Page 1

HP Integrated Lights-Out 2
J
User Guide
for Firmware 1.35
Part Number 394326-007
uly 2007 (Seventh Edition)
Page 2

© Copyright 2005-2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212,
Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S.
Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, and Windows XP are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Server 2003 is a U.S.
trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Vista is either a registered trademark or trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries. AMD is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. .Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. Intel, Pentium,
and Itanium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Audience assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems.
HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards
in products with hazardous energy levels.
Page 3

Contents
Operational overview ................................................................................................................... 8
Guide overview ........................................................................................................................................8
New in this release of iLO 2 ....................................................................................................................... 8
iLO 2 overview ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Typical usage ................................................................................................................................. 9
Differences between iLO 2 and iLO .................................................................................................10
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack Integration................................................................... 10
Server management through IPMI version 2.0 compliant applications................................................... 11
WS-Management compatibility overview.......................................................................................... 12
iLO 2 browser interface overview.............................................................................................................. 12
Supported browsers and client operating systems ..............................................................................13
Supported server operating system software......................................................................................13
Text-based remote console overview .......................................................................................................... 14
Virtual serial port and remote serial console...................................................................................... 15
iLO 2 setup ................................................................................................................................ 16
Quick setup............................................................................................................................................16
Preparing to setup iLO 2 ..........................................................................................................................16
Connecting to the network........................................................................................................................ 18
Configuring the IP address........................................................................................................................ 19
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time............................................................................................................ 19
Setting up user accounts........................................................................................................................... 20
Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU .................................................................................................. 20
Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option ............................................................................... 21
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser ...................................................................................... 21
Installing iLO 2 device drivers ................................................................................................................... 21
Microsoft device driver support .......................................................................................................22
Linux device driver support ............................................................................................................. 22
Novell NetWare device driver support............................................................................................. 23
Configuring iLO 2....................................................................................................................... 24
iLO 2 configuration overview.................................................................................................................... 24
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware ....................................................................................................................... 24
Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser ...................................................................................................25
Recovering from a failed iLO 2 firmware update ............................................................................... 26
Downgrading the iLO 2 firmware .................................................................................................... 27
Licensing................................................................................................................................................ 27
User administration.................................................................................................................................. 29
Adding a new user........................................................................................................................30
Viewing or modifying an existing user's settings ................................................................................32
Deleting a user.............................................................................................................................. 32
Group administration.....................................................................................................................33
Configuring iLO 2 access......................................................................................................................... 34
Services options ............................................................................................................................ 34
Access options .............................................................................................................................. 40
iLO 2 Remote Console and Remote Serial Console access ..................................................................42
Security.................................................................................................................................................. 42
Contents 3
Page 4

General security guidelines............................................................................................................. 43
User accounts and access............................................................................................................... 45
SSH key administration ..................................................................................................................46
SSL certificate administration........................................................................................................... 46
Two-factor authentication................................................................................................................ 47
Directory settings........................................................................................................................... 52
Encryption .................................................................................................................................... 55
HP SIM single sign-on (SSO) ........................................................................................................... 57
Remote Console Computer Lock....................................................................................................... 60
Network................................................................................................................................................. 62
Network Settings...........................................................................................................................62
DHCP/DNS Settings ...................................................................................................................... 68
SNMP/Insight Manager settings................................................................................................................ 69
Enabling SNMP alerts .................................................................................................................... 69
SNMP generated trap definitions..................................................................................................... 70
Configuring Insight Manager integration ..........................................................................................71
ProLiant BL p-Class configuration ............................................................................................................... 72
ProLiant BL p-Class user requirements ...............................................................................................72
Static IP bay configuration .............................................................................................................. 72
HP BladeSystem setup.................................................................................................................... 75
iLO 2 diagnostic port configuration parameters ................................................................................. 77
Using iLO 2 ............................................................................................................................... 79
System status and status summary information............................................................................................. 79
System Information Summary .......................................................................................................... 81
iLO 2 Log ..................................................................................................................................... 83
IML.............................................................................................................................................. 83
Diagnostics................................................................................................................................... 84
Insight Agents ...............................................................................................................................85
iLO 2 Remote Console ............................................................................................................................. 86
iLO 2 Remote Console and iLO 2 licensing options............................................................................ 87
Remote Console settings ................................................................................................................. 88
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen............................................................................................... 92
Integrated Remote Console option ................................................................................................... 92
Shared Remote Console ................................................................................................................. 96
Using Console Capture ..................................................................................................................96
Acquiring the Remote Console ........................................................................................................ 97
Remote Console ............................................................................................................................98
Remote Serial Console ................................................................................................................. 100
Virtual media........................................................................................................................................ 104
Using iLO 2 Virtual Media devices................................................................................................. 105
Virtual folder............................................................................................................................... 112
Power management............................................................................................................................... 113
Server power settings................................................................................................................... 114
Server power data....................................................................................................................... 115
Processor states........................................................................................................................... 116
Graceful shutdown ...................................................................................................................... 117
ProLiant BL p-Class Advanced management .............................................................................................. 117
Rack View .................................................................................................................................. 119
iLO 2 control of ProLiant BL p-Class server LEDs ............................................................................... 123
ProLiant BL p-Class alert forwarding ............................................................................................... 123
ProLiant BladeSystem HP Onboard Administrator ...................................................................................... 123
Enclosure bay IP addressing ......................................................................................................... 124
iLO option .................................................................................................................................. 127
Contents 4
Page 5

iLO 2 Virtual Fan......................................................................................................................... 128
Web Administration..................................................................................................................... 128
iLO 2 BL c-Class tab..................................................................................................................... 129
BL p-Class and BL c-Class features.................................................................................................. 129
Directory services...................................................................................................................... 130
Overview of directory integration ............................................................................................................ 130
Benefits of directory integration............................................................................................................... 130
Advantages and disadvantages of schema-free directories and HP schema directory .....................................131
Schema-free directory integration .................................................................................................. 132
HP schema directory integration .................................................................................................... 132
Setup for Schema-free directory integration............................................................................................... 134
Active Directory preparation ......................................................................................................... 134
Schema-free browser-based setup..................................................................................................135
Schema-free scripted setup............................................................................................................ 136
Schema-free HPLOMIG-based setup...............................................................................................136
Schema-free setup options ............................................................................................................136
Schema-free nested groups ........................................................................................................... 137
Setting up HP schema directory integration............................................................................................... 138
Features supported by HP schema directory integration .................................................................... 138
Setting up directory services.......................................................................................................... 138
Schema documentation ................................................................................................................ 139
Directory services support............................................................................................................. 139
Schema required software ............................................................................................................ 140
Schema installer .......................................................................................................................... 140
Management snap-in installer........................................................................................................ 142
Directory services for Active Directory ............................................................................................142
Directory services for eDirectory .................................................................................................... 152
User login using directory services.................................................................................................160
Directory-enabled remote management ....................................................................................... 161
Introduction to directory-enabled remote management................................................................................ 161
Creating roles to follow organizational structure........................................................................................ 161
Using existing groups................................................................................................................... 162
Using multiple roles...................................................................................................................... 162
How directory login restrictions are enforced ............................................................................................ 163
Restricting roles...........................................................................................................................163
User restrictions........................................................................................................................... 164
Creating multiple restrictions and roles ........................................................................................... 166
Using bulk import tools........................................................................................................................... 167
HPQLOMIG directory migration utility......................................................................................... 168
Introduction to HPQLOMIG utility ............................................................................................................ 168
Compatibility........................................................................................................................................ 168
HP Lights-Out directory package.............................................................................................................. 168
Using HPQLOMIG................................................................................................................................. 169
Finding management processors.................................................................................................... 169
Upgrading firmware on management processors............................................................................. 171
Selecting a directory access method .............................................................................................. 172
Naming management processors .................................................................................................. 173
Configuring directories when HP Extended schema is selected .......................................................... 174
Configuring directories when schema-free integration is selected .......................................................175
Setting up management processors for directories............................................................................ 176
HP Systems Insight Manager integration ...................................................................................... 178
Contents 5
Page 6

Integrating iLO 2 with HP SIM................................................................................................................. 178
HP SIM functional overview .................................................................................................................... 178
HP SIM identification and association ...................................................................................................... 179
HP SIM status.............................................................................................................................. 179
HP SIM links ...............................................................................................................................179
HP SIM systems lists ..................................................................................................................... 180
Receiving SNMP alerts in HP SIM............................................................................................................ 180
HP SIM port matching............................................................................................................................ 181
Reviewing Advanced Pack license information in HP SIM ...........................................................................181
Troubleshooting iLO 2 ............................................................................................................... 182
iLO 2 POST LED indicators .....................................................................................................................182
Event log entries.................................................................................................................................... 184
Hardware and software link-related issues................................................................................................ 186
JVM support .........................................................................................................................................187
Login issues .......................................................................................................................................... 187
Login name and password not accepted......................................................................................... 188
Directory user premature logout..................................................................................................... 188
iLO 2 Management Port not accessible by name .............................................................................188
iLO 2 RBSU unavailable after iLO 2 and server reset........................................................................ 189
Inability to access the login page................................................................................................... 189
Inability to access iLO 2 using telnet .............................................................................................. 189
Inability to access virtual media or graphical remote console ............................................................ 189
Inability to connect to iLO 2 after changing network settings .............................................................189
Inability to connect to the iLO 2 Diagnostic Port...............................................................................189
Inability to connect to the iLO 2 processor through the NIC............................................................... 190
Inability to log in to iLO 2 after installing the iLO 2 certificate............................................................ 190
Firewall issues............................................................................................................................. 191
Proxy server issues....................................................................................................................... 191
Two-factor authentication error ...................................................................................................... 191
Troubleshooting alert and trap problems .................................................................................................. 192
Inability to receive HP SIM alarms (SNMP traps) from iLO 2.............................................................. 192
iLO 2 Security Override switch...................................................................................................... 192
Authentication code error message ................................................................................................ 193
Troubleshooting directory problems .........................................................................................................193
Domain/name format login issues .................................................................................................193
ActiveX controls are enabled and I see a prompt but the domain/name login format does not work....... 193
User contexts do not appear to work.............................................................................................. 193
Troubleshooting Remote Console problems ............................................................................................... 193
Remote Console applet has a red X when running Linux client browser............................................... 194
Inability to navigate the single cursor of the Remote Console to corners of the Remote Console window.. 194
Remote Console no longer opens on the existing browser session ...................................................... 194
Remote console text window not updating properly.......................................................................... 195
Remote Console turns gray or black............................................................................................... 195
Remote Serial Console troubleshooting...........................................................................................195
Troubleshooting Integrated Remote Console problems ................................................................................ 195
Internet Explorer 7 and a flickering remote console screen ................................................................ 195
Configuring Apache to accept exported capture buffers ................................................................... 196
No console replay while server is powered down............................................................................ 197
Skipping information during boot and fault buffer playback .............................................................. 197
Out of Memory error starting Integrated Remote Console.................................................................. 197
Session leader does not receive connection request when IRC is in replay mode.................................. 197
Keyboard LED does not display correctly ........................................................................................ 197
Inactive IRC ................................................................................................................................198
Contents 6
Page 7

IRC Failed to connect to server error message .................................................................................198
IRC toolbar icons do not update .................................................................................................... 198
GNOME interface does not lock ...................................................................................................199
Repeating keys on the Remote Console .......................................................................................... 199
Remote Console playback does not work when the host server is powered down................................. 199
Troubleshooting SSH and Telnet problems ................................................................................................ 199
Initial PuTTY input slow................................................................................................................. 199
PuTTY client unresponsive with Shared Network Port ........................................................................ 199
SSH text support from a Remote Console session ............................................................................. 200
Troubleshooting terminal services problems............................................................................................... 200
Terminal Services button is not working .......................................................................................... 200
Terminal Services proxy stops responding....................................................................................... 200
Troubleshooting video and monitor problems............................................................................................200
General guidelines ...................................................................................................................... 200
Telnet displays incorrectly in DOS®...............................................................................................200
Video applications not displaying in the Remote Console.................................................................. 201
User interface is not displaying correctly......................................................................................... 201
Troubleshooting Virtual Media problems .................................................................................................. 201
Virtual drive listing....................................................................................................................... 201
Virtual Media applet has a red X and will not display ......................................................................201
Virtual Floppy media applet is unresponsive.................................................................................... 201
Troubleshooting miscellaneous problems ..................................................................................................202
Cookie sharing between browser instances and iLO 2 .....................................................................202
Inability to access ActiveX downloads ............................................................................................ 203
Inability to get SNMP information from HP SIM ...............................................................................203
Incorrect time or date of the entries in the event log..........................................................................204
Inability to upgrade iLO 2 firmware ............................................................................................... 204
iLO 2 does not respond to SSL requests..........................................................................................204
Testing SSL .................................................................................................................................205
Resetting iLO 2............................................................................................................................ 205
Server name still present after ERASE utility is executed .................................................................... 205
Troubleshooting a remote host....................................................................................................... 206
Directory services schema.......................................................................................................... 207
HP Management Core LDAP OID classes and attributes..............................................................................207
Core classes ............................................................................................................................... 207
Core attributes ............................................................................................................................207
Core class definitions................................................................................................................... 207
Core attribute definitions ..............................................................................................................208
Lights-Out Management specific LDAP OID classes and attributes ................................................................ 211
Lights-Out Management classes..................................................................................................... 211
Lights-Out Management attributes .................................................................................................. 211
Lights-Out Management class definitions.........................................................................................211
Lights-Out Management attribute definitions .................................................................................... 212
Technical support...................................................................................................................... 214
Software technical support and update service.......................................................................................... 214
HP contact information........................................................................................................................... 214
Before you contact HP............................................................................................................................ 215
Acronyms and abbreviations...................................................................................................... 216
Index....................................................................................................................................... 223
Contents 7
Page 8

Operational overview
In this section
Guide overview ....................................................................................................................................... 8
New in this release of iLO 2...................................................................................................................... 8
iLO 2 overview ........................................................................................................................................ 9
iLO 2 browser interface overview............................................................................................................. 12
Text-based remote console overview......................................................................................................... 14
Guide overview
HP iLO 2 provides multiple ways to configure, update, and operate servers remotely. The HP Integrated
Lights-Out 2 User Guide describes these features and how to use them with the browser-based interface
and RBSU. Some features are licensed features and may only be accessed after purchasing an optional
license. See the section, "Licensing (on page 27)" for more information.
The HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide
describes the syntax and tools available to use iLO 2 through a command-line or scripted interface.
This guide includes information about iLO 2 firmware version 1.11, 1.2x, and 1.30.
New in this release of iLO 2
iLO 2 version 1.30 added support for:
• WS-Management ("WS-Management compatibility overview" on page 12)
• Virtual media folder mapping ("Virtual folder" on page 112)
• Remote console screen capture and replay ("Using Console Capture" on page 96)
• Shared remote console (on page 96)
• HP SIM single sign-on ("HP SIM single sign-on (SSO)" on page 57)
• AES encryption (on page 55) for browser, XML, and SSH
• Infinite iLO 2 timeout setting ("Access options" on page 40)
• Automatic operating system locking when a remote console session terminates ("Remote Console
Computer Lock" on page 60)
• Remote Microsoft® Windows® Kernel Debugging ("Using a remote Windows Kernel Debugger" on
page 103)
• Schema-free nested groups (on page 137)
• Version 1.30 improved support for:
o Integrated Remote Console for international keyboards ("Hot keys and international keyboards"
on page 91)
o Authentication logging with iLO 2 records client hostname ("iLO 2 Log" on page 83)
Operational overview 8
Page 9

o
Default-schema directory support to navigate nested directory groups
o Virtual serial port performance ("Remote Serial Console" on page 100)
iLO 2 overview
Four versions of iLO 2 are available:
• iLO 2 Standard—Enables as standard features essential remote control and management
capabilities on next-generation HP ProLiant ML/DL servers. With iLO 2 Standard, you can remotely
perform basic system administration tasks. You can also access system management information at
any time. These remote control capabilities reduce the need for onsite support.
• iLO 2 Advanced—Provides comprehensive Lights-Out remote management capabilities for ProLiant
servers. iLO 2 Advanced also gives you the freedom to enable full remote control of your ProLiant
servers. You can perform the same tasks remotely that you can at the terminal, regardless of server
or operating system conditions. iLO 2 Advanced is also suitable for routine administration, giving
you a single tool for any situation. iLO 2 features comprehensive data encryption, enterprise-class
user authentication and the ability to isolate iLO 2 traffic on separate networks.
• iLO 2 Standard Blade Edition—Provides all of the remote control capabilities typically offered as
standard features on ProLiant servers, plus the new high-performance, Virtual KVM remote console
and browser-based virtual media that is essential to administering HP BladeSystem servers. In
addition, you can access system management information such as hardware health, event logs, and
configuration anytime to troubleshoot and maintain blades.
• iLO 2 Select—Provides Standard Blade Edition enabled servers an easy upgrade to full Lights-Out
functionality. It also provides a cost-effective upgrade to advanced Lights-Out functionality on ProLiant
300 and 500 Series servers that are managed using iLO 2 Standard text-based remote consoles,
typically found in Linux environments.
For information about the features available in each version iLO 2, see "Licensing (on page 27)."
Typical usage
iLO 2 can remotely perform most functions that otherwise require a visit to servers at the data center,
computer room, or remote location. The following are just a few examples of using iLO 2 features.
• iLO 2 Remote Console and virtual power enables you to view a stalled remote server with blue
screen conditions and restart the server without onsite assistance.
• iLO 2 Remote Console enables you to change BIOS settings when necessary.
• iLO 2 Virtual KVM technology provides a high-performance remote console that enables you to
remotely administer operating systems and applications in everyday situations.
• iLO 2 virtual CD/DVD-ROM or floppy enables you to install an operating system or flash system
firmware over the network from images on your workstations or on centralized web servers.
• iLO 2 Virtual Folder enables you to update operating system drivers or copy system files without
physical media or creating a disk image.
• iLO 2 scripting enables you to use virtual power and virtual media in other scripting tools to
automate deployment and provisioning.
Operational overview 9
Page 10

These examples are just a few ways iLO 2 is used to manage HP ProLiant servers from your office, home,
or travel location. As you begin using iLO 2 and defining your specific infrastructure requirements refer to
this guide for additional ways to simplify your remote server management needs.
Differences between iLO 2 and iLO
The iLO 2 product is based on the iLO product and shares many common features. However, to use iLO 2
to access a pre-operating system, text-based remote console, you must use the remote serial console. For
more information, see the section, "Text-based remote console overview (on page 14)."
The following highlights the differences between iLO 2 and iLO:
Feature iLO 2 iLO
Standard features
Text console Pre-OS Pre-OS and OS
Remote Serial Console (virtual serial
port)
Advanced features
Text console Pre-OS and OS Pre-OS and OS
Remote console Yes (Virtual KVM ) Yes
Integrated Remote Console Yes No
Support for Microsoft® JVM Yes No
Remote Console Acquire button Yes Yes
Terminal Services integration Yes Yes
HP schema directory integration Yes Yes
Schema-free directory integration Yes Yes
Two-factor authentication Yes Yes
Power Regulator reporting Yes Yes
Virtual Floppy and CD/DVD-ROM Yes Yes
USB key virtual media Yes Yes
Virtual folder Yes No
Pre-OS and OS Pre-OS and OS
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack Integration
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack integrates with iLO 2 to allow the management of remote
servers and the performance of remote console operations regardless of the state of the operating system
or hardware.
The Deployment Server provides the ability to use the power management features of iLO 2 to power on,
power off, or cycle power on the target server. Each time a server connects to the Deployment Server, the
Deployment Server polls the target server to see if a LOM management device is installed. If installed, the
server gathers information including the DNS name, IP address, and first user name. Security is
maintained by requiring the user to enter the correct password for that user name.
Operational overview 10
Page 11

For more information about the ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack, refer to the documentation that
ships on the ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack CD or the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/rdp
).
Server management through IPMI version 2.0 compliant applications
Server management through the IPMI is a standardized method for controlling and monitoring the server.
iLO 2 provides server management based on the IPMI version 2.0 specification.
The IPMI specification defines a standardized interface for platform management. The IPMI specification
defines the following types of platform management:
• Monitoring of system information, such as fans, temperatures, and power supplies
• Recovery capabilities, such as system resets and power on/off operations
• Logging capabilities, for abnormal events such as over temperature readings or fan failures
• Inventory capabilities, such as identifying failed hardware components
IPMI communications are dependent on the BMC and the SMS. The BMC manages the interface between
the SMS and the platform management hardware. iLO 2 emulates the BMC functionality and the SMS
functionality can be provided by various industry-standard tools. For additional information, see the IPMI
specification on the Intel® website (http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm
).
iLO 2 provides the KCS interface, or open interface, for SMS communications. The KCS interface provides
a set of I/O mapped communications registers. The default system base address for the I/O mapped
SMS Interface is 0xCA2 and is byte aligned at this system address.
The KCS interface is accessible to SMS software that is running on the local system. Examples of
compatible SMS software applications are as follows:
• IPMI version 2.0 Command Test Tool is a low-level MS-DOS command line tool that enables hex-
formatted IPMI commands to be sent to an IPMI BMC that implements the KCS interface. You can
locate this tool on the Intel® website (http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi/tools.htm
).
• IPMItool is a utility for managing and configuring devices that support the IPMI version 1.5 and
version 2.0 specifications and can be used in a Linux environment. You can locate this tool on the
IPMItool website (http://ipmitool.sourceforge.net/index.html
IPMI functionality provided by iLO 2
When emulating a BMC for the IPMI interface, iLO 2 supports all mandatory commands listed in the IPMI
version 2.0 specification. See the IPMI version 2.0 specification for a listing of these commands. Also, the
SMS should use the methods described in the specification for determining which IPMI features are
enabled or disabled in the BMC (for example, using the Get Device ID command).
If the server operating system is running and the health driver is enabled, any IPMI traffic through the KCS
interface can affect the performance of the health driver and overall health performance of the system. Do
not issue any IPMI commands through the KCS interface that could have a detrimental affect on the
monitoring performed by the health driver. These commands include any commands that sets or changes
IPMI parameters, such as Set Watchdog Timer and Set BMC Global Enabled. Any IPMI
command that simply returns data is safe to use, such as Get Device ID and Get Sensor Reading.
).
Operational overview 11
Page 12

WS-Management compatibility overview
The iLO 2 firmware implementation of WS-Management is in accordance with the specification, DTMF
Web Services for Management 1.0.0a.
Authentication
• iLO 2 uses basic authentication over SSL, compliant with profile:
wsman:secprofile/https/basic
• Authenticated users are authorized to execute WS-Management commands in accordance with
designated privileges in their local or directory accounts.
• To enable basic authentication on Microsoft® Windows Vista™, at the command prompt, enter
gpedit.msc to launch the Group Policy Object Editor. Select Computer Configuration>
Administrative Templates> Windows Components> Windows Remote Management (WinRM)>
WinRM Client. Set Allow Basic authentication to Enabled.
Compatibility
• WS-Management in iLO 2 are compatible with the Windows Vista™ WinRM utility, Microsoft®
Operations Manager 3, and the Management Pack provided by HP.
• The full set of WS-Management commands is available on iLO 2 servers that support embedded
system health. A greatly reduced subset of these commands is available on servers without
embedded systems health support.
Commands are available for remote invocation of the following devices:
• Server power
• UID
Status
The WS-Management in iLO 2 returns status information for fans, temperatures, power supplies, and
VRMs.
iLO 2 browser interface overview
The iLO 2 browser interface groups similar tasks for easy navigation and workflow. These tasks are
organized under high-level tabs across the top of the iLO 2 interface. These tabs are always visible and
include System Status, Remote Console, Virtual Media, Power Management, and Administration.
Each high-level iLO 2 tab has a menu on the left side of the interface with various options. This menu
changes every time you select a different high-level tab, displaying the options available from that tab.
Each menu option displays a page title, which is a description of the information or settings available on
that page. This page title might not reflect the name displayed on the menu option.
Assistance for all iLO 2 pages is available from iLO 2 Help. Links on each iLO 2 page provide summary
information about the features of iLO 2 and helpful information to optimize its operation. To access pagespecific help, click the question mark (?) on the right side of the browser window.
Typical user tasks are found under the System Status, Remote Console, Virtual Media, and Power
Management tabs of the iLO 2 interface. These tasks are described in the "Using iLO 2 (on page 79)"
section.
The Administration tab is typically used by an advanced or administrative user who must manage users,
configure global and network settings as well as configure or enable the more advanced functions of iLO
Operational overview 12
Page 13

