Page 1

HP Integrity iLO 2 MP Operations Guide
HP Part Number: 5991-6005
Published: January 2008
Page 2

© Copyright 2008, Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Legal Notices
The informationcontained hereinis subjectto changewithout notice.The onlywarranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Intel, Pentium, Intel Inside, Itanium, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in
the United States and other countries.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Acrobat is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Java is a US trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Table of Contents
About This Document.......................................................................................................15
Intended Audience................................................................................................................................15
New and Changed Information in This Edition...................................................................................15
Publishing History................................................................................................................................15
Document Organization.......................................................................................................................16
Typographic Conventions.....................................................................................................................17
Related Information..............................................................................................................................17
Warranty Information...........................................................................................................................18
HP Encourages Your Comments..........................................................................................................18
1 Introduction to iLO 2 MP.............................................................................................19
Features.................................................................................................................................................19
Standard Features............................................................................................................................19
Always-on Capability.................................................................................................................20
Virtual Front Panel.....................................................................................................................20
Multiple Access Methods...........................................................................................................20
Security.......................................................................................................................................20
User Access Control...................................................................................................................20
Multiple Users............................................................................................................................20
IPMI over LAN...........................................................................................................................21
Firmware Upgrades...................................................................................................................21
Internal Subsystem Information................................................................................................21
DHCP and DNS Support...........................................................................................................21
HP SIM Group Actions..............................................................................................................21
SNMP.........................................................................................................................................22
SMASH.......................................................................................................................................22
SM CLP.......................................................................................................................................22
Mirrored Console.......................................................................................................................22
Remote Power Control...............................................................................................................22
Event Logging............................................................................................................................22
Advanced Features..........................................................................................................................22
Virtual Media.............................................................................................................................22
IRC..............................................................................................................................................22
Directory-Based Secure Authorization Using LDAP.................................................................22
LDAP Lite...................................................................................................................................23
Power Meter Readings...............................................................................................................23
HP Insight Power Manager........................................................................................................23
Advanced Pack License.........................................................................................................................23
Obtaining and Activating iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack Licensing.....................................................24
Supported Systems and Required Components and Cables................................................................24
iLO 2 MP Supported Browsers and Client Operating Systems............................................................24
Security.................................................................................................................................................25
Protecting SNMP Traffic..................................................................................................................26
Lights-Out Advanced/KVM Card........................................................................................................26
2 Ports and LEDs..............................................................................................................27
HP Integrity Server Blade Components...............................................................................................27
Onboard Administrator...................................................................................................................27
HP Integrity rx2660 Server Components..............................................................................................29
Table of Contents 3
Page 4

HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600 Server Components...........................................................................29
iLO 2 MP Status LEDs...........................................................................................................................30
iLO 2 MP Reset Button..........................................................................................................................31
Resetting Local User Accounts and Passwords to Default Values..................................................31
Console Serial Port and Auxiliary Serial Port.......................................................................................31
iLO 2 MP LAN Port...............................................................................................................................32
iLO 2 MP LAN LEDs.......................................................................................................................32
3 Setting Up and Connecting the Console...................................................................33
Setup Checklist......................................................................................................................................34
Setup Flowchart....................................................................................................................................35
Preparing to Set Up iLO 2 MP..............................................................................................................36
Determining the Physical iLO 2 MP Access Method......................................................................36
Determining the iLO 2 MP LAN Configuration Method................................................................36
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using DHCP and DNS.....................................................................37
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using ARP Ping................................................................................37
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using the Console Serial Port...........................................................39
Logging In to the iLO 2 MP..................................................................................................................40
Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP.....................................................................40
Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP Using the Onboard Administrator.........................41
Auto-Login.................................................................................................................................41
Initiating an Auto-Login Session..........................................................................................42
Terminating an Auto-Login Session.....................................................................................43
User Account Cleanup during IPF Blade Initialization........................................................43
Auto-Login Troubleshooting................................................................................................43
Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP Using the Console Serial Port.................................43
Connecting the SUV Cable to the Server Blade.........................................................................44
Additional Setup...................................................................................................................................46
Modifying User Accounts and Default Passwords.........................................................................46
Setting Up Security..........................................................................................................................47
Setting Security Access...............................................................................................................47
4 Accessing the Host Console........................................................................................49
Interacting with the iLO 2 MP Using the Web GUI..............................................................................49
Accessing Online Help....................................................................................................................50
Accessing the Host Console Using the TUI..........................................................................................50
Help System.....................................................................................................................................50
Accessing the Host Console Using vKVM (Integrated Remote Console)............................................51
Accessing the Host Console Using SMASH SM CLP...........................................................................51
Accessing iLO 2 MP Using Onboard Administrator............................................................................51
Accessing the Graphic Console Using VGA ........................................................................................51
5 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite........................................................53
Configuring DHCP...............................................................................................................................53
Configuring DNS..................................................................................................................................54
Configuring LDAP Extended Schema..................................................................................................55
Login Process Using Directory Services with Extended LDAP......................................................56
Configuring LDAP Lite Default Schema..............................................................................................56
Setting up Directory Security Groups.............................................................................................57
Login Process Using Directory Services Without Schema Extensions............................................58
6 Using iLO 2 MP............................................................................................................59
4 Table of Contents
Page 5

Text User Interface................................................................................................................................59
MP Command Interfaces.................................................................................................................59
MP Main Menu................................................................................................................................60
MP Main Menu Commands.......................................................................................................60
CO (Console): Leave the Main Menu and enter console mode.............................................61
VFP (Virtual Front Panel): Simulate the display panel.........................................................61
CM (Command Mode): Enter command mode.....................................................................61
SMCLP (Server Management Command Line Protocol): Switch to the SMASH SMCLP.....61
CL (Console Log): View the history of the console output...................................................61
SL (Show Logs): View events in the log history...................................................................61
HE (Help): Display help for the menu or command in the MP Main Menu........................63
X (Exit): Exit the iLO 2 MP....................................................................................................63
Command Menu..............................................................................................................................63
Command Line Interface Scripting.................................................................................................64
Expect Script Example................................................................................................................65
Command Menu Commands and Standard Command Line Scripting Syntax.............................66
BP: Reset BMC passwords..........................................................................................................67
BLADE: Display BLADE parameters.........................................................................................67
CA: Configure asynchronous local serial port............................................................................68
DATE: Display date.....................................................................................................................69
DC (Default Configuration): Reset all parameters to default configurations.............................69
DF: Display FRU information.....................................................................................................69
DI: Disconnect LAN, WEB, SSH or Console..............................................................................70
DNS: DNS settings......................................................................................................................70
FW: Upgrade the MP firmware...................................................................................................70
HE: Display help for menu or command in command menu interface.....................................70
ID: System information settings................................................................................................71
IT: Inactivity timeout settings...................................................................................................71
LC: LAN configuration usage.....................................................................................................72
LDAP: LDAP directory settings..................................................................................................72
LDAP: LDAP group administration......................................................................................74
LDAP: LDAP Lite...................................................................................................................74
LM: License management............................................................................................................74
LOC: Locator UID LED configuration........................................................................................74
LS: LAN status...........................................................................................................................74
PC: Power control access............................................................................................................75
PM: Power regulator mode.........................................................................................................75
PR: Power restore policy configuration......................................................................................76
PS: Power status.........................................................................................................................76
RB: Reset BMC............................................................................................................................76
RS: Reset system through the RST signal...................................................................................77
SA: Set access LAN/WEB/SSH/IPMI over LAN ports................................................................77
SNMP: Configure SNMP parameters..........................................................................................77
SO: Security option help.............................................................................................................78
SS: System Status.......................................................................................................................78
SYSREV: Firmware revisions......................................................................................................79
TC: System reset through INIT or TOC signal...........................................................................79
TE: Send a message to other mirroring terminals......................................................................79
UC: User Configuration (users, passwords, and so on).............................................................80
WHO: Display a list of iLO 2 MP connected users.......................................................................81
XD: iLO 2 MP Diagnostics or reset..............................................................................................81
Web GUI................................................................................................................................................82
System Status...................................................................................................................................82
Status Summary > General ........................................................................................................82
Table of Contents 5
Page 6

Status Summary > Active Users.................................................................................................83
Server Status > General..............................................................................................................84
Server Status > Identification.....................................................................................................85
System Event Log.......................................................................................................................86
Events....................................................................................................................................87
Integrated Remote Console (vKVM)...............................................................................................88
IRC Requirements and Usage....................................................................................................88
Limitations of the vKVM Mouse and Keyboard..................................................................89
Browsers and Client Operating Systems that Support vKVM.............................................89
vKVM-Supported Resolutions and Browser Configurations...............................................89
Accessing the IRC.......................................................................................................................90
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen.................................................................................92
Remote Serial Console.....................................................................................................................93
Virtual Serial Port.......................................................................................................................95
Virtual Media...................................................................................................................................95
Using iLO 2 MP Virtual Media Devices.....................................................................................96
Virtual CD/DVD....................................................................................................................97
Creating the iLO 2 MP Disk Image Files.............................................................................100
Virtual Floppy/USB Key......................................................................................................101
Virtual Media Applet Timeout...........................................................................................102
Supported Operating Systems and USB Support for vMedia.................................................102
Java Plug-in Version.................................................................................................................103
Client Operating System and Browser Support for vMedia....................................................103
Power Management.......................................................................................................................103
Power & Reset...........................................................................................................................103
Power Meter Readings.............................................................................................................105
Power Regulator.......................................................................................................................107
Administration...............................................................................................................................108
Firmware Upgrade...................................................................................................................109
Licensing...................................................................................................................................109
User Administration > Local Accounts....................................................................................111
Group Accounts.......................................................................................................................112
Access Settings..........................................................................................................................113
LAN..........................................................................................................................................113
Serial Page.................................................................................................................................114
Login Options Page..................................................................................................................115
Current LDAP Parameters.......................................................................................................116
Network Settings......................................................................................................................117
Network Settings > Standard...................................................................................................117
Domain Name Server...............................................................................................................118
SNMP Settings..........................................................................................................................119
BL c-Class.......................................................................................................................................121
Help...............................................................................................................................................122
SMASH Server Management Command Line Protocol.....................................................................123
SM CLP Features and Functionality Overview.............................................................................123
SM CLP Session........................................................................................................................124
Accessing the SM CLP Interface....................................................................................................124
Exiting the SM CLP Interface...................................................................................................124
Changing the iLO 2 Default Interface to SM CLP....................................................................124
Using the SM CLP Interface...........................................................................................................125
SM CLP Syntax..............................................................................................................................126
Command Line Terms..............................................................................................................126
Command Verbs.......................................................................................................................126
Command Targets....................................................................................................................127
Command Target Properties....................................................................................................127
6 Table of Contents
Page 7

Command Options...................................................................................................................128
Level Option........................................................................................................................128
Display Option....................................................................................................................128
Character Set, Delimiters, Special, and Reserved Characters..................................................129
System1 Target...............................................................................................................................130
Target: SYSTEM1......................................................................................................................130
System Reset Power Status and Power Control.............................................................................130
Resetting the System................................................................................................................130
Displaying Power Status..........................................................................................................131
Powering Off the System..........................................................................................................131
Powering On the System..........................................................................................................131
Map1 (iLO 2) Target.......................................................................................................................131
Target: map1.............................................................................................................................131
Map1 Example..........................................................................................................................132
Resetting the iLO 2 MP.............................................................................................................132
Text Console Services.....................................................................................................................132
Opening the MP Main Menu from SM CLP............................................................................132
Target: map1/textredirectsap1.............................................................................................132
Opening the System Console Interface from SM CLP.............................................................133
Target: system1/consoles1/textredirectsap1........................................................................133
Switching Between the System Console and the SM CLP.......................................................133
Starting a System Console Session......................................................................................134
Determining the Session Termination Character Sequence for the System Console.........134
Exiting the System Console Session and Returning to SM CLP.........................................134
Entering the MP Main Menu Interface From SM CLP.......................................................134
Exiting the MP Main Menu Session and Returning to SM CLP.........................................134
Firmware Revision Display and Upgrade.....................................................................................134
SM CLP Firmware Targets........................................................................................................134
Target: map1/swinstallsvc1.................................................................................................134
Target: map1/swinventory1................................................................................................135
Target: map1/swinventory1/swid#......................................................................................135
Displaying Firmware Revisions...............................................................................................135
Firmware Upgrade...................................................................................................................136
Remote Access Configuration.......................................................................................................136
Telnet SM CLP Targets.............................................................................................................136
Target: map1/telnetsvc1......................................................................................................137
Telnet Examples..................................................................................................................137
SSH...........................................................................................................................................137
Target: map1/sshsvc1................................................................................................................137
SSH Examples...........................................................................................................................138
Network Configuration.................................................................................................................138
SM CLP Network Targets, Properties, and Verbs....................................................................138
Target: map1/enetport1.......................................................................................................138
Target: map1/enetport1/lanendpt1.....................................................................................138
Target: map1/enetport1/lanendpt1/ipendpt1......................................................................139
Target: map1/dhcpendpt1...................................................................................................139
Target: map1/dnsendpt1.....................................................................................................140
Target: map1/enetport1/lanendpt1/ipendpt1/gateway1.....................................................140
Target: map1/dnsserver1, map1/dnsserver2, map1/dnsserver3.........................................140
Target: map1/settings1/dnssettings1...................................................................................141
SM CLP Network Command Examples...................................................................................141
vMedia......................................................................................................................................142
Target: map1/oemhp_vm1/cddr1........................................................................................142
SM CLP vMedia Use Cases.................................................................................................143
User Accounts Configuration........................................................................................................143
Table of Contents 7
Page 8

Target: map1/group1................................................................................................................143
Target: map1/group1/account#.................................................................................................143
User Account Examples...........................................................................................................144
LDAP Configuration......................................................................................................................144
Target: map1/settings1/oemhp_ldapsettings1..........................................................................144
LDAP Configuration Examples................................................................................................145
7 Installing and Configuring Directory Services .......................................................147
Directory Services...............................................................................................................................147
Features Supported by Directory Integration...............................................................................148
Directory Services Installation Prerequisites.................................................................................148
Installing Directory Services..........................................................................................................148
Schema Documentation.................................................................................................................149
Directory Services Support............................................................................................................149
eDirectory Installation Prerequisites.............................................................................................149
Required Schema Software............................................................................................................150
Schema Installer.............................................................................................................................150
Schema Preview Screen............................................................................................................150
Setup Screen.............................................................................................................................150
Results Screen...........................................................................................................................151
Management Snap-In Installer......................................................................................................152
Directory Services for Active Directory..............................................................................................152
Active Directory Installation Prerequisites....................................................................................152
Preparing Directory Services for Active Directory........................................................................153
Installing and Initializing Snap-Ins for Active Directory..............................................................154
Example: Creating and Configuring Directory Objects for Use with iLO 2 in Active Directory...154
Directory Services Objects.............................................................................................................158
Active Directory Snap-Ins........................................................................................................158
Managing HP Devices In a Role.........................................................................................158
Managing Users In a Role...................................................................................................159
Setting Login Restrictions.........................................................................................................160
Setting Time Restrictions....................................................................................................160
Defining Client IP Address or DNS Name Access.............................................................161
Setting User or Group Role Rights................................................................................................162
Directory Services for eDirectory........................................................................................................163
Installing and Initializing Snap-In for eDirectory.........................................................................163
Example: Creating and Configuring Directory Objects for Use with iLO 2 MP Devices in
eDirectory......................................................................................................................................163
Creating Objects.......................................................................................................................163
Creating Roles..........................................................................................................................164
Directory Services Objects for eDirectory......................................................................................166
Adding Role Managed Devices................................................................................................166
Adding Members......................................................................................................................166
Setting Role Restrictions................................................................................................................167
Setting Time Restrictions...............................................................................................................168
Defining Client IP Address or DNS Name Access...................................................................168
Setting Lights-Out Management Device Rights............................................................................168
Installing Snap-Ins and Extending Schema for eDirectory on a Linux Platform..........................169
Installing the Java Runtime Environment................................................................................169
Installing Snap-Ins....................................................................................................................170
Extending Schema....................................................................................................................170
Verifying Snap-In Installation and Schema Extension.............................................................171
Using the LDAP Command to Configure Directory Settings in the iLO 2 MP.............................171
User Login Using Directory Services..................................................................................................172
8 Table of Contents
Page 9

Certificate Services..............................................................................................................................173
Installing Certificate Services........................................................................................................173
Verifying Directory Services..........................................................................................................173
Configuring an Automatic Certificate Request.............................................................................173
Directory-Enabled Remote Management...........................................................................................173
Using Existing Groups...................................................................................................................174
Using Multiple Roles.....................................................................................................................174
Creating Roles that Follow Organizational Structure...................................................................175
Restricting Roles............................................................................................................................175
Role Time Restrictions..............................................................................................................175
IP Address Range Restrictions.................................................................................................176
IP Address and Subnet Mask Restrictions...............................................................................176
DNS-Based Restrictions............................................................................................................176
Role Address Restrictions........................................................................................................176
How Directory Login Restrictions Are Enforced..........................................................................176
How User Time Restrictions Are Enforced...................................................................................177
User Address Restrictions.............................................................................................................178
Creating Multiple Restrictions and Roles......................................................................................178
Directory Services Schema (LDAP)....................................................................................................179
HP Management Core LDAP Object Identifier Classes and Attributes........................................179
Core Classes..............................................................................................................................180
Core Attributes.........................................................................................................................180
Core Class Definitions..............................................................................................................180
hpqTarget............................................................................................................................180
hpqRole...............................................................................................................................181
hpqPolicy.............................................................................................................................181
Core Attribute Definitions........................................................................................................181
hpqPolicyDN.......................................................................................................................181
hpqRoleMembership...........................................................................................................181
hpqTargetMembership........................................................................................................182
hpqRoleIPRestrictionDefault..............................................................................................182
hpqRoleIPRestrictions.........................................................................................................182
hpqRoleTimeRestriction.....................................................................................................182
iLO 2 MP-Specific LDAP OID Classes and Attributes..................................................................183
iLO 2 MP Classes......................................................................................................................183
iLO 2 MP Attributes.................................................................................................................183
iLO 2 MP Class Definitions......................................................................................................183
hpqLOMv100......................................................................................................................183
iLO 2 MP Attribute Definitions................................................................................................184
hpqLOMRightLogin............................................................................................................184
hpqLOMRightRemoteConsole............................................................................................184
hpqLOMRightRemoteConsole............................................................................................184
hpqLOMRightServerReset..................................................................................................184
hpqLOMRightLocalUserAdmin.........................................................................................185
hpqLOMRightConfigureSettings........................................................................................185
Glossary.........................................................................................................................187
Index...............................................................................................................................195
Table of Contents 9
Page 10

10
Page 11

List of Figures
2-1 OA/iLO Network Port and Components......................................................................................28
2-2 Onboard Administrator LEDs and Buttons..................................................................................28
2-3 HP Integrity rx2660 Server Rear View..........................................................................................29
2-4 HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600 Server Rear Ports and LEDs.......................................................30
2-5 Console Serial Port (RS-232) Connector........................................................................................31
2-6 iLO 2 MP LAN Port.......................................................................................................................32
3-1 Setup Flowchart.............................................................................................................................35
3-2 SUV Cable......................................................................................................................................45
3-3 Connecting the SUV Cable to the Server Blade.............................................................................46
4-1 Web Login Page.............................................................................................................................49
4-2 Status Summary Page....................................................................................................................50
6-1 MP Command Interfaces...............................................................................................................60
6-2 Status Summary General Page......................................................................................................83
6-3 Status Summary Active Users Page..............................................................................................84
6-4 Server Status General Page............................................................................................................85
6-5 Server Status Identification Page...................................................................................................86
6-6 System Event Log Page.................................................................................................................87
6-7 Integrated Remote Console Page..................................................................................................91
6-8 Integrated Remote Console Window............................................................................................92
6-9 Remote Serial Console Page..........................................................................................................93
6-10 Remote Serial Console Window....................................................................................................94
6-11 Virtual Media Page........................................................................................................................96
6-12 Virtual Media Dialog Box (Before Connection)............................................................................98
6-13 Virtual Media Dialog Box (after connection)................................................................................99
6-14 Local Image File Dialog Box........................................................................................................100
6-15 Create Media Image Dialog Box..................................................................................................101
6-16 Virtual Floppy/USB Key..............................................................................................................102
6-17 Power & Reset Page.....................................................................................................................104
6-18 Power Meter Readings Page........................................................................................................106
6-19 Power Regulator Page..................................................................................................................107
6-20 Licensing Page.............................................................................................................................110
6-21 Local Accounts Page....................................................................................................................111
6-22 Group Accounts Page..................................................................................................................112
6-23 LAN Page.....................................................................................................................................113
6-24 Serial Page....................................................................................................................................114
6-25 Login Options Page.....................................................................................................................115
6-26 Current LDAP Parameters Page..................................................................................................116
6-27 Standard Page..............................................................................................................................118
6-28 Domain Name Server Page..........................................................................................................119
6-29 SNMP Settings Page....................................................................................................................120
6-30 Onboard Administrator...............................................................................................................121
6-31 Help Page.....................................................................................................................................123
7-1 Schema Preview Screen...............................................................................................................150
7-2 Schema Setup Screen...................................................................................................................151
7-3 Schema Results Screen.................................................................................................................152
7-4 Directory Example.......................................................................................................................155
7-5 Create New HP Management Object Dialog Box........................................................................156
7-6 Select Users Dialog Box...............................................................................................................157
7-7 Lights-Out Management Tab.......................................................................................................157
7-8 HP Devices Tab............................................................................................................................159
7-9 Members Tab...............................................................................................................................159
7-10 Role Restrictions Tab...................................................................................................................160
11
Page 12

7-11 Logon Hours Screen....................................................................................................................161
7-12 New IP/Mask Dialog Box............................................................................................................161
7-13 Lights Out Management Tab.......................................................................................................162
7-14 Roles and Devices Example.........................................................................................................163
7-15 Select Object Subtype Dialog Box................................................................................................164
7-16 Setting Role Rights.......................................................................................................................165
7-17 Role Managed Devices Subtab....................................................................................................166
7-18 Members Tab (eDirectory)...........................................................................................................167
7-19 Role Restrictions Subtab (eDirectory)..........................................................................................167
7-20 Add New Restriction Dialog Box................................................................................................168
7-21 Lights-Out Management Device Rights Tab...............................................................................169
7-22 Admin User Gaining Admin Role Right, Example 1..................................................................175
7-23 Admin User Gaining Admin Role Right, Example 2..................................................................175
7-24 User and Role Access Restrictions...............................................................................................177
7-25 User Time Restrictions.................................................................................................................178
7-26 Restricting General Use...............................................................................................................179
7-27 Restricting the Reset Role............................................................................................................179
12 List of Figures
Page 13

List of Tables
1 Publishing History Details............................................................................................................16
1-1 Supported Systems and Required Components Matrix...............................................................24
1-2 iLO 2 MP Supported Browsers and Client Operating Systems....................................................25
2-1 iLO 2 MP Status LEDs...................................................................................................................30
2-2 Console Serial Port Pinouts...........................................................................................................31
2-3 iLO 2 MP LAN Port Pinouts..........................................................................................................32
2-4 iLO 2 MP LAN Link Status LEDs..................................................................................................32
2-5 iLO 2 MP LAN Link Speed LEDs..................................................................................................32
3-1 Setup Checklist..............................................................................................................................34
3-2 Physical Connection Matrix..........................................................................................................36
3-3 LAN Configuration Methods........................................................................................................36
3-4 ARP Ping Commands....................................................................................................................38
6-1 MP Command Interfaces...............................................................................................................59
6-2 MP Main Menu Commands..........................................................................................................60
6-3 Events............................................................................................................................................62
6-4 Alert Levels....................................................................................................................................62
6-5 Command Menu Commands........................................................................................................63
6-6 Status Summary General Page Description..................................................................................83
6-7 Active Users Page Description......................................................................................................84
6-8 Server Status General Page Description........................................................................................85
6-9 Server Status Identification Page Description...............................................................................86
6-10 System Event Log Page Description..............................................................................................87
6-11 IRC Page Description.....................................................................................................................91
6-12 IRC Window Description..............................................................................................................92
6-13 Operating System Support for vMedia.......................................................................................103
6-14 Client Operating System and Browser Support for vMedia.......................................................103
6-15 Power & Reset Page Description.................................................................................................104
6-16 Power Meter Readings Page Description....................................................................................106
6-17 Power Regulator Page Description..............................................................................................108
6-18 Licensing Page Description.........................................................................................................110
6-19 Local Accounts Page Description................................................................................................112
6-20 Group Accounts Page Description..............................................................................................113
6-21 LAN Page Description.................................................................................................................114
6-22 Serial Page Description................................................................................................................115
6-23 Login Options Page Description..................................................................................................115
6-24 Current LDAP Parameters Page Description..............................................................................117
6-25 Standard Page Description..........................................................................................................118
6-26 DNS Page Description.................................................................................................................119
6-27 SNMP Settings Page Description.................................................................................................120
6-28 Onboard Administrator Page Description..................................................................................121
6-29 Supported Command Verbs........................................................................................................126
6-30 Command Options......................................................................................................................129
6-31 SM CLP Reserved Characters and Character Sequences............................................................129
6-32 system1 Properties.......................................................................................................................130
6-33 map1 Properties...........................................................................................................................131
6-34 /map1/textredirectsap1 Properties..............................................................................................133
6-35 /system1/consoles1/textredirectsap1 Properties..........................................................................133
6-36 swinstallsvc1 Properties..............................................................................................................134
6-37 swinventory1 Properties..............................................................................................................135
6-38 swid# Properties..........................................................................................................................135
6-39 telnetsvc1 Properties....................................................................................................................137
6-40 sshsvc1 Properties........................................................................................................................137
13
Page 14

