Page 1

g
DEH203 R02
EntelliGuard™ Power Circuit Breakers
800–2000 A Frames, 240–600 Vac
Maintenance Manual
Page 2

Page 3

WARNINGS
CAUTIONS
NOTES
DEH203
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, AND NOTES
AS USED IN THIS PUBLICATION
Warning notices are used in this publication to emphasize that hazardous voltages, currents, or
other conditions that could cause personal injury are present in this equipment or may be associated with its use.
Warning notices are also used for situations in which inattention or lack of equipment knowledge
could cause either personal injury or damage to equipment.
Caution notices are used for situations in which equipment might be damaged if care is not taken.
Notes call attention to information that is especially significant to understanding and operating the
equipment.
This document is based on information available at the time of its publication. While efforts have
been made to ensure accuracy, the information contained herein does not cover all details or variations in hardware and software, nor does it provide for every possible contingency in connection
with installation, operation, and maintenance. Features may be described herein that are not present in all hardware and software systems. GE Consumer & Industrial assumes no obligation of
notice to holders of this document with respect to changes subsequently made.
GE Consumer & Industrial makes no representation or warranty, expressed, implied, or statutory,
with respect to, and assumes no responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, sufficiency, or
usefulness of the information contained herein. No warrantees of merchantability or fitness for
purpose shall apply.
The following are trademarks of GE Company:
EntelliGuard™, EntelliGuard Messenger™, Entellisys™
© Copyright 2005 GE Company
All Rights Reserved
i
Page 4

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview...................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Inspection and Maintenance..................................................................................................................1
1.3 Renewal Parts...........................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 2. Description
2.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................3
2.2 Frame Sizes.............................................................................................................................................. 3
2.3 Operation ................................................................................................................................................3
2.4 Fused Models...........................................................................................................................................3
2.5 Mounting.................................................................................................................................................3
2.6 Trip Units................................................................................................................................................3
2.7 Interruption Ratings ...............................................................................................................................3
Chapter 3. Storage, Safety, and Maintenance
3.1 Storage.....................................................................................................................................................5
3.2 Safety........................................................................................................................................................5
3.3 Maintenance............................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 4. Breaker Operation
4.1 Operating Instructions............................................................................................................................7
Sequence of Operations ..................................................................................................................7
Operation of the Breaker................................................................................................................7
Padlock Operation...........................................................................................................................8
4.2 Control Wiring ........................................................................................................................................8
4.3 Breaker Interlocks ...................................................................................................................................8
Drawout Interlock............................................................................................................................ 8
Contact Interlock.............................................................................................................................8
Spring Discharge Interlock .............................................................................................................8
4.4 Equipment Interlocks.............................................................................................................................. 8
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
5.1 Lubrication............................................................................................................................................11
5.2 Removing and Reinstalling the Breaker ..............................................................................................11
Removing the Breaker...................................................................................................................11
Installing the Breaker.................................................................................................................... 11
5.3 Slow Closing the Breaker ......................................................................................................................13
5.4 Separation and Reconnection of Front and Back Frames................................................................... 13
Separation of Front and Back Frames for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08......................................13
Reconnection of Front and Back Frames for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08.................................14
Separation of Front and Back Frames for EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20.............................................................................................................................................16
Reconnection of Front and Back Frames for EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20.............................................................................................................................................16
ii
Page 5

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
5.5 Breaker Mechanism Operation and Adjustment.................................................................................18
Trip Latch Adjustment..................................................................................................................19
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
6.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................20
6.2 Arc Chute Removal and Replacement .................................................................................................20
Arc Chutes in EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 Breakers....................................................................20
Arc Chutes in EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers............................20
6.3 Back Frame Assembly............................................................................................................................21
6.4 Replacement of Contacts ......................................................................................................................21
Contact Replacement on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 Breakers.................................................21
Contact Replacement on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers..........24
6.5 Adjusting the Contacts..........................................................................................................................26
Contact Adjustment on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 Breakers....................................................26
Contact Adjustment on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers............26
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
7.1 Primary Disconnects..............................................................................................................................28
Primary Disconnect Replacement on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 Breakers..............................28
Primary Disconnect Removal on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20
Breakers..........................................................................................................................................28
Primary Disconnect Installation on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20
Breakers..........................................................................................................................................29
7.2 Secondary Disconnect...........................................................................................................................31
Secondary Disconnect Removal....................................................................................................31
Secondary Disconnect Installation................................................................................................31
7.3 Flux Shifter ............................................................................................................................................32
Flux Shifter Adjustment.................................................................................................................32
Removing the Flux Shifter ............................................................................................................32
Installing the Flux Shifter..............................................................................................................32
7.4 Draw-Out Mechanism............................................................................................................................34
Draw-Out Mechanism Removal ....................................................................................................34
Draw-Out Mechanism Installation................................................................................................34
Draw-Out Mechanism Adjustment................................................................................................34
7.5 Escutcheon.............................................................................................................................................36
Escutcheon Removal .....................................................................................................................36
Escutcheon Installation.................................................................................................................36
7.6 Charging Handle...................................................................................................................................36
Removing the Charging Handle...................................................................................................36
Installing the Charging Handle....................................................................................................36
Table of Contents
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
8.1 Bell Alarm with Lockout........................................................................................................................38
Removing the Bell Alarm with Lockout........................................................................................38
Installing the Bell Alarm with Lockout.........................................................................................39
8.2 Shunt Trip .............................................................................................................................................39
iii
Page 6

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Table of Contents
Removing the Shunt Trip............................................................................................................. 40
Installing the Shunt Trip ..............................................................................................................40
8.3 Charging Motor..................................................................................................................................... 41
Removing the Charging Motor.....................................................................................................41
Installing the Charging Motor...................................................................................................... 41
Removing the Motor Cut-Off Switch ............................................................................................41
Installing the Motor Cut-Off Switch..............................................................................................41
Adjusting the Motor Cut-Off Switch............................................................................................. 43
8.4 Remote Close......................................................................................................................................... 43
Removing the Remote Close......................................................................................................... 44
Installing the Remote Close.......................................................................................................... 44
8.5 Open-Fuse Lockout ...............................................................................................................................45
Removing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 800 A and 1600 A Breakers..................................................45
Installing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 800 A and 1600 A Breakers................................................... 45
Removing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 2000 A Breakers...................................................................45
Installing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 2000 A Breakers ....................................................................46
8.6 Remote Charge-Indication Switch........................................................................................................47
Removing the Remote Charge-Indication Switch........................................................................ 47
Installing the Remote Charge-Indication Switch.........................................................................47
8.7 Network Interlock..................................................................................................................................48
iv
Page 7

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
List of Figures
1. Front of the EntelliGuard circuit breaker, showing the locations of standard and optional
features....................................................................................................................................................... 2
2. Elementary diagram of the breaker control circuits. ...............................................................................9
3. Location of the secondary disconnect...................................................................................................... 9
4. Installing the breaker into the compartment......................................................................................... 12
5. Disconnecting the closing spring assembly. ........................................................................................... 13
6. Removing or installing the secondary disconnect ................................................................................. 14
7. Movable contact connection to the breaker main shaft on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers...... 14
8. Separating the front and back frames on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.................................. 15
9. Movable contact connection to the breaker main shaft on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16,
EGS20, and EGF20 breakers. .................................................................................................................. 16
10. Separating the front and back frames on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20
breakers.................................................................................................................................................... 17
11. Breaker mechanism in the CLOSED position. ...................................................................................... 18
12. Breaker mechanism in the TRIPPED position. ..................................................................................... 18
13. Breaker mechanism in the RESET position........................................................................................... 18
14. Adjusting the trip latch. .......................................................................................................................... 19
15. Typical back frame assembly, EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08. .................................................................. 21
16. Typical back frame assembly, EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20............................ 21
17. Upper (stationary) contact assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers................................... 22
18. Lower (movable) contact assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers...................................... 22
19. Removal and installation of contact assemblies on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers .................. 23
20. Removal and installation of contact assemblies on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20 breakers........................................................................................................................................ 25
21. Stationary main and intermediate contact styles. ..................................................................................25
22. Replacement of stationary arcing contacts............................................................................................. 25
23. Contact adjustment on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers............................................................... 26
24. Contact adjustment on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, EGF20 breakers. ............................. 27
25. Primary disconnect assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers ............................................... 28
26. Primary disconnect assembly for EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers........ 28
27. Primary disconnect removal and installation on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers...................... 29
28. Primary disconnect removal and installation on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20 breakers........................................................................................................................................ 30
29. Primary disconnect adjustment on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20 and EGF20 breakers. ....30
30. Secondary disconnect.............................................................................................................................. 31
31. Secondary disconnect terminal numbering. ..........................................................................................31
32. Removing or installing the secondary disconnect. ................................................................................ 31
33. Flux shifter............................................................................................................................................... 32
34. Flux shifter adjustment............................................................................................................................ 32
35. Removal or installation of a flux shifter ................................................................................................. 33
36. Draw-out racking mechanism. ................................................................................................................ 34
v
Page 8

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
List of Figures
37. Draw-out mechanism adjustment............................................................................................................34
38. Draw-out racking mechanism removal and installation.........................................................................35
39. Escutcheon kit and related parts. ............................................................................................................36
40. Charging handle ......................................................................................................................................37
41. Charging handle removal and installation.............................................................................................37
42. Charging handle mounting detail ..........................................................................................................37
43. Bell Alarm with Lockout connections on the secondary disconnect. ....................................................38
44. Bell Alarm with Lockout accessory kit. ....................................................................................................38
45. Bell Alarm with Lockout installation or removal. ...................................................................................38
46. Front view of the Bell Alarm with Lockout installation, showing the breaker mechanism tab
engaging the mounting plate slot............................................................................................................39
47. Orientation of the label on the Bell Alarm module for installation. .....................................................39
48. Shunt Trip connections to the auxiliary switch and secondary disconnect. .........................................40
49. Shunt Trip accessory kit...........................................................................................................................40
50. Shunt Trip module removal and installation. ........................................................................................40
51. Charging Motor and cut-off switch..........................................................................................................41
52. Removal and installation of the Charging Motor and cut-off switch.....................................................42
53. Cut-off switch adjustment.........................................................................................................................43
54. Remote Close accessory kit.......................................................................................................................43
55. Remote Close installation and removal...................................................................................................44
56. Open-Fuse Lockout accessory ..................................................................................................................45
57. Open-Fuse Lockout connections to the secondary disconnect for EGF-20 breakers.............................45
58. Open-Fuse Lockout installation and removal .........................................................................................46
59. Remote charge-indication switch............................................................................................................47
60. Remote charge-indication switch removal and installation...................................................................47
61. Remote charge-indication switch side view.............................................................................................47
62. Network Interlock connections to the secondary disconnect. ................................................................48
63. Network Interlock assembly mounting to the circuit breaker bottom frame .........................................49
64. Network Interlock module fastening to the mounting plate. .................................................................49
65. Manual reset assembly mounting............................................................................................................49
66. Trip paddle and set lever gap calibration .............................................................................................49
vi
Page 9

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
List of Tables
1. Recommended service intervals, in number of ON-OFF operations, for EntelliGuard breakers........... 1
2. Breaker interruption ratings..................................................................................................................... 4
3. Sequence of operations that may be performed with the EntelliGuard circuit breaker......................... 7
4. Secondary disconnect terminals with standard and optional connections. ......................................... 10
5. Key to numbered parts in Figure 11, Figure 12, and Figure 13 ............................................................. 18
6. Bell Alarm with Lockout wires and corresponding secondary disconnect terminals. ..........................39
7. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Shunt Trip accessory. ................................................. 40
8. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Charging Motor accessory.......................................... 41
9. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Remote Close accessory.............................................. 43
vii
Page 10