2. These tasks are discussed in the sections, "iLO 2 setup (on page 16)" and "Configuring iLO 2 (on
page 24)".
Subject-specific areas of iLO 2 functionality and integration are detailed in:
• Directory services (on page 130)
• Directory-enabled remote management (on page 161)
• HPQLOMIG directory migration utility (on page 168)
• HP Systems Insight Manager integration (on page 178)
• Troubleshooting iLO 2 (on page 182)
• Directory services schema (on page 207)
Supported browsers and client operating systems
• Microsoft® Internet Explorer 7
o This browser is supported on Microsoft® Windows® products.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM
for your system configuration, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm
• Microsoft® Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later
o This browser is supported on Microsoft® Windows® products.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM
for your system configuration, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm
• Firefox 2.0
o This browser is supported on Red Hat Enterprise Linux Desktop 4 and Novell Linux Desktop 9.
o HP supports Microsoft® JVM and SUN Java™ 1.4.2_13. To download the recommended JVM
for your system configuration, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/manage/jvm
).
).
).
Certain browsers and operating system combinations might not work correctly, depending on the
implementation of the required browser technologies.
Supported server operating system software
iLO 2 is an independent microprocessor running an embedded operating system. The architecture ensures
that the majority of iLO 2 functionality is available, regardless of the host operating system.
For graceful host operating system shutdown, HP SIM integration requires health drivers and Management
Agents or remote console access.
iLO 2 provides two interface drivers:
• iLO 2 Advanced Server Management Controller Driver (health driver)—Provides system management
support, including monitoring of server components, event logging, and support for the Management
Agents.
• iLO 2 Management Interface Driver—Enables system software and SNMP Insight Agents to
communicate with iLO 2.
Operational overview 13
Page 14

These drivers and agents are available for the following network operating systems:
• Microsoft®
o Windows® 2000 Server
o Windows® 2000 Advanced Server
o Windows Server™ 2003
o Windows Server™ 2003, Web Edition
o Windows® Small Business Server 2003 (ML300 series)
o Windows Vista™
• Red Hat
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 (AMD64/EM64T)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (AMD64/EM64T)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (x86)
o Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (AMD64/EM64T)
• SUSE
o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 9 (x86)
o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server (AMD64/EM64T)
o SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 10
Text-based remote console overview
iLO and its predecessors support a true text-based remote console. Video information is obtained from the
server and the contents of the video memory are sent to the management processor, compressed,
encrypted, and forwarded to the management client application. iLO uses a screen-frame buffer, which
detects changes in text information, encrypts the changes, and sends the characters (including screen
positioning information) to text-based client applications. This method provides compatibility with standard
text-based clients, good performance, and simplicity. However, you cannot display non-ASCII or
graphical information, and screen positioning information (displayed characters) might be sent out of
order.
New video technology (known as Virtual KVM on HP ProLiant servers) used in the iLO 2 high-performance
remote console does not provide a true text-based console. iLO 2 uses the video adapter DVO port to
access video memory directly. This method significantly increases iLO 2 performance. However, the
digital video stream does not contain useful text data. Data obtained from the DVO port represents
graphical data (non-character-based), and is not comprehensible ASCII or text data. This video data
cannot be rendered by a text-based client application such as telnet or SSH.
The iLO 2 text-based remote console remains available on iLO 2 until the operating system POST is
complete. iLO 2 firmware continues to use the virtualized serial-port functionality of the management
processor. The virtual serial port capability is available in iLO and iLO 2. However, on the iLO 2
firmware, the virtual serial port was renamed Remote Serial Console. iLO 2 uses the Remote Serial
Console to access a pre-operating system, text-based remote console. The iLO 2 Remote Serial Console
applet appears as a text-based console, but the information is rendered using graphical video data.
Operational overview 14
Page 15

iLO 2 displays this information through the remote console applet while in the server pre-operating system
state, enabling a non-licensed iLO 2 to observe and interact with the server during POST activities. A nonlicensed iLO 2 cannot use remote console access after the server completes POST and begins to load the
operating system. The iLO 2 Advanced License enables access to the remote console at all times. For
more information, see the section, "Licensing (on page 27)."
Virtual serial port and remote serial console
The management processor contains serial-port hardware that can replace the physical serial port on the
server's motherboard. Using an electronic switch, the iLO 2 firmware disconnects the server's physical
serial port and commands its own serial-port hardware to connect. The iLO 2 serial-port hardware
establishes a connection between the server and the management processor network. The firmware
encapsulates the characters sent by the server to the serial port into network packets and sends the
network packets to the remote serial console applet or application (the application may be a telnet or SSH
client). Characters sent by the remote applet or application are encapsulated into network packets and
sent to the iLO 2 firmware, which then extracts the characters and feeds them to the server. The iLO 2
remote serial console provides a bi-directional serial communication path between the remote user and
the server.
Using the iLO 2 remote serial console, the remote user is able to perform operations such as interacting
with the server POST sequence and operating system boot sequence; establishing a login session with the
operating system, interacting with the operating system; and executing and interacting with applications
on the server operating system. Users of the Microsoft® Windows Server™ 2003 operating system have
the ability to execute the EMS subsystem through the remote serial console. EMS is useful for debugging
operating system boot and problems at the operating system kernel level.
Operational overview 15
Page 16

iLO 2 setup
In this section
Quick setup ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Preparing to setup iLO 2 ......................................................................................................................... 16
Connecting to the network....................................................................................................................... 18
Configuring the IP address ...................................................................................................................... 19
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time........................................................................................................... 19
Setting up user accounts.......................................................................................................................... 20
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser..................................................................................... 21
Installing iLO 2 device drivers.................................................................................................................. 21
Quick setup
To quickly setup iLO 2 using the default settings for iLO 2 Standard and iLO Advanced features, follow
the steps below:
1. Prepare—Decide how you want to handle networking and security ("Preparing to setup iLO 2" on
page 16)
2. Connect iLO 2 to the network ("Connecting to the network" on page 18).
3. If you are not using dynamic IP addressing, use the iLO 2 RBSU to configure a static IP address
("Configuring the IP address" on page 19).
4. Log into iLO 2 from a supported browser or command line using the default user name, password,
and DNS name provided on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the server ("Logging into
iLO 2 for the first time" on page 19).
5. Change the default user name and password on the administrator account to your predefined
selections
6. If you are using the local accounts feature, set up your user accounts ("Setting up user accounts" on
page 20).
7. Activate iLO 2 advanced features ("Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser" on page
21).
8. Install the iLO 2 device drivers ("Installing iLO 2 device drivers" on page 21).
Preparing to setup iLO 2
Before setting up your iLO 2 management processors, you must decide how to handle networking and
security. The following questions can help you configure iLO 2 for your needs:
1. How should iLO 2 connect to the network? For a graphical representation and explanation of the
available connections, see the section, "Connect to the network ("Connecting to the network" on
page 18)."
Typically iLO 2 is connected to the network using either:
iLO 2 setup 16
Page 17

o
A corporate network where both the NIC and the iLO 2 port are connected to the corporate
network. This connection enables access to iLO 2 from anywhere on the network and reduces the
amount of networking hardware and infrastructure required to support iLO 2. However, on a
corporate network, network traffic can hinder iLO 2 performance.
o A dedicated management network with the iLO 2 port on a separate network. A separate
network improves performance and security because you can physically control which
workstations are connected to the network. A separate network also provides redundant access
to the server when a hardware failure occurs on the corporate network. In this configuration, iLO
2 cannot be accessed directly from the corporate network.
2. How will iLO 2 acquire an IP address?
To access iLO 2 after connecting it to the network, the management processor must acquire an IP
address and subnet mask using either a dynamic or static process:
o Dynamic IP address is set by default. iLO 2 obtains the IP address and subnet mask from
DNS/DHCP servers. This method is the simplest.
o Static IP address is used to configure a static IP address if DNS/DHCP servers are not available
on the network. A static IP address can be configured in iLO 2 using the RBSU.
If using a static IP, you must have an IP address before starting iLO 2 setup.
3. What access security is required and what user accounts and privileges are needed?
iLO 2 provides several options to control user access. You must select one of the following methods
to prevent unauthorized access to corporate IT assets:
o Local accounts with up to 12 user names and passwords can be stored on iLO 2. This is ideal for
small environments such as labs and small- and medium-sized businesses.
o Directory services use the corporate directory (Microsoft® Active Directory or Novell eDirectory)
to manage iLO 2 user access. This is ideal for environments with a large number of frequently
changing users. If you plan to use Directory services leave at least one local account enabled for
alternate access.
For more information about iLO 2 access security see the section, "Security (on page 42)."
4. How do you want to configure iLO 2?
iLO 2 supports various interfaces for configuration and operation. This guide discusses the following
interfaces:
o iLO 2 RBSU ("Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU" on page 20) can be used when the system
environment does not use DHCP, DNS, or WINS.
o Browser-based setup ("Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option" on page 21) can be
used when you can connect to iLO 2 on the network using a browser. This method can also
reconfigure a previously configured iLO 2.
o SMASH CLP can be used when a command line is accessible through telnet, SSH, or physical
serial port. See the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command
Line Resource Guide.
The iLO 2 default settings enable you to use most features with no additional configuration. However, the
extensive configuration flexibility of iLO 2 enables customization for multiple enterprise environments. See
the section, "Configuring iLO 2 (on page 24)" for all available options.
For advanced setup of multiple iLO 2 management processors using scripting commands, the following
methods are available. Scripts are text files written in an XML-based scripting language called RIBCL. You
can use RIBCL scripts to configure iLO 2 on the network, during initial deployment, or from an already
iLO 2 setup 17
Page 18

deployed host. Each method is described in the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting
and Command Line Resource Guide.
• CPQLOCFG is a Microsoft® Windows® utility that sends RIBCL scripts to iLO 2 over the network.
• HPONCFG is a local online scripted-setup utility that runs on the host and passes RIBCL scripts to the
local iLO 2. There are Windows® and Linux versions of this utility, which require the HP iLO 2
Management Interface Driver.
• Perl is a scripting language that can be used from Linux clients to send RIBCL scripts to iLO 2 over
the network.
Connecting to the network
Typically iLO 2 is connected to the network in one of two ways. iLO 2 can be connected through a:
• Corporate network where both ports are connected to the corporate network. In this configuration,
the server has two network ports (one server NIC, and one iLO 2 NIC) connected to a corporate
network.
iLO 2 setup 18
Page 19

• Dedicated management network where the iLO 2 port is on a separate network.
Configuring the IP address
This step is necessary only if you are using a static IP address. When using dynamic IP addressing, your
DHCP server will automatically assign an IP address for iLO 2. HP recommends using DNS or DHCP with
iLO 2 to simplify installation
To configure a static IP address, use the iLO 2 RBSU with the following procedure to disable DNS and
DHCP and configure the IP address and the subnet mask:
1. Restart or power up the server.
2. Press the F8 key when prompted during POST. The iLO 2 RBSU runs.
3. Select Network>DNS/DHCP, press the Enter key, and then select DHCP Enable. Press the spacebar to
turn off DHCP. Be sure that DHCP Enable is set to Off, and save the changes.
4. Select Network>NIC>TCP/IP, press the Enter key, and enter the appropriate information in the IP
Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address fields.
5. Save the changes.
6. Exit iLO 2 RBSU. The changes take effect when you exit iLO 2 RBSU.
Logging into iLO 2 for the first time
iLO 2 is configured with a default user name, password, and DNS name. Default user information is
located on the iLO 2 Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management
processor. Use these values to access iLO 2 remotely from a network client using a standard Web
browser.
For security reasons, HP recommends changing the default settings after logging in to iLO 2 for the first
time.
The default values are:
iLO 2 setup 19
Page 20

• User name—Administrator
• Password—A random, eight-character, alphanumeric string
• DNS Name—ILOXXXXXXXXXXXX, where the Xs represent the serial number of the server
NOTE: User names and passwords are case sensitive.
If you enter an incorrect user name and password or a log in attempt fails, iLO 2 imposes a security
delay. For more information on login security, refer to "Login security (on page 45)."
Setting up user accounts
iLO 2 comes preconfigured with default factory settings, including a default user account and password.
For security reasons, HP recommends changing the default settings after logging in to iLO 2 for the first
time. These changes can be made using any of the iLO 2 user interfaces. RBSU and browser procedures
are explained in this user guide. Other options including the SMASH CLP and scripting methods are
described in the "HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource
Guide".
If iLO 2 is connected to a network running DNS or DHCP, you can use it immediately without changing
any settings.
Setting up iLO 2 using iLO 2 RBSU
HP recommends iLO 2 RBSU to initially set up iLO 2 and configure iLO 2 network parameters for
environments that do not use DHCP and DNS or WINS. RBSU provides the basic tools to configure iLO 2
network settings and user accounts to get iLO 2 on the network.
You can use RBSU to configure network parameters, directory settings, global settings, and user accounts.
iLO 2 RBSU is not intended for continued administration. RBSU is available every time the server is booted
and can be run remotely using the iLO 2 Remote Console.
iLO 2 RBSU can be disabled in the Global Settings preferences. Disabling iLO 2 RBSU prevents
reconfiguration from the host unless the iLO 2 Security Override Switch is set.
To run iLO 2 RBSU to set up local accounts:
1. Restart or power up the server.
2. Press the F8 key when prompted during POST. The iLO 2 RBSU runs.
3. If prompted, enter a valid iLO 2 user ID and password with the appropriate iLO 2 privileges
(Administer User Accounts>Configure iLO 2 Settings). Default account information is located on the
iLO 2 Default Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management
processor. If iLO 2 has not been configured to present a login challenge to the RBSU, no prompt will
appear.
4. Make and save any necessary changes to the iLO 2 configuration.
5. Exit iLO 2 RBSU.
iLO 2 setup 20
Page 21
Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option
Use the browser-based setup method if you can connect to iLO 2 on the network using a browser. You
can also use this method to reconfigure a previously configured iLO 2.
Access iLO 2 from a remote network client using a supported browser, and provide the default DNS
name, user name, and password. Default DNS name and account information is located on the iLO 2
Network Settings tag attached to the server containing the iLO 2 management processor.
When you successfully log onto iLO 2, you can change the default values of the local user accounts by
selecting User Administration under the iLO 2 Administration tab.
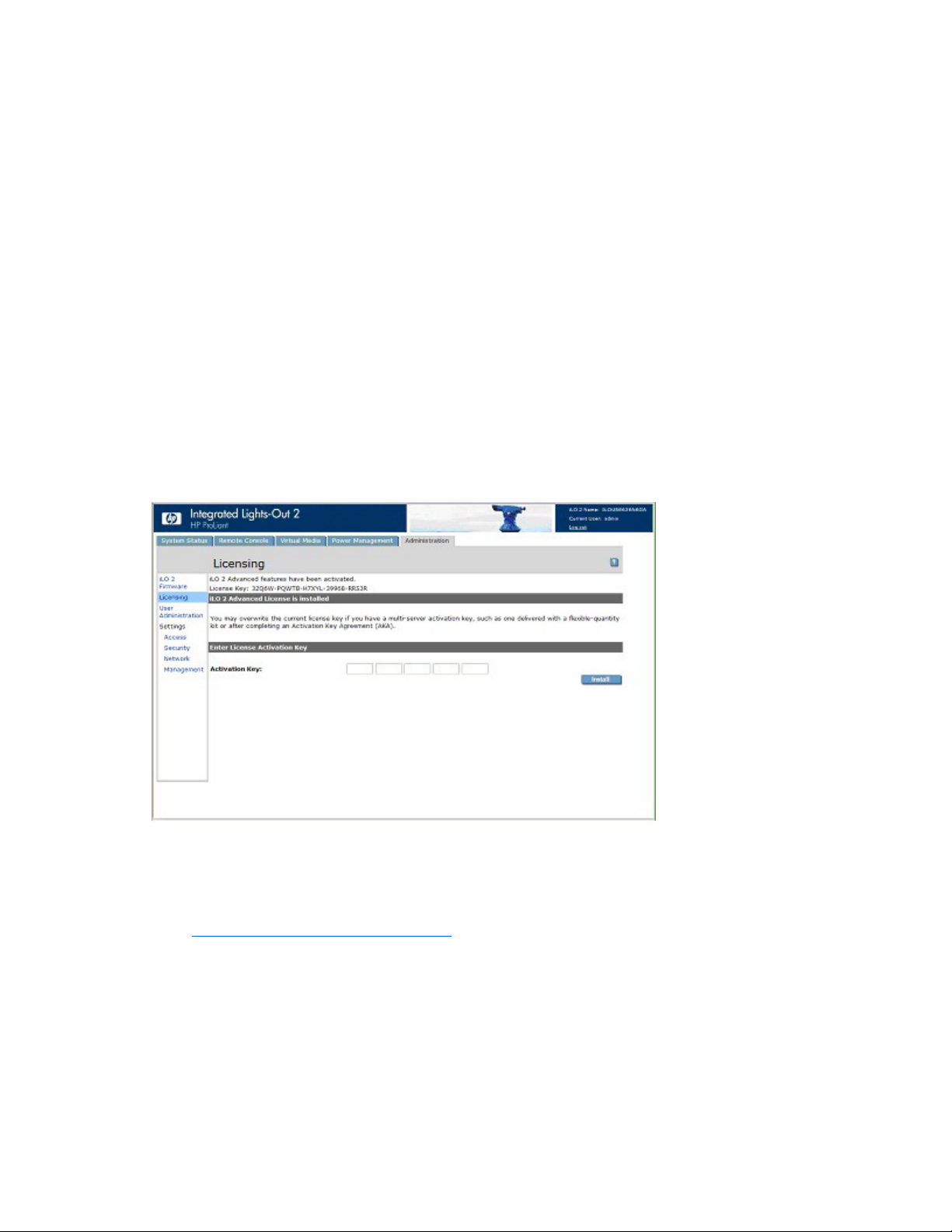
Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser
The Licensing page enables you to view the current license status and enter a key to activate iLO 2 license
features. The iLO 2 version and current license information is displayed in this section. If a license is
installed (including an evaluation license), the license number is displayed. See "Licensing (on page 27)"
for more information about iLO 2 license options.
1. Log into iLO 2 through a supported browser.
2. Click Administration>Licensing to display the iLO 2 license activation screen.
3. Enter the license key. Press the Tab key or click inside a field to move between fields. The Activation
Key field advances automatically as you enter data. Click Licensing to clear the fields and reload the
page.
4. Click Install. The EULA confirmation appears. The EULA details are available on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
5. Click OK.
The advanced features of iLO 2 are now enabled.
) and with the license kit.
Installing iLO 2 device drivers
The iLO 2 Management Interface Driver enables system software such as SNMP Insight Agents and the
Terminal Services Pass-Through service to communicate with iLO 2.
iLO 2 setup 21
Page 22

The device drivers required to support iLO 2 are part of the PSP located on the SmartStart CD,
Management CD, or on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
).
All the support drivers for your server and iLO 2 can be downloaded from the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
).
To download the drivers:
1. Click the iLO 2 graphic.
2. Select Software and Drivers.
Microsoft device driver support
The device drivers that support the iLO 2 are part of the PSP that is located on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support
the Windows® documentation and the latest Windows® Service Pack.
iLO 2 prerequisite files:
• CPQCIDRV.SYS provides the iLO 2 Management Interface Driver support.
• CPQASM2.SYS, SYSMGMT.SYS, and SYSDOWN.SYS provide the iLO 2 Advanced Server
Management Controller Driver support.
PSP for Microsoft® Windows® products includes an installer that analyzes system requirements and
installs all drivers. The PSP is available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
SmartStart CD.
To install the drivers in the PSP:
1. Download the PSP from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
2. Run the SETUP.EXE file included in the download, and follow the installation instructions.
For additional information about the PSP installation, read the text file included in the PSP download.
) or on the SmartStart CD. Before you install the Windows® drivers, obtain
) or on the
Linux device driver support
You can download the LSP files containing the iLO 2 driver, the foundation agents, and health agents
from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
driver are available on the website. The HP Management Agents for Linux are:
• ASM package (hpasm) which combines the health driver, IML viewer, foundation agents, health
agent, and standard equipment agent into one package.
• RSM package (hprsm) which combines the RIB driver, rack daemon, RIB agent, and rack agent into
one package.
To load the health and iLO 2 driver packages, use the following commands:
rpm –ivh hpasm-d.vv.v-pp.Linux_version.i386.rpm
rpm –ivh hprsm-d.vv.v-pp.Linux_version.i386.rpm
where d is the Linux distribution and version and
vv.v-pp are version numbers.
For additional information, refer to the Software and Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support
To remove the health and iLO 2 drivers, use the following commands:
rpm –e hpasm
). The instructions on how to install or update the iLO 2
).
iLO 2 setup 22
Page 23

rpm –e hprsm
For additional information, refer to the Software and Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support
Novell NetWare device driver support
The device drivers required to support iLO 2 are part of the PSP that is located on the SmartStart CD and
the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
analyzes system requirements and installs all drivers.
iLO 2 requires the following files:
• The CPQHLTH.NLM file provides the Health Driver for Novell NetWare.
• The CPQCI.NLM file provides iLO 2 Management Interface Driver support.
When updating iLO 2 drivers, be sure iLO 2 is running the latest version of iLO 2 firmware. You can
obtain the latest version as a Smart Component from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-
out).
To install the drivers download the PSP from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
server. After downloading the PSP, follow the Novell NetWare component installation instructions to
complete the installation. For additional information about the PSP installation, read the text file included
in the PSP download.
When using Novell NetWare 6.X, use the ATI ES1000 video driver that is provided by the operating
system for best results.
). The PSP for Novell NetWare includes an installer that
).
) to a NetWare
iLO 2 setup 23
Page 24

Configuring iLO 2
In this section
iLO 2 configuration overview................................................................................................................... 24
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware ...................................................................................................................... 24
Licensing............................................................................................................................................... 27
User administration................................................................................................................................. 29
Configuring iLO 2 access........................................................................................................................ 34
Security................................................................................................................................................. 42
Network................................................................................................................................................ 62
SNMP/Insight Manager settings .............................................................................................................. 69
ProLiant BL p-Class configuration.............................................................................................................. 72
iLO 2 configuration overview
Typically, an advanced or administrative user who must manage users and configure global and network
settings configures iLO 2. You can configure iLO 2 using the iLO 2 browser-based GUI or scripting tools
such as CPQLOCFG and HPONCFG (described in the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor
Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.)
The iLO 2 Administration tab enables you to configure and manage user settings, SNMP alerting (through
integration with HP SIM), security settings, licensing, certificate administration, directory settings, and
network environment settings. The Administration tab includes the following menu options:
• iLO 2 Firmware ("Upgrading iLO 2 firmware" on page 24)
• Licensing (on page 27)
• User Administration (on page 29)
• Settings
o Access ("Configuring iLO 2 access" on page 34)
o Security (on page 42)
o Network (on page 62)
o Management ("SNMP/Insight Manager settings" on page 69)
Upgrading iLO 2 firmware
Firmware upgrades enhance the functionality of iLO 2. You can find the latest firmware on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
After the software and drivers page appears, select your iLO 2 product and operating system, and then
click Locate Software. You can also locate your iLO 2 software by selecting the Operating System and
Category options.
You must have the Configure iLO 2 privilege (configure local device settings) to update the firmware
unless you set then the security override switch ("iLO 2 Security Override Switch administration" on page
). Select your iLO 2 product and then select Software & Drivers.
Configuring iLO 2 24
Page 25

44). If the security override switch is set, any iLO 2 user can update the firmware. You must run firmware
updates from an Administrator or root context on the host operating system.
To update the iLO 2 choose one of the following methods:
• Online firmware update—Download the appropriate operating system component and run it from
the Administrator or root context of the operating system. The online firmware update software runs
on the host operating system and updates the iLO 2 firmware without requiring you to log in to iLO
2.
• Offline firmware update for SmartStart maintenance—Download the iLO 2 firmware image file you
plan to install and see the section, "Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser (on page 25)."
• Firmware Maintenance CD-ROM—Download the component to create a bootable CD that contains
many firmware updates for ProLiant servers and options.
• Scripting with CPQLOCFG—Download the CPQLOCFG component to get the network-based
scripting utility, CPQLOCFG. CPQLOCFG enables you to use RIBCL scripts that perform firmware
updates, iLO 2 configuration, and iLO 2 operations in bulk, securely over the network. Linux users
should consider reviewing the HP Lights-Out XML PERL Scripting Samples for Linux.
• Scripting with HPONCFG—Download the HPONCFG component to get the host-based scripting
utility, HPONCFG. This utility enables you to use RIBCL scripts that perform firmware updates, Lights-
Out processor configuration and operations in bulk, from Administrator or root account access on
supported host operating systems.
• HP Directories Support for Management Processors—-Download the HP Directories Support for
Management Processors executable file to get the directory support components. One of the
components, HPLOMIG, can be used to discover iLO, iLO 2, RILOE, and RILOE II processors, and
update their firmware. You do not have to use directory integration to take advantage of this
functionality.
Upgrading iLO 2 using a browser
You can complete the firmware upgrade from any network client using a supported browser. You must
have the Update iLO 2 Firmware privilege to upgrade the iLO 2 firmware. The most recent firmware for
iLO 2 is available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
To upgrade the iLO 2 firmware using a supported browser:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
).
Configuring iLO 2 25
Page 26

