Honda GX240, GX270, GX340, GX390, UT2 Technical Manual
...
GX240
GX270
GX340
GX390
UT2/RT2
Technical Manual
©2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
All Rights Reserved
PTR54179


GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
Preface
This manual covers engine selection, engine installation design and engine installation testing, so the combination of a
Honda engine and your equipment will make the best possible product.
Please feel free to contact your Honda Engine Distributor at any time for additional technical information or to discuss
your engine application needs.
All information contained in this manual is based on the latest product information available at the time of printing. We
reserve the right to make changes at anytime without notice.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical
photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. This includes text, figures
and tables.
Contents
Design Features .......................................................... 2
Emission Regulations ................................................. 2
Recommended Power Range ..................................... 3
Maximum Operation ............................................... 3
Continuous Operation ............................................ 3
Power Curve .......................................................... 3
Output Confirmation Methods ................................ 5
Cooling ....................................................................... 5
Minimum Cooling Air Flow Requirement ................ 5
Ambient Temperature Limits .................................. 5
Testing ................................................................... 5
Engine Enclosures ................................................. 6
Fuel System ................................................................ 7
Fuel Tank Position ................................................. 7
Fuel Line ................................................................ 7
Fuel Valve Installation ............................................ 7
Fuel Pump ............................................................. 7
Fuel Tank Filter Installation .................................... 7
Controls ....................................................................... 7
Engine Switch ........................................................ 7
Carburetor Controls ............................................... 8
Exhaust System .......................................................... 9
Recommended Muffler ........................................... 9
Fabricated Exhaust Systems ................................. 9
Engine Mounting ....................................................... 10
Inclination ............................................................. 10
Resonance Check ............................................... 10
Electrical System ...................................................... 11
Battery ................................................................ 11
Fuse ..................................................................... 11
Engine Switch ...................................................... 11
Charging Coil Selection ....................................... 12
Lamp Coil Kit (optional) ........................................ 12
Oil Alert® System (optional) ................................ 12
Wiring Precautions ............................................... 12
Wiring Diagrams ....................................................... 13
No Charge Coil Models ........................................ 13
Electric Start Models ............................................ 13
Power Transmission ................................................. 15
V-Belt Connections .............................................. 15
Starting Performance ...........................................16
Installation Considerations ........................................17
Maintenance Points Accessibility ........................17
Dimensional Drawings ...............................................19
GX240-270 ...........................................................19
GX340-390 ...........................................................23
PTO Dimensional Drawings ......................................27
H Type (with reduction) ........................................27
L Type (with reduction) .........................................27
P Type ..................................................................28
Q Type ..................................................................28
S Type ..................................................................29
V Type ..................................................................29
W Type .................................................................30
Dimensions and Weights ...........................................31
GX240 ..................................................................31
GX270 ..................................................................33
GX340 ..................................................................34
GX390 ..................................................................35
Specifications ............................................................36
GX240 ..................................................................36
GX270 ..................................................................36
GX340 ..................................................................37
GX390 ..................................................................38
Serviceability .............................................................39
Maintenance Schedule .........................................39
Engine Oil Level Check ........................................40
Engine Oil Change ...............................................41
Air Cleaner Check/Cleaning and Replacement ....41
Sediment Cup Cleaning .......................................44
Spark Plug Check/Adjustment ..............................45
Spark Plug Replacement ......................................46
Spark Arrester Cleaning (if equipped) ..................46
Idle Speed Check/Adjustment ..............................47
Valve Clearance Check/Adjustment .....................48
Combustion Chamber Cleaning ...........................49
Fuel Tank and Filter Cleaning ..............................50
Fuel Tube Check ..................................................50
Evaporative emissions ...............................................51
Types with OEM provided fuel tanks ....................51
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 1

GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
INTRODUCTION
Honda engines are designed for minimal maintenance.
When maintenance is required, the task is kept simple by
providing convenient maintenance access and procedures.
Honda engines use proven engine technology and design
innovations to make them highly reliable engines.
DESIGN FEATURES
High Performance
OHV design reduces thermal distortion of the cylinder. This
helps maintain the optimum seal between the piston rings
and cylinder, which minimizes oil and fuel consumption.
Power is also maintained in extreme operating conditions.
Smooth and Quiet Operation
OHV design provides a reduced reciprocating mass and
balanced weight distribution. The 25° inclined cylinder
produces a low center of gravity for the moving parts, which
further reduces vibration for quiet operation. These features,
and the compact design result in extremely smooth
operation.
Use of proven design technologies reduces noise from
internal engine components. The hardness of reciprocating
parts, the helical cut gears on the crankshaft and camshaft
and the use of select materials makes these engines
exceptionally quiet. The large muffler is designed to further
reduce noise.
Durability/Reliability
Honda engines are built with quality that provides proven
durability and reliability. Proven features such as OHV
design and cast iron cylinder sleeve provide long life in all
types of operating conditions. To further enhance the
reliability of these engines, a 2-stage air cleaner system,
digital electronic ignition system, mechanical centrifugal
governor and proven side-draft carburetor are standard
features.
EMISSION REGULATIONS
The Honda GX390 engines meet U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency and the California Air Resources Board
regulations.
Honda engine distributors and equipment manufacturers
that use Honda engines are required by regulation to follow
this OEM technical manual. Correct engine matching
ensures that the engine will be durable (and emission
durable) in use.
