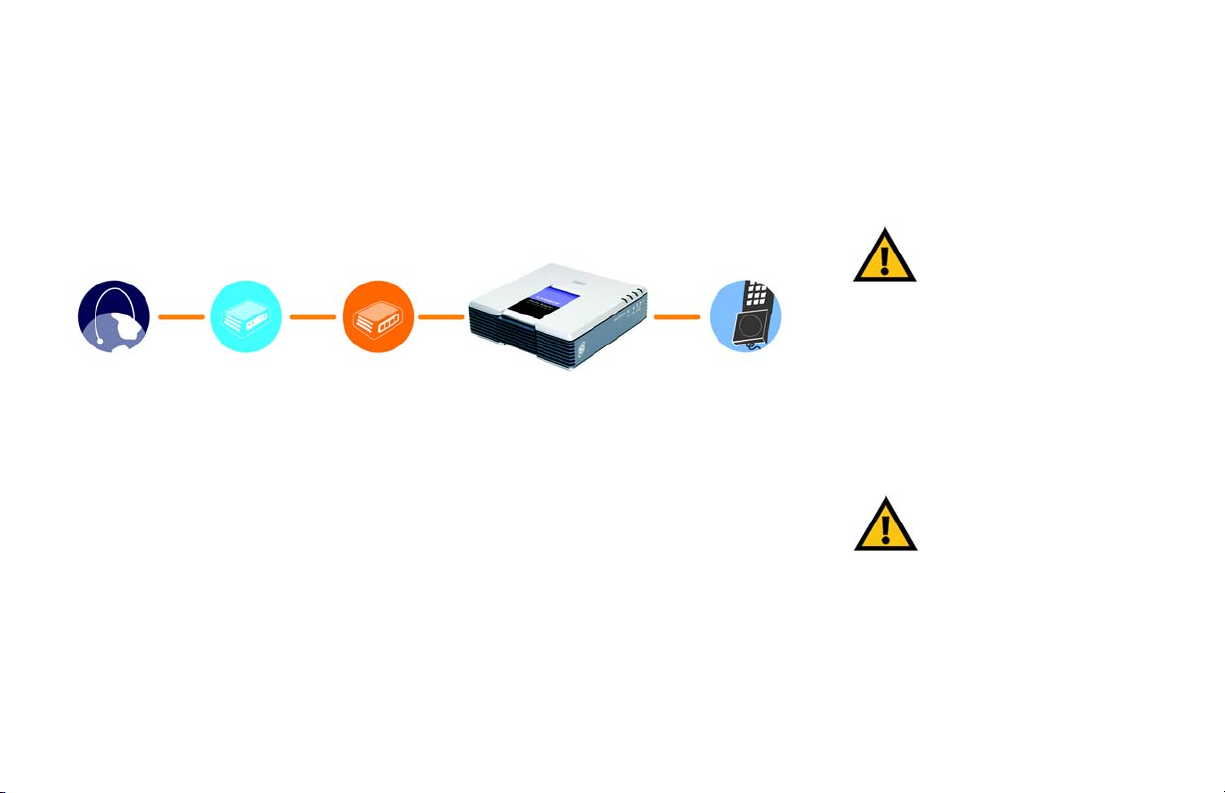
machines. Shown below is a connection diagram displaying a typical setup.
Internet
This chapter also describes the Phone Adapter’s placement options. You can place it flat on a surface, attach
the Phone Adapter’s base so it can stand in place, or mount the Phone Adapter on a wall.
Cable/DSL
Modem
Figure 3-1: Connect the Phone Adapter to Your Network and Telephone
Router
Phone Adapter
Instructions for Connecting the Phone Adapter
If you already have an account set up with your Internet phone service provider, then proceed to step 1.
If you do not have an account, contact your Internet phone service provider to activate the Phone Adapter. After
you have set up an account, then proceed to step 1.
Telephone
IMPORTANT: The Phone
Adapter includes a ringer (ring
signal generator), which is a
source of hazardous voltage.
When the ringer is activated by
an incoming call, do not touch
the Phone port wires, the wires
of a cable connected to either
of the Phone ports, or the
internal circuitry of the Phone
Adapter.
IMPORTANT: Do not connect
either of the Phone ports to a
telephone wall jack. Make sure
you only connect a telephone or
fax machine to either of the
Phone ports. Otherwise, the
Phone Adapter or the telephone
wiring in your home or office
may be damaged.
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
Overview
5
Page 11

