Page 1

USER MANUAL
Ethernet Option
OPC-G11S-ETN
For
GE Fuji AF-300G11/P11
Firmware Version 1.XXX
Document SDM-7583-006
Version 1.0 - Dec 19, 2003
HMS Industrial Networks
Germany
Japan
Sweden
U.S.A
℡
+ 49 - 721 - 96472 - 0 sales-ge@hms-networks.com
+ 81 – 45 - 478 -5340 sales-jp@hms-networks.com
+ 46 - 35 - 17 29 20 sales@hms-networks.com
+ 1 - 773 - 404 - 2271 sales-us@hms-networks.com
!
Page 2

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................. I
About This Manual ............................................................................................................ IV
How To Use This Manual.........................................................................................................................................................IV
Important User Information.....................................................................................................................................................IV
Related Documentation.............................................................................................................................................................IV
Revision List................................................................................................................................................................................IV
Conventions Used in This Manual............................................................................................................................................ V
About the OPC-G11S-ETN...................................................................................................1
Key Features.................................................................................................................................................................................. 1
General........................................................................................................................................................................................ 1
Ethernet Global Data (EGD)..................................................................................................................................................... 1
EtherNet/IP............................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Modbus/TCP ............................................................................................................................................................................. 1
EtherNet/IP Network Overview............................................................................................................................................... 2
Ethernet Global Data (EGD) Network Overview.................................................................................................................. 2
Modbus/TCP Network Overview............................................................................................................................................. 3
Applicable Inverters..................................................................................................................................................................... 4
I
Installation ............................................................................................................................5
Receiving Inspection.................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Installation of Option Card......................................................................................................................................................... 6
Installation Checklist.................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Installation and Configuration .............................................................................................8
Module Overview......................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Network Connection ................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Status Indicators ........................................................................................................................................................................... 9
LED 1 – Ethernet Link/Activity.............................................................................................................................................. 9
LED 2 – Module Status............................................................................................................................................................. 9
LED 3 – Network Status .......................................................................................................................................................... 9
Assigning a Network Address................................................................................................................................................... 10
Example Using HICP .............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Bus Configuration Parameters.................................................................................................................................................. 12
Operation Configuration Parameters....................................................................................................................................... 12
Fault Detection and Action....................................................................................................................................................... 13
EGD .................................................................................................................................... 14
Configuration .............................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Data Messages............................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Command Messages................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Configuration Messages............................................................................................................................................................. 16
Modbus/TCP......................................................................................................................17
Page 3

Table of Contents
Addressing................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Commands .................................................................................................................................................................................. 17
Exception Codes......................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Timeout........................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
EtherNet/IP ....................................................................................................................... 19
IO Connection............................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Idle action .................................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Example PLC configuration ...................................................................................................................................................... 19
Explicit Messaging...................................................................................................................................................................... 21
Get Attribute Single Example................................................................................................................................................... 21
Set Attribute Single Example.................................................................................................................................................... 23
Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) File ............................................................................................................................................24
Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format.................................................................... 25
Data Consumed by the Drive................................................................................................................................................... 25
Run Command Word ................................................................................................................................................................ 25
Frequency Setting (S01) ............................................................................................................................................................. 25
Data Produced by the Drive..................................................................................................................................................... 26
Operation Status Monitor 1 ....................................................................................................................................................... 26
Operation Status Monitor 2 ....................................................................................................................................................... 26
Output Frequency Monitor (M06).............................................................................................................................................. 27
II
Appendix B - Drive Parameters.......................................................................................... 28
Parameter List............................................................................................................................................................................. 28
Data Format Specification......................................................................................................................................................... 33
Data Format [1]: Integer Data (Positive): Min. Unit 1 ............................................................................................................ 33
Data Format [2]: Integer Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 1............................................................................................. 33
Data Format [3]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.1....................................................................................................... 33
Data Format [4]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.1........................................................................................ 33
Data Format [5]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.01..................................................................................................... 33
Data Format [6]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.01 ..................................................................................... 33
Data Format [7]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.001................................................................................................... 33
Data Format [8]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.001 ................................................................................... 34
Data Format [10]: Alarm Code............................................................................................................................................... 34
Data Format [11]: Capacity Code............................................................................................................................................ 34
Data Format [12]: Index Data (ACC/DEC Time, Display Coefficient).................................................................................. 35
Data Format [14]: Operation Command................................................................................................................................... 35
Data Format [15]: Universal Output Terminal......................................................................................................................... 35
Data Format [16]: Operating State........................................................................................................................................... 36
Data Format [17]: Type Code.................................................................................................................................................. 36
Data Format [18]: Code Setting (1 – 4 Figures)........................................................................................................................36
Data Format [19]: Amperage Value Decimal Data (Positive)................................................................................................... 37
Data Format [20]: Transmission Error Code............................................................................................................................ 37
Data Format [21]: Auto Tuning............................................................................................................................................... 37
Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects.................................................................................... 38
Identity Object, Class 0x01 ....................................................................................................................................................... 39
Services ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Class Attributes......................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Instance Attributes..................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Assembly Object (Class 0x04) ..................................................................................................................................................40
Services ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Class Attributes......................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x03 (3d).......................................................................................................... 40
Page 4

Table of Contents
III
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x64 (100d) .....................................................................................................40
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x65 (101d) .....................................................................................................40
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x96 (150d) .....................................................................................................40
Fuji Vendor Specific Object (Class 0x64) ............................................................................................................................... 41
Services ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Class Attributes......................................................................................................................................................................... 41
Instance Attributes..................................................................................................................................................................... 41
TCP/IP Interface Object (Class 0xF5).................................................................................................................................... 42
Services ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Class Attributes......................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Instance Attributes..................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6).......................................................................................................................................... 43
Services ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Class Attributes......................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Instance Attributes..................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Appendix D - EGD Exchanges ..........................................................................................44
Exchange C1 ............................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Exchange P1................................................................................................................................................................................ 44
Exchange P2................................................................................................................................................................................ 44
Exchange P3................................................................................................................................................................................ 45
Page 5
About This Manual
About This Manual
How To Use This Manual
This manual is intended to provide a good understanding of the functionality of the OPC-G11S-ETN
module. This manual only covers the Ethernet communication module, for more info about the drive’s
capabilities refer to the drive manual. For more information about a specific fieldbus contact the respective
fieldbus organization.
Important User Information
The data and illustrations found in this document are not binding. We reserve the right to modify our
products in line with our policy of continuous product development. The information in this document is
subject to change without notice and should not be considered as a commitment by HMS Industrial Networks
AB. HMS Industrial Networks AB assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
AnyBus® is a registered trademark of HMS Industrial Networks AB. All other trademarks are the property of
their respective holders.
IV
Related Documentation
Document Author
EtherNet/IP specification ODVA
Open Modbus/TCP specification Schneider Electric
Ethernet Global Data, Protocol specification GE Fanuc / GE Industrial Systems
AF-300G11 Instruction Manual GE Fuji
AF-300P11 Instruction Manual GE Fuji
Revision List
Revision Date Author Chapter Description
1.0 Dec 19, 2003 MaH All Document created
Page 6

