Page 1

R
Intel® Celeron® Processor in the
478-Pin Package
Specification Update
October 2006
Notice: The Intel
defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are documented in this
Specification Update.
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package may contain design
Document Number: 290749-030
Page 2

R
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL
DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR
WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT,
COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining
applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
®
The Intel
deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
The Specification Update should be publicly available following the last shipment date for a period of time equal to the specific product’s warranty
period. Hardcopy Specification Updates will be available for one (1) year following End of Life (EOL). Web access will be available for three (3)
years following EOL.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Intel, Celeron Pentium, Intel Xeon, and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United
States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2003–2005, Intel Corporation
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to
2 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 3

R
Contents
Revision History..................................................................................................................4
Preface................................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes .............................................................................................8
General Information ..........................................................................................................14
Component Identification Information...............................................................................15
Errata.................................................................................................................................19
Specification Changes ......................................................................................................46
Specification Clarifications................................................................................................47
Documentation Changes ..................................................................................................50
§
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 3
Page 4
Revision History
Revision History
Version Description Date
-001 Initial release. May 2002
-002 Added erratum AC35. Added Documentation Changes AC4- AC5.
Updated processor identification information table.
-003 Added erratum AC37. Added Documentation Changes AC3- AC12. July 2002
-004 Updated with Intel® Celeron® Processor on 0.13 Micron Process and in
the 478-Pin Package. Added erratum AC38. Updated Erratum AC17.
Added Documentation Changes AC3- AC24.
-005 Added erratum AC39. Added Documentation Changes AC25- AC32. October 2002
-006 Added Erratum AC40. Added Spec Change V1. Added Documentation
Changes AC1- AC10. Updated processor identification information table.
-007 Added Erratum AC41. January 2003
-008 Added Erratum AC42. February 2003
-009 Updated Erratum AC41. Added erratum AC43.
Updated processor identification information table
-010 Added Specification clarification AC1. Updated processor identification
information table. Added Errata AC44 and AC45.
-011 Updated processor identification information table. Updated Erratum
AC40.
-012 Updated processor identification information table. Added D1 step
update.
-013 Added Erratum AC46, AC47 and AC49. Updated processor identification
information table.
-014 Added Erratum AC49, AC50 and AC51. Updated processor identification
information table.
-015 Updated Erratum AC51. Updated processor identification information
table.
-016 Added Errata AC52- AC56. March 2004
-017 Updated Erratum AC16. Added Erratum AC57. April 2004
-018 Removed Errata that were previously called AC54 & AC55. Added Errata
AC56 and AC57.
-019 Updated Erratum AC11 & added Erratum AC58. August 2004
-020
-021
-022
Added Errata AC59- AC61.
Added Erratum AC62- AC63
Updated processor identification information table. Added Erratum V64
R
June 2002
September
2002
November
2002
March 2003
May 2003
June 2003
June 2003
August 2003
September
2003
November
2003
June 2004
September
2004
October 2004
November
2004
4 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 5
Revision History
R
Version Description Date
-023
-024 • Added specification clarification AC1. April 2005
-025 • Changed the Errata ID tag from “V” to “AC”. Updated Summary table of
-026 • Updated erratum AC40. January 2006
-027 • Updated document numbers for Software Developers Manuals. March 2006
-028 • Added erratum AC67 and AC68. Updated Summary Table of Changes. April 2006
-029 • Added erratum AC69. Updated Summary Table of Changes. June 2006
-030 • Updated the names of the Software Developer Manuals. Updated
Added Erratum AC65
changes. Updated Microcode Update Guide and .PDB file guide.
Added Erratum AC66.
Summary Table of Changes. Updated Links.
December
October 2005
October 2006
2004
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 5
Page 6
Preface
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the documents listed in the
following Affected Documents/Related Documents table. It is a compilation of device and
document errata and specification clarifications and changes, and is intended for hardware system
manufacturers and for software developers of applications, operating system, and tools.
Information types defined in the Nomenclature section of this document are consolidated into this
update document and are no longer published in other documents. This document may also
contain information that has not been previously published.
Affected Documents
R
Document Title Document Number
Intel® Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package up to 1.80 GHz
Datasheet
Intel® Celeron® Processor on 0.13 Micron Process in the 478-Pin
Package
Related Documents
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 1: Basic Architecture
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference, A-M
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 2B: Instruction Set Reference, N-Z
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 3A: System Programming Guide
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
http://developer.intel.com/design/
celeron/datashts/251748.htm
http://developer.intel.com/support
/processors/celeron/478/
Document Title Document Number
253665
253666
253667
253668
253669
6 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 7

Preface
R
Nomenclature
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are differentiated by their
unique characteristics (e.g., core speed, L2 cache size, package type, etc.) as described in the
processor identification information table. Care should be taken to read all notes associated with
each S-Spec number
®
Errata are design defects or errors. Errata may cause the Intel
package behavior to deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be
used with any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are present
on all devices.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications. These changes
will be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further highlight a
specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will be incorporated in
the next release of the specifications.
Celeron® processor in the 478-pn
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current published
specifications. These changes will be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 7
Page 8

Summary Tables of Changes
Summary Tables of Changes
The following table indicates the Specification Changes, Errata, Specification Clarifications, or
Documentation Changes that apply to the listed component steppings. Intel intends to fix some of
the errata in a future stepping of the component, and to account for the other outstanding issues
through documentation or Specification Changes as noted. This table uses the following
notations:
Codes Used in Summary Table
Stepping
X: Erratum, Specification Change or Clarification that applies
to this stepping.
R
(No mark) or (Blank Box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification
Status
Doc: Document change or update that will be implemented.
PlanFix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
NoFix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
PKG: This column refers to errata on the Celeron processor in
AP: APIC related erratum.
Shaded: This item is either new or modified from the previous
change does not apply to listed stepping.
product.
the 478-pin package substrate
version of the document.
8 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 9

Summary Tables of Changes
R
Note: Each Specification Update item is prefixed with a capital letter to distinguish the product. The key
below details the letters that are used in Intel’s microprocessor Specification Updates:
A = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 7000 sequence
B = Mobile Intel ® Pentium ® II processor
C = Intel ® Celeron ® processor
E = Intel ® Pentium ® III processor
F = Intel® Pentium® processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Pentium® D processor
G = Intel ® Pentium ® III Xeon™ processor
H = Mobile Intel ® Celeron ® processor at 466/433/400/366/333/300 and 266 MHz
J = 64-bit Intel® Xeon™ processor MP with 1MB L2 Cache
K = Mobile Intel ® Pentium ® III processor
L = Intel ® Celeron ® D processor
M = Mobile Intel ® Celeron ® processor
N = Intel ® Pentium ® 4 processor
O = Intel ® Xeon™ processor MP
P = Intel ® Xeon™ processor
Q = Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor supporting Hyper-Threading Technology on 90-
nm process technology
R = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor on 90 nm process
S = 64-bit Intel® Xeon™ processor with 800 MHz system bus (1 MB and 2 MB L2
cache versions)
T = Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M
V = Mobile Intel® Celeron® processor on .13 Micron Process in Micro-FCPGA
Package
W= Intel® Celeron® M processor
X = Intel® Pentium® M processor on 90nm process with 2-MB L2 Cache
Y = Intel® Pentium® M processor
Z = Mobile Intel ® Pentium ® 4 processor with 533 MHz system bus
AA = Intel® Pentium® processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Pentium® D processor on
65nm
AB = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor on 65 nm process
AC = Intel® Celeron® processor in 478 Pin Package
AD = Intel® Celeron® D processor on 65nm process
AE = Intel
®
CoreTM Duo Processor and Intel® CoreTM Solo processor on 65nm process
AF = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor LV
AG = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5100 Series
AH = Intel® Core™2 Duo mobile processor
AI = Intel® Core™2 Extreme Processor X6800Δ and Intel® Core™2 Duo Desktop
Processor E6000Δ Sequence
AL = Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 7100 Series
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 Plans ERRATA
AC1 X X X NoFix
AC2 X X X NoFix
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 9
I/O restart in SMM may fail after simultaneous machine check
exception (MCE)
MCA registers may contain invalid information if RESET#
occurs and PWRGOOD is not held asserted
Page 10

