Icom IC-M501EURO Service Manual

VHF MARINE TRANSCEIVER
SERVICE
MANUAL
iM501EURO

SYMBOL
ITA
UK
EUR
HOL
FRG
INTRODUCTION
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the IC-M501EURO VHF MARINE TRANSCEIVER at the
time of publication
DANGER
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or to a DC
power supply that uses more than 16 V. This will ruin the
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOT reverse the polarities of the power supply when
connecting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100 mW)
to the antenna connector. This could damage the
transceIer’s front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1110003200 S.IC TA31136FN IC-M501EURO MAIN UNIT 15 pieces
8810006050 Screw Icom screw E7 IC-M501EURO CHASSIS 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling the
transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is
disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insulated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the trans-
ceiver is defective.
6. DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a
sweep generator.
7. ALWAYS connect a 40 dB to 50 dB attenuator between
the transceiver and a deviation meter or spectrum analyzer when using such test equipment.
8. READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
MODEL
IC-M501EURO
To upgrade quality, any electrical or mechanical parts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
VERSION
Italy
United Kingdom
Europe
Holland
Germany

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
SECTION 3 OPTIONONAL UNIT INSTALLATION
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4 - 1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 1
4 - 2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 2
4 - 3 PLL CIRCUIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 3
4 - 4 DSC CIRCUIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 3
4 - 5 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 4
4 - 6 LOGIC CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 4
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5 - 1 PREPARATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 1
5 - 2 PLL ADJUSTMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 2
5 - 3 TRANSMITTER ADJUSTMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 2
5 - 4 RECEIVER ADJUSTMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 4
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS
7 - 1 IC-M501EURO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 - 1
7 - 2 HM-126 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 - 1
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9 - 1 LOGIC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 1
9 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 3
9 - 3 DSC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 4 ANT UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 5 PWR-CORD UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 6 VR UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 7 SQL UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 8 DIAL UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 5