2 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
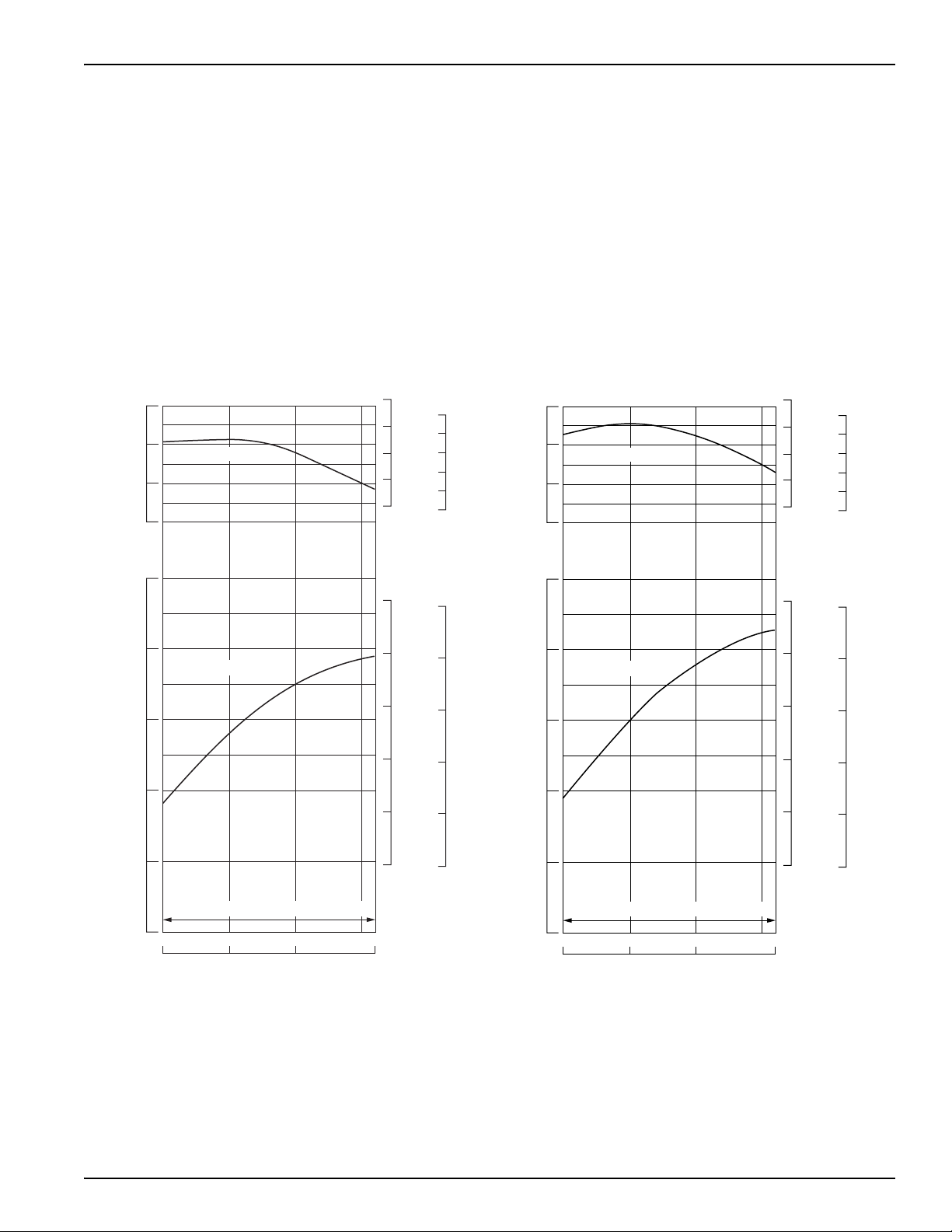
ENGINE SPEED
(rpm)
2000 36003000
(KW)
(HP)
OUTPUT
TORQUE
13
14
15
7
6
5
4
8
9
(PS)
7
6
5
4
8
9
20
NET POWER
NET TORQUE
12
11
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
1.5
18
16
14
3
2
4
5
6
7
(N·m)
(lbf·ft)
(kgf·m)
RECOMMENDED OPERATING SPEED RANGE
ENGINE SPEED
(rpm)
2000 36003000
(KW)
(HP)
OUTPUT
TORQUE
13
14
15
7
6
5
4
8
9
(PS)
7
6
5
4
8
9
20
NET POWER
NET TORQUE
12
11
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
1.5
18
16
14
3
2
4
5
6
7
(N·m)
(lbf·ft)
(kgf·m)
RECOMMENDED OPERATING SPEED RANGE
RECOMMENDED POWER RANGE
Maximum Operation
Operate the engine at not more than 90% of the maximum horsepower available at a given rpm.
Recommended maximum operating hp = 0.9 x maximum hp
Continuous Operation
For continuous operation (more than 30 minutes), operate the engine at not more than 80% of the maximum
horsepower available at a given rpm.
Continuous recommended operating hp = 0.8 x maximum hp
Power Curve
GX240 GX270
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 3
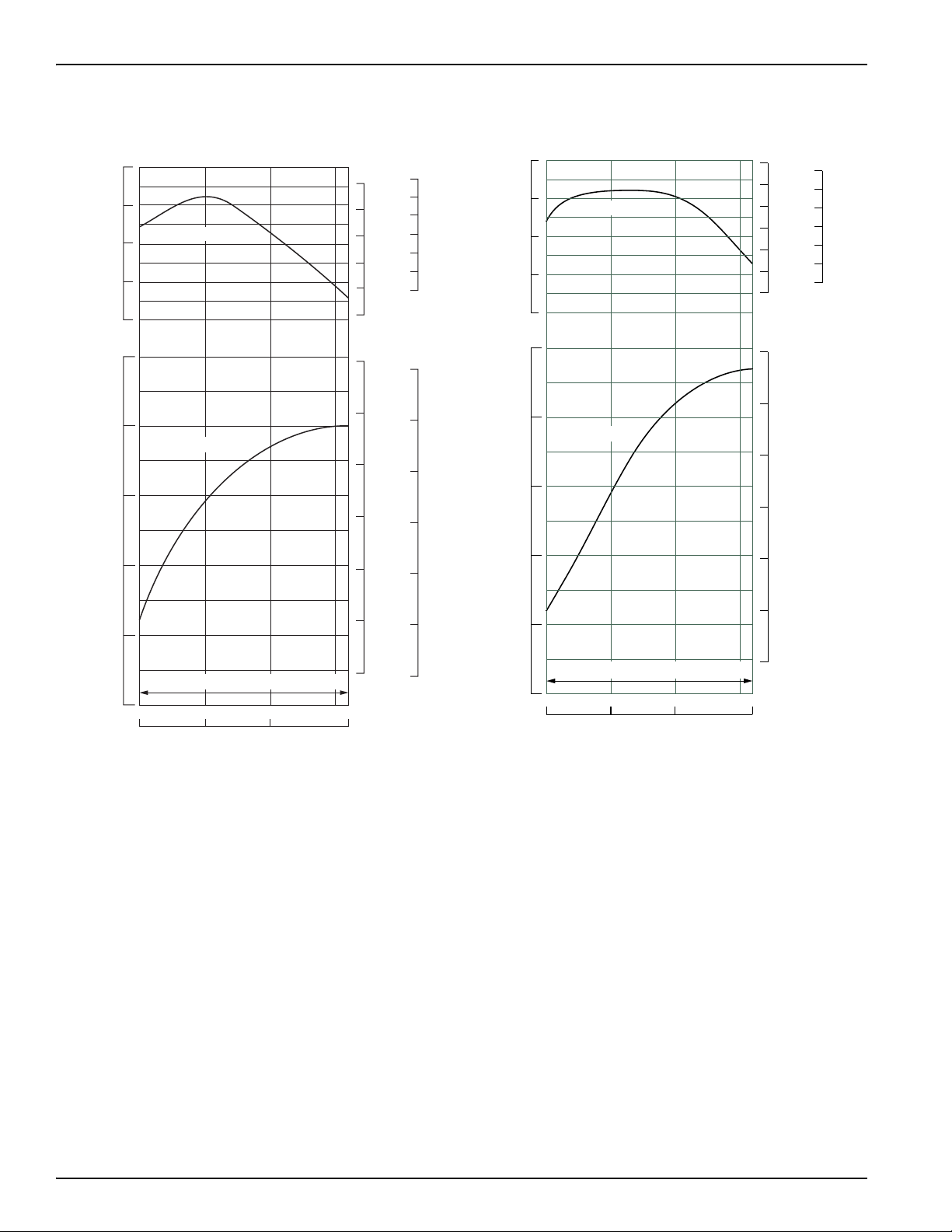
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
ENGINE SPEED
2000 36003000
RECOMMENDED OPERATING SPEED RANGE
(min-1 [TRO])
(N·m)
28
(KW)
(HP)
(lbf·ft)
(kgf·m)
9
8
7
OUTPUT
TORQUE
6
6
19
2.6
2.7
2.8
20
21
7
8
9
10
11
12
5
4
26
24
NET POWER
NET TORQUE
16
17
18
15
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.2
22
20
GX340 GX390
(N·m)
28
26
24
TORQUE
22
20
(KW)
9
8
7
OUTPUT
6
NET TORQUE
NET POWER
(lbf·ft)
20
19
18
17
16
15
(HP)
12
11
10
9
8
(kgf·m)
2.8
2.7
2.6
2.5
2.4
2.3
2.2
(PS)
12
11
10
9
8
5
RECOMMENDED OPERATING SPEED RANGE
4
2000 36003000
ENGINE SPEED
(rpm)
7
6
7
6
4 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved

GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
rpm with load
rpm without load
1-
()
100% ≤ 5%
Output Confirmation Methods
Governor Rod Measurement
When the engine is properly matched and operating at
its continuous rated load, the carburetor throttle angle
should be approximately half way between full open
and full closed positions.
