Page 1

User’s
Manual
Decoding Laser Scanner
P/N 063496-003
Page 2

Intermec Corporation
6001 36th Avenue West
P.O. Box 4280
Everett, WA 98203-9280
U.S. service and technical support: 1-800-755-5505
U.S. media supplies ordering information: 1-800-227-9947
Canadian service and technical support: 1-800-688-7043
Canadian media supplies ordering information: 1-800-268-6936
Outside U.S. and Canada: Contact your local Intermec service
supplier.
The information contained herein is proprietary and is provided
solely for the purpose of allowing customers to operate and/or
service Intermec manufactured equipment and is not to be released,
reproduced, or used for any other purpose without written
permission of Intermec.
Information and specifications in this manual are subject to change
without notice.
1996 by Intermec Corporation
All Rights Reserved
The word Intermec, the Intermec logo, JANUS, IRL, TRAKKER,
Duratherm, Precision Print, PrintSet, Virtual Wedge, and
CrossBar are trademarks of Intermec Corporation.
Throughout this manual, trademarked names may be used.
Rather than put a trademark () symbol in every occurrence of
a trademarked name, we state that we are using the names only
in an editorial fashion, and to the benefit of the trademark
owner, with no intention of infringement.
Page 3

Manual Change Record
This page records the changes to this manual. The manual was
originally released as version 001.
Version Date Description of Change
002 6/96 Revised and reorganized to
include the 1551 scanners.
003 12/96 Revised to include international
keyboards, caps lock, remote
beep, and connecting to a
laptop or pen-based terminal.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Before You Begin ix
Connecting the Scanner
1
Getting Started 1-3
Connecting the Scanner 1-4
Contents
Warranty Information ix
Safety Summary ix
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes x
About This Manual xi
Unpacking the Scanner 1-3
Installation Equipment 1-4
15XXX02 Decoding Laser Scanner 1-5
15XXX03 Decoding Laser Scanner 1-6
15XXX07 Decoding Laser Scanner 1-9
Operating the Scanner
2
General Instructions 2-3
Scanner Light 2-3
Scanner Beeps 2-4
Operating the Scanner 2-4
Hand-Held Scanning 2-4
Hands-Free Scanning 2-6
Troubleshooting 2-7
Maintenance 2-8
v
Page 6

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Configuring the Scanner
3
About Configuring the Scanner 3-3
Configuring by Scanning Bar Codes 3-3
Configuring the Scanner From a Host Terminal 3-3
Waking Up the Scanner to Process Commands
3-5
Remote Beep 3-5
Acknowledging Commands Between Host and
Scanner 3-5
Displaying Current Configuration 3-6
Resetting Default Values 3-6
Configuring Bar Code Symbologies 3-7
UPC-A and UPC-E 3-8
UPC Number System Digit 3-9
UPC Check Digit 3-9
EAN/JAN 3-9
EAN/JAN Number System Digit 3-10
EAN/JAN Check Digit 3-10
Code 39 3-11
Standard 2 of 5 3-12
Interleaved 2 of 5 3-12
Code 128 3-13
Codabar 3-14
Code 93 3-15
Code 11 3-16
Configuring Bar Code Parameters 3-17
Prefix 3-17
Suffix 3-18
Terminal ID 3-19
Bar Code ID 3-19
Preamble and Postamble 3-20
vi
Page 7

Contents
Configuring Operating Parameters 3-21
Power Consumption 3-21
Beep Volume 3-22
Laser Redundancy 3-22
Spotter Beam 3-23
External Trigger 3-23
Reading Uppercase Letters 3-24
Reading Symbols 3-25
International Keyboards 3-25
Configuring the 15XXX02 Serial Parameters 3-27
Baud Rate 3-27
Intercharacter Delay 3-28
Label Buffer 3-29
Setting Up the Bar Code Data String 3-29
Selecting a Protocol 3-31
Configuring the Scanner for Wand Emulation to Use With
a Portable Reader 3-33
Scanning Unreadable Symbologies 3-34
Configuring Bar Code Polarity 3-34
Configuring the Transmission Rate 3-34
Switching Back to a Terminal 3-35
Configuring the Scanner for Use With an Intermec 94XX
and 95XX Reader 3-36
vii
Page 8

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
A
Configuration Command List
B
Glossary
G
Index
I
viii
Page 9

Before You Begin
Before You Begin
This section introduces you to standard warranty provisions,
safety precautions, warnings and cautions, document
formatting conventions, and sources of additional product
information.
Warranty Information
To receive a copy of the standard warranty provision for this
product, contact your local Intermec support services
organization. In the U.S. call 1-800-755-5505, and in Canada call
1-800-688-7043.
Safety Summary
Your safety is extremely important. Read and follow all
warnings and cautions in this book before handling and
operating Intermec equipment. You can be seriously injured,
and equipment and data can be damaged if you do not follow
the safety warnings and cautions.
Do not repair or adjust alone Do not repair or adjust energized
equipment alone under any circumstances. Someone capable of
providing first aid must always be present for your safety.
First aid Always obtain first aid or medical attention
immediately after an injury. Never neglect an injury, no matter
how slight it seems.
Resuscitation Begin resuscitation immediately if someone is
injured and stops breathing. Any delay could result in death. To
work on or near high voltage, you should be familiar with
approved industrial first aid methods.
ix
Page 10

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Energized equipment Never work on energized equipment
unless authorized by a responsible authority. Energized
electrical equipment is dangerous. Electrical shock from
energized equipment can cause death. If you must perform
authorized emergency work on energized equipment, be sure
that you comply strictly with approved safety regulations.
Warnings, Cautions, and Notes
The warnings, cautions, and notes in this manual use the
following format.
Warning
A warning alerts you of an operating procedure,
practice, condition, or statement that must be strictly
observed to avoid death or serious injury to the
persons working on the equipment.
Avertissement
Un avertissement vous avertit d’une procédure de
fonctionnement, d’une méthode, d’un état ou d’un
rapport qui doit être strictement respecté pour éviter
l’occurrence de mort ou de blessures graves aux
personnes manupulant l’équipement.
Caution
A caution alerts you to an operating procedure,
practice, condition, or statement that must be strictly
observed to prevent equipment damage or
destruction, or corruption or loss of data.
Conseil
Une précaution vous avertit d’une procédure de
fonctionnement, d’une méthode, d’un état ou d’un
rapport qui doit être strictement respecté pour
empêcher l’endommagement ou la destruction de
l’équipement, ou l’altération ou la perte de données.
x
Page 11

Before You Begin
Notes: Notes are statements that either provide extra information
about a topic or contain special instructions for handling a particular
condition or set of circumstances.
About This Manual
This manual contains all of the information necessary to install,
operate, configure, troubleshoot, and maintain the decoding
laser scanners.
What You Will Find in This Manual
This table summarizes the information in each chapter and
appendix of this manual:
For Information On Refer To
Connecting the scanner Chapter 1 tells you how to connect
the scanner to your terminal.
Operating the scanner Chapter 2 explains how to
operate, troubleshoot, and
maintain the scanner.
Configuring the scanner Chapter 3 describes how to
configure the scanner.
Converting to hexadecimal Appendix A contains an ASCII
conversion chart.
Configuration commands Appendix B has an alphabetical
Terms
“Scanner” refers to the decoding laser scanners.
“Reader” refers to a device that receives data sent from the
scanner.
“Terminal” refers to the point-of-sale (POS) terminal, PC,
laptop, pen-based terminal, or other device that receives data
sent from the scanner.
list of configuration commands by
the command’s two-letter bar
code syntax.
xi
Page 12

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
For definitions of the technical terms used in this manual, see
the glossary.
Conventions for Bar Codes
You can use your laser scanner to scan the bar codes listed in
this manual to enter data or perform a command. The bar codes
are Code 128. The bar code is listed along with the command
name and syntax. For example:
Command Syntax Bar Code
Select 300 baud DA
Conventions for Input From a Keyboard or Keypad
When you need to press keys on your terminal or reader, they
are emphasized in bold. For example, “press Enter” means you
press the key labeled “Enter” on your keyboard or keypad.
Conventions for Commands
This example illustrates the format conventions used for
commands:
To send serial commands, use this syntax (spaces
have been added for clarity):
STX ESC XX [optional parameters] ETX
where:
STX is the ASCII start of text
command.
ESC is the ASCII escape command.
XX is the two-letter bar code
syntax for the command.
ETX is the ASCII end of text
command.
xii
Page 13

Before You Begin
Tthe conventions used in the example are:
Convention Description
Special font
Commands appear in this monospaced
font.
Italic text
[ ] Brackets enclose a parameter that you
where This word introduces a list of the
Italics indicate a variable, which you
must replace with a real value, such as
a two-letter bar code syntax.
may omit from the command. Do not
include the brackets in the command.
command’s parameters and explains
the values you can specify for them.
xiii
Page 14

Page 15

1
Connecting the Scanner
Page 16

Page 17

Connecting the Scanner
This chapter describes the different types of scanners and how to
connect the scanners to a terminal.
1
Getting Started
Each type of decoding laser scanner is designed for collecting
data for a specific type of terminal, as summarized in this list:
Scanner Description of terminal
15XXX02 Compatible with devices equipped with an
RS-232 serial communications port.
15XXX03 For use with an IBM 4683/4684/4693/4694 point-
of-sale terminal.
Also for the 1551X03 scanner only: Can be use
with an optical coupled interface adapter
(OCIA) and Data Checker terminals. See the
quick reference guide for your scanner or
contact your local Intermec representative for a
list of the specific terminals.
15XXX07 Keyboard wedge interface for use with personal
computers (PC) through a keyboard, or with a
laptop through the auxiliary keyboard port.
All scanners can be used with a portable terminal in Wand
Emulation mode (see Chapter 3), or with the scanner stand (see
Chapter 2).
Unpacking the Scanner
The shipping box contains the laser scanner and a quick
reference guide.
Note: You must order the appropriate interface cables separately. See
the quick reference guide for your scanner or call your local Intermec
representative for help ordering cables.
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact
your local Intermec representative. Retain the shipping box in
case you need to ship the scanner.
1-3
Page 18

