Page 1

g
GE Energy
Industrial Solutions
DC OEM Module
For use with Gerapid DC Circuit Breaker
Installation and Maintenance Instructions
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 1
Page 2

2 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 3

INDEX
INTRODUCTION ............................ ................................ ................................ .........................5
1-1 General Notes ..................... ................. .................. ................. .................. ................. 5
TESTING AND INSPECTION............................................................................................. 15
6-1 General Notes .................... ........................................ ........................................ ..... 15
Prior to Test .............................. ................................................. ................................. 15
Connecting Control Circuits ............................... .............................. .................. 15
1-2 Instruction Book Arrangement ........................................... .............................. 5
1-3 Related Publications...............................................................................................5
RECEIVING, HANDLING AND STORAGE .......................................................................6
2-1 Receiving ................... ...................... ...................... ....................... ...................... ..........6
Module and Trolley Package ......................................... ............... ............... ..........6
Inspecting for Damage .................................................. ........................... ...............6
Filing a Claim .......... ............................................... ............................................. ..........6
2-2 Handling and unpacking ........................... ........................ ......................... ..........6
Module handling and unpacking .................... ................................... .................6
Trolley handling and unpacking ............................... ..........................................7
2-3 Storage ....................... ................. ................. .................. ................. .................. ............7
Circuit Breakers ................................... ........ ....... ....... ........ ....... ........ ....... ........ ....... .....7
Modules and Trolleys ....... .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .....................................................................................................8
3-1 General Notes ..................... ................. .................. ................. .................. ................. 8
3-2 Summary Description ............... ...................... ......................... ....................... .......8
Ratings ................................................... ........................ ......................... ......................... 8
Interlocks ................................. ......................... ......................... ......................... ............8
Accessories .............. .................... .................... .................... .................... .................... ..8
3-3 The Module ............ ............... ............... ............... ................. ............... ............... ..........8
Breaker Compartment ...................................... .................... ....................... ............8
Cable Compartment ............................... ..... ..... ....... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... 9
Control Compartment ..... ............... .............. ............... ............... ............... ............... 9
3-4 The Trolley ............. ........................... ............................ ........................... ....................9
3-5 Gerapid Breakers ............................ ........................... ............................ .............. 10
INSTALLING THE MODULE ............................................................................................. 11
4-1 General Notes ..................... ................. .................. ................. ............... ................. 11
Environmental Requirements ............................ ........................................... .... 11
Foundation Requirements ................................... ........................................... .... 11
4-2 Module Configuration and Assembly ......................................................... 11
Multiple Modules Side by Side Assembly ........................ ............................. 11
Module Preparation ............................................................................................... 11
Module Rejection Interlock ............................. ......................... ......................... .. 12
Main Busbars Connection .... ..................................... ...................................... .... 12
Ground Bus Connection ........................................... .......................................... .. 12
Connecting Secondary Controls ........................................... ........................... 12
Device mounting on control compartment door .................................... 12
6-2 Field Testing Procedure ............. .................................................... .................... 15
Testing the Module with Remote Racking System .................................. 15
Testing the Module w/o Remote Racking System ................................... 15
High Potential Tests .......... ......................................................... ............................ 15
Grounding Circuit Check ............................ ......................... ............................ ..... 15
OPERATING THE MODULE .............................................................................................. 16
7.1 Mechanisms and Interlocks ........... .... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ... 16
Racking Mechanism................................................ ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ... 16
Access Interlocks ............................... .................................................. .................... 16
Secondary Control Interlock ................................. ............................................. 16
Remote Racking .................................... ............. ............ ............. ............ ............. ..... 17
Trolley Operated Switches ......... ................................... ................................... ... 17
Padlocks................................. ..... ..... .... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ... 17
7.2 Trolley with Manual Racking ...... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... .......... 18
Operational Positions ............................................... ................................ ............. 18
Racking – In Procedure .................................... ............................................. ........ 18
Rack-Out Procedure .............................. ................................... .............................. 19
7.3 Trolley with Remote Racking .. ............................................. ............................ 19
Operational positions. .............................................. ............ ............. ............ ........ 19
Remote Rack–In Procedure. .................................... ........................................... 20
Manual Rack-Out Procedure.
7.4 Operate the breaker. ........................................................................................... 21
TROUBLESHOOTING AND MAINTENANCE ............................................................... 22
8.1 Troubleshooting ........... ........................................ ........................................ .......... 22
Manually operated trolley ............... .................... .................... .................... ........ 22
Motor driven trolley .............................................. ............... ............... ............... ..... 22
8.2 Maintenance ........... ...................................................... ........................................... 22
CUSTOMER SUPPORT ....................................................................................................... 23
8.1 Warranty ..................... ............. ............ ............ ............. ............ ............. ............ ........ 23
8.2 Field Service Support ........ .................................................. ................................. 23
8.3 Publications and other support .......................................... ............. ............ ... 23
APPENDIX “A” – MODULE & TROLLEY DRAWINGS ................................................ 24
APPENDIX B – PRIMARY TERMINALS DRAWINGS .................................................. 26
APPENDIX C – LAYOUT DRAWINGS ............................................................................ 29
........................... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... ..... 21
INSTALLING THE BREAKER ............................................................................................ 13
5-1 General Notes ..................... ................. .................. ................. ............... ................. 13
5-2 Installing Gerapid Breaker ............... ................................... ............................. 13
Prior to Installation ................................................................................................ 13
Installation Procedure .................................. ................................................. ....... 13
Configuration of the Rejection Interlock .............................................. ....... 14
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 3
APPENDIX D – TIGHTENING TORQUES TABLES...................................................... 30
APPENDIX E – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS...................................................................... 31
APPENDIX F – RATING TABLES ..................................................................................... 39
APPENDIX G – ACCESSORIES & INSTALLATION DRAWINGS ............................. 40
APPENDIX H – FIELD TEST PROCEDURE ................................................................... 43
Page 4

4 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 5
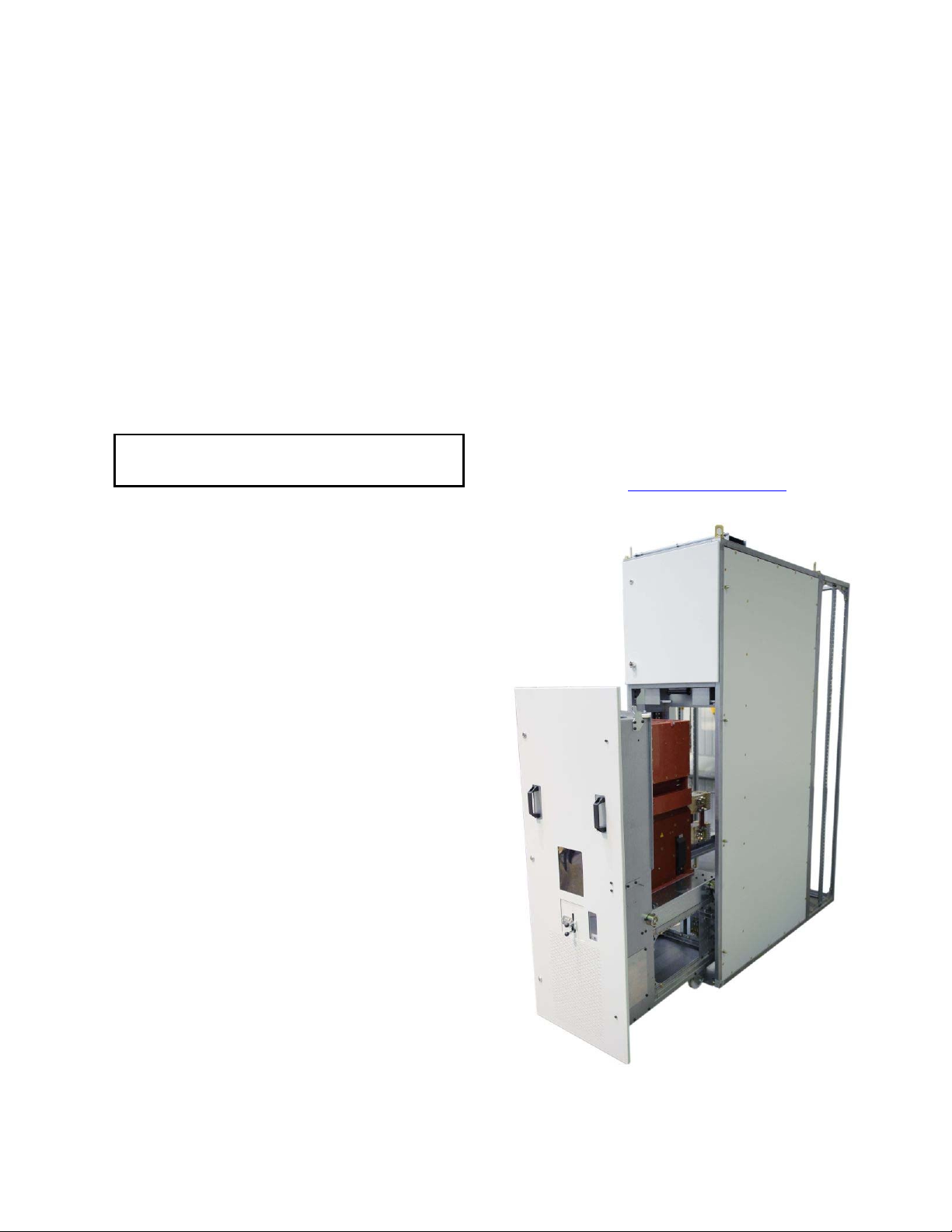
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 1 Introduction
Introduction
1-1 General Notes
This manual contains procedures for receiving, handling,
storage, operation, and maintenance of GE’s DC OEM Module
(called also the Module in this document) with withdrawable DC
OEM Trolley (referred to as Trolley in this document) for use with
Gerapid high speed DC circuit breaker (referred to as Breaker in
this document).
The OEM Module is designed to simplify the construction of a DC
switchgear assembly. Typical applications for such equipment
are Heavy and Light Rail Transit systems, commercial IT
systems (Data Centers), heavy industrial applications in mining
and metals. Other applications include equipment to supply DC
motors, excitation systems or high power DC testing and
research facilities.
DC OEM Module and Trolley described in this document are UL
Recognized components for use with GE’s UL listed Gerapid
high-speed circuit breaker.
NOTE: The personnel responsible for installing, operating,
and servicing this equipment should be thoroughly familiar
with the contents of this manual.
Before any installation work is performed, thoroughly read and
understand the material in this instruction manual. A copy of
the instruction manual is shipped with each module, in the
control compartment. When requesting additional information
from GE Energy, include the complete data appearing on the
equipment nameplate, including requisition number. The
module’s label is located inside the control compartment. The
trolley’s nameplate is located on the right side of the trolley,
next to doors.
When requesting information concerning any specific item
furnished with module and/or trolley, refer to that item by
description, part number, its location within this manual, and
any applicable drawing number. Any materials, which may be
required to meet local codes, such as mats, screens, railings,
etc., are not included, and not furnished by GE Energy.
If there are any questions or requirements not covered in this
manual or in the accompanying drawings, please contact the
local sales office of GE Energy.
Chapter 5 Installing and Removing the Breaker - gives a
step-by-step procedure for lifting the breaker from the
floor, and installing it on the trolley. Information on
configuring the Rejection Interlock on the trolley is
included.
Chapter 6 Testing and Inspection - reviews items which
should be field-tested or inspected prior to energizing and
operating the switchgear.
Chapter 7 Operating the Module - covers how to operate
the trolley, the module and the breaker. This section
contains information concerning drawout provisions, and
functions of various accessories.
Chapter 8 Energizing the Module - outlines the steps to be
taken before and during the electrical energization of the
completed equipment.
Chapter 9 Maintaining the Module - provides instructions
for recommended preventive maintenance, servicing, and
lubrication information for the module.
Appendixes - contains information covering ratings,
dimensional drawings, electric diagrams; screw and bolt
torque values, field testing procedures, and accessories.
1-3 Related Publications
Detailed Users Guides and Instruction Books for the Gerapid
breaker and other devices not fully described in this instruction
book are available at: http://www.geindustrial.com
Go to: Products -> Circuit Breakers -> Gerapid
1-2 Instruction Book Arrangement
Information and procedures in this instruction book are divided
into Chapters as follows:
Chapter 1 Introduction - provides applicable data for the
module and its components.
Chapter 2 Receiving, Handling and Storage - describes
procedures required for receiving, handling and storage
the module and trolley.
Chapter 3 Component Description - describes the module
and its various components. Included are the cable
compartment, breaker compartment, and instrument
compartment. This section also lists the electrical and
mechanical components and explains their assigned
functions.
Chapter 4 Module Installation - provides the information
needed prior to installation, site location and foundation
requirements, and how to anchor the equipment properly
and safely. It also covers information on electrical
connections and mechanical construction.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 5
Fig. 11-1 DC OEM Module and Trolley with Gerapid High
Speed Circuit Breaker
Page 6