2.
Click Administration>Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware. The Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware page appears.
3. Enter the file name in the New firmware image field or browse for the file.
4. Click Send firmware image. The firmware upgrade takes a few minutes. A progress bar displays the
progress of the firmware upgrade.
Do not interrupt an Upgrade iLO 2 Firmware session. The iLO 2 system automatically resets after a
successful firmware upgrade. The iLO 2 system reset does not affect the host operating system and server.
If the firmware upgrade is interrupted or fails, attempt the upgrade again immediately. Do not reset the
iLO 2 system before reattempting a firmware upgrade.
Recovering from a failed iLO 2 firmware update
To recover from a failed firmware update using the HP Drive Key Boot Utility:
1. Copy the iLO 2 offline flash component to your USB drive key.
2. Verify that the iLO 2 security override switch is set to disabled.
3. Boot the USB drive key drive containing the iLO 2 flash component.
To download the HP Drive Key Boot Utility and for information on how to create a boot USB key, see
the HP website (http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/download/23839.html
4. After the first screen displays, switch to text console by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+F1 keys.
5. Switch to the directory where the flash component is stored by entering cd
/mnt/usb/components/ at the # prompt.
6. Remove the loaded HP Lights-Out driver by entering /etc/init.d/hprsm stop.
7. Run the component using the --direct option. For example:
./CP00xxxx.scexe –-direct
).
8. Enter y at the Continue (y/N)? prompt.
9. After programming is successfully completed, set the security override switch to enabled and reboot
the server.
Configuring iLO 2 26
Page 27

Downgrading the iLO 2 firmware
If you downgrade the iLO 2 firmware, you must remove the iLO 2 1.30 Remote Console ActiveX applet
1.3.0.19 from your Internet Explorer client browser. To remove the applet:
1. Open Internet Explorer.
2. Select Tools>Internet Options>Settings>View objects.
3. To remove 1.30.19, right-click iLO2 Remote console 1.3.0.18.
Licensing
HP iLO Advanced Pack and HP iLO Select Pack software support both iLO and iLO 2 and activate
optional iLO 2 features that are not bundled with an unlicensed system. For additional information, see
the HP website
(http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/proliantessentials/valuepack/licensing.html
Effective July 9, 2007, you can purchase iLO Advanced Packs and iLO Select Packs individually or as
part of an Insight Control software suite.
If you purchase the iLO Advanced Pack or the iLO Select Pack with any Insight Control software suite or
iLO Power Management Pack, HP provides Technical Support and Update Services. See the "Software
technical support and update service (on page 214)" section for more information.
If you purchase the iLO Advanced Pack or the iLO Select Pack as a one-time activation of licensed
features, you must purchase future functional upgrades. See the "Software technical support and update
service (on page 214)" section for more information.
One iLO Advanced or iLO Select license is required for each server on which the product is installed and
used. Licenses are nontransferable. Full details are contained in the EULA.
HP will continue to provide maintenance releases with fixes as well as iLO Standard, and iLO Standard
Blade Edition feature enhancements at no extra charge.
).
A 60-day evaluation license key is available for download from the HP website
(http://h10018.www1.hp.com/wwsolutions/ilo/iloeval.html
). The evaluation license activates and
enables access to iLO 2 Advanced features. You can only install one evaluation license per iLO 2. When
the evaluation period expires, the iLO 2 features deactivate. To install a license, see the section,
"Activating iLO 2 licensed features using a browser (on page 21)."
The following versions of iLO 2 are available:
NOTE: The features annotated with an asterisk (*) are not supported on all systems.
• iLO 2 Standard (unlicensed:)
o Virtual Power and Reset control
o Remote serial console through POST only
o Event logs
o UID light*
o DMTF SMASH CLP
o RIBCL/XML scripting
o Browser access
Configuring iLO 2 27
Page 28

o
SSH access
o Shared network port*
o Serial access*
o Remote Console Computer Lock
• iLO 2 Standard Blade Edition (unlicensed blade server):
o Virtual power and reset control
o Remote Console and IRC
o Event logs
o UID light*
o DMTF SMASH CLP
o RIBCL/XML scripting
o Browser access
o SSH access
o Shared network port*
o Serial access*
o Applet-based virtual media
o Terminal Services integration
• iLO 2 Select:
o Directory integration
o Power Regulator for ProLiant
o Scripted virtual media
o Applet-based virtual media
o Two-factor authentication
o Console replay
o Shared Remote Console
o HP SIM SSO
• iLO 2 Advanced:
o Directory integration
o Power Regulator for ProLiant
o Scripted virtual media
o Applet-based virtual media
o Two-factor authentication
o Remote Console and IRC
o Terminal Services integration
o Console replay
o Shared Remote Console
o HP SIM SSO
In addition to the standard iLO 2 single-server licenses, two other licensing options are available:
Configuring iLO 2 28
Page 29

• The Flexible Quantity License Kit allows you to purchase a single software package, one copy of the
documentation, and a single license key to activate the exact number of licenses requested.
• The Activation Key Agreement allows a volume purchase of ProLiant Essentials and Insight Control
software over time, typically in conjunction with new ProLiant servers that are acquired on a regular
basis.
User administration
iLO 2 enables you to manage user accounts stored locally in the secure iLO 2 memory and directory
group accounts. Use MMC or ConsoleOne to manage directory user accounts.
iLO 2 supports up to 12 users with customizable access rights, login names, and advanced password
encryption. Privileges control individual user settings. Users can have privileges customized to their
individual access requirements. To support more than 12 users, you must have the Advanced Pack, which
enables integration with an unlimited number of directory-based user accounts.
You must have the Administer User Accounts privilege to view iLO 2 users, add new users, and modify or
delete existing users. If you do not have this privilege, you can view and modify only your account.
To access local accounts, click Administration>User Administration>Local Accounts.
Configuring iLO 2 29
Page 30

iLO 2 Directory Accounts enables you to view iLO 2 groups and modify the settings for those groups. You
must have the Administer Directory Groups privilege. To access Directory Accounts, click
Administration>User Administration>Group Accounts.
Adding a new user
IMPORTANT: Only users with the Administer User Accounts privilege can manage other users
You can assign a different access privilege to each user. Each user can have a unique set of privileges
designed for the tasks that the user must perform. You can grant or deny access to critical functions such
as remote access, user management, virtual power, and other features.
To add a new user to iLO 2:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Administer User Accounts privilege.
2. Click Administration.
3. Select User Administration>Local Accounts.
on iLO 2.
Configuring iLO 2 30
Page 31

4.
Click New.
5. Complete the fields. The following options are available:
o User Name is displayed in the user list and on the home page. It is not necessarily the same as
the Login name. The maximum length for a User Name is 39 characters. The User Name must
use printable characters.
o Login Name is the name that you must use when logging into iLO 2. The maximum length for a
Login Name is 39 characters. The Login Name may only use printable characters.
o Password and Confirm Password fields set and confirm the password that is used when logging
into iLO 2. The minimum length for a password is set in the Access Options page. The maximum
length for a password is 39 characters. Enter the password twice for verification.
o Administer User Accounts is a user privilege that allows you to add, modify, and delete local iLO
2 user accounts. It also allows you to alter privileges for all users, including granting all
permissions to yourself. Without this privilege, you can only view your own settings and change
your own password.
o Remote Console Access is a user privilege that allows you to remotely access the host system
Remote Console and Remote Serial Console, including video, keyboard and mouse control. You
are still required to have access to the remote system to use this capability.
o Virtual Power and Reset is a user privilege that allows you to power-cycle or reset the host
platform. Any of these activities interrupts the availability of the system. You can also diagnose
the system using the virtual NMI button.
o Virtual Media is a user privilege that allows you to use virtual media on the host platform.
o Configure iLO 2 Settings is a privilege that allows you to configure most iLO 2 settings, including
security settings. It enables you to remotely update iLO 2 firmware. It does not include user
account administration. These settings rarely change.
After correctly configuring iLO 2, revoking this privilege from all users prevents reconfiguration.
A user with the Administer User Accounts privilege can enable or disable this privilege. If iLO 2
RBSU is enabled, you can also reconfigure iLO 2.
o User Certificate Information maps a certificate to a user. User certificates are only required for
Two-Factor Authentication. If a certificate is not mapped to the user account, the message A
certificate has NOT been mapped to this user appears along with the Add a
Certificate button. Click this button to map a certificate to the user. After a certificate is mapped
Configuring iLO 2 31
Page 32

to the user account, a 40-digit thumbprint of the certificate appears, along with the Remove this
Certificate button, which can be used to remove the certificate. If Two-Factor Authentication is
enabled, a different certificate should be mapped to each user. A user who presents a certificate
when connecting to iLO 2 is authenticated as the user to whom the certificate is mapped. TwoFactor Authentication must be enabled to authenticate using a certificate.
6. When the user profile is complete, click Save User Information to return to the User Administration
screen. To clear the user profile while entering a new user, click Restore User Information.
Viewing or modifying an existing user's settings
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Administer User Accounts privilege.
You must have the Administer User Accounts privilege to manage other users on iLO 2. All users can
change their own password using the View/Modify User feature.
2. Click Administration>User Administration, and select the name of the user whose information you
want to modify.
3. Click View/Modify.
4. Change user information as required.
5. After changing the fields, click Save User Information to return to the User Administration screen. To
recover the original user information, click Restore User Information. All changes made to the profile
are discarded.
Deleting a user
IMPORTANT: Only users with the Administer User Accounts privilege can manage other users
To delete an existing user's information:
1. Log on to iLO 2 using an account that has the Administer User Accounts privilege. Click
2. Click User Administration and select from the list the name of the user whose information you want to
on iLO 2.
Administration.
change.
Configuring iLO 2 32
Page 33

Click Delete User. A pop-up window is displayed asking, Are you sure you want to delete
3.
the selected user? Click OK.
Group administration
iLO 2 enables you to view iLO 2 groups and modify settings for those groups. You must have the
Administer Directory Groups privilege. To view or modify a group:
1. Click Administration>User Administration>Group Accounts.
2. Select the group, and click View/Modify Group. The Modify Group page appears.
Click Cancel to return to the Group Administration page.
The following settings are available:
• Security Group Distinguished Name is the distinguished name of a group within the directory. All
members of this group are granted the privileges set for the group. The group specified in the
Security Group Distinguished Name must exist within the directory, and users who need access to
iLO 2 should be members of this group. Complete this field with a Distinguished Name from the
directory (for example, CN=Group1,OU=Managed Groups, DC=domain, DC=extension).
• Administer Group Accounts allows users who belong to this group to alter privileges for any group.
• Remote Console Access allows you to remotely access the host system Remote Console, including the
Remote Serial Console. You must have access to the remote system to use this capability.
• Virtual Power and Reset allows you to power cycle or reset the host platform. These activities
interrupt the availability of the system. If selected, this option also allows you to diagnose the system
using the virtual NMI button.
• Virtual Media allows you to use virtual media on the host platform.
• Configure iLO 2 Settings allows you to configure most iLO 2 settings, including security settings. If
selected, you can remotely update iLO 2 firmware. This setting does not include group account
administration. These settings rarely change.
After iLO 2 is correctly configured, revoking this privilege from all groups prevents reconfiguration.
Users with the Administer Group Accounts privilege can enable or disable this privilege. iLO 2 can
also be reconfigured if iLO 2 RBSU is enabled.
Configuring iLO 2 33
Page 34

Click Save Group Information to save updated information, or click Cancel to discard changes and return
to the Group Administration page.
Configuring iLO 2 access
iLO 2 allows you to configure which services are enabled on iLO 2 and user access to iLO 2. To
configure iLO 2 services options (on page 34), click Administration>Access. The Services page (tab)
appears. To configure iLO 2 access options (on page 40), click Administration>Access>Options (tab).
Services options
You must have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege to modify iLO 2 services and access options.
The Services tab enables you to select which services you want to enable on iLO 2, including SSH, SSL,
Remote Console, telnet, and Terminal Services. The Services tab also enables you to set the ports for each
selected option. Settings on the Services page apply to all iLO 2 users. You must have the Configure iLO
2 Settings privilege to modify settings on this page.
To access Services, click Administration>Access>Services. Click Apply to save any updated information.
Click Apply to save updated information. You must restart iLO 2 before any changes take effect. If any
changes have been made to enable or disable Lights-Out functionality, clicking Apply terminates your
browser connection and restarts iLO 2. You must wait at least 30 seconds before attempting to reestablish
a connection.
The Services tab includes the following settings:
Parameter Default value Description
Secure Shell (SSH)
Access
Secure shell (SSH)
Port
Enabled This setting enables you to specify whether the SSH feature
on the iLO 2 is enabled or disabled.
22 This setting enables you to configure the iLO 2 SSH port to
be used for SSH communications.
Configuring iLO 2 34
Page 35

Parameter Default value Description
Telnet Access Disabled This setting enables you to connect a telnet client to the
Remote Console/Telnet port, providing access to the iLO 2
CLP. The following settings are valid:
• Enabled—iLO 2 enables telnet clients to connect to the
Remote Console/Telnet port. Network port scanners can
detect that iLO 2 is listening on this port. Unencrypted
communication is allowed between the iLO 2 CLP and
telnet clients.
• Disabled— iLO 2 does not allow telnet clients to connect
to the Remote Console/Telnet port. Network port
scanners will not normally detect if this port is open on
iLO 2. iLO 2 listens on this port for a few seconds when
the Remote Console is opened, but telnet connections are
not accepted.
Communication between the iLO 2 and Remote Console is
always encrypted.
Remote
Console/Telnet Port
Web Server Non-SSL
Port
Web Server SSL Port 443 This setting enables you to specify which port the embedded
Terminal Services
Passthrough
23 This setting enables you to specify which port the iLO 2
Remote Console uses for remote console communications.
80 This setting enables you to specify which port the embedded
web server in iLO 2 uses for unencrypted communications.
web server in iLO 2 uses for encrypted communications.
Disabled This setting enables you to control the ability to support a
connection through iLO 2 between a Microsoft® Terminal
Services client and Terminal Services server running on the
host. The following settings are valid:
• Automatic—When remote console is started, the Terminal
Services client is launched.
• Enabled—The pass-through feature is enabled and can
connect the Terminal Services client directly to the iLO 2
without logging-into the iLO 2.
• Disabled—The pass-through feature is off.
Terminal Services Port 3389 This setting enables you to specify the Terminal Services Port
that the iLO 2 uses for encrypted communications with
Terminal Services Passthrough software on the server. If the
Terminal Services port is configured to anything other than
the default, you must manually change the port number in
Windows® 2000 to match it.
Virtual Media Port 17988 This setting enables you to specify the port for virtual media
support in iLO 2 communications.
Shared Remote
Console Port
9300 This setting enables you to specify the Shared Remote
Console Port. The Shared Remote Console Port is opened on
the client to allow additional users to connect to remote
console in a peer-to-peer fashion. This port is only open when
Shared Remote Console is in use.
Configuring iLO 2 35
Page 36

Parameter Default value Description
Console Replay Port 17990 This setting enables you to specify the Console Replay Port.
Terminal Services Passthrough option
Terminal Services is provided by the Microsoft® Windows® operating systems. The iLO 2 Terminal
Services Passthrough option provides a connection between the Terminal Services server on the host
system and the Terminal Services client on the client system. When the Terminal Services Passthrough
option is enabled, the iLO 2 firmware enables a socket, listening by default on port 3389. All data
received from Terminal Services on this port is forwarded to the server and all data Terminal Services
receives from the server is forwarded back to the socket. The iLO 2 firmware reads anything received on
this port as an RDP packet. RDP packets are exchanged between the iLO 2 firmware and the server
Terminal Services (RDP) server through the local host address on the server. The service provided
facilitates communications between the iLO 2 firmware and the RDP server. The RDP server interprets the
service as an established external RDP connection. For more information on RDP service, see the section,
"Windows® RDP Passthrough service ("Windows RDP passthrough service" on page 37)."
The Console Replay Port is opened on the client to enable the
transfer of internal capture buffers to the client for replay.
This port is only open when a capture buffer is being
transferred to the client.
A Terminal Services session provides a performance-enhanced view of the host system console. When the
operating system is unavailable (or the Terminal Services server or client is unavailable), the traditional
iLO 2 Remote Console provides a view of the host system console. For more information on Remote
Console and Terminal Services, see the section, "Remote Console and Terminal Services clients (on page
39)."
To configure the Terminal Services Passthrough option, see the sections, "Terminal Services Client
requirements (on page 36)" and "Terminal Services Passthrough installation (on page 37)."
Terminal Services client requirements
The Terminal Services client is available on Microsoft® Windows® client machines running:
• Windows® 2000
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 servers require the installation of Microsoft® .NET Framework to
support the use of iLO 2 Terminal Services. After the .NET Framework is installed, the Terminal
Services client must be installed from diskettes created by the Terminal Services server. See your
Windows® operating guides or help files for instructions.
• Windows® 2000 Professional
When installing the Terminal Services client on Windows® 2000 Professional, use the default
installation location. The Terminal Services client in Windows® 2000 Professional displays a dialog
box asking for a Terminal Services server.
• Windows Server™ 2003
On Windows Server™ 2003 servers, the Terminal Services client and RDP connection is built-in. The
client is part of the operating system and is activated using Remote Desktop sharing. To activate
desktop sharing, select My Computer>Properties>Remote>Remote Desktop. The Terminal Services
client in Windows Server™ 2003 provides command line options and seamless launches from the
Remote Console applet.
Configuring iLO 2 36
Page 37

• Windows® XP
On Windows® XP servers, the Terminal Services client and RDP connection is built in. The client is
part of the operating system and is activated using Remote Desktop sharing. To activate desktop
sharing, select Start>Programs>Accessories>Communications>Remote Desktop. The Terminal
Services client in Windows® XP provides command line options and launches from the remote
console applet.
Windows RDP passthrough service
To use the iLO 2 Terminal Services Passthrough feature, you must install a passthrough service on the host
system. This service displays the name of the iLO 2 Proxy in the host list of available services. The service
utilizes Microsoft® .NET framework security and reliability. After the service is started, the service polls
iLO 2 to detect if an RDP connection with the client is established. If an RDP connection with the client is
established, the service establishes a TCP connection with local host and begins exchanging packets. The
port used to communicate with the local host is read from the Windows® registry at:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\Wds\r
dpwd\Tds\tcp\PortNumber
The port is typically port 3389.
Terminal Services passthrough installation
The following section describes how to install Terminal Services passthrough on Microsoft® Windows®
2000, Windows Server™ 2003, and Microsoft® Windows® XP.
• Microsoft® Windows® 2000 and Windows Server™ 2003
Windows® 2000 servers require Microsoft® .NET Framework to support the use of iLO 2 Terminal
Services. The Terminal Services passthrough service and the iLO 2 Management Interface driver for
Windows® 2000 and Windows Server™ 2003 must be installed on the server that has the iLO 2.
a. Install the iLO 2 Management Interface driver.
b. Install the passthrough service. To install the service, launch the component installer and follow
the directions in the installation wizard.
If the service is already installed, then you must manually restart or reboot the server when the
driver is installed.
c. Install or activate the Terminal Services client.
Windows® 2000 servers require the installation of Microsoft® .NET Framework to support the
use of Terminal Services. After the .NET Framework is installed, the Terminal Services client must
be installed from diskettes created by the Terminal Services server, or by downloading the client
from the Microsoft website and installing it through the Control Panel using Add or Remove
Programs. Consult your Windows® operating guides or help files for instructions. When
installing the Terminal Services client on Windows® 2000, use the default installation location.
On Windows Server™ 2003, you can activate Remote Desktop sharing by clicking the Remote
tab under My Computer and Properties.
If the iLO 2 installation is complete, and if iLO 2 Terminal Services Passthrough option is set to
automatic, then Terminal Services launches when the installation is complete.
• Microsoft® Windows® XP
On Windows® XP, the Remote Desktop Connection is built-in and has no other installation
requirements.
Configuring iLO 2 37
Page 38

Errors that occur during installation and execution of the passthrough service are logged in the server
Application Event Log. You can remove the passthrough service using Add or Remove Programs in the
Control Panel.
Windows® 2000 Terminal Services port change
If the Terminal Services port is changed, Windows® 2000 client must manually configure the Terminal
Services Client Connection Manager.
1. Start the Terminal Services Client Connection Manager, and create a new connection to the terminal
server.
2. Highlight the icon created, and select File>Export. Rename the file with a .cns extension. For
example: myilo.cns.
3. Edit the myilo.cns file by looking for the line Server Port=3389. Replace 3389 with your new port
number and save the file.
4. From the Client Connection Manager, highlight the New Connection icon, and click File>Import.
5. Double-click the newly created icon to launch terminal server and connect to the new port.
Enabling the Terminal Services Passthrough option
By default, the Terminal Services Passthrough feature is disabled and can be enabled on the
Administration>Access>Services page. The Terminal Services button in the Remote Console is deactivated
until the Terminal Services Pass-Through feature is enabled.
To use of the Terminal Services Passthrough feature, install the latest Lights-Out Management Interface
Driver and then install Terminal Services passthrough service for Microsoft® Windows® on the server.
When the Terminal Services Passthrough option is set to Enabled or Automatic on the
Administration>Access>Services page and the Terminal Services Client is installed on the Windows®
client (installs by default on Windows® XP), the Terminal Services button is enabled. When you click the
Terminal Services button, the applet tries to launch the Terminal Services, even if the server is not running
a Windows® operating system.
You must comply with Microsoft® license requirements which are the same as connecting through the
server's NIC. For instance, when set for administrative access, Terminal Services does not allow more
than two connections, regardless of whether the connections are through the server's NIC, or iLO 2, or
both.
Terminal Services warning message
Terminals Services users operating on Windows® 2003 Server might notice the following when using the
Terminal Services pass-through feature of iLO 2. If a Terminal Services session is established through iLO
2 and a second Terminal Services session is established by a Windows® administrator (Console mode),
the first Terminal Services session is disconnected. However, the first Terminal Services session does not
receive the warning message indicating the disconnection until approximately one minute later. During
this one-minute period, the first Terminal Services session is available or active. This is normal behavior,
but it is different than the behavior observed when both Terminal Services sessions are established by
Windows® administrators. In that case, the warning message is received by the first Terminal Services
session immediately.
Configuring iLO 2 38
Page 39

Terminal Services Passthrough option display
The iLO 2 firmware might not accurately display the Terminal Services Passthrough option. The Terminal
Services Passthrough option might appear active even if the operating system is not Terminal Services
enabled (for example, if the host operating system is Linux, which does not support Terminal Services
operation).
Remote Console and Terminal Services clients
Using the management network connection to the iLO 2, an iLO 2 Remote Console session can be used to
display a Terminal Services session to the host. When the iLO 2 Remote Console applet runs, it launches
the Terminal Services client based on user preference. The Sun JVM must be installed to obtain full
functionality of this feature. If the Sun JVM is not installed, then the Remote Console cannot automatically
launch the Terminal Services client.
If Terminal Services pass-through is enabled, and the Terminal Services server is available, switching
between iLO 2 Remote Console and the Terminal Services client will be seamless as the server progresses
from pre-operating system environment to operating system-running environment, to operating system-not
available environment. The seamless operation is available as long as the Terminal Services client is not
started before Remote Console is available. If Remote Console is available and the Terminal Services
client is available, Remote Console will start the Terminal Services client when appropriate.
When using the Terminal Services pass-through option with Windows® 2000, there is approximately a
one-minute delay after the CTRL-ALT-DEL dialog box appears before the Terminal Services client launches.
On Windows Server 2003™, the delay is about 30 seconds. The 30 second delay represents how long it
takes for the service to connect to the RDP client running on the server. If the server is rebooted from the
Terminal Services client, the Remote Console screen turns grey or black for up to one minute while iLO 2
determines that the Terminal Services server is no longer available.
If Terminal Services mode is set to Enabled but you want to use the Remote Console, then the Terminal
Services client should be launched directly from the Terminal Services client menu. Launching directly from
the client menu allows simultaneous use of the Terminal Services client and the Remote Console.
Terminal Services can be disabled or enabled at any time. Changing the Terminal Services configuration
causes the iLO 2 firmware to reset. Resetting the iLO 2 firmware interrupts any open connections to iLO 2.
When the Terminal Services client is launched by the Remote Console, Remote Console goes into a sleep
mode to avoid consuming CPU bandwidth. Remote Console still listens to the Remote Console default port
23 for any commands from the iLO 2.
iLO 2 passes through only one Terminal Services connection at a time. Terminal Services has a limit of
two concurrent sessions.
The Remote Console activates and becomes available if the Remote Console is in sleep mode and the
Terminal Services client is interrupted by any of the following events:
• The Terminal Services client is closed by the user.
• The Windows® operating system is shut down.
• The Windows® operating system locks up.
Terminal Services troubleshooting
To resolve problems with iLO 2 Terminal Services Passthrough:
Configuring iLO 2 39
Page 40

1.
Verify that Terminal Services is enabled on the host by selecting My
Computer>Properties>Remote>Remote Desktop.
2. Verify that the iLO 2 pass-through configuration is enabled or automatic in the iLO 2 Global Settings.
3. Verify that iLO Advanced Pack is licensed.
4. Verify that the iLO 2 Management Interface Driver is installed on the host. To verify the driver, select
My Computer>Properties>Hardware>Device Manager>Multifunction Adapters.
5. Verify that the Terminal Services Pass-Through service and iLO 2 Proxy are installed and running on
the host. To verify these services, select Control Panel>Administrative Tools>Services and attempting
to restart the service.
6. Verify that the Application Event Log is not full.
The Terminal Services Pass-Through service might experience start-up problems when the operating
system Application Event Log is full. To view the event log, select Computer Management>System
Tools>Event Viewer>Application.
7. Verify that the Terminal Services port assignment is correct.
8. Verify that the Terminal Services client, mstsc.exe is located in \WINDOWS\SYSTEM32.
If not, set the pass-through configuration to Enabled, and manually activate the terminal services
client.
Access options
iLO 2 enables you to modify iLO 2 access, including connection idle time, iLO 2 functionality, iLO 2
RBSU, login requirements, CLI parameters, minimum password length, and server name. Settings on the
Access Options page apply to all iLO 2 users. You must have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege to
modify settings on this page.
To view or modify iLO 2 access, click Administration>Access>Options. Click Apply to save any updated
information. You must restart iLO 2 before any changes take effect. If any changes have been made to
enable or disable Lights-Out functionality, clicking Apply terminates your browser connection and restarts
iLO 2. You must wait at least 30 seconds before attempting to reestablish a connection.
The Options tab includes the following:
Configuring iLO 2 40
Page 41

