Page 1

Jøtul F 602 USA
Jøtul F 602 USA
Installation and Operating Instructions for the USA and Canada
Kindly save these instructions for future reference.
Ce document doit être conservé pendant toute la vie de l'appareil.
Page 2

USA
Table of contents
General information
Possible hazards to avoid
when using the Jøtul F 602 USA ..................................... 2
Installation
Safety notice .......................................................................... 3
Top Exit or Rear Exit............................................................. 3
Fasten the Legs ..................................................................... 3
Plan Ahead
Chimney connector ............................................................. 3
Wall Pass-Through................................................................ 4
Chimneys................................................................................ 4
Masonry Chimneys .............................................................. 5
Listed Metal Prefabricated Chimneys ............................. 5
Connection to the Chimney
Masonry Chimneys .............................................................. 5
Prefabricated Chimneys ..................................................... 5
Clearances to Combustibles
Floor Protection .................................................................... 6
Alternate Floor Protection .................................................. 6
Clearances to Adjacent Combustible Materials .......... 6
Using a Rear Heat Shield .................................................... 6
to Reduce Clearance in Alcove Installations ................. 6
Using Wall Protectors
to Reduce Clearances in Alcove Installations ............... 6
Alcove Installation ................................................................ 6
Operation
Wood Storage ........................................................................ 8
Creosote and Soot Formation and
the Need for Removal......................................................... 8
Breaking in Your Stove ....................................................... 8
Controls
Front Door Latch ...................................................................8
Air Control .............................................................................. 9
Building a Fire ....................................................................... 9
Reloading ............................................................................... 9
Reloading Procedure ........................................................... 9
Ash Removal .......................................................................... 9
Maintenance
General .................................................................................. 10
Glass Replacement ............................................................ 10
Glass Cleaning ..................................................................... 10
Jøtul F 602 Woodstove Clearances ......... 7
Figures and Diagrams ..................... 21-26
General Information
The Owner's Manual describes the installation and
operation of the Jøtul F 602 USA non-catalytic wood
heater. This heater meets the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency's emission limits for wood heaters sold
after July 1, 1990. Under specific test conditions, this heater
has shown heat output at rates ranging from 9,600 to
42,000 BTU's per hour.
When installing, operating, and maintaining your Jøtul F
602 USA, follow the guidelines given in these instructions.
Save these instructions, and make them available to
anyone using the stove.
A number of areas of the U.S. and Canada require a building
permit to install a solid-fuel burning appliance. NFPA 211
(National Fire Protection Association, Standard for
Chimneys, Fireplaces, Vents, and Solid Fuel Burning
Appliances) or CAN/CSA B-365 (Installation Code for SolidFuel Burning Appliances and Equipment) may apply to the
installation of solid fuel burning appliances in your area.
Your Jøtul dealer has knowledge of your local codes and
can provide assistance in making sure your installation is
safe and legal. Also contact your insurance representative,
building inspector, or fire officials to determine what
regulations apply in your area.
The Jøtul F 602 USA has been tested and listed to
ANSI-UL 1482, and ULC S627 by Intertek Testing ServicesWarnock Hersey of Middelton, Wisconsin.
Possible Hazards to Avoid When
Using the Jøtul F 602 USA
Any use of fire in a house represents a certain danger.
With intense overfiring, temperatures on the surface of
the Jøtul F 602 USA can exceed 1 000 0F (536 0C).
Comply with the following guidelines:
• Never overfire the stove. If any part of the stove or
chimney glows, you are overfiring, and a house fire or
serious damage to the stove or chimney could result.
Immediately close down the air control if you notice
this condition.
• Teach children that the stove is hot and must not be
touched.
• Never use gasoline, gasoline-type lantern fuel,
• Never use kerosene, charcoal lighter fluid or similar
liquids to start or "freshen up" a fire in this heater.
They can ignite with explosive force, causing bodily
injury or death. Keep all such liquids far away from the
heater while it is in use.
• Never use the stove if there are combustible gases in
the house. The fumes from certain cleaning fluids,
2
Page 3

USA
adhesives, and paints are a few examples of
combustible gases. Remember, the operating
woodstove is a source of "open flame".
• Avoid creating a "low pressure" condition in the room
where the stove is operating, such as by operating an
exhaust fan or a clothes dryer. A low-pressure
condition could cause poisonous gases to be drawn
out of the stove into the room. Some fuel will during
combustion separate carbon monoxide and generate
it in the burnchamber. Carbon monoxide is toxic, so
please follow the guidelines in this manual to avoid
smoke "roll out" from the burnchamber. You can
prevent a low-pressure condition by providing
adequate outside combustion air within 24" of the
stove.
• Never operate the Jøtul F 602 USA if it has cracked or
broken glass. Replace damaged glass only with the
proper glass panel available from your Jøtul dealer.
• Never burn trash of any kind in the stove.
• Keep combustible materials far away from the stove.
• Never modify the stove in any way.
• Do not dry clothes over the stove, since they could fall
and ignite.
• Use only seasoned wood in your stove. Never use
fireplace coal or synthetic logs that have not been
approved for the stove.
• Always wear protective gloves when adding fuel to
the fire.
• If you for some reason experience smoke "roll out"
from the fireplace, it might activate smoke detectors
(if installed).
• Do not connect this heater to any air distribution duct.
Note! This stove is not approved for use in mobile homes.
Top Exit or Rear Exit
The Jøtul F 602 USA has two flue outlet positions. If you
wish to top-exit the stove, place the cover plate in the
rear position and secure it with the screws and nuts, then
secure the flue collar to the top with the two remaining
screws.
To rear -exit the stove, secure the cover plate in the top
position with the two screws, then secure the flue collar
to the rear with the two remaining screws and two nuts.
When fastening the plate or flue collar to the rear, it may
be necessary to reach in through the top opening and
hold the nuts with a wrench.
Attaching the Legs
The Jøtul F 602 USA has four tapped leg bolt holes in the
bottom plate. Fasten each leg to the bottom with a bolt
and with a washer between the bolt head and the leg.
Plan Ahead
A safe stove installation involves several elements,
including: (A) the chimney connector, (B) the chimney itself,
(C) the connection between the chimney connector and
chimney, and (D) protection of combustible materials in
the vicinity of the stove. Each of these elements is equally
important for a safe stove installation.
Installation
Safety Notice
If this solid fuel room heater is not properly installed a
house fire may result. For your safety, follow the
installation directions. Contact local building or fire officials
about restrictions and installation inspection requirements
in your area.
Please read this entire manual before you install and use
your new stove. Failure to follow instructions may result
in property damage, bodily injury, or even death.
We recommend that you have your Jøtul F 602 USA
installed by a professional installer of solid fuel room
heaters.
A. Chimney Connector (Stove Pipe)
Chimney connector is also sometimes called stove pipe
or flue pipe, and it is used to connect the stove to the
chimney. The chimney connector should be 6" diameter
black steel, with a minimum thickness of 24 gauge.
Do not use aluminium or galvanized steel pipe as a chimney
connector. These materials cannot withstand the extreme
temperatures of a wood fire and can give off toxic fumes
when heated.
Matching enamel pipe is available for your Jøtul F 602
USA. Contact your Authorised Jøtul dealer for more
information.
Do not use chimney connector pipe as a chimney.
The factory-supplied adapter must be used for fitting the
stove's flue collar to the chimney connector.
Chimney connector sections must be attached to the
3
Page 4

USA
stove's flue collar adapter and to each other with the
crimped end toward the stove (fig. 2, page 20).
The space between the flue collar adapter and the
chimney connector should be sealed with stove cement
or an appropriately size piece of gasket. This allows any
small amounts of condensed creosote to run into the
stove rather then onto the outside of the pipe or the stove
top. All joints, including the adapter to the flue collar, should
be secured with three sheet metal screws to ensure that
the sections will not separate.
For proper operation the chimney connector should be as
short as possible. Horizontal lengths should have an
upward slope from the stove of 1/4" per foot. Avoid using
more than two 90 degree elbows or total runs of pipe
greater than 1 0'.
No part of the chimney connector may pass through an
attic or roof space, closet or other concealed space, or
through a floor or ceiling. Whenever possible, avoid
passing the chimney connector through a combustible
wall.
Wall Pass-Through
When your installation unavoidably requires that the
chimney connector pass through a combustible wall to
reach the chimney, extreme care must be taken. In the
U.S., the National Fire Protection Association's publication
NFPA 21 1, Standard for Chimneys, Fireplaces, Vents, and
Solid Fuel Burning Appliances, permits four methods for
passing through a combustible wall. In Canada, refer to
CAN/CGA B356. Before beginning the installation, contact
local building officials to make sure the proposed passthrough method meets local building code requirements.
An approved installation that uses a section of listed solid
fuel insulated factory-built chimney as a pass- through
for the chimney connector, must have an inside diameter
which is 2" larger than the chimney connector- a minimum
length of 12" -and at least 1" of insulation thickness. The
chimney section is installed with at least 2" of air space
between the outer chimney wall and adjacent combustible
materials.
Sheet steel support plates are used on both ends of the
chimney section to keep the connector centred. The
opening around the chimney section is closed on both
sides of the wall with sheet steel plates and the chimney
section is securely fastened to the plates. Fasteners used
to support the chimney section should never penetrate
the inner flue liner.
See NFPA-211 for other approved wall passthrough
methods.
B. Chimneys
There are two types of chimneys suitable for the
Jøtul F 602 USA. An approved masonry chimney, or a listed
residential-type building heating appliance chimney.
When selecting a chimney type and the location for the
chimney in the house, keep this in mind: it is the chimney
that makes the stove work, not the stove that makes the
chimney work. This is because a chimney actually creates
suction, called draft, which pulls air through the stove.
Several factors affect draft: the height, cross-sectional
area, and temperature of the chimney, as well as the
proximity of surrounding trees or buildings.
A commonly used method to pass through a wall directly
to a masonry chimney requires removal of all combustible
material from at least 12" around the entire chimney
connector. The space is then filled with at least 12" of
brick around a fireclay liner. Be sure to locate it so that
the top of the chimney connector will be at least 18" below
the ceiling.
To construct the brick pass-through, you will need an
opening of 30" x 30" minimum. It will be necessary to cut
wall studs, install headers, and construct a sill frame to
maintain proper dimensions and to hold the weight of
the brick. Minimum 3-1/2" (4" nominal) thick solid bricks
are to be used.
The fireclay liner (ASTM C35 or equivalent), minimum 5/8"
wall thickness, must not penetrate into the chimney
beyond the inner surface of the chimney flue liner and
must be firmly cemented in place. If it is necessary to cut
a hole in the chimney liner, use extreme care to keep it
from shattering. Refractory mortar must be used at the
junction to the chimney liner. (See figure 3, page 21)
4
In general, a short masonry chimney on the exterior of
the house will give the poorest performance. This is
because it can be very difficult to warm up, and in
extremely cold northern areas it may not work at all.
A tall masonry chimney inside the house is easier to keep
warm and will work best.
This guideline gives the necessary chimney requirements
based on the U.S. national code (NFPA-211). However, many
local codes differ from the national code to take into
account climate, altitude, or other factors. It is important
that you check with your local building officials to find out
what codes apply in your area before constructing a
chimney.
Page 5