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 2 Receiving, handling and storage
Receiving, handling and storage
2-1 Receiving
Module and Trolley Package
Every package leaving the factory is plainly marked with the
case number, requisition number, and customer's order
number.
The Module and the trolley are shipped in separate wooden
crates. The contents of each shipping package are listed on
the crate.
NOTE: Breakers, Trolleys and Modules are ordered
individually and shipped separately. Module accessories, if
ordered, are shipped separately.
See Fig. 21-1 for crates dimensions. Crates load weights are:
Crate with module, 6.5x2.6x8.0 [ft] / ~850 [lbs],
Crate with trolley, 3.9x2.6x5.8 [ft] / ~ 500 [lbs],
D
W
Remove the carton box and check plastic covers for any
damages. Do not remove the plastic if the breaker will be
stored for long periods. (See. Fig. 21-2 and 21-3)
Fig. 21-2 Gerapid circuit breaker package
H
Fig. 21-1 Typical wooden module crate for shipment
Inspecting for Damage
All equipment leaving the factory is carefully inspected and
packed by personnel experienced in the proper handling and
packing of electrical equipment. Upon receipt of any
equipment, immediately perform a visual inspection to
ascertain if any damage has been sustained in shipping or if
there are any loose parts. Be sure to inspect all devices
mounted inside compartments of each section to see if any
have been dislodged or damaged.
Gerapid circuit breakers are shipped separately in individual
boxes with the breaker in the open position. (See Fig. 21-2)
Circuit breakers should be unpacked and visually inspected for
damage or loose parts as soon as possible after they have
been received.
Fig. 21-3 Breaker plastic shrink-wrap protection
Filing a Claim
If any damage is evident, or indication of rough handling is
visible, file a claim for damage at once with the transportation
company and notify the nearest GE Energy Sales Office
immediately. Information on damaged parts, part number,
case number, requisition number, etc., should accompany the
claim.
2-2 Handling and unpacking
Module handling and unpacking
NOTE: The Module should be transported and installed in
its final location prior to installing the trolley.
The module shipping crate should be transported using forklift
only. During transport, the module should remain in its original
package. To unpack the module, start by removing the top
cover, then remove sidewalls and all inner supports.
CAUTION: Never use a forklift to transport an unpacked
module, as the module is not bolted to the shipping
palette.
6 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 7
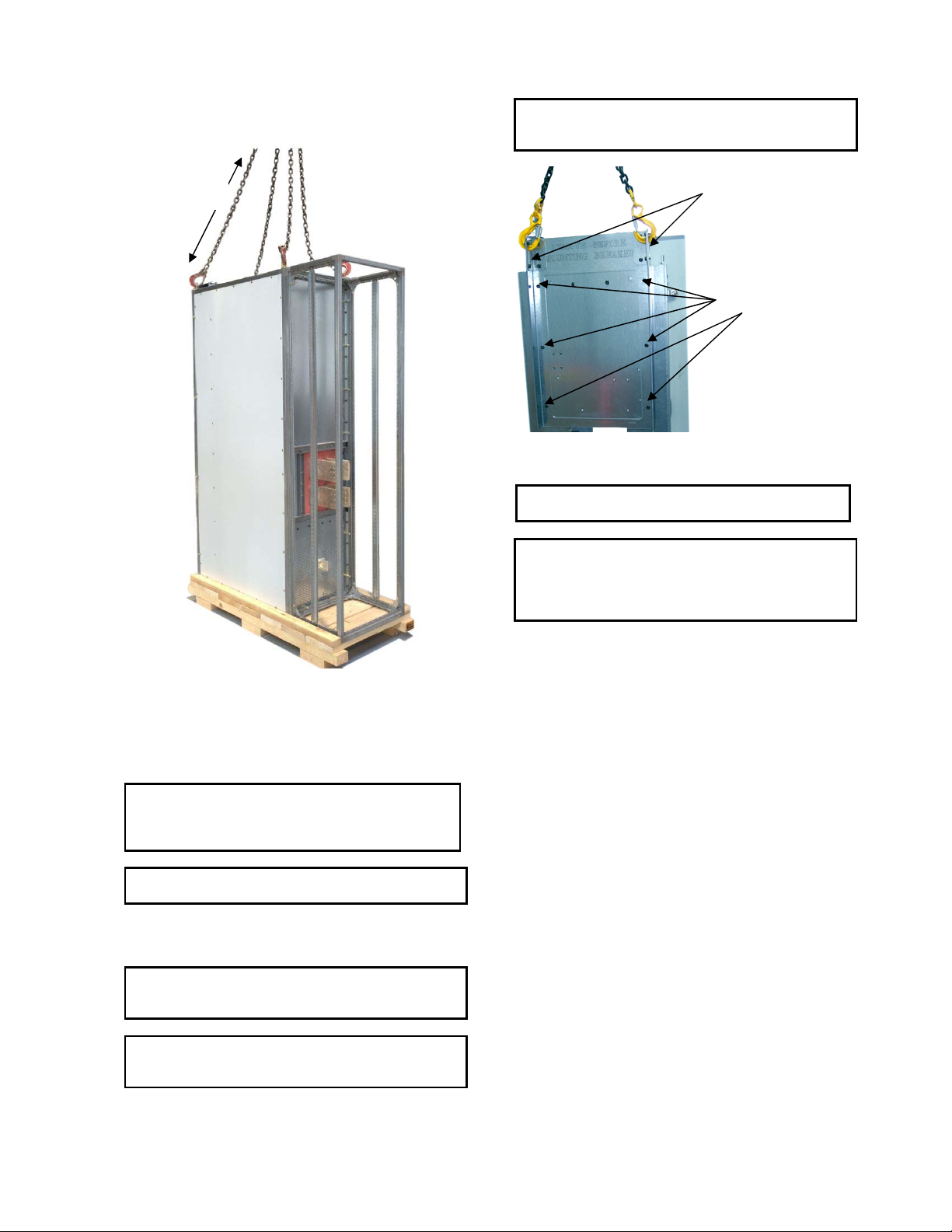
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 2 Receiving, handling and storage
Removable lifting plates are provided on the top of each
module, as standard equipment. Using a crane or overhead
hoist, carefully lift the module from the palette using the four
lifting plates. (See Fig. 22-1)
Min. 4 ft
NOTE: After transportation, but before installing of the
breaker, loosen six attachment screws and remove lifting
frame from the trolley. Replace and tighten these screws!
Lifting slots.
Fixing screws.
Fig. 22-2 Lifting of the trolley
CAUTION: Never use forklift to transport unpacked trolley,
as it is not bolted or fixed to the shipping palette
NOTE: Do not lift or transport the trolley, using forklift.
Never lift the trolley with a breaker mounted. Never roll the
trolley on the floor with a breaker set in place, unless the
breaker is properly bolted to the trolley and arc chutes
properly secured to the breaker (if installed).
2-3 Storage
Fig. 22-1 Overhead lifting of the module
To preserve the external appearance of the equipment, it is
suggested that the lifting plates be left in place. Utilize four
equal length cables or slings, each with a minimum load rating
of twice the weight of the Module package. See section 2.1.
NOTE: The angle between the cables and the top of the
equipment must be at least 45 degrees. This requires the
use of chains/slings at least 4 ft long. If this is not possible,
spreader bars must be used.
NOTE: Do not move, lift or handle the module with a trolley
installed.
Take up the slack in the lifting device very carefully and
manually stabilize the module to prevent it from rotating.
WARNING: Do not stand under the module while it is being
moved. Serious injury may occur if the cables or lifting
device fail.
CAUTION: Gently lower the module onto the level site
location. If the module is roughly handled or jarred, it is
possible to damage or misalign internal components.
Trolley handling and unpacking
The trolley, in its original package, should be transported using
forklift only. To unpack the trolley, remove the top cover first,
and then remove sidewalls and all inner supports. To lift the
trolley, use special lifting frame available. See Fig. 22-2.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 7
Circuit Breakers
Open shipping cartons and thoroughly inspect shipping
materials for damage. If shipping plastic is in satisfactory
condition, leave the breakers in their shipping cartons for
storage. Do not remove the circuit breaker shipping material
(shrink wrap) at this time.
Store the circuit breakers in a clean, dry location in an upright
position. If shipping plastic is damaged, a plastic or canvastype cover should be provided to reduce the possibility of
damage or contamination to the breakers due to dust and
water. For details concerning Gerapid breakers handling
consult the breaker’s User Guide, S47183De.
Modules and Trolleys
Remove protective covering. Check thoroughly for damage.
Store in a clean, dry, rodent-free location with moderate
temperature and provide protective coverings to prevent dirt,
water, or other foreign substances from entering the
equipment.
If dampness or condensation may be encountered in the
storage location, heaters must be placed inside the module
breaker compartment (module must be without trolley) and in
the front of the trolley with trolley door open to prevent
condensation. Approximately 250 watts of heat in each
section is required. Incandescent lamps can be used and
located in the bottom of the breaker compartment and
supported so the bulbs will not touch adjacent materials.
Page 8
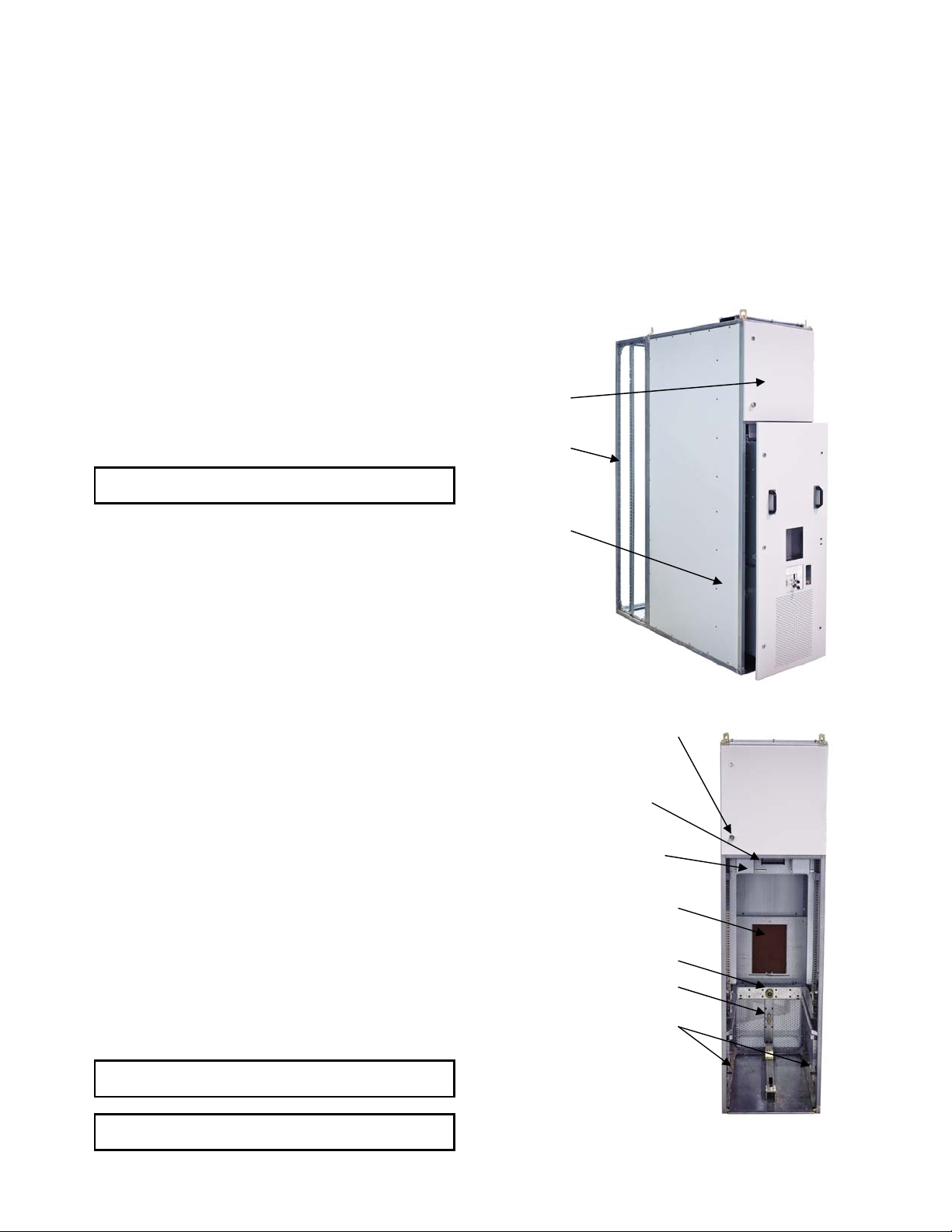
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 4 Installing the Module
General Description
3-1 General Notes
This section contains a description of the GE DC OEM Module and
Trolley for use with Gerapid high speed DC circuit breaker. It also
describes the functions of the electrical and mechanical systems.
3-2 Summary Description
The DC OEM Module is an individual, freestanding, metal-enclosed
switchgear section, designed to be used in conjunction with the
withdrawable trolley, containing a Gerapid circuit breaker,
auxiliary contacts, primary finger clusters and secondary
disconnect.
Ratings
The module is designed to be used on DC systems operating up to
800VDC and 6000A continuous.
The module is available in two continuous current ratings:
4000A for use with 2500A and 4000A Gerapid breaker,
6000A for use with 5000A and 6000A Gerapid breaker,
NOTE: See Appendix “F” for complete ratings of the Module
and the breaker.
Interlocks
Module and trolley are equipped with variety of safety interlocks
that minimize risk of incorrect operations. The following interlocks
are incorporated into the module and trolley:
Positive Interlock preventing movement of the trolley to or
from CONNECTED position when breaker is closed.
Negative Interlock preventing breaker closing unless the
trolley is in CONNECTED or TEST position.
Access Interlock – ensures breaker opening before any
manual operations.
Secondary Control Interlock preventing movement of the
trolley from TEST position to CONNECTED position unless
secondary disconnect is connected. The same interlock
prevents the trolley from being fully withdrawn from the
module unless the secondary disconnect is unplugged.
Breaker Disconnected Padlock Provisions allows padlocking
the trolley in DISCONNECTED position.
Control Compartment Padlock Provisions allows for
padlocking of the controls compartment door.
Rejection Interlock prevents trolley coded for particular
breaker current rating from being inserted into the module
that is coded to different rating.
Shutter Safety Padlock allows padlocking of the safety
shutters in closed position.
Accessories
Several accessories are available with the module and the trolley
for user convenience:
Side Covers for cable compartment,
Crank Handle for trolley racking operations,
Cable Channel connectors and covers,
Attachment Hardware Kits for different components,
Hinges for user furnished compartment doors,
NOTE: See Appendix “G” for full list of accessories, their codes
and illustrations.
NOTE: Detailed description of all accessories functions is given
in Chapter 7.
3-3 The Module
Breaker Compartment
The module is metal-enclosed construction, and consists of the
front breaker compartment, upper controls compartment and
rear cable compartment. Fig. 33-1 shows the location of the
module compartments.
Dead-front, drawout circuit breaker compartment is a standard
construction feature with all modules. The breaker compartment
door remains closed and latched while the breaker is racked out
from the CONNECTED position through TEST position, to the
DISCONNECTED position. See chapter 7.
Control
Compartment
Cable
Compartment
Breaker
Compartment
Fig. 33-1 Front view of the Module with Trolley inside
Control Compartment
Padlock Provisions
Secondary Disconnect
Secondary Control Interlock
Primary Disconnect Shutters
In front of Primary Stabs
Racking Drive Socket
Grounding Circuit Stab
Rejection Interlocks
Fig. 33-2 Front view of the module
8 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 9
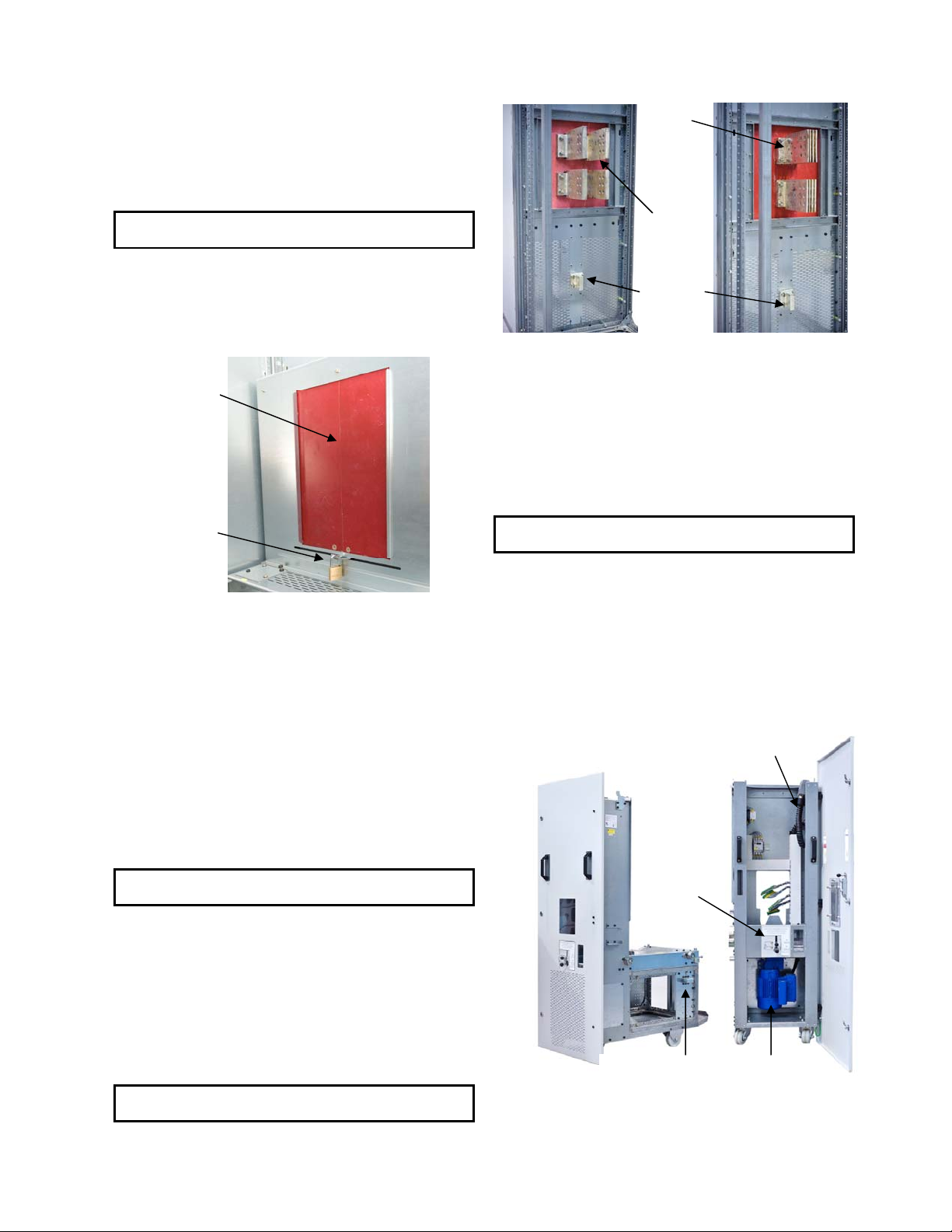
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
g
Rej
Chapter 4 Installing the Module
Grounded steel barriers on the top, sides, bottom, and front
enclose the breaker compartment. In the back, a flame-retardant,
track resistant, glass-filled polyester base minimizes the possibility
of fault communication between compartments or to the bus.
Breaker compartment has primary stabs for connecting the
breaker. Insulated shutters cover primary stabs. See Fig 33-2.
NOTE: See Appendix A for all dimensional drawings of the
breaker Compartment.
Primary disconnect shutters are provided as standard feature to
provide protection against contact with the energized stationary
primary stabs when the trolley is removed from its compartment.
The shutters are constructed from fiberglass reinforced thermoset
polyester. A padlock can lock the shutters in the closed position.
See Fig. 33-3.
4000A
Terminals
6000A
Terminals
Ground
Bus
Connection
Fig. 33-4 Rear views of 4000A and 6000A Modules
Shutters
Padlock
Fig. 33-3 Safety padlock on the shutters
Every module is equipped with rejection Interlock that must be
properly configured by the OEM. This interlock allows
configurations for all current ratings. It is placed on both sides of
the breaker compartment. See Fig. 33-2.
Cable Compartment
The primary stabs extend into the cable compartment and are
suitable for connection with ANSI type busbars. Fig 33-4 shows
primary terminals for 4000A and 6000 A rated modules. Ground
bus connection in the cable compartment is the same on all
module types. Cable compartment is provided without side
covers. See Fig. 33-1. Painted and pre-punched side covers can
be ordered as separate accessories.
NOTE: See Appendix A for all dimensional drawings of the
primary terminals and cable compartment.
Module is also equipped with trolley-operated contacts that are
activated in CONNECTED and TEST position as well as with some
other limit switches that are used for internal interlocks.
3-4 The Trolley
The module is designed to be used with Gerapid high-speed
circuit breaker installed on the withdrawable trolley. The trolley
can be ordered in two different versions, with manual racking or
with motor operated remote racking system.
Remote racking trolley equipped with motor drive can also be
operated manually by the crank handle.
NOTE: The crank handle is an accessory and has to be
ordered separately.
Trolley structure is compatible with all the modules and all
Gerapid circuit breakers listed in Section 3-5. The OEM must
correctly configure the rejection Interlock on the trolley and in the
module for the specific rating of breaker being installed.
All breaker controls, control power supply and auxiliary contacts
are extended to the control compartment via the secondary
disconnect and harness. Negative and positive interlocks are
operated from access console at the front of the trolley. The
access opening for the manual crank handle is there as well.
Secondary Disconnect Plu
Access
Console
Control Compartment
The secondary control plug located in the breaker compartment
is prewired, with a 3ft tagged wire harness brought into the
controls compartment for User’s connections. The matching
secondary disconnect plug is mounted on the trolley.
NOTE: See Appendix A for all dimensional drawings of the
Control Compartment.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 9
Fig. 34-1 Trolley features (motorized racking shown)
ection Interlock
Motordrive
Page 10
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 4 Installing the Module
3-5 Gerapid Breakers
The GE Gerapid DC Circuit Breaker is a high speed, single pole breaker
used for protection of high power DC supply systems. The main features
of the Gerapid circuit breaker are:
Modular construction, easy to inspect and maintain
Non-flammable and non-toxic insulation materials
High speed, current limiting short circuit characteristics
Up to 24kA tripping threshold for OC release
High speed remote impulse release for distant faults
Shunt or zero voltage releases for opening operation
Powerful closing solenoid enables quick closing operation
Easy and safe remote and local control of the breaker,
Wide variety of accessories, such as counter, indicators,
interlocks, manual handle, etc..
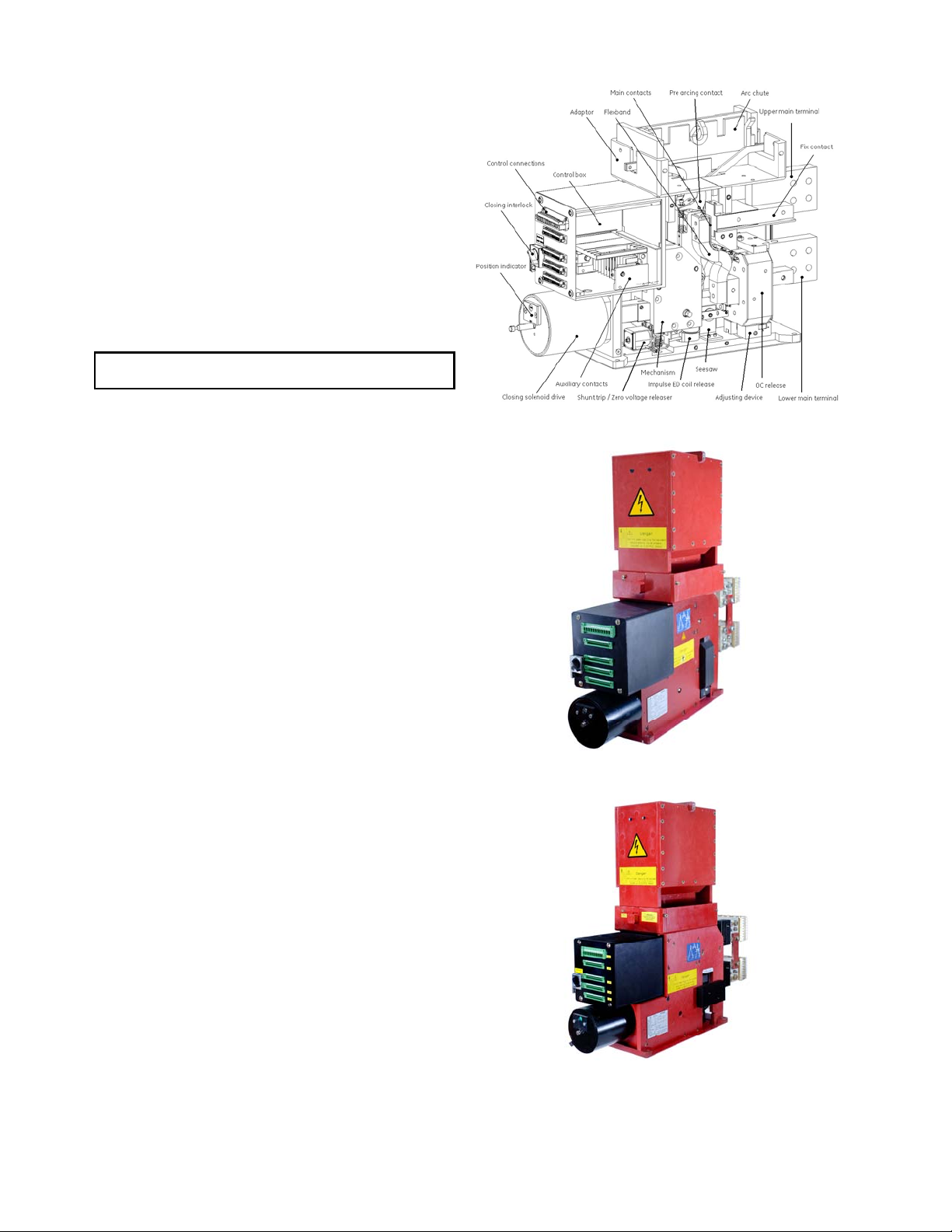
See Fig. 35-1 for overview of the breaker construction.
NOTE: See Appendix F for all ratings and see User Manual
S47183De for breaker details and accessories.
Four current ratings of Gerapid circuit breakers are available for
mounting on the trolley and used in the module. These circuit
breakers are UL Listed and type tested in accordance with
IEEE/ANSI C37.14-2000 Standards. Continuous current ratings
range from 2500 to 6000 ampere frame size. All Gerapid circuit
breakers of the same type and rating may be interchanged,
provided the breaker accessories have the same ratings.
Gerapid 2508 (See Fig. 35-2)
2500A frame size
Standard 200kA peak interrupting current at 800VDC
3700V power frequency withstand level
Current limiting characteristic
Tested for duty type a, b, c and d according to ANSI C37.14
Trip-free capability according to ANSI C37.100
Gerapid 4008 (See Fig. 35-2)
4000A frame size
Standard 200kA peak interrupting current at 800VDC
3700V power frequency withstand level
Current limiting characteristic
Tested for duty type a, b, c and d according to ANSI C37.14
Trip-free capability according to ANSI C37.100
Gerapid 5008 (See Fig. 35-3)
5000A frame size
Standard 200kA peak interrupting current at 800VDC
3700V power frequency withstand level
Current limiting characteristic
Tested for duty type a, b, c and d according to ANSI C37.14
Trip-free capability according to ANSI C37.100
Gerapid 6008 (See Fig. 35-3)
6000A frame size
Standard 200kA peak interrupting current at 800VDC
3700V power frequency withstand level
Current limiting characteristic
Tested for duty type a, b, c and d according to ANSI C37.14
Trip-free capability according to ANSI C37.100
Fig. 35-1 Gerapid circuit breaker construction
Fig. 35-2 Gerapid 2508 and 4008 circuit breakers
Fig. 35-3 Gerapid 5008 and 6008 circuit breakers
10 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 11
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 4 Installing the Module
Installing the Module
4-1 General Notes
This chapter contains instructions for installing the GE DC OEM
Module.
CAUTION: Personnel installing this equipment must be
thoroughly familiar with this instruction manual and all articles
of the National Electrical Code applicable to the installation of
this equipment. In addition, all drawings, both mechanical
installation and electrical, must be understood and strictly
followed to prevent damage to the module.
Environmental Requirements
The module as provided is designed for indoor installations only
and should be placed in an indoor area where clean, dry air is free
to circulate around and above it. Since air is taken into the
equipment at the bottom of each section and exhausted at the
top, a location with good airflow must be provided for efficient
operation.
A minimum of 30 inches of clear space above the equipment is
recommended. In order to properly withdraw the trolley there
should be at least 7 foot of space in the front of the module.
NOTE: See Appendix C for sketches concerning layout.
The foundation must be flat and level in all planes with maximum
deviation of 0.8 inch at the length of 3 foot. The module should be
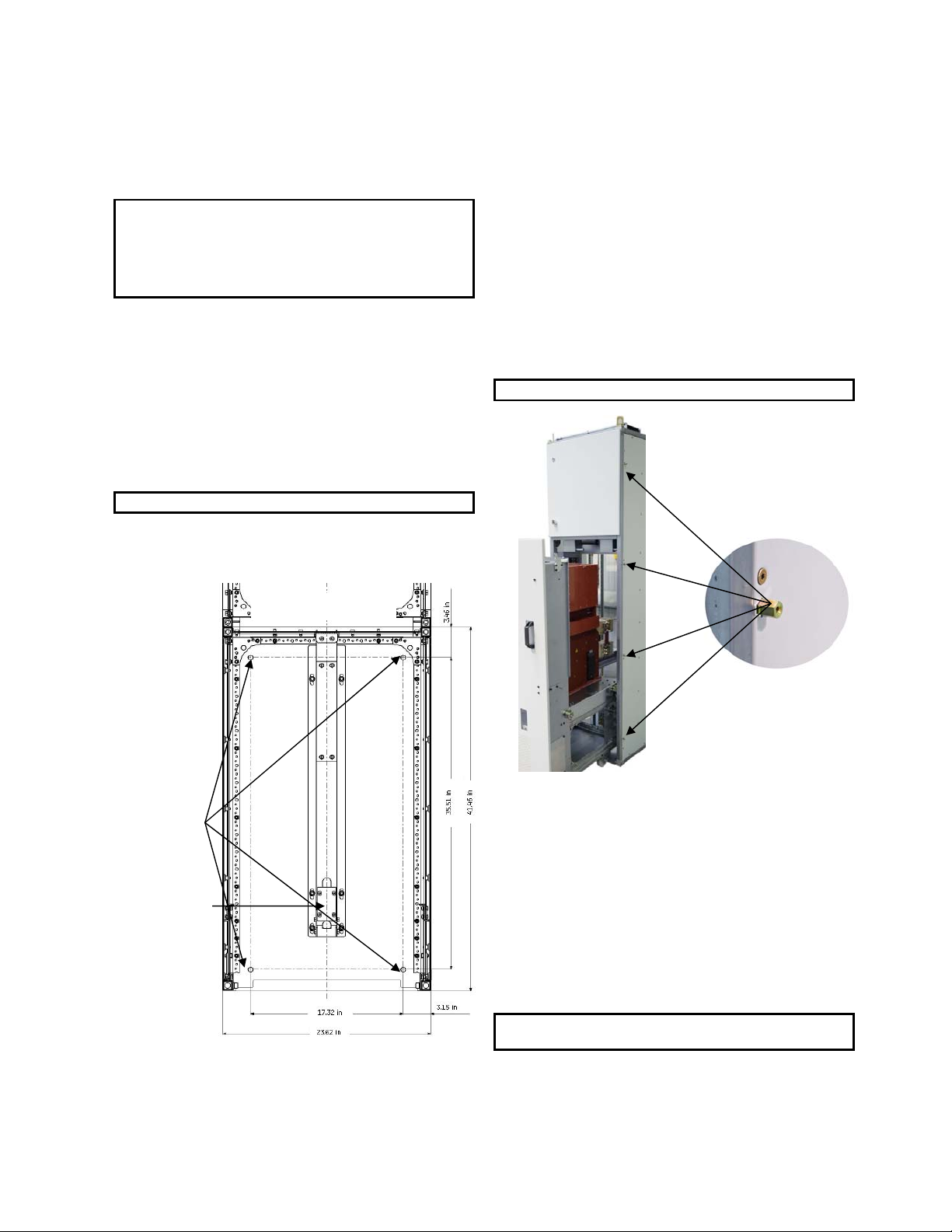
anchored to the floor through holes shown on Fig. 41-1 using
7/16” or metric M12 grade 5 steel bolts.
4-2 Module Configuration and Assembly
Multiple Modules Side by Side Assembly
Modules can be connected together to form switchgear lineups.
To bolt two modules together, edge trim strips must be removed.
Special connection spacers must be used and are inserted into 12
hex shaped cut outs visible in the sidewalls. Fig. 42-1 shows the
location of the front 4 connection spacer openings. Location of all
openings and installation tips are shown in Appendix G.
A Module Coupling Kit can be ordered under Cat. No.: 289169.
Each kit consists of 12 Connection spacers, bolts and washers
necessary to connect two adjacent modules.
NOTE: See Appendix D for connection drawings.
Foundation Requirements
The foundation requirements detailed in this chapter should be
strictly adhered to.
Top View on the floor.
Anchor Points
Use M12 or
7/16” grade 5
bolts.
Locking Plate
Fig.41-1 Module anchor bolt hole locations
The foundation must be strong enough to prevent sagging due to
the weight of the completed switchgear structure and to
withstand the impact loading caused by the opening of the
breakers under fault conditions. The impact loading is
approximately 1-1/2 times the static load.
Connection Spacers
12 per side-by-side.
Fig. 42-1 Location of front module connection spacers
Module Preparation
Every module is suitable for operating either with manually or
motor operated trolley. Depending on the type of trolley being
utilized, a locking plate in the module may need to be removed:
If motor operated trolley is going to be used with the
Module, remove the locking plate.
If manually operated trolley is going to be used with the
module, keep the locking plate in place
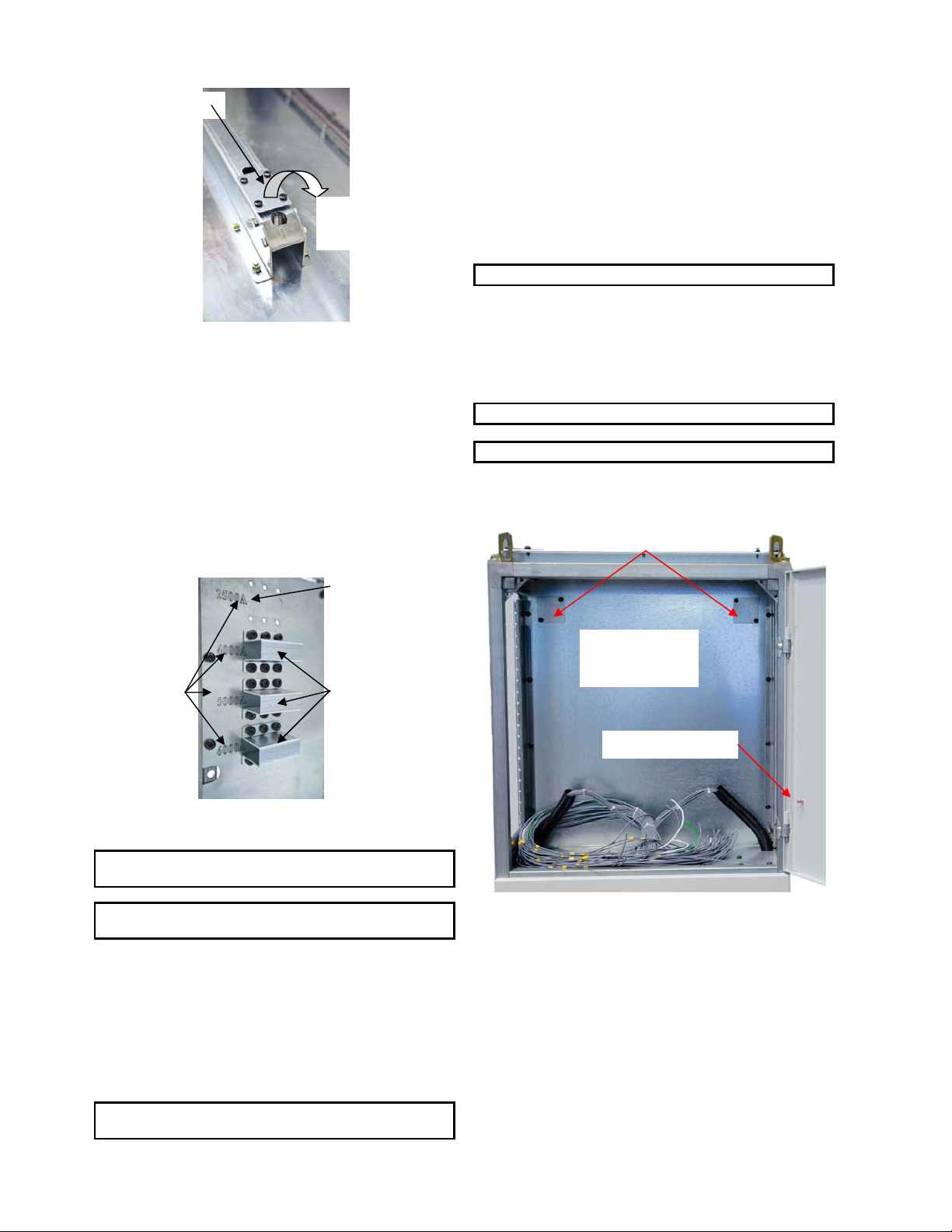
See Fig. 41-1 and Fig. 42-2 to locate locking plate.
NOTE: Look for the yellow warning label placed on the
module’s floor to find bottom guide rail and the plate.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 11
Page 12
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Rej
Chapter 4 Installing the Module
Locking Plate
Remove for motor
operated trolley !
Fig. 42-2 Locking Plate
Module Rejection Interlock
OEM must configure the rejection interlock in the module, before
its usage. Four different configurations are possible: 2500A,
4000A, 5000A or 6000A. In the module, rejection markers must be
screwed in place aligned with all current ratings except the one
that module is dedicated to. This should be done on the right and
left side of the module.
Fig. 42-3 illustrates a correctly configured module rejection
Interlock for a 2500A rated Gerapid breaker. Rejection markers
must be fixed on both right and left sides of the breaker
compartment, aligned with ratings: 4000A, 5000A and 6000A.
Installed Breaker
Ground Bus Connection
Ground bus connection terminal is located at the bottom of the
module in the cable compartment. See Fig. 33-4. Circuit
connections to a ground bus are made so that it is not necessary
to open-circuit the ground bus to remove any connection made
to the ground bus. Ground connections are provided for all
removable elements to ensure that the frame and mechanism are
grounded until the primary circuit is disconnected and the
removable element is moved a safe distance.
NOTE: See Appendix B for ground terminal drawings.
Connecting Secondary Controls
Secondary disconnect plug in the module is pre-wired with the
harness going into control compartment. All wires that should be
used by OEM for completing the module and breaker control are
numbered and accessible inside the Control Compartment.
NOTE: See Appendix E for electrical schemes for connections.
NOTE: See Appendix A for control compartment dimensions.
All trolley control commands and supply connections are also
available thru the harness in the Control Compartment.
Top mounted wire way
access covers
Rating
Markers
Fig.42-3 Rejection interlock set up for rating of 2500A
NOTE: Always verify that the rating on rejection interlock is not
higher that the module rated current.
NOTE: Always configure rejection interlock on both sides of the
module breaker compartment.
ection Markers
Main Busbars Connection
Module primary terminals are silver plated copper and are
suitable to connect to copper bus bars as per IEEE Std. C37.14
Table 6. Connected bus bars should not have cross sections less
that recommend in Table 6.
Gerapid circuit breakers are not polarized. Therefore the load and
the supply line can be connected to either top or bottom terminal.
See Fig. 33-4 for primary terminals views.
NOTE: See Appendix B for primary terminals drawings and
recommend bus bar dimension.
Components
Mounting Plate
Grounding Stud
Fig.42-4 Control compartment
Device mounting on control compartment door
Control compartment’s door should be removed before making
any cutouts. To remove the door, open and remove grounding
connection. Lift the door up until the pins are free from hinges.
All auxiliary devices can be attached to the mounting plate
provided at the back of the control compartment. However it is
recommend prefabricating a separate metal sheet and installing
it in the control compartment using frame supports.
There are two cover plates that provide access to the top
mounted wire way (cable channel). Remove the covers to use
them. See Fig. 42-4.
12 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 13
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 5 Installing the Breaker
Installing the Breaker
5-1 General Notes
Before installing, operating, or removing a circuit breaker, refer to
the Gerapid breaker instruction manual S47183De for
preparation, inspection, and test. Check thoroughly for damaged
or loose parts and for any dirt or foreign matter, which may be in
the breaker.
To install the breaker, proceed as follows:
1) Before installing a breaker, check the contact areas
on each primary disconnect cluster of fingers for foreign
matter that may have accumulated. Clean these areas if
necessary. Be sure that a thin film of the red lubricating
grease “MOBIL GREASE 28” covers the fingers areas before
putting a breaker in the compartment.
2) Check to see that the breakers match their respective
trolley and compartment. Each breaker is assigned a serial
number and ratings. These are shown on the breaker’s
nameplate. The breaker may also be identified using the 20digit PST catalog number. See Fig 51-1.
5-2 Installing Gerapid Breaker
Prior to Installation
Prior to placing a breaker in its intended location on the trolley,
please check following precautions:
1) Find the foil bag with breaker bolting kit no. 700701
that is attached to the trolley’s platform. Remove it.
2) Ensure that the breaker is OPEN.
3) Ensure that arc chute is NOT on the breaker.
4) Ensure that lifting device can carry ~300 lbs and that
lifting slings are min. 6 ft long.
Installation Procedure
To install the Gerapid circuit breaker, proceed as follows:
1) Ensure that the lifting frame has been removed from
the trolley. See Fig. 22-2.
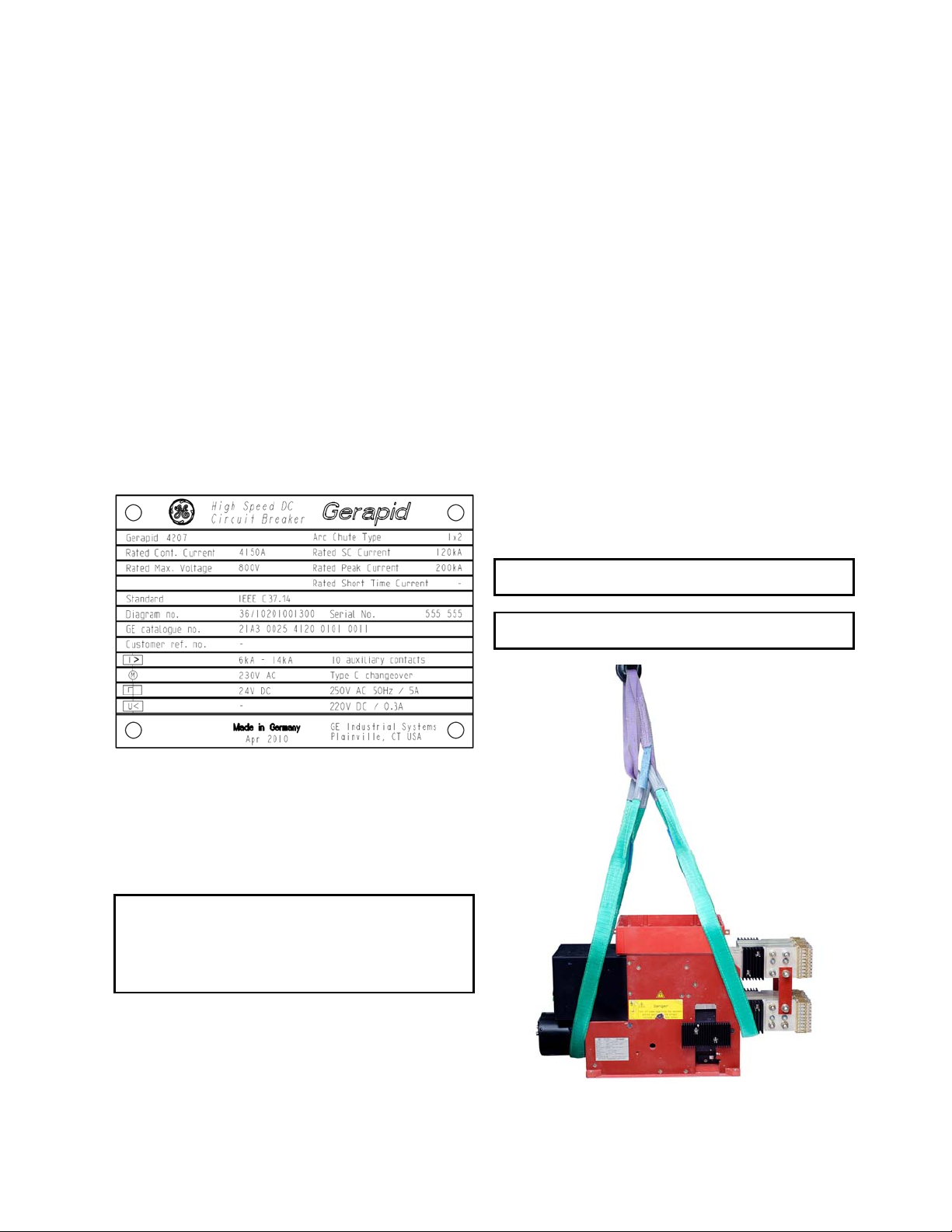
2) Place the lifting slings in position. See Fig. 52-1.
Carefully lift the breaker and place it on the trolley.
3) Slide in the breaker toward the front of the trolley,
until four attachment bolt holes in platform match the holes in
breaker baseplate. Install bolts provided and tighten with
torque listed in Table D-1. The fixing kit is attached to the
trolley’s platform.
4) Plug in all connectors to correct terminals at the front
of breaker’s control box. Tight the connectors. See Fig. 52-3.
WARNING: Do not stand under the circuit breaker during the
lifting and transport operations.
NOTE: Do not transport the circuit breaker with arc chute
installed.
Fig. 51-1 Nameplate of Gerapid breaker
Breakers of the same rating are interchangeable in their
equipment compartments, as long as they have the same
accessories equipped.
The trolley design is the same and universal, regardless of the
Gerapid breaker type intend to operate with.
WARNING: A breaker with different rating fit into any of the
trolleys. If the trolley’s rejection interlock does not match the
breaker’s rating, but it does match the compartment’s
rejection interlock, it is possible to rack-in an incorrect breaker
into the compartment. This may lead to serious damages and
could result in death or serious injury for operator!
Fig. 52-1 Lifting the breaker
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 13
Page 14
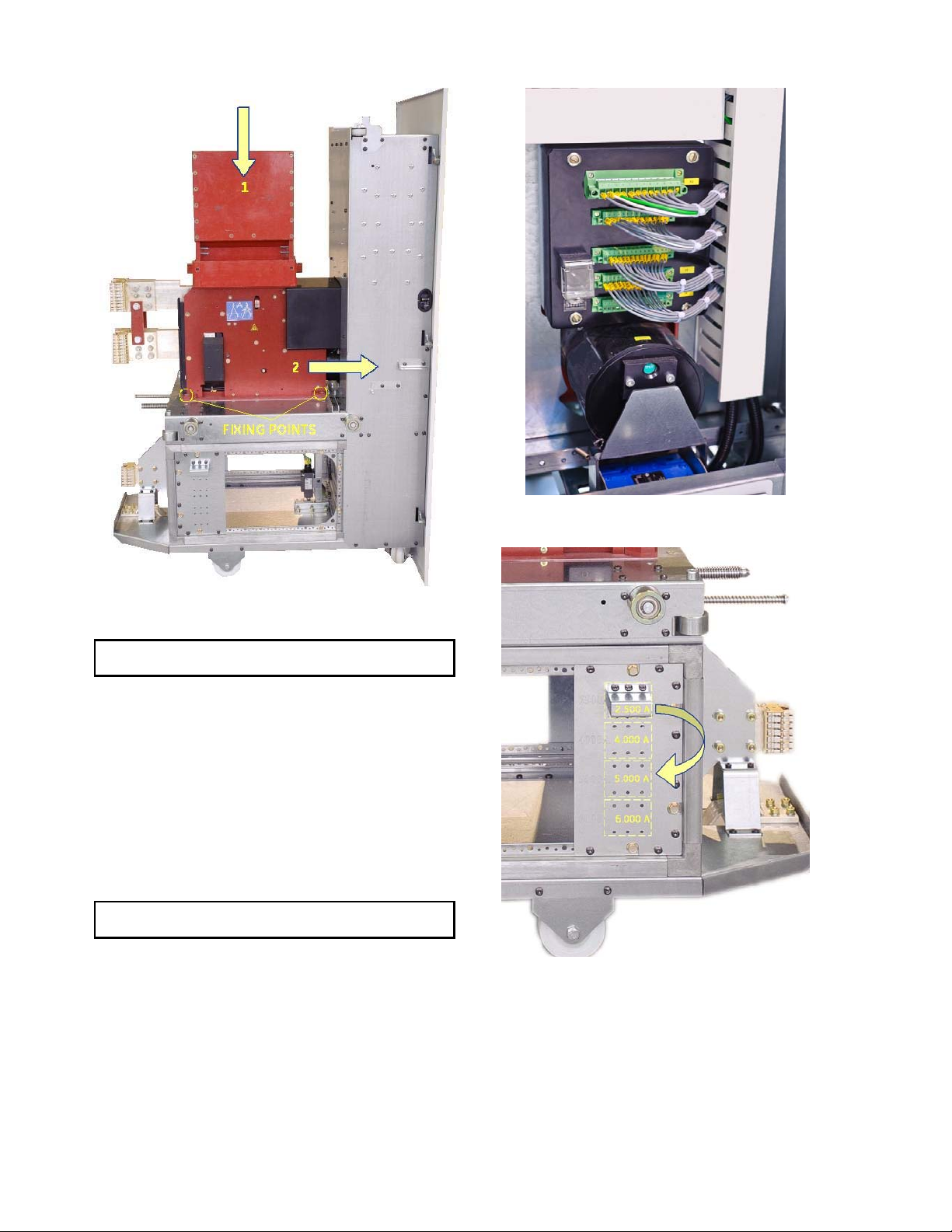
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 5 Installing the Breaker
Fig. 52-2 Breaker on the trolley
NOTE: Do not use attachment screws longer than ~1.2 in.
Longer screws may damage trolley’s components.
Configuration of the Rejection Interlock
It is strongly recommended to check and set up correct position
of the rejection interlock immediately after breaker is installed on
the trolley.
All trolleys have their rejection interlock set at 2500A, by default. If
the breaker has a different rating, the rejection interlock has to be
configured accordingly.
1) Remove both rejection markers from default positions.
2) Reattach them in to the positions which correspond to
the breaker’s current rating. In example from 2500A to 5000A,
see Fig. 52-4
CAUTION: Make sure both rejection markers on both sides of
the trolley match the breaker current rating.
Fig. 52-3 Control connectors for Gerapid breaker
Fig. 52-4 Rejection Interlock of the trolley
14 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 15