9 - 9 HM-126 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 6
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAM
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM
11 - 1 LOGIC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 - 1
11 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 - 2

1 - 1
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
‘‘
GENERAL
• Frequency coverage : 156.025–157.425 MHz (Tx)
156.025–162.025 MHz (Rx)
• Mode : 16K0G3E (FM)
• Usable channels : All international and USA* channels
*availability depending on version
• Power supply requirement : 13.8 V DC (negative ground)
• Usable temperature range : –20˚C to +60˚C
• Frequency stability : ±10 ppm (–20˚C to +60˚C)
• Current drain (at 13.8 V DC) : Transmit at 25 W 6.0 A
Receive max. audio 1.2 A
• Antenna connector : SO-239 (50 Ω)
• Dimensions (projections not included) : 165(W)×110(H)×109.4(D) mm
• Weight : 1130 g
‘‘
TRANSMITTER
• Output power (at 13.8 V DC) : High 25 W
Low 1 W
• Modulation : Variable reactance frequency modulation
• Maximum frequency deviation : ±5.0 kHz
• Spurious emissions : 0.25 µW
• Adjacent channel power : 70 dB
• Residual modulation : 40 dB
• Audio harmonic distortion : Less than 10% at 60% deviation
• Audio frequency response : +1 dB to –3 dB of 6 dB octave from 300 Hz to 3000 Hz
• Microphone impedance : 600 Ω
‘‘
RECEIVER
• Receive system : Double conversion superheterodyne system
• Intermediate frequencies : 1st 21.7 MHz
2nd 450 kHz
• Sensitivity : 6 dBµ emf at 20 dB SINAD
• Squelch sensitivity : –10 dBµ at threshhold
• Adjacent channel selectivity : 70 dB
• Spurious response : 70 dB
• Intermodulation rejection ratio : 68 dB
• Hum and noise : 40 dB
• Audio output power (at 13.8 V DC) : 3.5 W typical at 10% distortion with an 4 Ω load
• Audio frequency responce : +1 dB to –3 dB of –6 dB octave from 300 Hz to 3000 Hz
Specifications are measured in accordance with ETS300-162 2nd Edition
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
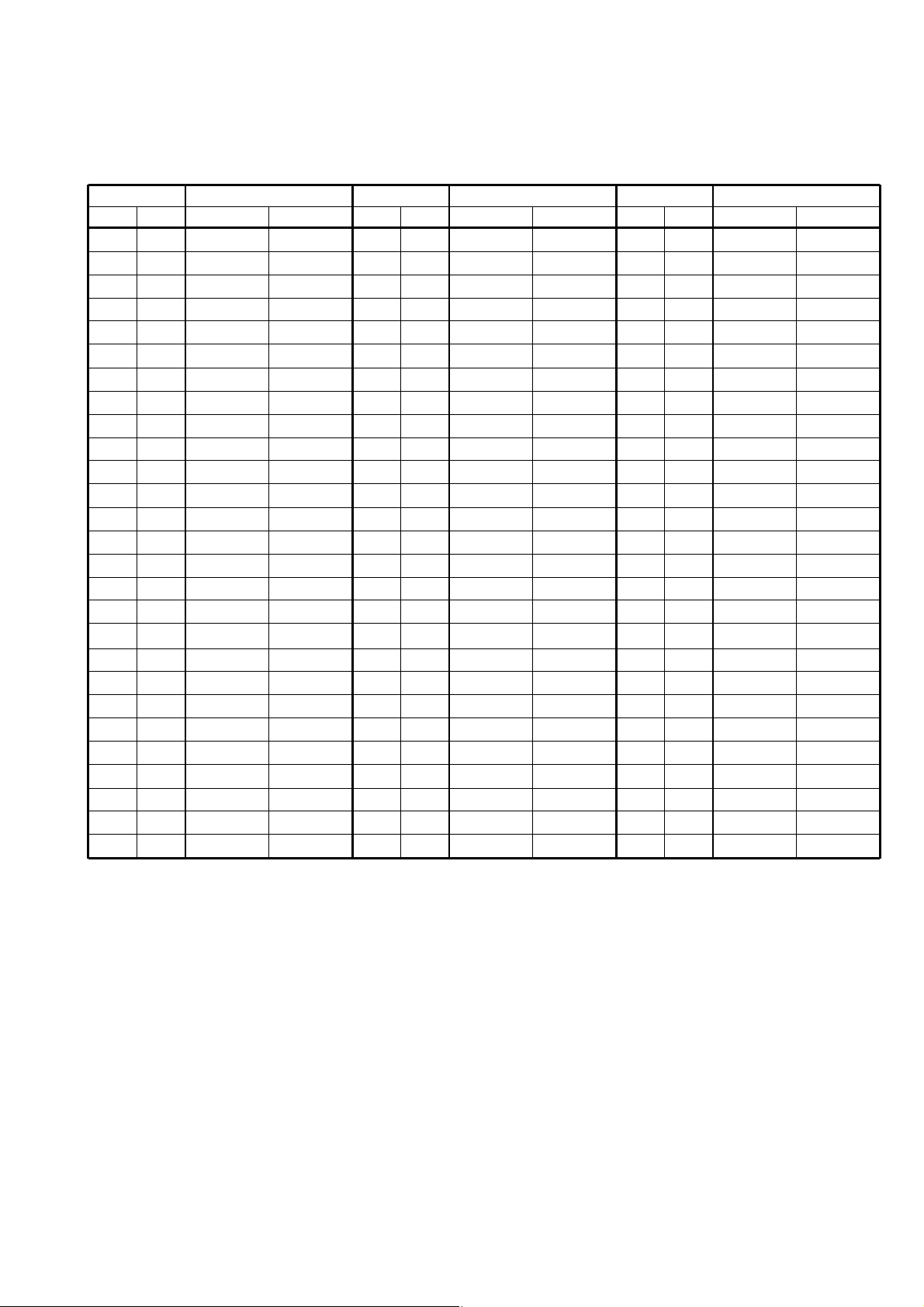
1 - 2
*1Low power only, *2Receive only
‘‘
VHF MARINE CHANNEL LIST
01A
02A
03A
04A
05A
06
07A
08
09
10
11
12
13*
1
14
15*
2
16
17*
1
18A
19A
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15*
1
16
17*
1
18
19
156.050
156.050
156.100
156.100
156.150
156.150
156.200
156.200
156.250
156.250
156.300
156.350
156.350
156.400
156.450
156.500
156.550
156.600
156.650
156.700
156.750
156.800
156.850
156.900
156.900
156.950
156.950
160.650
156.050
160.700
156.100
160.750
156.150
160.800
156.200
160.850
156.250
156.300
160.950
156.350
156.400
156.450
156.500
156.550
156.600
156.650
156.700
156.750
156.800
156.850
161.500
156.900
161.550
156.950
20
20A
21A
22A
23A
24
25
26
27
28
60A
61A
62A
63A
64A
65A
66A
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
157.000
157.000
157.050
157.050
157.100
157.100
157.150
157.150
157.200
157.250
157.300
157.350
157.400
156.025
156.025
156.075
156.075
156.125
156.125
156.175
156.175
156.225
156.225
156.275
156.275
156.325
156.325
