HP INTEGRITY RX2620 User Manual

User Service Guide
HP Integrity rx2620 Server
Manufacturing Part Number: AD117-9003A
First Edition
August 2006
© Copyright 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.

Legal Notices
Copyright Notices. © Copyright 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional
warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Printed in U.S.A.
Intel, Intel Inside, Itanium, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
2

About This Document
Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
New and Changed Information in This Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Publishing History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Document Organization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
HP-UX Release Name and Release Identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
HP Encourages Your Comments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
1. Introduction
Server Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Server Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Server Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
PCI Riser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Internal Core I/O. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
External Core I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Power Supply Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
System Board Manageability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Enhanced Server Manageability Using the Integrated Lights Out Management Processor . . . . . . . 20
Hard Disk Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
System Board Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Processor Sockets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Processor Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ZX1 I/O and Memory Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
I/O Bus Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Processor Dependent Hardware Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Dual Serial Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Field Programmable Gate Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Baseboard Management Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
SCSI Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
IDE Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1 Gb System LANs A and B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
USB Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Data Pathing Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Contents
2. Controls, Ports, and LEDs
Front Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Hot-Plug Disk Drive Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
LAN Gb A Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
LAN Gb B Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Management Processor LAN LEDs (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3

Contents
3. Powering Off and Powering On the Server
Power States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Powering Off the Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Powering Off the Server Using the iLO MP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Powering Off the Server Manually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Powering On the Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Powering On the Server Using the iLO MP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Powering On the Server Manually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
4. Removing and Replacing Components
ESD Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Service Tools Required. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Location of Internal Components and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Removing and Replacing System Top Metal Cover and Bezels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Rack-Mount System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Removing and Replacing the Top Metal Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Removing and Replacing the Front Bezel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Removing and Replacing Hot-Swap and Hot-Plug Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Removing and Replacing Server Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Removing and Replacing the Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Removing and Replacing an Internal Hard Disk Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Removing and Replacing Internal Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Removing and Replacing Airflow Guides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Removing and Replacing the Memory Airflow Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Removing and Replacing the Processor Airflow Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Removing and Replacing Memory DIMMs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Removing and Replacing a Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Removing and Replacing the System Battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Removing and Replacing PCI Card Cage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Removing and Replacing PCI Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Removing and Replacing the PCI Backplane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Removing and Replacing a Removable Media Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Removing and Replacing iLO MP Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Removing and Replacing the iLO MP Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Removing and Replacing the LED Status Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Removing and Replacing the System Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Removing and Replacing the Power Supply Interface Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Removing and Replacing the Hard Disk Drive (SCSI) Backplane. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Troubleshooting Methodology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Possible Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
The System Will Not Power-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
The System Will Not Boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
The System Has Intermittent Failures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
4

Contents
The System LED or Diagnostic LEDs are Not On and No Error Messages Appear. . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
The Server Powers Off but Doesn't Restart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Troubleshooting and FRU identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Verifying Hard Disk Drive Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Identifying and Diagnosing Hardware Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Power and System LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Command Line Interface Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Troubleshooting Example Using CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Troubleshooting Example Using CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
System Board Diagnostic LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Front Panel LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Rear Panel LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Optional Management Processor LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Online Diagnostics/Exercisers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Offline Support Tool Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Offline Support Tools List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
General Diagnostic Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Fault Management Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
HP-UX Fault Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Recommended Cleaning Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Where to Get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Information to Collect Before you Contact Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Online Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Phone Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
A. Parts Information
Field Replaceable Parts View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Field Replaceable Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
B. Booting the Operating System
Operating Systems Supported on HP Integrity Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Configuring System Boot Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Booting and Shutting Down HP-UX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Adding HP-UX to the Boot Options List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Standard HP-UX Booting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Single-User Mode HP-UX Booting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
LVM Maintenance Mode HP-UX Booting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Shutting Down HP-UX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Booting and Shutting Down HP OpenVMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Adding HP OpenVMS to the Boot Options List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Booting HP OpenVMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Shutting Down HP OpenVMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Booting and Shutting Down Microsoft Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
5

Contents
Adding Microsoft Windows to the Boot Options List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Booting the Microsoft Windows Operating System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Shutting Down Microsoft Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Booting and Shutting Down Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Adding Linux to the Boot Options List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Booting the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Operating System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Booting the SuSE Linux Enterprise Server Operating System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Shutting Down Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
C. Utilities
Extensible Firmware Interface Boot Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
EFI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
EFI/POSSE Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
baud . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
boottest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
cpuconfig . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
ioconfig. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
errdump. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
lanaddress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
monarch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
pdt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
sysmode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Specifying SCSI Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Using the SCSI Setup Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Using the Boot Configuration Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Using the System Configuration Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Using the Security Configuration Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
iLO MP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Configuring the iLO MP LAN Port IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Accessing the iLO MP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Configuring the iLO MP LAN Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
iLO MP Command Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
6

Tables
Table 1. Publishing History Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 2. HP-UX 11i Releases. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 1-1. Server Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 1-2. Memory Array Capacities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 1-3. Data Pathing - Part 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 1-4. Data Pathing - Part 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 1-5. Data Pathing - Part 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 2-1. Control Panel LEDs and Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 2-2. Power On/Off Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 2-3. Hard Disk Drive LED Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 2-4. Power Supply LED Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 2-5. DVD Drive LED Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 2-6. Rear Panel Connectors and Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 2-7. 10/100/1000 base-T ethernet Gb LAN A Connector LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 2-8. 10/100/1000 base-T ethernet Gb LAN B Connector LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 2-9. iLO MP LAN LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 3-1. Power States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 4-1. Component Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 4-2. Connector Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 5-1. Problem Symptoms Repair Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Table 5-2. System LED States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Table 5-3. Power and System LED States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Table 5-4. Diagnostic LEDs Fault and Warning Categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Table 5-5. Unknown Warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Table 5-6. Memory Warnings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Table 5-7. System Board Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Table 5-8. Fan Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Table 5-9. Processor Warnings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Table 5-10. Temperature Warnings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Table 5-11. Video Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Table 5-12. Power Supply Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Table 5-13. Unknown Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 5-14. Memory Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 5-15. Firmware Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 5-16. System Board Faults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Table 5-17. Fan Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Table 5-18. Processor Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 5-19. BMC Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 5-20. Temperature Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 5-21. Power Supply Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Table 5-22. System Board LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Table 5-23. Gb LAN A Connector LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 5-24. Gb LAN B Connector LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
7

Tables
Table 5-25. Optional Management Processor LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Table 5-26. Online Support Tools List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Table 5-27. Offline Support Tools List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Table 5-28. General Diagnostic Tools List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Table 5-29. Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Table A-1. Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Table C-1. EFI Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Table C-2. Communications Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Table C-3. HP Integrity rx2620 Slots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Table C-4. HP Integrity rx2620 Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Table C-5. Console Output Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Table C-6. Console Output Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Table C-7. Console Output Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Table C-8. Console Output Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Table C-9. iLO MP Main Menu Commands and Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Table C-10. Command Menu Commands and Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
8