Bring the engine to normal operating temperature and
then apply the expected continuous load. If the throttle
is more than halfway open, the engine is being
overloaded resulting in overheating and shortened
engine life.
Tachometer RPM Measurement
Normal governor droop can also be used to measure engine load.
At rated speed:
Engine is operating within the continuous recommended power range.
COOLING
Minimum Cooling Air Flow Requirement
Engine enclosure must have the minimum cooling air flow listed below.
3
GX240/GX270: 7 m
GX340/GX390: 8 m
Ambient Temperature Limits
-15 to +40°C (+5 to +104°F)
Testing
• Use thermocouple temperature probes at the specified locations.
• Operate the engine under worst-case conditions
• An electronic data logger is required for the temperature data collection
• Set up the data logger to take multiple readings per minute. If data is being taken manually, a reading every 5
minutes is adequate.
• Take readings until the engine oil temperature is stabilized at continuous rated load
• Run the application for one hour of continuous operation; the temperatures should be stabilized in that time. If the
application is used only for short intervals, note the normal run time in the application document.
• Shut the engine down and continue to take readings. Attempt to restart the engine after heat soaking for 5 minutes.
• For enclosed applications, fuel bowl temperature should be monitored after testing until the maximum is reached -
this may take several minutes
(247 ft3) per minute at 3,600 rpm
3
(282 ft3) per minute at 3,600 rpm
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 5
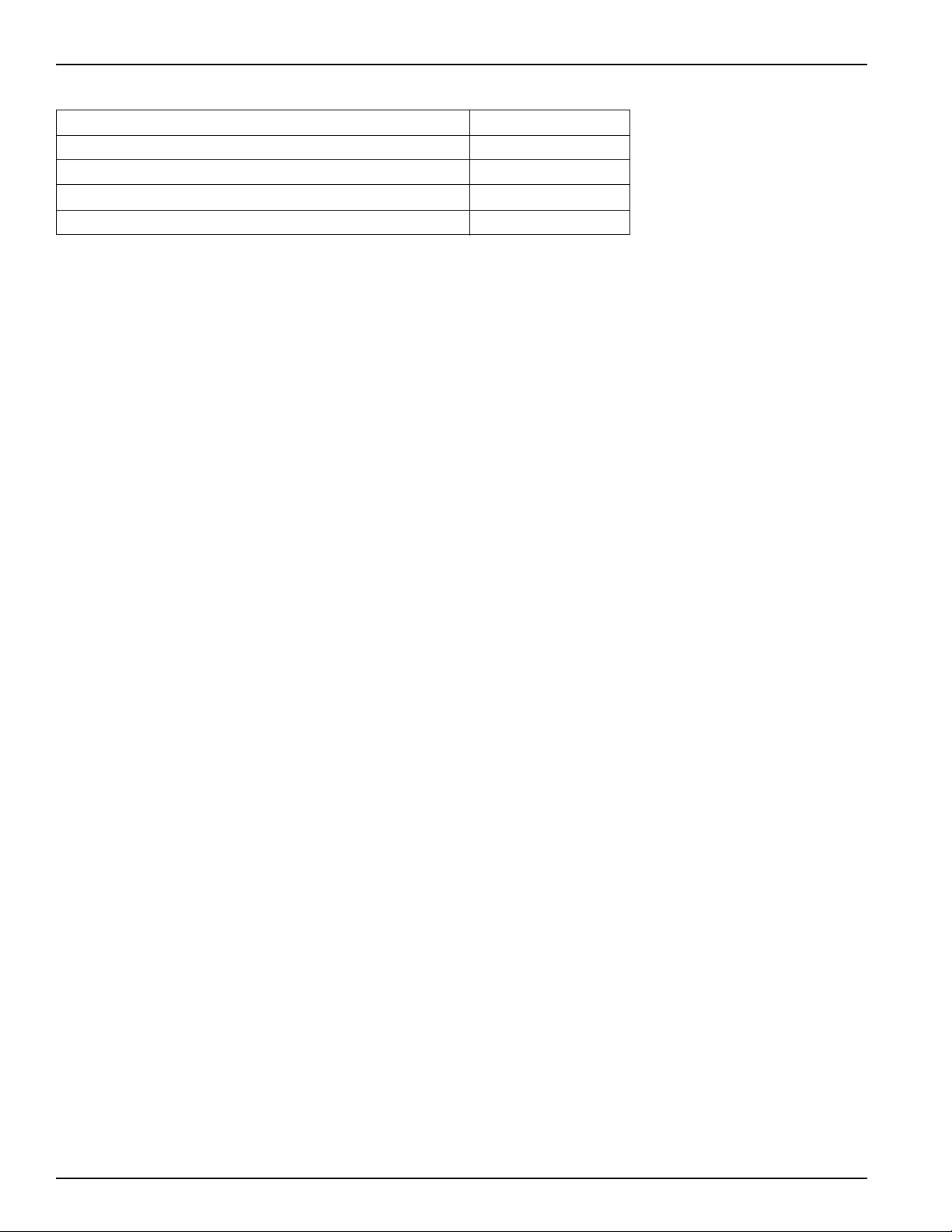
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
Maximum Operating Temperatures
Spark plug Seat 270 °C (482 °F)
Engine Oil 140 °C (284 °F)
Gasoline at Carburetor Float Bowl 60 °C (140 °F)
Gasoline at Carburetor Float Bowl (after 5 min. hot soak) <70 °C (158 °F)
Gasoline at Fuel Tank 60 °C (140 °F)
These temperatures are based on an ambient temperature of 40°C (104°F). Compensate for any deviation linearly; i.e.,
if the ambient temperature is 20°C (68°F), the maximum acceptable oil temperature is 120°C (248°F).
Adjusted oil temperatures of less than 40°C will require more frequent oil changes.
Engine Enclosures
When the engine installation in the equipment obscures the emission label, a duplicate label must be applied. In this
case, as part of the engine matching process, it will be necessary to establish a process for the OEM to obtain
duplicate labels. EPA requires full documentation, control, and record keeping of the duplicate label process.
