Page 1

HP Notebook Hard Drive
Measures of care, diagnosis and maintenance
Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 2
HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy............................................................................................................... 3
Notebook F10 Setup Hard Drive Self-Test ............................................................................................... 3
Minimum System BIOS Required............................................................................................................ 4
Hard Drive Mounting Screw.................................................................................................................. 4
HP Recommendations for Notebook Users .............................................................................................. 5
Hard Drive Troubleshooting Flowchart.................................................................................................... 6
Page 2

Introduction
HP has a passion to continuously improve upon the customer experience. This white paper explains
the measures that HP is providing to its customers to reduce the risk of hard drive failure. These
measures include a new power management policy, an enhanced hard drive self-test, and
recommendations for maintaining software integrity.
The hard drive in the notebook is in some respects a very fragile device. In each new generation
of hard drives, the manufacturers have made significant improvements to the drive’s susceptibility to
shock events. However, if the drive is exposed to shock events beyond the set specifications, the hard
drive can fail.
Shock events can cause read/write head misalignment, or contact between the read/write heads and
the media, resulting in symptoms such as a clicking noise, the failure to complete servo, and/or an
inaccessible boot device. Typically, such symptoms result from a significant bump or drop that occurs
• While the notebook is turned off (non-operational shock).
- or -
• While the unit is turned on and the hard drive is reading or writing data (operational shock).
Shock events may cause any of the following errors to be displayed:
Non-system disk
No boot device
1720 and/or 1782 errors
Hard drive performance can also be degraded if file fragmentation is not reduced by regular
software maintenance. Over time, the hard drive file structure can become fragmented due to
continuous creating, editing, copying, and deleting of files. New data is written to the hard drive on a
“first available space” basis. Fragmentation occurs when all of a given application or file is not stored
contiguously on the hard drive. When a file is fragmented, the hard drive throughput performance is
impacted because the hard drive reading/writing heads have to seek the data from multiple locations
across the hard drive.
Other types of hard drive performance issues that mimic hard drive failure are due to software
problems. Such software problems include but are not limited to viruses, application and/or operating
system bugs, and/or file corruption. The most difficult to trace of them all is file corruption, because of
how easily it can occur. For instance, powering off the notebook before the operating system shuts
down can create corrupted boot files, resulting in symptoms such as blue screens and continuous
reboots.
HP addresses these issues with the following measures.
2
Page 3
HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy
The opportunity for operational shock is at its greatest when an end user is mobile with his or her
notebook. Therefore HP has released a utility, the HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy, that works in
conjunction with the Microsoft Windows API for power management. This enhancement allows the
notebook to go into Standby mode when the display lid is closed while the notebook is operating
from the internal battery pack, e.g., on DC power, away from a docking device or external power
supply running on AC power. HP recommends use of this SoftPaq on all currently shipping notebooks.
The HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy is available from the following URL:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/support.html
After installing the application, access the HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy by selecting
Programs > HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy.
• Display status
• Enable HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy
Note 1: The HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy utility will not invoke Standby on an AC-powered
notebook having the display lid closed that subsequently transitions to DC power. The notebook must
first be undocked or removed from AC power before the display lid is closed.
Note 2: The Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP operating systems provide a feature called
Lid Switch Standby. However, it operates whether the notebook is operating on AC power or on DC
power. Since the purpose of docking is to allow the user to connect to AC power, close the notebook
display, and use an external keyboard and monitor, activating Standby upon lid closure in this
scenario is not an acceptable option.
The following options are displayed:
Start >
Notebook F10 Setup Hard Drive Self-Test
HP has enhanced the Hard Drive Self-Test routine which is accessible via the notebook’s F10 Setup
Tools menu. The new routine of the hard drive self-test increases its ability to detect a fault and fail the
hard drive. The short and long versions of the hard drive self-test have been combined as one test
option. Initiating the enhanced hard drive self-test includes the following:
1. The short test runs. If no errors occur, the long test automatically runs.
2. If no errors occur, SMART attribute checking automatically runs.
3. If a failure is detected in either of the tests, the process halts and failure occurs.
Note: Either test may be aborted at any time by pressing the
esc key.
The F10 Setup Hard Drive Self-Test enhancement is available as a commercial notebook system
BIOS upgrade. Please visit the HP Web site at http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/support.html
to download the latest BIOS update. HP recommends the latest system BIOS upgrade be applied to all
currently shipping notebooks, in addition to the Evo N400 and Evo N600 series. Refer to the
following table for the absolute minimum system BIOS required by each platform.
3
Page 4