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Installation Equipment
All scanners can be operated with this equipment:
• Connected to a terminal such as a point-of-sale terminal,
personal computer, or fixed reader
• Used with a portable terminal for mobile applications
• Used with the scanner stand for hands-free operation
You must order the appropriate interface cables separately. See
the quick reference guide for your scanner or call your local
Intermec representative for help ordering cables.
Connecting the Scanner
The procedures in this chapter prepare the decoding scanner for
operation using these bar code symbologies:
UPC-E
UPC-A
(not
expanded)
Code 39 Code 128
15XXX02
15XXX03
15XXX07
The scanner is automatically set up for scanning by hand and
sending data directly to the terminal.
1-4
üü üü
üü
üü üü
——
Page 19

Connecting the Scanner
1
15XXX02 Decoding Laser Scanner
The 15XXX02 is designed to interface with terminals equipped
with RS-232 serial communication ports. The interface cable
used with the terminal has a modular plug that resembles a
telephone connector and a D-type connector for the terminal
serial port.
To connect the 15XXX02 scanner
1. Connect the modular plug on the interface cable to the
bottom of the scanner handle. The 1551 models have a screw
to tighten that secures the plug in the handle.
2. Make sure the terminal is turned off. Then connect the
D-type connector end of the cable to the serial port.
3. Connect the external power supply cable to the side of the
D-type connector.
4. Plug the external power supply into an outlet or surge
protector.
5. Turn on the power to the terminal.
6. Scan this bar code to set default values:
Reset to Default Values ZA
The scanner is ready to be used as a hand-held scanner and will
send data directly to the terminal. The default symbologies are:
• UPC-A
• UPC-E (not expanded)
• Code 39
• Code 128
See Chapter 2 to learn basic scanning operation, scanning tips,
and how to use with the scanner stand for hands-free scanning.
To change the scanner configuration, see Chapter 3.
1-5
Page 20

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
15XXX03 Decoding Laser Scanner
The 15XXX03 is designed to interface with IBM
4683/4684/4693/4694 point-of-sale (POS) terminals. The 1551X03
can also interface with optical coupled interface adapter
(OCIA). See the quick reference guide for your scanner or
contact your local Intermec representative for a list of the
specific 1551X03 terminals.
To connect the 15XXX03 scanner to an IBM 4683/4684/4693/4694
1. Connect the modular plug on the cable to the bottom of the
scanner handle. The 1551 models have a screw to tighten
that secures the plug in the handle.
Note: The interface cable has either an 8-pin SDL (synchronous
data link) connector for the 5B port on the POS terminal, or a
4-pin SDL connector for the 9A or 9B port.
2. Make sure the power to the terminal is turned off. Then
connect the other end of the cable to the port in the POS
terminal.
Note: The scanner can function with either the 5B, 9A, or 9B
ports. The terminal must be configured for the port attached to the
scanner.
3. Turn on the power to the terminal.
4. Scan this bar code:
Select IBM
4683/4684/4693/4694
Configuration
CS
5. Scan this bar code to reset to the default value
communication mode for IBM 4683/4684/4693/4694:
Reset to Default Values ZA
1-6
Page 21

Connecting the Scanner
6. Scan a bar code to select the scanner emulation:
1
Select Laser Emulation*
Select CCD Emulation BL
* Default when using the Reset Default Values (ZA) command.
The scanner is ready to be used as a hand-held scanner and will
send data directly to the terminal. The default symbologies are:
• UPC-A
• UPC-E (not expanded)
See Chapter 2 to learn basic scanning operation, scanning tips,
and how to use with the scanner stand for hands-free scanning.
To change the scanner configuration, see Chapter 3.
To connect the 1551X03 scanner to an OCIA port
1. Insert the scanner end of the ten-position modular plug into
the opening at the bottom of the scanner handle. The 1551
models have a screw to tighten that secures the plug in the
handle.
2. Plug the other end into the receiving OCIA port in the
terminal.
BK
4. Scan this bar code to enable OCIA mode:
Select OCIA Configuration CL
5. Scan this bar code to reset to the default value, NCR “S”
(short) Format:
Reset to Default Values ZA
1-7
Page 22

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
6. Scan one of these bar codes to select an OCIA format:
NCR “S” (short) Format*
NCR “F” (full) Format NI
DTS Format NR
ICL Format NW
Nixdorf Format NS
NH
* Default when using the Reset to Default Values (ZA) command.
The scanner is ready to be used as a hand-held scanner and will
send data directly to the terminal. The default symbologies are:
• UPC-A
• UPC-E (not expanded)
See Chapter 2 to learn basic scanning operation, scanning tips,
and how to use with the scanner stand for hands-free scanning.
To change the scanner configuration, see Chapter 3.
1-8
Page 23

Connecting the Scanner
1
15XXX07 Decoding Laser Scanner
You can connect 15XXX07 scanner to a host terminal through
the keyboard and operate in keyboard wedge mode or you can
connect the scanner to an IBM laptop computer.
To connect to a wedge
1. Make sure the power to the terminal is turned off.
2. Connect the interface cable on the scanner cable to the
bottom of the scanner handle. The 1551 models have a screw
to tighten that secures the plug in the handle.
3. Unplug the keyboard from the terminal and plug it into the
short leg of the “Y” cable.
4. Plug the long leg of the “Y” cable into the terminal, where
the keyboard was plugged in.
To connect an external power supply, plug the power supply
into the connector. Then plug the other end of the power
supply into an outlet or surge protector.
5. Turn on the power to the terminal. You hear a series of beeps
that indicate power on reset (POR) routines.
6. Scan this bar code to reset to the default value:
Reset to Default Values ZA
7. Scan one of these bar codes to select your terminal type:
Apple Mac ADB CN
DEC VT220/320/420 CI
DEC VT510 CF
1-9
Page 24

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
15XXX07 Terminal Type (continued)
IBM 3151 CH
IBM 3477 CP
IBM 317X/8X/9X CT
IBM PC/AT*,
IBM PS/2 model 50/60/80
IBM PC/XT CG
IBM PS2 Model 25/30/57 CY
CF
* Default when using the Reset Default Values (ZA) command.
The scanner is ready to be used as a hand-held scanner and will
send data directly to the terminal. The default symbologies are:
• UPC-A
• UPC-E (not expanded)
• Code 39
• Code 128
To connect to a laptop or pen-based terminal
1. Make sure the power to the laptop or terminal is turned off.
2. Connect the interface cable on the scanner cable to the
bottom of the scanner handle. The 1551 models have a screw
to tighten that secures the plug in the handle.
3. Connect the cable to the laptop or terminal auxiliary port.
1-10
Page 25

Connecting the Scanner
4. Turn on the power to the laptop or terminal.
5. Scan a bar code to enable the laptop or terminal (US
keypad).
Note: If your laptop or terminal has an international keyboard, see
“International Keyboards” in Chapter 3 to enable a different
language.
1
IBM PS2 Model 57/25
laptop interface
IBM PC/AT laptop interface
(ThinkPad)
Zenith CruisePAD* CF
* Default.
6. (Laptops only.) Turn the laptop off and then back on to
restart communications.
The scanner is ready to be used. The default symbologies are:
• UPC-A
• UPC-E (not expanded)
• Code 39
• Code 128
C9
\A
1-11
Page 26

Page 27

2
Operating the Scanner
Page 28

Page 29

Code39Code39
This chapter provides basic operating procedures, troubleshooting,
and maintenance guidelines.
Operating the Scanner
2
General Instructions
Decoding laser scanners are easy to use and maintain, but you
should read this chapter to become familiar with the safety and
maintenance procedures and learn to get the most effective use
out of your scanner.
Note: Each scanner is shipped with a quick reference guide that
provides the same operating procedures and safety instructions in this
chapter. Keep that guide near your scanner for quick reference.
Scanner Light
The light indicates the status of the scanner.
Light Description
Yellow The device is scanning.
Green The bar code has been successfully scanned.
None The device is not scanning
Warning
Do not look directly into the window area or at
WARNING
a reflection of the laser beam while the laser is
scanning. Long term exposure to the laser beam
can damage your vision.
Avertissement
Ne regardez pas directement la réflexion d'un
rayon laser ou dans la fenêtre du laser lorsque
celui-ci est en opération. Si vous regardez trop
longtemps un rayon laser, cela peut endommager
votre vision.
2-3
Page 30

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Code39Code39
Scanner Beeps
The scanner emits these beeps to indicate either a successful
scan or a situation that requires your attention.
Beep Description
One short, high beep The bar code has been successfully read
and you can continue scanning.
Two beeps A command bar code has been
scanned.
High-low-high-low
beep sequence or,
low-medium-high
beep sequence
Three medium beeps The bar code information has not been
The scanner has been turned on and is
in Continuous Power mode. See
“Power Consumption” in Chapter 3.
sent to the terminal successfully. See
“Troubleshooting” later in this chapter.
You can also send a command to make the scanner beep. See
“Remote Beep” in Chapter 3.
Operating the Scanner
You can operate the scanner in two ways:
• As a hand-held device, using the trigger to initiate scanning.
• As a hands-free device, mounting in the scanner stand and
scanning automatically.
Before you start scanning, make sure the power to the
reader/terminal is on and all cable connections are secure.
Hand-Held Scanning
1. Aim the scanner at a sight angle or pitch to the bar code and
press the trigger.
2. When you get a successful read the laser beam turns off, the
scanner beeps once, and the light turns green.
2-4
Page 31

