Page 1

Powertrain DTC Summaries – OBD II
Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide
Jaguar X
Revised January, 2002:
P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 “POSSIBLE CAUSES” Revised
P0860 Added
P1606 Revised CK ENG
Evaporative System Monitor Drive Cycle Revised
Revised April, 2002: P0831, P0832, P1517, P1601
Revised August, 2002: P0507, P1260
Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of “Powertrain DTC Summaries”.
-
TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Page 2

KEY TO COLUMN HEADINGS
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code.
SYS The powertrain system with which the DTC is associated – EMS, TRANS, ABS/TC (DSC).
DTC retrieval tools:
OBD II – indicates that the DTC is an OBD II code and can be accessed via a generic scan tool or WDS.
JAG – indicates that the DTC is not an OBD II code and is accessed only via WDS.
FAULT DESCRIPTION Fault description.
MONITORING CONDITIONS “DIAGNOSTIC MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE” for the particular DTC. Operate the vehicle as described to check for a reoccurrence of
the DTC. Refer to pages 4 – 7.
Use WDS Datalogger or Scan Tool to monitor specified engine parameter(s).
CHECK ENGINE MIL 1 1 TRIP – indicates that the CHECK ENGINE MIL is activated by a fault occurring during ONE “TRIP”.
(CK ENG) 2 2 TRIPS – indicates that the CHECK ENGINE MIL is activated by a fault occurring during TWO CONSECUTIVE “TRIPS”.
N NO – indicates that the CHECK ENGINE MIL is not activated.
OTHER Driver Warnings:
N None
R RED MIL / Message or Powertrain Warning Indicator
A AMBER MIL / Message or Powertrain Warning Indicator
C Charge indicator
DEFAULT ACTION Control Module default action:
Logged – DTC stored in ECM memory buffer; Flagged – DTC stored in ECM memory / CHECK ENGINE MIL activated.
CM PIN ECM (SYS – EMS) / TCM (SYS – TRANS) Connector pin number(s)
POSSIBLE CAUSES Possible causes are listed in the order of diagnostic checking.
HIGH VOLTAGE – High voltage can be either sensor supply voltage (5 volts) or B+ voltage.
REFERENCE: It is recommended that the applicable “Electrical Guide” be referenced when using the information contained in this document.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
2
Page 3
CYLINDER NUMBERING
Engine cylinder numbering is as follows:
FRONT OF ENGINE
2 1
4 3
6 5
OBD SYSTEM READINESS – ENGINE MANAGEMENT
If DTC P1000 is flagged after DTCs have been cleared, all engine management OBD diagnostic monitor drive cycles HAVE NOT BEEN COMPLETED.
If DTC P1111 is flagged after DTCs have been cleared, all engine management OBD diagnostic monitor drive cycles HAVE BEEN COMPLETED.
OBD SYSTEM READINESS – TRANSMISSION
Use WDS Datalogger “TOTAL NUMBER OF DTC SET” to determine if transmission OBD monitoring has been completed. Refer to page 7.
OBD DIAGNOSTIC MONITORS
The Engine Management and Transmission Control systems are continuously checked during vehicle operation by the Engine Control Module (ECM) and Transmission
Control Module (TCM) on-board diagnostic (OBD) facilities. Powertrain OBD incorporates six diagnostic monitors. Each monitor has an associated group of DTCs. The
diagnostic monitors will complete the diagnostic test(s) if a specified service “drive cycle” is carried out.
The six diagnostic monitors are as follows:
– Heated Oxygen Sensors Monitor
– Adaptive Fuel Monitor
– Misfire Monitor
– Catalyst Efficiency Monitor
– Evaporative System Monitor
– Comprehensive Component Monitor (Engine Management / Transmission)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
3
Page 4

DIAGNOSTIC MONITORS DRIVE CYCLES
Technicians can ensure that an OBD Monitor drive cycle is completed and that all or specific components have been checked by completing a specified drive cycle.
Use the following service drive cycles to confirm that the components and subsystems covered by the Diagnostic Monitors are operating correctly.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE
Upstream (Universal) oxygen sensors:
1 Engine OFF; cooling fans inoperative > 20 seconds.
2 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
3 Drive the vehicle between 3000 – 4000 rpm at a steady speed. Lift foot completely off accelerator and coast to a stop within 30 seconds. Do not touch accelerator
pedal for 4 seconds after coming to a stop.
4 Repeat step 3.
5 Idle engine for 11 minutes.
Downstream oxygen sensors:
1 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
2 Drive the vehicle steadily between 48 – 97 km/h (30 – 60 mph) for 10 minutes.
3 Drive the vehicle above 3000 rpm in 4th gear at a steady speed. Lift foot completely off accelerator and coast for 30 seconds.
Oxygen sensor heaters:
1 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
2 Idle engine for 3 minutes.
ADAPTIVE FUEL MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE
1 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
2 Idle for a minimum of 10 minutes.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
4
Page 5

MISFIRE MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE
1 Record flagged DTC (s) and accompanying WDS DTC Monitor freeze frame(s) data.
2 Fuel level > 25%.
3 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
4 Drive vehicle to the recorded freeze frame conditions (from step 1).
5 Repeat several times.
Note regarding misfire monitor DTCs:
If on the first trip, the misfire is severe enough to cause excess exhaust emission, the individual cylinder DTC plus DTC P1316 will be logged. The CHECK ENGINE MIL
will not be activated. If the fault reoccurs on the second trip, the individual cylinder DTC plus DTC P1316 will be flagged, and the CHECK ENGINE MIL will be activated.
If on the first trip, the misfire is severe enough to cause catalyst damage (more severe than excess exhaust emission), the CHECK ENGINE MIL will flash while the
fault is present and the individual cylinder DTC plus DTC P1313 (bank 1), DTC P1314 (bank 2) will be logged. When the fault is no longer present the MIL will be deactivated. If the fault reoccurs on the second trip, the CHECK ENGINE MIL will flash while the fault is present and the individual cylinder DTC plus DTC P1313 (bank 1),
DTC P1314 (bank 2) will be flagged. When the fault is no longer present the CHECK ENGINE MIL will be activated.
CATALYST EFFICIENCY MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE
1 Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature > 82 °C (180 °F).
2 Drive vehicle steadily between 1700 – 2500 rpm for 5 minutes.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
5
Page 6

EVAPORATIVE SYSTEM MONITOR DRIVE CYCLE
1 Ensure that fuel filler cap is fully closed (minimum three clicks).
2 Fuel level > 30% and < 85%.
3 Using WDS, perform ECM DTC Clear (even if no DTCs are flagged).
4 Drive vehicle for a minimum of 2 minutes, and until engine is at normal operating temperature.
5 Using WDS, ensure that the EVAP Canister Purge Valve is operating by observing “PURGE VAPOR MANAGEMENT VALVE – DUTY CYCLE”. If the valve is not
active, ECM adaptions have not been learned. Conduct a “green ECM” Drive Cycle as described in Technical Service Bulletin.
6 Drive vehicle to the road where the EVAP System Drive Cycle will be conducted. Stop vehicle and switch OFF the ignition. Leave ignition OFF for 30 seconds,
then restart the engine.
7 Accelerate briskly to 80 km/h (50 mph) ensuring that the engine speed reaches a minimum of 3500 rpm for a minimum of 5 seconds.
8 (0.040 inch EVAP Test) View WDS “PURGE VAPOR MANAGEMENT VALVE – DUTY CYCLE”, “CANISTER CLOSE VALVE – VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM”, and
FUEL TANK PRESSURE – VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM”. Avoiding high engine loads, drive the vehicle steadily between 65 km/h (40 mph) and 100 km/h (60
mph). Avoid driving conditions that will produce excessive fuel movement. WDS should give an indication that the test is active (it may take up to 30 minutes
before the test will initialize). When the test has initialized (EVAP Canister Close Valve CLOSED), it will take approximately 90 seconds for the test to complete.
9 (0.020 inch EVAP Test) Continue driving vehicle as explained in Step 8 for an additional 10 minutes.
10 Gently coast the vehicle to a stop. Allow the engine to idle for 2 minutes and view WDS “PURGE VAPOR MANAGEMENT VALVE – DUTY CYCLE”, “CANISTER
CLOSE VALVE – VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM”, and FUEL TANK PRESSURE – VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM”. WDS should give an indication that the test is
active. When the test has initialized (EVAP Canister Close Valve CLOSED), it will take approximately 90 seconds for the test to complete.
11 If the 0.020 inch EVAP Test is not activated, the purge system vapor concentration may be too great. To reduce the vapor concentration proceed as follows:
12 Drive the vehicle for an additional 30 minutes avoiding driving conditions that will produce excessive fuel movement. Repeat Step 10. If the 0.020 inch EVAP
Test is still not activated, repeat the Drive Cycle from Step 6.
13 Using WDS, check for and clear flagged DTCs.
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENT MONITOR ENGINE MANAGEMENT DRIVE CYCLE
To avoid unnecessary complexity, a single comprehensive engine management drive cycle has not developed for X-TYPE. Refer to the individual DTC for specific drive
cycle / monitoring conditions.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
6
Page 7

COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENT MONITOR TRANSMISSION DRIVE CYCLE
The Comprehensive Component Monitor transmission drive cycle will “check” all transmission system components.
1 Engine and transmission at normal operating temperature. Ignition OFF
2 With gear selector in P and the ignition ON. Check gearshift interlock by attempting to move selector without pressing the brake pedal. Verify P state illumination.
3 Press and hold the brake pedal. Move the gear selector to R. Verify R state illumination.
4 Set the parking brake. Press and hold the brake pedal. Attempt to start the engine. The engine should not start.
5 Move the gear selector to N. Verify N state illumination. Start the engine.
6 With the hand brake set and the brake pedal pressed, move the gear selector to the remaining positions in the J Gate (D, 4, 3, 2) for five (5) seconds each. Verify
the state illumination in each position.
7 Move the gear selector back to 4. Verify 4 state illumination.
8 Move the gear selector to D. Verify D state illumination.
9 Move the gear selector to N. Verify N state illumination.
10 Select R, release the brakes and drive the vehicle in Reverse for a short distance.
11 Stop the vehicle.
12 Select 2 and drive the vehicle up to 65 km/h (40 mph). Hold 65 km/h (40 mph) for a minimum of five (5) seconds.
13 Select 3 and hold 65 km/h (40 mph) for a minimum of five (5) seconds.
14 Select 4 and hold 65 km/h (40 mph) for a minimum of five (5) seconds.
15 Select D and accelerate to a minimum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph). Hold 80 – 129 km/h (50 – 80 mph) for a minimum of 1.7 kilometers (1 mile).
16 Stop the vehicle; do not switch OFF the engine.
17 Use WDS Datalogger “TOTAL NUMBER OF DTC SET” to ensure that transmission DTC monitoring is complete.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
7
Page 8

