Page 1

Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Developer’s Manual
May 2005
Order Number: 278890-003US
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS
AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHA TSO EVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXP RESS
OR IMPLIED WARRANTY RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS, INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights that relate to the
presented subject matter. The furnishing of documents and other materials and information does not provide any license, express or implied, by
estoppel or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights.
Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
®
The Intel
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calli ng
1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
AnyPoint, AppChoice, BoardWatch, BunnyPeople, CablePort, Celeron, Chips, CT Media, Dialogic, DM3, EtherExpress, ETOX, FlashFile, i386, i486,
i960, iCOMP , InstantIP, Intel, Intel Centrino, Intel logo, Intel386, Intel486, Intel740, IntelDX2, IntelDX4, IntelSX2, Intel Create & Share, Intel GigaBlade,
Intel InBusiness, Intel Inside, Intel Inside logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel NetMerge, Intel NetStructure, Intel Play, Intel Play logo, Intel SingleDriver, Intel
SpeedStep, Intel StrataFlash, Intel TeamStation, Intel Xeon, Intel XScale, IPLink, Itanium, MCS, MMX, MMX logo, Optimizer logo, OverDrive,
Paragon, PC Dads, PC Parents, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium II Xeon, Pentium III Xeon, Performance at Your Command, RemoteExpress, SmartDie,
Solutions960, Sound Mark, StorageExpress, The Computer Inside., The Journey Inside, TokenExpress, VoiceBrick, VTune, and Xircom are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2005, Intel Corporation
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
2 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 3

Contents
Contents
1 Introduction..................................................................................................................................11
1.1 PCI Express* Interface Features ........................................................................................11
1.2 PCI-X Interface Features....................................................................................................11
1.3 Power Management............................................................................................................12
1.4 SMBus Interface .................................................................................................................12
1.5 JTAG...................................................................................................................................12
2 Signal Description.......................................................................................................................13
2.1 On-Die Termination (ODT) .................................................................................................13
2.2 PCI Express* Interface .......................................................................................................15
2.3 PCI Bus Interface (Two Instances).....................................................................................16
2.4 PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension (Two Interfaces) .........................................................18
2.5 PCI Bus Interface Clocks and, Reset and Power Management (Two Interfaces) ..............18
2.6 Interrupt Interface (Two Interfaces) ....................................................................................19
2.7 Reset Straps......................................................... ...... .............................................. ..........20
2.8 SMBus Interface .................................................................................................................21
2.9 Miscellaneous Pins......................................... ...... ....................................... ...... ....... ...... ....22
2.10 Voltage Pins........................................................................................................................23
3 PCI-X Interface.............................................................................................................................25
3.1 Initialization.........................................................................................................................25
3.2 Transactions Supported......................................................................................................26
3.2.1 PCI Mode...............................................................................................................26
3.2.2 PCI-X Mode ...........................................................................................................27
3.2.3 Read Transactions.................................................................................................27
3.2.4 Configuration Transactions....................................................................................28
3.2.5 LOCK Cycles .........................................................................................................29
3.2.6 Decoding................................................................................................................30
3.2.7 Transaction Termination ........................................................................................30
3.3 PCI-X Protocol Specifics.....................................................................................................34
3.3.1 Attributes................................................................................................................34
3.3.2 4 GB and 4 K Page Crossover ..............................................................................34
3.3.3 Wait States .................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .................34
3.3.4 Split Transactions ..................................................................................................35
3.4 Arbitration ...........................................................................................................................35
4 Power Management.....................................................................................................................37
4.1 Hardware-Controlled Active State Power Management .....................................................37
4.2 Software-Driven PCI-PM 1.1–Compatible Power Management.........................................37
4.3 PCI Bus Power Management .............................................................................................37
4.4 Intel
4.5 Power-Management Event Signaling .................................................................................38
5 Addressing...................................................................................................................................41
5.1 Addressable Spaces within the Intel
5.2 Secondary PCI Devices......................................................................................................42
5.3 Configuration-Space Access ..............................................................................................42
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Device Power Management .............................38
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge ........................41
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 3
Page 4

Contents
5.3.1 PCI Express* Configuration Access ......................................................................42
5.3.2 Type 0 Configuration Access from PCI-X Interface...............................................44
5.3.3 SMBus Configuration Access................................................................................45
5.4 I/O Space Access Mechanism............................................................................................45
5.5 Memory Space Access Mechanism....................................................................................47
5.5.1 Memory-Mapped I/O Window................................................................................48
5.5.2 Prefetchable Memory Window...............................................................................49
5.5.3 Opaque Memory Window ......................................................................................49
5.6 VGA Addressing.................................................................................................................49
6 Transaction Ordering..................................................................................................................51
6.1 Upstream Transaction Ordering .........................................................................................51
6.2 Downstream Transaction Ordering.....................................................................................52
6.3 Relaxed Ordering/No-Snoop Support.................................................................................52
7 Interrupt Support.........................................................................................................................53
7.1 Legacy Interrupt Sharing ....................................................................................................53
7.2 Interrupt Routing for Devices behind a Bridge....................................................................54
8 System Management Bus Interface...........................................................................................55
8.1 SMBus Commands.............................................................................................................56
8.2 Initialization Sequence........................................................................................................57
8.2.1 Configuration ........................................................................................................57
8.2.2 Configuration Writes ...................... ....... ...... ...... .............................................. .......60
8.3 Error Handling.....................................................................................................................61
8.4 SMBus Interface Reset.......................................................................................................62
9 Local Initialization .......................................................................................................................63
10 Clock and Reset...........................................................................................................................65
10.1 Clocking..............................................................................................................................65
10.2 Device Reset ......................................................................................................................65
10.2.1 PERST# Reset Mechanism...................................................................................66
10.2.2 RSTIN# Reset Mechanism ....................................................................................66
10.2.3 PCI Express* Reset Mechanism............................................................................66
10.2.4 Software PCI Reset (SBR—Secondary Bus Reset)..............................................67
11 Error Handling .............................................................................................................................69
11.1 PCI Express* Errors............................................................................................................69
11.2 PCI Errors...........................................................................................................................69
11.2.1 Error Types............................................................................................................70
11.2.2 Termination of Completion Required Transactions ...............................................70
12 Register Description ...................................................................................................................73
12.1 Register Nomenclature and Access Attributes...................................................................73
12.2 Configuration Registers .............................. ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ........................................74
12.2.1 Offset 00h: ID—Identifiers .....................................................................................78
12.2.2 Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register ...........................................................78
12.2.3 Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status............................................................79
12.2.4 Offset 08h: REVID—Revision ID...........................................................................80
12.2.5 Offset 09h: CC—Class Code.................................................................................81
4 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 5

Contents
12.2.6 Offset 0Ch: CLS—Cache-Line Size.......................................................................81
12.2.7 Offset 0Dh: PMLT—Primary Master Latency Timer ..............................................81
12.2.8 Offset 0Eh: HEADTYP—Header Type...................................................................81
12.2.9 Offset 18h: BNUM—Bus Numbers ........................................................................82
12.2.10 Offset 1Bh: SMLT—Secondary Master Latency Timer..........................................82
12.2.11 Offset 1Ch: IOBL—I/O Base and Limit ..................................................................83
12.2.12 Offset 1Eh: SSTS—Secondary Status ..................................................................84
12.2.13 Offset 20h: MBL—Memory Base and Limit............................................................85
12.2.14 Offset 24h: PMBL—Prefetchable Memory Base and Limit....................................86
12.2.15 Offset 28h: PMBU32—Prefetchable Memory Base Upper 32 Bits........................86
12.2.16 Offset 2Ch: PMLU32—Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper 32 Bits.........................87
12.2.17 Offset 30h: IOBLU16—I/O Base and Limit Uppe r 16 Bit s........ ....... ...... .................87
12.2.18 Offset 34h: CAPP—Capabilities List Pointer .........................................................87
12.2.19 Offset 3Ch: INTR—Interrupt Information ...............................................................87
12.2.20 Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control......................................................................88
12.2.21 Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register................................................90
12.2.22 Offset 42h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer............................................................91
12.2.23 Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control................................................................91
12.2.24 Offset 44h: EXP_CAPID—PCI Express* Capability Identifier................................91
12.2.25 Offset 45h: EXP_NXTP—Next Item Pointer..........................................................91
12.2.26 Offset 46h: EXP_CAP—PCI Express* Capability..................................................92
12.2.27 Offset 48h: EXP_DCAP—PCI Express* Device Capabilities Register ..................92
12.2.28 Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—PCI Express* Device Control Register .........................93
12.2.29 Offset 4Eh: EXP_DSTS—PCI Express* Device Status Register...........................94
12.2.30 Offset 50h: EXP_LCAP—PCI Express* Link Capabilities Register .......................94
12.2.31 Offset 54h: EXP_LCTL—PCI Express* Link Control Register...............................95
12.2.32 Offset 56h: EXP_LSTS—PCI Express* Link Status Register................................96
12.2.33 Offset 5Ch: MSI_CAPID—PCI Express* MSI Capability Identifier ........................96
12.2.34 Offset 5Dh: MSI_NXTP—PCI Express* Next Item Pointer....................................96
12.2.35 Offset 5Eh: MSI_MC—PCI Express* MSI Message Control .................................97
12.2.36 Offset 60h: MSI_MA—PCI Express* MSI Message Address ................................97
12.2.37 Offset 68h: MSI_MD—PCI Express* MSI Message Data......................................97
12.2.38 Offset 6Ch: PM_CAPID—Power Management Capabilities Identifier ...................97
12.2.39 Offset 6Dh: PM_NXTP—Power Management Next Item Pointer ..........................98
12.2.40 Offset 6Eh: PM_PMC—Power Management Capabilities.....................................98
12.2.41 Offset 70h: PM_PMCSR—Power Management Control/Status Register..............99
12.2.42 Offset 72h: PM_BSE—Power Management Bridge
Support Extensions............................................................ ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....99
12.2.43 Offset 73h: PM_DATA—Power Management Data Field ......................................99
12.2.44 Offset D8h: PX_CAPID—PCI-X Capabilities Identifier ........................................100
12.2.45 Offset D9h: PX_NXTP—PCI-X Next Item Pointer ...............................................100
12.2.46 Offset DAh: PX_SSTS—PCI-X Secondary Status ..............................................101
12.2.47 Offset DCh: PX_BSTS—PCI-X Bridge Status .....................................................102
12.2.48 Offset E0h: PX_USTC—PCI-X Upstream Split Transaction Control...................102
12.2.49 Offset E4h: PX_DSTC—PCI-X Downstream Split Transaction Control...............103
12.2.50 Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization Register................................................104
12.2.51 Offset 100h: EXPAERR_CAPID—PCI Express* Advanced
Error Capability Identifier .....................................................................................105
12.2.52 Offset 104h: ERRUNC_STS—PCI Express* Uncorrectable
Error Status Register ...........................................................................................105
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 5
Page 6

Contents
12.2.53 Offset 108h: ERRUNC_MSK—PCI Express*
Uncorrectable Error Mask....................................................................................106
12.2.54 Offset 10Ch: ERRUNC_SEV—PCI Express* Uncorrectable
Error Severity.......................................................................................................107
12.2.55 Offset 110h: ERRCOR_STS—PCI Ex pres s*
Correctable Error Status......................................................................................108
12.2.56 Offset 114h: ERRCOR_MSK—PCI Express*
Correctable Error Mask........................................................................................109
12.2.57 Offset 118h: ADVERR_CTL—A dv anced Er ror Control
and Capability Register........................................................................................109
12.2.58 Offset 11C–12Bh: HDR_LOG—PCI Express*
Transaction Header Log ......................................................................................110
12.2.59 Offset 12Ch: PCIXERRUNC_STS—Un co rrectab le
PCI-X Status Register..........................................................................................111
12.2.60 Offset 130h: PCIXERRUNC_MSK —Uncorrec tabl e
PCI-X Error Mask Register ..................................................................................113
12.2.61 Offset 134h: PCIXERRUNC_SEV —Uncorrec tab le
PCI-X Error Severity Register..............................................................................115
12.2.62 Offset 138h: PCIXERRUNC_PTR— Uncorrec table
PCI-X Error Pointer..............................................................................................116
12.2.63 Offset 13C–14Bh: PCIXHDR_LOG— Uncorrec tabl e
PCI-X Error Transaction Header Log...................................................................117
12.2.64 Offset 16Ah: ARB_CNTRL—Internal Arbiter Control Register ............................117
12.2.65 Offset 170h: SSR—Strap Status Register...........................................................118
12.2.66 Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register .........................................119
12.2.67 Offset 300h: PWRBGT_CAPID—Power Budgeting
Enhanced Capability Header...............................................................................120
12.2.68 Offset 304h: PWRBGT_DSEL—Power Budgeting
Data Select Register............................................................................................120
12.2.69 Offset 308h: PWRBGT_DATA—Power Budgeting Data Register.......................120
Figures
1 Internal Arbitration Scheme ........................................................................................................36
2 Type 1 to Type 0 Translation (PCI and PCI-X)...........................................................................44
3 Upstream Type 0 PCI-X Configuration Cycle Address Format ..................................................45
4 I/O Forwarding............................................................................................................................46
5 Memory Forwarding....................................................................................................................48
6 DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Block Write/Block Read, PEC Enabled) .............58
7 DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Word Write/Word Read, PEC Enabled) .............58
8 DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Block Write/Block Read, PEC Disabled) ............59
9 DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Word Write/Word Read, PEC Disabled).............59
10 DWord Configuration Write Protocol (SMBus Block Write, PEC Enabled).................................60
11 DWord Configuration Write Protocol (SMBus Byte Write, PEC Enabled) ..................................61
12 Intel
6 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Capabilities...............................................................75
Page 7

Contents
Tables
1 ODT Signals ...............................................................................................................................14
2 PCI Express* Interface Pins .......................................................................................................15
3 PCI Interface Pins.......................................................................................................................16
4 PCI Interface Pins: 64-Bit Extensions.........................................................................................18
5 PCI Clock and Reset Pins ..........................................................................................................18
6 Interrupt Interface Pins ...............................................................................................................19
7 Reset Strap Pins.........................................................................................................................20
8 SMBus Interface Pins .................................................................................................................21
9 Miscellaneous Pins.....................................................................................................................22
10 Miscellaneous Pins.....................................................................................................................23
11 PCI Mode Pin/Strap Encoding....................................................................................................25
12 PCI-X Initialization Pattern..........................................................................................................25
13 PCI Transactions Supported.......................................................................................................26
14 PCI-X Transactions Supported...................................................................................................27
15 LOCK Transaction Handling in the Intel
16 Intel
17 Intel
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Implementation of Requester Attribute Fields..........34
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Implementation of Completer Attribute Fields..........35
18 Split Completion Abort Registers................................................................................................35
19 Addressable Spaces within the Intel
20 Secondary PCI Device Addressing.............................................................................................42
21 Upstream Transaction Ordering ............................. ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .................51
22 Downstream Transaction Ordering.............................................................................................52
23 INTx Routing Table.....................................................................................................................53
24 Interrupt Binding for Devices behind a Bridge ............................................................................54
25 SMBus Address Assignments ....................................................................................................55
26 SMBus Command Encoding.......................................................................................................56
27 SMBus Status Byte Encoding.....................................................................................................57
28 Clock Domains............................................................................................................................65
29 Completion-Status Translation for Immediate Terminations.......................................................70
30 Completion-Status Translation for PCI-X Split-Completion Terminations ..................................71
31 Completion-Status Translation for PCI Express* Split-Completion Terminations.......................72
32 Bit Attribute Definitions ...............................................................................................................73
33 Legacy Configuration Space.......................................................................................................76
34 PCI Express* Extended Configuration Space ............................................................................77
35 Offset 00h: ID—Identifiers ..........................................................................................................78
36 Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register ................................................................................78
37 Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status.................................................................................79
38 Offset 08h: REVID—Revision ID................................................................................................80
39 Offset 09h: CC—Class Code......................................................................................................81
40 Offset 0Ch: CLS—Cache Line Size............................................................................................81
41 Offset 0Dh: PMLT—Primary Master Latency Timer ...................................................................81
42 Offset 0Eh: HEADTYP—Header Type .......................................................................................81
43 Offset 18h: BNUM—Bus Numbers.............................................................................................82
44 Offset 1Bh: SMLT—Secondary Master Latency Timer...............................................................82
45 Offset 1Ch: IOBL—I/O Base and Limit.......................................................................................83
46 Offset 1Eh: SSTS—Secondary Status .......................................................................................84
47 Offset 20h: MBL—Memory Base and Limit ........................ ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....85
48 Offset 24h: PMBL—Prefetchable Memory Base and Limit.........................................................86
49 Offset 28h: PMBU32—Prefetchable Memory Base Upper 32 Bits.............................................86
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge...........................29
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge................................41
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 7
Page 8

Contents
50 Offset 2Ch: PMLU32—Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper 32 Bits .............................................87
51 Offset 30h: IOBLU16—I/O Base and Limit Upper 16 Bits ...................................... ...... ....... ...... .87
52 Offset 34h: CAPP—Capabilities List Pointer..............................................................................87
53 Offset 3Ch: INTR—Interrupt Information....................................................................................87
54 Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control ..........................................................................................88
55 Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register ....................................................................90
56 Offset 42h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer ................................................................................91
57 Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control.....................................................................................91
58 Offset 44h: PCI Express*_CAPID—PCI Express* Capability Identifier......................................91
59 Offset 45h: PCI Express*_NXTP—Next Item Pointer.................................................................91
60 Offset 46h: EXP_CAP—PCI Express* Capability.......................................................................92
61 Offset 48h: EXP_DCAP—PCI Express* Device Capabilities Register.......................................92
62 Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—PCI Express* Device Control Register..............................................93
63 Offset 4Eh: EXP_DSTS—PCI Express* Device Status Register ...............................................94
64 Offset 50h: EXP_LCAP—PCI Express* Link Capabilities Register............................................94
65 Offset 54h: EXP_LCTL—PCI Express* Link Control Register ...................................................95
66 Offset 56h: EXP_LSTS—PCI Express* Link Status Register.....................................................96
67 Offset 5Ch: MSI_CAPID—PCI Express* MSI Capability Identifier.............................................96
68 Offset 5Dh: MSI_NXTP—PCI Express* Next Item Pointer.........................................................96
69 Offset 5Eh: MSI_MC—PCI Express* MSI Message Control......................................................97
70 Offset 60h: MSI_MA—PCI Express* MSI Message Address.....................................................97
71 Offset 68h: MSI_MD—PCI Express* MSI Message Data ..........................................................97
72 Offset 6Ch: PM_CAPID—Power Management Capabilities Identifier........................................97
73 Offset 6Dh: PM_NXTP—Power Management Next Item Pointer...............................................98
74 Offset 6Eh: PM_PMC—Power Management Capabilities..........................................................98
75 Offset 70h: PM_PMCSR—Power Management Control/Status Register...................................99
76 Offset 72h: PM_BSE—Power Management Bridge Support Extensions...................................99
77 Offset 73h: PM_DATA—Power Management Data Field...........................................................99
78 Offset D8h: PX_CAPID—PCI-X Capabilities Identifier .............................................................100
79 Offset D9h: PX_NXTP—PCI-X Next Item Pointer....................................................................100
80 Offset DAh: PX_SSTS—PCI-X Secondary Status ...................................................................101
81 Offset DCh: PX_BSTS—PCI-X Bridge Status..........................................................................102
82 Offset E0h: PX_USTC—PCI-X Upstream Split Transaction Control........................................102
83 Offset E4h: PX_DSTC—PCI-X Downstream Split Transaction Control ...................................103
84 Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization Register.....................................................................104
85 Offset 100h: EXPAERR_CAPID—PCI Express* Advanced Error Capability Identifier ............105
86 Offset 104h: ERRUNC_STS—PCI Express* Uncorrectable Error Status Register..................105
87 Offset 108h: ERRUNC_MSK—PCI Express* Uncorrectable Error Mask.................................106
88 Offset 10Ch: ERRUNC_SEV—PCI Express* Uncorrectable Error Severity ............................107
89 Offset 110h: ERRCOR_STS—PCI Express* Correctable Error Status....................................108
90 Offset 114h: ERRCOR_MSK—PCI Express* Correctable Error Mask ....................................109
91 Offset 118h: ADVERR_CTL—Advanced Error Control and Capability Register......................109
92 Offset 11C–12Bh: HDR_LOG—PCI Express* Transaction Header Log..................................110
93 Offset 12Ch: PCIXERRUNC_STS—Uncorrectable PCI-X Status Register .............................111
94 Offset 130h: PCIXERRUNC_MSK—Uncorrectable PCI-X Error Mask Register......................113
95 Offset 130h: PCIXERRUNC_SEV—Uncorrectable PCI-X Error Severity Register..................115
96 Offset 138h: PCIXERRUNC_PTR—Uncorrectable PCI-X Error Pointer Register....................116
97 Offset 13C–14Bh: PCIXHDR_LOG—Uncorrectable PCI-X Header Log..................................117
98 Offset 16Ah: ARB_CNTRL—Internal Arbiter Control Register.................................................117
99 Offset 170h: SSR—Strap Status Register................................................................................118
8 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 9

Contents
100 Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register ..............................................................119
101 Offset 300h: PWRBGT_HDR—Power Budgeting Enhanced Capability Header......................120
102 Offset 304h: PWRBGT_DSEL—Power Budgeting Data Select Register.................................120
103 Offset 308h: PWRBGT_DATA—Power Budgeting Data Register............................................120
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 9
Page 10

Contents
Revision History
Date Revision Description
May 2005 003 Revised Table1 and Table 9
October 2004 002
March 2004 001 Initial release
Updated PCI Express operation information in Section 1.1 and
Table 2 inSection 2.2.
Removed L0s state information throughout manual.
10 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 11

Introduction
Introduction 1
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (also called the 41210 Bridge or the 41210)
integrates two PCI Express*-to-PCI/PCI-X bridges. Each bridge follows the PCI-to-PCI Bridge
programming model. The PCI Express* port is compatible with the PCI Express* Specification,
Revision 1.0a. The two PCI bus interfaces are comparable with the PCI Local Bus Specification,
Revision 2.3 and the PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b.
1.1 PCI Express* Interface Features
• PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a
• Support for single ×8, single ×4 or single x1 PCI Express* operation
• 64-bit addressing support
• 32-bit CRC (cyclic redundancy checking) covering all transmitted data packets
• 16-bit CRC on all link message information
• Raw bit-rate on the data pins of 2.5 Gbit/s, resulting in a raw bandwidth per pin of 250 MB/s
• Maximum realized bandwidth on PCI Express* interface of 2 GB/s (in ×8 mode) in each
direction simultaneously, for an aggregate of 4 GB/s
1.2 PCI-X Interface Features
• PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.3
• PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.1
• PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b
• 64-bit 66 MHz, 3.3 V, not 5 V tolerant
• On-Die Termination (ODT) with 8.3 KΩ pul l-up to 3.3 V for PCI signals
• Six external REQ/GNT pairs for internal arbiter on segment A and B respectively
• Programmable bus parking on either the last agent or always on Intel
PCI Bridge
• Two-level programmable round-robin internal arbiter with Multi-Transaction Timer (MTT)
• External PCI clock-feed support for asynchronous primary and secondary domain operation
• 64-bit addressing for upstream and downstream transactions
• Downstream LOCK# support
• No upstream LOCK# support
• PCI fast Back-to-Back capable as target
• Up to four active and four pending upstream memory read transactions
®
41210 Serial to Parallel
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 11
Page 12

Introduction
• Up to two downstream delayed (memory read, I/O read/write and configuration read/write)
transactions
• Tunable inbound read prefetch algorithm for PCI MRM/MRL commands
• Device hiding support for secondary PCI devices
• Secondary bus private memory support via opaque memory region
• Local initialization via SMBus
• Secondary side initialization via Type 0 configuration cycles
• Full peer-to-peer read/write capability between the two secondary PCI segments
1.3 Power Management
• Support for PCI PM 1.1-compatible D0, D3hot and D3cold device power states
• Support for PME# event propagation on behalf of PCI devices
1.4 SMBus Interface
• Compatible with System Management Bus Specification, Revision 2.0
• Slave-mode operation only
• Full read/write access to all configuration registers
1.5 JTAG
• IEEE Standard Test Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture 1149.1a
12 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 13