161.600
157.000
161.650
157.050
161.700
157.100
161.750
157.150
161.800
161.850
161.900
161.950
162.000
160.625
156.025
160.675
156.075
160.725
156.125
160.775
156.175
160.825
156.225
160.875
156.275
160.925
156.325
67*
1
68
69
70*
2
71
72
73
74
77
78A
79A
80A
81A
82A
83A
84
85
86
87
88
88A
67
68
69
70*
2
71
72
73
74
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
156.375
156.425
156.475
156.525
156.575
156.625
156.675
156.725
156.875
156.925
156.925
156.975
156.975
157.025
157.025
157.075
157.075
157.125
157.125
157.175
157.175
157.225
157.275
157.325
157.375
157.425
157.425
156.375
156.425
156.475
156.525
156.575
156.625
156.675
156.725
156.875
161.525
156.925
161.575
156.975
161.625
157.025
161.675
157.075
161.725
157.125
161.775
157.175
161.825
161.875
161.925
161.975
162.025
157.425
Channel No. Frequency (MHz) Channel No.
Frequency (MHz) Channel No. Frequency (MHz)
USA INT
Transmit Receive
USA INT Transmit Receive USA INT Transmit
Receive
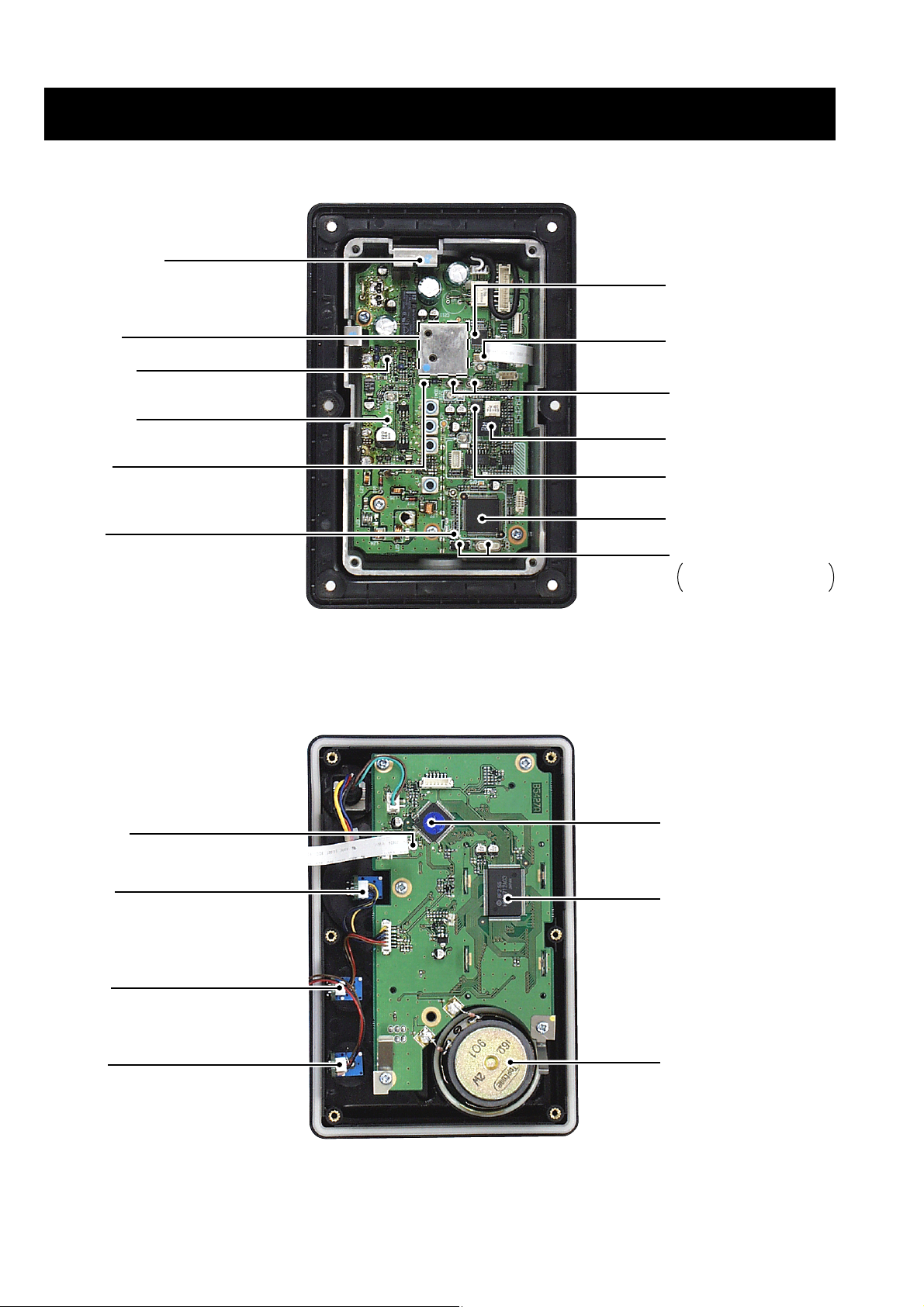
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2 - 1
• MAIN UNIT
• LOGIC UNIT
AF power amplifier
(IC14: LA4425A)
PLL IC
(IC2: µPD3140GS)
VCO circuit
Driver amplifier
(Q12: 2SC2954)
Power module*
(IC3: SC-1302)
1st mixer*
(Q3: 3SK166)
Reset IC
(IC15: S-80928ANMP)
Reference oscillator
(X2: CR-659 21.25 MHz)
1st IF filter
(FI1, FI2: FL-310)
2nd IF filter
(FI3: ALFY450E)
FM IF IC
(IC1: TA31136FN)
Main MPU
(IC16: MB90F583BPFV-G)
System clock
X3: DMX-26S 36.768 kHz,
X4: CR-610 7.9872 MHz
* Located under side of the point
System clock
(X1: PBRC 4.91BR 4.91 MHz)
DIAL UNIT
SQL UNIT
VR UNIT
SUB MPU
(IC1: µPD78F9418AGK-9EU)
LCD driver
(IC2: HD66712SA03FS)
Speaker
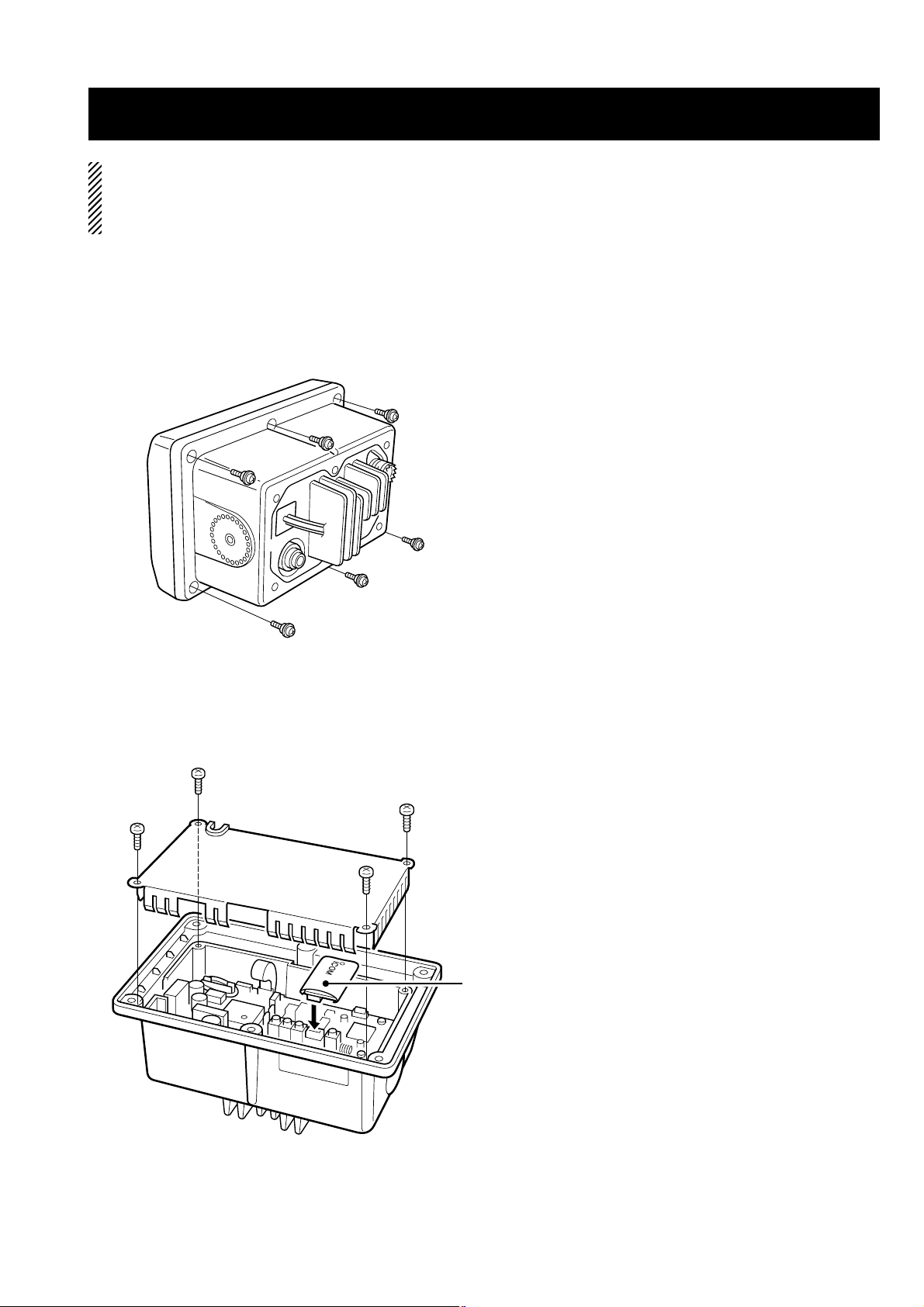
SECTION 3 OPTIONAL UNIT INSTALLATION
3 - 1
CAUTION: DISCONNECT the DC power cable from the
transceiver before performing any work on the transceiver.
Otherwise, there is danger of electric shock and/or equipment damage.
• Opening the transceiver case
Follow the case opening procedure shown here when you
want to install an optional unit, etc.
q Remove the 6 screws as shown below and open the trans-
ceiver.
w Remove the 4 screws from the shielding plate, then lift up
the shielding plate.
e Plug an optional unit to J6 on the MAIN unit as shown
below.
r Return the shielding plate and assemble the units to their
original positions.
Optional unit
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4 - 1
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
4-1-1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT
The antenna switching circuit functions as a low-pass filter
while receiving and as resonator circuit while transmitting.
The circuit does not allow transmit signals to enter receiver
circuits.
Received signals enter the MAIN unit from the antenna connector and pass through the low-pass filter (L23–L25, C134,
C136–C139). The signals are then applied to the RF circuit
via the antenna switching circuit (D17, L26, L27,
C141–C143).
4-1-2 RF CIRCUIT
The RF circuit amplifies signals within the range of frequency coverage and filters out-of-band signals.