6-41 enetport1 Properties....................................................................................................................138
6-42 lanedpt1 Properties......................................................................................................................138
6-43 ipendpt1 Properties.....................................................................................................................139
6-44 dhcpendpt1 Properties................................................................................................................139
6-45 dnsendpt1 Properties...................................................................................................................140
6-46 gateway1 Properties....................................................................................................................140
6-47 dnsserver1, dnsserver2, dnsserver3 Properties...........................................................................140
6-48 dnssettings1 Properties................................................................................................................141
6-49 cddr1 Properties..........................................................................................................................142
6-50 group1 Properties........................................................................................................................143
6-51 account# Properties.....................................................................................................................143
6-52 oemhp_ldapsettings1 Properties.................................................................................................145
7-1 Lights Out Management Rights..................................................................................................162
7-2 Management Device Rights.........................................................................................................169
7-3 Core Classes.................................................................................................................................180
7-4 Core Attributes............................................................................................................................180
7-5 hpqTarget.....................................................................................................................................180
7-6 hpqRole........................................................................................................................................181
7-7 hpqPolicy.....................................................................................................................................181
7-8 hpqPolicyDN...............................................................................................................................181
7-9 hpqRoleMembership...................................................................................................................181
7-10 hpqTargetMembership................................................................................................................182
7-11 hpqRoleIPRestrictionDefault.......................................................................................................182
7-12 hpqRoleIPRestrictions.................................................................................................................182
7-13 hpqRoleTimeRestriction..............................................................................................................182
7-14 iLO 2 MP Classes.........................................................................................................................183
7-15 iLO 2 MP Attributes....................................................................................................................183
7-16 hpqLOMv100...............................................................................................................................183
7-17 hpqLOMRightLogin....................................................................................................................184
7-18 hpqLOMRightRemoteConsole....................................................................................................184
7-19 hpqLOMRightRemoteConsole....................................................................................................184
7-20 hpqLOMRightServerReset...........................................................................................................184
7-21 hpqLOMRightLocalUserAdmin..................................................................................................185
7-22 hpqLOMRightConfigureSettings................................................................................................185
14 List of Tables
Page 15

About This Document
This document provides information and instructions on how to use the HP Integrated Lights
Out 2 Management Processor (iLO 2 MP) for Integrity.
The document printing date and part number indicate the document’s current edition. The
printing date changes when a new edition is printed. Minor changes may be made at reprint
without changingthe printing date. The document part number changes when extensive changes
are made.
Document updatesmay be issued betweeneditions to correct errors or document product changes.
To ensure that you receive the updated or new editions, subscribe to the appropriate product
support service. See your HP sales representative for details.
The latest version of this document can be found on the HP website
at:http://www.docs.hp.com
Intended Audience
This document provides technical product and support information for authorized service
providers, system administrators, and HP support personnel.
New and Changed Information in This Edition
The following information available for BL870c, BL860c, rx2660, rx3600, and rx6600 servers was
added to this guide:
• vMedia - virtual floppy/USB key capability, see “Virtual Floppy/USB Key” (page 101)
This document is also a reference for the following HP Integrity servers with Integrity iLO:
• rx7640
• rx8640
• Superdome sx2000
Publishing History
The publishing history below identifies the edition dates of this manual. Updates are made to
this publication on an unscheduled, as needed, basis. The updates consist of a complete replacement
manual and pertinent online or CD documentation.
Intended Audience 15
Page 16
Table 1 Publishing History Details
Manufacturing
Part Number
Publication DateSupported ServersOperating Systems SupportedDocument
5991–6005
5991-5992
5991-5983
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3 1H1
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3 1H1
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
BL860c
rx2660
rx3600
rx6600
1
rx7640
1
rx8640
Superdome sx2000
rx2660
rx3600
rx6600
1
rx7640
1
rx8640
Superdome sx2000
rx2660
rx3600
rx6600
January 2008BL870c
1
November 2007BL860c
1
June 2007BL860c
AD217-9001A
AB419-9006A
5971-4292
1 All of the iLO 2 functionality is not currently available on this server.
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
HP-UX 11i v2
OpenVMS 8.3
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Red Hat Linux and SuSE
Document Organization
This guide is divided into the following chapters.
Chapter 1 Introduction Use this chapter to learn about the iLO 2 MP functionality.
Chapter 2 Ports and LEDs Use this chapter to learn about ports and LEDs.
Chapter 3 Setting Up and Connecting the Console Use this chapter to set up and connect the
console.
Chapter 4 Accessing the Host Console Use this chapter to learn how to access the host console
of an HP Integrity server through the iLO 2 MP.
February 2007BL860c
rx2660
rx3600
rx6600
December 2006rx2660
rx3600
rx6600
September 2006rx3600
rx6600
16
Page 17

Chapter 5 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite Use this chapter to configure
DHCP, DNS, LDAP extended schema, and LDAP Lite default schema.
Chapter 6 Using the iLO 2 MP This chapter provides information on the different interfaces
you can use to interact with the iLO 2 MP such as text user interface, web GUI,
and SMASH SM CLP.
Chapter 7 Installing and Configuring Directory Services Use this chapter to learn about
installing and configuring directory services functions.
Glossary Use the glossary to learn iLO 2 MP terms and definitions.
Typographic Conventions
This document uses the following conventions.
WARNING! A warning lists requirements that you must meet to avoid personal injury.
CAUTION: A caution provides information required to avoid losing data or avoid losing system
functionality.
IMPORTANT: Important messages provide essential information to explain a concept or to
complete a task.
NOTE: A note highlights useful information such as restrictions,recommendations, or important
details about HP product features.
TIP: Tips provide you with helpful hints for completing a task. A tip is not used to give essential
information, but can be used to provide an alternate method for completing the task that precedes
it.
Command
Computer
Output
Ctrl+X A key sequence. A sequence such as Ctrl-X indicates that you must hold
Key The name of a keyboard key. Return and Enter both refer to the same key.
User Input
[ ] The contents are optional in formats and command descriptions. If the
{ } The contents are required in formats and command descriptions. If the
... The preceding element can be repeated an arbitrary number of times.
| Separates items in a list of choices.
A command name or qualified command phrase.
Text displayed by the computer.
down the key labeled Ctrl while you press another key or mouse button.
Commands and other text that you enter.
contents are a list separated by a pipe (|), you must select one of the items.
contents are a list separated by a pipe (|), you must select one of the items.
Related Information
You can find other information on HP server hardware management, Microsoft® Windows®,
and diagnostic support tools in the following publications.
HP Technical Documentation Website
http://www.docs.hp.com
Server Hardware Information
http://docs.hp.com/HP-UX/hw/
Typographic Conventions 17
Page 18

Windows Operating System Information
Find information about administration of the Microsoft Windows operating system at the
following websites
• http://www.docs.hp.com/windows_nt/
• http://www.microsoft.com/technet/
Diagnostics and Event Monitoring: Hardware Support Tools
Complete informationabout HP hardware support tools, including online and offline diagnostics
and event monitoring tools, is at:
http://www.docs.hp.com/HP-UX/diag/
Website for HP Technical Support
http://us-support2.external.hp.com/
Books about HP-UX Published by Prentice Hall
The HP Books website lists the HP books that Prentice Hall currently publishes, including the
following:
• HP-UX 11i System Administration Handbook
http://www.hp.com/hpbooks/prentice/ptr_0130600814.html
• HP-UX Virtual Partitions
http://www.hp.com/hpbooks/prentice/ptr_0130352128.html
HP Books are available worldwide through bookstores, online booksellers, and office and
computer stores.
Warranty Information
The latest versions of the BCS Global Limited Warranty and Technical Support documentation is
posted on the HP website in the Enterprise Servers, Workstations, and System Hardware collection
under each server to which it applies, at: http://www.docs.hp.com.
HP Encourages Your Comments
HP encourages your comments concerning this document. We are truly committed to providing
documentation that meets your needs.
Send comments to:
netinfo_feedback@cup.hp.com
Include title, manufacturing part number, and any comments, errors found, or suggestions for
improvement you have concerning this document. Also, please include what we did right so we
can incorporate it into other documents.
18
Page 19

1 Introduction to iLO 2 MP
The Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor (iLO MP) for entry class Integrity servers is
an autonomous management subsystem embedded directly on the server. It is the foundation
of the server’s High Availability (HA) embedded server and fault management. It also provides
system administrators secure remote management capabilities regardless of server status or
location. The iLO MP is available whenever the system is connected to a power source, even if
the server main power switch is in the off position.
HP has used several different names to describe the management functionality embedded in
servers, including “the management processor.” In addition, HP uses the term “management
processor” to refer to any embedded microprocessor that manages a system. Management
processor is a descriptive term (such as “server”), and iLO is a brand name or label (such as
“Integrity”).
Remote access is the key to maximizing efficiency of administration and troubleshooting for
enterprise servers. Integrity servers are designed so all administrative functions that can be
performed locally, can also be performed remotely. iLO enables remote access to the operating
system console, control over the server’s power and hardware reset functionality, and works
with the server to enable remote network booting through a variety of methods.
iLO 2 is an Integrated Lights Out 2 Management Processor (iLO 2 MP) with the latest advanced
digital video redirection technology. This new feature gives you a higher performance graphics
console redirection experience than with the previous iLO.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Features” (page 19)
• “Advanced Pack License” (page 23)
• “Supported Systems and Required Components and Cables” (page 24)
• “iLO 2 MP Supported Browsers and Client Operating Systems” (page 24)
• “Security” (page 25)
Features
iLO 2 MP functionality includes the following:
• Control of power, reset, and Transfer of Control (TOC) capabilities
• Console access
• Display and recording of system events
• Display of detailed information about the various internal subsystems and field replaceable
units (FRUs)
• A virtual front panel to monitor system status and see the state of front panel LEDs
The iLO 2 MP is completely independent of the host system and the operating system. It has its
own microprocessor and runs its own firmware. The operating system cannot send packets out
on the iLO 2 MP LAN, and packets on the iLO 2 MP LAN cannot go to the operating system.
The iLO 2 MP LAN is exclusive tothe iLO 2 MP and isdriven byan embedded realtime operating
system (RTOS) running on the iLO 2 MP.
The iLO 2 MP offers the following standard and advanced features.
Standard Features
The iLO 2 MP standard features provide the following basic system board management functions,
diagnostics, and essential Lights-Out functionality on iLO 2-supported HP servers:
Features 19
Page 20

Always-on Capability
The iLO 2 MP is active and available through the iLO 2 MP LAN connection and the local serial
port connection as long as the power cord is plugged in. In the event of a complete power failure,
the iLO 2 MP data is protected by an onboard battery backup.
Virtual Front Panel
The virtual front panel (VFP) presents a summary of the system front panel using direct console
addressing.
Multiple Access Methods
The available methods to access the iLO 2 MP are as follows:
IPMI/LAN Through the iLO 2 MP MAC address
LAN Using telnet, web, or SSH to access the iLO 2 MP LAN
Local Serial Port Using a terminal or laptop computer for direct connection
Web Using a GUI
Security
The iLO 2 MP provides strong security for remote management in IT environments, such as the
following:
• User-defined TCP/IP ports
• User accounts and access management
• Lightweight DirectoryAccess Protocol- (LDAP) based directory services authenticationand
authorization
• Encrypted communication using SSL and SSH
User Access Control
The iLO 2 MP is restricted by user accounts. User accounts are password protected and are
assigned access rights that define a specific level of access to the server and to the iLO 2 MP
commands. The iLO 2 MP supports both LDAP directory user authentication and locally stored
iLO 2 MP user accounts. iLO 2 MP users can have any of the following access rights:
Console Access Right to access the system console (the host operating
Power Control Access Right to power on, power off, or reset the server, and the
Local User Administration Access Right to configure locally stored user accounts.
iLO 2 MP Configuration Access Right to configure all iLO 2 MP settings and some system
Virtual Media Access Enables Advanced Pack license users the right to use the
Multiple Users
Multiple users can interact with the iLO 2 MP. However, iLO 2 MP command mode and console
mode are mirrored, allowing only one user at a time to have write access to the shared console.
When a command is completed, write access is released and any user can initiate another
command.
system). This does not bypass host authentication
requirements, if any.
right to configure the power restore policy.
settings, such as the power restore policy.
virtual media applet.
20 Introduction to iLO 2 MP
Page 21

IMPORTANT: Although the iLO 2 MP can support multiple simultaneous connections, to do
so can impact performance. HP does not recommend running more than eight simultaneous
connections.
The iLO 2 MP supports the following connections simultaneously:
• Four web (each web connection can have a remote serial console connection as well and not
be counted as part of the total number of connections allowed)
• Eight SSH
• One local console serial port (RS-232)
• Four IPMI over LAN
• Four telnet
• One Integrated Remote Console (IRC)
• One vMedia
IPMI over LAN
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) option provides direct access from the
iLO 2 MP LAN port to the server Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) monitoring and
controlling functions such as temperature, voltage, fans, and power supplies. IPMI defines a
common interface for platform management hardware. With IPMI over LAN enabled, BMC
functions are available to other management software applications. The iLO 2 MP supports up
to four simultaneous IPMI over LAN connections.
Firmware Upgrades
Firmware upgrades enhance the functionality of the iLO 2 MP.
The MP firmware is packaged along with system, BMC, and FPGA/PSOC firmware. You can
download and upgrade the firmware package from the HP website at:
http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport.
Internal Subsystem Information
The iLO 2 MP displays information about the following internal subsystems:
• FRU information
• System power state and fan status
• Processor Status
DHCP and DNS Support
The iLO 2 MP supports the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and the Domain
Name System (DNS) configuration options for acquiring network information through the iLO
2 MP LAN port. When the iLO 2 MP starts, it acquires the port configuration stored on a DHCP
server to assign an IP address to the iLO 2 MP LAN port. If DNS is configured, this information
is updated on the DNS server. The simplest method to initially connect to the iLO 2 MP is with
the default DNS name found on the toe-tag on the server, for example, mp0014c29c064f.
HP SIM Group Actions
HP SystemsInsight Manager (HP SIM) is a system-level management tool that supports executing
commands from HP SIM using the SSH interface. HP SIM enables you to perform similar
management activities across multiple iLO 2s (group actions) without requiring you to access
each iLO 2 MP individually. Group actions can be taken regardless of the server power state.
Fore more information about HP SIM, see:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim.
For the user guide, see the Information Library.
Features 21
Page 22

SNMP
The SNMP is part of the TCP/IP protocol suit developed to manage servers on an IP network.
SNMP enables you to manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan
for network growth.
SMASH
Server Management Architecture for Server Hardware(SMASH) is an initiative by the Distributed
Management Task Force (DMTF) that encompasses specifications (Server Management CLP, SM
ME Addressing, SM Profiles) that address the interoperable manageability requirements of small
to large scale heterogeneous computer environments.
SM CLP
The SM CLP specification defines a user friendly command-line protocol that provides command
line interface (CLI) standards for interoperability.
Mirrored Console
The system console output stream is reflected to all connected console users, and any user can
provide input.
Remote Power Control
The iLO 2 MP enables remote power cycle, power on and power off, and TOC. It also provides
options to reset the system, the BMC, or iLO 2 MP.
Event Logging
The iLO 2 MP provides event logging, display, and keyword search of console history and system
events.
Advanced Features
The iLO 2 MP advanced features provide additional functionality such as the graphical integrated
remote console and virtual media. In addition, the advanced features increase security by
integrating iLO 2 MP user administration with the Active Directory or eDirectory.
The advanced features require the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license. See “Advanced Pack License”
(page 23).
NOTE: A HP ProLiant iLO 2 Advanced Pack license key will not work on an HP Integrity
server, and vice versa.
iLO 2 MP advanced features include the iLO 2 MP standard features and the following features:
Virtual Media
Virtual Media (vMedia) enables connection of client-based USB CD and DVD devices and disk
image files as virtual devices on the server, and requires the vMedia right and the Java plug-in
version 1.4.2_10 and above.
IRC
The IRC provides a remote console on Windows clients running the Internet Explorer browser
to HP Integrity-based Windows servers. It combines virtual keyboard, video, and mouse (vKVM).
Directory-Based Secure Authorization Using LDAP
The directory-based authentication and authorization option enables iLO 2 MP user accounts to
be defined in a centralized database on an LDAP server. iLO 2 MP users are authenticated when
22 Introduction to iLO 2 MP
Page 23

logging in to the iLO 2 MP and authorization is given each time an iLO 2 MP command runs.
This provides a centralized database (LDAP server) of all user accounts and avoids the overhead
of creating users in each iLO 2 MP.
Directory authenticationoccurs by enabling Extended Schema or Default Schema. When Extended
Schema is used, the schema in the directory server must be extended. When Default Schema is
selected, schema extension is not needed.
LDAP Lite
LDAP Lite enables you to use directory authentication to log in to the iLO 2 MP without having
to do any schema extension on the directory server or snap-in installation on the client. In addition
to general directory integration benefits, iLO 2 MP schema-free integration provides the following:
• Minimal maintenance and administration
• Reliable security
• Complements two-factor authentication
Not extending the schema on the directory server means the directory server does not know
anything about the iLO 2 MP object or privileges, and the only thing the iLO 2 MP queries from
the directory server is to authenticate the user name and password.
Power Meter Readings
The power meter readings feature enables you to graphically view and monitor server power
usage, temperature, and power regulator settings.
HP Insight Power Manager
HP Insight Power Manager (HP IPM), a plug-in to HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM), is an
integrated power monitoring and management application that provides centralized control of
server power consumption and thermal output. It extends the unified infrastructure management
framework of HP SIM by providing new energy levers into the server.
Leveraging HP power regulator technology, HP IPM makes policy-based power and thermal
management possible by enabling you to view and modify the power efficiency regulator mode
of the system. It expands the capacity of data centers by reducing the amount of power and
cooling required for supported Integrity servers and the server blades.
Information on HP IPM is available at:
http://www.hp.com/go/ipm
Advanced Pack License
The iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license features sophisticated virtual administration and security
features for ultimate control of servers in data centers and remote sites. With an iLO 2 MP
Advanced Pack license key, you can activate powerful remote management features to install,
configure, monitor, update, and troubleshoot remote HP servers anywhere, anytime from a
standard web browser, command line or script.
Advanced Pack License 23
Page 24
IMPORTANT: On HP Integrity server blades, the AdvancedPack license is standard. Remember
to save the Advanced Pack license key information that was provided by HP. If you ever need
to replace your server blade under warranty, you will need to transfer the key by typing the code
on the replacement server blade.
NOTE: A HP ProLiant iLO 2 Advanced Pack license key will not work on an HP Integrity
server, and vice versa.
Obtaining and Activating iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack Licensing
A free 30-day evaluation license is available for download on the HP website. The evaluation
license activates and accesses iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack features. You can only install one
evaluation license per iLO 2 MP. After the evaluation period, an iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license
is required to continue using the advanced features. The iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license features
automatically deactivate when the evaluation license key expires.
Systems that do not have VGA support all other Advanced Pack license features.
For more information, see the HP website at:
http://h71028.www7.hp.com/enterprise/cache/279991-0-0-0-121.html
Follow the factory-install or manual install instructions located on the Integrated Lights-Out
Advanced Pack for HP Integrity Servers; Certificate of License to Use; License Installation Card to activate
your license.
Supported Systems and Required Components and Cables
Table 1-1 lists the systems on which the iLO 2 MP is supported and the components and cables
that are required to operate the iLO 2 MP.
Table 1-1 Supported Systems and Required Components Matrix
Required ComponentsSupported
Systems
BL860c
rx2660
board
rx6600
(This is only supported on Windows OS.)
See your server documentation.rx7640,
rx8640,
Superdome
sx2000
1 Cables are not provided with the server.
SUV or DB-9 cableFront console serial port (RS-232)
LAN cableRear OA/iLO network port
LAN, serial, and VGA cablesiLO 2 MP hardware is integrated into the system
LAN and serial cablesCore I/O board without VGA; factory installedrx3600,
LAN, serial, and VGA cablesCore I/O board with VGA (optional)
Required Cables
1
iLO 2 MP Supported Browsers and Client Operating Systems
The iLO 2 MP has an independent microprocessor. This architecture ensures that the majority
of iLO 2 MP functionality is available regardless of the host operating system.
Table 1-2 lists the client operating systems and browsers that are supported on iLO 2 MP:
24 Introduction to iLO 2 MP
Page 25
Table 1-2 iLO 2 MP Supported Browsers and Client Operating Systems
Client Operating SystemBrowsers
OpenVMSLinuxWindowsHP-UXJava Plug-in 1.5.0_08
11i
23/11.31
WS 2003
Enterprise
XXInternet Explorer 6.0
Red Hat
EnterpriseXP
XXXXXFirefox 2.0.0.4
Related Links
• Java for HP-UX
— http://www.hp.com/products1/unix/java/versions/index.html
— http://www.hp.com/products1/unix/java/archives/index.html
• Java for OpenVMS
— http://h18012.www1.hp.com/java/alpha
• Firefox for HP-UX
— http://www.hp.com/products1/unix/java/firefox/index.html
Note: 1.5.0.00 needs patch
— http://www.hp.com/go/firefox
• Firefox for Linux
— http://linuxcoe.corp.hp.com
• Firefox for Windows and Linux
— http://www.mozilla.com/firefox
• Browser Support 1.5.0
— http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/system-configurations.html
• Operating Systems for Montvale
— http://psweb1.cup.hp.com/~projects/sisl_prgm_mgmt/mvx%20(Low-end%20Montvale)/mvx%20info.htm
8.3SuSE
XHP Secure Web Browser 1.7.13
Security
It is important to have strong security surrounding the iLO 2 MP device. HP security requirements
of the enterprise and architected the iLO 2 MP include the following:
Authentication iLO 2 MP incorporates authentication techniques with the use of 128-bit
Authorization Using local accounts, iLO 2 MP enables you to define up to 19 separate
Integrity iLO 2 MP incorporates a trusted Java™ applet for vMedia.
Privacy iLO 2MP uses SSL for web connections, RSL-RC4 encryption for integrated
Login After initial failed login attempts (default three), a delay of approximately
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption. It is password based for web and
password- and key-based for secure shell (SSH).
users and to vary the server access rights of each user. The directory
services capabilities of iLO 2 MP enables you to maintain network user
accounts and security policies in a central, scalable database that supports
thousands of users, devices, and management roles.
remote console and remote serial console, and SSH-DES3/DES128 2.0
recommended encryption algorithms for SSH-based connections. You
can enable or disable telnet, IPMI over LAN, web, and SSH connectivity.
one second is imposed on the serial connection and the login banner
warnings are repeated. All other connection types are disconnected.
Security 25
Page 26

Because iLO 2 MP devices are completely autonomous and can be used to control the server,
treat them the same as other servers. For example, include the iLO 2 MP devices in the security
and network audits.
IMPORTANT: Ensure that physical access to the server is limited. Anyone can clear passwords
by pressing the power button for longer than four seconds.
Protecting SNMP Traffic
Because SNMP uses passwords, known as community strings, that are sent across the network
in clear text, you must enhance the network security when using SNMP traffic. To enhance
network security, do the following:
• Reset the community strings (read only) with the same frequency and according to the same
guidelines as the administrative passwords. For example, select alphanumeric strings with
at least one uppercase letter, one numeral, and one symbol.
• Set firewalls or routers to accept only specific source and destination addresses. For example,
you can allow inbound SNMP traffic into the host server only if it comes from one of the
predetermined management workstations.
TIP: Telnet sends data without encryption and is not a secure connection. HP recommends
using SSH instead of telnet because SSH uses encryption.
To enable and disable telnet access, use the SA command.
Lights-Out Advanced/KVM Card
The Lights-Out Advanced/KVM card (LOA) is a PCI-X card that you install into any sx2000-based
mid-range or high-end HP Integrity server.
The LOA card enables the Lights-Out Advanced vKVM and vMedia features of the iLO 2 MP
for the rx7640, rx8640, and Superdome sx2000 servers.
The LOA card is also a KVM card that offers physical video functionality for servers running
Windows, and USB functionality for servers running HP-UX, Windows, and OpenVMS.
All Lights-Out Advanced features are fully enabled on the LOA card--there is no additional
advanced pack license to purchase. At present, vKVM is only available for servers running
Windows and vMedia is available for servers running HP-UX, Windows, and OpenVMS.
The LOA card is not currently supported under Linux.
The Lights-Out Advanced features are accessed through the iLO 2 web interface.
26 Introduction to iLO 2 MP
Page 27