USA
Masonry Chimneys
The minimum requirements for a properly constructed
chimney include the following:
• The foundation must be large enough to support the
intended chimney without settling.
• The masonry wall of the chimney, if brick or modular
block, must be a minimum of 4" nominal thickness. A
mountain- or rubble-stone wall must be at least 12"
thick.
• The chimney must have a fireclay flue liner (or
equivalent with a minimum thickness of 5/8" and must
be installed with refractory mortar. There must be at1/
2" air space between the flue liner and chimney wall.
• The preferred fireclay flue liner size has a nominal
size of 8" x 8", and should not be larger than 8" x12". lf
round fireclay liners are used, the inside diameter
should be 6" and not larger than 8". lf an existing
chimney with larger tiles is used it should be relined
with an appropriate liner.
• No other appliance can be vented into the same flue.
• An airtight cleanout door should be located at the base
of the chimney.
A chimney inside the house must have at least 2" of
clearance to the combustible structure. A chimney outside
the house must have at least 1" clearance to the
combustible structure. Fire stops must be installed at the
spaces where the chimney passes through floors and/or
ceilings. Remember that there must be air space around
the chimney, and that insulation must be 2" or more from
the chimney.
A chimney, wether masonry or prefabricated metal, must
be the required height above the roof or other obstruction
for safety and for proper draft operation. The requirement
is that the chimney must at least 3' higher than the highest
point where it passes through the roof and at least 2'
higher than the be at least and highest part of the roof or
structure that is within 10' of the chimney, measured
horizontally (fig. 4, page 21).
Chimneys shorter than 14' may not provide adequate draft.
This could result in smoke spilling the room from the door
or joints in the stove or pipe. In addition, inadequate draft
can cause puffing. A too-strong draft, on the other hand,
cause excessive temperatures and can shorten burn
times. Excessive drafts can be corrected by having your
dealer install a barometric damper at 0.1 " of water
column. lf you suspect you have draft problem, consult
your dealer.
Listed Metal Prefabricated Chimneys
The heater must be connected to a listed Type HT per
UL 103 or ULC S629 prefabricated chimney. When a metal
prefabricated chimney is used, the manufacturer's
installation instructions must be followed precisely. You
must also purchase (from the same manufacturer) and
install the ceiling support package or wall pass through,
the "T" section package, the firestops (when needed), the
insulation shield, the roof flashing, the chimney cap, etc.
Maintain the proper clearance to the structure as
recommended by the manufacturer. This clearance is
usually a minimum of 2", although it may vary by
manufacturer or for certain components.
There are basically two methods of metal chimney
installation. One method is to install the chimney inside
the residence through the ceiling and the roof (fig. 5,
page 22).
The other method is to install an exterior chimney that
runs up the outside of the residence.
C. Connection to the Chimney
Masonry Chimneys
When connecting to a masonry chimney, the chimney
connector must slide completely inside the chimney
thimble (or breach) to the inner surface of flue liner, make
sure the connector does not protrude past the inside of
the flue liner as that will reduce the flow area available
for the smoke and ultimately cause problems with your
chimney system. The chimney connector should be sealed
into the thimble with refractory cement and the connector
should also be mechanically fastened to the chimney.
See fig. 6, page 22.
Prefabricated Chimneys
Always follow the chimney manufacturer's instructions
and use all the components required by the manufacturer.
Do not take shortcuts or use make shift methods for
securing the chimney connector to the chimney.
Note: The clearances expressed in inches are those
approved for installations in the United States. The
clearances in parentheses that are expressed in
centimeters are those approved for installations in Canada.
Different test standards for the respective countries may
result in differences in the clearance requirements.
5
Page 6

USA
Clearances to
Combustibles
Floor Protection
A bottom heat shield is required in all installations. In
addition, your stove must be placed on a noncombustible
surface that extends 8" beyond the sides and back of the
stove and 16" in the front of the stove. This will result in
an overall base that is 28 1/2" wide x 45- 1/2" deep . This
is the minimum floor protector size. Floor protection
must also be used under the stove pipe and must
extend 2" beyond either side of the pipe (fig. 7, page
22).
The floor protection must have a minimum R value of
D. 45.
Warning! Never put any type of floor protection on top of
carpeting.
Alternate Floor Protection
All floor protection materials must be non-combustible
(i.e., metals, brick, stone, mineral fiber boards, etc.). Any
organic materials (i.e., plastics, wood, paper products, etc.)
are combustible and must not be used. The floor protector
specified may include some form of thermal designation
such as R-value (thermal resistance), k-factor (thermal
conductivity), or C-factor (thermal conductance).
The easiest means of determining if a proposed alternate
floor material meets requirements listed in the appliance
manual is to follow the procedure: See page 26.
hearth in it that you plan to use, it is extremely
important that the entire system be examined for
safety. Many older homes may have faulty chimneys,
or previous owners may have covered combustible
walls or studs with brick veneers. Heat is conducted
readily through brick and could ignite unseen
combustibles behind it.
Contact local building or fire official about restrictions and
installation requirements in your area.
Using a Rear Heat Shield to Reduce
Clearance in Alcove lnstallations
The Jøtul F 602 USA optional rear heat shield, PN HS50,may
be used only in top-exiting parallel installations to reduce
clearance as shown in figures 11,12,13, page 23.
Using Wall Protectors to Reduce
Clearances
The wall protector must be non-combustible, such as a
minimum 24 gauge galvanized steel or its equivalent. The
wall protector must be elevated 1" from the floor to
provide an air space of at least 1" between the shield and
the combustible wall. See figures 16, 17, and 18 on pages 23
and 24 for approved sizing specifications.
Alcove installation
When installed with a listed double wall pipe and with
wall protection, the Jøtul F 602 USA can be placed in an
alcove that has a minimum height of 96”1 and a maximum
depth of 48", and a minimum width of 41". The clearances
for this installation are shown in figure 14-15, page 23.
Clearance to Adjacent Combustible
Materials
The diagrams in figures 8-9-10 - page 22, give the required
clearances you must maintain from unprotected
combustible materials or objects.
A combustible is anything that can burn, and in the case
of stove installations, these combustibles may not be
visible. lf you are not sure of the combustible nature of
any material in the vicinity of your planned stove
installation, you should check with your local fire off icials.
Remember that "fire resistant" materials are considered
combustible; they are difficult to ignite, but they will burn.
lf you have recently purchased a home that has a stove
6
When installed with a listed double wall pipe and with a
stove heat shield, the Jøtul F 602 USA can be placed in an
alcove that has a minimum height of 96”1 and a maximum
depth of 24”2, and a minimum width of 55". The clearances
for this installation are shown in fig. 12-13, page 23.
In an alcove, the height of the wall protector, including the
air space at the bottom, must be at least 41" (104 cm) (see
fig. 15, page 23). Both side walls and the rear wall must be
protected by the wall protector (fig. 14, page 22).
(1See NFPA 211 for ceiling clearance reductions with
protection.)
Page 7
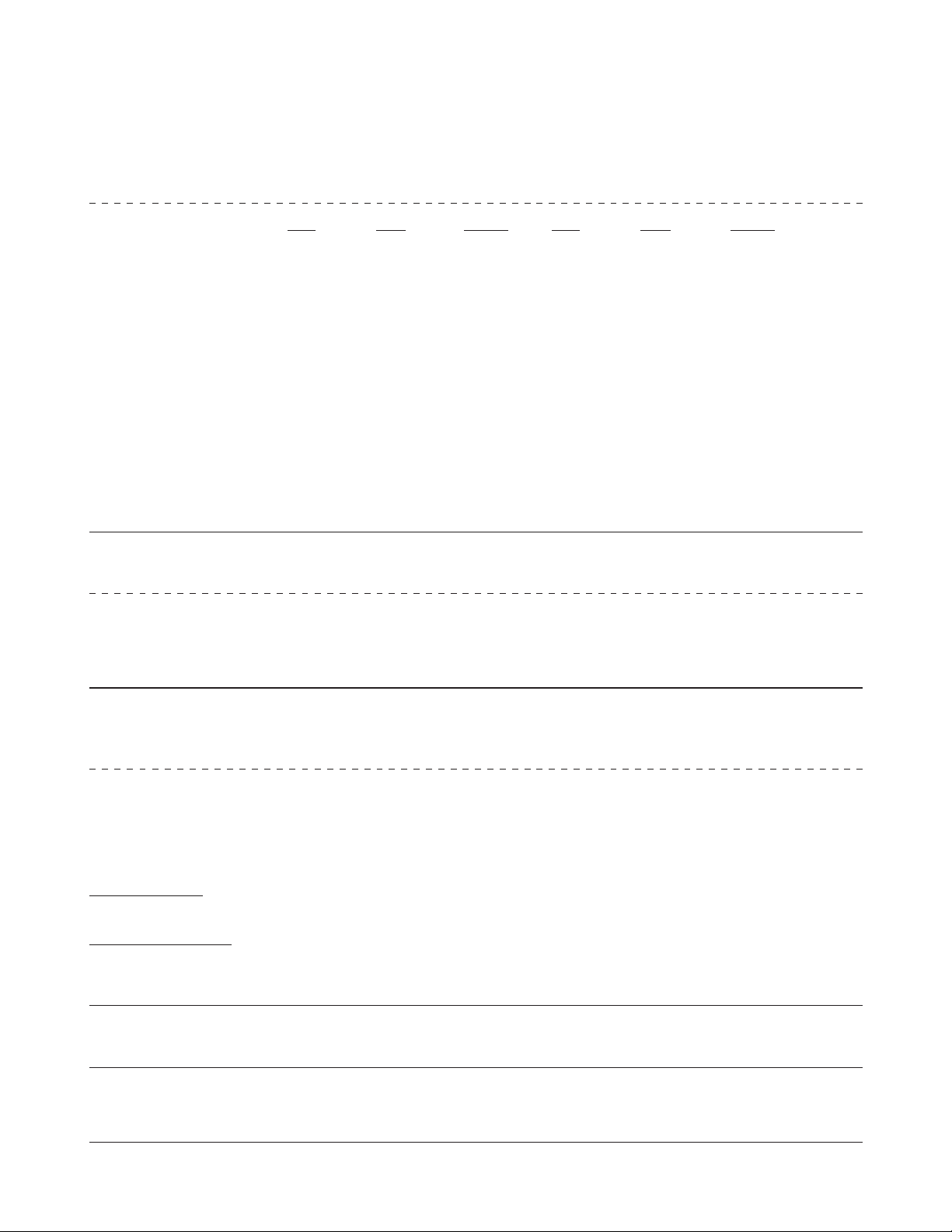
Jøtul F 602 Woodstove Clearances
Stove clearances Unprotected surfaces Protected surfaces (NFPA 211)
Top vent/vertical
Side Rear Corner Side Rear Corner
Single wall pipe 21" 13.5" 13" 13" 11" 9"
W/out rear heatshield 535mm 345mm 330mm 330mm 280mm 230mm
Single wall pipe 21" 11" 11" 13" 11" 9"
With rear heatshield 535mm 280mm 280mm 330mm 280mm 230mm
Shielded single wall pipe 21" 9" 9" 13" 8" 8"
With rear heatshield 535mm 230mm 230mm 330mm 205mm 205mm
Double wall pipe 24" 9" 9" 13" 8" 8"
With rear heatshield 610mm 230mm 230mm 300mm 205mm 205mm
Double wall pipe 24" 15" 15" 12" 8" 8"
W/out rear heatshield 610mm 380mm 380mm 305mm 205mm 205mm
USA
Connector Unprotected surface Protected surface (NFPA 211)
clearances (pipe) Vertical installation Vertical installation
Single wall pipe 18" 6"
460mm 150mm
Double wall pipe pipe mfgr.listing pipe mfgr.listing
Connector Unprotected surface Protected surface (NFPA 211)
clearances (pipe) Horizontal installation Horizontal installation
Single wall pipe 18" 9"
460mm 230mm
Double wall pipe pipe mfgr.listing pipe mfgr.listing
Very Important:
Top vent/vertical - assumes the connector pipe is exiting off the top of the stove and traveling vertically. If top vented
to any horizontal runs - the stove’s position is dictated by the connector pipe clearances.
Rear vent/horizontal - assumes the connector pipe exits from the rear of the stove and runs horizontally to the
chimney. If rear vented to vertical run - the stove position is dictated by the connector pipe clearances.
Minimum alcove dimensions:
Unprotected surface Protected surface (NFPA 211)
Vertical venting. Vertical venting
Assumes top exit: Assumes top exit:
Minimum alcove width 55” (1400mm) 41” (1040 mm)
Maximum alcove depth 48” (1220mm) 48” (1220 mm)
Height above the top of the stove 71” (1805mm) 71” (1805 mm)
7
Page 8