Parameter Default value Descriptions
Idle Connection
Timeout (minutes)
Lights-Out
Functionality
Require Login for iLO
2 RBSU
Show iLO 2 during
POST
Serial Command Line
Interface Status
30 minutes This setting specifies the interval of user inactivity, in minutes,
before the web server and Remote Console session
automatically terminate. The following settings are valid: 15,
30, 60, 120 minutes, or 0 (infinite). The infinite timeout value
does not log out inactive users.
Enabled This setting enables connection to iLO 2. If disabled, all
connections to iLO 2 are prevented.
The iLO 2 10/100 network and communications with
operating system drivers are turned off if Lights-Out
functionality is disabled. The iLO 2 Diagnostic Port for an HP
ProLiant BL p Class server is also disabled.
If iLO 2 functionality is disabled (including the iLO 2
Diagnostic Port), you must use the server's Security Override
Switch to enable iLO 2. See your server documentation to
locate the Security Override Switch and set it to override.
Power up the server and use the iLO 2 RBSU to set Lights-Out
Functionality to Enabled.
Disabled This setting enables RBSU access with or without a user-
credentials challenge. If this setting is Enabled, and you press
F8 during POST to enter iLO 2 RBSU. A login dialogue
appears.
Disabled This setting enables the display of the iLO 2 network IP
address during the host server POST process.
EnabledAuthentication
Required
This setting enables you to change the login model of the CLI
feature through the serial port. The following settings are
valid:
• Enabled—Authentication Required
• Enabled—No Authentication
• Disabled
Serial Command Line
Interface Speed
Minimum Password
Length
Server Name — This setting enables you to specify the host server name. This
9600 This setting enables you to use the serial port to change the
speed of the serial port for the CLI feature. The following
speeds (in bits/s) are valid: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600,
and 115200. The serial port configuration must be set to No
parity, 8 data bits, and 1 stop bit (N/8/1) for proper
operation. The serial port speed that is set by this parameter
must match the speed of the serial port set in the System
ROM RBSU setup.
8 This setting specifies the minimum number of characters
allowed when a user password is set or changed. The
character length can be set at a value from 0 to 39.
value is assigned when using HP ProLiant Management
Agents. If you do not use the agents and the host unnamed
message appears, you can change it here. If the agents are
running, the value you assign can be overwritten.
To force the browser to refresh, save this setting, and press
F5.
Configuring iLO 2 41
Page 42

Parameter Default value Descriptions
Authentication Failure
Logging
Enabled-Every
3rd Failure
This setting allows you to configure logging criteria for failed
authentications. All login types are supported and every
login type works independently. The following are valid
settings:
• Enabled-Every Failure—A failed login log entry is
recorded after every failed login attempt.
• Enabled-Every 2nd Failure—A failed login log entry is
recorded after every second failed login attempt.
• Enabled-Every 3rd Failure—A failed login log entry is
recorded after every third failed login attempt.
• Enabled-Every 5th Failure—A failed login log entry is
recorded after every fifth failed login attempt.
• Disabled—No failed login log entry is recorded.
When logging into iLO 2 with Telnet or SSH clients, the number of login name and password prompts
offered by iLO 2 matches the value of the Authentication Failure Logging parameter (or 3 when it is
disabled.) However, the number of prompts might also be affected by your Telnet and SSH client
configurations. Telnet and SSH logins also implement delays after login failure. During the delay, login is
disabled so no login failure occurs. As an example, to generate an SSH authentication failure log with a
default value (for instance, Enabled-Every 3rd Failure), three consecutive login failures occur as follows
(assuming the SSH client is configured with the number of password prompts >= 3):
1. Run the SSH client and log in with an incorrect login name and password. You will receive three
password prompts. After the third incorrect password, the connection terminates and the first login
failure is recorded. The SSH login failure counter is set to 1.
2. Run the SSH client until receiving the login prompt. Log in with an incorrect login name and
password. You will receive three password prompts. After the third incorrect password, the
connection terminates, and the second login failure is recorded. The SSH login failure counter is set
to 2.
3. Run the SSH client until receiving the login prompt. Log in with an incorrect login name and
password. You will receive three password prompts. After the third incorrect password, the
connection terminates and the third login failure is recorded. The SSH login failure counter is set to
3.
At this point, iLO 2 firmware records an SSH login failure log entry and sets the SSH login failure counter
to 0.
iLO 2 Remote Console and Remote Serial Console access
For iLO 2 Remote Console recommended client settings, server settings, optimizing mouse support, and
Remote Serial Console settings, see the section, "iLO 2 Remote Console (on page 86)."
Security
iLO 2 enables you to customize iLO 2 security settings. To access iLO 2 security settings, select
Administration>Security. iLO 2 security options include
• SSH key administration (on page 46)
Configuring iLO 2 42
Page 43

• SSL certificate administration (on page 46)
• Two-factor authentication (on page 47)
• Directory settings (on page 52)
• iLO 2 encryption
• HP SIM single sign-on ("HP SIM single sign-on (SSO)" on page 57)
• Remote Console Computer Lock (on page 60)
iLO 2 security options enables iLO 2 to provide the following security features:
• User-defined TCP/IP ports
• User actions logged in the iLO 2 Event Log
• Progressive delays for failed login attempts
• Support for X.509 CA signed certificates
• Support for securing RBSU
• Encrypted communication using:
o SSH key administration
o SSL certificate administration
• Support for optional LDAP-based directory services
Some of these options are licensed features. To verify your available options, see the section, "Licensing
(on page 27)."
General security guidelines
The following are general guidelines concerning security for iLO 2:
• For maximum security, iLO 2 should be set up on a separate management network.
• iLO 2 should not be connected directly to the Internet.
Password guidelines
• A 128-bit cipher strength browser must be used.
The following is a list of recommended password guidelines. Passwords should:
• Never be written down or recorded
• Never be shared with others
• Not be words generally found in a dictionary, or easy to guess words, such as the company name,
product names, the user's name, or the user's User ID
• Include at least three of the four following characteristics:
o At least one numeric character
o At least one special character
o At least one lowercase character
o At least one uppercase character
Configuring iLO 2 43
Page 44

Passwords issued for a temporary user ID, password reset, or a locked-out user ID should also conform to
these standards. Each password must be a minimum length of zero characters and a maximum length of
39 characters. The default minimum length is set to eight characters. Setting the minimum password length
to fewer than eight characters is not recommended unless you have a physically secure management
network that does not extend outside the secure data center.
Securing RBSU
iLO 2 RBSU enables you to view and modify the iLO 2 configuration. RBSU access settings can be
configured using RBSU, a web browser (Access options (on page 40)), RIBCL scripts, or the iLO 2 Security
Override Switch. RBSU has three levels of security:
• RBSU Login Not Required (default)
Anyone with access to the host during POST can enter the iLO 2 RBSU to view and modify
configuration settings. This is an acceptable setting if host access is controlled.
• RBSU Login Required (more secure)
If RBSU login is required, then the active configuration menus are controlled by the authenticated
user's access rights.
• RBSU Disabled (most secure)
If iLO 2 RBSU is disabled, user access is prohibited. This prevents modification using the RBSU
interface.
iLO 2 Security Override Switch administration
The iLO 2 Security Override Switch allows the administrator full access to the iLO 2 processor. This access
may be necessary for any of the following conditions:
• iLO 2 must be re-enabled after it has been disabled.
• All user accounts with the Administer User Accounts privilege have been locked out.
• A bad configuration keeps the iLO 2 from displaying on the network and RBSU has been disabled.
• The boot block must be flashed.
Ramifications of setting the Security Override Switch include:
• All security authorization checks are disabled while the switch is set.
• iLO 2 RBSU runs if the host server is reset.
• iLO 2 is not disabled and might display on the network as configured.
• iLO 2, if disabled while the Security Override Switch is set, does not log the user out and complete
the disable process until the power is cycled on the server.
• The boot block is exposed for programming.
A warning message is displayed on iLO 2 browser pages indicating that the iLO 2 Security Override
Switch is currently in use. An iLO 2 log entry records the use of the iLO 2 Security Override Switch. An
SNMP alert can also be sent upon setting or clearing the iLO 2 Security Override Switch.
Setting the iLO 2 Security Override Switch also enables you to flash the iLO 2 boot block. HP does not
anticipate that you will need to update the iLO 2 boot block. If an iLO 2 boot block update is ever
required, physical presence at the server will be required to reprogram the boot block and reset iLO 2.
The boot block will be exposed until iLO 2 is reset. For maximum security, HP recommends that you
Configuring iLO 2 44
Page 45

disconnect the iLO 2 from the network until the reset is complete. The iLO 2 Security Override Switch is
located inside the server and cannot be accessed without opening the server enclosure.
To set the iLO 2 Security Override Switch:
1. Power off the server.
2. Set the switch.
3. Power on the server.
Reverse the procedure to clear the iLO 2 Security Override Switch.
Depending on the server, the iLO 2 Security Override Switch might be a single jumper or a specific switch
position on a dip switch panel. To access and locate the iLO 2 Security Override Switch, refer to the
server documentation. The iLO 2 Security Override Switch can also be located using the diagrams on the
server access panel.
User accounts and access
iLO 2 supports the configuration of up to 12 local user accounts. Each of these accounts can be managed
through the use of the following features:
• Privileges (on page 45)
• Login security (on page 45)
iLO 2 can be configured to use a directory to authenticate and authorize its users. This configuration
enables a virtually unlimited number of users, and easily scales to the number of Lights-Out devices in an
enterprise. Additionally, the directory provides a central point of administration for Lights-Out devices and
users, and the directory can enforce a stronger password policy. iLO 2 enables you to use local users,
directory users, or both.
Two configuration options are available: using a directory that has been extended with HP Schema
("Setting up HP schema directory integration" on page 138) or using the directory’s default schema
(schema-free ("Setup for Schema-free directory integration" on page 134)).
Privileges
iLO 2 allows the administrator to control user account access to iLO 2 functions through the use of
privileges. When a user attempts to use a function, the iLO 2 system verifies that the user has the privilege
before the user is allowed to perform the function.
Each feature available through iLO 2 can be controlled through privileges, including Administer User
Accounts, Remote Console Access, Virtual Power and Reset, Virtual Media, and Configure iLO 2 Settings.
Privileges for each user can be configured on the User Administration page of the Administration tab.
Login security
iLO 2 provides several login security features. After an initial failed login attempt, iLO 2 imposes a delay
of five seconds. After a second failed attempt, iLO 2 imposes a delay of 10 seconds. After the third failed
attempt, and any subsequent attempts, iLO 2 imposes a delay of 60 seconds. All subsequent failed login
attempts cycles through these values. An information page is displayed during each delay. This will
continue until a valid login is completed. This feature assists in defending against possible dictionary
attacks against the browser login port.
iLO 2 saves a detailed log entry for failed login attempts, which imposes a delay of 60 seconds.
Configuring iLO 2 45
Page 46

SSH key administration
iLO 2 enables you to authorize up to four SSH keys at one time on the SSH Key tab. The SSH Key tab
also displays the owner (if any keys are authorized) of each authorized SSH key. Multiple keys can
belong to a single user.
To add an authorized key to iLO 2, the public key path must be submitted to iLO 2. The key file must
contain the user name after the end of the key. iLO 2 associates each key with a local user account. If the
local account does not exist or if it is deleted, the key is invalid (the key is not listed if the local account
does not exist).
Alternatively, you can authorize SSH keys for an HP SIM server by running the mxagentconfig tool from
the HP SIM server and specifying the address and user credentials for iLO 2. See your HP SIM
documentation for more details.
To authorize a new key:
1. In the iLO 2 interface, click Administration>Security>SSH Key.
2. Click Browse, and locate the key file.
3. Click Authorize Key.
You can view or delete any previously authorized key by selecting the key, and clicking View Selected
Key or Delete Selected Key. The View Selected Key and Delete Selected Key buttons only appear when
SSH keys are installed.
SSL certificate administration
iLO 2 enables you to create a certificate request, import a certificate, and view certificate administration
information associated with a stored certificate. Certificate information is encoded in the certificate by the
CA and is extracted by iLO 2.
By default, iLO 2 creates a self-signed certificate for use in SSL connections. This certificate enables iLO 2
to work without any additional configuration steps. The security features of the iLO 2 can be enhanced by
importing a trusted certificate. For more information on certificates and certificate services, see the
sections, "Introduction to certificate services (on page 134)" and "Installing certificate services (on page
134)."
To access certificate information, click Administration>Security>SSL Certificate. The SSL Certificate tab
displays the following information:
• The Issued To field lists the entity to which the certificate was issued.
• The Issued By field lists the CA that issued the certificate.
• The Valid From field lists the first date that the certificate is valid.
• The Valid Until field lists the date that the certificate will expire.
• The Serial Number field lists the serial number assigned to the certificate by the CA.
The following options are available on the SSL Certificate tab:
• Create Certificate Request—Use this button to create a certificate request. When you click this
button, a CR is created (in PKCS #10 format) that can be sent to a CA. This certificate request is
Base64-encoded. A CA processes this request and returns a response (X.509 certificate) that can be
imported into iLO 2.
Configuring iLO 2 46
Page 47

The CR contains a public/private key pair that validates communications between the client browser
and iLO 2. The generated CR is held in memory until a new CR is generated, iLO 2 is reset, or a
certificate is imported by the generation process. You can generate the CR and copy it to the client
clipboard, leave the iLO 2 website to retrieve the certificate, and then return to import the certificate.
When submitting the request to the CA, be sure to perform the following tasks:
a. Use the iLO 2 name as listed on the System Status screen as the URL for the server.
b. Request that the certificate is generated in the RAW format.
c. Include the Begin and End certificate lines.
Every time you click Create Certificate Request, a new certificate request is generated, even though
the iLO 2 name is the same.
• Import Certificate—Use this button when you are returning to the Certificate Administration page
with a certificate to import. Click Import Certificate to go directly to the Certificate Import screen
without generating a new CR. A certificate only works with the keys generated for the original CR
from which the certificate was generated. If iLO 2 has been reset, or another CR was generated
since the original CR was submitted to a CA, then a new CR must be generated and submitted to the
CA.
You can create a CR or import an existing certificate using RIBCL XML commands. These commands
enable you to script and automate certificate deployment on iLO 2 servers instead of manually deploying
certificates through the browser interface. For more information, see HP Integrated Lights-Out
Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
Two-factor authentication
Access to iLO 2 requires user authentication. This firmware release provides an enhanced authentication
scheme for iLO 2 using two factors of authentication: a password or PIN, and a private key for a digital
certificate. Using two-factor authentication requires that you verify your identity by providing both factors.
You can store your digital certificates and private keys wherever you choose, for example, on a smart
card, USB token, or hard drive.
The Two-Factor Authentication tab enables you to configure security settings and review, import, or delete
a trusted CA certificate. The Two-Factor Authentication Enforcement setting controls whether two-factor
authentication is used for user authentication during login. To require two-factor authentication, click
Enabled. To turn off the two-factor authentication requirement and allow login with user name and
password only, click Disabled. You cannot change the setting to Enabled if a trusted CA certificate is not
configured. To provide the necessary security, the following configuration changes are made when twofactor authentication is enabled:
• Telnet Access: Disabled
• Secure Shell (SSH) Access: Disabled
• Serial Command Line Interface Status: Disabled
If telnet, SSH, or Serial CLI access is required, re-enable these settings after two-factor authentication is
enabled. However, because these access methods do not provide a means of two-factor authentication,
only a single factor is required to access iLO 2 with telnet, SSH, or Serial CLI.
When two-factor authentication is enabled, access by the CPQLOCFG utility is disabled because
CPQLOCFG does not meet all authentication requirements. However, the HPONCFG utility works
because administrator privileges on the host system are required to execute the utility.
Configuring iLO 2 47
Page 48

A trusted CA certificate is required for two-factor authentication to function. You cannot change the TwoFactor Authentication Enforcement setting to Enabled if a trusted CA certificate is not configured. Also,
you must map a client certificate to a local user account if local user accounts are used. If iLO 2 is using
directory authentication, client certificate mapping to local user accounts is optional.
To change two-factor authentication security settings for iLO 2:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
2. Click Administration>Security>Two-Factor Authentication.
3. Change the settings by entering your selections in the fields.
4. Click Apply to save the changes.
The Certificate Revocation Checking setting controls whether iLO 2 uses the certificate CRL distribution
points attribute to download the latest CRL and verify revocation of the client certificate. If the client
certificate is contained in the CRL, or if you cannot download the CRL, access is denied. The CRL
distribution point must be available and accessible to iLO 2 when Certificate Revocation Checking is set
to Yes.
The Certificate Owner Field setting specifies which attribute of the client certificate to use when
authenticating with the directory. Only use the Certificate Owner Field setting if directory authentication is
enabled. Configuration of the Certificate Owner Field depends on the version of directory support used,
the directory configuration, and the certificate issuance policy of your organization. If SAN is specified,
iLO 2 extracts the User Principle Name from the Subject Alternative Name attribute and then uses the User
Principle Name when authenticating with the directory (for example, username@domain.extension). For
example, if the subject name is /DC=com/DC=domain/OU=organization/CN=user, iLO 2 will
derive CN=user,OU=organization,DC=domain,DC=com.
Setting up two-factor authentication for the first time
When setting up two-factor authentication for the first time, you can use either local user accounts or
directory user accounts. For more information on two-factor authentication settings, see the "Two-Factor
Authentication (on page 47)" section.
Setting up local user accounts
1. Obtain the public certificate from the CA that issues user certificates or smart cards in your
organization.
2. Export the certificate in Base64-encoded format to a file on your desktop (for example, CAcert.txt).
3. Obtain the public certificate of the user who needs access to iLO 2.
4. Export the certificate in Base64-encoded format to a file on your desktop (for example, Usercert.txt).
5. Open the file CAcert.txt in Notepad, select all of the text, and copy it by pressing the Ctrl+C keys.
6. Log in to iLO 2, and browse to the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page.
7. Click Import Trusted CA Certificate. The Import Root CA Certificate page appears.
8. Click inside the white text area so that your cursor is in the text area, and paste the contents of the
clipboard by pressing the Ctrl+V keys.
9. Click Import Root CA Certificate. The Two-Factor Authentication Settings page appears again with
information displayed under Trusted CA Certificate Information.
10. From your desktop, open the file for the user certificate in Notepad, select all the text, and copy the
text to the clipboard by pressing the Ctrl+C keys.
Configuring iLO 2 48
Page 49

11.
Browse to the User Administration page on iLO 2, and select the user for which you have obtained a
public certificate or create a new user.
12. Click View/Modify.
13. Click Add a certificate.
14. Click inside the white text area so that your cursor is in the text area, and paste the contents of the
clipboard by pressing the CTRL+V keys.
15. Click Add user Certificate. The Modify User page appears again with a 40-digit number in the
Thumbprint field. You can compare the number to the thumbprint displayed for the certificate by
using Microsoft® Certificate Viewer.
16. Browse to the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page.
17. Select Enabled for the Two-Factor Authentication option.
18. Select Disabled for the Certificate Revocation Checking option. This value is the default.
19. Click Apply. iLO 2 is reset. When iLO 2 attempts to go to the login page again, the browser
displays the Client Authentication page with a list of certificates that are available to the system.
If the user certificate is not registered on the client machine, you will not see it in the list. The user
certificate must be registered on the client system before you can use it. If there are no client
certificates on the client system you might not see the Client Authentication page and instead see a
Page cannot be displayed error. To resolve the error, the client certificate must be registered on the
client machine. For more information on exporting and registering client certificates, see the
documentation for your smart card or contact your certificate authority.
20. Select the certificate that was added to the user in iLO 2. Click OK.
21. If prompted to do so, insert your smart card, or enter your PIN or password.
After completing the authentication process, you have access to iLO 2.
Setting up directory user accounts
1. Obtain the public certificate from the CA that issues user certificates or smart cards in your
organization.
2. Export the certificate in Base64-encoded format to a file on your desktop (for example, CAcert.txt).
3. Open the file in Notepad, select all the text, and copy the contents to the clipboard by pressing the
Ctrl+C keys.
4. Log in to iLO 2, and browse to the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page.
5. Click Import Trusted CA Certificate. Another page appears.
6. Click inside the white text area so that your cursor is in the text area, and paste the contents of the
clipboard by pressing the Ctrl+V keys.
7. Click Import Root CA Certificate. The Two-Factor Authentication Settings page appears again with
information displayed under Trusted CA Certificate Information.
8. Change Enforce Two-Factor authentication to Yes.
9. Change Certificate Revocation Checking to No (default).
10. Change Certificate Owner Field to SAN. For more information, see the "Two-Factor Authentication
(on page 47)" section.
11. Click Apply. iLO 2 is reset. When iLO 2 attempts to go to the login page again, the browser
displays the Client Authentication page with a list of certificates that are available to the system.
12. Select the certificate added to the user in iLO 2. Click OK.
Configuring iLO 2 49
Page 50

13.
If prompted to do so, insert your smart card, or enter your PIN or password. The login page should
be displayed with the e-mail address for the user in the Directory User field. You cannot change the
Directory User field.
14. Enter the password for the directory user. Click Login.
After completing the authentication process, you have access to iLO 2. See the "Directory settings (on
page 52)" section for more information on configuring directory users and privileges.
Setting up a user for two-factor authentication
To authenticate a user with a local iLO 2 account, a certificate must be associated with the user's local
user name. On the Administration>Modify User page, if a certificate has been mapped to the user, a
thumbprint (an SHA1 hash of the certificate) appears with a button that removes the certificate. If a
certificate has not been mapped to the user, Thumbprint: A certificate has NOT been
mapped to this user appears with a button that starts the certificate import process.
To set up a user for two-factor authentication and add a user certificate:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
2. Click Administration>User Administration. Select a user.
3. Click View/Modify.
4. Under the User Certificate Information section, click Add a certificate.
5. On the Map User Certificate page, paste the user certificate into the text-box and click Import
Certificate. For more information on creating, copying, and pasting certificate information, see the
"Setting up two-factor authentication for the first time (on page 48)" section.
Two-factor authentication login
When you connect to iLO 2 and two-factor authentication is required, the Client Authentication page
prompts you to select the certificate you want to use. The Client Authentication page displays all of the
certificates available to authenticate a client. Select your certificate. The certificate can be a certificate
mapped to a local user in iLO 2, or a user specific certificate issued for authenticating to the domain.
Configuring iLO 2 50
Page 51