2 Ports and LEDs
All iLO 2 MP functions are available through the server iLO 2 MP LAN port and the local and
remote serial ports. On HP Integrity server blades, all iLO 2 MP functions are available on the
Onboard Administrator. This chapter describes the available iLO 2 MP ports, connectors, and
LEDs on the HP Integrity server blades, and the rx2660, rx3600, and rx6600 servers.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “HP Integrity Server Blade Components” (page 27)
• “HP Integrity rx2660 Server Components” (page 29)
• “HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600 Server Components” (page 29)
• “iLO 2 MP Reset Button” (page 31)
• “Console Serial Port and Auxiliary Serial Port” (page 31)
HP Integrity Server Blade Components
Onboard Administrator is the enclosure management processor, subsystem, and firmware base
used to support the HP Integrity server blades and all the managed devices contained within
the enclosure. Onboard Administrator provides a single point from which to perform basic
management tasks on server blades or switches within the enclosure. Using this hardwired
knowledge, OnboardAdministrator performs initial configuration steps for the enclosure, enables
runtime management and configuration of the enclosure components, and informs you of
problems within the enclosure through e-mail, SNMP, or the Insight Display.
Before setting up the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator, HP recommends that you read
the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator User Guide on the HP website at:
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00705292/c00705292.pdf
Reading this guide ensures that you understand the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator
and that you properly complete the initial setup to facilitate its proper functioning.
You can find other Onboard Administrator docs on the HP website at:
HP BladeSystem c-Class Onboard Administrator
Onboard Administrator
Figure 2-1 shows the Onboard Administrator OA/iLO network port and components.
HP Integrity Server Blade Components 27
Page 28
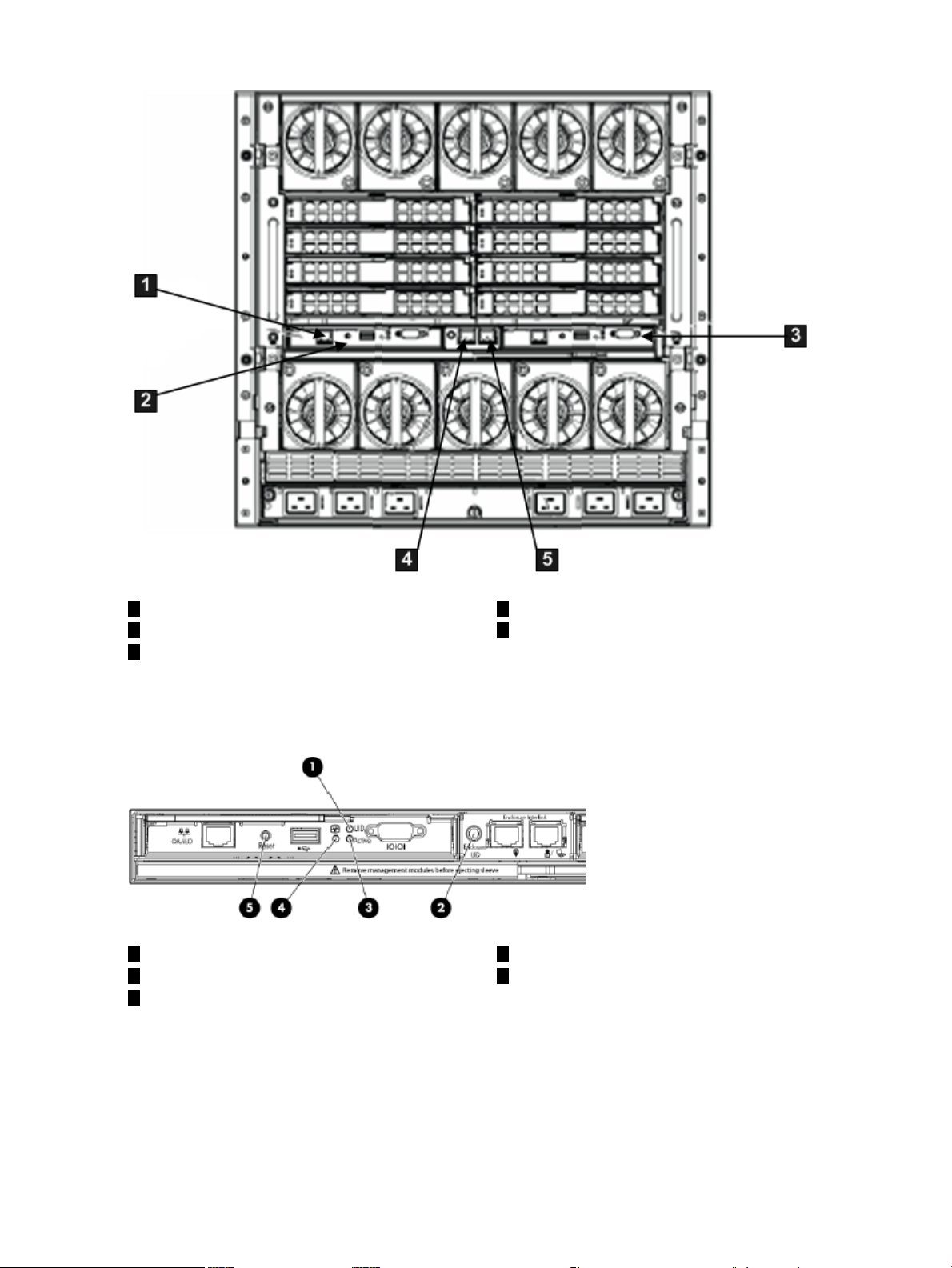
Figure 2-1 OA/iLO Network Port and Components
1
OA/iLO Network Port
2
Onboard Administrator Bay 1
3
Onboard Administrator Bay 2 (redundant
4
Enclosure Link-Up Port
5
Enclosure Link-Down Port
if used)
Figure 2-2 shows the Onboard Administrator LEDs and buttons.
Figure 2-2 Onboard Administrator LEDs and Buttons
1
Onboard Administrator UID LED
2
Enclosure UID LED
3
Onboard Administrator Active LED
4
Onboard Administrator Health LED
5
Onboard Administrator Reset Button
28 Ports and LEDs
Page 29
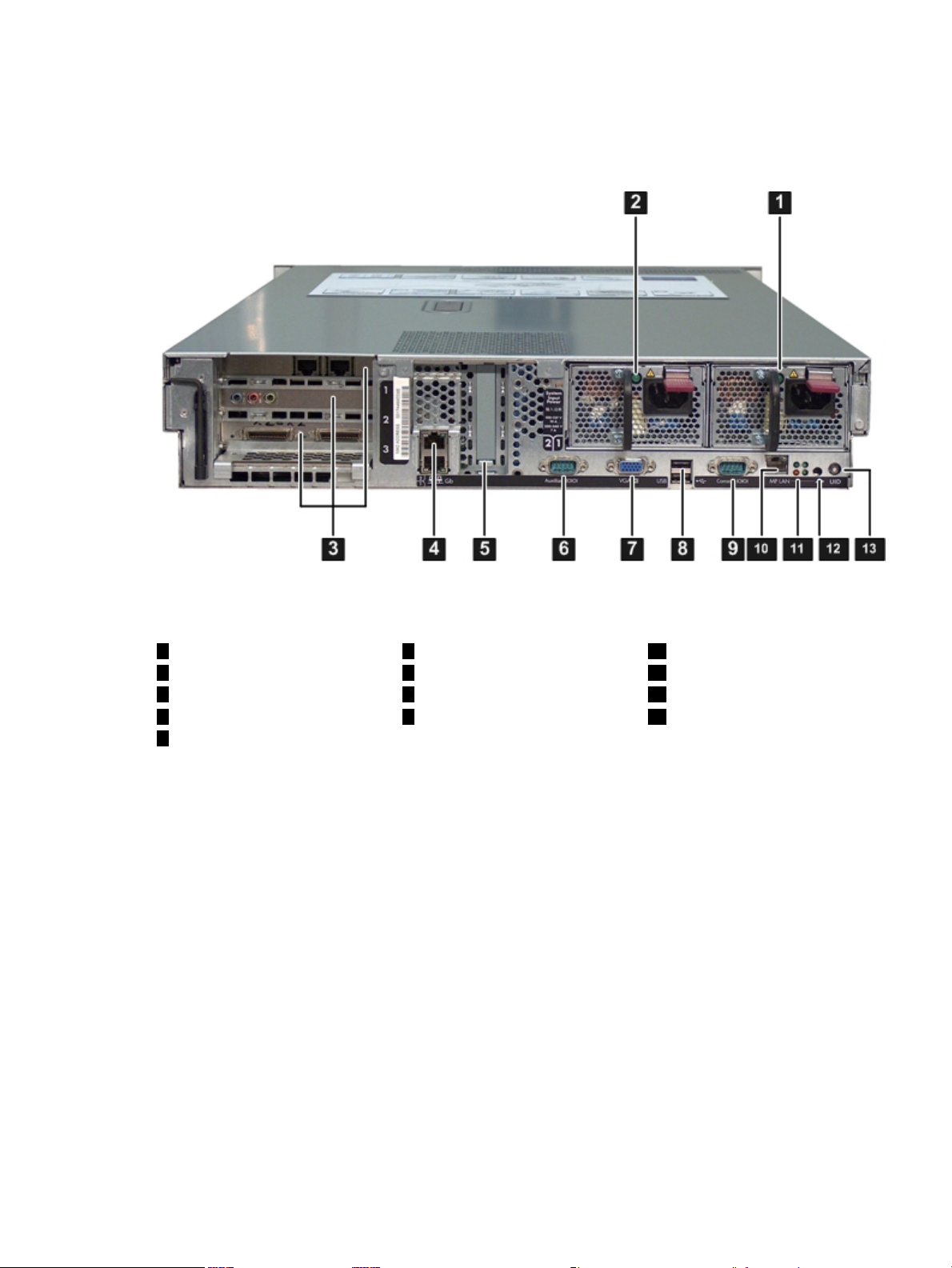
HP Integrity rx2660 Server Components
Figure 2-3 shows the rear view of the HP Integrity rx2660 server.
The system LAN functionality is integrated into the system board.
Figure 2-3 HP Integrity rx2660 Server Rear View
1
Power Supply 1 and LED
2
Power Supply 2 and LED
3
PCI-x/PCI-e Slots
6
Auxiliary Serial Port
7
VGA Port
8
USB Ports
Core LAN Ports UID Button/LEDConsole Serial Port
5
Smart Array P400
(RS-232)
10
11
12
1394
Controller Slot
HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600 Server Components
Figure 2-4 shows the controls, ports, and LEDs on the rear of the HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600
servers.
iLO 2 MP LAN Port
iLO 2 MP Status LEDs
iLO 2 MP Reset Button
HP Integrity rx2660 Server Components 29
Page 30
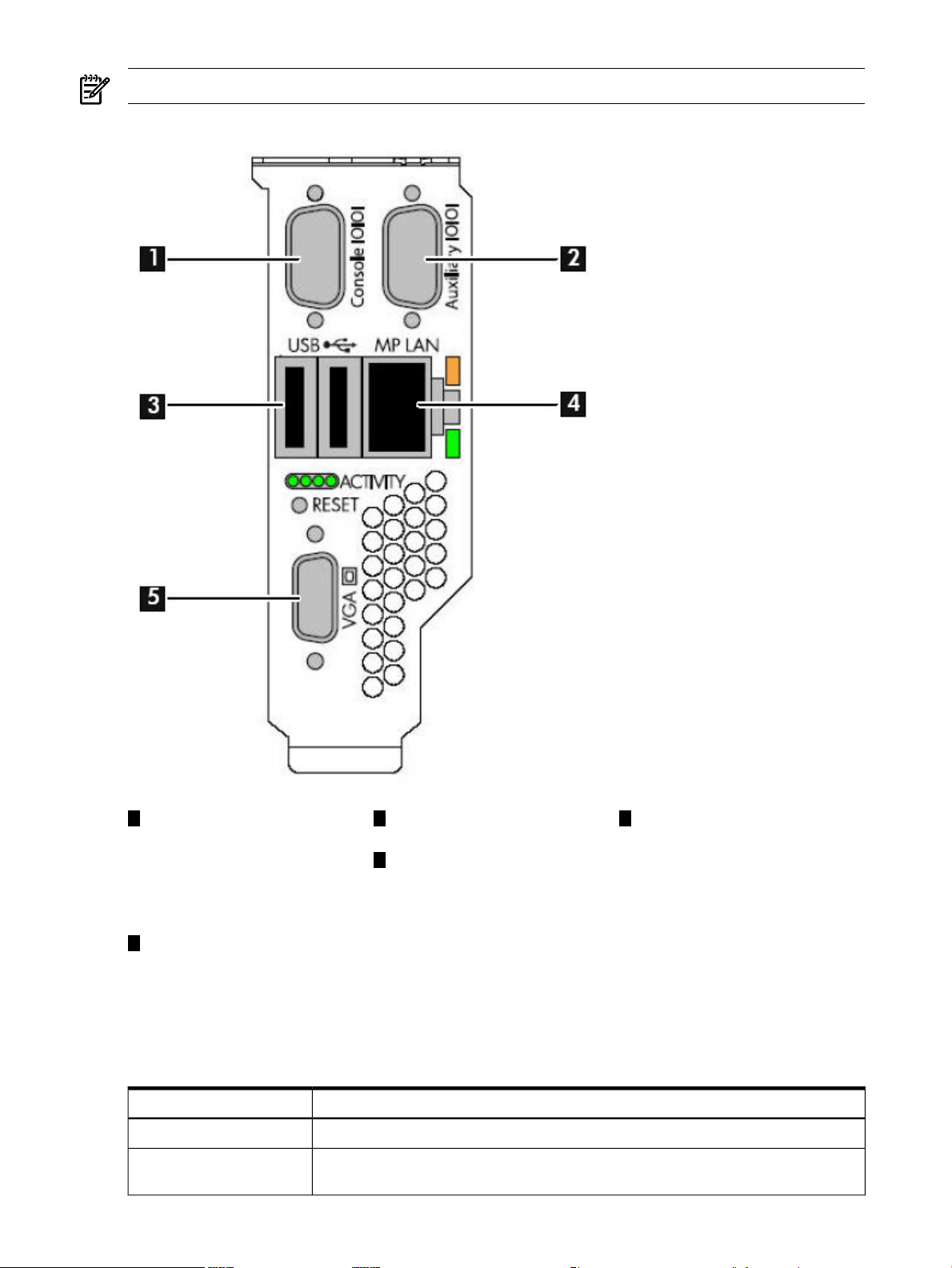
NOTE: This figure is oriented vertically to match the orientation of the core I/O board.
Figure 2-4 HP Integrity rx3600 and rx6600 Server Rear Ports and LEDs
1
iLO 2 MP Serial Console
Port (RS-232) (DB-9F to
DB-9F cable) Connected to
(PC, laptop, or ASCII
terminal)
2
General Use Serial Port
(Printers, etc.)
iLO 2 MP Status LEDs
Table 2-1 lists the state of the iLO 2 MP status LEDs during normal operation.
Table 2-1 iLO 2 MP Status LEDs
iLO 2 MP Self Test
30 Ports and LEDs
USB 2.0 Ports (any USB
device)
4
iLO 2 MP LAN Port (10/100
53
VGA Port (No iLO 2 MP
access; EFI only)
LAN)emulation terminal device
LED StateiLO 2 MP Status LED
Solid green.Standby Power
Off. The LED is solid amber when ac power is first applied. It remains solid amber for
a few seconds until the MP completes its self test; then the LED turns off.
Page 31

Table 2-1 iLO 2 MP Status LEDs (continued)
5
4
3
2
1
9
8
7
6
LED StateiLO 2 MP Status LED
Flashing green.iLO 2 MP Heartbeat
Flashing green.BMC Heartbeat
iLO 2 MP Reset Button
The iLO 2 MP Reset button enables you to reset the iLO 2 MP and reset the user-specific values
to factory default values. A momentary press causes a soft reset of the iLO 2 MP when the button
is released. A greater than four second press causes a soft reset of the iLO 2 MP upon release and
resets local user accounts and passwords to factory default values.
Resetting Local User Accounts and Passwords to Default Values
If iLO 2 MP user passwords are lost, or iLO 2 MP local user accounts are disabled and logging
in through LDAP directory server is unsuccessful because the directory server is down or directory
settings have not been configured properly in LDAP command, you can reset local user accounts
and passwords to their default values.
To reset local user accounts and passwords to default values, follow these steps:
1. Connect a serial terminal (or serial-cabled laptop with serial emulation) to the console serial
port.
2. Press and hold the iLO 2 MP Reset button for more than four seconds. The iLO 2 MP reboots
to factory default settings automatically.
3. Respond to the prompt to reset local user accounts and passwords to default values.
Console Serial Port and Auxiliary Serial Port
Figure 2-5 shows the console serial port connector with numbered labels for each pin on each
port.
Figure 2-5 Console Serial Port (RS-232) Connector
Table 2-2 maps the console serial port connector pin number to its signal description on each
port.
Table 2-2 Console Serial Port Pinouts
Signal DescriptionPin Number
Not used1
Receives data2
Transmits data3
Not used4
Ground5
Not used6
iLO 2 MP Reset Button 31
Page 32
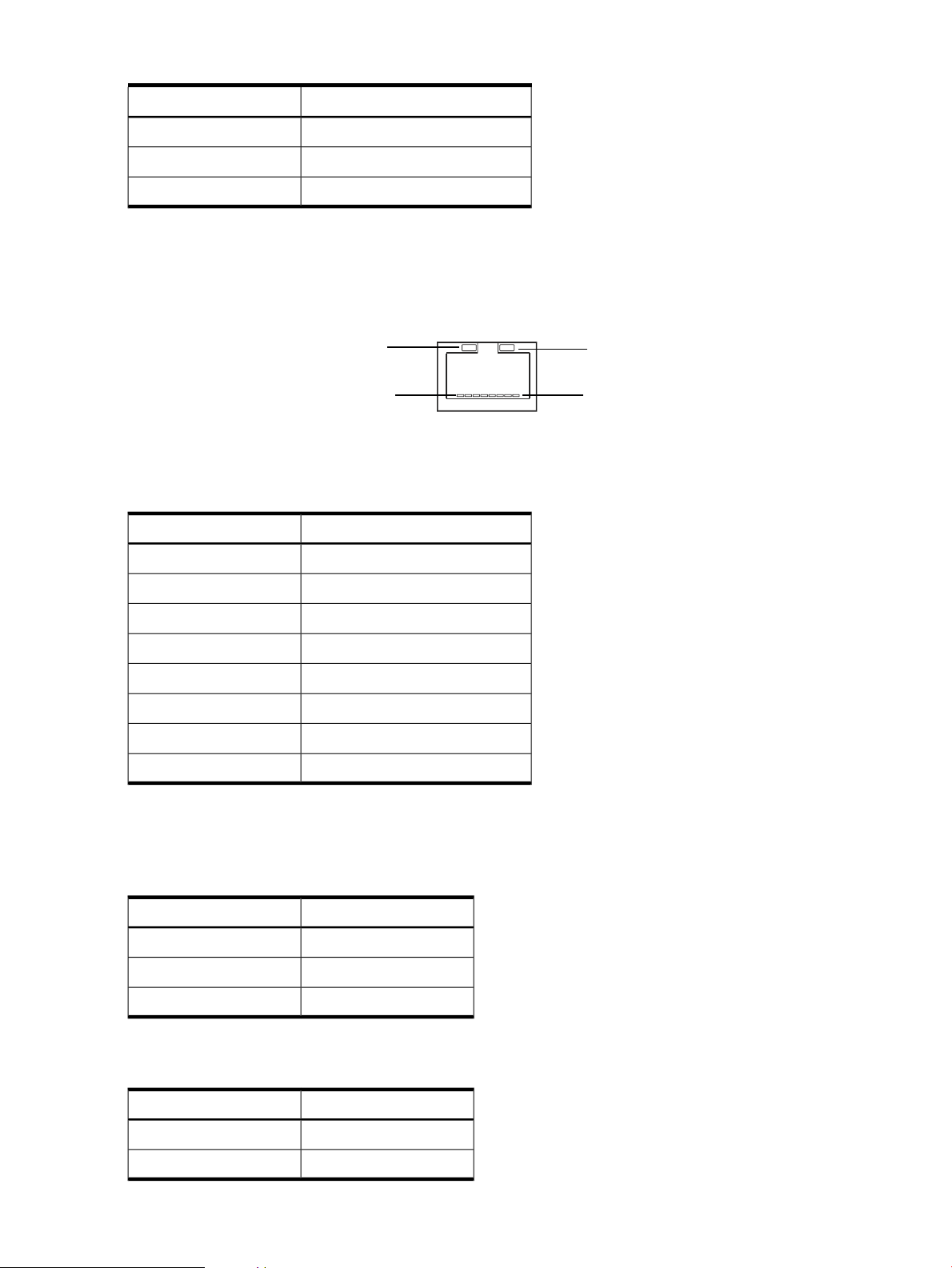
Table 2-2 Console Serial Port Pinouts (continued)
Amber Green
8
1
iLO 2 MP LAN Port
Figure 2-6 shows the iLO 2 MP LAN port connector pins and LEDs.
Figure 2-6 iLO 2 MP LAN Port
Table 2-3 maps the iLO 2 MP LAN port connector pin numbers to their signal descriptions.
Table 2-3 iLO 2 MP LAN Port Pinouts
Signal DescriptionPin Number
Requests to send7
Clears to send8
Not used9
Signal DescriptionPin Number
iLO 2 MP LAN LEDs
Table 2-4 lists the iLO 2 MP LAN link status LEDs and states.
Table 2-4 iLO 2 MP LAN Link Status LEDs
TXP1
TXN2
RXP3
Not used4
Not used5
RXN6
Not used7
Not used8
LED StateLink State
Blinking greenActivity
Solid greenLink with no activity
OffNo link
Table 2-5 lists the iLO 2 MP LAN link speed LEDs and states.
Table 2-5 iLO 2 MP LAN Link Speed LEDs
Solid amber100 Mb/s
Off10 Mb/s
32 Ports and LEDs
LED StateLink Speed
Page 33

3 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
To set up the console, follow these steps:
1. Determine the physical access method to connect cables. There are two physical connections
to the Integrity iLO 2 MP:
• Console serial port (RS-232)
• iLO 2 MP LAN port
2. Configure the Integrity iLO 2 MP and assign an IP address if necessary. Though there are
several methods to configuring the LAN, HP recommends DHCP with DNS. DHCP with
DNS comes preconfigured with default factory settings, including a default user account
and password. Other options include the following:
• ARP-Ping
• Console serial port (RS-232)
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Setup Checklist” (page 34)
• “Setup Flowchart” (page 35)
• “Preparing to Set Up iLO 2 MP” (page 36)
• “Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using DHCP and DNS” (page 37)
• “Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using ARP Ping” (page 37)
• “Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using the Console Serial Port” (page 39)
• “Logging In to the iLO 2 MP” (page 40)
• “Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP” (page 40)
• “Additional Setup” (page 46)
33
Page 34

Setup Checklist
Use the checklist in Table 3-1 to help set up iLO 2 MP.
Table 3-1 Setup Checklist
Standard
XActionStep
4
Advanced
Prepare1
Configure the iLO 2 MP LAN2
Log in to the iLO 2 MP3
Change default user name and
password
Set up user accounts5
Activate Advanced Pack features8
1. Determine the access method to select and connect
cables.
2. Determine the LAN configuration method and assign
an IP address if necessary.
Choose a method to configure the LAN for iLO 2 MP
access:
• DHCP with DNS
• ARP-Ping
• Console serial port (RS-232)
Log in to the iLO 2 MP from a supported web browser or
command lineusing the default user name and password.
Change the default user name and password on the
administrator account to your predefined selections.
Set up the user accountsif you are using the local accounts
feature.
Set up the security access settings.Set up security access6
Access the host console using your method of choice.Access the host console7
Activate advanced features by entering yourHP Integrity
Advanced Pack license key.
34 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 35
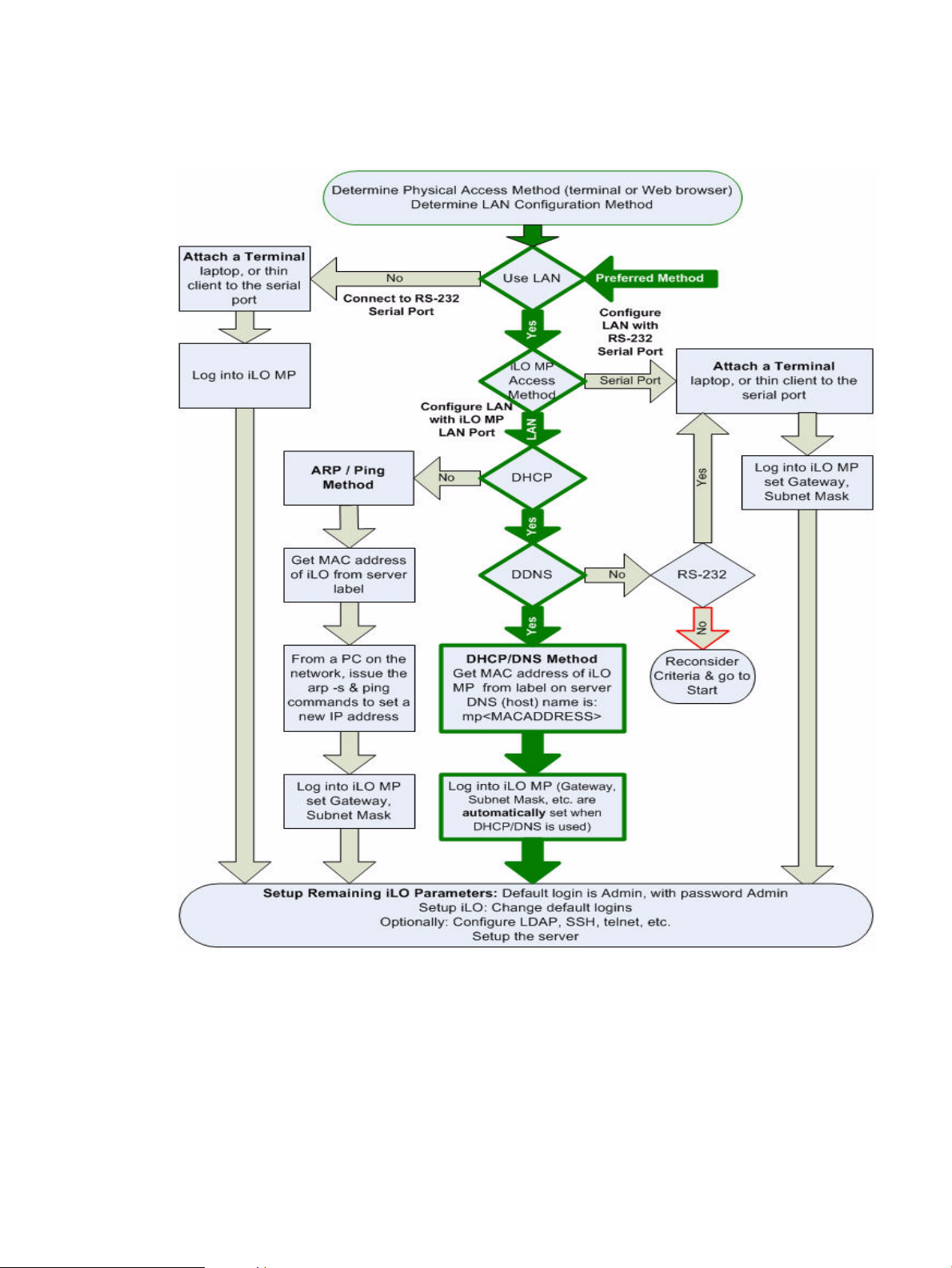
Setup Flowchart
Use this console setup flowchart as a guide to help set up the Integrity iLO 2 MP.
Figure 3-1 Setup Flowchart
Setup Flowchart 35
Page 36