Cool Air Intake
The engine must be provided with a cooling duct so that fresh air can be drawn directly from outside the enclosure
cover. Install the cooling air duct with the intake port in a place free from dust and dirt. The cooling air volume changes
according to the shape of the duct and screen and the engine installation conditions. Operate the engine under the
normal operating conditions and be sure that the engine meets all temperature requirements.
The cooling air duct must have a cross-sectional area of at least 300 cm
When the engine is operated in dusty areas, install a filter at the enclosure inlet for the cooling air. This will reduce the
effective area, so you must increase the size of the inlet accordingly. Increase the size of the inlet to the point where
the maximum operating temperatures are not exceeded when operated under maximum load.
Install the cooling air duct and filter so that the filter can be easily checked, and dust, dirt and foreign material removed.
2
(46.5 sq in).
Hot Air Discharge
Hot air must be discharged directly outside the enclosure. Provide a discharge duct if necessary. The minimum cross
section of the hot air discharge opening must be larger than that of the cooling air inlet.
Locate the discharge port so the hot discharge air does not flow back into the enclosure. Provide sufficient ventilation to
prevent the engine compartment temperature from rising above ambient temperature limits after the engine has been
stopped.
Exhaust Discharge
The exhaust system becomes hot during operation and remains hot for a while after operation. Separate the exhaust
system from the engine compartment with a partition wall and locate the exhaust system in the discharged cooling air
flow.
Be sure the exhaust gas is directly discharged outside the enclosure without being blocked or restricted by any
obstacles. The exhaust gas must not flow back or be drawn back into the enclosure.
Provide the engine with an exhaust deflector or exhaust pipe extension if necessary.
If an extension pipe is used:
• Keep the length of the pipe as short as possible to keep exhaust backpressure within limits (see page 10).
• The extension pipe must have an ID larger than the OD of the muffler outlet.
• Verify the exhaust pipe extension does not create excessive vibration at any given engine rpm. If necessary, use
an exhaust pipe holder to support the exhaust pipe extension.
Grass Cutting Applications
When the engine is operated on grass cutting equipment, install a rotary screen grid on the cooling air intake port to
prevent the accumulation of large clippings.
Do not allow the grass clippings shredded by the rotary screen grid to accumulate around the intake port.
6 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
FUEL SYSTEM
If the engine is supplied with an incomplete fuel system (no fuel tank, no fuel hose, etc.), the OEM is responsible for
ensuring evaporative emission requirements/regulations are met, including certification.
Fuel Tank Position
If a remote fuel tank is used, it must be installed so that its maximum gasoline level is within 50 cm (19.5 in) above the
carburetor gasoline level. If a fuel pump is used, the maximum fuel level should be within 50 cm (19.5 in) above or
below the carburetor gasoline level.
Fuel Line
Use a low permeation fuel line (displaying an Executive Order number) rated for use with gasoline. The fuel line should
have an inside dimension of 5.5 mm (0.22 in). Keep the fuel line as short as possible. Install the fuel line so it will not
rest against any sharp objects or make sharp bends that can restrict the flow of fuel. If the fuel line passes through an
enclosure wall, protect the line with a rubber grommet. Route the fuel line away from hot engine and exhaust system
components and away from electrical wiring. Secure the fuel line to prevent sagging and bending.
Fuel Valve Installation
If a remote fuel tank is used, a fuel valve should be installed so it is easily accessible. Install the fuel valve at the outlet
of the fuel tank and use an easily read label to indicate valve location and operation. If under the fuel tank is not the
ideal location, securely install the fuel valve in-line with the fuel tube in a cool location, so that engine heat cannot
cause vapor lock.
Fuel Pump
A fuel pump should be selected that provides a maximum operating pressure of 0.1 kgf/cm2 (1.4 psi) and delivers 15
liters/hr (4.0 US gal/hr). If a secondary fuel pump is used, to prevent carburetor flooding, its operating pressure must
not exceed the standard fuel pump’s operating pressure.
Fuel Tank Filter Installation
It is recommended that a fuel tank strainer with a mesh rating of #80 be installed at the fuel tank inlet to catch debris
when refueling. It is also recommended that a fuel tank sump be provided at the fuel tank outlet to reduce the chance of
contaminants entering the fuel system.
CONTROLS
Engine Switch
Use a three-position engine switch with continuity between its terminals as shown.
Wire Color
Switch Position
OFF
ON {{
START {{{{
EXT+
(Red)
EXT –
(Black)
ST
(Black/White)
BAT
(White)
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 7

GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
Flexible wire core
mounting
Solid wire core
mounting
WIRE
5mm
CIRCLIP
4 mm SCREW
WIRE HOLDER
THROTTLE
LEVER
OPTIONAL
THROTTLE LEVER
FRICTION NUT
WIRE HOLDER
4 mm SCREW
WIRE
5 mm CIRCLIP
SPRING
Carburetor Controls
Types of cable:
Two types can be used, flexible wire core or solid wire.
Installation:
The throttle and choke control levers are provided with holes for optional cable attachment. The following illustrations
show installation examples for a solid wire cable and for a flexible, braided wire cable. If using a flexible, braided wire
cable, add a return spring as shown. It is necessary to loosen the throttle lever friction nut when operating the throttle
with a remote-mounted control.
Remote Control Throttle
Remote Control Choke.
8 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Recommended Muffler
The recommended muffler and exhaust pipe are matched to the engine in terms of emissions performance, exhaust
backpressure, sound level, and durability.
Consider the following:
• Discharge the exhaust gas directly to the open air. Do not install flammable parts or any parts with poor heat
resistance properties around the exhaust system or near the discharge port.
• The exhaust gas must not enter the cooling-air intake port. Be especially careful when using the exhaust deflector
to change the discharge direction.
• The muffler and exhaust pipe become very hot during operation and remain hot after the engine has been shut off.
Install the muffler and exhaust pipe so the fuel system and other heat-sensitive components are isolated from the
exhaust heat.
Fabricated Exhaust Systems
The muffler type and the shape and length of the exhaust pipe(s) affect emissions performance and engine power. If
you use a muffler other than a recommended Honda muffler, observe the following precautions to maintain the
engine’s peak performance:
• The shape (bends and elbows) of the exhaust pipe can affect exhaust backpressure. If exhaust backpressure is
excessive, it can affect emissions performance and/or cause detonation.
• The exhaust pipe inside diameter must be the same size as the exhaust port diameter.There must be no gap
between the port inside diameter and the exhaust pipe ID.
• The exhaust backpressure increases if the diameter is less than specified. If the diameter is larger than specified,
the effective width of the exhaust gasket is reduced which could cause an exhaust leak.
• When the exhaust pipes are connected together before the muffler, make sure that the exhaust pipe length is as
short as possible to reduce backpressure.
• Muffler volume and design will affect exhaust backpressure. Increase the volume of the muffler if exhaust
backpressure is higher than specified.