Figures
Figure 1-1. HP Integrity rx2620 Server (front view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 1-2. HP Integrity rx2620 Server (front view with bezel removed) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 1-3. HP Integrity rx2620 Server (rear view). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 1-4. System Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 1-5. Memory Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 2-1. Front View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 2-2. Control Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 2-3. Hot-Plug Disk Drive LED Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 2-4. Power Supply LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 2-5. DVD LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 2-6. Rear View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 2-7. 10/100/1000 base-T ethernet Gb LAN A Connector LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 2-8. 10/100/1000 base-T ethernet Gb LAN B Connector LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 2-9. iLO MP LAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 4-1. Internal Physical Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 4-2. System Board Connectors and Slots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 4-3. Release the Rack Latches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 4-4. Removing and Replacing the Top Metal Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 4-5. Aligning the Top Metal Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 4-6. Closing the Top Metal Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 4-7. Front Bezel Retaining Clip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 4-8. Replacing the Front Bezel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 4-9. Fan 1A or Fan 1B Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 4-10. Fan 2 Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 4-11. Fan 3 Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 4-12. Releasing the Power Supply Retaining Clip. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 4-13. Removing the Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 4-14. Replacing the Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 4-15. Unlocking the Disk Drive (if necessary) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 4-16. Releasing the Disk Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 4-17. Removing the Disk Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 4-18. Airflow Guides Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 4-19. Removing the Memory Airflow Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Figure 4-20. Removing the Processor Airflow Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 4-21. Open the Release Clip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 4-22. Remove the Front Airflow Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 4-23. DIMM Slot Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 4-24. Inserting DIMM into Slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Figure 4-25. Processor Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Figure 4-26. Processor Location on System Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Figure 4-27. Removing the Processor Airflow Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Figure 4-28. Unscrew the Captive Screws. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Figure 4-29. Slide Sequencing Retainer Plate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
9

Figures
Figure 4-30. Unlock Processor Module Locking Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Figure 4-31. Unlocked ZIF Socket Lock. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 4-32. Processor Alignment Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 4-33. CPU Slot Alignment Holes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Figure 4-34. Installing the Processor Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Figure 4-35. Locking the Processor Module in Place . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Figure 4-36. Slide the Sequencing Retainer Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Figure 4-37. Secure the Captive Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 4-38. Removing the System Battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Figure 4-39. Removing the PCI Cage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 4-40. Removing the PCI Cage Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Figure 4-41. Installing a PCI Slot Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 4-42. Installing a PCI Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Figure 4-43. Removing the PCI Backplane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Figure 4-44. Replacing the PCI Backplane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Figure 4-45. Removable Media Drive Removal/Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 4-46. Removing the iLO MP Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 4-47. Replacing the iLO MP Blank. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 4-48. Removing the iLO MP Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Figure 4-49. Removing the LED Status Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 4-50. Remove System Board Mounting Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 4-51. Remove the System Board Mounting Screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 4-52. Remove the System Board. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 4-53. Slide System Board into Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 4-54. Align the System Board PCI Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Figure 4-55. Slide System Board in Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 4-56. Install the Rear Panel Mounting Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 4-57. Reinstall the Power Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Figure 4-58. Power Cables and Holding Clips. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Figure 4-59. Remove the Mounting Screw. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Figure 4-60. Remove the PSI Interface Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 4-61. Replacing the Power Supply Interface Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 4-62. Securing the Power Supply Interface Module and Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure 4-63. Open the Fan Power Bridge. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 4-64. Disconnect SCSI Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 4-65. Remove Mounting Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 4-66. Remove the SCSI Backplane. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 4-67. Remove the SCSI Backplane from Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 5-1. LED Apertures on Hard Disk Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Figure 5-2. Diagnostic LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Figure 5-3. Location of the STBY, F/W and BMC LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Figure A-1. Parts Identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Figure A-2. Tower Parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
10

Figures
Figure C-1. EFI Boot Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Figure C-2. Password Reset Jumper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
11

Figures
12
About This Document
This document provides information and instructions on servicing and troubleshooting the HP Integrity
rx2620 server.
The document printing date and part number indicate the document’s current edition. The printing date
changes when a new edition is printed. Minor changes may be made at reprint without changing the printing
date. The document part number changes when extensive changes are made.
Document updates may be issued between editions to correct errors or document product changes. To ensure
that you receive the updated or new editions, you should subscribe to the appropriate product support service.
See your HP sales representative for details.
The latest version of this document can be found on line at http://www.docs.hp.com.
Intended Audience
This document is intended to provide technical product and support information for authorized service
providers, system administrators, and HP support personnel.
This document is not a tutorial.
New and Changed Information in This Edition
This guide has been updated with:
• This document is being updated as part of a processor upgrade to the HP Integrity rx2620 server.
Publishing History
The publishing history below identifies the edition dates of this manual. Updates are made to this publication
on an unscheduled, as needed, basis. The updates will consist of a complete replacement manual and
pertinent on-line or CD documentation.
Table 1 Publishing History Details
Document
Manufacturing
Part Number
AD117-9003A HP-UX, Windows®,
Operating Systems
Supported
Linux®, OpenVMS®
Supported Product Versions
rx2620 August 2006
Publication
Date
13

Document Organization
This guide is divided into the following chapters.
Chapter 1 Introduction Use this chapter to learn about the features and specifications of the HP
Integrity rx2620 server.
Chapter 2 Controls, Ports, and LEDs Use this chapter to learn about the locations of the external
controls, ports, and LEDs on the server.
Chapter 3 Powering Off and Powering On the Server Use this chapter to learn about powering
the server off and on.
Chapter 4 Removing and Replacing Components Use this chapter to learn how to remove and
replace the field replaceable components (FRUs) on the server.
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting Use this chapter to learn about troubleshooting problems you may
encounter with the server.
Appendix A Parts Information Use this appendix to learn the location and part numbers of the server
components.
Appendix B Operating System Boot and Shutdown Use this appendix to learn about booting and
shutting down the operating system on the server.
Appendix C Utilities Use this appendix for information regarding the utilities available for the server.
Appendix D Console Setup and Connection Use this appendix to learn about the process for setting
up a console session and connecting to the server.
Typographic Conventions
This document uses the following conventions.
WAR NING A warning lists requirements that you must meet to avoid personal injury.
CAUTION A caution provides information required to avoid losing data or avoid losing server
functionality.
NOTE A note highlights useful information such as restrictions, recommendations, or important
details about HP product features.
Book Title The title of a book. On the Web and on the Instant Information CD, it may be a hot link to
the book itself.
KeyCap The name of a keyboard key or graphical interface item (such as buttons, tabs, and menu
items). Note that
Emphasis Text that is emphasized.
Bold Text that is strongly emphasized.
Bold The defined use of an important word or phrase.
Return and Enter both refer to the same key.
ComputerOut Text displayed by the computer.
UserInput Commands and other text that you type.
14