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
1. If necessary, disconnect the telephone cable from the telephone wall jack and connect that end to the
telephone jack adapter. Then connect the adapter to the PHONE 1 port of the Phone Adapter.
2. If you have a second phone line on your account, then connect another telephone or a fax machine to the
PHONE 2 port of the Phone Adapter.
3. Connect the included Ethernet network cable to the ETHERNET port of the Phone Adapter.
Connect the other end to the one of the Ethernet ports on your router or gateway.
4. Connect the included power adapter to the POWER port on the back panel of the Phone Adapter.
Connect the other end to a standard electrical outlet.
5. The Power, Ethernet, and Phone LEDs will be solidly lit when the Phone Adapter is ready for use.
6. Follow the instructions provided by your Internet phone service provider.
If you need to manually configure the Phone Adapter’s network settings, you can use the telephone; for
instructions, proceed to “Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu.”
The installation of the Phone Adapter is complete. Now you can pick up your phone and make calls.
Proceed to the next section, “Placement Options,” if you want to attach the Phone Adapter’s base.
6
Figure 3-2: Connect the Telephone Cable
Figure 3-3: Connect the Ethernet
Network Cable
Figure 3-4: Connect the Power
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
Instructions for Connecting the Phone Adapter
Page 12

Placement Options
There are three ways to place the Phone Adapter. The first way is to place the Phone Adapter horizontally on a
surface. The second way is to stand the Phone Adapter vertically on a surface. The third way is to mount the
Phone Adapter on a wall. The second and third options are explained in further detail below.
Stand Option
1. Remove the plate from the Phone Adapter’s bottom panel.
2. Line up the pegs of the Phone Adapter’s base with the mounting holes of the Phone Adapter’s bottom panel.
3. Insert the Phone Adapter’s base into the Phone Adapter’s bottom panel. Push the base in until it fits snugly.
4. Place the Phone Adapter in an appropriate location.
Congratulations! The installation of the Phone Adapter is complete.
If you need to change any of the Phone Adapter’s network settings, proceed to “Chapter 4: Using the
Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu.”
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Figure 3-5: Attaching the Phone
Adapter’s Base
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
Placement Options
Figure 3-6: Phone Adapter Standing
on Base
7
Page 13
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Wall-Mount Option
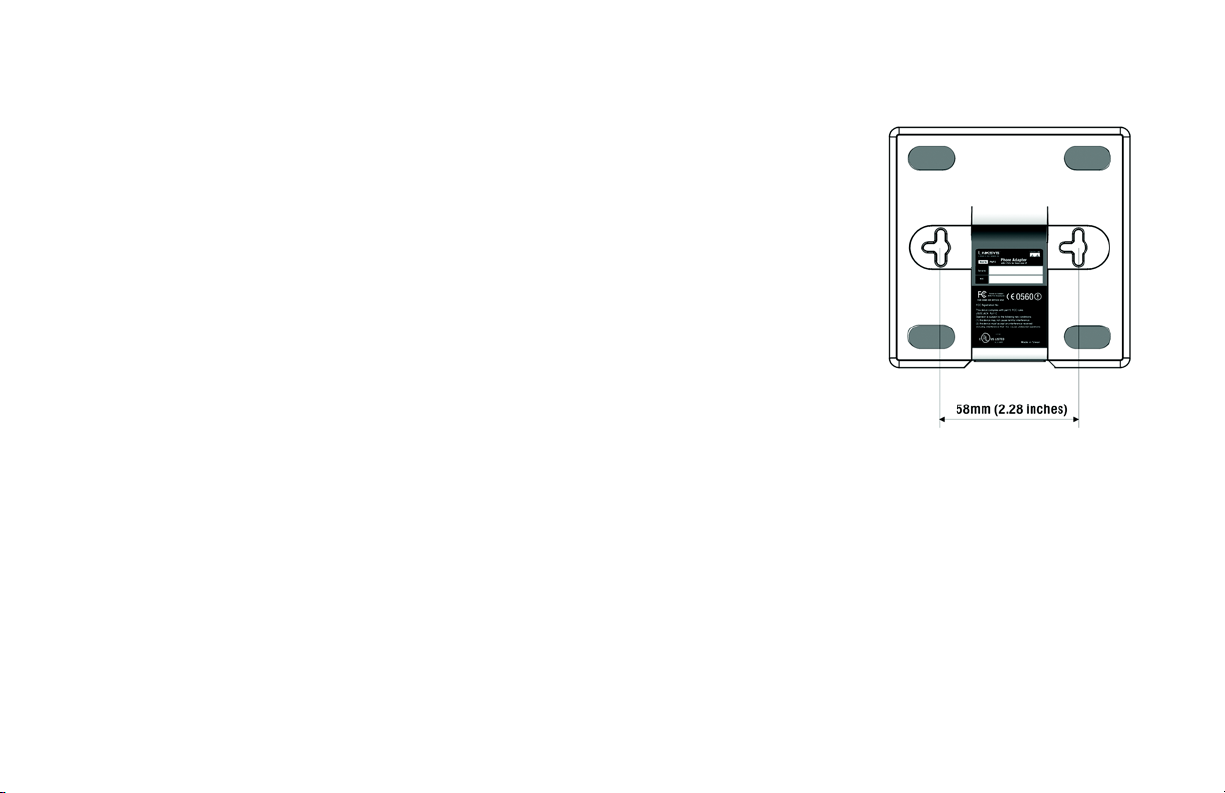
The Phone Adapter has two wall-mount slots on its back panel. The distance between the two slots is 58 mm
(2.28 inches).
1. Determine where you want to mount the Phone Adapter.
2. Drill two holes into the wall. Make sure the holes are 58 mm (2.28 inches) apart.
3. Insert a screw into each hole, and leave 5 mm (0.2 inches) of its head exposed.
4. Maneuver the Phone Adapter so the wall-mount slots line up with the two screws.
5. Place the wall-mount slots over the screws and slide the Phone Adapter down until the screws fit snugly into
the wall-mount slots.
Congratulations! The installation of the Phone Adapter is complete.
If you need to change any of the Phone Adapter’s network settings, proceed to “Chapter 4: Using the
Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu.”
8
Figure 3-7: Measurement between
Wall-Mount Slots
Chapter 3: Connecting the Phone Adapter
Placement Options
Page 14