Preparing to Set Up iLO 2 MP
Perform the following tasks before you configure the iLO 2 MP LAN:
• Determine the physical access method to select and connect cables.
• Determine the iLO 2 MP LAN configuration method and assign an IP address if necessary.
Determining the Physical iLO 2 MP Access Method
Before you can access the iLO 2 MP, you must determine the correct physical connection method.
The iLO 2 MP has a separate LAN port from the system LAN port. It requires a separate LAN
drop, IP address, and networking information from that of the operating system LAN port. See
Figure 2-3 and Figure 2-4 (page 30) and use Table 3-2 to determine your physical connection
method.
Table 3-2 lists the appropriate connection method, required connection components, and
connectors to the host console.
Table 3-2 Physical Connection Matrix
Required Connection ComponentsConnection Method
Console serial port
(RS-232)
• Host console
• Console serial port (RS-232) DB-9F to DB-9F cable (modem eliminator cable)
• Emulation terminal device (for example, a PC, laptop, or ASCII terminal)
10/100 LAN cableLAN port
Determining the iLO 2 MP LAN Configuration Method
To access the iLO 2 MP through the iLO 2 MP LAN, the iLO 2 MP must acquire an IP address.
The way the iLO 2 MP acquires an IP address is dependent upon whether DHCP is enabled or
disabled on the server, and if DHCP and DNS services are available to the server (see Table 3-3).
Once you have determined the iLO 2 MP access method, you must determine how you will
configure the iLO 2 MP LAN in order to acquire an IP address using the following methods:
• DHCP/DNS through the management LAN: use the DNS name on the toe-tag on the server.
• Setting up a staticIP number using a laptop with DHCP services and the management LAN.
• ARP Ping to set a static IP using a laptop and the management LAN
• Local RS-232 serial port and a serial console.
Table 3-3 provides all the possible IP address acquisition scenarios. Use this table to help you
select the appropriate LAN configuration method to obtain an IP address.
Table 3-3 LAN Configuration Methods
LAN Configuration MethodConsole Serial Port (RS-232)DNSDHCP
36 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
DHCPNoYesYes
DHCP or console serial portYesYesYes
ARP PingNoNoNo
ARP PingNoYesNo
ARP Ping or console serial portYesYesNo
Console serial portYesNoYes
Console serial port or ARP PingYesNoNo
Cannot set up the LAN; reconsider your criteriaNoNoYes
Page 37

Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using DHCP and DNS
DHCP automatically configures all DHCP-enabled servers with IP addresses, subnet masks, and
gateway addresses. All HP Integrity entry class servers with the iLO 2 MP are shipped from the
factory with DHCP enabled.
HP recommends using the DHCP and DNS method to simplify access to the iLO 2 MP.
NOTE: You can use ARP Ping regardless of the status of DHCP unless an IP address has ever
been acquiredusing DHCP. Once an IP address is assigned using DHCP, ARP Pingis permanently
disabled.
When you use DHCP and DNS, you can connect to the iLO 2 MP by entering the DNS name in
your browser rather than an IP address only if the following applies:
• DHCP must be enabled (DHCP is enabled by default).
• You are using a DHCP server that provides the domain name.
• The primary DNS server accepts dynamic DNS (DDNS) updates.
• The primary DNS server IP address was configured through the DHCP server.
IMPORTANT: You must know the DNS domain name, which is served out by the DHCP server,
unless its domain is local or the same domain.
To configure the iLO 2 MP using DHCP and DNS, follow these steps:
1. Obtain the factory-set DNS name from the toe-tag on the server. The DNS name is 14
characters long. It consists of the letters MP followed by the 12 characters of the MAC address.
For example:
mp0014c29c064f
This address is assigned to the iLO 2MP system board. Thesystem board has a unique MAC
address that identifies the hardware on the network.
2. Connect the iLO 2 MP LAN cable from the server to an active network port.
3. Apply ac power to the server.
4. Open a browser, telnet, or SSH client and enter the DNSname. The iLO 2 MP Log In window
appears.
5. Log in using the default user name and password (Admin/Admin).
CAUTION: When DHCP is enabled, the system is vulnerable to security risks because anyone
can access the iLO 2 MP until you change the default user name and password.
HP strongly recommends you assign user groups and rights before proceeding.
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using ARP Ping
NOTE: You can use ARP Ping regardless of the status of DHCP unless an IP address has ever
been acquiredusing DHCP. Once an IP address is assigned using DHCP, ARP Pingis permanently
disabled. Some DHCP server options can cause the apparent issuance of ARP Ping to the iLO 2
MP, which negates the DHCP over DNS method.
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Packet Internet Grouper (Ping) utility uses ARP
packets to ping (discover) a device on the local network segment. The IP address you assign to
the server must use the same network segment (subnet) as the system assigning the address.
ARP does not work across routed or switched networks.
Use the ARP Ping utility to assign a static IP address when you do not have access to the console
serial port (RS-232) or when DHCP is not available.
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using DHCP and DNS 37
Page 38

ARP Ping has the following operational issues:
• The PC and the server must be on the same physical subnet.
• When a new server is first booted, DHCP is automatically available (factory-set default),
but ARP Ping does not start until three minutes after the iLO 2 MP is booted. This applies
to every subsequent boot of the iLO 2 MP until an IP address is obtained by DHCP or is
assigned using the LC command.
• Upon successfully assigning an IP address using ARP Ping, DHCP is automatically disabled.
Select one of the following methods to use the ARP Ping utility:
1. Connect a PC to the network that is on the same physical subnet as the server and run the
ARP Ping commands from the PC.
2. Locate an existing server on the network and log in to it.
3. Run the ARP Ping commands from the server.
Table 3-4 lists the ARP Ping commands.
Table 3-4 ARP Ping Commands
DescriptionARP Command
arp -s
ping
Assigns the IP address to the iLO 2 MP MAC address. This ARP table entry maps the MAC
address of the iLO 2 MP LAN interface to the static IP address designated for that interface.
Tests network connections and verifies that the iLO 2 MP LAN port is configured with the
appropriate IP address.
NOTE: The following procedure explains how to use the ARP Ping utility using a PC that is
connected to the network that is on the same physical subnet as the server.
To configure a static IP address using the ARP Ping utility, follow these steps:
1. Obtain the iLO 2 MP MAC address. To set the IP address using ARP, you must know the
MAC address of the iLO 2 MP LAN. You can find the MAC address of the iLO 2 MP LAN
on a label on the server.
IMPORTANT: Make sure you obtain the MAC address to the iLO 2 MP LAN and not the
MAC address to the server core LAN.
2. Verify that an active LAN cable on the local subnet is connected to the iLO 2 MP LAN port
on the server.
3. Access a PC on the same physical subnet as the server.
4. Open a DOS window on the PC.
5. At the DOS command prompt (C: >) , enter arp -s to assign the IP address to the iLO
MAC address.
The syntax is as follows:
arp -s <IP address you want to assign to the iLO MAC address> <iLO 2 MAC address>
Example from Windows
arp -s 192.0.2.1 00-00-0c-07-ac-00
6. At the DOS command prompt, enter ping followed by the IP address to verify that the iLO
2 MP LAN port is configured with the appropriate IP address. The destination address is
the IP address that is mapped to the iLO MAC address. Perform this task from the PC that
has the ARP table entry.
The syntax is as follows:
ping <IP address just assigned to the iLO MAC address>
Example from Windows
38 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 39

ping 192.0.2.1
7. Use this IP address to connect to the iLO 2 MP LAN.
8. Use web or telnet access to connect to the iLO 2 MP from a host on the local subnet and
configure the rest of the LAN parameters (gateway, subnet).
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using the Console Serial Port
The terminal emulation device runs software that interfaces with the server. The software
emulates console output as it would appear on an ASCII terminal screen and displays it on a
console device screen.
To configure the iLO 2 MP LAN using the console serial port (RS-232), follow these steps:
IMPORTANT: Do not configure duplicate IP addresses on different servers within the same
network. The duplicate server IP addresses conflict and the servers cannot connect to the network.
The LC command enables you to configure a static IP address, host name, subnet mask, and
gateway address.
IMPORTANT: Ensure you have a console connection through the console serial port (RS-232)
or a network connection through the LAN to access the iLO 2 MP and use the LC command.
1. Ensure the emulation software is correctly configured:
a. Verify that the communication settings are configured as follows:
• 8/none (parity)
• 9600 baud
• None (receive)
• None (transmit)
b. Verify that the terminal type is configured appropriately. The following are supported
terminal types:
• hpterm
• vt100
• vt100+
• vt-utf8
IMPORTANT: Do not mix hpterm and vt100 terminal types at the same time.
Consult the help section of the emulation software application for instructions on how to
configure the software options.
2. Use Table 3-2 to determine the required connection components and the ports used to connect
the server to the console device.
3. Connect the cables.
4. Start the emulation software on the console device.
5. Log in to the iLO 2 MP. See “Logging In to the iLO 2 MP” (page 40).
6. At the MP Main Menu, enter CM and press Enter to select command mode.
7. At the command mode prompt, enter LS and press Enter. The screen displays the default
LAN configuration values. Write down the default values or log the information to a file.
8. To disable DHCP, enter the LC command.
a. From the LC command menu, enter D and press Enter.
b. Follow the instructions on the screen to change the DHCP status from enabled to
disabled.
c. Enter XD -R to reset the iLO 2 MP.
Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using the Console Serial Port 39
Page 40
9. Use the LC command to enter information for the IP address, host, subnet mask, gateway
parameters, and so on.
10. Enter XD -R -NC to reset the iLO 2 MP.
11. After the iLO 2 MP resets, log in to the iLO 2 MP again and enter CM at the MP> prompt.
12. To confirm that DHCP is disabled and display a list of updated LAN configuration settings,
enter the LS command.
Logging In to the iLO 2 MP
To log in to the iLO 2 MP, follow these steps:
1. Access the iLO 2 MP using the LAN, console serial port (RS-232), telnet, SSH, or web method.
The iLO 2 MP login prompt appears.
2. Log in using the default the iLO 2 MP user name and password (Admin/Admin).
TIP: For security reasons, HP strongly recommends you modify the default settings during
the initial login session. See “Modifying User Accounts and Default Passwords” (page 46).
Following is the MP Main Menu:
CO: Console
VFP: Virtual Front Panel
CM: Command Menu
CL: Console Logs
SL: Show Event Logs
SMCLP: Server Management Command Line Protocol
HE: Main Menu Help
X: Exit Connection
See Section : “Text User Interface” (page 59) for information on the iLO 2 MP menus and
commands.
TIP: When logging in using the local or remote console serial ports, the login prompt may not
display if another user is logged in through these ports. In this case, use Ctrl-B to access the MP
Main Menu and the MP> prompt.
Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP
Use one of the following methods to connect the server blade to the iLO 2 MP:
• Connect to the iLO 2 MP with DHCP enabled. Use the Onboard Administrator iLO (OA/iLO)
network port on the rear of the enclosure. If the OA/iLO network port on the enclosure is
connected to the local network that has a DHCP server, your iLO 2 MP IP address is
automatically generated by the DHCP server. The server blade is factory set with DHCP
enabled.
• Connect to the iLO 2 MP with no network connection. Use the console serial port on the
SUV cable. If the enclosure is not connected to any network, you must configure your server
through the console serial port (RS-232) on the SUV cable.
40 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 41

NOTE: The local video port can be used to access the console at EFI or potentially the OS, but
is not a connection to the iLO 2 MP. The USB provides keyboard and mouse to the operating
system on HP Integrity server blades. Also, server blades do not support directly connecting a
modem to the MP (called the remote RS-232 port on servers), so there is no remote RS-232
connection on the server blade. In addition, there is no LAN connection on the front of the server
blade.
Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP Using the Onboard Administrator
If the OA/iLO network port on the enclosure is connected to the local network that has a DHCP
server, your iLO 2 MP IP address is automatically generated by the DHCP server. The server
blade is factory set with DHCP enabled.
For complete Onboard Administrator information, the following guides can be found on the HP
website:
• For CLI, see the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator Command Line Interface User Guide.
• For web GUI, see the HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator User Guide.
To connect to the iLO 2 MP using the Onboard Administrator, follow these steps:
1. Connect a standard LAN cable to the OA/iLO network port on the rear of the server blade.
2. Connect the LAN cable to a local network that has a DHCP server. The LCD display panel
on the front of the enclosure displays the Main Menu.
3. Select Blade or Port Info from the options and click OK.
4. Select the appropriate server blade from the options on the screen and click OK. The screen
displays the iLO 2 MP IP address.
5. Write down the iLO 2 MP IP address.
6. Access the iLO 2 MP through telnet, SSH, or the web using the assigned DHCP iLO 2 MP
IP address.
NOTE: For the HP Integrity server blades, you can use the Onboard Administrator to set the
IP addresses for all the iLO 2 MPs. You can also find the iLO 2 MP address so you can log in.
Auto-Login
Auto-Login provides direct access to iLO 2 MP from the OA for users who already logged in to
the OA. A user who has authenticated their connection to the OA can follow a link to a server
blade in the enclosure without an additional login step. Auto-Login features and usage are as
follows:
• A user who has authenticated a connection to the OA is able to establish a connection with
• OA provides the following auto-login connection methods to iLO 2 MP links to users to
• Auto-Login is implemented using IPMI commands over I2C between OA and iLO 2 MP to
• Supports a maximum of four simultaneous OA user accounts. The OA keeps track of these
iLO 2 MP without providing the user login and password to iLO 2 MP.
launch these connections to iLO 2 MP:
iLO CLI SSH Connection If you logged in to the OA CLI through SSH, enter
connect server <bay number> to establish an
SSH/telnet connection with iLO 2 MP.
iLO Web GUI Connection If you logged in to the OA web GUI, click on the link to
launch the iLO's web GUI.
create and delete user commands.
users locally. The information maintained for each user is the username, password, and
privilege levels.
Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP 41
Page 42

• User accounts for the Auto-Login feature arecreated in the MP database when an Auto-Login
session is established. These accounts are deleted when the Auto-Login session is terminated.
• If a maximum number of user accounts has already been reached, and OA creates another
account on iLO 2 MP. The OA sends a request to iLO 2 MP to delete one of the previously
created accounts, before attempting to create a new one.
• If iLO 2 MP is rebooted or power-cycled, it checks if there are any previously created OA
user accounts in the iLO 2 MP user database when it boots up. If there are any
previously-created OA user accounts, it deletes those accounts.
• View and manage user accounts created in iLO 2 MP by OA like any other local user account
on iLO 2 MP. To view and manage user accounts, use the TUI WHO, UC commands; or use
the User Administration Page in the web GUI.
• View and disconnect user connections established through the Auto-Login feature just like
other connections to iLO 2 MP. To view and disconnect user connections, use the TUI WHO,
DI commands, or use the User Administration Page in the web GUI.
• OA supports three types of users: administrators, operators, and users. These user types
map to the following iLO 2 MP capabilities:
Administrators Can perform any function including iLO 2 MP configuration. This
level equates to an iLO 2 MP user with all privilege levels such as,
Administer User Accounts, Remote Console Access, Virtual Power
and Reset, Virtual Media, and Configure iLO settings. It allows access
to all aspects of the OA including configuration, firmware updates,
user management, and resetting default settings.
Operators Provided access to the host system IRC, serial console, and vMedia.
This level equates to an iLO 2 MP user with Remote Console Access,
Virtual Power and Reset, Virtual Media, and Configure iLO settings.
It allows access to all but configuration changes and user
management. This account is used for individuals who might be
required to periodically change configuration settings.
Users Provided read-only login access to the iLO 2 MP. This account is used
for individuals who need to see the configuration of the OA but do
not need the ability to change settings. This level equates to an iLO
2 MP user with no privileges set.
NOTE: For information on how to set user roles and privilege levels in the OA, see the HP
BladeSystem Onboard Administrator User Guide.
Initiating an Auto-Login Session
The Auto-Login session is initiated in the following way:
1. OA finds the first available auto-login user by finding the first user entry with a time-created
value of 0.(OAtmp1...OAtmp4).
2. If there are no available users, the oldest user is deleted.
NOTE: This could terminate a currently active session.
a. OA sends a request to iLO 2 MP to delete that user.
3. OA sends a command to create an OA user.
4. OA launches an SSH or Web GUI connection to iLO 2 MP and logs in with created user’s
credentials.
42 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 43

Terminating an Auto-Login Session
When the Auto-Login CLI or Web GUI session is terminated, the following user clean up is
preformed:
• For Auto-Login sessions, the temporary Auto-Login iLO 2 MP account is deleted when the
session with the iLO 2 MP is terminated.
User Account Cleanup during IPF Blade Initialization
OA and iLO 2 MP perform the following during an IPF blade initialization
• When a server blade is inserted, or iLO 2 MP or OA is reboot or reset, both OA and iLO
perform cleanup of the accounts that could have been created for auto-login before the reset.
• When iLO 2 MP initializes, OA marks all four user slots as unused.
• iLO scans its local user accounts. If there are any OA created user accounts, they are deleted
from iLO user database.
Auto-Login Troubleshooting
There may be times when Auto-Login fails. The following information provides possible reasons
for the failure
User Creation When OA sends a request to iLO 2 MP to create a new user, iLO attempts
to create a user inthe local iLO userdatabase. Creation of anOA user could
fail for a few of reasons:
• The local user database is disabled in iLO and LDAP authentication
is being used.
• MP user database has reached the maximum number of users (19
users).
• There is already a user registered with the same login name
User Login After an OA user has been created in the MP database, OA user login can
still fail for a number of reasons:
• iLO 2 MP upgrade is currently in progress, and no new connections
are allowed.
• Maximum number of connections for the requested connection type
(SSH, Telnet, web GUI) to iLO 2 MP has been reached.
• Requested connection type (SSH, Telnet or web) to iLO is currently
disabled.
User Deletion When OA sends a request to iLO 2 MP to delete a user, iLO 2 MP attempts
to delete that user from the local iLO user database. Deletion of an OA user
could fail for a couple of reasons
• A user with the specified login doesn't exist (could have been deleted
through other iLO UI)
• The specified user cannot be deleted because it is the only user in the
local database with user administration right.
Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP Using the Console Serial Port
If the enclosure is not connected to any network, you must configure your server through the
console serial port (RS-232) on the SUV cable. Use this procedure to configure the console serial
port to enable iLO 2 MP access. To perform this procedure, you need a terminal emulator (for
example, a laptop using hyperterm) to connect to the server blade.
Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP 43
Page 44

NOTE: On the HP Integrity server blades, you have access to two serial ports through the
RS-232 connector. The default setting is for the iLO 2 MP interface, the other is for an AUX UART
directly connected to the host operating system and can be used for any serial device (terminal,
debug port, and so on). HP recommends using the AUX UART for server blade setup and debug
purposes only.
You can use a command to toggle between the two ports. However, if access to the iLO 2 MP
TUI is not possible through telnet and if the port mode of operation is set to the AUX UART,
perform a hard reset of the iLO 2 MP to set it to the default shipping settings. To perform a hard
reset, push the recessed MP (iLO) Reset button.
TIP: It is not necessary to physically connect to the iLO 2 MP through the console serial port
to perform management tasks. Use the OA/iLO 2 LAN port to communicate with any iLO 2 MP
in the enclosure and the Onboard Administrator. You can use the LCD panel and the Onboard
Administrator to configure and determine the iLO 2 MP LAN address.
Connecting the SUV Cable to the Server Blade
This section describes how to connect your server blade to a terminal device using the SUV port.
CAUTION: Disconnect the SUV cable from the port when it is not in use. The port and connector
are not intended to provide a permanent connection.
On the SUV cable, locking buttons are located on the sides of the server blade connector. Always
squeeze the locking buttons on the SUV cable connector before disconnecting the SUV cable from
the SUV cable port. Failure to do so can result in damage to the port.
Use caution when walking near the server blade when the SUV cable is installed. Hitting or
bumping the cable can cause the port on the server blade to break. This can damage the system
board, requiring it to be replaced.
To establish a connection from the server blade to the terminal emulator, follow these steps:
1. Insert the SUV cable into the SUV port on the rear of the server blade. See Figure 3-2 and
Figure 3-3.
2. Connect a standard DB-9F to DB-9F modem eliminator cable to the RS-232 port on the SUV
cable.
3. Connect the other end of the DB-9F to DB-9F modem eliminator cable to the terminal
emulator.
4. Verify the parameters for serial console port communication are set to the following values
on your terminal or emulator device:
• VT 100 protocol
• 8/none (parity)
• 9600 baud
• None (receive)
• None (transmit)
5. Click OK to set the parameters.
6. If running an emulator, launch it now.
44 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 45

Figure 3-2 SUV Cable
1
Server Blade Connector
2
2-Port USB
3
VGA (no access to iLO 2 MP)
4
9-Pin Console Serial Port (RS-232)
5
USB Label
6
USB-1
7
USB-0
Physically Connecting the Server Blade to the iLO 2 MP 45
Page 46

Figure 3-3 Connecting the SUV Cable to the Server Blade
Additional Setup
This section provides additional information to set up the iLO 2 MP.
Modifying User Accounts and Default Passwords
The iLO 2 MP comes preconfigured with default factory settings, including a default user account
and password. The two default user accounts on initial login are:
• All Rights (Administrator) level user:
login = Admin
password = Admin
• Console Rights (Operator) level user:
login = Oper
password = Oper
Login and password are case sensitive.
TIP: For security reasons, HP strongly recommends you modify the default settings during the
initial login session.
Make the following changes using any of the iLO 2 MP user interfaces.
To modify default account configuration settings, follow these steps:
1. Log in as the administrator to modify default user configuration settings
2. To modify default passwords, follow these steps:
a. Access the MP Main Menu.
b. Enter CM at the MP> prompt.
c. Enter UC at the MP:CM> prompt and follow the prompts to modify default passwords.
3. To set up user accounts, follow these steps:
a. Access the MP Main Menu.
b. Enter CM at the MP> prompt.
c. Enter UC at the MP:CM> prompt and follow the prompts to modify user accounts.
46 Setting Up and Connecting the Console
Page 47

Setting Up Security
For greater security and reliability, HP recommends that iLO 2 MP management traffic be on a
separate dedicated management network and that only administrators be granted access to that
network. This not only improves performance by reducing traffic load across the main network,
it also acts as the first line of defense against security attacks. A separate network enables you
to physically control which workstations are connected to the network.
Setting Security Access
Determine the security access required and what user accounts and privileges are needed. The
iLO 2 MP provides options to control user access. Select one of the following options to prevent
unauthorized access to the iLO 2 MP:
• Change the default user name and password. See “Modifying User Accounts and Default
Passwords” (page 46).
CAUTION: When DHCP is enabled, the system is vulnerable to security risks because
anyone can access the iLO 2 MP until you change the default user name and password.
HP strongly recommends you assign user groups and rights before proceeding.
• Create local accounts. You can store up to 19 user names and passwords to manage iLO 2
MP access. This is ideal for small environments such as labs and small-to-medium sized
businesses.
• Use corporate directory services to manage iLO 2 MP user access. This is ideal for
environments with a large number of frequently changing users. If you plan to use directory
services, HP recommends leaving at least one local account enabled as an alternate method
of access.
For more information on how to create local accounts and use directory services, see Chapter 7:
“Installing and Configuring Directory Services ” (page 147).
Additional Setup 47
Page 48