Page 11
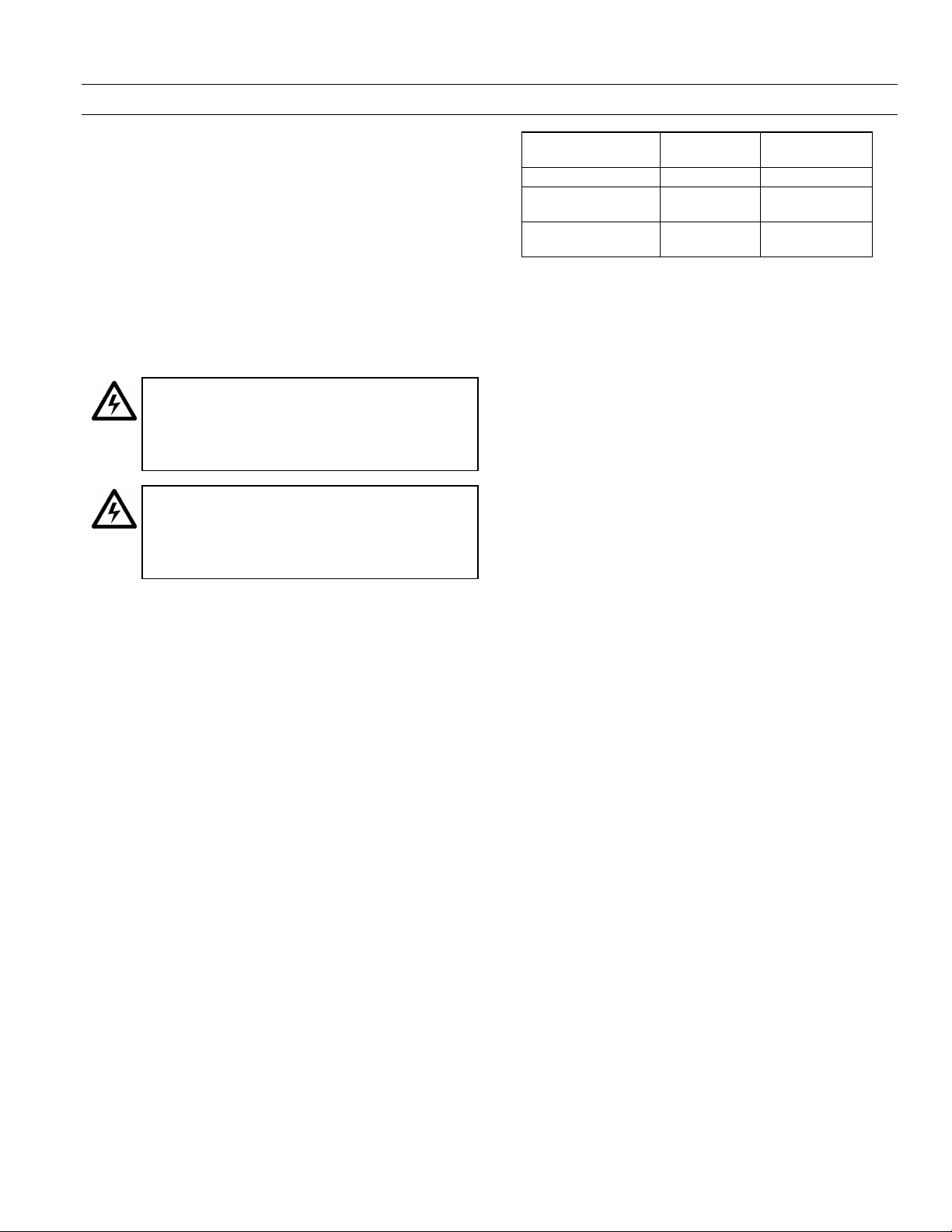
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview
These instructions describe the procedures for maintenance and operation of EntelliGuard 800-2000 ampere
low-voltage power circuit breakers. Figure 1 is a front view
of the breaker, with key features indicated.
The proper use, care, and maintenance of these breakers
is important both from the safety aspect of protecting personnel and for minimizing equipment damage when
faults occur. Persons who apply, use, and service these
breakers should be familiar with the information presented in this publication.
WARNING: Before inspecting or beginning
any maintenance work on a circuit breaker, the
breaker must be in the OPEN position and dis connected from all voltage sources, both power
and control.
AVERTISSEMENT: Avant d’inspecter ou de
débuter tout travail de maintenance d’un disjoncteur, celui-ci dout être en position OPEN et
débranché de toutes les sources de voltage, à la
fois de puissance et de contrôle.
1.2 Inspection and Maintenance
Circuit breakers should be maintained under a systematic
program. Take each breaker out of service periodically for
inspection and maintenance to help establish high reliability in service. This policy is facilitated by keeping one
or more spare breakers to install in place of breakers
requiring maintenance. Keeping a stock of recommended
renewal parts ensures that maintenance work can be done
quickly.
The frequency at which an individual breaker should be
inspected depends on the circumstances of its use. Table 1
lists the ANSI-recommended service interval with the GErecommended interval for EntelliGuard breakers.
EntelliGuard breakers should be inspected after every
short circuit interruption, after every number of ON-OFF
operations given in Table 1, or every two years, whichever
comes first. EntelliGuard breakers have been built and
tested to operate reliably with inspections at twice the
ANSI interval, thus saving time and money by reducing
breaker downtime.
Source of
Recommendation 800 A Frame
ANSI 1750 500
EntelliGuard, no
load
EntelliGuard, at
frame rating
Table 1. Recommended service intervals, in number of ON-OFF
operations, for EntelliGuard breakers.
If a breaker is installed in an area of high humidity or a
dusty atmosphere, it should be inspected more often.
Monthly inspections might be warranted for a breaker
operated under severe conditions.
Always inspect the breaker after it has interrupted a short
circuit or ground fault.
A standard inspection should consist of the following
steps:
1. Visual Check – Look for dirt, grease, or other
foreign material on all breaker parts. Check
insulating surfaces for conditions that could
degrade insulating properties, such as cracks or
evidence of overheating. Check for foreign objects
on the bottom of the breaker compartment. Check
for loose or damaged control wiring and for similar
problems.
2. Operation – Observe a few close-open operations
using the operating handle. If a breaker is seldom
operated, such that it remains open or closed for six
months or more, open and close the breaker several
times in succession.
3. Interlocks – During the operational check, verify
that the safety interlocks are working properly.
4. Arc Chutes and Contacts – Inspect the arc chutes
and contacts for excessive burning or breakage.
Check the amount of contact depression or wipe
when the breaker is closed.
5. Accessories – Verify that the various accessories are
working properly.
3500 1000
2800 800
1600 and
2000 A Frames
1.3 Renewal Parts
Many of the parts and assemblies contained in
EntelliGuard breakers are available as replacement parts.
See DEF004 for a complete listing.
1
Page 12
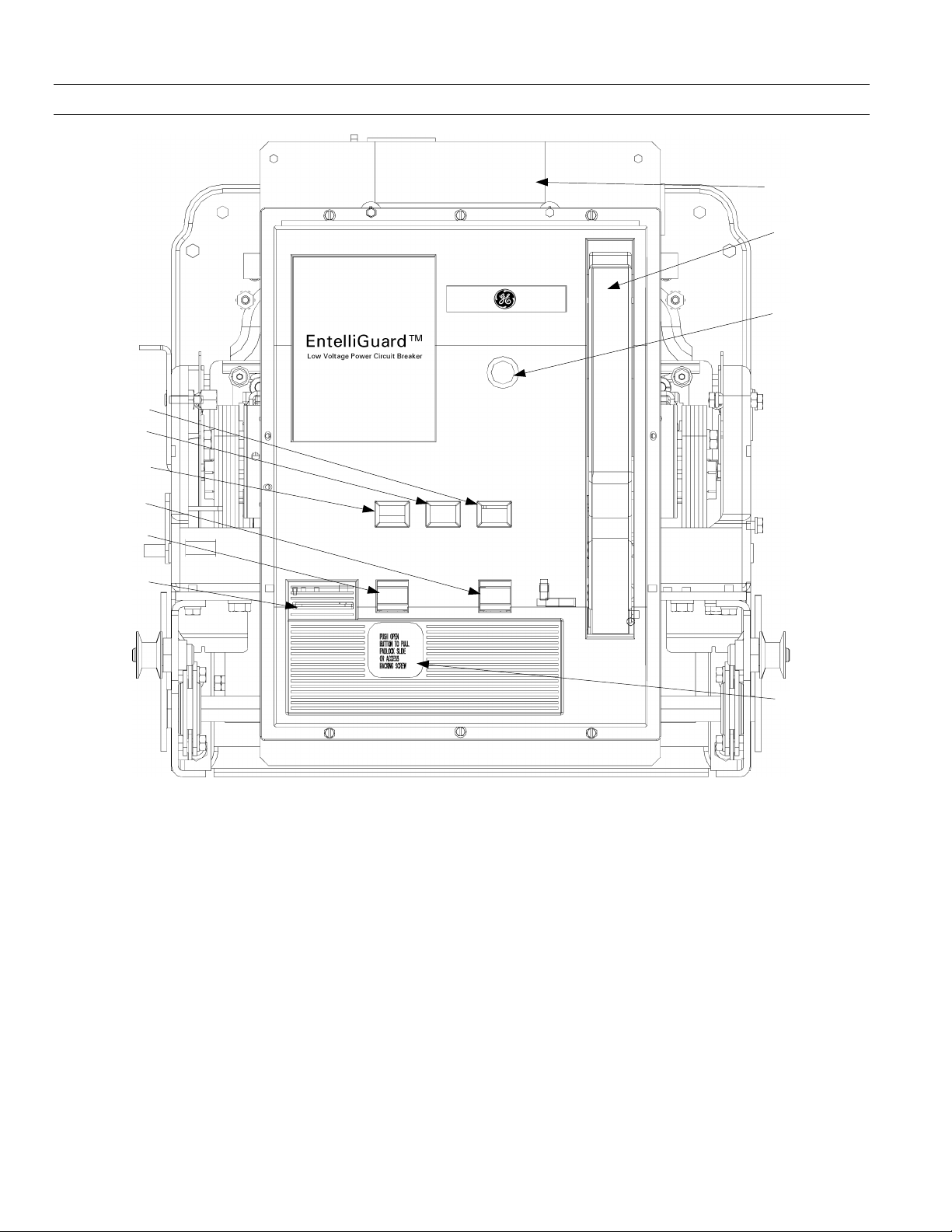
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
A B C D E F G H J K
Chapter 1. Introduction
Figure 1. Front of the EntelliGuard circuit breaker, showing the locations of standard and optional features.
A Indicator: DISC (white)
TEST (white)
CONN (white)
B Indicator: CHARGED (yellow)
DISCHARGED (white)
C Indicator: CLOSED (red)
OPEN (green)
D CLOSE button (black)
E OPEN button (red)
F Padlock provision
G Catalog number, rating, and date code nameplate
H Manual charging handle
J Bell Alarm with Lockout target/RESET button
K Draw-out racking screw (behind cover)
2
Page 13