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 5 Installing the Breaker
Testing and Inspection
6-1 General Notes
After the equipment has been installed and all connections made,
equipment must be tested and inspected before it is put in
service. Although each module and each breaker have been
tested at the factory, a final field test must be made to be sure
that the equipment has been properly installed and that all
interlocks operate correctly.
Directions for inspection and testing breakers are given in the
instruction book S47183De, furnished with each breaker. The
extent of the tests on the equipment as a whole is given below.
NOTE: See Appendix H for corresponding Field Test Procedure,
where all steps are listed in Tables H-2, H-3 and H-4.
Prior to Test
Before any operation on the module, it is required to check if
corresponding trolley is remote or manual racking type. Remote
racking trolley includes motor drive installed in a bottom-front
compartment of the trolley. See Fig. 34-1.
NOTE: Make sure that locking plate has been removed, if the
trolley is manual racking type. See section 4.2.
Connecting Control Circuits
Some of the field test procedures require control circuits to be
active and energized. Therefore it is necessary to connect the
wiring harness of the module to a dedicated system, which
enables control of the module. To see recommended connections,
please refer to Appendix H, Fig. H-1.
CAUTION: All wires, which are not connected, must be
insulated while test is running.
The Remote Racking option is available only with ~230 V 60 Hz
control voltage. For other values please contact GE Industrial
Solutions representatives. Supply source should be capable to
carry ~3 A permanent current.
NOTE: See Appendix F for details concerning electric
characteristics of auxiliary loads.
High Potential Tests
High-potential tests, to check the integrity of the insulation, are
not necessary if the installation instructions are carefully followed.
Each module and each trolley undergo High Potential Tests
before shipment. Passing of compete Factory Acceptance Test
sequence is marked by sticker note. See Fig. 61-1.
Fig. 61-1 Quality check markings after FAT tests
If local codes demand this test, or the purchaser wishes to make
high-potential tests, the voltage should not exceed, for the power
circuit, 2.8 kV RMS or 3.9 kV DC and for the control circuit
1.2 kV RMS. Testing procedure is described in Appendix H, Table
H-7.
Grounding Circuit Check
If local codes demand this test, or the purchaser wishes to make
earthing system test, refer to procedure described in Appendix H,
Table H-8.
Minimum current required for checking of grounding connections
is 10 A. Resistance for each measured grounding connection
must be less than 0.1 Ohm.
6-2 Field Testing Procedure
NOTE: Extended descriptions of the module operating modes
with illustrations are given in Chapter 7. Refer to these during
Field Testing execution.
Testing the Module with Remote Racking System
Proceed with steps 1.1 to 1.9 from Appendix H, Table H-4.
Testing the Module w/o Remote Racking System
Proceed with steps 1.1 to 1.9 from Appendix H, Table H-5.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 15
Page 16