Signal Description
Signal Description 2
The “#” symbol at the end of a signal name indicates that the active (asserted) state occurs when
the signal is at a low voltage level. When “#” is not present after the signal name, the signal is
asserted when at the high voltage level. The following notations are used to describe the signal
type:
I: Input pin
O: Output pin
OD: Open-drain Output pin
I/O: Bidirectional Input/Output pin
I/OD: Bidirectional Input/Open-drain Output pin
2.1 On-Die Termination (ODT)
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (also called the 41210 Bridge or the 41210)
incorporates On-Die Termination (ODT) for most of the PCI interface signals. ODT eliminates the
need for the system designer to incorporate external pull-up resistors in the design.
T a ble 1, “ODT Signals” on page 14 lists the signals that have an on-die termination of 8.33 KΩ @
40%.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 13
Page 14

Signal Description
Table 1. ODT Signals
A_ACK64# B_ACK64#
A_AD[63:32] B_AD[63:32]
A_CBE#[7:4] B_CBE#[7:4]
A_DEVSEL# B_DEVSEL#
A_FRAME# B_FRAME#
A_GNT#[5:0] B_GNT#[5:0]
A_IRDY# B_IRDY#
A_PAR B_PAR
A_PAR64 B_PAR64
A_PERR# B_PERR#
A_LOCK# B_LOCK#
A_REQ#[5:0] B_REQ#[5:0]
A_REQ64# B_REQ64#
A_SERR# B_SERR#
A_STOP# B_STOP#
A_TRDY# B_TRDY#
A_INTA# B_INTA#
A_INTB# B_INTB#
A_INTC# B_INTC#
A_INTD# B_INTD#
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
14 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 15
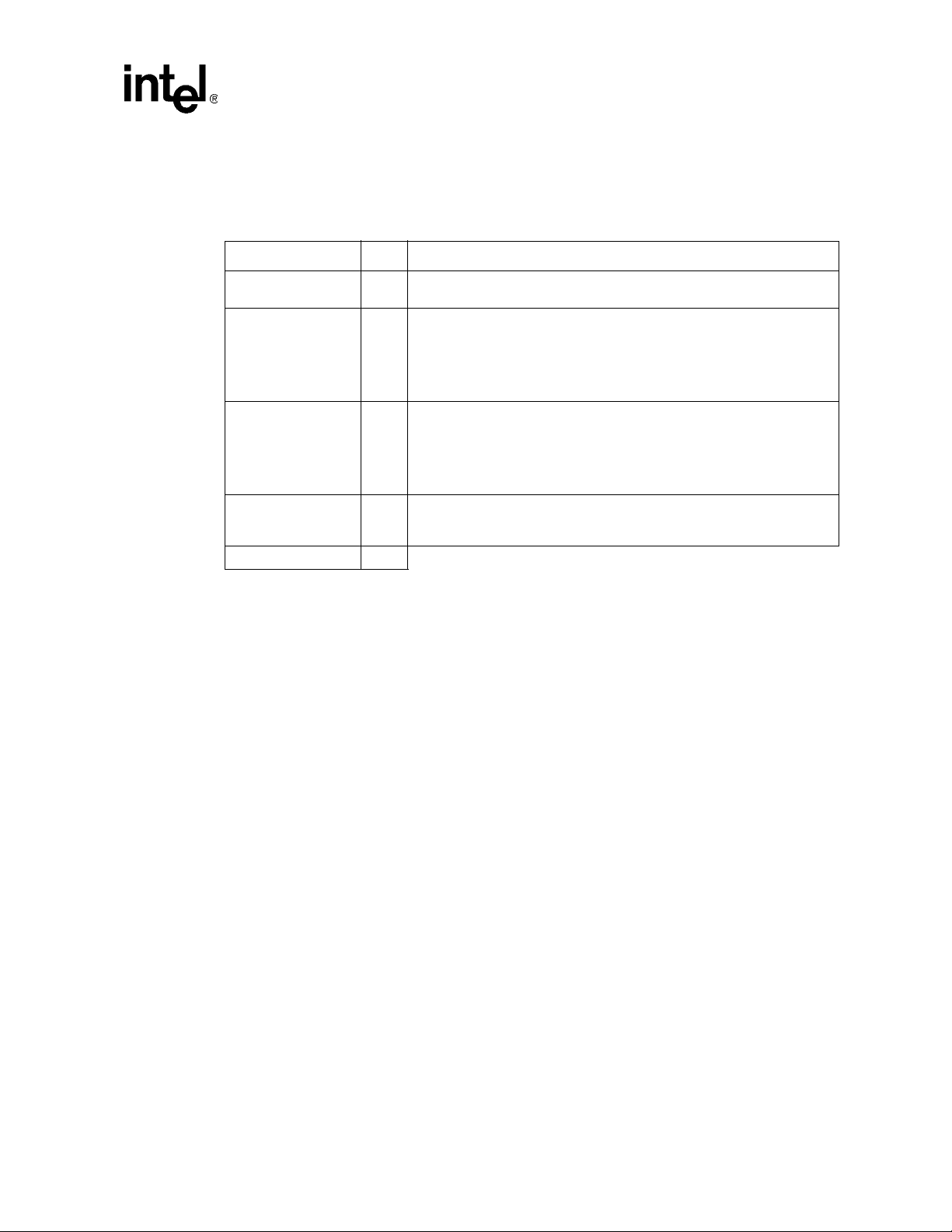
2.2 PCI Express* Interface
T able 2. PCI Express* Interface Pins
Signal I/O Description
Signal Description
REFCLKp/
REFCLKn
PETp[7:0]/
PETn[7:0]
PERp[7:0]/
PERn[7:0]
PE_RCOMP[1:0] I
Total 36
I PCI Express* Reference Clocks: 100 MHz differential clock pair
PCI Express* Serial Data Transmit: PCI Express* differential data transmit
signals
X8 Mode: All PETp[7:0]/PETn[7:0] are used.
O
X4 Mode: Only PETp[3:0]/PETn[3:0] are used.
X1 Mode: Either PETp[0]/PETn[0] is used or PETp[7]/PETn[7] is used.
PCI Express* Serial Data Receive: PCI Express* differential data receive
signals
X8 Mode: All PERp[7:0]/PERn[7:0] are used.
I
X4 Mode: Only PERp[3:0]/PERn[3:0] are used.
X1 Mode: Either PERp[0]/PERn[0] is used or PERp[7]/PERn[7] is used.
PCI Express* Compensation Inputs: Analog signals. Connect to a
24.9 Ω ±1% pull-up resistor to 1.5 V. A single resistor can be used for both
signals.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 15
Page 16
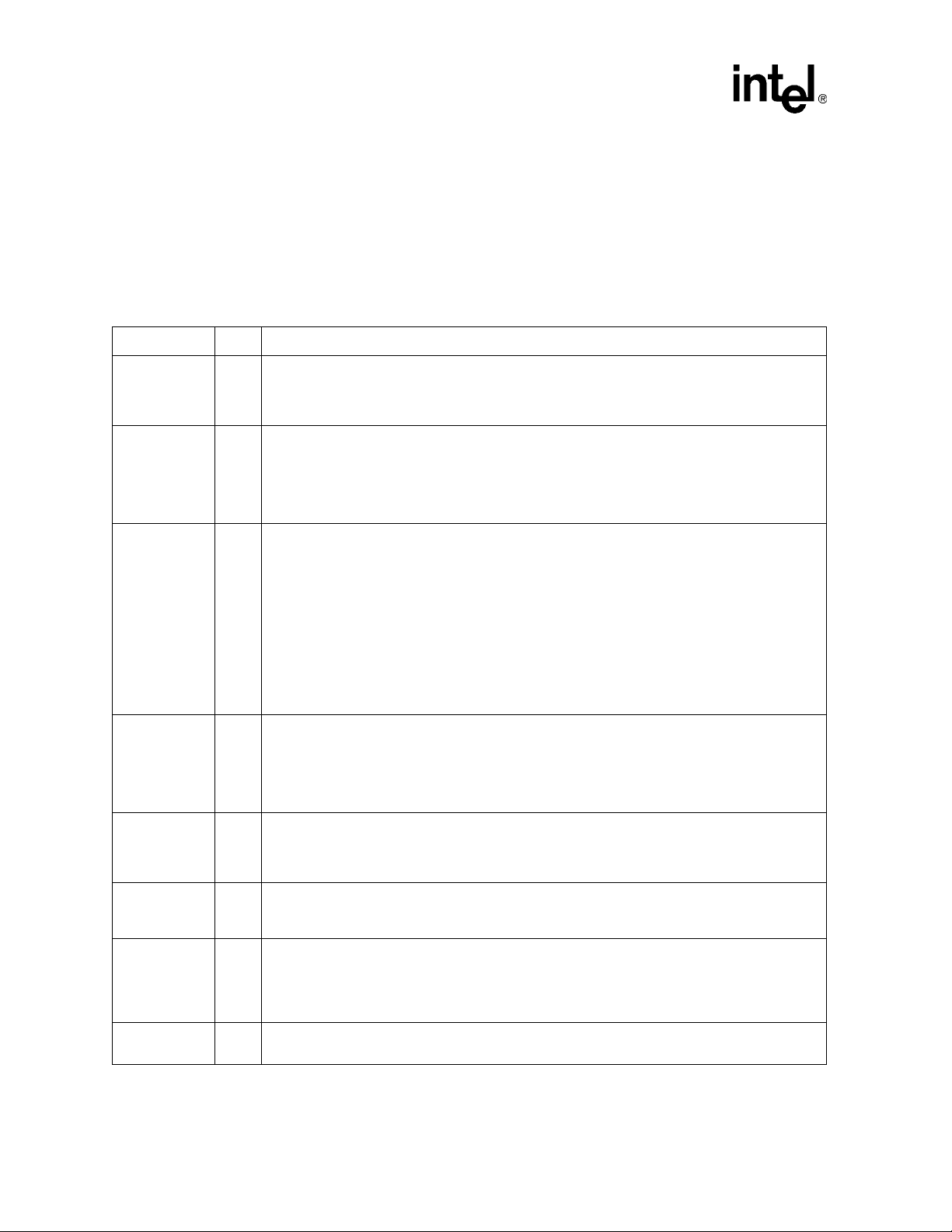
Signal Description
2.3 PCI Bus Interface (Two Instances)
Each interface is marked by either the letter “A” or “B” to signify the interface. For example,
A_AD refers to the AD bus on PCI bus A, and B_AD refers to the AD bus on PCI bus B. For pin
names described in the following sections, an “X” in the name indicates either A or B, for the PCI
bus A and PCI bus B sides, respectively. For example, “X_PAR” indicates A _PAR on the PCI bus
A and B_PAR on the PCI bus B.
Ta ble 3. PCI Interface Pins (Sheet 1 of 2)
Signal I/O Description
PCI Address/Data: These signals are a multiplexed address and data bus. During the address
A_AD[31:0]
B_AD[31:0]
A_C/BE#[3:0]
B_C/BE#[3:0]
A_PAR
B_PAR
A_DEVSEL#
B_DEVSEL#
A_FRAME#
B_FRAME#
A_IRDY#
B_IRDY#
A_TRDY#
B_TRDY#
A_STOP#
B_STOP#
phase or phases of a transaction, the initiator drives a physical address on X_AD[31:0]. During the
I/O
data phases of a transaction, the initiator drives write data, or the ta rget drives read data.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Bus Command and Byte Enables: These signals are a multiplexed command field and byte enable
field. During the address phase or phases of a transaction, the initiator drives the transaction type on
C/BE#[3:0]. When there are two address phases, the first address phase carries the dual address
I/O
command and the second address phase carries the transaction type. For both read and write
transactions, the initiator drives byte enables on C/BE#[3:0] during the data phases.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Parity: Even parity is calculated on 36 bits—AD[31:0] plus C/BE[3:0]#. It is calculated on all 36 bits
regardless of the valid byte enables. It is generated for address and data phases. It is driven
identically to the AD[31:0] lines, except it is delayed by exactly one PCI clock.
It is an output in the following cases:
• During the address phase for all transactions initiated by the Intel
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Bridge
• During all data phases when the 41210 is the initiator of a PCI write transaction
• When the 41210 is the target of a read transaction
The 41210 checks parity when it is the initiator of PCI read transactions and when it is the target of
PCI write transactions.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Device Select: The bridge asserts DEVSEL# to claim a PCI transaction. As a target, the 41210
asserts DEVSEL# when a PCI master peripheral attempts to access an address destined for PCI
Express*. As an initiator, DEVSEL# indicates the response to a transaction initiated by the 41210 on
the PCI bus. DEVSEL# is tristated from the leading edge of PCIRST#. DEVSEL# remains tristated by
the 41210 until driven as a target.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Frame: FRAME# is driven by the initiator to indicate the beginning and duration of an access. While
FRAME# is asserted, data transfers continue. When FRAME# is deasserted the transaction is in the
final data phase.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Initiator Ready: IRDY# indicates the ability of the initiator to complete the current data phase of the
transaction. A data phase is completed when both IRDY# and TRDY# are sampled asserted.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Target Ready: TRDY# indicates the ability of the target to complete the current data phase of the
transaction. A data phase is completed when both TRDY# and IRDY# are sampled asserted. TRDY#
is tristated from the leading edge of RST#. TRDY# remains tristated by the 41210 until driven as a
target.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Stop: This bit indicates that the target is requesting an initiator to stop the current transaction.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI
16 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 17
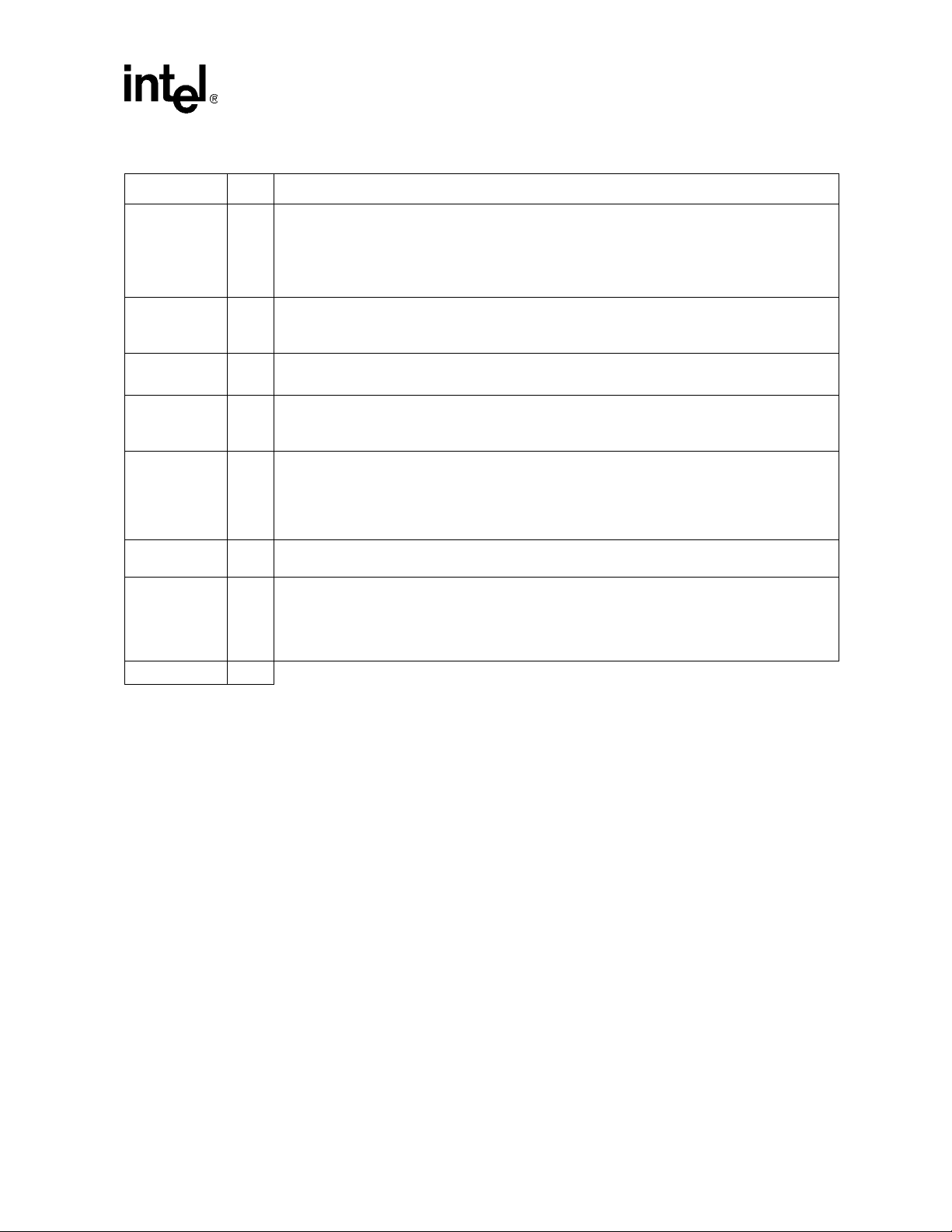
T a ble 3. PCI Interface Pins (Sheet 2 of 2)
Signal I/O Description
Parity Error: PERR# is driven by an external PCI device when it receives data that has a parity error.
A_PERR#
B_PERR#
A_SERR#
B_SERR#
A_REQ#[5:0]
B_REQ#[5:0]
A_GNT#[5:0]
B_GNT#[5:0]
A_M66EN
B_M66EN
A_PCIXCAP
B_PCIXCAP
A_LOCK#
B_LOCK#
Total 118
PERR# is driven by the 41210 in the following cases:
• when the 41210, as an initiator, detects a parity error during a read transaction
I/O
• when the 41210, as a target, detects a parity error during a write transaction
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
System Error: The 41210 samples SERR# as an input and conditionally forwards it to the PCI
Express*.
I
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
PCI Requests: REQ# receives request inputs into the internal arbiter.
I
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
PCI Grants: GNT# is the bus grant output corresponding to request input bits[5:0] from the internal
arbiter. GNT# indicates that an initiator can start a transaction on the PCI bus.
O
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
66 MHz Enable: M66EN is an input signal from the PCI bus that indicates the speed of the PCI bus.
When it is high, the bus speed is 66 MHz. When it is low, the bus speed is 33 MHz. This signal is
used to generate an appropriate clock (33 or 66 MHz) on the PCI bus.
I/OD
To tie high: Use an approximately 8.2 KΩ resistor to pull to VCC33.
To tie low: Pull down to ground.
PCI-X Capable: PCIXCAP indicates whether all devices on the PCI bus are PCI-X devices, so that
I
the 41210 can switch into PCI-X mode. Use an approximately 8.2 KΩ resistor to pull to VCC33.
PCI Lock: LOCK# indicates an exclusive bus operation and may require multiple transactions to
complete. This signal is an output from the bridge when it is initiating exclusive transactions on PCI.
LOCK# is ignored when PCI masters are granted the bus. Locked transaction do not propagate
O
upstream.
No external pull-up resistors are required on the system board for these signals.
Signal Description
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 17
Page 18
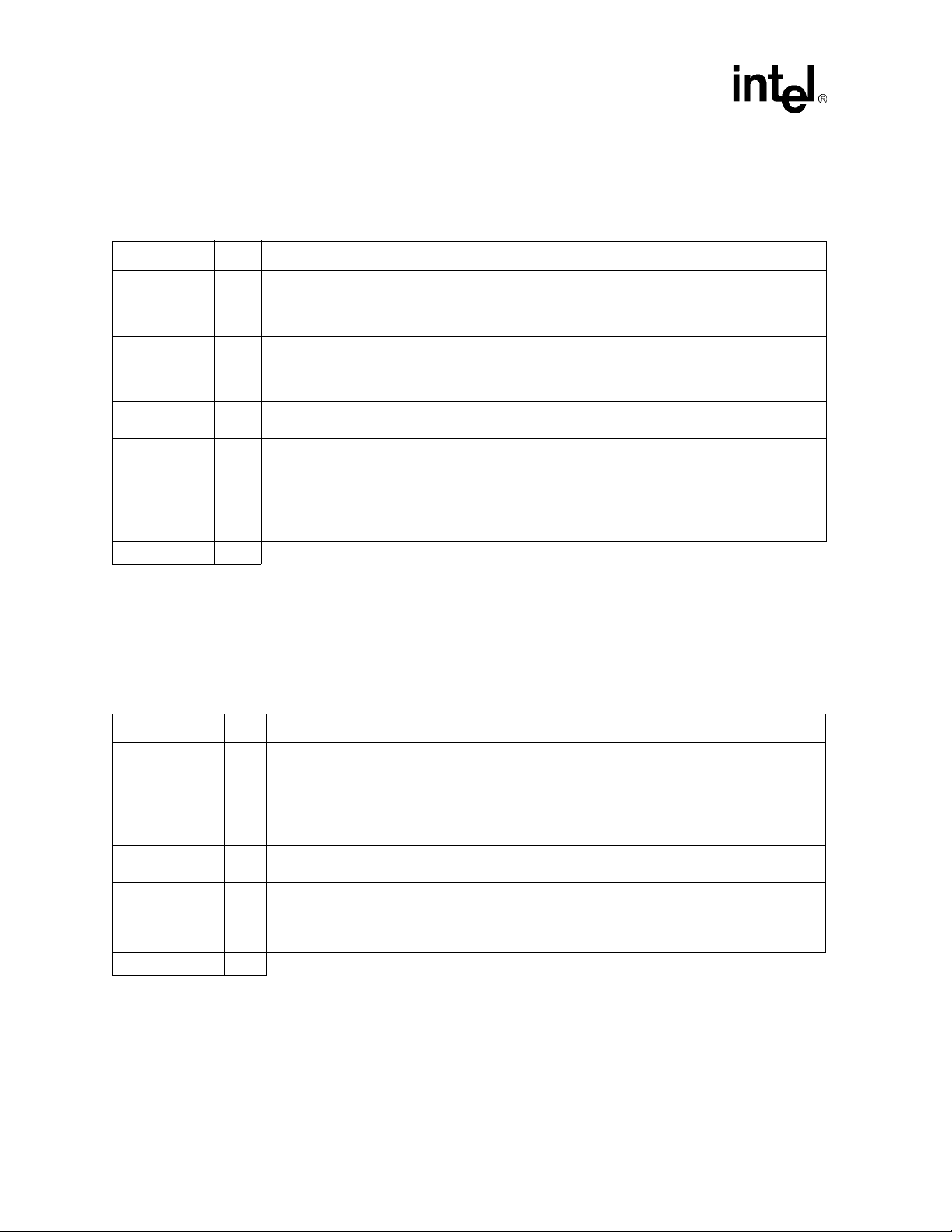
Signal Description
2.4 PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension (Two Interfaces)
Table 4. PCI Interface Pins: 64-Bit Extensions
Signal I/O Description
A_AD[63:32]
B_AD[63:32]
A_C/BE#[7:4]
B_C/BE#[7:4]
A_PAR64
B_PAR64
A_REQ64#
B_REQ64#
A_ACK64#
B_ACK64#
PCI Address/Data: The AD signals are a multiplexed address and data bus. This bus provides an
additional 32 bits to the PCI bus. During the data phases of a transaction, the initiator drives the
I/O
upper 32 bits of 64-bit write data, or the target drives the upper 32 bits of 64-bit read data, when
REQ64# and ACK64# are both asserted.
Bus Command and Byte enables upper 4 bits: The C/BE# signals are a multiplexed command
field and byte enable field. For both reads and write transactions, the initiator drives byte enables for
I/O
the AD[63:32] data bits on C/BE[7:4] during the data phases when REQ64# and ACK64# are both
asserted.
PCI interface upper 32 bits parity: PAR64 carries the even parity of the 36 bits of AD[63:32] and
I/O
C/BE#[7:4] for both address and data phases.
PCI interface request 64-bit transfer: REQ64# is asserted by the initiator to indicate that the
I/O
initiator is requesting a 64-bit data transfer. REQ64# has the same timing as FRAME#. When the
41210 is the initiator, this signal is an output. When the 41210 is the target, this signal is an input.
PCI interface acknowledge 64-bit transfer: ACK64# is asserted by the target only when REQ64# is
I/O
asserted by the initiator, to indicate the target ability to transfer data using 64 bits. ACK64# has the
same timing as DEVSEL#.
Total 78
2.5 PCI Bus Interface Clocks and, Reset and Power Management (Two Interfaces)
T able 5. PCI Clock and Reset Pins
Signal I/O Description
A_CLKO[6:0]
B_CLKO[6:0]
A_CLKIN
B_CLKIN
A_RST#
B_RST#
A_PME#
B_PME#
PCI Clock Output: CLKO is the 33/66/100/133 MHz clock for a PCI device. X_CLK[6] must be
connected to the respective X_CLKIN input for feeding the PCI interface logic. Unused clock outputs
O
may be disabled via the “Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control” register and should be treated as
no connects on the board.
PCI Clock In : CLKIN is the PCI clock feedback input. CLKIN must be connected to the
I
corresponding X_CLKO[6] through a 22 Ω ± 1% series resistor.
O PCI Reset: The bridge asserts RST# to reset devices that reside on the secondary PCI bus.
PCI Power Management Event: PME# is the PCI bus power management event signal. PME# is a
shared open-drain input from all the PCI cards on the corresponding PCI bus segment. PME# is a
I
level-sensitive signal that is converted to a PME event on PCI Express*.
PME# does not have on-die 8.3 KΩ pull-up. This pull-up must be provided externally.
Total 20
18 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 19
2.6 Interrupt Interface (Two Interfaces)
This section lists the interrupt interface signals. There are two sets of interrupt signals for the
standard INTA–INTD PCI signals.
T able 6. Interrupt Interface Pins
Signal I/O Description
A_INTA#
A_INTB#
A_INTC#
A_INTD#
B_INTA#
B_INTB#
B_INTC#
B_INTD#
Total 8
Interrupt Request Bu s: The interrupt lines from PCI interrupts INTA#–INTD# can be routed to
these interrupt lines.
I
Routing must be based on device number in accordance with the instructions given in Section 7,
“Interrupt Support” on page 53.
Signal Description
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 19
Page 20
Signal Description
2.7 Reset Straps
The following signals are used for static configuration. These signals are all sampled on the rising
edge of PERST#.
Table 7. Reset Strap Pins
Signal I/O Description
PCI-X 133 MHz Enable: The 133EN pin, when high, allows the PCI-X segment to run at 133 MHz
A_133EN
B_133EN
A_STRAP[6:0]
B_STRAP[6:0]
when X_PCIXCAP is sampled high. When 133EN is low, the PCI-X segment runs only at 100MHz
when X_PCIXCAP is sampled high.
I
To tie high: Use an approximately 8.2 KΩ resistor to pull to VCC33.
To tie low: Pull down to ground.
Internal Test Modes: For normal operation, X_STRAP[6] and [2:0] must be pulled low and
X_STRAP[5:3] must be pulled high, as shown in the table below.
X_STRAP Logic Level
00
10
I
20
31
41
51
60
A_TEST[2:1]
B_TEST{2:1]
CFGRETRY I
Total
To tie high: Use approximately an 8.2 KΩ resistor to pull up to VCC33.
To tie low: Pull down to VSS.
Internal Test Modes: These straps must be pulled high to VCC33. Use an approximately 8.2 KΩ
I
resistor to pull up to VCC33.
Configuration Retry: This pin, when sampled high, sets the Configuration Cycle Retry Bit (bit 3) in
the Bridge Initialization Register (“Offset FCh: BINIT— Bridge Initialization Register” on page 104).
When no local initialization is needed, this pin must be pulled low to VSS.
See Section 9, “Local Initialization” for additional details.
19
20 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 21
2.8 SMBus Interface
Ta ble 8. SMBus Interface Pins
Signal I/O Description
SMBCLK I/OD SMBus Clock: This signal must be pulled to 3.3 V through an 8.2 KΩ resistor.
SMBDAT I/OD SMBus Data: This signal must be pulled to 3.3 V through an 8.2 KΩ resistor.
SMBus Addressing Straps: These straps set the SMBus address for the 41210 Bridge. The address
is determined as indicated below:
•Bit[7]1
•Bit[6]1
SMBUS[5]
SMBUS[3:1]
Total
• Bit[5] SMBUS[5]
I
•Bit[4]0
• Bit[3] SMBUS[3]
• Bit[2] SMBUS[2]
• Bit[1] SMBUS[1]
These signals (bits[5], [3:1]) must be pulled up to 3.3 V or down to ground. Sampled at the rising edge
of PERST#.
6
Signal Description
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 21
Page 22
Signal Description
2.9 Miscellaneous Pins
Table 9. Miscellaneous Pins
Signal I/O Description
Configuration Reset : This signal is asserted low when ever the bridge goes
through a fundemental reset (PERST#, RSTIN#, or PCI Express Reset). This
CFGRST# O
PERST# I
RSTIN# I
TCK I
TDI I
TDO O
TMS I
TRST# I
RESERVED[8:1] I
NC[19:18], NC[16:1]
A_NC[10:1]
B_NC[10:1]
NC[17] O This signal requires an external pull-up, 8.2K ohm to 3.3V
O No Connect: (39 pins) These output pins should be left floating
Total
signal should be used to indicate when the local initialization methods should be
executed.
Refer to the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Design Guide for more
information.
PCI Express Fundamental Reset: When low, asynchronously resets the
internal logic (including sticky bits).
Reset In: When Asserted, this signal asynchronously resets the internal logic
and asserts X_RST# output for both PCI interfaces. This signal should be pulled
high for adapter card usage.
TAP Clock In: This is the input clock to the JTAG TAP controller. Acceptable
frequency is 0-16MHz
If not utilizing JTAG, this signal can be left as a no connect.
Test Data In: Th is is the serial data input to the JTAG BSCAN shift register
chain and to the JT AG BSCAN control logic. This is latched in on the rising edge
of TCK.
If not utilizing JTAG, this signal can be left as a no connect.
Test Data Output: This is the serial data output from the JTAG BS CAN logic
If not utilizing JTAG, this signal can be left as a no connect.
Test Mode Select: This signal controls the T A P controller state machine to
move to different states and is sampled on the rising edge of TCK.
If not utilizing JTAG, this signal can be left as a no connect.
Test Reset In: This signal is used to asynchronously reset the JTAG BSCAN
logic.
If not utilizing JTAG, connect this signal to ground through a 1KΩ pull-down
resistor.
Reserved: (8 pins) These input pins should be pulled low
Use an approximately 8.2KΩ resistor to pull-down to ground.
57
22 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 23
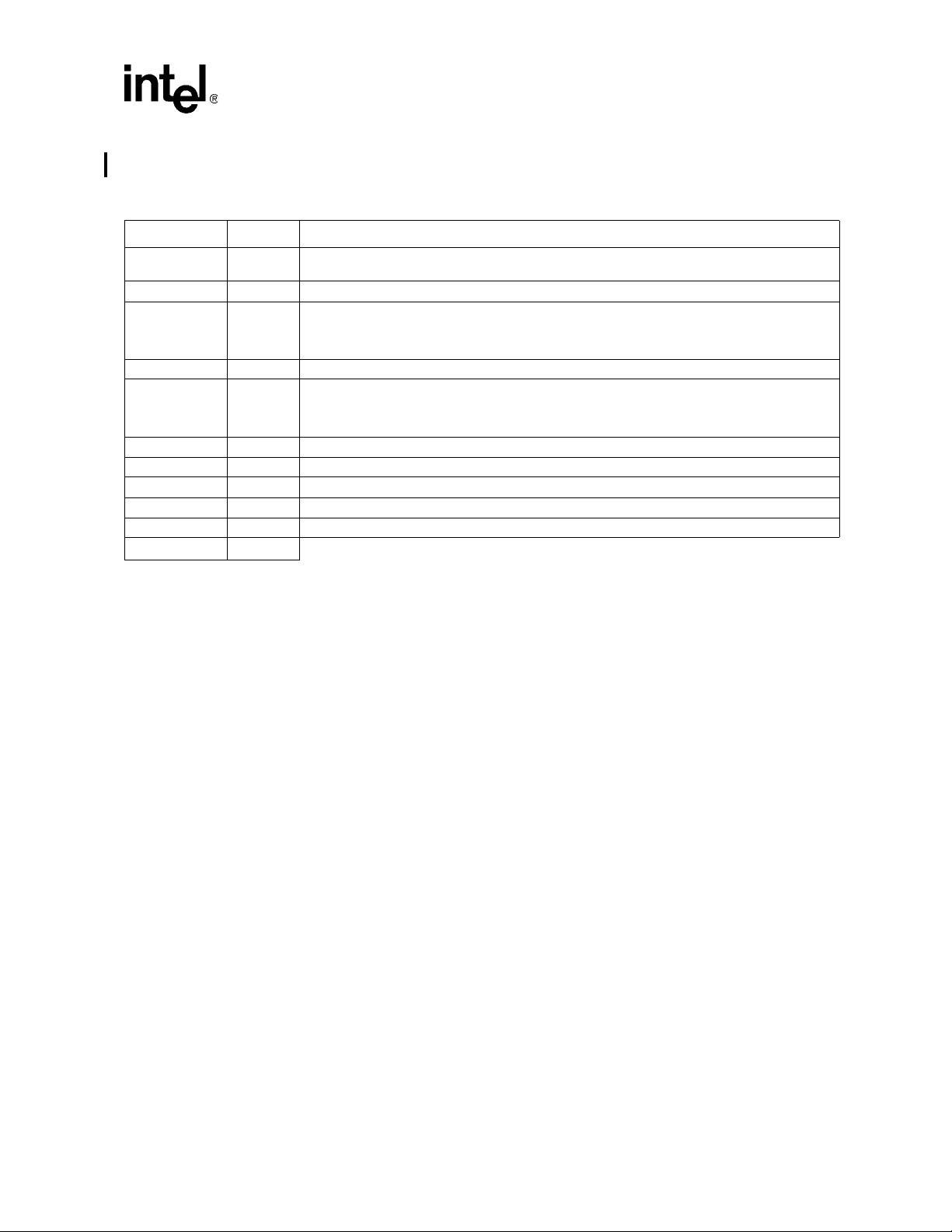
2.10 Voltage Pins
Table 10. Miscellaneous Pins
Signal Number Description
RCOMP 1
VCC 36 1.5 V Core Voltage: 1.5 V ± 5%.
VCCAPE 1
VCCAPCI[2:0] 3 Analog PCI Voltages: 1.5 V ±3%
VCCBGPE 1
VSSBGPE 1 Analog Band-gap Ground
VCCPE 9 1.5 V PCI Express* Voltage: 1.5 V ±3%
VCC33 30 3.3 V PCI I/O Voltage: 3. 3V ± 5%.
VSS 142 Ground: Ground for all voltage rails
VSSAPE 1 Analog PC I Express* Ground
Total
225
Analog Compensation Pin: RCOMP is the analog compensation pin for PCI. Pull down to
ground through a 100 Ω ±1% resistor.
Analog PCI Express* Voltage:
• DC: 1.5 V ± 3%
• AC: ±5 mV above 1 M Hz at package pin under DC load conditions
Analog Band-gap Voltage:
• DC: 2.5 V ±3%
• AC: ±10 mV above 1 MHz at package pin under DC load conditions
Signal Description
§ §
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 23
Page 24

