Page 1

GE
Measurement & Control Flow
T5 Flare Gas Transducer
(Standard and Extended Velocity Range)
Installation Guide
916-117 Rev. D
November 2014
Page 2

Page 3

GE
Measurement & Control
T5 Flare Gas Transducer
(Standard and Extended Velocity Range)
Installation Guide
916-117 Rev. D
November 2014
www.ge-mcs.com
©2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Technical content subject to change without notice.
Page 4

[no content intended for this page]
ii
Page 5

Preface
Information Paragraphs
Note: These paragraphs provide information that provides a deeper understanding of the situation, but is not
essential to the proper completion of the instructions.
IMPORTANT: These paragraphs provide information that emphasizes instructions that are essential to proper setup of
the equipment. Failure to follow these instructions carefully may cause unreliable performance.
CAUTION! This symbol indicates a risk of potential minor personal injury and/or severe damage to
the equipment, unless these instructions are followed carefully.
WARNING! This symbol indicates a risk of potential serious personal injury, unless these instructions
are followed carefully.
Safety Issues
WARNING! It is the responsibility of the user to make sure all local, county, state and national codes,
regulations, rules and laws related to safety and safe operating conditions are met for each
installation.
WARNING! For installations in potentially hazardous areas, be sure to read the Certification and
Safety Statements document at the end of this manual before beginning the installation.
Auxiliary Equipment
Local Safety Standards
The user must make sure that he operates all auxiliary equipment in accordance with local codes, standards,
regulations, or laws applicable to safety.
Working Area
WARNING! Auxiliary equipment may have both manual and automatic modes of operation. As
equipment can move suddenly and without warning, do not enter the work cell of this equipment
during automatic operation, and do not enter the work envelope of this equipment during manual
operation. If you do, serious injury can result.
WARNING! Make sure that power to the auxiliary equipment is turned OFF and locked out before
you perform maintenance procedures on the equipment.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide iii
Page 6
Preface
Qualification of Personnel
Make sure that all personnel have manufacturer-approved training applicable to the auxiliary equipment.
Personal Safety Equipment
Make sure that operators and maintenance personnel have all safety equipment applicable to the auxiliary equipment.
Examples include safety glasses, protective headgear, safety shoes, etc.
Unauthorized Operation
Make sure that unauthorized personnel cannot gain access to the operation of the equipment.
Environmental Compliance
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive
GE Measurement & Control is an active participant in Europe’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
take-back initiative, directive 2012/19/EU.
The equipment that you bought has required the extraction and use of natural resources for its production. It may
contain hazardous substances that could impact health and the environment.
In order to avoid the dissemination of those substances in our environment and to diminish the pressure on the natural
resources, we encourage you to use the appropriate take-back systems. Those systems will reuse or recycle most of the
materials of your end life equipment in a sound way.
The crossed-out wheeled bin symbol invites you to use those systems.
If you need more information on the collection, reuse and recycling systems, please contact your local or regional
waste administration.
Visit http://www.ge-mcs.com/en/about-us/environmental-health-and-safety/1741-weee-req.html
take-back instructions and more information about this initiative.
for
iv T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
1.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.2 Bias 90° Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
1.2.2 Selecting and Marking the Pipe for Nozzle Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.2.3 Installing the First Welding Boss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
1.2.4 Installing the First Nozzle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.2.5 Installing the Second Welding Boss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
1.2.6 Installing the Second Nozzle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
1.2.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
1.2.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
1.3 Tilted 45° Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
1.3.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
1.3.2 Selecting and Marking the First Nozzle Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
1.3.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
1.3.4 Installing the First Welding Boss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
1.3.5 Installing the First Nozzle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
1.3.6 Installing the Second Welding Boss and Nozzle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
1.3.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
1.3.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
2.1 Bias 90° Installation (Standard or Extended Velocity Range). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.1.1 For 3 inch Flanges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.1.2 For 2 inch Flanges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.2 Tilted 45° Installation (Standard Velocity Range). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.2.1 For 3 inch Flanges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.2.2 For 2 inch Flanges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.3 Tilted 45° Installation (Extended Velocity Range) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide v
Page 8

Contents
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
3.2 Using the Low-Pressure Insertion Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
3.2.1 Preparing for Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
3.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
3.3 Mounting the Bias 90 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
3.4 Inserting the Bias 90 Transducer into the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
3.5 Aligning the Transducers (Standard Velocity Range). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
3.6 Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.8 Inserting the Tilted 45 Transducer into the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
3.9 Connecting an XAMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Chapter 4. Specifications
4.1 T5 Transducer Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
4.2 T5 Transducer Certifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
vi T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 9