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
Operating the Module
7.1 Mechanisms and Interlocks
Racking Mechanism
The racking mechanism is designed for moving the trolley
between two (2) positions, TEST and CONNECTED. Clockwise
rotation of the racking shaft, Fig. 71-1, results in Trolley
movement toward the CONNECTED position. Counterclockwise
rotation of the racking mechanism results in trolley movement
from the CONNECTED to the TEST position.
Racking Shaft
Indicator Shaft
Access Interlocks
Front door Access Interlock, see Fig. 71-4, ensures tripping of
the breaker before the Crank Handle can be inserted for
racking. Lifting up of the Trip Lever causes breaker to trip open,
and additionally enable access to manual racking slot.
NOTE: The Access Lever is locked in lower position when
the breaker is closed.
Trip Lever
Fig. 71-1 Racking system
The racking mechanism can be manually or remotely
operated, closed-door drawout, designed to prevent overtravel, and equipped with guides for alignment of the breaker
in the module. The Crank Handle has a torque clutch. See
Fig. 71-2. This clutch protects the racking system against
damages caused by applying excessive force when Trolley is in
CONNECTED position.
Clutch
Fig 71-2 Crank Handle
An indicator is provided to show breaker position within the
compartment. See Fig. 71-3. The indicator is visible from the
exterior of the switchgear.
Access Lever
Fig. 71-4 Front door Access Interlock
Trip Lever is mechanically coupled with a vertical interlock
under the trolley. This interlock mechanically locks the trolley in
TEST or CONNECTD position.
When the Tri Lever is lifted up, the “Crank Lock” stop switch
(S3F) electrically cuts-off the closing circuit of the breaker and
blocks remote racking. This ensures no remote command
activates the trolley or closes the breaker with the Crank
Handle is inserted. See Fig. 71 5 and wiring circuit in Appendix
D.
Operating
Rod
-S3F stop
Lower position
switch
Upper position
Fig. 71-5 Locking rod with S3F end switch “Crank Lock”
Secondary Control Interlock
TEST CONNECTED
Fig. 71-3 Position Indicator
Trolley is equipped with integral wheels for moving the trolley
in and out of a cubicle and sized to carry the weight without
deforming or cutting into the concrete surface. The wheels roll,
but not slide, and guide the trolley to correctly align and
engage the racking mechanism.
16 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Secondary Disconnect consist of a receptacle installed in the
stationary cell and removable plug, which is a part of the
trolley. See Fig. 71-6. This disconnect is equipped with Rack-in
Interlock preventing movement of the trolley from TEST
position to CONNECTED position unless Secondary Disconnect
is connected. Rack-out Interlock prevents the trolley from
being fully withdrawn from the Module unless the secondary
disconnect is unplugged. See Fig. 71-6.
After removing the plug, both interlocks move to the right and
reset. This enables withdrawal operation and blocks rack-in
operation as shown at Fig. 71-7.
Page 17