The signals from the antenna switching circuit pass through
a tunable bandpass filter (D1, L1, C2–C4) where the object
signals are led to the RF amplifier circuit (Q2).
The amplified signals at Q2 are applied to the 3-stage tunable bandpass filter (D2–D4, L2–L4, C13, C14, C16–C18,
C20–C24) to suppress unwanted signals and improve the
selectivity. The signals are then applied to the 1st mixer circuit.
D1–D4 employ varactor diodes, that are controlled by the
PLL lock voltage, to track the band pass filters.
4-1-3 1ST MIXER AND 1ST IF CIRCUITS
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signal to a fixed
frequency of the 1st IF signal with a 1st LO (VCO output) frequency. By changing the 1st LO frequency, only the desired
frequency will pass through a pair of crystal filters at the next
stage of the mixer.
The signals from the RF circuit are mixed with the VCO signals at the 1st mixer circuit (Q3) to produce a 21.7 MHz 1st
IF signal.
The 1st IF signal is applied to a pair of crystal filters (FI1,
FI2) to suppress out-of-band signals and is then amplified at
the IF amplifier (Q4). The amplified signal is applied to the
2nd mixer circuit (IC1).
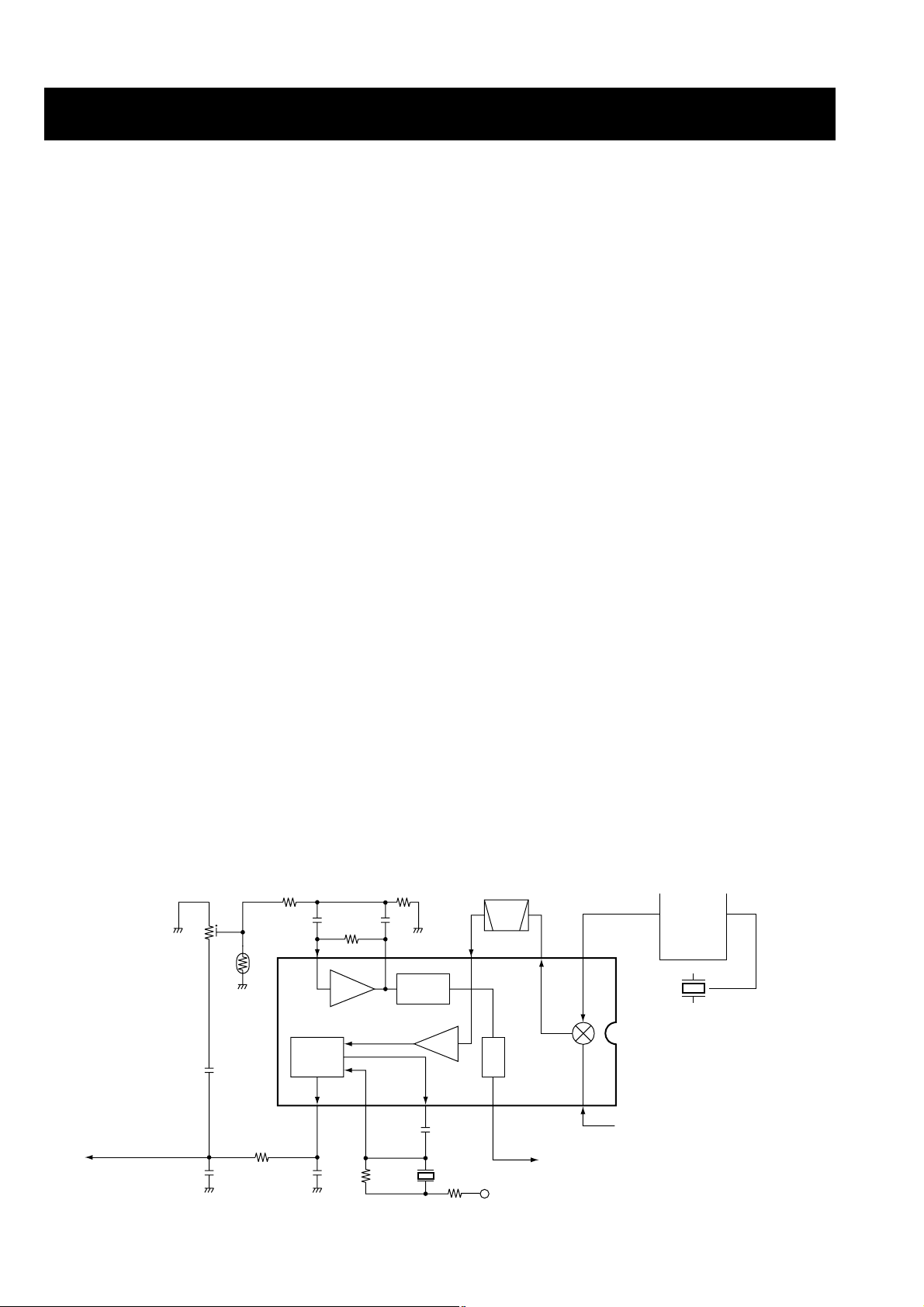
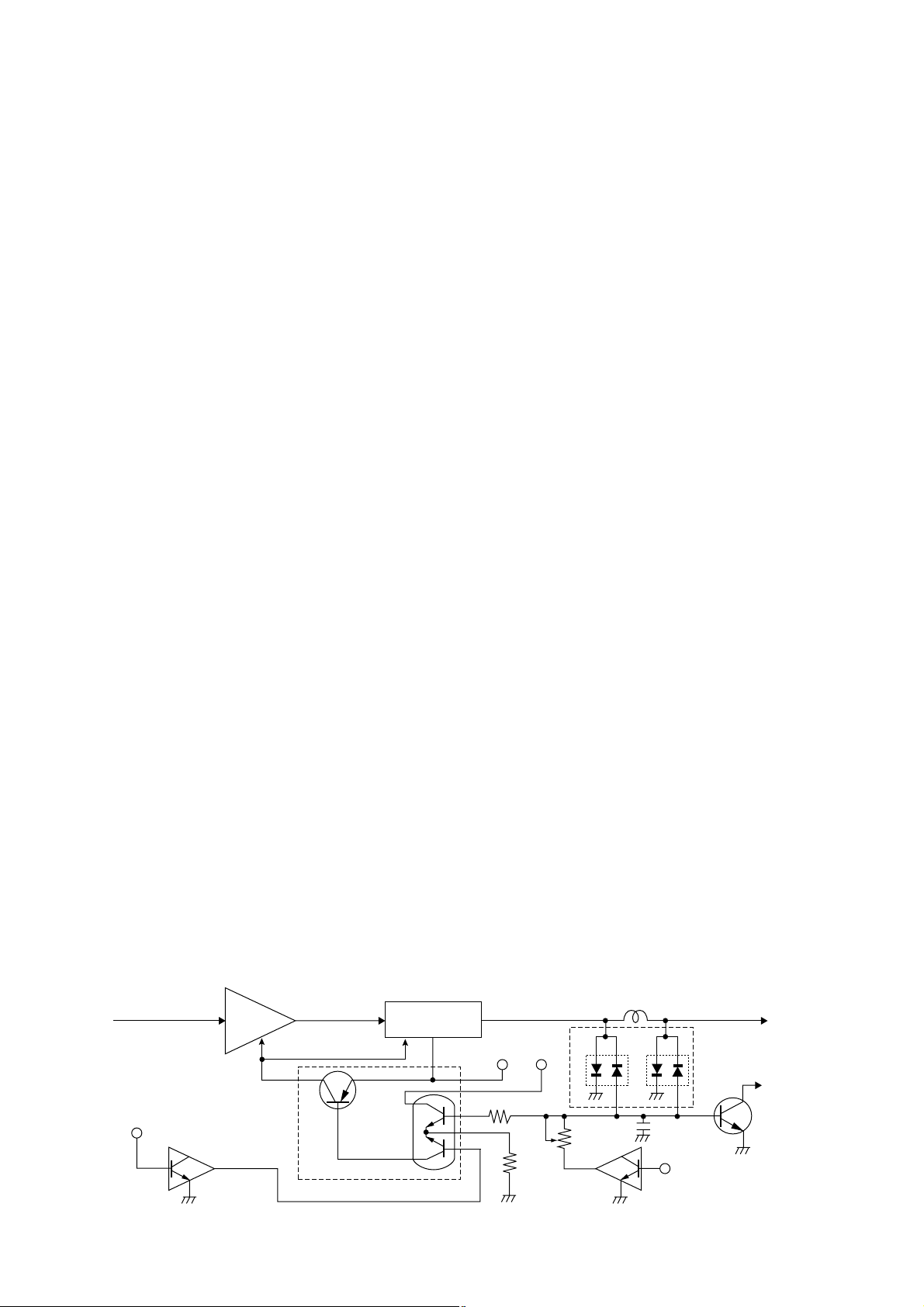
4-1-4 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st IF signal to a 2nd IF
signal. A double superheterodyne system (which converts
receive signals twice) improves the image rejection ratio and
obtains stable receiver gain.
The FM IF IC (IC1) contains the 2nd local oscillator, 2nd
mixer, limiter amplifier, quadrature detector, and noise
detector circuits, etc.
The 1st IF signal from Q4 is applied to the 2nd mixer section
of IC1 (pin 16), and is mixed with a 21.25 MHz 2nd LO signal generated at the PLL circuit using the reference frequency (21.25 MHz) to produce a 450 kHz 2nd IF signal.
The 2nd IF signal from IC1 (pin 3) is passed through the
ceramic filter (FI3), where unwanted signals are suppressed, and is then applied to the 2nd IF (limiter) amplifier
in IC1 (pin 5). The signal is applied to the FM detector section in IC1 for demodulation into AF signals.
The FM detector circuit employs a quadrature detection
method (linear phase detection), which uses a ceramic discriminator (X1) for phase delay to obtain a non-adjusting circuit. The detected signal from IC1 (pin 9) is applied to the AF
circuit.
• 2nd IF and demodulator circuits
Mixer
16
Limiter
amp.
2nd IF filter
450 kHz
PLL IC
IC2
X2
21.25 MHz
X1
(21.25 MHz)
RSSI
IC1 TA31136FN
14
1st IF (21.7 MHz) from Q4
"SQLI" signal to the DC amplifier (IC20, pin 1)
11109
87 5 3
AF signal "DEMOD"
R8V
Squelch level
adjustment pot
2
17
16
Active
filter
FI3
Noise
detector
FM
detector
4 - 2
4-1-5 AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The AF amplifier circuit amplifies the detected signals to
drive a speaker. The AF circuit includes an AF mute circuit
for the squelch.
AF signals from IC1 (pin 9) are passed through the analog