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Overview
Chapter 4 explains how you can use the Interactive Voice Response Menu to configure the Phone Adapter’s
network settings. You may need to change these settings depending on the specifics of your local network setup.
Use the phone’s keypad to enter your commands and select choices, and the Phone Adapter will respond with
voice responses.
Accessing the Interactive Voice Response Menu
1. Use a telephone connected to the PHONE 1 or PHONE 2 port of the Phone Adapter.
2. Press **** (in other words, press the star key four times).
3. You will hear, “Configuration menu. Please enter option followed by the # (hash) key or hang up to exit.”
Refer to the following table that lists actions, commands, menu choices, and descriptions. After you select
an option, press the # (hash) key. To exit the menu, hang up the telephone.
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
While entering a value, such as an IP address, you may exit without entering any changes. Press the * (star) key
twice within half a second. Otherwise, the * will be treated as a decimal point or dot.
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Overview
9
Page 15

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
After entering a value, such as an IP address, press the # (hash) key to indicate you have finished your selection.
To save the new setting, press 1. To review the new setting, press 2. To re-enter the new setting, press 3. To
cancel your entry and return to the main menu, press * (star).
For example, to enter the IP address 191.168.1.105 by keypad, press these keys: 191*168*1*105. Press the #
(hash) key to indicate that you have finished entering the IP address, and then press 1 to save the IP address. To
cancel your entry and return to the main menu, press * (star).
If the menu is inactive for more than one minute, the Phone Adapter will time out. You will need to re-enter the
menu by pressing ****.
The settings you have saved will take effect after you have hung up the telephone. The Phone Adapter may
reboot at this time.
Interactive Voice Response Menu
Action Command
(press these
keys on the
telephone)
Enter Interactive Voice
Response Menu
10
**** Use this command to enter the
Choices Description
Interactive Voice Response Menu. Do
not press any other keys until you
hear, “Configuration menu. Please
enter option followed by the # (hash)
key or hang up to exit.”
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
Page 16

Interactive Voice Response Menu
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Action Command
Choices Description
(press these
keys on the
telephone)
Check DHCP 100 Use this command to find out if DHCP
has been enabled or disabled. If
enabled, the Phone Adapter will be
automatically assigned an IP address
by your network router or gateway. If
disabled, then the Phone Adapter will
use a static IP address.
Enable/Disable DHCP 101 Enter 1 to enable
Enter 0 to disable
Check IP Address 110 You will hear the current IP address of
Enable or disable the Phone Adapter’s
DHCP feature. If your network router
or gateway assigns IP addresses, then
enter 1. Otherwise, enter 0.
the Phone Adapter.
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
11
Page 17