Summary Tables of Changes
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 Plans ERRATA
R
AC3 X Fixed
AC4 X X X NoFix Transaction is not retried after BINIT#
AC5 X X X NoFix Invalid opcode 0FFFh requires a ModRM byte
AC6 X X X NoFix
AC7 X X X NoFix
AC8 X X X NoFix
AC9 X X X NoFix
AC10 X Fixed Writing a performance counter may result in incorrect value
AC11 X X X NoFix IA32_MC0_STATUS register overflow bit not set correctly
AC12 X Fixed
AC13 X NoFix
AC14 X NoFix
AC15 X X X NoFix Debug mechanisms may not function as expected
AC16 X X X NoFix
AC17 X Fixed
AC18 X X X NoFix
AC19 X Fixed
AC20 X X X NoFix EMON event counting of x87 loads may not work as expected
AC21 X Fixed
AC22 X Fixed
AC23 X X X PlanFix
AC24 X X X PlanFix
AC25 X Fixed
AC26 X PlanFix Buffer on resistance may exceed specification
AC27 X X X NoFix
Uncacheable (UC) code in same line as write back (WB) data
may lead to data corruption
FSW may not be completely restored after page fault on
FRSTOR or FLDENV instructions
The processor flags #PF instead of #AC on an unlocked
CMPXCHG8B instruction
When in no-fill mode the memory type of large pages are
incorrectly forced to uncacheable
Processor may hang due to speculative page walks to nonexistent system memory
Performance counter may contain incorrect value after being
stopped
MCA error code field in IA32_MC0_STATUS register may
become out of sync with the rest of the register
The IA32_MC1_STATUS register may contain incorrect
information for correctable errors
Machine check architecture error reporting and recovery may
not work as expected
Processor may timeout waiting for a device to respond after
~0.67 seconds
Cascading of performance counters does not work correctly
when forced overflow is enabled
IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR ADDRESS VALID bit may be set
when no valid address is available
Software controlled clock modulation using a 12.5% or 25%
duty cycle may cause the processor to hang
SQRTPD and SQRTSD may return QnaN indefinite instead of
negative zero
Bus Invalidate Line requests that return unexpected data may
result in L1 cache corruption
Write Combining (WC) load may result in unintended address
on system bus
Incorrect data may be returned when page tables are in Write
Combining (WC) memory space
Processor issues inconsistent transaction size attributes for
locked operation
10 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 11
Summary Tables of Changes
R
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 Plans ERRATA
AC28 X Fixed
AC29 X Fixed Processor may hang when resuming from Deep Sleep state
AC30 X X X NoFix
AC31 X X X NoFix
AC32 X X X NoFix
AC33 X Fixed
AC34 X X X NoFix
AC35 X Fixed
AC36 X Fixed L2 cache may contain stale data in the Exclusive state
AC37 X X X NoFix
AC38
S
AC39 X Fixed CPUID Returns Incorrect Number of ITLB Entries
AC40 X X X NoFix
AC41 X Fixed
AC42 X X NoFix
AC43 X Fixed
AC44 X X Fixed
X X X NoFix
Multiple accesses to the same S-state L2 cache line and ECC
error combination may result in loss of cache coherency
When the processor is in the System Management Mode
(SMM), debug registers may be fully writeable
Associated counting logic must be configured when using
Event Selection Control (ESCR) MSR
IA32_MC0_ADDR and IA32_MC0_MISC registers will contain
invalid or stale data following a Data, Address, or Response
Parity Error
CR2 may be incorrect or an incorrect page fault error code
may be pushed onto stack after execution of an LSS
instruction
System may hang if a fatal cache error causes Bus Write Line
(BWL) transaction to occur to the same cache line address as
an outstanding Bus Read Line (BRL) or Bus Read-Invalidate
Line (BRIL)
Processor Does not Flag #GP on Non-zero Write to Certain
MSRs
Simultaneous assertion of A20M# and INIT# may result in
incorrect data fetch
Glitches on Address and Data Strobe Signals May Cause
System Shutdown
A Write to an APIC Register Sometimes May Appear to Have
Not Occurred
Store to Load Data Forwarding may Result in Switched Data
Bytes
Parity Error in the L1 Cache may Cause the Processor to
Hang
The TCK Input in the Test Access Port (TAP) is Sensitive to
Low Clock Edge Rates and Prone to Noise Coupling Onto
TCK's Rising or Falling Edges
Re-mapping the APIC base address to a value less than or
equal to 0xDC001000 may cause IO and Special Cycle failure
AC45 X X Fixed Erroneous BIST result found in EAX register after reset
AC46 X X X NoFix
AC47 X X X NoFix
AC48 X X X NoFix
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 11
The State of the Resume Flag (RF Flag) in a Task-State
Segment (TSS) May be Incorrect
Changes to CR3 Register do not Fence Pending Instruction
Page Walks
Processor Provides a 4-Byte Store Unlock After an 8-Byte
Load Lock
Page 12
Summary Tables of Changes
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 Plans ERRATA
R
AC49 X X X NoFix
AC50 X X X NoFix
AC51 X X X NoFix
AC52 X X NoFix
AC53 X X PlanFix
AC54 X X NoFix
AC55 X X X NoFix xAPIC May Not Report Some Illegal Vector Errors
AC56 X PlanFix
AC57 X X X NoFix
AC58 X X NoFix
AC59 X X X No Fix
AC60 X X No Fix
AC61 X PlanFix
AC62 X X X NoFix
AC63 X X X PlanFix
AC64 X X X NoFix
AC65 X X X NoFix
AC66 X X X NoFix
AC67 X X X NoFix
AC68 X X X NoFix
System Bus Interrupt Messages Without Data Which Receive
a HardFailure Response May Hang the Processor
Memory Type of the Load Lock Different from its
Corresponding Store Unlock
A 16-bit Address Wrap Resulting from a Near Branch (Jump or
Call) May Cause an Incorrect Address to Be Reported to the
#GP Exception Handler
ITP Cannot Continue Single Step Execution after the First
Breakpoint
PWRGOOD and TAP Signals Maximum Input Hysteresis
Higher Than Specified
Incorrect Debug Exception (#DB) May Occur When a Data
Breakpoint is set on an FP Instruction
A Timing Marginality in the Instruction Decoder Unit May
Cause an Unpredictable Application Behavior and/or System
Hang
Memory Aliasing of Pages as Uncacheable Memory Type and
Write Back (WB) May Hang the System
Using STPCLK and Executing Code From Very Slow Memory
Could Lead to a System Hang
Machine Check Exceptions May not Update Last-Exception
Record MSRs (LERs)
Stores to Page Tables May Not Be Visible to Pagewalks for
Subsequent Loads Without Serializing or Invalidating the Page
Table Entry
A Timing Marginality in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) May
Cause Indeterminate Behavior
With TF (Trap Flag) Asserted, FP Instruction That Triggers an
Unmasked FP Exception May Take Single Step Trap Before
Retirement of Instruction
BTS(Branch Trace Store) and PEBS(Precise Event Based
Sampling) May Update Memory outside the BTS/PEBS Buffer
Memory Ordering Failure May Occur with Snoop Filtering
Third Party Agents after Issuing and Completing a BWIL (Bus
Write Invalidate Line) or BLW (Bus Locked Write) Transaction
Control Register 2 (CR2) Can be Updated during a REP
MOVS/STOS Instruction with Fast Strings Enabled
Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is
Pending May Cause an Unexpected Interrupt
Using 2M/4M Pages When A20M# Is Asserted May Result in
Incorrect Address Translations
Writing Shared Unaligned Data that Crosses a Cache Line
without Proper Semaphores or Barriers May Expose a
Memory Ordering Issue
12 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 13
Summary Tables of Changes
R
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 Plans ERRATA
AC69 X X X NoFix
Debug Status Register (DR6) Breakpoint Condition Detected
Flags May be set Incorrectly
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 SPECIFICATION CHANGES
No update for this Month
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS
No Update for this month.
NO. E0 nC1 nD1 DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
Refer to Documentation Changes section
§
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 13
Page 14
General Information
©
©
f
f
General Information
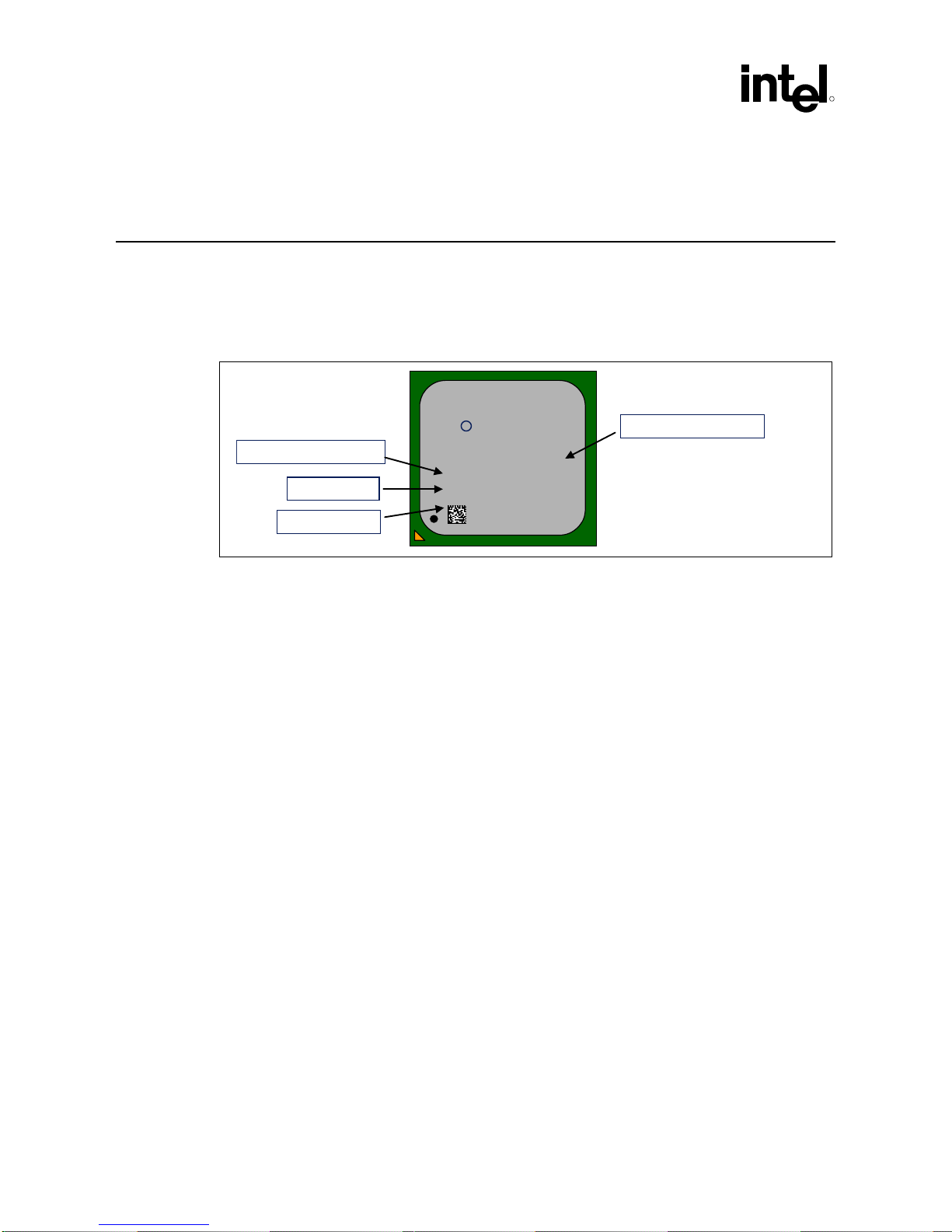
This section contains top marking information for the Intel® Celeron® processor in the 478-pn
package.
®
Figure 1. Example Markings for the Intel
in the 478-Pin Package
Celeron® Processor on 0.13 Micron Process and/or
R
S-
Spec/Country o
Spec/Country o
FPO
FPO
2-
D Matrix Mark
D Matrix Mark
m
‘03
i
Celeron®
S-
Assy
Assy
-
-
2-
2A GHZ/512/400/1.50V
2 GHZ/128/400
SYYYY XXXXXX
SYYYY XXXXXX
FFFFFFFF-NNNN
FFFFFFFF
i
-
m
‘01
ATPO LOT N
NNNN
Frequency/Cache/Bus
Frequency/Cache/Bus
§
14 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 15
Component Identification Information
R
Component Identification Information
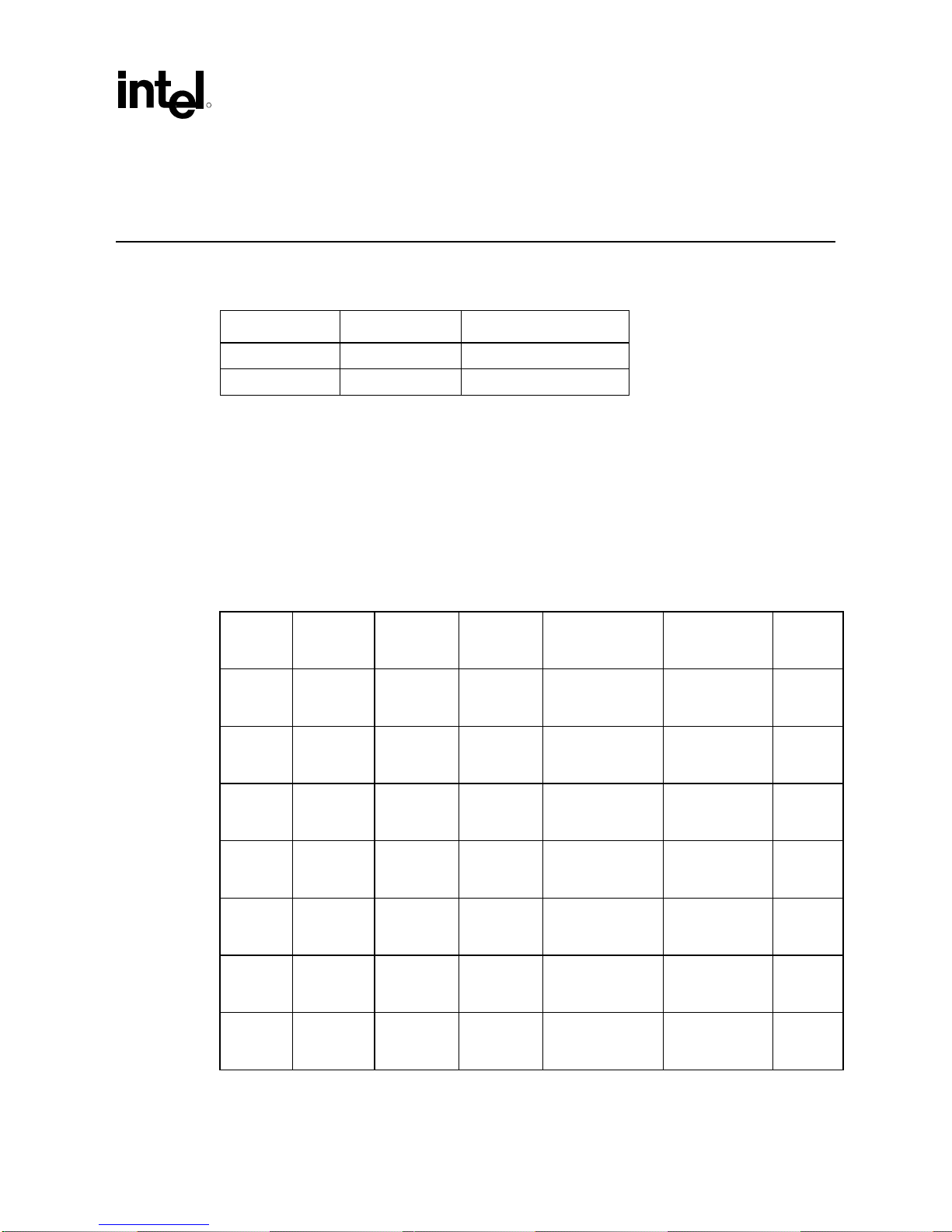
The Intel® Celeron® processor in the 478-pn package processor may be identified by the
following values.
Family1 Model2 Brand3
1111b 0001b 00001010b
1111b 0010b 00001010b
NOTES:
1. The Family corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [11:8] of the EAX register
after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of the
Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
2. The Model corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [7:4] of the EAX register after
the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the Device ID
register accessible through Boundary Scan.
3. The Brand ID corresponds to bits [7:0] of the EBX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a
1 in the EAX register.
®
Table 1. Intel
Identification Information
S-Spec
SL69Z E0 128K 0F13h 1.70 GHz/
SL68C E0 128K 0F13h 1.70 GHz/
SL6A2 E0 128K 0F13h 1.80 GHz/
SL68D E0 128K 0F13h 1.80 GHz/
SL6SW C1 128K 0F27h 2 GHz/
SL6LC C1 128K 0F27h 2 GHz/
SL6HY C1 128K 0F27h 2 GHz/
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Processor
Core
Stepping
L2 Cache
Size
(bytes)
Processor
Signature Speed Core/Bus
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
Package and
Revision Notes
FC-PGA2
35.0 mm, Rev
02
FC-PGA2
35.0 mm, Rev
02
FC-PGA2
35.0 mm, Rev
02
FC-PGA2
35.0 mm, Rev
02
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
2, 4, 8
1, 2
1
2, 3
3
2, 4
4
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 15
Page 16