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 2. Description
2.1 Introduction
EntelliGuard low-voltage power circuit breakers control
and protect power circuits up to 600 volts. They will safely
switch loads and automatically clear circuits during abnormal conditions when used with the EntelliGuard
Messenger™. These include short circuits, sustained
overloads, and ground faults.
EntelliGuard breakers contain a “quick-make, quickbreak” mechanism, which stores energy in a closing spring
for quick release. During closing, some energy is
transferred to an opening spring to be used subsequently
for fast tripping.
The three main functional components of the breaker are
its mechanism, an assembly consisting of the conductive
components, and the interrupter.
The mechanism is designed to receive energy, store it, and
later deliver it to close the breaker contacts. It must be able
to reverse the closing operation at any point upon receipt
of a trip signal from the EntelliGuard Messenger (that is,
it must be “trip-free”). Finally, it must also open a closed
breaker quickly enough to minimize contact erosion and
to effectively transfer the arc to the arc chutes.
The current-carrying components are assembled on the
back frame, which provides the required mechanical support and insulating structure. The conductive components are the studs for external connections, the movable
and stationary contact sets, and the pivots for the movable
contacts.
The interrupter components are the arcing contacts, the
arc runners mounted on the back base, and the removable
arc chute assemblies.
In addition to these basic components, a breaker may be
equipped with a combination of accessories and interlocking devices.
breaker, and a Shunt Trip to open the breaker. External
control power is required to energize the motor and its
control circuit. All breakers are equipped with a manual
charging handle so that the closing springs can be
charged without motor control power.
2.4 Fused Models
Internally fused breakers are available in 800- and 1600ampere frame sizes. They are not interchangeable with
unfused breakers, since fused breakers require deeper
compartments to accommodate the fuses.
2.5 Mounting
EntelliGuard breakers are designed for draw-out
mounting. Draw-out breakers are easily installed into or
removed from their switchgear cubicle. They are
equipped with a racking mechanism, which is used to
insert or withdraw the breaker, and primary and
secondary disconnects, which connect and disconnect
automatically.
2.6 EntelliGuard Messenger™
EntelliGuard low-voltage power circuit breakers are
intended for use in Entellisys™ Low-Voltage Switchgear
only. The breaker frames do not contain trip units or
current transformers. Thus, the EntelliGuard circuit
breaker must be used in concert with the EntelliGuard
Messenger and the current transformers mounted within
the switchgear cubicle. For installation and operation of
the EntelliGuard Messenger, see DEH231 and DEH234.
2.7 Interruption Ratings
2.2 Frame Sizes
The EntelliGuard breakers covered in this manual are
available in 800-ampere, 1600-ampere, and 2000-ampere
frame sizes. These values represent the maximum
continuous-current rating of each frame. In addition,
each breaker carries a specific rating that is determined by
the current sensor ampere rating or the maximum setting
of the EntelliGuard Messenger™ with which it is used.
2.3 Operation
EntelliGuard breakers are available with either manual or
electric operation. The mechanism closing springs of
manually operated breakers are charged by operating the
charging handle on the front of the breaker.
Electrically operated breakers contain an electric
Charging Motor that charges the closing springs, a
Remote Close accessory with antipump to close the
Table 2 lists the short-circuit current that each breaker
type is rated to interrupt for each maximum rated voltage.
3
Page 14
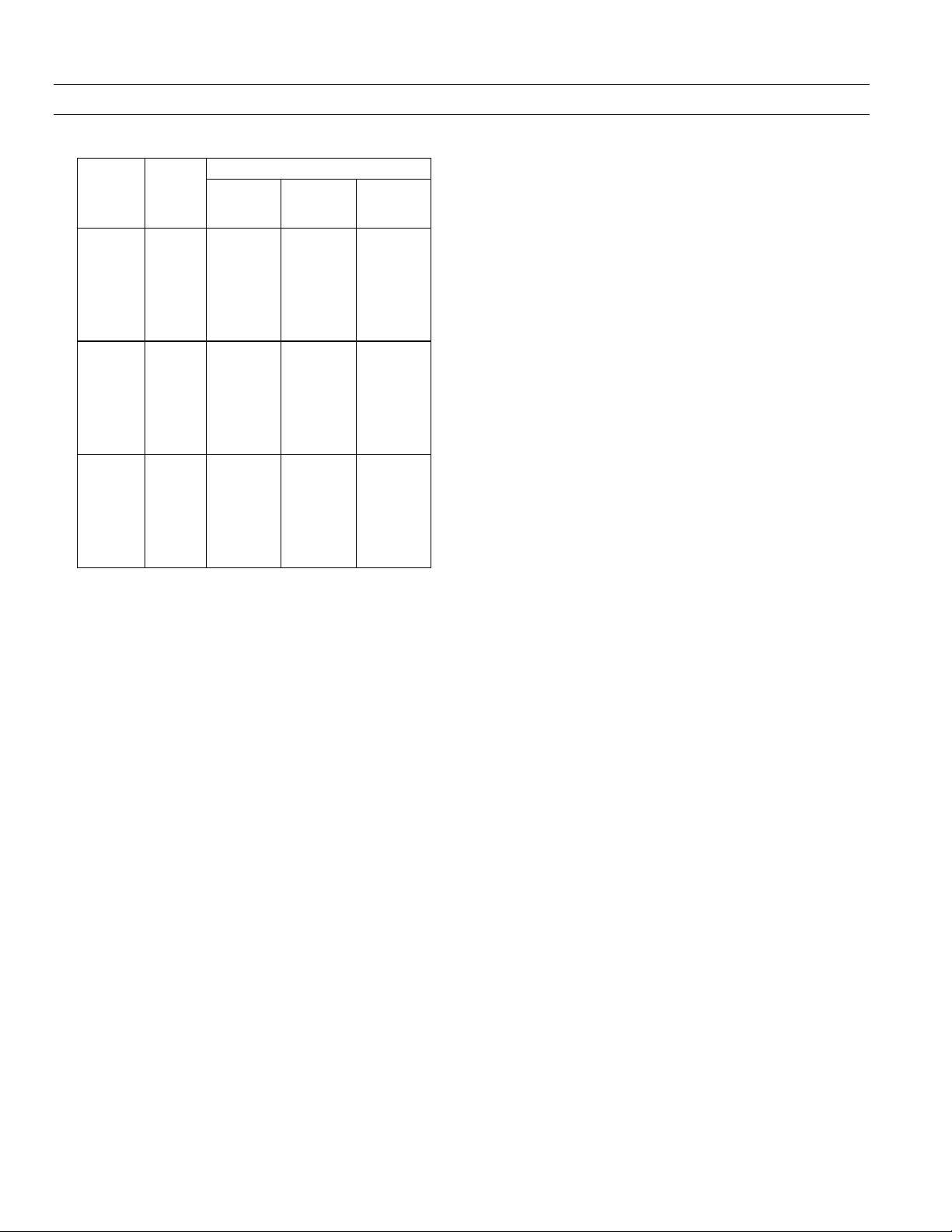
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 2. Description
Rated AC
Voltage,
Nominal
(max)
600
(635)
480
(508)
240
(254)
Short-Circuit RMS Symmetrical kA
Breaker
Type
EGS-08
EGH-08
EGX-08
EGS-16
EGH-16
EGS-20
EGS-08
EGH-08
EGX-08
EGS-16
EGH-16
EGS-20
EGS-08
EGH-08
EGX-08
EGS-16
EGH-16
EGS-20
Short-Time
Withstand
30
42
50
42
65
65
30
42
65
50
65
65
30
42
65
50
65
65
With
Inst. Trip
30
42
50
42
65
65
30
42
65
50
65
65
42
50
65
65
65
65
Without
Inst. Trip
30
42
50
42
65
65
30
42
65
50
65
65
30
42
65
50
65
65
Table 2. Breaker interruption ratings.
(EGF-08/16/20 rated at 200kA).
4
Page 15
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 3. Storage, Safety, and Maintenance
3.1 Storage
The breaker should be put into service immediately in its
permanent location. If this is not possible, the following
precautions must be taken to ensure proper storage of the
breaker
• Protect the breaker against condensation, preferably
by storing it in a warm, dry room, since water absorption has an adverse effect on the insulating parts.
• Store the breaker in a clean location free from corrosive gases or fumes. It is particularly important to
protect the equipment from moisture and cement
dust, as this combination is corrosive to many parts.
CAUTION: If the breaker is stored for any
length of time, inspect it periodically to ensure
that steel parts have not begun to rust and to
ensure good mechanical condition. If the
breaker has been stored under unfavorable
atmospheric conditions, it must be cleaned and
dried before being placed in service.
ATTENTION: Si le disjoncteur est remisé pour
peu importe la période de temps, inspectez-le
périodiquement afin de vous assurer que les
pièces d’acier n’ont pas commencé à rouiller et
de vous assurer de leur bonne condition
mécanique. Si le disjoncteur a été remisé à des
conditions atmosphériques défavorables, il doit
être nettoyé et séché avant d’être mis en service.
3.2 Safety
Each facility must maintain a safety program for the protection of personnel, as well as other equipment, from the
hazards associated with electrical equipment.
The following requirements are intended to augment a
facility’s safety program, not to supplant local responsibility for devising a complete safety program. The following
basic industry-accepted safety requirements are applicable
to all major electrical equipment, such as switchgear and
switchboards. General Electric neither condones nor
assumes any responsibility for practices that deviate from
these requirements.
1. All conductors must be assumed to be energized
unless their potential has been measured as ground
and suitable grounding conductors have been
applied to prevent energizing. Many accidents have
been caused by back feeds from various sources.
2. Although interlocks are provided to reduce some of
the risks, each individual’s actions are essential to
prevent accidents when performing service or main tenance. Each person’s knowledge, mental awareness, and planned and executed actions often
determine if an accident will occur. The most
important principle for avoiding accidents is that all
associated personnel carefully apply a thorough
understanding of the specific equipment with
regard to its purpose, its construction, its operation,
and situations that could be dangerous.
3. All personnel associated with installation, operation,
and maintenance of electrical equipment, such as
power circuit breakers and other power-handling
equipment, must be thoroughly instructed, with
periodic retraining, about power equipment in general and the specific equipment with which they will
be working in particular. Instruction books, actual
devices, and appropriate safety and maintenance
procedures, such as OSHA publications, the
National Electrical Safety Code (ANSI C2), the
National Electrical Code, and NFPA 7 OB Electrical
Equipment Maintenance, must be closely studied
and followed. During actual work, supervisors
should audit procedures to ensure conformance.
4. Excellent maintenance is essential for reliability and
safety of all electrical equipment. Industry publications of recommended maintenance practices, such
as ANSI/NFPA 70B, Electrical Equipment Maintenance,
are readily available.
3.3 Maintenance
Both long- and short-term maintenance of all electrical
equipment is essential for reliability and safety. Maintenance programs must be well-planned and carried out
consistently with both industry experience and the manufacturer’s recommendations. The local environment must
always be considered such programs, including such
variables as ambient temperature, extreme moisture,
number of operations, corrosive atmosphere, significant
insect problems, and any other unusual or abusive condition of the application.
One of the critical service activities, sometimes neglected,
is the calibration of various control devices. These monitor conditions in the primary and secondary circuits,
sometimes initiating emergency corrective action, such as
opening or closing circuit breakers. In view of the vital
roles of these devices, it is important to follow a periodic
test program.
General Electric recognizes that the interval between periodic checks will vary, depending on the environment, the
type of device, and the customer’s experience. GE recommends that, until the customer has accumulated sufficient
experience to select a test interval best suited to the local
requirements, all significant calibrations be checked at
one- to two-year intervals.
Operation and maintenance guides supplied by manufacturers normally address components that require service
or maintenance during the useful life of the equipment.
However, they cannot include every possible part that
could require attention, particularly over a long service
period or under adverse conditions. Maintenance
personnel must be alert to deterioration of any part of the
5
Page 16

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 3. Storage, Safety, and Maintenance
supplied switchgear, taking such action as necessary to
restore it to serviceable status.
If additional assistance is required in the planning and
performance of maintenance, contact GE Installation and
Field Service (1-888-434SERV / 1-888-434-7378) to
undertake the maintenance or to provide technical
assistance, such as the latest publications.
The performance and safety of this equipment may be
compromised by the modification or supplied parts or
their replacement by non-identical substitutes. All such
design changes must be qualified to ANSI/IEEE Standard
C37.59.
Each customer should methodically keep written maintenance records as an aid in future service planning and
equipment reliability improvement. Unusual experiences
should be promptly reported to General Electric (1-888GER-ESOLve).
6
Page 17
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 4. Breaker Operation
4.1 Operating Instructions
Sequence of Operations
The sequence of operations that may be performed on the
circuit breaker are listed in Table 3.
Operation of the Breaker
Manually Charging the Closing Springs
Pull the operating handle down about 90° (until it stops)
six times to fully charge the closing springs. This will
not close the breaker contacts. The charge indicator will
show CHARGED on a yellow background.
NOTE: The breaker cannot be closed unless
the springs are fully charged and the handle is
stored fully in.
NOTE: Le disjoncteur ne peut être fermé à
moins que les ressorts ne soient pleinement
chargés et que la poignée ne soit pleinement
rentrée.
Electrically Charging the Closing Springs
If the breaker is equipped with the (optional) Charging
Motor, the closing springs may also be charged with any
the following methods:
• With the breaker in the TEST position, install the
motor fuse in the fuse holder in the upper left corner
of the breaker compartment.
• Operate the Charging Motor by applying the rated
voltage to secondary disconnect terminals 8 and 17.
Power to the motor is removed automatically by a
cutoff switch when the springs are fully charged.
• If power is lost during the charging cycle, finish
charging the springs by cycling the charging handle
until the indicator shows CHARGED on a yellow
background.
The closing springs will automatically recharge after
closing if control power is maintained at terminals 8 and
17.
Open/Closed
Indicator
OPEN Open DISCHARGED Discharged Mechanism may be charged
OPEN Open CHARGED Charged Contacts may be closed
CLOSED Closed DISCHARGED Discharged
CLOSED Closed CHARGED Charged Contacts may be opened
Main Breaker
Contacts
Charge
Indicator
Condition of Close
Table 3. Sequence of operations that may be performed with the EntelliGuard circuit breaker
Closing the Breaker
Close the breaker contacts with any of the following
methods:
• Depress the CLOSE button on the front of the
breaker.
• Close the breaker using the Entellisys™ HMI.
• Energize the (optional) Remote Close accessory by
applying the rated voltage to secondary disconnect
terminals 9 and 18.
If the breaker is closed electrically and the closing voltage
is maintained, an antipump device prevents a second closing operation on the breaker in the event it is tripped
OPEN. The closing impulse must be released for 1 to 2.5
seconds and reapplied before a second closing operation
can occur.
If the closing voltage is applied while the closing springs
are not fully charged, the Remote Close coil energizes, but
operation of the closing mechanism is blocked. The
closing voltage must be removed and reapplied when the
springs are fully charged to close the breaker.
A mechanical interlock prevents the closing springs from
discharging if an attempt is made to close an already
CLOSED breaker.
NOTE: The main breaker contacts cannot be
closed if any of the following conditions apply:
• The draw-out mechanism is in any position other than TEST or CONN, as displayed on the breaker position indicator.
• The (optional) Bell Alarm with Lockout
was not reset after an overcurrent lockout.
• The (optional) Open Fuse Lockout was
not reset after replacement of a blown fuse.
• The (optional) Network Interlock was not
reset after a set operation.
These conditions must be corrected before the
breaker can be closed. Attempts to close the
breaker before these conditions are corrected
may result in discharge of the closing springs
without closing the main contacts.
Springs
Mechanism may be recharged or
Contacts may be opened
Next Permissible
Operating Function
7
Page 18
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 4. Breaker Operation
NOTE: Les contacts principaux du disjoncteur
ne peuvent être fermés si l’une ou l’autre des
conditions suivantes s’appliquent:
• Le mécanisme de retrait du ressort est en
tout autre position que: TEST ou DISC, tel
que montré à la position indicatrice du disjoncteur.
• L’alarme optionnelle avec cloche n’a pas
été remise en place après un blocage par
surintensité de courant.
• Le mécanisme optionnel de déclenchement par sous voltage n’a pas été
enclenché.
• Le verrouillage réciproque optionnel de
réseaun'était pas réenclenché après une
opération d'enclenchement.
Il faut que ces situations soient corrigées avant
de procéder à la fermeture du disjoncteur.
Opening the Breaker
Open the breaker contacts with any of the following
methods:
• Depress the OPEN button on the front of the breaker.
• Open or trip the breaker using the Entellisys™ HMI.
• Energize the (optional) Shunt Trip accessory by
applying the rated voltage to secondary disconnect
terminals 5 and 7.
Padlock Operation
The padlock provision prevents the breaker from closing
by holding the trip latch in the tripped position. Up to
three padlocks with 1/4" or 3/8" diameter shanks, or scissor-type safety lockout hasps may be inserted at one time.
To install a padlock, use the following procedure:
WARNING: Be sure to test for proper
operation of the mechanism, as described in
step 1, before using it to secure the breaker.
AVERTISSEMENT: Assurez-vous de tester que
le mécanisme opère correctement, tel que
décrit à l'étape 1, avant de l'utiliser pour fixer le
disjoncteur.
1. To check for proper installation of the padlock
mechanism, hold in the OPEN button, pull out the
padlock slide, insert a 1/8" rod or #10 gage solid
wire, and attempt to close the breaker.
The breaker must not close.
2. While holding the OPEN button in, slide the padlock plate out and hold it in place.
3. Put the padlock or safety lockout hasp into one of
the three holes in the padlock plate; this will
prevent the plate from returning to its unlocked
position and prevent the breaker from closing.
4.2 Control Wiring
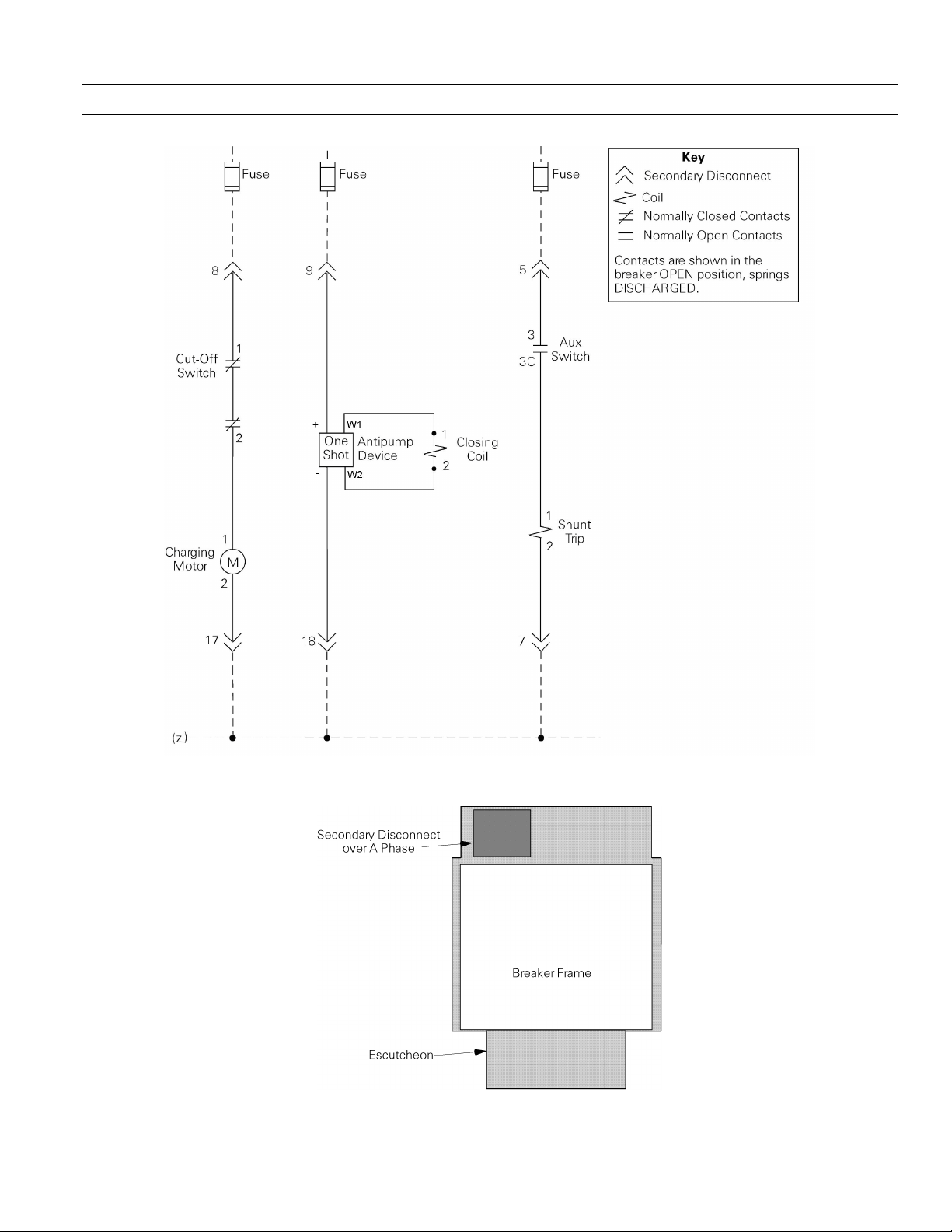
Figure 2 is the wiring diagram for the breaker control
circuits. Table 4 lists the secondary disconnect terminals
and the items connected to each. The location of the
secondary disconnect is illustrated in Figure 3.
4.3 Breaker Interlocks
EntelliGuard breakers are equipped with a number of
safety interlocks to prevent improper operation of the
breaker.
Draw-Out Interlock
The draw-out interlock prevents the breaker from being
closed when the breaker is in neither the CONN or TEST
position, but is between these positions. A pin on the side
of the breaker engages a ramped cam in the switchgear
cubicle. When the pin is lifted 3/8" the breaker is held tripfree.
An additional interlock holds the breaker trip-free whenever the access door to the racking mechanism is open.
Contact Interlock
The contact interlock keeps the door to the draw-out
mechanism racking screw closed whenever the breaker
contacts are CLOSED. This prevents changes to the
breaker’s position with the main contacts CLOSED.
Spring Discharge Interlock
The spring discharge interlock functions in conjunction
with the circuit breaker’s draw-out interlock and a
compartment-mounted cam to discharge the closing and
opening springs before the breaker can be withdrawn
from the compartment.
4.4 Equipment Interlocks
Additional optional interlocks may be furnished with the
breaker enclosure. The Key Interlock prevents the breaker
from closing when the interlock is engaged and requires
one or more keys to operate. The Door Interlock prevents
opening of the enclosure door when the breaker is in the
CONN position. It can be defeated for authorized access.
The door can be opened by racking the breaker to the
TEST or DISC position.
8
Page 19
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 4. Breaker Operation
Figure 2. Elementary diagram of the breaker control circuits.
Figure 3. Location of the secondary disconnect (top view of the breaker).
9
Page 20