POWERTRAIN CONTROL ACRONYMS:
A/C Air conditioning
APP Sensor Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
B+ Battery Voltage
Bank 1 RH Engine cylinder bank (cylinders 1, 3, 5) (A Bank)
Bank 2 LH Engine cylinder bank (cylinders 2, 4, 6) (B Bank)
BARO Sensor Barometric Pressure Sensor
CAN Controller Area Network
CKP Sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor 1 Camshaft Position Sensor – Bank 1
CMP Sensor 2 Camshaft Position Sensor – Bank 2
DLC Data Link Connector
ECM Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
EFT Sensor Engine Fuel Temperature Sensor
EOT Sensor Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
EVAP Canister Close Valve Evaporative Emission Canister Close Valve
EVAP Canister Purge Valve Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Valve
FTP Sensor Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
HO2 Sensor 1 / 1 Heated Oxygen Sensor – Bank 1 / Upstream
HO2 Sensor 1 / 2 Heated Oxygen Sensor – Bank 1 / Downstream
HO2 Sensor 2 / 1 Heated Oxygen Sensor – Bank 2 / Upstream
HO2 Sensor 2 / 2 Heated Oxygen Sensor – Bank 2 / Downstream
IAT Sensor Intake Air Temperature Sensor
IMT Valve 1 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve: Bottom
IMT Valve 2 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve: Top
IP Sensor Injection Pressure Sensor
KS 1 Knock Sensor – Bank 1
KS 2 Knock Sensor – Bank 2
MAF Sensor Mass Air Flow Sensor
MAP Sensor Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
TCC Torque converter clutch
TCM Transmission Control Module
TFT Sensor Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
TP Sensor Throttle Position Sensor
VVT Valve 1 Variable Valve Timing Valve – Bank 1
VVT Valve 2 Variable Valve Timing Valve – Bank 2
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
8
Page 9
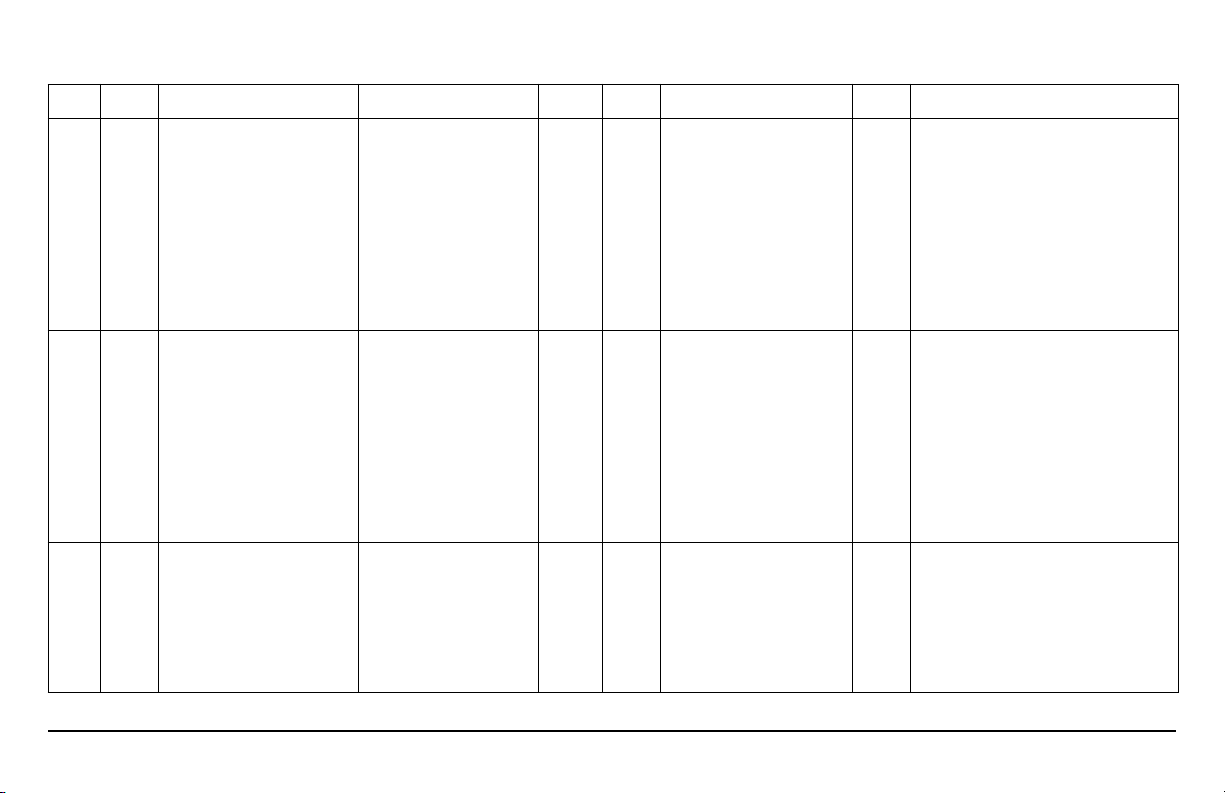
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0010 EMS
VVT circuit malfunction – bank 1 Idle engine 30 seconds
OBD II
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range
Coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 VVT hold current set at
a constant value of 450 mA
EN16
VVT solenoid valve to ECM PWM drive circuit:
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
-109
VVT solenoid failure
Idle engine 30 seconds
P0020 EMS
VVT circuit malfunction – bank 2 Idle engine 30 seconds
OBD II
P0031 EMS
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
low current –
OBD II
bank 1, upstream (1/1)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
Idle engine 30 seconds
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
2NECM Default:
– Bank 2 VVT hold current set at
a constant value of 450 mA
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering and adaptive fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Bank 1 upstream HO2S
heater control circuit switched
off
EN16
VVT solenoid valve to ECM PWM drive circuit:
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
-110
VVT solenoid failure
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater power supply circuit:
EN16
open circuit
-001
-002
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater control circuit:
-029
open circuit, high resistance
-030
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater ground circuit(s) fault
(EN16-029, EN16-030)
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater failure
9
Page 10
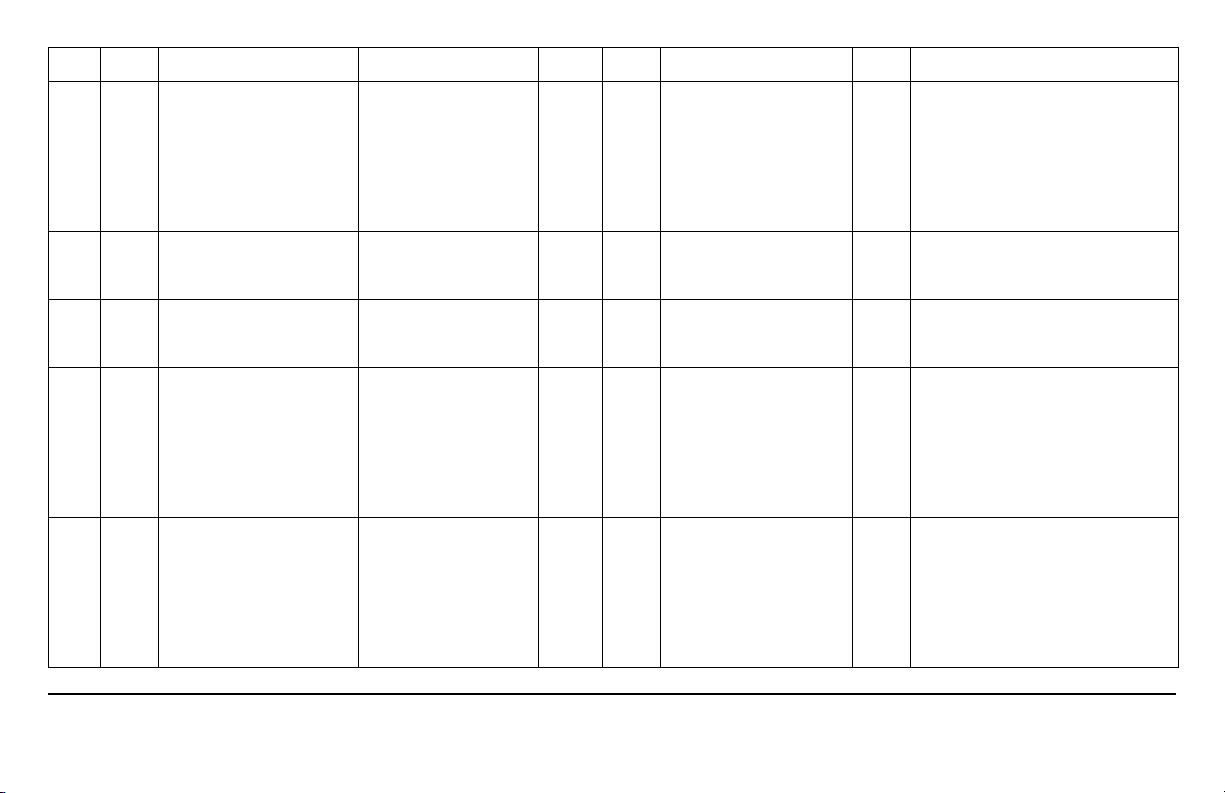
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0032 EMS
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
high current –
OBD II
bank 1, upstream (1/1)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering and adaptive fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Bank 1 upstream HO2S
heater control circuit switched
off
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater control circuit:
EN16
short circuit to ground
-001
-002
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater ground circuit(s) fault
-029
(EN16-029, EN16-030)
-030
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater failure
P0037 EMS
P0038 EMS
P0051 EMS
P0052 EMS
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
low resistance –
OBD II
bank 1, downstream (1/2)
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
high resistance –
OBD II
bank 1, downstream (1/2)
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
low current –
OBD II
bank 2, upstream (2/1)
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
high current –
OBD II
bank 2, upstream (2/1)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
2NNone EN16
2NNone EN16
2NECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering and adaptive fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Bank 2 upstream HO2S
heater control circuit switched
off
2NECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering and adaptive fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Bank 2 upstream HO2S
heater control circuit switched
off
-092
-092
EN16
-055
-056
-081
-082
EN16
-055
-056
-081
-082
HO2 Sensor 1/2 heater control circuit:
short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 1/2 heater failure
HO2 Sensor 1/2 heater control circuit:
open circuit; high resistance
HO2 Sensor 1/2 heater failure
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater power supply circuit:
open circuit
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater control circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater ground circuit(s) fault
(EN16-081, EN16-082)
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater failure
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater control circuit:
short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater ground circuit(s) fault
(EN16-081, EN16-082)
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater failure
10
Page 11