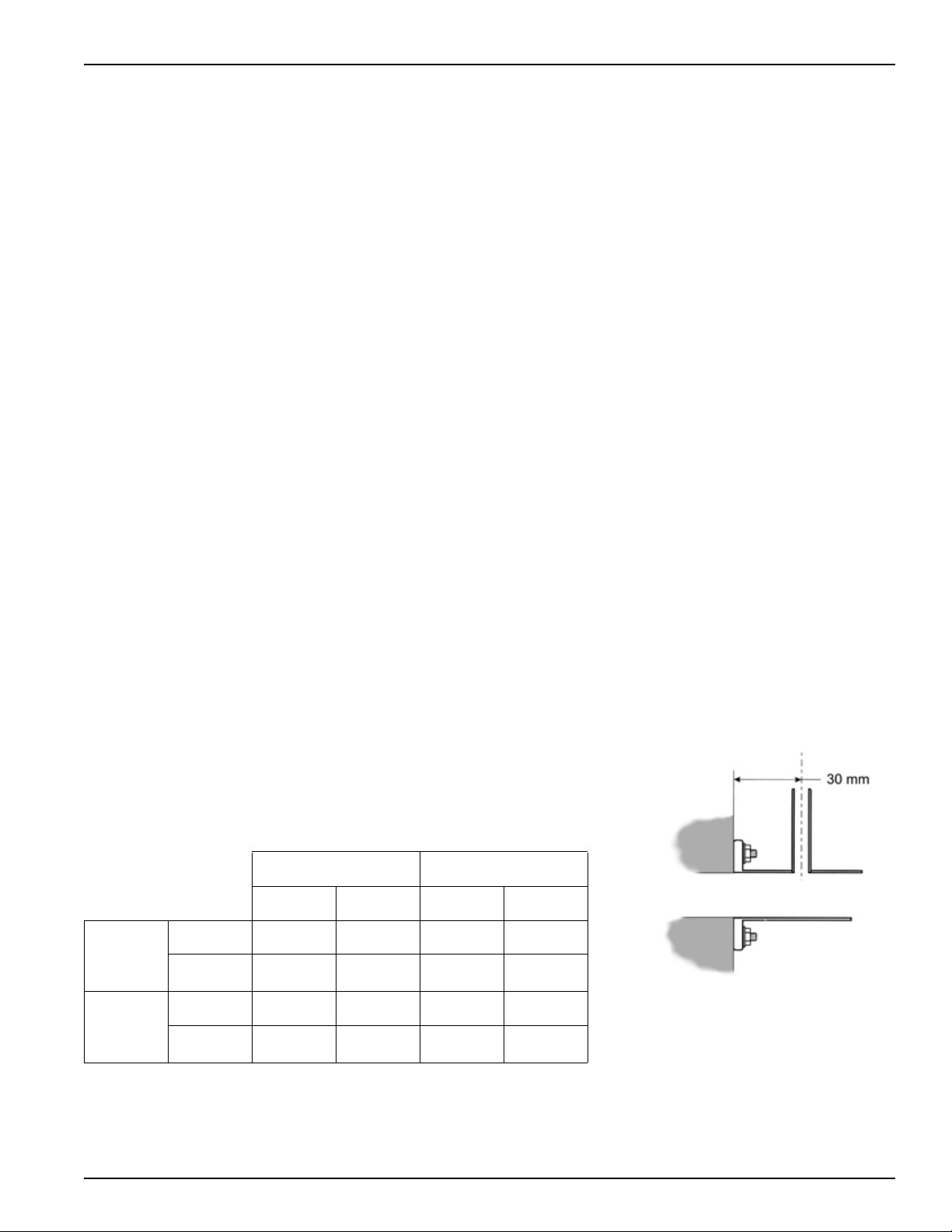
Exhaust Back Pressure Measurement
Measure the exhaust back pressure at the exhaust pipe with the engine under
continuous load (WOT), 30 mm (1.2 in) from the exhaust pipe mounting flange
as shown (make sure the test nipple does not extend beyond the inner wall of
the exhaust pipe).
3000 rpm 3600 rpm
Min. Max Min. Max
GX240
GX270
kPa 4.2 9.0 4.9 11.0
mmH
O 428 918 500 1122
2
GX340
GX390
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 9
kPa 4.6 10.5 6 12.5
mmH
O 469 1071 612 1275
2
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
Rigid Engine Mount Muffler Installation.
The frame must be rigid to prevent cracking when the exhaust pipe and muffler are connected. The muffler should be
installed securely with bolts and nuts.
The muffler should be supported at two points (or more) using special rubber mounts designed for muffler support
applications.
Check to see muffler vibration does not increase at any given engine speed, causing an abnormal increase in
resonance.
Rubber Engine Mount Muffler Installation
A flexible pipe should be used between the muffler and exhaust pipe when the engine is mounted to the engine bed
with rubber mounts. The flexible pipe ID must be the same as the exhaust pipe OD or larger.
The muffler should be supported at two points (or more) and should be installed securely with bolts and nuts to prevent
muffler cracking from vibration during starting and stopping.
Check to see muffler vibration does not increase at any given engine speed, causing an abnormal increase in
resonance.
ENGINE MOUNTING
Use an engine bed or frame with enough rigidity to allow maximum durability
of the engine and attachment installation.
The engine must not wobble on the engine bed. Use an engine bed or frame
that provides a flat surface for the engine to be mounted on. If there is a gap
between the engine and the engine bed, the engine-mounting surface may
be damaged.
Inclination
Horizontal mounting and operation of the engine is recommended. If the
engine must be operated on a slope, the incline position of the engine must
not exceed 20° in any direction.
Resonance Check
There must be no resonance when the engine and attachment are operated within the designated speed range. Slowly
raise the engine speed from idle to maximum and check for resonance at any engine speed.
General Methods for Preventing Resonance
When engine accessories or a part of the attachment is resonating, increase the rigidity of the resonating part to bring
the resonance point higher than the working engine speed range.
• Increase the rigidity of the engine bed and frame to bring the resonance point higher than the working engine
speed range.
• Install the muffler on the engine body, using a rigid stay to prevent resonance of the muffler when the engine speed
is within the specific operating speed range.