Signal Description
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
24 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 25
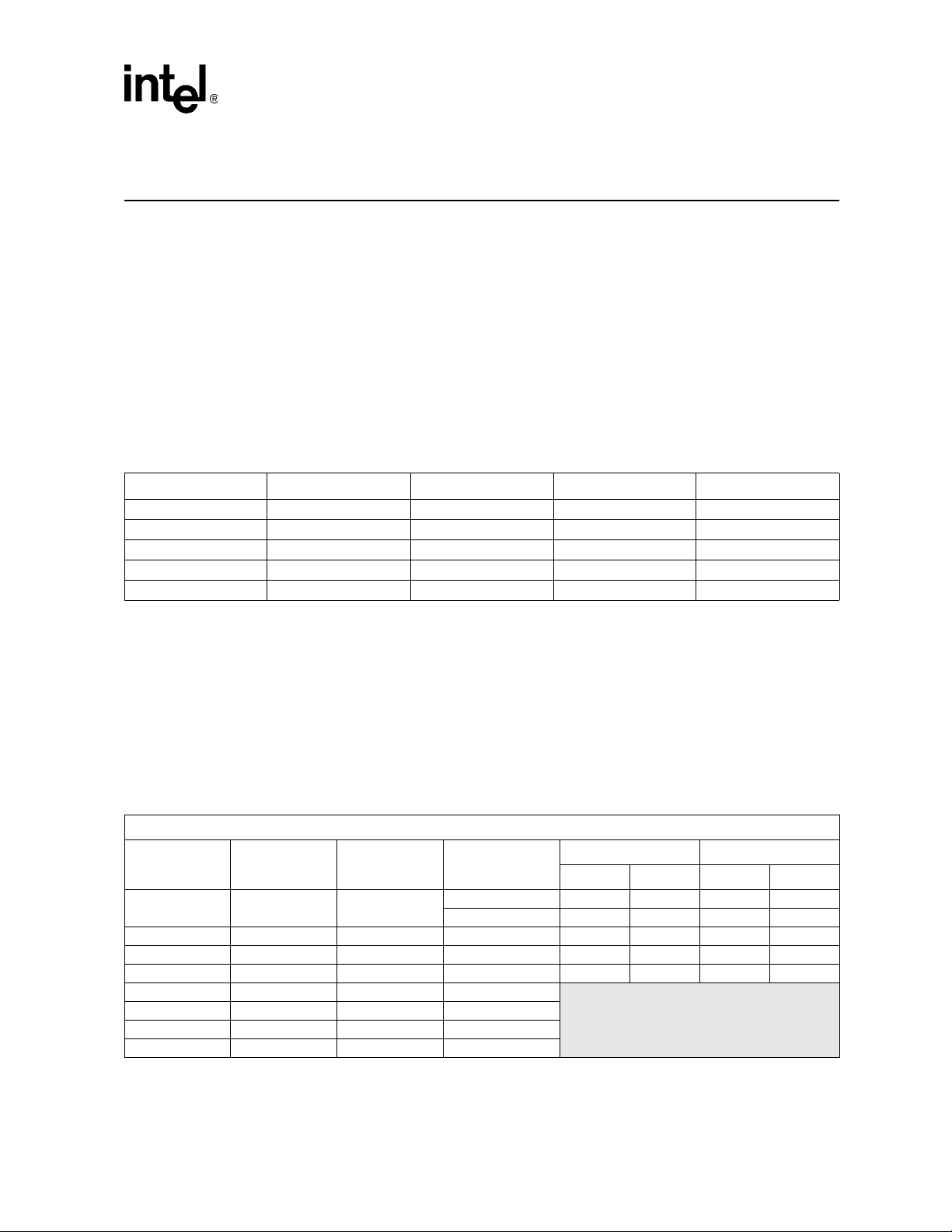
PCI-X Interface
PCI-X Interface 3
This section deals with the specifics of the operation and transaction flow details of the PCI
interfaces.
3.1 Initialization
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (also called the 41210 Bridge or the 41210) is the
source bridge for the PCI bus and senses the X_M66EN, X_133EN, and X_PCIXCAP pins to
decide the mode and frequency of operation. Encoding on the M66EN and PCIXCAP pins along
with the PCI reset straps is shown below; these encodings identify the capabilities of the sy stem .
Table 11. PCI Mode Pin/Strap Encoding
X_133EN
Not connected – Not connected PCI-X 133 MHz
NOTE:
1. This pin is used by the board designer to run the PCI-X bus at 100 MHz even when all the PCI-X devices on the bus are
133 MHz capable, so as to accommodate the board routing limitation on frequency. Note that to accommodate running a
PCI-X bus at 66 MHz, when all cards are capable of 133 MHz, the motherboard has to drive the PCIXCAP pin to VCC33/2.
1
– Ground Ground PCI conventional 33 MHz
– Not connected Ground PCI conventional 66 MHz
– – Pull-down PCI-X 66 MHz
Ground – Not connected PCI-X 100 MHz
X_M66EN X_PCIXCAP PCI Bus Mode PCI Frequency
As soon as the 41210 identifies the capabilities of the PCI bus devices, it drives the initialization
pattern on the DEVSEL#, STOP#, TRDY#, FRAME#, and IRDY# pins as per Table 12 to initialize
the PCI bus devices to the proper mode and frequency. The patterns shown in Table 12 below are
stable on the rising edge of the A_RST# and B_RST# pins. Refer to the PCI-X Addendum to the
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b for details on the timing of these patterns with respect
to the A_RST# and B_RST# pins.
Table 12. PCI-X Initialization Pattern
FRAME# and IRDY# are Deasserted
DEVSEL# STOP# TRDY# Mode
Deasserted Deasserted Deas serted
Deasserted Deasserted Asserted PCI-X 15 20 50 66
Deasserted Asserted Deasserted PCI-X 10 15 66 100
Deasserted Asserted A sserted PCI-X 7.5 10 100 133
Asserted Deasserted Deasserted PCI-X
Asserted Deasserted Asserted PCI-X
Asserted Asserted Deasserted PCI-X
Asserted Asserted Asserted PC I-X
PCI 33 30 — 0 33
PCI 66 15 30 33 66
Clock Period (ns) Clock Freq. (MHz)
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Reserved
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 25
Page 26
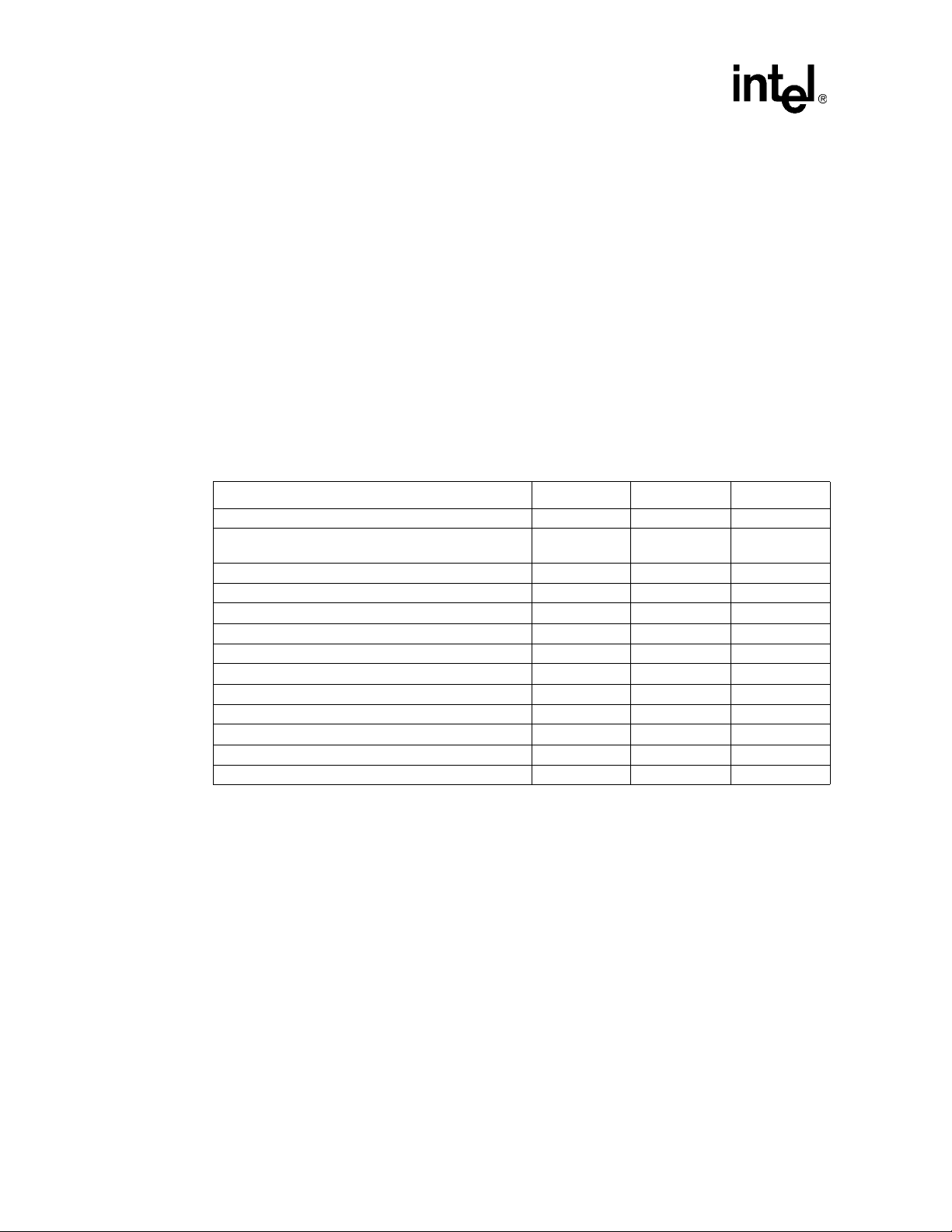
PCI-X Interface
In summary:
• A_RST# and B_RST# are outputs from the 41210.
• PCI clocks are actively driven out from the 41210.
• The 41210 drives X_AD[31:0], X_BE[3:0], and X_PAR low during PCI bus reset.
• The 41210 drives X_REQ64# low during reset.
3.2 Transactions Supported
3.2.1 PCI Mode
Table 13 lists all the transactions supported by the 41210 on the PCI bus. The 41210 supports full
64-bit addressing upstream and downstream and can both generate and accept dual address cycles.
Table 13. PCI Transactions Supported
Transaction Encoding
Interrupt acknowledge 0000 No No
Special cycle (PCI Express* Type1-t o-PC I Special
Cycle)
I/O read 0010 Yes Yes
I/O write 0011 Yes Yes
Memory read 0110 Yes Yes
Memory write 0111 Yes Yes
Configuration read 1010 Y es Y es
Configuration write 1011 Yes Yes
Memory read multiple 1100 No Yes
Dual address cycle 1101 Yes Yes
Memory read line 1110 No Yes
Memory write and invalidate 1111 No Yes
LOCK transaction – Yes No
NOTES:
1. PCI command encodings that are not shown in this table are ignored.
2. I/O transactions are forwarded from PCI to PCI Express* only when the inbound I/O enable bit is set in the
“Offset FCh: BINIT —Bridge Initialization Register” on page 104
3. Upstream Type 0 configuration cycles to the 41210 Bridge’s own configuration space are supported.
1
0001 Yes No
Master Target
2
3
26 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 27
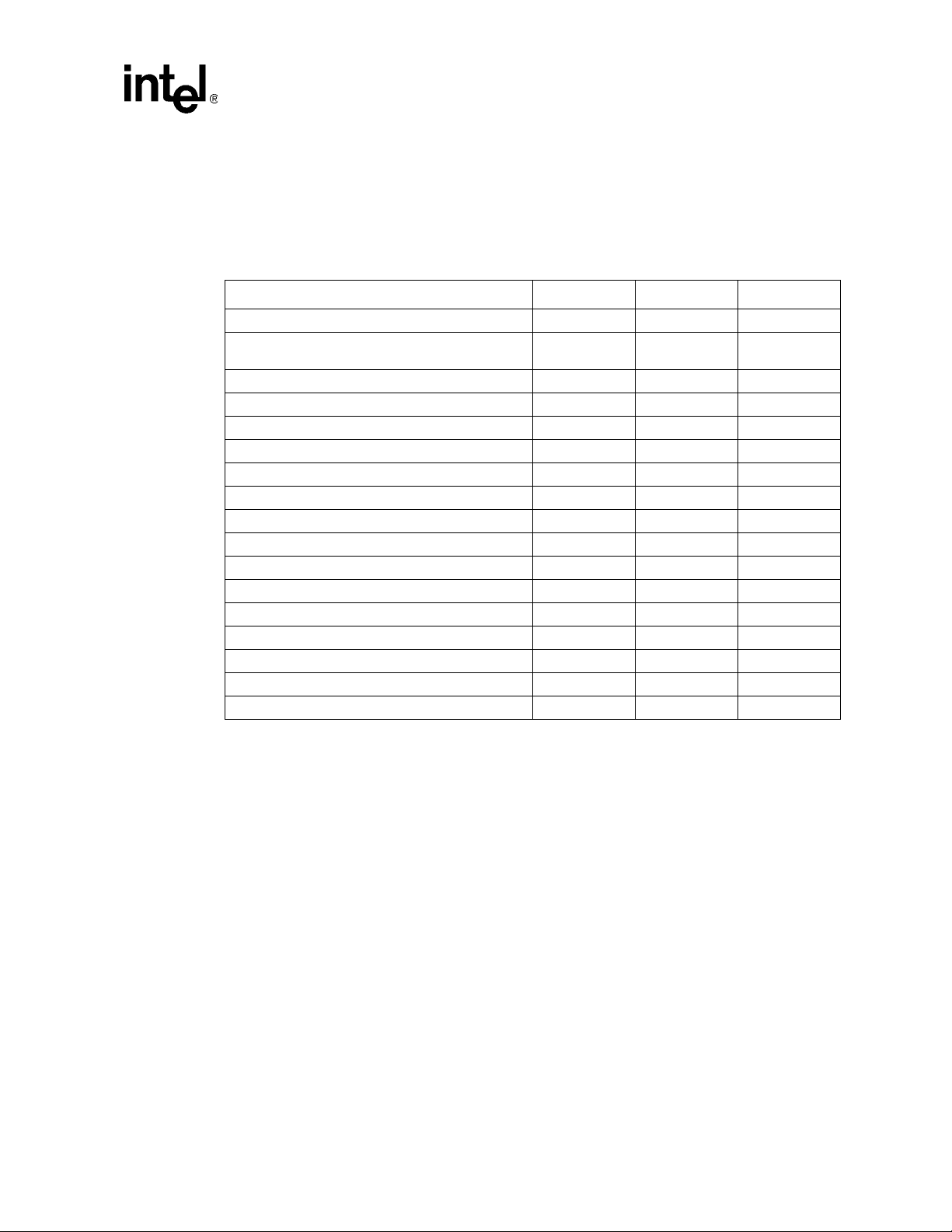
3.2.2 PCI-X Mode
Table 14 lists the transactions that the 41210 supports when the PCI interface is in the PCI-X mode.
As a master, the 41210 supports the memory write block command for writes that are multiples of
cache-line.
Table 14. PCI-X Transactions Supported
Transaction Encoding
Interrupt acknowledge 0000 No No
Special cycle
(PCI Express* Type1-to-PCI Special Cycle)
I/O read 0010 Yes Yes
I/O write 0011 Yes Yes
Reserved 0100 No No
Reserved 0101 No No
Memory read DWORD 0110 Yes Yes
Memory wri te 0111 Yes Y es
Alias to memory read block 1000 No Yes
Alias to memory write block 1001 No Yes
Configuration read 1010 Yes Y es
Configuration write 1011 Yes Yes
Split completion 1 100 Yes Yes
Dual address cycle 1101 Yes Yes
Memory read block 1110 Yes Yes
Memory write block 1111 Yes Yes
LOCK transaction – Yes No
NOTES:
1. PCI command encodings that are not detailed in this table are ignored.
2. Upstream Type 0 configuration cycles to the bridge’s own configuration space are supported.
PCI-X Interface
1
0001 Yes No
Master Target
2
3.2.3 Read Transactions
3.2.3.1 Prefetchable
Any memory read line or memory read multiple commands on PCI that are decoded by the 41210
are prefetched on the PCI Express* interface. The prefetchability of a given PCI read request is
determined by the prefetch policy (PP) bits[55:54] of the “Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch
Control Register” on page 119. The amount of data prefetched depends on the clock frequency,
x_REQ64#, and the command type. The 41210 does not prefetch past a 4 KB page boundary.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 27
Page 28