Command A command name or qualified command phrase.
Option An available option.
Screen Output Example of computer screen output.
[] The contents are optional in formats and command descriptions. If the contents are a list
separated by |, you must select one of the items.
{} The contents are required in formats and command descriptions. If the contents are a list
separated by |, you must select one of the items.
... The preceding element may be repeated an arbitrary number of times.
| Separates items in a list of choices.
HP-UX Release Name and Release Identifier
Each HP-UX 11i release has an associated release name and release identifier. The uname (1) command with
the -r option returns the release identifier. This table shows the releases available for HP-UX 11i.
Table 2 HP-U X 1 1i Rel ea se s
Release Identifier Release Name Supported Processor Architecture
B.11.11 HP-UX 11i v1 PA-RISC
B.11.20 HP-UX 11i v1.5 Intel® Itanium®
B.11.22 HP-UX 11i v1.6 Intel Itanium
B.11.23 HP-UX 11i v2.0 Intel Itanium
Related Documents
You can find other information on HP server hardware management, Microsoft® Windows®, and diagnostic
support tools in the following publications.
Web Site for HP Technical Documentation:
http://docs.hp.com
Server Hardware Information:
http://docs.hp.com/hpux/hw/
Windows Operating System Information
You can find information about administration of the Microsoft Windows operating system at the following
Web sites, among others:
• http://docs.hp.com/windows_nt/
• http://www.microsoft.com/technet/
Diagnostics and Event Monitoring: Hardware Support Tools
Complete information about HP’s hardware support tools, including online and offline diagnostics and event
monitoring tools, is at the http://docs.hp.com/hpux/diag/ Web site. This site has manuals, tutorials,
FAQs, and other reference material.
15

Web Site for HP Technical Support:
http://us-support2.external.hp.com/
Books about HP-UX Published by Prentice Hall
The http://www.hp.com/hpbooks/ Web site lists the HP books that Prentice Hall currently publishes, such
as HP-UX books including:
• HP-UX 11i System Administration Handbook
http://www.hp.com/hpbooks/prentice/ptr_0130600814.html
• HP-UX Virtual Partitions
http://www.hp.com/hpbooks/prentice/ptr_0130352128.html
HP Books are available worldwide through bookstores, online booksellers, and office and computer stores.
HP Encourages Your Comments
HP encourages your comments concerning this document. We are truly committed to providing
documentation that meets your needs.
Please send comments to: netinfo_feedback@cup.hp.com.
Please include title, manufacturing part number, and any comment, error found, or suggestion for
improvement you have concerning this document. Also, please include what we did right so we can
incorporate it into other documents.
16

1 Introduction
The HP Integrity rx2620 server is a 2-socket server based on the Itanium® processor architecture. The server
supports the following operating systems: Microsoft Windows®, HP-UX, Linux®, and OpenVMS. The server
is available in either rack-mount or pedestal configurations. The server accommodates up to 12 DIMMs and
internal peripherals including disks and a DVD. Its high availability features include hot-swap fans, power
supplies, and hot-plug disk drives.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Server Overview” on page 18.
• “Server Components” on page 19.
• “System Board Components” on page 22.
Chapter 1
17
Introduction
Server Overview
Server Overview
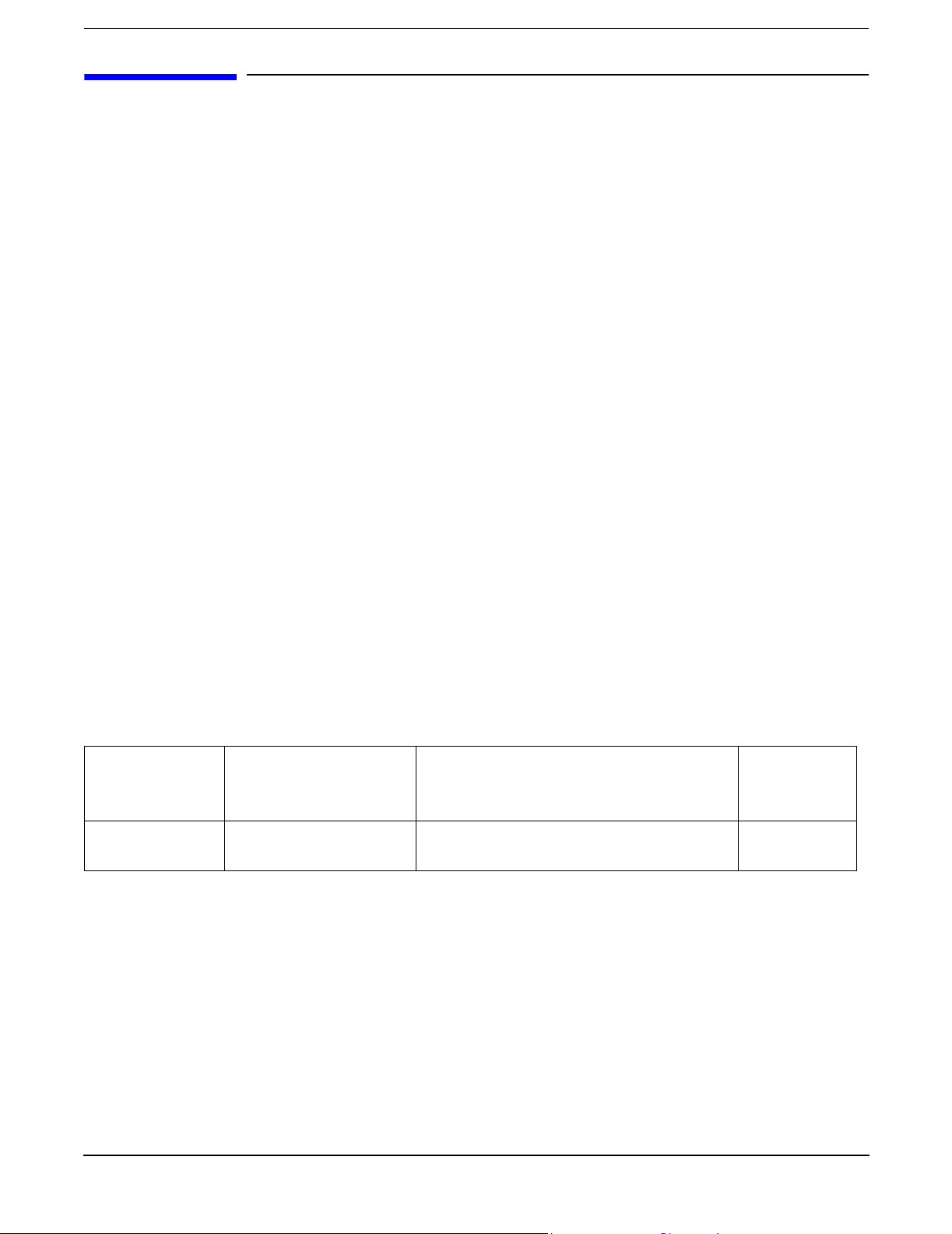
The HP Integrity rx2620 server chassis is a 2U Electronics Industry Association (EIA) enclosure, which
mounts in any standard 19 inch EIA rack. All external cabling connects from the rear of the enclosure. With
the server installed in the rack, service access is enhanced by the use of chassis slides. It has bays to
accommodate 1 + 1 redundant, hot-swappable power supplies, accessible from the front of the product. There
are three low-profile hot swappable hard disk drives accessible from the front, and a slim-line optical drive for
a CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R or DVD+RW. There are N + 1 redundant, hot-swappable server fans, all clearly
identified and easily accessible. Server status indication, a power switch, server locator switch and LED are
located in the front within the bezel. There is also a server locator switch and LED in the back of the server
for easy identification in the rack. See Figure 1-1, Figure 1-2, and Figure 1-3 for front and back views of the
server.
Figure 1-1 HP Integrity rx2620 Server (front view)
Figure 1-2 HP Integrity rx2620 Server (front view with bezel removed)
Figure 1-3 HP Integrity rx2620 Server (rear view)
WARNING Unplug all power cords from system before servicing
PWR
2
Automatic Internal SCSI Termination
SCSI LVD/SE
LAN 10/100
PWR
1
Management Card
LAN Gb A
MP
RESET
LAN Gb B
CONSOLE / REMOTE / UPS
TOC
USB
VGA
CONSOLE
SERIAL A
SERIAL B
18
Chapter 1
Server Dimensions
Table 1-1 shows the dimensions and weight of the rx2620 server.
Table 1-1 Serv e r Dime ns ions
Dimensions Value
Rack units 2U
Height 8.6 cm (3.4 in.)
Width 48.3 cm (19.0 in.)
Depth 67.9 cm (26.8 in.)
Weight
•Min
•Max
17.5 kg (38.6 lb.)
22.2 kg (49.0 lb.)
Introduction
Server Components
Server Components
The following components make up the HP Integrity rx2620 server.
Processor
• 1.4 GHz/12 MB L3 cache dual-core processor
• 1.6 GHz/18 MB L3 cache dual-core processor
Memory
• 12 memory DIMM slots
• 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, and 4 GB standard 184 pins 2.5 V DDR1, CL2, registered, ECC
• 133 MHz memory bus frequency, 266 MTransfers/s data, 8.5 Gb/s peak data bandwidth
• Minimum memory size of 1 GB with four 256 MB DIMMs
• Maximum memory size of 32 GB with eight 4 GB DIMMs
• Upgrades must be made by quads of DIMMs
• DIMMs loaded by quads enable interleaved mode and chip spare
PCI Riser
• Four independent PCI-X 133 MHz 64 bit, 3.3 V, 15 W slots. There is no 5 V card and hot plug support
NOTE Some 25 W cards are supported. See the following slot matrix (by server):
http://www.docs.hp.com/en/SSM1-EL/slotmatrix.htm
For more information regarding specific I/O cards, see:
http://www.docs.hp.com/en/netcom.html
Chapter 1
19