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
(
)
(
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
Receptacle Snap Lock
Trolley Operated Switches
Stationary part of the Module is equipped with set of trolley
position switches. See Fig. 71-9 for location.
Rack-Out Interlock
active)
Plug
Fig. 71-6 Secondary Disconnect with two interlocks
Rack-In Interlock activated
Park position for the plug.
Fig. 71-7 Operation of Rack-in Interlock
Rack-In Interlock
release
Remote Racking
A motor drive 230V 60 Hz and 250 W (0.34 Hp) is available for
Remote Racking option. The gear-motor is installed in the
front-bottom compartment of the trolley. See Fig. 34-1.
Complete rack-in or rack-out operation lasts ~8 seconds.
Access to 33-1 & 33-2
33-5/33-4
Fig. 71-9 Position switches 33-3, S4F, 33-4, 33-5
Following signal switches are available with the Module:
Switch S4F: NC dry contact available at (Y64 Y65).
Indicate coupling of the racking shaft with racking socket.
Switch 33-4: NO and NC dry contacts available at
(Y66 Y67) and (Y68 Y69). Indicate TEST position.
Switch 33-5: NO and NC dry contacts available at
(Y70 Y71) and (Y72 Y73). Indicate CONNECTED position.
33-3/S4F
Actuator Pins of 33-1
& 33-2
Racking Socket
Fig. 71-8 Limit switches 33-1 and 33-2.
The motor is protected by 2.5 A fuse element. Two
independent limit switches, 33-1 and 33-2, switch off the
motor drive’s supply when the trolley reaches CONNECTED
position. Limit switch 33-3 stops the trolley in TEST position.
See Fig. 71-9.
All three switches are wired to block the breaker CLOSE
operation if the trolley is between CONNECTED and TEST
positions. See circuit diagram E-2, Appendix E.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 17
Padlocks
There are three interlocks, which can be padlocked. Padlock’s
diameter shall not exceed 1/3 inch. Padlocks are not included.
Safety Shutters, see Fig. 33-3,
Access Console, see Fig. 71-10,
Control Compartment, see Fig. 71-10.
Fig. 71-10 Padlock set at Access Console (left) and
Control Compartment (right).
Page 18