After you have selected a certificate, if the certificate is protected with a password or if the certificate is
stored on a smart card, a second page appears prompting you to enter the PIN or password associated
with the chosen certificate.
The certificate is examined by iLO 2 to ensure it was issued by a trusted CA by checking the signature
against the CA certificate configured in iLO 2. iLO 2 determines if the certificate has been revoked and if
it maps to a user in the iLO 2 local user database. If all of these tests pass, then the normal iLO 2 user
interface appears.
If your credential authentication fails, the Login Failed page appears. If login fails, you are instructed to
close the browser, open a new browser page, and try connecting again. If directory authentication is
enabled, and local user authentication fails, iLO 2 displays a login page with the directory user name
field populated with either the User Principal Name from the certificate or the Distinguished Name
(derived from the subject of the certificate). iLO 2 requests the password for the account. After providing
the password, you are authenticated.
Using two-factor authentication with directory authentication
In some cases, configuring two-factor authentication with directory authentication is complicated. iLO 2
can use HP Extended schema or Default Directory schema to integrate with directory services. To ensure
security when two-factor authentication is enforced, iLO 2 uses an attribute from the client certificate as
the directory user's login name. Which client certificate attribute iLO 2 uses is determined by the
Certificate Owner Field configuration setting on the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page. If Certificate
Owner Field is set to SAN, iLO 2 obtains the directory user's login name from the UPN attribute of the
SAN. If the Certificate Owner Field setting is set to Subject, iLO 2 obtains the directory user's
distinguished name from the subject of the certificate.
Which Certificate Owner Field setting to choose depends on the directory integration method used, the
directory architecture, and what information is contained in the user certificates that are issued. The
following examples assume you have the appropriate permissions.
Authentication using Default Directory Schema, part 1: The distinguished name for a user in the directory
is CN=John Doe,OU=IT,DC=MyCompany,DC=com, and the following are the attributes of John Doe's
certificate:
• Subject: DC=com/DC=MyCompany/OU=IT/CN=John Doe
• SAN/UPN: john.doe@MyCompany.com
Authenticating to iLO 2 with username:john.doe@MyCompany.com and password, will work if two-factor
authentication is not enforced. After two-factor authentication is enforced, if SAN is selected on the TwoFactor Authentication Settings page, the login page automatically populates the Directory User field with
john.doe@MyCompany.com. The password can be entered, but the user will not be authenticated. The
user is not authenticated because john.doe@MyCompany.com, which was obtained from the certificate,
is not the distinguished name for the user in the directory. In this case, you must select Subject on the TwoFactor Authentication Settings page. Then the Directory User field on the login page will be populated
Configuring iLO 2 51
Page 52

with CN=John Doe,OU=IT,DC=MyCompany,DC=com, which is the user's actual distinguished name. If
the correct password is entered, the user is authenticated.
Authentication using Default Directory Schema, part 2: The distinguished name for a user in the directory
is CN=john.doe@MyCompany.com,OU=IT,DC=MyCompany,DC=com, and the following are the
attributes of John Doe's certificate:
• Subject: DC=com/DC=MyCompany/OU=Employees/CN=John
Doe/E=john.doe@MyCompany.com
• SAN/UPN: john.doe@MyCompany.com
• Search context on the Directory Settings page is set to: OU=IT,DC=MyCompany,DC=com
In this example, if SAN is selected on the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page, the Directory User field
on the login page is populated with john.doe@MyCompany.com. After the correct password is entered,
the user is authenticated. The user is authenticated even though john.doe@MyCompany.com is not the
distinguished name for the user. The user is authenticated because iLO 2 attempts to authenticate using
the search context fields (CN=john.doe@MyCompany.com, OU=IT, DC=MyCompany, DC=com)
configured on the Directory Settings page. Because this is the correct distinguished name for the user, iLO
2 successfully finds the user in the directory.
NOTE: Selecting Subject on the Two-Factor Authentication Settings page causes authentication
to fail, because the subject of the certificate is not the distinguished name for the user in the
directory.
When authenticating using the HP Extended Schema method, HP recommends selecting the SAN option
on the Two-factor Authentication Settings page.
Directory settings
iLO 2 connects to Microsoft® Active Directory, Novell e-Directory, and other LDAP 3.0-compliant directory
services for user authentication and authorization. You can configure iLO 2 to authenticate and authorize
users using the HP schema directory integration or the schema-free directory integration. iLO 2 only
connects to directory services using SSL-secured connections to the directory server LDAP port. The default
secure LDAP port is 636. Directory services support is a licensed feature available with the purchase of
optional licenses. For more information, see "Licensing (on page 27)". For additional information about
directories, see "Directory services (on page 130)."
Locally-stored user accounts (found on the User Administration page) can be active while iLO 2 directory
support is enabled. This support enables both local- and directory-based user directory-based user
accesses. Typically, an administrator can delete local user accounts (except, possibly an emergency
access account) after iLO 2 is successfully configured to access the directory service. You can also disable
access to these accounts if directory support is enabled.
Configuring iLO 2 52
Page 53

Configuring directory settings
iLO 2 enables administrators to centralize user account administration using directory services. You must
have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege to configure and test the iLO 2 directory services. To access
Directory Settings, click Administration>Security>Directory.
iLO 2 directory settings enable you to control directory-related behavior for the iLO 2 directory you are
logged into. These settings include:
• Disable Directory Authentication—Enables you to activate or deactivate directory support on this iLO
2 directory.
o If directory authentication is enabled and configured properly, users can log in using directory
credentials.
o If directory authentication is disabled, user credentials are not validated using the directory.
• Use HP Extended Schema—Selects directory authentication and authorization using directory objects
created with HP schema. Select this option if the directory has been extended with HP schema, and
you plan to use it.
• Use Directory Default Schema—Selects directory authentication and authorization using user
accounts in the directory. Select this option if the directory is not extended with HP schema. User
accounts and group memberships are used to authenticate and authorize users. After entering the
directory network information, click Administer Groups and enter one or more valid directory
distinguished names and privileges to grant users access to iLO 2.
• Enable Local User Accounts—Enables you to limit access to local users.
o If Local User Accounts are enabled, a user can login using locally stored user credentials.
o If Local User Accounts are disabled, user access is limited to valid directory credentials only.
Access using Local User Accounts is enabled if Directory Support is disabled and/or the iLO 2 Select
or iLO 2 Advanced License is revoked. You cannot disable local user access if you are logged in
using a local user account.
iLO 2 directory server settings enables you to identify the directory server address and port. These settings
include:
• Directory Server Address—Enables you to specify the network DNS name or IP address of the
directory server. You can specify multiple servers, separated by a comma (,) or space ( ). If Use
Configuring iLO 2 53
Page 54

Directory Default Schema is selected, enter a DNS name in the Directory Server Address field to
allow authentication with user ID. For example:
directory.hp.com
192.168.1.250, 192.168.1.251
• Directory Server LDAP Port—Specifies the port number for the secure LDAP service on the server. The
default value for this port is 636. However, you can specify a different value if your directory service
is configured to use a different port.
• iLO 2 Directory Properties—Identifies the LOM object in the directory tree. This information is used to
determine user access rights. You can configure iLO 2 with the password to the LOM object at this
time however, this information is not used until directory configuration support is provided.
• LOM Object Distinguished Name—Specifies where this LOM instance is listed in the directory tree.
For example: cn=iLO 2 Mail Server,ou=Management Devices,o=hp
User search contexts are not applied to the LOM Object Distinguished Name when accessing the
directory server.
• LOM Object Password—Specifies the password to the iLO 2 object that iLO 2 uses to verify the
directory for updates (LOM Object Distinguished Name).
• Confirm Password—Verifies your LOM Object Password. If you alter the LOM Object Password,
reenter the new password in this field.
• User Login Search Contexts enables you to specify common directory subcontexts so that users do
not need to enter their full distinguished name at login.
You can identify all objects listed in a directory using their unique distinguished names. However,
distinguished names can be long and users might not know their distinguished names, or have
accounts in different directory contexts. iLO 2 attempts to contact the directory service by
distinguishing name, and then applies the search contexts in order until successful.
Directory User Contexts specify user name contexts that are applied to the login name.
Example 1:
Instead of logging in as cn=user,ou=engineering,o=hp a search context of
ou=engineering,o=hp allows login as user
Example 2:
If a system is managed by Information Management, Services, and Training, search contexts like:
Directory User Context 1:ou=IM,o=hp
Directory User Context 2:ou=Services,o=hp
Directory User Context 3:ou=Training,o=hp
Allow users in any of these organizations to log in using just their common names. If a user exists in
both the IM organizational unit and the Training organizational unit, login is first attempted as
cn=user,ou=IM,o=hp.
Example 3 (Active Directory only):
Microsoft Active Directory allows an alternate user credential format. Search contexts in this format
cannot be tested except by successful login attempt. A user may login as:
user@domain.hp.com
in which case a search context of
@domain.hp.com
allows the user to login as
user
To test the communication between the directory server and iLO 2, click Test Settings. For more
information, see the section, "Directory Tests (on page 55)."
Configuring iLO 2 54
Page 55

Directory tests
To validate current directory settings for iLO 2, click Test Settings on the Directory Settings page. The
Directory Tests page appears.
The test page displays the results of a series of simple tests designed to validate the current directory
settings. Additionally, it includes a test log that shows test results and any problems that have been
detected. After your directory settings are configured correctly, you do not need to rerun these tests. The
Directory Tests screen does not require you to be logged in as a directory user.
To verify your directory settings:
1. Enter the distinguished name and password of a directory administrator. A good choice would be
the same credentials used when creating the iLO 2 objects in the directory. These credentials are not
stored by iLO 2. They are used to verify the iLO 2 object and user search contexts.
2. Enter a test user name and password. Typically, this account would be intended to access the iLO 2
being tested. It can be the same account as the directory administrator. However, the tests cannot
verify user authentication with a superuser account. These credentials are not stored by iLO 2.
3. Click Start Test. Several tests begin in the background, starting with a network ping of the directory
user through establishing an SSL connection to the server and evaluating user privileges as they
would be evaluated during a normal login.
While the tests are running, the page periodically refreshes. At any time during test execution, you can
stop the tests or manually refresh the page. Consult the help link on the page for test details and actions in
the event of trouble.
Encryption
iLO 2 provides enhanced security for remote management in distributed IT environments. Web browser
data is protected by SSL encryption. SSL encryption of HTTP data ensures that the data is secure as it is
transmitted across the network. iLO 2 provides support for two of the strongest available cipher strengths;
the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and the Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES). iLO 2 supports
the following cipher strengths:
• 256-bit AES with RSA, DHE and a SHA1 MAC
• 256-bit AES with RSA and a SHA1 MAC
Configuring iLO 2 55
Page 56

• 128-bit AES with RSA, DHE and a SHA1 MAC
• 128-bit AES with RSA and a SHA1 MAC
• 168-bit Triple DES with RSA and a SHA1 MAC
• 168-bit Triple DES with RSA, DHE and a SHA1 MAC
iLO 2 also provides enhanced encryption through the SSH port for secure CLP transactions. iLO 2
supports AES128-CBC and 3DES-CBC cipher strengths through the SSH port.
If enabled, iLO 2 enforces the usage of these enhanced ciphers (both AES and 3DES) over the secure
channels, including secure HTTP transmissions through the browser, SSH port, and XML port. When
AES/3DES encryption is enabled, you must use a cipher strength equal to or greater than AES/3DES to
connect to iLO 2 through these secure channels. Communications and connections over less secure
channels (such as the telnet port) are not affected by the AES/3DES encryption enforcement setting.
By default, remote console data uses 128-bit RC4 bi-directional encryption. The CPQLOCFG utility uses a
168-bit Triple DES with RSA and a SHA1 MAC cipher to securely send RIBCL scripts to iLO 2 over the
network.
Encryption settings
You can view or modify the current encryption settings using the iLO 2 interface, CLP, or RIBCL.
To view or modify current encryption settings using the iLO 2 interface:
1. Click Administration>Security>Encryption.
The Encryption page appears, displaying the current encryption settings for iLO 2. Both the current
negotiated cipher and the encryption enforcement settings appear on this page.
o Current Negotiated Cipher displays the cipher in use for the current browser session. After
logging into iLO 2 through the browser, the browser and iLO 2 negotiate a cipher setting to use
during the session. The Encryption page Current Negotiated Cipher section displays the
negotiated cipher.
Encryption Enforcement Settings displays the current encryption settings for iLO 2. Enforce
AES/3DES Encryption (if enabled) enables iLO 2 to only accept connections through the browser
and SSH interface that meet the minimum cipher strength. A cipher strength of at least AES or
3DES must be used to connect to iLO 2 if this setting is enabled. Enforce AES/3DES Encryption
can be enabled or disabled.
2. To save changes, click Apply.
When changing the Enforcement setting to Enable, close all open browsers after clicking Apply. Any
browsers that remain open might continue to use a non-AES/3DES cipher.
To view or modify current encryption settings through the CLP or RIBCL, see the HP Integrated Lights-Out
Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
Connecting to the iLO 2 using AES/3DES encryption
After enabling the Enforce AES/3DES Encryption setting, iLO 2 requires you to connect through secure
channels (web browser, SSH, or XML port) using a cipher strength of at least AES or 3DES.
To connect to iLO 2 through a browser, the browser must be configured with a cipher strength of at least
AES or 3DES. If the web browser is not using AES or 3DES ciphers, iLO 2 displays an error message
informing the user to close the current connection and select the correct cipher.
Configuring iLO 2 56
Page 57

See your browser documentation to select a cipher strength of at least AES or 3DES. Different browsers
use different methods of selecting a negotiated cipher. You must log out of iLO 2 through the current
browser before changing the browser's cipher strength. Any changes made to the browser cipher setting
while logged into iLO 2 might enable the browser to continue using a non-AES/3DES cipher.
All client operating systems and browsers supported by iLO 2, support the iLO 2 AES/3DES Encryption
feature except when using Windows 2000 Professional with Internet Explorer. By default, Windows 2000
Professional does not support AES or 3DES ciphers. If a client uses Windows® 2000 Professional, you
must use another browser, or update the operating system.
Internet Explorer does not have a user-selectable cipher strength setting. You must edit the registry to
enable Internet Explorer to connect to iLO 2 when the Enforce AES/3DES Encryption setting is enabled.
To enable AES/3DES encryption in Internet Explorer, open the registry and set
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\FIPSAlgorithmPolicy
to 1.
IMPORTANT: Incorrectly editing the registry can severely damage your system. HP
recommends creating a back up of any valued data on the computer before making changes
to the registry.
To connect to iLO 2 through an SSH connection, see your SSH utility documentation to set the cipher
strength.
When connecting through the XML channel, the CPQLOCFG utility uses a secure 3DES cipher by default.
CPQLOCFG 2.26 or later displays the following current-connection cipher strength on the XML output. For
example:
Connecting to Server..
Negotiated cipher: 168-bit Triple DES with RSA and a SHA1 MAC
AES encryption is not supported by Internet Explorer on a Windows® 2000 Professional client. To use
AES encryption with this operating system, use another browser (such as Mozilla).
HP SIM single sign-on (SSO)
HP SIM SSO enables you to browse directly from HP SIM to your LOM processor, bypassing an
intermediate login step. To use SSO, a current version of HP SIM is required, and you must configure your
LOM processor to accept the links from HP SIM. HP SIM requires the latest updates and patches to
function correctly. For more information about HP Systems Insight Manager and available updates, see
the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim
HP SIM SSO is a licensed feature available with the purchase of optional licenses. For more information,
see "Licensing (on page 27)".
The HP SIM SSO page enables you to view and configure SSO settings through the iLO 2 interface. For
more information, see the section, "Setting up HP SIM SSO (on page 59)."
You can also access HP SIM SSO configuration settings using scripts, text files, and through a commandline using text-based clients such as SSH over the network or from the operating system on the host
computer. Scripting SSO enables you to use the same SSO settings on all your LOM processors. For more
information, example scripts, and CLP extensions to read, modify, and write HP SIM SSO configuration
settings, see the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource
Guide.
).
Configuring iLO 2 57
Page 58

Setting up iLO 2 for HP SIM SSO
Before you start SSO setup, you must have the network address of HP SIM and ensure that a license key is
installed. To setup SSO:
1. Enable Single Sign-On Trust Mode by selecting either Trust by Certificate (recommended), Trust by
Name, or Trust All.
2. Add the HP SIM certificate of the server to iLO 2.
a. Click Add an HP SIM Server.
b. Enter the HP SIM server network address.
c. Click Import Certificate.
The certificate repository is sized to allow five typical iLO 2 certificates. However, certificate sizes
can vary if typical certificates are not issued. There is 6KB of combined storage allocated for
certificates and iLO 2 server names. When the allocated storage is used, no more imports are
accepted.
After setting up SSO in iLO 2, log into HP SIM, locate the LOM processor, select Tools>System
Information>iLO as... HP SIM launches a new browser that is logged in to the LOM management
processor.
Adding HP SIM trusted servers
You can install HP SIM server certificates using scripting that is suitable for mass deployment. For more
information, see the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line
Resource Guide. To add HP SIM server records using a browser:
1. Click Administration>Security>HP SIM SSO.
2. Click Add an HP SIM Server.
3. To authenticate the server, choose one of the following:
o To add an HP SIM server using Trust by Name authentication, enter the full network name of the
HP SIM server in the Add a Trusted HP SIM Server Name section. Click Add Server Name.
Trust by Name authentication uses fully qualified domain names; for example, sim-host.hp.com
instead of sim-host. If you are unsure of the fully qualified domain name, use the nslookup
host command.
o To retrieve and import a certificate from a trusted HP SIM server, enter the full network name of
an HP SIM Server in the Retrieve and import a certificate from a trusted HP SIM Server section.
Click Import Certificate to request the certificate from the HP SIM server and automatically import
it. This record supports SSO Trust by Name and SSO Trust by Certificate.
To prevent any certificate tampering directly import an HP SIM server certificate. To directly
import an HP SIM server certificate, retrieve the HP SIM certificate date using one of the
following options:
— Using a separate browser window, browse to the HP SIM server using the URL:
http://<sim network address>:280/GetCertificate
Cut and paste the certificate data from HP SIM into iLO 2.
— Export the HP SIM server certificate from the HP SIM user interface by selecting
Options>Security>Certificates>Server Certificate. Open the file using a text editor, and copy
and paste all the certificate raw data into iLO 2.
Configuring iLO 2 58
Page 59

— Using command-line tools on the HP SIM server, the HP SIM certificate can be extracted using
the tomcat-coded alias for the HP SIM certificate. For example:
mxcert -l tomcat
The certificate data resembles:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----several lines of encoded data
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
After pasting the HP SIM server base-64 encoded x.509 certificate data into the Directly import a
HP SIM Server Certificate section, click Import Certificate to record the data. This type of record
supports SSO Trust by Name and SSO Trust by Certificate.
There are other ways to retrieve HP SIM server certificate data. For more information, see your HP SIM
documentation.
Setting up HP SIM SSO
The HP SIM SSO page allows you to view and configure the existing iLO 2 Single Sign-On settings. You
must have the Configure iLO 2 privilege to alter these settings. To access iLO 2 SSO settings, click
Administration>Security>HP SIM SSO.
The HP Systems Insight Manager Single Sign-On Settings page includes the following fields and options:
• Single Sign-On Trust Mode— Enables you to control how SSO-initiated connections are accepted:
o Trust None (default)—Rejects all SSO connection requests.
o Trust by Certificate (most secure)—Enables only SSO connections from an HP SIM server
matching a certificate previously imported into iLO 2.
o Trust by Name—Enables SSO connections from an HP SIM server matching a DNS name or
certificate previously imported into iLO 2.
o Trust All (least secure)—Accepts any SSO connections initiated from any HP SIM server.
Users who log in to HP SIM are authorized based upon the role assignment at the HP SIM server.
The role assignment is passed to the LOM processor when SSO is attempted. You can configure iLO
2 privileges for each role in the Single Sign-On Settings section. For more information about each
privilege, see the section, "User administration (on page 29)."
Configuring iLO 2 59
Page 60

Using directory-based user accounts, SSO attempts to receive only the privileges assigned in this
section. Lights-Out directory settings do not apply. Default privilege assignments are:
o User—Login only
o Operator—Login, Remote Console, Power and Reset, and Virtual Media
o Administrator—Login, Remote Console, Power and Reset, Virtual Media, Configure iLO 2, and
Administer Users
• HP SIM Trusted Servers—Enables you to view the status of trusted HP SIM servers configured to use
SSO with the current LOM processor. Click Add a SIM Server to add a server name, import a server
certificate, or directly install a server certificate. For more information, see the section, "Adding HP
SIM trusted servers (on page 58)."
The server table displays a list of registered HP SIM servers with the status of each. The actual
number of systems allowed depends on the size of the stored certificate data.
Although a system might be registered, SSO might be refused because of the current trust level or
certificate status. For example, if an HP SIM server name is registered and the trust level is set to Trust
by Certificate, SSO is not allowed from that server. Likewise, if a HP SIM server certificate is
imported, but the certificate has expired, SSO is not allowed from that server. Additionally, the
records are not used when SSO is disabled. iLO 2 does not enforce SSO server certificate
revocation.
o Status—Indicates the status of the record (if any are installed).
o Description—Displays the server name (or certificate subject). A thumbnail of a certificate
indicates that the record contains a stored certificate.
o Actions—Displays the actions you can take on a selected record. The actions displayed depend
on the type and number of records installed:
— Remove Name—Removes the server name record.
— Remove Certificate—Removes the certificate record.
Remote Console Computer Lock
Remote Console Computer Lock enhances the security of an iLO 2 managed server by automatically
locking an operating system, or logging out a user when a remote console session terminates or the
network link to iLO 2 is lost. Unlike Remote Console or Integrated Remote Console, this feature is standard
and does not require an additional license. As a result, if you open a Remote Console Session or an
Integrated Remote Console window and have this feature configured, it will lock the operating system
when the window is closed even if additional feature licenses are not installed.
You can view and configure the Remote Console Computer Lock settings through the Administration or
Remote Console tabs in the iLO 2 interface. The Remote Console Computer Lock feature is disabled by
default.
To change the Remote Console Computer Lock settings:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
2. Click Administration>Security>Remote Console. The Computer Lock Settings page appears.
Configuring iLO 2 60
Page 61

3.
Modify the settings as required:
o Windows—Use this option to configure iLO 2 to lock a managed server running a Windows®
operating system. The server automatically displays the Computer Locked dialog box when a
remote console session is terminated or the iLO 2 network link is lost.
o Custom—Use this option to configure iLO 2 to use a custom key sequence to lock a managed
server or log out a user on that server. You can select up to five keys from the list. The selected
key sequence is automatically sent to the server operating system when a remote console session
is terminated or the iLO 2 network link is lost.
o Disabled—Use this option to disable the Remote Console Computer Lock feature. Terminating a
remote console session or losing an iLO 2 network link will not lock the managed server.
You can create a Remote Console Computer Lock key sequence using the keys listed in the following
table.
ESC F4 1 e
L_ALT F5 2 f
R_ALT F6 3 g
L_SHIFT F7 4 h
R_SHIFT F8 5 i
L-CTRL F9 6 j
R_CTRL F10 7 k
L_GUI F11 8 l
R_GUI F12 9 m
INS " " (Space) : n
DEL ! ; o
HOME " < p
END # = q
PG_UP $ > r
PG_DN % ? s
ENTER & @ t
TAB ' [ u
BREAK ( \ v
BACKSPACE ) ] w
NUM PLUS * ^ x
NUM MINUS + _ y
SCRL LCK , ' z
SYS RQ - a {
F1 . b }
F2 / c |
F3 0 d ~
4. Click Apply to save changes.
This feature can also be configured using scripting or command lines. For more information, see the HP
Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
Configuring iLO 2 61
Page 62

Network
The Network Settings and DCHP/DNS tabs of the Network section enable you to view and modify
network settings for iLO 2.
Only users with the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can change these settings. Users that do not have
the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can view the assigned settings.
To change network settings for iLO 2:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege. Click
Administration>Network.
2. Select Network Settings or DHCP/DNS.
3. Change the settings as needed.
4. After completing any parameter changes, click Apply to complete the changes.
iLO 2 restarts, and the connection of your browser to iLO 2 terminates. To reestablish a connection, wait
Network Settings
60 seconds before launching another browser session and logging in.
The Network Settings page displays the NIC IP address, subnet mask, and other TCP/IP-related
information and settings. From the Network Settings screen, you can enable or disable DHCP and
configure a static IP address for servers not using DHCP. All users can view the network settings, but only
users with the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can change these settings. To access the Network
Settings page, click Administration>Network>Network. The Network Settings page appears.
The Network Settings page has the following information and settings available:
• NIC enables you to set the iLO 2 NIC to Enabled, Disabled, or to Shared Network Port.
o Enabled—Enables the primary iLO 2 network interface.
o Disabled—Disables the iLO 2 network interface. You must use the iLO 2 RBSU or other host-
based scripting utility to re-enable the network interface.
Configuring iLO 2 62
Page 63

o
Shared Network Port—Enables networking using the designated host Ethernet port. The port
appears as two separate Ethernet MACs and IP addresses on the network. See the section, "iLO
2 Shared Network Port (on page 64)" for more information.
• DHCP enables you to select static IP (disabled) or enables the use of a DHCP server to obtain an IP
address for the Integrated Lights-Out 2 subsystem.
You cannot set the iLO 2 IP Address and Subnet Mask if DHCP is enabled. Disabling DHCP enables
you to configure the IP address. The IP Address field also appears on the DHCP/DNS Settings page
for convenience. Changing the value on either page changes the DHCP setting.
• VLAN (when enabled) makes the iLO 2 Shared Network Port part of a Virtual LAN. All network
devices with the same Virtual LAN tag appear to be on a separate LAN even if they are physically
connected to the same LAN.
• VLAN Tag identifies all network devices on the same Virtual LAN. The Virtual LAN tag can be any
number between 1 and 4094.
• IP Address is the iLO 2 IP address. If DHCP is used, the iLO 2 IP address is automatically supplied. If
not, enter a static IP address. The IP Address field appears on the DHCP/DNS page for
convenience. Entering values in the field on either page changes the IP address of the iLO 2.
• Subnet Mask is the subnet mask of the iLO 2 IP network. If DHCP is used, the Subnet Mask is
automatically supplied. If not, enter the subnet mask for the network.
• Gateway IP Address displays the IP address of the network gateway. If DHCP is in use, the Gateway
IP Address is automatically supplied. If not, enter the network gateway address.
• iLO 2 Subsystem Name is a name used by the iLO 2 subsystem. If DHCP and DNS are configured
correctly, this name can be used to connect to the iLO 2 subsystem instead of the IP address. See
"iLO 2 subsystem name limitations (on page 63)" for more information.
• Link controls the speed and duplex of the iLO 2 network transceiver. The current link speed of the
primary dedicated iLO 2 NIC can be highlighted. Link settings include the following:
o Automatic (default) enables iLO 2 to negotiate the highest supported link speed and duplex when
connected to the network.
o 100Mb/FD forces a 100-Mb connection using full duplex
o 100Mb/HD forces a 100-Mb connection using half duplex
o 10Mb/FD forces a 10-Mb connection using full duplex
o 10Mb/HD forces a 10-Mb connection using half duplex
iLO 2 subsystem name limitations
The iLO 2 subsystem name represents the DNS name of the iLO 2 subsystem. For example, ilo instead of
ilo.hp.com. This name can only be used, if DHCP and DNS are configured properly to connect to the
iLO 2 subsystem name instead of the IP address.
• Name service limitations—The subsystem name is used as part of the DNS name and WINS name.
However DNS and WINS limitations differ:
o DNS allows alphanumeric and hyphen. WINS allows alphanumeric, hyphen and underscore.
o WINS subsystem names are truncated at 15 characters, DNS are not.
If you require underscores, they can be entered in RBSU or using the iLO 2 scripting utility.
Configuring iLO 2 63
Page 64