Component Identification Information
R
Table 1. Intel
Identification Information
S-Spec
SL6RV C1 128K 0F27h 2 GHz/
SL6VR D1 128K 0F29h 2 GHz/
SL6VY D1 128K 0F29h 2 GHz/
SL6RT C1 128K 0F27h 2.10 GHz/
SL6RS C1 128K 0F27h 2.10 GHz/
SL6VS D1 128K 0F29h 2.10 GHz/
SL6SY C1 128K 0F27h 2.10 GHz/
SL6VZ D1 128K 0F29h 2.10 GHz/
SL6RT C1 128K 0F27h 2.10 GHz/
SL6LB C1 128K 0F27h 2.20 GHz/
SL6RW C1 128K 0F27h 2.20 GHz/
SL6SX C1 128K 0F27h 2.20 GHz/
SL6LB C1 128K 0F27h 2.20 GHz/
SL6VT D1 128K 0F29h 2.20 GHz/
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Processor
Core
Stepping
L2 Cache
Size
(bytes)
Processor
Signature Speed Core/Bus
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
Package and
Revision Notes
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
4, 8, 9
4, 8, 9
2, 4, 8
5, 8, 10
5, 8, 9
2, 5, 8
2, 5, 8
2, 5, 8
6, 8, 9
2, 6, 8
6, 8, 9
2, 5
2, 6
6, 8
16 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 17

Component Identification Information
R
Table 1. Intel
Identification Information
S-Spec
SL6W2 D1 128K 0F29h 2.20 GHz/
SL6XJ C1 128K 0F27h 2.30 GHz/
SL6WC D1 128K 0F29h 2.30 GHz/
SL6WD D1 128K 0F29h 2.30 GHz/
SL6T2 C1 128K 0F27h 2.30 GHz/
SL6T5 C1 128K 0F27h 2.30 GHz/
SL6VU C1 128K 0F27h 2.40 GHz/
SL6W4 D1 128K 0F29h 2.40 GHz/
SL6XG C1 128K 0F27h 2.40 GHz/
SL6V2 C1 128K 0F27h 2.40 GHz/
SL6VU D1 128K 0F29h 2.40 GHz/
SL6ZY D1 128K 0F29h 2.50 GHz/
SL72B D1 128K 0F29h 2.50 GHz/
SL6W5 C1 128K 0F27h 2.60 GHz/
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Processor
Core
Stepping
L2 Cache
Size
(bytes)
Processor
Signature Speed Core/Bus
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
Package and
Revision Notes
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
2, 6, 8
6, 8, 9
2, 6, 8
2, 6, 8
2, 7, 8
7, 8, 9
2, 8, 11
2, 8, 11
6, 8
2, 6
7, 8
7, 8
7, 8
8
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 17
Page 18

Component Identification Information
R
Table 1. Intel
Identification Information
S-Spec
SL6VV C1 128K 0F27h 2.60 GHz/
SL77U D1 128K 0F29h 2.70 GHz/
SL77S D1 128K 0F29h 2.70 GHz/
SL77T D1 128K 0F29h 2.80 GHz/
SL77V D1 128K 0F29h 2.80 GHz/
SL7EZ D1 128K 0F29h 1.60GHz/400MHz
SL7RU D1 128K 0F29h 1.80GHz/400MHz
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Processor
Core
Stepping
L2 Cache
Size
(bytes)
Processor
Signature Speed Core/Bus
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
400 MHz
Package and
Revision Notes
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
FC-PGA2
31.0 mm , rev
1.0
31.0 mm FC,
Rev 1.0
31.0 mm FC,
Rev 1.0
8, 11
2, 8
8
8, 9
2, 8
2,8
2,8
NOTES:
1. This processor has maximum Tcase of 76 °C
2. This is a boxed processor with an unattached fan heatsink.
3. This processor has maximum Tcase of 77 °C.
4. This processor has maximum Tcase of 68 °C
5. This processor has maximum Tcase of 69 °C
6. This processor has maximum Tcase of 70 °C
7. This processor has maximum Tcase of 71 °C
8. This part has Multiple VID
9. Some of these processors are offered as boxed processors with an unattached fan heatsink
10. This is a Desktop product only
11. This processor has maximum Tcase of 72 °C
§
18 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 19

Errata
R
Errata
AC1. I/O Restart in SMM May Fail after Simultaneous Machine Check Exception
(MCE)
Problem: If an I/O instruction (IN, INS, REP INS, OUT, OUTS, or REP OUTS) is being executed, and if
the data for this instruction becomes corrupted, the processor will signal a Machine Check
Exception (MCE). If the instruction is directed at a device that is powered down, the processor
may also receive an assertion of SMI#. Since MCEs have higher priority, the processor will call
the MCE handler, and the SMI# assertion will remain pending. However, upon attempting to
execute the first instruction of the MCE handler, the SMI# will be recognized and the processor
will attempt to execute the SMM handler. If the SMM handler is completed successfully, it will
attempt to restart the I/O instruction, but will not have the correct machine state, due to the call to
the MCE handler.
Implication: A simultaneous MCE and SMI# assertion may occur for one of the I/O instructions above. The
SMM handler may attempt to restart such an I/O instruction, but will have an incorrect state due
to the MCE handler call, leading to failure of the restart and shutdown of the processor.
Workaround: If a system implementation must support both SMM and board I/O restart, the first thing the
SMM handler code should do is check for a pending MCE. If there is an MCE pending, the SMM
handler should immediately exit via an RSM instruction and allow the MCE handler to execute. If
there is no MCE pending, the SMM handler may proceed with its normal operation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC2. MCA Registers May Contain Invalid Information If RESET# Occurs and
PWRGOOD Is Not Held Asserted
Problem: This erratum can occur as a result either of the following events:
• PWRGOOD is de-asserted during a RESET# assertion causing internal glitches that may
result in the possibility that the MCA registers latch invalid information.
• Or, during a reset sequence if the processor’s power remains valid regardless of the state of
PWRGOOD, and RESET# is re-asserted before the processor has cleared the MCA registers,
the processor will begin the reset process again but may not clear these registers.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the information in the MCA registers may not be reliable.
Workaround: Ensure that PWRGOOD remains asserted throughout any RESET# assertion and that RESET# is
not re-asserted while PWRGOOD is de-asserted.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 19
Page 20