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 4. Breaker Operation
10 Aux Switch (NO contact)
1 Aux Switch
2 Aux Switch
11 Aux Switch (NC contact)
13 Flux Shifter
12 Flux Shifter common
5 Shunt Trip
7 Shunt Trip common
9 Close Circuit
18 Close Circuit common
8 Closing Spring Charging Motor
17 Closing Spring Charging Motor common
3 Remote Charge Indicator
4 Remote Charge Indicator
14 Bell Alarm Trip
6 Bell Alarm Trip Common
16 Bell Alarm Status
19 Bell Alarm Status Comon
OR
15 Network Interlock SET
20 Network Interlock RESET
21 Network Interlock SET/RESET common
16 Network Interlock Status
19 Network Interlock Status common
22 OFLO (phase A)
23 OFLO (phase A)
24 OFLO (phase B)
25 OFLO (phase B)
26 OFLO (phase C)
27 OFLO (phase C)
28 Spare
29 Spare
30 Spare
31 Spare
32 Spare
33 Spare
34 Spare
35 Spare
36 Spare
Table 4. Secondary disconnect terminals with standard and optional connections.
10
Page 21

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
WARNING: Before inspecting a breaker or
beginning any maintenance, the breaker must
be disconnected from all voltage sources, both
power and control, and the breaker must be in
the OPEN position.
AVERTISSEMENT: Avant d’inspecter ou de
débuter tout travail de maintenance d’un disjoncteur, celui-ci dout être en position OPEN et
débranché de toutes les sources de voltage, à la
fois de puissance et de contrôle.
5.1 Lubrication
Bearing points and sliding surfaces should be lubricated
with a thin film of GE Lubricant D6A15A1 (MobilGrease
28, catalog number 193A1751P1). Clean the surfaces to be
lubricated with an industry-approved solvent.
Note: Remove all excess lubricant with a clean, lint free cloth to avoid accumulation of dirt or dust.
The contact surfaces of the primary disconnect fingers
should be cleaned and lubricated with GE Lubricant
D6A15A1.
Note: Do not lubricate the main, intermediate, or
arcing breaker contacts or the outside diameters of
rollers. Also do not lubricate the ground radius on the
closing prop or trip latch, as this will cause
accumulation of dirt and dust.
5.2 Removing and Reinstalling the
Breaker
Maintenance or inspection should be performed with the
breaker removed from the compartment and placed on a
workbench. Figure 4 illustrates these procedures.
Removing the Breaker
1. With the compartment door closed and latched,
trip the breaker.
2. Push the OPEN button and slide the racking screw
access door to the right, exposing the racking screw.
3. Engage the Remote Racker accessory (WPEGRRLV)
or the Racking Handle (0324B4721G001) with the
racking screw. Rotate the screw counterclockwise
using either the Remote Racker or the Racking
Handle until the breaker travels from the
Connected position through the Test position (as
indicated by the legends CONN and TEST,
respectively, on the draw-out position indicator)
and comes to a solid stop in the Disconnected
position (as indicated by the legend DISC on the
position indicator). At this point, the primary and
secondary disconnects are disengaged.
4. Open the compartment door. Pull out the rails,
then pull the breaker out to the withdrawn position
at the track travel limit
5. Verify that the indicators on the front of the breaker
show that the springs are DISCHARGED and the
breaker is OPEN.
6. Attach the lifting bracket (catalog number
0324B4551G1) by locating the hooks in the slots on
the side of the breaker and on the closing spring
anchor pin. Raise the breaker until its mounting
wheels clear the rails.
7. Push the rails back into the compartment, then
move the breaker forward until the primary disconnects clear the compartment. Lower the breaker
onto a flat surface free of protrusions that could
damage the breaker’s internal parts. Close the compartment door.
8. Place the draw-out mechanism in the Connect position to deactivate the interlocks that would otherwise prevent the breaker mechanism or contacts
from closing. Engage the Racking Handle to the
racking screw and turn it clockwise until it stops, as
indicated by the legend CONN on the position indicator.
Installing the Breaker
Use the following procedure to install the draw-out
breaker into its compartment.
1. Before lifting a breaker to its intended compartment
location, observe the following precautions:
• Check the compartment to ensure that it is free of
foreign objects.
• Verify that the breaker is the correct type for the
compartment.
• Ensure that the breaker is OPEN.
• Apply a thin coat of GE lubricant D6A15A1 to the
breaker’s primary disconnects.
• Insert the racking handle and rotate it fully counterclockwise to ensure that the racking cams on
the breaker are correctly positioned for initial
engagement with the pins in the breaker cubicle.
The position indicator on the front of the breaker
should show DISC.
2. Attach the lifting bracket by locating the hooks in
the slots on the side of the breaker and on the closing spring anchor pin.
3. Pull the rails all the way out to their withdrawn position.
4. Slowly lower the breaker onto the rails so that the
grooves in the rollers on the side of the breaker
align with the rails.
11
Page 22

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
Figure 4. Installing the breaker into the compartment.
12
Page 23

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
5. Push the breaker into the compartment until it
reaches the stops. This is the Disconnect position
(as shown by the legend DISC on the draw-out position indicator). At this point the racking arms are
positioned to engage the fixed racking pins in the
compartment and are ready to begin the racking
motion. Push the rails back into the compartment.
6. Close the compartment door. Push the OPEN button
and slide the racking screw access door to the right,
exposing the racking screw.
7. Engage the Remote Racker accessory or the Racking
Handle with the racking screw. Rotate the screw
clockwise using either the Remote Racker or the
Racking Handle through the Test position, until
the racking screw comes to a solid stop. The breaker
is now in the Connected position, as shown by the
legend CONN on the position indicator flag. Note
that a loud click will be heard as the spring-loaded
secondary disconnect detent releases as the breaker
moves beyond the TEST position.
8. Depress the red OPEN button to close the racking
screw access door to permit breaker closing.
5.3 Slow Closing the Breaker
3. After the bolt is removed, use the maintenance
handle (catalog number 568B386P1) to rotate the
ratchet assembly roller onto the closing prop.
4. Remove the closing prop by either pushing the
CLOSE button or by pushing the solenoid armature
of the Remote Close.
5. Continue turning the camshaft until the contacts
and mechanism are in the fully closed position. The
cam then supports the cam roller and the contacts
develop maximum depression.
6. Push the TRIP button to release the mechanism and
open the contacts.
CAUTION: The mechanism and contacts will
open with normal speed and force.
ATTENTION: Le mécanisme et les contacts
s’ouvriront à une vitesse et une force normales.
When replacing the hex-head bolt, turn the camshaft with
the charging handle to align the mating holes in the
lower spring assembly and camshaft linkage. Tighten the
bolt to 360 lb-in.
Closing the breaker slowly, while observing the action of
the mechanism and contacts, is a good way to judge the
correctness of mechanical and contact relationships.
Some of the maintenance procedures described later
involve slow closing the breaker. Use the following procedure to slow close the breaker:
1. Remove the escutcheon. (See Section 7.5)
2. The closing spring must be isolated from the
mechanism camshaft. Make sure that the breaker
mechanism is DISCHARGED and the spring is at
minimum extension, then remove the hex-head bolt
shown in Figure 5 to disconnect the lower spring
assembly from the mating camshaft linkage.
Figure 5. Disconnecting the closing spring assembly.
5.4 Separation and Reconnection of
Front and Back Frames
Some repair operations require separation of the front
and back frames, per the following procedure. The
breaker must first be removed from its compartment, as
described in Section 5.2, and placed on a suitable work
surface.
Separation of Front and Back Frames for
EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 8.
1. Verify that the breaker contacts are open and that
the closing springs are discharged.
2. Remove the mounting bolt securing each of the arc
chutes and lift out the arc chutes. Remove the four
interphase barriers.
3. Remove the two screws and standoffs securing the
secondary disconnect to the mounting plate, taking
care to retain the spring washer from the pin on the
underside of the disconnect, as illustrated in Figure
6. Cut the wire ties securing the secondary disconnect leads to the mounting plate and to the breaker
back frame. Slide the secondary disconnect off the
support bracket. Secure the secondary disconnect to
the front frame assembly.
4. Remove the bolt, lock washer, and nut connecting
each tie bar to the front frame. Lift off the tie bars.
13
Page 24