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0057 EMS
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
low resistance –
OBD II
bank 2, downstream (2/2)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
2NNone EN16
-93
HO2 Sensor 2/2 heater control circuit:
short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 2/2 heater failure
P0058 EMS
P0101 EMS
P0102 EMS
HO2 Sensor heater control circuit
high resistance –
OBD II
bank 2, downstream (2/2)
MAF Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
MAF Sensor circuit low voltage Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Oxygen sensor heaters)
Fuel level > 25%.
Start engine and bring to
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Drive the vehicle steadily in
4th or 5th gear on a level road
between 1700 – 2300 rpm;
hold the engine speed
constant for 40 seconds while
maintaining a steady throttle
2NNone EN16
2AECM Default:
– Default air mass used
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
-93
EN16
-044
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
– Default air mass used
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
-044
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
HO2 Sensor 2/2 heater control circuit:
open circuit; high resistance
HO2 Sensor 2/2 heater failure
Blocked air cleaner
Air intake leak
Engine breather leak
Throttle control malfunction
MAF Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, intermittent short circuit
to ground
MAF Sensor supply circuit: high resistance
MAF Sensor failure
Blocked air cleaner
MAF Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, intermittent
short circuit to ground
MAF Sensor supply circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground
MAF Sensor failure
11
Page 12
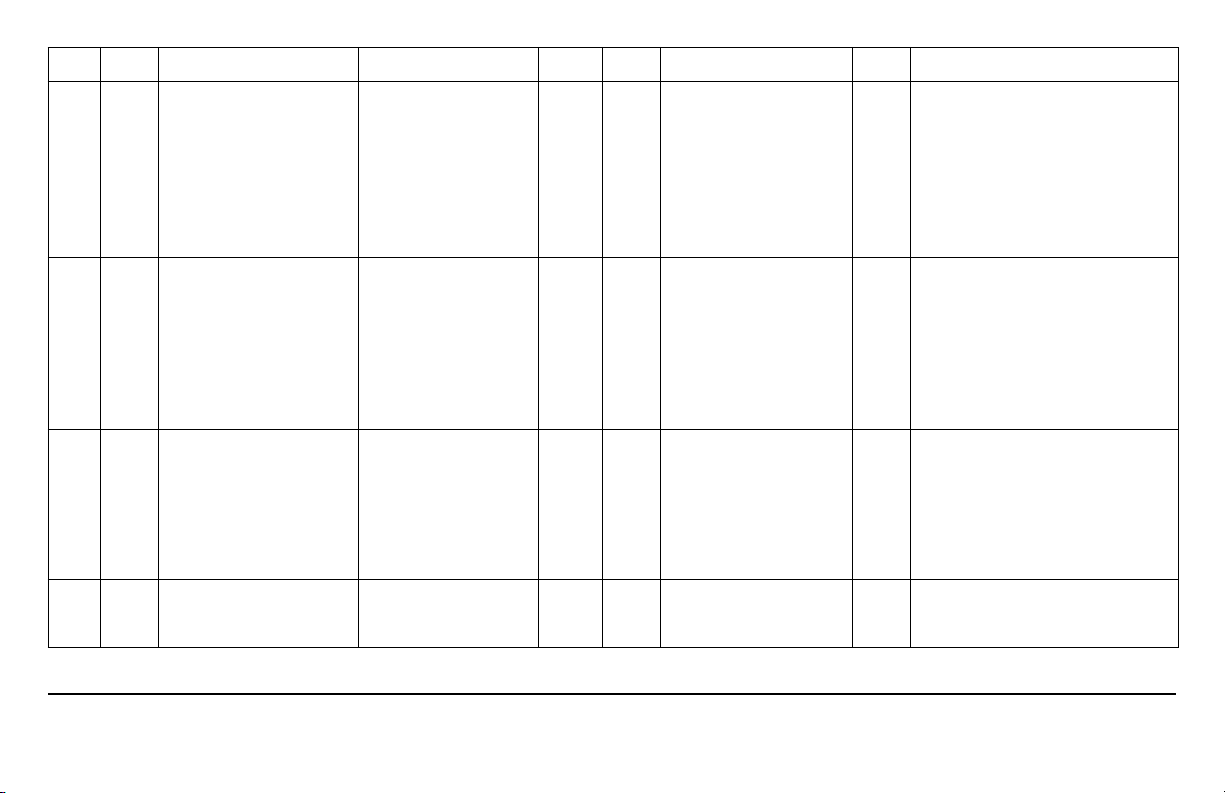
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0103 EMS
MAF Sensor circuit high voltage Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
OBD II
– Default air mass used
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
EN16
MAF Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
short circuit to B+ voltage
-044
MAF Sensor to ECM sensor ground circuit:
-045
open circuit
-046
MAF Sensor failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P0105 EMS
MAP Sensor circuit malfunction Fuel level > 25%
OBD II
P0106 EMS
P0107 EMS
BARO Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
BARO Sensor circuit low voltage Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine and bring to
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Drive the vehicle steadily in
4th or 5th gear on a level road
between 1700 – 2300 rpm;
hold the engine speed
constant for 40 seconds while
maintaining a steady throttle
Engine temperature cool
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle twice more
2NECM Default:
– Default value of 1.013 BAR
(29.92 in hg) used
2NECM Default:
– Default value of 1 BAR (29.53
in hg) used
– Default value of 1 BAR (29.53
in hg) used
EN16
MAP Sensor to ECM circuit(s) fault
-127
MAP Sensor failure
— BARO Sensor failure (internal ECM fault)
— BARO Sensor failure (internal ECM fault)
12
Page 13

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0108 EMS
BARO Sensor circuit high voltage Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
OBD II
– Default value of 1 BAR (29.53
in hg) used
— BARO Sensor failure (internal ECM fault)
P0111 EMS
P0112 EMS
P0113 EMS
IAT Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
IAT Sensor circuit high voltage
(low air temperature)
OBD II
IAT Sensor circuit low voltage
(high air temperature)
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Engine OFF; coolant
temperature <35 °C (95 °F)
Start engine and hold 3000
rpm in P or N for 30 seconds
2NECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
EN16
Blocked air cleaner
-071
Air intake leak
Engine breather leak
IAT Sensor to ECM wiring:
open circuit or high resistance
IAT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
IAT Sensor failure
EN16
IAT Sensor to ECM wiring:
open circuit or high resistance
-071
IAT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
short circuit to B+ voltage
IAT Sensor failure
EN16
IAT Sensor to ECM wiring:
short circuit to ground
-071
IAT Sensor failure
13
Page 14

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0116 EMS
ECT Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
Engine coolant temperature
and ambient temperature
within 10 °C (50 °F)
Drive the vehicle steadily in
4th or 5th gear above 1700
rpm for 5 minutes
Idle engine until engine
coolant temperature reaches
80 °C (176 °F)
CAUTION: Overheating is
possible if the ECT sensor is
faulty and cooling fans do not
operate
2AECM Default:
– EOT value substituted (no
greater than 95 °C (203 °F)
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm-up ignition
retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Low coolant level
-070
Contaminated coolant
Engine thermostat failure
ECT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance when hot, intermittent high
resistance
ECT Sensor failure
P0117 EMS
ECT Sensor circuit high voltage
(low coolant temperature)
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
– EOT value substituted (no
greater than 95 °C (203 °F)
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm-up ignition
retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
ECT Sensor disconnected
-070
ECT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit
to B+ voltage
ECT Sensor failure
14
Page 15
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0118 EMS
ECT Sensor circuit low voltage
(high coolant temperature)
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
– EOT value substituted (no
greater than 95 °C (203 °F)
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm-up ignition
retard inhibited
EN16
Engine overheat condition
-070
ECT Sensor to ECM wiring:
short circuit to ground
ECT Sensor failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P0121 EMS
P0122 EMS
TP Sensor range / performance
(TP1 compared to TP2)
OBD II
TP Sensor circuit 1 low voltage Battery voltage > 10 v
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
EN16
TP Sensor to ECM wiring:
open circuit, high resistance
-075
-076
TP Sensor to ECM sensing circuits (TP1 or
TP2): short circuit to B+ voltage
TP Sensor failure
EN16
TP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit (TP1):
open circuit, high resistance
-075
TP Sensor failure
15
Page 16
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0123 EMS
TP Sensor circuit 1 high voltage Battery voltage > 10 v
OBD II
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
EN16
TP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit (TP1):
short circuit to high voltage
-075
TP Sensor failure
P0125 EMS
ECT Sensor response
(for closed loop fuel control)
OBD II
(Coolant thermostat monitor)
P0128 EMS
Coolant thermostat range /
performance
OBD II
P0131 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit low
current – bank 1, upstream (1/1)
OBD II
(Universal oxygen sensor: lean
condition at ECM – high current at
sensor)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Engine coolant temperature
and ambient temperature
within 10 °C (50 °F)
Drive the vehicle steadily in
4th or 5th gear above 1700
rpm for 5 minutes
Idle engine until engine
coolant temperature reaches
80 °C (176 °F)
CAUTION: Overheating is
possible if the ECT sensor is
faulty and cooling fans do not
operate
Engine OFF; coolant
temperature <35 °C (95 °F)
Start engine and drive until
normal engine operating
temperature > 82 °C (180 °F)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
2AECM Default:
– EOT value substituted (no
greater than 95 °C (203 °F)
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm-up ignition
retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Low coolant level
-070
Contaminated coolant
Engine coolant thermostat failure
ECT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit or short circuit
to high voltage
Engine cooling fan stuck on high speed
Above normal air flow through engine
compartment due to accident damage and/
or missing panels
2NNone — Contaminated coolant
Engine coolant thermostat failure
ECT Sensor failure
(ECT Sensor DTC(s) also flagged)
2NNone EN16
HO2 Sensor 1/1 disconnected
-083
HO2 Sensor 1/1 to ECM variable current
-084
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 3)
ECM to HO2 Sensor 1/1 constant current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 4)
HO2 Sensor 1/1 failure
16
Page 17
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0132 EMS
OBD II
HO2 Sensor sense circuit high
current – bank 1, upstream (1/1)
(Universal oxygen sensor: rich
condition at ECM – low current at
sensor)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
2NNone EN16
-083
-084
HO2 Sensor 1/1 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 1/1 to ECM variable current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 3)
ECM to HO2 Sensor 1/1 constant current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 4)
HO2 Sensor 1/1 failure
P0133 EMS
P0137 EMS
P0138 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
slow response –
OBD II
bank 1, upstream (1/1)
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
low voltage –
OBD II
bank 1, downstream (1/2)
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
high voltage –
OBD II
bank 1, downstream (1/2)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
EN16
-083
-084
– Canister purge inhibited
2NNone EN16
2NNone EN16
-128
-128
Engine misfire
HO2 Sensor 1/1 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 1/1 mechanical damage
HO2 Sensor 1/1 to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor 1/1 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 1/1 to ECM wiring shield open
circuit
HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater circuit fault
Exhaust leak
Low exhaust temperature
Injector flow partially blocked
Catalyst efficiency decrease
HO2 Sensor 1/1 failure
HO2 Sensor 1/2 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 1/2 to ECM wiring open circuit
HO2 Sensor 1/2 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 1/2 failure
HO2 Sensor 1/2 sensing circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
HO2 Sensor 1/2 ground (BRD – braided shield)
open circuit
HO2 Sensor 1/2 failure
17
Page 18