Errata
AC3. Uncacheable (UC) Code in Same Line As Write Back (WB) Data May Lead to
Data Corruption
Problem: When both code (being accessed as UC or WC) and data (being accessed as WB) are aliased into
the same cache line, the UC fetch will cause the processor to self-snoop and generate an implicit
writeback. The data supplied by this implicit writeback may be corrupted due to the way the
processor handles self-modifying code.
Implication: UC or WC code located in the same cache line as WB data may lead to data corruption.
Workaround: UC or WC code should not be located in the same physical 64-byte cache line as any location that
is being stored to with WB data
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC4. Transaction Is Not Retried after BINIT#
Problem: If the first transaction of a locked sequence receives a HITM# and DEFER# during the snoop
phase it should be retried and the locked sequence restarted. However, if BINIT# is also asserted
during this transaction, it will not be retried.
R
Implication: When this erratum occurs, locked transactions will unexpectedly not be retried.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC5. Invalid Opcode 0FFFh Requires a ModRM Byte
Problem: Some invalid opcodes require a ModRM byte (or other following bytes), while others do not. The
invalid opcode 0FFFh did not require a ModRM byte in previous generation Intel® architecture
processors, but does in the Intel® Pentium® 4 processor.
Implication: The use of an invalid opcode 0FFFh without the ModRM byte may result in a page or limit fault
on the Pentium 4 processor.
Workaround: Use a ModRM byte with invalid 0FFFh opcode.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
20 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 21

Errata
R
AC6. FSW May Not Be Completely Restored after Page Fault on FRSTOR or
FLDENV Instructions
Problem: If the FPU operating environment or FPU state (operating environment and register stack) being
loaded by an FLDENV or FRSTOR instruction wraps around a 64-Kbyte or 4-Gbyte boundary
and a page fault (#PF) or segment limit fault (#GP or #SS) occurs on the instruction near the wrap
boundary, the upper byte of the FPU status word (FSW) might not be restored. If the fault handler
does not restart program execution at the faulting instruction, stale data may exist in the FSW.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, stale data will exist in the FSW.
Workaround: Ensure that the FPU operating environment and FPU state do not cross 64Kbyte or 4Gbyte
boundaries. Alternately, ensure that the page fault handler restarts program execution at the
faulting instruction after correcting the paging problem.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC7. The Processor Flags #PF Instead of #AC on an Unlocked CMPXCHG8B
Instruction
Problem: If a data page fault (#PF) and alignment check fault (#AC) both occur for an unlocked
CMPXCHG8B instruction, then #PF will be flagged.
Implication: Software that depends #AC before #PF will be affected since #PF is flagged in this case.
Workaround: Workaround: Remove the software’s dependency on the fact that #AC has precedence over #PF.
Alternately, reload the page in the page fault handler and then restart the faulting instruction.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC8. When in No-Fill Mode the Memory Type of Large Pages Are Incorrectly
Forced to Uncacheable
Problem: When the processor is operating in No-Fill Mode (CR0.CD=1), the paging hardware incorrectly
forces the memory type of large (PSE-4M and PAE-2M) pages to uncacheable (UC) memory type
regardless of the MTRR settings. By forcing the memory type of these pages to UC, load
operations, which should hit valid data in the L1 cache, are forced to load the data from system
memory. Some applications will lose the performance advantage associated with the caching
permitted by other memory types
Implication: This erratum may result in some performance degradation when using no-fill mode with large
pages.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 21
Page 22

Errata
AC9. Processor May Hang Due to Speculative Page Walks to Non-Existent
System Memory
Problem: A load operation that misses the Data Translation Lookaside Buffer (DTLB) will result in a page-
walk. If the page-walk loads the Page Directory Entry (PDE) from cacheable memory and that
PDE load returns data that points to a valid Page Table Entry (PTE) in uncacheable memory the
processor will access the address referenced by the PTE. If the address referenced does not exist
the processor will hang with no response from system memory.
Implication: Processor may hang due to speculative page walks to non-existent system memory.
Workaround: Page directories and page tables in UC memory space which are marked valid must point to
physical addresses that will return a data response to the processor.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC10. Writing a Performance Counter May Result in Incorrect Value
R
Problem: When a performance counter is written and the event counter for the event being monitored is
non-zero, the performance counter will be incremented by the value on that event counter.
Because the upper eight bits of the performance counter are not written at the same time as the
lower 32 bits, the increment due to the non-zero event counter may cause a carry to the upper bits
such that the performance counter contains a value about four billion (232) higher than what was
written.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the performance counter will contain a different value from that which
was written.
Workaround: If the performance counter is set to select a null event and the counter configuration and control
register (CCCR) for that counter has its compare bit set to zero, before the performance counter is
written, this erratum will not occur. Since the lower 32 bits will always be correct, event counting
which does not exceed 232 events will not be affected.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC11. IA32_MC0_STATUS Register Overflow Bit Not Set Correctly
Problem: The Overflow Error bit (bit 62) in the IA32_MC0_STATUS register indicates, when set, that a
machine check error occurred while the results of a previous error were still in the error reporting
bank (i.e. the valid bit was set when the new error occurred). In the case of this erratum, if an
uncorrectable error is logged in the error-reporting bank and another error occurs, the overflow bit
will not be set
Implication: When this erratum occurs the overflow bit will not be set.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
22 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 23

Errata
R
AC12. Performance Counter May Contain Incorrect Value after Being Stopped
Problem: If a performance counter is stopped on the precise internal clock cycle where the intermediate
carry from the lower 32 bits of the counter to the upper eight bits occurs, the intermediate carry is
lost.
32
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the performance counter will contain a value about 4 billion (2
) less
than it should.
Workaround: Since this erratum does not occur if the performance counters are read when running, a possible
workaround is to read the counter before stopping it. Since the lower 32 bits will always be
correct, event counting which does not exceed 2
32
events will not be affected.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC13. MCA Error Code Field in IA32_MC0_STATUS Register May become out of
Sync with the Rest of the Register
Problem: The MCA Error Code field of the IA32_MC0_STATUS register gets written by a different
mechanism than the rest of the register. For uncorrectable errors, the other fields in the
IA32_MC0_STATUS register are only updated by the first error. Any subsequent errors cause the
Overflow Error bit to be asserted until this register is cleared. Because of this erratum, any further
errors that are detected will update the MCA Error Code field without updating the rest of the
register, thereby leaving the IA32_MC0_STATUS register with stale information.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the IA32_MC0_STATUS register contains stale information.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC14. The IA32_MC1_STATUS Register May Contain Incorrect Information for
Correctable Errors
Problem: When a speculative load operation hits the L2 cache and receives a correctable error, the
IA32_MC1_STATUS register may be updated with incorrect information. The
IA32_MC1_STATUS register should not be updated for speculative loads.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the IA32_MC1_STATUS register will contain incorrect information
for correctable errors.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 23
Page 24

Errata
AC15. Debug Mechanisms May Not Function As Expected
Problem: Certain debug mechanisms may not function as expected on the processor. The cases are as
follows:
• When the following conditions occur: 1) An FLD instruction signals a stack overflow or
underflow, 2) the FLD instruction splits a page-boundary or a 64-byte cache line boundary,
3) the instruction matches a Debug Register on the high page or cache line respectively, and
4) the FLD has a stack fault and a memory fault on a split access, the processor will only
signal the stack fault and the debug exception will not be taken.
• When a data breakpoint is set on the ninth and/or tenth byte(s) of a floating point store using
the Extended Real data type, and an unmasked floating point exception occurs on the store,
the break point will not be captured.
• When any instruction has multiple debug register matches, and any one of those debug
registers is enabled in DR7, all of the matches should be reported in DR6 when the processor
goes to the debug handler. This is not true during a REP instruction. As an example, during
execution of a REP MOVSW instruction the first iteration a load matches DR0 and DR2 and
sets DR6 as FFFF0FF5h. On a subsequent iteration of the instruction, a load matches only
DR0. The DR6 register is expected to still contain FFFF0FF5h, but the processor will update
DR6 to FFFF0FF1h.
R
• A data breakpoint that is set on a load to uncacheable memory may be ignored due to an
internal segment register access conflict. In this case the system will continue to execute
instructions, bypassing the intended breakpoint. Avoiding having instructions that access
segment descriptor registers e.g., LGDT, LIDT close to the UC load, and avoiding serialized
instructions before the UC load will reduce the occurrence of this erratum.
Implication: Certain debug mechanisms do not function as expected on the processor.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
24 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 25

Errata
R
AC16. Machine Check Architecture Error Reporting and Recovery May Not Work
As Expected
Problem: When the processor detects errors it should attempt to report and/or recover from the error. In the
situations described below, the processor does not report and/or recover from the error(s) as
intended.
• When a transaction is deferred during the snoop phase and subsequently receives a Hard
Failure response, the transaction should be removed from the bus queue so that the processor
may proceed. Instead, the transaction is not properly removed from the bus queue, the bus
queue is blocked, and the processor will hang.
• When a hardware prefetch results in an uncorrectable tag error in the L2 cache,
IA32_MC0_STATUS.UNCOR and IA32_MC0_STATUS.PCC are set but no Machine
Check Exception (MCE) is signaled. No data loss or corruption occurs because the data being
prefetched has not been used. If the data location with the uncorrectable tag error is
subsequently accessed, an MCE will occur. However, upon this MCE, or any other
subsequent MCE, the information for that error will not be logged because
IA32_MC0_STATUS.UNCOR has already been set and the MCA status registers will not
contain information about the error which caused the MCE assertion but instead will contain
information about the prefetch error event.
• When the reporting of errors is disabled for Machine Check Architecture (MCA) Bank 2 by
setting all IA32_MC2_CTL register bits to 0, uncorrectable errors should be logged in the
IA32_MC2_STATUS register but no machine-check exception should be generated.
Uncorrectable loads on bank 2, which would normally be logged in the
IA32_MC2_STATUS register, are not logged.
• When one half of a 64 byte instruction fetch from the L2 cache has an uncorrectable error
and the other 32 byte half of the same fetch from the L2 cache has a correctable error, the
processor will attempt to correct the correctable error but cannot proceed due to the
uncorrectable error. When this occurs the processor will hang.
• When an L1 cache parity error occurs, the cache controller logic should write the physical
address of the data memory location that produced that error into the IA32_MC1_ADDR
register. In some instances of a parity error on a load operation that hits the L1 cache,
however, the cache controller logic may write the physical address from a subsequent load or
store operation into the IA32_MC1_ADDR register.
• If an instruction fetch results in an uncorrectable error and there is also a debug breakpoint at
this address, the processor will livelock and the uncorrectable error will not be logged in the
machine check registers.
• The MCA Overflow bit should be set when an uncorrectable error resides within the register
bank (valid bit is already set) and any subsequent errors occur. The Overflow bit being set
indicates that more than one error has occurred. Because of this erratum, if any further errors
occur, the MCA Overflow bit will not be updated; thereby incorrectly indicating only one
error has been received.
Implication: The processor is unable to correctly report and/or recover from certain errors.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 25
Page 26