10 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
HORIZONTAL
VERTICAL
LATERAL
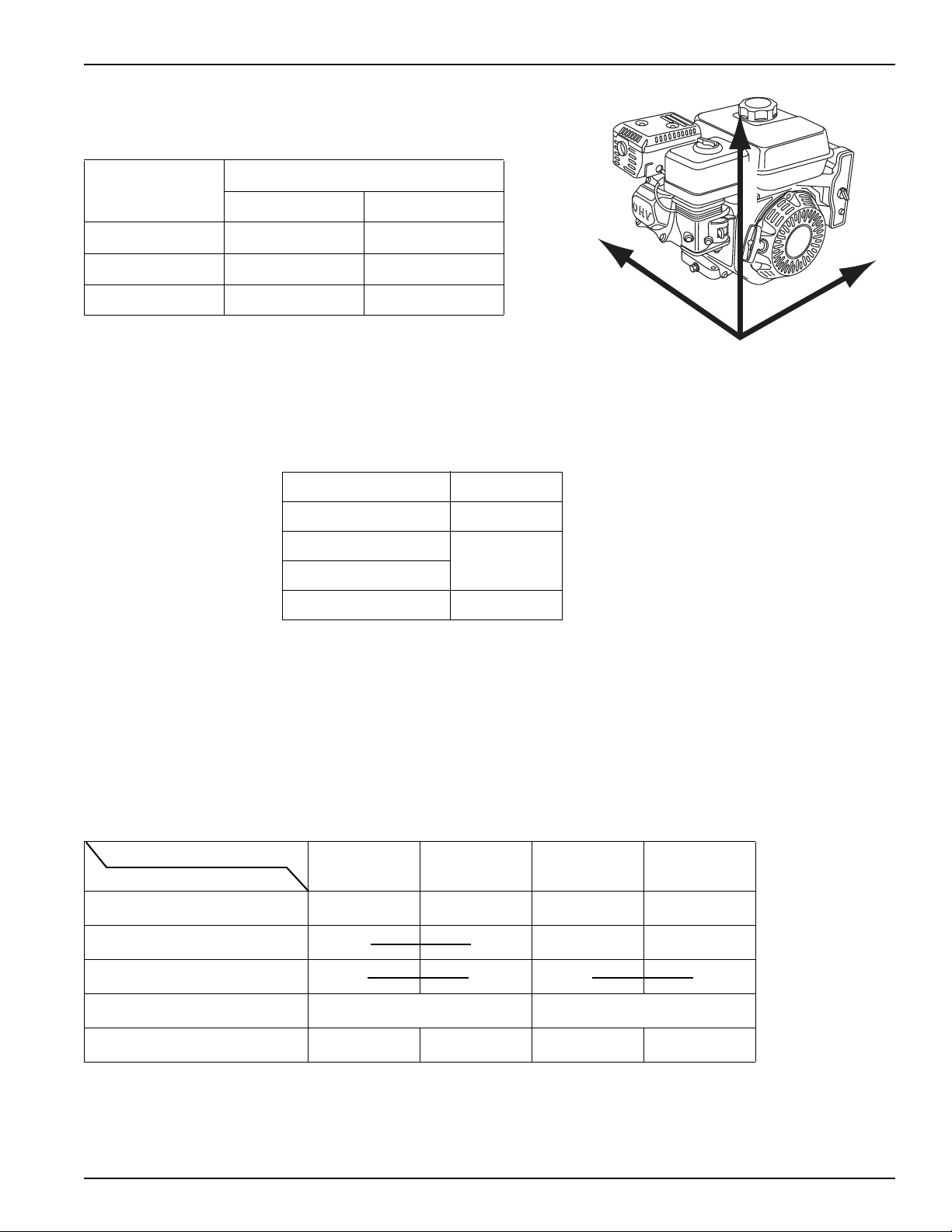
Engine Acceleration/Vibration
Using a vibration meter, measure the vibration amplitude at the base
on three axis (vertical, lateral and horizontal).
Direction Allowable G value
(Peak) (RMS)
Vertical 10 (98 m/s
Horizontal 5.9 (58 m/s
Lateral 6.9 (68 m/s
2
)6.9 (68 m/s
2
)4.2 (41 m/s
2
)4.9 (48 m/s
2
)
2
)
2
)
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Battery
Use a 12 V battery with a minimum capacity of 24AH.
Fuse
Recommended fuse size:
Charging system (A) Fuse (A)
1.0 5
3.0
10.0
18.0 25
15
Battery Cables
Select battery cables to avoid greater than 0.5 volt drop in the cable during starter motor operation.
Battery cable size and length: (Gauge x Length)
Positive cable: AWG No. 4 x 1.5 m (5.0 ft) maximum
Negative cable: AWG No. 4 x 2.3 m (7.5 ft) maximum
Engine Switch
Electric start
Use a three-position engine switch with continuity between its terminals as shown.
Wire Color
Switch Position
OFF
ON {{
EXT+
(Red)
EXT –
(Black)
ST
(Black/White)
BAT
(White)
START {{{{
Vdc/A (rated) AC300V, 220mA (PEAK) 12/15A
Dia. (recommended) AV0.5 AV0.5 AV2.0* AV0.75
* In combination with 1A/3A/10A charge coil, AV1.25 is acceptable.
AV0.5 = Automotive Vinyl, 0.5 mm
2
cross-sectional area
Do not run the starter motor for more than 5 seconds at a time. Always allow resting for 10 seconds before each
starting attempt.
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 11

GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
Manual start
Use a two-position engine switch with continuity between its terminals as shown.
Wire Color
Switch Position
OFF
ON {{
EXT+
(Red)
EXT –
(Black)
Charging Coil Selection
Four types of coils are available:
Coil Output (A) Regulated RPM
1A 0.9 No
3A 2.7 No
10A 9.5 Yes
18A 17.0 Yes
The 1A and 3A coils are only suitable for recharging a starting battery. Use the 10A or 18A coils when powering
accessories.
3,600
Lamp Coil Kit (optional)
Three types of lamp coils are available: 6v –25w, 12v –15w, 12v –25w. Two coils can be installed in parallel to provide
12V-50W, if no charging coils are applied. Use parallel connector (No. 32105-ZE1-000) to connect two coils in parallel.
A single coil (12v-25w) can be used in combination with the 3A charge coil as required.
Oil Alert® System (optional)
The Oil Alert System uses a float type switch located inside the crankcase. When the engine oil level falls below a safe
operating level, the float falls and the circuit is completed through the control box, grounding the primary side of the
ignition coil. The Oil Alert System is only recommended for use on equipment that is stationary while operating.
Wiring Precautions
• Connect the battery positive (+) cable to the positive terminal of the starter solenoid.
• Connect the battery negative (–) cable to the engine crankcase or engine frame mounting bolt.
• Do not route the battery cables on or near any hot, moving, or rotating parts, or sharp edges. Keep the battery
cables and electrical wires away from the fuel line.
• Protect positive electrical connections with a cover or insulation.