48
Page 49

4 Accessing the Host Console
This chapter describes several ways to access the host console of an HP Integrity server.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Interacting with the iLO 2 MP Using the Web GUI” (page 49)
• “Accessing the Host Console Using the TUI” (page 50)
• “Accessing the Host Console Using vKVM (Integrated Remote Console)” (page 51)
• “Accessing the Host Console Using SMASH SM CLP” (page 51)
• “Accessing iLO 2 MP Using Onboard Administrator” (page 51)
• “Accessing the Graphic Console Using VGA ” (page 51)
Interacting with the iLO 2 MP Using the Web GUI
Web browser access is an embedded feature of the iLO 2 MP.
Before starting this procedure, you must have the following information:
• DNS name for the iLO 2 MP LAN. This is found on the toe-tag on the server.
• Host name
To interact with the iLO 2 MP through the web, follow these steps:
1. Open a web browser and enter the DNS name or the IP address for the iLO 2 MP.
2. Log in using your user account name and password at the login page. (Figure 4-1).
Figure 4-1 Web Login Page
NOTE: The iLO 2 MP web interface session times out after five minutes if there is no
activity. If you open a remote console terminal window, the system remains open in the
web interface session until you sign out. Also, the web session does not timeout if vMedia
is connected.
3. Click Sign In. The Status Summary page (Figure 4-2) appears after login.
Interacting with the iLO 2 MP Using the Web GUI 49
Page 50
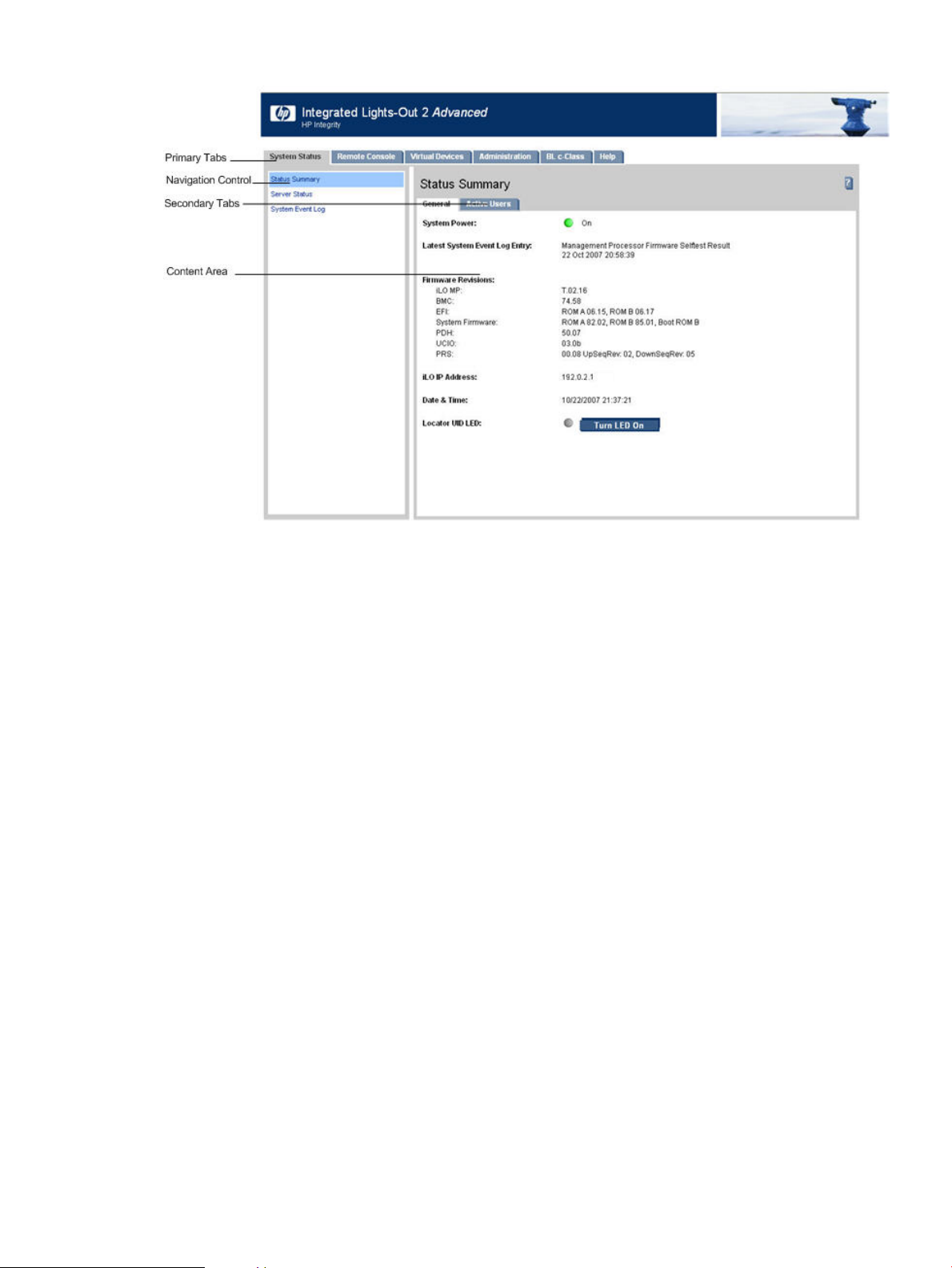
Figure 4-2 Status Summary Page
4. Select the web interface functions by clicking the Primary tabs at the top of the page. Each
function lists options in the Navigation Control on the left side of the page.
5. To display data in the content area; select an option and click Refresh to update the display.
6. Click the Remote Console tab. The remote console provides the following options to access
the console:
• A serial console that behaves similarly to the TUI
• The virtual KVM console
Accessing Online Help
The iLO 2 MP web interface has a robust help system. To launch iLO 2 MP help, click Help.
Alternately, click the ? at the top right corner of each page to display help about that page.
Accessing the Host Console Using the TUI
To access the host console using the text user interface (TUI), follow these steps:
1. Log in using your user account name and password at the login page.
2. To switch the console terminal from the MP Main Menu to mirrored/redirected console
mode, enter the CO command at the MP> login prompt. All mirrored data appears.
3. To return to the iLO 2 MP command interface, enter Ctrl-B or Esc (.
Help System
The iLO 2 MP has a robust help system.
To access the Help menu from the TUI, enter HE at the MP> prompt. The following is the MP
Help Main Menu:
==== MP Help: Main Menu ===============================================
Integrated Lights-Out for HP Integrity and HP 9000 - Management Processor (MP) MP Help System
Enter a command at the help prompt:
OVerview : Launch the help overview
LIst : Show the list of MP Main Menu commands
50 Accessing the Host Console
Page 51
<COMMAND> : Enter the command name for help on individual command
TOPics : Show all MP Help topics and commands
HElp : Display this screen
Q : Quit help
====
MP:HE
To display the Main Menu Command List, enter LI at the MP HE: prompt.
To return to the MP Main Menu, enter Q.
To access help from the web GUI, click Help. You can also click the ? at the top right corner of
each page to display help about that page.
Accessing the Host Console Using vKVM (Integrated Remote Console)
For information on how to access the host console using the vKVM feature through the Integrated
Remote Console (IRC), see “Accessing the IRC” (page 90).
Accessing the Host Console Using SMASH SM CLP
For information on how to access the host console using the SMASH SM CLP, see “Accessing
the SM CLP Interface” (page 124).
Accessing iLO 2 MP Using Onboard Administrator
NOTE: The HP BladeSystem Onboard Administrator is only available on HP Integrity server
blades.
To access the iLO 2 MP using Onboard Administrator, follow these steps:
1. Establish a network connection through the OA/iLO network port.
2. Enter the iLO MP IP address you obtained previously through the OA/iLO port in the
appropriate screen. You now have access to the iLO 2 MP functionality through a telnet
session.
3. Ensure that you have an MP prompt.
4. To log into the iLO 2 MP, enter the following default values for the login ID and password
(case sensitive):
• Login: Admin
• Password: Admin
The MP Main Menu screen appears.
Accessing the Graphic Console Using VGA
NOTE: You cannot access the iLO 2 MP using VGA.
Accessing the graphics console using VGA requires three items:
• Monitor (VGA connector)
• Keyboard (USB connector)
• Mouse (USB connector)
The graphic console output displays on the monitor screen.
Accessing the Host Console Using vKVM (Integrated Remote Console) 51
Page 52

IMPORTANT: The server console output does not display on the console device screen until
the server boots to the EFI Shell. Start a console session using the console serial port (RS-232)
method to view console output prior to booting to the EFI Shell, or to access the iLO 2 MP.
See“Configuring the iLO 2 MP LAN Using the Console Serial Port” (page 39).
To access the graphic console with VGA, follow these steps:
1. Perform preparation tasks.
2. Connect the cables. See Figure 2-3 and Figure 2-4 (page 30) for specific port information.
a. Connect the monitor VGA cable to the appropriate VGA port.
b. Connect the keyboard USB cable to the appropriate USB port.
c. Connect the mouse USB cable to the appropriate USB port.
3. Power on the server. The EFI Shell prompt appears.
52 Accessing the Host Console
Page 53

5 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite
This chapter provides information on how to configure DHCP, DNS, LDAP extended schema,
and LDAP Lite default schema.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Configuring DHCP” (page 53)
• “Configuring DNS” (page 54)
• “Configuring LDAP Extended Schema” (page 55)
• “Configuring LDAP Lite Default Schema” (page 56)
Configuring DHCP
DHCP enables you to automatically assign reusable IP addresses to DHCP clients. This section
provides information on how to configure DHCP options such as the Domain Name System
(DNS).
The iLO 2 MP host name you set through this method displays at the iLO 2 MP command mode
prompt. Its primary purpose is to identify the iLO 2 MP LAN interface in a DNS database.
NOTE: The HP-UX system name displayed by the uname -a command is different than the
iLO 2 MP host name.
If the IP address, gateway IP address, and subnet mask are obtained through DHCP, you cannot
change them without first disabling DHCP. If you change the host name and the IP address was
obtained through DHCP and registered with dynamic DNS (DDNS), a “delete old name” request
for the old host name and an “add name request” for the new host name are sent to the DDNS
server.
If you change the DHCP status between enabled and disabled, the IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway IP address are set to default values (127.0.0.1:0xffffff00). Also, the DNS parameters are
voided. When you change the DHCP status from enabled to disabled, the DNS parameters for
using DHCP are set to disabled, and the Register with DDNS parameter is set to No. When
you change the DHCP status from disabled to enabled, the DNS parameters for using DHCP are
set to enabled, and the Register with DDNS parameter is set to Yes.
NOTE: DNS is the comprehensive RFC standard; DDNS provides only a part of the DNS
standard functionality.
Use the LC command to perform the following actions to configure DHCP:
• Set all default LAN settings.
MP:CM> LC -all DEFAULT –nc
• Display current LAN settings.
MP:CM> LC –nc
• Modify the MP DHCP status.
MP:CM> LC –dhcp disabled
• Modify the MP IP address.
MP:CM> LC -ip 192.0.2.1
• Modify the MP host name.
MP:CM> LC -h hostname
Configuring DHCP 53
Page 54

• Modify the MP subnet mask.
MP:CM> LC -s 192.0.2.1
• Modify the MP gateway address.
MP:CM> LC -g 192.0.2.1
• Set the link state to autonegotiate.
MP:CM> LC –link auto
• Set the link state to 10 BaseT.
MP:CM> LC –link t
• Set the remote console serial port address.
MP:CM> LC –web 2023
• Set the SSH console port address.
MP:CM> LC –ssh 22
Configuring DNS
To use the DNS command to display and modify the DNS configuration, follow these steps:
1. From the MP Main Menu, enter command mode.
2. At the MP:CM> prompt, enter DNS. The screen appears current DNS data.
3. When prompted, enter A to select all parameters. The screen displays the current DHCP for
DNS servers status.
4. When prompted, enter Enabled or Disabled. The screen displays the current DHCP for
DNS domain name status.
5. When prompted, enter Enabled or Disabled. The screen displays the current register
with DDNS server value.
6. When prompted, enter Yes or No. The screen displays the current DNS domain name.
7. When prompted, enter a new value. The screen displays the primary DNS server IP address.
8. When prompted, enter a new value. The screen displays the optional secondary DNS server
IP address.
9. When prompted, enter a new value. The screen displays the optional tertiary DNS server
IP address.
10. When prompted, enter a new value.
The DNS configuration is updated as follows:
New DNS Configuration (* modified values):
* S - DHCP for DNS Servers : Disabled
* D - DHCP for DNS Domain Name : Disabled
R - Register with DDNS Server : Yes
* N - DNS Domain Name : mpdns.company.com
* 1 - Primary DNS Server IP : 192.0.2.1
2 - Secondary DNS Server IP :
3 - Tertiary DNS Server IP :
Enter parameter(s) to revise, Y to confirm, or [Q] to Quit: Y
-> DNS Configuration has been updated
[mpserver] MP:CM>
54 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite
Page 55

Configuring LDAP Extended Schema
The following procedure shows how to configure the iLO 2 MP to use a directory server to
authenticate a user login using the iLO 2 MP TUI.
NOTE: The LDAP connection times out after 30 minutes of inactivity in Active Directory. For
Novell directory, there is no inactivity timeout.
To configure using the web interface, see “Group Accounts” (page 112).
NOTE: The LDAP feature is only available if you have the iLO 2 Advanced Pack license.
To configure LDAP extended schema, follow these steps:
1. From the MP Main Menu, enter command mode.
2. At the MP:CM> prompt, enter LDAP.
3. To select Directory Settings, enter D. The current LDAP directory settings appear.
4. To select all parameters enter A. The current LDAP directory authentication status appears.
The local iLO 2 MP user accounts database status also appears. If enabled, the local iLO 2
MP user database is used if there is an authentication failure using the LDAP Directory.
5. Enter D for disabled, or E for enabled. You must enter E if LDAP directory authentication
is disabled. The current LDAP server IP address appears.
6. Enter the IP address of the LDAP server. The current LDAP server port address appears.
7. Enter a new port number. The screen displays the current object distinguished name. This
specifies the full distinguished name of the iLO 2 MP device object in the directory service.
For example, CN=RILOE2OBJECT, CN=Users, DC=HP, DC=com. Distinguished names
are limited to 255 characters maximum plus one for the NULL terminator character.
8. Enter a new name. The Current User Search Context 1 appears.
9. Enter a new search setting. The Current User Search Context 2 appears.
NOTE: The context settings 1, 2, and 3 point to areas in the directory service where users
are located, so that users do not have to enter the complete tree structure when logging in.
For example, CN=Users, DC=HP, DC=com. Directory user contexts are limited to 127
characters maximum plus one for the NULL terminator character for each directory user
context.
10. Enter a new search setting. The screen displays the Current User Search Context 3.
11. When prompted, enter a new search setting.
Following is the updated LDAP configuration:
New Directory Configuration (* modified values):
* L - LDAP Directory Authentication : Enabled
M - Local MP User database : Enabled
* I - Directory Server IP Address : 192.0.2.1
P - Directory Server LDAP Port : 636
D - Distinguished Name (DN) : cn=mp,o=demo
1 - User Search Context 1 : o=mp
2 - User Search Context 2 : o=demo
3 - User Search Context 3 : o=test
Enter Parameter(s) to revise, Y to confirm, or [Q] to Quit: y
-> LDAP Configuration has been updated
Configuring LDAP Extended Schema 55
Page 56

Login Process Using Directory Services with Extended LDAP
You can choose to enable directory services to authenticate users and authorize user privileges
for groups of iLO 2 MPs. The iLO 2 MP directory services feature uses the industry-standard
LDAP. HP layers LDAP on top of SSL to transmit the directory services information securely to
the directory servers. More information about directoryservices is available from theHP website
at:
http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
Using directory services after users enter their login and password, the browser sends the cookie
to the iLO 2 MP. The iLO 2 MP processor accesses the directory service to determine which roles
are available for that user login. The iLO 2 MP first uses the credentials to access the iLO 2 MP
device object in the directory. The directory service returns only the roles for which the user has
rights. If the user credentials allow read access to the iLO 2 MP device object and the role object,
the iLO 2 MP determines the role object’s distinguished name and the associated user privileges.
The iLO 2 MP then calculates the current user privileges based on those roles and grants them
to that user.
Configuring LDAP Lite Default Schema
IMPORTANT: Due to command syntax changes in LDAP Lite, some customer-developed scripts
may not run. You must change any scripts you developed to enable them to run with the new
LDAP Lite syntax.
The iLO 2 MP schema-free directory integration enables you to use the standard directory schema
instead of adding HP’s schema to the directory database. You accomplish this by authenticating
users from the directory database and authorizing iLO 2 MP privileges based on matching groups
stored on each iLO 2 MP.
NOTE: The LDAP Lite feature is available only if you have the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license.
In addition to general directory integration benefits, the iLO 2 MP schema-free integration
provides the following advantages:
56 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite
Page 57

• Easy implementation without schema extensions.
The iLO 2 MP schema-free integration is configured from any iLO 2 MP user interface
(browser, command line, or script).
• Minimal administration and maintenance.
— After initial setup, only groups and permissions require maintenance support on the
iLO 2 MP; typically group and permission changes occur infrequently.
— The schema-free approach does notrequire updating directory databases with newiLO
2 MP devices objects.
• Reliable security.
iLO 2 MP schema-free integration does not affect standard directory attributes, avoiding
conflicting use of attributes that can result over time.
• Complements two-factor authentication.
iLO 2 MP schema-free integration can be used in conjunction with iLO 2 MP two-factor
authentication to provide asset protection using strong authentication.
NOTE: If you have already extended your directory with HP schema, there is no need to switch
to the schema-free approach. Schema extension provides the lowest maintenance approach for
directory integration. Once this process has taken place, there is no advantage for the schema-free
approach until a schema change is required.
To configure LDAP Lite, follow these steps:
1. Follow the procedure for “Configuring LDAP Extended Schema” (page 55), but omit Step
8. It is not necessary to enter a new port number.
2. Set up directory security groups.
Setting up Directory Security Groups
The following procedure describes how to set up directory security groups in LDAP Lite using
the iLO 2 MP TUI. To use the web interface, see “Group Accounts” (page 112).
NOTE: Due to command syntax changes in LDAP Lite, some customer-developed scripts may
not run. You must change any scripts you developed to enable them to run with the new LDAP
Lite syntax.
NOTE: You must select the default schema from the LDAP command for the LDAP Lite settings
to work.
To set up directory security groups, follow these steps.
1. At the MP:CM> prompt, enter LDAP. The screen displays the current LDAP options.
[hqgstlb3] MP:CM> ldap
LDAP
Current LDAP options:
D - Directory settings
G - Security Group Administration
2. Enter G. The current group configuration appears.
Enter menu item or [Q] to Quit:G
Current Group Configuration:
Group Names Group Distinguished Names Access Rights
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Configuring LDAP Lite Default Schema 57
Page 58

1 - Administrator C, P, M, U
2 - User C, P
3 - Custom1 None
4 - Custom2 None
5 - Custom3 None
6 - Custom4 None
Only the first 30 characters of the Group Distinguished Names are displayed.
Enter number to view or modify, or [Q] to Quit:
3. Enter the number for the group you want to view or modify. The current LDAP group
settings appear.
4. Set up a group distinguished name.
5. Select rights for the group.
6. Enter Y to confirm.
Login Process Using Directory Services Without Schema Extensions
You can control access to the iLO 2 MP using directories without schema extensions. The iLO 2
MP acquires the user name to determine group membership from the directory. The iLO 2 MP
then cross-references the group names with its locally stored names to determine user privilege
level. The iLO 2 MP must be configured with the appropriate group names and their associated
privileges. To configure the iLO 2 MP, use one of the following methods:
• Web GUI (Administration > Directory Settings > Group Administration page)
• iLO 2 MP TUI (LDAP command)
58 Configuring DHCP, DNS, LDAP, and LDAP Lite
Page 59

6 Using iLO 2 MP
This chapter provides information and instructions on how to use the iLO 2 MP.
This chapter addresses the following topics:
• “Text User Interface” (page 59)
• “Web GUI” (page 82)
• “Integrated Remote Console (vKVM)” (page 88)
• “Virtual Media” (page 95)
• “Power Management” (page 103)
• “SMASH Server Management Command Line Protocol” (page 123)
Text User Interface
This section provides information on the text user interface commands you can run in the iLO
2 MP.
NOTE: HP Integrity server blades do not have fans or power supplies. Therefore, their response
to certain commands are different than a rack-mount server.
MP Command Interfaces
Table 6-1 lists and describes the available MP command interfaces.
Table 6-1 MP Command Interfaces
DescriptionMP Command Interface
MP Main Menu
Command Menu
SMASH SM CLP
The MP Main Menu appears when you first access the iLO 2 MP. The MP Main Menu
supports the basic MP commands for server control and the iLO 2 MP configuration,
such as setting up the iLO 2 MP LAN, retrievingevents, resetting and powering on control
of the server, switching to the console, and so on. You can enter the MP Main Menu
commands at the MP> prompt.
The Command menu provides a set of commands that help monitor and manage the
server. It switches the console terminal from the MP Main Menu to command interface
mode. You can access commands that are not displayed in the MP Main Menu by entering
CM at the MP Main Menu and entering HE LI at the MP:CM> prompt to get a list of the
available commands.
The Systems Management Architecture for Server Hardware (SMASH), Server
Management Command Line Protocol (SM CLP) initiative is an effort within the
Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) to standardize commands for servers. The
SMASH SMCLP specifies common command line syntax and message protocolsemantics
for server management.
For information on using SMASH SM CLP scripting commands, see Section : “SMASH
Server Management Command Line Protocol” (page 123).
Figure 6-1 displays the MP command interface options.
Text User Interface 59
Page 60

Figure 6-1 MP Command Interfaces
MP Main Menu
After logging in to the iLO 2 MP, the MP Main Menu appears. The MP Main Menu runs as a
private session. Other iLO 2 MP users do not see the actions you perform in the private session.
The iLO 2 MP can support multiple sessions to perform independent tasks:
• Multiple windows logged into the iLO 2 MP to monitor VFP or study event logs in one
window while administering the server from another window.
• Resetting a server from one window and monitoring the boot from another window while
interacting with the console from a third window.
Table 6-2 lists the MP Main Menu commands.
Table 6-2 MP Main Menu Commands
CO
VFP
CM
SMCLP
CL
SL
HE
X
TIP: An effective method for using the iLO 2 MP is to log in more than once with different
views for each session. For instance, one window logged in viewing the console, and another
viewing the virtual front panel.
MP Main Menu Commands
DescriptionCommand
Selects console mode
Displays the virtual front panel
Enters command interface mode
Accesses the SMASH SM CLP
Views the console log
Shows event logs
Displays help for the menu or command
Exits
MP Main Menu command descriptions are listed as follows:
60 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 61

CO (Console): Leave the Main Menu and enter console mode
CO switches the console terminal from the MP Main Menu to mirrored/redirected console mode.
All console output is mirrored to all users in console mode. Only one of the mirrored users at a
time has write access to the console. To get console write access, press Ctrl-Ecf.
Press either Ctrl-B or Esc and ( to return to the iLO 2 MP command interface. Verify that all
mirrored consoles are of the same terminal type for proper operation.
To run an ASCII screen-oriented application (SAM) or a file transfer program (ftp), the console
is not the recommended connection. HP recommends using the LAN and connecting directly
with telnet or the web to the system over the system LAN.
VFP (Virtual Front Panel): Simulate the display panel
VFP simulates the display panel on the front of the server. It gives realtime feedback on the results
of system events and user actions. VFP works by decoding system events. It provides a live
display of major states of the system, the latest system activity, and the state of front panel LEDs.
VFP shows forward progress during boot by indicating how many events have been received
since the boot started and whether there have been any errors (events with alert level 3 or greater)
since the last boot. To clear the yellow attention indicator on the front of the system, use the SL
command and access the System Event Log (SEL).
Each user viewing VFP is in private session mode.
See also: LOC (locator LED) and, SL (show logs).
CM (Command Mode): Enter command mode
CM switches the console terminal from the MP Main Menu tomirrored command interface mode.
The Command menu provides you with a set of standard command line interface commands
that help monitor and manage the server.
To display the list of MP command mode commands that are not displayed in the MP Main
Menu , follow these steps:
1. From the MP Main Menu , enter HE.
2. Enter LI after the MP HELP:> prompt.
If a command is in progress, a system status message appears.
To return to the MP Main Menu , press CTRL-B.
SMCLP (Server Management Command Line Protocol): Switch to the SMASH SMCLP
SMCLP switches the console terminal from the MP Main Menu to the SMASH SMCLP interface.
For information on SMASHSM CLPsee “SMASHServer Management CommandLine Protocol”
(page 123).
CL (Console Log): View the history of the console output
CL displays up to 60 KB of logged console data (about 60 pages of display in text mode) sent
from the system to the console path and stored for later analysis.
Console data is stored in a buffer in nonvolatile memory. By default, data is displayed from the
beginning of the buffer to end of the buffer. You can control the starting point from which the
data displays and navigate through the data.
An image of the console history appears when you enter the CL command. Console output
continues to be logged while this buffer is read, and nothing is lost.
SL (Show Logs): View events in the log history
SL displays the contents of the event logs that are stored in nonvolatile memory.
Text User Interface 61
Page 62

Events are data items that communicate system information from the source of the event to other
parts of the system, then to you. Events are produced by intelligent hardware modules, the
operating system,and system firmware. Events funnelinto BMC from different sources throughout
the server. The iLO 2 MP polls the BMC for new events and stores them in nonvolatile memory.
• SEL: High attention events and errors.
• Forward progress: All events.
• Boot log: All events between start of boot and boot complete.
• Previous boot log: The events from the previous boot.
Reading the SEL is the only way to turn off the attention LED (flashing yellow light).
Table 6-3 shows the events and actions used to navigate within the logs.
Table 6-3 Events
ActionEvent
Displays the next block (forward in time)+
Displays the previous block (backward in time)-
Continues to the next or previous blockEnter (<CR>)
Dumps the entire log for capture or analysisD
Displays the first entryF
Displays the last entryL
Jumps to entry numberJ
Displays the mode configuration (hex)H
Displays the mode configuration (keyword)K
Displays the view mode configuration (text)T
Displays the alert level filter optionsA
Displays the alert level unfilteredU
Q
?
Ctrl-B
Quits and returns to the Event Log Viewer Menu
Displays the view mode configuration (text, keyword, hex)V
Displays the Help menu
Exits and returns to the MP Main Menu
Table 6-4 defines alert (severity) levels.
Table 6-4 Alert Levels
Minor forward progress0
Major forward progress1
Informational2
DefinitionSeverity
See also: DC (default configuration) and VFP (virtual front panel).
62 Using iLO 2 MP
Warning3
Critical5
Fatal7
Page 63