USA
Operation
Before building a fire in your new stove, please read
the following section carefully.
The stove is designed to burn natural wood only. Higher
efficiencies and lower emissions generally result when
burning air-dried seasoned hardwoods, as compared to
softwoods or to green or freshly-cut hardwoods.
Do not burn:
• Coal
• Garbage
• Cardboard
• Treated or painted Wood Solvents
• Treated or painted Wood
• Chemical Chimney Cleaners
• Colored Paper
• Any syntethic fuel or logs that have not been approved
for wood stoves.
Burning treated wood, garbage, solvents, colored paper,
chemical chimney cleaners, or trash may result in release of
toxic fumes.
will depend on how you operate your stove, but it is
important to inspect the flue after every two weeks of
use. An accumulation of 1/4" or more on the sides of the
flue or connector is considered hazardous and should be
removed.
In the event that creosote in your chimney or flue
connector ignites, the resulting fire is often accompanied
by a roaring noise and a crackling sound as flakes of burned
creosote break loose. lf you suspect you are having a
chimney fire, immediately close the draft regulator and
make sure the stove door is closed. Call the fire
department and get everyone safely out of the house.
Trying to extinguish the fire in the stove will not help. In
fact it can make the matter worse by allowing oxygen
through the door, which then supports the fire in the
chimney. When the roaring and crackling has stopped, you
should resist the temptation to open the door and look at
the fire. The fire may have suffocated, but could rekindle
when you open the door. After a chimney fire, do not use
your stove until the chimney and the flue connector has
been cleaned and inspected to ensure that no damage
has been sustained.
Never use gasoline, gasoline-type lantern fuel, kerosene,
charcoal lighter fluid, or similar liquids to start or "freshen
up" a fire in this heater. Keep all such liquids far away
from the heater while it is in use.
Wood Storage
When storing wood outside, it should be covered and
stored off the ground to protect it from the elements.
Make certain that the woodpile has good air circulation
through it in order to promote drying to aid in the seasoning
process.
To obtain the best performance from your stove, we
recommend using seasoned hardwood that has been dried
and stored under cover for at least one year. Burning
unseasoned or wet wood causes the rapid development
of creosote and reduces the heat value of the wood.
Creosote and Soot Formation and
the Need for Removal
When wood is burned slowly, it produces tar and other
organic vapors which combine with expelled moisture to
form creosote. These creosote vapors condense in the
relatively cool chimney flue of a slow burning fire. The
creosote that accumulates in the flue is highly flammable
and is the fuel of chimney fires. To prevent a chimney fire,
the creosote needs to be removed by sweeping the
chimney and flue connector. The frequency of sweeping
Breaking in Your Stove
A cast iron stove should be "broken in" gradually. Five
consecutive small fires must be built in the stove prior to
operating the stove continuously. Each fire should be a
little larger than the previous one, and the last fire should
be a full-sized load. Allow the stove to cool completely
between fires.
It is normal for new painted stoves to emit a smell or
even some smoke during the first few fires. This is caused
by the seasoning of the high temperature paint, and the
odor will diminish with each fire and eventually disappear.
Opening a window or door near the stove will help provide
additional ventilation and reduce the odor.
Controls
Front Door Latch
The latch for the front door is conveniently located to the
left of the door's center. To open the door, simply raise
the latch and pull the door toward you. To shut the door,
raise the latch, push the door tightly against the stove
front, and lower the latch. See fig. 19 A, page 24.
8
Page 9

USA
Air Control
The sliding air control (See fig. 19 B, page 24) is located
in the bottom center of the front door.
Sliding the control to the right opens the air control and
increases the heat output; sliding it to the left closes the
control and decreases the heat output.
Slide the control fully to the right when first starting or
reviving a fire, or when maximum heat is required. Position
the control in the middle or left of the middle when less
heat is needed and when longer burn times are desired.
You will determine the best settings for your particular
needs as you gain experience with your stove.
Hot while in operation. Keep children, clothing and
furniture away. Do not store fuel within the clearances
listed previously.
Building a Fire
A good fire will efficiently utilize your fuel, keep the glass
in the door clean, keep emissions and creosote to an
absolute minimum, require less work, and be very
predictable.
A Good Foundation
Reloading
Reload the stove while it is still hot and there are plenty
of hot to ignite the fresh fuel load. It is a good idea to
include a smaller piece or two of wood at the base of the
new load to help the stove recover more quickly to its
operating temperature.
Reloading Procedure
• Always wear gloves when tending your stove.
• Push the air control to the right to the full open
position.
• Wait a few seconds and open the door.
• Use a stove shovel or similar tool to break up any
remaining charcoal and to drag some live embers
toward the front where combustion air enters.
• Load the fuel (Smaller pieces first).
• Close the door.
• Wait 5-10 minutes and adjust the air control to desired
setting.
Note: lf the charcoal bed present at reloading time is
relatively deep (2"-3") and your wood is well seasoned, it
is possible to add the fresh fuel load, close the door and
reset the air control for the desired heat output rate
within 5 minutes.
• Make sure the air control handle is fully to the right.
Open the front door and cover the bottom of the stove
with tightly crupled newspaper. Criss-cross a generous
double handful of dry kindling, such as split pieces of
scrap lumber, on top of the paper. lf you don't have
scrap lumber, split some of your best dry wood down
to finger-sized pieces and use that. Place three or
four 1 " -2" split pieces of dry wood on top of the kindling.
• Light the paper evenly across the front and close the
door.
• Continue to add 1" - 2" pieces of split dry wood until a
healthy bed of glowing coals has formed.
• You can now add three or four small-to-medium pieces
of wood. Allow this wood to burn for several minutes.
Once you are sure the wood is burning well, adjust the
air control to your desired heat output level. Moving it
to the right increases the heat; moving it to the left
decreases the heat. Avoid operating the stove with
the air control closed completely.
• In order for secondary combustion to occur, the fire
must be well established with temperatures above
1.0000F (6000C) in the firebox.
• lf the fire dies out, this cause is most likely either an
insufficient bed of coals, reducing the air supply too
soon, or using wood that is either too large or not dry
enough.
Ash Removal
Ash removal will be required every day or two during
normal operation, and is most easily done when the fire
has burned down to coals.
Use a shovel to push or rake any hot coals first to one
side. Shovel out the exposed ash, and push or rake the hot
coal to the other side. Remove the ash from the second
side as well, and then spread the hot coals evenly across
the firebox. Wood may now be added to start a new fire.
When removing ash from a stove that is in operation,
close and latch the door before taking the ashes outside
for safe disposal. It is always a good idea to wear heavy
protective gloves while removing and disposing of the
ashes from your stove.
Ashes should be placed in a metal container used
exclusively for ashes, with a tight fitting lid. The closed
container of ashes should be placed outdoors, well away
from all combustible materials, pending final disposal. lf
ashes are disposed of by burisl in soil or otherwise
dispersed, they should be retained in the closed container
until all cinders have thoroughly cooled.
Overfiring will result if the stove is operated with the
door open. This could cause damage to the stove, void the
warranty or lead to a house fire.
9
Page 10