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Interactive Voice Response Menu
Action Command
Choices Description
(press these
keys on the
telephone)
Set Static IP Address 111 Enter the IP
address using
numbers on the
telephone keypad.
Use the * (star) key
when entering a
decimal point.
Check Network Mask
(or Subnet Mask)
Set Network Mask (or
Subnet Mask)
Check Static Gateway
IP Address
120 You will hear the current network
121 Enter the network
mask using
numbers on the
telephone keypad.
Use the * (star) key
when entering a
decimal point.
130 You will hear the current gateway IP
To set a static IP address, the DHCP
feature must be disabled. If the DHCP
feature is enabled, then you will hear,
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set a
static IP address.
mask of the Phone Adapter.
To set the network mask, the DHCP
feature must be disabled. If the DHCP
feature is enabled, then you will hear,
“Invalid Option,” if you try to set the
network mask.
address of the Phone Adapter.
12
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
Page 18

Interactive Voice Response Menu
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Action Command
Choices Description
(press these
keys on the
telephone)
Set Static Gateway IP
Address
Check MAC Address 140 You will hear the MAC address of the
Check Firmware
Version
Manual Reboot 732668 After you hear, “Option successful,”
131 Enter the IP
address using
numbers on the
telephone keypad.
Use the * (star) key
when entering a
decimal point.
150 You will hear the version number of
To set a static gateway IP address, the
DHCP feature must be disabled. If the
DHCP feature is enabled, then you will
hear, “Invalid Option,” if you try to set
a static gateway IP address.
Phone Adapter in hexadecimal string
format.
the firmware currently installed on the
Phone Adapter.
hang up the phone. The Phone
Adapter will automatically reboot.
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Using the Interactive Voice Response Menu
13
Page 19

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Configuring the Settings for Your Internet Phone Service
If you want to change the settings for your Internet phone service, contact your Internet phone service provider.
14
Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu
Configuring the Settings for Your Internet Phone Service
Page 20

Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix provides solutions to problems that may occur during the installation and operation of the Phone
Adapter. Read the description below to solve your problems. If you can't find an answer here, check the Linksys
website at www.linksys.com.
Common Problems and Solutions
1. I don’t hear a dial tone, and the PHONE1 (or PHONE2) LED is not lit.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Make sure the telephone is plugged into the appropriate port, PHONE 1 or PHONE 2. (You should use the
Phone 2 port only if you have more than one phone line.)
• Make sure the ETHERNET LED on the front panel of the Phone Adapter is lit. If it is not lit, then check your
router and network connection to the Internet.
• Pick up the telephone. Press 80#. Hang up the telephone. Wait approximately 30 seconds. Then pick up
the telephone; you should now have a dial tone.
• Follow these instructions to reboot your cable or DSL modem, Phone Adapter, and router:
1. Power off your cable or DSL modem by unplugging its power adapter.
2. Power off the router by unplugging its power adapter.
3. Power off the Phone Adapter by unplugging its power adapter.
4. Wait two minutes, and then power on your cable or DSL modem by plugging its power adapter into
an electrical outlet.
5. Wait two minutes, and then power on the router by plugging its power adapter into an electrical
outlet.
6. Wait five minutes, and then power on the Phone Adapter by plugging its power adapter into an
electrical outlet.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
15
Page 21

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
7. Reboot one of your networked computers, and check to see if you have an active Internet
connection.
8. Pick up the telephone. You should now have a dial tone.
• Set up port forwarding on your router. You must specify that four port ranges be forwarded to the IP
address of the Phone Adapter. These four port ranges are as follows: 5060-5061 (UDP), 53-53 (UDP),
69-69 (UDP), and 10000-20000 (UDP).
Before you set up port forwarding on your router, change two of the Phone Adapter’s settings using its
Interactive Voice Response Menu. First, disable its DHCP feature, and then assign a static IP address to
the Phone Adapter. Refer to “Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu” for
instructions.
If you have a non-Linksys router, refer to its documentation for instructions.
If you have a Linksys router, then follow these instructions:
1. On one of your networked computers, open your web browser.
2. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the
Router.
3. A login screen will appear. Leave the User Name field blank. Enter the Router’s password (the
default is admin) in the Password field. Then click the OK button.
4. Click the Applications & Gaming tab, and then click the Port Range Forwarding tab.
5. For each port range you must specify, enter a different name in the Application field. Then enter the
number or range of external port(s) used by the Phone Adapter.
6. Select the protocol you will be using, UDP.
7. Enter the IP address of the Phone Adapter. For example, if the Phone Adapter’s IP address is
192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided.
16
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 22