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0140 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
no activity –
OBD II
bank 1, downstream (1/2)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
2NNone EN16
-128
HO2 Sensor 1/2 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 1/2 mechanical damage
HO2 Sensor 1/2 to ECM wiring open circuit
HO2 Sensor 1/2 sensing circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
HO2 Sensor 1/2 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 1/2 ground (BRD – braided shield)
open circuit
Exhaust leak
Low exhaust temperature
HO2 Sensor 1/2 failure
P0151 EMS
OBD II
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
low current –
bank 2, upstream (2/1)
(Universal oxygen sensor: lean
condition at ECM – high current at
sensor)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
2NNone EN16
-107
-108
HO2 Sensor 2/1 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 2/1 to ECM variable current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 3)
ECM to HO2 Sensor 2/1 constant current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 4)
HO2 Sensor 2/1 failure
P0152 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
high current –
OBD II
bank 2, upstream (2/1)
(Universal oxygen sensor: rich
condition at ECM – low current at
sensor)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
2NNone EN16
-107
-108
HO2 Sensor 2/1 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 2/1 to ECM variable current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 3)
ECM to HO2 Sensor 2/1 constant current
circuit fault (HO2 Sensor pin 4)
HO2 Sensor 2/1 failure
18
Page 19
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0153 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
slow response –
OBD II
bank 2, upstream (2/1)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Upstream oxygen sensors)
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
EN16
Engine misfire
-107
HO2 Sensor 2/1 disconnected
-108
HO2 Sensor 2/1 mechanical damage
HO2 Sensor 2/1 to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor 2/1 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 2/1 to ECM wiring shield open
circuit
HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater circuit fault
Exhaust leak
Low exhaust temperature
Injector flow partially blocked
Catalyst efficiency decrease
HO2 Sensor 2/1 failure
P0157 EMS
P0158 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
low voltage –
OBD II
bank 2, downstream (2/2)
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
high voltage –
OBD II
bank 2, downstream (2/2)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
2NNone EN16
2NNone EN16
-129
-129
HO2 Sensor 2/2 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 2/2 to ECM wiring open circuit
HO2 Sensor 2/2 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 2/2 failure
HO2 Sensor 2/2 sensing circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
HO2 Sensor 2/2 ground (BRD – braided shield)
open circuit
HO2 Sensor 2/2 failure
19
Page 20
DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0160 EMS
HO2 Sensor sense circuit
no activity –
OBD II
bank 2, downstream (2/2)
Heated oxygen sensors
monitor drive cycle – page 4
(Downstream oxygen
sensors)
2NNone EN16
-129
HO2 Sensor 2/2 disconnected
HO2 Sensor 2/2 mechanical damage
HO2 Sensor 2/2 to ECM wiring open circuit
HO2 Sensor 2/2 sensing circuit short circuit to
high voltage
HO2 Sensor 2/2 short circuit to ground
HO2 Sensor 2/2 ground (BRD – braided shield)
open circuit
Exhaust leak
Low exhaust temperature
HO2 Sensor 2/2 failure
P0171 EMS
Bank 1 combustion too lean Start engine and bring to
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Idle for 10 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 catalyst warm-up
ignition retard inhibited
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
— Engine misfire
Air intake leak between MAF Sensor and
throttle
Fuel filter / system restriction
Fuel injector restriction
Fuel pressure sensor failure (low fuel
pressure)
Low fuel pump output
HO2 Sensor(s) (1/1, 1/2)
harness wiring condition fault
Exhaust leak (before catalyst)
ECM receiving incorrect signal from one or
more of the following components:
ECT Sensor, MAF Sensor, IAT Sensor,
IP Sensor, EFT Sensor, TP Sensor
20
Page 21

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0172 EMS
Bank 1 combustion too rich Start engine and bring to
OBD II
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Idle for 10 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 catalyst warm-up
ignition retard inhibited
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
— Restricted air filter
Leaking fuel injector(s)
Fuel pressure sensor failure
(high fuel pressure)
ECM receiving incorrect signal from one or
more of the following components:
ECT Sensor, MAF Sensor, IAT Sensor,
IP Sensor, EFT Sensor, TP Sensor
P0174 EMS
Bank 2 combustion too lean Start engine and bring to
OBD II
P0175 EMS
Bank 2 combustion too rich Start engine and bring to
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Idle for 10 minutes
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Idle for 10 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 catalyst warm-up
ignition retard inhibited
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 catalyst warm-up
ignition retard inhibited
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
— Engine misfire
Air intake leak between MAF Sensor and
throttle
Fuel filter / system restriction
Fuel injector restriction
Fuel pressure sensor failure
(low fuel pressure)
Low fuel pump output
HO2 Sensor(s) (2/1, 2/2)
harness wiring condition fault
Exhaust leak (before catalyst)
ECM receiving incorrect signal from one or
more of the following components:
ECT Sensor, MAF Sensor, IAT Sensor,
IP Sensor, EFT Sensor, TP Sensor
— Restricted air filter
Leaking fuel injector(s)
Fuel pressure sensor failure
(high fuel pressure)
ECM receiving incorrect signal from one or
more of the following components:
ECT Sensor, MAF Sensor, IAT Sensor,
IP Sensor, EFT Sensor, TP Sensor
21
Page 22

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0181 EMS
EFT Sensor range / performance Engine OFF; coolant
OBD II
temperature <35 °C (95 °F)
Start engine and drive until
normal engine operating
temperature > 82 °C (180 °F)
Drive for an additional 25
minutes
2NECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
EN16
EFT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit to
-050
ground short circuit to high voltage
EFT Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
high resistance, open circuit
EFT Sensor failure
P0182 EMS
P0183 EMS
P0191 EMS
EFT Sensor circuit low voltage
(high temperature)
OBD II
EFT Sensor circuit high voltage
(low temperature)
OBD II
IP Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 25 °C (77 °F)
used
Fuel level > 25%
Idle engine 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2NECM Default:
– Default value of 3.80 BAR
(55.11 psi) used
– Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
Idle engine 30 seconds
EN16
EFT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
short circuit to ground
-050
EFT Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
short circuit
EFT Sensor failure
EN16
EFT Sensor disconnected
-050
EFT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit
to high voltage
EFT Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
high resistance, open circuit
EFT Sensor failure
EN16
Fuel filter / system restriction
-073
Fuel system leak
Incorrect fuel pump output
IP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit
to ground, short circuit to high voltage
IP Sensor to splice sensor supply circuit:
high resistance, open circuit
IP Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit
to ground, short circuit to high voltage
IP Sensor failure
22
Page 23

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0192 EMS
IP Sensor sensor circuit
low voltage (low pressure)
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 3.80 BAR
(55.11 psi) used
Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
EN16
IP Sensor disconnected
-073
IP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
open circuit or short circuit to ground
IP Sensor to splice sensor supply circuit:
high resistance open circuit
IP Sensor failure
P0193 EMS
P0196 EMS
IP Sensor sensor circuit
high voltage (high pressure)
OBD II
EOT Sensor range / performance Engine OFF; coolant
OBD II
P0197 EMS
P0198 EMS
EOT Sensor low voltage
(high temperature)
OBD II
EOT Sensor high voltage
(low temperature)
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 3.80 BAR
(55.11 psi) used
Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
temperature <35 °C (95 °F)
Start engine and drive until
normal engine operating
temperature > 82 °C (180 °F)
2NECM Default:
– ECT substituted
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– ECT substituted
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– ECT substituted
EN16
IP Sensor to ECM wiring (supply, sense):
short circuit to each other
-073
IP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
IP Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
open circuit
IP Sensor failure
EN16
EOT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit;
high resistance when hot, intermittent
-078
high resistance
EOT Sensor failure
EN16
EOT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
short circuit to ground
-078
EOT Sensor failure
EN16
EOT Sensor disconnected
-078
EOT Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
high resistance, open circuit, short circuit
to B+ voltage
EOT Sensor failure
23
Page 24

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0201 EMS
Fuel injector 1 circuit malfunction Start engine
OBD II
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
Injector disconnected
-115
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P0202 EMS
Fuel injector 2 circuit malfunction Start engine
OBD II
P0203 EMS
Fuel injector 3 circuit malfunction Start engine
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Injector disconnected
-120
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
EN16
Injector disconnected
-114
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
24
Page 25

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0204 EMS
Fuel injector 4 circuit malfunction Start engine
OBD II
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
Injector disconnected
-119
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P0205 EMS
Fuel injector 5 circuit malfunction Start engine.
OBD II
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes.
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
Injector disconnected
-113
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P0206 EMS
Fuel injector 6 circuit malfunction Start engine.
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes.
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Injector disconnected
-118
Injector harness wiring:
open circuit, short circuit
Injector failure
25
Page 26

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0222 EMS
TP Sensor sense circuit 2 (TP2)
low voltage
OBD II
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
EN16
TP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit (TP2):
open circuit, high resistance
-076
TP Sensor failure
P0223 EMS
P0300 EMS
TP Sensor sense circuit 2 (TP2)
high voltage
OBD II
Random misfire detected
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
EN16
TP Sensor to ECM sensing circuit (TP2):
short circuit to high voltage
-076
TP Sensor failure
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
1 or 2* N None — Cylinder compression low
Worn camshaft / broken valve spring(s)
Fuel delivery pressure (low / high)
Fuel injector(s) restricted / leaking
Fuel injector(s) continuously open
Fuel contamination
Fuel injector circuit fault(s)
(Injector DTCs also flagged)
Spark plug failure / fouled / incorrect gap
ECM to ignition coil primary circuit fault
(Cylinder misfire detected DTC also
flagged)
Ignition coil failure
26
Page 27

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0301 EMS
P0302 EMS
P0303 EMS
P0304 EMS
P0305 EMS
P0306 EMS
P0332 EMS
Misfire detected – cylinder 1
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Misfire detected – cylinder 2
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Misfire detected – cylinder 3
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Misfire detected – cylinder 4
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Misfire detected – cylinder 5
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
Misfire detected – cylinder 6
OBD II
*Refer to Misfire Note, page 5
KS sense circuit out of range –
low voltage
OBD II
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
1 or 2* N None — Refer to P0300 Possible Causes
2AECM Default:
– Maximum ignition retard
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Poor sensor contact with the cylinder block
-098
KS to ECM sense circuit short circuit to
ground
KS failure
P0333 EMS
KS sense circuit out of range –
high voltage
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Maximum ignition retard
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Poor sensor contact with the cylinder block
-098
KS to ECM sense circuit: high resistance,
open circuit, short circuit to high voltage
KS failure
27
Page 28

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0335 EMS
OBD II
CKP Sensor circuit malfunction Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine; idle 30 seconds.
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2AECM Default:
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
CKP Sensor disconnected
-036
CKP Sensor gap incorrect / foreign matter on
-037
sensor face
CKP Sensor sensing circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CKP Sensor failure
Idle engine 30 seconds
Note: If CKP Sensor fault
exists and engine will not
start, battery voltage must
drop below 10.5 V during
cranking for DTC to be
flagged. (Crank period – 30
seconds.) If CKP Sensor fault
exists, engine will start on the
second crank as the ECM will
default to CMP signals for
synchronization.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
28
Page 29