switch (IC12, pins 10, 11), and are applied to the de-emphasis circuit (R118, C182). The de-emphasis circuit is an integrated circuit with frequency characteristic of –6 dB/octave.
The integrated signals are applied to the active filters (Q24,
Q25). Q24 functions as a high-pass filter to suppress
unwanted lower noise signals and Q25 functions as a lowpass filter to suppress higher noise signals.
The filtered signals are passed through the [VOLUME] control, and are then applied to the AF power amplifier (IC14,
pin 1). The output signal from IC14 (pin 4) drives the internal (external) speaker.
4-1-6 SQUELCH CIRCUIT
Asquelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF signals are
received. By detecting noise components in the AF signals,
the squelch circuit switches the AF mute switch.
A portion of the AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9)
pass through the squelch adjustment pot (R33), and are
then applied to the active filter section (IC1, pin 8). The
active filter section amplifies and filters noise components.
The filtered signals are applied to the noise detector section
and output from pin 14 as the “SQLI” signal. The “SQLI” signal is amplified at the DC amplifier (IC20) and applied to the
CPU (IC16, pin 39) as the “SQL” signal. The CPU analyzes
the noise condition and outputs the “RMUTM”, “RMUTS”
signals to toggle the AF mute switches (Q26, Q27).
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals with
+6 dB/octave pre-emphasis from the microphone to a level
needed at the modulation circuit.
The AF signals from the microphone are amplified at the
microphone amplifier (IC11a) via the analog switch (IC10,
pins 11, 10). A capacitor (C214) and resistor (R147) are connected to the amplifier to obtain the pre-emphasis characteristics.
The amplified signals are applied to the IDC amplifier
(IC13a, pin 2) via the analog switch (IC12, pins 8, 9 and pins
4, 3) and are passed through the splatter filter (IC13b) to
suppress unwanted 3 kHz or higher signals. The filtered signals are then applied to the modulation circuit.
4-2-2 MODULATION CIRCUIT
The modulation circuit modulates the VCO oscillating signal
(RF signal) using the microphone audio signals.
Audio signals from the splatter filter (IC13b) pass through
the frequency deviation adjustment pot (R172) and are then
applied to the modulation circuit (D8) to change the reactance of D8, and modulate the oscillated signal at the TXVCO (Q7).
4-2-3 DRIVE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The drive amplifier circuit amplifies the VCO oscillating signal to a level needed at the power amplifier.
The VCO output is buffer-amplified by Q9 and Q10, and is
then applied to the Tx/Rx switch (D12). The transmit signal
from the Tx/Rx switch is amplified to the pre-drive (Q11) and
drive (Q12) amplifiers to obtain an approximate 200 mW signal level. The amplified signal is then applied to the RF
power amplifier (IC3).
4-2-4 POWER AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The power amplifier circuit amplifies the driver signal to an
output power level.