Errata
AC17. Processor May Timeout Waiting for a Device to Respond after 0.67
Seconds
Problem: The PCI 2.1 target initial latency specification allows two seconds for a device to respond during
initialization-time. The processor may timeout after only approximately 0.67 seconds. When the
processor times out it will hang with IERR# asserted. PCI devices that take longer than 0.67
seconds to initialize may not be initialized properly.
Implication: System may hang with IERR# asserted.
Workaround: Due to the long initialization time observed on some commercially available PCI cards, it may be
necessary to disable the timeout counter during the PCI initialization sequence. This can be
accomplished by temporarily setting Bit 5 of the MISC_ENABLES_MSR located at address
1A0H to 1. This model specific register (MSR) is software visible but should only be set for the
duration of the PCI initialization sequence. It is necessary to re-enable the timeout counter by
clearing this bit after completing the PCI initialization sequence. CAUTION: The processor's
Thermal Monitor feature may not function if the timeout counter is not re-enabled after
completing the PCI initialization.
After the system is fully initialized, this erratum may occur either when a PCI device is hot added
into the system or when a PCI device is transitioned from D3 cold. System software responsible
for completing the hot add and the power state transition from D3 cold should allow for a delay of
the target initial latency prior to initiating configuration accesses to the PCI device.
R
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC18. Cascading of Performance Counters Does Not Work Correctly When
Forced Overflow Is Enabled
Problem: The performance counters are organized into pairs. When the CASCADE bit of the Counter
Configuration Control Register (CCCR) is set, a counter that overflows will continue to count in
the other counter of the pair. The FORCE_OVF bit forces the counters to overflow on every nonzero increment. When the FORCE_OVF bit is set, the counter overflow bit will be set but the
counter no longer cascades.
Implication: The performance counters do not cascade when the FORCE_OVF bit is set.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
26 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 27

Errata
R
AC19. IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR ADDRESS VALID Bit May Be Set When No Valid
Address Is Available
Problem: The processor should only log the address for L1 parity errors in the IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR
if a valid address is available. If a valid address is not available, the ADDRESS VALID bit in the
IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR should not be set. In instances where an L1 parity error occurs and
the address is not available because the linear to physical address translation is not complete or an
internal resource conflict has occurred, the ADDRESS VALID bit is incorrectly set.
Implication: The ADDRESS VALID bit is set even though the address is not valid.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC20. EMON Event Counting of x87 Loads May Not Work As Expected
Problem: If a performance counter is set to count x87 loads and floating-point exceptions are unmasked, the
FPU Operand Data Pointer (FDP) may become corrupted.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the FPU Operand Data Pointer (FDP) may become corrupted.
Workaround: This erratum will not occur with floating point exceptions masked. If floating-point exceptions
are unmasked, then performance counting of x87 loads should be disabled.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC21. Software Controlled Clock Modulation Using a 12.5% or 25% Duty Cycle
May Cause the Processor to Hang
Problem: Processor clock modulation may be controlled via a processor register
(IA32_THERM_CONTROL). The On-Demand Clock Modulation Duty Cycle is controlled by
bits 3:1. If these bits are set to a duty cycle of 12.5% or 25%, the processor may hang while
attempting to execute a floating-point instruction. In this failure, the last instruction pointer (LIP)
is pointing to a floating-point instruction whose instruction bytes are in UC space and which takes
an exception 16 (floating point error exception). The processor stalls trying to fetch the bytes of
the faulting floating-point instruction and those following it. This processor hang is caused by
interactions between thermal control circuit and floating-point event handler.
Implication: The processor will go into a sleep state from which it fails to return.
Workaround: Use a duty cycle other than 12.5% or 25%.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 27
Page 28

Errata
AC22. SQRTPD and SQRTSD May Return QNaN Indefinite Instead of Negative
Zero
Problem: When DAZ mode is enabled, and a SQRTPD or SQRTSD instruction has a negative denormal
operand, the instruction will return a QNaN indefinite when the specified response should be a
negative zero.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the instruction will return a QNaN indefinite when a negative zero is
expected.
Workaround: Ensure that negative denormals are not used as operands to the SQRTPD or SQRTSD instructions
when DAZ mode is enabled. Software could enable FTZ mode to ensure that negative denormals
are not generated by computation prior to execution of a SQRTPD or SQRTSD instruction.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC23. Bus Invalidate Line Requests That Return Unexpected Data May Result in
L1 Cache Corruption
R
Problem: When a Bus Invalidate Line (BIL) request receives unexpected data from a deferred reply, and a
store operation write combines to the same address, there is a small window where the L0 is
corrupt, and loads can retire with this corrupted data. This erratum occurs in the following
scenario:
• A Read-For-Ownership (RFO) transaction is issued by the processor and hits a line in shared
state in the L1 cache.
• The RFO is then issued on the system bus as a 0 length Read-Invalidate (a BIL), since it
doesn't need data, just ownership of the cache line.
• This transaction is deferred by the chipset.
• At some later point, the chipset sends a deferred reply for this transaction with an implicit
write-back response. For this erratum to occur, no snoop of this cache line can be issued
between the BIL and the deferred reply.
• The processor issues a write-combining store to the same cache line while data is returning to
the processor. This store straddles an 8-byte boundary.
• Due to an internal boundary condition, a time window exists where the L1 cache contains
corrupt data which could be accessed by a load.
Implication: No known commercially available chipsets trigger the failure conditions.
Workaround: The chipset could issue a BIL (snoop) to the deferred processor to eliminate the failure
conditions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
28 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 29

Errata
R
AC24. Write Combining (WC) Load May Result in Unintended Address on System
Bus
Problem: When the processor performs a speculative write combining (WC) load, down the path of a
mispredicted branch, and the address happens to match a valid UnCacheable (UC) address
translation with the Data Translation Look-Aside Buffer, an unintended UnCacheable load
operation may be sent out on the system bus.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an unintended load may be sent on system bus. Intel has only
encountered this erratum during pre-silicon simulation.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC25. Incorrect Data May be Returned When Page Tables Are In Write Combining
(WC) Memory Space
Problem: If page directories and/or page tables are located in Write Combining (WC) memory, speculative
loads to cacheable memory may complete with incorrect data.
Implication: Cacheable loads to memory mapped using page tables located in write combining memory may
return incorrect data. Intel has not been able to reproduce this erratum with commercially
available software.
Workaround: Do not place page directories and/or page tables in WC memory.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC26. Buffer on Resistance May Exceed Specification
Problem: The datasheet specifies the resistance range for RON (Buffer on Resistance) for the AGTL+ and
Asynchronous GTL+ buffers as 5 to 11 Ω. Due to this erratum, RON may be as high as 13.11 Ω.
Implication: The RON value affects the voltage level of the signals when the buffer is driving the signal low.
A higher RON may adversely affect the system's ability to meet specifications such as VIL. As
the system design also affects margin to specification, designs may or may not have sufficient
margin to function properly with an increased RON. System designers should evaluate whether a
particular system is affected by this erratum. Designs that follow the recommendations in the
®
Pentium® 4 Processor and Intel® 850 Chipset Platform Design Guide are not expected to
Intel
be affected.
Workaround: No workaround is necessary for systems with margin sufficient to accept a higher RON.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 29
Page 30

Errata
AC27. Processor Issues Inconsistent Transaction Size Attributes for Locked
Operation
Problem: When the processor is in the Page Address Extension (PAE) mode and detects the need to set the
Access and/or Dirty bits in the page directory or page table entries, the processor sends an 8-byte
load lock onto the system bus. A subsequent 8-byte store unlock is expected, but instead a 4-byte
store unlock occurs. Correct data is provided since only the lower bytes change, however external
logic monitoring the data transfer may be expecting an 8-byte store unlock.
Implication: No known commercially available chipsets are affected by this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC28. Multiple Accesses to the Same S-State L2 Cache Line and ECC Error
Combination May Result in Loss of Cache Coherency
R
Problem: When a Read for Ownership (RFO) cycle has a 64-bit address match with an outstanding read hit
on a line in the L2 cache which is in the S-state AND that line contains an ECC error, the
processor should recycle the RFO until the ECC error is handled. Due to this erratum, the
processor does not recycle the RFO and attempts to service both the RFO and the read hit at the
same time.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, cache may become incoherent.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC29. Processor May Hang When Resuming from Deep Sleep State
Problem: When resuming from the Deep Sleep state the address strobe signals (ADSTB[1:0]#) may become
out of phase with respect to the system bus clock (BCLK).
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will hang.
Workaround: The system BIOS should prevent the processor from going to the Deep Sleep state.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
30 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 31

Errata
R
AC30. When the Processor Is in the System Management Mode (SMM), Debug
Registers May Be Fully Writeable
Problem: When in System Management Mode (SMM), the processor executes code and stores data in the
SMRAM space. When the processor is in this mode and writes are made to DR6 and DR7, the
processor should block writes to the reserved bit locations. Due to this erratum, the processor may
not block these writes. This may result in invalid data in the reserved bit locations.
Implication: Reserved bit locations within DR6 and DR7 may become invalid.
Workaround: Software may perform a read/modify/write when writing to DR6 and DR7 to ensure that the
values in the reserved bits are maintained.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC31. Associated Counting Logic Must Be Configured When Using Event
Selection Control (ESCR) MSR
Problem: ESCR MSRs allow software to select specific events to be counted, with each ESCR usually
associated with a pair of performance counters. ESCRs may also be used to qualify the detection
of at-retirement events that support precise-event-based sampling (PEBS). A number of
performance metrics that support PEBS require a 2nd ESCR to tag uops for the qualification of
at-retirement events. (The first ESCR is required to program the at-retirement event.) Counting is
enabled via counter configuration control registers (CCCR) while the event count is read from
one of the associated counters. When counting logic is configured for the subset of at-retirement
events that require a 2nd ESCR to tag uops, at least one of the CCCRs in the same group of the
2nd ESCR must be enabled.
Implication: If no CCCR/counter is enabled in a given group, the ESCR in that group that is programmed for
tagging uops will have no effect. Hence a subset of performance metrics that require a 2nd ESCR
for tagging uops may result in 0 count.
Workaround: Ensure that at least one CCCR/counter in the same group as the tagging ESCR is enabled for
those performance metrics that require two ESCRs and tagging uops for at-retirement counting.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC32. IA32_MC0_ADDR and IA32_MC0_MISC Registers Will Contain Invalid or
Stale Data Following a Data, Address, or Response Parity Error
Problem: If the processor experiences a data, address, or response parity error, the ADDRV and MISCV
bits of the IA32_MC0_STATUS register are set, but the IA32_MC0_ADDR and
IA32_MC0_MISC registers are not loaded with data regarding the error.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the IA32_MC0_ADDR and IA32_MC0_MISC registers will contain
invalid or stale data.
Workaround: Ignore any information in the IA32_MC0_ADDR and IA32_MC0_MISC registers after a data,
address or response parity error.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 31
Page 32