8. Repeat steps 5-7 until you have entered all four port ranges for the Phone Adapter.
Application Start and End Protocol IP Address Enable
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Internet phone 1 5060 to 5061 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 2 53 to 53 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 3 69 to 69 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 4 10000 to 20000 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
9. Check the Enable option for the port services you want to use.
10. When you have completed the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
2. When I make a telephone call, the call doesn’t go through; instead, I hear a fast busy signal.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Follow these instructions to reboot your cable or DSL modem, Phone Adapter, and router:
1. Power off your cable or DSL modem by unplugging its power adapter.
2. Power off the router by unplugging its power adapter.
3. Power off the Phone Adapter by unplugging its power adapter.
4. Wait two minutes, and then power on your cable or DSL modem by plugging its power adapter into
an electrical outlet.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
17
Page 23

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
5. Wait two minutes, and then power on the router by plugging its power adapter into an electrical
outlet.
6. Wait five minutes, and then power on the Phone Adapter by plugging its power adapter into an
electrical outlet.
7. Reboot one of your networked computers, and check to see if you have an active Internet
connection.
8. Pick up the telephone. You should now have a dial tone.
• Set up port forwarding on your router. You must specify that four port ranges be forwarded to the IP
address of the Phone Adapter. These four port ranges are as follows: 5060-5061 (UDP), 53-53 (UDP),
69-69 (UDP), and 10000-20000 (UDP).
Before you set up port forwarding on your router, change two of the Phone Adapter’s settings using its
Interactive Voice Response Menu. First, disable its DHCP feature, and then assign a static IP address to
the Phone Adapter. Refer to “Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu” for
instructions.
If you have a non-Linksys router, refer to its documentation for instructions.
If you have a Linksys router, then follow these instructions:
1. On one of your networked computers, open your web browser.
2. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the
Router.
3. A login screen will appear. Leave the User Name field blank. Enter the Router’s password (the
default is admin) in the Password field. Then click the OK button.
4. Click the Applications & Gaming tab, and then click the Port Range Forwarding tab.
5. For each port range you must specify, enter a different name in the Application field. Then enter the
number or range of external port(s) used by the Phone Adapter.
6. Select the protocol you will be using, UDP.
18
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 24

7. Enter the IP address of the Phone Adapter. For example, if the Phone Adapter’s IP address is
192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided.
8. Repeat steps 5-7 until you have entered all four port ranges for the Phone Adapter.
Application Start and End Protocol IP Address Enable
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Internet phone 1 5060 to 5061 UDP (IP address of
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 2 53 to 53 UDP (IP address of
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 3 69 to 69 UDP (IP address of
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 4 10000 to 20000 UDP (IP address of
Phone Adapter)
9. Check the Enable option for the port services you want to use.
10. When you have completed the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
X
X
X
X
19
Page 25

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
3. When I’m on a telephone call, words are dropped intermittently.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Are you using a wireless router and cordless phone? If so, the router and cordless phone may be using
the same frequency and interfere with each other. Move the cordless phone farther away from the
router.
• There may be heavy network activity, particularly if you are running a server or using a file sharing
program. Try to limit network or Internet activity during any Internet telephone call. For example, if you
are running a file sharing program, files may be uploaded in the background even though you are not
downloading any files, so make sure you exit the program before you make an Internet phone call.
• There may not be enough bandwidth available for your call. You can test your bandwidth at
http://www.pcpitstop.com/internet/Bandwidth.asp. If necessary, you can lower your service’s default
codec setting, which is High (90k). First, access your service account at your Internet phone service
provider’s website. Then lower the codec setting to Med (50k) or Low (30k).
4. My telephone does not ring, and my calls automatically go to voicemail.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Make sure the telephone is plugged into the appropriate port, PHONE 1 or PHONE 2. (You should use the
Phone 2 port only if you have more than one phone line.)
• Make sure the ringer volume on your telephone is set to an audible level.
• Follow these instructions to reboot your cable or DSL modem, Phone Adapter, and router:
1. Power off your cable or DSL modem by unplugging its power adapter.
2. Power off the router by unplugging its power adapter.
3. Power off the Phone Adapter by unplugging its power adapter.
4. Wait two minutes, and then power on your cable or DSL modem by plugging its power adapter into
an electrical outlet.
5. Wait two minutes, and then power on the router by plugging its power adapter into an electrical
outlet.
20
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 26