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
1.1 Introduction
Before the T5 transducers can be installed into the pipe, you will need to install pipe nozzles. Nozzles may be installed
as part of a fabricated spoolpiece or by using the hot or cold tap process with a GE Sensing Nozzle Installation Kit.
IMPORTANT: This procedure only applies if you are using a Nozzle Installation Kit. If you are tapping the pipe
without using a Nozzle Installation Kit, refer to the supplied drawings in your shipment. This procedure
is written and illustrated for installations on horizontal pipes. However, the procedure is the same for
vertical pipe installations.
This section describes how to install nozzles in the following configurations:
1. Bias 90
• Standard transducer spacings of 10” and 9”, with both transducers facing straight at each other, are for
• A shorter transducer spacing of 6.4”, with only the downstream transducer rotated 6° into the flow is for
o
Installation
applications with gas velocities up to 100 m/s (328 ft/s). This is the standard velocity range.
applications with gas velocities up to 120 m/s (394 ft/s). This is the extended velocity range.
o
2. Tilted 45
Installation
• Standard transducer face to face spacings, with both transducer body axes concentric and parallel to each
other are for applications with gas velocities up to 100 m/s (328 ft/s). This is the standard velocity range.
• A shorter transducer face to face spacing of approximately 7.85”, with only the downstream transducer
tilted 6° into the flow, is for applications with gas velocities up to 120 m/s (394 ft/s). This is the extended
velocity range.
1.2 Bias 90
This procedure includes the following steps:
°
Installation
• Identifying and checking the nozzle installation kit components
• Selecting and marking the pipe for nozzle locations
• Installing the first welding boss
• Installing the first nozzle
• Installing the second welding boss
• Installing the second nozzle
• Tapping the pipe
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 1
Page 10
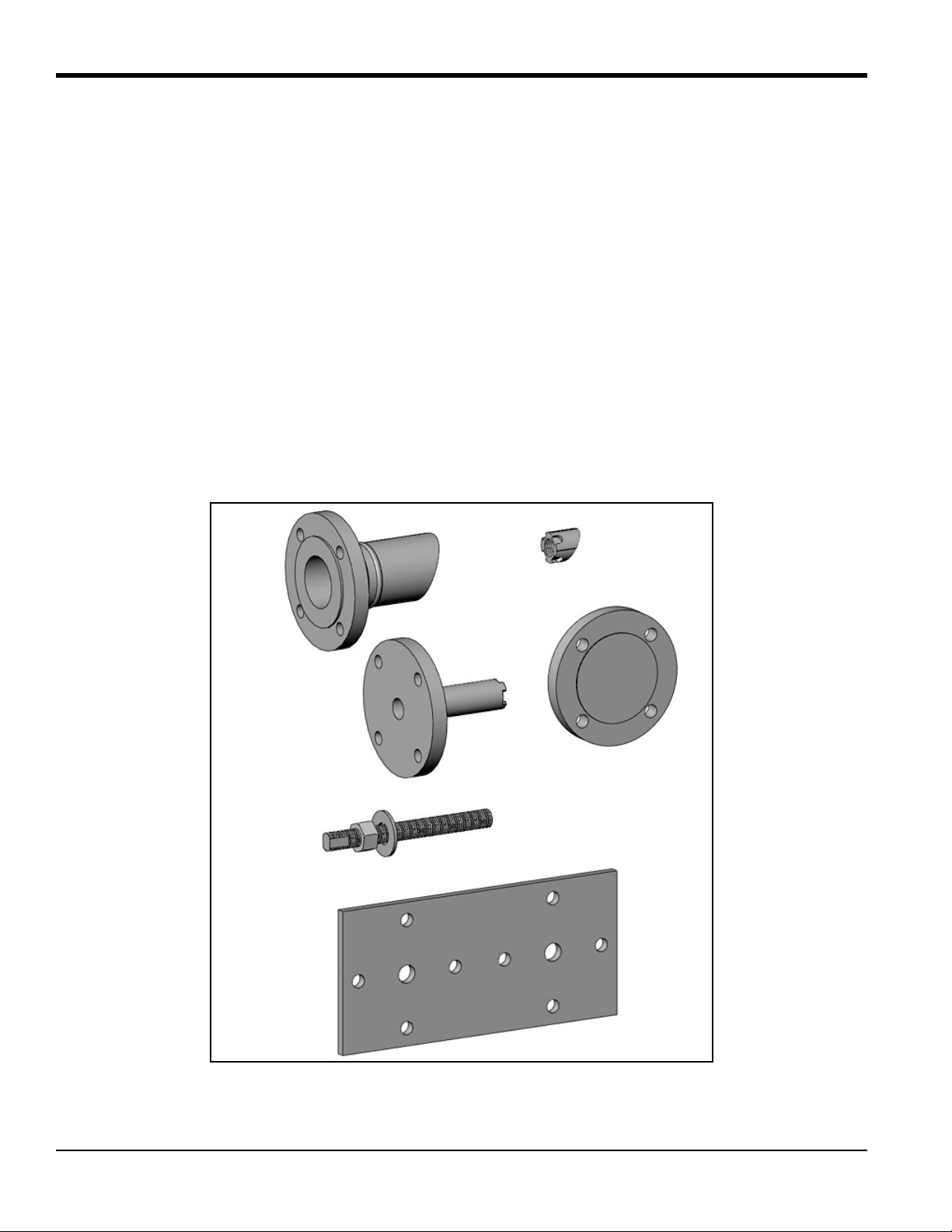
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Welding Boss
Nozzle
Jig
Spacer Flange
Alignment
Threaded Rod
with Washer and Nut
Plate
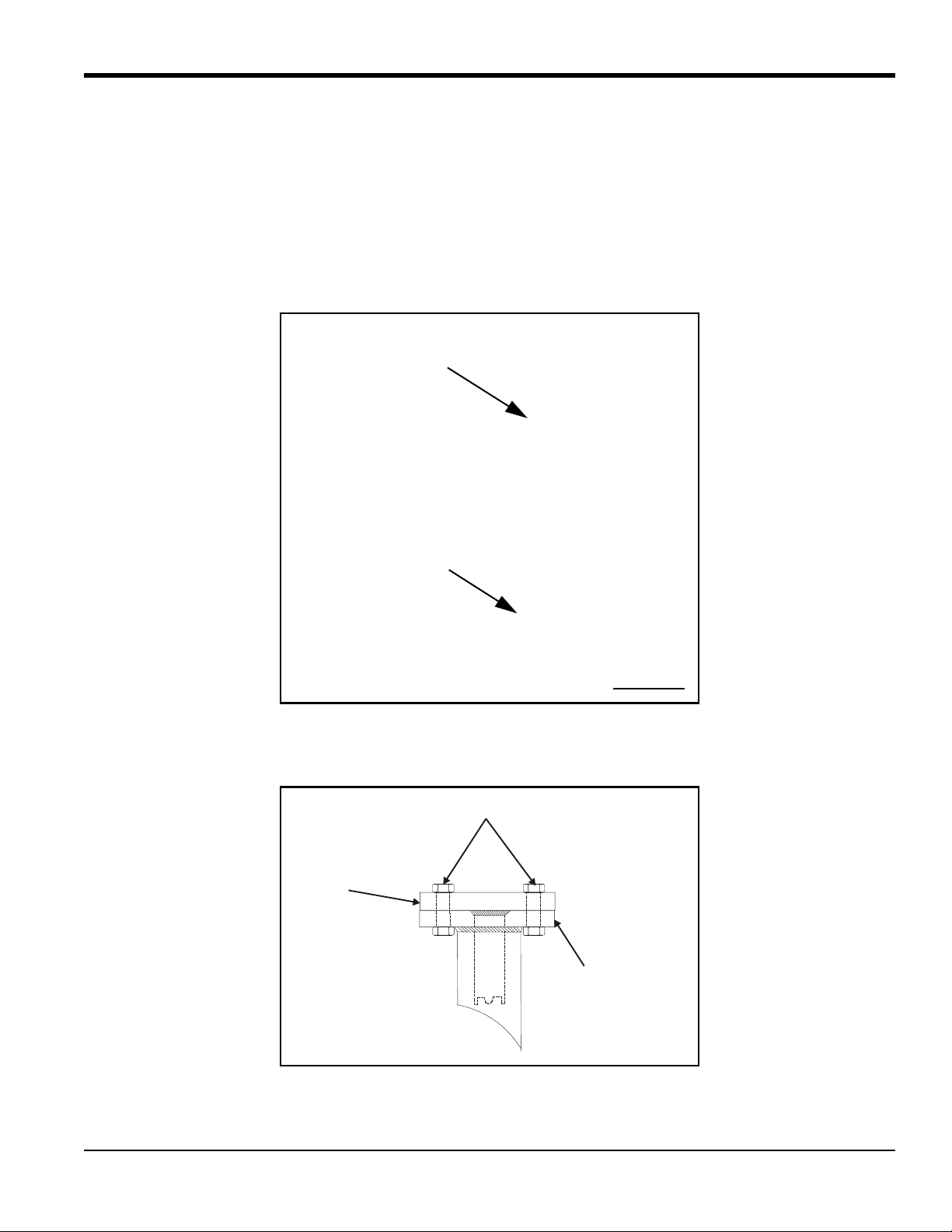
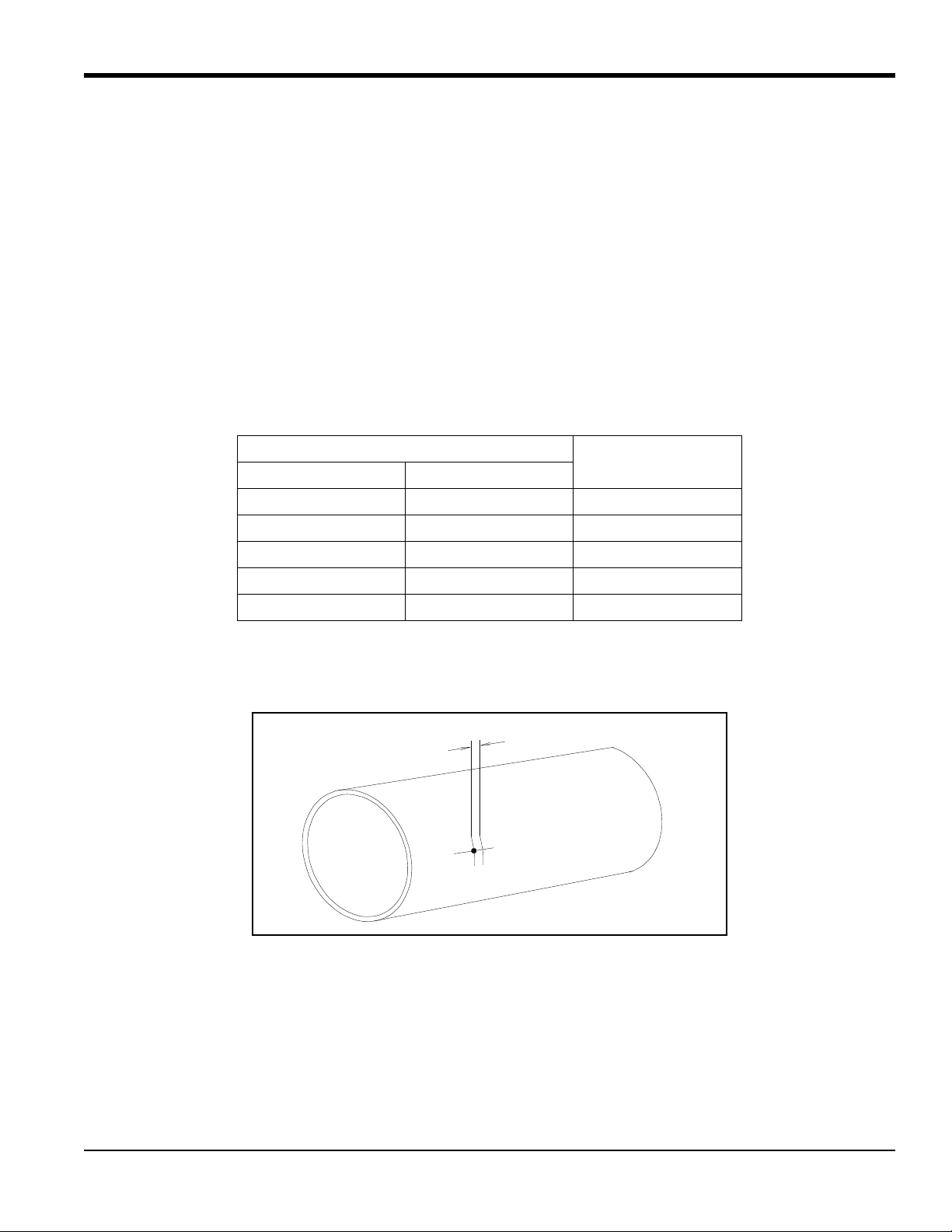
1.2.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components
The Nozzle Installation Kit contains the materials listed below. Use Figure 1 below to help identify each component.
• 2 Nozzles (if purchased)
• 2 Welding bosses
• 1 Jig
• 1 Alignment plate (9”, 10” or 6.4” spacing)
• 1 Spacer flange
• 1 Threaded rod (1” diameter), with washer and nut
IMPORTANT: You will need eight 5/8” studs with two nuts each, or 3/4” studs with two nuts each. The 5/8” studs are
needed for 2”-150#, 2”-300# and 3”-150# flanges. The 3/4” studs are needed for 3”-300# flanges.
After you are familiar with each component, verify that the welding bosses and alignment plate shipped are for the
required transducer spacing and the pipe size described in the following steps.
Figure 1: Components for Nozzle Installation Kit
2 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 11
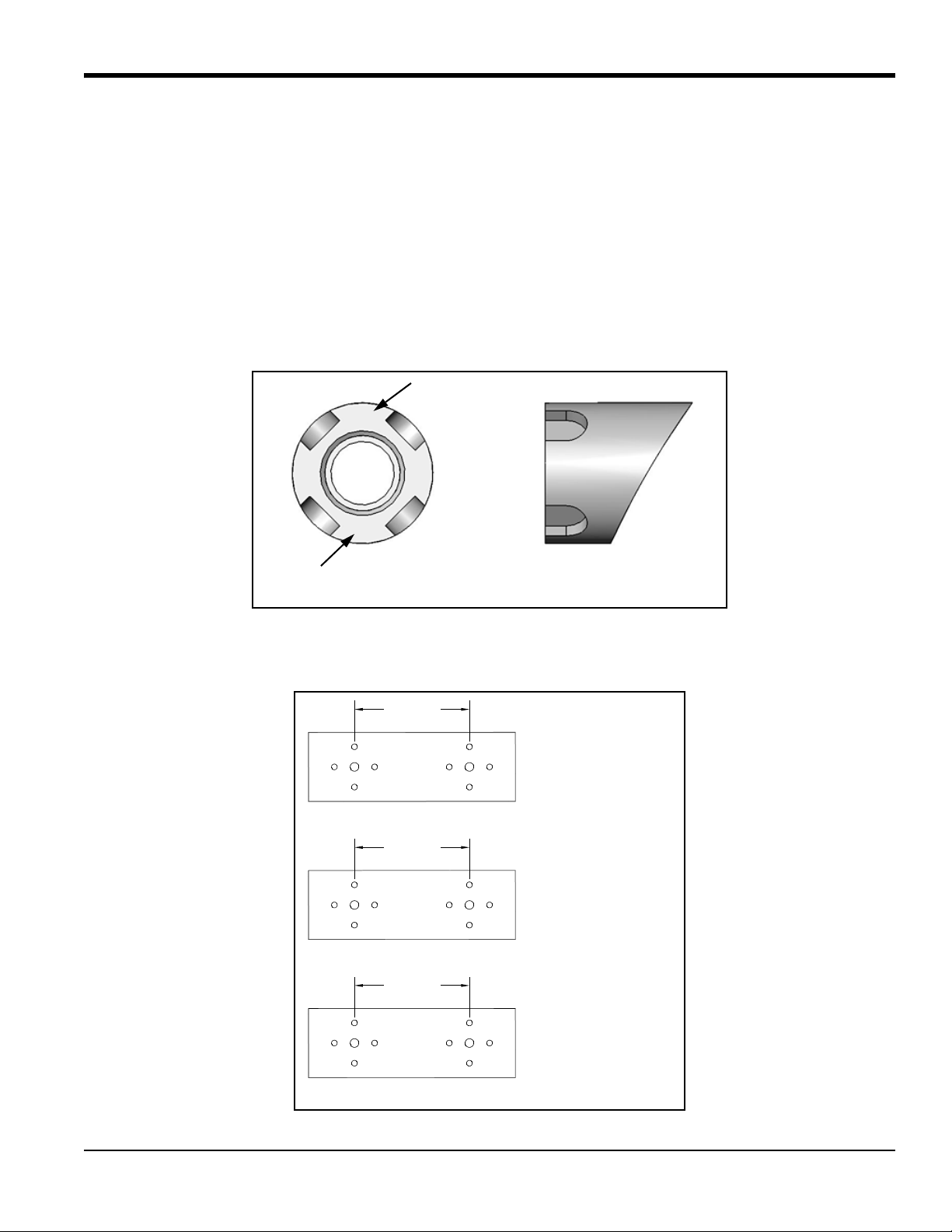
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
36 in.
5 in.
Bias Dimension (Spacing)
Pipe O.D.
3.4 in. Bias = 6.4 in. Spacing
4.5 in. Bias = 9 in. Spacing
5 in. Bias = 10 in. Spacing
12.73 in.
4.5 in. Bias (9 in. Spacing)
14.14 in.
5 in. Bias (10 in. Spacing)
9.05 in.
3.2 in. Bias (6.4 in. Spacing)
Bolt location shown
for 150# rating.
1.2.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components (cont.)
1. Check the marking on the end of the welding boss. The pipe O.D. and the bias dimension (i.e., the transducer
spacing) are engraved on the boss as shown below. Typically,
• For flow velocities up to 100 m/s (328 ft/s), the 10 in. spacing is used on pipes 18 in. (450 mm) in diameter
or larger, while the 9 in. spacing is used on pipes 16 in. (400 mm) in diameter or on larger pipes when
attenuating gases are present.
• For flow velocities up to 120 m/s (394 ft/s), the 6.4 in. spacing is used on pipes 14 in. (356 mm) in
diameter or larger.
Note: Bias dimension refers to the distance between the center of the nozzle location and the center line of the pipe.
2. Check the spacing between the holes on the alignment plate, as shown below. The dimensions should
correspond to the bias/spacing dimension on the welding boss.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 3
Page 12
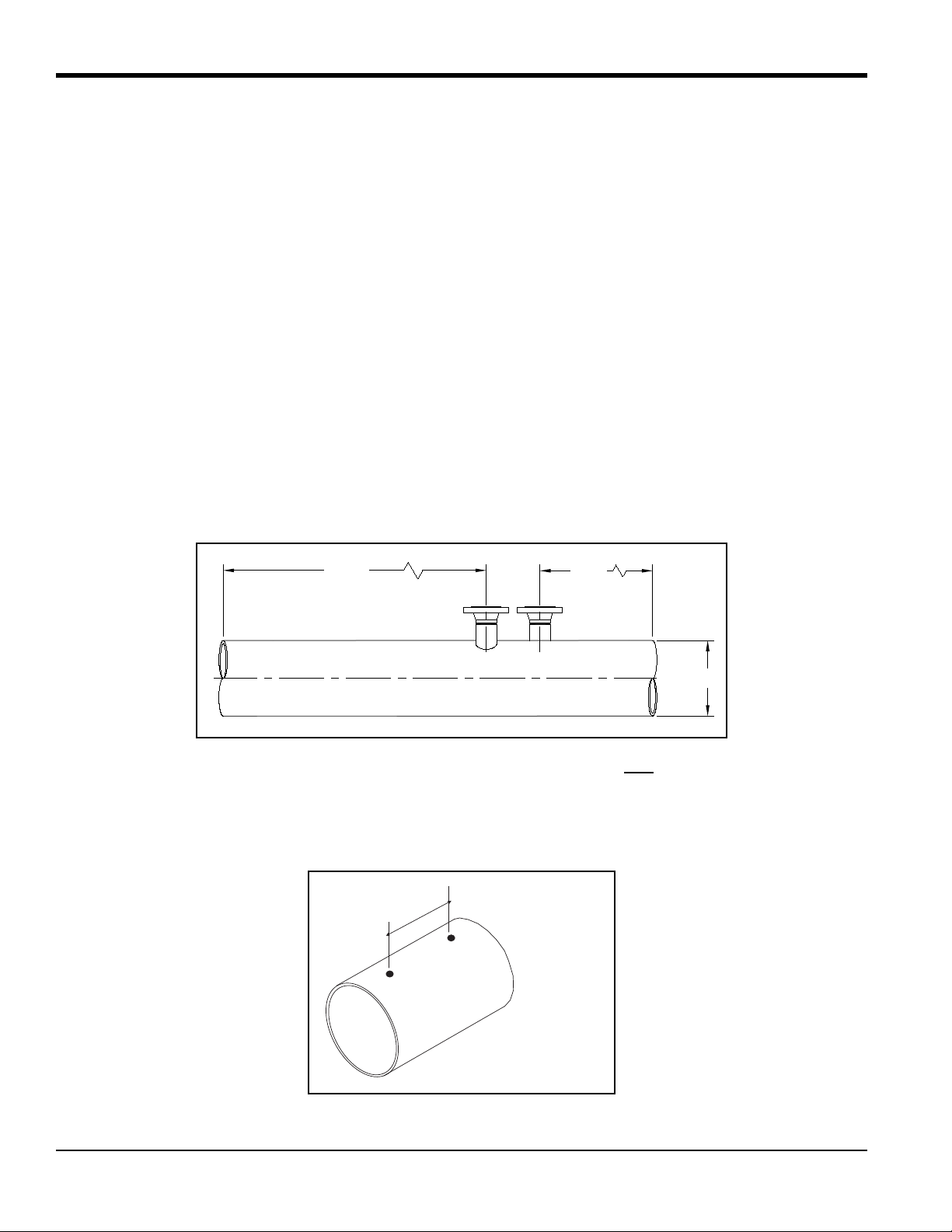
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
10D
20D
D
~ 16 in.
Top View
1.2.2 Selecting and Marking the Pipe for Nozzle Locations
CAUTION! Correct nozzle alignment is critical to the successful operation of the flowmeter.
Therefore, all marking, positioning and welding operations must be carried out with the utmost
attention to accuracy. Unless otherwise stated, dimensional positioning of the nozzles must be held
to a tolerance of ±1/16 in. (±1.6 mm) relative to each other and with respect to the pipe centerline.
The angular tolerance must be held to ±1
using hot tapping equipment.
WARNING! Be sure to adhere to all applicable safety regulations.
1. For optimum performance, you should select a location that has at least 20 pipe diameters of straight,
undisturbed flow upstream and 10 pipe diameters of straight, undisturbed flow downstream from the point of
measurement. Undisturbed flow means avoiding sources of turbulence such as flanges, elbows and tees;
avoiding swirl; and avoiding disturbed flow profiles. Never install the flowmeter downstream of control
valves, especially butterfly valves. If you cann ot find a proper location, please consult with GE Flow
Application engineering.
O
. All hole cutting in process piping must be performed
2. Use a center finder device to locate the center of the pipe.
FLOW MEASUREMENT!
“EYEBALLING” IS NOT ADEQUATE FOR ACCURATE
3. Lightly punch two marks approximately 16 in. apart on the top of the pipe, running along the center line. The
two nozzle locations will be located between these two center punch marks.
4 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 13
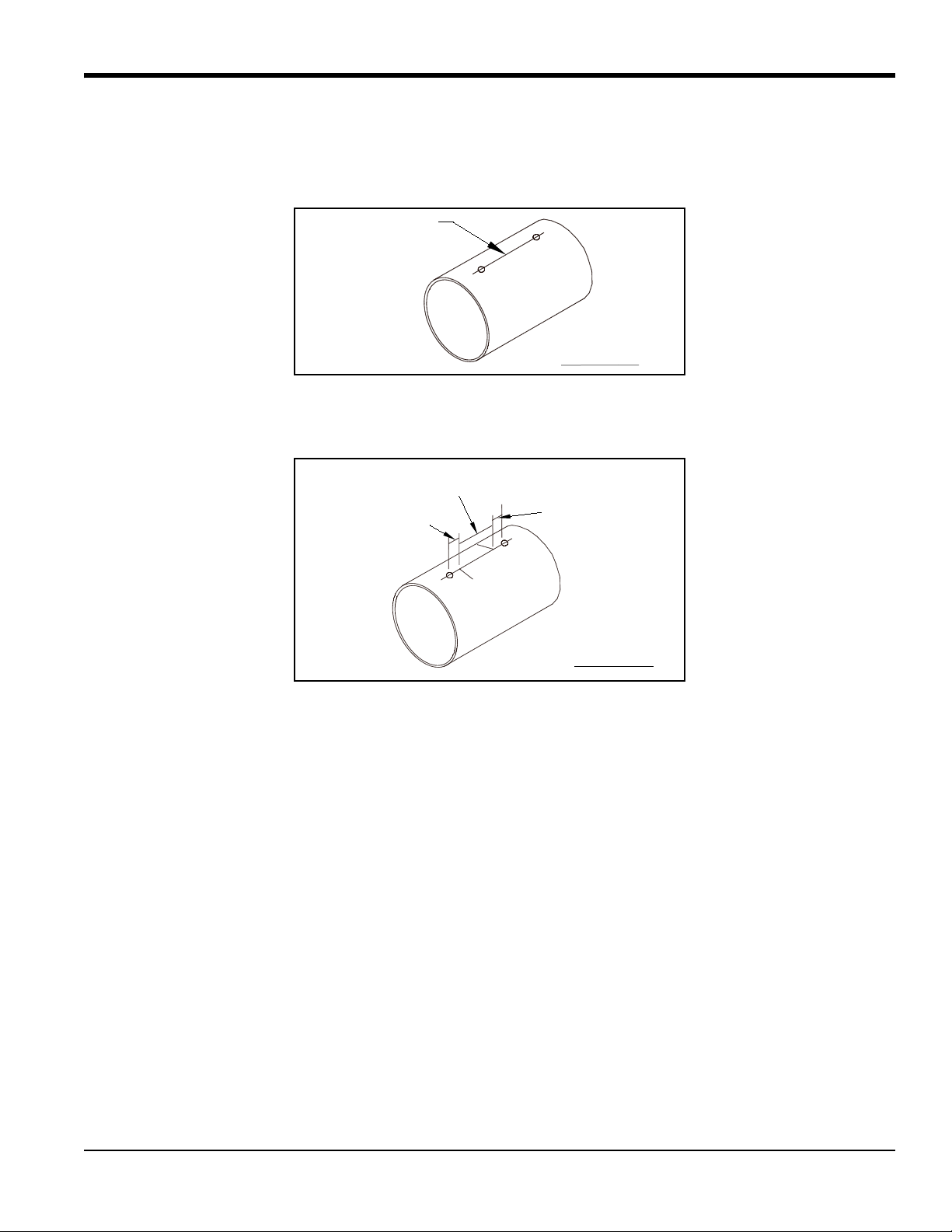
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Scribe Line
Top View
10", 9" or 6.4"
3", 3.5" or 4.8"
3", 3.5" or 4.8"
Top View
1.2.2 Selecting and Marking the Pipe for Nozzle Locations (cont.)
4. Spray the area between the two punch marks on the to p of the pipe with a marking dye product. Using a metal
straight edge, scribe a line between the two punch marks.
5. Along the new scribe lin e, mark off a length equ al to your transducer spacing (10 in., 9 in. or 6.4 in.) and scribe
two lines at least 10 in. in length and perpendicular to the scribe line on different sides of the scribe line.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 5
6. Along each of the perpendicular scribe lines, lightly punch a mark at a distance equal to half of your transducer
spacing (5 in., 4.5 in. or 3.2 in.) from the center line, depending on the bias distance for your transducers. Keep
in mind that the distance along the arc of the pipe (L) from the pipe centerline is slightly greater than the
point-to-point distance through the pipe. These marks pinpoint the centers for the nozzles. Refer to Table 1 on
page 7 for arc distances for the most commonly used pipe sizes. If your pipe size is not shown in Table 1, use
the equation in the figure on page 6 to calculate the arc distance.
Page 14
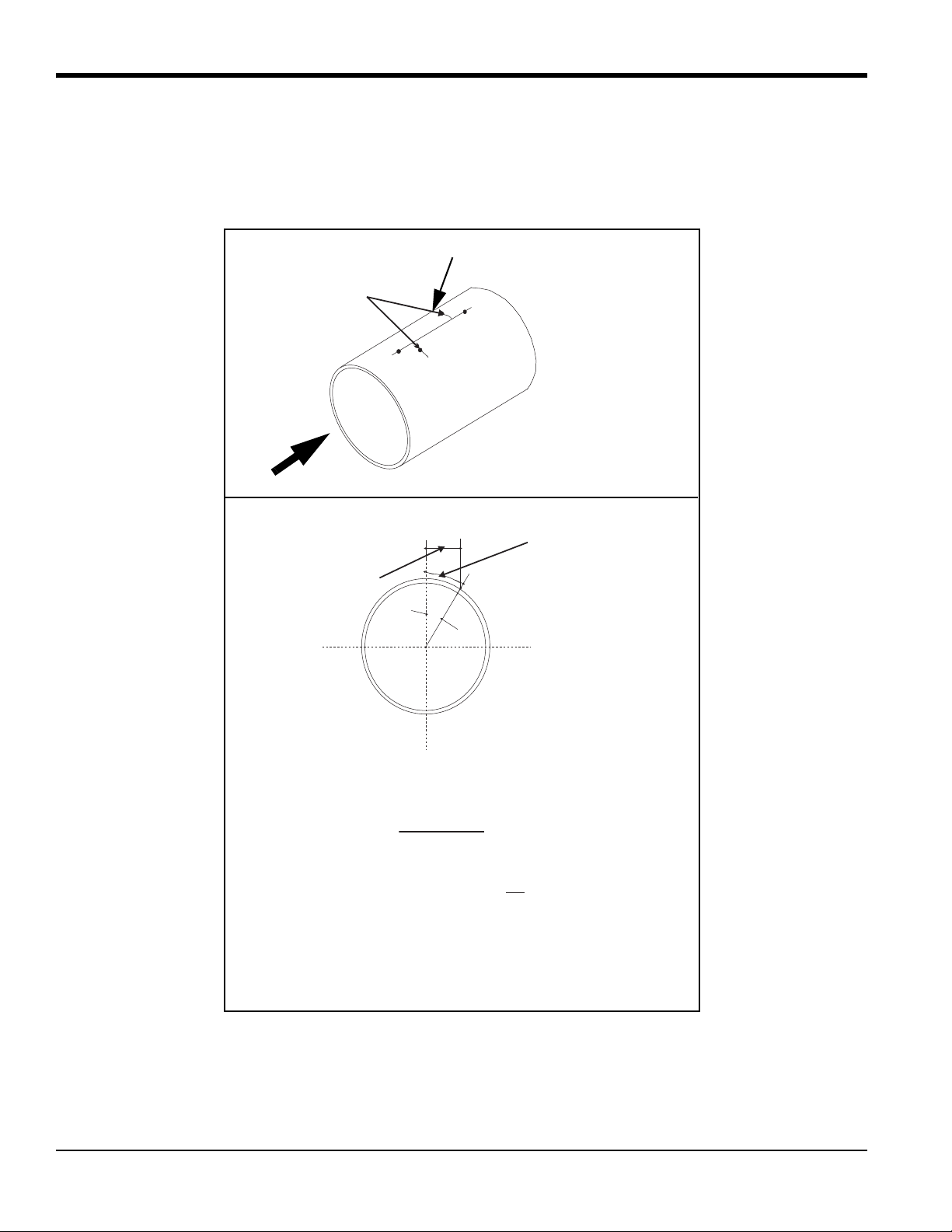
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Punch Marks
S
L = Arc Length
along pipe
surface
R
A
Spacing
Calculate L as follows:
L = 3.142 x R x A
180
Where A = Sin
-1
R = Radius in inches
S = Bias in inches
S
R
( )
End View
Flow
Downstream Port Location
for 3.2 in. bias
1.2.2 Selecting and Marking the Pipe for Nozzle Locations (cont.)
IMPORTANT: For a 3.2 in.bias distance, the downstream port must be located on the right side of the long scribe line
when viewed from the downstream end of the pipe (see the figure below). This convention is mandatory
for the 6.4 in. transducer spacing and is optional (not required) for a 10 in. or 9 in. spacing.
6 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 15
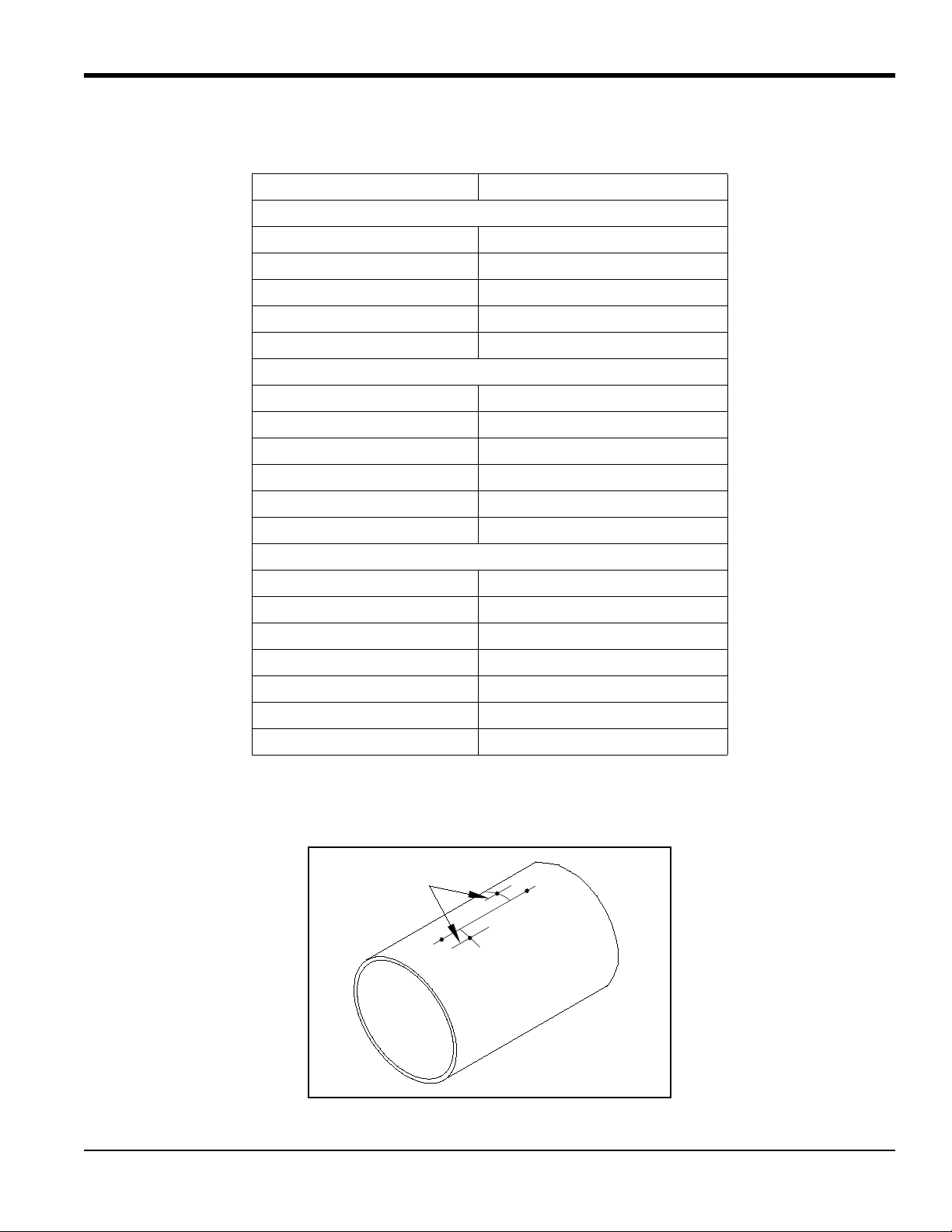
1.2.2 Selecting and Marking the Pipe for Nozzle Locations (cont.)
Scribe Lines
Top View