NOTE: Name service limitations also apply to the domain name.
To avoid name space issues:
o Do not use the underscore character.
o Limit subsystem names to 15 characters.
o Verify you can PING iLO by IP address and by DNS/WINS name.
o Verify NSLOOKUP correctly resolves the iLO network address and that there are no namespace
conflicts.
o Verify DNS and WINS both correctly resolve the name (if you are using both).
o Flush the DNS name if you make any name space changes.
iLO 2 Shared Network Port
The iLO 2 Shared Network Port enables you to choose either the system NIC or dedicated iLO 2
Dedicated Management NIC for server management. When you enable the iLO 2 Shared Network Port,
both regular network traffic, and network traffic intended for iLO 2 pass through the system NIC.
iLO 2 provides support for servers that might not have an iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC. On servers
using the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC, the standard hardware configuration provides iLO 2
network connectivity only through the iLO 2 Shared Network Port connection. iLO 2 detects the lack of an
iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC and automatically defaults to the Shared Network Port. On some of
these servers, an iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC might be available as a hardware option. If an iLO
2 Dedicated Management NIC is available as a hardware option, iLO 2 defaults to the installed iLO 2
Dedicated Management NIC. On servers using the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC, you can enable
shared network port operation through the iLO 2 interface.
The iLO 2 Shared Network Port uses the network port labeled NIC 1 on the rear panel of the server. NIC
numbering in the operating system can be different from system numbering. The iLO 2 Shared Network
Port does not incur an iLO 2 performance penalty. Peak iLO 2 traffic is less than 2 MB (on a NIC capable
of 1000-Mb speeds), and average iLO 2 traffic is infrequent and low.
The Shared Network Port is not available on HP ProLiant ML310 G3, ML310 G4, BL20p G4, and all cClass blade servers.
iLO 2 Shared Management Port features and restrictions
iLO 2 Shared Network Port and the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC port are used for iLO 2 server
management. You can only use the iLO 2 Shared Network Port and the iLO 2 Dedicated Management
NIC port for iLO 2 server management. The iLO 2 Shared Network Port and the iLO 2 Dedicated
Management NIC port cannot operate simultaneously. If you enable the dedicated iLO 2 NIC, you will
disable the iLO 2 Shared Network Port. If you enable the iLO 2 Shared Network Port, you will disable the
dedicated iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC.
However, disabling the Shared Network Port does not completely disable the system NIC. Regular
network traffic still passes through the system NIC. When Shared Network Port network traffic is disabled,
any traffic going to or originating from iLO 2 will not pass on to iLO 2 through the Shared Network Port
because the Shared Network Port is no longer shared with iLO 2.
The Shared Network Port should not be considered an availability feature. The Shared Network Port is
intended to allow managed network port consolidation. The use of this feature can create a single failure
point, that is, if the port fails or is unplugged, both the host and iLO 2 become unavailable to the network.
Configuring iLO 2 64
Page 65

You can use VLAN tagging with the iLO 2 Shared Network Port to separate host traffic from iLO 2 traffic.
VLAN tagging requires a switch that supports VLAN. For more information, see the section, "Shared
Network Port VLAN (on page 66)."
Enabling the iLO 2 Shared Network Port feature
The iLO 2 Shared Network Port feature is disabled by default. This feature can be enabled through and of
the following:
• iLO 2 RBSU
• The iLO 2 web interface
• XML scripting
Enabling the iLO 2 Shared Network Port feature through iLO 2 RBSU
1. Connect the server's NIC port 1 to a LAN.
2. When prompted during POST, press the F8 key to enter iLO 2 RBSU.
3. Select Network>NIC>TCP/IP, and press the Enter key.
4. In the Network Configuration menu, toggle the Network Interface Adapter Field to Shared Network
Port by pressing the space bar. The Shared Network Port option is only available on supported
servers.
5. Press the F10 key to save the configuration.
6. Select File>Exit, and press the Enter key.
After iLO 2 resets, the Shared Network Port feature is active. Any network traffic going to or originating
from iLO 2 is directed through the system's NIC port 1.
Enabling the iLO 2 Shared Network Port feature through the web interface
1. Connect iLO 2 NIC port 1 to a LAN.
2. Open a browser, and browse to the iLO 2 IP address or DNS name.
3. Select Administration>Network Settings.
4. On the Network Settings page, select Shared Network Port. The Shared Network feature is available
on supported servers only.
Configuring iLO 2 65
Page 66

5.
Click Apply at the bottom of the page.
6. Click Yes in the warning dialog box, and click OK.
After iLO 2 resets, the Shared Network Port feature is active. Any network traffic going to or originating
from iLO 2 is directed through the system's NIC port 1.
Only the Shared Network Port or the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC is active for server management.
They cannot be enabled at the same time.
Shared Network Port VLAN
The Shared Network Port VLAN feature is designed for customers who want to use the Shared Network
Port but want to keep their management network traffic separate from their regular network traffic. For
example, you can configure the management traffic for all of the iLO 2 Shared Network Ports on a
network to be on the same VLAN. Regular network traffic traveling through the Shared network Ports
could be on the same LAN, different LANs, different VLAN, and so on.
To communicate with iLO 2 through a client system, the client must be on the same VLAN as the iLO 2
Shared Network Ports, and any network switches between the iLO 2 Shared Network Port and the client
must be IEEE 802.1q compliant. IEEE 802.1q managed switches might need to be configured to enable
VLAN support.
The iLO 2 Shared Network Port VLAN feature is disabled by default. This feature can be enabled and
configured through:
• iLO 2 RBSU
• iLO 2 web interface
• XML scripting
The VLAN feature is only available on systems that support SNP NIC. All VLANs must be configured with
a VLAN ID. The VLAN ID can be any number between 1 and 4094. Only users with the Configure iLO 2
Settings privilege are allowed change enable or disable VLAN support and to configure VLAN IDs.
Enabling and configuring VLAN using the iLO 2 interface
1. Log on to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege. Click
Administration.
IMPORTANT: Only users with the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can change these settings.
Users that do not have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can only view the assigned
2. Click Network Settings.
3. Click Yes in the Enable Virtual LAN option to enable the VLAN feature.
4. Enter a number between 1 and 4094 in the Virtual LAN ID field.
settings.
If the Shared Network Port is not selected, the choices for the Enable Virtual LAN radio button and
the VLAN ID field are deactivated and cannot be configured.
If the Virtual LAN feature is disabled, the Virtual LAN ID field is deactivated and cannot be
configured.
5. Click Apply. iLO 2 will reset with the current VLAN ID settings.
Configuring iLO 2 66
Page 67

Enabling and configuring VLAN using RBSU
1. Reboot the server and press the F8 key. When prompted, enter iLO 2 RBSU.
2. Navigate to Network>NIC>TCP/IP, and press the Enter key.
3. Use the space bar to select Shared Network Port in the Network Interface Adapter field.
4. Navigate to the Virtual LAN field, and use the space bar to select Enabled. A user definable VLAN
ID field appears.
5. Navigate to the Virtual LAN ID field, and enter any number between 1 and 4094.
Enabling and configuring VLAN using XML
You can enable or disable VLAN support through XML scripting using RIBCL. For more information, see
the scripting and command line resource guide.
Re-enabling the dedicated iLO 2 management port
The iLO 2 web interface, RBSU, or XML (described in the scripting and command line reference guide)
scripting must be used to re-enable the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC. Re-enabling iLO 2 through
RBSU requires that the system be rebooted.
To re-enable the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC using RBSU:
1. Connect the iLO 2 dedicated management NIC port to a LAN from which the server is managed.
2. Reboot the server.
3. When prompted during POST, press the F8 key to enter iLO 2 RBSU.
4. Select Network>NIC>TCP/IP, and press the Enter key.
5. In the Network Configuration menu, toggle the Network Interface Adapter Field to ON by pressing
the space bar.
6. Press the F10 key to save the configuration.
7. Select File>Exit, and press the Enter key.
After iLO 2 resets, the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC port is active.
To re-enable the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC using iLO 2 interface:
Configuring iLO 2 67
Page 68

1.
Open a browser and navigate to the iLO 2 IP address or DNS name
2. On the Network Settings page, select Enabled for the iLO 2 NIC.
3. Click Apply. A warning dialog appears.
4. Click Yes, and then OK.
After iLO 2 resets, the iLO 2 Dedicated Management NIC is active. When using IRC through iLO 2
Dedicated Management NIC port and depending on the network traffic, you might not have sufficient
time to press the RBSU keys during POST.
DHCP/DNS Settings
The iLO 2 DHCP/DNS Settings page displays DHCP/DNS configuration information for iLO 2. All users
can view the DHCP/DNS settings, but you must have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege to change
them. These settings can also be changed using the iLO 2 RBSU (F8 during POST). To access DHCP/DNS
settings, click Administration>Network>DHCP/DNS. The DHCP/DNS Settings page appears.
The following options are available:
• DHCP allows you to select static IP (disabled) or enable the use of a DHCP server to obtain an IP
address for the iLO 2 subsystem.
You cannot set the iLO 2 IP address if DHCP is enabled. Disabling DHCP allows you to configure the
IP address. The IP Address field also appears on the Network Settings page for your convenience.
Changing the value on either page changes the DHCP setting.
• IP Address is the iLO 2 IP address. If DHCP is used, the iLO 2 IP address is automatically supplied. If
not, enter a static IP address. The IP Address field appears on the Network Settings page for your
convenience. Changing the value on either page changes the IP address of iLO 2.
• Domain Name is the name of the domain where the iLO 2 subsystem resides. This name is assigned
by DHCP (if DHCP is enabled). Enabling DHCP allows you to configure the following DHCP options:
o Use DHCP Supplied Gateway—Toggles if iLO 2 uses the DHCP server-supplied gateway. If not,
enter an gateway address in the Gateway IP Address box.
Configuring iLO 2 68
Page 69

o
Use DHCP Supplied DNS Servers—Toggles if iLO 2 uses the DHCP server-supplied DNS server
list. If not, enter the DNS server address in the Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary DNS Server
fields.
o Use DHCP Supplied WINS Servers—Toggles if iLO 2 uses the DHCP server-supplied WINS
server list. If not, enter the WINS server address in the Primary and Secondary WINS Server
fields.
o Use DHCP Supplied Static Routes—Toggles if iLO 2 uses the DHCP server-supplied static route. If
not, enter the static route address in Static Route #1, Static Route #2, or Static Route #3 fields.
o Use DHCP Supplied Domain Name—Toggles if iLO 2 uses the DHCP server-supplied domain
name. If not, enter a domain name in the Domain Name box.
• WINS Server Registration toggles if iLO 2 registers its name with a WINS server.
• DDNS Server Registration toggles if iLO 2 registers its name with a DDNS server.
• Ping Gateway on Startup option causes iLO 2 to send four ICMP echo request packets to the
gateway when iLO 2 initializes. This option ensures that the ARP cache entry for iLO 2 is up-to-date
on the router responsible for routing packets to and from iLO 2.
• DHCP Server is the IP address of the DHCP server. This field cannot be assigned. It is received from
DHCP if DHCP is enabled and represents the last known valid DHCP server address.
• Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary DNS Server are the IP addresses of the DNS servers. If supplied by
the DHCP server, these fields are automatically populated. Otherwise, enter the IP addresses
manually.
• Primary and Secondary WINS Server are the IP addresses of the WINS servers. If supplied by the
DHCP server, these fields are automatically populated. Otherwise, enter the IP addresses manually.
• Static Route #1, Static Route #2, and Static Route #3 (destination, gateway) are the network
destination gateway addresses. Enter up to three network destination/gateway routing pairs.
SNMP/Insight Manager settings
The Management option of the Administration section displays the SNMP/Insight Manager Settings page.
The SNMP/Insight Manager Settings page enables you to configure SNMP alerts, generate a test alert,
Enabling SNMP alerts
and configure integration with HP SIM.
iLO 2 supports up to three IP addresses to receive SNMP alerts. Typically, the addresses used are the
same as the IP address of the HP SIM server console.
Only users with the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can change these settings. Users that do not have
the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can only view the assigned settings.
The following alert options are available in the SNMP/Insight Manager Settings screen:
• SNMP Alert Destination(s)
• iLO 2 SNMP Alerts
• Forward Insight Manager Agent SNMP Alerts
• SNMP Pass-thru
• p-Class Alert Forwarding (displayed on p-Class servers only)
Configuring iLO 2 69
Page 70

For more information see to the HP Integrated Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command
Line Resource Guide.
To configure alerts:
1. Log in to iLO 2 using an account that has the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
2. Select Management in the Administration tab. The SNMP/Insight Manager Settings screen appears.
3. In the SNMP Alert Destination(s) fields, enter up to three IP addresses that you want to receive the
SNMP alerts and select the alert options you want iLO 2 to support.
4. Click Apply Settings.
Test alerts include an Insight Manager SNMP trap and are used to verify the network connectivity of iLO 2
in HP SIM. Only users with the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege can send test alerts.
Be sure you have saved any changes to the SNMP Alert Destination(s) fields before sending a test alert.
To send a test alert:
1. Select Management in the Administration tab. The SNMP/Insight Manager Settings screen appears.
2. Click Send Test Alert in the Configure and Test SNMP Alerts section to generate a test alert and send
it to the TCP/IP addresses saved in the SNMP Alert Destinations fields.
3. After generating the alert, a confirmation screen appears.
4. Check the HP SIM console for receipt of the trap.
SNMP generated trap definitions
You can generate the following SNMP traps on BL c-Class servers and iLO 2:
• ALERT_TEST is used to verify that the SNMP configuration, client SNMP console, and network are
operating correctly. You can use the iLO 2 interface to generate this alert to verify receipt of the alert
at the SNMP console. You can also generate this alert using the iLO 2 Option ROM to verify SNMP
configuration settings.
• ALERT_SERVER_POWER occurs when the iLO 2 management processor detects an unexpected
transition of the host system power, either from ON to OFF, or OFF to ON. Transitions of the host
system power are unexpected when the change takes place because of events unknown to the
management processor. This alert is not generated when the system is powered up or down using
Configuring iLO 2 70
Page 71

the iLO 2 interface, CLI, RIBCL or other management feature. If the server is powered down because
of the operating system, physical power button presses, or other methods, the alert is generated and
sent.
• ALERT_SERVER_RESET occurs when the iLO 2 management processor is used to perform a cold boot
or warm boot of the host system. This alert is also sent when the iLO 2 management processor
detects the host system is in reset because of events unknown to the management processor. Certain
operating system behavior or actions can cause this type of event to be detected, and the alert
transmitted.
• ALERT_ILLEGAL_LOGIN is an SNMP alert transmitted when a connection is attempted using an
invalid username and password. This alert is transmitted regardless of connection type; web
interface, serial port, telnet, SSH, or RIBCL.
• ALERT_LOGS_FULL is an SNMP alert transmitted when the iLO 2 Event Log is full and an attempt to
log a new event occurs.
• ALERT_SELFTEST_FAILURE is an SNMP alert transmitted when iLO 2 detects an error in any one of
the monitored internal components. If an error is detected an SNMP alert is transmitted.
• ALERT_SECURITY_ENABLED alert is transmitted when the iLO 2 management processor detects a
change in the Security Override Switch to enabled.
• ALERT_SECURITY_DISABLED alert is transmitted when the iLO 2 management processor detects a
change in the Security Override Switch to disabled.
• ALERT_HOST_GENERATED alert is generated when the iLO 2 management processor was asked to
transmit a Host (SNMP passthrough) alert and the management processor was unable to transmit the
original SNMP alert. iLO 2 attempts to transmit this generic alert in order to notify the SNMP
management console that an alert intended to be transmitted from the host system was not
transmitted.
Configuring Insight Manager integration
The Insight Manager Web Agent URL (DNS name or IP address) sets the browser destination of the Insight
Agent link on iLO 2 pages. Typically, this link is the IP address or DNS name of the management agent
running on the host server operating system.
Enter the IP address of the host server. The protocol (https://) and port number (:2381) are automatically
added to the IP address or DNS name to allow access to the Insight Management Web Agents from iLO
2.
If the Insight Manager Web Agent URL is set through another method (for example, CPQLOCFG), click
the refresh button of your browser to display the updated URL.
The Level of Data Returned setting controls the content of an anonymous discovery message received by
iLO 2. The information returned is used for Insight Manager HTTP identification requests. The following
options are available:
• Enabled (default) allows Insight Manager to associate the management processor with the host
server and provides sufficient data to allow integration with HP SIM.
• Disabled prevents iLO 2 from responding to the HP SIM requests.
• View XML Reply enables you to examine the data returned at the settings.
View the response that will be returned to Insight Manager when it requests Management Processor
identification using this link.
Configuring iLO 2 71
Page 72

To see the results of changes made, click Apply Settings to save the changes. Click Reset Settings to return
the page to its clear the fields and return to its previous state. The Reset Settings button does not save any
changes.
For more information on Insight Agents, click System Status>Insight Agent.
ProLiant BL p-Class configuration
ProLiant BL p-Class servers can be accessed and configured through the:
• iLO 2 Diagnostic Port on the front of the server
• "Browser-based setup ("Setting up iLO 2 using the browser-based option" on page 21)" which
initially configures the system through the iLO 2 Diagnostic Port
• Step-by-step installation wizard through HP BladeSystem Setup
On select p-Class blades in enclosures with updated management backplanes that support high-density
blades, iLO 2 can be used for initial enclosure static IP configuration. Initial configuration of the blade in
bay 1 allows all subsequent iLO 2s in the enclosure to receive predetermined static IP assignments. This
ProLiant BL p-Class user requirements
feature is supported in iLO 1.55 and later.
• Users must have the Configure iLO 2 Settings privilege.
• A network connection to iLO 2 must be available and functioning properly.
Static IP bay configuration
Static IP bay configuration is implemented using the Static IP Bay Settings option on the BL p-Class tab.
This option eases the initial deployment of an entire enclosure or the subsequent deployment of blades
within an existing enclosure. While the preferred method for assigning IP addresses to the iLO 2 in each
blade server is through DHCP and DNS, these protocols are not always available on nonproduction
networks.
For example, after configuring Static IP Bay configuration for the blade in bay 1, subsequent blade
additions to the enclosure assume subsequent addresses without DHCP. The network addresses are
assigned by blade position bay 1: 192.168.1.1, bay 2: 192.168.1.2, and so on. Deploying subsequent
blades does not demand extra configuration, and the network address corresponds to the bay number.
Static IP bay configuration automates the first step of BL p-Class blade deployment by enabling the iLO 2
management processor in each blade slot to obtain a predefined IP address without relying on DHCP. iLO
2 is immediately accessible for server deployment using Virtual Media and other remote administration
functions.
Static IP bay configuration uses the Static IP Bay Configuration addressing method, which enables you to
assign IP addresses to each iLO 2 based on slot location in the respective server enclosure. By providing
a set of IP addresses in the enclosure, you gain the advantages of a static IP bay configuration without
requiring each individual iLO 2 to be configured locally.
Using iLO 2 static IP bay configuration:
• Helps avoid the costs of a DHCP infrastructure to support the blade environment
• Provides easier setup with automatic iLO 2 address generation for all or a few selected bays
Configuring iLO 2 72
Page 73

Static IP Bay Configuration is not supported in G1 BL-series blade enclosures. To view the enclosure
generation, click BL p-Class>Rack View>Details for a specific enclosure. Static IP Bay configuration is not
supported on an enclosure when Enclosure Type details displays the message BL Enclosure G1.
When a blade is redeployed, Static IP Bay Configuration might not complete as expected. To correct this,
verify that the blade is using the current iLO 2 firmware, and then reset the iLO 2 configuration to factory
default settings using iLO 2 RBSU.
Configuring a ProLiant BL p-Class blade enclosure
To configure a BL p-Class blade enclosure using static IP bay addressing:
1. Install a server blade in bay 1 of the BL p-Class enclosure. The server blade does not need to be
configured or have an operating system installed. The server blade must be configured before
installing any additional blades in the enclosure.
2. Connect a client device to the front-panel iLO 2 port of the blade using the local I/O cable. The local
I/O cable connects to the I/O port on the front of the server blade. This connection enables the
static IP 192.168.1.1 for the iLO 2 Web interface.
3. Configure the enclosure setting. Using the iLO 2 Web interface, select the BL p-Class tab to access
the Enclosure Static IP Settings. The BL p-Class tab provides a user interface for configuring the
enclosure-level static IP addresses.
4. Select a reasonable starting IP address, with the last digit(s) of the address corresponding to the bay
number of each blade (example: 192.168.100.1 through 192.168.100.16), to build an easy-toremember numbering system.
5. Reset bay #1, if necessary. The blade in bay #1 must only be reset if you intend the blade to use a
Static IP bay Configuration address by marking the feature enable mask for bay #1. Before resetting
the blade, browse to the Network Settings page, select Enable Static IP Settings and click Apply to
force the blade to reboot and use the newly assigned enclosure static IP.
If multiple enclosures are deployed at the same time, the process can be repeated easily by moving a
single blade to bay #1 of each enclosure to perform the configuration.
Configuring static IP bay settings
Static IP bay settings are available on the BL p-Class tab and enable you to configure and deploy the
blade server. When configuring these settings, you must use the blade in bay 1.
Configuring iLO 2 73
Page 74

The Enable Static IP Bay Configuration Settings checkbox, available on the Network Settings tab (not
shown), allows you to enable or disable Static IP Bay Configuration. The new Enable Static IP Bay
Configuration Settings option is only available on blade servers. When Static IP Bay Configuration is
enabled, all fields except iLO 2 Subsystem Name are disabled. Only Static IP Bay Configuration or DHCP
can be enabled at one time. Disabling both Static IP Bay Configuration and DHCP signals iLO 2 to use a
user-defined IP address. The Enable Static IP Bay Configuration Settings option remains disabled if the
infrastructure does not support Static IP Bay Configuration.
ProLiant BL p-Class standard configuration parameters
Beginning IP Address (Bay 1)—Assigns the starting IP address. All IP addresses must be valid addresses.
Ending IP Address (Bay 16)—Assigns the ending IP address. All IP addresses must be valid addresses.
Subnet Mask—Assigns the subnet mask for the default gateway. This field may be filled in if either Static
IP Bay Configuration or DHCP is enabled. The entire IP address range must conform to the subnet mask.
Gateway IP Address—Assigns the IP address of the network router that connects the Remote Insight subnet
to another subnet where the management PC resides. This field may be filled in if either Static IP Bay
Configuration or DHCP is enabled.
ProLiant BL p-Class advanced configuration parameters
Domain Name—Enables you to assign the name of the domain in which the iLO 2 will participate.
Primary DNS Server—Assigns a unique DNS server IP address on your network.
Secondary DNS Server—Assigns a unique DNS server IP address on your network.
Tertiary DNS Server—Assigns a unique DNS server IP address on your network.
Primary WINS Server—Assigns a unique WINS server IP address on your network.
Secondary WINS Server—Assigns a unique WINS server IP address on your network.
Configuring iLO 2 74
Page 75

Static Route #1, #2, and #3 (destination gateway)—Assigns the appropriate static route destination and
gateway IP address on your network (the default IP values are 0.0.0.0 and 0.0.0.0, where the first IP
address corresponds to the destination IP, and the second IP address corresponds to the gateway IP).
Enabling iLO 2 IP address assignment
The bay #1 through bay #16 checkboxes enable you to select which BL p-Class blade servers will be
configured. You can Enable All, Clear All, or Apply your selection.
HP BladeSystem setup
The HP BladeSystem setup wizard provides step-by-step instructions to simplify single blade setup without
requiring DHCP or PXE. The HP BladeSystem Setup page launches after you authenticate to iLO 2 from
the front port.
The server blade must be properly cabled for iLO 2 connectivity. Connect to the server blade through the
server blade I/O port, while the blade is in the rack. This method requires you to connect the local I/O
cable to the I/O port and a client PC. Using the static IP address listed on the I/O cable label and the
initial access information on the front of the server blade, you can access the server blade through iLO 2
through its standard Web browser interface.
Although any blade can be used for access, if static IP bay configuration will be used to configure iLO 2
network settings, then the first blade in the enclosure should be used for access.
The first page of the wizard automatically launches if:
• This blade is new from the factory, and you have logged into iLO 2 from the front port.
• You did not fully complete the wizard by selecting Finish on the final page, and you did not select
Do not show setup wizard again and clicked Cancel on the beginning page.
• You have set iLO 2 back to factory default settings.
Click Cancel to close the automated setup wizard. Click Next to set up your blade server. The setup
wizard will guide you through:
Configuring iLO 2 75
Page 76