Code39Code39
Operating the Scanner
2
Scanning Tips
Hold the scanner at a slight angle or pitch to the bar code. The
scanner’s Automatic Laser Power Control adjusts the beam to
be the brightest and scan the quickest at an angle. If the bar
code is on a reflective surface or you are scanning straight at
(perpendicular to) the bar code, the beam temporarily dims or
disappears but the scanner can still read the bar code.
*123*
Vertical
reading
angles (pitch)
Adjust the scanner distance to the bar code and the position of
the laser beam to make sure every bar and space is scanned.
*HI* *HI*
INCORRECT CORRECT
155XQRG.005
155XQRG.006
2-5
Page 32

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Code39Code39
Hands-Free Scanning
You can use your laser scanner with a scanner stand for handsfree scanning. To order a scanner stand, contact your local
Intermec representative. See scanner stand documentation to
assemble the scanner stand and insert the scanner.
Configure the scanner to enable the Stand mode before inserting
the scanner into the stand.
To scan bar code using the scanner stand
1. Scan this bar code to enable Stand mode.
Enable Stand
2. Place the scanner into the scanner stand.
3. Align the scanner and adjust the column height so the
scanner laser beam covers the entire reflective label.
4. Place a bar code right-side up over the reflective label.
When the scanner emits a single beep and/or the scanner light
turns green, the bar code has been successfully read. If you
remove the scanner from the stand, you can scan bar codes by
pressing the trigger. When you return the scanner to the stand,
the scanner will scan bar codes placed over the reflective label.
Switching Back to Hand-Held Scanning
1. Remove the scanner from the stand.
2. The scanner beam resets after 2 to 6 seconds.
3. Aim the scanner at a sight angle or pitch to the bar code and
press the trigger.
If you use the scanner for extended hand-held scanning, disable
the Stand mode to conserve power. Scan this bar code:
Disable Stand
2-6
Page 33

Code39Code39
Operating the Scanner
2
Troubleshooting
This table lists common scanner problems and their solutions.
Symptom Solution
System is
“jammed” and
scanner will not
operate.
The scanner could not process the
information. Turn off the power to the
terminal and then turn it on. The scanner will
retain its configuration.
Scanner cannot
read certain bar
codes.
Scanner does not
read the correct
uppercase or
lowercase letter, or
number and
symbol.
Scanner does not
read bar codes
quickly and
sometimes requires
multiple scans.
The reader/terminal was not set up to read this
type of bar code, or the bar code is damaged,
covered up, or poor quality.
Scan another bar code on a similar item. If it
scans, clean the bar code giving you trouble.
If you are still unable to scan the bar code,
enable other bar code symbologies (see
“Configuring Bar Code Symbologies” in
Chapter 3.).
If you use the Caps Lock on your terminal,
you must enable the Shift Alphabetic
Characters (EO) command for the scanner to
read and correctly decode bar code labels with
uppercase letters.
If you use the Shift key on your terminal, you
must enable the Shift Lock (ES) command for
the scanner to read and correctly decode bar
code labels with symbols (for example:
!@#$%).
Clean the window with a cotton cloth
moistened with an ammonia or water
solution. Dry with a soft cotton cloth or allow
to air dry.
Make sure the bar code is free of dirt and
grime. If it is damaged, try to repair.
Scan at a slight angle or pitch to the bar code
(see “Scanning Tips” earlier in this chapter).
2-7
Page 34

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Symptom Solution
Laser beam dims
and sometimes
disappears when
scanning at
different angles.
It is normal for the laser beam brightness to
vary. If the bar code is on a reflective surface
or you are scanning straight at the bar code
(perpendicular to), the beam disappears but
the scanner still reads the bar code.
Scan at a slight angle or pitch to the bar code
(see “Scanning Tips” earlier in this chapter).
Code39Code39
Scanner emits three
beeps and the item
scanned does not
appear on the
terminal.
Scanner does not
emit a beam and
does not operate.
Make sure the cables are securely connected
and the terminal is ready to receive data.
Turn the terminal off, then turn it on.
The scanner is not receiving power. Make sure
the scanner cables are securely plugged in and
the terminal is on. Replace damaged cables.
If you continue to encounter problems with your scanner,
contact your local Intermec representative.
Maintenance
Water or grime on the window of the scanner distorts the laser
beam and impair performance. Moving from one temperature
extreme to another causes condensation to form on the optical
surfaces and also affects scanner performance.
Follow these guidelines to maintain the scanner:
• Clean the window with a cotton cloth and ammonia or
water. Dry with a soft cotton cloth or allow to air dry.
• Do not use a dry tissue to wipe the window. This causes
small scratches on the window.
• Do not immerse the unit in water.
• Operate and store in an environment with 5% to 95% relative
humidity.
2-8
Page 35

3
Configuring the Scanner
Page 36

Page 37
Configuring the Scanner
This chapter describes how to configure your scanner for different
bar code symbologies, bar code parameters, operating parameters,
serial parameters. This chapter also describes how to configure
wand emulation for use with a portable reader.
3
About Configuring the Scanner
There are two ways to configure the scanner parameters:
scanning bar codes and configuring from a host using the twoletter bar code syntax.
Configuring by Scanning Bar Codes
You can scan the bar codes in this chapter to configure the
scanner parameters. If you are use the 15XXX02 with a portable
reader you must scan the bar codes. When the 15XXX02 is used
with a portable reader all serial communications functions are
disabled. (Serial communications parameters and portable
reader parameters are activated with the same components and
cannot be implemented simultaneously.)
The bar codes are listed along with the command name and the
two-letter syntax. For example:
Command Syntax Bar Code (Code 128)
Select 300 baud DA
Configuring the Scanner From a Host Terminal
If you have a 15XXX02 scanner in Serial mode (CA), you can
configure the scanner from a host terminal using the two-letter
syntax provided with the bar code.
Note: Do not mix configuring from a host and configuring by
scanning a bar code. The scanner does not resolve conflicts between the
two methods and gives priority to commands from the host.
3-3
Page 38

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
y
Commands are active as soon as they are received. For this
reason, configure communications parameters last so they do
not disrupt your scanner operation.
To send a serial commands, use this syntax (spaces have been
added for clarity):
STX ESC XX [optional parameters] ETX
where:
STX is the ASCII start of text command.
ESC is the ASCII escape command.
XX is the two-letter bar code s
ntax for the
command.
ETX is the ASCII end of text command.
If a parameter is required (such as values for minimum length),
use the two-letter bar code for the command. For example:
Command* Function
STX ESC PC ETX Enable I 2 of 5 with check digit
STX ESC PD12 ETX Set I 2 of 5 minimum length to 12
STX ESC PE14 ETX Set I 2 of 5 maximum length to 14
STX ESC KB31323334 ETX Set preamble to 1234
STX ESC LB61626364 ETX Set postamble to abcd
* Spaces added for clarity.
Note: The ASCII codes STX (02H), ESC (1BH), and ETX (03H) can
be generated with ASCII control characters. To create STX press Ctrl
B, to create ETX press Ctrl C. See the conversion chart in Appendix A
for a complete list of hex codes and control characters.
For specific help downloading the commands to the scanner,
see the manual for your host terminal.
3-4
Page 39

Configuring the Scanner
3
Waking Up the Scanner to Process Commands
If the scanner is programmed for Standby Power mode during
idle times, transmit an extra space before STX to “wake up” the
scanner (the space is ignored). Include a pause of 150 to 200 ms
to allow the CPU to initialize, accept, and process commands.
Remote Beep
In Serial mode, the scanner will beep when this command is
sent from the host terminal:
STX BEL ETX
or 02H 07H 03H in Hex command, or ^B ^G ^C through the
keyboard.
Acknowledging Commands Between Host and Scanner
The scanners use ACK/NAK protocol during serial
programming to acknowledge receiving commands. When the
scanner receives a correctly formatted command, it sends a
confirmation back to the host followed by an ACK (06H). If the
scanner receives an unknown command, an improperly
formatted command, or a command accompanied by incorrect
parameters, it sends a NAK (15H) code. NAK prevents downloading commands faster than the scanner can receive them.
Avoid these commands when configuring serial parameters:
CB Portable Reader, Code 39 output
CC Portable Reader, same code output
YA Portable Reader, 5 inches per second
YB Portable Reader, 10 inches per second
YC Portable Reader, 15 inches per second
YD Portable Reader, 20 inches per second
YE Portable Reader, 30 inches per second
YF Portable Reader, 50 inches per second
YG Portable Reader, 70 inches per second
They cause the scanner to enter Portable Reader mode and
disable serial communications without sending ACK or NAK.
3-5
Page 40

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Displaying Current Configuration
You can display the current parameter settings for your scanner
by scanning these bar codes (will not work in Wand mode or
with a 1551X03):
Note: The Display Current Configuration option (ZB) may interfere
with terminal software, depending on the application.
Display Current Configuration ZB
Transmit Program Version ZC
Transmit Program Version number displays as two decimal
places followed by commands for carriage return and line feed.
Resetting Default Values
The default bar code symbologies for the scanners are:
UPC-E
UPC-A
(not
expanded)
Code 39 Code 128
15XXX02
15XXX03
15XXX07
You can enable or disable any symbology as well as UPC
supplements, EAN supplements, Interleaved 2 of 5 (I 2 of 5)
with check digit, and Code 39 modulo 43 check digit.
üü üü
üü
üü üü
——
3-6
Page 41

Configuring the Scanner
The minimum label lengths are set to one character, except for
I 2 of 5, which is set to 14 characters, and standard 2 of 5, which
is set to 4 characters. If maximum length is not programmed,
the scanner will limit the bar code length to 32 characters.
To reset your scanner to default values, scan this bar code:
Reset to Default Values ZA
To set up Intermec default values, scan this bar code:
Intermec Default
Wand emulation: white high, 50 ips
Communications: 9600, e, 7, 1
Z5
3
Configuring Bar Code Symbologies
You can configure these symbologies on your scanner:
• UPC-A • UPC-E
• EAN/JAN • Code 39
• Standard 2 of 5 • Interleaved 2 of 5
• Code 128 • Codabar
• Code 93 • Code 11
Configure only the symbologies you will use and disable any
symbologies you will not use. This will help increase scanning
speed. For example, if you are using a 15XXX02 scanner, four
symbologies including Code 39 are automatically activated. If
you will not scan Code 39 bar codes, disable the Code 39
symbology by scanning the Disable Code 39 (OA) bar code
command found later in this section or in Appendix B.
3-7
Page 42