Table 1: Calculated Arc Distances for Common Pipe Sizes
Pipe O.D. Arc Distance
5 in. Bias
18 in. (450 mm) 5.301 in. (134.6 mm)
24 in. (600 mm) 5.157 in. (131.0 mm)
30 in. (750 mm) 5.098 in. (129.5 mm)
36 in. (900 mm) 5.067 in. (128.7 mm)
42 in. (1050 mm) 5.048 in. (128.2 mm)
4.5 in. Bias
16 in. (400 mm) 4.779 in. (121.4 mm)
18 in. (450 mm) 4.713 in. (119.7 mm)
24 in. (600 mm) 4.613 in. (117.2 mm)
30 in. (750 mm) 4.571 in. (116.1 mm)
36 in. (900 mm) 4.549 in. (115.5 mm)
42 in. (1050 mm) 4. 536 in. (115.2 mm)
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
3.2 in. Bias
14 in. (350 mm) 3.323 in. (84.4 mm)
16 in. (400 mm) 3.292 in. (83.6 mm)
18 in. (450 mm) 3.272 in. (83.1 mm)
24 in. (600 mm) 3.239 in. (82.3 mm)
30 in. (750 mm) 3.225 in. (81.9 mm)
36 in. (900 mm) 3.217 in. (81.7 mm)
42 in. (1050 mm) 3.213 in. (81.6 mm)
7. Scribe a 6 in. long horizontal centerline through each nozzle center location point and parallel to the original
centerline.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 7
Page 16
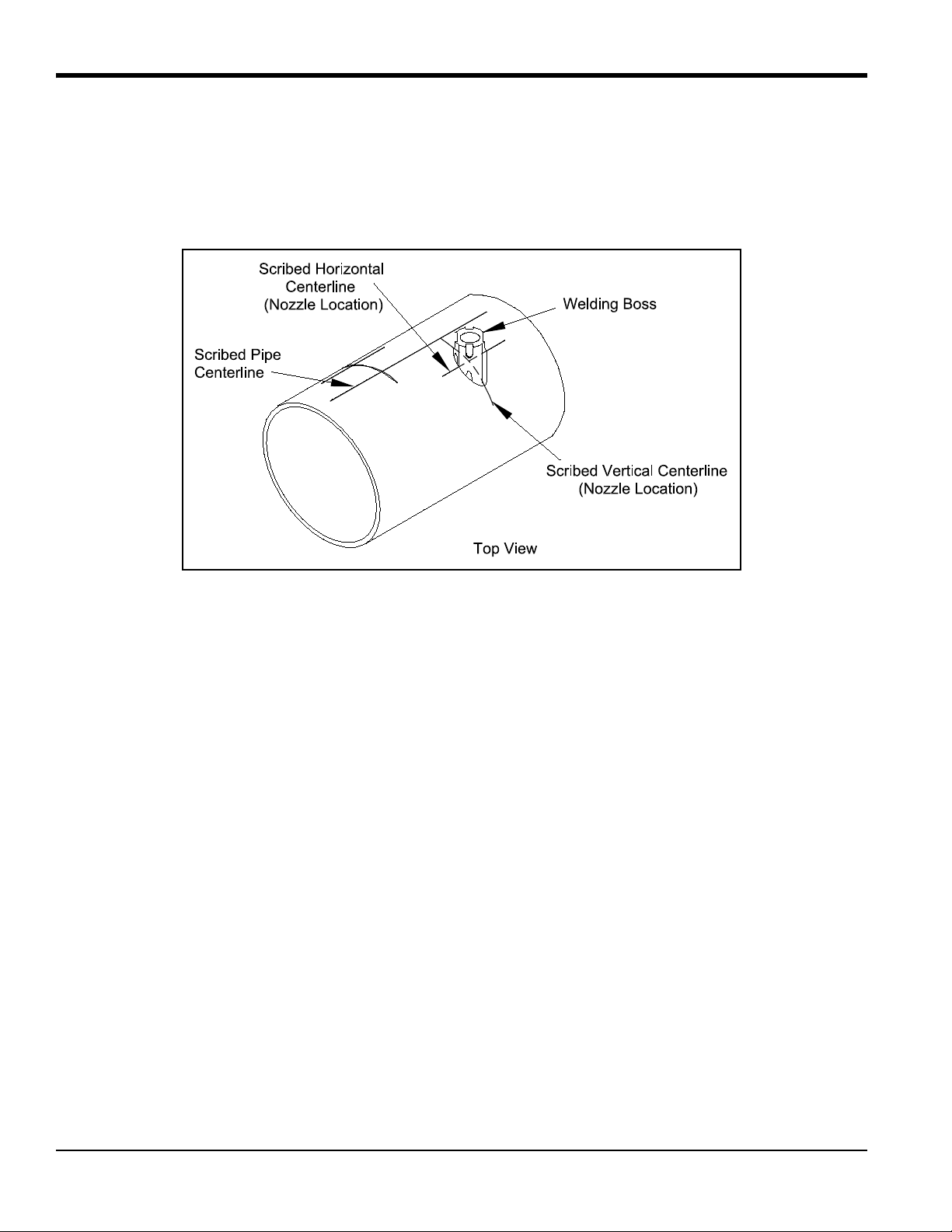
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
1.2.3 Installing the First Welding Boss
1. Each welding boss has four scribe marks indicating the center of the bias.Take one welding boss and line up its
scribe marks with the horizontal and perpendicular scribe marks on the pipe as shown below. Make sure you
position the boss on the pipe so that the contoured end of the boss matches the pipe arc. That is, the shorter side
of the boss should be closer to the original scribed pipe centerline.
2. Clamp the boss in place, using a pipe strap or equivalent, so that it cannot move during tack welding.
3. Check the boss alignment again, and then tack weld the boss in each of the four grooves between the boss
scribe marks. Make sure you keep the boss contour flush with the pipe contour during the entire tack welding
operation. The boss is constructed of carbon steel.
4. Check the alignment again. If the boss is misaligned by 0.02 in. (0.5 mm) or more, remove the boss, grind off
the welds and reinstall the boss.
8 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 17
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Threaded Rod
Welding Boss
End View
Bolts
Nozzle
Jig
Side View
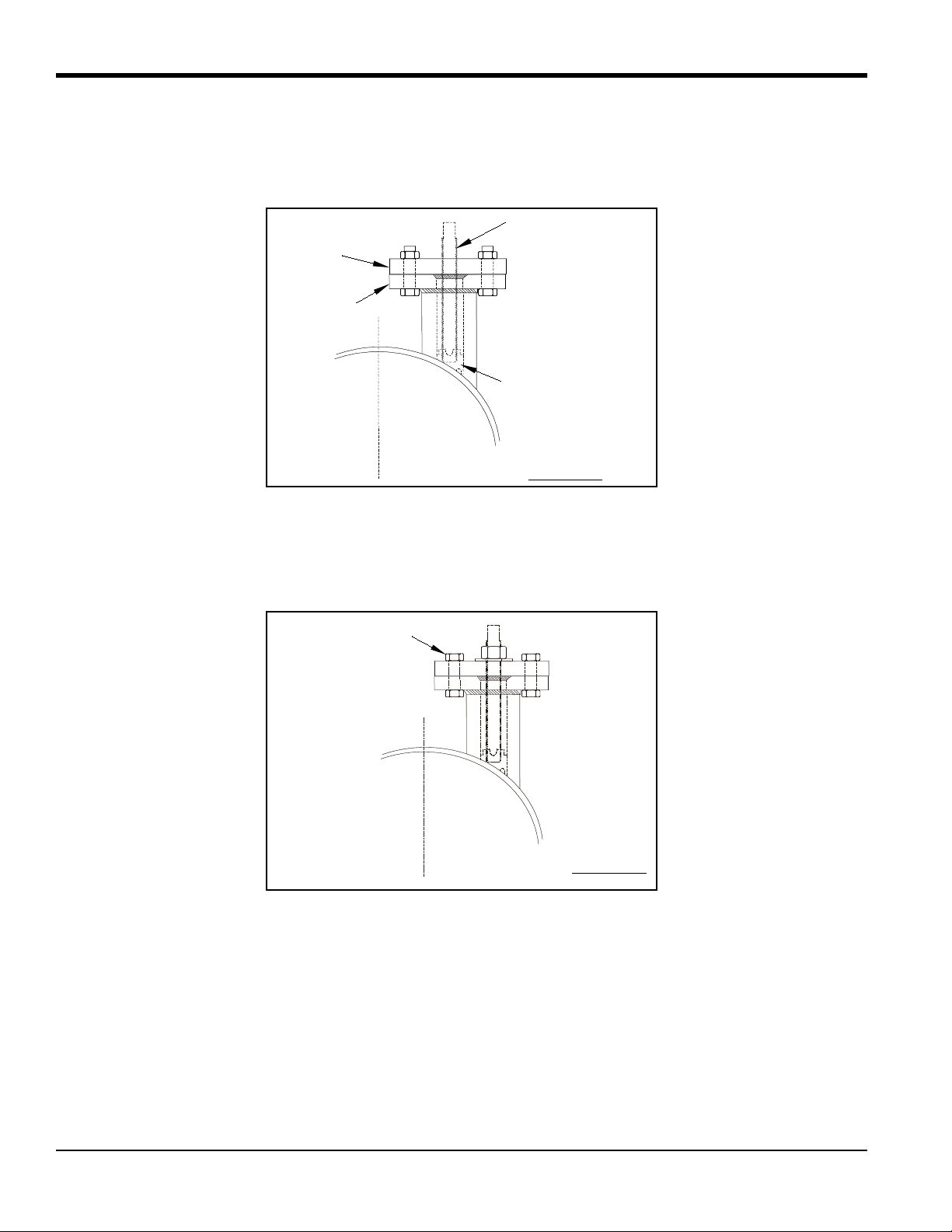
1.2.4 Installing the First Nozzle
CAUTION! It is essential that the nozzles are set up and fixed in position using the jig and alignment
plate provided, prior to welding the nozzle.
1. Screw the threaded rod into the boss that is welded onto the pipe. If necessary, remove the washer and nut from
the threaded rod.
2. Insert the pipe section of the jig (the key cut section) into the pipe section of the nozzle, and fasten the
assembly together using four nuts and bolts.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 9
Page 18
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Jig
Nozzle
Threaded Rod
Welding Boss
End View
Washer and Nut
End View
1.2.4 Installing the First Nozzle (cont.)
3. Slide the jig/nozzle assembly over the threaded rod, fitting the jig into the key cut end of the welding boss
while aligning the contoured end of the nozzle to the pipe arc.
4. Align the nozzle scribe marks with the pipe scribe marks and tighten the assembly in place using the 1-in.
washer and nut provided. If slight misalignment occurs between the nozzle scribe marks and pipe scribe marks,
loosen the four bolts holding the jig and nozzle assembly, and rotate the nozzle for the best alignment. After the
nozzle has been accurately aligned, retighten the four bolts.
5. The jig, boss, and nozzle assembly is designed to provide a 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) root gap between the beveled
edge of the nozzle and the outside diameter of the pipe. If this gap is not present all the way around the nozzle,
the nozzle must be removed and ground appropriately to provide the required clearance. If the root gap is larger
than the 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) dimension evenly all the way around the nozzle, then suitably sized washers may
be inserted between the jig and the nozzle to reduce the root gap dimension.
10 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 19
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Jig
Alignment Plate
Side View
Threaded Rod
Welding Boss
Side View
Washer and Nut
to Secure
Side View
Threaded Rod
Welding Boss
1.2.4 Installing the First Nozzle (cont.)
WARNING! Only qualified personnel should weld bosses and nozzles, using a suitable ASME IX
qualified welding procedure. All applicable safety codes should be observed.
6. Tack weld the nozzle to the pipe at four diametrically opposed points, each tack being approximately
0.2 in. (5 mm) in length. Allow the weld to cool for 30 seconds between tacks.
7. Complete the root pass and subsequent filler passes as required.
8. Allow the weld to cool, and then remove the nut, washer, jig and threaded rod.
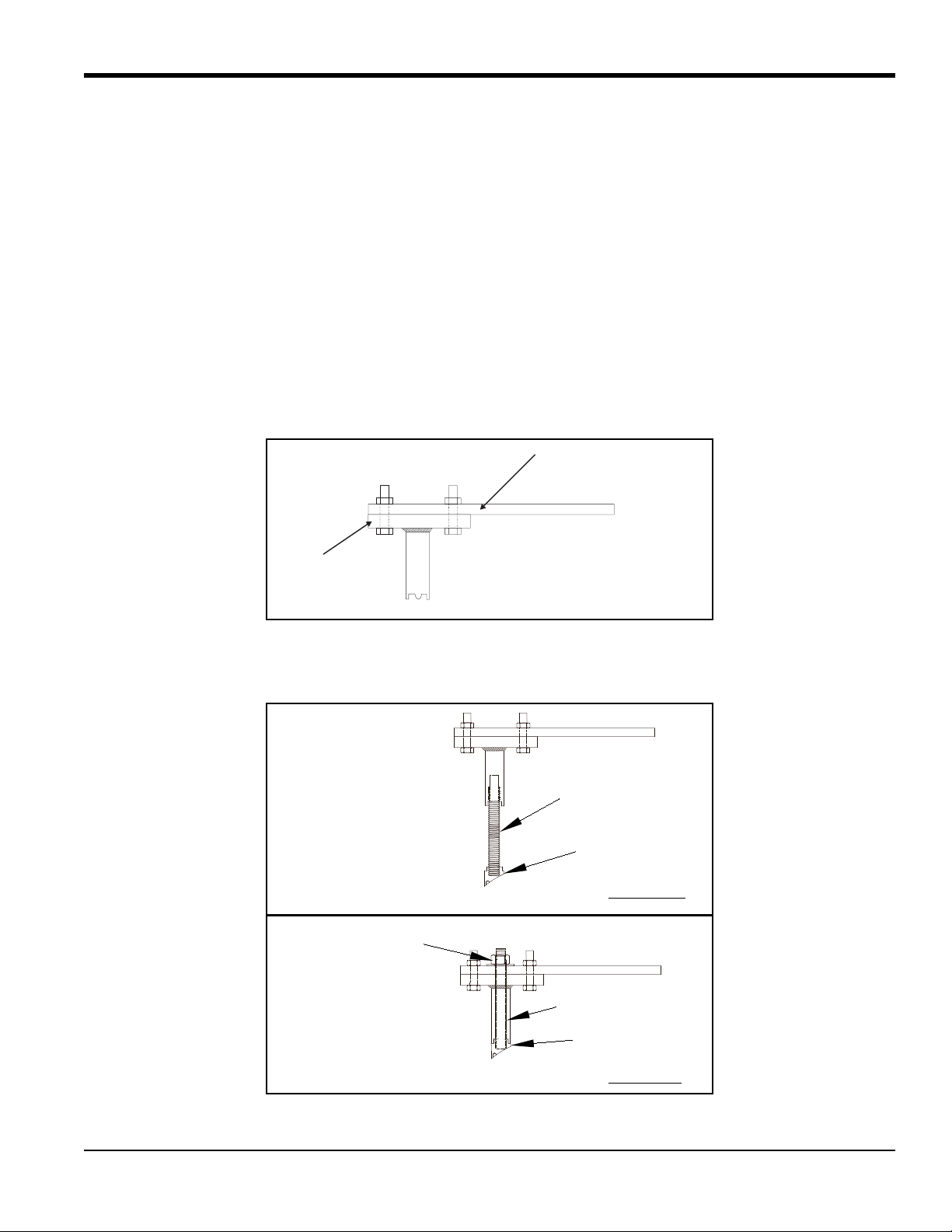
1.2.5 Installing the Second Welding Boss
1. Bolt the jig to one end of the alignment plate using four bolts.
2. Screw the threaded rod into the second boss. Then, insert the bolt/boss assembly into the jig key cut grooves
and secure it with a washer and nut on top.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 11
Page 20
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Jig
Spacer
Flange
Welded
Nozzle
End View
Top View
1.2.5 Installing the Second Welding Boss (cont.)
3. Remember to orient the boss in the jig to maintain the proper contour location to the pipe for installation.
4. Place the spacer flange on top of the welded nozzle and then mount the second end of the alignment plate on
top of the spacer flange. Bolt the alignment plate into position with the remaining bolts.
5. The second welding boss should now be positioned over the second nozzle location scribe marks. Align the
boss scribe marks with the pipe scribe marks, and then tighten all of the nuts securely.
6. Check the boss alignment again, then tack weld the boss in each of the four grooves between the boss scribe
marks.
7. After tacking, check the boss alignment once more. If the boss is misaligned by 0.02 in. (0.5 mm) or more,
remove the boss by grinding off the welds, and then reinstall the boss.
8. Remove the threaded rod and the jig. Leave the alignment plate bolted to the first nozzle, with the spacer flange
sandwiched between them.
12 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 21
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Jig
Nozzle
End View
Spacer
Flange
Alignment Plate
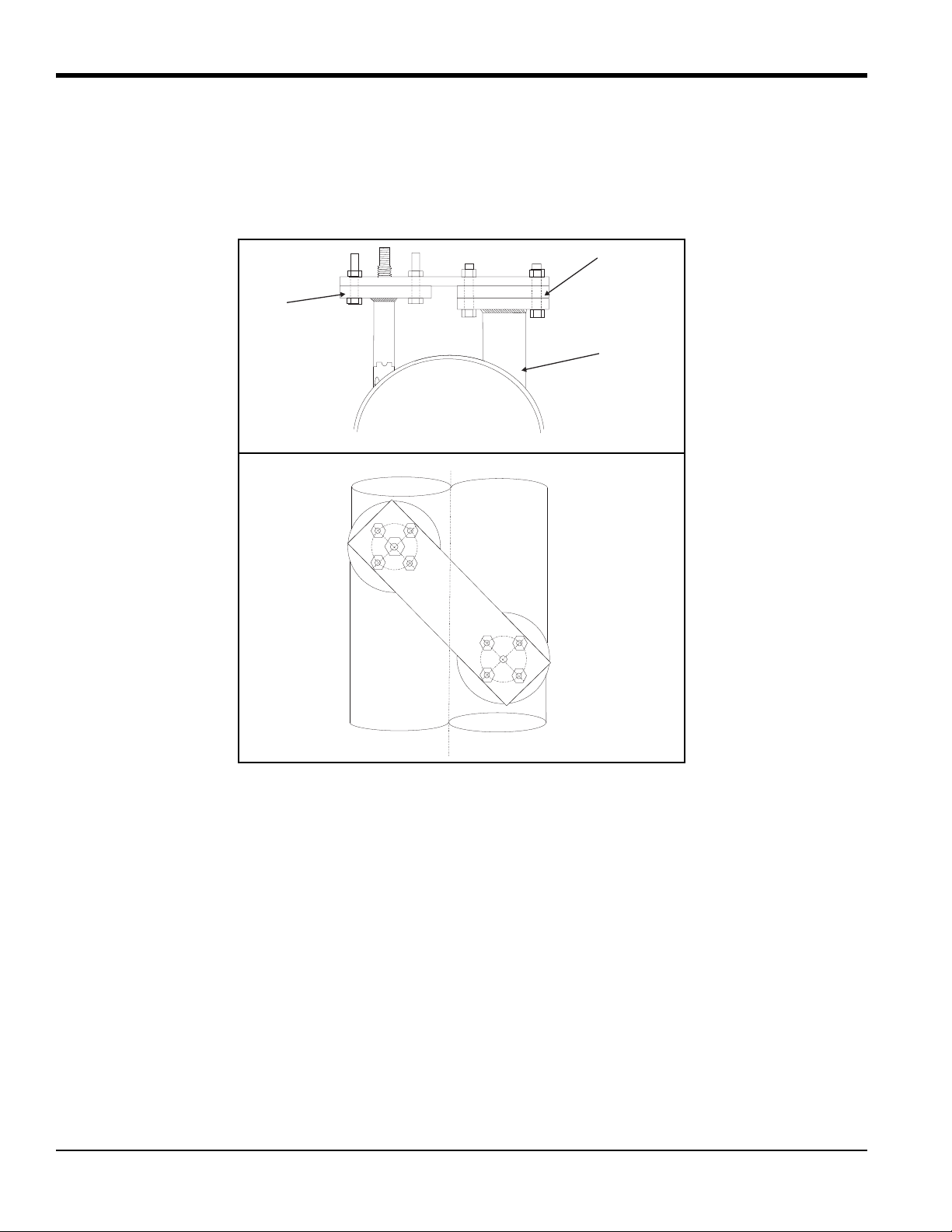
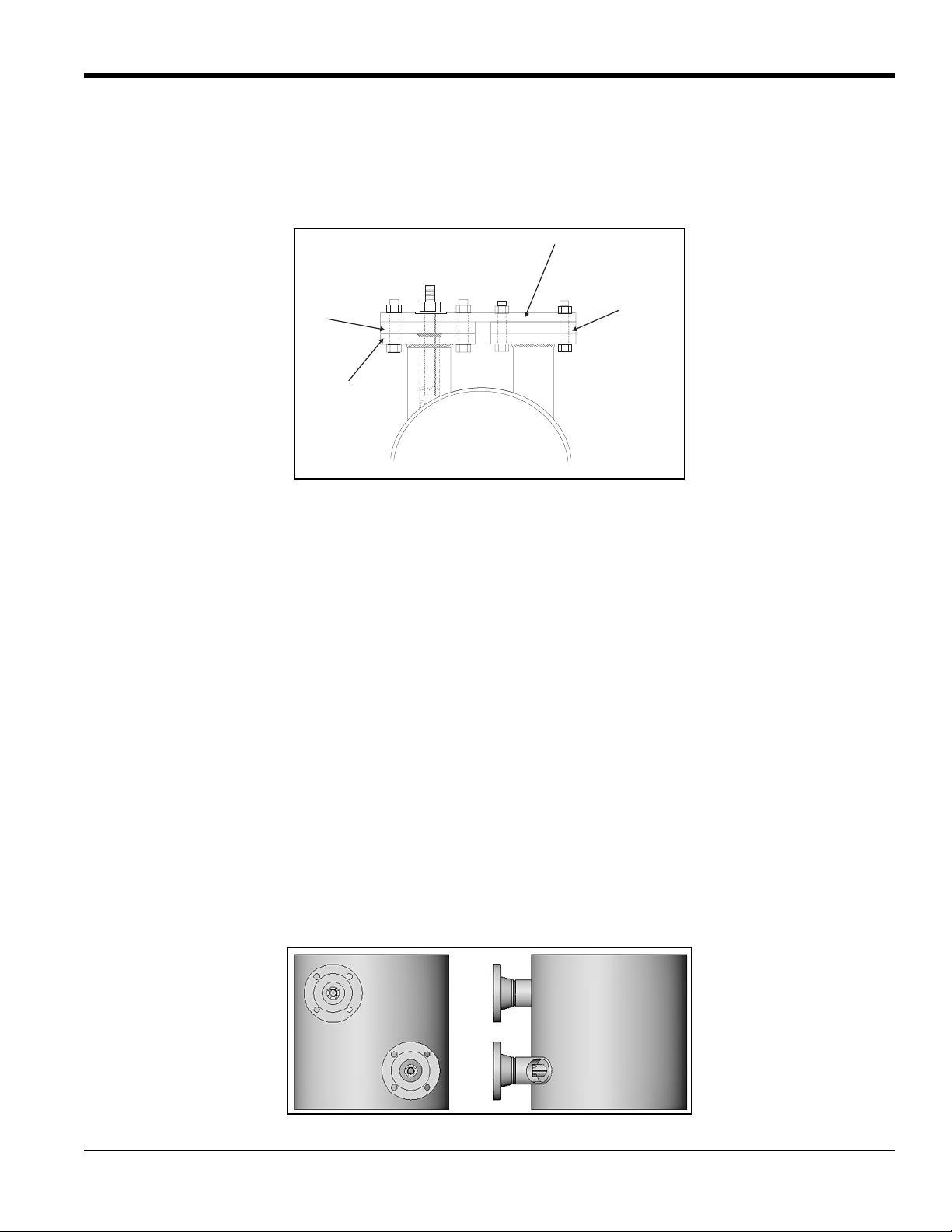
1.2.6 Installing the Second Nozzle
To install the second nozzle, complete the following steps:
1. Insert the jig into the second nozzle and position this assembly over the boss and under the alignment plate.
Then, insert the threaded rod.
2. The jig, boss, and nozzle assembly is designed to provide a 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) root gap between the beveled
edge of the nozzle and the outside diameter of the pipe. If this gap is not present all the way around the nozzle,
the nozzle must be removed and ground appropriately to provide the required clearance. If the root gap is larger
than the 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) dimension evenly all the way around the nozzle, then suitably sized washers may
be inserted between the jig and the nozzle to reduce the root gap dimension.
3. Secure the alignment plate by installing the two sets of four bolts on the alignment plate. Also, install the
washer and nut on the threaded rod.
4. Line up the nozzle scribe marks with the pipe scribe marks and tighten all the nuts.
5. Make sure the nozzle is still in alignment.
WARNING! Only qualified personnel should weld bosses and nozzles, using a suitable ASME IX
qualified welding procedure. All applicable safety codes should be observed.
6. Tack weld the nozzle to the pipe at four diametrically opposed points, each tack being approximately
0.2 in. (5 mm) in length. Allow the weld to cool for 30 seconds between tacks.
7. Complete the root pass and subsequent filler passes as required.
8. Allow the weld to cool, and then remove all nuts and bolts, the alignment plate, the jig, the spacer flange and
the threaded rod. The completed installation should appear as shown below.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 13
Page 22