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
5. Remove the four bolts, washers, and nuts that attach
the secondary disconnect mounting plate to the
back frame. Remove the mounting plate.
6. Remove one of the snap rings and slide out the pin
connecting each of the movable contact assemblies
to the breaker main shaft, as illustrated in Figure 7.
7. Carefully place the breaker on its back, resting on
the primary disconnects.
8. Remove the six bolts and lock washers attaching the
front and back frames on the side panels.
9. Lift the front frame straight off the back frame.
Reconnection of Front and Back Frames for
EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 8.
1. Carefully place the back frame on a suitable work
surface, resting on the primary disconnects.
2. Place the front frame assembly onto the back frame,
being careful to line up the mounting holes in the
side panels. Insert the six bolts and lock washers and
tighten them to 200 in-lb.
3. Carefully place the breaker upright, resting on its
bottom surface.
4. Reconnect the movable contact assemblies to the
breaker main shaft by inserting the connecting pin
and reattaching the snap ring, as illustrated in
Figure 7.
5. Place the secondary disconnect mounting plate in
position and secure with the four bolts, washers, and
nuts.
6. Connect the ends of the tie bars to the secondary
disconnect mounting plate and attach the other
ends to the front frame with the bolt, lock washer,
and nut removed earlier. Tighten to 96 in-lb.
7. Place the flexible washer on the molded pin on the
bottom of the secondary disconnect, then slide the
two feet into the slots on the mounting plate. Secure
with the two screws and standoffs, as illustrated in
Figure 6. Replace the wire bundle into the channel
on the top of the frame and secure with wire ties.
8. Insert the four interphase barriers into their mounting slots.
9. Slide the arc chutes into position, with the slots over
the movable contact arms. Secure with the bolts and
lock washers removed on disassembly.
10. Check that no wires are interfering with breaker
operation and that all bolts and nuts are tight.
Operate the breaker a few times to verify proper
operation.
Figure 6. Removing or installing the secondary disconnect.
Figure 7. Movable contact connection to the breaker main shaft on
EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.
14
Page 25

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
Figure 8. Separating the front and back frames on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.
15
Page 26

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
Separation of Front and Back Frames for
EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 10.
1. Verify that the breaker contacts are open and that
the closing springs are discharged.
2. Remove the two bolts and lock washers that attach
the arc chute retainer to the front frame and
remove the retainer. Slide out the arc chutes and
interphase barriers. Note that there are three distinct types of phase barriers: right, inner (2), and
left.
3. Remove the two screws and standoffs securing each
secondary disconnect to the mounting plate, taking
care to retain the spring washer from the pin on the
underside of the disconnect, as illustrated in Figure
6. Cut the wire ties securing the secondary disconnect leads to the mounting plate and to the breaker
back frame. Slide the secondary disconnect off the
support bracket. Secure the secondary disconnect to
the front frame assembly.
4. Remove the three screws and washers that attach
the secondary disconnect mounting plate to the
back frame. Remove the mounting plate.
5. Remove one of the snap rings and slide out the pin
connecting each of the movable contact assemblies
to the breaker main shaft, as illustrated in Figure 9.
On the two outer poles, first remove the bolt and
cover over the outer end of the pin.
6. Carefully place the breaker on its back, resting on
the primary disconnects.
7. Remove the two nuts and lock washers attaching the
tie bars to the front frame.
8. Remove the six nuts and lock washers (the top connections also have spacers) connecting the front
and back frames.
9. Lift the front frame straight off the back frame.
Reconnection of Front and Back Frames for
EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 10.
1. Carefully place the back frame on a suitable work
surface, resting on the primary disconnects.
2. Carefully lower the front frame onto the back frame,
lining up the six studs in the sides of the back frame
with the corresponding holes in the front frame.
Attach the six nuts and lock washers, with the two
spacers on the top studs, and tighten to 250 in-lb.
Figure 9. Movable contact connection to the breaker main shaft on
EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
3. Attach the two nuts and lock washers to secure the
tie bars to the front frame. Tighten to 250 in-lb.
4. Carefully place the breaker upright, resting on its
bottom surface.
5. Reconnect the movable contact assemblies to the
breaker main shaft by inserting the connecting pin
and reattaching the snap ring, as illustrated in
Figure 9. Reattach the cover and bolt on the two
outer poles.
6. Reattach the secondary disconnect mounting plate
with three screws and washers to the back frame.
7. Place the flexible washer on the molded pin on the
bottom of the secondary disconnect, then slide the
two feet into the slots on the mounting plate. Secure
with the two screws and standoffs, as illustrated in
Figure 6. Replace the wire bundle into the channel
on the top of the frame and secure with wire ties.
8. Insert the four interphase barriers into position,
noting the proper locations for the three different
types.
9. Slide the arc chutes into position. Place the arc
chute retainer in position and secure with the two
bolts and lock washers to the front frame. Tighten
securely.
10. Check that no wires are interfering with breaker
operation and that all bolts and nuts are tight.
Operate the breaker a few times to verify proper
operation.
16
Page 27

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
left
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
Figure 10. Separating the front and back frames on EGX08, EGPS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers (EGS20 illustrated).
17
Page 28

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
5.5 Breaker Mechanism Operation
and Adjustment
Figure 11, Figure 12, and Figure 13 show the mechanism
components in the CLOSED, TRIPPED, and RESET
conditions, respectively. Numbers in parentheses refer to
the indicated items in the figures listed in Table 5. The
closing spring is in the charged position for all of these
details.
Closed Position – The movable contacts are pushed against
the stationary contacts by the toggle linkage, as illustrated
in Figure 11. The toggle linkage is held in position
through the engagement of its cam roller (4), with the
prop (1), the secondary latch/roller (5), the secondary
latch (10), and the trip latch (7).
Tripped Position – The mechanism goes from the CLOSED
position to the TRIPPED position, illustrated in Figure 12,
when the trip shaft (6) is rotated by either the manual trip
button or one of the other trip devices. The trip latch (7)
is assembled to the trip shaft. When the trip shaft rotates,
the trip latch disengages from the secondary latch roller
(5). The secondary latch pivots, resulting in the collapse
of the toggle linkage. This collapse, along with the opening spring (11), shown in Figure 13, causes the breaker
contacts to open.
Reset Position – The closing cam (2), assembled to the
cam shaft (3), is rotated by the Charging Motor, manual
charging handle, or maintenance handle. The cam
engages the cam roller and partially extends the toggle
linkage. This allows the secondary latch (10) to pivot
against the front frame, as illustrated in Figure 13, leaving
a gap between the trip latch (7) and secondary latch roller
(5). The secondary latch is now in a position to engage
both the trip latch and cam roller (4).
The breaker closes when the closing springs discharge
and rotate the cam (2) against the cam roller (4). The
toggle linkage is fully extended, pivoting the secondary
latch (10) from the front frame and engaging it with the
trip latch (7) and cam roller (4), as shown in Figure 11.
When the breaker is closed and the closing spring is discharged, the upper cam roller (4) is supported by the cam
(2) rather than the prop (1). The mechanism must be in
this position to check contact adjustment, as described in
Chapter 6.
Figure 11. Breaker mechanism in the CLOSED position.
Figure 12. Breaker mechanism in the TRIPPED position.
Figure 13. Breaker mechanism in the RESET position.
1 Prop 7 Trip latch
2 Cam 8 Insulated coupling
3 Camshaft 9 Main shaft
4 Cam roller 10 Secondary latch
Secondary latch
5
roller
6 Trip shaft
Table 5. Key to numbered parts in Figure 11, Figure 12, and
11 Opening spring
Figure 13.
18
Page 29

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Trip Latch Adjustment
Use the following procedure to adjust the trip latch, as
illustrated in Figure 14.
1. Remove the breaker from its compartment and
place it on a suitable work surface.
2. Remove the arc chutes and phase barriers, as
described in Section 6.2.
3. Charge the closing springs with the manual charging handle and close the breaker.
4. Turn the trip latch adjustment screw in (clockwise)
until the breaker trips. Withdraw the screw
(counter-clockwise) 41/2 turns.
Chapter 5. Breaker Maintenance
Figure 14. Adjusting the trip latch.
19
Page 30

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
6.1 Introduction
Breakers subjected to frequent interruption of high currents may eventually require replacement of their contacts. The general rule for determining if replacement is
required is the loss of one-half or more of the mass of the
contact tip material. Roughening or light pitting of the
contact surface does not indicate loss of ability to carry or
interrupt current.
When contacts are replaced, they must be adjusted to
ensure that the proper force and contact depression is
developed between the movable and stationary contacts
when the breaker is closed. This is called the wipe adjustment. Wipe is the distance through which the stationary
contacts move when the breaker closes. It is measured
between the point of contact on a stationary contact when
the breaker is open and the position of the same point
when the breaker is closed. The actual wiping motion is
greater than this measurement, since the contacts overtravel.
The wipe adjustment provides proper depression to assure
full current-carrying capacity without overheating and
influences proper current transfer during interruption of
fault currents. Transfer of the current is the forced
sequential movement from the main to the intermediate
contacts, then to the arcing contacts, to the arc runner,
and finally to the arc chutes, where energy is dissipated
and the arc is extinguished. Contact wipe should be
checked periodically during normal maintenance inspections and after any overcurrent trip.
CAUTION: Before performing any contact
adjustment or replacement, disable the closing
springs, as described in Section 5.3.
ATTENTION: Avant d’effectuer tout
ajustement ou remplacement de contact,
neutraliser les ressorts de fermeture, tel que
décrit à la Section 5.3.
6.2 Arc Chute Removal and
Replacement
The arc chutes should be removed and inspected at the
regular inspection period. Arc chutes and interphase barriers are available as renewal parts.
The breaker must be removed from its compartment, as
described in Section 5.2, and placed on a suitable work
surface.
There are two types of arc chutes used in these breakers,
depending on frame size.
Arc Chutes in EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08
Breakers
Use the following procedure to remove and replace the
arc chutes, as illustrated in Figure 8.
1. Verify that the breaker contacts are open and the
closing springs are discharged.
2. Remove the mounting bolt and lock washer securing each of the arc chutes and lift out the arc
chutes. Remove the four interphase barriers.
3. Check the arc chutes and barriers for damage and
replace them, if necessary.
4. Replace the four interphase barriers into their slots.
5. Slide the arc chutes into place, with the slots over
the movable contact arms.
6. Replace the mounting bolt and lock washer securing each arc chute to the breaker frame.
CAUTION: All insulating barriers must be in
place before the breaker is placed back into
service.
ATTENTION: Toutes les barriéres isolatrices
doivent être en place avant que le disjoncteur
ne soit replacé en service.
Arc Chutes in EGX08, EGS16, EGF16,
EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers
Use the following procedure to remove and replace the
arc chutes, as illustrated in Figure 10.
1. Verify that the breaker contacts are open and the
closing springs are discharged.
2. Remove the two bolts and lock washers that attach
the arc chute retainer to the front frame and
remove the retainer.
3. Slide out the arc chutes and interphase barriers.
Note that there are three distinct types of phase barriers: right, inner (2), and left.
4. Check the arc chutes and barriers for damage and
replace them, if necessary.
5. Replace the four interphase barriers into their correct slots.
6. Slide the arc chutes into place, with the slots over
the movable contact arms.
7. Replace the arc chute retainer bar and secure it with
two bolts and lock washers.
CAUTION: All insulating barriers must be in
place before the breaker is placed back into
service.
20
Page 31

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
ATTENTION: Toutes les barriéres isolatrices
doivent être en place avant que le disjoncteur
ne soit replacé en service.
6.3 Back Frame Assembly
The breaker back frame assembly consists of a frame to
which the pole units are mounted. Each pole unit is connected to the breaker main shaft. Typical examples of the
two styles of back frame are shown in Figure 15 and Figure
16. Complete back frame assemblies are available as
renewal parts.
Each pole consists of a separately mounted upper (stationary) and lower (movable) contact assembly, including
the line and load mounting studs.
6.4 Replacement of Contacts
Contact assemblies are different between the EGS08,
EGF08, and EGH08 frames and the EGX08, EGS16,
EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 frames. The
procedures for contact replacement for each type follow.
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
Contact Replacement on EGS08, EGF08, and
EGH08 Breakers
Complete upper and lower contact assemblies are available as renewal parts, as illustrated in Figure 17 and Figure
18. In addition, arcing and main contact springs are
available for the upper contact assemblies. The insulator
link assembly and movable contact springs are available
for the lower contact assemblies.
Use the following procedure to replace a contact assembly,
as illustrated in Figure 19. It is not necessary to separate
the front and back frames.
1. Remove the breaker from its compartment and
place it on a suitable work surface.
2. Remove the primary disconnect from the pole on
which the contact assembly is to be changed, as
described in Section 7.1.
3. Remove the arc chutes and interphase barriers, as
described in Section 6.2.
4. For a lower contact assembly, remove one of the
snap rings from the pin connecting the contact arm
to the breaker main shaft, then slide out the pin.
5. Remove the nut, lock washer, and flat washer from
each of the four studs attaching the contact assembly to the breaker back frame.
6. Slide the contact assembly forward, then lift it out
through the top of the breaker.
Figure 15. Typical back frame assembly, EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08.
Figure 16. Typical back frame assembly, EGX08, EGS16, EGF16,
EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20.
21
Page 32