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
UPC-A and UPC-E
Scan the appropriate bar code to enable or disable UPC
symbology. When enabled, the UPC codes, with or without a
supplement, can be scanned. Enabling the supplement (2 or 5
digits) lets the scanner read the supplement as well.
Enable UPC-A and UPC-E
Supplement allowed
Enable UPC-A and UPC-E
Supplement disabled*
Enable Expanded UPC-E QI
Disable Expanded UPC-E QH
Enable Transmit UPC-A as
EAN-13
Disable Transmit UPC-A as
EAN-13**
Disabled (A and E) QA
QB
QC
QJ
QK
* Default for all scanners.
**
Default for all modes.
Continue to the next section to configure a number system digit
and a check digit.
3-8
Page 43

Configuring the Scanner
3
UPC Number System Digit
Scan the appropriate bar code to enable or disable the number
system digit (the first character in a UPC symbol).
Enable UPC Transmit of
Number System Digit
Disable UPC Transmit of
Number System Digit
QE
QD
UPC Check Digit
Scan a bar code to enable or disable the check digit (the last
character in a UPC symbol).
Enabled*
Disabled QF
*
Default for all modes.
QG
EAN/JAN
Scan the appropriate code to enable or disable EAN 8 digit and
13 digit. When EAN/JAN is enabled, all EAN/JAN codes, with
or without a supplement, can be scanned. Enabling the
supplement (2 or 5 digits) lets the scanner read the supplement
as well.
Disabled - both 8 and 13 digit* RA
Enabled - Supplement enabled
(2 or 5 digit)
Enabled - Supplement disabled
(2 or 5 digit)
Continue to the next section to configure a number system digit
and a check digit.
RB
RC
3-9
Page 44

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
EAN/JAN Number System Digit
Scan the appropriate bar code to enable or disable the number
system digit (the first character in a UPC symbol).
Disable Number System Digit RD
Enable Number System Digit* RE
EAN/JAN Check Digit
Scan a bar code to enable or disable the check digit (the last
character in a UPC symbol).
Enable Check Digit* RG
Disable Check Digit RF
*
Default for all modes.
3-10
Page 45
Configuring the Scanner
3
Code 39
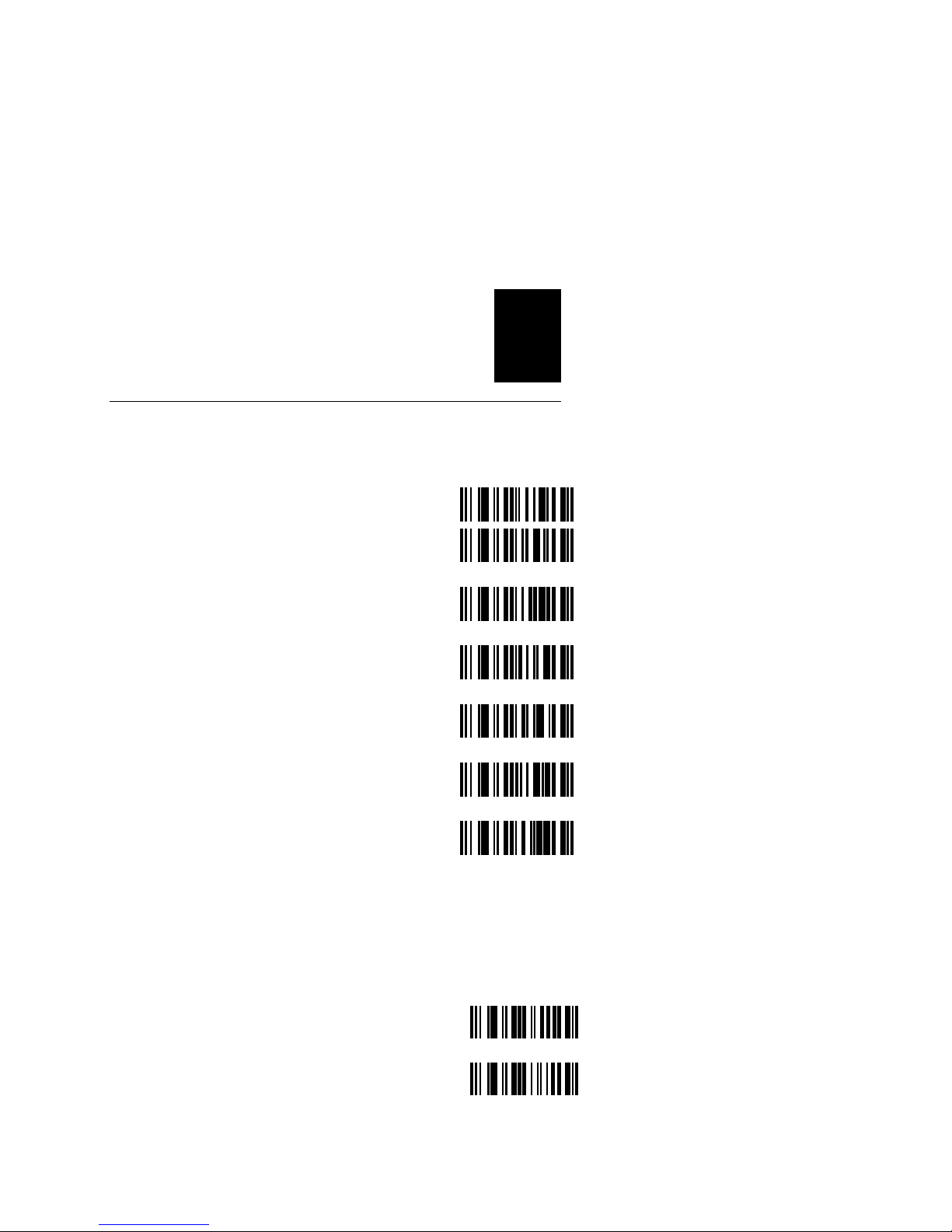
These bar codes configure your scanner for Code 39 scanning
capabilities.
Disable OA
Enable Standard Code 39* OB
Full ASCII Code 39 OC
Disable Modulo 43 Check
Character**
Enable Modulo 43 Check Character OE
Transmit START and STOP
Characters
Do not transmit START and STOP
Characters
* Default for 15XXX02 and 15XXX07 scanners.
Default for all modes.
**
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length OH
Maximum Length OI
**
OD
OG
OF
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3-11
Page 46

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Standard 2 of 5
These bar codes configure your scanner for 2 of 5 scanning
capabilities.
Enable PG
Disable* PF
*
Default for all modes.
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length PH
Maximum Length PI
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
Interleaved 2 of 5
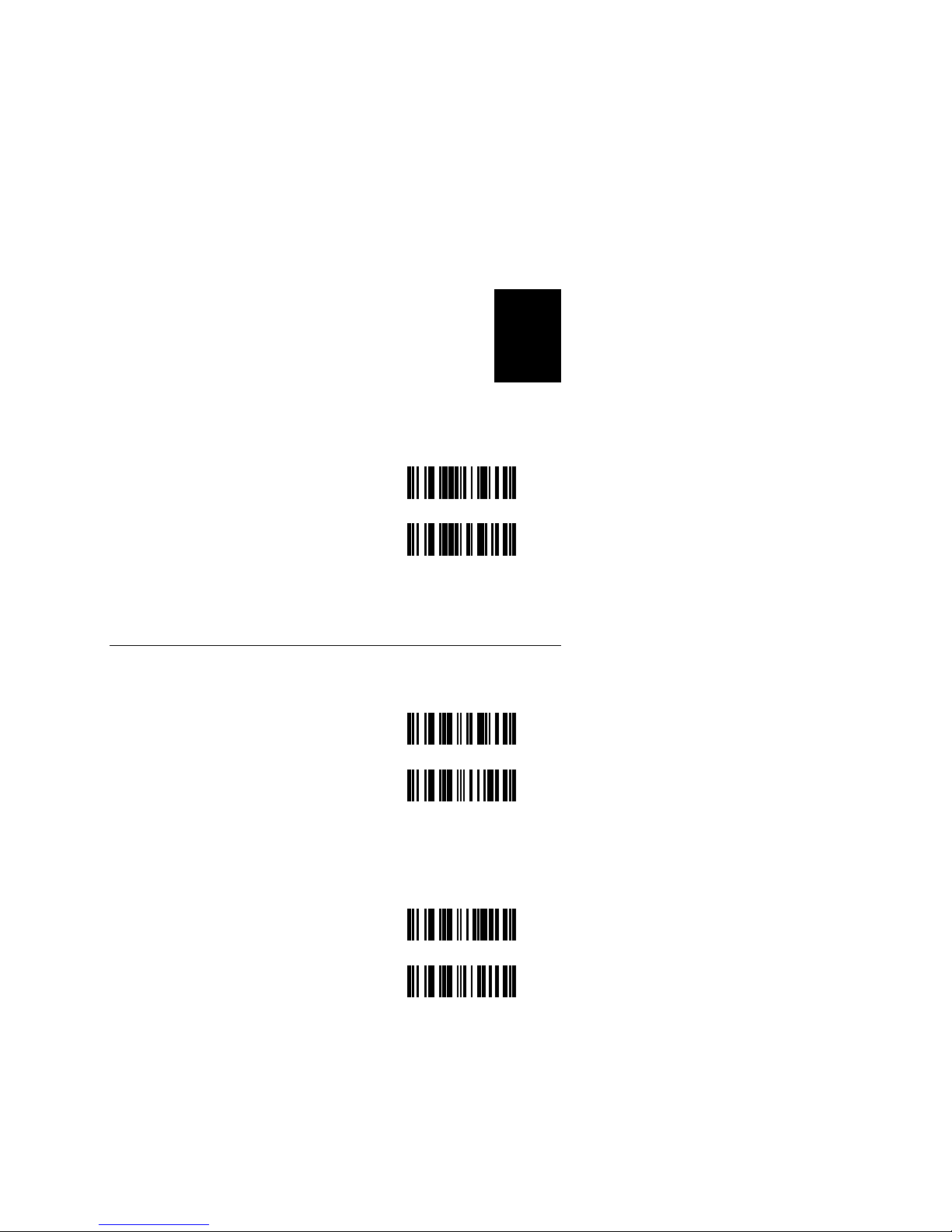
These bar codes configure your scanner for I 2 of 5 scanning
capabilities.
Disable*
Enable with Check Digit PC
Enable without Check Digit PB
* Default for all modes.
3-12
PA
Page 47
Configuring the Scanner
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length PD
Maximum Length PE
2. Enter a length between 02 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3
Code 128
These bar codes configure your scanner for Code 128 scanning.
Enable* TB
Disable TA
* Default for 15XXX02 and 15XXX07 scanners.
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length TC
Maximum Length TD
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3-13
Page 48