6. Wait five minutes, and then power on the Phone Adapter by plugging its power adapter into an
electrical outlet.
7. Reboot one of your networked computers, and check to see if you have an active Internet
connection.
• Set up port forwarding on your router. You must specify that four port ranges be forwarded to the IP
address of the Phone Adapter. These four port ranges are as follows: 5060-5061 (UDP), 53-53 (UDP),
69-69 (UDP), and 10000-20000 (UDP).
Before you set up port forwarding on your router, change two of the Phone Adapter’s settings using its
Interactive Voice Response Menu. First, disable its DHCP feature, and then assign a static IP address to
the Phone Adapter. Refer to “Chapter 4: Using the Phone Adapter’s Interactive Voice Response Menu” for
instructions.
If you have a non-Linksys router, refer to its documentation for instructions.
If you have a Linksys router, then follow these instructions:
1. On one of your networked computers, open your web browser.
2. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the
Router.
3. A login screen will appear. Leave the User Name field blank. Enter the Router’s password (the
default is admin) in the Password field. Then click the OK button.
4. Click the Applications & Gaming tab, and then click the Port Range Forwarding tab.
5. For each port range you must specify, enter a different name in the Application field. Then enter the
number or range of external port(s) used by the Phone Adapter.
6. Select the protocol you will be using, UDP.
7. Enter the IP address of the Phone Adapter. For example, if the Phone Adapter’s IP address is
192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
21
Page 27

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
8. Repeat steps 5-7 until you have entered all four port ranges for the Phone Adapter.
Application Start and End Protocol IP Address Enable
Internet phone 1 5060 to 5061 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 2 53 to 53 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 3 69 to 69 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
Internet phone 4 10000 to 20000 UDP (IP address of
X
Phone Adapter)
9. Check the Enable option for the port services you want to use.
10. When you have completed the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
5. The Power LED does not light up or lights up red.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Unplug the power adapter from the Phone Adapter. Wait five seconds. Then plug the power adapter into
the Phone Adapter again.
• You may be using the wrong power adapter. Make sure the power adapter you are using is the one
included with the Phone Adapter.
22
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 28

6. The ETHERNET LED does not light up.
Go through this checklist until your problem is solved:
• Check the cable connecting the Phone Adapter to your router.
• Make sure your network has an active Internet connection. If it does not, follow these instructions to
reboot your cable or DSL modem, Phone Adapter, and router:
1. Power off your cable or DSL modem by unplugging its power adapter.
2. Power off the router by unplugging its power adapter.
3. Power off the Phone Adapter by unplugging its power adapter.
4. Wait two minutes, and then power on your cable or DSL modem by plugging its power adapter into
an electrical outlet.
5. Wait two minutes, and then power on the router by plugging its power adapter into an electrical
outlet.
6. Wait five minutes, and then power on the Phone Adapter by plugging its power adapter into an
electrical outlet.
7. Reboot one of your networked computers, and check to see if you have an active Internet
connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I make a phone call?
Pick up the phone and dial as you normally would.
Can I make calls if my Internet connection is down?
No. Your high-speed Internet connection must be active when you make Internet phone or fax calls.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
23
Page 29

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Can I make calls while I’m browsing the Internet?
Yes. You can make Internet phone or fax calls while browsing the Internet. However, your web browsing may
affect the quality of your telephone call, depending on the amount of upstream data traffic passing through your
Internet connection.
Can I receive calls while my network is down?
You cannot directly receive calls while your network is down. However, your Internet phone service provider may
be able to forward calls to a different telephone number, such as a cellular phone number, if you activate a
feature called Network Availability Number. You can configure this feature through your service account.
24
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
Page 30

Appendix B: Windows Help
Almost all Linksys products require Microsoft Windows. Windows is the most used operating system in the world
and comes with many features that help make networking easier. These features can be accessed through
Windows Help and are described in this appendix.
TCP/IP
Before a computer can communicate with a network router, TCP/IP must be enabled. TCP/IP is a set of
instructions, or protocol, all PCs follow to communicate over a network. This is true for wireless networks as
well. Your PCs will not be able to utilize wireless networking without having TCP/IP enabled. Windows Help
provides complete instructions on enabling TCP/IP.
Shared Resources
If you wish to share printers, folder, or files over your network, Windows Help provides complete instructions on
utilizing shared resources.
Network Neighborhood/My Network Places
Other PCs on your network will appear under Network Neighborhood or My Network Places (depending upon the
version of Windows you're running). Windows Help provides complete instructions on adding PCs to your
network.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix B: Windows Help
25
Page 31

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
26
Appendix B: Windows Help
Page 32