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
7. To replace only the stationary contact springs, use
the following procedure:
a. Remove the insulating caps over the bolt head
and nut securing the arcing contacts. Remove the
nut, two flat washers, two springs, and bolt.
Remove the arcing contacts.
b. Remove the bolt, flat washer, nut, and lock washer
securing the main contacts to the assembly.
Remove the main contacts and springs.
c. Insert the new main contact springs and the exist-
ing main contacts into position on the contact
assembly. Replace the bolt, nut, and washers to
secure the main contacts.
d. Place one of the new arcing contact springs and a
flat washer onto the bolt removed in b. Place the
arcing contacts in position, slide the bolt through
the holes, and place the other new spring and a
flat washer and nut onto the bolt. Replace the
insulating caps on the bolt head and nut.
8. To replace only the movable contact springs and
insulator link assembly, use the following procedure:
a. Remove the bolt, flat washer, lock washer, nut,
and two bushings securing the insulator link
assembly and movable main contacts to the contact arm and remove the link assembly and main
contacts.
b. Remove the bolt, nut, two small flat washers, two
springs, and two large flat washers from the movable contact arm pivot.
c. Place a small flat washer, replacement spring, and
large flat washer onto the bolt removed in b.; slide
the bolt through the contact arm pivot; and place
a large flat washer, replacement spring, small flat
washer, and nut onto the bolt.
d. Place a flat washer and bushing onto the bolt
removed in a.; slide the bolt through the replacement insulator link assembly, movable main contacts, and contact arm; and place a bushing, flat
washer, and nut on the bolt.
9. Place the contact assembly back into position, with
the four studs through the appropriate holes in the
back frame. Replace the nuts, flat washers, and lock
washers on the studs.
10. For a lower contact assembly replace the pin attaching the insulator link assembly to the breaker main
shaft and secure with the snap ring removed earlier.
11. Adjust the contacts as described in Section 6.5.
12. Replace the arc chutes and interphase barriers
13. Replace the primary disconnect.
Figure 17. Upper (stationary) contact assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and
EGH08 breakers (EGH08 has two additional main contacts).
Figure 18. Lower (movable) contact assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and
EGH08 breakers (EGH08 has two additional main contacts).
22
Page 33

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
Figure 19. Removal and installation of contact assemblies on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.
23
Page 34

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
Contact Replacement on EGX08, EGS16,
EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers
For the following procedures, illustrated in Figure 20, the
breaker must be removed from its compartment and
placed on a suitable working surface. Remove the arc
chutes and interphase barriers, as described in Section
6.2.
Stationary Contacts
Use the following procedure to replace the stationary contacts.
1. Remove the four screws holding the arc runner in
place and remove the arc runner. Take care not to
damage or lose the insulating washer underneath
the lock washer and flat washer on the two lower
screws.
2. For replacement of stationary main and intermediate contacts:
a. Release each contact spring by holding the corre-
sponding intermediate or main contact, extending the spring, and removing the spring from the
contact. The end pieces of each spring have a
small hole for inserting a spring puller.
b. Remove each contact as its spring is disengaged.
Clean off the existing lubricant on the pivot area.
Replace with a small amount of GE Lubricant
D6A15A1 (MobilGrease 28, catalog number
193A1751P1).
c. Insert each replacement main and intermediate
contact and secure with its contact spring. Note
that main and intermediate contacts are
differentiated by the number of chamfers on the
corners of the contact surfaces, as illustrated in
Figure 21. It is important that this distinction be
observed when replacing the contacts.
3. For replacement of stationary arcing contacts, as
illustrated in Figure 22:
a. Remove the two screws and lock washers securing
the arcing contact pivot to the assembly and
remove the pivot.
b. Remove the insulating spacers, contact pin, and
arcing contacts.
c. Insert the replacement arcing contacts, the con-
tact pin, and insulating spacers.
d. Place the arcing contact pivot in position and
secure with its two screws and lock washers.
4. Place the arc runner in position and secure with its
four screws. Ensure that the insulating washers are
in place on the lower screws. Tighten the screws to
45 in-lb.
Movable Contacts
Use the following procedure to replace the movable contacts.
1. Remove the snap ring from the coupling pin and
slide out the pin.
2. Remove the screw, washer, and spring from one side
of the pivot pin. Carefully remove the pivot pin.
3. Slip out the contact arms.
4. Clean any existing lubricant from the pivot pin.
Place a small amount of GE Lubricant D6A15A1
(MobilGrease 28, catalog number 193A1751P1) on
the pivot pin and the pivot surfaces of the new
contact arms.
5. Install the new arm, insert the pivot pin, and replace
the pivot spring, washer, and screw. Tighten to 90
in-lb.
6. Install the coupling pin and secure with the snap
ring.
7. Adjust the contacts as described in Section 6.5.
24
Page 35

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
Figure 20. Removal and installation of contact assemblies on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
Figure 21. Stationary main and intermediate contact styles.
Figure 22. Replacement of stationary arcing contacts.
25
Page 36

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
6.5 Adjusting the Contacts
Adjust the contact depression whenever contacts are
replaced. In addition, check and adjust, as necessary, at
the normal maintenance interval.
Contact Adjustment on EGS08, EGF08, and
EGH08 Breakers
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 23.
1. Contact depression is correct if the center of the roll
pin falls within the two sides of the scribed adjustment mark on the side of the stationary main contact.
2. If adjustment is necessary, remove the nut, washer,
and bushing from the end of the pivot bolt securing
the insulator link assembly to the movable contact
arm, then remove the bolt and other washer and
bushing.
3. Turn the contact adjusting link in or out of the insulator link assembly. Increase its length to increase
contact depression and shorten the link to decrease
contact depression.
4. Reassemble the insulator link assembly to the contact arm with the pivot bolt, nut, two washers, and
two bushings.
Contact Adjustment on EGX08, EGS16,
EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 Breakers
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 24.
1. Remove the arc chutes and phase barriers, as
described in Section 6.2.
2. To establish a reference for measurement, fasten
the aluminum arc chute retainer to the breaker
mechanism frame with small C clamps, as shown.
Ensure that the C clamps do not interfere with any
moving parts.
3. Measure dimension ‘A’ with the contacts open and
again with the contacts closed. Note that the measurement is made from the second contact spring
end (first stationary main contact). The difference
in the measurements should be 0.06–0.10 inch,
which provides 0.05–0.08 inch main contact depression.
4. To adjust contact depression, do the following:
a. Remove the retaining ring from one side of the
pin connecting the drive link to the movable contact arms and remove the pin.
b. Adjust the depression by turning the link in one-
half-turn increments. Note that the link has lefthand threads. One-half turn changes dimension
A by about 0.03 inch, which is equivalent to about
0.02 inch in contact depression.
5. Repeat for all poles.
Figure 23. Contact adjustment on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.
26
Page 37

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 6. Contact Maintenance
Figure 24. Contact adjustment on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
27
Page 38

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
This section describes procedures for replacing the standard parts and assemblies available as renewal parts.
Before any of the operations in this chapter can be performed, the breaker must be removed from its compartment, as described in Section 5.2, and placed on a suitable
work surface.
7.1 Primary Disconnects
Primary disconnects provide the flexible connection
between the breaker line and load terminals and the
equipment line and load terminals.
Primary disconnect assemblies are different between the
EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 frames, as illustrated in Figure
25, and the EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and
EGF20 frames, as illustrated in Figure 26. The procedures
for removal and installation of the two types are described
below.
Primary Disconnect Replacement on EGS08,
EGF08, and EGH08 Breakers
Figure 25. Primary disconnect assembly for EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08
breakers.
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 27.
To remove a primary disconnect assembly, squeeze the
disconnect fingers together with a suitable tool until the
assembly releases from the stud, then slide it off.
To install a primary disconnect assembly, squeeze the disconnect fingers together with a suitable tool, slide the
assembly over the stud, then reduce the pressure on the
fingers until they close into the slots on the stud.
Primary Disconnect Removal on EGX08,
EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20
Breakers
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 28.
1. Remove the two nuts from one of the long bolts
holding the primary disconnect assembly together.
2. Carefully slide out the bolt while removing the flat
washer, spring, bushing, upper retainer, bow-tie
spacers, and disconnect fingers from the top and
the bow-tie spacers, lower retainer, and fingers from
the bottom of the assembly.
3. Repeat for the other assembly bolt and components.
4. Slide off the spring clips and remove the two stud
spacers.
5. Remove the main retainer from the stud.
Figure 26. Primary disconnect assembly for EGX08, EGS16, EGF16,
EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
28
Page 39

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
Figure 27. Primary disconnect removal and installation on EGS08, EGF08, and EGH08 breakers.
Primary Disconnect Installation on EGX08,
EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20
Breakers
1. Slide the main retainer over the stud.
2. Position each of the stud spacers, in turn, in the
holes in the stud and secure with the spring clips.
Note that the holes in the stud spacers are off center
and must be positioned with the hole toward the
back of the breaker to align with the holes in the
clips.
3. Set a pair of bow-tie spacers into one of the fingers,
place a retainer over the spacers to hold them in
position, then turn the subassembly over. Slide a
long bolt through the hole in the retainer and finger, then through the clip and stud spacer. Hold the
bottom finger subassembly in place.
4. Place a finger through the bolt from the top, then
place two bow-tie spacers in the finger and hold
them in position with a retainer.
5. Place a spring, bushing, and flat washer over the
bolt, then secure with the two nuts.
6. Repeat steps 3–5 for the other half of the pole.
7. The primary disconnect assembly on new breakers is
adjusted in the factory for a force of 85–105 pounds
on a 1/2-inch-thick copper bar between the fingers.
This force range can be obtained after installation
of a new primary disconnect assembly by adjusting
the finger spacing as shown in Figure 29. Loosen
the lock nuts to obtain a spacing of 0.766–0.797
inch between the top of the upper retainer and the
bottom of the flat washer. Tighten the lock nuts.
29
Page 40

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
Figure 28. Primary disconnect removal and installation on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16, EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
Figure 29. Primary disconnect adjustment on EGX08, EGS16, EGF16,
EGH16, EGS20, and EGF20 breakers.
30
Page 41

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
7.2 Secondary Disconnect
The secondary disconnect, illustrated in Figure 30, provides connections between the breaker control circuits and
external circuit elements. It is attached to a mounting
plate on the breaker back frame. It automatically makes or
breaks the control circuit connections as the breaker is
racked in or out of its compartment. Figure 31 illustrates
the numbering of the terminals in the secondary
disconnect.
Secondary Disconnect Removal
To remove a secondary disconnect, use the following procedure, as illustrated in Figure 32.
1. Unplug all control circuit wires from the secondary
disconnect, carefully marking each wire with its
position number in the disconnect.
2. Remove the two screws and standoffs securing the
disconnect to the mounting plate.
3. Slide the disconnect mounting feet out of the slots
in the mounting plate. Remove the spring washer if
it has detached from the molded pin on the underside of the disconnect.
Figure 30. Secondary disconnect.
Secondary Disconnect Installation
To replace a secondary disconnect, use the following
procedure, as illustrated in Figure 32.
1. Place the spring washer on the molded pin on the
underside of the disconnect body and hold it in
place.
2. Slide the mounting feet on the disconnect into the
two slots in the secondary disconnect mounting
plate.
3. Place the two screws and standoffs into the slots on
the front of the disconnect and into the tapped
holes in the mounting plate. Tighten to 40 in-lb.
4. Insert the control circuit wires into the correct positions in the secondary disconnect.
Figure 31. Secondary disconnect terminal numbering. (As seen from
the front of the breaker.)
Figure 32. Removing or installing the secondary disconnect.
31
Page 42

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
7.3 Flux Shifter
The function of the flux shifter, illustrated in Figure 33, is
to actuate the trip shaft and trip the breaker upon receiving a signal from the EntelliGuard Messenger™.
Flux Shifter Adjustment
The only adjustment required to the flux shifter mechanism is the trip rod length. As shown in Figure 34, the
clearance between the trip rod end and the trip paddle is
set to 0.11 ± 0.03 inch. To make this adjustment, open the
breaker and charge the closing springs to restore the
mechanism to the Reset position. Loosen the lock nut on
the trip rod, rotate the adjuster until the proper gap is
attained, then retighten the lock nut.
Removing the Flux Shifter
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 35.
1. Remove the snap ring connecting the reset arm to
the main shaft and slide the arm off its mounting
point.
2. Unplug the connector at the end of the flux shifter
leads.
3. Remove the two mounting bolts and lock washers
from underneath the breaker base, then lift off the
flux shifter.
Installing the Flux Shifter
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 35.
1. Put the replacement flux shifter into position, lining
up the solenoid plunger with the end of the trip rod
and the operations counter link (if present) with
the end of the reset arm. Insert the two bolts and
lock washers from beneath the bottom plate of the
breaker and tighten to 32 in-lb.
2. Slide the end of the reset arm onto the connection
on the breaker main shaft and secure with the snap
ring.
3. Connect the leads to the secondary disconnect.
Figure 33. Flux shifter.
Figure 34. Flux shifter adjustment.
32
Page 43

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
Figure 35. Removal or installation of a flux shifter.
33
Page 44