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0336 EMS
CKP Sensor circuit range /
performance
OBD II
Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine; idle 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2AECM Default:
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
CKP Sensor reluctor: foreign matter /
damaged teeth
-036
-037
CKP Sensor sensing circuit:
intermittent open circuit, short circuit
to ground, short circuit to high voltage
CKP Sensor failure
Idle engine 30 seconds
P0340 EMS
CMP Sensor 1 circuit malfunction
– bank 1
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine idle 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
Idle engine 30 seconds
2NNone EN16
-094
-095
CMP Sensor disconnected
CMP Sensor gap incorrect / foreign matter on
sensor face
CMP Sensor sensing circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CMP Sensor 1 failure
29
Page 30

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0341 EMS
CMP Sensor 1 circuit range /
performance – bank 1
OBD II
Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine; idle 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2NNone EN16
-094
-095
CMP Sensor disconnected
CMP Sensor gap incorrect / foreign matter on
sensor face
CMP Sensor sensing circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CMP Sensor 1 failure
Idle engine 30 seconds
P0351 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 1
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 1)
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-087
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
30
Page 31

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0352 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 2
OBD II
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-061
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 2)
P0353 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 3
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 3)
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-088
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
31
Page 32

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0354 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 4
OBD II
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-062
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 4)
P0355 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 5
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 1 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 1 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 1 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 5)
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-089
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
32
Page 33

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0356 EMS
Ignition module primary circuit
malfunction – cylinder 6
OBD II
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Bank 2 closed loop fuel
metering inhibited
– Bank 2 adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Bank 2 catalyst warm up
ignition retard inhibited
EN16
ECM to ignition module primary circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-063
high resistance
Ignition module ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Ignition module / coil failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off
(cylinder 6)
P0420 EMS
P0430 EMS
Catalytic converter system
efficiency below threshold –
OBD II
bank 1
Catalytic converter system
efficiency below threshold –
OBD II
bank 2
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Catalyst efficiency monitor
drive cycle – page 5
Catalyst efficiency monitor
drive cycle – page 5
2NNone — HO2 Sensor disconnected
HO2 Sensor to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor heater to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor heater failure
Upstream HO2 Sensor failure
Downstream HO2 Sensor failure
Catalyst failure
2NNone — HO2 Sensor disconnected
HO2 Sensor to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor heater to ECM wiring fault
HO2 Sensor heater failure
Upstream HO2 Sensor failure
Downstream HO2 Sensor failure
Catalyst failure
33
Page 34

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0442 EMS
EVAP system leak detected –
small (0.040 in.)
OBD II
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
— Fuel cap seal defective
EVAP system leak (canister damage,
pipework damage)
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
EVAP Canister purge valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
EVAP Canister purge valve to engine purge
pipe: restricted, leaking, disconnected
EVAP Canister purge valve operating vacuum
hose leak / restriction
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
Fuel tank leak
P0443 EMS
P0444 EMS
P0445 EMS
EVAP canister purge valve circuit
malfunction
OBD II
EVAP canister purge valve circuit
open circuit
OBD II
EVAP canister purge valve circuit
short circuit
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6.
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6.
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
EN16
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
-066
resistance
EVAP Canister purge valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
EVAP Canister purge valve operating vacuum
hose leak / restriction
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
EN16
EVAP Canister purge valve disconnected
-066
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, high resistance
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
EN16
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: short circuit to ground
-066
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
34
Page 35

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0446 EMS
EVAP canister close valve circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
EN16
EVAP canister close valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
-067
EVAP canister close valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, high resistance, short
circuit to B+ voltage
EVAP canister close valve failure
P0447 EMS
P0448 EMS
P0450 EMS
EVAP canister close valve circuit
open circuit
OBD II
EVAP canister close valve circuit
short circuit
OBD II
FTP Sensor circuit malfunction Evaporative system monitor
OBD II
P0452 EMS
FTP Sensor circuit low voltage
(low pressure)
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
drive cycle – page 6
2NNone EN16
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
EN16
-067
EN16
-067
-104
-104
EVAP canister close valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
EVAP canister close valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, high resistance, short
circuit to B+ voltage
EVAP canister close valve failure
EVAP canister close valve to ECM drive
circuit: short to ground
EVAP canister close valve failure
FTP Sensor disconnected
FTP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to B+ voltage
FTP Sensor to splice sensor supply circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
FTP Sensor to splice ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
FTP Sensor failure
FTP Sensor disconnected
FTP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground
FTP Sensor to splice sensor supply circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
FTP Sensor failure
35
Page 36

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0453 EMS
FTP Sensor circuit high voltage
(high pressure)
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
-104
FTP Sensor to splice sensor ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
FTP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
FTP Sensor failure
P0455 EMS
EVAP system leak detected –
large
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
— Fuel cap off
Fuel cap seal defective
EVAP system leak
(canister damage, pipework damage)
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
EVAP Canister purge valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
EVAP Canister purge valve to engine purge
pipe: restricted, leaking, disconnected
EVAP Canister purge valve operating vacuum
hose leak / restriction
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
Fuel tank leak
36
Page 37

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0456 EMS
EVAP system leak detected –
very small (0.020 in.)
OBD II
Evaporative system monitor
drive cycle – page 6
2NECM Default:
– Canister purge inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
— Fuel cap seal defective
EVAP system leak
(canister damage, pipework damage)
EVAP Canister purge valve to ECM drive
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
EVAP Canister purge valve power supply
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
EVAP Canister purge valve to engine purge
pipe: restricted, leaking
EVAP Canister purge valve operating vacuum
hose leak / restriction
EVAP Canister purge valve failure
Fuel tank leak
P0460 EMS
P0480 EMS
Fuel level sensor(s) circuit range /
performance
OBD II
Radiator cooling fan module drive
circuit malfunction
JAG
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Fuel tank empty
Fill in stages: 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, full
Check fuel gauge reading at
each stage
Start and run engine > 2000
rpm for 2 minutes
(Ensures voltage stays above
14 V for the required time)
2NNone — Fuel level sensor to instrument pack circuit(s):
intermittent short circuit, open circuit, high
resistance
Fuel level sensor failure
Instrument pack fault (incorrect fuel level data)
NNECM Default:
– With ignition ON, fan operates
at maximum speed
EN16
ECM to radiator cooling fan module drive
circuit: short circuit, open circuit, high
-051
resistance
Radiator cooling fan module fault
37
Page 38

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0506 EMS
Idle RPM lower than expected Start engine and drive until
OBD II
normal engine operating
temperature > 82 °C (180 °F)
Stop vehicle and idle 30
seconds
Drive vehicle for 2 minutes
Stop vehicle and idle 30
seconds
Repeat drive / idle two
additional times
2NNone — Air intake restriction
Accessory drive overload
(defective / seized component)
Throttle valve stuck closed
Throttle body failure
P0507 EMS
Idle RPM higher than expected Start engine and drive until
OBD II
P0560 EMS
Battery power supply voltage
malfunction
OBD II
Note: This DTC can be flagged
due to fuel injection pressure
sensor fault. If P0193 is also
flagged, correct first.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
normal engine operating
temperature > 82 °C (180 °F)
Stop vehicle and idle 30
seconds
Drive vehicle for 2 minutes
Stop vehicle and idle 30
seconds
Repeat drive / idle two
additional times
Engine temperature cool
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times
2NNone — Intake air leak between MAF sensor and
throttle
Intake air leak between throttle and engine
Engine crankcase breather leak
Throttle valve stuck open
Throttle body failure
2NNone EN16
ECM battery power supply open circuit, high
resistance
-022
38
Page 39

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0565 EMS
Cruise control ON / OFF switch
fault
JAG
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: short circuit to ground
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel:
short circuit to ground
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
short circuit to ground
ON / OFF switch failure (stuck ON)
P0566 EMS
P0567 EMS
P0568 EMS
Cruise control CANCEL switch
ON fault
JAG
Cruise control RESUME switch
ON fault
JAG
Cruise control input signal low /
high resistance
JAG
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: short circuit to ground
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel:
short circuit to ground
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
short circuit to ground
CANCEL switch failure (stuck ON)
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: short circuit to ground
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel:
short circuit to ground
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
short circuit to ground
RESUME switch failure (stuck ON)
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: open circuit; high resistance
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel open circuit, high
resistance
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
39
Page 40

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0569 EMS
Cruise control SET / - switch ON
fault
JAG
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: short circuit to ground
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel:
short circuit to ground
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
short circuit to ground
SET / - switch failure
P0570 EMS
P0603 EMS
Cruise control SET / + switch ON
fault
JAG
ECM Keep alive memory error Engine temperature cool
OBD II
P0616 EMS
Starter relay drive circuit low
voltage / starter relay request off
OBD II
(ignition switch position III OFF)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 45 seconds N A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times.
Ignition ON
2NNone — ECM Failure
2NNone EN16
Battery voltage > 12 v
Automatic – P for 5 seconds;
manual – clutch fully pressed
for 5 seconds
Start engine
EN16
Cruise control switches internal steering
wheel circuit: short circuit to ground
-047
Steering wheel cassette reel:
short circuit to ground
Cassette reel to ECM circuit:
short circuit to ground
SET / + switch failure
Starter relay drive circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
-041
-006
Starter relay failure
40
Page 41

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0617 EMS
Starter relay drive circuit high
voltage / starter relay request on
OBD II
(ignition switch position III ON)
Ignition ON
Battery voltage > 12 v
Automatic – P for 5 seconds;
manual – clutch fully pressed
for 5 seconds
2NNone EN16
-041
-006
Starter relay drive circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
Starter relay failure
Start engine
P0646 EMS
P0647 EMS
P0706 TRANS
A/C Compressor clutch relay drive
circuit low voltage / A/C
OBD II
(compressor clutch request off
[CAN])
A/C Compressor clutch relay drive
circuit high voltage / A/C
OBD II
(compressor clutch request on
[CAN])
Transmission range sensor circuit
– no signal; incorrect signal(s)
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Climate control system OFF
Idle for 10 seconds
Start engine
Climate control system ON –
full cooling
Idle for 2 minutes
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2NNone EN16
2NNone EN16
2ATCM Default:
– 4, 3, 2 Cannot be selected
– No J Gate illumination
– Reverse disengaged above 10
km/h (6 mph)
(Poor shift quality)
-034
-034
JB131
-007
-008
-025
-026
-027
-030
-009
A/C Compressor clutch relay drive circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
A/C Compressor clutch relay failure
A/C Compressor clutch relay drive circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
A/C Compressor clutch relay failure
J Gate – incorrect setting
Selector cable adjustment / installation
incorrect
Range sensor incorrect installation /
adjustment
Range sensor to TCM circuit(s): open circuit,
short circuit to ground
TCM Ground circuit: open circuit, high
resistance
Range sensor failure
41
Page 42