About This Manual
Conventions Used in This Manual
The following conventions are used throughout this manual:
• Numbered lists provide sequential steps
• Bulleted lists provide information, not procedural steps
• The term ‘module’ is used when referring to the OPC-G11S-ETN
• Hexadecimal values are written in the format NNNNh or 0xNNNN, where NNNN is the
hexadecimal value.
V
Page 7

About the OPC-G11S-ETN
About the OPC-G11S-ETN
The OPC-G11S-ETN Ethernet adapter interfaces the G11 or P11 drive to an Ethernet network. The module
support three different communication protocols: EtherNet/IP, Ethernet Global Data (EGD), and
Modbus/TCP. It is not recommended that more than one protocol is used for controlling the drive at the
same time.
Key Features
General
• 10/100 Mbps operation
• DHCP support
• Supports HICP (Host IP Configuration Protocol)
• FTP server for configuration and firmware upgrade
1
Ethernet Global Data (EGD)
• Implements EGD class 3 functionality
• Data messages (Exchanges)
• Command messages
• Configuration messages
EtherNet/IP
• IO data connection
• EtherNet/IP explicit messaging
Modbus/TCP
• Supports 8 simultaneously connections
• Configurable time-out
Page 8

About the OPC-G11S-ETN
EtherNet/IP Network Overview
EtherNet/IP is an industrial networking standard that takes advantage of commercial off-the-shelf Ethernet
communication chips and physical media. IP, stands for 'industrial protocol' and is what distinguishes this
network. Unlike many options in the industrial Ethernet crowd, EtherNet/IP uses an open protocol at the
application layer. Further, more than one vendor or organization backs EtherNet/IP. It is the only standard
supported by three networking organizations: ControlNet International (CI), the Industrial Ethernet
Association (IEA) and the Open DeviceNet Vendor Association (ODVA)
For further information:
ODVA
1099 Highland Drive, Suite A
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48108
Phone: 1-734-975-8840
Fax: 1-734-922-0027
Email: odva@odva.org
http://www.odva.org
2
Ethernet Global Data (EGD) Network Overview
Ethernet Global Data (EGD) supports the ability to share information between controllers (nodes) in a
networked environment. EGD allows one controller, referred to as the producer of the data, to simultaneously
send information to any number of peer controllers (consumers) at a fixed periodic rate.
In addition, EGD supports a set of commands for accessing data and protocol information on EGD nodes.
EGD also defines a mechanism for sharing configuration information among nodes.
EGD protocol messages are categorized as command, data, or configuration messages.
Command messages can be used to monitor and control the operation of EGD on the destination node.
Data messages are individually configured to send a sample of data at a fixed periodic rate. Each data message
that a node sends or receives is associated with a specific identifier, which uniquely defines the configuration
of the data sample. This configuration is referred to as an exchange. EGD allows the configuration of
exchanges that are sent to a single destination address (IP Unicast addressing), a group of addresses (IP
Multicast addressing), or to all EGD nodes (IP Broadcast addressing). An assigned set of 32 IP Multicast
addresses has been defined for use by applications requiring the transmission of data exchanges to a group of
nodes.
EGD configuration messages are transferred using HTTP on the connection based TCP/IP transport layer,
utilizing XML as a data abstraction layer.
Page 9

About the OPC-G11S-ETN
Modbus/TCP Network Overview
Modbus/TCP was invented by Modicon/Group Schneider and is today is one of the most popular protocols
embedded inside the TCP/IP frames of Ethernet.
The Modbus protocol was first published back in the 1970's and has been adopted by users and vendors alike
in the industrial automation world. No changes have been made to the protocol itself but changes have been
made in the way or the rate that messages are sent in order to fulfill the real-time needs of industrial
applications. This has given us Modbus/TCP.
Modbus/TCP basically embeds a Modbus frame into a TCP frame in a simple manner. This is a connectionoriented transaction, which means every query expects a response.
This query/response technique fits well with the master/slave nature of Modbus, adding to the deterministic
advantage that Switched Ethernet offers industrial users.
For further information:
The Modbus Organization
PO Box 628
Hopkinton, MA 01748-0628
3
Phone: 508-435-7170
http://www.modbus.org
Page 10