1.
iLO 2 configuration
2. Server RAID verification
3. Virtual media connection
4. Software installation
iLO 2 configuration screen
This screen enables you to change the following settings:
• Administrator password. HP recommends changing the default password.
• Network configuration settings. The following are the default settings:
o Enable DHCP—Yes
o Enable Static IP Bay Configuration—No
• If connected to the blade in enclosure slot 1, you can enable Static IP Bay configuration to
preconfigure the static address for other iLO 2 processors in the enclosure.
In the default configuration, the iLO 2 being updated gets its IP address through DHCP. Other iLO 2
processors in the enclosure must be configured separately. If these settings are not changed, clicking Next
displays the next page in the setup wizard. If either of these settings are changed, iLO 2 reboots to invoke
the updated settings.
The following configuration combinations are also available (the default setting is in parentheses):
• Enable DHCP (Yes) and Enable Static IP Bay Configuration (Yes)
This configuration causes the iLO 2 being configured to get its IP address through DHCP. Clicking
Next displays the Static IP Bay Configuration page, enabling you to specify the IP addresses for
other iLO 2s in the enclosure. After you click Next, you are prompted to verify that you want to use
DHCP for this iLO 2 IP address.
• Enable DHCP (No) and Enable Static IP Bay Configuration (Yes)
This configuration causes the iLO 2 being configured to set its IP address according to the settings
specified through the Static IP Bay Configuration. Clicking Next displays the Static IP Bay
Configuration page.
• Enable DHCP (No) and Enable Static IP Bay Configuration (No)
This configuration causes the iLO 2 being configured to set its IP address according to the settings
specified through the Network Settings page. Clicking Next displays the Network Settings page.
To save any network changes, you must have the Configure iLO 2 privilege.
Click Next to save changes and continue.
Verify Server RAID Configuration screen
This step of the installation wizard enables you to verify and accept server RAID configuration settings.
Verify the detected RAID level for the hard drives on the blade server displayed on the web page and do
one of the following:
• Click Next to keep current RAID settings.
• Click Default Settings to automatically configure the RAID level based on the number of installed
drives. You are prompted to verify that you want to reset the RAID level because this could result in
loss of data. Resetting the RAID level requires a server power-on or reboot. iLO 2 displays a page
Configuring iLO 2 76
Page 77

indicating that this action is occurring. The page is refreshed automatically every 10 seconds. After
the server reboots, the next page in the installation wizard displays again. If an error occurs during
the RAID reset process, the RAID Configuration page will redisplay with an indication of the error.
An error is most likely to occur if the server is in POST. If this is the case, exit any RBSU program you
are running, allow POST to complete, and try the operation again.
You can change the RAID level manually through RBSU. If the operating system is already installed,
changing the RAID level results in a loss of data.
Connect Virtual Media screen
This step of the installation wizard enables you to verify and accept the drive you will use during the
installation of the operating system. Under Settings, select the local drive and media type you intend to
use during operating system installation. Click Launch Virtual Media to launch the Virtual Media applet.
• Ensure the operating system media is connected. In the Virtual Media applet, a green icon appears
next to the media currently selected.
• Verify that the operating system media is in the appropriate local drive.
• Accept security certificates as they appear.
After making your selection, click Next to save your settings and continue. The virtual media applet
appears. After the applet is available, you can change the selected drive, or select other options not
available on the installation wizard page.
Install Software screen
This step of the installation wizard enables you to launch the Remote Console and install the operating
system. To start the operating system installation process:
• Click Launch Software Installation to launch the Remote Console. iLO 2 automatically initiates a
server power-on or reboot to start the operating system installation through the previously selected
virtual media.
• Accept security certificates as they appear.
Click Finish to complete the setup process.
iLO 2 diagnostic port configuration parameters
The iLO 2 Diagnostic Port on the front of ProLiant BL p-Class servers enables you to access and
troubleshoot server issues by using a diagnostic cable. The iLO 2 Diagnostic Port uses a static IP address.
It does not use DHCP to obtain an IP address, register with WINS or dynamic DNS, or use a gateway.
The diagnostic port cable should not be left plugged in without an active network connection because it
will cause degraded network performance on the standard iLO 2 network port.
In Network Settings, you can configure specific diagnostic port information. For more information on
using the diagnostic port and the diagnostic cable, see to the setup and installation guide for the blade
server.
The following are the fields that can be configured for the Diagnostic Port:
• Enable NIC
If Enable NIC is set to Yes, the diagnostic port is enabled.
• Transceiver Speed Autoselect
Configuring iLO 2 77
Page 78

• Speed
• Duplex
• IP Address
Use this parameter to assign a static IP address to iLO 2 on your network. By default, the IP address
is assigned by DHCP. By default, the IP address is 192.168.1.1 for all iLO 2 Diagnostic Ports.
• Subnet Mask
o Use the subnet mask parameter to assign the subnet mask for the iLO 2 Diagnostic Port. By
default, the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 for all iLO 2 Diagnostic Ports.
o The use of the Diagnostic Port is automatically sensed when an active network cable is plugged
in to it. When switching between the diagnostic and back ports, you must allow 90 seconds for
the network switchover to complete before attempting connection through the web browser.
NOTE: The diagnostic port will not switch over if an active Remote Console session or a
firmware update is in progress.
Configuring iLO 2 78
Page 79

Using iLO 2
In this section
System status and status summary information ........................................................................................... 79
iLO 2 Remote Console ............................................................................................................................ 86
Virtual media....................................................................................................................................... 104
Power management.............................................................................................................................. 113
ProLiant BL p-Class Advanced management............................................................................................. 117
ProLiant BladeSystem HP Onboard Administrator..................................................................................... 123
System status and status summary information
When you first access iLO 2, the interface displays the Status Summary page with system status and status
summary information, and provides access to health information, system logs, and Insight Agent
information. The options available in the System Status section are: Summary, System Information, iLO 2
Log, IML, Diagnostics, iLO 2 User Tips, and Insight Agents.
The Status Summary page displays high-level details about the system and iLO 2 subsystem, as well as
links to commonly used features. To access the Status Summary page from other areas of the iLO 2
interface, click System Status>Summary.
Status information includes:
• Server Name—Displays the name of the server.
• Server UUID—Displays the ID of the server.
• Server Serial Number/Product ID—Displays the serial number of the server, which is assigned when
the system is manufactured. You can change this setting using the system RBSU during POST. Product
ID is used to distinguish between different systems with similar serial numbers. Although the Product
ID is assigned when the system is manufactured, you can change this setting using the system RBSU
during POST.
Using iLO 2 79
Page 80

• System ROM—Displays the family and version of the active system ROM. If the system supports a
backup system ROM, the backup date is also shown.
• System Health—Summarizes the condition of the monitored subsystems including overall status and
redundancy (ability to handle a failure). The subsystems might include fans, temperature sensors,
power supplies, and VRM information.
• Internal Health LED—Represents the server internal health indicator (if supported). It summarizes
problems with fans, temperature sensors, VRMs, and other monitored subsystems in the server. See
the section, "System Information Summary (on page 81)" for details.
• Server Power—Displays the current power state of the server (ON/STANDBY) when the page was
loaded. Users with virtual power and reset privilege can also send a momentary power button press.
• UID Light—Displays the state of the UID light when the page was loaded. You can control the UID
state using the button below the UID icon in addition to the physical UID buttons on the server
chassis.
The UID helps you identify and locate a system, especially in high-density rack environments.
Additionally, the UID is used to indicate that a critical operation is underway on the host, such as
Remote Console access or firmware update. Never remove power from a server with a flashing UID.
The current state of the UID (on or off) is the last state chosen using one of these methods. If a new
state is chosen while the UID is blinking, the new state becomes the current state and takes effect
when the UID stops blinking. While the UID is blinking, the current state of the UID is shown along
with the tag flashing. When the UID stops blinking, the tag is removed.
The UID is not supported on the HP ProLiant ML310 G3.
• Last Used Remote Console—Displays the previously launched remote console and its availability,
which enables you to quickly launch your preferred Remote Console. You can use the Remote
Console if it is available and you have the appropriate user privilege. You can pick a different
console by following the Last Used Remote Console link.
• Latest IML Entry—Displays the most recent entry in the IML.
• iLO 2 Name displays the name assigned to the iLO 2 subsystem. By default, this is the word iLO
added to the system serial number. This value is used for the network name and should be unique.
• License Type—Displays whether the system has a feature license installed. Some features of iLO 2
cannot be accessed unless licensed.
• iLO 2 Firmware Version—Displays information about the version of iLO 2 firmware currently installed
and provides a link to the iLO 2 Release Notes page which highlights new capabilities in the current
firmware release and in selected previous releases
• IP Address—Displays the network IP address of the iLO 2 subsystem.
• Active Sessions—Displays all users currently logged into Integrated Lights-Out 2.
• Latest iLO 2 Event Log Entry— displays the most recent entry in the iLO 2 Event Log.
• iLO 2 Date—Displays the date (MM/DD/YYYY) as indicated by the iLO 2 subsystem internal
calendar. The iLO 2 internal calendar is synchronized with the host system at POST and when the
Insight Agents run.
• iLO 2 Time—Displays the iLO 2 subsystem internal clock. The iLO 2 internal clock is synchronized
with the host system at POST and when the Insight Agents run.
Using iLO 2 80
Page 81

System Information Summary
System Information displays the health of the monitored system. Many of the features necessary to operate
and manage the components of the HP ProLiant server have migrated from the health driver to the iLO 2
microprocessor. These features are available without installing and loading the health driver for the
installed operating system. The iLO 2 microprocessor monitors these devices when the server is powered
on during server boot, operating system initialization, and operation. Monitoring continues through an
unexpected operating system failure. To access System Information, click System Status>System
Information. The System Health Summary tab appears. System Information also displays the following
embedded health tabs: Fans (on page 81), Temperatures (on page 82), Power (on page 82), Processors
(on page 83), Memory (on page 83), and NIC (on page 83).
The Summary tab displays the state of monitored host-platform subsystems status at a glance, summarizing
the condition of the monitored subsystems, including overall status and redundancy (ability to handle a
failure). The subsystems can include fans, temperature sensors, power supplies, and voltage regulator
modules.
• Fans—Displays the state of the replaceable fans in the server chassis. This data includes the area
that is cooled by each fan and current fan speeds.
• Temperatures—Displays the temperature conditions monitored at sensors in various locations in the
server chassis, and the processor temperature. The temperature is monitored to maintain the location
temperature below the caution threshold. If the temperature exceeds the caution threshold, the fan
speed is increased to maximum.
Fans
• VRMs—Displays VRM status. A VRM is required for each processor in the system. The VRM adjusts
the power to meet the power requirements of the processor supported. A failed VRM prevents the
processor from being supported and should be replaced.
• Power Supplies—Displays the presence and condition of installed power supplies.
o OK—Indicates that the power supply is installed and operational.
o Unpowered—Indicates that the power supply is installed, but not operational. Verify that the
power cord is connected.
o Not present—Indicates that the power supply is not installed. Power is not redundant in this
condition.
o Failed—Indicates that the power supply should be replaced.
To access the Summary tab from other areas of the iLO 2 interface, click System Status>System
Information>Summary.
iLO 2, in conjunction with additional hardware, controls the operation and speed of the fans. Fans
provide essential cooling of components to ensure reliability and correct operation. Fan location,
placement, design and speed control take into account various temperatures monitored throughout the
system to provide appropriate cooling with minimal noise levels.
Fan operation policies might differ from server to server based on fan configuration and cooling
demands. Fan control takes into account the internal temperature of the system, increasing the fan speed
to provide more cooling, and decreasing the fan speed if cooling is sufficient. In the unlikely event of a
fan failure, some fan operation policies might increase the speed of the other fans, record the event in the
IML, and turn LED indicators on.
Using iLO 2 81
Page 82

Monitoring the fan sub-system includes the sufficient, redundant, and non-redundant configurations of the
fans. Fan failure is a rare occurrence, but to ensure reliability and uptime, ProLiant servers have redundant
fan configurations. In ProLiant servers that support redundant configurations, fan or fans might fail and still
provide sufficient cooling to continue operation. iLO 2 increases fan control to continue safe operation of
the server in the event of fan failure, maintenance operations, or any event that alters cooling of the
server.
In non-redundant configurations, or redundant configurations where multiple fan failures occur, the system
might become incapable of providing the necessary cooling to protect the system from damage and to
ensure data integrity. In this condition, in addition to the cooling policies, the system might start a graceful
shutdown of the operating system and server.
The Fan tab displays the state of the replaceable fans within the server chassis. This data includes the
area cooled by each fan and the current fan speed.
Temperatures
The Temperatures tab displays the location, status, temperature, and threshold settings of temperature
sensors in the server chassis. The temperature is monitored to maintain the location temperature below the
caution threshold. If one or more sensors exceed this threshold, iLO 2 implements the recovery policy to
prevent damage to server components.
Power
• If the temperature exceeds the caution threshold, the fan speed is increased to maximum.
• If the temperature exceeds the critical temperature, a graceful server shutdown is attempted.
• If the temperature exceeds the fatal threshold, the server is immediately turned off to prevent
permanent damage.
Monitoring policies differ depending on server requirements. Policies usually include increasing fan speed
to maximum cooling, logging the temperature event in the IML log, providing visual indication of the event
using LED indicators, and starting a graceful shutdown of the operating system to avoid data corruption.
After correcting the excessive temperature conditions additional polices are implemented including
returning the fan speed to normal, recording the event in the IML, turning off the LED indicators, and if
appropriate, canceling shutdowns in progress.
The VRMs/Power Supplies tab displays the state of each VRM or power supply. VRMs are required for
each processor in the system. VRMs adjust the power to meet the needs of the processor supported. A
VRM can be replaced if it fails. A failed VRM prevents the processor from being supported.
iLO 2 also monitors power supplies in the system to ensure the longest available uptime of the server and
operating system. Power supplies can be affected by the brownouts and other electrical conditions, or AC
cords can be accidentally unplugged. These conditions result in a loss of redundancy if redundant power
supplies are configured, or result in loss of operation if redundant power supplies are not in use.
Additionally, should a power supply failure be detected (hardware failure) or the AC power cord
disconnected, appropriate events are recorded in the IML and LED indicators used.
iLO 2 monitors power supplies to ensure that they are correctly installed. This information is displayed on
the System Information page. Reviewing the System Information page and IML will assist you in deciding
when to repair or replace a power supply, preventing a disruption in service.
Using iLO 2 82
Page 83

Processors
The Processors tab displays the available processor slots, the type of processor installed in the slot, and a
brief status summary of the processor subsystem. If available, installed processor speed in MHz and
cache capabilities are displayed.
Memory
The Memory tab displays the available memory slots and the type of memory, if any, installed in the slot.
NIC
The NIC tab displays the MAC addresses of the integrated NICs. This page does not display add-in
network adapters.
iLO 2 Log
The iLO 2 Log page displays the iLO 2 Event Log, which is a record of significant events detected by iLO
2. Logged events include major server events such as a server power outage or a server reset and iLO 2
events such as unauthorized login attempts. Other logged events include successful or unsuccessful
browser and Remote Console logins, virtual power and power cycle events, clear event log actions, and
some configuration changes, such as creating or deleting a user.
iLO 2 provides secure password encryption, tracking all login attempts and maintaining a record of all
login failures. Authentication Failure Logging allows you to configure logging criteria for failed
authentications. You can configure tracking failed login attempts for every attempt or every second, third,
or fifth attempt, and captures the client name for each logged entry to improve auditing capabilities in
DHCP environments, as well as recording account name, computer name, and IP address. When login
attempts fail, iLO 2 also generates alerts and sends them to a remote management console.
Events logged by higher versions of iLO 2 firmware might not be supported by earlier versions. If an event
is logged by an unsupported firmware, the event is listed as UNKNOWN EVENT TYPE. You can clear the
event log to eliminate these entries, or update the firmware to the latest supported version.
IML
To access the iLO 2 Log, click System Status>iLO 2 Log.
To clear the event log:
1. Click Clear Event Log to clear the event log of all previously logged information.
2. Click OK to confirm that you want to clear the event log. A line indicating that the log has been
cleared is logged.
The IML page displays the Integrated Management Log, which is a record of historical events that have
occurred on the server as reported by various software components. Events are generated by the system
ROM and by services like the System Management (health) driver. The IML enables you to view logged
remote server events. Logged events include all server-specific events recorded by the system health driver,
including operating system information and ROM-based POST codes. For more information, see to the
server guide.
Entries in the IML can assist during problem diagnosis or help identify possible problems before they
occur. Preventative action might be recommended to avoid possible disruption of service. iLO 2 manages
the IML, which can be accessed using a supported browser, even when the server is off. The ability to
Using iLO 2 83
Page 84

view the event log even when the server is off can be helpful when troubleshooting remote host server
problems.
You can sort the log by clicking the header of any column of data. After the sort completes, clicking the
same column header again sorts the log in reverse of its current order. Very large logs will take several
minutes to sort and display. You can clear the events in this log on the server's Insight Manager Web
Agents home page.
The iLO 2 processor records the following information to the IML based upon the occurrences in the
system.
• Fan inserted
• Fan removed
• Fan failure
• Fan degraded
• Fan repaired
• Fan redundancy lost
• Fans redundant
• Power supply inserted
• Power supply removed
• Power supply failure
• Power supplies redundancy lost
• Power supplies redundant
• Temperature over threshold
• Temperature normal
• Automatic shutdown started
• Automatic shutdown cancelled
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics option on the System Status tab displays the Server and iLO 2 Diagnostics screen. The
Server and iLO 2 Diagnostic screen displays iLO 2 self-test results, and provides options to generate an
NMI to the system and to reset iLO 2.
NOTE: When connected through the Diagnostics Port, the directory server is not available.
The Diagnostics page contains the following sections:
You can log in using a local account only.
• Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) button
The Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) button section contains the Generate NMI to System button which
enables you to halt the operating system for debugging. This functionality is an advanced function
and should only be used for kernel-level debugging. The possible uses of the Generate NMI to
System feature include the following:
o Use the Demonstrate ASR feature only if the System Management (health) driver is loaded and
ASR is enabled. The host automatically reboots after an NMI has occurred.
Using iLO 2 84
Page 85

o
Use the Debug feature if a software application hangs the system. The Generate NMI to System
button can be used to engage the operating system debugger.
o Initiate the dump of an unresponsive host if you want to capture the server context.
The Virtual Power and Reset privilege is required to generate an NMI. An unexpected NMI typically
signals a fatal condition on the host platform. A blue-screen, panic, ABEND, or other fatal exception
occurs when an unexpected NMI is received by the host operating system, even when the operating
system is unresponsive or locked-up. Generating an unexpected NMI can be used to diagnose a
catatonic or deadlocked operating system. Generating an NMI crashes the operating system,
resulting in lost service and data.
Generating an NMI should only be used in extreme diagnostic cases in which the operating system
is not functioning properly and an experienced support organization has recommended that you
proceed with an NMI. Generating an NMI as a diagnostic and debugging tool is primarily used
when the operating system is no longer available. Generating an NMI should not be used during
normal operation of the server. The Generate NMI to System button does not gracefully shut down
the operating system.
• iLO 2 Self-Test Results
The iLO 2 Self-Test Results sections displays the results of iLO 2 internal diagnostics. iLO 2 performs a
series of initialization and diagnostic procedures on the subsystems of the iLO 2 system. The results
are displayed on the Server and iLO 2 Diagnostics screen. All tested subsystems should display
Passed under normal circumstances. Each test displays one of three results: Passed, Fault, or N/A.
The status of these self-tests is indicated by the test results and is intended to identify problem areas.
If a Fault test condition is indicated, follow information noted on the screen. The specific tests that are
run is system-dependant. Not all tests are run on all systems. See the iLO 2 Diagnostics page to
verify which tests are automatically performed on your system.
• Reset Integrated Lights-Out 2
The Reset Integrated Lights-Out 2 section contains the Reset button which enables you to reboot the
iLO 2 processor. Using Reset does not make any configuration changes. Reset disconnects any
active connections to iLO 2 and completes any firmware updates in progress. You must have the
Configure iLO 2 privilege (configure local device settings) to reset iLO 2 using this option.
Insight Agents
The HP Insight Management Agents support a browser interface for access to runtime management data
through the HP System Management Homepage. The HP System Management Homepage is a secure
web-based interface that consolidates and simplifies the management of individual servers and operating
systems. By aggregating data from HP Insight Management Agents and other management tools, the
System Management Homepage provides an intuitive interface to review in-depth hardware configuration
and status data, performance metrics, system thresholds and software version control information.
The agents can automatically provide the link to iLO 2, or you can manually enter the link using
Administration/Management.
For more information, see "HP Systems Insight Manager integration" and the HP web site
(http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
).
Using iLO 2 85
Page 86

iLO 2 Remote Console
iLO 2 Remote Console redirects the host server console to the network client browser, providing full text
(standard), graphical mode video, keyboard, and mouse access to the remote host server (if licensed).
iLO 2 uses virtual KVM technology to improve remote console performance comparable with other KVM
solutions.
With remote console access, you can observe POST boot messages as the remote host server restarts and
initiate ROM-based setup routines to configure the hardware of the remote host server. When installing
operating systems remotely, the graphical remote consoles (if licensed) enable you to view and control the
host server screen throughout the installation process.
Remote console access provides you complete control over a remote host server as if you were in front of
the system, including access to the remote file system and network drives. Remote Console enables you to
change hardware and software settings of the remote host server, install applications and drivers, change
remote server screen resolution, and gracefully shut down the remote system.
Up to 10 users are allowed to simultaneously log in to iLO 2. However, only four users can access a
shared Integrated Remote Console. If you attempt to open the Remote Console while it is already in use, a
warning message appears, indicating that it is in use by another user. To view the remote console session
already in progress, see the section, "Shared Remote Console (on page 96)" for more information. To
take control of the session, use the Remote Console Acquire feature. See the section, "Acquiring the
Remote console (on page 97)" for more information.
The Remote Console Information page provides access links to the different remote console access
options. After deciding which console option you want to use, click the appropriate link. iLO 2 provides
the following remote console access options:
• Integrated Remote Console ("Integrated Remote Console option" on page 92)—Provides access to
the system KVM, allowing control of Virtual Power and Virtual Media from a single console using
Microsoft® Internet Explorer.
• Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen (on page 92)—Resizes the Integrated Remote Console to the
same display resolution as the remote host.
The Integrated Remote Console and Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen uses ActiveX and requires
Microsoft® Internet Explorer™.
• Remote Console (on page 98)—Provides access to the system KVM through a Java applet-based
console. Remote Console is the familiar Remote Console support carried forward from the original
iLO product. Remote Console support requires that Java™ be installed on the client system. Remote
Console operates with all operating systems and browsers supported by iLO 2.
• Remote Serial Console (on page 100)—Provides access to a VT320 serial console through a Java
applet-based console connected to the iLO 2 Virtual Serial Port. The Remote Serial Console is
available without an additional license and is suitable for host operating systems that do not require
access to the graphical console.
Standard iLO 2 provides server console access from server power-on through POST. Integrated Remote
Console, Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen, and Remote Console are graphical remote consoles that
turn a supported browser into a virtual desktop, allowing you full control over the display, keyboard, and
mouse of the host server. The operating-system-independent console supports graphic modes that display
remote host server activities, including shutdown and startup operations (if licensed).
Using iLO 2 86
Page 87

Remote console access to the host server after server POST is a licensed feature available with the
purchase of optional licenses. For more information, see "Licensing (on page 27)". To access iLO 2
Remote Console, click Remote Console. The Remote Console Information page appears.
iLO 2 Remote Console and iLO 2 licensing options
All iLO 2 Remote Console connection options are graphical and must be rendered using a client program
that can process iLO 2 graphics commands. Two clients are provided to render the iLO 2 graphics: a
Java™-based Remote Console and a Windows® Active X-based Integrated Remote Console. For those
clients that do not understand iLO 2 graphics (SSH and telnet), the iLO 2 Remote Serial Console must be
used.
iLO 2 blades ship with the iLO 2 Standard Blade Edition, which includes the Remote Console. However,
the HP ProLiant ML and HP ProLiant DL models ship with the iLO Standard license, which does not include
the Remote Console. Previous iLO Standard licenses on the HP ProLiant ML and ProLiant DL models
included a text-based Remote Console. Because there is no true text protocol in the iLO 2 Remote
Console, the iLO 2 Standard Remote Console on the HP ProLiant ML and ProLiant DL models is limited to
pre-operating system only. As soon as the server starts to boot an operating system, the iLO 2 Standard
on the HP ProLiant ML and ProLiant DL models displays a message that indicates the need for the iLO 2
Advanced license.
For system using SSH and the CLP to display iLO 2 Remote Console information, the CLP command
currently used is start /system1/console1. This command is only valid for the iLO 2 blade for as
long as the operating system is in text-only mode. If start /system1/console1 is used with an iLO 2
blade, you will not see anything because even if the operating system is in text-only mode, the protocol
stream sent by iLO 2 in response to this command is graphical. The iLO 2 firmware will not send
graphical data to the SSH port.
For an iLO 2 blade (and an iLO blade running Linux in a graphical format), enter getty() on the
server's serial port, and then use iLO 2 Remote Serial Console or iLO Virtual Serial Port (CLP command
start /system1/oemhp_vsp1) to view a login session to the Linux operating system through the
serial port.
Using iLO 2 87
Page 88