PCI-X Interface
3.2.3.2 Delayed
All memory read transactions are delayed read transactions. When the 41210 accepts a delayed
read request, it samples the address, command, and address parity. This information is entered into
the delayed transaction queue. When the 41210 is in PCI-X mode, transactions follow the split
transaction model of PCI-X. Read data returned from PCI Express* for an active delayed
transaction entry is forwarded to the PCI-X master as a split completion.
3.2.3.3 Inbound Read Request Algorithm
In PCI mode:
• Each read stream always gets exactly 1 K buffer—no more or no less.
• A maximum of four requests can be outstanding per stream/buffer.
• A maximum of eight requests can be outstanding per PCI segment.
In PCI-X mode:
• Each read stream requests and gets buffer in 512 B chunks.
• There is no limit on how many 512 B chunks a read stream can occupy.
• A maximum of four requests can be outstanding per stream.
• A maximum of one request can be outstanding per 512 B buffer.
• A maximum of eight requests can be outstanding per PCI-X segment.
3.2.4 Configuration Transactions
Type 0 configuration transactions are issued when the intended target resides on the same PCI bus
as the initiator. A Type 0 configuration transaction is identified by the configuration command and
by the lowest two bits of the address being set to 00b.
Type 1 configuration transactions are issued when the intended target resides on another PCI bus,
or when a special cycle is to be generated on another PCI bus. A Type 1 configuration transaction
is identified by the configuration command and by the lowest two bits of the address being set to
01b.
The register number is found in both Type 0 and Type 1 formats and gives the Dword address of
the configuration register to be accessed. The function number is also included in both Type 0 and
Type 1 formats and indicates which function of a multifunction device is to be accessed. For singlefunction devices, this value is not decoded. Type 1 configuration transaction addresses also include
a five-bit field designating the device number that identifies the device on the target PCI bus that is
to be accessed. In addition, the bus number in Type 1 transactions specifies the PCI bus to which
the transaction is targeted.
28 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 29

3.2.5 LOCK Cycles
A lock is established when all the following conditions are true:
• A PCI Express* device initiates a Memory Read Lock (MRdLk) request to read from a target
PCI device.
• LOCK# is asserted on the PCI bus.
• The target PCI device responds with a TRDY#.
The bus is unlocked when the Unlock Message is received on PCI Express*.
When the PCI bus is locked, all upstream mem ory transactions fr om that bus are retried. T he 41210
upstream read prefetch engine stops issuin g any mo re req uests o n the PCI Ex pres s* bus. However ,
note that the 41210 accepts read completions for upstream read requests that were issue d before the
lock was established on the PCI bus when they return on PCI Express*.
As soon as the bus is locked, any PCI Express* cycle to PCI is driven with the LOCK# pin
asserted, even when that particular cycle is not locked. This is not expected to occur, because under
lock, peer-to-peer accesses are internally blocked and the upstream component must not send any
non-locked transactions downstream.
When one PCI bus segment is locked, the other is still free to accept cycles (in other words, that
bus is not locked. However, these transactions are not allowed to proceed on PCI Express* or the
locked PCI segment). Therefore, as soon as the PCI bus is locked, additional cycles d o not pr oceed
onto PCI Express* from the non-locked PCI segment.
PCI-X Interface
During the LOCK sequence, when the initial locked read command results in a master or target abort
(either on the PCI bus or the internal switch interconnect), the 41210 does not esta blish lo ck, and i t
sends a completion packet on PCI Express* with an error status. In case of a subsequent memory read
or memory write receiving a target or master abort during a LOCK sequence, the 41210 unlocks only
after the unlock message is received on PCI Express*.
• Downstrea m LOCK is supported by th e 41210.
• Upstream LOCK transactions are treated with the LOCK signal ignored.
See Table 15 below for a summary of the 41210 responses to LOCK transactions.
Table 15. LOCK Transaction Handling in the Intel
End Point
PCI – Forward to PCI w/ LOCK#
PCI Express* Ignore
NOTE:
1. Transaction is treated as if it is a normal read or write transaction.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Source
PCI PCI Express*
1
–
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 29
Page 30

PCI-X Interface
3.2.6 Decoding
In the PCI mode, the 41210 supports only the linear i ncrement address mode for bursting memory
transfers (indicated when the lowest two address bits are equal to 0). When either of these address bits
is non-zero, the 41210 disconnects the transaction after the first data transfer. The 41210 decodes all
PCI cycles with medium DEVSEL# timing. In the PCI-X mode, 41210 always decodes as a Type A
target. Also, in PCI-X mode, the 41210 decodes split completions using the primary bus number
field.
Refer to Section 5, “Addressing” on page 41 for a general description of addressing and decoding.
3.2.7 Transaction Termination
3.2.7.1 PCI Mode Transaction Termination
• Normal Termination
As a PCI master, the 41210 uses normal termination when DEVSEL# is returned by the target
within five clock cycles of FRAME# assertion. It terminates a transaction when one of the
following conditions are met:
— All write data for a write transaction are transferred from the 41210 data buffers to the
target (the 41210 does not generate fast back-to-back transactions).
— All read data for a read transaction are transferred from the target to the 41210.
— The master latency timer expires and the bus grant of the 41210 is de-asserted.
• Master Abort
When the transaction initiated by the 41210 does not receive a DEVSEL# response within five
clocks of FRAME# assertion, the 41210 terminates the transaction with a master abort. The
41210 sets the received master abort bit in the secondary status register. Read requests
(configuration, I/O, memory) that receive master abort termination are sent back to PCI
Express*/peer PCI with a master abort status.
Note that when the 41210 performs a Type 1 to special cycle translation, a master abort is the
expected termination for the special cycle on the target bus. In this case, the master abort
received bit is not set, and the Type 1 configuration transaction is disconnected after the first
data phase.
• Tar g et Abort
When the 41210 receives a target abort, and the cycle requires completion on PCI Express*,
the bridge returns the target abort status to PCI Express*. The 41210 sets the received target
abort status bit in the secondary status register for all target aborts it receives on the PCI bus.
Tar get abort can occur dur ing any data phase of a PCI-X transaction. A read com pletion packet
to PCI Express*/peer PCI, incurring a target abort in the middle of the packet, returns valid
data to the point of target abort and a target abort completion status for the reminder.
• Disconnect and Retry
When the 41210 receives a disconnect response from a target, it re-initiates the transfer with
the remaining length. When the 41210 receives a retry , it waits at least two PCI clocks before it
retries the transaction. When the retried transaction is a write, the 41210 retries the write until
it completes normally or with a target or master abort. When the retried transaction is a
delayed read or delayed write transaction, the 41210 allows memory reads and writes to pass
the transaction. Refer to Section 6, “Transaction Orderin g” on page51 for details on the k i nds
30 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 31

PCI-X Interface
of reordering allowed. Retry is not considered an error condition, so there is no error logging
or reporting done on a retry.
• The 41210 terminates a transaction with retry to an initiator when one of the following
conditions is met:
— The 41210 receives a new memory read transaction, and the 41210 delayed transaction
queue is full.
— The 41210 receives a memory read that has already been queued, but has not completed
on PCI Express*.
— The 41210 receives a memory read that has been queued and completed on PCI Expres s*,
but ordering rules require a downstream posted write to complete ahead of it.
— A LOCK transaction has been established from PCI Express*-to-PCI.
— The 41210 receives a memory write transaction, and the 41210 has no fr ee buf fer sp ace to
accept the write.
— A memory write transaction is from a master other than the master that was previously
retried (starvation prevention mechanis m).
• The 41210 disconnects an initiator when one of the following conditions is met:
— The 41210 cannot accept any more write data.
— The 41210 has no more read data to deliver.
— The memory address is non-linear.
— The inverse decode window ends.
• The 41210 returns a target abort to PCI when the following condition is met.
— The cycle master aborted, or the target aborted on PCI Express*/peer PCI.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 31
Page 32

PCI-X Interface
3.2.7.2 PCI-X Mode Transaction Termination
• Initiator Disconnect or Satisfaction of Byte Count
As a PCI-X master, the 41210 uses normal termination (initiator disconnect or satisfaction of
byte count) if DEVSEL# is returned by the target within six clock cycles after address phase.
The 41210 terminates a transaction when one of the following conditions are met:
— Initiator disconnect occurs when all write data indicated in the byte count of the write
transaction is transferred from the 41210 data buffers to the target. The 41210 does not
perform an initiator disconnect on a write before the byte count size has been satisfied.
— Initiator disconnect at the next ADB on a split read completion because the 41210 data
buffer has run dry.
— Initiator disconnect occurs at the next ADB when the master latency timer expires and the
bus grant of the 41210 is de-asserted.
• Master Abort Termination
When a transaction initiated by the 41210 does not receive a DEVSEL# response within six
clocks after address phase, the 41210 terminates the transaction with a master abort. The
41210 sets the received master abort bit in the secondary status register. Read requests
(configuration, I/O, memory) that receive master abort termination are sent back to PCI
Express*/peer PCI with a master abort status. Delayed write requests that receive master abort
are sent back to PCI Express* with a master abort status.
Note: When the 41210 performs a Type 1 to special cycle translation, a master abort is the expected
termination for the special cycle on the target bus. In this case, the master abort received bit is not
set, and the Type 1 configuration transaction is disconnected after the first data phase.
• Tar g et Abort
When the 41210 receives a target abort, and the cycle requires completion on PCI Express*,
the 41210 returns the target abort status to PCI Express*. The 41210 sets the received target
abort status bit in the secondary status register for all target aborts it receives on the PCI bus.
Tar get abort can happ en on any dat a phase of a PCI-X transaction. A read com pletion packet to
PCI Express*/peer PCI that incurs a target abort in the middle of the packet returns valid data
to the point of target abort, all 1s for the reminder of the length, and a target abort completion
status for the entire packet.
• Disconnect and Retry
When the 41210 receives a disconnect response (single data phase or at next ADB) from a
target, it re-initiates the transfer with the remaining length. When the 41210 receives a retry, it
waits at least two PCI clocks before it retries the transaction. When the retried transaction is a
write, the 41210 retries the write until it completes normally or with a target or master abort.
When the retried transaction is a delayed read or delayed write transaction, the 41210 allows
memory reads, split completions, and writes to pass the transaction. Refer to Section 6,
“Transaction Order i ng” on page 51 for details on the kinds of reordering allowed. Retry is not
considered an error condition, so there is no error logging or reporting done on a retry.
• Split Response
The 41210 can receive split response for memory reads, and I/O and configuration read and
write transactions.
32 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 33

PCI-X Interface
• Target Terminations Initiated by the 41210
The 41210 responds with a retry to PCI-X when one of the following conditions is met:
— A memory read transaction occurs and the 41210 delayed transaction queue is full.
— A LOCK transaction is established from PCI Express*-to-PCI.
— A memory write transaction occurs and the 41210 has no free buffer space to accept the
write.
— A memory write is from a master other than the master that was previously retried
(starvation prevention mechanism).
Note: The 41210 never retries a completion since it always has enough buffer space for all split requests
it sends out. No transaction information is retained on any writes.
• Disconnect
The 41210 disconnects a transaction on PCI-X when one of the following conditions is met:
— The 41210 cannot accept any more write data and an ADB is reached.
— A split completion packet being sent, ADB is reached, and the 41210 read buffers are
running dry.
— Inverse decode window ends, and an upstream write is in progress, irrespective of the
availability of the write-buffer.
• Target Abort
The 41210 returns a target abort to PCI-X when one of the following conditions is met:
— The initial request received a target-abort on the peer PCI bus or a Completion with
Completer Abort status on the PCI Express* interface.
— All requests with address parity error and the parity error response bit is set.
• Master Abort
— The 41210 master aborts all memory transactions on PCI-X when the bus master enable
(BME) bit is cleared.
— The 41210 returns a master abort response in a split completion when the split cycle
master aborted on PCI Express*/peer PCI.
• Split Response
All memory read cycles that cross the 41210 receive this termination, if they are not retried.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 33
Page 34

PCI-X Interface
3.3 PCI-X Protocol Specifics
3.3.1 Attributes
Table 16 describes how the 41210 fills in attribute fields where the PCI-to-PCI Bridge
Specification, Revision 1.1 allow s some implementation flexibility.
Table 16. Intel
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Implementation of Requester Attribute
Fields
Attribute Function
No Snoop (NS)
Relaxed Ordering (RO)
Tag
Byte counts
The Intel
directions and does nothing with it internally.
This bit allows relaxed ordering of transactions, which the 41210 does not permit.
This bit is only forwarded in the 41210, and is never generated on PCI-X from an
PCI Express* packet or vice-versa.
Since the 41210 can have two outstanding requests on PCI-X at a time, this field can
be either 0 or 1.
From PCI Express*, this attribute is based on the length field from PCI Express*,
which is DWord-based.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge only forwards this attribute in both
3.3.2 4 GB and 4 K Page Crossover
The PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b, allows burst transactions
to cross page boundaries (in the case of the 41210, this is 4 K) and 4 GB address boundaries. As a
PCI-X master, the 41210 always ends the transaction at a 4 K boundary. As a PCI-X target, the
41210 allows a burst beyond a 4 K page boundary. Note that on PCI Express*, neither read nor
write requests ever cross a 4 K boundary.
3.3.3 Wait States
The 41210 does not generate wait states as a targ et.
34 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 35

3.3.4 Split Transactions
• Completer attributes are given in Table 17.
®
T a ble 17. Intel
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Implementation of Completer Attribute
Fields
Attribute Function
Byte Count Modified (BCM) The 41210 does not set this bit.
Split Completion Error (SCE)
Split Completion Message (SCM) This bit shadows the SCE bit.
• Unexpected Split Completions
The 41210 asserts DEVSEL# and discard s the data when th e Requester ID matches th e bridge
but the tag does not match that of any outstanding requests (0 or 1) from this device.
• Split Completion Messages
The 41210 can generate error messages only for cycles that cross the bridge that master- or
target-abort. At this point, Dword cycles cross the bridge that requires completion (in other
words, I/O cycles). Therefore, the 41210 can generate only a “PCI-X Bridge Error”
completion message for the memory read commands, as indicated in Table 18.
PCI-X Interface
The 41210 sets this bit only in the following
circumstances:
• when a memory read command from PCI-X
master is target aborted on PCI Express*
• when the 41210 does a queue discard operation
of upstream queues
Table 18. Split Completion Abort Registers
Index Message
00h Master-Abort: The 41210 encountered a Master-Abort on the destination bus.
01h Target-Abort: The 41210 encountered a Master-Abort on the destination bus
3.4 Arbitration
The 41210 supports a high-performance internal PCI arbiter that supports up to five external masters on
each PCI segment. The request inputs into the internal arbiter include five external request inputs and
one internal request input. All request inputs to the internal arbiter are split into two groups: a high
priority group and a low priority group. Any master, including the internal master, can be programmed
to be in either of the two groups. The request inputs into the arbiter can be in one single group. Within a
group, priority is round-robin. The entire low-priority group represents one slot in the high-priority
group. The 41210 provides a 16-bit arbiter control register to control two aspects of the internal arbiter
behavior:
• Priority group for a master (in other words, whether a master is in the low-priority group or the
high-priority group)
• Bus parking on last PCI agent or the bridge
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 35
Page 36

PCI-X Interface
For controlling the priority level, there is one bit for each of the PCI REQ# inputs and one bit for the
internal request input. Bit[7] in the control register is for the bridge, bit[5] is for REQ[5]#, bit[4] is for
REQ[4]#, and so on. A value of 1 in a bit position puts the corresponding master in the high-priority
group.
Figure 1 represents the arbiter scheme with bits[7:0] in the arbiter control register set to “110 0011”. In
Figure 1, M0 represents master 0 (REQ[0]#), M1 represents master 1 (REQ[1]#) and so on. Bit[8] in the
arbiter control register controls the bus parking behavior of the internal arbiter. A value of 0 i nstructs the
internal arbiter to always park the bus on the bridge. A value of 1 instructs the internal arbiter to park the
bus on the last PCI master.
The 41 210 al s o s upports an 8-bit MTT (Multi-Transaction T imer) register that influences the behavior
of the internal arbiter. This register controls the amount of time that the arbiter allows a PCI initiator to
perform multiple back-to-back transactions on the PCI bus. The number of clocks programmed in the
MTT represents the minimum length of time on the PCI bus that the master is granted the bus as long as
the REQ of that master is asserted, before the GNT is given to the next master.
Figure 1. Internal Arbitration Scheme
Bridge
M0
High Priority
Group
M1
lpg
M2
Low Priority
Group
M3
M4
B3173-01
§ §
36 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 37

Power Management
Power Management 4
4.1 Hardware-Controlled Active State Power Management
PCI Express* defines a hardware-initiated power management of the PCI Express* Link called
active state power management. Under hardware control, the link can be put into a low-power L0s
link state or an even lower-power L1 link state. The Intel
(also called the 41210 Bridge or the 41210) supports only the PCI Express* active state power
management link state L0s. The 41210 does not support optional active state power management
link state L1. Active state power management is entirely dependent on traffic and is not initiated by
software. The software, however, can enable and disable the active state management by means of
the capability structure.
Note: Due to the unreliable behavior described in the Intel 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Specification Update, Errata #19, L0s active state power management is not supported.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Refer to the PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a for more details on the active state power
management.
Note: Link state L1 is not supported for hardware-driven active state power management. However, link
state L1 is supported for software-driven power managem ent.
4.2 Software-Driven PCI-PM 1.1–Compatible Power
Management
The 41210 supports PCI Express* link states L0, L1, and L3, as required to implement
PCI-PM 1.1–compatible device states (D0, D3hot, D3cold). When both bridge segments in the
41210 are programmed to the D3hot state, the PCI Express* link enters the link state L1. When the
PCI Express* link is in L1 because of software-driven power management, the only message that
can cause the link to come out of L1 is a PME message.
Refer to the PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a for details of the protocol involved in
transitioning the link to the L1 state.
The 41210 also supports the PM_TURN_OFF/PM_TO_ACK protocol to support D3cold/L3
device/link states.
4.3 PCI Bus Power Management
The 41210 supports bus st ates B0 and B3 corres ponding to t he bridge device st ates D0 and D3cold.
The 41210 does not support stopping the PCI bus clocks when in D3hot state and hence does not
support the bus state B2.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 37
Page 38

Power Management
4.4 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Device Power Management
Each bridge segment supports PCI-PM 1.1 device power management states D0, D3hot, and
D3cold. Each function, when programmed to the D3hot state, behaves as follows:
• The function responds to configuration cycles from PCI Express*.
• The function initiates and accepts PCI Express* completion transactions.
• The function does not respond to memory cycles on PCI Express*.
• The function does not respond to I/O cycles on PCI Express*.
• The function does not initiate PCI Express* request transactions.
• The function does not reset its registers, when programmed to D0 from D3hot.
• The 41210 does not assert PCIRST# when in the D3hot state.
4.5 Power-Management Event Signaling
The 41210 supports conveying PCI power-management events (PME#) over PCI Express* by
means of an in-band mechanism. Power-management events are generated on behalf of PCI
devices that require a change in their power state. The 41210 does not support any method to
“wake” the PCI Express* hierarchy before it signals a PME message (in other words, the 41210
supports neit her the WAKE# side band signal nor the in-band tone-generation mechanism).
W aking is needed when the ups tream component is in a non- communicative state with clock an d/or
power removed. The expectation for this component is that both ends of the link are fully powered
and clocked (in other words, the link is fully communicative) when signaling the PCI powermanagement events.
The 41210 supports a PME# event pin for conveying power-management events that occur on the
secondary PCI bus segments of the 41210. The PME output from all the PCI devices on the
segment are wire-ORed to o btain a compos ite P ME si gnal whi ch is rout ed to t he 41 210. T he 41210
converts the level-sensitive PME# signal into a PCI Express* message. This message carries the
bus number of the PCI bus that caused the PME# assertion. The power-manager software needs the
bus-number information when invoked.
Note: Since the bus number of the PCI bus must be passed in the PME_MSG, this scheme functions
correctly only for waking from the PCI buses directly below the 41210.
The exact mechanism for generating the PME_MSG packet in the 41210 involves sending a
message over PCI Express* whenever the PME input pin is asserted. Note that this packet must
carry the bus number of the PCI bus generating the PME#. This means that the 41210 must
construct the requestor ID of the PME_MSG packet with the secondary bus-number register in the
corresponding PCI-to-PCI Bridge header space. There is a chance that PME messages could be
lost. Thus the 41210 implements a counter to periodically sample the PME# pin and generate a
message. Refer to the PCI Express* specifications for more details. This polling mechanism
creates spurious interrupts t o the p owe r-manager software, and the power manager must be able to
handle this.
38 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 39

Power Management
To support the PCI Express* power-management event-signaling protocol, the 41210 supports the
following messa ges:
• PME_Turn_Off
• PME_TO_ACK
PME_Turn_Off is used to turn off PME generation from all PCI Express* devices before the
system power-manager disconnects the power from the PCI Express* link hierarchy. The 41210
acknowledges the reception of a PME_Turn_Off message with a PME_TO_ACK message to the
north device. Refer to the PCI Express* Specification, Revis i on 1.0a for more details on the PME
handshake mechanism.
The 41210 does not use Vaux power. As a result, the 41210 does not support PME# ass ert ion from
the D3cold state.
§ §
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 39
Page 40

Power Management
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
40 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 41