Introduction
Server Components
Internal Core I/O
• Dual channel SCSI U320 interface, two internal 68-pin connectors, one 68-pin external connector
• The three internal SCSI drive connectors are the 80-pin type and provide drive electrical hot-plug
capability
• One internal IDE connector for a slim-line optical device (CD and DVD)
External Core I/O
• One SCSI U320 68 pin connector
• Two 10/100/1000Base-T ethernet LAN connectors for twisted-pair cable
• Four USB 2.0 ports
• Two general purpose or 9-pin serial ports, 16550 compatible
Power Supply Unit
• 600 W output power
• The power supply is split in a front-end block (the actual power supply case) that converts the line voltage
into a high DC voltage. Back-end voltage regulation modules (on the system board) step down the front
end DC voltage to the required voltages
• Redundant and hot-pluggable power supplies (front-end block only)
System Board Manageability
• Baseboard Management Controller (BMC)
• Temperature monitoring and fans regulation by BMC
• BMC manageability console shared with server console and general purpose serial port
• IPMI protocol for communication between BMC/server/iLO MP hardware
• BMC hardware diagnostics display on the front status panel
• Locator front/rear LEDs
• Field replacement units monitoring by BMC
• Serial port for local and modem console
• Wake-on-LAN and Alert-on-LAN capabilities from the 10/100/1000 BT LAN port
Enhanced Server Manageability Using the Integrated Lights Out Management Processor
The integrated Lights Out Management Processor (iLO MP) provides the following enhancements to server
manageability:
• Web Graphical User Interface (GUI)
• LAN telnet console
• Web console
20
Chapter 1