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
1.2.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe
WARNING! Hot tapping should only be performed by qualified personnel. Follow all applicable code
and safety practices during these procedures.
1.2.7a Hot Tapping For 3” Flanges
To hot tap the pipe for 3” flanges, complete the following steps:
1. Obtain two suitable 3 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 11.125 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
either 5/8 in. studs and nuts for 150# flanges or 3/4 in. studs and nuts for 300# flanges.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
4. Hot tap holes in the pipe using a hot tap machine equipped with a 3/4 in. (19.05 mm) drill bit.
5. Then use a coupon retaining hole saw to cut a hole with a diameter of 2.36 in. (60 mm) minimum to
2.875 in. (73 mm) maximum.
1.2.7b Hot Tapping For 2” Flanges
To hot tap the pipe for 2” flanges, complete the following steps:
1. Obtain two suitable 2 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 7 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8.50 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
5/8 in. studs and nuts.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
4. Hot tap holes in the pipe using a hot tap machine equipped with a 3/4 in. (19.05 mm) drill bit.
5. Then use a coupon retaining hole saw to cut a hole with a diameter of 1.81 in. (46 mm) minimum to
1.89 in. (48 mm) maximum.
1.2.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe
WARNING! Cold tapping should only be performed by qualified personnel. Follow all applicable code
and safety practices during these procedures.
The procedure for cold tapping a pipe is the same as the hot tapping procedure described above. However, isolation
valves are not necessary during the tapping process. The hot tap machine is used directly on the nozzles. The isolation
valves are added after the tapping process has been completed.
14 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 23
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Welding Boss
Threaded Rod
with Washer and Nut
Nozzle
Jig
1.3 Tilted 45° Installation
This procedure includes the following steps:
• Identifying and checking the nozzle installation kit components
• Selecting and marking the pipe for nozzle locations
• Installing the first welding boss
• Installing the first nozzle
• Installing the second welding boss
• Installing the second nozzle
• Tapping the pipe
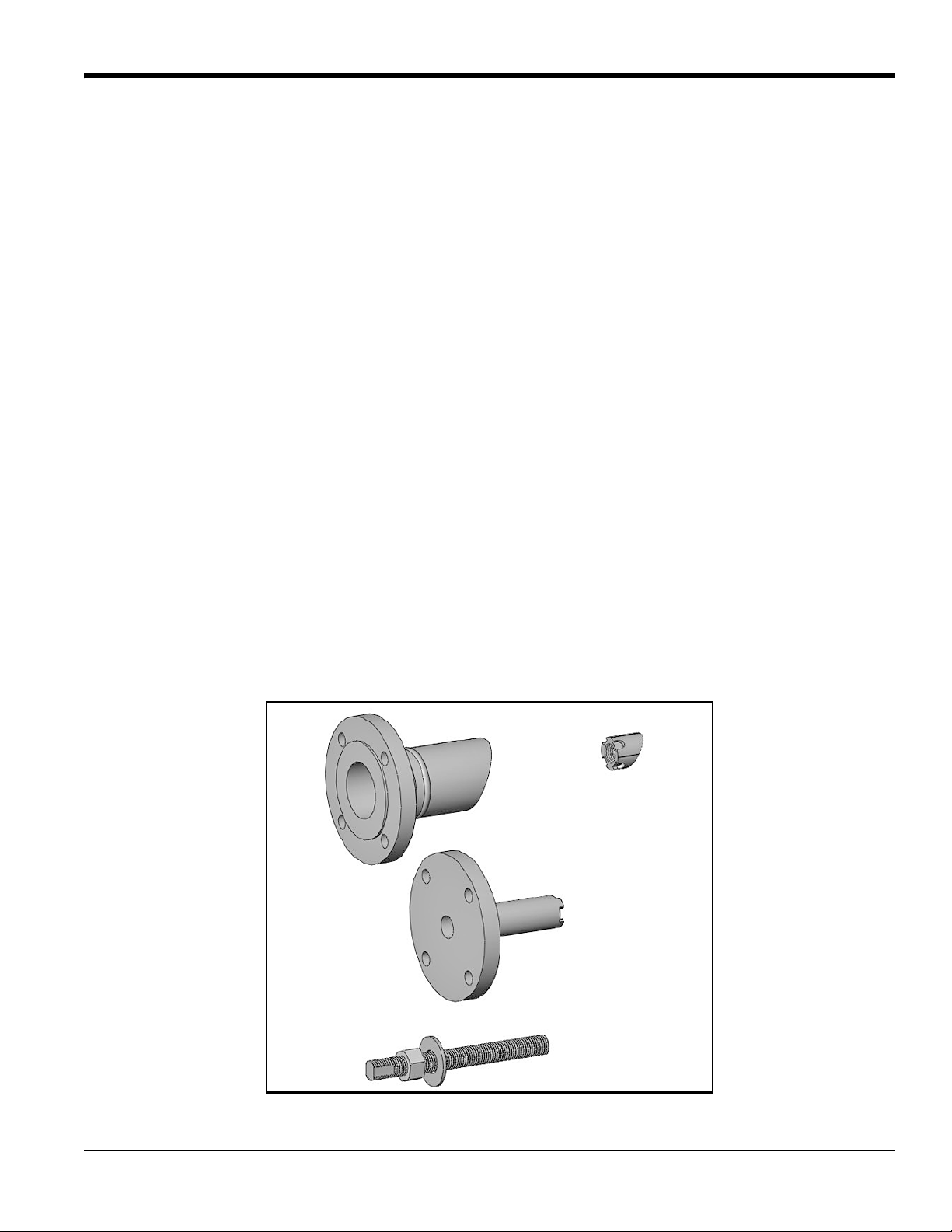
1.3.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components
The Nozzle Installation Kit contains the materials listed below. Use Figure 2 below to help identify each component.
• 2 Nozzles (if purchased)
• 2 Welding bosses
• 1 Jig
• 1 Threaded rod (1” diameter), with washer and nut
IMPORTANT: You will need eight 5/8” studs with two nuts each, or 3/4” studs with two nuts each. The 5/8” studs are
needed for 2”-150#, 2”-300# and 3”-150# flanges. The 3/4” studs are needed for 3”-300# flanges.
Figure 2: Components for Nozzle Installation Kit
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 15
Page 24
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Pipe O.D.
Mounting Angle
FLOW
NOZZLE
2 PLACES
10D
20D
D
45°
TOP VIEW
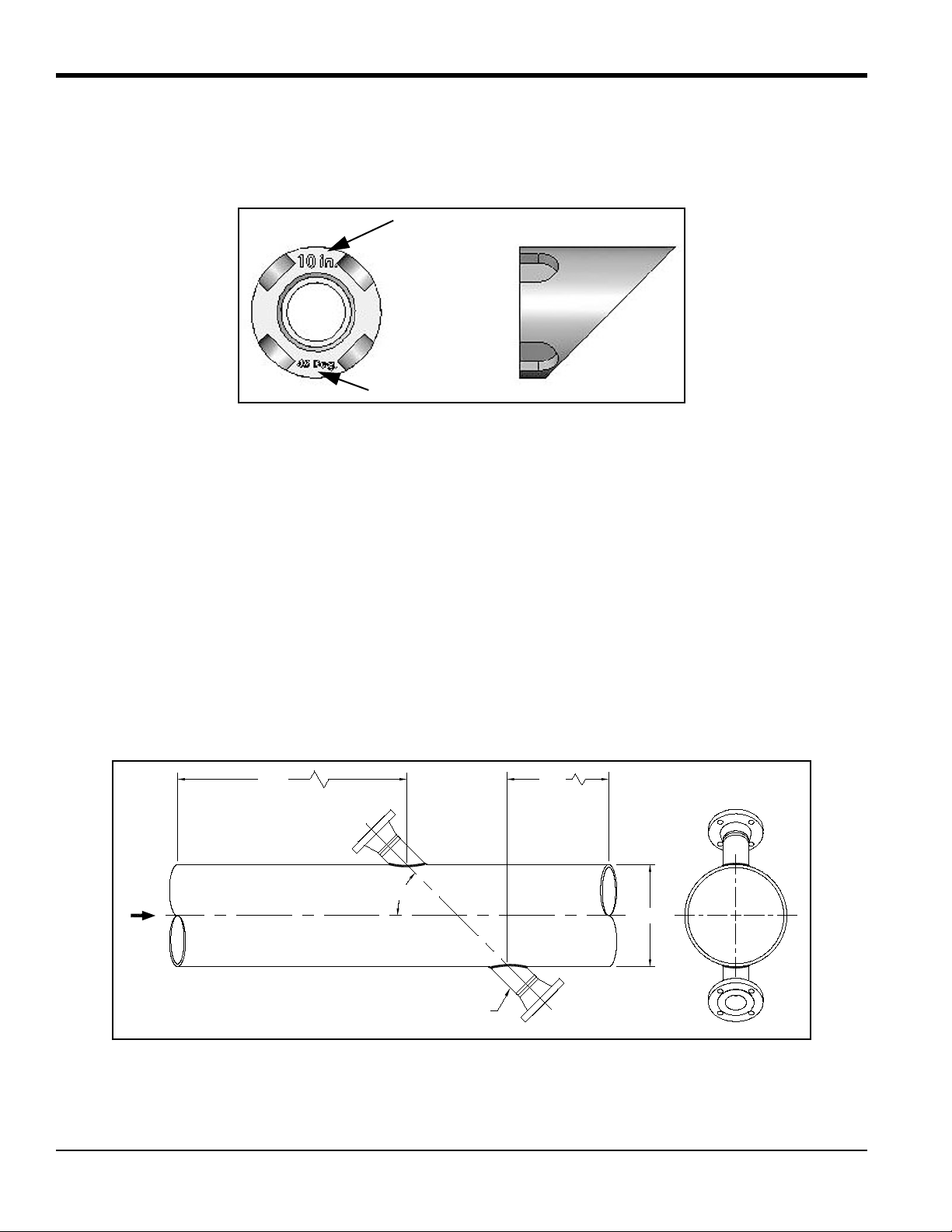
1.3.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components (cont.)
Check the markings on the end of the welding boss. The pipe OD and the mounting angle are engraved on the boss, as
shown below.
1.3.2 Selecting and Marking the First Nozzle Location
CAUTION! Correct nozzle alignment is critical to the successful operation of the flowmeter.
Therefore, all marking, positioning and welding operations must be carried out with the utmost
attention to accuracy. Unless otherwise stated, dimensional positioning of the nozzles must be held
to a tolerance of ±1/16 in. (±1.6 mm) relative to each other and with respect to the pipe centerline.
The angular tolerance must be held to ±1
using hot tapping equipment.
O
. All hole cutting in process piping must be performed
1. For optimum performance, you should select a location that has at least 20 pipe diameters of straight,
undisturbed flow upstream and 10 pipe diameters of straight, undisturbed flow downstream from the point of
measurement. Undisturbed flow means avoiding sources of turbulence such as flanges, elbows and tees;
avoiding swirl; and avoiding disturbed flow profiles. Never install the flowmeter downstream of control
valves, especially butterfly valves. If you cann ot find a proper location, please consult with GE Flow
Application engineering.
16 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 25