IC3 is a power module which has amplification output capabilities of about 35 W with 300 mW input. The output from
IC3 (pin 4) is passed through the antenna switching circuit
(D16) and is then applied to the antenna connector via the
low-pass filter.
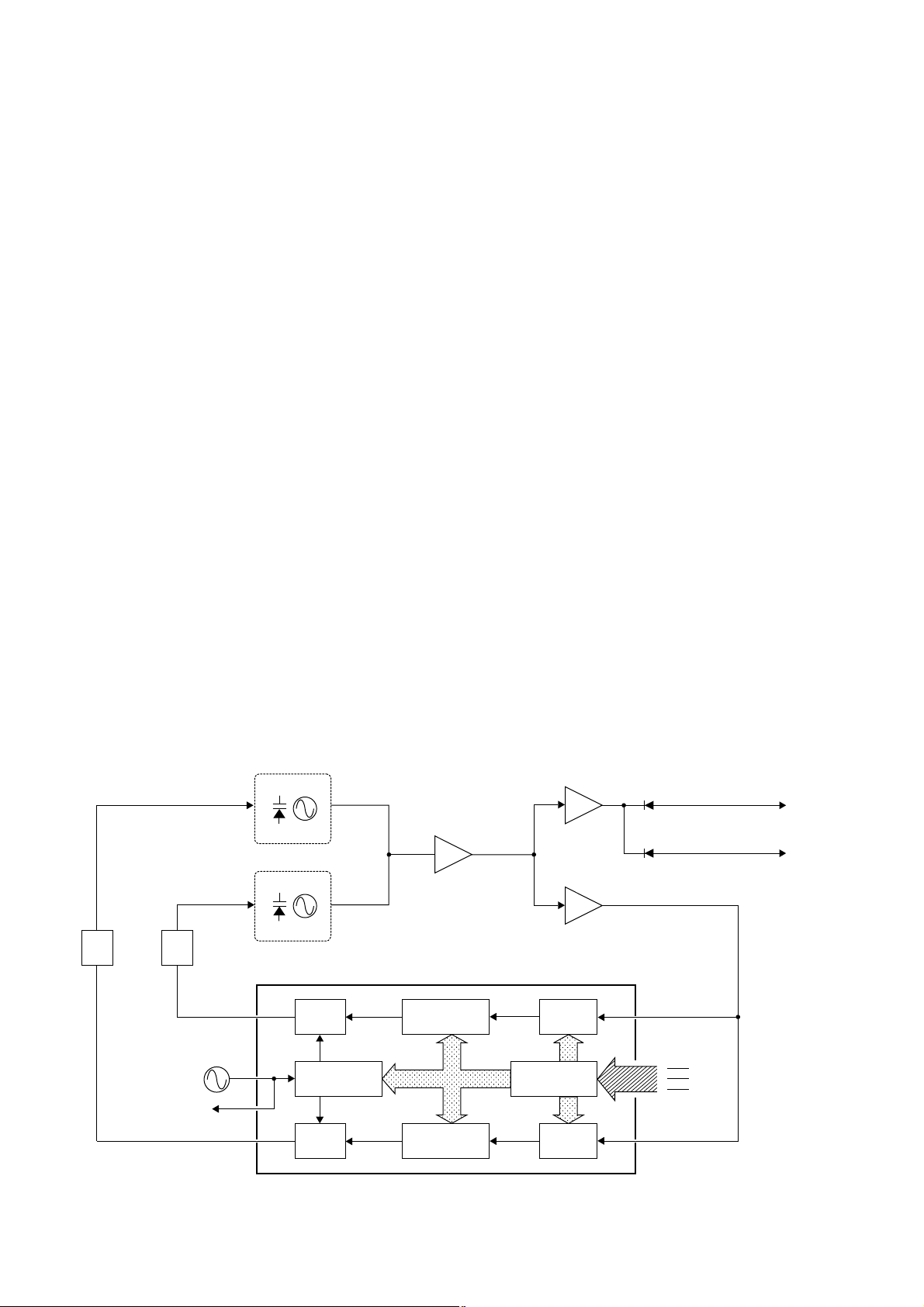
4-2-5 APC CIRCUIT
The APC circuit stabilizes transmit output power.
The RF output signal from the power amplifier (IC3) is
detected at the power detector circuit (D14, D15, L21) and
is then applied to one of the differential amplifier inputs
(Q16, pin 5) via the High/Low control circuit (R84, Q17). The
applied voltage controls the differential amplifier output
(Q16, pin 2) and the bias voltage control (Q14). Thus the
APC circuit maintains a constant output power.
• APC circuit
RF signal
from PLL
/TMUT
Q15
Q12
Drive
amp.
Q14
Q16
APC control circuit
Power module
IC3
VCC
T8
D14
R84
Q17
L21
D15
RF detector
circuit
HI/LO
Q14
to antenna
"TXDET" signal
to the CPU
4 - 3
4-3 PLL CIRCUITS
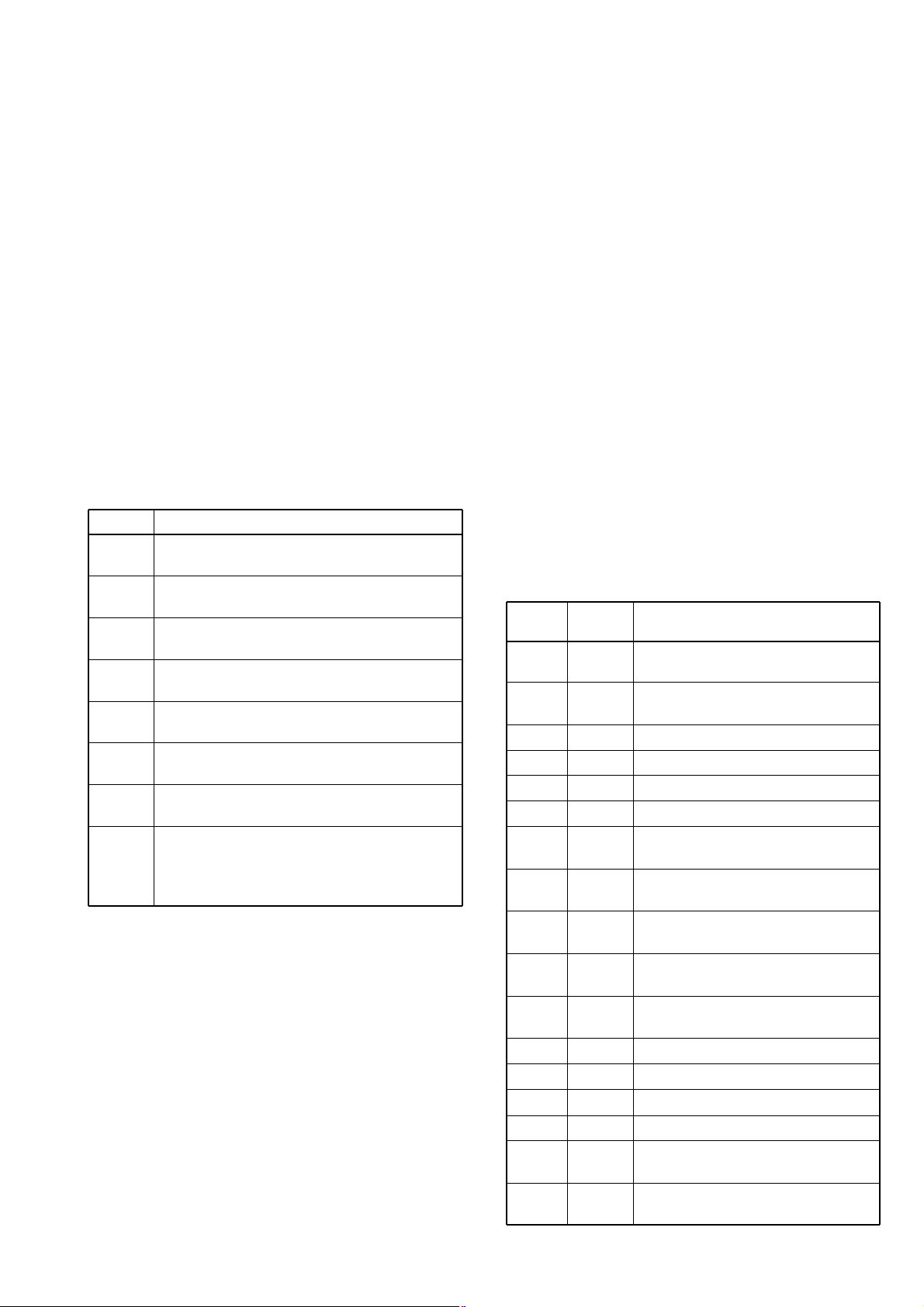
4-3-1 GENERAL
The PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit frequency and receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL circuit compares the phase of the divided VCO frequency to the reference frequency. The PLL output frequency is controlled by a
crystal oscillator and the divided ratio of the programmable
divider.
IC2 is a dual PLL IC which controls both VCO circuits for Tx
and Rx, and contains a prescaler, programmable counter,
programmable divider phase detector, charge pomp and etc.
The PLL circuit, using a one chip PLL IC (IC2), directly generates the transmit frequency and receive 1st IF frequency
with VCOs. The PLL sets the divided ratio based on serial
data from the CPU and compares the phases of VCO signals with the reference oscillator frequency. The PLL IC
detects the out-of-step phase and output from pins 8 and 13
for Tx and Rx, respectively. The reference frequency (21.25
MHz) is oscillated at X2.
4-3-2 TX LOOP
The generated signal at the TX-VCO (Q7, D6–D8) enters
the PLL IC (IC2, pin 2) and is divided at the programmable
divider section and is then applied to the phase detector
section.
The phase detector compares the input signal with a reference frequency, and then outputs the out-of-phase signal
(pulse-type signal) from pin 8.
The pulse-type signal is converted into DC voltage (lock
voltage) at the loop filter (R252–R254, C292–C294), and is
then applied to varactor diodes (D6, D7) of the TX-VCO to
stabilize the oscillated frequency.
4-3-3 RX LOOP
The generated signal at the RX-VCO (Q8, D9, D10) enters
the PLL IC (IC2, pin 19) and is divided at the programmable
divider section and is then applied to the phase detector