Appendix C: Glossary
Adapter - A device that adds network functionality to your PC.
Backbone - The part of a network that connects most of the systems and networks together, and handles the most data.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given device or network.
Bit - A binary digit.
Boot - To start a device and cause it to start executing instructions.
Bridge - A device that connects different networks.
Broadband - An always-on, fast Internet connection.
Browser - An application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the information on the World Wide Web.
Buffer - A shared or assigned memory area that is used to support and coordinate different computing and networking
activities so one isn't held up by the other.
Byte - A unit of data that is usually eight bits long
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in turn connects to the Internet.
CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance) - A method of data transfer that is used to prevent data
collisions.
CTS (Clear To Send) - A signal sent by a wireless device, signifying that it is ready to receive data.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Daisy Chain - A method used to connect devices in a series, one after the other.
Appendix C: Glossary
27
Page 33

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Database - A collection of data that is organized so that its contents can easily be accessed, managed, and updated.
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) - Allows the hosting of a website, FTP server, or e-mail server with a fixed domain
name (e.g., www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP address.
Default Gateway - A device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A networking protocol that allows administrators to assign temporary IP
addresses to network computers by “leasing” an IP address to a user for a limited amount of time, instead of assigning
permanent IP addresses.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Removes the Router's firewall protection from one PC, allowing it to be “seen” from the Internet.
DNS (Domain Name Server) - The IP address of your ISP's server, which translates the names of websites into IP addresses.
Domain - A specific name for a network of computers.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - An always-on broadband connection over traditional phone lines.
DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) - A message included in data packets that can increase wireless efficiency.
Dynamic IP Address - A temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
Encryption - Encoding data transmitted in a network.
Ethernet - A networking protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission medium.
Finger - A program that tells you the name associated with an e-mail address.
Firewall - A set of related programs located at a network gateway server that protects the resources of a network from users
from other networks.
28
Appendix C: Glossary
Page 34

Firmware - The programming code that runs a networking device.
Fragmentation -Breaking a packet into smaller units when transmitting over a network medium that cannot support the
original size of the packet.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network.
Full Duplex - The ability of a networking device to receive and transmit data simultaneously.
Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible communications protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single line, but only one direction at a time.
Hardware - The physical aspect of computers, telecommunications, and other information technology devices.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used to connect to servers on the World Wide Web.
Infrastructure - A wireless network that is bridged to a wired network via an access point.
IP (Internet Protocol) - A protocol used to send data over a network.
IP Address - The address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
IPCONFIG - A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays the IP address for a particular networking device.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A VPN protocol used to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
ISM band - Radio bandwidth utilized in wireless transmissions.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
LAN (Local Area Network) - The computers and networking products that make up your local network.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address that a manufacturer assigns to each networking device.
Appendix C: Glossary
29
Page 35

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) - One million bits per second; a unit of measurement for data transmission.
mIRC - An Internet Relay Chat program that runs under Windows.
Multicasting - Sending data to a group of destinations at once.
NAT (Network Address Translation) - NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a different IP address
for the Internet.
NAT (Network Address Translation) Tr ave rs al -A method of enabling specialized applications, such as Internet phone calls,
video, and audio, to travel between your local network and the Internet. STUN is a specific type of NAT traversal.
Network - A series of computers or devices connected for the purpose of data sharing, storage, and/or transmission between
users.
NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) - The protocol used to connect to Usenet groups on the Internet.
Packet - A unit of data sent over a network.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether a particular IP address is online.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) - A standard mail server commonly used on the Internet.
Port - The connection point on a computer or networking device used for plugging in cables or adapters.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - An Ethernet connector that holds up to eight wires.
Router - A networking device that connects multiple networks together.
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) - A protocol that enables specialized applications, such as Internet phone calls, video, and
audio, to occur in real time.
RTS (Request To Send) - A networking method of coordinating large packets through the RTS Threshold setting.
30
Appendix C: Glossary
Page 36

Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access to files, printing, communications, and other
services.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The standard e-mail protocol on the Internet.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - A widely used network monitoring and control protocol.
Software - Instructions for the computer. A series of instructions that performs a particular task is called a “program”.
SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) - Market segment of professionals who work at home or in small offices.
Static IP Address - A fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a network.
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path.
STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs) - A protocol that enables specialized applications, such as Internet phone calls,
video, and audio, to travel between your local network and the Internet. STUN is a specific type of NAT traversal.
Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network.
Switch - 1. A data switch that connects computing devices to host computers, allowing a large number of devices to share a
limited number of ports. 2. A device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that requires acknowledgement from the
recipient of data sent.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - A set of instructions PCs use to communicate over a network.
Tel ne t - A user command and TCP/IP protocol used for accessing remote PCs.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no directory or password capability.
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Throughput - The amount of data moved successfully from one node to another in a given time period.
Appendix C: Glossary
31
Page 37