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Codabar
These bar codes configure your scanner for Codabar scanning
capabilities.
Enable VB
Disable* VA
Transmit START and STOP
characters
Do not transmit START and
STOP characters
VD
VC
* Default for all scanners.
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length VE
Maximum Length VF
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3-14
Page 49

Configuring the Scanner
3
Code 93
These bar codes configure your scanner for Code 93 scanning
capabilities.
Disable* UA
Enable Code 93 UB
Standard Code 93 UC
Enable Full ASCII Code 93 UD
* Default for 15XXX02 and 15XXX07 scanners.
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length UE
Maximum Length UF
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3-15
Page 50

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Code 11
These bar codes configure your scanner for Code 11 scanning
capabilities.
Disable Code 11 SA
Enable Code 11 With One
Check Digit
Enable Code 11 With Two
Check Digits
Disable Transmit of Code 11
Check Digits
Enable Transmit of Code 11
Check Digits
SB
SC
SD
SE
To set the bar code length (optional)
1. Scan the appropriate bar code below.
Minimum Length SF
Maximum Length SG
2. Enter a length between 01 and 32 using the conversion chart
in Appendix A.
3-16
Page 51
Configuring the Scanner
3
Configuring Bar Code Parameters
You can configure these bar code parameters (not available for
15XXX03):
• Prefix
• Suffix
• Terminal ID
• Bar code ID
• Preamble
• Postamble
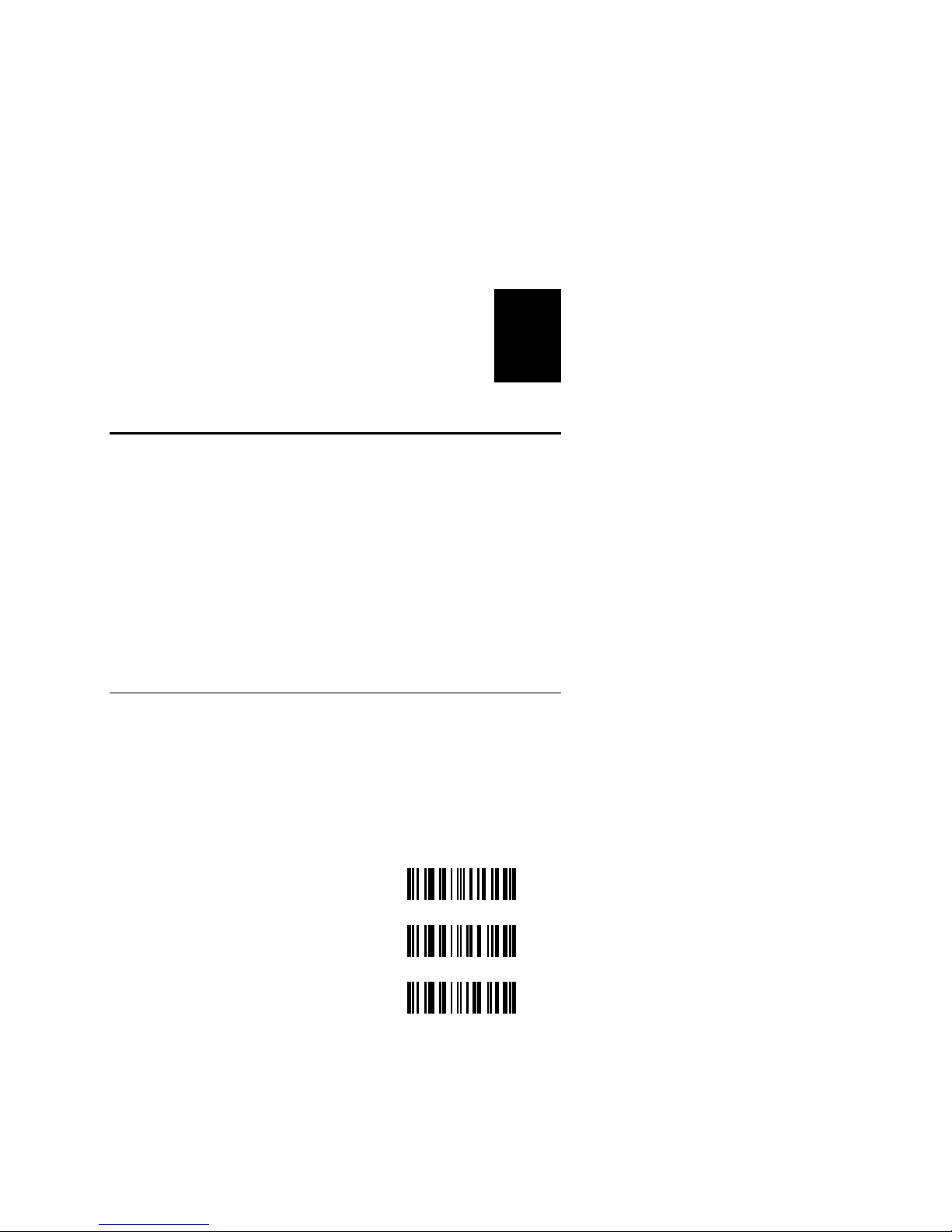
Prefix
The prefix identifies the start of a data string and is represented
by a code that is determined by an industry standard. The
prefixes available are STX (start of transmission code) and SOH
(start of header code).
Scan a bar code to enable the prefix used by your system
(not available for 15XXX03).
No Prefix*
STX IB
SOH IC
* Default
IA
3-17
Page 52

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Suffix
The suffix marks the end of a data string and, like the prefix, it
is assigned a specific ASCII code that conforms to a standard.
The available suffixes are CR (carriage return), LF (line feed),
CR and LF, ETX (end of transmission), and HT (horizontal tab).
Scan a bar code to enable the suffix used with your system
(not available for 15XXX03).
No suffix*
ETX MB
CR MC
LF MD
HT ME
CR and LF**
MA
MF
* Default for Keyboard Wedge mode.
** Default for Serial mode.
3-18
Page 53

Configuring the Scanner
3
Terminal ID
Terminal IDs are used to identify individual scanners for host
systems that interface with many scanners. Two digits (01 to 99)
are used for terminal IDs.
To configure terminal ID
1. Scan a bar code (not available for 15XXX03):
Terminal ID Disabled*
Terminal ID JB
* Default.
2. If you scan “Terminal ID,” enter two digits between 01 and 99
using the conversion chart in Appendix A.
JA
Bar Code ID
If your system uses different types of bar code symbologies, it
may require a bar code ID. The ID is a single character that is
transmitted with each message identifying the bar code
scanned. ID characters are:
Code 39 a UPC/EAN/JA
N
Interleaved 2 of 5 b Code 128 f
Standard 2 of 5 c Codabar h
To configure a bar code ID
Scan one of these bar codes to enable or disable the bar code ID
(not available for 15XXX03):
d
Disable Bar Code ID*
Enable Bar Code ID FB
* Default.
FA
3-19
Page 54

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Preamble and Postamble
Preambles and postambles are character strings that precede
and follow the actual message. Each preamble and postamble
consists of four ASCII characters, each is represented by two
hexadecimal numbers.
If they are used in your system, only those codes with the
correct preamble and postamble are accepted.
To configure a preamble or a postamble
1. Scan one of these bar codes (not available for 15XXX03):
No Preamble*
No Postamble*
Enter Preamble KB
Enter Postamble LB
KA
LA
* Default.
2. If you scanned “Enter Preamble” or “Enter Postamble,” enter
four characters using the conversion chart in Appendix A.
3-20
Page 55

Configuring the Scanner
3
Configuring Operating Parameters
You can configure these scanner operating parameters:
• Power consumption
• Beeper volume
• Laser redundancy
• Spotter beam
• External trigger
• Reading Uppercase Letters
• Reading Special Characters
• International Keyboards
Power Consumption
Power consumption parameters determine if the scanner reverts
to standby when not scanning. With standby enabled, the
scanner draws very little power between scans and conserves
power.
Scan a bar code to select the type of power consumption for
your scanner (not available for 15XXX03):
Continuous Full Power* @A
Standby Enabled** @B
* Default for 1551X03 and 15XXX07 scanners.
** Default for 15XXX02 scanners.
3-21
Page 56