USA
Warning: Operate your Jøtul F 602 USA only with the
door fully closed. Keep the door fully closed except
when loading fuel or removing ashes. A partially open
door may result in overfiring.
Maintenance
General
At least once a year, perform a routine maintenance
check. A good time to do this is when you are cleaning
the chimney and the connector. You should clean the
chimney and connector whenever accumulations of
soot and creosote reach 1/4" thick, which may be several
times a year, depending on how the stove is operated.
Thoroughly clean the entire stove. Brush all ash and soot
out of the stove. It is better to brush out the ash and soot
than to vacuum it out because soot particles are small
enough to pass through most vacuum bags.
In a dark room, use a strong light to inspect the stove
inside and out for cracks or leaks at corners and joints.
Cracked pants should be replaced. Leaks at joints can be
patched with stove furnace cement.
Check the door and window gaskets for tightness. To check
the front door gasket, put a dollar bill halfway into the
stove, close and latch the door, and try pulling the dollar
out. lf it can be removed easily the, seal is too loose. Check
several spots around the door. To replace the gasket,
scrape out all old gasket material and gasket cement.
Spread a 1/8" bead of stove cement into the bottom of
the groove and press in new gasket.
The door requires 36" of 1/4" diameter high density gasket.
The gasket between the glass panel and the door receives
very little wear. The best indication that it needs to be
replaced is streaks on the glass caused by air leaking
around the gasket.
Glass Replacement
To prevent cracking of the glass operate the doors gently.
Do not shut the door by striking or slamming.
working surface. The steps are the same:
Clean off any residual gasket material from the door using
a wire brush if necessary.
The replacement gasket is self-adeshive. Measure enough
gasket to go from the upper right corner of the glass,
down the right side, across the bottom and back up to the
upper left corner and then add about 2-1/2". Please note
that the top of the glass is not gasketed. A small amount
of air is allowed to enter through the that area to help
keep the glass clean.
• Peel off about 10" of the self-adhesive backing strip.
Leaving about 1-1/4"of gasket "tail" overlapping, apply
the gasket to the groove on the door, making sure that
the adhesive is facing the door.
• Press the gasket firmly in place.
• Peel off the remaining adhesive backing and apply the
remaining gasket, again leaving a "tail" at the upper
left corner.
• Press the gasket firmly in place.
• Center the glass panel left and right on top of the
gasket. Slide the glass toward the bottom of the door
until it hits stops.
• Hold the glass in place with your hand and wrap the
gasket "tails" over the top of the glass and down the
outer edges. You will have to twist the gasket so the
adhesive will face the glass. Press the "tails" firmly on
the glass.
• Replace the air control slide and the upper and lower
retainer manifolds and screws.
It is extremely important that the retainers be tightened
a small amount at a time and following a pattern similar
to tightening the lug bolts on an automobile wheel. They
should end up equally tightened and not over-tightened.
It may be necessary to retighten once again after the
stove has been burned and the new gasket has been
seated.
Glass Cleaning
From time to time, clean off the accumulated ash from
the inside surfaces of the glass panels. lf this fly ash is
allowed to remain on the surface for extended periods, it
could eventually cause the glass to become permanently
etched and somewhat cloudy. Any creosote which might
deposit on the glass will burn off during the next hot fire.
lf the stove's glass is cracked or broken, you must replace
it before operating your stove. Carefully remove any
broken pieces. Replace the panel only with the correct
Jøtul replacement glass, and do not use substitutes.
The glass can be replaced with the door still mounted to
the stove or the door can be removed and placed on a flat
10
Never clean the glass while it is hot and never use any
abrasive materials to clean the glass. Cool water and a
soft cloth or paper towel are usually all that is required.
Rinse thoroughly with clean water after washing and dry
completely before burning your stove.
Page 11

CANADA
Table des matières
Information d’ordre général
Dangers possibles à éviter pendant L’ utilisation
du “Jøtul F 602 USA” ................................................................ 11
Installation
Avis de sécurité .......................................................................... 12
Sortie des fumées par le dessus ou par l’arrière ..............12
Fixation des pieds ..................................................................... 12
Organisez-vous d´avance
Raccord de cheminée (tuyau de poêle) .............................. 13
Traverse murale..........................................................................13
Cheminées ................................................................................. 14
Cheminées de maçonnerie ................................................... 14
Cheminées métalliques préfabriquées homologuées ...15
Connexion à la cheminée .......................................................15
Dégagement jusqu’aux matériaux
Protection de plancher ............................................................15
Dégagements jusqu´aux matériaux combustibles ........ 15
Utilisation de protège-murs pour diminuer les
dégagements d’installations en alcôve ............................. 16
Installation en alcôve .............................................................. 16
Fonctionnement
Entreposage/Rangement du bois....................................... 16
Formation de créosote et de suie et nécessité
de les éliminer ............................................................................17
Rodage de poêle .......................................................................17
Commandes
Loquet - Porte de devant ........................................................17
Préparation de feu .................................................................... 17
Bonne fondation ...................................................................... 18
Rechargement ........................................................................... 18
Information d’ordre
général
Le manuel du propriétaire décrit l’installation et le
fonctionnement du poêle à bois, non catalytique, Jøtul F
602 USA. Ce poêle est conforme aux limites imposées par
l’agence américaine pour la protection contre les
émissions des poêles à bois vendus après le 1er juillet
1990. Ce poêle a en outre démontré, sous conditions de
test spécifiques, que sa puissance calorifique pouvait
s’étendre entre 9 600 et 42 000 Btu/h.
Pendant l’installation, le fonctionnement ou l’entretien
du poêle Jøtul F 602 USA, veillez à suivre les directives du
présent manuel. Conservez-les et tenez-les à la disposition
de toute personne susceptible de se servir de ce poêle.
Plusieurs régions des États-Unis et du Canada requièrent
un permis de construction pour l’installation d’un appareil
de chauffage à combustible solide. La norme canadienne
CAN/CSA(ACNOR) B-365 (Code d’installation pour appareils
et équipement à combustible solide) ou codes similaires
pourront s’appliquer à l’installation d’appareils de
chauffage à combustible solide dans votre région. Votre
concessionnaire Jøtul est au courant de ces codes locaux
et pourra vous renseigner sur la sûreté et la légalité de
votre installation. Communiquez, en outre, avec votre
agent d’assurance, votre inspecteur de la construction ou
les responsables officiels de la prévention des incendies
afin de déterminer quels règlements s’appliquent dans
votre région.
Le Jøtul F 602 USA a été testé et homologué
conformément à la norme CAN-ULC S627 de Scarborough,
Ontario.
Entretien
Généralités ................................................................................. 19
Remplacement du verre......................................................... 19
Nettoyage de panneau du verre..........................................20
Jøtul F 602 Woodstove Clearances ............. 7
Diagrammes......................................... 21-26
Dangers possibles à éviter lorsque
vous employez un poêle à bois
Jøtul F 602 USA
Un feu allumé dans une maison représente toujours
certains dangers. Les surfaces d’un poêle Jøtul F 602 USA
soumises à une surchauffe intense pourront en pousser
la température au-delà de 1 000°F (536°C).
Conformez-vous aux directives suivantes :
• Ne surchauffez jamais le poêle. L’incandescence de
l’une quelconque des parties du poêle signifie
surchauffe et risque éventuel d’un incendie ou de
graves dommages au poêle ou à la cheminée. En
l’occurrence, fermez immédiatement le distributeur
d’air.
11
Page 12

CANADA
• Faites comprendre aux enfants qu’un poêle chauffe
et qu’ils risquent de se brûler en y touchant.
• N’employez jamais de l’essence, du carburant pour
lanternes genre essence, kérosène, allumeur liquide
de charbon de bois ou autre liquide similaire dans ce
poêle pour commencer un feu ni pour le raviver. Ceuxci risquent de s’enflammer avec une vigueur explosive
pouvant causer des blessures graves et parfois
mortelles. Conservez tous ces liquides éloignés du
poêle en fonctionnement.
• N’employez jamais ce poêle dans une résidence où
sont conservées des sources de gaz de combustion
tels que certains liquides nettoyants d’usage
domestique, adhésifs et peintures pour n’en nommer
que quelques-uns. Souvenez-vous qu’un poêle à bois
est, lui-même, une «source de flammes nues».
• Évitez de créer une pression basse dans la pièce
chauffée généralement causée par l’utilisation d’un
appareil tel qu’un ventilateur d’échappement, une
sécheuse à linge etc., ceci pouvant libérer les vapeurs
toxiques du poêle dans la pièce chauffée. Pour parer à
cette condition, prévoyez suffisamment d’air de
combustion extérieur dans un rayon de 24 po. (61 cm)
autour du poêle.
• N’employez jamais un poêle Jøtul F 602 USA si une
vitre est fêlée ou brisée. Ne remplacez le verre
endommagé que par un panneau Jøtul F 602 USA
approprié acheté chez votre concessionnaire Jøtul.
• Ne brûlez jamais aucun déchet quel qu’il soit dans ce
poêle.
• Éloignez tous matériaux combustibles à une distance
considérable du poêle.
• Ne modifiez jamais le poêle de quelque manière que
ce soit.
• Ne suspendez jamais du linge au-dessus du poêle; il
risquerait en effet de s’enflammer en tombant.
• N’employez que du bois sec dans votre poêle.
• N’utilisez jamais de charbon de bois pour cheminées
ni des bûches synthétiques non approuvés pour poêles
à bois.
• Portez toujours des gants protecteurs pour ajouter
du carburant au feu.
• Si des fumées s’échappent du foyer, cela peut activer
les détecteurs de fumées (s’ils sont installés).
• Ne reliez pas ce poêle à un conduit de distribution
d’air.
• Ce poêle n’a pas été approuvé pour usage dans les
maisons mobiles.
Installation
Avis de sécurité
L’installation non appropriée de ce poêle à combustible
solide risque de causer un incendie. Assurez votre sécurité
en respectant les directives d’installation et consultez les
autorités locales de la construction et de la prévention
des incendies au sujet des limitations et des exigences
relatives aux inspections particulières à votre région.
Veuillez lire ce manuel tout entier avant d’installer et
d’utiliser votre nouveau poêle. Tout manquement à
observer ces directives risque de causer dommages
matériels, blessures graves ou même la mort de
personnes présentes.
Nous vous recommandons de faire installer votre poêle
Jøtul F 602 USA par un installateur professionnel de poêles
à combustible solide.
Sortie des fumées par le dessus ou
par I’arrière
Votre poêle Jøtul F 602 USA vous offre deux positions de
sortie de fumée.
Si vous choisissez la position supérieure, posez la plaquette
appropriée en position arrière, maintenez-la avec vis et
écrous puis fixez la virole du conduit de fumée à la partie
supérieure au moyen des deux vis restantes.
Si vous préférez la position arrière, posez la plaquette
appropriée en position par le dessus, maintenez-la avec
les deux vis, puis fixez la virole du conduit de fumée à
l’arrière au moyen des deux vis restantes et des deux
écrous.
Lorsque vous attachez la plaquette ou la virole du conduit
de fumée à l’arrière, il sera peut-être nécessaire
d’introduire votre main dans l’orifice supérieur et de
maintenir les écrous avec une clé anglaise.
Fixation des pieds
Le Jøtul F 602 USA est fourni avec quatre orifices
prépercés dans la plaque du fond. Attachez chaque pied à
cette plaque de fond avec un boulon et une rondelle entre
la tête de boulon et le pied.
12
Page 13