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Side View
Side View
1.3.2 Selecting and Marking the First Nozzle Location (cont.)
2. Install the pipe nozzles on a pipe diameter as near as possible to the horizontal plane. This would be at the
3 o’clock and 9 o’clock positions for a horizontal pipe.
Note: If you cannot find a proper location, please consult with GE Flow Application engineering.
3. At the 3 o’clock position, center punch the pipe to mark the position for the center of the first nozzle.
4. Spray this area with a marking dye product. Using a metal straight edge, scribe 6 in. long vertical and
horizontal lines that intersect at the center punch mark.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 17
Page 26
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
D1
D2
D3
D4
Side View
Average
O.D.
4 X O.D.
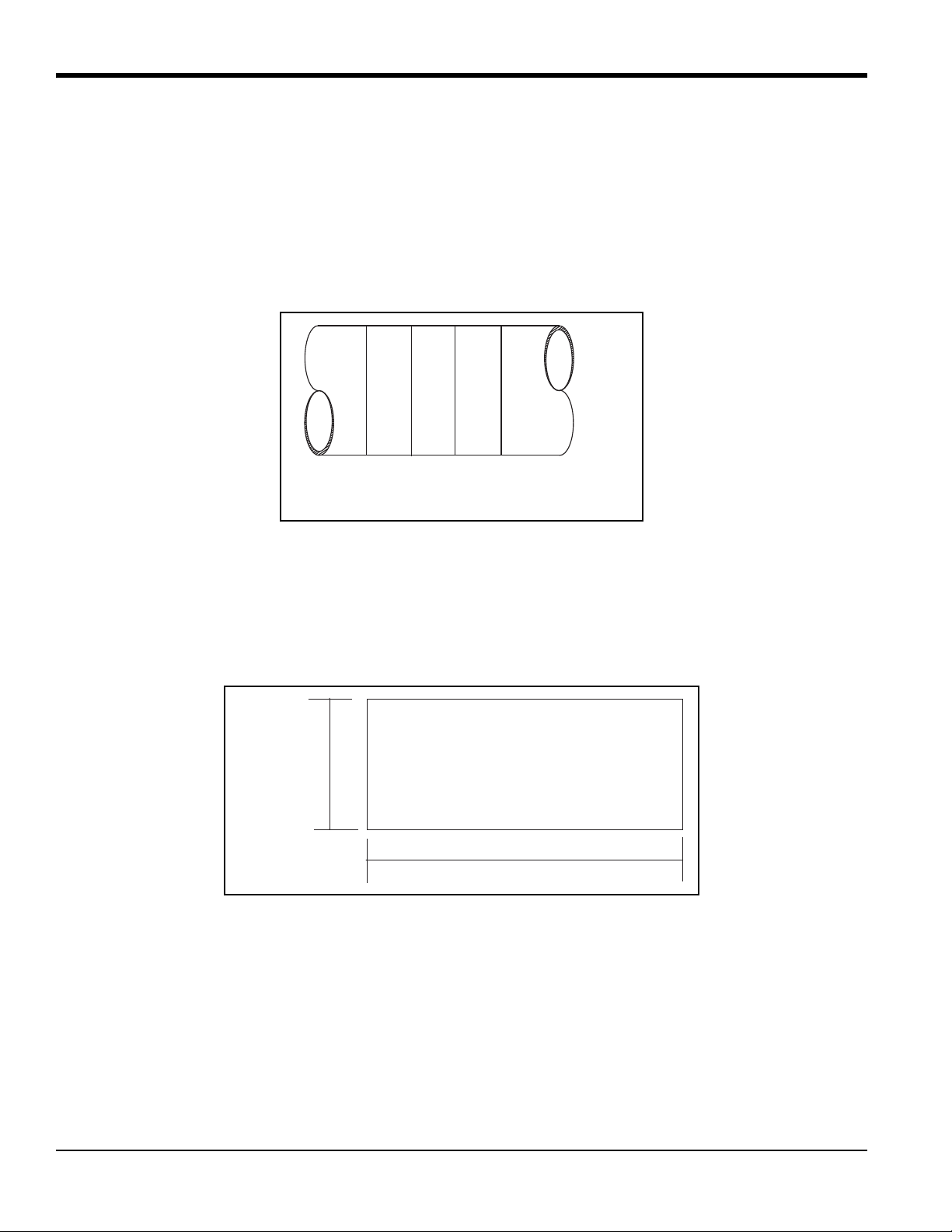
1.3.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location
1. The second nozzle is located a distance equal to one pipe O.D. along the pipe centerline and on the opposite
side of the pipe (180
Note: For installation angles other than 45°, the distance along the pipe centerline i s equal to the pipe O.D. times the
tangent of the installation angle.
2. To account for possible variations in the O.D. of the pipe, measure the pipe O.D. at four location between the
nozzle centers. Calculate the average outside diameter based on these measurements.
°
around the circumference). Spray this area with a marking dy e product.
3. Using a roll of polyester film (or equivalent), cut a strip of film to the following width and length:
IMPORTANT: Ensure that the sides of the film are cut parallel to each other.
• Width - equal to the average pipe O.D., as calculated in Step 1 above.
• Length - equal to 4 times the average pipe O.D., as calculated in Step 1 above.
18 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 27