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Beep Volume
Scan one of these bar codes to set the scanner beep volume (not
available for 15XXX03):
Off (no beeper) AA
Softest AB
Medium AC
Loudest*
AD
* Default.
Laser Redundancy
Laser redundancy checks each scan by creating a duplicate scan
and comparing the information, which must match for a
successful read. This feature increases the integrity of the
scanners since it creates an automatic error check.
Scan a bar code to enable or disable laser redundancy
(not available for 15XXX03):
Disabled*
Enable (2X) BD
Enable (4X) BE
* Default.
BC
3-22
Page 57
Configuring the Scanner
3
Spotter Beam
The spotter beam lets you see where the laser beam will scan
before a bar code is actually read. With the spotter beam
enabled, you can press the scanner trigger and have a small
laser dot appear (for a preset time) where the full laser beam
will scan, and then the scanner will read that bar code.
Use the spotter beam if you have trouble scanning bar codes
that are far away, in a group of closely printed bar codes (for
example, Appendix B), in a bright environment, or in a glass
showcase.
To configure spotter beam
1. Scan a bar code to enable or disable the spotter beam:
Disable Spotter Beam NP
Enable Spotter Beam NQ
2. If you sca n “Enab le Spot ter Beam,” enter a spotter beam
duration between 0 and 9 using the conversion chart in
Appendix A.
External Trigger
The external trigger lets you program your scanner to be
enabled from a computer or other external device. Unlike the
scanner stand, which activates the scanner when the beam path
is interrupted, the external trigger responds to a signal at the
CTS input. This signal starts the scan and continues until the
label is decoded, or the signal times out (approximately 6
seconds).
The external trigger can be activated as External Trigger (+),
which activates scanning when the CTS input is high, or
External Trigger (-), which activates scanning when the CTS
input is low. When CTS is not connected, it is treated as if it
3-23
Page 58

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
were a high input (for both settings). See the modular connector
for the voltage levels.
Note: The trigger must be deactivated for a minimum of 50 ms
between scans to verify trigger cycling. Forcing the signal to active at
all times does not create continuous scanning and decoding.
Scan a bar code below to set the external trigger (not available if
using 15XXX03 or 1551X07):
Disabled*
External Trigger (+) HE
External Trigger (-) HF
HA
* Default.
Reading Uppercase Letters
When the Caps Lock key is used on the reader/terminal, you
must also configure the scanner to read and decode the
uppercase letters in a bar code. Scan the Shift Alphabetic
Characters bar code (EO) to configure the scanner to read all
uppercase letters. Scan the Normal Alphabetic Character (EP) to
return to reading lowercase letters. (Not available for 15XXX02
and 15XXX03.)
Note: To use the symbols above the number keys (for example:
!@#$%^&*), see the next section “Reading Symbols.”
Shift Alphabetic Characters EO
Normal Alphabetic Characters EP
3-24
Page 59

Configuring the Scanner
3
Reading Symbols
When the Shift key is used on the reader/terminal, you must
also configure the scanner to read and decode the symbols (for
example: !@#$%^&*) in a bar code. Scan a bar code to enable or
disable shift lock (not available for 15XXX02 and 15XXX03):
Enable Shift Lock ES
Disable Shift Lock ET
Note: To read uppercase letters, see the previous section “Reading
Uppercase Letters.”
International Keyboards
Scan a bar code to configure a 15XXX07 for one of these
keyboards (not available on 15XXX02 and 15XXX03):
PC/AT German CV
PC/AT French CW
PC/AT United Kingdom CX
PC/AT Belgian \B
PC/AT Swiss \C
PC/AT Danish \D
3-25
Page 60

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
International Keyboards (continued)
PC/AT Spanish \F
PC/AT Swedish \G
PC/AT Portuguese \H
DEC VT 220/320/420 German
Keyboard Wedge
DEC VT 220/320/420 French
Keyboard Wedge
\L
\M
Using an International Keyboard With a Laptop
If you use a laptop with an international keyboard you need to
enable the keyboard. Scan a bar code to enable or disable the
keyboard:
Enable Execution of Keyboard
POR (Power on Reset)
Disable Execution of Keyboard
POR (Power on Reset)
\J
\M
3-26
Page 61
Configuring the Scanner
3
Configuring the 15XXX02 Serial Parameters
You can configure these serial communications parameters for a
15XXX02 scanner:
• Baud rate
• Intercharacter delay
• Data bits
• Protocol
• Label buffer
Note: If you are using your 15XXX02 scanner with a portable reader,
you must configure the scanner by scanning the bar codes in this
manual. If you are configuring the scanner from a host terminal see
“Configuring the Scanner From a Host Terminal” earlier in this
chapter.
Baud Rate
The baud rate is the rate at which information reaches the
terminal in data bits per second.
Scan one of these bar codes to set the baud rate:
300 DA
600 DB
1200 DC
2400 DD
3-27
Page 62

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Baud Rate in Data Bits per Second (continued)
4800 DE
9600*
19200 DG
DF
* Default for Serial mode.
Intercharacter Delay
Some host terminals require an intercharacter delay to process
information properly. The intercharacter delay simulates
keystroke input by inserting a delay between transmission of
characters. The delay is a certain number of milliseconds, set
separately when you enable this parameter.
To set the intercharacter delay
1. Scan a bar code:
No Intercharacter Delay GA
Set Intercharacter Delay GB
2. If you select “Set Intercharacter Delay,” enter the number of
milliseconds using the conversion chart in Appendix A.
Note: Intercharacter Delay cannot exceed 99 ms.
3-28
Page 63
Configuring the Scanner
3
Label Buffer
The label buffer controls the operation of the transmit queue by
determining how labels are placed in the scanner memory
before transmission and how long you must wait before
scanning the next label. The buffering methods are:
Full buffer Each label is read entirely and then placed in the
transmit queue. Labels are transmitted immediately (unless
prevented by the protocol), and you may scan the next label
without waiting for the previous label to be transmitted.
No buffer You cannot scan the next label until the previous one
has been completely transmitted.
One label buffer You can scan ahead one label only.
Scan a bar code for the buffering method of your system:
Full Label Buffer*
No Label Buffer NF
One Label Buffer NG
* Default.
NE
Setting Up the Bar Code Data String
Each bar code is a string of data that consists of these elements:
• 1 start bit
• 7 or 8 data bits
• 1 or 2 stop bits
• Parity bits for error checking (optional)
Each system and application requires different combinations of
data string elements. For example, some systems require a
prefix in front of the data while others do not.
3-29
Page 64

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Scan a bar code for the data string setup used with your system.
Data Setup: 1 start bit, 7 data bits, 1 stop bit
Odd Parity ED
Even Parity EC
Mark Parity EB
Space Parity*
EA
* Default for Serial mode.
Data Setup: 1 start bit, 7 data bits, 2 stop bit
Odd Parity EH
Even Parity EG
Mark Parity EF
Space Parity EE
Data Setup: 1 start bit, 8 data bits, 2 stop bits
No Parity EN
3-30
Page 65

Configuring the Scanner
Data Setup: 1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
No Parity EM
Odd Parity EL
Even Parity EK
Mark Parity EJ
Space Parity EI
3
Selecting a Protocol
Protocol controls data flow between the scanner and the host
terminal and determines acknowledgment of data transmission
between the two devices. The available protocols are:
XON/XOFF Terminal sends the ASCII XON character to the
scanner when it is ready to receive data, and sends the XOFF
character when the buffer is full and cannot accept data. No
additional hardware is needed; only transmit, receive, and
signal ground are required.
Clear to send (CTS) The host uses a signal that informs the
scanner when it is ready to accept data. CTS (+) causes the
scanner to wait for a high input level to send data. CTS (-)
causes the scanner to wait for a low input level to send data.
Request to send (RTS) RTS has three different operating modes:
scanner sends an RTS when it is ready to receive data; RTS is set
to remain fixed; and RTS sent when scanner has data to
transmit.
3-31
Page 66

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Scan a bar code for the protocol for your system.
XON/XOFF HB
CTS (-) HC
CTS (+) HD
CTS = None. RTS high when
scanner ready to receive.
Note: CTS may be programmed independently of RTS, however the polarities must
match. You cannot select CTS (+) and fix RTS (-).
RTS low when scanner ready
to receive
RTS high when scanner ready to
transmit
RTS low when scanner ready to
transmit
RTS always high HG
RTS always low HH
*
HA
HI
HJ
HK
* Default.
3-32
Page 67

Configuring the Scanner
3
Configuring the Scanner for Wand
Emulation to Use With a Portable Reader
You can configure your scanner for wand emulation to use it
with a portable reader.
To use the scanner with a portable reader
1. Scan this bar code to disable using the scanner stand:
Disable Stand NN
2. Turn off the power to the terminal before you disconnect the
scanner (or remove it from the scanner stand). Otherwise,
your terminal may register a scanner failure or you may
cause damage to the terminal or the scanner.
3. Connect the scanner to the reader using the cables for your
scanner. For help see your scanner quick reference guide.
4. Scan this bar code to set parameters:
Intermec Default
Wand emulation: white high 50
ips
Communications: 9600, e, 7, 1
5. Scan a bar code to configure portable reader use:
Select Same Code
Wand Emulation
Your scanner now has these default values:
Parameter Setting
Transmitted symbology Same code and length
Bar code polarity White
Transmission rate 50 inches per second
Z5
CC
3-33
Page 68

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Or,
Select Code 39
Wand Emulation
Continue to next sections to configure for bar code conversion
to Code 39 before transmission, bar code polarity, and
transmission rates.
CB
Scanning Unreadable Symbologies
If the portable reader cannot process a bar code symbology, you
can configure your scanner to convert to Code 39 before it
transmits the data to the portable reader.
To convert to Code 39 (full ASCII) before transmitting, scan this
code:
Transmit Code 39 only CB
Configuring Bar Code Polarity
Select one of these options for bar code polarity:
Black High WA
White High*
* Default.
WB
Configuring the Transmission Rate
Select the transmission rate (in inches per second) for your
portable reader by scanning one of these bar codes:
5 ips YA
3-34
Page 69

Configuring the Scanner
Configuring the Transmission Rate (continued)
10 ips YB
15 ips YC
20 ips YD
30 ips YE
3
50 ips*
70 ips YG
* Default.
YF
Switching Back to a Terminal
To start scanning at the terminal again, scan this bar code:
Note for 15XXX07 users: If your scanner is interfaced through a
keyboard, scanning CA will enable Serial mode. Scan CE (next bar
code) before reconnecting your scanner to the keyboard.
Cancel Wand Emulation CA
Wedge Mode Enable (for
15XXX07 scanners)
Connect your scanner to the terminal or place it in the scanner
stand and turn on the terminal power.
CE
3-35
Page 70