Addressing
Addressing 5
5.1 Addressable Spaces within the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Before dis cussing all the addressin g/configuration aspects of the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel
PCI Bridge (also called the 41210 Bridge or the 41210), this section provides a brief summary of
the addressable spaces within the 41210 PCI Express*-to-PCI Bridges (functions 0 and 2), the
corresponding access mechanism, and a description of when they are applicable. A detailed
description of each of these spaces follows in the later chapters.
®
T a ble 19. Addressable Spaces within the Intel
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
Addressable Space
PCI-to-PCI Bridge A Configuration Space
(Function 0)
PCI-to-PCI Bridge B Configuration Space
(Function 2)
Access
PCI Express* PCIA PCIB SMBus
Yes
(Type 0)
Yes
(Type 0)
Yes
(Type 0)
No
No Yes
Yes
(Type 0)
Yes
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 41
Page 42

Addressing
5.2 Secondary PCI Devices
Devices on the secondary PCI bus can b e co nfigu red as private devices and h idden fr om BIOS and
host software. Devices are hidden by inhibiting the assertion of the IDSEL input of the device
during configuration cy cles. This feat ure is config ured thr ough t he BINIT r e gister. P u blic a n d priv ate
devices are supported accordin g to Table 20.
T a ble 20. Secondary PCI Device Addressing
Device Number
0 AD16 Reserved Dedicated for bridge
1AD17
2AD18
3AD19
4AD20
5AD21
6AD22
7AD23
8AD24
9AD25
10 (0xA) AD26
11 (0xB) AD27
12 (0xC) AD28
13 (0xD) AD29
14 (0xE) AD30
15 (0xF) AD31
Signal Used for
IDSEL Input
Public/Private Notes
Public or Private
Reserved
Public Available for secondary PCI devices
5.3 Configuration-Space Access
The 41210 supports configuration-sp ace accesses from PCI Express* using both the legacy PCI-toPCI Bridge Specification, Revision 2.3 access mechanism and the enhanced PCI Express*
configuration-space access mechanism. For local initialization, the 41210 also supports
configuration-pace accesses from the SMBus port and secondary PCI bus.
Based on the device-hiding enable bit
(bit[2] of the BINIT register)
Available for secondary PCI devices
Used to address extended configuration
space of bridge
Based on the upstream-configuration
enable bit (bit[1] of the BINIT register)
5.3.1 PCI Express* Configuration Access
The PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.1 defines the configuration-space region of a PCI
function to be up to 256 B. PCI Express* extends the PCI configuration space from 256 B to 4 K.
The region up to 256 B can be accessed using the mechanism for configuration accesses defined in
the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.1. The region above 256 B is accessible only by
means of the enhanced configuration access mechanism defined in PCI Express*. This mechanism
utilizes a flat memory-mapped address region to access the configuration space. The core-logic
chipset converts the legacy PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.1 or the enhanced PCI
Express* configuration-space accesses into PCI Express* configuration cycles.
42 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 43

Addressing
The extended address bits used to access the configuration region above 256 B are all 0s when the
access mechanism compatible with the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.1 is used, or
when accessing devices on PCI. Note that 41210, when it translates Type 1 configuration
transactions from PCI Express*-to-PCI and finds the extended address bits to be non-zero,
terminates the transaction with an unsupported request response on PCI Express*. All
configuration accesses on PCI Express* are aligned DWORD only.
• Type 0 accesses to the 41210:
The bridge configuration spaces are accessed from PCI Express* by a Type 0 configuration
transaction. Type 0 transactions from PCI Express* (not peer PCI or SMBus) to the bridge
segments return a configuration retry response on PCI Express* when the “Configuration
Cycle Retry” bit is set in the BINIT register (“Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization
Register” on page 104).
The 41210 captures the bus and device numbers from Type 0 configuration writes, to its
internal functions, from PCI Express*. The 41210 does not capture the bus/device number
from Type 0 configuratio n writes to its internal function s, from either the PCI segment or
SMBus. The captured bus/device number from Type 0 PCI Express* configuration writes are
used by the 41210 in forming the Requester ID/Completer ID on PCI Express* and PCI-X
requests/completions. Also, the 41210 does not decode the device number field for Type 0
configuration transactions from PCI Express*.
• Type 1 accesses to the 41210:
Type 1 accesses from PCI Express* are intended for the PCI bus only and not for the internal
configuration spaces. Type 1 configuration transactions to PCI that do not complete within
40 µs from the time they are received on PCI Express* receive a configuration retry response
on PCI Express* when the retry response is enabled by means of the “Bridge Configuration
Retry Enable” bit in the PCI Express* Device Control Register (“Of fs et 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—
PCI Express* Device Control Register” on page93). The 41210 continues to retry the
transaction on PCI even when a retry response has been signaled on PCI Express*, and when
completed, the transaction is discarded.
• Type 1 to Type 0 translation:
The 41210 performs a Type 1 to Type 0 translation when the Type 1 transaction is generated
on PCI Express* and is intended fo r a device attach ed directly to its secon dary bu s. The bridg e
must convert the configuration command to a Type 0 format so that the secondary bus device
can respond to it. The resulting Type 0 address is driven on the PCI bus, as shown in Figure 2.
Device numbers are decoded to assert a single bit (IDSEL) in address bits[31:16]. A device
number of 0 converts to PCI AD[16] being a 1; a device number of 2 converts to PCI AD[17]
being a 1; and so on. When the device number is greater than 16, all bits (bits[31:16]) are 0.
See Table 20, “Sec ondary PCI D evice Addres sing” on page 42.
Note: When the device-hiding bit in the BINIT register is set, the 41210 master-aborts all Type 0
transactions to the PCI bus targeting device numbers 0 to 9. Device numbers 10 to 15 are never
hidden; in other words, they are never master-aborted.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 43
Page 44

Addressing
Figure 2. Type 1 to Type 0 Translation (PCI and PCI-X)
PCI Express Header
PCI Address
Reserved Bus No Dev No Fnc Register
31
Ext.
Add=0
2627282930
2324
25 19202122 15161718 1214 13 891011 4567 3
Only one '1'
0000
Fnc Register
R
210
00
B3183-01
• Type 1-to-Type 1 Forwarding:
The 41210 passes a Type 1 PCI Express* configuration cycle as a Type 1 configuration cycle
on PCI when it is intended for a device attached to a bus below the bridge and beyond the bus
directly attached to the secondary side of the br idge.
The 41210 forwards a Type 1 configuration cycle unchanged to the PCI bus when the Type 1
configuration cycle on PCI Express* has a bus number that falls in the range defined by the
lower limit (exclusive) in the secondary bus number register and the upper limit (inclusive) in
the subordinate bus number register.
As an error response, the 41210 returns an “unsupported request” completion when the
extended address bits are non-zero.
Note: The device-hiding bit in the BINIT register has no effect when forwarding a Type 1 transaction to
PCI as a Type 1 transaction.
• Type 1 to Special Cycle Forwarding
The 41210 translates a Type 1 configuration write transaction on PCI Express* into a special
cycle on PCI, but does not translate a Type 1 configuration access on PCI to a special cycle on
PCI Express*. A PCI Express* Type 1 configuration cycle is be converted to a special cycle on
the PCI interface when all of the following conditions are true:
— The device number field is equal to 11111b.
— The function number field is equal to 111b.
— The register number field is equal to 00 0000b.
— The bus number is equal to the value in the secondary bus number register in
configuration space.
The address and data are forwarded unchanged. Devices ignore the address and decode only
the bus command. The data phase contains the special cycle message. The transaction masteraborts on PCI, but results in a normal completion on the opposite bus (normal completion
status on PCI Express*; no DEVSEL# on PCI).
5.3.2 Type 0 Configuration Access from PCI-X Interface
The 41210 supports inbound Type 0 configuration accesses from PCI-X to access registers on the
corresponding source bridge segment. Type 0 accesses from PCI-X cannot be used to access
registers in any other fun ctions with in the 4121 0 other than the source br idge segment ; nor can it b e
used to access devices upstream of the 41210.
44 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 45

Instead of having a secondary IDSEL# pi n, the 4 121 0 r eserv es a device n umber of 0 fo r itself. The
41210 claims a Type 0 configuration transaction from PCI-X when the Upstream Configuration
Enable bit is set in the Bridge Initialization Register (“Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization
Register” on page 104) and the AD[16] signal of the transaction is asserted (HIGH) during the
address phase of the configuration transaction. The format for the Type 0 configuration cycle on
PCI-X is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Upstream Type 0 PCI-X Configuration Cycle Address Format
Addressing
Type 0 Header
31
Reserved
2627282930
2324
25 19202122 15161718 1214 13 891011 45673
The 41210 ignores the device number and function number fields during Type 0 decode. The
41210 does not use the device n umber in the PCI -X Type 0 configuration transaction to program its
internal (primary) device number field in the PCI-X Bridge Status register.
Note: Platforms supporting inbound Type 0 configuration cycles to the 41210 must not use address
bit[16] or bits[27:24] for IDSEL on the motherboard.
5.3.3 SMBus Configuration Access
The 41210 provides a mechanism for SMBus access to its internal configuration registers. This
mechanism provides a means for server management controllers to access the registers for
debugging, and also provides a means for custom configuration of the bridge based on usage
models. See Section 8, “System Management Bus Interface” on page 55 for more details.
5.4 I/O Space Access Mechanism
One I/O window can be set up in the PCI-to-PCI Bridge space for forwarding I/O transactions from
PCI Express*-to-PCI. Refer to Section 5.6, “VGA Addressing” on page 49 to see how I/O cycles in
the VGA range are handled. The registers and register bits listed below define the setup and control
of this I/O window:
• I/O Base and Limit (IOBL) registers in the PCI-to-PCI Bridge configuration space
Dev No
FncExt. Add 0000000 1 Register
2 1 0
00
B3184-01
• I/O enable bit (IOSE) in the command register in the PCI-to-PCI Bridge configuration space
To enable downstream I/O transactions, the I/O enable bit must be set in the command register in
the 41210 configuration space (bit 0 at offset 04h–05h). When the I/O enable bit is not set, all I/O
transactions initiated on PCI Express* receive a master-abort completion. The 41210 implements
one set of I/O base and limit address registers in configuration space that define an I/O address
range for the bridge. PCI Express* I/O transactions with addresses t hat fall inside the range defined
by the I/O base and limit registers are forwarded to PCI, and PCI I/O transactions with addresses
that fall outside this range are master-aborted.
Setting the base address to a value greater than that of the limit address turns off the I/O range.
When the I/O range is turned off, no I/O transactions are forwarded to PCI even when the I/O
enable bit is set.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 45
Page 46

Addressing
The base register consists of an 8-bit field at configuration address 1Ch, and a 16-bit field at
address 30h. The top four bits (bits[7:4] of address 1Ch) of the 8-bit field define bits[15:12] of the
I/O base address. The bottom four bits (bits[3:0]) read only as 0h to indicate that the 41210
supports 16-bit I/O addressing only. Bits[11:0] of the base address are assumed to be 0, which
naturally aligns the base address to a 4 KB boundary. The I/O base upper 16-bit register at offset
30H is reserved. After chip reset, the value of the I/O base address is initialized to 0000H.
The I/O limit register consists of an 8-bit f ield at off set 1Dh and a 16-bi t field at o ff set 32h. The t op
four bits (bits[7:4] of address 1Dh) of the 8-b it fi eld defi ne bit s[15:12 ] of t he I/O l imit ad dress. The
bottom four bits (bits[3:0]) read only as 0h to indicate that 16-bit I/O addressing is supported.
Bits[11:0] of the limit address are assumed to be FFFh, which naturally aligns the limit address to
the top of a 4 KB I/O address block. The 16 bits I/O base and limit registers at offsets 30h and 32h
are not implemented, since the 41210 supports only 16-bit I/O addressing. After chip reset, the
value of the I/O limit address is reset to 0FFFh (in other words, the lower 4 K in the 64 K space).
Figure 4. I/O Forwarding
Primary
64 K
Limit
Base
0
Secondary
Forward
Forward
Forward
B3185-01
Error Response: I/O transactions from PCI Express* that do not match the I/O address forwarding
window of either PCI-to-PCI Bridges results in a UR response. Note that software is responsible
for making sure that the I/O window programmed into the registers of the two PCI-to-PCI Bridg es
do not overlap.
46 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 47

5.5 Memory Space Access Mechanism
The 41210 supports 64 bits of memory addressing on both interfaces.
Two memory windows can be setup for forwarding memory transactions from PCI Express*-to-
PCI. These windows are defined as part of the standard PCI-to-PCI Bridge configuration space.
Inverse decoding is used for forwarding transactions from PCI-to-PCI Express*. Refer to
Section 5.6, “VGA Addressin g” on page 49 to see how memory cycles in the VGA range are
handled. The registers and register bits listed below control the setup and operation of these
memory windows:
• Memory-mapped I/O base and limit (MBL) registers
• Prefetchable memory base and limit (PMBL) registers
• Prefetchable memory base and limit upper 32 bits (PMBLU32) register
• Memory enable (MSE) bit in the command register
• Master enable bit (BME) in the command register
T o enable downst ream memory transaction s, the memory space enable bit in the comm and register
must be set (bit[1] of of fs et 04h–0 5h) . To enable upstream memory transactions, the mast er enable
bit in the command register must be set (bit[2] of offset 04h–05h). The 41210 does not prefetch
data from downstream PCI devices. U pst ream p refet ch ing is cont ro ll abl e by sett ings i n th e “Offset
178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register” on page 119.
Addressing
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 47
Page 48

Addressing
5.5.1 Memory-Mapped I/O Window
Software uses the memory-mapped I/O window to map all no n-p refet ch able (in other words, reads
that have side effects, such as reads to FIFOs, or “read-to-clear” status registers) memory space
into PCI memory space.
The memory-mapped I/O base address register and memory-mapped I/O limit address register
define an address range that the bridge us es to determine when to forward memory commands. The
41210 forwards a memory transaction from PCI Express* to PCI when the address falls within the
range. The 41210 forwards it from PCI to PCI Express* (or the peer PCI segment) when the
address is outside the range and does not fall into the prefetchable memory range. This memory
range supports 32-bit addressing only (addresses 4 GB). It has a granularity and alignment of
1MB.
This range is defined by a 16-bit bas e address register at o ff set 20h in the conf iguration s pace and a
16-bit limit address register at offset 22h. The most significant 12 bits of each of these registers
correspond to bits[31:20] o f the memory address. The least s ignificant four bits are hard-wired to 0.
The least significant 20 bits of the base address are assumed to be all 0s, which results in a natural
alignment to a 1 MB boundary. The least significant 20 bits of the limit address are assume d to be
all 1s, which results in an alignment to the top of a 1 MB block.
Note: Setting the base to a value greater than that of the limit turns off the memory range.
Figure 5. Memory Forwarding
Prefetchable Base
Non-Prefetchable Limit
Non-Prefetchable Base
Primary Secondary
Private A-Segment Memory
(optional)
Prefetchable Limit
Prefetchable Memory
Memory Mapped I/O
64
2
63
2
4 GB
0 K
B3186-01
48 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 49

5.5.2 Prefetchable Memory Window
The prefetchable memory base and address registers, along with their upper 32-bit counterparts,
define an additional address range that the 41210 uses to forward accesses. Software maps the
prefetchable PCI memory spaces to this window. The 41210 still treats the memory reads in this
region as non-prefetchable. The 41210 forwards a memory transaction from PCI Express* to PCI
when the address falls within the range. The 41210 forwards transactions from PCI to PCI
Express* (or the peer PCI segment) when the address is outside the range and does not fall into the
regular memory range. This memory range supports 64-bit addressing, and has a granularity and
alignment of 1 MB.
The least-significant 32 bits of the range are defined by a 16-bit base register at offset 24h in the
configuration space and a 16-bit limit regis t er at offset 28h. The most-significant 12 bits of each of
these registers correspond to bits[31:20] of the memory address. The least-significant 4 bits are
hard-wired to 1h, indicating 64-bit address support. The least-significant 20 bits of the base address
are assumed to be all 0s, which results in a natural alignment to a 1 MB boundary. The leastsignificant 20 bits of the limit address are assumed to be all 1s, which results in an alignment to the
top of a 1 MB block.
The most-significant 32-bits of the range are defined by a 32-bit base register at offset 28h in the
configuration space, and a 32-bit limit register at offset 2Ch.
Addressing
Note: Setting the entire base (with the most-significant 32-bits) to a value greater than that of the limit
turns off the memory range.
5.5.3 Opaque Memory Window
When the opaque memory window is enabled, the 41210 hard codes certain address ranges to the
secondary segment of each bridge.The hard-coded address ranges are as follows:
• A[63:62] = 10 Secondary side of A-Segment
• A[63:62] = 11 Secondary side of B-Segment
These address ranges are not forwarded from the PCI Express* interface to the corresponding
secondary side and are also never forwarded from the secondary to the PCI Express* interface,
regardless of the setting of the prefetchable base and limit registers.
Note: Even when the opaque memory window is enabled, the normal behavior defined for the BME,
MSE, and IOSE bits in the PCICMD register is still applicable.
5.6 VGA Addressing
When a VGA-compatible device exists behind a 41210 bridge, the VGA enable bit in the bridge
control register is set (offset 3 at 3Eh–3Fh).
When this bit is set, the 41210 forwards all transactions addressing the VGA frame buffer memory
and VGA I/O registers from PCI Express* to PCI, regardless of the values of the 41210 base and
limit address registers. When set, the 41210 does not forward VGA frame buffer memory accesses
to PCI Express* regardless of the values of the memory address ranges. However, the I/O enable
and memory enable bit in the command register must still be set.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 49
Page 50

Addressing
When this bit is cleared, the 41210 forwards transactions addressing the VGA frame buffer
memory and VGA I/O registers from PCI Express* to PCI when the defined memory and I/O
address ranges enable forwarding. When cleared, accesses to the VGA frame buffer memory are
forwarded from PCI to PCI Express* when the defined memory ad dres s ran ges enab le fo rward ing.
However, the master enable bit must still be set. The VGA I/O addresses are never forwarded to
PCI Express* when the upstream I/O enable bit in BINIT register is cleared. When this bit is set
and also the VGA enable bit is set, the 41210 does not forward the VGA I/O addresses from PCI to
PCI Express*.
The VGA frame buffer consists of the memory address range 000A 0000h–000B FFFFh.
The VGA I/O addresses consist of the I/O addresses 3B0h–3BBh and 3C0h–3DFh. These I/O
addresses are aliased every 1 KB throughout the first 64 KB of I/O space, when the VGA 16-bit
decode bit in the bridge control register (bit[4]) is cleared. This means that address bits[9:0]
(3B0h–3BBh and 3C0 h–3DFh) ar e decoded, bits [15:10] are not d ecoded and can be any val ue, and
address bits[31:16] must be all 0s. When the VGA 16-bit decode bit is set, the 41210 does the
entire 16-bit decode on the VGA I/O addresses. When software sets the VGA enable bit in one
bridge, the ISA enable bit must be set in the other bridge.
§ §
50 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 51

Transaction Ordering
Transaction Ordering 6
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the 41210 Bridge or 41210)
follows the producer-consumer model of a standard PCI Express*-to-PCI bridge. Based on this
model, the 41210 implements a set of ordering rules in the upstream and downstream directions.
The ordering plane covered by these rules spans the transaction domain covered by PCI Express*
and either of the two PCI segments. The 41210 uses a single PCI Express* virtual channel, for both
PCI segments.
Accesses to the internal 41210 configuration registers follow no ordering relationship with respect
to transactions moving to and from PCI and PCI Express* buses. This means that upstream
memory and configuration reads and writes (when enabled via the BINIT register) are completed
out of order with the transactions pending in the 41210 upstream queues towards PCI Express*.
Downstream memory/configuration transactions to the internal register space can complete out of
order with respect to transactions pending in the downstream queues towards PCI. Software must
be aware that any semaphore mechanism implemented through the internal 41210 register space
requires a dummy read to the PCI or PCI Express* space to push the writes that are pending in the
41210 queues in either direction. The orde ring tabl es in the next two sections do not consider these
transactions.
6.1 Upstream Transaction Ordering
Table 21 lists the combined set of ordering rules in the upstream path of the 41210 for PCI
transactions.
T a ble 21. Upstream Transaction Ordering
Row Pass Column Posted Write
Posted write No Yes No No
Delayed/split read request No Yes
Delayed/split write request No Yes Yes No
Delayed/split read completion No Yes Yes No
Delayed/split write completion No Yes Yes No
NOTE:
1. Subsequent requests only (prefetches). All upstream initial requests are in order.
Delayed/Split Read
Request
1
Delayed/Split Read
Completion
Yes No
Delayed/Split Write
Completion
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 51
Page 52

Transaction Ordering
6.2 Downstream Transaction Ordering
Table 22 lists the combined set of ordering rules in the downstream path of the 41210.
T a ble 22. Downstream Transaction Ordering
Row pass Column Posted Write
Posted write No Yes Yes Yes
Delayed/split read request No Yes
Delayed/split write request No Yes Yes Yes
Delayed/split read completion No Yes Yes Yes
Delayed/split write completion No Yes Yes Yes
NOTE:
1. The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge supports two downstream completion required requests per PCI segment.
Downstream delayed/split read requests can pass each other when issued on the PCI bus.
Delayed/Split Read
Request
1
Delayed/Split Write
Request
Yes Yes
Delayed/Split Read
Completion
6.3 Relaxed Ordering/No-Snoop Support
The 41210 forwards the PCI Express*/PCI-X relaxed ordering and no-snoop attributes to
PCI-X/PCI Express*. No internal optimization is done with the relaxed ordering attribute.
§ §
52 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 53

Interrupt Support
Interrupt Support 7
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the 41210 Bridge or 41210) can
generate an in-band interru pt requ est o n P CI Ex pres s * fo r bo ot devices and for systems that do not
support Message Signaled Interrupts (MSI).
7.1 Legacy Interrupt Sharing
PCI Express* provides interrupt messages that emulate the legacy wired mechanism. This feature
allows I/O devices to signal PCI-style interrupts using a pair of ASSERT and DEASSERT
messages. This message pairing preserves the level-sensitive semantics of the PCI interrupts on
PCI Express*.
The four virtual wire interrupts (INTA–INTD) correspond to the four inte rrupt wir es defin ed in the
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.3. The 41210 routes its P CI int err upt pi ns an d t h e i nternal
interrupts to the PCI Express* INTx interrupts as shown in Table 23.
Table 23. INTx Routing Table
A_INTx# Interrupt Pins B_INTx# Interrupt Pins PCI Express* INTx Message
A_INTA# B_INTA# INTA
A_INTB# B_INTB# INTB
A_INTC# B_INTC# INTC
A_INTD# B_INTD# INTD
Each row in Table 23 indicates a logical ORing of the interrupts in th at row. The
ASSER T/DEASSER T message sent out on PCI Express* capt ures the assert ing/deasserti ng edge of
the signal that represents the logical OR of the interrupts in that row.
The 41210 uses its primary bus number and device number in the Requester ID field for the PCI
Express* INTx messages. As stated in the PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a, the function
number is reserved for interrupt messages and is always 0.
Note: PCI Express* Assert_INTx/Deassert_INTx messages are not inhibited by the Bus Master Enable
(BME) bit.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 53
Page 54

Interrupt Support
7.2 Interrupt Routing for Devices behind a Bridge
Given the legacy interrupt sharing scheme shown in Table 23, to get the best legacy interrupt
performance (by reducing interrupt sharing), adapter boards must select the appropriate INTA#–
INTD# input pin to use on each PCI bus segment. The chosen interrupt input also imposes a PCI
device number requirement for the interrupt source as shown in Table 24.
Table 24. Interrupt Binding for Devices behind a Bridge
Device Number on
Secondary Bus
01, 4, 82, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28
2
1, 5, 9
, 13, 17, 21, 25, 29
2
2, 6, 10
3, 7, 11
NOTES:
, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30
2
, 15, 19, 23, 27, 31
1. Device number 0 is reserved for the bridge and must not be assigned to secondary devices.
2. AD[27:24], which correspond to devices[11:8], must not be used for IDSEL# connections, because these
signals are used when accessing the extended configuration space in the bridge from the secondary bus.
Interrupt Pin on Device
INTA # INTA#
INTB# INTB#
INTC# INTC#
INTD# INTD#
INTA# INTB#
INTB# INTC#
INTC# INTD#
INTD# INTA#
INTA # INTC#
INTB# INTD#
INTC# INTA#
INTD# INTB#
INTA # INTD#
INTB# INTA#
INTC# INTB#
INTD# INTC#
Interrupt Pin on the Intel® 41210
Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
§ §
54 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 55