About the OPC-G11S-ETN
Applicable Inverters
Item Description
Inverter type AF-300G11/P11
Compatible inverter Model number The two last digits of the model number should be B1 or later
Example: 6KG1123X1B1
Up to 22kW (30HP) S08000 Minimum inverter ROM version
30 kW (40HP) and above H08004
Note: This product can only be used for Inverters with ROM version numbers greater than or equal to the versions
shown above.
1. Check the ROM number of your Inverter as follows, using the inverter keypad.
2. Check that the Inverter Operation monitor (Operation mode) screen is displayed.
3. Press the [PRG] key of the Inverter once.
4. Select the "5. MAINTENANC" with the cursor and press the [FUNC/DATA] key.
5. Press the down cursor key to increment the display at the MAINTENANC screen. Finally, the ROM
number is shown in the maintenance information, as indicated by the display "INV=Hxxxxx or
Sxxxxx".
4
The maintenance and inspection items are similar to the Inverter unit, for detail refer to the Inverter
Instruction Manual.
Page 11
Installation
Receiving Inspection
Confirm the following items upon a receipt.
1. The model number matches your purchase order?
2. Check the model number printed on the circuit board.
Model: OPC – G11S – ETN
Inverter type
G11S = AF-300 G11/P11 Series
Installation
5
Option Type
ETN = Ethernet Interface Option
3. Inspection for damage during transportation. Report damage to transportation carrier.
Page 12
Installation
yp
p
p
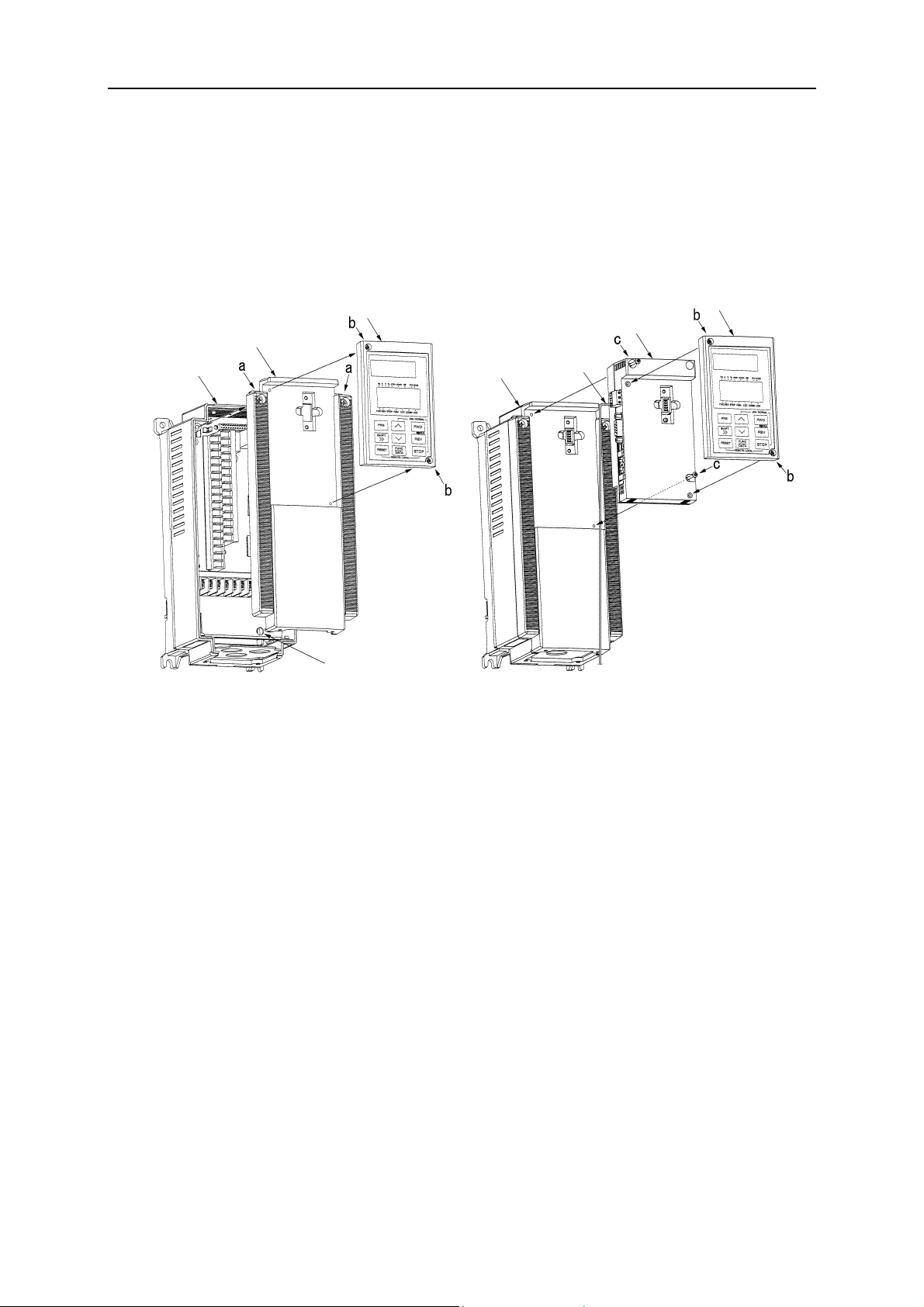
Installation of Option Card
Please follow the installation procedure described as follows. Please install or detach the option after turning
off the input power supply of the inverter and confirming the charge lamp (CHARGE or CRG) is gone out.
The shape, the dimensions and the position of the charge lamp of the inverter are different by each capacity.
Ke
To
Inverter Unit
Cover
Keypad
Inverter Unit
PE Line
tion Unit
O
6
ad
Charge Lamp
Step 1 Step 2 to 4
Step 1
Loosen two screws (M4) at a and remove the top cover. Loosen two screws (M3) at b and detach the keypad
panel. (For the 30kW[40HP] and above inverters, the keypad panel can be detached if the front cover is
removed and the screws loosened at b.)
Step 2
Reassemble the top cover, push-in the option unit and secure it with two screws (M3) at c.
Step 3
Secure the keypad panel to the option unit with two screws at b.
Step 4
Connect the ground cable to the PE terminal of the option unit (The rightmost screw terminal, besides the
RJ45 Ethernet connector).
Page 13