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Side View
Overlap Mark
Overlap Mark Fold to Here
Mark the Edge
1.3.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location (cont.)
4. Wrap the strip of film around the pipe with one edge running along the vertical scribe line at the first nozzle
location. Make sure the strip overlaps squarely
the strip. This equals the circumference of the pipe.
all the way around the pipe, and mark the overlap location of
5. Remove the strip of film and fold it as shown below to determine the position which is diametrically opposite
the overlap position when the film is reapplied to the pipe.
6. Mark the outside of the fold for reference.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 19
Page 28

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Overlap Mark
First Edge
Side View
Fold Mark
Side View
Punch Here
Second Edge
Scribe Lines
Side View
1.3.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location (cont.)
7. Wrap the strip of film around the pipe again. This time, line up the overlap mark with the horizontal and
vertical scribe lines. Again, make sure you wrap the strip of film squarely all the way around the pipe.
8. The new location of the center of the second nozzle is now identified as the intersection of the fold line and the
second edge of the strip of film. Center punch this location prior to removing the strip of film.
9. Remove the strip of film from the pipe.
10. Scribe 6 in. long vertical and horizontal lines which intersect at the new center-punch mark.
20 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 29
Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
XD2⁄
d2⁄
sin
-1
dD⁄()[]tan
---------------------------------------- -
–=
True Center Line
Oblique Center Line
Side View
1.3.4 Installing the First Welding Boss
1. Before welding the first boss, you must add another scribe line known as the oblique center line. The oblique
center line compensates for the slope or oblique of the boss. The oblique center line is offset from the true
center (vertical) scribe line marked earlier by a distance of
2. ” which is dependent on the pipe outside diameter as follows:
where, D = pipe outside diameter
d = welding boss outside diameter (1.660 in.)
X,
Table 2 below shows values of
3. Scribe the o blique center line on th e pipe at the calcula ted distance from the true center line. The oblique center
line should be marked on the side of the true center line that is closer to the second nozzle location.
X for various pipe sizes.
Table 2: X Values for Various Pipe Sizes
Pipe Size
X DimensionsNPS (DN) O.D.
6 in. (150 mm) 6.625 in. (168 mm) 0.106 in. (2.69 mm)
8 in. (200 mm) 8.625 in. (219 mm) 0.081 in. (2.06 mm)
10 in. (250 mm) 10.750 in. (273 mm) 0.064 in. (1.62 mm)
12 in. (300 mm) 12.750 in. (324 mm) 0.054 in. (1.37 mm)
14 in. (350 mm) 14.000 in. (356 mm) 0.049 in. (1.24 mm)
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 21
Page 30

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Oblique Center Line Scribe Mark
Horizontal Scribe Mark
1.3.4 Installing the First Welding Boss (cont.)
4. Position the welding boss such that the four scribe lines on the welding boss are lined up with the horizontal
scribe mark and the oblique center line on the pipe. Make sure you orient the boss as shown below.
5. Clamp the boss in place using a pipe strap or equivalent so that it cannot move during tack welding.
6. Check the boss alignment, then tack weld the carbon steel b oss to the pipe in each of the four grooves between
the boss scribe marks.
7. Remove the clamp and check the alignment again. If the boss is misaligned by 0.02 in. (0.5 mm) or more,
remove the boss, grind off the welds and reinstall the boss.
22 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 31

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Threaded Rod
Welded Boss
Jig
Threaded Rod
Nozzle
1.3.5 Installing the First Nozzle
IMPORTANT: Prior to welding the nozzle, it is essential that the nozzle is set up and fixed in position using the jig and
the 1-in. threaded rod provided in the kit.
1. Screw the threaded rod into boss that is welded onto the pipe. If necessary, remove the washer and nut from the
threaded rod.
2. Slide the nozzle over the threaded rod, and align the contoured end of the nozzle so that it matches the pipe arc.
Then slide the jig over the threaded rod and fit the jig into the welding boss.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 23
Page 32