Errata
AC33. CR2 May Be Incorrect or an Incorrect Page Fault Error Code May Be
Pushed onto Stack after Execution of an LSS Instruction
Problem: Under certain timing conditions, the internal load of the selector portion of the LSS instruction
may complete with potentially incorrect speculative data before the load of the offset portion of
the address completes. The incorrect data is corrected before the completion of the LSS
instruction but the value of CR2 and the error code pushed on the stack are reflective of the
speculative state. Intel has not observed this erratum with commercially available software.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the contents of CR2 may be off by two, or an incorrect page fault error
code may be pushed onto the stack.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC34. ProSystem May Hang If a Fatal Cache Error Causes Bus Write Line (BWL)
Transaction to Occur to the Same Cache Line Address As an Outstanding
Bus Read Line (BRL) or Bus Read-Invalidate Line (BRIL)
R
Problem: A processor internal cache fatal data ECC error may cause the processor to issue a BWL
transaction to the same cache line address as an outstanding BRL or BRIL. As it is not typical
behavior for a single processor to have a BWL and a BRL/BRIL concurrently outstanding to the
same address, this may represent an unexpected scenario to system logic within the chipset.
Implication: The processor may not be able to fully execute the machine check handler in response to the fatal
cache error if system logic does not ensure forward progress on the system bus under this
scenario.
Workaround: System logic should ensure completion of the outstanding transactions. Note that during recovery
from a fatal data ECC error, memory image coherency of the BWL with respect to BRL/BRIL
transactions is not important. Forward progress is the primary requirement.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC35. Processor Does Not Flag #GP on Non-Zero Write to Certain MSRs
Problem: When a non-zero write occurs to the upper 32 bits of IA32_CR_SYSENTER_EIP or
IA32_CR_SYSENTER_ESP, the processor should indicate a general protection fault by flagging
#GP. Due to this erratum, the processor does not flag #GP.
Implication: The processor unexpectedly does not flag #GP on a non-zero write to the upper 32 bits of
IA32_CR_SYSENTER_EIP or IA32_CR_SYSENTER_ESP. No known commercially available
operating system has been identified to be affected by this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
32 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 33

Errata
R
AC36. L2 Cache May Contain Stale Data in the Exclusive State
Problem: If a cacheline (A) is in Modified (M) state in the write-combining (WC) buffers and in the Invalid
(I) state in the L2 cache and its adjacent sector (B) is in the Invalid (I) state and the following
scenario occurs:
1. A read to B misses in the L2 cache and allocates cacheline B and its associated second-sector
pre-fetch into an almost full bus queue,
2. A Bus Read Line (BRL) to cacheline B completes with HIT# and fills data in Shared (S)
state,
3. The bus queue full condition causes the prefetch to cacheline A to be cancelled, cacheline A
will remain M in the WC buffers and I in the L2 while cacheline B will be in the S state.
Then, if the further conditions occur:
4. Cacheline A is evicted from the WC Buffers to the bus queue which is still almost full,
5. A hardware prefetch Read for Ownership (RFO) to cacheline B, hits the S state in the L2 and
observes cacheline A in the I state, allocates both cachelines,
6. An RFO to cacheline A completes before the WC Buffers write modified data back, filling
the L2 with stale data,
7. The writeback from the WC Buffers completes leaving stale data, for cacheline A, in the
Exclusive (E) state in the L2 cache.
Implication: Stale data may be consumed leading to unpredictable program execution. Intel has not been able
to reproduce this erratum with commercial software.
Workaround: It is possible for BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC37. Simultaneous Assertion of A20M# and INIT# May Result in Incorrect Data
Fetch
Problem: If A20M# and INIT# are simultaneously asserted by software, followed by a data access to the
0xFFFFFXXX memory region, with A20M# still asserted, incorrect data will be accessed. With
A20M# asserted, an access to 0xFFFFFXXX should result in a load from physical address
0xFFEFFXXX. However, in the case of A20M# and INIT# being asserted together, the data load
will actually be from the physical address 0xFFFFFXXX. Code accesses are not affected by this
erratum
Implication: Processor may fetch incorrect data, resulting in BIOS failure.
Workaround: Deasserting and reasserting A20M# prior to the data access will workaround this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 33
Page 34

Errata
AC38. Glitches on Address or Data Strobe Signals May Cause System Shutdown
Problem: When a Machine Check Exception is generated due to a glitch on the address or data strobe
signals, the exception may be reported repeatedly, resulting in system shutdown.
Implication: If a glitch occurs on the address or data strobe signals, an operating system shutdown will occur if
Machine Check Exceptions (MCE) are enabled. IERR# assertion and shutdown will occur if
MCE is disabled.
Workaround: Correct design and implementation of the processor system bus will remove the possibility of this
failure.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC39. CPUID Instruction Returns Incorrect Number of ITLB Entries
Problem: When CPUID instruction is executed with EAX = 2 it should return a value of 51h in EAX[15:8]
to indicate that the Instruction Translation Lookaside Buffer (ITLB) has 128 entries. Due to this
erratum, the processor returns 50h (64 entries).
R
Implication: Software may incorrectly report the number of ITLB entries. Operation of the processor is not
affected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC40. A Write to an APIC Register Sometimes May Appear to Have Not Occurred
Problem: With respect to the retirement of instructions, stores to the uncacheable memory-based APIC
register space are handled in a non-synchronized way. For example if an instruction that masks
the interrupt flag, e.g. CLI, is executed soon after an uncacheable write to the Task Priority
Register (TPR) that lowers the APIC priority, the interrupt masking operation may take effect
before the actual priority has been lowered. This may cause interrupts whose priority is lower
than the initial TPR, but higher than the final TPR, to not be serviced until the interrupt enabled
flag is finally set, i.e. by STI instruction. Interrupts will remain pending and are not
lost.
Implication: In this example the processor may allow interrupts to be accepted but may delay their service.
Workaround: This non-synchronization can be avoided by issuing an APIC register read after the APIC register
write. This will force the store to the APIC register before any subsequent instructions are
executed. No commercial operating system is known to be impacted by this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
34 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 35

Errata
R
AC41. Store to Load Data Forwarding may Result in Switched Data Bytes
Problem: If in a short window after an instruction that updates a segment register has executed, but has not
yet retired, there is a load occurring to an address, that matches a recent previous store operation,
but the data size is smaller than the size of the store, the resulting data forwarded from the store to
the load may have some of the lower bytes switched.
Implication: If this erratum occurs, the processor may execute with incorrect data.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC42. Parity Error in the L1 Cache May Cause the Processor to Hang
Problem: If a locked operation accesses a line in the L1 cache that has a parity error, it is possible that the
processor may hang while trying to evict the line.
Implication:
If this erratum occurs, it may result in a system hang. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software
Workaround: None
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC43. The TCK Input in the Test Access Port (TAP) Is Sensitive to Low Clock
Edge Rates and Prone to Noise Coupling onto TCK's Rising or Falling
Edges
Problem: TCK is susceptible to double clocking when low amplitude noise occurs on TCK edge, while it is
crossing the receiver's transition region. TAP failures tend to increase with increases in
background system noise.
Implication: This only impacts JTAG/TAP accesses to the processor. Other bus accesses are not affected.
Workaround: To minimize the effects of this issue, reduce noise on the TCK-net at the processor relative to
ground, and position TCK relative to BCLK to minimize the TAP error rate. Decreasing rise
times to under 800 ps reduces the failure rate but does not stop all failures.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 35
Page 36

Errata
AC44. Re-Mapping the APIC Base Address to a Value Less Than or Equal to
0xDC001000 May Cause IO and Special Cycle Failure
Problem: Remapping the APIC base address from its default can cause conflicts with either I/O or special
cycle bus transactions.
Implication: Either I/O or special cycle bus transactions can be redirected to the APIC, instead of appearing on
the front-side bus.
Workaround: Use any APIC base addresses above 0xDC001000 as the relocation address.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC45. Erroneous BIST Result Found in EAX Register after Reset
Problem: The processor may show an erroneous BIST (built-in self test) result in the EAX register bit 0
after coming out of reset.
R
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an erroneous BIST failure will be reported in the EAX register bit 0,
however this failure can be ignored since it is not accurate.
Workaround: It is possible for BIOS to workaround this issue by masking off bit 0 in the EAX register where
BIST results are written.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC46. The State of the Resume Flag (RF Flag) in a Task-State Segment (TSS) May
Be Incorrect
Problem: After executing a JMP instruction to the next (or other) task through a hardware task switch, it is
possible for the state of the RF flag (in the EFLAGS register image) to be incorrect.
Implication: The RF flag is normally used for code breakpoint management during debug of an application. It
is not typically used during normal program execution. Code breakpoints or single step debug
behavior in the presence of hardware task switches, therefore, may be unpredictable as a result of
this erratum. This erratum has not been observed in commercially available software.
Workaround: None
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
36 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 37

Errata
R
AC47. Changes to CR3 Register Do Not Fence Pending Instruction Page Walks
Problem: When software writes to the CR3 register, it is expected that all previous/outstanding code, data
accesses and page walks are completed using the previous value in CR3 register. Due to this
erratum, it is possible that a pending instruction page walk is still in progress, resulting in an
access (to the PDE portion of the page table) that may be directed to an incorrect memory address.
Implication: The results of the access to the PDE will not be consumed by the processor so the return of
incorrect data is benign. However, the system may hang if the access to the PDE does not
complete with data (e.g. infinite number of retries).
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to have a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC48. Processor Provides a 4-Byte Store Unlock after an 8-Byte Load Lock
Problem: When the processor is in the Page Address Extension (PAE) mode and detects the need to set the
Access and/or Dirty bits in the page directory or page table entries, the processor sends an 8 byte
load lock onto the system bus. A subsequent 8 byte store unlock is expected, but instead a 4 byte
store unlock occurs. Correct data is provided since only the lower bytes change, however
external logic monitoring the data transfer may be expecting an 8 byte load lock.
Implication: No known commercially available chipsets are affected by this erratum.
Workaround: None identified at this time
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
AC49. System Bus Interrupt Messages without Data Which Receive a HardFailure
Response May Hang the Processor
Problem: When a system bus agent (processor or chipset) issues an interrupt transaction without data onto
the system bus and the transaction receives a HardFailure response, a potential processor hang can
occur. The processor, which generates an inter-processor interrupt (IPI) that receives the
HardFailure response, will still log the MCA error event cause as HardFailure, even if the APIC
causes a hang. Other processors, which are true targets of the IPI, will also hang on hardfailwithout-data, but will not record an MCA HardFailure event as the cause. If a HardFailure
response occurs on a system bus interrupt message with data, the APIC will complete the
operation so as not to hang the processor.
Implication: The processor may hang.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 37
Page 38