• Serial port for local console
• Serial port for modem console
• Duplication of console screen content across all consoles
• VGA and 2D graphics display
• Advanced Features:
— Secure Shell (SSH) access
— Group actions through the HP Systems Insight Manager (HPSIM)
— Directory-based authentication and authorization (LDAP)
Hard Disk Drives
The following hard disk drives are supported by the rx2620 server:
• 36 GB 15K HotPlug Ultra320 SCSI drive
• 73 GB 15K HotPlug Ultra320 SCSI drive
• 146 GB 10K HotPlug Ultra320 SCSI drive
Introduction
Server Components
• 300 GB 10K HotPlug Ultra320 SCSI drive
The server holds up to three hard disk drives
Chapter 1
21
Introduction
System Board Components
System Board Components
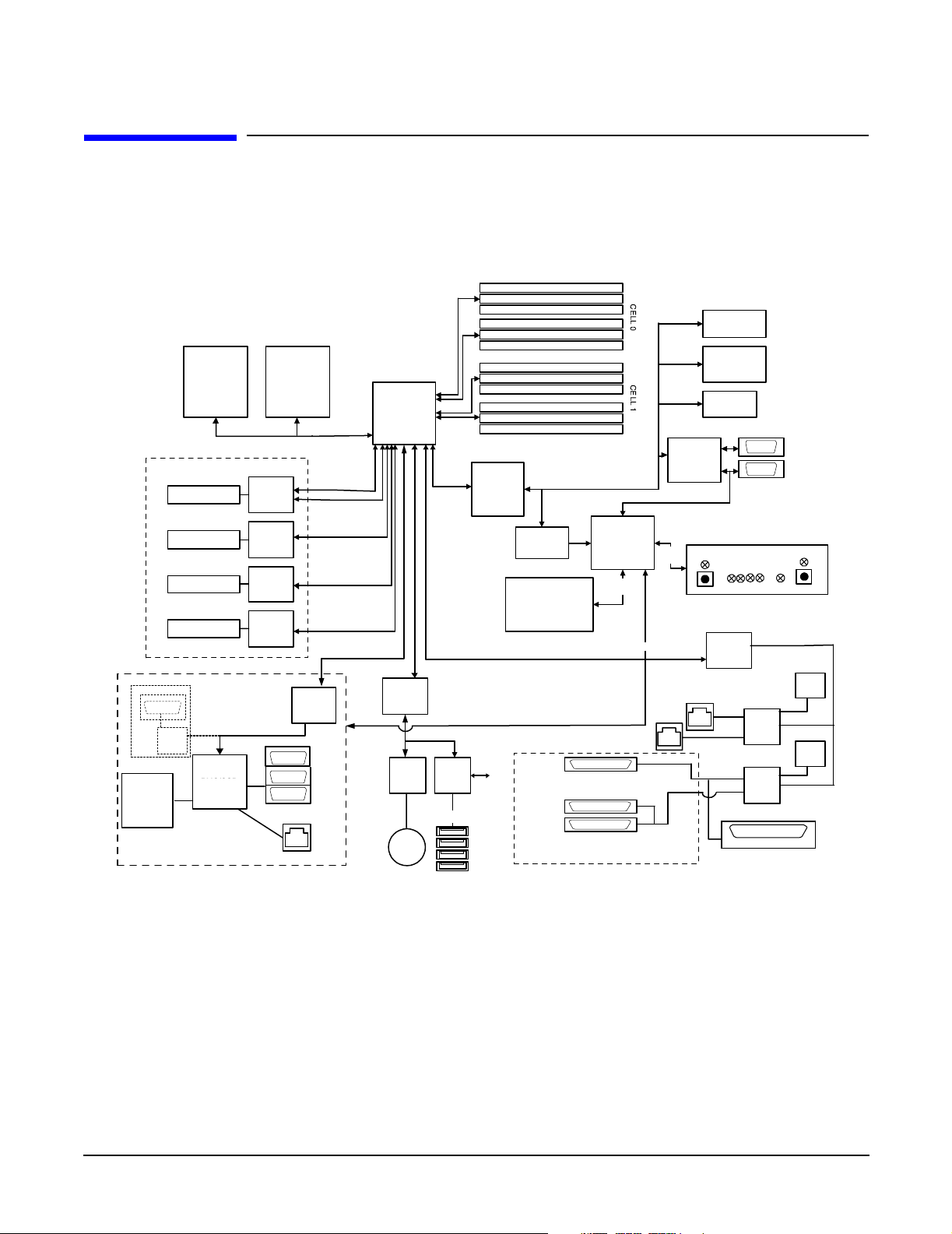
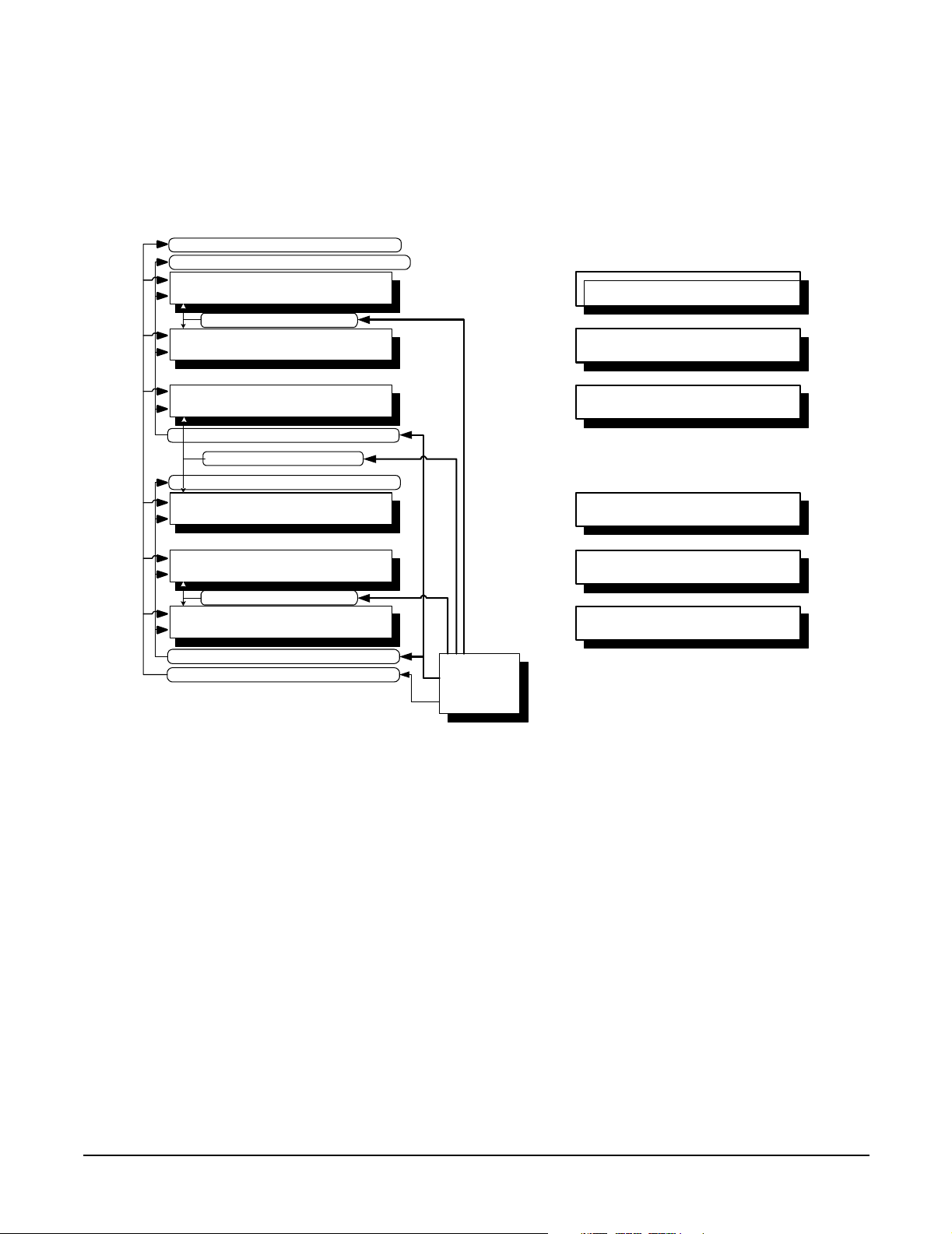
This section provides a block diagram of the system board and descriptions of key components (integrated
circuits) on the board. Figure 1-4 shows a block diagram of the rx2620 server.
Figure 1-4 System Block Diagram
Optional
Battery•
SRAM
DRAM
Flash
etc...
PCI-X 133
PCI-X 133 "Slot2"
PCI-X 133 "Slot3"
PCI-X 133 "Slot4"
VGA
VGA
Management Processor
Itanium-2
IPF
267MHz 8.5GB/S Peak Data BandWidth
200MHz 6.4GB/S Peak Data BandWidth
PCI-X Interface
ASIC
PCI 33/32
LAN100BT
Bus
Interface
ASIC
Bus
Interface
ASIC
Bus
Interface
ASIC
Bus
Interface
"Slot1"
iLO MP
RMC/GSP
Itanium-2
IPF
Interface
UPS
Console
Modem
ASIC
Bus
ROPE 4
ROPE 5
ROPE 3
ROPE 2
ROPE 6
ROPE 7
ASIC
Bus
Interface
ROPE 0
ASIC
Bus
Interface
IDE
DVD RW
Slim
Line
DMD
267MHz 8b data
533MB/s Peak Data
Bandwidth per rope
ROPE 1
PCI 33/32
USB
2.0
Keyboard
Mouse
Industry Standard DDR1 DIMM
133 MHz bus clock
267 MT/s data rate
8.5GB/s peak data bandwidth
ASIC
Bus
Interface
To AGP
Riser
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
MEMORY
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
PDH Bus
LPC
FPGA
LPC + ACPI
BMC SRAM 512KB
(on battery, scratch RAM•
+NVM+ FPL •
forward progress log)
BMC FLASH
SCSI ID 2
SCSI ID 1
SCSI ID 0
Bus
1MB
SCSI BACKPLANE
Manageability
Controller
HDD #3
HDD #2
HDD #1
BMC
I2C
etc...
BMC
bus
I2C, etc...
(SE-LVDS SCA-2 80pin)
DUART
LOCATOR
FMW/PDC
Flash
8 MB
16MB
FMW SRAM
(on battery, scratch
RAM + NVM)
512KB
RTC
COM1
COM2
LED STATUS PANEL
DIAG LEDs
ASIC
Bus
Interface
LAN
LAN
10/100/
10/100/
1000
1G
Channel B
SCSI
SCSI
Channel A
U320
U320
External
external (se-lvds 68p)
System/BMC
Console
& Serial Port
Serial Port
OS Enabled
ON-OFF
LAN
Activity
PCI-X 133
(SE-LVDS 68p)
FLASH
FLASH
The following describes the main components of the system board:
• “Processor Sockets” on page 23
• “Processor Bus” on page 23
• “ZX1 I/O and Memory Controller” on page 23
• “Memory” on page 23
• “I/O Bus Interface” on page 25
• “Processor Dependent Hardware Controller” on page 26
22
Chapter 1