HE (Help): Display help for the menu or command in the MP Main Menu
HE displays the MP hardware and firmware version identity, and the date and time of firmware
generation. If executed from the MP Main Menu, HE displays general information about the iLO
2 MP, and those commands available in the MP Main Menu. If executed in command mode, HE
displays a list of Command menu commands available. It also displays detailed help information
in response to a topic or command at the help prompt.
X (Exit): Exit the iLO 2 MP
X exits you from the MP Main Menu. If the terminal is the local serial port, the login prompt
appears. For all other types of terminals, you are disconnected from the iLO 2 MP.
Command Menu
The Command menu provides you with a set of standard command line interface commands
that help monitor and manage the server.
Table 6-5 lists the Command Menu commands.
Table 6-5 Command Menu Commands
DescriptionCommand
BP
BLADE
CA
DATE
DC
DF
DI
DNS
FW
HE
ID
IT
LC
LDAP
LM
Resets the BMC passwords
Displays blade parameters
NOTE: This command is available only on a server blade.
Configures asynchronous local serial port
Displays the current date
Resets all parameters to default configuration
Displays field replaceable unit (FRU) information
Disconnects the LAN console
Sets the DNS configuration
This command is only available to authorized HP service personnel
Displays help for the menu or command
Displays or modifies system information
Modifies the iLO 2 MP inactivity timeouts
Displays the LAN configuration
Displays the LDAP configuration
License management
LOC
LS
PC
PM
PR
PS
RB
RS
Displays and configures locator LED
Displays the LAN status
Remote power control
Remote power mode control
Configures the power restore policy
Displays the power management module status
Resets the BMC
Resets the system through the RST signal
Text User Interface 63
Page 64
Table 6-5 Command Menu Commands (continued)
DescriptionCommand
SA
SNMP
SO
SS
SYSREV
TC
TE
UC
WHO
XD
Sets access options
Configures SNMP parameters
Configures security options
Displays system processor status
Displays all firmware revisions
Resets through transfer of control (TOC)
“Tell” (sends a message to other users)
Displays a user configuration
Displays connected the iLO 2 MP users
Diagnoses or resets the iLO 2 MP
The following is a quick reference list that provides MP Command mode activities:
To access the Command menu, enter CM at the MP Main Menu.
To see all the available commands, enter HE LI at the MP:CM> prompt.
To access the Command menu help, enter HE at the MP:CM> prompt. The Command menu help
provides information on all the Command menu items.
To modify the inactivity timeout, enter the IT command. The inactivity timer aborts a command
if you do not complete it within a certain time period.
To abort most commands, enter Q at the point when the iLO 2 MP is asking for input.
To return to the MP Main Menu from any of these commands, press Ctrl-B.
Command Line Interface Scripting
A command line interface is provided for all commands to assist you in scripting. This section
provides syntax examples used in the iLO 2 MP command-line or scripted interface.
Typically, tools like Expect (see “Expect Script Example” (page 65)) and (http://expect.nist.gov/)
are used to string together several commands to accomplish a task. These scripting tools enable
you to write a script for one iLO 2 MP, and use it to apply the same commands to additional iLO
2 MPs. Scripting tools have capabilities that enable you to do the following:
• Write scripts that make decisions based on the output of commands
• Use variables in the script to customize it for each target automatically
• Compensate for delays in output
Scripting tools and the command-line interfaces enable you to carry out commands to multiple
iLO 2 MPs such as setting the IP address on 10 iLO 2 MPs pulled from a list of 10 IP addresses
read from a file local to your script. To automatically administer any part of the system during
any stage of its operation, you can use the scripting tool to log in to the iLO 2 MP, access the
console, and send and receive commands in EFI or the OS.
64 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 65

NOTE: This guide is not meant as a substitute for instruction on various scripting tools that
are available for automating command-line interfaces. The iLO 2 MP TUI (when used with
command-line arguments) and the SMASH command-line interface were created with these
types of scripting tools in mind to facilitate powerful automation capabilities.
Expect Script Example
The following provides a simple Expect script example with no timeouts and no error checking
using telnet instead of SSH.
#!/usr/local/bin/expect -f
#
# (Portions of) this Expect script (were) was generated by autoexpect on
# Tue Nov 21 08:45:11 2006
# Expect and autoexpect were both written by Don Libes, NIST.
#
# Note that autoexpect does not guarantee a working script. It
# necessarily has to guess about certain things. Two reasons a script
# might fail are:
#
# 1) timing - A surprising number of programs (rn, ksh, zsh, telnet,
# etc.) and devices discard or ignore keystrokes that arrive "too
# quickly" after prompts. If you find your new script hanging up at
# one spot, try adding a short sleep just before the previous send.
# Setting "force_conservative" to 1 (see below) makes Expect do this
# automatically - pausing briefly before sending each character. This
# pacifies every program I know of. The -c flag makes the script do
# this in the first place. The -C flag allows you to define a
# character to toggle this mode off and on.
set force_conservative 0 ;# set to 1 to force conservative mode even if
;# script wasn't run conservatively originally
if {$force_conservative} {
set send_slow {1 .1}
proc send {ignore arg} {
sleep .1
exp_send -s -- $arg
}
}
#2) differing output - Some programs produce different output each time
# they run. The "date" command is an obvious example. Another is
# ftp, if it produces throughput statistics at the end of a file
# transfer. If this causes a problem, delete these patterns or replace
# them with wildcards. An alternative is to use the -p flag (for
# "prompt") which makes Expect only look for the last line of output
# (i.e., the prompt). The -P flag allows you to define a character to
# toggle this mode off and on.
#
# Read the man page for more info.
#
# -Don
#
# (End of auto-expect generated content)
#######################################################################
# USER
set mp_user "Admin"
# PASSWORD- get password from terminal instead of storing it in the script
stty -echo
send_user "For user $mp_user\n"
Text User Interface 65
Page 66

send_user "Password: "
expect_user -re "(.*)\n"
set mp_password $expect_out(1,string)
stty echo
# Other Constants
set timeout 20
########################################################################
## BEGIN
##
spawn $env(SHELL)
match_max 100000
#foreach mp_name {puma_mp lion_mp cougar_mp} {
set mp_name "puma_mp"
send_user "\n\n----- $mp_name -----\n\n"
# Frequently used Strings
set MA_PROMPT "$mp_name\] MP> $"
set CM_PROMPT "$mp_name\] MP:CM> $"
# Expect the UNIX prompt...
#expect "-> $"
#### Log into the MP #####
send -- "telnet $mp_name\r"
expect ".*MP login: $"
send -- "$mp_user\r"
expect "MP password: $"
send -- "$mp_password\r"
expect "$MA_PROMPT"
#Run SL command to dump logs
#send "sl -forward -view text -nc\r"
send -- "cm\r"
expect "$CM_PROMPT"
#Run PC command to power on the system
send -- "pc -on -nc\r"
expect "$CM_PROMPT"
send "ma\r"
expect "$MA_PROMPT"
send "x\r"
#}
expect eof
Command Menu Commands and Standard Command Line Scripting Syntax
The following list of commands is provided to help you learn about the Command menu
commands. Command-line interface scripting syntax for each command is provided to help you
accomplish a scripting task. The following rules apply to scripting syntax:
• The -nc (no confirmation) is optional. This special keyword designates that no user
confirmation isrequired to execute the command. If you enter -nc at the end of the command
line, the command is executed without asking you for user input. Without the -nc option,
you are asked to confirm the changes. The only exception to this rule is when a password
must be entered. In that case, you are prompted for a password separately. However,
66 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 67

commands that require a password can have that password entered on the command line
(FW, UC).
If -nc is specifiedon a command with no other parameters or with only a specific multilevel
selector, the command displays all or just the specific multilevel parameters. The absence
of a specific multilevel parameter on a command that has multilevels causes all the multilevel
parameters to display.
• Most commands accept -all default. This causes all parameters for that command to
be set to their default values.
• In some multilevel commands, you can use default to set that level to its default values.
• Further use of default on many individual parameters causes that parameter to be set to
its default value.
• -? (MP command-specific help) is optional. If you enter -? by itself with the command, a
usage display appears. In the event of an incorrect command line usage, in addition to the
error message, the usage display appears.
• Arguments in brackets [ ] are optional.
• Without arguments, the system prompts you for answers to questions.
• Entering a command without parameters takes you through the command interactively and
prompts you for all the options.
BP: Reset BMC passwords
Command access level: MP configuration access
BP resets the BMC user and administrator passwords.
Command line usage and scripting:
BP [ -nc ]
-?
See also: DC, RB, UC
BLADE: Display BLADE parameters
NOTE: This command is available only on a server blade.
Command access level: Login access
BLADE facilitates the cabling and initial installation ofHP Integrity server blades. It also provides
a quick view of the enclosure status. You must have configuration access right to turn the enclosure
locator UID LED on or off.
Onboard Administrator Configuration
OA IP Address IP address of the Onboard Administrator.
OA MAC Address MAC address of the Onboard Administrator.
Server Blade Configuration
Rack Name Logically groups together enclosures in a rack. The rack name is shared with
the other enclosures in the rack.
Rack UID Rack unique identifier.
Bay Number The blade enclosure can support up to eight HP Integrity server blades. When
viewed from the rack front, the bays are numbered from left to right, from 1 to
8. The bay number is used to locate and identify a blade.
Enclosure Information
Enclosure Name Logically groups together the server blades installed in the same enclosure.
The enclosure name is shared with the other server blades in the enclosure.
Health Indicates one of three states of health of this enclosure.
Text User Interface 67
Page 68

OK Normal operation, any issues have been acknowledged.
Degraded Typically loss of redundancy or partial failure of a component.
Critical Failure with loss or imminent loss of system function.
Command line usage and scripting:
BLADE [ -nc ]
blade -?
Example of the BLADE Command With Output
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM> blade
BLADE
Onboard Administrator Information:
IP Address : 192.0.2.1
MAC Address : 0x00xxxxxexxbb
Server Blade Information:
Rack name : RACK
Rack UID : 000z00xx0000
Bay Number : 3
Enclosure Information:
Enclosure name : encl
Health : OK
-> Command successful.
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM>
CA: Configure asynchronous local serial port
Command access level: MP configuration access
CA sets the parameters for the local and the remote serial console. Input and output data rates
are the same. The value returned by the stty command on HP-UX is the local serial port console
speed.
Set up the local serial port parameters as follows:
BAUD RATES Input and output data rates are the same. Possible values are as follows:
4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 115200 bit/sec.
FLOW
CONTROL
For HP Integrity server blades, the CA command also provides an option to change between the
Integrity iLO mode or the dedicated AUX UART mode. Switching to AUX UART mode when
MP remote access is disabled or LAN parameters are not configured requires a push button reset
to change back to iLO MP mode.
NOTE: Inconsistent bit rate settings can result in improper MP UI while switching between
these modes.
Hardware uses RTS/CTS; software uses Xon/Xoff.
The operation mode settings are saved on the MP NVRAM and are permanent for reset and
firmware upgrade of the iLO 2 MP, but the settings are not permanent for power cycles or blade
ejection. For power cycle to the blade, the console serial port is set back to the iLO mode.
If you cannot access the iLO 2 MP through telnet and the port mode of operation is AUX UART,
you must change the port operation mode to Integrity iLO mode to access the MP through the
serial port. To change the port operation mode to iLO, perform a hard reset to the MP by pushing
the recessed push button through a hole in the front panel. The hard reset resets the MP hardware
and sets the MP to the default settings. The hard reset returns the port default connection to MP.
68 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 69
NOTE: Both short and long reset button presses return the port default connection to the MP.
The iLO 2 MP mirrors the system console to the iLO 2 MP local and LAN ports. One console
output stream is reflected to all connected console users. If several different terminal types are
used simultaneously, some users can see unexpected results.
Command line usage and scripting:
CA [ -local ] [ -bit <n> ] [ -flow >software|hardware> ] ] [ -nc ]
-?
Server blade usage
CA [ -local ] [ -bit <n> ] [ -flow >software|hardware> ]
[ -mode ,aux|ilo> ] ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: SA
DATE: Display date
Command access level: Login access
DATE displays the date, as best known to the iLO 2 MP. The iLO 2 MP clock is updated from the
BMC/SFW and cannot be modified. The realtime clock is used only when the iLO 2 MP is first
powered on or rebooted, until it can obtain the correct date from the BMC.
Command line usage and scripting:
DATE [ -nc ]
-?
DC (Default Configuration): Reset all parameters to default configurations
Command access level: MP configuration access
DC sets all iLO 2 MP parameters back to their default values. To restore specific configurations
to their default values, use the following commands:
MP IP configuration : LC -all DEFAULT
Remote Access Configuration : SA -all DEFAULT
Command Interface configuration : IT -all DEFAULT
MP Security configuration : SO -opt DEFAULT
MP Session configuration : IT -all DEFAULT
MP User configuration : UC -all DEFAULT
MP LDAP directory configuration : LDAP -all DEFAULT
SNMP Configuration : SNMP - all DEFAULT
Use any of the following methods to reset passwords in the iLO 2 MP:
• In the UC command, change individual users or reset all users to default values.
• Reset passwords by pressing the iLO 2 MP reset button on the back panel of your HP server
for longer than four seconds. After the iLO 2 MP reboots, the local console terminal displays
a message for five seconds. Responding to this message in time enables a local user to reset
the passwords.
NOTE: All user information (logins, passwords, and so on) is erased when you use any of
the previous reset methods.
Command line usage and scripting:
DC [ -all default [ -nc ] ]
-?
DF: Display FRU information
Command access level: Login access
Text User Interface 69
Page 70

DF displays FRU information for FRU devices located behind the BMC. Information provided
includes serial number, part number, model designation, name and version number, and
manufacturer.
Command line usage and scripting:
DF [ -specific[ <fruid> ] | -all ] [ -view <text|hex> ] [ -nc ]
-?
DI: Disconnect LAN, WEB, SSH or Console
Command access level: MP configuration access
DI disconnects LAN, web SSL, or SSH users from the iLO 2 MP. It does not disable the ports. To
disable the ports, see the SA command for LAN/WEB/SSH/IPMI over LAN access. Use the TE
and WHO commands to identify the connected users before running this command.
Command line usage and scripting:
DI [ -telnet] [ —web ] [ -ssh ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: EX, SA, TE, WHO
DNS: DNS settings
Command access level: MP configuration access
DNS configures the DNS domain name and up to three DNS servers either manually or
automatically with DHCP. You can use this command only with DHCP enabled. You can also
perform a DDNS update through the primary DNS server as long as it is authoritative for the
zone.
If no DNS server IP addresses are specified, or the DNS domain is undefined, DNS is not used.
If an IP address was obtained through DHCP, an add name request is sent to the DDNS server
if it is enabled and registered.
Command line usage and scripting:
DNS [ [ -server <e|d> ] [ -domain <text> ] [ -name <e|d> ]
[ -register <y|n> ] [ -1ip <ipaddr> ] [ -2ip <ipaddr> ]
[ -3ip <ipaddr> ] ] | [ -all default ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: LC
FW: Upgrade the MP firmware
This command is only available to authorized HP service personnel.
The MP firmware is packaged along with system, BMC, and FPGA/PSOC firmware. You can
download and upgrade the firmware package from the HP website at:
http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport.
IMPORTANT: When performing a firmware upgrade that contains system programmable
hardware, you must properly shut down any OS that is running before starting the firmware
upgrade process.
Select the download for Integrity firmware and follow the directions provided in the release
notes.
After the upgrade, reconnect and log in as user Admin and password Admin (case sensitive).
HE: Display help for menu or command in command menu interface
Command access level: Login access
70 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 71
HE displays the MP hardware and firmware version identity, and the date and time of firmware
generation.
• If executed from the MP Main Menu, HE displays general information about the iLO 2 MP
and those commands available in the MP Main Menu.
• If executed in command mode, HE displays the MP Help: Command Menu List. HE also
displays detailed help information in response to a topic or command at the help prompt.
Command line usage and scripting:
HE [ -topic | command ] [ -nc ]
-?
ID: System information settings
Command access level: MP configuration access
ID displays and modifies the following:
SNMP contact person Name, telephone, e-mail, and pager number.
Server information Location, rack ID, position, asset tag.
System host name The system host name of the operating system.
Command line usage and scripting:
ID [ { -host [ <text> ] }
| { -person [ -name <text> ] [ -telephone <text> ]
[ -email <text> ] [-pager <text> ] }
| { -server [ -location <text> ] [ -rackid <text> ]
[ -position <text> ] } ]
[ -tag <text> } ] [ -nc ]
-?
NOTE: The system host name information is not retained across
iLO 2 MP reboots.
IT: Inactivity timeout settings
Command access level: MP configuration access
IT prevents sessions on the system from being inadvertently left open. When you initiate an iLO
2 MP command, other users are prohibitedfrom running any commands until thefirst command
has been completed or until it times out. Command interface inactivity timeout specifies that
timeout value. This prevents a user from inadvertently keeping the iLO MP locked in a command,
preventing other users from running iLO 2 MP commands.
NOTE: The iLO 2 MP command interface inactivity timeout cannot be deactivated.
Use the flow control timeout to prevent any user who is using a terminal that does not obey flow
control from locking the system out from other users.
The following are IT command parameters:
iLO 2 MP inactivity timeout One to 30 minutes (default is three minutes).
Flow control timeout Zero to 60 minutes. If the flow control timeout is set to
Command line usage and scripting:
IT [ -command <n> ] [ -flow <n> ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: SA
zero, no timeout is applied. A mirroring flow control
condition ceases when no flow control condition exists on
any port. This timeout prevents mirrored flow control from
blocking other ports when inactive.
Text User Interface 71
Page 72

LC: LAN configuration usage
Command access level: MP configuration access
LC modifies the LAN configuration parameters.
IMPORTANT: If you are connected through a network and you make any changes to DHCP
status, IP address, subnet mask, or gateway IP address, the iLO 2 MP automatically resets once
you confirm the change.
If you are connected through a serial console and you make any changes to DHCP status, IP
address, subnet mask, or gateway IP address, the iLO 2 MP alerts you to manually reset the iLO
2 MP.
Configurable parameters include the following:
• iLO 2 MP IP address
• DHCP status (default is enabled)
— If the IP address, gateway IP address, or subnet mask was obtained through DHCP,
you cannot change the DHCP status without first disabling DHCP.
— If you change the DHCP status to enabled or disabled, the IP address, subnet mask,
and gateway address are set to their default values (127.0.0.1:0xffffff00), and the DNS
parameters are voided.
— When you change the DHCP status from enabled to disabled, the DNS parameters for
DHCP are set to disabled, and the Register with DDNS parameter is set to No.
— When you change the DHCP status from disabled to enabled, the DNS parameters for
DHCP are set to enabled, and the Register with DDNS parameter is set to Yes .
• iLO 2 MP host name
— The iLO 2 MP host name set in this command is displayed at the iLO 2 MP command
mode prompt. Its primary purpose is to identify the iLO 2 MP LAN interface in a DNS
database.
— If you change the iLO 2 MP host name and the IP address was obtained through DHCP
and DDNS is registered, a delete old name request for the old host name and an add name
request for the new host name are sent to the DDNS server.
— Typically you enter the DNS name for the LAN IP. You can program this field to any
useful name or phrase. For clarity, enter MPNAME-on-SYSTEM as the MP Host name,
so both names show up in the prompt. The limit is 19 characters, and no spaces are
allowed.
• Subnet mask
• Gateway IP address
• Local console serial port
• Link state
• SSH access port number
Command line usage and scripting:
LC [ -ip <ipaddr> ] [ -subnet <subnet> ] [ -gateway <ipaddr> ]
[ -host <text> ] [ -web <n> ] [ -link <auto|T<10baseT)> ]
[ -ssh <n> ] [ -dhcp <e|d> ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: DNS, LS, SA
LDAP: LDAP directory settings
Command access level: MP configuration access
72 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 73

LDAP displays and modifies the following LDAP directory settings:
• Directory Authentication: Activates or deactivates directory support on the iLO 2 MP.
— Enable with Extended Schema: Selects directory authentication and authorization using
directory objects created with the HP schema. Select this option if the directory server
is extended with the HP schema and you plan to use it.
— Enable with Default Schema: Selects directory authentication and authorization using
user accounts in the directory which has not been extended with the HP schema. User
accounts and group memberships are used to authenticate and authorize users. Data
in the Group Administration page must be configured after you select this option. In
the Group Administration page, configure one or more directory groups by entering
the distinguished name of the group and privileges to be granted to users who are
members of that group.
— Disable: Deactivates directory support on the iLO 2 MP.
• Local User Accounts: Includes or excludes access to local iLO 2 MP user accounts. If local
user accounts are enabled, you can log in to the iLO 2 MP using locally stored user credentials.
If they are disabled, access is limited to valid directory credentials only.
NOTE: Locally stored user accounts can be active while directory support is enabled. This
enables both local- and directory-based user access. If both directory authentication and
local user accounts are enabled, login is attempted using the directory first, then using local
accounts.
• Directory Server IP Address: IP address or host name of the directory server.
• Directory Server LDAP Port: Port number for the secure LDAP service on the server. The
default value for this port is 636.
• Distinguished Name: Specifies where this iLO 2 MP instance is listed in the directory tree.
For example: cn=MP Server,ou=Management Devices,o=hp
• User Search Contexts (1,2,3): User name contexts that are applied to the login name entered
to access the iLO 2 MP.
User name contexts are used to locate an object in the tree structure of the directory server
and applied to the login name entered to access the iLO 2 MP. All objects listed in the
directory can be identified using their unique distinguished name. However, distinguished
names can be long, users might not know their distinguished names, or they might have
accounts in different directory contexts. Search contexts enables users to specify common
directory contexts, so that they do not have to enter their full distinguished name at login.
iLO 2 MP attempts to authenticate a user in the directory first by the login name entered,
and then by applying user search contexts to that login name until login succeeds. For
example:
Instead of logging in as cn=user,ou=engineering,o=hp, search context of
ou=engineering,o=hp enables a user to log in as user
When extended schema is selected and Active Directory is used as a directory server.
Microsoft Active Directory has an alternate user credential format. A user can log in as:
user@domain.hp.com, in which case a search context of @domain.hp.com enables the
user to login as user.
Command line usage and scripting:
LDAP [ -directory [ -ldap <d|x|s> ] [ -mp <e|d>]
[ -ip <hostname/ipaddr> ] [ -port <n>]
[ -dn <text> ] [ -1context <test>]
[ -2context <text>] [ -3context <text>]
| -groups [ -change <groupNo.> [ -dn <text>]
[ rights <e|d>]
<console|mp|power|user|virtual|all|none> ]
[ -list <groupNo.> ]]
Text User Interface 73
Page 74

| -nc ]
-?
See also: LOGIN, US
LDAP: LDAP group administration
LDAP enters one or more directory groups by specifying the distinguished name of the group
and privileges to be granted to users who are members of that group.
You must configure group administration information when the directory is enabled with the
default schema.
The group administration section of the LDAP command enables users to enter one or more
directory groups by specifying the distinguished name of the group and privileges to be granted
to users who are members of that group.
When a user attempts to log in to the iLO 2 MP, the iLO 2 MP reads that user’s directory name
in the directory to determine which groups the user is a member of. The iLO 2 MP compares this
information with a list of configured groups. The rights of all the matched groups are combined
and assigned to that user.
LDAP: LDAP Lite
LDAP Lite enables you to use directory authentication for logging in to the iLO 2 MP without
having to do any schema extension on the directory server or snap-in installation on the client.
For information on LDAP Lite, see “Configuring LDAP Lite Default Schema” (page 56).
LM: License management
Command access level: MP configuration access
LM displays your current license status. Use it to enter a license key to enable the Advanced Pack
license features.
Command line usage and scripting:
LM [ -key <license key> ] [ -nc ]
-?
LOC: Locator UID LED configuration
Command access level: MP configuration access
LOC displays the current status of the locator UID LED and enables you to turn the locator UID
LED on or off.
In HP Integrity server blades, this command also enables you to turn the enclosure locator UID
LED on or off. The UID LED physically identifies the blade in a data center environment. It emits
a blue light when turned on. It does not have an associated button. You can control the UID LED
from the BMC only.
Command line usage and scripting:
LOC [ -on | -off [ -nc ] ]
-?
Server blade usage
LOC [ -server <on | off> ] [-enclosure <on | -off>] [ -nc ]
-?
LS: LAN status
Command access level: Login access
LS displays all parameters and the current status of the iLO 2 MP LAN connections. The LAN
parameters are not modified by this command.
74 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 75

Command line usage and scripting:
LS [ -nc ]
-?
See also: DNS, LC, SA
PC: Power control access
Command access level: Power control access
PC enables control of the power management module. It provides the following options for
remote control of system power:
ON
OFF
CYCLE
Graceful Shutdown
Command line usage and scripting:
PC [ -on | -off | -graceful | -cycle ] [ -nc ]
-?
Example:
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM> pc -on -nc
Turns the system power on. This command has no affect if the power
is already on.
Turns the system power off. This command is equivalent to turning
the system power off at the front panel switch. There is no signal sent
to the OS to shut the software down before power is turned off. To
turn the system off gracefully, ensure that the OS is shut down before
running this command.
Turns the system power off, then on. The delay between off and on
is 30 seconds.
The BMC sends a signal to the OS to shut down prior to turning off
the system power.
PC -on -nc
System will be powered on.
-> System is being powered on.
-> Command successful.
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM>
See also: PR, PS
PM: Power regulator mode
Command access level: Power control access
PM provides the following options for remote control of the system power regulator:
Dynamic Enables the system to dynamically change the processor power level when needed
based on current operating conditions. The system remains in this mode unless the
system is reset or an OS-hosted application requests a processor state change. In
these cases, power management mode changes to OS Control Mode.
Low Sets the processor to the lowest supported processor state and forces it to stay in
that lowest state until the system is reset. If the processor is reset, the power mode
changes to OS Control Mode.
High Sets the processor to the highest supported processor state and forces it to stay in
that highest state unless the system is reset or an OS- hosted application requests a
state change. If the processor is reset, the power mode changes to OS Control Mode.
OS Sets the control of the power regulator to the OS.
Command line usage and scripting
Text User Interface 75
Page 76