System Management Bus Interface
System Management Bus Interface 8
The SMBus interface allows the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the
41210 Bridge or 41210) to serve as a slave device residing on the SMBus for system management
functions and provides for full access to the configuration registers in each function. The SMBus
implementation has the following characteristics:
• Is based on the System Management Bus Specification, Revision 2.0 (SMBus)
• Allows for slave-mode operation only
• Provides full read/write access to internal configuration and memory spaces
The SMBus address is set up on PERST# by sampling the SMBUS pins. When the pins are
sampled, the resulting address is assigned as shown in Table 25:
T able 25. SMBus Address Assignments
Bit Value
71
61
5SMBUS[5]
40
3SMBUS[3]
2SMBUS[2]
1SMBUS[1]
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 55
Page 56

System Management Bus Interface
8.1 SMBus Commands
The 41210 supports six SMBus commands:
• Block Write • Word Write • Byte Write
• Block Read • Word Read • Byte Read
Sequencing these commands initiates accesses to the internal configuration and memory registers.
For high reliability, the 41210 also supports the optional packet-error-checking feature (CRC-8)
and is enabled or disabled with each transaction.
Every configuration and memory read or write consists first of an SMBus write sequence that
initializes the bus number, device, fu nction number , register offset, and so on. The term sequen ce is
used because these variables can be initialized by the SMBus master with a single block write or
multiple word or byte writes. The last write in the sequence that completes the initialization
performs the internal configuration/memory read or write. The SMBus master can then initiate a
read sequence, which returns the status of the internal read or write command and also the data in
case of a read.
Each SMBus transaction has an 8-bit command driven by the master. The command encodes the
information shown in Table 26:
Table 26. SMBus Command Encoding
Bit Description
7 Begin: When set, this bit indicates the first transaction of the read or write sequence.
6
End: When set, this bit indicates the last transaction of the read or write sequence.
5
Reserved: Must be set to 0.
PEC Enable: When set, indicates that PEC is enabled. When set, each transaction in the sequence
ends with an extra CRC byte. CRC is checked on writes and generated on reads.
4
PEC does not include the command byte itself.
Internal Command:
00 Read Dword
3:2
1:0
01 Write Byte
10 Write Word
11 Write Dword
All accesses are naturally aligned to the access width. This field specifies the command to be issued
by the SMBus slave logic to the internal registers.
SMBus
command:
00 Byte
01 Word
10 Block
11 Reserved
This field specifies the SMBus command to be issued on the SMBus. This field is used as an
indication of the length of transfer so that the slave knows when to expect the PEC packet (when
enabled).
56 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 57

8.2 Initialization Sequence
All configuration read and writes are accomplished through SMBus write(s) followed by an
SMBus read (for a read command). For con figur at ion access , the SMBus write sequence is u sed to
initialize the following parameters:
• Bus number
• Device/function number
• 12-bit register number (in two separate bytes on SMBus)
Each of the parameters above is sent on the SMBus in separate bytes. The register number
parameter is initialized with two bytes, and the 41210 ignores the most significant four bits of the
second byte that initializes the register number.
The initialization of the information can be accomplished through any combination of the
supported SMBus write commands (Block, Word or Byte). The internal command field for each
write must specify the same internal command every time (read or write). After all the information
is set up, the last write (end bit is set) initiates an internal read or write command. On an internal
read, when the data is not available before the slave interface acknowledges this last write
command (ACK), the slave “clock stretches” until the data returns to the SMBus interface unit. On
an internal write, when the write is not complete before the slave interface acknowledges this last
write command (ACK), the slave “clock stretches” until the write completes internally. When an
error occurs (internal time-out or internal abort) during the internal access, the last write comman d
receives a NACK.
System Management Bus Interface
8.2.1 Configuration
The 41210 supports only read Dword to internal register space. All configuration reads are
accomplished through an SMBus write (or writes) and are followed later by an SMBus read to read
the status and the read data. For SMBus read transactions, the last byte of data (or the PEC byte
when enabled), is NACKed by the master to indicate the end of the transaction. The SMBus read
command returns the status of the previous internal command and the data associated previous
internal read command. The status field encoding is shown in Table 27:
Table 27. SMBus Status Byte Encoding
Bit Description
7 Internal time-out. This bit is set when an SMBus request is not completed in 2 ms internally .
6 Reserved
5 Internal master abort
4 Internal target abort
3:1 Reserved
0 Successful
Examples of configuration reads are shown in Figure 6 through Figure 9. For the definition of the
diagram conventions below, refer to the System Management Bus Specification, Revision 2.0.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 57
Page 58

System Management Bus Interface
Figure 6. DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Block Write/Block Read, PEC Enabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 11010010 A Byte Count = 4 A Bus Number A A Reg Number [15:8] ADevice/Function
Reg Number [7:0]
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
A Data[7:0]
A PEC Clock Stretch A
W Cmd = 11010010
R A Byte Count = 5 A
PEC
AA
Status A Data[31:24] A A Data[15:8]Data[23:16]
P
NA
P
B3187-01
Figure 7. DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Word Write/Word Read, PEC Enabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 10010001 A
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 01010001 A
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
W Cmd = 10010001
RA A
W Cmd = 00010001
RA A
Status AData[31:24] N PPEC
Data[23:16] AData[15:8] N PPEC
Bus Number A Device/Function A A
Register Num [15:8]
AA
AA
Register Num [7:0]
A PEC Clock Stretch A
A
PPEC
P
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
W Cmd = 01010000
RA A
Data[7:0] PEC N P
AA
B3188-01
58 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 59

System Management Bus Interface
Figure 8. DWord Configuration Read Protocol (SMBus Block Write/Block Read, PEC
Disabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 11000010 A Byte Count = 4 A Bus Number A A Reg Number [15:8] ADevice/Function
Reg Number [7:0]
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
Clock Stretch A
W Cmd = 11000010
R A Byte Count = 5 A
P
AA
Status A Data[31:24] A A Data[15:8] A
Data[7:0] N PData[23:16]
B3189-01
Figure 9. DWord Configuration Read Proto col (SMBus Word Write/Word Read, PEC Disabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 10000001 A
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 01000001 A
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
W Cmd = 10000001
RA A
Status Data[31:24] N P
W Cmd = 00000001
RA A
Data[23:16] Data[15:8] N P
Bus Number A Device/Function A
Register Num[7:0]Register Num[15:8]
A Clock Stretch A
AA
AA
P
P
S 11X0_XXX
Sr
11X0_XXX
W Cmd = 01000000
RA
Data[7:0] N P
AA
B3190-01
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 59
Page 60

System Management Bus Interface
8.2.2 Configuration Writes
Configuration writes are accomplished through a series of SMBus writes. As with reads, a write
sequence is used first to initialize the bus number, device, function, and register number for the
configuration access. The writing of this information can be accomplished through any
combination of the supported SMBus write commands (Block, Word or Byte).
Note: On SMBus, there is no concept of byte enables. Therefore, the register number written to the slave
is assumed to be aligned to the length of the internal command. In other words, for a Write Byte
internal command, the register number specifies the byte address. For a Write DWord in ternal
command, the two least-significant bits of the register number are ignored. This is different than
PCI; with PCI, the byte enables are used to indicate the byte of interest.
After all the information is set up, the SMBus master initiates one or more writes which set up th e
data to be written. The final write (end bit is set) initiates an internal configuration. The slave
interface can potentially “clock-stretch” the last data write until the write completes without error.
When an error occurs, the SMBus interface NACKs the last write oper ation just befor e the stop b it.
Examples of configuration writes are illustrated in Figure 10 and Figure 11. All the figures are
shown with PEC enabled. When PEC is disabled, there is no PEC byte in any of the sequences, and
the PEC enable bit in the command field is 0.
For the definition of the diagram conventions used in Figure 10 and Figure 11, refer to the System
Management Bus Specification, Revision 2.0.
Figure 10. DWord Configuration Write Protocol (SMBus Block Write, PEC Enabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 11011110 A Byte Count = 8 A
A Data[23:16] Data[16:8]
A
A
Data[7:0]
Bus
Number
A
PEC Clock Stretch A
Device/
AA
Function
Reg Number
[15:8]
P
Reg Number
A
[7:0]
A
Data[31:21]
B3191-01
60 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 61

System Management Bus Interface
Figure 11. DWord Configuration Write Protocol (SMBus Byte Write, PEC Enabled)
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 10011000 A Bus Number A PEC A P
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 00011000 A Device/Function A PEC A P
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 00011000 A Reg Number[15:8] A PEC A P
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 00011000 A Reg Number[7:0] A PEC A P
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 00011000 A Data[W:X] A PEC A P
S 11X0_XXX W A Cmd = 01011000 A Data[Y:Z] A PEC
8.3 Error Handling
The SMBus slave interface handles two types of errors: internal and PEC.
Internal errors can occur when the target function is busy servicing a request from the PCI
Express* interface. The SMBus unit may time-out these transactions and return a NACK for the
read or write command. Additionally , an internal error can occur when the read or write command
receives a master or target abort on the internal interface. When the master receives a NACK, the
entire transaction must be reattempted.
When the master supports packet error checking (PEC), and the PEC enable bit in the command is
set, the PEC byte is checked in the slave interface. When the check indicates a failure, the slave
NACKs the PEC packet and does not issue the command on the internal interface.
Note: An SMBus master must either do PEC on all transactions in a sequence or not do it at all. PEC
cannot be disabled in the middle of a sequence. A PEC error in the middle of a sequence must be
re-started from the beginning of the sequence that set the begin bit.
Clock Stretch A P
B3192-01
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 61
Page 62

System Management Bus Interface
8.4 SMBus Interface Reset
The master has two ways to reset the slave interface state machine in the 41210:
• The master holds SCLK low for 25 ms cumulative. “Cumulative” in this case means that all
the “low time” for SCLK is counted between the start and stop bit. When this count totals
25 ms before reaching the stop bit, the interface is reset.
• The master holds SCLK continuousl y high for 50 ms.
Besides these methods, the SMBus interface in the 41210 is also reset on a PERST#, RSTIN#, or
an in-band warm reset from PCI Express*.
§ §
62 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 63

Local Initialization
Local Initialization 9
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the 41210 Bridge or 41210)
includes device-specific registers that allow for control of the bridges’s behavior, both internally
and externally. Examples of these device-specific registers are the arbiter control register, the
prefetch control register, and so on. Depending on the usage model, these registers might need to
be programmed to a different value than the reset-default, every time 41210 goes through a
component reset.
When application-specific initialization of the 41210 is required, the CFGRETRY strap must be
asserted at the rising edge of PERST#. This places the 41210 Bridge in a local initialization mode,
and all configuration accesses from PCI Express* is retried by returning a completion with the
configuration request retry status. As soon as the local configuration is completed, the “Local
Initialization In Progress bit” in the “Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization Register” on
page 104 must be cleared to enable host access to the bridge configuration registers.
Local initialization can be accomplished via SMBus access or Type 0 configuration cycles fr om the
secondary bus. The CFGRST# output is asserted whenever the config uration space is reset and can
be used as a control signal to re-initialize the application-specific parameters. The X_RST# signal
must not be used since the configuration space is not cleared due to a software-initiated secondary
bus reset.
Device-specific registers are listed below:
• “Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register” on page 90
• “Offset 42h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer” on page 91
• “Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control” on page 91
• “Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization Register” on page 104
• “Offset 16Ah: ARB_CNTRL—Internal Arbiter Control Register” on page 117
• “Offset 170h: SSR—Strap Status Register” on page 118
• “Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register” on page 119
§ §
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 63
Page 64

Local Initialization
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
64 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 65

Clock and Reset
Clock and Reset 10
10.1 Clocking
The Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the 41210 Bridge or the 41210)
always uses the PCI Express* REFCLK as its primary clock input and drives the PCI clock
outputs. The clock domains are shown in Table 28:
Table 28. Clock Domains
Clock
Domain
PCI Express* 100 MHz Differential External PCI Express* differential clocks
PCI 133/100/66/33 MHz Internal PCI bus clock outputs
SMBus 10–100 KHz Source Synchronous
TCK 0–16 MHz Ext ernal JTAG clock
Frequency Source Usage
10.2 Device Reset
Four types of resets can be perf ormed on the 41 210. These ar e listed from th e h ighest-level reset to
the lowest-level reset:
• PERST#: This signal indicates stable power when high and causes an asynchronous reset of
the entire chip when low. This signal must be connected to the PERST# pin on the PCI
Express* connector.
• RSTIN#: When asserted, this signal causes an asynchronous reset of the 41210. This reset is
used for debugging purposes only and must be pulled high for normal operation.
• PCI Express* Reset: This reset is a message coming on the PCI Express* interface and resets
all configuration registers with the exception of sticky bits.
• Software PCI Reset: This reset is initiated by writing to the bridge control register of the PCI
configuration space. This reset affects only the associated bridge segment and is commonly
referred to as the Secondary Bus Reset (SBR).
This pin is controlled by the driver of the
SMBus interface, and typically runs between
10 and 100 KHz
These resets are described in more detail in the following sections.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 65
Page 66

Clock and Reset
10.2.1 PERST# Reset Mechanism
All the voltage sources in the system are tracked by a system component that asserts the PERST#
signal only after all the voltages have been stable fo r some predetermined time. Th e 41210 receives
the PERST# signal as an asynchronous input, meaning that there is no assumed relationship
between the assertion or the de-assertio n of PERST# and the r eference clock. W hile the PERST# is
de-asserted, the 41210 holds all logic in reset.
The PERST# reset clears all internal state machines and logic, and initializes all registers to their
default states, including “sticky” error bits that are persistent through all other reset classes. To
eliminate potential system-reliability problems, all devices are also required to either tristate their
outputs or to drive them to safe levels during such a power-on reset.
The 41210 keeps PCIRST# asserted for a minimum of 320 ms after the deassertion of PERST#.
Refer to the PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a for details of the relationship between
PERST# assertion and the stability of the clocks and power at the inputs of the 41210.
10.2.2 RSTIN# Reset Mechanism
As soon as the system is up and running, a full system reset may be required to recover from
system-error conditions related to various device or subsystem failures. The RSTIN# reset
mechanism is a hot-reset mechanism that accomplishes this recovery without clearing the “sticky”
error-status bits which track the cause of the error conditions of the device or subsystem.
A hot reset can be initiated by asserting the RSTIN# signal. This signal is treated as an
asynchronous input to the 41210, meaning that there is no assumed relationship between the host
reference clock and the assertion or the de-assertion of RSTIN#.
When the 41210 goes through a reset due to RSTIN# assertion, the link goes down, which is
interpreted by the upstream component as a surprise extraction which may cause system instability.
The 41210 keeps PCIRST# asserted for a minimum of 320 ms after the deassertion of RSTIN#.
10.2.3 PCI Express* Reset Mechanism
There is no reset signal on the PCI Express*, and all reset communication is in-band. The upstream
PCI Express* device communicates the fact that it is entering and coming out of a reset using
messages. The 41210 responds by also going through a reset. In accordance with the PCI Express*
protocol, this incoming message is asynchronous to the reference clock.
When the upstream device puts the 41210 Bridge in reset through the in-band reset mechanism, the
41210 resets its core and PCI interfaces. Sticky bits are reserved
The 41210 keeps PCIRST# asserted for a minimum of 320 ms after the deassertion of the PCI
Express* in-band reset message.
66 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 67

Clock and Reset
10.2.4 S oftware PCI Reset (SBR—Secondary Bus Reset)
Commonly referred to as the Secondary Bus Reset (SBR), the software PCI reset is initiated by a
write to the bridge control register and resets only the particular PCI segment. This reset can be
used for various reasons, including but not limited to the following:
• Recovering from error conditions on the secondary bus
• Redoing enumeration
• Changing the operating frequency of the bus (33/66/100/133 MHz)
• Changing the operating mode of the bus (PCI or PCI-X)
This reset is synchronous to the PCI clock domain in which it is used. SBR is strictly restricted to
the particular PCI segment and affects neither the other PCI segment nor the rest of the 41210
Bridge logic. Writes to the bridge configuration register with a new frequency or bus mode have no
effect until the SBR is completed (see “Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register” on
page 90).
§ §
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 67
Page 68

Clock and Reset
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
68 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 69

Error Handling
Error Handling 11
For each interface, the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge (called hereafter the 41210
Bridge or 41210) implements the specified error-l ogg ing and escalation actions a s per the interface
rules. For example, errors encountered on the PCI interface follow the logging and escalation rules
of PCI. The error escalation mechanisms implemented by the 41210 can be fully masked. This
feature provides the platform software with the ability to pick and choose what it wants to do on
any of the error conditions. All logging registers specific to the 41210 are “sticky” (these registers
retain their values) through any chip reset except a PERST# reset cycle.
11.1 PCI Express* Errors
The 41210 supports the PCI Express* advanced error-reporting capability, which allows for
system-level error recovery and debugging. The capability includes both the base error-reporting
features and the bridge-specific extensions for reporting PCI and PCI-X errors.
PCI Express* errors are classified as either correctable errors or uncorrectable errors:
• Correctable errors are those for which hardware exists to correct the errors.
• Uncorrectable errors are errors for which hardware does not exist to correct the errors.
Uncorrectable errors are further classified into fatal and non-fatal errors, with non-fatal errors
indicating an unreliable link.
PCI Express* supports three different error messages to support these error classes: ERR_COR,
ERR_UNC and ERR_F ATAL. Refer to the PCI Express* Specification, Revision 1.0a for details of
the various PCI Express* errors and how they are signaled and escalated.
PCI Express* error logging specifies a set of advanced transaction-logging registers as an added
capability.
11.2 PCI Errors
PCI and PCI-X errors include several sources of error, such as the following:
• Address errors
• Data-parity errors
• Split-completion errors
• Master aborts
• Target aborts
Some of these errors are fatal and some are non-fatal. The PCI-X specifications specify a set of
rules for the behavior of a bridge under a variety of error conditions that could happen on the bus.
To aid the system software/driver in error recovery and debugging, the 41210 implements those
rules on PCI along with the error-logging and routing control specific to the 41210.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 69
Page 70

Error Handling
11.2.1 Error Types
PCI errors are classified into two categories: fatal and non-fatal:
• Fatal errors are those that have the potential to cause data corruption. Software must be careful
to contain and escalate these errors (when needed).
• Non-fatal errors are those that do not cause any data corruption. These errors include driver
errors such as master-abort on PCI and target errors such as target-abort.
All errors on PCI are uncorrectable and are forwarded to PCI Express* as such.
The fatal class of errors includes:
• Data parity errors on PCI
• Address and attribute parity errors on PCI
The non-fatal class of errors includes:
• Target Aborts on PCI
• Master Aborts on PCI
11 .2. 2 Term in ation of Compl e tion Required Transactions
11.2.2.1 Immediate Termination on the PCI-X Interface
An immediate termination occurs when the 41210 Bridge masters a transaction on PCI or PCI-X
and receives an “immediate termination” response for that transaction. Table 29 describes the
completion-status translation for immediate terminations. The behavior described for completionrequired cycles is independent of the setting of the Master Abort Mode bit, and is als o independent
of whether the cycle is exclusive (locked) or not.
T a ble 29. Completion-Status Translation for Immediate Terminations
PCI-X Termination PCI Express* Completion
Normal completion Successful
Memory, I/O, configuration reads Successful with poisoned TLP
Normal completion with
data parity error
Master abort UR
Target abort CA
NOTES:
1. In PCI mode, the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge samples PERR# asserted and generates the
UR completion.
2. PERR# is not signaled for a special cycle data parity error. SERR# is asserted instead.
Configuration, I/O writes
Configuration write to special cycle
conversion
2
1
UR
Successful
70 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 71

Error Handling
11.2.2.2 Split Termination on PCI-X Interface
A split-termination error translation occurs when a completion-required transaction receives a
“split termination” response when originally mastered on the PCI-X bus, and a “split completion”
error message is later received for the original request. Table 30 describes the completion-status
translation for PCI-X split-completion terminations. The behavior described in Table 30 is
independent of the Master Abort Mode bit and whether or not the cycle is exclusive (locked).
Note: When a target or master abort is returned on PCI Express* for the first read of an exclusive access,
the secondary PCI-X bus is not locked. This is especially important in regard to the completion
messages “byte count out of range, “device specific”, and “reserved/invalid codes”. The 41210
Bridge does not lock its bus on these errors, even though they are not explicitly master- or targetaborts on the PCI-X interface.
Table 30. Completion-Status Translation for PCI-X Split-Completion Terminations
PCI-X Split Termination
Message
Class Index
Successful 0 00h Successful
Master abort 1 00h UR
T arget abort 1 01h CA
Write data parity error 1 02h UR
Byte count out of range 2 00h UR
Write data parity error 2 01h UR
Device-specific 2 8Xh CA
Reserved/invalid Others CA
PCI Express*
Completion Status
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 71
Page 72

Error Handling
11.2.2.3 Split Termination on PCI Express* Interface
Table 31 shows the split-completion errors received on the PCI Express* interface and how they
translate to PCI-X.
T able 31. Completion-Status Translation for PCI Express* Split-Completion Terminations
PCI Express* Completion Status PCI Completion
Successful (SC) Successful
Memory reads: PCI target abort
MAM = 1
Unsupported Request (UR)
MAM = 0
PCI-X spli t master
2
abort
Completer Abort (CA)
NOTES:
1. Data is returned to the point of error, and then a target abort is signaled.
2. The 41210 Bridge issues a split-completion error message and either master aborts or target aborts the
remaining completion sequence when an abort is detected on the PCI Express*/peer interface. If several
bytes of data return successfully for the request, the data is returned to the point of error (rounded to the
nearest ADB), and then the split-completion error message is generated.
PCI target abort
PCI-X split target abort
I/O reads: PCI target abort
I/O writes: PCI target abort
Memory reads: PCI return all Fs
I/O reads: PCI return all Fs
I/O writes: Normal completion
1
1
1
§ §
72 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 73

Register Description
Register Description 12
This chapter describes the registers of the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge.
12.1 Register Nomenclature and Access Attributes
Table 32 describes the nomenclature used for describing bit attributes throughout this chapter.
Table 32. Bit Attribute Definitions
Mnemonic Attribute
RO
RsvdP
RsvdZ
ROS
RZSet
RW
RW1Set
RWS
RWC
RWCS
Strap
WT
Read-Only: This bit cannot be altered by software. This bit can be hard-wired to return a
fixed value at all times, or it can be set by hardware on an event.
Reserved and Preserved: These bits are reserved for future RW implementations; software
must preserve the value read for writes to bits. The Intel
hardware implements these bits as read-only 0s.
Reserved and Zero: These bits are reserved for future RWC implementations; software must
use 0 for writes to bits. The 41210 hardware implements these bits as read-only 0s.
Read-Only Sticky: These bits are read-only and cannot be altered by software. The bits are
not cleared by reset and can be reset only with the
Read Zero to Set: Reading this bit when the current value of the bit is 0 causes the bit to flip
to a 1. Software must write a 1 to clear this bit. Writing a 0 has no effect.
Read-Write: Software can do a full read and write of this bit.
Read and Write One to Set: Software must write a 1 to set this bit. Writing a 0 has no effect
on this bit. Software can clear this bit through a separate RWC bit, or it can be reset by
hardware.
Read-Write and Sticky: Software can read and write this bit. The bit can be reset only by a
PERST# reset.
Read and Write One to Clear: When this bit is set, software must write a 1 to this bit to clear
it. Writing a 0 has no effect.
Read and Write One to Clear and Sticky through reset: When this bit is set, sof tware must
write a 1 to this bit to clear it. Writing a 0 has no effect. The bit can be reset only by a
reset.
Strap: This is a read-only register. The power-on default is based on sampling a strap pin at
the rising edge of
Write Transient: This bit is always read as a 0. Writing a 1 to this bit causes other side-
effects that are specific to every WT bit.
PERST#.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
PERST# reset condition.
PERST#
Note: Software must not attempt to write to the registers that are marked “reserved”. Writing to these
registers yields undetermined results. Reads of these registers can yield either value. Note that the
behavior of individual register bits that are marked “reserved” is in accordance with the attribute
definiti on for that bit.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 73
Page 74

Register Description
12.2 Configuration Registers
The bridge configuration space follows the standard PCI Express*-to-PCI Bridge configuration
space format. Refer to the PCI Express*-to-PCI Bridge Specification, Revision 1.0a fo r details on
the format. Each 41210 Bridge contains an identical set of registers as descri bed i n this secti on for
its respective PCI se gment.
Table 33 and Table 34 show the configuration registers of the 41210 and their address byte offset
values. Figure 12 presents the capabilities supported by the 41210.
74 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 75