Introduction
System Board Components
• “Dual Serial Controller” on page 26
• “Field Programmable Gate Array” on page 26
• “Baseboard Management Controller” on page 27
• “SCSI Controller” on page 27
• “IDE Interface” on page 27
• “1 Gb System LANs A and B” on page 28
• “USB Connectors” on page 28
• “Data Pathing Information” on page 28
Processor Sockets
The system board consists of two zero insertion force (ZIF) processor sockets, the core electronic complex
(CEC), and circuitry for clock and power generation and distribution, boundary scan, in-target probe, and
debug.
The front side bus (FSB) is the IA64 processor bus, based on bus protocol from Intel. Unlike previous PA-RISC
microprocessors that utilized HP's proprietary processor bus, this processor is designed to utilize the FSB.
This allows processor field replaceable units (FRUs) to be dropped in, provided that electrical and mechanical
compatibility and support circuitry exist. For the purposes of this document, a FRU consists of a single
processor with power pod, and the heatsink assembly.
Each processor plugs directly into, and is powered by its own 12 V to 1.2 V power pod. Other power for the
system board comes from multiple on-board DC to DC converters. Each processor is attached to the board
through a ZIF socket and the entire FRU secured by a heatsink.
Processor Bus
The FSB in this product runs at 200 MHz. Data on the FSB are transferred at a double data rate, which
allows a peak FSB bandwidth of 6.4 Gb/sec.
ZX1 I/O and Memory Controller
The HP Integrity rx2620 server supports the following features of the ZX1 I/O and memory controller chip
• 8.5 Gb/s peak I/O bandwidth
• Seven communication paths
• Peak memory bandwidth of 8.5 Gb/s
• Two memory cells, 144 data bits each
Memory
The memory subsystem provides two memory cells, each of which is 144 data bits wide. Each cell has six
DIMM slots, which means a total of 12 DIMM slots are available. The memory bus clock speed is 133 MHz,
and the data transfer rate is 266 Mtransfers/second as data is clocked on both edges of the clock. The peak
data bandwidth for this memory subsystem design is 8.5 Gb/s. Load DIMMs in quads with qualified modules.
Memory is protected by data ECC, and the hardware implementation supports chip-spare.
The minimum amount of memory supported by the server is 1 GB (four 256 MB modules). The maximum
amount of memory supported by the server is 32 GB (eight 4 GB modules).
Chapter 1
23
Introduction
System Board Components
This design does not support any non industry standard DDR DIMMs. Only qualified DIMMs are supported.
Figure 1-5 shows a block diagram of the server memory.
Figure 1-5 Memory Block Diagram
MC0
Parallel Termination Resistors for Address and Control Rt=27 ohms
Parallel Termination Resistors for DQ[143:72] and associated DQS Rt=27 ohms
SA0=1
SA1=0
SA2=0
SA0=1
SA1=0
SA2=1
SA0=1
SA1=1
SA2=0
Stub Isolation Resistors for DQ[143:72] and associated DQS Rs=18 ohms
Parallel Termination Resistors for DQ [71:0] and associated DQS Rt=27 ohms
SA0=0
SA1=0
SA2=0
SA0=0
SA1=0
SA2=1
SA0=0
SA1=1
SA2=0
Stub Isolation Resistors for DQ[71:0] and associated DQS Rs=18 ohms
Stub Isolation Resistors for Address and Control Rs=18 ohms
DIMM0B
DIMM CLK Stub Isolation Resistors Rs=0 ohms
DIMM4B
DIMM2B
DIMM CLK Stub Isolation Resistors Rs=0 ohms
DIMM0A
DIMM4A
DIMM CLK Stub Isolation Resistors Rs=0 ohms
DIMM2A
CS1(0)
CS1(4)
CS1(2)
CS1(6)
CS1(1)
CS1(5)
CS1(0)
CS1(4)
CS1(2)
CS1(6)
CS1(1)
CS1(5)
Memory
Controller
MC1
SA0=1
SA1=0
SA2=0
SA0=1
SA1=0
SA2=1
SA0=1
SA1=1
SA2=0
SA0=0
SA1=0
SA2=0
SA0=0
SA1=0
SA2=1
SA0=0
SA1=1
SA2=0
DIMM1B
DIMM5B
DIMM3B
Same connection scheme
for MC1 as for MC0
DIMM1A
DIMM5A
DIMM3A
CS1(0)
CS1(4)
CS1(2)
CS1(6)
CS1(1)
CS1(5)
CS1(0)
CS1(4)
CS1(2)
CS1(6)
CS1(1)
CS1(5)
Memory Architecture
The I/O ASIC memory interface supports two DDR cells, each of which is 144 data bits wide. The memory
subsystem physical design uses a comb-filter termination scheme for both the data and the address and
control buses. This part of the topology is similar to other DDR designs in the computer industry. Clocks are
distributed directly from the I/O ASIC; each clock pair drives two DIMMs.
Memory data is protected by the ECC. Eight ECC bits per DIMM protect 64 bits of data. The use of ECC
allows correction of single-bit errors, and detection of multi-bit errors. Only DIMMs with ECC are qualified or
supported.
DIMMs
The memory subsystem supports only DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random
Access Memory) technology utilizing industry-standard PC-1600 type DDR SDRAM DIMMs, 1.2" tall. The
DIMMs use a 184-pin JEDEC standard connector.
24
Chapter 1
Introduction
System Board Components
DIMMs are loaded in groups of four, known as a quad. All four DIMMs in a quad must be the same size.
Table 1-2 summarizes the memory solutions.
Table 1-2 Memory Array Capacities
Min / Max Memory Size Single DIMM Size
1 GB / 3 GB 256 MB DIMM 18 x 32 MB x 4 DDR1 SDRAMs (128 MB)
2 GB / 6 GB 512 MB DIMM 36 x 32 MB x 4 DDR1 SDRAMs (128 MB)
4 GB / 12 GB 1024 MB DIMM 36 x 64 MB x 4 DDR1 SDRAMs (256 MB)
8 GB / 24 GB 2048 MB DIMM 36 x 128 MB x 4 DDR1 SDRAMs (512 MB)
32 GB / 32 GB 4096 MB DIMM 36 x 256 MB x 4 DDR1 SDRAMs (1024 MB)
Chip Spare Functionality
Chip spare enables an entire DDR SDRAM chip on a DIMM to be bypassed in the event that a multi-bit error
is detected on the DDR SDRAM. In order to use the chip spare functionality on your server, only DIMMs built
with ×4 DDR SDRAM parts can be used, and these DIMMs must be loaded in quads.
The memory subsystem design supports the I/O ASIC chip’s spare functionality. Chip spare enables an entire
SDRAM chip on a DIMM to be bypassed/replaced in the event that a multi-bit error is detected on that
SDRAM. In order to use the chip spare functionality on, only DIMMs built with x4 SDRAM parts can be used,
and these DIMMs must be loaded in quads (two DIMMs per memory cell, loaded in the same location in each
memory cell). Each DIMM within a quad must be identical to all the other DIMMs in the quad.
Chip spare is achieved if four identical DIMMs are loaded into a quad. If more DIMMs are added, they must
be loaded in quads in order to maintain the chip spare functionality. So, if more DIMMs are added in to the
example case, four identical DIMMs (identical to each other, but can be different from the original quad that
was loaded) must be loaded into the next quad. However, if you are using 4 GB DIMMS, the only
configuration supported is eight 4 GB DIMMS in the first three quads, with no other DIMMs in the remaining
quad. For slot and quad locations, see Figure 4-23 on page 66.
DDR SDRAM Count, Type and
Technology
Serial Presence Detect
Each DIMM contains an I2C electronically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) whose
content describes the module's characteristics: speed, revision, vendor, etc. This feature is called serial
presence detect (SPD). Firmware typically uses this information to detect unmatched pairs of DIMMs, and
configure certain memory subsystem parameters. The SPD information for DIMMs loaded in the server is
also accessible to the BMC through the I2C bus.
I/O Bus Interface
The I/O bus interface provides these features:
• Industry standard PCI 33 MHz and 66 MHz, PCI-X 66 MHz to 133 MHz, 32 or 64 data bit support
• 3.3 V PCI only, it does not support 5 V PCI.
• Optimizes for DMA performance.
• Supports 3.3 V or Universal keyed PCI cards. 5 V keyed PCI cards are not supported
• Supports up to four PCI sockets.
Chapter 1
25