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0710 TRANS
TFT Sensor circuit malfunction Comprehensive component
OBD II
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ANone
(Poor shift quality)
JB131
Transmission to TCM temperature sensor
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
-039
resistance
-020
Transmission internal temperature sensor
circuit (internal harness): open circuit, short
circuit; high resistance
Sensor ground circuit fault
TFT Sensor failure
P0715 TRANS
P0720 TRANS
P0731 TRANS
Turbine speed sensor circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Output speed sensor circuit
malfunction
OBD II
(Automatic Transmission)
1st Gear ratio error
OBD II
Note: If a shift solenoid failure
DTC is also flagged, correct shift
solenoid DTC first.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start and run engine – 10
seconds
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ANone
(Poor shift quality)
2ATCM Default:
– ABS Wheel speed (CAN)
substituted
(Poor shift quality)
– If ABS Wheel speed message
incorrect – fixed 4th gear
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
Transmission to TCM turbine speed sensor
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
-024
resistance
-020
Transmission internal turbine speed sensor
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
Transmission to TCM turbine speed sensor
circuit: shielding defective
Sensor ground circuit fault
Turbine speed sensor failure
JB131
Transmission to TCM output speed sensor
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
-005
resistance
-020
Transmission internal output speed sensor
circuit: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
Transmission to TCM output speed sensor
circuit: shielding defective
Sensor ground circuit fault
Output speed sensor failure
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
42
Page 43

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0732 TRANS
2nd Gear ratio error
OBD II
Note: If a shift solenoid failure
DTC is also flagged, correct shift
solenoid DTC first.
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
P0733 TRANS
P0734 TRANS
P0735 TRANS
P0736 TRANS
3rd Gear ratio error
OBD II
Note: If a shift solenoid failure
DTC is also flagged, correct shift
solenoid DTC first.
4th Gear ratio error
OBD II
Note: If a shift solenoid failure
DTC is also flagged, correct shift
solenoid DTC first.
5th Gear ratio error
OBD II
Note: If a shift solenoid failure
DTC is also flagged, correct shift
solenoid DTC first.
Reverse gear ratio error Comprehensive component
JAG
P0740 TRANS
TCC malfunction Comprehensive component
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
NATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear in D
(R range not effected)
2ATCM Default:
– No TCC control
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
—J Gate – incorrect setting
Transmission oil level low
Transmission mechanical failure
43
Page 44

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0743 TRANS
TCC Solenoid circuit malfunction Comprehensive component
OBD II
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– If short circuit to B+ V – TCC
permanently engaged
– If other cause – TCC
inoperative
JB131
Transmission to TCM TCC solenoid circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to B+ V, short
-016
circuit to ground
-009
Transmission internal TCC solenoid circuit:
open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
TCC Solenoid failure
P0748 TRANS
P0753 TRANS
P0758 TRANS
Line pressure control solenoid
circuit malfunction
OBD II
Shift solenoid A circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Shift solenoid B circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start and run engine – 10
seconds
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
2ATCM Default:
– If short circuit to B+ V – fixed
2nd gear at low vehicle speed;
fixed 5th gear at high vehicle
speed
– If other cause – fixed 3rd gear
at low vehicle speed; fixed 4th
gear at high vehicle speed
2ATCM Default:
– If short circuit to B+ V: fixed
3nd gear
– If other cause: fixed 4rd gear
JB131
Transmission to TCM line pressure solenoid
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
-018
-009
Transmission internal line pressure solenoid
circuit: open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Line pressure solenoid failure
JB131
Transmission to TCM shift solenoid A circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to B+ V, short
-015
circuit to ground
-009
Transmission internal shift solenoid A circuit:
open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Shift solenoid A pressure solenoid failure
JB131
Transmission to TCM shift solenoid B circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to B+ V, short
-014
circuit to ground
-009
Transmission internal shift solenoid B circuit:
open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Shift solenoid B pressure solenoid failure
44
Page 45

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0763 TRANS
Shift solenoid C circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
Transmission to TCM shift solenoid C circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to B+ V, short
-052
circuit to ground
-009
Transmission internal shift solenoid C circuit:
open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Shift solenoid C pressure solenoid failure
P0778 TRANS
P0791 TRANS
P0791 TRANS
2/4 Brake pressure control
solenoid circuit malfunction
OBD II
Intermediate speed sensor circuit
malfunction
OBD II
(Automatic transmission)
Output speed sensor circuit
malfunction
(ECM*)
(Manual transmission)
JAG
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start and run engine – 10
seconds
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
Drive vehicle above 16 km/h
(10 mph) for 15 seconds
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
2ANone
(Poor shift quality)
NNNone EN16
JB131
-003
-009
JB131
-021
-020
-026
Transmission to TCM 2/4 Brake pressure
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
Transmission internal 2/4 Brake pressure
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
2/4 Brake pressure solenoid failure
Transmission to TCM intermediate speed
sensor circuit: open circuit, short circuit,
high resistance
Transmission internal intermediate speed
sensor circuit: open circuit, short circuit,
high resistance
Transmission to TCM intermediate speed
sensor circuit: shielding defective
Sensor ground circuit fault
Intermediate speed sensor failure
Output speed sensor power supply circuit:
open circuit, short circuit
Transmission to ECM output speed sensor
circuits: open circuit, short circuit, high
resistance
Output speed sensor failure
45
Page 46

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P0831 TRANS
Clutch cancel switch low voltage
(switch normally closed)
(ECM*)
* Manual transmission input to
OBD II
ECM
Drive vehicle 60 – 100 km/h
(37 – 62 mph); 1800 – 2500
rpm; engine load > 0.40 g/rpm
2NNone EN16
-033
Clutch cancel switch supply circuit:
open circuit
Clutch cancel switch to ECM circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Clutch cancel switch failure
P0832 TRANS
P0834 TRANS
P0835 TRANS
P0860 TRANS
Clutch cancel switch high voltage
(switch normally closed)
(ECM*)
* Manual transmission input to
OBD II
(ECM*)
JAG
(ECM*)
JAG
ECM
Clutch pedal safety switch low
voltage (switch normally open)
* Manual transmission input to
ECM
Clutch pedal safety switch high
voltage (switch normally open)
* Manual transmission input to
ECM
J Gate CAN network malfunction
(ECM*)
JAG
* J Gate / CAN monitored by ECM
P1000 EMS
System (OBD) check not
complete since last memory clear
JAG
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Drive vehicle; shift from 1st to
2nd; stop vehicle
Repeat 5 times
Drive vehicle; shift from 1st to
2nd; stop vehicle
Repeat 5 times
2NNone EN16
NNNone EN16
-033
-031
Clutch cancel switch to ECM circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
Clutch cancel switch failure
Clutch pedal safety switch supply circuit:
open circuit
Clutch pedal safety switch to ECM circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Clutch pedal safety switch failure
Drive vehicle 60 – 100 km/h
(37 – 62 mph); 1800 – 2500
rpm; engine load > 0.40 g/rpm
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
NNNone EN16
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum throttle opening for
N range inhibited
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
-031
EN16
-123
-124
Clutch pedal safety switch to ECM circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
Clutch pedal safety switch failure
CAN open circuit fault
CAN short circuit fault
J Gate failure
System Readiness Test N N None — Refer to page 3
46
Page 47

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1104 EMS
MAF Sensor ground malfunction Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
OBD II
– Default air mass used
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
EN16
MAF Sensor to ECM sensor ground circuit
open circuit, short circuit to high voltage,
-045
high resistance
-046
MAF Sensor to ECM sensing circuit:
open circuit
MAF Sensor failure
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
P1107 EMS
P1108 EMS
P1111 EMS
P1122 EMS
MAP Sensor sense circuit
low voltage
OBD II
MAP Sensor sense circuit
high voltage
OBD II
System (OBD) checks complete
since last memory clear
JAG
APP Sensor sense circuit low
voltage – APP1
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 1.013 BAR
(29.92 in hg) used
EN16
MAP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground
-127
MAP Sensor sensor supply circuit (to splice):
open circuit
MAP Sensor failure
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N ECM Default:
– Default value of 1.013 BAR
(29.92 in hg) used
EN16
MAP Sensor sensor ground circuit (to splice):
open circuit
-127
MAP Sensor to ECM sense circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
MAP Sensor failure
System Readiness Test N N None — Refer to page 3
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period.
Slowly return the pedal to rest
2RECM Default:
– APP angle default value used
– Speed control inhibited
– APP adaptions (wear,
variance) inhibited
EN16
APP Sensor to ECM sense circuit (APP1):
open circuit, high resistance
-103
APP Sensor sensor supply circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
APP Sensor failure
Repeat 3 times
47
Page 48

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1123 EMS
OBD II
APP Sensor sense circuit high
voltage – APP1
Note: This DTC could be flagged
by both sensor element sensing
circuit having faults.
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
2RECM Default:
– APP angle default value used
– Speed control inhibited
– APP adaptions (wear,
variance) inhibited
EN16
APP Sensor sensor to ECM sense circuit(s)
(APP1 or APP2): short circuit to B+ voltage
-103
-102
APP Sensor sensor ground circuit(s): open
circuit
APP Sensor failure
Repeat 3 times
P1146 EMS
P1215 EMS
P1216 EMS
Generator “CHARGE” circuit low
voltage / request high
OBD II
APP Sensor sense circuit low
voltage – APP2
OBD II
APP Sensor sense circuit high
voltage – APP2
OBD II
Note: This DTC could be flagged
by both sensor element sensing
circuit having faults.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 12 v
Switch OFF all electrical
consumers
Start engine; idle for 16
minutes with all electrical
consumers switched OFF
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2CNone EN16
2RECM Default:
– APP angle default value used
-053
EN16
-102
– Speed control inhibited
– APP adaptions (wear,
variance) inhibited
2RECM Default:
– APP angle default value used
– Speed control inhibited
– APP adaptions (wear,
variance) inhibited
EN16
-102
-103
Generator to ECM “CHARGE” circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Generator regulator failure
APP Sensor to ECM sense circuit (APP2):
open circuit, high resistance
APP Sensor sensor supply circuit (to splice):
open circuit, high resistance
APP Sensor failure
APP Sensor sensor to ECM sense circuit(s)
(APP2 or APP1): short circuit to B+ voltage
APP Sensor sensor ground circuit(s) (to
splice): open circuit
APP Sensor failure
48
Page 49

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1224 EMS
Throttle control position error Battery voltage > 10 v
OBD II
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
— Throttle adaptions not performed after battery
disconnect
TP Sensor disconnected
TP Sensor to ECM sense circuits:
open circuit, high resistance
Throttle motor relay failure
Throttle motor relay to ECM circuit fault
Throttle motor relay power supply open circuit
ECM ground circuit fault (relay coil drive)
Throttle motor to ECM drive circuits:
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
Throttle motor failure
Throttle body failure
P1229 EMS
P1234 EMS
P1236 EMS
Throttle motor control circuit
malfunction
OBD II
No fuel pump commands
received by ECM
OBD II
Fuel pump not activated when
requested by ECM
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
2NECM Default:
– Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
2NECM Default:
– Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
— Throttle motor disconnected
Throttle motor to ECM drive circuits:
short circuit or open circuit
Throttle motor failure
EN16
ECM to fuel pump control module control and
/ or feedback circuits:
-025
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
-027
Fuel pump control module failure
EN16
ECM to fuel pump control module control and
/ or feedback circuits:
-025
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
-027
Fuel pump control module failure
49
Page 50