Figure 12. Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Capabilities
Register Description
n
o
i
t
a
r
u
g
i
f
n
o
e
C
c
a
d
p
e
S
d
n
e
t
x
E
Power Budgeting Capability
PCI Express Advanced Error
Reporting Capability
PCI-X Capability
PCI-PM 1.1 Capability
MSI Capability
PCI Express Capability
0xFFF
0x300
0x100
CAP_PTR
PCI/PCI-X Compatible
configuration region
0x40
0x00
B3174-02
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 75
Page 76

Register Description
T a ble 33. Legacy Configuration Space
Byte
Offset
DID VID 00h
PSTS PCICMD 04h 84h
Class Code (CC) REVID 08h 88h
Reserved HEADTYP PMLT CLS 0Ch 8Ch
Reserved
SMLT BNUM 18h 98h
SSTS IOBL 1Ch 9Ch
MBL 20h A0h
PMBL 24h A4h
PMBU32 28h A8h
PMLU32 2Ch ACh
IOBLU16 30h B0h
Reserved CAPP 34h B4h
Reserved 38h B8h
BCTRL INTR 3Ch BCh
PCLKC MTT BCNF 40h C0h
EXP_CAP EXP_NXTP
EXP_DCAP 48h C8h
EXP_DSTS EXP_DCTL 4Ch CCh
EXP_LCAP 50h D0h
EXP_LSTS EXP_LCTL 54h D4h
Reserved 58h PX_SSTS PX_NXTP PX_CAPID D8h
MSI_MC MSI_NXTP MSI_CAPID 5Ch PX_BSTS DCh
MSI_MA
Reserved MSI_MD 68h
PM_PMC PM_NXTP PM_CAPID 6Ch ECh
PM_DATA PM_BSE PM_PMCSR 70h F0h
Reserved
EXP
_CAPID
10h 90h
14h 94h
Reserved
44h C4h
60h PX_USTC E0h
64h PX_DSTC E4h
Reserved
74h F4h
78h F8h
7Ch BINIT FCh
Byte
Offset
80h
E8h
76 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 77

Table 34. PCI Express* Extended Configuration Space
Register Description
Reserved
Register
EXPAERR_CAPID 100
ERRUNC_STS 104
ERRUNC_MSK 108
ERRUNC_SEV 10C
ERRCOR_STS 110
ERRCOR_MSK 114
ADVERR_CTL 118
HDR_LOG
PCIXERRUNC_STS 12C
PCIXERRUNC_MSK 130
PCIXERRUNC_SEV 134
PCIXERRUNC_PTR 138
PCIXHDR_LOG
Reserved 14C–167
Byte
Offset
11C
120
124
128
13C
140
144
148
ARB_CNTRL
Reserved
Reserved
SSR 170
Reserved 174
PREFCTRL
Reserved 180–2FF
PWRBGT_CAPID 300
Reserved PWRBGT_DSEL 304
PWRBGT_DATA 308
Reserved 30C–3FF
168
16C
178
17C
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 77
Page 78

Register Description
12.2.1 Offse t 00h: ID—Identifiers
Contains the vendor and device identifiers for software.
Table 35. Offset 00h: ID—Identifiers
Bits Type Reset Description
31:16 RO
15:0 RO 8086h
AB
0340h 0341h
Device ID (DID): These bits indicate the device number assigned by Intel to the Intel
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge.
Vendor ID (VID): This 16-bit field indicates that Intel is the vendor.
12.2.2 Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register
This register controls how the device behaves on the primary interface (PCI Express*). As this
component is a bridge, additional command information is located in a separate Bridge Control
register (“Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control” on page 88).
Table 36. Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register (Sheet 1 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
15:11 RO 00h Reserved
10 RW 0b
9RO 0b
8RW 0b
7RO 0b
6RW 0b
5RO 0b
4RO 0b
3RO 0b
INTx Mask: The bridge does not generate internal interrupts. The value of this bit has no
meaning.
Fast Back-to-back enable (FBE): This bit has no meaning on PCI Express*.
This bit must be hard-wired to 0.
SERR# Enable (SEE): This bit enables reporting of non-fatal and fatal errors to the root
complex.
0 = Disable reporting errors
1 = Enable reporting of non-fatal and fatal errors to the root complex
NOTE: Errors are reported when enabled either through this bit or through the PCI
Express*-specific bits in the Device Control Register (“Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—
PCI Express* Device Control Register” on page 93).
Wait Cycle Control (WCC): Reserved
Parity Error Response Enable (PERE): This bit controls the setting of the master data
parity error bit in the Status Register (“Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status” on
page 79) in response to a parity error received on the PCI Express* interface (poisoned
TLP) or peer PCI interface.
0 = The 41210 ignores these errors on the PCI Express*/peer-PCI interface.
1 = The 41210 reports read completion data parity errors on PCI Express* and sets the
MDPD bit in the status register.
VGA Palette Sn oop Enable (VGA_PSE): Reserved
Memory Write and Invalidate Enable (MWIE): Memory write and invalidate transactions
are not generated, since PCI Express* does not have a corresponding transfer type.
Special Cycle Enable (SCE): Reserved
®
78 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 79

Table 36. Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register (Sheet 2 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
Bus Master Enable (BME): This bit controls the ability of the 41210 to issue memory and
I/O read/write requests on the PCI Express* interface.
0 = The 41210 does not respond to any memory or I/O transactions on the PCI interface
and stops issuing new requests on PCI Express*.
2RW 0b
1RW 0b
0RW 0b
1 = The 41210 processes transactions normally.
NOTE: This bit does not stop completions on PCI Express* from being issued. Software
must ensure that all upstream posted transactions are flushed in the bridge
segment when this bit is set. Otherwise, delayed completions (such as configuration
read completions) can be stuck behind a posted write and cannot proceed from PCI
to PCI Express*.
Memory Space Enable (MSE): This bit controls the response of the 41210 when the 41210
is the target of a memory transaction from a primary or secondary interface.
0 = Every memory transaction targeting a secondary interface is master-aborted, and every
memory transaction from secondary to primary is claimed.
1 = Primary-to-secondary and secondary-to-primary forwarding follows the normal rules for
memory forwarding.
I/O Space Enable (IOSE): This bit controls the response of the 41210 when the 41210 is
the target of I/O transactions from primary or secondary interfaces.
0 = Every I/O transaction targeting secondary is master-aborted, and every memory
transaction from secondary to primary is claimed, provided that the upstream I/O
enable bit in the BINIT register is also set.
1 = Primary-to-secondary and secondary-to-primary forwarding follows the normal rules for
memory forwarding.
Register Description
12.2.3 Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status
For the writable bits in this register, writing a 1 clears the bit. Writing a 0 to the bit has no effect.
T a ble 37. Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status (Sheet 1 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
Detected Parity Error (DPE): This bit is set when a poisoned TLP is received from PCI
Express* or a data parity error is detected from the peer PCI segment (writes or read
15 RWC 0b
14 RWC 0b
13 RWC 0b
12 RWC 0b
completions). This bit is set even when the parity error response enable bit (bit[6] of the
PCICMD Register—“Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register” on page 78) is not set.
0 = No error
1 = Poisoned TLP received or Data Parity Error detected
Signaled System Error (SSE): This bit is set when ERR_FATAL or ERR_NONFATAL
messages are sent to the root complex and the SERR enable bit in the PCICMD Register
(“Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register” on page 78) is set.
0 = No error
1 = ERR_FATAL or ERR_NONFATAL message sent
Received Master Abort (RMA): This bit is set when the 41210 receives a completion with
“Unsupported Request Completion” status on the PCI Express* interface.
0 = No error
1 = “Unsupported Request Completion” status received on PCI Express* interface
Received Target Abort (RTA): This bit is set when the 41210 receives a completion with
“Completer Abort” (CA) status on the PCI Express* interface.
0 = No error
1 = Completer Abort (CA) status received on PCI Express* interface
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 79
Page 80

Register Description
T able 37. Offset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status (Sheet 2 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
Signaled Target Abort (STA): This bit is set when a completion packet with Completer
11 RWC 0b
10:9 RO 00b
8RWC0b
7RO0b
6 RO 0b Reserved
5RO0b
4RO1b
3RO0b
2:0 RO 0h Reserved
Abort (CA) status is generated on PCI Express*.
0 = No error.
1 = Completer Abort (CA) status transmitted on PCI Express* interface
DEVSEL# Timing (DVT): These bits have no meaning on PCI Express*. Fast decode
timing is reported.
Master Data Parity Error Detected (MDPD): This bit is set when the 41210 detects an
uncorrectable data error. This bit is set when the parity error response enable bit (PERE) in
the Command Register (“Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command Register” on page 78) is set and
one of the following conditions occurs:
• The bridge receives a completion with a poisoned TLP on the PCI Express* interface.
• The bridge receives a completion with poisoned data on the peer PCI segment.
• The bridge poisons a write request on the PCI Express* interface.
0 = No error
1 = Data Parity Error in completion packet received or a write request transmitted
Fast Back-to-Back Capable (FBC): This bit has no meaning on PCI Express*.
66 MHz Capable (C66): This bit has no meaning on PCI Express*.
Capabilities List Enable (CAPE): This bit indicates the capabilities pointer in the 41210.
Offset 34H indicates the offset for the first entry in the linked list of capabilities.
0 = No capabilities enabled
1 = Capabilities enabled and accessible from 34H
Interrupt Status: The 41210 does not generate internal interrupts. This bit is hard-wired
to 0.
12.2.4 Offset 08h: REVID—Revision ID
This register is the Revision ID Register.
T a ble 38. Offset 08h: REVID—Revision ID
Bits Type Reset Description
Revision ID (RID): These bits indicate the stepping (die version) of the Intel
7:0 RO 00h
to Parallel PCI Bridge.
0000 0000 A-0 stepping
80 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
®
41210 Serial
Page 81

Register Description
12.2.5 Offset 09h: CC—Class Code
This register contains the class code, sub-class code, and programming interface for the device.
Table 39. Offset 09h: CC—Class Code
Bits Type Reset Description
23:16 RO 06h Base Class Code (BCC): The value of 06h indicates that this is a bridge device.
15:8 RO 04h
7:0 RO 00h
Sub Class Code (SCC): This 8-bit value indicates that this device is a PCI-to-PCI Bridge.
Programming Interface (PIF): This bit indicates that this device is standard (non-
subtractive) PCI-to-PCI Bridge.
12.2.6 Offset 0Ch: CLS—Cache-Line Size
This register indicates the cache-line size of the system.
T a ble 40. Offset 0Ch: CLS—Cache Line Size
Bits Type Reset Description
Cache Line Size (CLS): These bits specify the system cache-line size in units of Dwords:
• 08h: 32-byte line (8 DWords)
7:0 RW 00h
• 10h 64-byte line
• 20h 128-byte line
Any value outside this range defaults to a 64-byte line. When creating read requests to PCI
Express*, this value is used to partition speculative PCI read requests on cache-line–
aligned boundaries. This register has no other effect on the 41210.
12.2.7 Offset 0Dh: PMLT—Primary Master Latency Timer
This register does not apply to PCI Express*, and is maintained as R/W for software compatibility.
Table 41. Offset 0Dh: PMLT—Primary Master Latency Timer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:3 RO 00h Time Value (TV): Not applicable for PCI Express*
2:0 RO 000b Reserved
12.2.8 Offset 0Eh: HEADTYP—Header Type
This register determines how the rest of the configuration space is laid out.
T a ble 42. Offset 0Eh: HEADTYP—Header Type
Bits Type Reset Description
7RO 1b
6:0 RO 01h
Multi-function device (MFD): Reserved as 1 to indicate that the 41210 is a multi-function
device.
Header Type (HTYPE): These bits define the layout of addresses 10h through 3Fh in the
configuration space. These bits read as 01h to indicate that the register layout conforms to
the standard PCI-to-PCI Bridge layout.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 81
Page 82

Register Description
12.2.9 Offset 18h: BNUM—Bus Numbers
This register contains the primary, secondary, and maximum subordinate bus number registers.
Table 43. Offset 18h: BNUM—Bus Numbers
Bits Type Reset Description
Subordinate Bus Number (SBBN): These bits indicate the highest PCI bus number
23:16 RW 00h
15:8 RW 00h
7:0 RW 00h
downstream of this bridge. Every Type 1 configuration cycle on PCI Express* with a bus
number greater than the secondary bus number and less than or equal to the subordinate
bus number is forwarded as a Type 1 configuration cycle to the secondary PCI bus.
Secondary Bus Number (SCBN): These bits indicate the bus number of the PCI device to
which the secondary interface is connected. Any Type 1 configuration cycle matching this
bus number is translated to a Type 0 configuration cycle and run on the PCI bus.
Primary Bus Number (PBN): These bits indicate the PCI Express* bus number. Any
Type 1 configuration cycle with a bus number less than this number is not accepted by this
bridge (in other words, it may still match the other bridge).
12.2.10 Offset 1Bh: SMLT—Secondary Master Latency Timer
This timer controls the amount of time that the 41210 continues to burst data on its secondary
interface. The counter starts counting down from the assertion of FRAME#. When the grant is
removed, then the expiration of this counter results in the de-assertion of FRAME#. When the
grant is not removed, then the 41210 may continue ownership of the bus. The secondary master
latency timer default value is 64 in PCI-X mode (see Section 8.6.1 of the PCI-X Addendum to the
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b).
Table 44. Offset 1Bh: SMLT—Secondary Master Latency Timer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:3 RW
2:0 RO 000b Reserved
00h: PCI
40h: PCI-X
Secondary Latenc y Timer (TV): This 5-bit value indicates the number of PCI clocks, in
8-clock increments, during which the bridge remains as a master of the PCI bus when
another master is requesting use of the PCI bus.
82 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 83

12.2.11 Offset 1Ch: IOBL—I/O Base and Limit
This register defines the base and limit, aligned to a 4 KB boundary, of the I/O area of the bridge.
Accesses from PCI Express* that are within the ranges specified in this register are sent to PCI
when the I/O space enable bit is set. Accesses from PCI Express* that are outside the ranges
specified result in an Unsupported Request response.
Table 45. Offset 1Ch: IOBL—I/O Base and Limit
Bits Type Reset Description
I/O Limit Address Bits [15:12] (IOLA): These bits define the top address of an address
15:12 RW 0h
11:8 RO 0h
7:4 RW 0h
3:0 RO 0h
range to determine when to forward I/O transactions from PCI Express* to PCI. These bits
correspond to address lines[15:12] for 4 KB aligned window. Bits[11: 0] are assumed to be
FFFh.
I/O Limit Addressing Capability (IOLC): Each of these bits is hard-wired to 0, indicating
support for 16-bit I/O addressing only.
I/O Base Address Bits [15:12] (IOBA): These bits define the bottom address of an
address range to determine when to forward I/O transactions from one interface to another.
These bits correspond to address lines[15:12] for 4 KB alignment. Bits[11:0] are assumed to
be 000h.
I/O Base Addressing Capability (IOBC): Each of these bits is hard-wired to 0, indicating
support for 16-bit I/O addressing only.
Register Description
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 83
Page 84

Register Description
12.2.12 Offset 1Eh: SSTS—Secondary Status
For the writable bits in this register, writing 1 to the bit clears the bit. Writing 0 to the bit has
no effect.
Table 46. Offset 1Eh: SSTS—Secondary Status
Bits Type Reset Description
Detected Parity Error (DPE): This bit is set to 1 whenever the bridge detects an address or
15 RWC 0b
14 RWC 0b
13 RWC 0b
12 RWC 0b
11 RWC 0b
10:9 RO 01b
8RWC 0b
7RO 1b
6 RO 0b Reserved
5RO 1b
4:0 RO 00h Reserved
data parity error on the PCI bus. This bit is set even when the Parity Error Response Enable
bit of the Bridge Control Register (bit[0], “Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control” on page 88)
is not set.
Received System Error (RSE): This bit is set to 1 when a SERR# assertion is received
on PCI.
Received Master Abort (RMA): This bit is set to 1 whenever the bridge, as an initiator on
the PCI bus, receives a master-abort, or when the bridge receives a PCI-X split completion
packet with a master-abort.
Received Target Abort (RTA): This bit is set to 1 whenever the bridge, as an initiator on
PCI, receives a target-abort on PCI. For “completion required” PCI Express* packets, this
event forces a completion status of “target abort” on PCI Express*, and sets the Signaled
T arget Abort in the Primary S tatus Register (“Of fset 06h: PSTS—Primary Device Status” on
page 79).
Signaled Target Abor t (STA): This bit is set to 1 when the bridge, as a target on the PCI
bus, signals a target abort.
DEVSEL# Timing (DVT): These bits indicate that the 41210 responds in medium decode
time to transactions on the PCI interface (secondary bus).
Master Data Parity Error Detected (MDPD): This bit is set to 1 when all of the following
are true:
• The bridge is the initiator on PCI.
• PERR# is detected to be asserted.
• The Parity Error Response Enable bit in the Bridge Control Register (bit[0], “Offset 3Eh:
BCTRL—Bridge Control” on page 88) is set.
This bit is also set when the 41210 receives a split-completion message from PCI-X, which
indicates a write data parity error (regardless of the setting of the Parity Error Response
Enable bit). Refer to
details.
Fast Back-to-Back Capable (FBC): This bit indicates that the secondary interface can
receive fast back-to-back cycles.
66 MHz Capable (C66): This bit indicates that the secondary interface of the bridge is
66 MHz-capable.
PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 1.0b for
84 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 85

12.2.13 Offset 20h: MBL—Memory Base and Limit
Defines the base and limit, aligned to a 1 MB boundary, of the non-prefetchable memory area of
the bridge. Accesses from PCI Express* that are within the ranges specified in this reg ister are sent
to PCI when the Memory Space Enable bit is set. Accesses from PCI that are outside the ranges
specified are forwarded to PCI Express* when the Bus Master Enable bit is set.
Note: Even though this region is non-prefetchable, peer reads from PCI can potentially prefetch through
this window. This prefetching can be turned off with the Prefetch Policy bits (PP bits[42:41],
“Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register” on page 119).
These registers are cleared to all 0s on reset.
Note: This register must be programmed appropriately to enable or disable the space.
T able 47. Offset 20h: MBL—Memory Base and Limit
Bits Type Reset Description
Register Description
31:20 RW 000h
19:16 RO 0h Reserved
15:4 RW 000h
3:0 RO 0h Reserved
Memory Limit (ML): These bits are compared with bits[31:20] of the incoming address to
determine the upper 1 MB-aligned value (exclusive) of the range. The incoming address
must be less than this value.
Memory Base (MB): These bits are compared with bits[31:20] of the incoming address to
determine the lower 1 MB-aligned value (inclusive) of the range. The incoming address
must be greater than or equal to this value.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 85
Page 86

Register Description
12.2.14 Offset 24h: PMBL—Prefetchable Memory Base and Limit
This register defines the base and limit, aligned to a 1 MB boundary, of the prefetchable memory
area of the bridge. Accesses from PCI Express* that are within the ranges specified in this register
are sent to PCI when the Memory Space Enable bit is set. Accesses from PCI that are outside the
ranges specified are forwarded to PCI Express* when the Bus Master Enable bit is set.
Note: Even though this register specifies a valid prefetchable memory window, the bridge never
prefetches through this window in the downstream direction (reads from PCI Express*-to-PCI).
Also, the bridge does not do any byte-merging in this window.
Note: Peer reads from PCI can prefetch through this window. This prefetching can be turned off with the
prefetch policy bits (PP bits 42:41, “Offset 178h: PREFCTRL—Prefetch Control Register” on
page 119).
These registers are cleared to all 0s on reset.
Note: This register must be programmed appropriately to enable or disable the space.
Table 48. Offset 24h: PMBL—Prefetchable Memory Base and Limit
Bits Type Reset Description
31:20 RW 000h
19:16 RO 1h
15:4 RW 000h
3:0 RO 1h
Prefetchable Memory Limit (PML): These bits are compared with bits[31:20] of the
incoming address to determine the upper 1 MB-aligned value (inclusive) of the range. The
incoming address must be less than this value.
64-bit Indicator (IS64L): These bits indicate that 64-bit addressing is supported for the
limit. This value must be in agreement with the IS64B field (bits[3:0], below).
Prefetchable Memory Base (PMB): These bits are compared with bits[31:20] of the
incoming address to determine the lower 1 MB-aligned value (inclusive) of the range. The
incoming address must be greater than or equal to this value.
64-bit Indicator (IS64B): These bits indicate that 64-bit addressing is supported for the
limit. This value must be in agreement with the IS64L field (bits[19:16], above).
12.2.15 Offset 28h: PMBU32—Prefetchable Memory Base Upper
32 Bits
This register defines the upper 32 bits of the prefetchable address base register.
T a ble 49. Offset 28h: PMBU32—Prefetchable Memory Base Upper 32 Bits
Bits Type Reset Description
31:0 RW 0000 0000h
86 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Prefetchable Memory Base Upper Portion (PMBU): These bits indicate that full 64-bit
addressing is supported.
Page 87

Register Description
12.2.16 Offset 2Ch: PMLU32—Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper
32 Bits
This register defines the upper 32 bits of the prefetchable address base register.
T a ble 50. Offset 2Ch: PMLU32—Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper 32 Bits
Bits Type Reset Description
31:0 RW 0000 0000h
Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper Portion (PMLU): These bits indicate that full 64-bit
addressing is supported.
12.2.17 Offset 30h: IOBLU16—I/O Base and Limit Upper 16 Bits
Since I/O is limited to 64 KB, this register is reserved and not used.
T able 51. Offset 30h: IOBLU16—I/O Base and Limit Upper 16 Bits
Bits Type Reset Description
31:16 RO 0000h I/O Base High 16 Bits (IOBH): Reserved
15:0 RO 0000h
I/O Limit High 16Bits (IOLH): Reserved
12.2.18 Offset 34h: CAPP—Capabilities List Pointer
This register contains the pointer for the first entry in the capabilities list.
T able 52. Offset 34h: CAPP—Capabilities List Pointer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 44h
Capabilities Pointer (PTR): These bits indicate that the pointer for the first entry in the
capabilities list is at 44h (PCI Express* capability) in the configuration space.
12.2.19 Offset 3Ch: INTR—Interrupt Information
This register contains information on interrupts on the bridge.
T a ble 53. Offset 3Ch: INTR—Interrupt Information
Bits Type Reset Description
15:8 RO 00h Interrupt Pin (PIN ): These bits indicate that no interrupt is used by the bridge segment.
7:0 RW 00h
Interrupt Line (LINE): This register is used to convey the interrupt line routing information
between the initialization code and the device driver.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 87
Page 88

Register Description
12.2.20 Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control
This register provides extensions to the Command Register (“Offset 04h: PCICMD—Command
Register” on page 78) that are specific to a bridge. The Bridge Control Register provides many of
the same controls for the secondary interface that are provided by the Command Register for the
primary interface. Some bits affect operation of both interfaces of the bridge.
Table 54. Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control (Sheet 1 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
15:12 RO 0h Reserved
Discard Timer SERR# Enable (DTSE): This bit controls the generation of
ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FATAL messages on the primary interface in response to a timer
discard on the secondary interface.
0 = The 41210 does not generate ERR_NONFATA L/ERR_FATAL on a secondary timer
discard.
11 RW 0b
10 RWC 0b
9RW 0b
8RW 0b
7RO 0b
6RW 0b
1 = When the appropriate mask bit in the advanced capability register is clear, the 41210
does generate ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FAT AL in response to a secondary timer
discard.
NOTE: ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FATAL messages may also be generated when the
corresponding mask bit in the Uncorrectable Error Mask Register (“Offset 108h:
ERRUNC_MSK—PCI Express* Uncorrectable Error Mask” on page 106) is
cleared.
Discard Timer Status (DTS): This bit is set to 1 when the secondary discard timer expires
(there is no discard timer for the primary interface).
Secondary Discard Timer (SDT): This bit sets the maximum number of PCI clock cycles
during which the bridge waits for an initiator on PCI to repeat a delayed transaction request.
The counter starts as soon as the delayed transaction completion is at the head of the
queue. When the master has not repeated the transaction at least once before the counter
expires, the bridge discards the transaction from its queues.
0 = The PCI master time-out value is between 2
1 = The PCI master time-out value is between 2
Primary Discard Timer (PDT): This bit is not relevant to PCI Express*.
Fast Back-to-Back Enable (FBE): The bridge cannot generate fast back-to-back cycles on
the PCI bus from PCI Express*-initiated transactions.
Secondary Bus Reset (SBR): This bit controls x_RST# assertion on PCI.
0 = The bridge does
1 = The bridge asserts PCIRST#. Bridge configuration registers are not reset when this bit
is set.
As soon as this bit is set, the bridge completes the currently running transaction on PCI and
then resets the bus. Note that it is the responsibility of the software to ensure that all
pending transactions with the bus segment are complete before setting this bit. When the
software fails to do this, transactions can be lost.
NOTE: Software must ensure the secondary bus x_RST# timing requirements when
clearing this bit.
not force x_RST# assertion on the secondary interface.
15
and 216 PCI clocks.
10
and 211 PCI clocks.
88 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 89