Minimum System BIOS Required
Notebook Platform BIOS Version BIOS Date
HP Compaq Business nc8000 F.0A 12 Dec 03
HP Compaq Business nw8000 F.0A 12 Dec 03
HP Compaq Business nc6000 F.09 09 Feb 04
HP Compaq Business nc4000 Series F.25 06 Feb 04
HP Compaq Business nx9000 Series KG.M1.15 19 Dec 03
HP Compaq Business nx5000 F.05 04 Feb 04
Compaq Evo N620c F.0E 21 Nov 03
Compaq Evo N610c/v F.18 09 Dec 03
Compaq Evo N600c 686DF 31 Dec 03
Compaq Evo N800c F.14 08 Mar 04
Compaq Evo N410c F.14 15 Dec 03
Compaq Evo N400c 686AW_2004.03.8A 08 Mar 04
Hard Drive Mounting Screw
All HP and Compaq branded commercial and SMB notebooks come equipped with one or more hard
drive mounting screws, which are designed to reliably support the installed hard drive. Therefore,
these screws must be correctly installed at all times. Without the hard drive mounting screws, the
chance of hard drive failure over time is greatly increased. Because the screws are an integral part of
the design of the notebook, they should always be replaced after they are removed or when they are
missing from the notebook altogether.
Hard drive mounting screw kit—Whenever one of the following commercial notebooks is
serviced and one or more of the hard drive mounting screws are missing, they can be replaced from
one of the following bulk screw kits (100 screws per kit):
• For N600c/N610c/N620c/Nc6000 models, use bulk HDD spare kit part number 360670-001.
• For N800c/N800v/N800w models use bulk HDD spare kit part number 360380-001.
• For HP Pavilion ze4300/ze4400/ze4500/ze5300/ze5400/ze5500 and HP Compaq nx9000/
nx9005/nx9010 models, use bulk HDD spare kit part number 361188-001.
Note: Customers should contact their local service partner to obtain the hard drive mounting screws.
4
Page 5