Introduction
System Board Components
Processor Dependent Hardware Controller
The PDH controller provides these features:
• 16-bit PDH bus with reserved address space for
— Flash memory
— Non-volatile memory
— Scratch RAM
— Real Time Clock
— UARTs
— External Registers
— Firmware read/writable registers
— Two general purpose 32-bit registers
— Semaphore registers
— Monarch selection registers
— Test and Reset register
• Reset and INIT generation
Dual Serial Controller
The dual serial controller is a dual universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter (DUART). This chip
provides enhanced UART functions with 16-byte first-in, first-out (FIFO), a modem control interface.
Registers on this chip provide onboard error indications and operation status. An internal loopback capability
provides onboard diagnostics.
Features include:
• Data rates up to 115.2 kbps
• 16550A fully compatible controller
• A 16-byte transmit FIFO to reduce the bandwidth requirement of the external CPU
• A 16-byte receive FIFO with four selectable interrupt trigger levels and error flags to reduce the
bandwidth requirement of the external CPU
• UART control that provides independent transmit and receive
• Modem control signals (-CTS, -RTS, -DSR, -DTR, -RI, -CD, and software controllable line break)
• Programmable character lengths (5, 6, 7, 8) with Even, Odd or No Parity
• A status report register
Field Programmable Gate Array
The field programmable gate array (FPGA) provides ACPI and LPC support for the PDH bus and provides
these features:
• ACPI 2.0 interface
• LPC bus interface to support BMC
26
Chapter 1