Installation Checklist
After installation and wiring, check the following items.
• The wiring is correct.
• No loose wires or screws remain inside the Inverter.
• The screws and terminals are all tight.
• There are no loose threads of wires at terminals that may contact other terminals.
• Inverter parameters such as H30, o27, o28, o31 to o40, are set correctly. (H30: Link Active/Inactive,
o27 and o28: for network loss action, o31 to o40: for fieldbus specific options)
Installation
7
Page 14
Installation and Configuration
Installation and Configuration
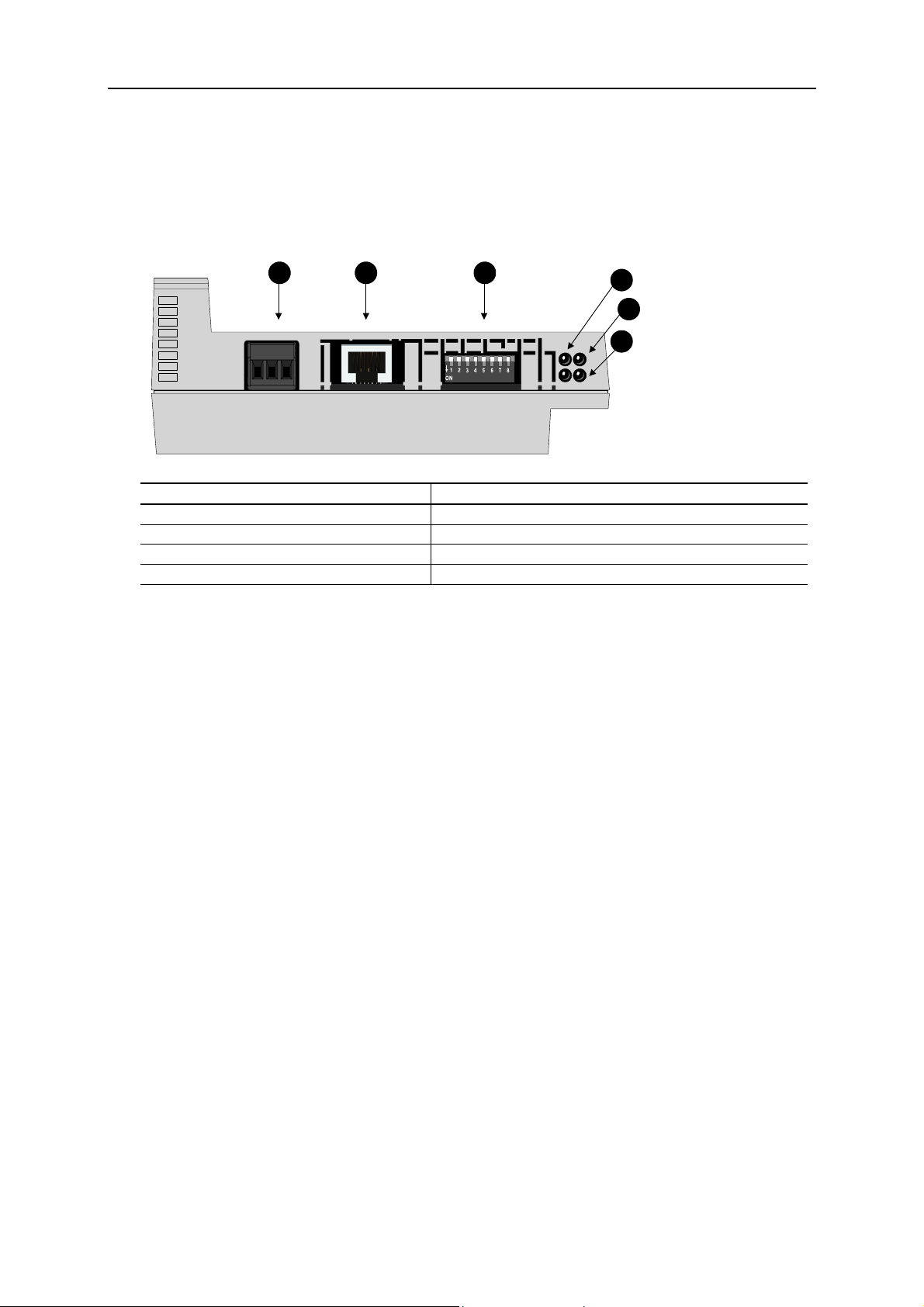
Module Overview
8
A B C
1
2
3
Figure Description
A PE Connector
B RJ45 Ethernet connector
C Network address switch
1-3 LED indicators
Network Connection
Connect the module to a 10 or 100 Mbps Ethernet network.
LED 1 lit green when the module detects link, the LED will flash when the module is receiving/transmitting
data on the network.
Default, auto negotiation will be used for speed and duplex. If speed and duplex settings need to be
configured manually, i.e., no link is established, see the bus configuration parameters.
Page 15
Installation and Configuration
Status Indicators
LED 1 – Ethernet Link/Activity
Color LED state Description
Green
LED 2 – Module Status
LED state Device State Description
Steady Off No power Steady Green Device operational
Flashing Green Standby
Flashing Red Minor fault
Steady Red Major fault
Flashing Green/Red Self-test The module is performing its power up testing.
On The module sense link
Off The module does not sense link
Flash The module is receiving/transmitting data on Ethernet
The module has an Ethernet/IP connection OR has a
healthy EGD exchange OR has a Modbus/TCP
connection.
The module has no active data exchange but is ready to
be controlled.
A recoverable minor fault has been detected. E.g., a
connection time out or EGD exchange in unhealthy state.
A major internal error has been detected. E.g., hardware
fault or invalid drive type detected.
9
LED 3 – Network Status
LED state Network State Description
Steady Off
Flashing Green No connections
Steady Green Connected
Flashing Red Connection timeout
Steady Red Duplicate IP
Flashing Green/Red Self-test The module is performing its power up testing.
No power or
no IP address
The module has no power or no IP address is configured.
There are no Ethernet/IP connections established to the
module.
The module has at least one established Ethernet/IP
connection.
One or more of the EtherNet/IP connections, where this
module is the target, has timed out. This state is only left if
all timed out connections are re-established or if the
module is reset.
The module has detected that its IP address is already in
use.
Page 16
Installation and Configuration
Assigning a Network Address
When the module is connected to the network it must me assigned a unique IP address on the network. There
are four methods available for setting the IP address:
Method Description Comment
Network address switch
DHCP
HICP
(Windows program)
EtherNet/IP
The module will use the IP address
192.168.0.X where X is set with the
network address switch. The address
is set binary with DIP1 as MSB.
The module will automatically receive
the configuration from a DHCP server.
Use “Anybus IPconfig” software to find
the module on the network and
configure it.
Send IP parameters to the TCP/IP
interface object-
Must be set before power-on. This
configuration can only be used in a
private network.
DHCP is enabled by default.
HICP can be disable, see bus config
parameters.
Module needs to be restarted before
new configuration will be used.
10
Page 17
Installation and Configuration
11
Example Using HICP
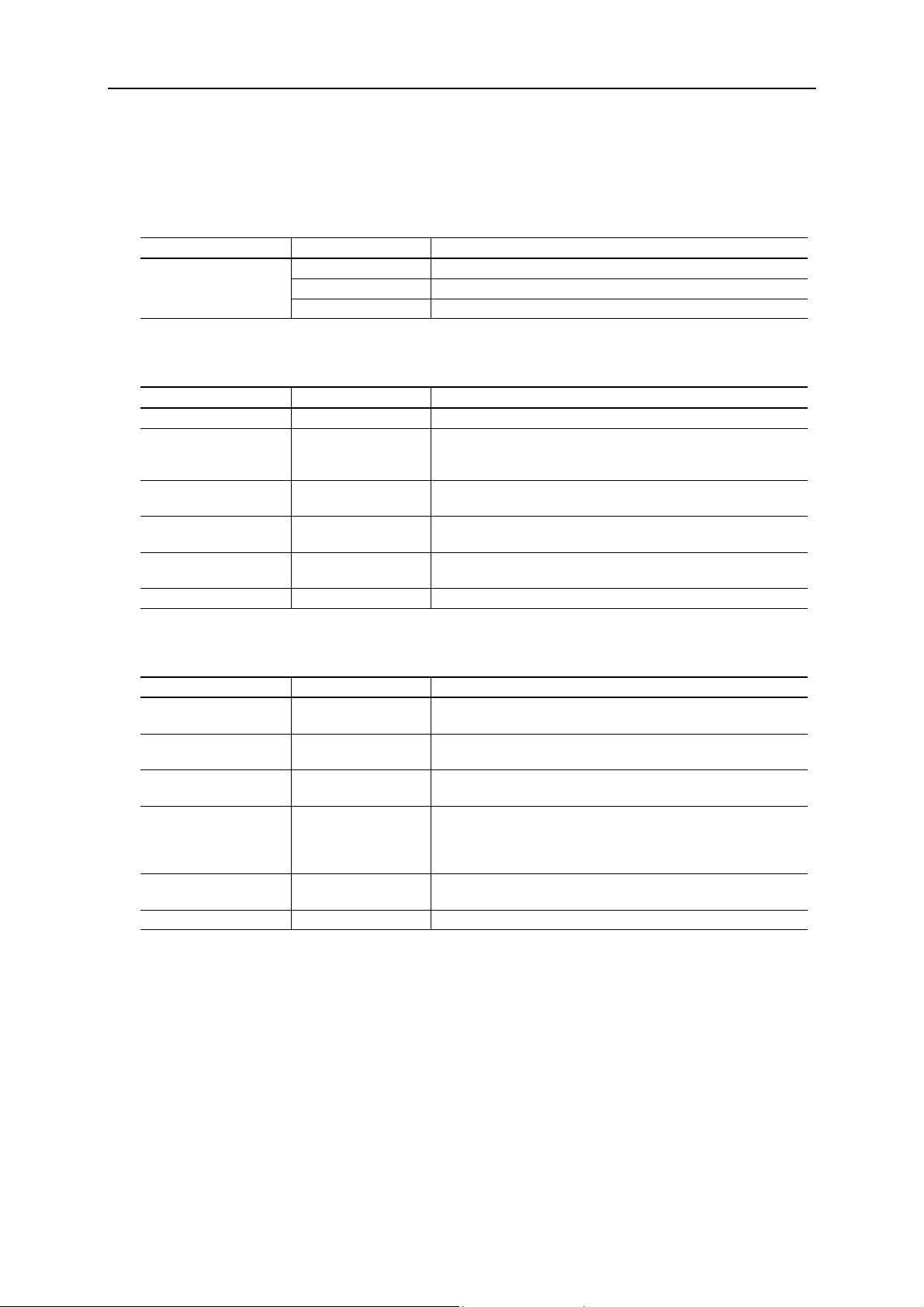
Install “Anybus IPconfig” software on a PC with MS Windows. The software is located on the diskette
delivered with the module and can also be downloaded from the web at http://www.hms-networks.com.
1. Start the configuration program and hit the Scan button, the module(s) shall appear in the window: If
the module does not appear, make sure that it is connected to the same network and that it has link.
2. Double click on the line with the module you want to configure. If you have several nodes connected
to the network, the MAC address shall match the MAC address that is printed on the side of the
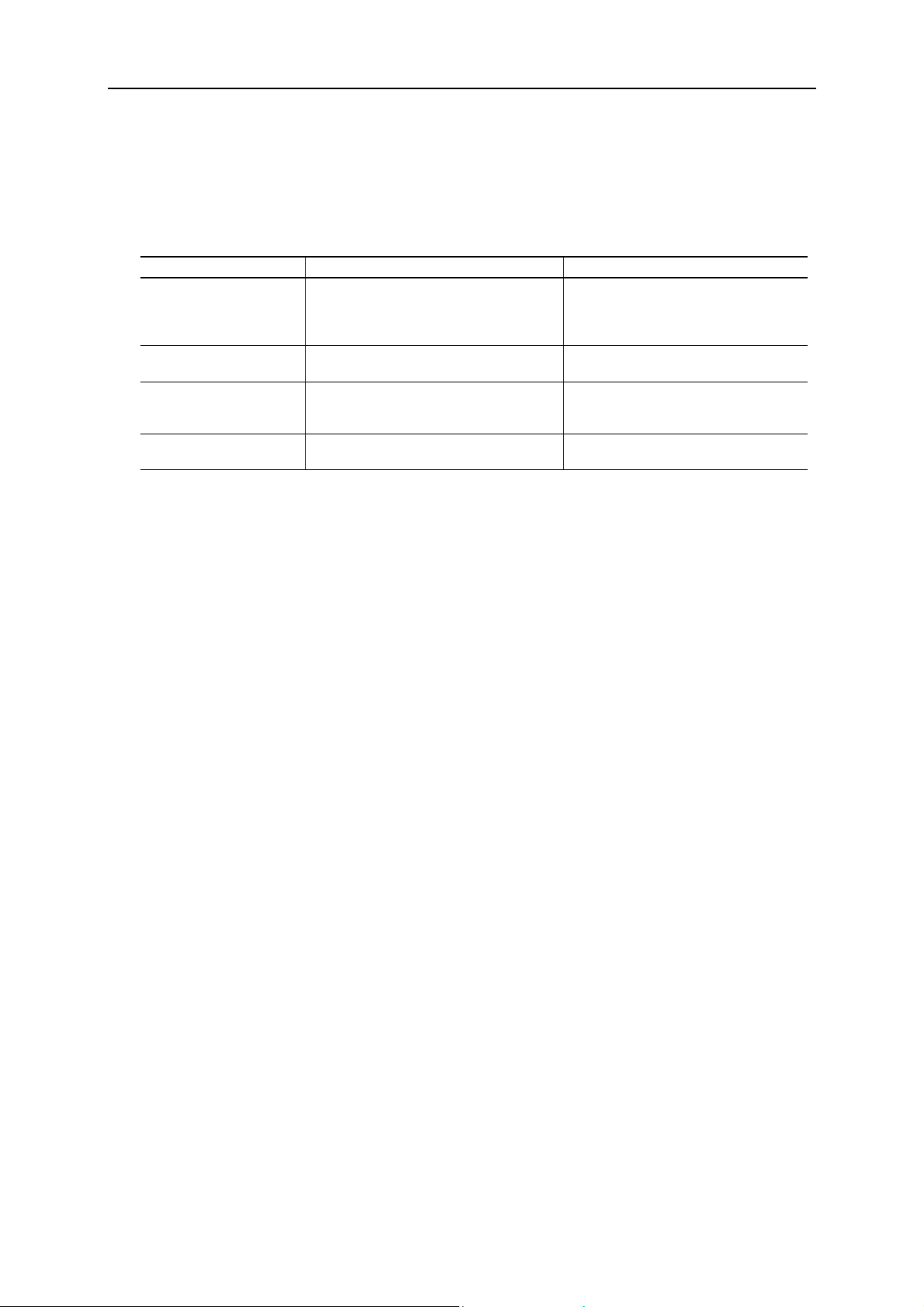
module. The following window will open:
3. Enter the desired settings and turn DHCP off. The settings can optionally be protected by a
password. Hit set and the module is configured. The DNS settings are not used in this product.
Page 18