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
7.4 Draw-Out Mechanism
EntelliGuard circuit breakers are installed in GE
Entellisys™ Low-Voltage Switchgear. Draw-out
construction permits activation of a new feeder, allows
rapid replacement of a circuit breaker, and facilitates
inspection and maintenance of the breaker with no need
to deenergize the entire switchgear lineup. The draw-out
racking mechanism, illustrated in Figure 36, is available as
a replacement assembly.
Figure 36. Draw-out racking mechanism.
Draw-Out Mechanism Removal
The following procedure describes the removal of the
draw-out mechanism, as illustrated in Figure 38.
1. Position the breaker on a suitable work surface so
that its underside is accessible.
2. Remove the snap ring connecting the interlock link
to the breaker mechanism.
3. Remove the two bolts, lock washers, and nuts connecting each side mounting bracket to the sides of
the breaker.
4. Remove the four bolts and lock washers connecting
the bottom mounting brackets to the tapped holes
in the bottom plate of the breaker and lift off the
mechanism.
Draw-Out Mechanism Installation
The following procedure describes the installation of the
draw-out mechanism, as illustrated in Figure 38.
1. Put the replacement mechanism in position on the
bottom of the breaker, then insert the four bolts and
lock washers through the bottom mounting brackets
into the tapped holes in the bottom plate of the
breaker. Tighten to 96 in-lb.
2. Attach the two side mounting brackets to the sides
of the breaker with two bolts, lock washers, and nuts
each. Tighten to 96 in-lb.
3. Position the interlock link on the mounting pin of
the breaker mechanism and secure with the snap
ring.
Draw-Out Mechanism Adjustment
After installation of a replacement draw-out mechanism,
adjust the draw-out mechanism
1. With the trunnion against the jamb nut washers,
check that the distance between the edge of the
washers and the collar is 6.16 inch, as illustrated in
Figure 37. To adjust this dimension, loosen and
rotate the jamb nuts appropriately, then retighten
the nuts.
2. The length of the sleeve is adjusted to stop the
trunnion when the distance between the ends of the
equipment and breaker studs in 0.03 to 0.22 inch.
To adjust this dimension, loosen the set screw in the
collar, turn the sleeve to increase or decrease its
length appropriately, then retighten the set screw.
Figure 37. Draw-out mechanism adjustment.
34
Page 45

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
Figure 38. Draw-out racking mechanism removal and installation.
35
Page 46

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
¼” Hex
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
7.5 Escutcheon
The escutcheon is illustrated in Figure 39.
Figure 39. Escutcheon and related parts.
Escutcheon Installation
Use the following procedure to install the escutcheon:
1. Pull the manual charging handle out part way, then
slide the handle through the slot in the replacement
escutcheon and move the escutcheon into place.
Insert the six mounting screws and tighten to 14–20
in-lb.
2. Replace the trim ring around the escutcheon, with
the narrow side at the bottom. Insert the trim plate
mounting rods into the rear of the escutcheon.
7.6 Charging Handle
The charging handle, illustrated in Figure 40, is avail able
as a renewal part. See DEF004.
Removing the Charging Handle
Use the following procedure to remove the charging handle, as illustrated in Figure 41 and Figure 42.
1. Remove the escutcheon, as described in Section 7.5.
2. Disconnect the handle return spring from the link
on the rear of the handle.
3. Remove the nut and lock washer from the bolt connecting the handle to the charging mechanism,
then slide out the bolt and flat washer.
4. Remove the nut and lock washer from the mounting
bolt, then slide out the bolt and flat washer. Remove
the handle from the breaker.
Installing the Charging Handle
Escutcheon Removal
Use the following procedure to remove the escutcheon:
1. Pull the ends of the two trim plate mounting rods
out of the holes at the rear of both sides of the
escutcheon, then remove the trim plate.
2. Remove the six screws securing the escutcheon to
the breaker. Pull the manual charging handle out
part way, then slide off the escutcheon.
Use the following procedure to install the charging handle, as illustrated in Figure 41 and Figure 42.
1. Insert the pivot bushing into the replacement handle, then place the handle in position on the charging mechanism. Insert the mounting bolt with flat
washer and secure it with the lock washer and nut.
Tighten to 200 in-lb.
2. Slide the other bolt through the mechanism link,
flat washer, and handle, then secure it with the lock
washer and nut. Tighten to 96 in-lb.
3. Connect the handle return spring to the link on the
rear of the handle.
4. Replace the escutcheon, as described in Section 7.5.
36
Page 47

Figure 40. Charging handle.
EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 7. Maintenance of Standard Parts and Assemblies
Figure 42. Charging handle mounting detail.
Figure 41. Charging handle removal and installation.
37
Page 48

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
1421
6 1643
19
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
This section describes the removal, replacement, and
adjustment of the various accessories available with
EntelliGuard breakers.
Before any of the operations in this chapter can be performed, the breaker must be removed from its compartment, as described in Section 5.2, and placed on a suitable
work surface.
8.1 Bell Alarm with Lockout
The Bell Alarm with Lockout locks out the breaker in the
event of a protection trip. The device has one normally
open output switch and a trip circuit that are connected to
the secondary disconnect as illustrated in Figure 43. The
switch output provides status feedback to the EntelliGuard
Messenger. The Bell Alarm with Lockout can only be reset
manually by pressing the yellow target/RESET button on
the breaker escutcheon.
Renewal parts for the Bell Alarm with Lockout are a
complete kit including mounting hardware, illustrated in
Figure 44, or the module only.
Removing the Bell Alarm with Lockout
Use the following procedure to remove the Bell Alarm
with Lockout module and mounting plate, as illustrated in
Figure 45. If only the Bell Alarm module is to be replaced,
it is not necessary to remove the mounting plate (perform
steps 1–3 only).
1. Remove the breaker escutcheon, as described in
Section 7.5.
2. Remove the four Bell Alarm wires from the
secondary disconnect, as listed in Table 6. Cut the
wire ties securing the wire bundle to the breaker
frame so that the four wires can be removed with
the Bell Alarm.
3. Remove the two screws and bushings securing the
Bell Alarm module to the mounting plate and
remove the module.
4. Remove the three nuts and lock washers securing
the mounting plate to the breaker frame.
5. Disengage the mounting plate from the breaker
mechanism and remove the plate.
Figure 44. Bell alarm with Lockout accessory kit.
Figure 43. Bell Alarm with Lockout connections to the secondary
disconnect. The contact is shown in the RESET state.
Lockout
Trip Coil
Status
Contact
Figure 45. Bell Alarm with Lockout installation or removal.
38
Page 49

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Connection
Lockout trip white 14
Lockout trip COM green 6
Status switch N/O blue 16
Status switch COM black 19
Table 6. Bell Alarm with Lockout wires and corresponding secondary
disconnect terminals.
Wire Color
Sec. Disc.
Terminal #
Installing the Bell Alarm with Lockout
Use the following procedure to install the Bell Alarm with
Lockout mounting plate and module. If this is a new
installation into a breaker that was not equipped at the
factory with a Bell Alarm with Lockout, see the installation
instructions in DEH238, supplied with the Bell Alarm with
Lockout kit. If only the module is to be replaced, begin at
step 3.
1. Place the Bell Alarm mounting plate over the three
standoffs on the breaker front frame and secure
with three lock washers and nuts. Ensure that the
actuating tab from the breaker mechanism engages
the slot in the bottom of the mounting plate, as
illustrated in the front view in Figure 46.
2. Line up the Bell Alarm module on the mounting
plate, as shown in Figure 45, so that the solenoid
plunger and locating pin fit in the appropriate
holes. The label on the end of the module should
appear as in Figure 47, with the legend ↑ SF LO
(Small Frame Lockout) horizontal.
3. Attach the Bell Alarm module to the mounting
bracket with the two screws provided.
4. Run the four wires from the Bell Alarm to the secondary disconnect A block and connect to the terminals listed in Table 6. Use wire ties to secure the wire
bundle to the breaker frame.
5. Replace the breaker escutcheon, as described in Section 7.5.
Figure 46. Front view of the Bell Alarm with Lockout installation,
showing the breaker mechanism tab engaging the mounting plate slot.
Figure 47. Orientation of the label on the Bell Alarm module for
installation.
8.2 Shunt Trip
The Shunt Trip allows the breaker to be opened remotely
by the EntelliGuard Messenger™. It is always provided on
electrically operated breakers. The device causes the
circuit breaker to open when its coil is energized. An “A”
auxiliary switch, which is closed when the breaker is
closed, is connected in series with the Shunt Trip coil, as
illustrated in Figure 48. The voltage source is connected to
terminals 5 and 7 on the secondary disconnect.
Renewal parts for the Shunt Trip are a complete kit, illustrated in Figure 49, and the module. Electrical ratings for
the Shunt Trip are listed in Table 7.
39
Page 50

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
5 7
Aux Switch
3C 321Shunt Trip
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Figure 48. Shunt Trip connections to the auxiliary switch and
secondary disconnect.
Figure 50. Shunt Trip module removal and installation.
Installing the Shunt Trip
Use the following procedure to install the Shunt Trip
module as a replacement, as illustrated in Figure 50.
1. Insert the two mounting studs on the top of the
Shunt Trip module into the holes on the top of the
mounting bracket and secure with the two lock
washers and nuts supplied.
2. Run one wire from the Shunt Trip module to
auxiliary switch terminal 3C. Cut all wires to the
Figure 49. Shunt trip accessory kit.
Catalog
Number
WPS1SF60120 120 Vac, 60 Hz
Voltage
Rating
Table 7. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Shunt Trip
accessory.
Removing the Shunt Trip
Use the following procedure to remove the Shunt Trip
module for replacement, as illustrated in Figure 50. The
mounting bracket does not normally require replacement.
1. Carefully place the breaker on a suitable working
surface, resting on the primary disconnects, so that
the bottom of the breaker is accessible.
2. Disconnect the wire at the secondary disconnect
terminal 7. Disconnect the other wire from the
auxiliary switch, terminal 3C. Bring the wires back
to the Shunt Trip, removing wire ties as necessary.
3. Remove the two nuts and washers securing the
Shunt Trip module to the mounting bracket, then
remove the module.
appropriate length and crimp on the terminals
provided (the right-angle flag for the auxiliary
switch, the spade terminal for the secondary
disconnect connection).
3. Attach the wires to the breaker frame with wire ties
as appropriate.
4. To verify that the Shunt Trip will trip the breaker,
place a 0.03-inch shim between the armature and
magnet of the Shunt Trip and manually operate the
armature to trip the breaker.
5. If the breaker does not trip in this test, verify that
the mounting fasteners are tight. If they are, bend
the trip paddle on the trip shaft to slightly reduce
the distance between the trip arm of the Shunt Trip
and the trip paddle and recheck for positive trip.
Verify that there is a 0.03–0.05-inch gap between the
trip arm and the trip paddle with the breaker
closed. A gap greater than 0.05 inch is allowable
and may sometimes be necessary to prevent nuisance tripping.
40
Page 51

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
8.3 Charging Motor
The Charging Motor provides a means of electrically
charging the springs that close the breaker. The Charging
Motor is available only as a factory-installed option. It is
always provided on electrically operated breakers.
The circuit breaker closing springs are charged automatically when control voltage is applied to terminals 8 and 17
of the secondary disconnects. When the springs are fully
charged, a cutoff switch automatically de-energizes the
motor. The closing springs will recharge automatically
after the breaker closes.
Renewal parts for the Charging Motor are the motor and
the cut-off switch, illustrated in Figure 51. The catalog
number and electrical characteristics of the Charging
Motor are listed in Table 8.
Figure 51. Charging Motor and cut-off switch.
Catalog
Number
568B596G5 104–127
Table 8. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Charging Motor
Voltage
Range, Vac
accessory.
Removing the Charging Motor
Use the following procedure to remove the Charging
Motor for replacement, as illustrated in Figure 52.
1. Carefully place the breaker on a suitable working
surface, so that the right front of the breaker is
accessible.
2. Disconnect the motor wires at the connector.
3. Remove the three bolts and lock washers securing
the motor to the breaker mechanism.
4. Remove the motor and the three mounting spacers.
Installing the Charging Motor
Use the following procedure to install a replacement
Charging Motor, as illustrated in Figure 52.
1. Place the motor in position with the three mounting
spacers on the breaker mechanism and insert the
three mounting bolts and lock washers. Tighten the
bolts to 110 in-lb.
2. Connect the motor wires by plugging the connector
into place.
Removing the Motor Cut-Off Switch
Use the following procedure to remove the motor cut-off
switch, as illustrated in Figure 52.
1. Carefully place the breaker on a suitable working
surface, so that the right front of the breaker is
accessible.
2. Remove the breaker escutcheon, as described in
Section 7.5.
3. Disconnect the wires at the screw terminals on the
switch.
4. Remove the nut from the switch stem under the
hole in the mounting bracket.
5. Remove the cut-off switch.
Installing the Motor Cut-Off Switch
Use the following procedure to install the replacement
motor cut-off switch, as illustrated in Figure 52.
1. Screw one of the locking nuts onto the switch barrel
and place the flat washer over the nut.
2. Place the cut-off switch in position with the switch
stem through the hole in the mounting bracket.
Attach the mounting nut and secure the switch.
3. Connect the wires at the screw terminals on the
switch.
41
Page 52

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Figure 52. Removal and installation of the Charging Motor and cut-off switch.
42
Page 53