Example
[gstl0074] MP:CM> pm
PM [ -dynamic | -low | -high | -os ] [ -nc ]
PM -?
[gstl0074] MP:CM> pm
PM
Current System Power Mode : Dynamic Mode
Power Regulator Menu:
D - Dynamic Power Savings Mode
L - Static Low Power Mode
H - Static High Performance Mode
O - OS Control Mode
Enter menu item or [Q] to Quit: O
O
Power mode will be set to OS Control.
Confirm? (Y/[N]): y
y
Please wait ..
-> Power mode has been successfully changed
See also: PC, PR
PR: Power restore policy configuration
Command access level: MP configuration access
PR configures the power restore policy. The power restore policy determines how the system
behaves when ac power returns after an ac power loss.
• If PR is set to On, the system powers on after ac is applied.
• If PR is set to Off, the system stays powered off after ac is applied. Push the system power
button or run the PC command to power on the system.
• If PR is set to Previous, the power is restored to the state that was in effect when the ac
power was removed or lost.
Command line usage and scripting:
PR [ -on | -off | -previous ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: PC
PS: Power status
Command access level: Login access
PS displays the system power state, the temperature, and status of the power supplies and fans.
Command line usage and scripting:
PS [ -nc ]
-?
See also: PC, SS
RB: Reset BMC
Command access level: MP configuration access
RB resets the BMC by toggling the GPIO BMC reset line.
Command line usage and scripting:
76 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 77

RB [ -nc ]
-?
See also: PC, SS
RS: Reset system through the RST signal
Command access level: Power control access
IMPORTANT: During normal system operation, shut down the OS before issuing the RS
command.
RS resets the system (except iLO 2 MP) through the RST signal.
Running this command irrecoverably halts all system processing and I/O activity and restarts
the system. The effect of this command is similar to cycling the system power. The OS is not
notified, no dump is taken as the system shuts down, and so on.
Command line usage and scripting:
RS [ -nc ]
-?
See also: TC
SA: Set access LAN/WEB/SSH/IPMI over LAN ports
Command access level: MP configuration access
SA sets access permissions for users logging in to the iLO 2 MP over the LAN. You can set the
iLO 2 MP to allow telnet access, web access, SSH, IPMI over LAN, or all four.
If LANor web users are connected when a disable from this command runs, they are disconnected.
Any future incoming connection request to the corresponding port is rejected.
Command line usage and scripting:
SA [ -telnet <e|d> ] [ -web <e|d> ] [ -ssh <e|d> ]
[ -lanipmi <e|d> ] [ -command <mpmenu|smclp> ] [ -nc ]
-?
SNMP: Configure SNMP parameters
Command access level: MP configuration access
SNMP performs the following actions:
• Enable or disable the SNMP server. Disabling the SNMP server prevents all access to the
SNMP management information base (MIB) objects and alsoprevents sending of any SNMP
alerts.
• Enable or disable the SNMP alerts feature separate from the general SNMP server.
NOTE: Currently, the SNMP alert feature is only supported on HP Integrity server blades.
• Configure up to four destination IP addresses where SNMP alerts will be sent. Alerts are
sent by the iLO 2 MP to these destinations for power shutdown, system reset, and system
fatal error events.
• Configure the community string, thereby securing the access to the MIB objects.
To configure SNMP parameters, follow these steps:
1. At the MP:CM> prompt, enter SNMP.
2. To change the SNMP status, enter N. Enabled is the default.
3. Enter E to enable or D to disable all SNMP access. The screen displays the new SNMP
configuration settings.
4. To change the SNMP alert status, enter T. Disabled is the default.
Text User Interface 77
Page 78

5. Enter E to enable or D to disable all SNMP alerts. The screen displays the new SNMP
configuration settings.
NOTE: Currently, the SNMP alert feature is supported on HP Integrity server blades only.
6. To configure a destination IP address for SNMP alerts, enter 1 2 3 4. The default is blank
(unused).
7. To configure the community string to secure the access to the MIB objects, enter C. The
default is public.
Command line usage and scripting
SNMP [ -status <e|d> ] [ -community [ <text> ] ] [ -nc ]
-?
Command line usage and scripting for server blades:
SA [ -status <e|d> ] [ -community [ <text> ] ] [ -traps <e|d> ]
[ -1dest <ipaddr> ] [ -2dest <ipaddr> ] [ -3dest <ipaddr> ]
[ -4dest <ipaddr> ] [ -nc ]
-?
See also: ID
SO: Security option help
Command access level: MP configuration access
SO modifies the security option of the iLO 2 MP (login timeouts, password faulty, SSL certificate
generation, SSH keys).
The following are SO command parameters:
• Login timeout: Zero to five minutes. This is the maximum time allowed to enter login name
and password after the connection is established. The connection is interrupted when the
timeout value is reached. The local console restarts the login; for all other terminal types,
the connection is closed. A timeout value of 0 means there is no timeout set for the login.
The login timeout and the timeout value is effective on all ports including the local port.
However, the local port cannot be disconnectedlike other ports on login timeout. For example,
if a local port user sits at the MP Login : prompt, nothing happens even if a timeout occurs.
But, if a local port user enters a login name, sits at the MP Password : prompt, and if a
timeout occurs at this stage, this login is cancelled and the MP Login: prompt reappears.
• Number of password faults allowed: 1 to 10. This parameter defines the number of times a
user can attempt to log in to a console before being rejected and having its connection closed.
• SSL certificate: Enables the generation of SSL certificates.
• SSH keys generation: Enables SSH keys authorization.
• iLO 2 MP reset: Enables an iLO 2 MP reset through IPMI from BMC, system, or IPMI over
LAN.
• iLO 2 MP password reset: Enables iLO 2 MP password reset through IPMI from BMC,
system, or IPMI over LAN.
Command line usage and scripting:
SO [ { -options [ -login <n> ] [ -number <n> ] [ -fwpci <e|d> ]
[ -reset <e|d> ] [ -pwdreset <e|d> ] }
| { -ss1 [ -name <text> ] [ -organization <text>] [ -unit <text> ]
[ country <text> ] [ -region <text> ] [ -locality <text> ]
[ -email <text> ] }
| { -ssh } ] [-nc ]
-?
SS: System Status
Command access level: Login access
78 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 79

SS displays the status of the system processors and which processor is the monarch.
The iLO 2 MP learns the system configuration through the events it receives from the system.
There is usually a delay between any processor configuration change and what is displayed by
this command. For the most up-to-date processor configuration information, use the EFI or BCH
prompt.
Command line usage and scripting:
SS [ -nc ]
-?
See also: PS
SYSREV: Firmware revisions
Command access level: Login access
SYSREV displays the current firmware revisions in the system.
Command line usage and scripting:
SYSREV [ -nc ]
-?
Example:
MP:CM> SYSREV
Current firmware revisions
MP FW : F.01.57
BMC FW : 75.12
EFI FW : ROM A 05.63, ROM B 05.60
System FW : 01.40
PDH FW : 00.0d
UCIO FW : 03.0a
PRS FW : 00.08 UpSeqRev: 01, DownSeqRev: 01
TC: System reset through INIT or TOC signal
Command access level: MP configuration access
NOTE: During normal operation, shut down the OS before issuing this command.
TC resets the system through the INIT or TOC signal. Running this command irrecoverably halts
all system processing and I/O activity and restarts the computer system. It is different from the
RS command in that the processors are signaled to dump state as they shut down.
Command line usage and scripting:
TC [ -nc ]
-?
See also: RS
TE: Send a message to other mirroring terminals
Command access level: MP configuration access
TE treats all displayable characters following the command as a comment. Characters typed are
broadcast to the connected console clients when you press Enter. The string size is limited to 80
characters. Any extra characters are not broadcast to other console clients.
NOTE: The broadcast message is sent only to Command Menu clients, and does not include
users connected to MP Main Menu functions.
Command line usage and scripting:
Text User Interface 79
Page 80

TE <text> [ -nc ]
-?
UC: User Configuration (users, passwords, and so on)
Command access level: User administration access
UC adds, modifies, re-enables, or deletes any of the following user parameters:
• Login ID
• Password
• User Name
• User Workgroup
• User Access Rights
• User Operating Mode
• User Enabled
There are two default users, Admin and Oper. The Admin user has all rights (C, P, M, U,
and V). The Oper user has the console access right by default. You can change the configuration
of these default users with the UC command.
All users have the right to log in to the iLO 2 MP and to run Status (Read-only) commands (view
event logs, check system status, power status, and so on), but not to run any commands that alter
the state of the iLO 2 MP or the system.
The following commands are available to all users: CL, DATE, DF, HE, LS, PS, SL, SS, SYSREV,
TE, VFP, WHO, XD (status options)
An iLO 2 MP user can also have any or all of the following rights:
Console Access Right to access the system console (the host OS). This does
not bypass host authentication requirements, if any.
Command: CO
Power Control Access Right to power on, power off, or reset the server, and to
configure the power restore policy.
Commands: PC,PR, RS, TC
Local User Administration Access Right to configure locally stored user accounts.
Commands: UC
iLO 2 MP Configuration Access Right to configure all iLO 2 MP settings (and some system
settings, such as the power restore policy).
Commands: BP, CA, CL, DC, DI, FW, ID, IT, LC, LDAP, LOC,
PG, RB, SA, SO, XD
Virtual Media Access Enables Advanced Pack license users the right to use the
vMedia applet.
NOTE: The vMedia feature is available only if you have
the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license and the user vMedia
access right.
Command line usage and scripting:
UC [ -new <login> —user <text> [ -workgroup <text> ]
[ -rights <e|d> <console|mp|power|user|virtual|all|none> ]
[ -mode <single|multiple> ] [ -enable <e|d> ]
[ -password <value> ] ]
[ -change <login> [-login<newlogin> ] [ -user <text> ]
[ -rights <e|d> <console|mp|power|user|virtual|all|none> ]
[ -workgroup <text> ] [ -mode <single|multiple> ]
80 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 81

[ -enable <e|d> \ [ -password [ <value> ]
[ -delete <login> ] | [ -list <login> ] ] [ -nc ]
-?
Example:
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM> uc -delete Oper -nc
UC -delete Oper -nc
Current User Parameters:
User Login ID : Oper
User Password : ************
User Name : Default Operator
User Workgroup :
User Access Rights : Console access, Virtual Media
User Operating Mode : Multiple
User Enabled/Disabled : Enabled
-> Current User will be deleted
User may be disconnected in this process
-> User Configuration has been updated.
-> Command successful.
[gstlhpg1] MP:CM>
See also: CA, SO, LDAP
WHO: Display a list of iLO 2 MP connected users
Command access level: Login access
WHO displays the login name of the connected console client users, the ports on which they are
connected, and the mode used for the connection.
• Login name
• Login type (LDAP or local authentication)
• User access rights
• Connection port (local, remote, telnet, web, SSH)
• IP address (for telnet, web, SSH)
• Current MP mode that user is in (MA—MP Main Menu, CM—Command menu, LIVE—live
event viewer, VFP—VFP mode)
For LANand serial console clients, the command displays the IP address. When DNS is integrated,
the host name appears as well.
The local port now requires a login. A user must be logged into the system, or no local port
displays.
Command line usage and scripting:
WHO [ -nc ]
-?
See also: DI, TE
XD: iLO 2 MP Diagnostics or reset
Command access level: MP configuration access for resetting the iLO 2 MP, console access for
all other XD options
Text User Interface 81
Page 82

XD performs simple checks to confirm the iLO 2 MP health and its connectivity status. The
following tests are available:
• iLO 2 MP Parameter Checksum in NVRAM
• Verify I2C connection (get BMC device ID)
• LAN connectivity test using the ping command
• History of firmware updates and other activities
You can use the XD command plus its R command option to reset the iLO 2 MP. You can safely
perform an iLO 2 MP reset without affecting the operation of the server.
You can also reset the iLO 2 MP through the web interface or by pressing the iLO 2 MP reset
button.
Command line usage and scripting:
XD -parameter | -i2c |-lan <ipaddr> | -reset | -hist ] [ -nc ]
-?
Web GUI
This section describes the functions and features of the web graphical user interface (GUI).
Some of the functionality in the web GUI only display if you have the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack
license. For more information on the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license, see “Advanced Pack
License” (page 23) and the HP website at:
http://h71028.www7.hp.com/enterprise/cache/279991-0-0-0-121.html
NOTE: Cookies must be enabled on the web browser in order to successfully login to the iLO
2 MP web GUI.
System Status
The System Status tab enables you to access the following pages:
• Status Summary: General and Active Users
• Server Status: General and Identification
• SEL
Status Summary > General
The Status Summary General page (Figure 6-2) displays a brief status summary of the system.
82 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 83

Figure 6-2 Status Summary General Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
Table 6-6 lists the fields and descriptions.
Table 6-6 Status Summary General Page Description
System Power
Firmware Revisions
Locator UID LED
Status Summary > Active Users
The Active Users page (Figure 6-3) displays information about the users currently logged in to
the iLO 2 MP.
DescriptionField
The current power state (ON/OFF/STANDBY) of the system and the corresponding
power LED state.
The most recent entry in the SEL.Latest SEL Entry
Displays the current firmware revisions for iLO MP, BMC,EFI, system firmware, PDH,
UCIO, and PRS.
The IP address of the iLO 2 MP subsystem.iLO 2 MP IP Address
Displays the date and time as known to the iLO 2 MP.Date & Time
Displays the status of the blue locator or UID LED and enables you to turn the Locator
LED on or off.
Note: The system's (Yellow) attention LED, which is separate from the locator LED, is
lit automatically if a Warning event is present in the SEL. To clear the attention LED,
read the SEL.
Web GUI 83
Page 84

Figure 6-3 Status Summary Active Users Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
Table 6-7 lists the fields and descriptions.
Table 6-7 Active Users Page Description
Access Type
Authorized
Rights
Mode
Server Status > General
DescriptionField
Multiple access methods are available: Serial, telnet, SSH, SSL web or IPMI over LAN.
IPMI, vMedia, and vKVM/IRC users are not listed in web GUI sessions.
The user currently logged in through a particular access type.User Login
The IP address of the active user.IP Address
The type of authentication: LDAP directory user authentication (LDAP) or locally
stored iLO 2 MP user accounts (local).
Rights control the iLO functions a user can perform. There are five user access rights:
console access, iLO 2 MP configuration, power control, virtual media, and user
administration. A user can be configured to have some, none, or all the access rights.
Current iLO 2 MP mode that the user is in. Text user interface modes are: MA, MP
Main Menu; CM, MP Command menu; CO, console; LIVE, Live event viewer; VFP,
VFP mode.
Enables a user with sufficient privileges to disconnect users of a certain access type.Disconnect
The Server Status General page (Figure 6-4) displays the status of server components. It also
displays the status of the system processors and which processor is the monarch.
84 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 85

Figure 6-4 Server Status General Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
Table 6-8 lists the fields and descriptions.
Table 6-8 Server Status General Page Description
System Processors
Server Status > Identification
The Identification page enables you to configure system information for identifying the server.
DescriptionField
Displays the current power state of thesystem and the corresponding power LED state.System Power
Displays the temperature status.Temperature
Lists the power supplies and their status and type.Power Supplies
Lists the fans and fan status.Fans
Displays the status of the processor.
NOTE: For BL c-Class servers, you can obtain information on power supplies and
fans through the Onboard Administrator. See “BL c-Class” (page 121).
Web GUI 85
Page 86

Figure 6-5 Server Status Identification Page
Table 6-9 lists the fields and descriptions.
Table 6-9 Server Status Identification Page Description
Bay
NOTE: Many of the fields are published by the iLO 2 MP's SNMP for visibility to management
applications on the network.
System Event Log
The System Event Log (SEL) page (Figure 6-6) enables you to view the contents of the event logs
that have been stored in nonvolatile memory. A user with login rights can view the SEL. You
must have iLO configuration access right to clear the logs.
DescriptionField
Displays the server host name.Server Host Name
Displays the rack unique identifier: a known unique identifier for the rack.Rack UID
Displays thebay number. The blade enclosure cansupport as many as eightHP Integrity
server blades. When viewed from the rack front, the bays are numbered from left to
right and from 1 to 8. The bay number is used to locate and identify a blade.
Enter the contact information in these fields.Contact Person
86 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 87

Figure 6-6 System Event Log Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
Table 6-10 lists the fields, buttons, and descriptions.
Table 6-10 System Event Log Page Description
DescriptionFields and Buttons
System Event Log
Forward Progress Log
Boot Log
High attention events and errors. Reading the SEL off the attention LED (blinking
yellow light).
Contains events of all types. Does not need to be cleared. In a web GUI session you
cannot view forward progress logs, only SEL logs.
All events between start of boot and boot complete. You cannot view boot logs or
previous boot logs from a web session.
The boot log from the previous boot.Previous Boot Log
Deletes the log.Delete Log
NOTE: You can view only the most pertinent fields for each event on the web. For a more
complete decoding of the events, use the TUI available by logging in to the iLO 2 MP through
telnet or SSH.
Events
Events can be a result of a failure or an error (such as fan failure, Machine-Check Abort, and so
on). They can indicate a major change in system state (such as, firmware boot start or, system
power on/off), or they can be forward progress markers (such as CPU selftest complete).
Events are produced by intelligent hardware modules, the OS, and system firmware. Events
funnel into BMC from different sources throughout the server. The iLO 2 MP polls the BMC for
new events and stores them in nonvolatile memory. Events communicate system information
Web GUI 87
Page 88

from the source of the event to other parts of the system, and ultimately to the system
administrator.
The log viewer contains an event decoder to help you interpret events.
The following event severity (or alert) levels are defined:
0: Minor forward progress
1: Major forward progress
2: Informational
3: Warning
5: Critical
7: Fatal
Integrated Remote Console (vKVM)
The Integrated Remote Console (IRC) offers a remote console interface for Windows clients
running Internet Explorer. The iLO 2 MP graphical IRC provides Virtual Keyboard, Video
(monitor), and Mouse (vKVM) capabilities with KVM over IP performance. The IRC data stream
is encrypted, enabling you to securely view and manage the server.
The vKVM functionality enables a user with console access right and the Advanced Pack license
to do the following:
• View the server graphics console and control the keyboard and mouse, as if you were
standing in front of the remote server
• Access the server from any location on the same network
• Perform maintenance activities.
• Diagnose server failures interactively
• Perform a controlled reset of the server, regardless of the state of the host operating system,
and remain connected to monitor the reboot process
• View a complete boot sequence following an automatic server recovery event
• View a log of remote console events
• Modify login passwords without administrator access right
• Remotely change the configuration parameters of the IRC
Because the iLO 2 MP IRC is hardware-based, it is available regardless of the state of the operating
system.
IRC Requirements and Usage
The IRC feature is only available if you have the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license. If the iLO 2
MP is not licensed to use the IRC, see the Licensing page under the Administration tab to activate
the Advance Pack license.
Internet Explorer version 6 with Service Pack 1 and above is the only supported browser for this
feature. Windows is the only supported client operating system on HP Integrity servers for
vKVM. Additionally you must allow downloading and usage of signed ActiveX controls.
Only one user has access to the IRC at a time. You must have console access right to use this
feature. If you do not have console access right, see the User Administration page under the
Administration tab to add this access right.
The IRC runs as an ActiveX control that is downloaded to clients running Internet Explorer 6.0
with Service Pack 1 and above on Windows clients. No additional software is required on the
remote server or client system.
The ActiveX control automatically downloads from the iLO 2 MP on the first client connection.
The IRC uses encryption and compression to provide a secure connection.
88 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 89
NOTE: When working on multiple systems, controls for each system are displayed on a separate
screen for each server. Additionally, you must allow downloading and usage of signed ActiveX
controls.
Before running the IRC, note the following:
1. Verify that the IRC is available. Only one user can control the IRC at a time. If a remote
console session already exists on the system, you are notified that IRC use is unavailable.
To determine if the remote console/IRC isavailable for use, click Remote Console Integrated
Remote Console. If Launch is grayed out and the Maximum console number has
been reached status message appears, the remote console/IRC is in use by another client.
2. Verify that you have console access right on the User Administration page, or if the right
must be granted.
3. Verify that the system is licensed for IRC use. View this information on the
Administration Licensing tab. For more information, see “Advanced Pack License”
(page 23).
4. Disable any popup-blocking applications. Popup-blocking applications prevent the IRC
from running.
5. Accept the IRC certificate. Refusing to accept the IRC certificate causes a red X to be displayed
in the IRC and prevents the IRC from working on that client.
Limitations of the vKVM Mouse and Keyboard
IRC does not yet provide identical virtualization of the Windows keyboard. Some known issues
are:
• No support for system-level commands such as Ctrl + Esc, or Print Screen.
• Pressing the Ctrl key locks the virtual mouse. Releasing the Ctrl key unlocks the virtual
mouse.
• No support for simultaneous mouse click and keystroke combinations.
• The IRC closes after 15 minutes if there is no mouse or keyboard activity.
• A slight delay might be observed between the physical and virtual mouse pointer.
NOTE: If you run system discovery utilities such as MAPPER or IOSCAN, the output might
display an extra keyboard and mouse that are not physically connected. This is a consequence
of the vKVM feature.
Browsers and Client Operating Systems that Support vKVM
Currently, the only browser that supports vKVM is Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 with Service
Pack 1 and above.
Client operating systems that support vKVM are as follows:
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
• Microsoft Windows XP Professional
• Microsoft Windows 2003
NOTE: Currently, vKVM is not supported on HP-UX, Linux, or OpenVMS.
vKVM-Supported Resolutions and Browser Configurations
Set your Windows-based HP Integrity server to the following specifications to properly access
and view the IRC and optimize performance.
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Console Resolution Settings for vKVM
The following settings are suggested for display and mouse properties:
Web GUI 89
Page 90

Server Display Properties
• Set the background to plain (no wallpaper pattern) on the host server.
• Set the client screen resolution higher than the host server for best remote console
performance.
• Set the display resolution to 800 x 600 pixels, or the maximum supported resolution of 1024
x 768 pixels.
NOTE: The resolution on the host server must not exceed 1024 x 768 pixels. Higher
resolutions can produce unpredictable results.
• Set the display color mode to 256 colors, or 24-bit colors.
Server Mouse Properties
• Select None for mouse pointer scheme.
• Select Disable Pointer Trails.
• Deselect Enable Pointer Shadow.
• Select Motion or Pointer Options, and set the pointer speed slider to the middle position.
• Deselect Enhanced pointer precision.
To automate setting an optimal mouse configuration, download the Lights-Out Optimization
utility from the HP website at:
http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
Click the Best Practices graphic and click the Maximize Performance links.
Accessing the IRC
To access the IRC, select Remote Console > Integrated Remote Console and click Launch.
The IRC might experience a slight delay as it first loads on your browser.
The IRC page refreshes every 10 seconds.
Figure 6-7 shows the IRC page.
90 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 91

Figure 6-7 Integrated Remote Console Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
Table 6-11 lists the fields, buttons, and actions.
Table 6-11 IRC Page Description
ActionFields and Buttons
Fullscreen
Launch
Resizes the IRC page.
For fullscreen with multi-head client, launch the browser from the primary display.
Resizes the IRC page to the same display resolution as the remote host. To open the
server’s graphic console in a new browser window, click Launch.
The IRC displays the host server’s graphics console (Figure 6-8).
Web GUI 91
Page 92