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
7.2 Trolley with Manual Racking
Operational Positions
The trolley has four separate operating positions:
1. CONNECTED position – Primary Disconnects and
Secondary Disconnect in full contact, breaker ready for normal
operation. Position Interlock, see Fig. 72-1, keeps the trolley in
this position.
Secondary Disconnect
Secondary Disconnect
2. TEST position - Primary Disconnect separated by a safe
distance and shutters closed. The Secondary Disconnect is in
full contact. Trolley is withdrawn ~5 inches and locked by
Position Interlock. See Fig. 72-2.
3. DISCONNECTED position - Primary Disconnects separated
by a safe distance and shutters closed. Secondary Disconnect
is disengaged. Trolley positioned in the TEST position.
4. WITHDRAWN position – Trolley outside of the Module.
Position Interlock
Fig. 72-1 CONNECTED position of the trolley
NOTE: Manual racking-in and racking-out does not
require control voltage to be present. Although, switching
ON/OFF the breaker will not possible in such case.
Primary Disconnects
Position Interlock
Fig. 72-2 TEST position of the trolley
Primary Disconnects
Racking – In Procedure
NOTE: Crank Handle is necessary for racking operations.
Crank Handle has to be ordered separately.
1. Trolley WITHDRAWN. Push trolley toward the module until
it stops at DISCONNECTED position.
2. Open the trolley’s door and install Secondary Disconnect.
Now the trolley is at the TEST position.
NOTE: .Use the Door Key to open all Door Locks and
release Door Interlock. See Fig. 72-3.
NOTE: Make sure that Receptacle Snap Lock is engaged.
3. Lift up the Access Lever (Fig. 71-4) and push the trolley in
further until racking shaft (Fig. 71-1) couples with socket
(Fig. 71-8).
NOTE: S4F contact should indicate the coupling position if
connected (Y64 Y65) to any external indication device.
18 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 19

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
y
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
Lift to release
Door Interlock
Door Ke
Door Locks
Rack-Out Procedure
NOTE: Crank Handle is necessary for racking operations.
Crank Handle has to be ordered separately.
1. Trolley CONNECTED. Open the breaker either using OPEN
command or pulling up the Trip Lever (Fig. 71-4).
2. Lift up the Access Lever (Fig. 71-4) and insert Crank
Handle. Rotate the crank counterclockwise until trolley
stops. Breaker is now at TEST position.
NOTE: TEST position is indicated by Position Indicator,
(Fig. 71-3) or by contacts of the switch 33-4 (Fig. 71-9).
3. Open the trolley’s door and disconnect the Secondary
Disconnect. Hang it on the frame to the right (Fig. 71-7).
Now the trolley is at the DISCONNECTED position.
NOTE: Use the Door Key to open all Door Locks and
release Door Interlock. See Fig. 72-3.
4. Remove the crank. Lift up the Access Lever (Fig. 71-4) and
pull the trolley out from the module.
Fig. 72-3 Door locks positions
4. Insert Crank Handle into the Access Console slot, Fig. 72-4
and rotate the crank clockwise until trolley reaches
CONNECTED position.
NOTE: CONNECTED position is indicated by Position
Indicator, (Fig. 71-3) or by contacts of the switch 33-5.
5. Remove the Crank Handle. Push down the Trip Lever,
(Fig. 71-4), to make sure that both levers of the Access
Console are in their maximum lower positions.
NOTE: If the Access Lever is not at its maximum lower
position, closing of the breaker will not be possible.
7.3 Trolley with Remote Racking
Operational positions.
The trolley has distinguished four operational positions:
Secondary Disconnect
Fig. 72-4 Crank Handle installed
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 19
Position Interlock
Fig. 73-1 CONNECTED position for the remote racking
trolley
Primary Disconnects
Page 20

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
1. CONNECTED position – Primary Disconnects and
Secondary Disconnect in full contact, breaker ready for normal
operation. Position Interlock, see Fig. 73-1, keeps the trolley in
this position.
2. TEST position - Primary Disconnect open and separated by
a safe distance with shutters closed. The Secondary
Disconnect is in full contact. The Trolley is withdrawn ~4 inches
and locked by Position Interlock. See Fig. 72-3.
Secondary Disconnect
Secondary Disconnect
Position Interlock
Fig. 73-2 TEST position for remote racking trolley
3. DISCONNECTED position - Primary Disconnects open and
separated by a safe distance with shutters closed. Secondary
Disconnect is open. Trolley is withdrawn ~5 inches. See Fig. 72-
3.
4. WITHDRAWN position – Trolley outside of the module.
NOTE: Remote racking-operations require control voltage
and control commands to be provided. See Appendix E for
electrical circuit drawings.
Primary Disconnects
Fig. 73-3 DISCONNECTED position for remote racking
trolley.
Position Interlock
Primary Disconnects
Remote Rack–In Procedure.
NOTE: Crank Handle is necessary for completing racking
operations. Crank Handle has to be ordered separately.
WARNING: EMERGENCY RACKING STOP circuit (Y58 Y59)
must be wired to a pushbutton (furnished by OEM). It is
recommended the STOP PB be installed on the control
compartment door. See example Fig. 73-4.
Use this pushbutton for immediate interruption of racking
operation and stop the trolley regardless of its position.
EMERGENCY RACKING STOP
Fig. 73-4 EMERGENCY STOP pushbutton (by OEM)
20 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 21

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
y
Chapter 7 Operating the Module
1. Trolley WITHDRAWN. Push trolley toward the module
until it stops at DISCONNECTED position.
2. Open the trolley’s door and install Secondary
Disconnect.
NOTE: Use the Door Key provided to open all Door Locks
and release Door Interlock. See Fig. 73-4.
NOTE: Make sure that Receptacle Snap Lock is engaged.
3. Lift up the Access Lever (Fig. 71-4) and push the
trolley in further until racking shaft (Fig. 71-1) couples with
socket (Fig. 71-8).
NOTE: S4F contact should indicate the coupling position if
connected (Y64 Y65) to any external indication device.
4. Insert Crank Handle into the Access Console slot,
Fig. 72-4 and rotate Crank Handle clockwise until trolley
reaches TEST position.
NOTE: TEST position is indicated by Position Indicator,
(Fig. 71-3) or by indication of switch 33-4 (Fig. 71-9).
5. Remove Crank Handle. Push the Trip Lever down,
(Fig. 71-4), making sure that both levers of the Access
Console are in their maximum lower positions.
NOTE: If the Access Lever is not at its maximum lower
position, closing of the breaker or remote rack-in will not
be possible.
6. Use RACK BREAKER-IN command (Y60 Y61) to start
motor for rack in operation. Trolley will stop at
CONNECTED position.
WARNING: Use EMERGENCY STOP pushbutton in case of
emergency situation. See Fig.73-4.
Lift to release
Door Interlock
Manual Rack-Out Procedure.
NOTE: Crank Handle is necessary for completing of
racking operations. Crank Handle has to be ordered
separately.
1. Trolley CONNECTED. Open the breaker either using
OPEN command or pulling up the Trip Lever (Fig. 71-
4).
2. Use RACK BREAKER-OUT command (Y62 Y63) to start
motor for rack out operation. Trolley will stop at TEST
position.
NOTE: TEST position is indicated by Position Indicator,
(Fig. 71-3) or by indication of switch 33-4 (Fig. 71-9).
3. Open the trolley’s door and disconnect the
Secondary Disconnect. Hang it on the frame to the
right (Fig. 71-7).
NOTE: Use the Door Key to open all Door Locks and
release Door Interlock. See Fig. 73-4.
4. Lift up the Access Lever (Fig. 71-4) and insert Crank
Handle. Rotate Crank Handle counterclockwise until
trolley stops. Now the trolley is in the DISCONNECTED
position.
5. Remove Crank Handle. Lift up the Access Lever
(Fig. 71-4) and pull the trolley out from the module.
7.4 Operate the breaker.
Gerapid circuit breakers can be operated electrically and
manually.
NOTE: Manual CLOSE operation at the breaker is possible
only at WITHDRAWN position of the trolley. Manual closing
should only be performed for maintenance.
Manual OPEN operation at CONNECTED or TEST positions is
possible by means of Trip Lever. For maintenance purposes
breaker can be operated by means of dedicated hand lever at
WITHDRAWN position.
NOTE: See User Manual S47183De for breaker operation
details and accessories.
All electric control commands and signals are wired thru
available harness (Y01 Y54). See Appendix E for details of
available commands and signals.
Door Ke
Door Locks
Fig. 73-4 Door locks
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 21
Page 22

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Chapter 9 Customer Support.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
8.1 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting section describes potential issues that user
may experience during operation of the trolley. Contact GE
Energy service in case the problem is not resolved.
NOTE: See User Manual S47183De for breaker
troubleshooting information.
Manually operated trolley
A. Cannot lift Access Lever to insert Crank Handle
Check if the breaker is OPEN. When CLOSED,
breaker’s drive rod activates interlock, which
locks the Access Lever.
Check the length of four M8 mounting screws
for the breaker. Screws may limit the movement
of the Access Lever if are longer than 25 mm
(1”).
B. Cannot trip the breaker by means of Trip Lever
Check the length of four M8 mounting screws
for the breaker. Screws may limit the movement
of the Trip Lever if are longer than 25 mm (1”).
Check the Forced Tripping Release pin under the
breaker’s base. The pin should be able to be fully
pressed against base. If this does not work, the
pin may be damaged inside the breaker.
C. Cannot move the trolley using Crank Handle
Check if Crank Handle is properly and fully
inserted into Access Slot. The crank engages
fully with the shaft only with proper orientation
of the handle.
Check if Crank’s clutch is set at minimum 50 Nm.
D. Cannot rack-in the trolley into DISCONNECT / TEST
position
Check point C.
Check if rating Rejection Interlock of the trolley
and the module match.
Check if Racking Shaft is bent.
Check if Indicator Shaft is jammed.
E. Cannot rack-in the trolley into CONNECTED
position.
Check point C.
Check if Secondary Disconnect is connected.
Check if shutters are jammed or closed.
F. Cannot rack-out the trolley from TEST position.
Check if Secondary Disconnect is disconnected.
Check if Access Lever is lifted up.
8.2 Maintenance
NOTE: See User Manual S47183De for complete breaker
inspection and maintenance routines.
Expected service life of the OEM module is 20 years, with MTBF
exceeds 2,000 racking operations. The module and trolley
construction is nearly maintenance free. The system is
designed to operate during specified period and in prescribed
conditions without functional part replacement. Only simple
preventive maintenance is recommended to be performed
every two years:
Check the racking shaft of the trolley and grease it with
molybdenum based grease, such as MOLYKOTE G4700
or NYE Rheolube® 373. Also grease racking socket in
the structure.
Check the Primary Disconnect clusters. Clean and
apply a light coating of red Mobile 28 grease,
manufactured by ExxonMobil.
Perform testing routine as listed in Appendix H, tables
H3 or H4.
Motor driven trolley
NOTE: Check points A thru F are also valid for motor driven
trolley. Refer to them in case of related issues.
G. Cannot rack-in the trolley to CONNECTED position.
Check if Access Lever is in down position.
Check if motor thermal overload protection
GPS1B is activated.
Check if end switch S4F is activated.
Check if end switch S3F is activated.
H. Cannot rack-out the trolley from CONNECTED
position.
Make sure the breaker contacts are OPEN.
Check point G.
22 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 23