Errata
AC50. Memory Type of the Load Lock Different from Its Corresponding Store
Unlock
Problem: A use-once protocol is employed to ensure that the processor in a multi-agent system may access
data that is loaded into its cache on a Read-for-Ownership operation at least once before it is
snooped out by another agent. This protocol is necessary to avoid a multi-agent livelock scenario
in which the processor cannot gain ownership of a line and modify it before that data is snooped
out by another agent. In the case of this erratum, split load lock instructions incorrectly trigger the
use-once protocol. A load lock operation accesses data that splits across a page boundary with
both pages of WB memory type. The use-once protocol activates and the memory type for the
split halves get forced to UC. Since use-once does not apply to stores, the store unlock
instructions go out as WB memory type. The full sequence on the bus is: locked partial read (UC),
partial read (UC), partial write (WB), locked partial write (WB). The use-once protocol should
not be applied to load locks.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the memory type of the load lock will be different than the memory
type of the store unlock operation. This behavior (load locks and store unlocks having different
memory types) does not introduce any functional failures such as system hangs or memory
corruption.
R
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
AC51. A 16-bit Address Wrap Resulting from a Near Branch (Jump or Call) May
Cause an Incorrect Address to Be Reported to the #GP Exception Handler
Problem: If a 16-bit application executes a branch instruction that causes an address wrap to a target
address outside of the code segment, the address of the branch instruction should be provided to
the general protection exception handler. It is possible that, as a result of this erratum, that the
general protection handler may be called with the address of the branch target.
Implication: The 16-bit software environment which is affected by this erratum, will see that the address
reported by the exception handler points to the target of the branch, rather than the address of the
branch instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
AC52. ITP Cannot Continue Single Step Execution after the First Breakpoint
Problem: ITP will not continue in single step execution after the first software breakpoint. ITP is unable to
reset the Resume Flag (RF) bit in the EFLAGS Register.
Implication: The processor repeatedly breaks at the instruction breakpoint address instead of single stepping.
Workaround: Execution after the break will continue, if you manually clear DR7 bit 1 (Global Breakpoint
Enable).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
38 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 39

Errata
R
AC53. PWRGOOD and TAP Signals Maximum Input Hysteresis Higher Than
Specified
Problem: The maximum input hysteresis for the PWRGOOD and TAP input signals is specified at 350 mV.
The actual value could be as high as 800 mV.
Implication: The PWRGOOD and TAP inputs may switch at different levels than previously documented
specifications. Intel has not observed any issues in validation or simulation as a result of this
erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC54. Incorrect Debug Exception (#DB) May Occur When a Data Breakpoint Is Set
on an FP Instruction
Problem: The default Microcode Floating Point Event Handler routine executes a series of loads to obtain
data about the FP instruction that is causing the FP event. If a data breakpoint is set on the
instruction causing the FP event, the load in the microcode routine will trigger the data breakpoint
resulting in a Debug Exception.
Implication: An incorrect Debug Exception (#DB) may occur if data breakpoint is placed on an FP instruction.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software or system.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC55. xAPIC May Not Report Some Illegal Vector Errors
Problem: The local xAPIC has an Error Status Register, which records all errors. The bit 6 (the Receive
Illegal Vector bit) of this register, is set when the local xAPIC detects an illegal vector in a
received message. When an illegal vector error is received on the same internal clock that the
error status register is being written (due to a previous error), bit 6 does not get set and illegal
vector errors are not flagged.
Workaround: The xAPIC may not report some Illegal Vector errors when they occur at approximately the same
time as other xAPIC errors. The other xAPIC errors will continue to be reported
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 39
Page 40

Errata
AC56. A Timing Marginality in the Instruction Decoder Unit May Cause an
Unpredictable Application Behavior and/or System Hang
Problem: A timing marginality may exist in the clocking of the instruction decoder unit which leads to a
circuit slowdown in the read path from the Instruction Decode PLA circuit. This timing
marginality may not be visible for some period of time.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an incorrect instruction stream may be executed resulting in an
unpredictable application behavior and/or system hang.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. BIOS must load the
microcode update during the BIOS POST time prior to memory initialization.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC57. Memory Aliasing of Pages as Uncacheable Memory Type and Write Back
(WB) May Hang the System
R
Problem: When a page is being accessed as either Uncacheable (UC) or Write Combining (WC) and WB,
under certain bus and memory timing conditions, the system may loop in a continual sequence of
UC fetch, implicit writeback, and Request For Ownership (RFO) retries.
Implication: This erratum has not been observed in any commercially available operating system or
application. The aliasing of memory regions, a condition necessary for this erratum to occur, is
documented as being unsupported in the IA-32 Intel
®
Architecture Software Developer's Manual,
Volume 3, section 10.12.4, Programming the PAT. However, if this erratum occurs the system
may hang.
Workaround: The pages should not be mapped as either UC or WC and WB at the same time.
Status: For the stepping affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
AC58. Using STPCLK and Executing Code from Very Slow Memory Could Lead to
a System Hang
Problem: The system may hang when the following conditions are met:
1. Periodic STPCLK mechanism is enabled via the chipset
2. Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled
3. One logical processor is waiting for an event (i.e. hardware interrupt)
4. The other logical processor executes code from very slow memory such that every code fetch
is deferred long enough for the STPCLK to be re-asserted.
Implication: If this erratum occurs, the processor will go into and out of the sleep state without making
forward progress, since the logical processor will not be able to service any pending event. This
erratum has not been observed in any commercial platform running commercial software.
Workaround: None
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
40 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 41

Errata
R
AC59. Machine Check Exceptions May Not Update Last-Exception Record MSRs
(LERs)
Problem: The Last-Exception Record MSRs (LERs) may not get updated when Machine Check Exceptions
occur.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the LER may not contain information relating to the machine check
exception. They will contain information relating to the exception prior to the machine check
exception.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC60. Stores to Page Tables May Not Be Visible to Pagewalks for Subsequent
Loads without Serializing or Invalidating the Page Table Entry
Problem: Under rare timing circumstances, a page table load on behalf of a programmatically younger
memory access may not get data from a programmatically older store to the page table entry if
there is not a fencing operation or page translation invalidate operation between the store and the
younger memory access. Refer to the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer's Manual for
the correct way to update page tables. Software that conforms to the Software Developer's Manual
will operate correctly.
Implication: If the guidelines in the Software Developer's Manual are not followed, stale data may be loaded
into the processor's Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) and used for memory operations. This
erratum has not been observed with any commercially available software.
Workaround: The guidelines in the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer's Manual should be
followed.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC61. A Timing Marginality in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) May Cause
Indeterminate Behavior
Problem: A timing marginality may exist in the clocking of the ALU which leads to a slowdown in the
speed of the circuit’s operation. This could lead to incorrect behavior of the ALU.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, unpredictable application behavior and/or system hang may occur.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 41
Page 42

Errata
AC62. With TF (Trap Flag) Asserted, FP Instruction That Triggers an Unmasked
FP Exception May Take Single Step Trap before Retirement of Instruction
Problem: If an FP instruction generates an unmasked exception with the EFLAGS.TF=1, it is possible for
external events to occur, including a transition to a lower power state. When resuming from the
lower power state, it may be possible to take the single step trap before the execution of the
original FP instruction completes.
Implication: A Single Step trap will be taken when not expected.
Workaround: None Identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC63. BTS (Branch Tree Store) and PEBS (Precise Event Based Sampling) May
Update Memory outside the BTS/PEBS Buffer
Problem: If the BTS/PEBS buffer is defined such that:
• The difference between BTS/PEBS buffer base and BTS/PEBS absolute maximum is
not an integer multiple of the corresponding record sizes
• BTS/PEBS absolute maximum is less than a record size from the end of the virtual
address space
• The record that would cross BTS/PEBS absolute maximum will also continue past the
end of the virtual address space
A BTS/PEBS record can be written that will wrap at the 4G boundary (IA32) or 2^64 boundary
(EMT64 mode), and write memory outside of the BTS/PEBS buffer.
R
Implication: Software that uses BTS/PEBS near the 4G boundary (IA32) or 2^64 boundary (EMT64 mode),
and defines the buffer such that it does not hold an integer multiple of records can update memory
outside the BTS/PEBS buffer.
Implication: A Single Step trap will be taken when not expected.
Workaround: Define BTS/PEBS buffer such that BTS/PEBS absolute maximum minus BTS/PEBS buffer base
is integer multiple of the corresponding record sizes as recommended in the Programmers
Reference Manual Volume 3.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC64. Memory Ordering Failure May Occur with Snoop Filtering Third-Party
Agents after Issuing and Completing a BWIL (Bus Write Invalidate Line) or
BLW (Bus Locked Write) Transaction
Problem: Under limited circumstances, the processors may, after issuing and completing a BWIL or BLW
transaction, retain data from the addressed cache line in shared state even though the specification
requires complete invalidation. This data retention may also occur when a BWIL transaction’s
self-snooping yields HITM snoop results.
Implication: A system may suffer memory ordering failures if its central agent incorporates coherence
sequencing which depends on full self-invalidation of the cache line associated with (1) BWIL
42 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 43

Errata
R
and BLW transactions, or (2) all HITM snoop results without regard to the transaction type and
snoop results’ source.
Workaround: 1. The central agent can issue a bus cycle that causes a cache line to be invalidated (Bus Read
Invalidate Line (BRIL) or BWIL transaction) in response to a processor-generated BWIL (or
BLW) transaction to insure complete invalidation of the associated cache line. If there are no
intervening processor-originated transactions to that cache line, the central agent’s invalidating
snoop will get a clean snoop result.
Or
2. Snoop filtering central agents can:
a. Not use processor-originated BWIL or BLW transactions to update their snoop filter
information, or
b. Update the associated cache line state information to shared state on the originating bus
(rather than invalid state) in reaction to a BWIL or BLW.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC65. Memory Control Register 2 (CR2) Can be Updated during a REP
MOVS/STOS Instruction with Fast Strings Enabled Transaction
Problem: Under limited circumstances while executing a REP MOVS/STOS string instruction, with fast
strings enabled, it is possible for the value in CR2 to be changed as a result of an interim paging
event, normally invisible to the user. Any higher priority architectural event that arrives and is
handled while the interim paging event is occurring may see the modified value of CR2.
Implication: The value in CR2 is correct at the time that an architectural page fault is signaled. Intel has not
observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC66. Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending May
Cause an Unexpected Interrupt
Problem: If a local interrupt is pending when the LVT entry is written, an interrupt may be taken on the
new interrupt vector even if the mask bit is set.
Implication: An interrupt may immediately be generated with the new vector when a LVT entry is written,
even if the new LVT entry has the mask bit set. If there is no Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) set
up for that vector the system will GP fault. If the ISR does not do an End of Interrupt
(EOI) the bit for the vector will be left set in the in-service register and mask all interrupts at the
same or lower priority.
Workaround: Any vector programmed into an LVT entry must have an ISR associated with it, even if that
vector was programmed as masked. This ISR routine must do an EOI to clear any unexpected
interrupts that may occur. The ISR associated with the spurious vector does not generate an EOI,
therefore the spurious vector should not be used when writing the LVT.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 43
Page 44