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1240 EMS
Sensor power supply circuit
malfunction
OBD II
(APP Sensor, TP Sensor,
IP Sensor, MAP Sensor,
FTP Sensor)
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
-012
-013
ECM to sensors sensor supply voltage
circuit(s): short circuit to ground, short
circuit to high voltage, open circuit, high
resistance
APP Sensor, TP Sensor, IP Sensor, MAP
Sensor, FTP Sensor failure(s)
P1241 EMS
P1242 EMS
P1243 EMS
Sensor power supply circuit
low voltage
OBD II
(APP Sensor, TP Sensor,
IP Sensor, MAP Sensor,
FTP Sensor)
Sensor power supply circuit
high voltage
OBD II
(APP Sensor, TP Sensor,
IP Sensor, MAP Sensor,
FTP Sensor)
Sensor ground circuits
open circuit
OBD II
(APP Sensor, TP Sensor,
IP Sensor, MAP Sensor,
FTP Sensor)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 R ECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
EN16
-012
-013
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 R ECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
EN16
-012
-013
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
-019
-020
ECM to sensors sensor supply voltage
circuit(s): short circuit to ground
APP Sensor, TP Sensor, IP Sensor,
MAP Sensor, FTP Sensor failure(s)
ECM to sensors supply voltage circuit(s):
open circuit, high resistance, short circuit to
high voltage
APP Sensor, TP Sensor, IP Sensor,
MAP Sensor, FTP Sensor failure(s)
ECM to sensors sensor ground circuit(s):
open circuit, high resistance
APP Sensor, TP Sensor, IP Sensor,
MAP Sensor, FTP Sensor failure(s)
50
Page 51

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1244 EMS
Generator “CHARGE” circuit
high voltage / request low
OBD II
Battery voltage > 12 v
Switch OFF all electrical
consumers
Start engine; idle for 16
minutes with all electrical
consumers switched OFF
2CECM Default:
– Cooling fan speed increased
EN16
Generator to ECM “CHARGE” circuit:
short circuit to high voltage
-053
Generator regulator failure
Generator failure
P1245 EMS
Engine crank signal low voltage Start engine
OBD II
P1246 EMS
Engine crank signal high voltage Drive vehicle > 32 km/h (20
OBD II
P1250 EMS
P1251 EMS
Throttle valve return spring
malfunction
OBD II
Throttle motor relay OFF failure Engine temperature cool
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Starter should stop when the
key is released from position
III (CRANK)
mph) between 2000 – 2500
rpm for10 seconds; stop
vehicle
Repeat 10 times
Idle engine
Switch OFF ignition for 10
seconds
Start engine and repeat
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times
2NNone EN16
2NNone EN16
2RECM Default:
-006
-006
— Throttle return spring failure
– Limp home unavailable
– Vehicle speed limited
– Speed control inhibited
– Possible engine shut down
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
EN16
-052
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
Starter relay coil to ECM / ignition switch
circuit: open circuit
Starter relay coil to ECM / ignition switch
circuit: short circuit to high voltage
Ignition switch failure
(throttle body failure)
Throttle motor relay coil power supply circuit:
open circuit (fuse)
Throttle motor relay failure
Throttle motor relay coil to ECM circuit:
open circuit
ECM ground circuit fault (relay coil drive)
51
Page 52

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1254 EMS
Throttle “limp home” spring
malfunction
OBD II
Idle engine
Switch OFF ignition for 10
seconds
Start engine and repeat
2RECM Default:
– Limp home unavailable
– Vehicle speed limited
– Speed control inhibited
— Throttle limp home spring failure
(throttle body failure)
– Possible engine shut down
P1260 EMS
Security input malfunction Start engine N N None — Invalid ignition key code
JAG
Passive anti-theft system (PATS) signal to
instrument pack missing or corrupted
Security message (PATS) CAN failure
NOTE: To clear this DTC, the failure must first
be rectified, followed by an ignition ON cycle
to allow a successful PATS identification
exchange between the ECM and the IC. The
fault code can then be cleared.
P1313 EMS
OBD II
Misfire rate catalyst damage –
bank 1
NOTE: This DTC will flag only
when accompanied by an
individual cylinder misfire DTC:
P0300 – P0306
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
2AECM Default:
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
— Cylinder compression low
Worn camshaft / broken valve spring(s)
Fuel delivery pressure (low / high)
Fuel injector(s) restricted / leaking
Fuel injector(s) continuously open
Fuel contamination
Fuel injector circuit fault(s)
(Injector DTCs also flagged)
Spark plug failure / fouled / incorrect gap
ECM to ignition coil primary circuit fault
(Cylinder misfire detected DTC also
flagged)
Ignition coil failure
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
52
Page 53

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1314 EMS
OBD II
Misfire rate catalyst damage –
bank 2
NOTE: This DTC will flag only
when accompanied by an
individual cylinder misfire DTC:
P0300 – P0306
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
2AECM Default:
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
— Cylinder compression low
Worn camshaft / broken valve spring(s)
Fuel delivery pressure (low / high)
Fuel injector(s) restricted / leaking
Fuel injector(s) continuously open
Fuel contamination
Fuel injector circuit fault(s)
(Injector DTCs also flagged)
Spark plug failure / fouled / incorrect gap
ECM to ignition coil primary circuit fault
(Cylinder misfire detected DTC also
flagged)
Ignition coil failure
P1316 EMS
OBD II
Misfire excess emission
NOTE: This DTC will flag only
when accompanied by an
individual cylinder misfire DTC:
P0300 – P0306
Misfire monitor drive cycle –
page 5
2NNone — Cylinder compression low
Worn camshaft / broken valve spring(s)
Fuel delivery pressure (low / high)
Fuel injector(s) restricted / leaking
Fuel injector(s) continuously open
Fuel contamination
Fuel injector circuit fault(s)
(Injector DTCs also flagged)
Spark plug failure / fouled / incorrect gap
ECM to ignition coil primary circuit fault
(Cylinder misfire detected DTC also
flagged)
Ignition coil failure
P1338 EMS
Fuel pump feedback circuit low /
high voltage
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2NECM Default:
– Fuel pump feedback control
inhibited
EN16
ECM to fuel pump control module control and
/ or feedback circuits:
-025
open circuit, short circuit, high resistance
-027
Fuel pump control module failure
53
Page 54

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1340 EMS
CMP Sensor 2 circuit malfunction
– bank 2
OBD II
Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine; idle 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2NNone EN16
-068
-069
CMP Sensor disconnected
CMP Sensor gap incorrect / foreign matter on
sensor face
CMP Sensor sensing circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CMP Sensor 2 failure
Idle engine 30 seconds
P1341 EMS
CMP Sensor 2 circuit range /
performance – bank 2
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine; momentarily
race the engine; stop engine
Repeat two additional times
Start engine; idle 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
Idle engine 30 seconds
2NNone EN16
-068
-069
CMP Sensor disconnected
CMP Sensor gap incorrect / foreign matter on
sensor face
CMP Sensor sensing circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to high voltage
CMP Sensor 2 failure
54
Page 55

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1344 EMS
APP Sensor sense circuits APP1
and APP2 range / performance
OBD II
Battery voltage > 10 v
Ignition ON
Slowly press accelerator
pedal to the floor over a 5
second period
Slowly return the pedal to rest
Repeat 3 times
2RECM Default:
– APP angle default value used
– Speed control inhibited
– APP adaptions (wear,
variance) inhibited
EN16
APP Sensor to ECM sense circuits:
short circuit, open circuit, high resistance
-102
-103
APP Sensor sensor supply circuits:
short circuit, open circuit, high resistance
APP Sensor sensor ground circuits:
open circuit
APP Sensor failure
P1367 EMS
P1368 EMS
Ignition amplifier bank 1 (1, 3, 5)
fault
OBD II
Ignition amplifier bank 2 (2, 4, 6)
fault
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
Start engine
Battery voltage > 12 v
Idle for 2 minutes
2AECM Default:
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off (cylinders
1, 3, 5)
2AECM Default:
– Closed loop fuel metering
inhibited
– Adaptive fuel metering
inhibited
– Catalyst warm up ignition
retard inhibited
– Canister purge inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Fuel injection cut off (cylinders
2, 4, 6
EN16
Ignition monitoring circuit between splice and
ECM: open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-131
short circuit to B+ voltage
Ignition module / coil bank 1 ground circuit
fault
EN16
Ignition monitoring circuit between splice and
ECM: open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-132
short circuit to B+ voltage
Ignition module / coil bank 2 ground circuit
fault
55
Page 56

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1384 EMS
VVT solenoid malfunction –
bank 1
OBD II
Idle engine 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
2NECM Default:
– Bank 1 VVT hold current set at
a constant valve of 450 mA
EN16
VVT solenoid valve 1 to ECM PWM drive
circuit fault
-109
VVT solenoid valve 1 ground circuit fault
VVT solenoid 1 failure
VVT 1 oil flow fault
VVT / camshaft mechanical failure – bank 1
Idle engine 30 seconds
P1396 EMS
P1516 EMS
VVT solenoid malfunction –
bank 2
OBD II
Gear change P / N driving
malfunction
OBD II
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Idle engine 30 seconds
Accelerate from stop through
complete engine rpm range;
coast to a stop
Drive the vehicle steadily
between 48 – 97 km/h (30 –
60 mph) for 5 minutes; coast
to a stop
Accelerate smoothly through
complete accelerator pedal
travel; coast to a stop
Idle engine 30 seconds
Drive vehicle > 24 km/h (15
mph) between 1500 – 4000
rpm for30 seconds
2NECM Default:
– Bank 2 VVT hold current set at
a constant valve of 450 mA
2AECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
VVT solenoid valve 2 to ECM PWM drive
circuit fault
-110
VVT solenoid valve 2 ground circuit fault
VVT solenoid 2 failure
VVT 2 oil flow fault
VVT / camshaft mechanical failure – bank 2
EN16
Gear selector cable setting incorrect
-031
Transmission range sensor to ECM circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Transmission range sensor failure
D – 4 Switch to TCM circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
D – 4 Switch failure
56
Page 57