CANADA
Organisez-vous d’avance
Plusieurs éléments, d’importance égale, contribuent à
l’installation sûre de votre poêle : (A) le raccord de
cheminée; (B) la cheminée-même; (C) la connexion entre
le raccord et la cheminée et (D) la protection des
matériaux combustibles dans la proximité immédiate du
poêle.
A. Raccord de cheminée (Tuyau de
poêle)
Le raccord de cheminée, également appelé tuyau de poêle
ou conduit de fumée est employé pour relier le poêle à la
cheminée. Il se composera d’acier noir, son diamètre sera
de 15-1/4 cm et son calibre d’épaisseur #24.
Ne vous servez jamais d’un raccord composé de tuyau
d’aluminium ou d’acier galvanisé, ces matériaux chauffés
ne pouvant soutenir les températures extrêmes d’un feu
de bois et risquant de dégager des vapeurs toxiques.
Un tuyau d’émail assorti est disponible pour votre poêle
Jøtul F 602 USA. Veuillez demander de plus amples
renseignements à votre concessionnaire Jøtul.
travers combles ou vides sous toits, armoires ou autres
espaces dissimulés, planchers ni plafonds. Évitez autant
que possible de faire passer un raccord de cheminée à
travers un mur combustible.
Traverses murales
Lorsque votre installation requiert inévitablement de faire
passer le raccord de cheminée de votre poêle à travers
un mur combustible, d’extrêmes précautions devront être
prises. La norme CAN/CSA(ACNOR) B-365 (Code
d’installation pour appareils et équipement à combustible
solide) prévoit quatre méthodes à cet effet.
Avant de commencer votre installation, renseignez-vous
auprès de vos autorités locales de la construction sur la
méthode de traverse proposée, pour votre poêle,
compatible avec les codes locaux de la construction.
La méthode la plus commune de traverser un mur pour
atteindre une cheminée de maçonnerie exige le retrait
de tous matériaux combustibles dans un rayon d’au moins
30.5 cm autour du raccord tout entier pour être remplacés
par une épaisseur de briques de 30.5 cm (35.5 cm) cm au
moins autour d’une chemise argileuse. Veillez à placer
celle-ci de sorte que le dessus du raccord de cheminée
soit au moins 45-314 cm plus bas que le plafond.
N’employez jamais un tuyau de raccord en guise de
cheminée.
L’adaptateur fourni en usine servira à ajuster l’orifice
d’échappement de fumée de votre poêle au raccord de
cheminée.
Les sections de raccord de cheminée doivent être
attachées à l’adaptateur de sortie de fumée du poêle puis
l’une à l’autre - l’extrémité plissée dirigée vers le poêle.
(Illustr. 2, page 21).
L’espace entre l’adaptateur de sortie des fumées du poêle
et le raccord de cheminée doit être scellé avec un ciment
à poêle ou un joint de mastic de poêle à bois,
approximativement dimensionné. Ceci permettra à toute
petite quantité de créosote condensée de passer dans le
poêle plutôt que de s’accumuler à l’extérieur du tuyau ou
à l’orifice du dessus de poêle. Tous les joints, y compris
l’adaptateur de sortie des fumées seront fermement
maintenus par trois vis à tôle, pour empêcher les sections
de se séparer.
Pour un fonctionnement approprié, le raccord de cheminée
sera aussi court que possible. Les tuyaux horizontaux
auront une pente ascendante, depuis le poêle, d’ 0.6 cm.
Évitez d’utiliser plus de deux coudes à 90° ou une longueur
totale de tuyau supérieure à 305 cm.
Aucune partie du raccord de cheminée ne passera à
Pour construire le «passe muraille» de brique, une
ouverture d’au moins 76 cm x 76 cm est nécessaire. Des
poteaux muraux seront en outre coupés, des boutisses
installées et un encadrement construit conformément
aux dimensions appropriées pour soutenir le poids des
briques. Des briques solides de 9 cm (format nominal
10 cm seront employées. La chemise argileuse (ASTM C35
ou équivalent) d’une épaisseur murale de 1 -1 /2 cm ne
pénétrera pas la cheminée au-delà de la surface
intérieure de la chemise de celle-ci et sera fermement
cimentée en position.
S’il s’avère nécessaire de découper un cercle dans la
chemise de la cheminée, prenez toutes précautions
possibles pour l’empêcher de se briser. Un mortier
réfractaire sera employé au point de jonction de la
chemise de cheminée.(Illustr. 3, page 21)
Une installation approuvée utilisant une section de
cheminée isolée homologuée pour combustible solide,
construite en usine en guise de traverse murale (passemuraille) pour le raccord de cheminée.
Le diamètre intérieur de la section de cheminée sera 5 cm
plus large que celui du raccord de cheminée; il mesurera
30.5 cm au moins et sera isolé sur une épaisseur d’au moins
2-1/2 cm.
Cette section installée présentera un espace d’air d’au
moins 5 cm entre la paroi extérieure de la cheminée
proprement dite et les matériaux combustibles adjacents.
13
Page 14

CANADA
Des plaques d’appui en feuille d’acier sont utilisées à
chaque extrémité de la section de cheminée afin que le
raccord demeure bien centré. L’orifice autour de la section
de cheminée est bouché de chaque côté de la paroi murale
avec des plaques en feuille d’acier auxquelles la section
de cheminée est alors fermement attachée. Les attaches
utilisées pour soutenir la section de cheminée ne pourront,
en aucune circonstance, pénétrer la chemise intérieure
du conduit de fumée.
Voyez la norme ; La norme CAN/CSA(ACNOR) B-365 pour
toute autre méthode passe-muraille, approuvée.
B. Cheminées
Deux types de cheminée conviennent pour votre poêle
Jøtul F 602 USA : une cheminée de maçonnerie approuvée
ou une cheminée d’appareil de chauffage de type
résidentiel, homologuée pour sa sûreté.
Rappelez-vous, lorsque vous choisissez un type de
cheminée et son emplacement dans la maison que c’est
grâce à elle que le poêle peut fonctionner et non pas grâce
au poêle que la cheminée fonctionne. Cela est dû au fait
que la cheminée crée une aspiration appelée tirage qui
attire I’air à travers le poêle.
Cheminées de maçonnerie
Les exigences minimales pour construction appropriée
d’une cheminée de maçonnerie comprennent ce qui suit :
La fondation doit être suffisamment large pour soutenir
la cheminée envisagée sans affaissement.
Le mur de maçonnerie de la cheminée, soit en briques,
soit en blocs modulaires, sera d’une épaisseur nominale
d’au moins 10 cm. Un mur de blocaille ou de moellons
bruts aura au moins 30.5 cm d’épaisseur.
La cheminée doit être doublée d’une chemise argileuse
(ou équivalente) d’au moins 1 -1 /2 cm et doit être installée
au moyen de mortier réfractaire. Un espace minimal d’11/4doit séparer la chemise du conduit de fumée du mur
de la cheminée.
Le diamètre nominal préférable de la chemise argileuse
de cheminée est de 20-1/4 x 20-1/4 cm; il ne pourra, en
aucun cas, dépasser un diamètre maximal 20-1/4 x 30.5
cm. Une chemise circulaire requiert un diamètre intérieur
de 15-1/4 cm - jamais plus de 20-1/4 cm. Si une cheminée à
tuiles de plus grande dimension est employée, elle sera
redoublée avec une chemise appropriée.
Aucun autre appareil ne sera aéré par le même conduit.
Le tirage réagit à plusieurs facteurs : hauteur, superficie
en coupe et température de la cheminée, ainsi que la
proximité d’arbres ou de constructions environnants.
Une courte cheminée de maçonnerie à I’extérieur de la
maison donne, généralement la performance la moins
satisfaisante du fait qu’elle s’avère exceptionnellement
difficile à chauffer et même impossible dans certaines
régions extrêmement froides du Grand Nord.
Une haute cheminée de maçonnerie à I’intérieur de la
maison facilite le chauffage et fonctionne le mieux.
Les présentes directives vous indiquent les exigences
spéciales requises d’après le code national canadien, la
norme CAN/CSA(ACNOR) B-365. Néanmoins, de nombreux
codes locaux diffèrent du code national afin de tenir
compte de facteurs tels que climat et altitude etc. Il est
important que vous vérifiiez, auprès des autorités locales
de la construction quels codes s’appliquent dans votre
région avant de procéder à la construction d’une
cheminée.
Une trappe de nettoyage hermétique sera située à la base
de la cheminée.
Le dégagement d’une cheminée à I’intérieur de la maison
doit être d’au moins 5 cm jusqu’à la structure combustible.
Celui d’une cheminée extérieure sera d’au moins 2.5 cm
jusqu’à la structure combustible. Des coupe-feu doivent
être installés aux endroits où la cheminée traverse le
plancher et (ou) le plafond .
Souvenez-vous que la cheminée doit être entourée d’un
vide d’air suffisant et que le matériau isolant doit être
éloigné de 5 cm ou plus de la cheminée.
Une cheminée, de maçonnerie ou métallique
préfabriquée, sera de la hauteur requise, au-dessus du
toit, ou de toute autre obstruction, pour en assurer la
sécurité et le tirage approprié. Il est par conséquent
nécessaire qu’elle soit d’au moins 3 pieds (91-1/2 cm) plus
haut que le point le plus élevé auquel elle traverse le toit
et d’au moins 2 pieds (61 cm) plus haut que la partie du
toit ou de la structure la plus élevée dans une limite de 10
pieds (305 cm) de distance de la cheminée, mesurés
horizontalement. (Illustr. 4, page 21).
14
Aucune cheminée de moins de 14 pieds ne peut assurer
un tirage adéquat ; elle permettra, au contraire, à la fumée
de s’échapper dans la pièce par la porte ou les joints du
poêle ou du conduit de fumée. En outre, un tirage
Page 15