12 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
LED
OIL_ALT
EXT ( - )
EXT ( + )
R
Bl
R
Bl
Y
Y
C2
C1
1
4 3 1 2
C3
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
OIL LEVEL
SWITCH
ENGINE STOP
SWITCH
Bl Black
Y Yellow
Bu Blue
G Green
R Red
W White
Br Brown
O Orange
Lb Light blue
Lg Light green
P Pink
Gr Gray
TWO COLORED WIRE (EXAMPLE:YELLOW/RED)
EXT ( + ) EXT ( - )
OFF
ON
ENGINE STOP SWITCH
LED
OIL_ALT
EXT ( - )
EXT ( + )
ST
EXT ( + )
EXT ( - )
BAT
( Bl/W )
( W )
R
Gr
Gr
Gr
Gr
W
W
Bl
Gr
Gr
Gr
Gr
Bl/Y
W
Bl
W/Bu
Bl
Y
Y
Bl/W
( Bl )
R
Bl
W
W W
(W)
R
Bl
(W)
R
Bl
Bl
3
C10
C2
C1
C9
C8
T2
T3
1
4312
C3
C11
C4T1
T4
CONTROL BOX
COMBINATION
SWITCH
STARTER MOTORBATTERY
CHARGE
COIL
REGULATOR/
RECTIFIER
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
OIL LEVEL
SWITCH
Bl Black
Y Yellow
Bu Blue
G Green
RRed
W White
Br Brown
O Orange
Lb Light blue
Lg Light green
P Pink
Gr Gray
TWO COLORED WIRE (EXAMPLE:YELLOW/RED)
EXT ( + ) EXT ( - ) ST BAT
OFF
ON
START
461235
COMBINATION
SWITCH
MAIN FUSE
CHARGE
COIL
FLYWHEEL
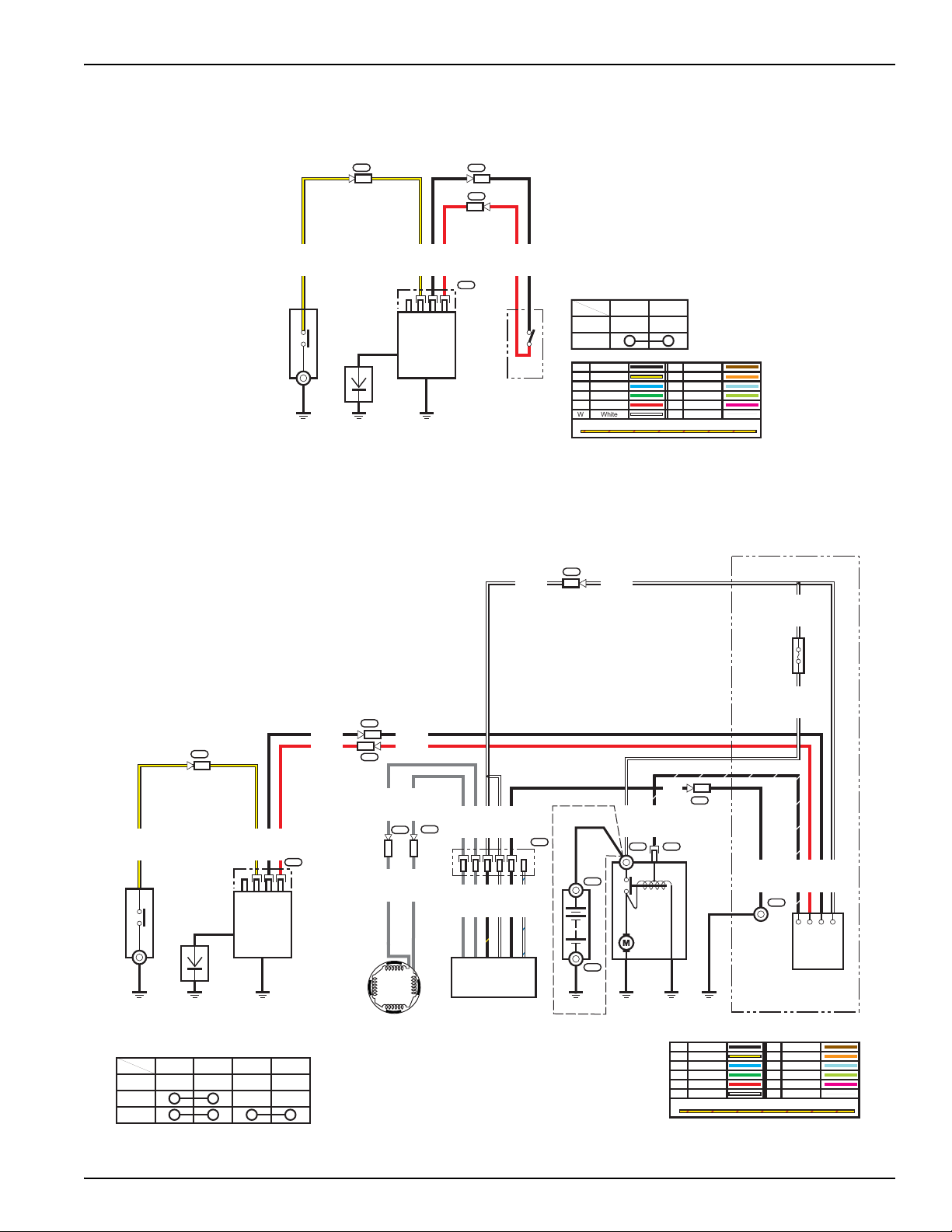
WIRING DIAGRAMS
No Charge Coil Models
Electric Start Models
18A Charging System
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 13
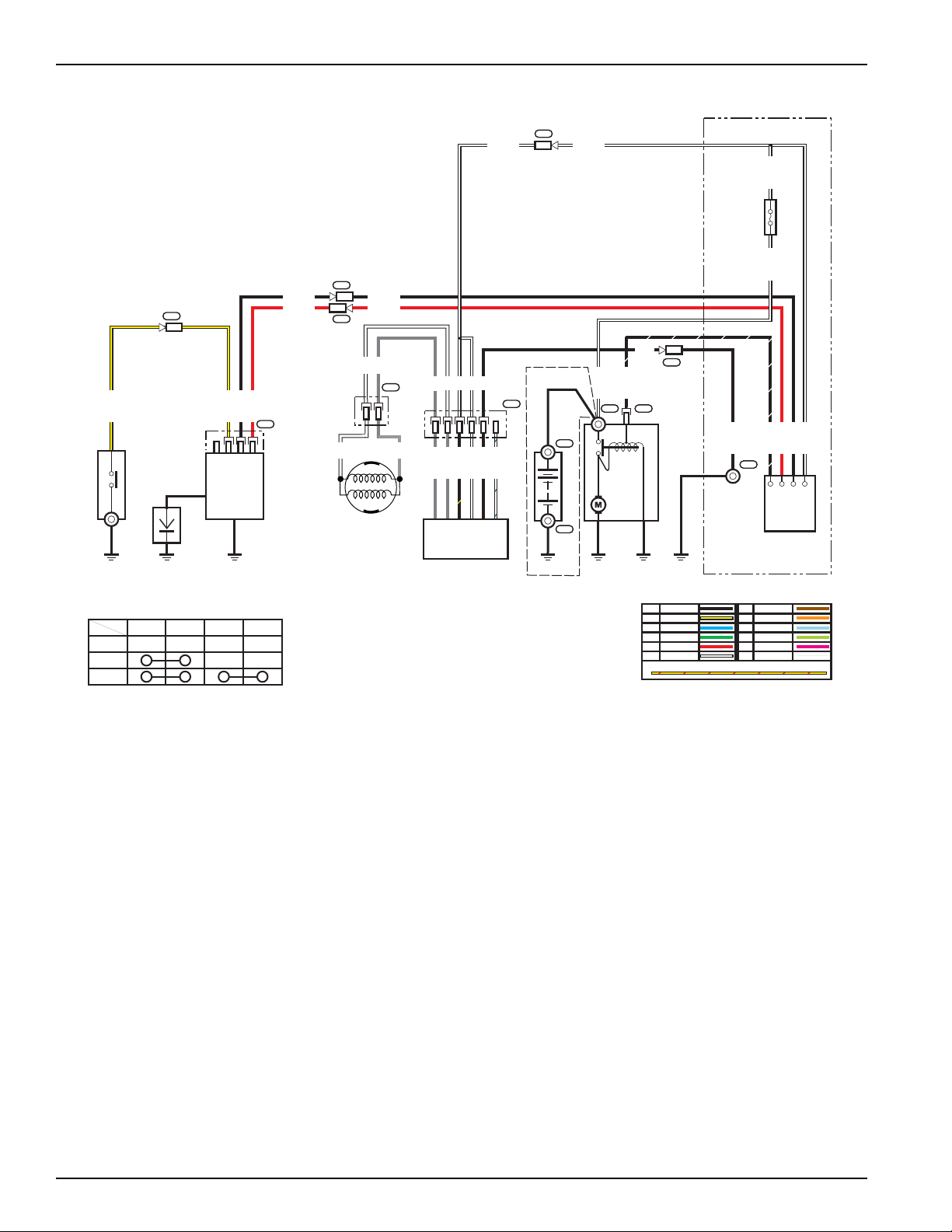
10A Charging System
LED
OIL_ALT
EXT ( - )
EXT ( + )
ST
EXT ( + )
EXT ( - )
BAT
( Bl/W )
( W )
R
W
WGrW
Bl
Gr
Gr
Bl/Y
W
Bl
W/Bu
Bl
Y
Y
Bl/W
( Bl )