HP Recommendations for Notebook Users
• Install HP Notebook LidSwitch Policy, or as an alternative, place the notebook into Standby mode
before transporting it from one location to another.
• Upgrade to the latest system BIOS, as given in the “F10 Setup Hard Drive Self-Test” section.
• Whenever possible, adjust power management settings (power schemes) in Control Panel to permit
the hard drive to be turned off when it will be unused for an extended period of time, e.g., when
you are working in applications such as a word processor that executes primarily from electronic
memory without having to access the hard drive very often.
• Perform the Defrag operation periodically to optimize the reading and writing of data to the hard
drive. During Defrag, data is moved to contiguous space. As a result, movement of the hard drive
reading/writing heads is decreased. Please refer to the following Microsoft Knowledge Base
articles for information on how to defragment your hard drive:
– Windows XP: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;314848
– Windows XP command line: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;283080
– Windows 2000: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;227463
• Periodically use the Microsoft Recovery Console to run, at a minimum, the chkdsk /p /r commands
to check your hard drive for any errors, bad sectors and/or recovery of readable information.
Please refer to the following Microsoft Knowledge Base articles for information:
– Windows XP: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;314058&Product=winxp
– Windows 2000: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;229716
• Install and maintain a virus protection program to prevent failures due to viruses.
• Regularly back up critical email and documents to removable media.
• Regularly check the HP Web site for system BIOS and driver enhancements.
5
Page 6
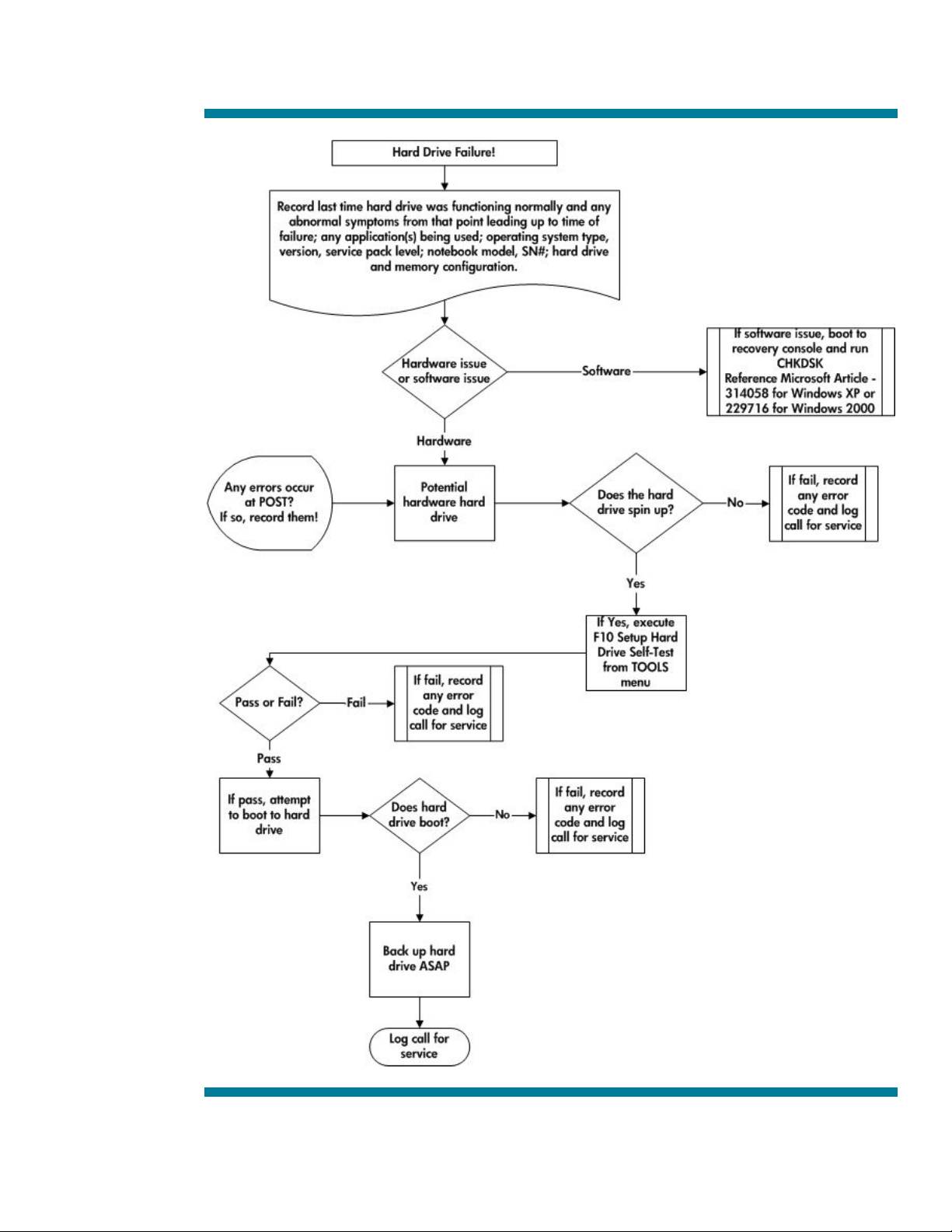
Hard Drive Troubleshooting Flowchart
6
Page 7

© Copyright 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only
warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty
statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should
be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
5982-4726ENUC, 05/2004
7
 Loading...
Loading...