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
If your scanner does not work when you reconnect it, you may
have forgotten to turn off the terminal before removing the
scanner. With some terminals, this records a failure and the
scanner is deactivated. To reactivate the scanner, leave it
attached to the terminal, and then turn off the terminal and turn
it back on again.
Configuring the Scanner for Use With an
Intermec 94XX and 95XX Reader
These steps are a quick way to enable wand emulation to an
Intermec 94XX or 95XX reader when the scanner is connected
with a “smart” cable (a cable that causes the scanner to
automatically switch to Wand Emulation mode).
To use the scanner with an Intermec 94XX or 95XX reader
1. Scan this bar code to reset the scanner:
Reset to Default Values ZA
2. Scan this bar code to enable wand emulation:
Wand Emulation, White High WB
3. Scan this bar code to increase the beeper volume:
Beeper Volume Control
(Loud)
3-36
AD
Page 71

A
Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
Page 72

Page 73

Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
This appendix contains the hexadecimal conversion chart and
instructions for converting ASCII characters to hexadecial characters.
A
Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
Use the hexadecimal chart in this appendix to find the
hexadecimal equivalents to ASCII characters and control
characters. Use this chart to set preambles and postambles, and
to program your computer using serial commands.
To enter the hexadecimal equivalent for ASCII characters
1. Find the ASCII character within the table.
2. Locate the number at the top of the table, in bold, for the
column containing the character.
3. Scan the bar code for that number. This number must be
scanned first.
4. Locate the number or letter at the left of the table, in bold,
for the row containing the character.
5. Scan the bar code for that number or letter.
For example, the hexadecimal number for “Q” is 51, which is in
the column under 5 and in the row next to 1. To enter “Q” as a
character, scan the bar code for 5 and then 1.
To enter a digit less than ten, scan a zero first. For example, 01 is
30 and then 31.
Entering Control Codes
When programming from a host, you can generate the
characters listed in column 0 by pressing Ctrl and then the
character listed in column 4. For example, to create STX, press
Ctrl and then B. You must always use a 4-character hex
representation for preambles and postambles even when
programming from a host terminal. For example, if you want a
two-character preamble, pad the preamble with two null
characters.
A-3
Page 74

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Hexadecimal Conversion Table
0
1
0123
NUL
0
2
3
4
5
A
B
C
D
1
2
3
4
ENQ
5
ACK
6
7
8
9
E
F
SOH
STX
ETX
EOT
BEL
BS
HT
LF
VT
FF
CR
SO
SI
DLE
DC1
DC2
DC3
DC4
NAK
SYN
ETB
CAN
EM
SUB
ESC
FS
GS
RS
US
SP
%
&
0
!
“
#
$
’
(
)
*
+
,
-
.
/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
:
;
<
=
>
?
6
7
A-4
Page 75

Hexadecimal Conversion Chart
g
j
y
4567
A
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
@
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[
\
]
^
_
‘
a
b
c
d
e
f
h
i
k
l
m
n
o
DEL
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
z
{
|
}
~
A
B
C
D
E
F
A-5
Page 76

Page 77
B
Configuration Command List
Page 78

Page 79
Configuration Command List
This appendix lists all the configuration commands for the 15XX
decoding laser scanner.
B
Summary of Commands
This table lists all of the configuration commands available for
the decoding laser scanners. You can scan bar codes, or you can
program the scanners from a host terminal with a 15XXX02
scanner in Serial mode using the two-letter bar code syntax. See
“Configuring the Scanner” in Chapter 3.
The commands are listed in alphabetic order by syntax.
Command Syntax Bar Code
Continuous Power @A
Power Conservation @B
Transmit Program ID @C
Select Intermec Wedge Function Key
Table
Emulate Compsee Wedge Function
Key Table
Disable Bypass Command Label @Z
IBM PC/AT laptop interface \A
Commands \B to \M are international keyboard commands.
PC/AT Belgian \B
PC/AT Swiss \C
PC/AT Danish \D
PC/AT Italian \E
PC/AT Spanish \F
@Q
@R
B-3
Page 80

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Commands \B to \M are international keyboard commands (continued)
PC/AT Swedish \G
PC/AT Portuguese \H
Enable Execution of Keyboard
POR (Power On Reset)
Disable Execution of Keyboard
POR (Power On Reset)
DEC VT220/320/420/ German
Keyboard Wedge
DEC VT220/320/420/ French
Keyboard Wedge
Beeper Volume Control (Off) AA
Beeper Volume Control (Low) AB
Beeper Volume Control (Medium) AC
Beeper Volume Control (Loud) AD
Enable Parameter Messages BA
Disable Parameter Messages BB
Disable LASER Redundancy BC
Enable LASER Redundancy (2X) BD
\J
\K
\L
\M
Enable LASER Redundancy (4X) BE
Set 6 Second Software Timeout BH
Set 4 Second Software Timeout BI
Set 2 Second Software Timeout BJ
B-4
Page 81

Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
Select 4683 LASER Emulation BK
Select 4683 CCD Emulation BL
B
Enable Redundant Transmit Feature
(used with LASER redundancy)
Disable Redundant Transmit Feature BN
Set Software Timeout to 1 Second BO
IBM PS2 Model 57/25
laptop interface
Select Primary Communications
Port/Cancel Wand Emulation
Select Wand Emulation (Code 39, Full
ASCII)
Select Wand Emulation (Same Code
Emulation)
Inverted Serial Communications CD
Wedge Mode Enable CE
Select AT Keyboard and Wedge Mode CF
Select XT Keyboard and Wedge Mode CG
Select IBM 3151 Terminal CH
BM
C9
CA
CB
CC
Select DEC VT220 Terminal CI
Select IBM Primary Table of Key Code CQ
Select IBM Secondary Table CR
Select IBM 317X, IBM 318X, IBM 319X CT
PC/AT German Keyboard CV
B-5
Page 82

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
PC/AT French Keyboard CW
PC/AT United Kingdom CX
Select IBM PS/2 Mod 57 / 25 CY
Select Data General D216/D217
Terminal
Select NEC Powermate SX20
Keyboard
Select IBM 3151 With Break Codes C1
Select Sperry PC With Keytronics
Keyboard
Select Unisys B26 Keyboard Wedge C6
Enable Fast PC-AT Keyboard (Hong
Kong)
Enable Link 125 Terminal C8
Select 300 baud DA
Select 600 baud DB
Select 1200 baud DC
Select 2400 baud DD
CZ
C0
C4
C7
Select 4800 baud DE
Select 9600 baud DF
Select 19200 baud DG
B-6
Page 83

Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
Commands EA to EN are serial data word commands.
7,Low,1 EA
7,High,1 EB
7,Even,1 EC
7,Odd,1 ED
7,Low,2 EE
7,High,2 EF
7,Even,2 EG
7,Odd,2 EH
B
8,Low,1 EI
8,High,1 EJ
8,Even,1 EK
8,Odd,1 EL
8, no parity,1 EM
8, no parity,2 EN
B-7
Page 84

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Enable Shift Alphanumeric Keys in
Wedge Mode
Disable Shift Alphanumeric Keys in
Wedge Mode
Enable Shift Lock ES
Disable Shift Lock ET
Turn Off the Intercharacter Delay GA
Set the Intercharacter Delay. Two digit
argument is the delay time in
milliseconds (00-99).
Turn Off the Interlabel Delay GC
Set the Interlabel Delay. Two digit
argument is the delay time in 100
milliseconds intervals (00-99).
EO
EP
GB
GD
HA to HK are serial communication commands
Turn Off All Protocols HA
Enable XON/XOFF Protocol. All CTS
protocols are disabled.
HB
Enable CTS High to Transmit.
XON/XOFF is disabled.
Enable CTS Low to Transmit.
XON/XOFF is disabled.
Enable External Trigger +.
XON/XOFF is disabled
Enable External Trigger -. XON/XOFF
is disabled
RTS Always High HG
HC
HD
HE
HF
B-8
Page 85
Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
HA to HK are serial communication commands (continued)
RTS Always Low HH
RTS Low = Ready to Receive HI
RTS High = Transmit Ready HJ
RTS Low = Transmit Ready HK
Disable Prefix IA
Set Prefix to STX IB
Set Prefix to SOH IC
Disable Unit ID JA
B
Enable Unit ID. The arguments are a
two digit unit ID number ID’s are in
the range (01-99).
Disable Preamble KA
Set Four Character Preamble. Unused
characters are set to Null. The four
character hex value is contained in the
arguments.
Disable Postamble LA
Set Four Character Postamble. Unused
characters are set to Null. The four
character hex value is contained in the
arguments.
Set Suffix to None MA
Set Suffix to ETX MB
Set Suffix to CR MC
JB
KB
LB
B-9
Page 86

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Set Suffix to LF MD
Set Suffix to HT ME
Set Suffix to CR/LF MF
Set Suffix to ETB/NULL MI
Set User Programmable Suffix
Character
Select Full Duplex NA
Select Half Duplex NB
Disable Label Buffering NC
Enable Label Buffering and Power
Conservation. Clear the label buffer.
Enable Full Serial Buffering NE
Enable No Serial Buffering NF
One Label Buffer NG
Select Wide (Normal) Scan Angle NL
Select Narrow (Reduced) Scan Angle NM
Disable Stand Mode NN
Enable Stand Mode NO
Disable Spotter Beam NP
MJ
ND
Enable Spotter Beam. Single digit
argument is the marker duration.
Enable “No Read” Message Option NX
Disable “No Read” Message Option NY
NQ
B-10
Page 87
Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
Commands OA to OK are for Code 39 only.
Disable Code 39 OA
Enable Standard Code 39 OB
Enable Full ASCII Code 39 OC
Disable Modulo 43 Check Character OD
Enable Modulo 43 Check Character OE
B
Disable Transmit of The Start/Stop
Characters
Enable Transmit of The Start/Stop
Characters
Set Minimum Length. Two digit
argument is the length (01-32)
Set Maximum Length. Two digit
argument is the length (01-32)
Enable Transmit of Check Character.
This command and the next are
responsible for controlling the
transmission of the check character in
Code 39 ONLY when the check
character is required for decode. If the
Modulo 43 check character is NOT
enabled (with command OE), the
check character is simply part of the
label and is always transmitted.
Disable Transmit of Check Character OK
Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 PA
OF
OG
OH
OI
OJ
Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 Without
Check Digit
PB
B-11
Page 88