Introduction
System Board Components
• Decoding logic for PDH devices
Baseboard Management Controller
The baseboard management controller (BMC) supports the industry-standard Intelligent Platform
Management Interface (IPMI) specification. This specification describes the management features that have
been built into the system board. These features include: local and remote diagnostics, console support,
configuration management, hardware management, and troubleshooting.
The baseboard management controller provides the following:
• Compliance with Intelligent Platform Management Interface 1.0
• Tachometer inputs for fan speed monitoring
• Pulse width modulator outputs for fan speed control
• Push-button inputs for front panel buttons and switches
• One serial port, multiplexed with the server console port
• Remote access and intelligent chassis management bus (ICMB) support
• Three I
2
C primary/secondary ports (one the ports is used for IPMB
• Low pin count (LPC) bus provides access to three keyboard controller style (KCS) and one-block transfer
(BT) interface
• 32-bit ARM7 processor
• 160-pin low profile flat pack (LQFP) package
• Firmware is provided for the following interfaces:
— Intelligent platform management interface (IPMI)
— Intelligent platform management bus (IPMB)
SCSI Controller
The SCSI controller is an LSI Logic 53C1030 chip. This chip is fully compliant with the SCSI Peripheral
Interface-3 Specification (SPI-3). It has two independent SCSI channels supporting devices at speeds up to
320 Mb/second each. The 53C1030 adheres to the PCI-X addendum to the PCI Local Specification and is
hard-wired to PCI ID 1 which corresponds to bit 17 of the PCI AD bus.
IDE Interface
The IDE controller (PCI649) supports the ATAPI zero to five modes (from 16 to 100 Mb/s). The usable speed
on this server is limited to 16 MHz (ATA-33 mode, 33 Mb/s) because the slimline CD/DVD devices do not
support the ATA-66 and 100 modes.
The primary IDE channel is the only channel that is implemented. The IDE cable provides only one drive
connector, of the primary type, for the DVD peripheral.
Chapter 1
27
Introduction
System Board Components
1 Gb System LANs A and B
The 1 Gb system LAN ports A and B provide:
•Main server LANs
• 10/100/1000 Mb capability
USB Connectors
The USB connectors provide:
• High speed 480 Mb/sec. capability
• Full speed 12 Mb/sec. and low speed 1.5 Mb/sec
• Support for USB keyboard and mouse
• HP-UX supports HP USB keyboard and mouse
Data Pathing Information
Table 1-3 shows information about data pathing in the HP Integrity rx2620 server.
Table 1-3 Data Pathing - Part 1
PCI Slot PCI Card Function Physical Location ACPI Path
1 PCI-X 133 Mhz/64 bit Top slot (HWP0002,400)/PCI(1|0)
2 PCI-X 133 Mhz/64 bit 2nd from top (HWP0002,300)/PCI(1|0)
3 PCI-X 133 Mhz/64 bit 3rd from top (HWP0002,200)/PCI(1|0)
4 PCI-X 133 Mhz/64 bit Bottom slot (HWP0002,600)/PCI(1|0)
Core I/O -1 USB Port Rear bulkhead - “Mouse icon” (HWP0002,0)/PCI(1|0)/USB(0, 0)
Core I/O -2 USB Port Rear bulkhead - stacked top (HWP0002,0)/PCI(1|0)/USB(1, 0)
Core I/O -3 USB Port Rear bulkhead - “Kybd icon” (HWP0002,0)/PCI(1|1)/USB(0, 0)
Core I/O -4 USB Port Rear bulkhead - stacked bottom (HWP0002,0)/PCI(1|1)/USB(1, 0)
Core I/O -5 IDE Controller System board (HWP0002,0)/PCI(2|0)
Core I/O -6 1 Gb LAN Rear bulkhead - LAN Gb B (HWP0002,100)/PCI(3|0)
Core I/O -7 1 Gb LAN Rear bulkhead - LAN Gb A (HWP0002,0)/PCI(2|0)
Core I/O -8 SCSI - Channel A System board (HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|0)
Core I/O -9 SCSI - Channel A ID0 Bottom (#3) HDD (HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|0)/SCSI
(Pun0,Lun0)
Core I/O -10 SCSI - Channel A ID1 Middle (#2) HDD (HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|0)/SCSI
(Pun1,Lun0)
Core I/O -11 SCSI - Channel B System board (HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|1)
Core I/O -12 SCSI - Channel B ID2 Top (#1) HDD (HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|1)/SCSI
(Pun2, Lun0)
28
Chapter 1
System Board Components
Table 1-3 Data Pathing - Part 1 (Continued)
PCI Slot PCI Card Function Physical Location ACPI Path
Introduction
Core I/O -13 SCSI - Channel B Ext. Rear bulkhead - SCSI LVD/SE
connector
Core I/O -14 Internal IDE device Front DVD drive slot (HWP0002,0)/PCI(2|0)/ATA
Opt MP -1 MP Serial Controller Rear bulkhead - MP
Console/Remote/UPS conn.
Opt MP -2 MP Console Controller Rear bulkhead - MP
Console/Remote/UPS conn.
Opt MP -3 MP VGA Controller Rear bulkhead - MP VGA conn. HWP0002,700)/PCI(2|0)
N/A System board Console
port (CLI)
N/A System board Serial
port
Rear bulkhead - Serial
A/Console connector.
Rear bulkhead - Serial B
connector
(HWP0002,100)/PCI(1|1)/SCSI
(Punx, Luny)
(HWP0002,700)/PCI(1|0)
HWP0002,700)/PCI(1|1)
N/A
N/A
Table 1-4 Data Pathing - Part 2
PCI Slot MAPPER Path HP-UX Path Linux Path Windows Path
1 0/4/1/0 0/4/1/0 80:01.0
2 0/3/1/0 0/3/1/0 60:01.0
3 0/2/1/0 0/2/1/0 40:01.0
4 0/6/1/0 0/5/1/0 C0:01.0
Core I/O -1 0/0/1/0 0/0/1/0 00:01.0
Core I/O -2 0/0/1/0 0/0/1/0 00:01.0
Core I/O -3 0/0/1/1 0/0/1/1 00:01.1
Core I/O -4 0/0/1/1 0/0/1/1 00:01.1
Core I/O -5 0/0/2/0 0/0/2/0 00:02.0
Core I/O -6 0/0/3/0 0/0/3/0 00:03.0
Core I/O -7 0/1/2/0 0/1/2/0 20:02.0
Core I/O -8 0/1/1/0 0/1/1/0 20:01.0
Core I/O -9 0/1/1/0.0.0 0/1/1/0.0.0
Core I/O -10 0/1/1/0.1.0 0/1/1/0.1.0
Core I/O -11 0/1/1/1 0/1/1/1 20:01.1
Core I/O -12 0/1/1/1.2.0 0/1/1/1.2.0
Core I/O -13 0/1/1/1.x.y 0/1/1/1.x.y
Chapter 1
29
Introduction
System Board Components
Table 1-4 Data Pathing - Part 2 (Continued)
PCI Slot MAPPER Path HP-UX Path Linux Path Windows Path
Core I/O -14 0/0/2/0.0.0 0/0/2/0.0.0
Opt MP -1 0/7/1/0 0/6/1/0 E0:01.0
Opt MP -2 0/7/1/1 0/6/1/1 E0:01.1
Opt MP -3 0/7/2/0 0/6/2/0 E0:02.0
Table 1-5 Data Pathing - Part 3
PCI Slot
1 4/5 HWP0002 0x400 0x80-0xBF 4 4
2 3 HWP0002 0x300 0x60-0x7F 3 3
3 2 HWP0002 0x200 0x40-0x5F 2 2
4 6 HWP0002 0x600 0xC0-0xDF 6 5
Core I/O -1 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -2 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -3 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -4 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -5 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -6 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Core I/O -7 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -8 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -9 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Rope
Number
ACPI
HID
ACPI
UID
PCI Bus
Address
PCI Bus
Number
PCI Host
Controller
Number
Core I/O -10 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -11 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -12 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -13 1 HWP0002 0x100 0x20-0x3F 1 1
Core I/O -14 0 HWP0002 0x000 0x00-0x1F 0 0
Opt. MP -1 7 HWP0002 0x700 0xE0-0xFF N/A 7
Opt MP -2 7 HWP0002 0x700 0xE0-0xFF N/A 7
Opt MP -3 7 HWP0002 0x700 0xE0-0xFF N/A 7
30
Chapter 1
 Loading...
Loading...