CANADA
inadéquat pourra causer des retours de flammes dans la
boîte à feu. D’autre part, un tirage trop vigoureux, en
causant des températures excessives, risque de
raccourcir les durées de combustion. Vous pourrez
remédier à des tirages excessifs en faisant installer, par
votre concessionnaire, un registre barométrique réglé
pour une colonne d’eau de 0-1/4 cm. Si vous soupçonnez
un problème de tirage, consultez donc votre
concessionnaire.
Cheminées métalliques
préfabriquées, homologuées.
Lorsque vous employez une cheminée métallique
préfabriquée, suivez à la lettre les directives d’installation
du fabricant. Vous devrez en outre acheter et installer
I’ensemble de support de plafond, ou de «passe-muraille»,
I’ensemble de section en Té, les coupe-feu éventuellement
requis, I’écran isolant, le chaperon de toiture, chapiteau
de cheminée etc., tous provenant du même fabricant.
Respectez le dégagement approprié jusqu’à la structure,
tel que recommandé par le fabricant. De règle générale,
ce dégagement doit être d’au moins 5 cm bien qu’il puisse
varier selon le fabricant ou le type de certaines
composantes. (Illustr. 5 page 22)
C. Connexion à la cheminée
Cheminées de maçonnerie
Lorsque vous raccordez votre poêle à une cheminée de
maçonnerie, le raccord doit glisser complètement à
I’intérieur de la rosace (ou «trouée») jusqu’à la surface
intérieure de la chemise argileuse. Assurez-vous que le
raccord ne fasse pas saillie au-delà de I’intérieur de la
chemise, ce qui risquerait de diminuer la section de
passage de fumée et de causer, en conséquence, des
problèmes pour votre système de cheminée. Le raccord
de cheminée sera scellé dans la rosace au moyen d’un
ciment réfractaire et sera, en outre, attaché
mécaniquement à la cheminée. (Illustr. 6, page 22).
Cheminés préfabriquées
Suivez toujours les directives du fabricant de cheminée
et n’employez que les composantes recommandées par
lui. Ne vous laissez pas tenter par des «raccourcis» ou
des solutions de facilité lorsque vous fixez le raccord à la
cheminée.
Dégagements jusqu’aux
combustibles
Protection de plancher
Un écran de fond thermique est inclus aux éléments
standard du poêle Jøtul F 602 USA et doit être présent
dans toutes installations. De plus, le poêle sera placé sur
une protection de plancher non combustible s’étalant sur
20-1/4 cm au moins au-delà des côtés et de I’arrière du
poêle et de 40-1/2 cm par-devant ce qui vous donnera une
protection de plancher de 84 cm de long par 115-1/2 cm de
côté. Cette protection doit aussi recouvrir la surface pardessous toutes sections horizontales de raccord de
cheminée (tuyau de poêle) et doit s’étaler sur au moins 5
cm au-delà de chaque côté du tuyau. (Illustr. 7, page 22).
Le poêle sera posé sur un protège-plancher non
combustible, homologué, comprendra de 0.9 cm
d’épaisseur de carton à I’enrouleuse, d’une conductivité
thermique de K-0.84 Btu-po. par pi.
qu’il n’y ait aucun espace entre les briques ou les tuiles
éventuellement utilisées afin d’éviter que des étincelles
ou des braises n’enflamment le plancher.
Une bonne méthode à suivre pour la fabrication de votre
protection de plancher est de couvrir la couche de
protection avec une plaque décorative non combustible
ou d’un renfort de carrelage tel que Wonderboard (MD)
ou Durock (MD)
Ne posez jamais aucun genre de protection de plancher
par-dessus tapis ou moquette.
Dégagements jusqu’aux matériaux
combustibles adjacents
Le diagramme de I’illustr 8-9-10-page 22, stipule les
dégagements requis à respecter jusqu’aux matériaux ou
objets combustibles, non protégés.
Un combustible signifie tout ce qui est susceptible de
brûler et peut parfois être invisible, en ce qui concerne les
installations de poêle. Si vous n’êtes pas rassuré sur la
combustibilité des matériaux environnant la surface
d’installation prévue pour votre poêle, vérifiez auprès des
responsables locaux de la prévention des incendies.
Souvenez-vous que les matériaux soi-disant «résistants
au feu» bien que longs à s’allumer, brûleront
éventuellement. Ils sont, par conséquent, considérés
comme combustibles.
2
/hre -°F. Veillez à ce
15
Page 16

CANADA
Si vous avez récemment acheté une maison avec un âtre
que vous prévoyez d’utiliser, il s’avère essentiel que la
sécurité du système soit vérifiée auparavant. De
nombreuses maisons anciennes ont des cheminées
défectueuses ou les murs et poteaux combustibles
peuvent avoir été recouverts d’un placage de briques par
les propriétaires précédents. La brique étant un excellent
conducteur de chaleur risque d’enflammer les
combustibles qu’elle dissimule.
Communiquez avec vos autorités locales de la construction
et de la prévention des incendies au sujet des limitations et
exigences d’installation imposées dans votre région.
Utilisation d’écrans thermiques pour diminuer les
dégagements
L’écran thermique arrière facultatif du poêle Jøtul F 602
USA peut être employé pour sortie des fumées par le
dessus pour diminuer le dégagement d’installations
parallèles, (Illustr. 11,12,13, page 23).
Utilisation de protège-murs pour
diminuer les dégagements
d’installations en alcôve
Le protège-mur d’une installation en aIcôve sera non
combustible - en acier galvanisé, par exemple, de calibre
minimal #24 ou équivalent. Il sera élevé d’2.5 cm d’espace
d’air au-dessus du plancher et sera monté de manière à
ménager également 2.5 cm d’espace d’air au moins entre
I’écran et le combustible. La hauteur du protège-mur, y
compris celle de I’espace d’air au bas du mur doit être
d’au moins 102-1/2 cm (Illustr. 15, page 21). Les deux murs
latéraux ainsi que le mur arrière seront protégés par ce
matériau. (Illustr. 14, page 23).
Notes :
1
Renseignez-vous auprès de votre concessionnaire sur les
diminutions de dégagement de plafond avec protection.
2.
Si la largeur de I’un des deux murs latéraux est supérieure
à 61 cm, (le dégagement du mur latéral le plus large sera de
63-1/2 cm.
Fonctionnement
Avant de préparer un feu dans votre nouveau poêle,
veuillez lire attentivement le chapitre suivant.
Ce poêle a été conçu uniquement pour le brûlage de bois
naturel. Le brûlage de bois séché à I’air a pour résultat
des rendements plus efficaces et des émissions moins
élevées comparativement au brûlage de bois tendre, vert
ou bois dur fraîchement coupé.
Ne brûlez jamais :
*ni charbon
*ni ordures ménagères
* ni carton
* ni solvants
* ni bois sec peint
* ni nettoyants chimiques de cheminée
* ni papier peint
*- ni déchets
* ni aucun carburant ou bûche synthétique quel qu’il soit,
non approuvé pour poêles à bois.
Le brûlage de bois traité, ordures ménagères, solvants,
papier peint, nettoyants chimiques de cheminée et
déchets risque de libérer des vapeurs toxiques.
Installation en alcôve
Lorsque vous installez votre poêle Jøtul F 602 USA avec
un tuyau homologué à double paroi et une protection
murale, vous pourrez le poser dans une aIcôve dont la
hauteur minimale est de 244 cm et la largeur maximale
122 cm et la longueur minimale 103 cm.
Les dégagements pour une installation de ce genre sont
indiqués dans l’illustration 14-15, page 23.
Lorsque vous installez votre poêle Jøtul F 602 USA avec
un tuyau homologué à double paroi et un écran thermique
pour poêle, vous pourrez le poser dans une alcôve dont la
hauteur minimale est de 244 cm(1). l et la largeur maximale
61 cm(2) et la longueur minimale 139-3/4 cm. Les
dégagements pour une installation de ce genre sont
indiqués dans l’illustr. 12-13, page 23.
16
N’employez jamais de I’essence, du carburant pour
lanternes genre essence, kérosène, allumeur liquide de
charbon de bois ou autre liquide similaire dans ce poêle
pour commencer un feu ni pour le raviver. Conservez tous
ces liquides éloignés du poêle en fonctionnement.
Entreposage/Rangement du bois.
Entreposage/Rangement du bois
Tout bois entreposé à I’extérieur sera couvert et le tas
sera surélevé au-dessus du sol pour le protéger des
intempéries. Veillez à I’entasser de manière à laisser
suffisamment d’espace pour la circulation d’air afin de
faciliter le processus de séchage.
Pour que votre poêle vous offre le meilleur rendement
possible, nous vous recommandons d’utiliser du bois dur,
séché et entreposé couvert pendant au moins un an. Le
Page 17

CANADA
brûlage de bois non séché ou encore humide en diminuera
la capacité calorifique en causant I’accumulation rapide
de créosote et diminuera la puissance calorifique du bois
employé.
Formation de créosote et de suie et
nécessité de les éliminer
Lorsque le bois brûle lentement, il produit du goudron et
d’autres vapeurs organiques qui, combinés à I’humidité
expulsée, forment de la créosote, dont les vapeurs se
condensent dans le conduit de fumée relativement froid
du tuyau de cheminée. Cette créosote accumulée est
extrêmement inflammable ; elle est à l’origine de la
plupart des feux de cheminée. Pour éviter un feu de
cheminée, il vous faudra donc I’éliminer en ramonant la
cheminée et le raccord du tuyau de fumée. La fréquence
de ramonage dépendra du fonctionnement de votre poêle;
néanmoins, il sera prudent de vérifier le tuyau de cheminée
toutes les deux semaines d’utilisation du poêle. Une
accumulation d’1/4 po. (0.6 cm) ou plus sur les parois de
tuyau ou de raccord est considérée dangereuse et doit
être nettoyée.
Au cas où la créosote accumulée dans le tuyau de
cheminée ou le raccord s’enflammerait, le feu de cheminée
est généralement signalé par un ronflement bruyant et
des crépitements au fur et à mesure que la créosote se
détache. Si vous soupçonnez un feu de cheminée, fermez
immédiatement le régulateur de tirage et assurez-vous
que la porte du poêle est close. Appelez les pompiers et
faites sortir toutes les personnes présentes pour les
mettre à I’abri.
Vous ne pouvez essayer d’éteindre le feu depuis I’intérieur
du poêle; en fait, vous risqueriez d’empirer la situation en
permettant la pénétration d’oxygène par la porte qui à
son tour, continuerait d’alimenter le feu de cheminée.
Lorsque le ronflement et les crépitements cessent,
résistez à la tentation d’ouvrir la porte du poêle pour
examiner le feu. Même si vous êtes parvenu à le suffoquer,
il risque de se raviver lorsque vous ouvrez la porte. Après
un feu de cheminée, n’employez votre poêle que lorsque
la cheminée et le raccord auront été nettoyés et inspectés
afin de vous assurer de I’absence de tout dommage.
Une certaine odeur et même de la fumée sont normales
pendant les quelques premiers feux. Ceci est dû au
traitement de la peinture soumise à une température
élevée ; I’odeur devrait diminuer avec chaque feu et
éventuellement disparaître. Une fenêtre ou porte ouverte
à proximité du poêle produira un supplément d’aération
et aidera à diminuer l’odeur.
Commandes
Loquet - Porte de devant
Le loquet de la porte avant est situé de manière pratique
à gauche du centre de la porte. Pour ouvrir celle-ci,
soulevez simplement le loquet et tirez la porte vers vous.
Pour fermer, soulevez le loquet, pressez la porte
fermement contre I’avant du poêle et abaissez le loquet.
(Voyez illustr. 19 A, page 24)
Commande d’air
La commande d’air coulissante (Illustr. 19 B, page 24) est
située sur le panneau avant, au-dessus de la porte de
chargement de combustible.
Le glissement de la commande vers la droite augmente
I’admission d’air et la sortie de chaleur ; son glissement
vers la gauche diminue I’admission d’air et la sortie de
chaleur.
Glissez intégralement la commande vers la droite pour
mettre un feu en marche, pour le raviver ou lorsqu’un
chauffage maximal est désiré. Positionnez la commande
au milieu ou à gauche du milieu pour une chaleur moins
forte et lorsque des durées prolongées de brûlage sont
requises. Vous déterminerez les meilleurs réglages pour
votre usage personnel au fur et à mesure que vous vous familiariserez avec votre poêle.
Le poêle est chaud pendant son fonctionnement. Eloignez
les enfants et ne gardez pas de vêtements ou de meubles
à proximité. Ne stockez pas de combustible à l’intérieur
des dégagements énumérés précédemment.
Rodage du poêle
Un poêle de fonte doit être «rodé» graduellement. Cinq
petits feux seront allumés consécutivement avant
d’utiliser le poêle en continu. Chaque feu sera un peu plus
conséquent que le précédent et le dernier sera
d’importance normale. Laissez le poêle refroidir
complètement entre les feux.
Préparation d’un feu
Un feu bien préparé utilisera efficacement votre
combustible, conservera la vitre propre, les émissions et
la créosote au minimum, demandera moins de travail et
ses réactions seront extrêmement faciles à prévoir.
17
Page 18