Installation and Configuration
Bus Configuration Parameters
Some basic settings can be accessed via the keypad. For instructions how to use the keypad, see the drive’s
user manual.
Drive
parameter
o30 Communication rate
o31 Disable FTP
o32 Reserved o33 IDLE action
o34 Modbus/TCP timeout
Name Description
0 = Auto negotiate
1 = 100 Mbps, Full duplex
2 = 100 Mbps, half duplex
3 = 10 Mbps, Full duplex
4 = 10 Mbps, half duplex
0 = Enable FTP server
1 = Disable FTP server
0 = If the EtherNet/IP header indicates idle, an error is sent to
the drive
1 = The run/idle bit is ignored
Sets the maximum time between Modbus/TCP commands
before a time-out is detected.
The value is multiplied with 100 ms to give the timeout from
100ms-25.5s.
12
Operation Configuration Parameters
These parameters configure the link option control and set the drive’s reaction upon a network loss event.
Drive
parameter
H30 Link function
o27
o28
Name Description
0 = Command and freq. from drive
1 = Command from drive, freq. from option card
2 = Command from option card, freq. from drive
3 = Command and freq. from option card
Loss of network
behaviour
ERR5 timer setting
(used with o27)
0 = Immediate trip (ERR5)
1 = Trip after timer setting, o28
2 = Re-check after timer setting o28
3 = Ignore communication error
ERR5 timer setting, 0.0 – 60s
Page 19