R
Bl
W
W W
(W)
R
Bl
(W)
R
Bl
Bl
3
C10
C2
C1
T2
T3
1
4312
C3
C11
C4T1
T4
CONTROL BOX
COMBINATION
SWITCH
STARTER MOTORBATTERY
REGULATOR/
RECTIFIER
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
OIL LEVEL
SWITCH
Bl Black
Y Yellow
Bu Blue
G Green
RRed
W White
Br Brown
O Orange
Lb Light blue
Lg Light green
P Pink
Gr Gray
TWO COLORED WIRE (EXAMPLE:YELLOW/RED)
EXT ( + ) EXT ( - ) ST BAT
OFF
ON
START
461235
COMBINATION
SWITCH
MAIN FUSE
4
12
Gr
W
Gr
W
CHARGE COIL
FLYWHEEL
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
14 © 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved
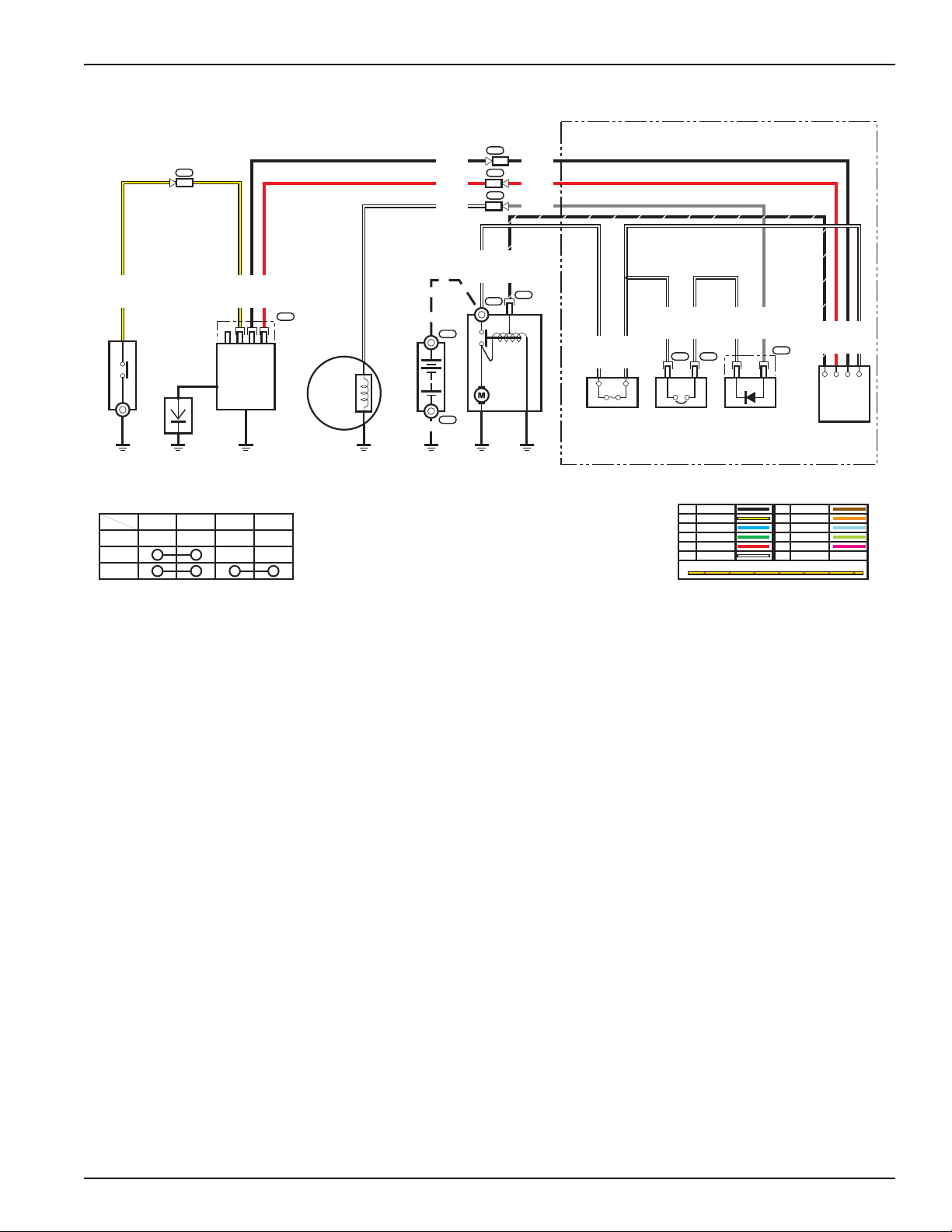
GX240 • GX270 • GX340 • GX390 (UT2/RT2) Technical Manual
LED
OIL_ALT
EXT ( - )
EXT ( + )
ST
EXT ( + )
EXT ( - )
BAT
( Bl/W )
( W )
R
Bl
Y
( Y )
( W )
( W )
( W )
( W )
( W )
( Gr )
( Bl/W )
( R )
( Bl )
( W )
W
( R )
( Bl )
Gr
( R )
( Bl )
C6
C4
C5
C2
C1
T1
T2
T3
1
4 3 1 2
2 1
C3
C7
2
CONTROL BOX
COMBINATION
SWITCH
SILICON
RECTIFIER
CIRCUIT
PROTECTOR
MAIN FUSE
STARTER MOTOR BATTERY CHARGE
COIL
IGNITION
COIL
SPARK
PLUG
OIL LEVEL
SWITCH
Bl Black
Y Yellow
Bu Blue
G Green
R Red
W White
Br Brown
O Orange
Lb Light blue
Lg Light green
P Pink
Gr Gray
TWO COLORED WIRE (EXAMPLE:YELLOW/RED)
EXT ( + ) EXT ( - ) ST BAT
OFF
ON
START
COMBINATION
SWITCH
1A/3A Charging System
© 2010 American Honda Motor Co., Inc — All Rights Reserved 15
 Loading...
Loading...