Remote Console settings
iLO 2 Remote Console settings and options are configured on the Remote Console Settings page. To
access the Remote Console Settings page, click Remote Console>Settings.
The Remote Console Settings page includes three tabs:
Settings
• High Performance Mouse settings can help alleviate remote console mouse synchronization issues,
but this feature is not supported on all operating systems. The effects of changing the settings take
place when remote console is started or restarted. The following options are available:
o Disabled—Enables the mouse to use the relative coordinates mode which is compatible with most
host operating systems.
o Enabled—Enables the mouse to use the absolute coordinates mode, eliminating synchronization
issues on supported operating systems.
o Automatic—Enables iLO 2 to select the appropriate mouse mode when the iLO 2 driver is loaded
on the host operating system. The selected mode is persistent unless a different mode is indicated
when the operating system driver is loaded or if you choose another setting.
• Remote Console Acquire enables one user to take the remote console session away from another
user. This setting enables or disables the acquire functionality.
• Shared Remote Console enables multiple users to view and control the server console at the same
time. This setting enables or disables the shared functionality.
• Interactive Console Replay allows you to replay the captured console video of boot and fault
sequences along with user-initiated manual console captures.
• The Key-Up/Key-Down setting allows you toggle between using the HID report keyboard model and
the ASCII and ESC codes keyboard model in the IRC. The HID report keyboard model is enabled by
default but might cause repeating characters on high latency networks. If you experience repeating
characters when using IRC, set Key-Up/Key-Down to Disabled.
• Boot/Fault Console Capture enables you to capture console video to internal buffers of any boot and
fault sequences. Internal buffer space is limited to the capture of the most recent boot or fault
Using iLO 2 88
Page 89

sequence. Buffer space is limited. The more dynamic and the higher the graphical resolution of the
server console, the less amount of data that can be stored in the buffer. Select which type of video to
capture using the following options:
o Console Capture buffer allows you to select which type of console sequence to capture. You can
enable either buffer or enable both buffers at the same time. The buffers share the same internal
data area, so enabling both reduces the amount of console video that can be captured. You can
change the enabled buffers at any time to maximize buffer utilization. When the buffer
configuration is changed, both buffers are reset and information currently in the buffers at that
time is lost.
o Auto Export/Fault Buffer allows you to enable or disable automatically exporting captured
console data.
• Export Boot/Fault Buffer enables you to specify the URL location of a web server that accepts a PUT
or POST Method data transfer. For example:
http://192.168.1.1/images/capture%h%t.ilo transfers the internal-capture buffers to a
web server at the IP address 192.168.1.1, and stores the data in the images folder using the
filename captureServerNameDateTime-Boot(or Fault).ilo, where:
— %h specifies the addition of the server name to the filename
— %t specifies that a time stamp will be included in the filename
— Boot or Fault is automatically added to denote the buffer type as either a boot-sequence or
fault-sequence event
For more information about web server configuration, and how to configure an Apache web
server to accept exported capture buffers, see the section, "Configuring Apache to accept
exported capture buffers (on page 196)."
o Export enables you to trigger an export manually.
o Export username is the username for the web server that is specified in the URL.
o Password is the password of the web server that is specified in the URL.
After making changes, click Apply.
• Serial Port Configuration displays the current settings of the system serial ports and the Virtual Serial
Port. The Settings for the system and virtual serial ports are also displayed, showing the COM ports
in use and IRQ numbers.
• iLO 2 Virtual Serial Port displays the current status of the Virtual Serial Port connection. The possible
modes available are: in use raw mode, or in use normal mode. If the connection is in use, the
Disconnect button is available and can be used to disconnect a Virtual Serial Port connection. Raw
mode indicates that a client is connected using the WiLODbg.exe utility which is used for remote
Windows® kernel debugging.
Hot Keys enables you to define keystroke sequences that will be transmitted to the remote host server by
pressing a hot key. Remote Console hot keys allow specific key sequences such as Alt+Tab and Alt+SysRq
to be passed to the server from the Remote Console Java™ session. See the section, "Remote Console hot
keys (on page 90)" for more information.
Java displays the Java™ requirements for each supported operating system and a link to download
Java™. For more information, see the section, "Supported browsers and client operating systems (on
page 13)."
Using iLO 2 89
Page 90

Remote console hot keys
The Program Remote Console Hot Keys page enables you to define up to six multiple key combinations
assigned to each hot key. When a hot key is pressed in the Remote Console, on client systems, the
defined key combination (all keys pressed at the same time) are transmitted in place of the hot key to the
remote host server. To access AltGr symbols on international keyboards, use hot keys to define these
symbols. For a list of support hot keys, see the section, "Supported hot keys (on page 90)."
Remote console hot keys are active during a Remote Console session through the IRC, Remote Console
applet, and during a text Remote Console session through a telnet client. When using the IRC, keyboard
LED states for NumLock, CapsLock and ScrollLock on the client keyboard do not necessarily reflect the
state of the server keyboard. However, pressing any of the locking keys will change that Lock state on the
server.
To define a Remote Console hot key:
1. Click Remote Console>Hot Keys.
2. Select the hot key you want to define, and use the dropdown boxes to select the key sequence to be
transmitted to the host server when you press the hot key.
3. Click Save Hot Keys when you have finished defining the key sequences.
The Program Remote Console Hot Keys page also contains a Reset Hot Keys option. This option clears all
entries in the hot key fields. Click Save Hot Keys to save the cleared fields.
Supported hot keys
The Program Remote Console Hot Keys page allows you to define up to 6 different sets of hot keys for use
during a Remote Console session. Each hot key represents a combination of up to 5 different keys which
are sent to the host machine whenever the hot key is pressed during a Remote Console session. The
selected key combination (all keys pressed at the same time) are transmitted in its place. For more
information, refer to "Remote Console hot keys (on page 90)." The following table lists keys available to
combine in a Remote Console hot key sequence.
ESC F12 : o
L_ALT " "
R_ALT ! > q
L_SHIFT # = r
R_SHIFT $ ? s
INS % @ t
DEL & [ u
HOME ~ ] v
END ( \ w
PG UP ) ^ x
PG DN * _ y
ENTER + a z
TAB - b {
< p
(Space)
BREAK . c }
F1 / d |
Using iLO 2 90
Page 91

F2 0 e ;
F3 1 f ’
F4 2 g L_CTRL
F5 3 h R_CTRL
F6 4 i NUM PLUS
F7 5 j NUM MINUS
F8 6 k SCRL LCK
F9 7 l BACKSPACE
F10 8 m SYS RQ
F11 9 n
Hot keys and international keyboards
To set up hot keys on an international keyboard, select keys on your keyboard in the same position on a
US keyboard. To create a hot key using the international AltGR key, use R_ALT in the key list. Use the US
keyboard layout shown to select your keys.
Shaded keys do not exist on a US keyboard.
• The green shaded key is known as the Non-US \ and | keys on an international keyboard.
• The purple shaded key is known as the Non-US # and ~ key on an international keyboard.
Hot keys and Virtual Serial Port
When connected to the Virtual Serial Port feature of iLO 2 using telnet, the key sequence CTRL+P+! (CTRL
key, P key, SHIFT key, and 1 key pressed simultaneously) normally causes the remote server to reboot.
However, when using this key sequence from a client running Microsoft® Windows 2000, the command
might fail, causing iLO 2 to become unresponsive.
To power off the remote server, use the key sequence CTRL+P 6 and the key sequence CTRL+P 1 to power
up the remote server.
If iLO 2 becomes unresponsive, close the Virtual Serial Port session. iLO 2 will automatically reset in
approximately three minutes and return to normal operation.
Using iLO 2 91
Page 92

Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen allows you to re-size the IRC to the same display resolution as the
remote host. To return to your client desktop, exit the console.
Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen causes your client to resize to the same resolution as the remote
server. Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen attempts to pick the best client display settings for that
resolution; however, some monitors might have trouble with the highest screen refresh rates supported by
the video adapter. If this occurs, check your desktop properties by right-clicking on the Desktop and
selecting Properties>Settings>Advanced>Monitor and select a lower screen refresh rate.
For more information on the Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen display, refer to the "Integrated Remote
Console ("Integrated Remote Console option" on page 92)" section.
Integrated Remote Console option
The Integrated Remote Console offers a high-performance remote console interface for Windows® clients,
combining KVM, Virtual Power, and Virtual Media functionality. The Integrated Remote Console option is
an ActiveX control that runs from Microsoft® Internet Explorer. Integrated Remote Console is a licensed
feature available with the purchase of optional licenses. For more information, see "Licensing (on page
27)".
The Integrated Remote Console supports four simultaneous remote console sessions with the same server if
enabled through the Remote Console Settings screen, SMASH CLI (OEM), or RIBCL. For more information
about using multiple remote console sessions, see the section, "Shared Remote Console (on page 96)."
Integrated Remote Console and Integrated Remote Console Fullscreen display a menu bar and buttons
rendered on the screen. The menu bar has the following options:
• Remote Console Replay (play icon)—Displays the Replay Menu dialog (if Boot/Fault Console
Capture is enabled) or starts the Open File dialog box if Boot/Fault Console Capture is not enabled.
o Replay Current BOOT buffer and Replay Current FAULT buffer—Enables you to transfer the
internally captured buffers to the client using the Console Replay port specified on the
Using iLO 2 92
Page 93

Administration>Access tab. Click Replay Current BOOT buffer or Replay Current FAULT buffer to
change the Remote Console menu to the Replay Console menu.
o Replay file—Displays an Open dialog box enabling you to view a previously saved file. After
you select a file and click Open, the Remote Console menu changes to the Replay Console menu.
• Replay (play icon on the main menu)—Displays the Replay Console. The Replay Console provides
playback control of the selected data buffer and displays elapsed playback time.
The Replay Console has the following options:
o Click Play to start the playback. After you click Play, you can:
— Click Pause to stop the playback and hold the current position. To resume playback, click
Play from the paused state and the playback resumes from the current position.
— Click Stop to halt the playback and reset the playback to the beginning of the data buffer.
— Click Fast-forward to increases the playback rate 2x, 4x, or 8x of normal speed.
o Close appears when playback is complete. Click Close to exit the Replay Console and display
the Remote Console menu bar.
• Record (camera icon)—Enables you to manually record current server console video. Press Record to
display a Save dialog box enabling you to specify the file name and the location to save the current
recording session. During a recording session, Record will appear depressed and change to green.
While enabled, any server console activity appearing on the Integrated Remote Console is saved to
the file specified. If you click Record during a recording session, the recording session stops and
returns the Record button to the normal unpressed state. To replay the recording, click Replay.
• Control—Enables the session leader to reclaim full control if control was authorized for a satellite
client.
• Lock—Enables you to prevent any additional satellite client requests from appearing on the session
leader console.
Using iLO 2 93
Page 94

• Client List—Displays the user name and DNS name (if available) or IP address of the current satellite
clients.
• Drive—Displays all available media.
• Power (green power icon)—Displays the power status and allows you to access the power options.
The power button is green when the server is powered up. When you press Power the Virtual Power
Button screen appears with four options: Momentary Press, Press and Hold, Cold Boot, and Reset
System.
When either the Drives or Power button is pressed, the menu displayed remains open even when the
mouse is moved away from the menu bar.
• CAD—Enables you to start a dialog to send the Ctrl-Alt-Del keys (or any one of the six hotkeys) to the
server.
• Thumb tack—Enables you to keep the Remote Console main menu open or to retract the main menu
when the mouse is moved away.
• Exit (red X icon)—Enables you to close and exit the remote console.
Internet Explorer 7 security enhancements display the address bar in any recently opened windows. If you
want to remove the address bar from the IRC, you must change the Security setting from the default level.
To remove the address bar, set "Set Allow websites to open windows without address or status bars" to
Enable.
Optimizing mouse performance for Remote Console or Integrated Remote Console
In some Microsoft® Windows® configurations the mouse acceleration must be set correctly for remote
console mouse to behave properly.
SLES 9
Determine which mouse device is the Remote Console mouse by using the xsetpointer -l command
to list all mice.
1. Determine which mouse you want to modify by cross-referencing the output of xsetpointer with the X
configuration (either /etc/X11/XF86Config or /etc/X11/xorg.conf)
2. Select the remote console mouse as the mouse you want to modify. For example:
xsetpointer Mouse[2]
3. Set the acceleration parameters. For example:
xset m 1/1 1.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Set the acceleration parameters using:
xset m 1/1 1
Windows® mouse synchronization
The default High Performance mouse setting on the Global Setting page is designed to use the best setting
based on the server operating system. To function correctly requires the HP ProLiant Lights-Out
Management Interface Driver is loaded and the server has been rebooted after the driver installation. If
you experience mouse synchronization problems under Windows, change the High Performance Mouse
setting to Yes.
Using iLO 2 94
Page 95

High Performance Mouse settings
When using the Remote Console, you can enable the High Performance Mouse feature. This feature
greatly improves pointer performance and accuracy on supported operating systems. iLO 2 High
Performance Mouse is a pointing device that provides absolute position coordinates to describe its
location similar to a USB tablet mouse. A conventional mouse sends relative position information (such as
the mouse has moved 12 pixels to the right). The host computer can modify relative position information
to enable features like mouse acceleration. When using the Remote Console, the client is not aware of
these modifications. Therefore, synchronization between the client and host mouse cursors fails.
Both the Integrated Remote Console and the Remote Console applets send absolute and relative mouse
cursor coordinates to iLO 2. When iLO 2 is in High Performance Mouse mode, it discards the relative
coordinates and sends the absolute coordinates to the USB tablet mouse emulator. The result is that the
server "sees" the mouse move as if the coordinate information had originated from a local USB tablet
mouse. When iLO 2 is not in High Performance Mouse mode, the absolute coordinates are discarded
and the relative coordinates are sent to the USB relative mouse emulator.
High-Performance Mouse is supported only on operating systems that support USB tablet mouse.
Windows® users should enable the High Performance Mouse option on the Remote Console Settings
screen. Linux users should enable the High Performance mouse option once the iLO 2 High Performance
Mouse for Linux driver is installed. Other operating system servers experiencing Remote Console mouse
trouble should disable the High Performance Mouse option.
When using Integrated Remote Console from iLO 2 and SmartStart, the local mouse and remote mouse
do not stay aligned. The High Performance Mouse setting should be disabled while in SmartStart. If the
local mouse and remote mouse get out of alignment while you are using the High Performance Mouse
feature, you can use the right Ctrl key to realign them. Alternatively, you can use the Java™ Remote
Console instead of Integrated Remote Console.
The High Performance Mouse option alleviates all mouse synchronization issues on supported host
operating systems. You can select this mode on the Remote Console Settings page before starting a
Remote Console. However, it might not be supported by all operating systems, particularly during
installation. For best performance:
• Select a lower remote server screen resolution to improve the performance of the Remote Console.
The maximum supported resolution is 1280 x 1024 pixels.
• Set the client screen resolution higher than the remote server resolution to maximize Remote Console
visibility.
• The color quality of the remote server has no effect on the performance of the remote console. The
Remote Console is rendered in 4096 (12-bit) colors.
• Use a non-animated mouse pointer on the remote system.
• Disable mouse trails on the remote system.
To configure the host server adjust the following settings in the Control Panel:
1. Select Mouse>Pointers>Scheme>Windows Default scheme. Click OK.
2. From the Mouse>Pointers page, select Enable pointer shadow. Click OK.
3. Select Display>Settings>Advanced>Troubleshoot>Hardware Acceleration>Full. Click OK.
4. Select System>Advanced>Performance Settings>Visual Effects>Adjust for best performance. Click
OK.
Alternatively, the HP online configuration utility (HPONCFG) can automatically adjust these settings. You
can also edit High Performance Mouse settings using the XML command MOD_GLOBAL_SETTINGS. For
Using iLO 2 95
Page 96

more information about using the RIBCL command MOD_GLOBAL_SETTINGS, see the HP Integrated
Lights-Out Management Processor Scripting and Command Line Resource Guide.
Shared Remote Console
Shared Remote Console is an iLO 2 feature that allows the connection of up to four sessions on the same
on the same server. This feature does not replace the Acquire feature described in "Acquiring the Remote
console (on page 97)" or allow full-access clients (read/write) to control power. Shared Remote Console
does not support passing server host designation to another user or a failed user connection to reconnect
after failure. You must restart the remote console session to allow user access after failure.
Shared Remote Console is a licensed feature available with the purchase of optional licenses. For more
information, see "Licensing (on page 27)".
Shared Remote Console and Forced Switch mode are disabled by default. You must enable and configure
these features through the browser, SMASH CLI (OEM), or RIBCL. All console sessions are encrypted by
authenticating the client first, and then the session leader decides whether to allow the new connection.
The first user to initiate a Remote Console session connects to the server normally and is designated as the
session leader (session host.) Any subsequent user requesting Remote Console access initiates an access
request, requesting a satellite client connection, calling the session leader. A pop-up for each satellite
client request appears on the session leader's desktop, identifying the requester's user name and DNS
name (if available) or IP address.
Session hosts have the option to grant or deny access. A list of users and session host names appears
within the remote console browser frame. Satellite client sessions terminate when the session host is
terminated.
Shared sessions do not operate well with the Console Capture and replay features of iLO 2. If a satellite
session is viewing a captured session, during the playback time, the satellite session will not receive
session leader control messages. If the session host starts to view captured video data during a shared
session, the video is displayed on all satellite Remote Console sessions.
Using Console Capture
Console Capture is a Remote Console feature that enables you to record and replay a video stream of
events such as booting, ASR events, and sensed operating system faults. You can also manually start and
stop the recording of console video. Console Capture is only available through the iLO 2 user interface
and cannot be accessed through XML scripting or the CLP. Console Capture is a licensed feature
available with the purchase of optional licenses. For more information, see "Licensing (on page 27)".
A buffer area is set aside in the management processor to store captured video data. This buffer area is
shared with the firmware update buffer, so any information captured is lost when you start the firmware
update process. You cannot capture video data during the firmware update process.
Buffer space is limited. Only one of each type of event is stored in the buffer area at a time. You can
transfer captured data buffers to a client running the IRC for replay. You can also configure iLO 2 to
automatically send captured video data to a web server on the same network as the iLO 2 when an event
occurs. The web server must accept POST-method data transfers. You can select Boot buffer only, Fault
buffer, or combine them both as one large buffer to have more room to capture Linux boot sequences.
Exported buffer data is given a unique name to easily identify the data for playback. Playback requires a
licensed iLO 2 on the network. Some operating systems (such as Linux) can fill the buffer quickly. If you
Using iLO 2 96
Page 97

leave the system console in text mode, it helps maximize the amount of information captured. Also,
closing or reducing the number of active graphical console elements helps optimize internal buffer space.
You can manually capture video of the server console using the IRC Record feature. All manually captured
data is stored in a local file on the client for later playback.
Acquiring the Remote Console
When the Remote Console Acquire setting on the Remote Console Settings screen is enabled, the Remote
Console page displays the Acquire button. If you have opened the Remote Console page and are notified
that another user is currently using Remote Console, clicking the Acquire button ends the other user's
Remote Console session and starts a Remote Console session in your current window.
When you click Acquire, you are prompted to verify that you want to interrupt the other user's Remote
Console session. The other user receives a notification that another user has acquired the Remote Console
session after losing the connection. No prior warning is given. After you confirm you want to proceed
with the acquire operation, you are notified by an alert window that the operation could take 30 seconds
or longer to complete. The Acquire button becomes disabled after it is clicked and the Acquire operation
is started. On browsers that support it, the button will change to a light gray color to indicate it is
disabled. On other browsers, there may be no visible indication that the button is disabled.
Only one acquire command is allowed every five minutes for all users. If another user has recently
acquired the Remote Console, clicking the Acquire button can result in a page informing you that the fiveminute acquire disabled period is in effect. Close the window and re-launch Remote Console again. The
Acquire button is disabled in the new page until the acquire disable period expires. When the Acquire
button is enabled (this operation happens automatically, and you do not have to refresh the page), you
can attempt to acquire the Remote Console session again. On browsers that support it, the button will
appear in a light gray color to indicate it is disabled during this five-minute time period. On other
browsers, there may be no visible indication that the button is disabled, and thus there will be no visual
indication when the timeout period expires.
Only one acquire attempt may be made per Remote Console session window. If you have successfully
acquired the Remote Console, and someone subsequently acquires it from you, you must open a new
Remote Console window to attempt to acquire the Remote Console session again.
Using iLO 2 97
Page 98

Remote Console
Remote Console is a Java™ applet that renders the remote console with broad browser compatibility
including Windows® and Linux browsers. Supported browsers are listed in the "Supported browsers and
client operating systems (on page 13)" section. Remote Console is a licensed feature available with the
purchase of optional licenses. For more information, see "Licensing (on page 27)".
Remote Console uses dual cursors to help you distinguish between the local and remote mouse pointers.
The client computer's mouse cursor appears in the Remote Console as a crosshair symbol. For best
performance, be sure to configure the host operating system display as described in the sections,
"Recommended client settings (on page 99)" and "Recommended server settings (on page 99)."
To synchronize the remote and local cursors if they drift apart, do one following:
• Right-click, drag, and move the local crosshair cursor to align with the mouse cursor of the remote
server.
• Press and hold the right Ctrl key, and move the local crosshair cursor to align with the mouse cursor
of the remote server.
The local cursor takes the shape of the remote cursor. The cursor appears as a single cursor if the local
cursor and the remote cursor are perfectly aligned and the hardware acceleration is set to Full on the
managed server.
Remote Console features and controls
The Remote Console applet contains buttons that provide iLO 2 with enhanced features and control. These
options are:
• Refresh causes iLO 2 to refresh the screen.
• Terminal Svcs launches the Microsoft® Terminal Services client installed on the system. This button is
deactivated if Terminal Services is disabled or is not installed on the server.
• Ctrl-Alt-Del enters the key sequence Ctrl+Alt+Del in the Remote Console.
Using iLO 2 98
Page 99

• Alt Lock, when selected, sends any key pressed to the server as if you pressed the Alt key and
another key simultaneously.
• Character Set changes the default character set used by the Remote Console. Modifying the Remote
Console character set ensures the correct display of characters.
• Close ends the Remote Console session and closes the Remote Console window.
Recommended client settings
Ideally, the remote server operating system display resolution should be the same resolution, or smaller,
than that of the browser computer. Higher server resolutions transmit more information, slowing the overall
performance.
Use the following client and browser settings to optimize performance:
• Display Properties
o Select an option greater than 256 colors.
o Select a greater screen resolution than the screen resolution of the remote server.
o Linux X Display Properties—On the X Preferences screen, set the font size to 12.
• Remote Console
o For Remote Console speed, HP recommends using a 700-MHz or faster client with 128 MB or
more of memory.
o For the Remote Console Java™ applet execution, HP recommends using a single processor client.
• Mouse Properties
o Set the Mouse Pointer speed to the middle setting.
o Set the Mouse Pointer Acceleration to low or disable the pointer acceleration.
Recommended server settings
The following is a list of recommended server settings based on the operating system used.
NOTE: To display the entire host server screen on the client Remote Console applet, set the
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 settings
To optimize performance, set server Display Properties to a plain background (no wallpaper pattern).
Microsoft® Windows® Server 2003 settings
To optimize performance, set the server Display Properties to plain background (no wallpaper pattern)
and set the Server Mouse Properties to Disable Pointer Trails.
Red Hat Linux and SUSE Linux server settings
To optimize performance, set the server Mouse Properties>Pointer Acceleration to 1x. For KDE, access the
Control Center, select Peripherals/Mouse, then select the Advanced tab.
server display resolution less than or equal to that of the client.
Using iLO 2 99
Page 100

Remote Serial Console
The Remote Serial Console enables you to access a VT320 serial console from a Java™ applet-based
console connected to the iLO 2 Virtual Serial Port through a browser. Launching the Remote Serial
Console enables you to exchange text data with the host. The Remote Serial Console option is compatible
with both Windows® and Linux host operating systems and requires JVM.
The flow of data is a bi-directional stream sent to the server serial port. Three types of data can appear on
a HP ProLiant server serial port:
• Windows® EMS console
• Linux user session through serial tty (ttyS0)
• System POST dialog (if BIOS serial console redirection is enabled)
The current configuration is displayed on the Remote Console Information page when you click the
Remote Console tab. You can alter the current settings using the host system RBSU, accessed during a
server reset.
Configuring Remote Serial Console
To successfully use the Remote Serial Console, the server software and firmware must be configured
correctly. To configure the server POST firmware, the server System RBSU must be invoked to set the serial
port parameters. You must configure the RBSU to enable BIOS Serial Console Redirection mode. This
mode instructs the server system ROM to send data to, and receive data from, the server serial port.
When the iLO 2 firmware enters Remote Serial Console mode, iLO 2 enables a serial port in place of the
server serial port, intercepts and retransmits outgoing data to the Remote Serial Console client, receives
incoming data (from the Remote Serial Console client), and retransmits it to the system ROM.
After the server completes POST, the server system ROM transfers control to the operating system boot
loader. If you are using Linux, you can configure the operating system boot loader to interact with the
server serial port instead of the keyboard, mouse, and VGA console. This configuration enables you to
view and interact with the operating system boot sequence through the Remote Serial console. See the
Using iLO 2 100
 Loading...
Loading...