Installation and Configuration
Fault Detection and Action
A network loss event will be generated to the drive from the Ethernet option board when any of the following
events occur:
Event Source Condition Fault cleared when
Link lost Hardware Link was established. Network cable connected
Connection time-out -
Connection Idle
A consumed data exchange
enters the UNHEALTY
state.
The time from last
Modbus/TCP message has
exceeded the configured
Modbus time-out action.
EtherNet/IP
EGD
Modus/TCP
Configured to set error
on IDLE. See drive
parameter o33.
The configured
consumption time must
not be set to zero.
Configured Modbus
timeout action must not
be set to zero.
See drive parameter
o34.
Connection is deleted or
module receives information
on connection again.
Master is set in run mode
Exchange enters the
HEALTHY state
A new Modbus/TCP
message is received.
13
After an error is cleared, the error must be acknowledged to the drive before drive control will start again. The
drive’s reaction to a network loss event can be set, see the “Operation Configuration Parameters” section.
Page 20

EGD
EGD
Configuration
The EGD configuration is stored in a file called “egd.cfg” in the module’s file system. Altering this file
configures the EGD protocol.
To configure the module follow these steps:
1. Make sure that the module’s FTP server is enabled (default). See the “Bus Configuration Parameters”
section.
2. Connect to the module from an FTP client, such as Internet Explorer, by typing ftp://[IP address]
3. Open/download the file called “egd.cfg”
4. Alter the file to reflect your configuration
5. Store/Download the file to the module again
6. Restart the drive
14
The file contains settings in a format where the configuration parameter name, e.g., [Producer ID], is defined
on the first line and next line contains the value for that parameter.
The following configuration parameters are located in the file:
Parameter Description
[Producer ID]
[Network Name]
[Multicast TTL]
[Production 1 Address] Destination address of produced exchange 1
[Production 1 Period]
[Production 2 Address] Destination address of produced exchange 2
[Production 2 Period]
[Consumption 1 Address]
[Consumption 1 ProducerID]
[Consumption 1 ExchangeID]
[Consumption 1 Timeout]
[Consumption 1 Signature]
[Consumption 1 CfgTime]
ID number that uniquely identifies the EGD node. Format should be
either a dotted decimal IP address (e.g., 10.10.12.210) or an unsigned
decimal integer value. If set to zero, the module’s IP address will be
used for ProducerID.
A symbolic name of the network that the device is connected to
(Optional)
Time to live setting of multicast packages. Need normally not be
changed from default value = 1
Produce rate of exchange 1. Set between 20-65535 ms. A value of 0
disables the production of this exchange.
Produce rate of exchange 2. Set between 1000-65535 ms. A value of 0
disables the production of this exchange.
Consumes messages sent to this IP address, e.g., modules configured
IP address or a multicast address.
Must match the ProducerID of the consumed exchange, formatted as
either a dotted decimal IP address (e.g., 10.10.12.63) or an unsigned
decimal integer value. A value of zero disables consumption of this
exchange.
Must match the ExchangeID of the consumed exchange A value of zero
disables consumption of this exchange.
Specifies the maximum time between consumed exchanges before the
exchange state transits to UNHEALTHY state. The UNHEALTHY state
generates a network loss event. Set between 20 – 65535 ms. A value
of zero disables consumption of this exchange.
For the consumed exchange to be used, the major number of the
configured signature must match the major number of the signature in
the consumed exchange. If set to 0, the signature is not checked.
For the consumed exchange to be used, this value must match the
CfgTime in the consumed exchange. If set to 0, the CfgTime is not
checked.
Page 21