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Topology - The physical layout of a network.
TX Rate - Transmission Rate.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that does not require acknowledgement from the
recipient of the data that is sent.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload - To transmit a file over a network.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address of a file located on the Internet.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - A security measure to protect data as it leaves one network and goes to another over the
Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network)- The Internet.
WINIPCFG - A Windows 98 and Me utility that displays the IP address for a particular networking device.
32
Appendix C: Glossary
Page 38

Appendix D: Specifications
Model PAP2-VU
Standards SIP v2 Session Initiation Protocol (RFC 3261, 3262, 3263, 3264)
Voice Codecs G.729 A, G.711 a-law, G.711µ-law, G.726, G.723
Ports Power, Ethernet, Phone 1, Phone 2
Cabling Type CAT 5 (RJ45) for Ethernet Port and RJ11 for Phone Ports
LEDs Power, Ethernet, Phone 1, Phone 2
Maximum Ringer Load 5 REN
Ring Frequency 10-40 Hz
FXS Port Impedance Eight Configurable Settings Including North America 600 ohms,
European CTR21
Ring Voltage 60-90 Vrms Configurable
Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Security Features Password Protected Administration
Appendix D: Specifications
33
Page 39

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Dimensions 101 mm x 101 mm x 15 mm
(W x H x D)
Unit Weight 0.13 kg
Power 5 V DC, 2.0 A
Certifications FCC, cUL, CE
Operating Temp. 5º~45ºC
Storage Temp. -25º~85ºC
Operating Humidity 10~90% Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 5~90% Non-Condensing
34
Appendix D: Specifications
Page 40

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix E: Warranty Information
LIMITED WARRANTY
Your Internet phone service provider warrants to You that, for a period of two years (the “Warranty Period”), your Linksys Product will be substantially free of
defects in materials and workmanship under normal use. Your exclusive remedy and Your Internet phone service provider’s entire liability under this
warranty will be for Your Internet phone service provider at its option to repair or replace the Product or refund Your purchase price less any rebates. This
limited warranty extends only to the original purchaser.
If the Product proves defective during the Warranty Period call Your Internet phone service provider Technical Support in order to obtain a Return
Authorization Number, if applicable. If You are requested to return the Product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package.
You are responsible for shipping defective Products to Your Internet phone service provider.
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE
WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED. Some jurisdictions do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to
You. This warranty gives You specific legal rights, and You may also have other rights which vary by jurisdiction.
This warranty does not apply if the Product (a) has been altered, except by Your Internet phone service provider, (b) has not been installed, operated, repaired,
or maintained in accordance with instructions supplied by Your Internet phone service provider, or (c) has been subjected to abnormal physical or electrical
stress, misuse, negligence, or accident. In addition, due to the continual development of new techniques for intruding upon and attacking networks, Your
Internet phone service provider does not warrant that the Product will be free of vulnerability to intrusion or attack.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL YOUR INTERNET PHONE SERVICE PROVIDER BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE OR
PROFIT, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE), ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT (INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN IF Your Internet phone
service provider HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT WILL Your Internet phone service provider’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE
AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT. The foregoing limitations will apply even if any warranty or remedy provided under this Agreement fails of its
essential purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion
may not apply to You.
Please contact your Internet phone service provider regarding the warranty for the Product.
Appendix E: Warranty Information
35
Page 41

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
36
Appendix E: Warranty Information
Page 42

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix F: Regulatory Information
FCC STATEMENT
This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver's
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
SAFETY NOTICES
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY (EUROPE)
In compliance with the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC, and Amendment Directive 93/68/EEC, this product meets
the requirements of the following standards:
• EN55022 Emission
EN55024 Immunity
Appendix F: Regulatory Information
37
Page 43

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
38
Appendix F: Regulatory Information
Page 44

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
Appendix G: Contact Information
Need to contact Linksys?
Visit us online for information on the latest products and updates
to your existing products at: http://www.linksys.com
If you experience problems with any Linksys product, you can e-mail us at:
United Kingdom & Ireland support.uk@linksys.com
Appendix G: Contact Information
39
Page 45

Phone Adapter with 2 Ports for Voice-over-IP
40
Appendix G: Contact Information
Page 46

www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...