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX A Module & Trolley Drawings.
Customer support
8.1 Warranty
For warranty issues or other after sales service, contact
the GE Energy GE Resolve Customer support line at :
1-888-437-3765.
8.2 Field Service Support
To request and schedule GE Energy Service Engineering
support, call :
1-800-533-5885.
8.3 Publications and other support
Instruction Books, Drawings and other technical
documents can be found and downloaded from the
GE Energy web site at
http://www.geindustrial.com
Go to: Products -> Circuit Breakers -> DC High Speed
Circuit Breakers -> Gerapid.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 23
Page 24
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX A Module & Trolley Drawings.
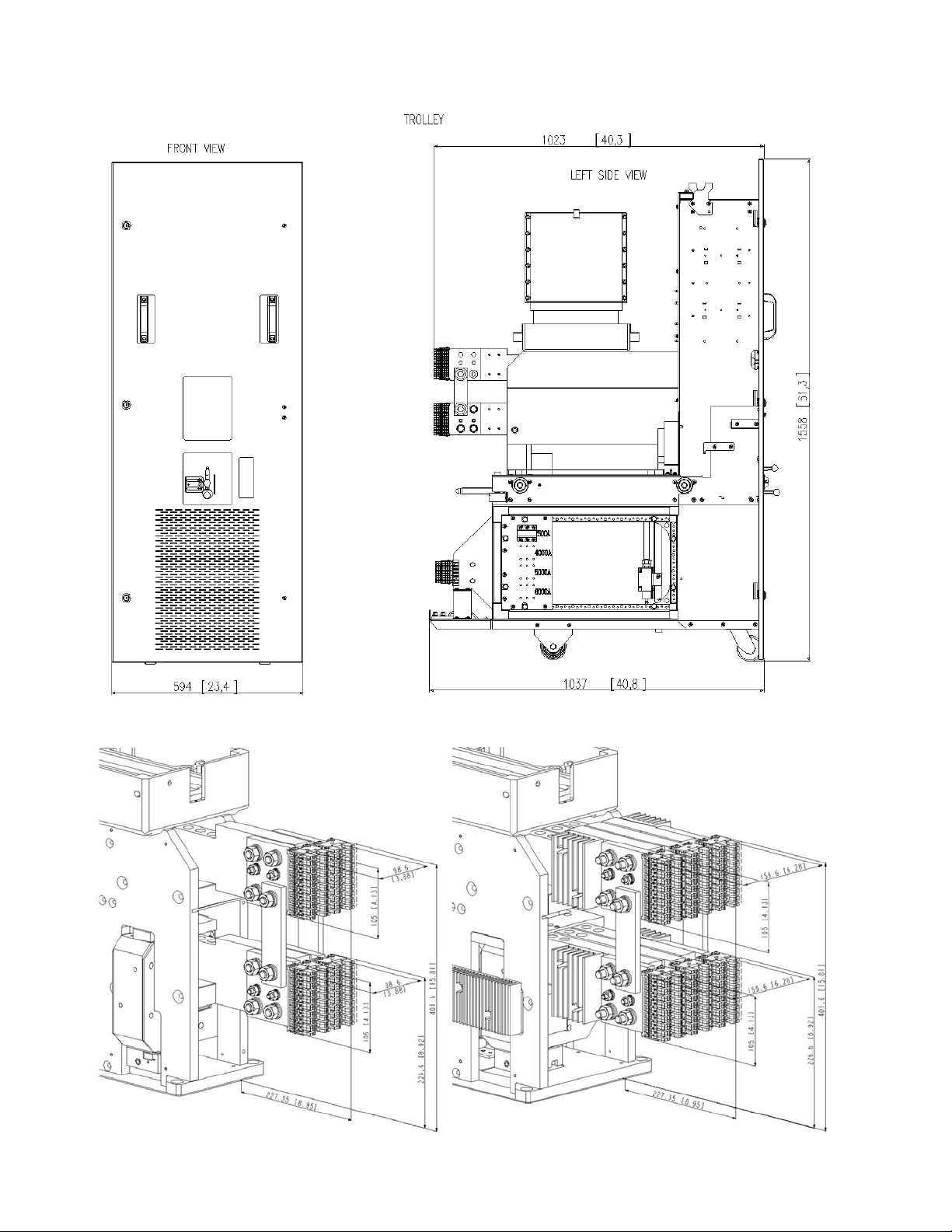
APPENDIX “A” – Module & Trolley Drawings
Fig. A-1 Outline dimensions of the trolley. Units are mm [inches]
Fig. A-2 Primary disconnect clusters for 2508, 4008 (left) and 5008, 6008 (right) Gerapid breakers. Units are mm [inches]
24 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 25

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX A Module & Trolley Drawings.
Fig. A-3 Outline dimensions for OEM Module with 750 mm [ 29.53 inches ] Cable Compartment
Fig. A-4 Outline dimensions for OEM Module with 450 mm [ 17.72 inches ] Cable Compartment
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 25
Page 26
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX B Primary Terminals Drawings.
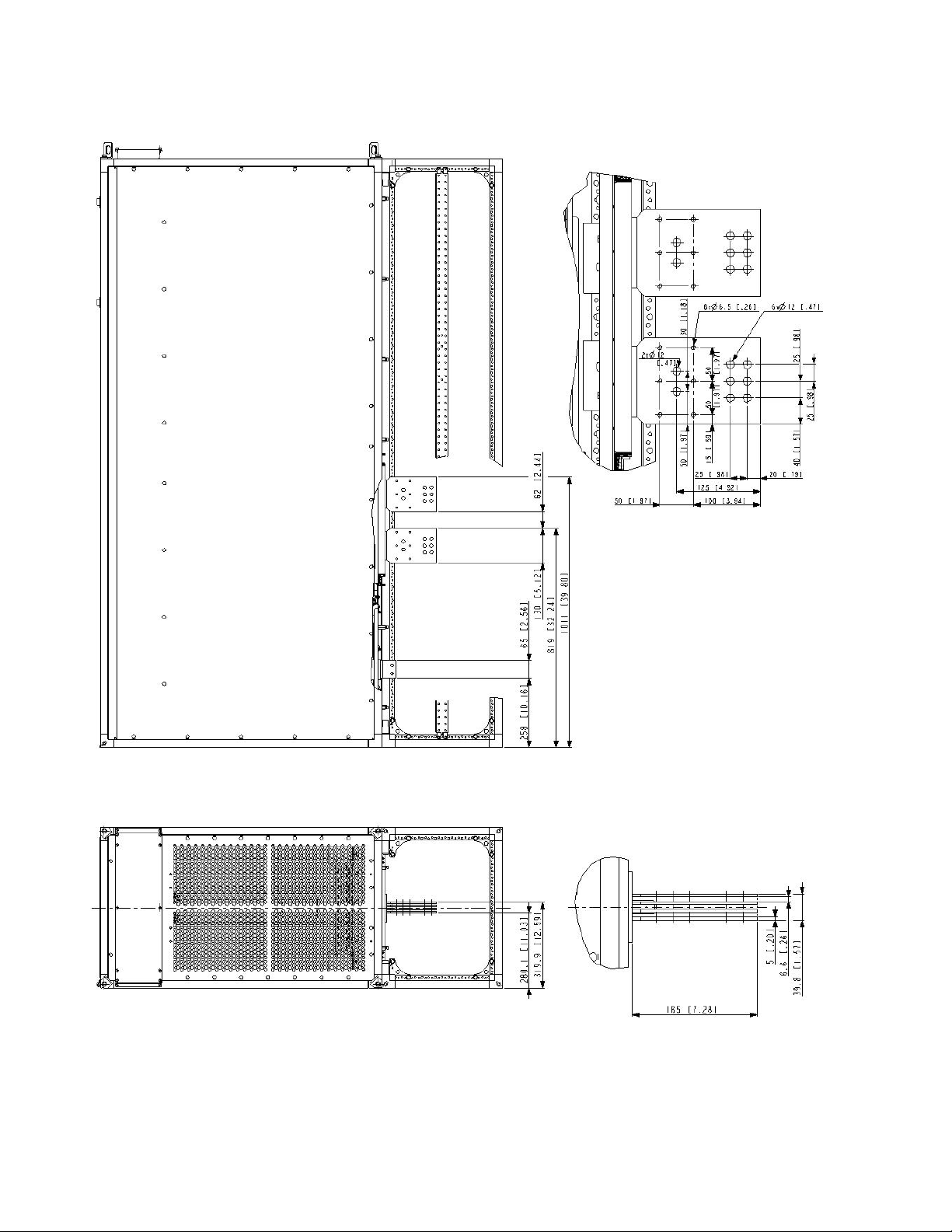
APPENDIX B – Primary Terminals Drawings
Fig. B-1 2500A and 4000A Primary Terminals of OEM DC Module. Units are mm [inches]
26 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 27

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX B Primary Terminals Drawings.
Fig. B-2 5000A and 6000A Primary Terminals of OEM DC Module. Units are mm [inches]
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 27
Page 28

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX B Primary Terminals Drawings.
Side View
Fig. B-3 Ground bus main connection
Top View
28 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 29

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX B Primary Terminals Drawings.
APPENDIX C – Layout drawings
TOP VIEW :
Dimension A:
Dimension B:
Dimension C:
NOTE: Minium free space over the Module’s roof should be 1.5 ft.
- min. 0.3 ft
- min. 7 ft
- min. 0.3 ft in case of no need for rear access,
- min. 1.5 ft in case of need for rear access.
Trolley
Fig. C-1 Minimum required distances for installing the DC OEM Module
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 29
Page 30

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX C Layout Drawings.
APPENDIX D – Tightening Torques Tables
All the tightening torques listed below are applicable for Module, Trolley and Breaker.
Table D-1 Tightening torques for mechanical construction elements
Screw size Hex-head screws
Class 5.8
Inch-pounds Inch-pounds Inch-pounds
Less M3 3 – 4 5 - 6 -
M3 7 – 8 10 - 11 -
M3.5 9 - 10 15 - 17 8 - 10
M4 14 - 15 22 - 24 15 - 17
M5 26 - 29 44 - 49 62 - 68
M6 47 - 51 75 - 83 132 - 146
M8 106 - 117 177 - 194 177 - 194
M10 230 - 253 362 - 398 -
M12 362 - 398 620 - 681 -
M16 885 – 973 1500 - 1650 -
Hex-head screws
Class 8.8
Self-tapping
screws
Table D-2 Tightening torques for electric circuits connections
Screw size Auxiliary & control
circuits
Inch-pounds Inch-pounds
Less M3 - -
M3 9 - 10 -
M3.5 10 - 11 -
M4 13 - 15 -
M5 26 - 29 -
M6 52 - 58 71 - 78
M8 124 - 136 177 - 194
M10 230 - 253 354 - 390
M12 354 - 390 620 - 681
M16 531 - 584 1240 - 1360
Copper bus bar
connections
30 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 31

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX E Electrical Diagrams.
APPENDIX E – Electrical Diagrams
Fig. E-1 Remote Racking Module - Gerapid connections
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 31
Page 32

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX F Rating Tables.
Fig. E-2 Remote Racking Module – Control diagram
32 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 33

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX E Electrical Diagrams.
Fig. E-3 Remote Racking Module – Secondary Disconnect coding
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 33
Page 34

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX F Rating Tables.
Fig. E-4 Remote Racking Module – Wiring Harness coding
34 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 35

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX E Electrical Diagrams.
Fig. E-5 Manual Racking Module - Gerapid connections
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 35
Page 36

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX F Rating Tables.
Fig. E-6 Manual Racking Module – Control diagram
36 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 37

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX E Electrical Diagrams.
Fig. E-7 Manual Racking Module – Secondary Disconnect coding
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 37
Page 38

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX F Rating Tables.
Fig. E-8 Manual Racking Module – Wiring Harness coding
38 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 39