Table 54. Offset 3Eh: BCTRL—Bridge Control (Sheet 2 of 2)
Bits Type Reset Description
Master Abort Mode (MAM ): This bit controls the bridge’s behavior when a master-abort (or
unsupported request) occurs on either interface. This bit does not affect the behavior when
the bridge forwards a UR completion from PCI Express* to master-abort on PCI-X.
0 = Do not report master-aborts. When a UR response is received from PCI Express* for
non-posted transactions, and when the secondary side is operating in conventional
5RW 0b
4RW 0b
3RW 0b
2RW 0b
1RW 0b
0RW 0b
PCI mode, the device returns FFFF FFFFh on reads and completes I/O writes
normally. For posted transactions, the data is discarded and no additional action is
taken.
1 = Report UR completions by signaling a target-abort on the secondary/peer interface
when operating in conventional PCI mode. The device returns
ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FATAL messages for posted transactions initiated from PCI
Express*.
VGA 16-bit Decode: This bit enables the bridge to provide 16-bit decoding of VGA I/O
address precluding the decoding of VGA alias addresses every 1 KB. This bit requires the
VGA enable bit (bit 3 of this register) to be set to 1.
VGA Enable (VGAE): This bit modifies the response to VGA-compatible addresses. When
set to 1, the bridge forwards the following transactions from PCI Express*-to-PCI regardless
of the value of the I/O base and limit registers. The transactions are qualified by the memory
enable and I/O enable in the command register.
Memory addresses: 000A 0000h–000B FFFFh
I/O addresses: 3B0h–3BBh and 3C0h–3DFh. For the I/O addresses, bits[63:16] of the
address must be 0, and bits[15:10] of the address are ignored (aliased).
The same holds true from secondary accesses to the primary interface in reverse for
memory accesses and also for I/O when the upstream I/O enable bit is set in the BINIT
register, from secondary to primary.
ISA Enable (IE): This bit modifies the response by the bridge to ISA I/O addresses. This
function applies only to I/O addresses that are enabled by the I/O base and I/O limit
registers and are in the first 64 KB of PCI I/O space. When this bit is set, the bridge blocks
all forwarding from primary to secondary of I/O transactions addressing the last 768 bytes in
each 1 KB block (offsets 100h to 3FFh). This bit has the reverse effect on I/O transfers
originating on the secondary bus when the upstream I/O enable bit is set in the BINIT
Register (“Offset FCh: BINIT—Bridge Initialization Register” on page 104).
SERR# Enable (SE): This bit controls the forwarding of secondary interface SERR#
assertions on the primary interface. When set, the bridge sends a PCI Express*
ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FATAL cycle (based on Advanced Error capability’s PCI SERR
detected severity bit) when all of the following conditions are true:
• SERR# is asserted on the secondary interface.
• This bit is set.
• The SERR# detected mask bit in the Advanced Error capability is set.
• ERR_NONFATAL/ERR_FATAL messages are enabled to be sent.
Parity Err or Res ponse Enable (PER E): This bit cont rols the response to address and data
parity errors on the secondary interface. When the bit is cleared, the bridge must ignore any
parity errors that it detects and continue normal operation. The bridge must generate parity
even when parity error reporting is disabled.
Register Description
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 89
Page 90

Register Description
12.2.21 Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register
The bridge control bits specific to the Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge are listed in
Table 55.
Table 55. Offset 40h: BCNF—Bridge Configuration Register
Bits Type Reset Description
15 RsvdP 0h Preserved
PCI Mode (PMODE): This bit determines the mode of operation of the PCI bus. This bit
14 RW
13:11 RsvdP 101b Preserved
See
T able1 1 on
page 25.
reflects the status of the current PCI bus mode and also allows the software to change the
mode by writing to this bit. The power-up value of this register is written based upon
Table 11, “PCI Mode Pin/Strap Encoding” on page 25.
0 = Conventional PCI
1 = PCI-X
PCI Frequency (PF REQ) : This bit det ermines the frequency at which the PCI bus operates.
The power-up value of this register is written based upon Table 12, “PCI-X Initialization
Pattern” on page 25. After the software determines the capabilities of the bus, it sets this
value, and the PMODE bit (bit[14] of this register) to the desired frequency and resets the
PCI bus. The values are encoded as follows:
10:9 RW
8 RsvdP 0b Preserved
7RW 1b
6:4 RsvdP 000b Preserved
3 RsvdP 0b Preserved
2 RsvdP 0b Preserved
1:0 RW 00b
See
T able12 on
page 25.
Results are indeterminate when invalid combinations are written by the software.
Peer Memory Read Enable (PMRE):
0 = Normal operation. Peer memory reads are not allowed. All memory reads from a PCI
bridge are sent to PCI Express* regardless of address.
1 = Peer memory reads from one PCI segment to another are supported.
Maximum Upstream Delayed Transactions (MDT): This bit controls the maximum number
of upstream delayed transactions the Intel
have:
Bit[10:9] Frequency Comments
00 33 MHz Valid only when PMODE is 0.
01 66 MHz
10 100 MHz Valid only when PMODE is 1.
11 133 MHz Valid only when PMODE is 1.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge is allowed to
Bit Maximum Number of Upstream Delayed Transactions
00 4 active, 4 pending
01 1 active, 1 pending
10 2 active, 2 pending
11 Reserved
90 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 91

12.2.22 Offset 42h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer
This register controls the amount of time that the 41210 arbiter allows for a PCI initiator to perform
multiple back-to-back transactions on the PCI bus. The number of clocks programmed in the MTT
represents the time slice (measured in PCI clocks) to be allotted to the current agent, after which
the arbiter grants the bus to another agent that is requesting it.
T a ble 56. Offset 42h: MTT—Multi-Transaction Timer
Bits Type Reset Description
Register Description
7:3 RW 00h
2:0 RsvdP 000b Preserved
Timer Count Value (MTC): This field specifies the amount of time that the grant remains
asserted to a master that is continuously asserting its request for multiple transfers. This
field specifies the count in an 8-clock (PCI clock) granularity.
12.2.23 Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control
This register controls the enable and disable of the 41210 PCI clock outputs.
T a ble 57. Offset 43h: PCLKC—PCI Clock Control
Bits Type Reset Description
7 RsvdP 1b Reserved
PCI Feedback Clock Control:
6RW 1b
5:0 RW 1 1111b
0 = PCI feedback clock output buffer, X_CLK[6], is tristated.
1 = PCI feedback clock output buffer, X_CLK[6], is enabled.
PCI Clock Control: These bits enable the PCI clock output buffers, when all 1s. Otherwise
the buffers are tristated. Bit[0] corresponds to X_CLKO[0], bit[1] corresponds to X_CLKO[1],
etc.
The tristating of the clock is asynchronous to the output clocks.
12.2.24 Offset 44h: EXP_CAPID—PCI Express* Capability Identifier
This register stores the PCI Express* capability ID value.
T a ble 58. Offset 44h: PCI Express*_CAPID—PCI Express* Capability Identifier
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 10h
PCI Express* Capability ID: These bits indicate that the Intel
Bridge has PCI Express* capability.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI
12.2.25 Offset 45h: EXP_NXTP—Next Item Pointer
This register stores the byte offset pointer to the next capability list item of the bridge.
T able 59. Offset 45h: PCI Express*_NXTP—Next Item Pointer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 5Ch
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 91
Next Capability Po inter: This field indicates the offset of the next capabilities list item,
which is the MSI capability.
Page 92

Register Description
12.2.26 Offset 46h: EXP_CAP—PCI Express* Capability
This register stores the versio n n umber o f th e capab ility item an d o ther bas e inf ormation co ntained
in the capability structure.
Table 60. Offset 46h: EXP_CAP—PCI Express* Capability
Bits Type Default Description
15:14 RsvdP 00b Preserved
13:9 RO 0 0000b
8RO 0b
7:4 RO 7h
3:0 RO 1h
Interrupt Message Number: Not relevant for the Intel
Slot Implemented: Not relevant for the 41210
Device/Port Type: These bits indicate that the 41210 is a PCI Express* end-point device.
Version Number: These bits indicate the version number of the PCI Express* capability
structure.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge
12.2.27 Offset 48h: EXP_DCAP—PCI Express* Device Capabilit ies
Register
This register stores information on the PCI Express* link capabilities.
Table 61. Offset 48h: EXP_DCAP—PCI Express* Device Capabilities Register
Bits Type Default Description
31:28 RsvdP 0h Preserved
Captured Slot Power Limit Scale: In combination with the Slot Power Limit value
27:26 RO 00b
25:18 RO 00h
17:15 RsvdP 000b Preserved
14 RO 0b
13 RO 0b
12 RO 0b
11:9 RO 000b
8:6 RO 000b
5RO 0b
4:3 RO 00b
2:0 RO 001b
(bits[25:18], this field specifies the upper limit of the power supplied by slot. The power limit
(in Watts) is calculated by multiplying the value in this field by the value in the Slot Power
Limit Value field. This value is set by the Set_Slot_Power_Limit message.
Captured Slot Power Limit Value: In combination with the Slot Power Limit Scale value
(bits[27:26]), this field specifies the upper limit of the power supplied by slot. The power limit
(in Watts) is calculated by multiplying the value in this field by the value in the Slot Power
Limit Scale field. This value is set by the Set_Slot_Power_Limit message.
Power Indicator Present: Not supported
Attention Indicator Present: Not supported
Attention Button Present: Not supported
Endpoint L1 Acce ptable Latency: L1 ASPM is not supported.
Endpoint L0s Acceptable Latency: The least latency possible out of L0s is supported.
NOTE: L0s ASPM is not supported in the 41210 Bridge.
Extended Tag Field Supported: Only a 5-bit tag is supported.
Phantom Functions Supported: Not supported
Supported Max Payloa d sizes: 256-byte packets are the maximum supported.
92 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 93

Register Description
12.2.28 Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—PCI Express* Device Control
Register
This register stores command bits that control the 41210 behavior on PCI Express*.
T a ble 62. Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—PCI Express* Device Control Register (Sheet 1 of 2)
Bits Typ e Default Description
Bridge Configuration Re t r y Enable: When set, the bridge is enabled to return a
15 RW 0b
14:12 RW 010b
completion with Completion Retry Status (CRS) on PCI Express* when a configuration
transaction to the secondary interface did not complete within the PCI completion time-out
period.
Max_Read_Request_Size: This field applies to the bridge segment when the segment is in
PCI mode only. When in PCI-X mode, this field does not apply. The Intel
Parallel PCI Bridge cannot send requests larger than the size indicated by this field.
Encodings are as follows:
Bit Max_Read_Request_Size
000b 128-byte maximum read request size
001b 256-byte maximum read request size
010b 512-byte maximum read request size
011b 1024-byte maximum read request size
100b 2048-byte maximum read request size
101b 4096-byte maximum read request size
110b Reserved (the 41210 defaults to 512 bytes)
111b Reserved (the 41210 defaults to 512 bytes)
®
41210 Serial to
11 RO 0b
10 RO 0b
9RO 0b
8RO 0b
7:5 RW 000b
4RO 0b
3RW 0b
Enable No Snoop: Hard-wired to 0
Auxiliary (AUX) Power PM Enable: Not supported
Phantom Function Enable: Not supported
Extended Tag Field Enable: Ignored because only 5-bit tag is supported
Maximum Payload Size: These bits indicate the maximum payload size supported for
TLPs. Supported encodings are as follows:
Bit Max_Payload_Size
000b 128-byte maximum payload size
001b 256-byte maximum payload size
All other values default to 128 bytes.
Enable Relaxed Ordering: Hard-wired to 0
Unsupported Request Reporting Enable: This bit controls the enabling of
ERR_NONFATAL or ERR_FATAL messages on PCI Express* for reporting “Unsupported
Request” errors. Note that the following requests use this enable bit:
• requests from PCI Express* that are unsupported
• requests from PCI Express* that master-abort on the internal switch
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 93
Page 94

Register Description
T able 62. Offset 4Ch: EXP_DCTL—PCI Express* Device Control Register (Sheet 2 of 2)
Bits Type Default Description
2RW 0b
1RW 0b
0RW 0b
Report Fatal Errors: When this bit is set, generation of the ERR_FATAL message is
enabled.
Report NonFatal Errors: When this bit is set, generation of the ERR_NONFATAL message
is enabled.
Report Correctable Errors: When this bit is set, generation of the ERR_CORR message is
enabled.
12.2.29 Offset 4Eh: EXP_DSTS—PCI Express* Device Status
Register
This register stores information on the PCI Express* device status.
T a ble 63. Offset 4Eh: EXP_DSTS—PCI Express* Device Status Register
Bits Type Default Description
15:6 RsvdZ 000h Reserved Zero: Software must always write a 0 to these bits.
Transactions Pending: This bit is set when any non-posted request has been issued but
5RO 0b
4RO 0b
3RWC 0b
2RWC 0b
1RWC 0b
0RWC 0b
has not been completed. The bit is cleared only when all completions for all outstanding
non-posted requests are received. Note that this is a dynamic bit; in other words, this bit
goes on and off based on current traffic.
Auxiliary Power Detected: Auxiliary Power is not supported.
Unsupported Request Detected: This bit is set when any unsupported request from PCI
Express* is received. Unsupported requests include all requests that are not claimed by any
function in the Intel
forwarded to the PCI interface with completions returned with an “unsupported request”
status.
Detected Fatal Error: This bit is set when a fatal error is detected (regardless of whether
an error message is generated) on either interface or internally. The bit remains set until the
software writes a 1 to clear it.
Detected Non-Fatal Error: This bit is set when a non-fatal error is detected (regardless of
whether the mask bit is set in the advanced error capability) on eit her int er face or internally.
The bit remains set until the software writes a 1 to clear it.
Detected Correctable Error: This bit is set when a correctable error is detected
(regardless of whether the mask bit is set in the advanced error capability) on either
interface or internally. The bit remains set until the software writes a 1 to clear it.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge, but do not include requests
12.2.30 Offset 50h: EXP_LCAP—PCI Express* Link Capabilities
Register
Table 64. Offset 50h: EXP_LCAP—PCI Express* Link Capabilities Register (Sheet 1 of 2)
Bits Type Default Description
31:24 RO 00h Port Number: Not applicable
23:18 RsvdP 00h Preserved
17:15 RO 111b
94 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
L1 Exit Latency: L1 transition is not supported.
Page 95

Register Description
Table 64. Offset 50h: EXP_LCAP—PCI Express* Link Capabilities Register (Sheet 2 of 2)
Bits Typ e Default Description
L0s Exit Latency: The value in these bits is determined by the setting of the Common
Clock Configuration bit (bit[6]) in the Link Control Register (Offset 54h: EXP_LCTL—PCI
Express* Link Control Register). Note that software can write bit[6] in the Link Control
Register to either a 1 or 0 and these bits then change accordingly. The mapping is shown
below:
14:12 RO 110b
11:10 RO 01b L0s ASPM is not supported in the 41210 Bridge.
9:4 RO 08h
3:0 RO 1h
Bit 6 in LCTL L0s Exit Latency
0
1 010b
NOTE: L0s ASPM is not supported in the 41210 Bridge.
Maximum Link Width: X8 link width is supported.
Maximum Link Speed: 2.5 Gb/s link speed is supported.
110b (because currently L0s cannot work with different reference
clocks)
12.2.31 Offset 54h: EXP_LCTL—PCI Express* Link Control Register
T able 65. Offset 54h: EXP_LCTL—PCI Express* Link Control Register
Bits Typ e Default Description
15:8 RsvdP 00h Preserved
Extended Synch.: When set, this bit forces extended transmission of 4096 FTS ordered
7RW 0b
6RW 0b
5RO 0b
4RO 0b
3RO 0b
2 RsvdP 0b Preserved
1:0 RW 00b
sets in FTS and an extra 1024 TS1 at exit from L1 prior to entering L0. This mode provides
external devices monitoring the link time to achieve bit and symbol lock before the link
enters L0 state and resumes communication. Default value for this bit is 0.
Common Clock Configurat ion: This bit indicates the relationship of the reference clock
between the Intel
end of the 41210 Upstream PCI Express* interface:
0 = Clock is asynchronous .
1 = Clock is comm on.
NOTE: T his bit de term ines the proper L0s exit latency value in the EXP_LSTS register.
NOTE: L0s ASPM is not supported in the 41210 Bridge.
Retrain Link: Not applicable
Disable Link: Not applicable
Read Completion Boundary Control: Not used
ASPM Control: Enables bridge upstream interface to enter L0s:
• 00b = L0s entry is disabled.
• 01b = The Intel
• 10b = L0s entry is disabled.
• 11b = The 41210 enters L0s as per the specification requirement for L0s entry.
NOTE: L0s ASPM is not supported in the 41210 Bridge.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge and the component at the opposite
®
requirement for L0s entry.
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge enters L0s as per the specification
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 95
Page 96

Register Description
12.2.32 Offset 56h: EXP_LSTS—PCI Express* Link Status Register
Table 66. Offset 56h: EXP_LSTS—PCI Express* Link Status Register
Bits Type Default Description
15:13 RsvdZ 000b Reserved Zero: Software must always write 0 to these bits.
®
41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge is on a PCI
12 RO 1b
11 RO 0b
10 RO 0b
Set by PCI
Express*
9:4 RO
3:0 RO 1h
Link Layer
after
training is
complete
Slot Clock Co nfiguration: When the Intel
Express* connector, this bit indicates whether it is using the same reference clock that is
provided at the connector.
0 = Indicates independent reference clock
1 = Indicates same reference clock.
Link Training: Not applicable
Link Width Negot iation Error: Not applicable
Negotiated Link Width: This field indicates the negotiated width of the PCI Express* link.
• 00 0001b X1
• 00 0010b X2—not supported
• 00 0100b X4
• 00 1000b X8
• 00 1100b X12—not supported
• 01 0000b X16—not supported
• 10 0000b X32—not supported
• All other values are reserved.
Link Speed: The only speed supported is 2.5 Gbps.
12.2.33 Offset 5Ch: MSI_CAPID—PCI Express* MSI Capability
Identifier
Note: MSI generation is used for internal debugging purposes and does not occur in normal operation.
Table 67. Offset 5Ch: MSI_CAPID—PCI Express* MSI Capability Identifier
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 05h Capability ID (MCID): Capabilities ID indicates MSI.
12.2.34 Offset 5Dh: MSI_NXTP—PCI Express* Next Item Pointer
Table 68. Offset 5Dh: MSI_NXTP—PCI Express* Next Item Pointer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 6Ch
Next Pointer (MNPTR): This field points to the next capabilities list pointer, which is the PCI
Express* Power Management capability item.
96 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 97

Register Description
12.2.35 Offset 5Eh: MSI_MC—PCI Express* MSI Message Control
T able 69. Offset 5Eh: MSI_MC—PCI Express* MSI Message Control
Bits Type Reset Description
15:8 RO 00h Reserved
7RO 1b
6:4 RW 000b
3:1 RO 000b
0RW 0b
64-Bit Address Capable: When set, this bit indicates that the Intel
Parallel PCI Bridge is capable of generating a 64-bit message address. (Set by default.)
Multiple Message Enable: Only one message is supported. These bits are R/W for
software compatibility.
Multiple Message Capable: Only one message is supported.
MSI Enable: When set, MSI is enabled and traditional interrupt pins are not used to
generate interrupts.
®
41210 Serial to
12.2.36 Offset 60h: MSI_MA—PCI Express* MSI Message Address
T able 70. Offset 60h: MSI_MA—PCI Express* MSI Message Address
Bits Type Reset Description
63:2 RW 0 Address (ADDR): Message address specified by the system, always DWORD aligned
1:0 RO 00b Reserved
12.2.37 Offset 68h: MSI_MD—PCI Express* MSI Message Data
T able 71. Offset 68h: MSI_MD—PCI Express* MSI Message Data
Bits Type Reset Description
15:0 RW 0000h
Data (DATA): This 16-bit field is programmed by system software when MSI is enabled. Its
content is driven onto the lower word (D[15:0]) of the MSI memory write transaction.
12.2.38 Offset 6Ch: PM_CAPID—Power Management Capabilities
Identifier
T a ble 72. Offset 6Ch: PM_CAPID—Power Management Capabilities Identifier
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 01h Identifier (ID): These bits indicate that this is a PCI-compatible PM.
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 97
Page 98

Register Description
12.2.39 Offset 6Dh: PM_NXTP—Power Management Next Item
Pointer
Table 73. Offset 6Dh: PM_NXTP—Power Management Next Item Pointer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO D8h Next Pointer: This field points to the PCI-X capability as the next capability.
12.2.40 Offset 6Eh: PM_PMC—Power Management Capabilities
Table 74. Offset 6Eh: PM_PMC—Power Management Capabilities
Bits Type Reset Description
15:11 RO 19h
10 RO 0b
9RO 0b
8:6 RO 000b
5RO 0b
4 RsvdP 0b Preserved
3RO 0b
2:0 RO 2h
PME_Support: PME assertion is supported when in D3hot. PME assertion from D3cold is
not supported.
D2 Support: Not supported
D1 Support: Not supported
Auxiliary Current: Auxiliary power is not supported.
DSI: Device-specific initialization is not required when transitioning to D0 from D3hot state.
This bit is zero.
PME Clock: Does not apply to PCI Express*. Hard-wired to 0.
Version: PM implementation is compliant with PCI Bus Power Management Interface
Specification
, Revision 1.1.
98 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
Page 99

Register Description
12.2.41 Offset 70h: PM_PMCSR—Power Management
Control/Status Register
T a ble 75. Offset 70h: PM_PMCSR—Power Management Control/Status Register
Bits Type Reset Description
15 RO 0b PME Status: Not supported
14:13 RO 00h
12:9 RO 0h
8RWS 0b
7:2 RsvdP 00 0000b Preserved
1:0 RW 00b
Data Scale: Not supported
Data Select: Not supported
PME En: Not supported
Power State: This 2-bit field is used both to det ermine the current power state of a f unction
and to set the function into a new power state. Supported field values are given below.
• 00b = D0
• 01b = Reserved
• 10b = Reserved
• 11b = D3 hot
When the software attempts to write an unsupported, optional state to this field, the write
operation must complete normally on the bus; however, the data is discarded and no state
change occurs.
12.2.42 Offset 72h: PM_BSE—Power Management Bridge
Support Extensions
Table 76. Offset 72h: PM_BSE—Power Management Bridge Support Extensions
Bits Type Reset Description
7RO 0b
6RO 0b
5:0 RsvdP 00h Preserved
BPCC_En (Bus Power/Clock Control Enable): Neither bus or clock control of PCI is
supported when in D3hot state. This bit is hard-wired to 0.
B2/B3#: Not supported. This bit has no meaning since the BPCC_En bit is hard-wired to 0.
12.2.43 Offset 73h: PM_DATA—Power Management Data Field
Table 77. Offset 73h: PM_DATA—Power Management Data Field
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 00h Data: Not supported
Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual 99
Page 100

Register Description
12.2.44 Offset D8h: PX_CAPID—PCI-X Capabilities Identifier
This register identifies this item in the capabilities list as a PCI-X register set.
Table 78. Offset D8h: PX_CAPID—PCI-X Capabilities Identifier
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 07h Identifier (ID): These bits indicate that this is a PCI-X capabilities list.
12.2.45 Offset D9h: PX_NXTP—PCI-X Next Item Pointer
This register indicates where the next item in the capabilities list resides. This is the end of the list,
so “00H” is returned.
T able 79. Offset D9h: PX_NXTP—PCI-X Next Item Pointer
Bits Type Reset Description
7:0 RO 00h PCI-X is the last capability list item and hence these bits are all 0s.
100 Intel® 41210 Serial to Parallel PCI Bridge Developer’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...