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1517 EMS
Gear change P / N starting
malfunction
OBD II
Start engine in P
Start engine in N
Check that engine does not
start in R, D, 4, 3, 2
CAUTION: If the P/N switch is
faulty, the engine may start
while in gear
2AECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum throttle opening for
N range inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
Gear selector cable setting incorrect
-031
Transmission range sensor to ECM circuit:
open circuit or high resistance
Transmission range sensor failure
P1532 EMS
P1549 EMS
P1571 EMS
IMT valve 2 (bottom) circuit
malfunction
OBD II
IMT valve 1 (top) circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Brake ON / OFF switch; brake
cancel switch malfunction
JAG
(Brake ON / OFF switch –
normally open; brake cancel
switch – normally closed)
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year
Battery voltage > 12 v
Start engine and bring to
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Run engine at 5000 rpm in N
for 20 seconds
Battery voltage > 12 v
Start engine and bring to
normal operating temperature
> 82 °C (180 °F)
Run engine at 5000 rpm in N
for 20 seconds
Start engine; idle in P, N
Press brake pedal for > 30
seconds; release brake pedal
Repeat 5 times
Momentarily press brake
pedal and release; press again
and hold > 30 seconds;
release brake pedal
Repeat 5 times
2NECM Default:
– IMT 2 Inhibited
2NECM Default:
– IMT 1 Inhibited
NAECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
IMT Valve 2 (bottom) disconnected
-039
IMT Valve 2 (bottom) to ECM drive circuit fault
IMT Valve 2 (bottom) power supply circuit
fault
IMT Valve 2 (bottom) failure
EN16
IMT Valve 1 (top) disconnected
-038
IMT Valve 1 (top) to ECM drive circuit fault
IMT Valve 1 (top) power supply circuit fault
IMT Valve 1 (top) failure
EN16
Brake ON / OFF switch to ECM circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
-008
high resistance
-009
Brake ON / OFF power supply circuit:
open circuit
Brake ON / OFF switch failure
Brake cancel switch to ECM circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground,
high resistance
Brake cancel switch power supply circuit:
open circuit
Brake cancel switch failure
57
Page 58

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1573 TRANS
CAN throttle angle error Ignition ON – 5 seconds N A None
JAG
(Poor shift quality)
JB131
TP Sensor fault (TP Sensor DTC flagged –
P0121, P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223)
-012
-013
ECM CAN message error
P1582 EMS
“Flight recorder” data is stored if
any one of five conditions occur:
JAG
1 Inertia switch activated
2 Throttle Limp Home mode
3 Engine starts and stumbles
4 Engine fail to start
NNNone EN16
-010
If none of the five conditions occur, check:
Inertia switch to ECM circuit:
short circuit to B+ voltage
Inertia switch failure
5 Engine stall
P1601 TRANS
OBD II
P1603 TRANS
OBD II
Incorrect ECM or TCM fitted to
vehicle
Ignition ON – 5 seconds 1 A TCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
TCM EEPROM failure Ignition ON – 5 seconds 1 A None JB131
Configure ECM and TCM using WDS
JB131
-012
-013
-033
-034
Battery disconnected while the ignition is
switched ON
-009
B+ power supply circuit: open circuit
TCM failure
P1606 EMS
EMS control relay malfunction
OBD II
Note: This DTC could be flagged
along with P0032 and P0052,
which if flagged, should be
corrected first.
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 58
Engine temperature cool
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times
1
N None
2*
EN16
ECM control relay failure
-040
ECM control relay to ECM circuit fault
ECM control relay coil power supply open
circuit
ECM ground circuit fault (relay coil drive)
* Early production vehicles
Page 59

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1609 EMS
ECM microprocessor to
microprocessor communication
OBD II
failure
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 R ECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
— ECM Failure
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
P1611 EMS
ECM sub CPU failure Drive vehicle
OBD II
If fitted, engage speed control
Refer to Owner’s Handbook
and ensure that speed control
engages normally
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
— ECM Failure
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
P1629 EMS
Generator “FIELD” circuit failure Battery voltage > 12 v
OBD II
Switch OFF all electrical
consumers
Ignition ON 15 seconds
Start engine; momentarily idle
with all electrical consumers
switched OFF
2CNone EN16
-065
ECM to generator “FIELD” return circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Generator regulator failure
Generator failure
Switch ignition OFF
Switch ignition ON
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 59
Page 60

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1631 EMS
Throttle motor relay coil drive
circuit OFF failure
OBD II
Engine temperature cool
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle twice more
2RECM Default:
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
EN16
Throttle motor relay coil power supply circuit:
open circuit (fuse)
-052
Throttle motor relay failure
Throttle motor relay coil to ECM drive circuit:
open circuit, short circuit to ground
P1632 EMS
P1633 EMS
Generator charge system failure /
generator “LOAD” feedback
OBD II
circuit failure
Battery voltage > 12 v
Switch OFF all electrical
consumers
Start engine; idle for 16
minutes with all electrical
consumers switched OFF
If no reoccurrence of DTC(s):
hold engine > 1500 rpm for
one minute in N
2CNone —
ECM main CPU failure Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 R ECM Default:
OBD II
– Throttle motor and throttle
motor relay disabled
– Throttle valve opening set to
default value
– Idle speed controlled by fuel
injection intervention
ECM to generator “LOAD” feedback circuit:
EN16
short circuit, open circuit, high resistance
Generator regulator failure
-079
Generator failure
— ECM Failure
– Idle speed adaption inhibited
P1634 EMS
Throttle “watch dog” circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Idle engine
Switch OFF ignition for 10
seconds
Start engine and repeat
2RECM Default:
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Vehicle speed limited
— ECM Failure
– Speed control limited
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 60
Page 61

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1637 EMS
CAN ECM to ABS/TCCM
(DSCCM) network malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum throttle opening for
N range inhibited
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
CAN open circuit fault –
ABS/TCCM (DSCCM) to ECM
-123
-124
CAN short circuit fault
ABS/TCCM (DSCCM) failure
ECM failure
P1638 EMS
CAN ECM / INST network
malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
-123
-124
CAN open circuit fault – INST to ECM
CAN short circuit fault
INST failure
ECM failure
P1642 EMS
P1643 EMS
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 61
CAN circuit malfunction Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
OBD II
CAN ECM / TCM network
malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum throttle opening for
N range inhibited
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
– Speed control inhibited
– Maximum throttle opening for
N range inhibited
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
EN16
CAN short circuit fault
-123
Control module failure –
-124
check for additional flagged DTC(s) to locate
control module source
EN16
CAN open circuit fault – TCM to ECM
-123
CAN short circuit fault
-124
TCM failure
ECM failure
Page 62

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1646 EMS
ECM HO2 Sensor control
malfunction –
OBD II
bank 1 upstream (1/1)
Drive vehicle for 10 minutes 2 N ECM Default:
– HO2S 1/1 control circuit
inhibited
— HO2 Sensor 1/1 heater failure
HO2 Sensor 1/1 sensing circuit:
short circuit to ground, short circuit to
high voltage, open circuit
ECM Failure
P1647 EMS
ECM HO2 Sensor control
malfunction –
OBD II
bank 2 upstream (2/1)
Drive vehicle for 10 minutes 2 N ECM Default:
– HO2S 2/1 control circuit
inhibited
— HO2 Sensor 2/1 heater failure
HO2 Sensor 2/1 sensing circuit:
short circuit to ground, short circuit to
high voltage, open circuit
ECM Failure
P1648 EMS
P1656 EMS
P1657 EMS
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 62
ECM KS self test failure Start engine
OBD II
TP Sensor amplifier circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Throttle motor relay coil drive
circuit ON failure
OBD II
Battery voltage > 12 v.
Idle for 2 minutes
– Maximum ignition retard
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 A ECM Default:
– Maximum engine speed
reduced
2AECM Default:
Engine temperature cool
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Vehicle speed limited
– Speed control inhibited
— ECM Failure
EN16
ECM Failure
-075
EN16
Throttle motor relay failure
-052
Throttle motor relay coil to ECM drive circuit:
short circuit to B+ voltage
Page 63

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1658 EMS
Throttle motor relay ON failure Engine temperature cool
OBD II
(cooling fans not running)
Remove ignition key for 20
seconds (cooling fans not
running)
Ignition key in, position II for 5
seconds (do not start)
Repeat cycle two additional
times
2RECM Default:
– Throttle opening limited to
30%
– Vehicle speed limited
– Speed control inhibited
EN16
Throttle motor relay failure
-052
Throttle motor relay coil to ECM drive circuit:
short circuit to B+ voltage
P1699 EMS
CAN ECM / A/CCM network
malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON 10 seconds 2 N None EN16
-123
-124
CAN open circuit fault – A/CCM to ECM
CAN short circuit fault
A/CCM failure
ECM failure
P1710 TRANS
P1745 TRANS
Control valve solenoids ground
circuit malfunction
OBD II
Low clutch timing solenoid circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON – 5 seconds 2 A TCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
TCM to transmission sensor ground circuit:
open circuit
-017
-009
TCM ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
JB131
Transmission to TCM low clutch timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
-053
-009
Transmission internal low clutch timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
TCM ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Low clutch timing solenoid failure
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 63
Page 64

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1746 TRANS
Reduction timing solenoid circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– If short circuit to B+ V: no
engine braking in D, 4, 3, 2
– If other cause: poor shift
quality
JB131
Transmission to TCM reduction timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit to
-010
B+ V, short circuit to ground
-009
Transmission internal reduction timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
TCM ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Reduction timing solenoid failure
P1747 TRANS
2/4 Brake timing solenoid circuit
malfunction
OBD II
Comprehensive component
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ATCM Default:
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
Transmission to TCM 2/4 brake timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
-004
-009
Transmission internal 2/4 brake timing
solenoid circuit: open circuit, short circuit
TCM ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
2/4 Brake timing solenoid failure
P1777 TRANS
P1780 TRANS
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 64
CAN torque reduction error Comprehensive component
OBD II
D – 4 Switch circuit malfunction Comprehensive component
OBD II
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
monitor transmission drive
cycle – page 7
2ANone
(D poor shift quality)
2ANone
(D – 4 Switch signal ignored)
JB131
ECM CAN message error
-012
-013
JB131
J Gate – incorrect setting
-045
Selector cable adjustment / installation
-009
incorrect
Range sensor incorrect installation /
adjustment
D – 4 Switch to TCM circuit:
short circuit, open circuit, high resistance
J-Gate ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
Page 65

DTC SYS FAULT DESCRIPTION MONITORING CONDITIONS CK ENG OTHER DEFAULT ACTION CM PIN POSSIBLE CAUSES
P1793 TRANS
TCM Ignition switched power
supply circuit malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON – 5 seconds 2 A TCM Default
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
TCM Power supply circuit: open circuit (fuse)
-036
TCM Relay failure
-054
TCM Relay ground circuit:
-009
open circuit, high resistance
TCM Relay supply circuits: open circuit (fuse)
TCM Ground circuit:
open circuit, high resistance
P1796 TRANS
P1797 TRANS
CAN network malfunction Ignition ON – 5 seconds 2 A TCM Default
OBD II
CAN TCM / ECM network
malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON – 5 seconds 2 A TCM Default
– Fixed 4th gear
– Fixed 4th gear
JB131
CAN open circuit fault
-012
CAN short circuit fault
-013
TCM failure
JB131
CAN open circuit fault – TCM to ECM
-012
CAN short circuit fault
-013
ECM failure
TCM failure
P1799 TRANS
CAN TCM / ABS/TC (DSCCM)
network malfunction
OBD II
Ignition ON – 5 seconds 2 A None JB131
-012
-013
CAN open circuit fault – TCM to ABS/TC
(DSCCM)
CAN short circuit fault
ABS/TC (DSCCM) failure
TCM failure
Jaguar X-TYPE P DTC OBD II 2002 Model Year 65
 Loading...
Loading...