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
Washer and Nut
Bolt Holes
1.3.5 Installing the First Nozzle (cont.)
3. Align the jig bolt holes with the nozzle bolt holes. Then, tighten the assembly together, using the washer and
nut on the threaded rod.
4. The jig, boss, and nozzle assembly is designed to provide a 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) root gap between the beveled
edge of the nozzle and the outside diameter of the pipe. If this gap is not present all the way around the nozzle,
the nozzle must be removed and ground appropriately to provide the required clearance. If the root gap is larger
than the 0.094 in. (2.4 mm) dimension evenly all the way around the nozzle, then suitably sized washers may
be inserted between the jig and the nozzle to reduce the root gap dimension.
WARNING! Only qualified personnel should weld bosses and nozzles, using a suitable ASME IX
qualified welding procedure. All applicable safety codes should be observed.
5. Tack weld the nozzle to the pipe at four diametrically opposed points, each tack being approximately
0.6 in. (15 mm) in length. Allow the weld to cool for 30 seconds between tacks.
6. Complete the root pass and subsequent filler passes as required.
7. Allow the weld to cool, and then remove the nut, washer, jig and threaded rod.
24 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 33

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
45°
FLOW
WELDING BOSS
NOZZLE
2 PLACES
2 PLACES
1.3.6 Installing the Second Welding Boss and Nozzle
Using the same procedures used for installing the first welding boss and nozzle, install the second welding boss and
nozzle at the marked position on the pipe.
The completed installation should appear as shown below.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 25
Page 34

Chapter 1. Installing Pipe Nozzles
1.3.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe
Note: Hot tapping a tilted 45° installation is possible only for the standar d velocity range (100 m/s, 328 ft/s). For the
extended velocity range (120 m/s, 394 ft/s), only the 4” pipe size can be hot topped.
WARNING! Hot tapping should only be performed by qualified personnel. Follow all applicable code
and safety practices during these procedures.
1.3.7a Hot Tapping For 3” Flanges
To hot tap the pipe for 3” flanges, complete the following steps:
1. Obtain two suitable 3 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 11.125 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
either 5/8 in. studs and nuts for 150# flanges or 3/4 in. studs and nuts for 300# flanges.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
4. Hot tap holes in the pipe using a hot tap machine equipped with a 3/4 in. (19.05 mm) drill bit.
5. Then use a coupon retaining hole saw to cut a hole with a diameter of 2.36 in. (60 mm) minimum to
2.875 in. (73 mm) maximum.
1.3.7b Hot Tapping For 2” Flanges
To hot tap the pipe for 2” flanges, complete the following steps:
1. Obtain two suitable 2 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 7 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8.50 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
5/8 in. studs and nuts.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
4. Hot tap holes in the pipe using a hot tap machine equipped with a 3/4 in. (19.05 mm) drill bit.
5. Then use a coupon retaining hole saw to cut a hole with a diameter of 1.81 in. (46 mm) minimum to
1.89 in. (48 mm) maximum.
1.3.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe
WARNING! Cold tapping should only be performed by qualified personnel. Follow all applicable code
and safety practices during these procedures.
The cold tapping procedure is the same as the hot tapping procedure described above for a standard velocity range
(100 m/s, 328 ft/s) installation. Except for the 4 in. pipe size, cold tapping can be performed only before the isolation
valve is installed. The hot tap machine is used directly on the nozzles, and the isolation valves are added after the
tapping process has been completed.
26 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 35

Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
This chapter provides instructions for installing an isolation valve onto a nozzle for applications using the flare gas
insertion mechanism.
Note: Installation of the isolation valves may have been done already during the hot tapping operation.
2.1 Bias 90° Installation (Standard or Extended Velocity Range)
2.1.1 For 3 inch Flanges
1. Obtain two suitable 3 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 11.125 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
either 5/8 in. studs and nuts for 150# flanges or 3/4 in. studs and nuts for 300# flanges.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
2.1.2 For 2 inch Flanges
1. Obtain two suitable 2 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 7 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8.50 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
5/8 in. studs and nuts.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
2.2 Tilted 45° Installation (Standard Velocity Range)
2.2.1 For 3 inch Flanges
1. Obtain two suitable 3 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 11.125 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
either 5/8 in. studs and nuts for 150# flanges or 3/4 in. studs and nuts for 300# flanges.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
2.2.2 For 2 inch Flanges
1. Obtain two suitable 2 in. ANSI flanged isolation valves. The valves should be a full bore type with either
150# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 7 in. or 300# RF flanges and a face-to-face length of 8.50 in.
2. Install one of the isolation valves, including a suitable gasket, on each of the nozzles. Secure the valves with
5/8 in. studs and nuts.
3. Orient the isolation valve handles to minimize interference during operation of the valves.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 27
Page 36

Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
6° Wedge
Gaskets
Adjustment Screws
Hardware
Bolt Spacer
Flow Direction
Valve Face Marking on 6° Wedge
Nut Side Marking on Bolt Spacer
Nozzle Face Marking on 6° Wedge
2.3 Tilted 45° Installation (Extended Velocity Range)
Note: The upstream valve and transducer are installed without wedges, as described in the previous section.
To install the downstream isolation valve, the items shown in Figure 3 below are required.
Figure 3: Parts for 150# RF Flange Isolation Valve Installation
1. Insert the four bolts into the nozzle flange holes.
2. With the Nut Side marking facing the pipe, place the split bolt spacer halves over the bolts behind the flange,
with the thin ends corresponding to what will be the thickest side of the other wedge (see Figure 4 below).
Note: The wedge positions are based on the need to tilt the transducer 6° against the flow.
28 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Figure 4: Mounting Bolts, Bolt Spacers, Wedge and Gaskets Positions
Page 37

Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
Nut Side Marking on Bolt Spacer
2.3 Tilted 45° Installation (Extended Velocity Range) (cont.)
3. With the Nozzle Face marking facing the pipe and the Valve Face marking facing outward, hold the
gasket/ wedge/gasket combination in line with the insertion hole and oriented as shown in Figure 4 on page 28.
4. While one person holds the gaskets and wedges in place, another person should line up the isolation valve
mounting holes with the bolts in the nozzle flange, push the isolation valve against the gasket/wedge/gasket
combination, and install the washers and nuts to secure the isolation valve to the nozzle flange (see Figure 5
below).
Figure 5: Mounting the Isolation Valve
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 29
Page 38

Chapter 2. Installing the Isolation Valves
Adjustment Screw
Adjustment Screw
Scribe Line
2.3 Tilted 45° Installation (Extended Velocity Range) (cont.)
5. Insert the two adjustment screws into the threaded holes on the 6° wedge (see Figure 6 below) and use them to
rotate the wedge until the scribe line is centered between the two bolts.
Figure 6: Adjusting the Wedge Position
6. After the wedge is positioned correctly, use two wrenches to tighten the hardware and secure the isolation
valve to the nozzle. Then remove the adjustment screws from the wedge.
Figure 7: Completed Isolation Valve Installation
Note: The upstream valve and transducer are installed without wedges, as described in the previous section.
30 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 39

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.1 Introduction
Transducers and their holder assemblies are installed into a meter body, which is a section of pipe that contains the
ports for mounting the transducer assemblies. The meter body may be prefabricated or created by installing ports on an
existing pipe. The transducers can be inserted into the meter body using the following holder methods:
• Low-pressure insertion mechanism
• Barrel holder
• Flanged holder
Note: As an example, this chapter describes the use of the low-pressure insertion mechanism type only.
3.2 Using the Low-Pressure Insertion Mechanism
Note: The Low-Pressure Insertion Mechanism is designed for manual (non-assisted) transducer insertion into
operating pipes at low pressure. The mechanism uses an isolation valve and a packing gland for sealing.
Inserting the transducers into the pipe requires the following steps:
• Preparing for installation
• Mounting the insertion mechanism
• Inserting the transducer into the pipe
• Aligning the transducers
WARNING! The manual insertion mechanism is used for low-pressure applications (80 psig/6.5 bar
absolute or less). Use the appropriate safety precautions when inserting or withdrawing the insertion
mechanism.
3.2.1 Preparing for Installation
Before you begin, find a work area where you can stand the insertion mechanism upright without placing any weight
on the transducer (e.g., a bench with a cutout large enough for the transducer to slide through).
You will need the following items for installation:
• A packing tool (may be shipped with the flowmeter)
• A gasket for the isolation valve
• A straight edge ruler
• A tag to place on the isolation valve
• Bolts
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 31
Page 40

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Junction Box
Packing Gland
Barrel
Transducer
(90° head shown)
Transducer
(180° head shown)
3.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism
1. Before mounting the insertion mechanism on the isolation valve you should familiarize yourself with its
components (see the figure below):
• Junction box
• Barrel
• Packing gland
• Transducer
Note: Explosion-proof junction boxes are not pre-mounted on the end of the transducer when shipped.
32 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 41

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Top Compression Fitting
Four Bolts
Stop Ring
3.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism (cont.)
2. Visually inspect the transducer, and make sure the top compression fitting is not loose.
IMPORTANT: The stop ring at the end of the barrel should be loose. DO NOT tighten the compression fitting or you
could change the transducer alignment.
3. Remove the four bolts that fasten the barrel to the packing gland.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 33
Page 42

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Compression Fitting
(hand tight)
3.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism (cont.)
4. Retract the barrel from the packing gland so that the transducer head is recessed in the packing gland. You will
hear the stop ring click into place when the transducer is fully recessed.
34 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 43

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Bias 90 Assembly
with 90° Head
Transducer
Recessed in
Packing Gland
Tilted Diameter Assembly
with 180° Head
Transducer
Recessed in
Packing Gland
3.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism (cont.)
5. Visually inspect the mechanism. Make sure the transducer is recessed in the packing gland. Again, make sure
the top compression fitting is secure and hand tight.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 35
Page 44
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Gasket
Barrel
Packing
Tool
Gasket
Gasket
Isolation
Isolation
Downstream
Transducer Location
Upstream
Transducer Location
F
l
o
w
Valve
Valve
3.3 Mounting the Bias 90 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly
1. Lift the gasket and insert the packing tool into the packing nut. By turning the packing tool clockwise, tighten
the packing material so that the barrel stays up without support.
2. Verify that the isolation valves are securely installed with gaskets and hardware. Then, place a gasket on the
face of each isolation valve.
36 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 45

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Downstream Transducer Assy.
Identification Ring
(on Extended Range Version)
3.3 Mounting the Bias 90 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
3. Identify the upstream and downstream nozzles as follows:
• For a Standard Velocity Range application, the upstream and downstream nozzles are interchangeable,
because the system is bi-directional.
• For an Extended Velocity Range application, the system is not bi-directional. Note which nozzle is
designated as upstream and which is designated as downstream on the pipe. Then, identify the upstream
and downstream insertion mechanism assemblies. The downstream assembly is labeled with a ring marked
Downstream at the end of the assembly near the junction box (see the figure below).
4. Proceed with either the upstream or downstream assembly.
5. Lift the insertion mechanism by the barrel and place the insertion mechanism on the isolation valve.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 37
Page 46

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Bolts
Packing Tool
3.3 Mounting the Bias 90 Insertion Mechanism Transducer Assembly (cont.)
6. Line up the flange holes and bolt the packing gland to the isolation valve.
7. Using the packing tool, tighten the packing nut again so the nut is recessed.
WARNING! The packing material must be securely packed before the isolation valve is opened.
38 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 47

3.4 Inserting the Bias 90 Transducer into the Pipe
Barrel
Packing
Gland
Bolts
1. Before you open the isolation valve, carefully verify the following:
• The barrel is pulled up as far as it can go
• All bolts are secure
• The transducer head is recessed in the packing gland
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
WARNING! Follow all applicable safety codes and practices before opening the isolation valve.
2. Open the isolation valve.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 39
Page 48

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Place
Hands Here
Transducer
Alignment Marks
3.4 Inserting the Bias 90 Transducer into the Pipe (cont.)
3. Placing your hands on top of the barrel, push the barrel/transducer down into the pipe so that the barrel flange
and the packing gland flange meet. You may have to twist the barrel to get it moving.
4. For this Bias 90 configuration, orient the alignment marks on each barrel flange so that they are facing each
other. The alignment mark, which is marked with yellow paint, is scribed on the top and outside of the flange.
40 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 49

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Bolts
3.4 Inserting the Bias 90 Transducer into the Pipe (cont.)
5. Place two bolts into the flange in holes opposite each other , but not in the hole with the scribe mark. Then, hand
tighten the nuts.
Note:
DO NOT insert the remaining bolts until instructed to do so in the following section.
6. Install the second insertion mechanism by repeating the steps in the two previous sections. After the second
insertion mechanism is installed, proceed to one of the following sections:
• “Aligning the Transducers (Standard Velocity Range)” on page 42
• “Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range)” on page 42
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 41
Page 50

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Upstream
Transducer
F
l
o
w
Downstream
Transducer
3.5 Aligning the Transducers (Standard Velocity Range)
For applications with gas flow velocities up to 100 m/s, align the transducers as follows:
Note: These instructions apply to both the upstream and downstream transducer assemblies.
1. Use a straight edge to line up the alignment marks on the two barrel flanges.
2. Place the remaining bolts into the flanges and tighten them securely.
3. Place a tag on each isolation valve stating the following:
DO NOT OPERATE (CLOSE) WHEN
TRANSDUCER IS INSERTED INTO PIPE.
4. Refer to your flowmeter Startup Guide to make the transducer electrical connections.
3.6 Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range)
For applications with gas flow velocities up to 120 m/s, align the transducers as follows:
Note: The downstream transducer is pre-installed at the factory in the barrel of the downstream insertion
mechanism, to shift the signal direction 6° away from the upstream transducer signal.
1. Verify that the downstream transducer is located on the right to a person looking from the downstream end of
the pipe (see Figure 8 below). Contact GE if the port locations do not follow this convention.
Figure 8: Extended Range Transducer Installation
42 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 51

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Upstream
Downstream
Transducer
Transducer
Guide Plate
Upstream
Transducer
Cover Plate
3.6 Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range) (cont.)
2. Slide the end slot of the guide plate around the upstream transducer, and rotate the plate until the side slot is
around the downstream transducer (see Figure 9 below). Then, align the mark on the upstream transducer
barrel with the guide plate mark. Slightly tighten the upstream barrel flange bolts to maintain the alignment.
Figure 9: Installing the Guide Plate
3. Place the cover plate on top of the guide plate and slide it as far as possible until it is positioned around the
upstream transducer, as shown in Figure 10 below. Then, tighten the screws to secure it.
Figure 10: Installing the Cover Plate
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 43
Page 52