Figure 6-8 Integrated Remote Console Window
Table 6-12 lists the menu bar, buttons, and actions you can perform in the IRC window.
Table 6-12 IRC Window Description
ActionMenu Bar Buttons
Thumb Tack
Ctrl+Alt+Del
Enables you to keep the menu open, or retracts it when the mouse is moved
away.
Enables you to simulate the Ctrl Alt Del keyboard sequence on a remote
console.
Enables you to close and exit the console and return to the client desktop.Exit (red button)
IMPORTANT: For security purposes, if you log in to a host server through the IRC, you should
log out before closing the IRC.
NOTE: When you run system discovery utilities such as MAPPER or IOSCAN, the output
might display an extra keyboard and mouse that are not physically connected. This is a
consequence of the vKVM feature.
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen
The IRC Fullscreen causes your client to resize its screen to the same resolution as the remote
server. The IRC Fullscreen automatically chooses the best client display settings for that resolution;
92 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 93

however, some monitors have trouble with the highest screen refresh rates supported by the
video adapter. If this occurs, follow these steps:
1. To check our desktop properties, right-click the desktop and select
Properties>Settings>Advanced>Monitor.
2. Select a lower screen refresh rate.
3. To resize the IRC to the same display resolution as the remote host, select Fullscreen before
you click Launch.
4. Use the red X to exit the IRC and return to your client desktop.
Remote Serial Console
The Remote Serial Console page (Figure 6-9) enables you to securely view and manage a remote
server. You must have console access right to use this feature.
You can also connect to the system console by launching View Console from the Remote Serial
Console page.
Figure 6-9 Remote Serial Console Page
NOTE: The BL c-Class tab is available only on HP Integrity server blades.
The remote serial console is a Java applet that requires Java Plug-in 1.4.2-10 to be installed on
the client system. This applet enables connection to the server serial console over default port
2023. You can configure this port through the Administration > Access Settings page. All data
on this port is encrypted using RC4. The remote serial console provides terminal emulation.
Remote serial console operates with all the operating systems and browsers supported by the
iLO 2 MP.
NOTE: Pop-up blocking applications prevent remote serial console from running. Disable any
pop-up blocking applications before starting the remote serial console.
The iLO 2 MP mirrors the system console to the iLO 2 MP local, remote, and LAN ports. One
console output stream is reflected to all of the connected console users. If several different terminal
Web GUI 93
Page 94

types are used simultaneously by the users, some users may see unexpected results. Only one
of the mirrored users at a time has write access to the console. Write access is retained until
another user requests console write access. To get console write access, enter Ctrl-Ecf.
To ensure proper operation of the remote serial console, verify the following conditions:
• Your emulator can run the supported terminal type.
• The iLO 2 MP terminal setting in the applet is a supported setting.
• The operating system environment settings and your client terminal type are set properly.
• All mirrored consoles are of the same terminal type for proper operation. Supported terminal
types are:
— VT100
— VT100+
— VT-UTF8
IMPORTANT: Do not mix hpterm and vt100 terminal types at the same time.
To connect to the system console (Figure 6-10), click Launch.
NOTE: If Launch is disabled, the user does not have console access right. See the User
Administration page under the Administration tab to add the access right.
Figure 6-10 Remote Serial Console Window
Using this feature you can do the following:
94 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 95

• View and interact with the boot sequence of your server.
• Perform maintenance activities in text mode.
• Manage non-graphical mode operating systems.
The console window remains open until you sign out of the iLO 2 MP interface using the provided
link in the banner, leave the iLO 2 MP site, or refresh the entire page.
The remote serial console provides the console, and the GUI provides the iLO 2 MP Main Menu
functionality.
Output from the console is stored in nonvolatile memory in the console log, regardless of whether
or not any users are connected to a console. The Remote Serial Console page refreshes every 10
seconds.
The remote serial console option relies on the virtual serial port.
Virtual Serial Port
The iLO 2 MP contains a virtual serial port that enables it to actually be the console hardware
device for the OS. This port is a serial interface between the host system and the iLO 2 MP. The
iLO 2 MP converts the serial data stream to be available remotely through the remote serial
console (a VT320 Java applet). The virtual serial port must be correctly enabled and configured
in the host.
The virtual serial port function is a bidirectional data flow of the data stream appearing on the
server's serial port. Using the remote console paradigm, a remote user can operate as if a physical
serial connection is present on the server's serial port.
With the virtual serial port feature of iLO, an administrator can access a console application such
as Windows EMS remotely over the network. The iLO 2 MP contains the functional equivalent
of the standard serial port (16550 UART) register set, and the iLO firmware provides a Java applet
that connects to the server serial port. If the serial redirection feature is enabled on the host server,
iLO intercepts the data coming from the serial port, encrypts it, and sends it to the web browser
applet.
For Linux users, the iLO virtual serial port feature provides an important function for remote
access to the Linux server. By configuring a Linux login process attached to the server’s serial
port, you can use the iLO virtual serial port feature to remotely login to the Linux operating
system over the network.
For more information on using the virtual serial port, see Integrated Lights-Out Virtual Serial Port
configuration and operation HOW TO on the HP website at:
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00263709/c00263709.pdf
Virtual Media
Virtual Media (vMedia) provides you with virtual devices that mimic physical hardware devices
such as a virtual floppy disk drive and a CD/DVD drive that connects through the network to
the managed server just as if it was physically connected. The vMedia device can be a physical
CD/DVD drive on the management workstation, or it can be an image file stored on a local disk
drive or network drive.
Booting from the iLO 2 MP CD/DVD enables administrators to upgrade the host system ROM,
upgrade device drivers, deploy an OS from network drives, and perform disaster recovery of
failed operating systems, among other tasks.
The iLO 2 MP device uses a client-server model to perform the vMedia functions. The iLO 2 MP
device streamsthe vMedia data across a live network connectionbetween the remote management
console and the host server. The vMedia Java applet provides data to the iLO 2 MP as it requests
it.
The Virtual Media page refreshes every 10 seconds. Only one user can connect a virtual device
at a time.
Web GUI 95
Page 96
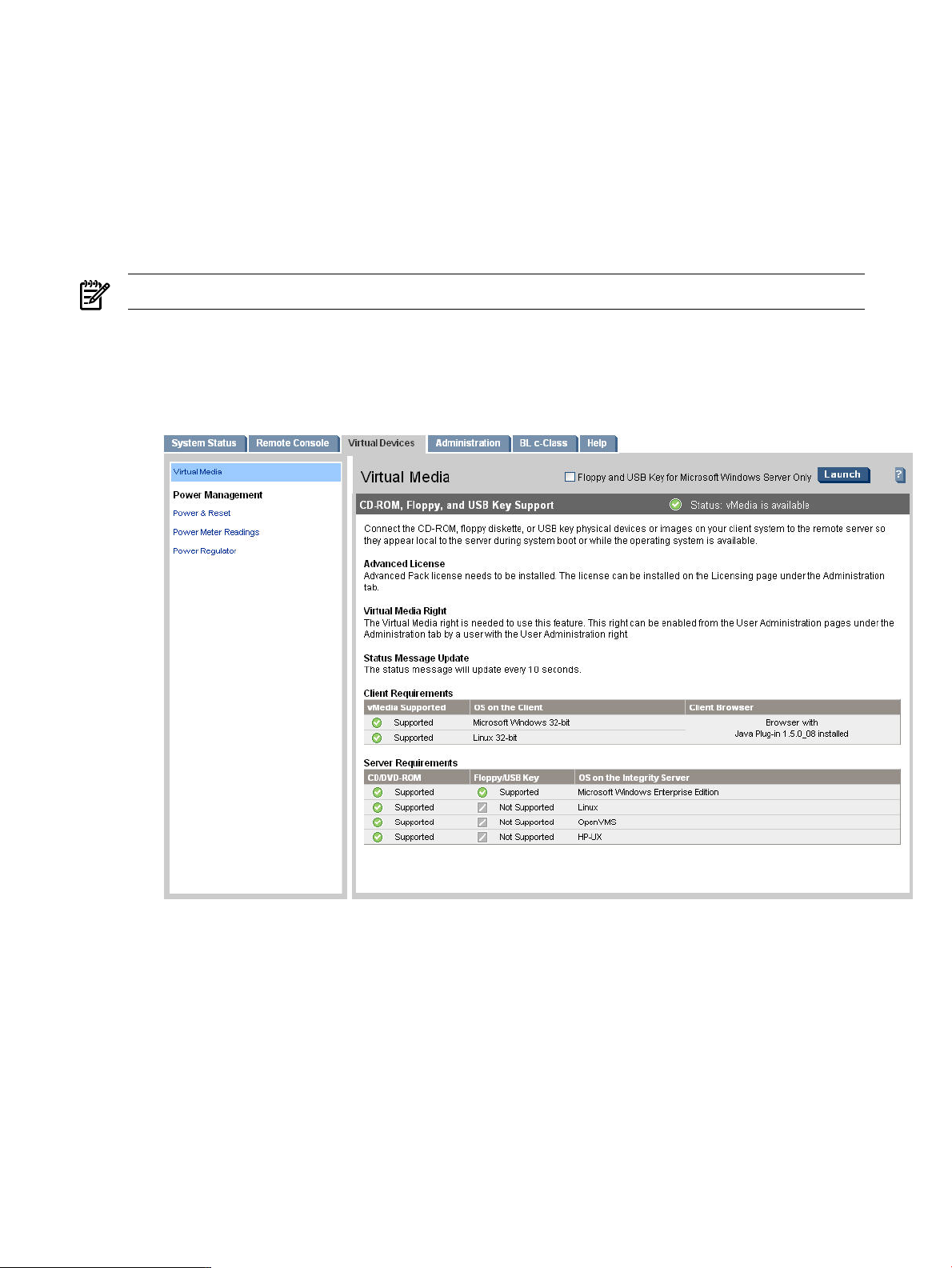
Using iLO 2 MP Virtual Media Devices
Connect client-based vMedia to a host HP Integrity server through a graphical interface using
a signed Java applet. Refusing to accept the applet certificate prevents browser-based vMedia
from functioning (a red X appears). It also prevents the remote console applet from functioning
because it is also signed using the same certificate.
The vMedia functionality is part of the iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack feature set and is enabled by
purchasing the optional iLO 2 MP Advanced Pack license and granting the vMedia right. If not
licensed, the message “iLO 2 feature not licensed” appears. For more information, see
“Advanced Pack License” (page 23).
NOTE: You can use the vMedia applet only on x86 clients.
To access the iLO 2 MP vMedia devices using the graphical interface, follow these steps:
1. From the Virtual Devices tab, select Virtual Media. The Virtual Media page appears
(Figure 6-11)
Figure 6-11 Virtual Media Page
2. Click Launch to load the vMedia applet. The vMedia applet loads in support of the vMedia
device.
3. At this point, you can connect to a virtual CD/DVD or virtual floppy/USB key device or
create an iLO 2 MP disk image file.
96 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 97

NOTE: When you disconnect the iLO 2 MP vMedia, you might receive a warning message
from the host operating system regarding unsafe removal of a device. This warning can be
avoided by using the operating system's-stop-device function before disconnecting it from the
vMedia.
Virtual CD/DVD
The iLO 2 MP virtual CD/DVD is available during server boot for operating systems specified
in “Supported Operating Systems and USB Support for vMedia” (page 102).
Booting from the iLO 2 MP virtual CD/DVD enables you to deploy an operating system from
network drives with DVDs or CDs that contain data in the El Torito Bootable CD format, as well
as perform other tasks.
If the host server operating system supports USB mass storage devices, the iLO 2 MP virtual
CD/DVD is also available after the host server operating system loads. Use the iLO 2 MP virtual
CD/DVD when the host server operating system is running to upgrade device drivers, install
software, and perform other tasks. Having the virtual CD/DVD available when the server is
running can be especially useful if you must diagnose and repair a problem with the NIC driver.
The virtual CD/DVD can be the physical CD/DVD drive on the client system (which you are
running on the web browser), or an image file stored on the client or network drive. For maximum
performance, HP recommends using local image files stored either on the hard drive of your
client system or on a network drive accessible through a high-speed network link.
The iLO 2 MP vMedia CD/DVD appears to your operating system just like any other CD/DVD.
When using the iLO 2 MP for the first time, the host operating system might prompt you to
complete a New Hardware Found wizard.
NOTE: This features requires that the Java Plug-in 1.4.2 or 1.5 is installed.
This feature requires the vMedia right and the Advance Pack License. For more information, see
“Advanced Pack License” (page 23). If a user does not have the vMedia right, it can be granted
from theUser Administration page under the Administration tab by a user with Admin privileges.
To use a physical CD/DVD drive in your client system, follow these steps:
1. From the Virtual Devices tab, select Virtual Media. The Virtual Media content page appears.
Web GUI 97
Page 98
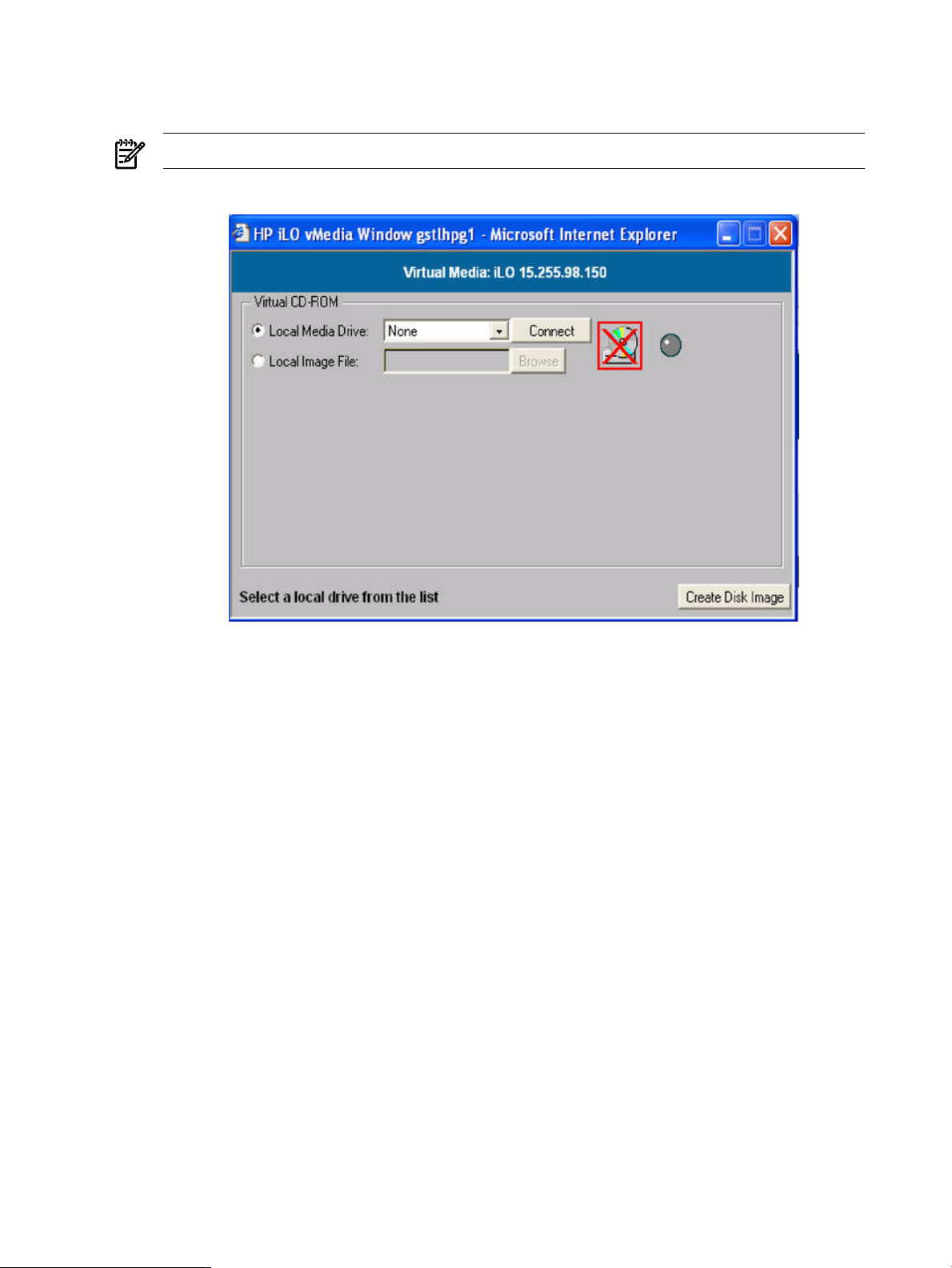
2. Click Launch to load the applet and connect to USB CD/DVD devices and disk image files
available on the client as virtual devices on the server. The vMedia applet appears
(Figure 6-12).
NOTE: Only one user and one device can be connected at a time.
Figure 6-12 Virtual Media Dialog Box (Before Connection)
3. Select Local Media Drive.
4. Select the drive letter of the desired physical CD/DVD drive on your client system from the
list.
98 Using iLO 2 MP
Page 99
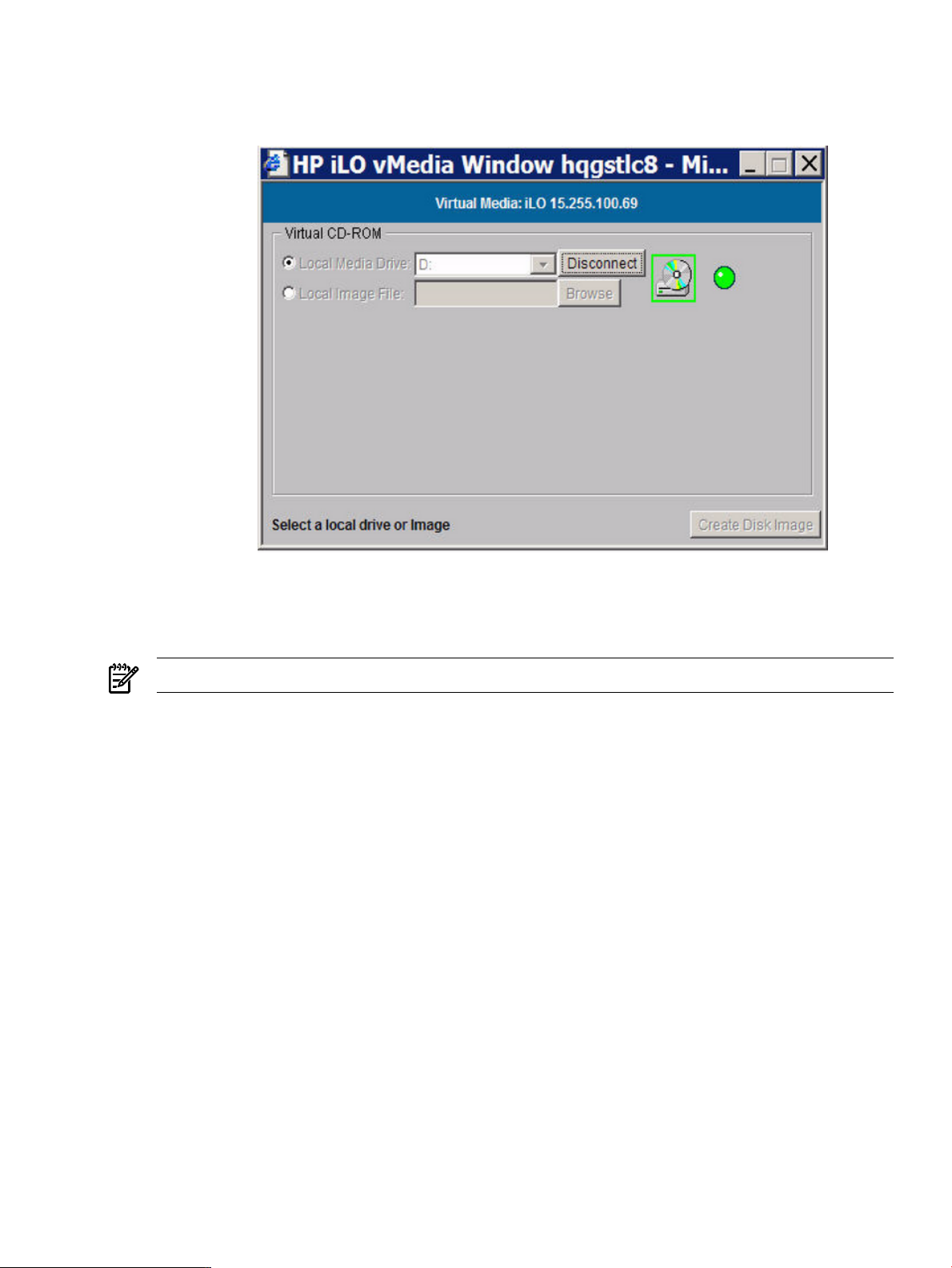
5. Click Connect. The connected drive icon and LED changes states to reflect the current status
of the virtual CD/DVD.
Figure 6-13 Virtual Media Dialog Box (after connection)
After you are connected, virtual devices are available to the host server until you close the vMedia
applet or sign out from a web session. When you are finished using the virtual CD/DVD,
disconnect the device from the host server or close the applet.
NOTE: The vMedia applet must remain open when using a vMedia device.
Virtual Media CD/DVD Operating System
vMedia CD/DVD operating systems information is listed as follows:
• Currently, EFI console only supports El Torito bootable CD format media.
• Windows Server 2003:
The virtual CD/DVD displays automatically after Windows has recognized the mounting
of the USB device. Use it as you would a locally attached CD/DVD device.
• Linux:
On servers with a locally attached IDE CD/DVD, the virtual CD/DVD device is accessible
at /dev/cdrom1. However, on servers without a locally attached CD/DVD (such as the HP
Integrity server blades) the virtual CD/DVD is the first CD/DVD accessible at/dev/cdrom.
The virtual CD/DVD can be mounted as a normal CD/DVD device using: mount
/mnt/cdrom1.
• HP-UX 11.23
To recognize the hardware path and special files, run the ioscan -kfnC disk command.
To mount the virtual CD/DVD/image file on a directory, use the # mount <special
files path> /<dir-name> command.
• Open VMS
Web GUI 99
Page 100
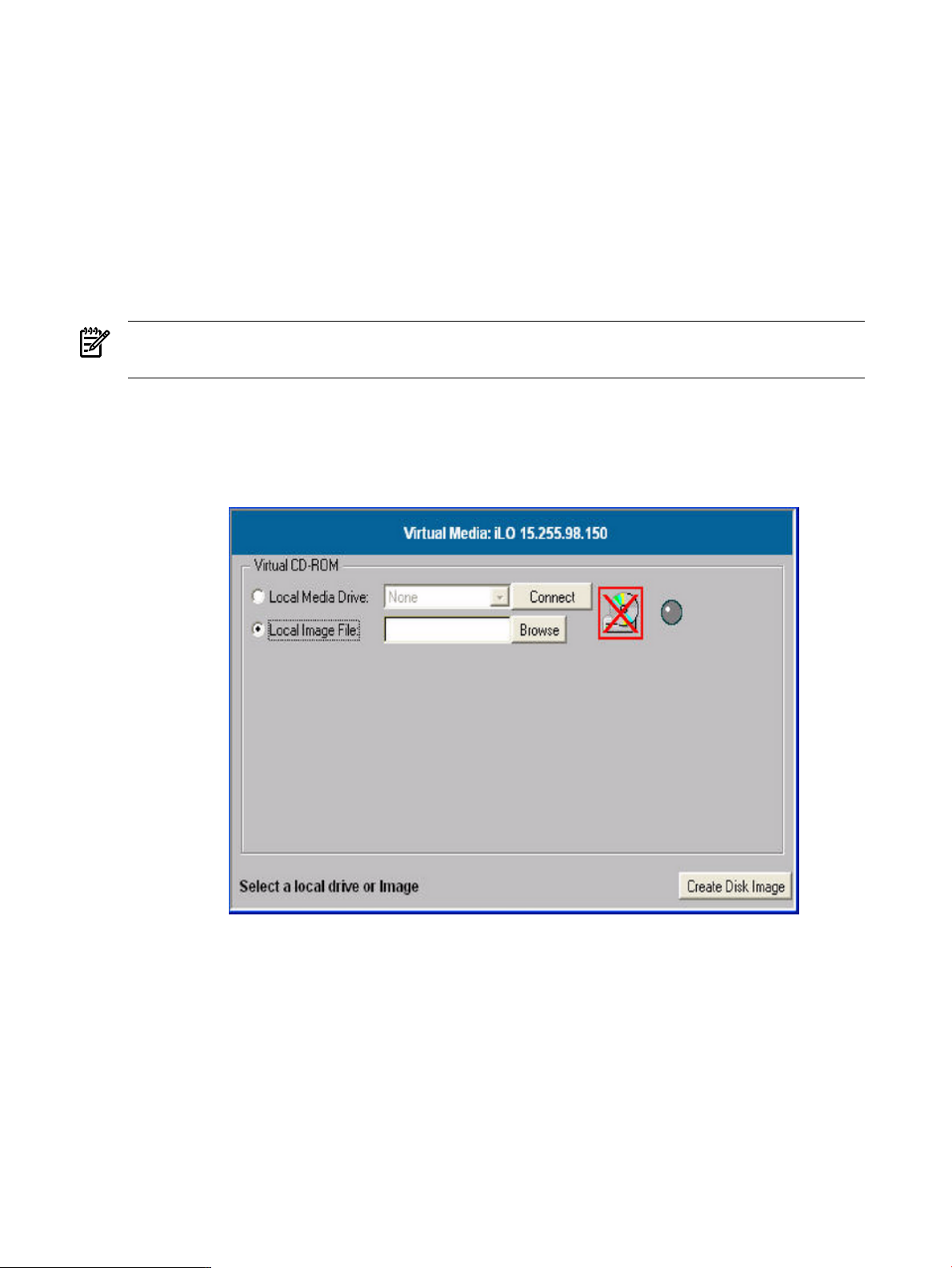
Creating the iLO 2 MP Disk Image Files
The iLO 2 MP vMedia feature enables you to create CD and DVD image files within the same
applet. The image files created are ISO-9660 file system images and El Torito bootable CD images.
The performance of the iLO 2 MP vMedia is faster when image files are used. The utility to create
the iLO 2 MP CD/DVD disk image files is integrated into the vMedia applet.
Store image files on your client computer or on a network drive that can be accessed from the
client using a fast network segment. A disk image file produces better performance than using
a physical CD in your client computer.
Use the Disk>>Image option to create image files from physical diskettes, CDs, or DVDs. The
Image>>Disk option is not valid for a virtual CD/DVD image. The Disk>>Image button changes
to Image>>Disk when clicked.
NOTE: The iLO 2 MP Create Media Image utility does not currently support USB devices in
Linux or NetWare.
The following procedure explains how to create an iLO 2 MP disk image file:
1. Select Local Image File in the Virtual CD-ROM section of the vMedia applet.
2. Select Local Media Drive from the list.
Figure 6-14 Local Image File Dialog Box
3. Enter the path or file name of the image in the text box or click Browse to open the Create
Media Image dialog box and locate the image file.
100 Using iLO 2 MP
 Loading...
Loading...