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 With Check
Digit
Set Minimum Length for Interleaved 2
of 5. Two digit argument is the length
(02-32). Length must be a multiple of
two. Round all entries up to the next
even number. Becomes 1st fixed
length for 3 fixed length option.
Set Maximum Length for Interleaved 2
of 5. Two digit argument is the length
(02-32). Length must be a multiple of
two. Round all entries up to the next
even number. Becomes 2nd fixed
length for 3 fixed length option.
Disable Standard 2 of 5 PF
Enable Standard 2 of 5 PG
Set Minimum Length for Standard 2 of
5. Two digit argument is the length
(01-32).
Set Maximum Length for Standard 2
of 5. Two digit argument is the length
(01-32).
PC
PD
PE
PH
PI
Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 Check Digit
Transmission
Enable Interleaved 2 of 5 Check Digit
Transmission
Transmit All Characters of I 2 of 5
Labels
Transmit Only First Eight Characters
of I 2 of 5 Labels
B-12
PO
PP
PR
PS
Page 89

Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
Disable UPC QA
Enable UPC With Supplements QB
Enable UPC Without Supplements QC
B
Disable UPC Transmit of Number
System Digit
Enable UPC Transmit of Number
System Digit
Disable Transmit of The UPC Check
Digit (UPC-A and UPC-E only).
Enable Transmit of the UPC Check
Digit. (UPC-A and UPC-E only)
Disable Expansion of UPC-E QH
Enable Expansion of UPC-E QI
Enable EAN Emulation by UPC-A
Symbols. Forces UPC-A to be decoded
as EAN13.
Disable EAN Emulation by UPC-A
Symbols
Enable UPC-E Only QL
Disable Second Beep on Supplements QN
Enable Second Beep on Supplements QO
QD
QE
QF
QG
QJ
QK
Set Up Supplement Retry Counter QP
Disable UPC-E Transmission of Check
Character
Enable UPC-E Transmission of Check
Character
QR
QS
B-13
Page 90

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Disable UPC-E Transmission of The
Number System Digit
Enable UPC-E Transmission of The
Number System Digit
Disable UPC-E QV
Enable UPC-E With Supplements QW
Enable UPC-E Without Supplements QX
Disable Supplement Delimiter QY
Enable Supplement Delimiter QZ
Disable Mandatory Supplements for
UPC/ EAN
Enable Mandatory Supplements for
UPC / EAN
Disable UPC-E1 Symbology Q2
Enable All UPC Symbologies (UPC-A,
UPC-E0 and -E1)
Disable EAN RA
QT
QU
Q0
Q1
Q3
Enable EAN With Supplements RB
Enable EAN Without Supplements RC
Disable EAN Transmit of Number
System Digit
Enable EAN Transmit of Number
System Digit
Disable Transmit of The EAN Check
Digit
RD
RE
RF
B-14
Page 91

Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
B
Enable Transmit of The EAN Check
Digit
Disable Stacked EAN-13.
Stacked EAN-13 is not a true stacked
bar code function. When enabled, you
can read two EAN-13 (and/or UPC-A)
bar codes on one trigger pull. The
scanner will decode the two dissimilar
bar codes of EAN-13 or UPC-A, turn
off the laser, and transmit the labels
one after the other.
Note: These bar codes will not be
concatenated upon transmit.
Enable Stacked EAN-13 RI
Disable EAN-8 Transmission of Check
Character
Enable EAN-8 Transmission of Check
Character
Disable EAN-8 Transmission of The
Number System Digit
RG
RH
RJ
RK
RL
Enable EAN-8 Transmission of The
Number System Digit
Disable EAN-8 RN
Enable EAN-8 With Supplements RO
Enable EAN-8 Without Supplements RP
Disable Code 11 SA
Enable Code 11 With One Check Digit SB
Enable Code 11 With Two Check
Digits
RM
SC
B-15
Page 92

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
Disable Transmit of Code 11 Check
Digits
Enable Transmit of Code 11 Check
Digits
Set Minimum Length for Code 11.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Set Maximum Length for Code 11.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Disable Code 128 TA
Enable Code 128 TB
Set Minimum Length for Code 128.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Set Maximum Length for Code 128.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Disable Code 93 UA
SD
SE
SF
SG
TC
TD
Enable Code 93 UB
Standard Code 93 UC
Enable Full ASCII Code 93 UD
Set Minimum Length for Code 93.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Set Maximum Length for Code 93.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
UE
UF
B-16
Page 93
Configuration Command List
Command Syntax Bar Code
Disable Codabar VA
Enable Codabar VB
B
Disable Transmit of Codabar
Start/Stop Characters
Enable Transmit of Codabar
Start/Stop as Uppercase Characters
Set Minimum Length for Codabar.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Set Maximum Length for Codabar.
Two digit argument is the length (01-
32).
Enable Transmit of Codabar
Start/Stop as Lowercase Characters
Wand Emulation, Black High WA
Wand Emulation, White High WB
Wand Emulation, White High,
Quiescent High (Intermec)
VC
VD
VE
VF
VG
WC
Commands YA to YG are wand emulation transmission speeds in
inches per second
5 ips YA
10 ips YB
15 ips YC
20 ips YD
30 ips YE
B-17
Page 94

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Command Syntax Bar Code
50 ips YF
70 ips YG
Disable Control and Command Keys YI
Enable Command Key YJ
Enable Control Key YK
Reset to Primary Communications
Defaults
Dump Status, Serial Communications
Models Only.
Dump Version, Serial
Communications Models Only.
Scan and Transmit Label, Serial
Communications Models Only.
Requires a two digit argument.
Reset to Wand Emulation Defaults ZR
Intermec Default.
Wand emulation: white high, 50 ips.
Communications: 9600, e, 7 ,1
ZA
ZB
ZC
ZD
Z5
B-18
Page 95

G
Glossary
Page 96

Page 97
Glossary
This glossary contains definitions for terms specific to this manual
and the decoding laser scanners.
ASCII chart
A chart containing ASCII (American Standard Code for
Information Interchange) characters and their equivalent
hexadecimal numbers and control characters.
bar code
A printed machine-readable code that consists of parallel bars
of varied width and spacing.
bar code scanner
See scanner
baud rate
The rate at which information is transmitted from one device to
another. The number of bits, symbols, or digits per second that
are transmitted.
G
check digit
A bar coded character in some UPC symbols that follows the
bar coded information and serves as an error check.
Codabar
A numeric symbology most commonly used in libraries, blood
banks, and air parcel express applications, developed in 1972.
Code 2 of 5
A straightforward numeric symbology developed in the late
1960’s. It has been used for warehouse sorting systems,
photofinishing envelope identification, and for tracking
sequentially numbered airline tickets.
Code 39
The first alphanumeric symbology ever developed, used mostly
by the automobile and medical industries.
G-3
Page 98

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
Code 128
A very high density, alphanumeric symbology, introduced in
1981. It is a variable length, continuous code that employs
multiple element widths.
configuration
The current parameter settings that determine the
characteristics of the scanner.
decode
To translate information encoded in a bar code format.
EAN
European Article Numbering system (abbreviated as EAN) that
is a numeric superset of UPC. EAN has both a version that uses
8 digits and a version that uses 13 digits.
EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory. A
form of semiconductor memory in which the entire contents can
be erased with electrical signals and reprogrammed.
hand-held scanning
A scanning method that requires the scanner to be held by the
operator while scanning.
hands-free scanning
A scanning method that uses a special stand to hold the scanner
while scanning.
host terminal
The device used to receive and process information collected
through the scanner. Point-of-sale terminals, cash registers and
personal computers are examples of host terminals.
G-4
Page 99
Glossary
Interleaved 2 of 5
A high density, self checking, continuous numeric symbology,
used in the distribution industry.
keyboard wedge mode
An operating method for the scanner that lets it be connected to
a PC by attaching it to the keyboard. This mode is useful for
PCs that do not have an extra serial communication port.
laser redundancy
A feature that checks each scan by creating a duplicate scan and
comparing the information.
laser scanner
See Scanner
modulo 43
A character within a string of data that performs a
mathematical check to ensure the accuracy of the data.
G
number system digit
The character in some UPC symbols that precedes the bar coded
information.
OCIA
Optical Coupled Interface Adapter. A type of interface that
allows the scanner to transmit bar code data to cash registers.
OCR
Optical Character Recognition. A process in which a machine
processes scanned information in an optical character format.
G-5
Page 100

Decoding Laser Scanner User’s Manual
operating parameter
An adjustable operating feature. Examples of operating
parameters are bar code symbology and baud rate.
parameter
See operating parameter.
portable reader
A hand-held device that lets the user move around with the
scanner to scan items. The scanned information is stored in the
reader and transferred later to a terminal.
protocol
The type of communications between two devices (such as a
scanner and a host terminal) that controls data flow.
RS-232
A widely used standard interface for connections between data
communication equipment.
scan
To read a bar code by scanning with a laser scanner, that
converts optical information into electrical signals.
scannable
A bar code that can be successfully scanned and correctly
decoded.
scanner
Also Bar Code Scanner, Laser Scanner. A device that can
capture an image, such as a bar code, and convert the pattern
into a unique set of electrical signals that can be read by a host
terminal.
scanner holder
A plastic holder that is used to hold the scanner when it is not
being used, or when it is used with the Scanner Stand.
G-6
 Loading...
Loading...