CANADA
Bonne fondation
Assurez-vous que la poignée de commande d’air primaire
est bien poussée intégralement vers la droite et que le
tisonnier de la commande de mise en marche est en
position ouverte (tiré intégralement vers I’extérieur).
Ouvrez la porte du devant et couvrez le fond du poêle de
papier journal chiffonné serré. Entrecroisez une généreuse
double poignée de bûchettes sèches - des morceaux de
bois de retaille fendu par exemple, par-dessus le papier.
Si vous ne disposez pas de bois de retaille, fendez-en vousmême dans du bois sec, en bâtonnets d’un doigt
d’épaisseur environ et servez-vous en comme de
bûchettes. Placez alors quatre morceaux de 2-1/2 à 5 cm
de bois sec fendu sur le dessus des bûchettes.
Allumez uniformément le papier tout au long de I’avant
du poêle et fermez la porte.
Continuez à ajouter des morceaux de 2-1/2 à 5 cm de bois
sec fendu jusqu’ à ce qu’un lit de braises incandescentes
ait bien pris.
Vous pouvez maintenant ajouter trois ou quatre morceaux
de bois - petite à moyenne dimension, que vous laisserez
brûler plusieurs minutes. Dès que vous êtes convaincu
que ce bois brûle bien, fermez I’admission d’air de mise en
marche (tisonnier intégralement enfoncé) et réglez la
commande d’air primaire au niveau de sortie de chaleur
désiré et pour maintenir des températures de
fonctionnement sûres et sans danger. Un déplacement
vers la droite augmente la chaleur ; vers la gauche, il la
diminue. Évitez d’employer le poêle si la commande d’air
est complètement fermée.
Lorsqu’un feu meurt, cela est probablement dû à un lit de
braises insuffisant, lequel diminue I’admission d’air trop
rapidement ou à I’usage d’un bois trop épais ou
insuffisamment séché.
Rechargement
Rechargez le poêle encore chaud et dont les braises
restantes suffisent à enflammer la nouvelle charge de
combustible. Il sera bon d’insérer un morceau ou deux de
bois plus petits à la base de la nouvelle charge pour aider
le poêle à récupérer plus rapidement sa température de
fonctionnement.
Méthode de rechargement
• Portez toujours des gants lorsque vous prenez soin de
votre poêle.
• Poussez la commande d’air à droite, en position ouverte
intégrale.
• Attendez quelques secondes avant d’ouvrir la porte.
• Employez une pelle à poêle ou un outil similaire pour
briser les restes de charbon de bois et pour attirer
quelques braises vers I’avant du poêle par lequel entre
I’air de combustion.
• Chargez le combustible (morceaux plus petits d’abord).
• Fermez la porte.
• Attendez 5 à 10 minutes puis réglez la commande d’air
au niveau désiré.
Avis : Si le lit de charbon de bois présent au moment de
recharger est relativement profond ( 5 à 7 1/2 cm) et si
votre bois est bien sec, le moment est venu d’ajouter une
nouvelle charge de combustible, de fermer la porte, de
régler à nouveau la commande d’air au taux désiré de
sortie de chaleur - tout cela en 5 minutes seulement.
Retrait des cendres
Le retrait des cendres est requis chaque jour ou deux
pendant une saison de fonctionnement normal ; il est bien
plus facile à effectuer lorsque le bois brûlé est calciné en
charbons.
Avec une pelle, poussez tout d’abord les braises chaudes
d’un côté ou de I’autre. Ramassez à la pelle les cendres
exposées et repoussez les braises chaudes de l’autre côté.
Enlevez également les cendres de ce côté puis étalez
uniformément les braises chaudes à travers la boîte à
feu. Vous pouvez maintenant ajouter du nouveau bois pour
commencer un nouveau feu.
Lorsque vous enlevez les cendres d’un poêle en
fonctionnement, fermez et loquetez la porte avant de
sortir les cendres à I’extérieur pour en disposer sans
danger. Le port de gants protecteurs épais est toujours
une bonne idée tandis que vous enlevez et disposez des
cendres de votre poêle.
Les cendres devraient être placées dans un contenant de
métal avec couvercle bien serré, uniquement réservé à
cet effet et que vous conserverez à I’extérieur, bien
éloigné de tous les matériaux combustibles, jusqu’à ce
que vous puissiez en disposer définitivement. Si votre
intention est d’enfouir les cendres dans le sol ou de les
dispenser, conservez-les dans le contenant bien fermé
jusqu’à ce que toutes les escarbilles soient éteintes et
aient eu le temps de refroidir.
18
Page 19

CANADA
Une porte de poêle restant ouverte pourra causer de
dangereuses conditions de surchauffe qui risqueraient
d’endommager I’appareil, de rendre la garantie nulle et
non avenue ou de causer un incendie.
Mise en garde : N’employez votre poêle Jøtul F 602 USA
que lorsoue la porte est absolument fermée et n’ouvrez
celle-ci que pour recharger le poêle ou enlever les cendres.
Une porte partiellement ouverte risque de causer une
surchauffe.
Entretien
Généralités
Une fois par an, au moins, soumettez votre système à un
entretien de routine. Le meilleur moment pour cela est
lorsque vous nettoyez la cheminée et le raccord. Ce
nettoyage devrait être effectué chaque fois que
I’accumulation de créosote et de suie atteint 0.6 cm
d’épaisseur, ceci pouvant se produire plusieurs fois par an
selon le fonctionnement de I’appareil.
1. Nettoyez à fond le poêle tout entier. Brossez toutes
les cendres et la suie du poêle pour les éliminer. Il est
préférable de brosser les cendres et la suie plutôt que
de les nettoyer à I’aspirateur à cause de particules de
suie si fines qu’elles peuvent passer à travers la plupart
des sacs d’aspirateur.
2. Servez-vous d’une forte lampe dans une pièce sombre
pour inspecter I’intérieur et I’extérieur du poêle afin
de déceler les fêlures et fuites possibles des coins et
des joints. Les parties fêlées seront remplacées ; les
fuites de joints pourront être bouchées avec du ciment
pour poêle.
3. Vérifiez si la porte et les joints de fenêtre sont
parfaitement étanches. Pour vérifier le joint de porte
avant, introduisez à demi un dollar dans le poêle,
fermez la porte, loquetez-la puis tentez de retirer le
dollar sans le déchirer. S’il s’enlève facilement, le joint
n’est pas assez serré. Vérifiez plusieurs endroits autour
de la porte. Pour remplacer I’ancien joint défectueux,
grattez toute trace du matériau de joint et de ciment.
Etalez un cordon de ciment pour poêle d’1/8 po.(0.3 cm)
au fond de la rainure et pressez le nouveau joint
pardessus.
La porte requiert environ 91-1/2 cm de joint pour poêle, en
fibre de verre d’ 0.6 cm, haute densité. Ce joint s’use très
peu entre le panneau de verre et la porte. La meilleure
preuve de la nécessité d’un remplacement est I’apparition
de stries sur le verre, causées par les fuites d’air autour
du joint.
Remplacement du verre
Si une vitre de poêle se fêle ou se brise, vous devez la
remplacer avant de pouvoir utiliser le poêle de nouveau.
Enlevez soigneusement tout morceau de verre brisé. Ne
remplacez le panneau qu’avec un panneau de verre Jøtul
identique sans possibilité de substitut.
Le verre peut être remplacé sans démonter la porte du
poêle ou vous pouvez démonter celle-ci et la poser sur
une surface plate.
• Nettoyez la porte de tout résidu de joint au moyen
d’une brosse métallique, si nécessaire.
• Le joint sera auto-adhésif. Mesurez une longueur de
joint suffisante pour entourer la vitre - depuis le coin
supérieur de droite, au long du côté droit et du bord
inférieur puis en remontant vers le coin supérieur de
gauche plus 5 cm environ. Vous remarquerez que le
côté supérieur de la vitre ne requiert pas de joint. La
petite quantité d’air qui pénétrera par cet endroit
aidera à conserver la vitre propre.
• Pelez environ 25 cm de revêtement protecteur du
collant auto-adhésif. Prévoyez environ 3 cm de joint
pour chevauchement puis insérez le joint dans la
rainure de la porte en vous assurant que le côté
adhésif est dirigé vers la porte. Pressez le joint
fermement en position; continuez à peler I’adhésif et
à appliquer le joint jusqu’à ce qu’il vous reste un court
morceau lorsque vous atteindrez le coin supérieur de
gauche. Pressez alors le joint fermement en position.
• Centrez le panneau de verre de remplacement en le
déplaçant de gauche à droite sur le joint. Glissez la
vitre vers le bas de la porte jusqu’à ce qu’elle se bloque,
maintenez le verre en position d’une main tandis que
vous passez les morceaux de chevauchement par
dessus le côté supérieur du verre et au long des bords
extérieurs. Il vous faudra tordre le joint de sorte que
I’adhésif soit dirigé vers le verre. Pressez ces morceaux
fermement en position sur le verre.
• Replacez la glissière de la commande d’air, les pattes
de fixation supérieures et les vis.
Il est extrêmement important que les pattes soient
serrées un peu à la fois et qu’elles imitent le serrage des
19
Page 20