section.
The phase detector compares the input signal with a reference frequency, and then outputs the out-of-phase signal
(pulse-type signal) from pin 13.
The pulse-type signal is converted into DC voltage (lock
voltage) at the loop filter (R255–R257, C295, C296), and is
then applied to varactor diodes (D9, D10) of the RX-VCO to
stabilize the oscillated frequency. The lock voltage is also
used for the receiver circuit for the bandpass filter center frequency. The lock voltage from the loop filter is amplified at
the buffer-amplifier (Q6) and then applied to the RF circuit.
4-3-4 VCO CIRCUIT
The VCO outputs from TX-VCO (Q7) and RX-VCO (Q8) are
amplified at the buffer amplifiers (Q9 and Q10), and are then
sent to the Tx/Rx switch (D11, D12). The receive LO signal
is applied to the 1st mixer circuit (Q3) through a low-pass filter, and the transmit signal is applied to the pre-drive amplifier (Q11). A portion of the VCO output is reapplied to the
PLL IC (IC2, pin 2 or pin 13) via the buffer amplifier (Q5).
• PLL circuit
Loop
filter
21.25 MHz signal
to the FM IF IC
Loop
filter
21.25 MHz
X2
RX-VCO
Q8, D9, D10
TX-VCO
Q7, D6–D8
8
16
17
13
Phase
detector
Programmable
divider
Phase
detector
Buffer
Q9
Programmable
counter
Programmable
counter
Buffer
Q10
Buffer
Q5
IC2 (PLL IC)
Prescaler
Shift register/
data latch
Prescaler
D11
to 1st mixer circuit
D12
to transmitter circuit
2
3
PSTB
4
CK
5
DATA
19
4 - 4
4-4 DSC CIRCUITS (DSC UNIT)
4-4-1 DATA INTERFACE CIRCUIT
The control signals from DS-100 CLASS D/DSC TERMINAL
are shaped waveform at the SCHMITT circuit (IC3) via the
photo-coupler (IC2), and are then applied to the MAIN unit
via J2 (pin 11).
4-4-2 DSC MODULATION CIRCUT
The modulation signals from DS-100 are converted into a
600 Ω impedance at T1 and passed through the high-pass
filter (IC1a) with +6 dB/octave characteristics.
The signals from the high-pass filter (IC1a) are passed
through the splatter filter (IC1b) to suppress unwanted 3 kHz
or higher signals. The filtered signals are then applied to the
TX modulation circuit via the buffer amplifier (Q30) and analog switch (IC12, pins 1, 2) on the MAIN unit as a DSC modulation signal.
4-5 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
4-5-1 VOLTAGE LINE (MAIN UNIT)
4-6 LOGIC CIRCUITS
4-6-1 MAIN UNIT
• MPU
IC16 is a 16 bit multifunction micro-computer and contains
FLASH memory, serial I/O, timer, A/D converter, D/A converter, programmable I/O, ROM and RAM.
• SYSTEM CLOCK CIRCUIT
X3, X4 are crystal oscillators and oscillate 7.9872 MHz and
32.768 kHz system clocks for the MPU (IC16) respectively.
• RESET CIRCUIT
IC15 is a reset IC. When turn power ON, IC15 outputs a
reset signal (“LOW” pulse) to MPU (IC16, pin 75).