EGD
15
[Consumption 1 DataOffset]
The number of 16-bit words into the data portion of the exchange from
which consumed data is copied. Using different offsets on different
devices allows a single exchange to be sent to a group of devices,
improving network bandwidth utilization and coordination among
devices.
To set the configuration to default, delete the file and restart the drive.
Data Messages
This product defines four EGD exchanges:
Exchange Description
Exchange C1
Exchange P1
Exchange P2
Exchange P3
Consumed exchange 1, this exchange contains control information to the
drive. Data format is described in “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO
Format”.
Produced exchange 1, this exchange contains operation status monitor
words and frequency output monitor. Data format is described in
“Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format”.
Produced exchange 2, this exchange contains control and monitor values
from the drive. The values in this exchange is updated at low priority, e.g.,
other protocols, like Modbus/TCP, are prioritized when requesting data.
Data format is described in “Appendix D - EGD Exchanges”.
Produced exchange 3, this exchange is used for accessing drive registers
with Command messages and cannot be set up for cyclic production.
Data format is described in “Appendix D - EGD Exchanges”.
Command Messages
Command messages are used for monitoring and control of the module.
The following commands are used for this product:
Command Description
Retrieve Configuration Returns configuration information for an exchange
Summary Returns a summary of the exchanges
Capabilities Returns the supported capabilities of the module
Statistics Returns the operating statistics of a specified exchange
Read Returns the contents of one or more continuous groups of memory
Write Changes the contents of one or more continuous groups of memory
Page 22

EGD
Configuration Messages
EGD configuration messages are sent using the HTTP protocol on TCP port 7937, a message request have
the following format:
http://[IP Address]:7937/EGD?Action=[Action]&Type=[Type]&ProducerID=[Producer ID]
The brackets shall be substituted as:
Field Description
IP Address The modules assigned IP address
Action GetVersion - Get version information
GetDoc - Retrieve specified configuration document
Type Specifies document to be retrieved. Used for GetDoc
ProducerID Producer ID of module. Used for GetDoc
The following documents can be retrieved:
Document Description
ProducedData Describes the produced data exchanges
ConsumedData Describes the needs for consumed data exchanges
EGDProfile Describes the EGD capabilities
SymbolTable Describes the contents of the exchanges
16
Examples:
http://10.10.12.210:7937/EGD?Action=GetDoc&Type=SymbolTable&ProducerID=10.10.12.210
http://10.10.12.210:7937/EGD?Action=GetVersion
Page 23

Modbus/TCP
Modbus/TCP
This product incorporates a Modbus/TCP server according to version 1.0 of the Modbus/TCP specification.
The product listens for incoming connections on TCP port 502.
Up to 8 simultaneously connections can be set-up. A connection will be closed if no data has been exchanged
during 1 minute.
Addressing
This product supports the Modbus area for output/holding registers (4XXXX).
Register 40001-40255 corresponds to Communication No. 1-255.
Commands
The module supports the following Modbus/TCP commands:
17
Function
code
3 Read multiple registers Read one ore more registers in the drive
6 Write single register Write to a single register
16 Write multiple registers Write to multiple registers
23 Read/Write registers Read and write to multiple registers with one command
Function name Description
Exception Codes
If a command cannot be executed an exception code is returned. The following exception codes can be
returned:
Exception
code
01 Illegal function The function code in the query is not supported
02 Illegal data address
03 Illegal data value
06 Slave device busy
Exception name Description
The data address in the query is outside the valid address
range or the address is invalid.
This code will be returned if:
1. Trying to write to a read only register in the drive or
2. The requested register cannot be changed while the drive
is running.
This code will be returned if:
1. The inverter is busy or
2. There is a communication error between the drive and the
communication adapter.
Page 24

Modbus/TCP
18
Timeout
When a Modbus/TCP timeout value is configured, see the “Bus Configuration Parameters” chapter, a
network error will be generated to the drive if the time between two Modbus messages exceeds the configured
value.
Note: If the Modbus/TCP protocol is used for controlling the drive, a timeout value shall be configured so that the
drive trips if the connection with the master fails.
Page 25

EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP
IO Connection
An IO connection is used for data that is cyclically exchanged with the drive, i.e., Frequency command and
operation command. Other drive parameters can be exchanged by explicit messaging, see the “Explicit
Messaging” section.
Idle action
For security reasons, when the PLC is put into program/idle mode it defaults generates a network loss event
to stop the drive. This functionality can be disabled by bus configuration parameter IDLE action, see the “Bus
Configuration Parameters” section.
Example PLC configuration
In this example a connection is set up to a Rockwell Automation ControlLogix PLC, equipped with a 1756ENBT/A Ethernet bridge. The configuration program used is RSLogix 5000 from Rockwell Software.
19
1. Start RSLogix 5000
2. Right-click on the Ethernet bridge module and choose “New module”
Page 26

EtherNet/IP
20
3. Select type “ETHERNET MODULE” and click OK
4. Configure the IP address to the module and Input and Output instances. The configuration instance
is not used but requires a value. Input is set to three words and output is to two words, the data
format shall be set to “Data – INT”. Click Next>
5. Set the RPI value to 20ms or higher. Click Finish>>>
The module is now added to the PLC configuration and can be used in the PLC program. For example, to
access the drive speed, use the tag OPCG11SETN:I.Data[2].
Save the configuration and download to the PLC.
The format of the IO data is described in “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format”.
Page 27

EtherNet/IP
Explicit Messaging
Many of the drive’s parameters are mapped as Communication No:s, see “Appendix B - Drive Parameters”,
for EtherNet/IP the CommunicationNo:s are accessed via the Fuji Vendor Specific Object (Class 0x64).
Various configuration softwares or, for example, ControlLogix from Rockwell Automation can perform
EtherNet/IP explicit messaging. The examples in the chapter demonstrate how explicit read/writes can be
performed with the ControlLogix PLC. The PLC is configured in RSLogix 5000.
Get Attribute Single Example
This example shows how to get the “DC link circuit voltage” (M21) by explicit messaging.
1. In Controller tags, create a tag of MESSAGE type for the read instruction and create a tag of INT
type for storing the value.
21
2. Add the message instruction (MSG) to a rung and use the created tag as value for the “Message
Control” field.
Page 28