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Downstream
Transducer
Collar 6° Mark
Line on Transducer Tube
6° Mark
0° Mark
Downstream
Transducer
Collar 0° Mark
Guide Plate Line
Nuts on Flange
3.6 Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range) (cont.)
4. Slide the locking collar over the downstream transducer to the cavity on top of the guide plate. Align the 6°
mark on the top of the collar with the line on the transducer (see Figure 11 below). Then, tighten the collar set
screws until the collar is secured to the transducer.
5. Check to see if the 0° mark on the side of the locking collar is aligned with the line on the guide plate. If they
are not aligned, then loosen the nuts on top of the barrel flange and rotate the transducer assembly until the two
lines are aligned (see Figure 12 below). Then, re-tighten the nuts.
Figure 11: Installing the Locking Collar
Figure 12: Locking Collar 0° Mark Aligned with Guide Plate Line
44 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 53

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Upstream
Transducer
Upstream Transducer Line
Cover Plate Line
3.6 Aligning the Transducers (Extended Velocity Range) (cont.)
6. Check to see if the line on the upstream transducer tube is aligned with the line on the cover plate. If they are
not aligned, loosen the nuts on top of the barrel flange and rotate the transducer assembly until the two lines are
aligned (see Figure 13 below). Then, re-tighten the nuts.
7. Upon completion of the above steps, remove the cover plate, locking collar and guide plate from the transducer
assemblies.
8. Place the remaining bolts into the flanges and tighten them securely.
9. Place a tag on each isolation valve stating the following:
10. Refer to your flowmeter Startup Guide to make the transducer electrical connections.
Figure 13: Upstream Transducer Mark Aligned with Cover Plate Line
DO NOT OPERATE (CLOSE) WHEN
TRANSDUCER IS INSERTED INTO PIPE.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 45
Page 54

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Gasket
Barrel
Packing Tool
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly
1. Lift the gasket and insert the packing tool into the packing nut. Turning the packing tool clockwise, tighten the
packing material so that the barrel will stay up without support.
46 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 55

3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
2 PLACES; REF ONLY
3 INCH SCH 80 PIPE NOZZLE
3 INCH 150 LB, RF WELDING NECK FLANGE
2 PLACES; REF ONLY
FLOW
TRANSDUCER PORT
UPSTREAM
TRANSDUCER PORT
DOWNSTREAM
GASKET
GASKET
2. Check and make sure the isolation valves are securely installed with gaskets and hardware. Then, place a
gasket on the face of each isolation valve (see either Figure 14 below or Figure 15 on page 48).
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Figure 14: Standard Velocity Range Assembly
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 47
Page 56

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
ISOLATION BALL VALVE
2 PLACES; REF ONLY
3 INCH 150 LB RF,
FULL OPENING
RECOVERY ANGLE BOLT/NUT SPACER
RECOVERY ANGLE WEDGE
GASKET(S)
GASKET
TRANSDUCER PORT
FLOW
UPSTREAM
TRANSDUCER PORT
DOWNSTREAM
GASKET
2 PLACES; REF ONLY
3 INCH SCH 80 PIPE NOZZLE
3 INCH 150 LB, RF WELDING NECK FLANGE
2 PLACES; REF ONLY
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
48 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Figure 15: Extended Velocity Range Assembly
Page 57

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Downstream Transducer Assy.
Identification Ring
(on Extended Range Version)
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
3. Identify the upstream and downstream nozzles as follows:
• For a Standard Velocity Range application, the upstream and downstream nozzles are interchangeable,
because the system is bi-directional.
• For an Extended Velocity Range application, the system is not bi-directional. Note which nozzle is
designated as upstream and which is designated as downstream on the pipe. Then, identify the upstream
and downstream insertion mechanism assemblies. The downstream assembly is labeled with a ring marked
Downstream at the end of the assembly near the junction box (see the figure below).
4. Proceed with either the upstream or downstream assembly.
5. Lift the insertion mechanism by the barrel and place the insertion mechanism on the isolation valve.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 49
Page 58

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Bolts
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
6. Line up the flange holes and bolt the packing gland to the isolation valve.
50 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 59

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Packing Tool
3.7 Mounting the Tilted 45 Insertion Mechanism/Transducer Assembly (cont.)
7. Using the packing tool, tighten the packing nut again until the nut is recessed.
WARNING! The packing material must be securely packed before the isolation valve is opened.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 51
Page 60

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Barrel
Packing
Gland
Bolts
3.8 Inserting the Tilted 45 Transducer into the Pipe
1. Before you open the isolation valve, carefully verify the following:
• The barrel is pulled up as far as it can go
• All bolts are secure
• The transducer head is recessed in the packing gland
WARNING! Follow all applicable safety codes and practices before opening the isolation valve.
2. Open the isolation valve.
52 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 61

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Place
Hands Here
Transducer
Bolts
3.8 Inserting the Tilted 45 Transducer into the Pipe (cont.)
3. Placing your hands on top of the barrel, push the barrel/transducer down into the pipe so that the barrel flange
and the packing gland flange meet. You may have to twist the barrel to get it moving.
4. Place the bolts into the flange joining the barrel flange to the packing gland flange.
5. Tighten the bolts securely.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 53
Page 62

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.8 Inserting the Tilted 45 Transducer into the Pipe (cont.)
6. Install the second insertion mechanism by repeating the steps in the previous sections. Confirm that the
downstream transducer assembly is in the downstream port and the upstream transducer assembly is in the
upstream port.
Note: The following steps apply to both the upstream and downstream assemblies equally.
7. Place a tag on each isolation valve stating the following:
DO NOT OPERATE (CLOSE) WHEN
TRANSDUCER IS INSERTED INTO PIPE.
8. Refer to your flowmeter Startup Guide to make the transducer electrical connections.
3.9 Connecting an XAMP
This section explains how to correctly install and assemble an XAMP into a transducer junction box. It applies to all
three possible junction box options (see drawing #752-063 in Figure 24 on page 59), but only one of the junction box
options is used as an example in the steps below.
1. Place a 3/4” NPT compression fitting on the stem of the transducer closest to the BNC connector.
2. Torque the fitting into one of the 3/4” NPT ports of the junction box with at least 5 threads engaged. After the
fitting is torqued into place, ensure that the BNC head of the transducer extends slightly past the ground screw
bosses, as shown in Figure 16 below:
Figure 16: Torquing the NPT Reducer
3. If the BNC head extends too far into the junction box, it will make the assembly more difficult to install by
reducing the amount of area needed to properly store the excess cable. If the BNC head is not positioned
approximately where it is pictured in Figure 16 above, loosen the compression fitting and adjust the transducer .
Then, re-tighten the compression fitting.
54 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 63

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.9 Connecting an XAMP (cont.)
4. Torque the cable gland coming from the flowmeter electronics main hous ing into the other 3/4” NPT port in
the junction box until there are at least 5 threads of engagement (see Figure 17 below).
Figure 17: Torquing the Cable Gland
5. Verify that, with the transducer and the cable gland assembled, the junction box looks like Figure 18 below:
Figure 18: Assembled Transducer and Cable Gland
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 55
Page 64

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.9 Connecting an XAMP (cont.)
6. Connect the right angle male BNC plug to the exposed BNC cable from the cable gland assembly, as shown in
Figure 19 below.
Figure 19: Connecting BNC Plug to the Cable
7. Connect the female BNC plug of the XAMP to the male BNC transducer head as shown in Figure 20 below:
Figure 20: Female Plug to Male BNC Head
56 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 65

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.9 Connecting an XAMP (cont.)
8. Wrap the extra length of cable around the inside of the junction box such that the BNC heads do not rest on
other cables or on each other. The assembly should now look like Figure 21 below.
Figure 21: BNC Heads
9. Place the XAMP body into the junction box, resting the puck gently on the cables below it. To reduce stress
and strain on the joint. ensure that the cables of the XAMP rest naturally according to the slant at which they
exit the epoxy. The XAMP should remain still, and the cap of the junction box should rotate freely around the
XAMP.
Figure 22: Junction Box Cap
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 57
Page 66

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
3.9 Connecting an XAMP (cont.)
10. Place the cap of the junction box over the XAMP and tighten the cap until the junction box is firmly closed. Engage
the set screw (see Figure 23 below) to secure the cap in place.
Figure 23: Junction Box Set Screw
Note: To disconnect or uninstall the XAMP from the assembly, perform the above steps in reverse order.
58 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 67

3.9 Connecting an XAMP (cont.)
GE Sensing
1100 Techn ology P ark Dr.
Billerica, MA 0182 1 USA
1180
Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
Figure 24: Transducer Arrangement (dwg. #752-063, rev. L)
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 59
Page 68

Chapter 3. Installing the Transducer Assemblies
[no content intended for this page]
60 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 69

Chapter 4. Specifications
Chapter 4. Specifications
4.1 T5 Transducer Physical Specifications
Applications: Hazardous Area, Flare Gas, Hydrocarbon Gases, Saturated Steam
Installation Type: Wetted
Material: Standard: Titanium
Optional: 316 Stainless Steel, Monel
Field Mounting: Flowcell, Hot or Cold Tap
Process Connection: Flanged, 1.5 in. to 3 in. (40 mm to 80 mm)
Holder Type: Insertion Mechanism
Holder Ratings: 150#, 300#, 600#
Operating Frequency: Standard: 100 kHz
Optional: 50 kHz and 200 kHz
Pressure Range: 0 to 2700 psig
Electrical Rating: 200 V peak-to-peak, 5 mA
Ambient Temperature Range: –40° to +140°F (–40° to +60°C)
Process Temperature Range: –364° to +500°F (–220° to +260°C)
or Hastelloy
4.2 T5 Transducer Certifications
North American Explosion proof:
Class I, Division 1, Group C, D
Class II, Class III, Division 1, Group E, F, G
European/International Flameproof:
North American Weatherproof:
European/International Weatherproof:
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 61
II 2 G Ex d IIC T6...T2 Gb (T code dependent on Process Temperature)
Tamb –40° to +140
KEMA 01ATEX2045X: IECEx KEM09.0009X
Standards used: EN 60079-0:2012, EN 60079-1:2007, IEC 60079-0:2011,
IEC 60079-1:2007, Ed. 6.
IP66, TYPE 4X
200Vpp, 5mA
IP 66
o
F (–40° to +60oC)
Page 70

Chapter 4. Specifications
[no content intended for this page]
62 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 71

Warranty
Warranty
Each instrument manufactured by GE Sensing is warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship.
Liability under this warranty is limited to restoring the instrument to normal operation or replacing the instrument, at
the sole discretion of GE Sensing. Fuses and batteries are specifically excluded from any liability. This warranty is
effective from the date of delivery to the original purchaser. If GE Sensing determines that the equipment was
defective, the warranty period is:
• one year from delivery for electronic or mechanical failures
• one year from delivery for sensor shelf life
If GE Sensing determines that the equipment was damaged by misuse, improper installation, the use of unauthorized
replacement parts, or operating conditions outside the guidelines specified by GE Sensing, the repairs are not covered
under this warranty.
The warranties set forth herein are exclusive and are in lieu of all other warranties whether
statutory, express or implied (including warranties or merchantability and fitness for a
particular purpose, and warranties arising from course of dealing or usage or trade).
Return Policy
If a GE Sensing instrument malfunctions within the warranty period, the following procedure must be completed:
1. Notify GE Se n sin g , giv ing full details of the prob lem, and p rovi de the model number and serial number of th e
instrument. If the nature of the problem indicates the need for factory service, GE Sensing will issue a
RETURN AUTHORIZATION NUMBER (RAN), and shipping instructions for the return of the instrument to
a service center will be provided.
2. If GE Sensing instructs you to send your instrument to a service center, it must be shipped prepaid to the
authorized repair station indicated in the shipping instructions.
3. Upon receipt, GE Sensing will evaluate the instrument to determine the cause of the malfunction.
Then, one of the following courses of action will then be taken:
• If the damage is covered under the terms of the warranty , the instrument will be repai red at no cost to the owner
and returned.
• If GE Sensing determines that the damage is not covered under the terms of the warranty , or if the warranty has
expired, an estimate for the cost of the repairs at standard rates will be provided. Upon receipt of the owner’s
approval to proceed, the instrument will be repaired and returned.
T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide 63
Page 72

Warranty
[no content intended for this page]
64 T5 Flare Gas Transducer Installation Guide
Page 73

GE
Sensing
DECLARATION
OF
CONFORMITY
DOC-0028, Rev. G
We, GE Sensing
1100 Technology Park Drive
Billerica, MA 01821
USA
declare under our sole responsibility that the
Models T3, T5, T8, T11, T14 and T17 Wetted Ultrasonic Flow Transducers
Series BWT1 / F...PA / XAMP... Ultrasonic Flowmeter Transducer Assembly
to which this declaration relates, are in conformity with the following standards:
• EN 60079-0: 2012
• EN 60079-1: 2007
• II 2 G Ex d IIC T6...615°C Gb T3: KEMA06ATEX0052, T5: KEMA01ATEX2045X, T8: KEMA02ATEX2283X,
T11: KEMA02ATEX2252, T14: KEMA04ATEX2054X, T17: KEMA01ATEX2045X
Series BWT1 / F...PA / XAMP...: KEMA01ATEX2051X; IEC Ex KEM09.0010X
(DEKRA, Ultrechtseweg, 310 Arnhem, The Netherlands - NoBo 0344)
• EN 61326-1: 2006, Class A, Table 2, Industrial Locations
• EN 61326-2-3: 2006
• EN 61010-1: 2012, Overvoltage Category II
Other standards used:
• EN 50014: 1997 + A1, A2
• EN 50018: 2000
following the provisions of the 2004/108/EC EMC and 94/9/EC ATEX Directives.
Where products were initially assessed for compliance with the Essential Health and Safety Requirements of the
ATEX Directive 94/9/EC using earlier harmonized standards, a subsequent review has determined that “technical
knowledge” is unaffected by the current harmonized standards listed above.
The units listed above and any ancillary equipment supplied with them do not bear CE marking for the Pressure
Equipment Directive. They are supplied in accordance with Article 3, Section 3 (sound engineering practices and
codes of good workmanship) of the Pressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC for DN<25.
Billerica - January 2014
Issued Mr. Gary Kozinski
Certification & Standards, Lead Engineer
Page 74

[no content intended for this page]
Page 75

Page 76

Customer Support Centers
U.S.A .
The Boston Center
1100 Technology Park Drive
Billerica, MA 01821
U.S.A.
Tel: 800 833 9438 (toll-free)
978 437 1000
E-mail: sensing@ge.com
Ireland
Sensing House
Shannon Free Zone East
Shannon, County Clare
Ireland
Tel: +353 (0)61 470200
E-mail: gesensingsnnservices@ge.com
916-117 Rev. D
An ISO 9001-2008 Certified Company
www.ge-mcs.com/en/about-us/quality.html
www.ge-mcs.com
©2014 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Technical content subject to change without notice.
 Loading...
Loading...