Errata
AC67. Using 2M/4M Pages When A20M# Is Asserted May Result in Incorrect
Address Translations
Problem: An external A20M# pin if enabled forces address bit 20 to be masked (forced to zero) to emulates
real-address mode address wraparound at 1 megabyte. However, if all of the following conditions
are met, address bit 20 may not be masked.
• paging is enabled
• a linear address has bit 20 set
• the address references a large page
• A20M# is enabled
Implication: When A20M# is enabled and an address references a large page the resulting translated physical
address may be incorrect. This erratum has not been observed with any commercially available
operating system.
Workaround: Operating systems should not allow A20M# to be enabled if the masking of address bit 20 could
be applied to an address that references a large page. A20M# is normally only used with the first
megabyte of memory.
R
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC68. Writing Shared Unaligned Data that Crosses a Cache Line without Proper
Semaphores or Barriers May Expose a Memory Ordering Issue
Problem: Software which is written so that multiple agents can modify the same shared unaligned memory
location at the same time may experience a memory ordering issue if multiple loads access this
shared data shortly thereafter. Exposure to this problem requires the use of a data write which
spans a cache line boundary.
Implication: This erratum may cause loads to be observed out of order. Intel has not observed this erratum
with any commercially available software or system.
Workaround: Software should ensure at least one of the following is true when modifying shared data by
multiple agents:
• The shared data is aligned
• Proper semaphores or barriers are used in order to prevent concurrent data accesses.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AC69. Debug Status Register (DR6) Breakpoint Condition Detected Flags May be
set Incorrectly
Problem: The Debug Status Register (DR6) may report detection of a spurious breakpoint condition under
certain boundary conditions when either:
• A "MOV SS" or "POP SS" instruction is immediately followed by a hardware
debugger breakpoint instruction, or
44 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 45

Errata
R
• Any debug register access ("MOV DRx, r32" or "MOV r32, DRx") results in a
general-detect exception condition.
Implication: Due to this erratum the breakpoint condition detected flags may be set incorrectly.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 45
Page 46

Specification Changes
Specification Changes
The Specification Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
• Intel
• Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel
All Specification Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate Celeron
processor documentation.
No update for this month
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Datasheet
®
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volumes 1, 2-A, 2-
B, 3-A, and 3-B
R
§
46 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 47

Specification Clarifications
R
Specification Clarifications
The Specification Clarifications listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
• Intel
• Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel
All Specification Clarifications will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
Celeron processor documentation.
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Datasheet
®
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volumes 1, 2-A, 2-
B, 3-A, and 3-B
1. Specification Clarification with respect to Time Stamp Counter
In the “Debugging and Performance Monitoring” chapter (Sections 15.8, 15.10.9 and 15.10.9.3)
of the IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual Volume 3: System Programming
Guide, the Time Stamp Counter definition has been updated to include support for the future
processors. This change will be incorporated in the next revision of the IA-32 Intel® Architecture
Software Developer’s Manual.
15.8 Time-Stamp Counter
The IA-32 architecture (beginning with the Pentium processor) defines a time-stamp counter
mechanism that can be used to monitor and identify the relative time occurrence of processor
events. The counter’s architecture includes the following components:
• TSC flag — A feature bit that indicates the availability of the time-stamp counter. The
counter is available in an IA-32 processor implementation if the function
CPUID.1:EDX.TSC[bit 4] = 1.
• IA32_TIME_STAMP_COUNTER MSR (called TSC MSR in P6 family and Pentium
processors) — The MSR used as the counter.
• RDTSC instruction — An instruction used to read the time-stamp counter.
• TSD flag — A control register flag is used to enable or disable the time-stamp counter
(enabled if CR4.TSD[bit 2] = 1).
The time-stamp counter (as implemented in the P6 family, Pentium, Pentium M, Pentium 4, and
Intel Xeon processors) is a 64-bit counter that is set to 0 following a RESET of the processor.
Following a RESET, the counter will increment even when the processor is halted by the HLT
instruction or the external STPCLK# pin. Note that the assertion of the external DPSLP# pin may
cause the time-stamp counter to stop.
Members of the processor families increment the time-stamp counter differently:
• For Pentium M processors (family [06H], models [09H, 0DH]); for Pentium 4 processors,
Intel Xeon processors (family [0FH], models [00H, 01H, or 02H]); and for P6 family
processors: the time-stamp counter increments with every internal processor clock cycle. The
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 47
Page 48

Specification Clarifications
internal processor clock cycle is determined by the current core-clock to bus-clock ratio.
Intel® SpeedStep® technology transitions may also impact the processor clock.
• For Pentium 4 processors, Intel Xeon processors (family [0FH], models [03H and higher]):
the time-stamp counter increments at a constant rate. That rate may be set by the maximum
core-clock to bus-clock ratio of the processor or may be set by the frequency at which the
processor is booted. The specific processor configuration determines the behavior. Constant
TSC behavior ensures that the duration of each clock tick is uniform and supports the use of
the TSC as a wall clock timer even if the processor core changes frequency. This is the
architectural behavior moving forward.
To determine average processor clock frequency, Intel recommends the use of Performance
Monitoring logic to count processor core clocks over the period of time for which the average is
required. See Section 15.10.9 and Appendix A in this manual for more information.
The RDTSC instruction reads the time-stamp counter and is guaranteed to return a monotonically
increasing unique value whenever executed, except for a 64-bit counter wraparound. Intel
guarantees that the time-stamp counter will not wraparound within 10 years after being reset. The
period for counter wrap is longer for Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, P6 family, and Pentium processors.
R
NOTE
Normally, the RDTSC instruction can be executed by programs and procedures running at any
privilege level and in virtual-8086 mode. The TSD flag allows use of this instruction to be
restricted to programs and procedures running at privilege level 0. A secure operating system
would set the TSD flag during system initialization to disable user access to the time-stamp
counter. An operating system that disables user access to the time-stamp counter should emulate
the instruction through a user-accessible programming interface.
The RDTSC instruction is not serializing or ordered with other instructions. It does not
necessarily wait until all previous instructions have been executed before reading the counter.
Similarly, subsequent instructions may begin execution before the RDTSC instruction operation is
performed.
The RDMSR and WRMSR instructions read and write the time-stamp counter, treating the timestamp counter as an ordinary MSR (address 10H). In the Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 family
processors, all 64-bits of the time-stamp counter are read using RDMSR (just as with RDTSC).
When WRMSR is used to write the time-stamp counter on processors before family [0FH],
models [03H, 04H]: only the low order 32-bits of the time-stamp counter can be written (the highorder 32 bits are cleared to 0). For family [0FH], models [03H, 04H]: all 64 bits are writeable.
15.10.9 Counting Clocks
The count of cycles, also known as clockticks, forms a the basis for measuring how long a
program takes to execute. Clockticks are also used as part of efficiency ratios like cycles per
instruction (CPI). Processor clocks may stop ticking under circumstances like the following:
• The processor is halted when there is nothing for the CPU to do. For example, the processor
may halt to save power while the computer is servicing an I/O request. When HyperThreading Technology is enabled, both logical processors must be halted for performancemonitoring counters to be powered down.
48 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
Page 49

Specification Clarifications
R
• The processor is asleep as a result of being halted or because of a power-management
scheme. There are different levels of sleep. In the some deep sleep levels, the time-stamp
counter stops counting.
There are three ways to count processor clock cycles to monitor performance. These are:
• Non-halted clockticks — Measures clock cycles in which the specified logical processor is
not halted and is not in any power-saving state. When Hyper-Threading Technology is
enabled, this these ticks can be measured on a per-logical-processor basis.
• Non-sleep clockticks — Measures clock cycles in which the specified physical processor is
not in a sleep mode or in a power-saving state. These ticks cannot be measured on a logicalprocessor basis.
• Time-stamp counter — Some processor models permit clock cycles to be measured when the
physical processor is not in deep sleep (by using the time-stamp counter and the RDTSC
instruction). Note that such ticks cannot be measured on a per-logical-processor basis. See
Section 10.8 for detail on processor capabilities.
The first two methods use performance counters and can be set up to cause an interrupt upon
overflow (for sampling). They may also be useful where it is easier for a tool to read a
performance counter than to use a time stamp counter (the timestamp counter is accessed using
the RDTSC instruction).
For applications with a significant amount of I/O, there are two ratios of interest:
• Non-halted CPI — Non-halted clockticks/instructions retired measures the CPI for phases
where the CPU was being used. This ratio can be measured on a logical-processor basis when
Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled.
• Nominal CPI — Time-stamp counter ticks/instructions retired measures the CPI over the
duration of a program, including those periods when the machine halts while waiting for I/O.
15.10.9.3 Incrementing the Time-Stamp Counter
The time-stamp counter increments when the clock signal on the system bus is active and when
the sleep pin is not asserted. The counter value can be read with the RDTSC instruction.
The time-stamp counter and the non-sleep clockticks count may not agree in all cases and for all
processors. See Section 10.8 for more information on counter operation.
§
®
Intel
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update 49
Page 50

Documentation Changes
Documentation Changes
The Documentation Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
• Intel
• Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel
All Documentation Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate Celeron
processor documentation.
Note: Documentation changes for IA-32 Intel(R) Architecture Software Developer’s Manual
volumes 1, 2, and 3 will be posted in a separate document " IA-32 Intel(R) Architecture Software
Developer’s Manual Documentation Changes". Please follow the link below to become familiar
with this file.
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Datasheet
®
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volumes 1, 2-A, 2-
B, 3-A, and 3-B
R
http://developer.intel.com/design/pentium4/specupdt/252046.htm
§
50 Intel
®
Celeron® Processor in the 478-Pin Package Specification Update
 Loading...
Loading...