CANADA
goujons d’une roue d’automobile. Elles seront toutes aussi
serrées les unes que les autres, sans forcer. Veillez à ce
que le panneau de verre demeure centré dans I’ouverture
et qu’il ne glisse pas vers le bas. Il pourra s’avérer
nécessaire de serrer à nouveau lorsque le poêle aura
fonctionné et lorsque le joint se sera placé définitivement
en position.
Nettoyage du panneau de verre
Nettoyez, de temps à autre, la cendre fine accumulée sur
la surface intérieure du panneau de verre étant donné
qu’elle risquerait, en demeurant attachée trop longtemps
sur le panneau de verre, de le rayer sans remède au point
de le brouiller. La créosote éventuellement déposée sur
le panneau de verre sera éliminée en brûlant pendant le
prochain grand feu.
Ne nettoyez jamais le verre encore chaud et n’utilisez
jamais de nettoyant abrasif. De l’eau fraîche et un chiffon
doux ou une serviette de papier suffisent habituellement.
Rincez à fond à l’eau fraîche après le lavage et séchez
complètement avant de vous servir à nouveau de votre
poêle.
20
Page 21

Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Clearance to Chimney
Pass through
construction: 12”-(30,5)
Brick from thimble to
combustibles
Fig. 4
Header
12”
(30.5 cm)
Thimble: 5/8”-(1,6cm)
Fireclay Liner or
equivalent
Sill / Support
Flue LinerWood Stud 2”-(5cm)
12”
At least 3 feet
(91,5 cm)
At least 2 feet
(61 cm)
At least 10 feet
(305 cm)
(Measurements in cm - for Canada)
21
Page 22

Fig. 5
Listed Cap
Storm Collar
Flashing
Specified
clearance
Listed
Chimney
Attic
Insulation
Shield
Fig. 7
Hearth protection
2”
(5 cm)
A
A
A
B
28 1/2”
(75 cm)
A: 8” (20 cm)
B: 16” (46 cm)
Clearance to Adjacent Combustible
43 1/2”
(115 cm)
Fig. 6
Connector pipe must
be flush with the
inside of the flue tile
Combustible
Ceiling Joists
Chimney
Connector
Floor
Protector
to
Stove
Ceiling
Support
Fig. 8
A
B
A: 21” (53,5cm)
B: 13,5 ” (34,5 cm)
Fig. 9
A
B
A
C
C
B
A: 13” (33,5 cm)
B: 20 1/4” (51,5cm)
Chimney
Connector
Pipe
Thimble
(Measurements in cm - for Canada)
22
Flue Tile
Fig. 10
A
B
A: 24” (61 cm)
B: 19” (48,3cm)
Page 23

Fig. 11
Rear Heat Shield to reduce clearance
Single wall pipe, top exit only
A
Fig. 14
Alcove - double wall pipe and
wall protection
B
A: 21” - (53,5 cm)
B: 11” -( 28 cm)
Fig. 12
Alcove Installation
Double wall pipe and stove heat shield
A: 55” - (140 cm)
B: 15” - (39,5 cm)
C: 21” - (53,5 cm)
D: 48” - (122 cm)
A: 41” - (104 cm)
B: 8” - (20,5cm)
C: 14” - (36 cm)
D: 48” - (122 cm)
Fig. 15
A: Min. 96” - (244 cm)
B: Max. 48” - (122 cm)
C: Min. 41” - (104 cm)
D: 1” - (2,5 cm)
Alcove with wall protection
Fig.13
A: Min. 96” - (244 cm)
B: Max. 24” - (61 cm)
Alcove with rear heatshield
Fig. 16
Parallel installation with wall shield
Combustible wall
Wall shield
• Must be 27” wide
and centered
behind the stove.
• Must be 1” off the
wall and 1” off the
floor.
• With single wall
pipe, the shield
must be 49” high
measured off the
floor.
• With double wall
pipe, the shield
must be 37” high
measured off the
floor.
1
1
(Measurements in cm - for Canada)
23
Page 24

Fig. 17
Parallel installation in a corner with
wall shield
Wall shield
• Must be 1” off the
wall and 1” off the
floor.
• With single wall
pipe, the shield
must be 49” high
measured off the
floor.
• With double wall
pipe, the shield
must be 37” high
measured off the
floor.
• Both shields
extend and join in
the corner.
MUST
Combustible wall
The wall
shield must
extend a
minimum of
4” (102 mm)
past the side
of the stove
The wall shield must extend a
minimum of 7” (178mm) past the
ash lip of the stove
Fig. 18
Corner installation with wall shield
Wall shield
• Must be 1” off
the wall and 1”
off the floor.
• With single wall
pipe, the shield
must be 49”.
• With the double
wall pipe, the
shield must be
37” high.
• Both shields
MUST extend
and join in the
corner.
Fig. 19
Combustible wall
The wall shield
must extend a
minimum of 7”
(178mm) past
the front
corner of the
stove.
The wall shield must
extend a minimum of 7”
(178mm) past the front
corner of the stove.
A
A: Lift to open
B: Left - closed, Right - open
(Measurements in cm - for Canada)
24
B
Page 25

25
Page 26

Partlist Jøtul F 602 USA
Pos Description .........................................Dim./Spec.
1 Hot plate ........................................... 240 mm
2 Gasket ................................................ LD 360 Ø8.7x850
3 Screw, panhead...............................M6x12 DIN 7985
4 Air deflector
5 Nut ..................................................... M8
6 Gasket................................................ LD 187-1 Ø4.8x600
7 Gasket ................................................V-125 8x150
8 Spring for glass-door ....................Ø7.6x13
9 Door vent baffle
10 Screw, self thread ........................... M6 x 16
11 Flue outlet
12 Back plate
13 Side panel
14 Rivet ................................................... Ø3x12
15 Rivet ................................................... Ø2,4x4
16 Label
17 Label shield
18 Cover for smoke outlet
19 Countersunk screw ........................ M6x16
20 Baffle plate
21 Air manifold
22 Air chamber, complete
23 Air chamber
24 Screw, collar head........................... M6x10
25 Screw, collar head........................... M6x25
26 Rivet ................................................... Ø8x16 mm
27 Knob, wood
28 Screw, filister head ......................... M6x70
29 Nut w/ collar ................................... M6
30 Door catch
31 Door handle
32 Screw, cylinder head ...................... M6x30 DIN 84 S.krom.
33 screw, collar head ........................... M 6x35
34 Insulating blanket .......................... 360x185
35 Burnplate, side, with insulation
36 Burnplate, bottom
37 Insulating blanket .......................... 360x330
38 Screw, hex......................................... M6x25
39 Washer .............................................. Ø18x06,4x1.6
40 Top plate
41 Pin, door
42 Glass door, complete incl. handle
44 Glass, ceramic .................................. 4x147x154
45 Air slide vent
46 Front plate, complete
47 Front plate
48 Base plate
49 Legs, package of four
50 Leg, 1 pcs
51 Heatshield - bottom
52 Increaser ........................................... Ø 126xØ154 mm
53 Decorative top
54 Casing
55 Washer
56 Washer, black crom.
Appendix A:
Alternate floor protection
All floor protection materials must be non-combustible ie.
Metal, brick, stone, mineral fiber boards). Any combustible
material may not be used.
The easiest means of determining if a proposed alternate floor
material meets requirements listed in this manual is to follow
this procedure.
R-value = thermal resistance
K-value = thermal conductivity
C-value = thermal conductance
1. Convert the specification to r-value;
a. If r-value is given, no conversion is needed.
b. If k-value is given with a required thickness (t) in
inches: R=1/k X T.
c. If c-value is given: R=1/C.
2. Determine the r-value of the proposed alternate floor
protector.
a. Use the formula in step 1 to convert values not
expressed as “R”.
b. For multiple layers, add r-values of each layer to
determine overall r-value.
3. If the overall R-value of the sustem is greater than the
R-value of the specified floor protector, the alternate is
acceptable.
Example:
The specified floor protector should be 3/4” thick material
with a k-factor of 0.84. The proposed alternate is 4” brick with
a c-factor of 1.25 over 1/8” mineral board witha k-factor of
0.29.
Step A. Use formula above to convert specifications to
R-value. R=1/k x t= 1/.84 x .75 = .893
Step B. Calculate r of proposed system.
4” brick of c-1.25, therefore
R brick = 1/c = 1/1.25 = 0.80
1/8” mineral board of K = 0.29 therefore
R mineral board = 1/.29 x 0.125 = 0.431
Total R = R brick + R mineral board= 0.8 + 0.431=1.231
Step C. Compare proposed system R = 1.231 to specified R
of 0.893. Since R is greater than required, the system
is acceptable.
Definitions:
Thermal conductance =
C = btu = W
(Hr)(ft2)(f) (m2)(k)
Thermal conductivity =
K = btu = W = (btu)
(Hr)(ft2)(f) (m2)(k) (hr)(ft)(f)
Thermal resistance =
R = btu = (m2)(k) = (btu)(inch)
(Hr)(ft2)(f) W (hr)(ft2)(f)
For the 3 requires floor protection with a minimum insulating
R-value of 1.1.
26
Alcove installation require a minimum R-value of 1.1. (If a UL/
ULC or whi listed hearth pad is not used.)
Page 27

27
Page 28

Møklegaards Trykkeri as -Jun. 04
Draw.no. 4-3436-P03
Cat.no. 128765
Jøtul maintains a policy of constant product development. Products supplied may therefore
differ in specification, colour and type of accessories from those illustrated and described in
this manual.
Jøtul vise sans cesse à améliorer ses produits. C’est pourquoi, il se réserve le droit de modifier
les specifications, couleurs et équipements sans avis prélable.
Quality
Jøtul AS has a quality system that conforms to NS-EN ISO 9001 for product development,
manufacturing, and distribution of stoves and fireplaces. This policy gives our customers
quality and safety piece of mind as a result of Jøtul’s vast experience dating back to when the
company first started in 1853.
We appreciate your trust in welcoming our product into your home and invite your comment
and appraisal of our efforts to provide you with the finest in home hearth products.
Qualité
Le système de contrôle de la qualité de Jøtul AS est conforme à la norme NS-EN ISO 9001
relative à la conception, à la fabrication et à la distribution de poêles, foyers et inserts. Cette
politique nous permet d’offrir à nos clients une qualité et une sécurité reposant sur la vaste
expérience accumulée par Jøtul depuis sa création en 1853.
Jøtul North America
400 Riverside Street
Portland, Maine 04104
Jøtul AS,
P.o. box 1411
N-1 Fredrikstad,
Norway
This product has been controlled by:
Ce produit a été contrôlé par :
____________________________ __________________
Date: Sign:
 Loading...
Loading...