• LOW BATTERY DETECTOR
VCC voltage is divided by R204, R205 and is applied to the
low battery detector section in the MPU (IC16, pin 42).
4-6-2 LOGIC UNIT
• CPU
IC1 is an 8 bit single chip micro-computer and contains LCD
driver, serial I/O, timer, A/D converter, programmable I/O,
ROM and RAM.
• SYSTEM CLOCK CIRCUIT
X1 is a ceramic oscillator and oscillates a 4.91 MHz system
clock for the CPU (IC1).
• LCD DRIVER
IC2 is a LCD driver for a dot matrix LCD.
• DIMMER CIRCUIT
CPU (IC1) and Q2, Q3, Q8 are dimmer circuit and control
the LCD backlight (LED).
• CONTRAST CIRCUIT
CPU (IC1) and Q1, Q4 are contrast circuit and control the 8
step display contrast.
4-7 PORT ALLOCATIONS
4-7-1 SUB CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1)
LINE
HV
HVS
VCC
8V
A5V
D5V
T8
R8
DESCRIPTION
The voltage from the connected DC power supply.
Same voltage as the HV line which is passed
through the [PWR] switch (LOGIC unit; S1).
Same voltage as the HVS line which is passed
through the power controller (RL1).
Common 8 V converted from the VCC line at the
8V regulator circuit (IC8).
Common 5 V converted from the 8V line at the
analog 5V regulator circuit (IC9).
Common 5 V converted from the 8V line at the
digital 5V regulator circuit (IC7).
Transmit 8 V controlled by the T8 control circuit
(Q20, Q21) using the SEND signal from CPU.
Receive 8 V controlled by the R8 control circuit
(Q22, Q23) using the RCV signal from CPU. The
controlled voltage is applied to the receiver circuits.
27,
28, 29, 30
31–38
42
43
44
46
47
51, 52
54
55
58–60
61
62
63
64
75–77
78–80
LRESET,
E, RW, RS
DB7–
DB0
SCAN
CHWX
CH16
SQLV
KEYM
DIALA,
DIALB
SRXD
STXD
CONTSEG3–
CONTSEG1
DTRS
IC
DSC
HL
DIM3–
DIM1
CONDOT3–
CONDOT1
Output ports for the LCD driver (IC2)
control signals.
I/O port for the LCD driver (IC2) control
signals.
Input port for the [SCAN] key.
Input port for the [DIAL] key.
Input port for the [CALL] key.
Input port for the squelch volume level.
Input port from the microphone (HM-
126) for remote control signal
Input ports for the [CHANNEL].
Outputs communication data for main
CPU (MAIN unit; IC16).
Input port for the communication data
from main CPU (MIAN unit; IC16).
Output port for the LCD contrast.
Input port for the [16] key.
Input port for the [DIMMER] key.
Input port for the [DUAL] key.
Input port for the [HI/LO] key.
Output LCD backlight control signal for
the dimmer circuit (Q2, Q3, Q8).
Output port for the LCD contrast.
Pin Port
Description
number name
4 - 5
4-7-2 MAIN CPU (MAIN unit; IC17)
Outputs serial data signal for EEPROM (IC17).
Outputs select signal to the analog
switch (IC12) for the microphone audio
signal or DSC signal.
D/A output port for the ATIS/DSC
encode signal to the buffer amplifier
(Q33).
Input port from the FM IF IC (IC1) for
the squelch operation.
Input port for the connected power
supply voltage detection (low battery
indicator).
Input port for the “TX” indicator from
the power detector circuit (D14, D15).
Input port for the ATIS/DSC decode
signal.
Input port for the PLL unlock signal.
Low : While PLL is locked.
Input port for the communication data
from DS-100 via the DSC connector
(DSC unit; J1), photo coupler (DSC
unit; IC2) and buffer amplifier (DSC
unit; IC3).
Outputs the communication data to
DS-100 via the buffer amplifier (DSC
unit; Q1, Q2, D4).
Input port for the PTT switch.
Input port for the microphone hanger
detection signal.
Low : Microphone on hook
Input port for the optional unit connection detection.
Outputs the R8 regulator (Q22, Q23)
control signal.
Low : While receiving
Outputs the AF mute switch (Q26)
control signal for main body.
Low : While squelched
Outputs the AF mute switch (Q27)
control signal for the optional remote
microphone (HM-127).
Low : While squelched
Outputs beep audio for main body.
Outputs beep audio for the optional
remote microphone (HM-127).
Input port for the reset signal.
Outputs the reset signal for sub CPU
(LOGIC unit; IC1).
EDA
MICDSC
DSC
SQL
LBAT
TXDET
DSDEC
UNLK
DATAS
DATAM
PTT
HANG
OPTIN
RCV
RMUTM
RMUTS
BEEPM
BPLVM
RESET
SRESET
24
27
30
39
42
44
45
46
57
58
60
61
62
66
67
68
69
71
75
100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
19
20
23
STRU
SCON
OPSTB
PSTB
CK
DATA
PTTM
PTTS
MMUTE
SMUTE
SP
HI/LO
SEND
TMUTE
SRXD
STXD
CLRX
CLTX
ECK
Outputs control signal to the analog
switch (IC12) for passing through the
optional VOICE SCRAMBLER unit
(UT98 or UT-112).
Outputs ON/OFF control signal for the
optional VOICE SCRAMBLER unit
(UT-98 or UT-112).
Outputs strobe signals for the optional
VOICE SCRAMBLER unit UT-98 or
UT-112.
Outputs strobe signals to PLL IC (IC2,
pin 2).
Outputs clock signal to PLL IC (IC2,
pin 3).
Outputs clock signal to PLL IC (IC2,
pin 4).
Outputs main microphone (HM-126)
select signal to the analog switch
(IC10) while intercom operation.
Outputs optional remote microphone
(HM-127) select signal to the analog
switch (IC10) while intercom
operation.
Outputs select signal for the speaker
of main microphone (HM-126) to the
analog switch (IC10) while intercom
operation.
Outputs select signal for the speaker
of optional remote microphone (HM-
127) to the analog switch (IC10) while
intercom operation.
Outputs ON/OFF control signal for the
internal speaker to the AF mute circuit
(Q32, D23, RL2).
Low : While internal speaker is ON.
Output port for RF output power (High
or Low) select signal.
Low : While low power is selected.
Outputs the T8 regulator (Q20, Q21)
control signal.
Low : While transmitting
Outputs transmit mute signal.
High : While transmitting
Input port for the communication data
from sub CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1).
Outputs communication data for sub
CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1).
Input port for the cloning data from the
buffer (D24).
Output port for the cloning data to the
buffer (MAIN unit; Q37).
Outputs clock signal for EEPROM
(IC17).
Pin Port
Description
number name
Pin Port
Description
number name
 Loading...
Loading...