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX G Accessories and Installation Drawings..
APPENDIX F – Rating Tables
Breaker Rating Gerapid 2508
Arc chute type 1x2 1x2 1x2 1x2
Rated continuous current 2,500 A 4,000 A 5,000 A 6,000 A
Rated short circuit peak/sustained current 200/120 kA 200/120 kA 200/120 kA 200/120 kA
Short circuit characteristics Duties a b, c, d Duties a b, c, d Duties a b, c, d Duties a b, c, d
Rated maximum system voltage 800 V 800 V 800 V 800 V
Power frequency withstand voltage 3,700 V / 60 sec 3,700 V / 60 sec 3,700 V / 60 sec 3,700 V / 60 sec
Maximum arc voltage 1,500 V 1,500 V 1,500 V 1,500 V
Mechanical endurance w/o maintenance* 20,000 cycles 20,000 cycles 20,000 cycles 20,000 cycles
Breaker weight 310 lbs 310 lbs 480 lbs 480 lbs
Table F-1 UL listed Gerapid Ratings according to IEEE Std. C37-14-2002
Module Rating DCOEM 4000
Rated continuous current of the primary circuit 4,000 A 6,000 A
Type of Gerapid breaker for installation 2508 & 4008 5008 & 6008
Rated short circuit peak/sustained current 200/120 kA 200/120 kA
Rated maximum voltage 800 V 800 V
Rated insulation level of the primary circuit 5,200 V d.c. 5,200 V d.c.
Rated insulation level of the secondary circuits
Mechanical endurance w/o maintenance* 500 cycles 500 cycles
Weight of the trolley without Gerapid breaker 300 lbs 300 lbs
Weight of the Module without Trolley 550 lbs 580 lbs
1,500 V
Gerapid 4008
DCOEM 6000
1,500 V
Gerapid 5008 Gerapid 6008
Table F-2 UL listed DC OEM Module. Ratings according to IEEE Std. C37.20.1-2002
No functional parts replaced during the listed number of operations. Breakers require servicing at recommended intervals.
Servicing consists of adjusting, cleaning, lubricating, tightening and similar procedures as recommended in Users Guide
S47183De.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 39
Page 40

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX G Accessories and Installation Drawings.
APPENDIX G – Accessories & Installation Drawings
Accessories
Table G-1 List of accessories for DC OEM Module
Catalogue Name Cat No. Description
A
DCOEMCRANK 700695
B
DCOEMCOVER15 700696
C
DCOEMCOVER18 700697
D
DCOEMCONNECTOR 700698
E
DCOEMCHANCOVER 700699
F
DCOEMM8x25KIT 700701
G
DCOEMM6x12KIT 289158
H
DCOEMCOVERFIX 289160
I
DCOEMCOUPLINGS 289169
J
DCOEMHINGES 289709
Crank handle for manual racking. Consists of:
1 pc of crank handle.
Side cover kit for 450 mm depth cable compartment. Consists of:
2 pcs of side cover
4 pcs of edge trim strip
16 pcs of bolting sets like in 289160.
Side cover kit for 750 mm depth cable compartment. Consists of:
2 pcs of side cover
4 pcs of edge trim strip
20 pcs of bolting sets, like in 289160.
Cable channel connector for connecting top cable channels. Sufficient for
connecting eleven (11) OEM modules side-by-side. Attachment requires four (4)
screws M6x12 (289158) per single cable duct connector. Consist of:
10 pcs of cable duct connector
10 pcs of cable duct connector cover
End covers for top cable channels. Fixation requires four (4) screws M6x12 (289158)
per single cover. Consist of:
10 pcs of cable channel covers
Screws for fixation of the single Gerapid breaker to the single Trolley. Consist of:
4 pcs of countersunk screws M8x25
Screws M6x12 use for fixation of user components to the skeleton frame. Consist of:
500 pcs of screws M6x12
Side covers fixing kit. Consist of:
100 fixing sets for side covers installing..
Module coupling kit. Consist of:
12 bolting sets for connecting two adjacent Module frames.
Hinges kit. Single hinge requires one screw M6x12 (289158). Consist of:
12 pcs of hinges for doors.
“A” – DCOEMCRANK “B” - DCOEMCOVER15 “C” - DCOEMCOVER18 “D” - DCOEMCONNECTOR
“E” – DCOEMCHANCOVER “F” – single M8x30 screw “G” – single M6x12 screw “H” – single side cover
connector
“I” – single frame bolting connector “J” – single hinge
40 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 41

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Installation Drawings
APPENDIX G Accessories and Installation Drawings.
12 bolting elements “I” for connecting of
rear, middle and front columns.
cable channel
connector “D”.
4 screws “G” for installing
cable channel connector “D”.
Fig. G-3 Bolting two frames together and installing cable channel connector “D”
cable channel cover “E”
2 screws “G” for installing
cable channel cover “E”
Fig. G-4 Installing end cover “E” for top cable channel.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 41
Page 42

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX G Accessories and Installation Drawings.
Part “H”
Edge Strips
NOTE: Cover “C” (750mm depth) has two additional “H” screws, centered at the top and bottom of the cover.
Fig G-5 Installing edge strips and side cover “B” or “C”
42 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 43

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
y
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
APPENDIX H – Field Test Procedure
This Appendix describes full recommended procedure for Field Testing of DC OEM Module equipped with Gerapid DC Circuit Breaker.
The description consists of four chapters:
Connecting control commands to the module. See Fig. H-1
Testing the module with Remote Racking. See Table H-3.
Testing the module with Manual Racking. See Table H-4.
High potential test (optional). See Table H-6.
Connecting control commands for testing
Following control commands are available for OEM wiring:
Name Wire Points Description
RACK BREAKER-IN (Y60-Y61) Moves trolley from TEST to CONNECTED position.
RACK BREAKER-OUT (Y62-Y63) Moves trolley from CONNECTED to TEST position.
GERAPID SOLENOID CLOSE– (Y04-Y05) Closes Gerapid breaker, possible only in TEST or CONNECTED positions.
GERAPID OPEN (Y06-Y07) Opens Gerapid breaker, possible only in TEST or CONNECTED positions.
POSITIONS CHECK (Y67/Y73) Signals when trolley reaches TEST or CONNECTED position.
EMERGENCY RACKING STOP (Y58-Y59) Immediately stops the trolley regardless of position.
Typical external
controls, furnished
b
OEM.
Fig. H-1 Wiring diagram for connection of control functions for the module.
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 43
Page 44

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
Testing the module with Remote Racking option
(d) Trip Lever
(e) Access Lever
(c) Access Slot
(a) Position Indicator
(b) Crank Handle
Fig. H-2 Access Console and Secondary Disconnect of the trolley
Table H-3 DC Module with Remote Racking - Field Test Procedure
Step Starting Point Check Points
1.1 Trolley is in WITHDRAWN position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot.
1.2 Trolley is in DISCONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank (b) into Access Slot (c).
Connect the Plug (g).
1.3 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Remove Crank Handle (b) from Access
Slot (c).
1.4 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.5 Trolley is in CONNECTED position.
CLOSE the breaker.
a. Try to rack-in the trolley to TEST position.
a. Manually rack-in the trolley to TEST position, using the
Crank Handle (b).
b. Try to CLOSE the breaker at TEST position.
a. CLOSE the breaker.
b. Check the position indication in TEST.
c. Send a command to rack-in the trolley to CONNECTED
position.
d. Try to lift up Access Lever (e).
e. Try to lift up Trip Lever (d).
a. Use Crank Handle (b) to rack the trolley between TEST
and CONNECTED positions.
b. Remove Crank Handle.
c. CLOSE the breaker.
a. Send a command to rack-out the trolley to TEST
position.
b. Try to lift up Access Lever (e).
c. Send a command to OPEN the breaker.
d. Check “Position Check” signal in CONNECTED position
(g) Secondary Plug
UNLOCK
(h) Rack-Out Interlock
(f) Receptacle Snap Latch
(i) Rack-In Interlock
NOTE: Please refer to section 7 for
module operating instructions and hints.
Pass Criteria
a. The trolley must not move into
TEST position, while Plug (g) is
disconnected.
a. The breaker must not
while Crank Handle (b) is inserted.
a. The breaker must CLOSE.
b. “Positions Check” signal must be
active.
c. The trolley must not move.
d. Access Lever must not open,
while breaker is CLOSED.
e. Trip Lever must release and open
the breaker.
c. The breaker must not
is not in TEST or CONNECTED
position.
a. The trolley must not move, while
the breaker is closed.
b. Access Slot (c) must not open, if
breaker is CLOSED.
c. The breaker must OPEN.
d. “Positions Check” signal must be
active.
LOCK
CLOSE,
CLOSE, if it
1.6 Trolley is in CONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.7 Trolley is in TEST position.
CLOSE the breaker.
Remove Crank Handle (b) from Access
Slot (c).
1.8 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.9 END OF PROCEDURE
a. Use Crank Handle (b) to rack-out the trolley into
position between TEST and CONNECTED.
b. Remove Crank Handle.
c. CLOSE the breaker.
d. OPEN and move the trolley to TEST position.
a. Send a command to rack-in the trolley to CONNECTED
position.
b. OPEN the breaker.
a. Use Crank Handle (b) to rack-out the trolley to
DISCONNECTED position.
b. Remove Crank Handle.
c. Try to manually pull trolley out of the module.
d. Disconnect Secondary Plug (g).
e. Try to manually pull trolley out of the module.
c. The breaker must not
is not in TEST or CONNECTED
position.
a. The trolley must not move, while
breaker is CLOSED.
c. The trolley must not move out of
the module, while Plug is
connected.
e. The trolley must move out of the
module.
CLOSE, if it
44 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 45

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
Table H-4 DC Module w/o Remote Racking - Field Test Procedure
Step Starting Point Check Points
1.1 Trolley is in WITHDRAWN position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.2 Trolley is in DISCONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c). Connect Secondary Plug (g).
1.3 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Remove Crank Handle (b) from the slot
(c).
1.4 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.5 Trolley is in CONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
1.6 Trolley is in CONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Insert Crank Handle (b) into Access Slot
(c).
1.7 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Remove Crank Handle (b) from slot (c).
1.8 Trolley is in TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
1.9 END OF PROCEDURE
a. Try to rack-in the trolley to CONNECTED
position.
a. Try to CLOSE the breaker.
a. CLOSE the breaker.
b. Check “Position Check” signal at this
position.
c. Try to lift up Access Lever (e).
d. Try to lift up Trip Lever (d).
a. Rack-in the trolley to a position between
TEST and CONNECTED.
b. Remove Crank Handle.
c. CLOSE the breaker.
d. Rack-in the trolley to CONNECTED
position.
a. Remove Crank Handle.
b. CLOSE the breaker.
c. Try to lift up Access Lever (e).
d. Try to lift up Trip Lever (d).
e. Check “Position Check” signal at this
position.
a. Rack-out the trolley into a position
between CONNECTED and TEST.
b. Remove Crank Handle.
d. CLOSE the breaker.
e. Rack-out the trolley into TEST position
a. CLOSE the breaker.
b. Try to lift up Access Lever (e).
c. Try to lift up Trip Lever (d).
d. Check “Position Check” signal at this
position.
a. Try to manually pull trolley out of the
module.
b. Disconnect Secondary Plug (g).
c. Try to manually pull trolley out of the
module.
Pass Criteria
a. The trolley must not
while Secondary Plug (g) is
disconnected
a. The breaker must not
while Crank Handle (b) is
inserted.
a. The breaker must
b. “Positions Check” signal must
be active.
c. The Access Lever must not
move, while breaker is CLOSED.
d. The breaker must OPEN.
c. The breaker must not
it is not in TEST or CONNECTED
position.
b. The Access Lever must not
open, while breaker is CLOSED.
c. The breaker must OPEN.
d. “Positions Check” signal must
be active.
c. The breaker must not
it is not in TEST or CONNECTED
position.
b. The Access Lever must not
open, while breaker is CLOSED.
c. The breaker must OPEN.
d. “Positions Check” signal must
be active.
a. The trolley must not
of the module, while Secondary
Plug is connected.
c. The trolley must move out of
the module.
move,
CLOSE,
CLOSE.
CLOSE, if
CLOSE, if
move out
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 45
Page 46

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
kV
kV
kV
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
Table H-6 High Potential Tests for the module and the trolley
Step Starting Status Check Points Pass Criteria
2.1 Trolley is at CONNECTED position.
CLOSE the breaker.
2.2 Trolley is at CONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Connect BOTTOM connector with frame.
2.3 Trolley is at CONNECTED position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Connect TOP connector with frame.
2.4 END OF PROCEDURE.
Apply 3.9
connectors and frame.
Apply 3.9
connector and frame
Apply 3.9
main connector and frame
DC or 2.8 kV RMS for 60 seconds between main
DC or 2.8 kV RMS for 60 seconds between TOP main
DC or 2.8 kV RMS for 60 seconds between BOTTOM
No flashover.
No flashover.
No flashover.
Rear view on the bus bars compartment.
Main TOP connector
Main BOTTOM connector
Step 2.2
Step 2.3
46 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 47

DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
Table H-7 High Potential Tests for control and auxiliary circuits
Step Starting Status Check Points Pass Criteria
3.1 Trolley is at TEST position.
Breaker is OPEN.
Connect all control wires together.
Disconnect all earthing wires.
3.2 END OF PROCEDURE
Apply 3.9 kV DC or 1.2 kV RMS for 60 seconds between
wiring harness and frame.
No flashover.
Step 3.1
Table H-8 Grounding Circuit Tests
Step Starting Status Check Points Pass Criteria
a. Check mounting screws of end switches no: 33-
4.1 Trolley WITHDRAWN
Rack-in the trolley into TEST
4.2
position.
Connect Secondary Plug (g), Fig. H-
2.
1 / 33-2 / 33-3 / S4F / 33-4 / 33-5,
b. Check door locks of the control compartment,
c. Check end switch S3F under the trolley.
a. Check the motor drive’s housing,
b. Check breaker’s grounding point at –X2:3,
c. Check door locks of the trolley,
d. Check handles at the front of the trolley.
Grounding path resistance,
between main ground bus
and measured point, must
be less 0.1 Ohm.
Step 4.1a Step 4.1a
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 47
Page 48
DC OEM MODULE FOR USE WITH GERAPID CIRCUIT BREAKERS
APPENDIX H Field Test Procedure.
Step 4.1b Step 4.1c
Step 4.2a
Step 4.2b
Step 4.2c
Step 4.2d
48 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183Ee rev.01 2011-04-26
Page 49

GE Industrial Solution
41 Woodford Ave.
Plainville, CT 06062
www.geindustrial.com
© 2010 General Electric Company
All Rights Reserved
S47183Ee rev 01
2011-04-26 S47183Ee rev.01 Design and specifications are subject to change without notice 49
 Loading...
Loading...