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Adjusting the Motor Cut-Off Switch
Adjust the cut-off switch as illustrated in Figure 533:
1. Charge the closing springs with the manual charging handle.
2. The main stem of the switch should be located
between 0.005 and 0.030 inch from the barrel.
3. If necessary, adjust switch depression by screwing
the switch button in or out of the threaded housing.
8.4 Remote Close
The Remote Close allows the breaker to be closed
remotely by the EntelliGuard Messenger™ after the
closing springs have been charged. It is always provided
on electrically operated breakers.
A circuit breaker equipped with the Remote Close accessory can be closed by applying the rated control voltage to
terminals 9 and 18 of the secondary disconnects.
The Remote Close accessory is continuously rated and has
an antipump feature that prevents a motor-operated
breaker from repeatedly closing if the closing signal is
maintained. The closing control voltage must be removed
for 1–2.5 seconds and then reapplied for each breaker
closure.
Renewal parts for the Remote Close are the complete kit,
illustrated in Figure 54, the circuit board, and the solenoid.
Electrical characteristics of the Remote Close are listed in
Table 9.
Figure 53. Cut-off switch adjustment.
Figure 54. Remote Close accessory kit.
Catalog Number Voltage Rating
WPRCSF60120 120 Vac, 60 Hz
Table 9. Catalog number and operating voltage for the Remote Close
accessory.
43
Page 54

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Removing the Remote Close
Use the following procedure to remove the Remote Close
solenoid and circuit board for replacement, as illustrated
in Figure 55. If only the solenoid or circuit board is to be
replaced, it is not necessary to remove both components.
1. Carefully place the breaker on a suitable working
surface, resting on the primary disconnects, so that
the bottom of the breaker is accessible.
2. Disconnect the two Remote Close wires at terminals
9 and 18 of the secondary disconnect. Cut the wire
ties, as needed, so that the wires can be removed
with the Remote Close.
3. Remove the two screws, lock washers, and flat washers connecting the Remote Close module to the
breaker frame.
4. Remove the snap ring connecting the Remote Close
actuator to the pin on the charging mechanism and
remove the module.
5. The Remote Close solenoid or circuit board can
now be separately replaced on the module.
Installing the Remote Close
Use the following procedure to install the replacement
Remote Close, as illustrated in Figure 55. If this is a new
installation into a breaker that was not equipped at the
factory with a Remote Close, see the installation
instructions in DEH172, supplied with the Remote Close
kit. (The circuit breaker should be resting on the
secondary disconnects with the right pole opening spring
removed, as in the removal procedure above.)
1. Insert the connecting pin on the breaker closing
mechanism through the hole in the end of the
Remote Close actuator and secure with the snap
ring.
2. Line up the mounting holes in the Remote Close
module with the two tapped holes in the bottom of
the breaker frame. Insert a screw with lock washer
and flat washer into each hole and tighten.
3. Run the wires from the Remote Close module to the
secondary disconnect and connect the wires to
terminals 9 and 18. Attach the wires to the breaker
frame with wire ties as needed.
Figure 55. Remote close installation and removal.
44
Page 55

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
24
25
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
8.5 Open-Fuse Lockout
The Open-Fuse Lockout, illustrated in Figure 56, trips the
breaker to prevent single-phasing when a primary fuse
blows. In 800 A and 1600 A breakers, it is connected
directly to the primary fuse terminals. In 2000 A breakers,
the device is used in combination with a fuse rollout
element and is connected to the secondary disconnect.
This accessory is available only as a factory-installed
option.
The Open-Fuse Lockout contains an individual trip solenoid for each pole, connected directly across the fuse in
that phase. When any fuse blows, its solenoid is energized
through connections to the secondary disconnect, illustrated in Figure 57, and trips the breaker. An indicator
shows which fuse has blown. The breaker cannot be
reclosed until the blown fuse is replaced and the RESET
button is pressed on the Open-Fuse Lockout.
Figure 56. Open-Fuse Lockout accessory.
1
2
22
OFLO
Phase A
3
4
OFLO
Phase B
5
6
26
OFLO
Phase C
Removing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 800 A
and 1600 A Breakers
Use the following procedure, illustrated in Figure 58, to
remove the Open-Fuse Lockout for replacement.
1. Follow the six wires from the Open-Fuse Lockout to
their connection points on either side of each
primary fuse. Disconnect the wires from the primary
conductors. Cut the wire ties as necessary to release
the wires back to the Open-Fuse Lockout.
2. Remove the three mounting bolts and lock washers
securing the Open-Fuse Lockout to the bottom plate
of the breaker.
3. Remove the Open-Fuse Lockout straight out from
the front of the breaker.
Installing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 800 A and
1600 A Breakers
Use the following procedure, illustrated in Figure 58, to
install a replacement Open-Fuse Lockout.
4. Place the replacement Open-Fuse Lockout in
position, carefully guiding the trip rod through the
hole in the trip rod guide.
5. Insert the three bolts and lock washers from the top
of the breaker bottom plate into the tapped holes in
the Open-Fuse Lockout mounting bracket. Tighten
to 96 in-lb.
6. Connect wires from each Open-Fuse Lockout coil
across the coil’s respective primary fuse. For
example, wires from the Phase A coil, marked “L”
on the Open-Fuse Lockout label, should be
connected on opposite sides of the Phase A
(leftmost from the front) primary fuse.
7. Adjust the Open-Fuse Lockout as follows:
a. Charge the closing springs with the manual
charging handle and close the breaker.
b. The dimension between the end of the trip rod
and the trip paddle should be 0.10–0.14 inch. If
necessary, loosen the trip rod lock nut and run
the rod in or out to attain the proper clearance.
c. With the Open-Fuse Lockout energized, the
breaker must TRIP and the RESET button must
move forward to the front plate. In this condition,
the breaker must be held trip free.
23
Figure 57. Open-Fuse Lockout connections to the secondary disconnect
for EGF-20 breakers
27
Removing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 2000 A
Breakers
Use the following procedure, illustrated in Figure 58, to
remove the Open-Fuse Lockout for replacement.
1. Disconnect the wires from the Open-Fuse Lockout at
terminals 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, and 27 of the secondary
disconnect block. Cut any wire ties, as necessary to
release the wires back to the Open-Fuse Lockout.
45
Page 56

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
2. Remove the three mounting bolts and lock washers
securing the Open-Fuse Lockout to the bottom plate
of the breaker.
3. Remove the Open-Fuse Lockout straight out from
the front of the breaker.
Installing the Open-Fuse Lockout, 2000 A
Breakers
Use the following procedure, illustrated in Figure 58, to
install a replacement Open-Fuse Lockout.
1. Place the replacement Open-Fuse Lockout in
position, carefully guiding the trip rod through the
hole in the trip rod guide.
2. Insert the three bolts and lock washers from the top
of the breaker bottom plate into the tapped holes in
the Open-Fuse Lockout mounting bracket. Tighten
to 96 in-lb.
3. Connect the wires from the coils on the Open-Fuse
Lockout to the secondary disconnect block as follows:
• Phase A to terminals 22 and 23.
• Phase B to terminals 24 and 25.
• Phase C to terminals 26 and 27.
4. Adjust the Open-Fuse Lockout as follows:
a. Charge the closing springs with the manual
charging handle and close the breaker.
b. The dimension between the end of the trip rod
and the trip paddle should be 0.10–0.14 inch. If
necessary, loosen the trip rod lock nut and run
the rod in or out to attain the proper clearance.
c. With the Open-Fuse Lockout energized, the
breaker must TRIP and the RESET button must
move forward to the front plate. In this condition,
the breaker must be held trip free.
Figure 58. Open-fuse lockout installation and removal.
46
Page 57

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
8.6 Remote Charge-Indication Switch
The remote charge-indication switch, illustrated in Figure
59, allows the EntelliGuard Messenger to remotely
monitor the state of the closing springs on electrically
operated breakers. When the springs are charged,
terminals 3 and 4 at the secondary disconnect are shorted
and are open when the springs are discharged.
Figure 59. Remote charge-indication switch.
a. Charge the breaker closing springs with the man-
ual charging handle.
b. Rotate the switch until the switch trigger is fully
depressed against the trigger pin, as illustrated in
Figure 61.
c. Tighten the switch mounting bolt to 32 in-lb.
d. Close and trip the breaker.
3. Run the two wires from the switch to the secondary
disconnect block and connect them to terminals 3
and 4.
4. Replace the breaker escutcheon, as described in Section 7.5.
Removing the Remote Charge-Indication
Switch
Use the following procedure to remove the remote chargeindication switch for replacement, as illustrated in Figure
60.
1. Remove the breaker escutcheon, as described in
Section 7.5.
2. Disconnect the two wires from terminals 3 and 4 of
the secondary disconnect block and bring them
back to the switch.
3. Remove the bolt, lock washer, and flat washer
attaching the switch to the flag shaft support plate,
then slide off the switch.
Installing the Remote Charge-Indication
Switch
Use the following procedure to install the replacement
remote charge-indication switch, as illustrated in Figure
60.
1. Place the replacement switch in position on the flag
shaft. Insert the mounting bolt, lock washer, and flat
washer through the rectangular hole in the switch
and into the tapped hole in the flag shaft support
plate. Do not tighten the bolt.
2. Adjust the switch position as follows:
Figure 60. Remote charge-indication switch removal and installation.
Figure 61. Remote charge-indication switch side view.
47
Page 58

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
15 NI Set
20 21 NI Reset
1 3 2 16 19 4 5 NI Status
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
8.7 Network Interlock
The Network Interlock provides a means of locking out a
breaker to coordinate its operation with other breakers in
the distribution network. When activated by the
EntelliGuard Messenger, the Network Interlock prevents
the breaker from closing. When the EntelliGuard
Messenger issues a RESET signal, the breaker can be
closed either remotely or locally. The Network Interlock
accessory includes a manual reset lever to reset the device
in the absence of a signal from the EntelliGuard
Messenger.
The Network Interlock consists of a trip coil, a reset coil,
and a status switch. The device connections to the
secondary disconnect are shown in Figure 62. When
voltage is applied across the trip coil, the device locks out
the breaker. Conversely, when voltage is applied to the
reset coil or when the reset lever is depressed, the Network
Interlock resets, allowing the breaker to close. The
Network Interlock does not close the breaker itself.
Renewal parts for the Network Interlock are available as a
complete kit or as a module only. The Network Interlock
accessory is only available on electrically operated
breakers.
Figure 62. Network Interlock connections to the secondary disconnect.
Coil
Removing the Network Interlock Module
Use the following procedure to remove the Network
Interlock.
1. Disconnect the six wires from the Network Interlock
device. Label each wire as it is removed. Cut wire ties
as necessary.
2. Remove the manual reset assembly by removing the
two hex-head screws as shown in Figure 65.
3. Remove the accessory mounting plate as shown in
Figure 63.
4. Remove the Network Interlock module from the
mounting plate by removing the three sets of nuts
and washers, as shown in Figure 64.
Coil
Contact
Installing the Network Interlock Module
Use the following procedure to install the Network
Interlock module as a replacement.
1. Open the circuit breaker and remove it from the
cubicle or substructure. Check to ensure the breaker
closing springs are DISCHARGED.
2. Carefully place the circuit breaker on a suitable
working surface, resting on the primary disconnects,
so that the bottom of the circuit breaker is accessible.
3. Fasten the Network Interlock module to the accessory
mounting plate using three sets of # 8-32 nuts, spring
washers, and flat washers as shown in Figure 64.
4. Fasten the Shunt Trip accessory to the mounting plate
beside the Network Interlock. See Section 8.2 or DEH168 for detailed instructions.
5. Assemble the accessory mounting plate to the circuit
breaker frame using four sets of # 10-32 screws, spring
washers, and flat washers as shown in Figure 63
6. Ensure the Network Interlock is in the RESET state
(shown in Figure 66) by manually rotating the reset
lever counterclockwise. If the Network Interlock was
SET, this operation will cause the set lever to retract
(counterclockwise) away from the trip paddle.
7. With the breaker open, charge the breaker closing
springs. Do not close the breaker. Adjust the gap
between the Network Interlock set lever and trip
paddle by rotating the socket-head adjusting screw as
shown in Figure 66. The distance between the set lever
and the trip paddle must be between 0.060 and 0.090
inch.
8. Connect the six wires to their corresponding terminals
on the Network Interlock device.
9. Reset the Network Interlock by pushing the manual
reset button. The Network Interlock status circuit
should be open. Close the breaker manually or
electrically. The breaker should close properly.
10. Set the Network Interlock by applying 120 VAC across
terminals 15 and 21 on the secondary disconnect. The
breaker should trip open and the status circuit should
change from open to close.
11. Charge the breaker manually or electrically. Close the
breaker. The breaker should trip open, discharging
the closing springs.
12. Reset the Network Interlock by applying 120 VAC
across terminals 20 and 21 on the secondary
disconnect. The status circuit should change from
closed to open.
13. Charge and close the breaker. The breaker should
close properly.
14. Set the Network Interlock, and repeat Steps 9 through
13.
48
Page 59

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Manual Reset Assembly
Manual Reset Button
0.06”
-
0.09”
Reset Lever
Set Lever
Trip Paddle
Screw
Bottom Frame
Mounting Plate
Reset Sole
noid Set Solenoid
Chapter 8. Accessory Maintenance
Figure 63. Network Interlock assembly mounting to the circuit breaker
bottom frame. (Shunt Trip omitted for clarity.)
Figure 64. Network Interlock module fastening to the mounting plate.
Figure 65. Manual reset assembly mounting
Figure 66. Trip paddle and set lever gap calibration. (Breaker charged.
NI module shown in RESET position.)
Adjusting
49
Page 60

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Notes
50
Page 61

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Notes
51
Page 62

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Notes
52
Page 63

EntelliGuard™ 800–2000 A Power Circuit Breakers
Notes
53
Page 64

g
GE Consumer & Industrial
General Electric Company
41 Woodford Avenue, Plainville, CT 06062
DEH203 R02 1005 © 2005 General Electric Company
 Loading...
Loading...