EtherNet/IP
3. Click the button with the three dots in the MSG instruction to bring up the MESSAGE
configuration window. Do the following settings:
Field Value Description
Message Type CIP Generic CIP Message
Service Type Get attribute single CIP Service
Class 64 Fuji Vendor Specific Object
Instance 1 Instance 1
Attribute 23
Destination DC_Voltage Name of created destination tag
Path OPCG11SETN
M21 – DC link circuit voltage = Communication No.
35 = 23 hex
Name of device. Click Browse and locate the module.
Must have been added as described in the IO
connection example chapter
22
When GetDcValue in the example is activated, DC voltage is read and stored in the DC_Voltage Tag.
Page 29

EtherNet/IP
23
Set Attribute Single Example
This example shows how to set the “LED Monitor (Function)” (E43) to show the output current on the LED
display, by explicit messaging.
In Controller tags, create a tag of MESSAGE type for the write instruction and create a tag of INT type for
the value to send.
1. In Controller tags, create a tag of MESSAGE type for the write instruction and create a tag of INT
type for the value to be sent. Set the value tag to 3 for “Output current”.
2. Add the message instruction (MSG) to a rung and use the created tag as value for the “Message
Control” field.
Page 30

EtherNet/IP
3. Click the button with the three dots in the MSG instruction to bring up the MESSAGE
configuration window. Do the following settings:
Field Value Description
Message Type CIP Generic CIP Message
Service Type Set attribute single CIP Service
Class 64 Fuji Vendor Specific Object
Instance 1 Instance 1
Attribute 8A
Source
Element
Source Length
Path OPCG11SETN
SetDisplayValue Name of created source tag
2 1 word
E43 – LED Monitor (Function) = Communication No.
138 = 8A hex
Name of device. Click Browse and locate the module.
Must have been added as described in the IO
connection example chapter
24
When SetDisplay in the example is activated, the value in the SetDisplayValue Tag is written to parameter E43
in the drive.
Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) File
An EtherNet/IP node needs an EDS file with information about the device, the EDS file is used by network
configuration tools. The EDS file for this product is located on the diskette supplied together with the module
or can be downloaded from http://www.hms-networks.com/private/fujilogin.asp. Username: fuji, Password:
400024.
Page 31

Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format
Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format
This chapter specifies the format of data that is cyclically exchange with the drive, here called IO data. This
format is used for the assembly instances on EtherNet/IP and for the exchanges P1 and C1 on EGD.
Data Consumed by the Drive
Consumed data is located in assembly instance 150 on EtherNet/IP and Produced Exchange 1(P1) on EGD.
Position Description
Word 0 (16 Bit) Run command word
Word 1 (16 Bit) Frequency setting (S01)
Run Command Word
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
25
RST - BX RT4 - X9 X8 X7 X6 X5 X4 X3 X2 X1 REV FWD
FWD 1: Run forward command
REV 1: Run reverse command
X1 – X9 1: Digital input
RT4 1: Acceleration/Deceleration time 4 (Has priority over the Acc/Dec time selection by X terminal)
BX 1: Coast-to-stop command
RST Alarm reset:
(Each function is set by inverter’s parameter E01-E09, See drive manual)
0 to 1 and 1 to 0
t
min
= 20ms
Frequency Setting (S01)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Frequency command data
Frequency is set as: Output Frequency * 20000 / Max frequency
Max frequency = F03
Reverse direction is set with a negative value
Page 32

Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format
Data Produced by the Drive
Produced data is located in assembly instance 100 on EtherNet/IP and Consumed Exchange 1(C1) on EGD.
Position Description
Word 0 (16 Bit) Operation status monitor 1
Word 1 (16 Bit) Operation status monitor 2
Word 2 (16 Bit) Output frequency monitor
Operation Status Monitor 1
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - WR RL ALM DEC ACC IL VL TL NUV BRK INT EXT REV FWD
FWD 1: In forward command
REV 1: In reverse command
EXT 1: In DC breaking or in preparatory excitation
INT 1: No output
BRK 1: In breaking
NUV 1: DC link voltage is establishment
(Under voltage condition at 0)
TL 1: In torque limiting
VL 1: In voltage limiting
IL 1: In current limiting
ACC 1: In acceleration
DEC 1: In deceleration
ALM 1: Alarm
RL 1: Remote (Run command or Frequency command is valid from link)
WR 1: Fieldbus writing right, 0: Keypad writing right
26
Operation Status Monitor 2
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- - - - - - - - - - - - SWM2 RDY FDT FAR
FAR 1: Frequency (speed) arrival
FDT 1: Frequency (speed) detection
RDY 1: Ready for operation
SWM2 1: Motor 2 switching
Page 33

Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format
Output Frequency Monitor (M06)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Output frequency
27
Page 34

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
Appendix B - Drive Parameters
Parameter List
This table shows the mapping between Communication No. and drive parameter number. The
Communication No. is used when accessing parameters from the fieldbus.
G11/P11
Code
- 0 (0) - S01 1 (1) Frequency command 2
- 2 (2)
- 3 (3) - -
- 4 (4) - S05 5 (5) Frequency command 5
S06 6 (6) Operation command 14
S07 7 (7) Universal Do 15
S08 8 (8) Accel Time F07 3
S09 9 (9) Deccel Time F08 3
S10 10 (A) Driving Torque Limit F40 5
S11 11 (B) Braking Torque Limit F41 5
S12 12 (C) Universal Ao 2
- 13 (D) - -
- 14 (E) - M01 15 (F) Frequency command (final) 2
- 16 (10) - -
- 17 (11) - -
- 18 (12) - M05 19 (13) Frequency command (final) 5
M06 20 (14) Actual frequency 2
M07 21 (15) Actual value of torque 6
M08 22 (16) Torque current 6
M09 23 (17) Output frequency 5
M10 24 (18) Motor output 5
M11 25 (19) Output current (rms) 5
M12 26 (1A) Output voltage (rms) 3
M13 27 (1B) Operation (final) 14
M14 28 (1C) Operation state 16
M15 29 (1D) General-purpose output terminal 15
M16 30 (1E) Alarm content latest 10
M17 31 (1F) Alarm content 1st previous 10
M18 32 (20) Alarm content 2nd previous 10
M19 33 (21) Alarm content 3rd previous 10
M20 34 (22) Total operation time 1
M21 35 (23) DC link voltage 1
- 36 (24) - M23 37 (25) Type code 17
M24 38 (26) Capacity code 11
M25 39 (27) ROM version 1
M26 40 (28) Processing code in abnormal transmission 20
Communication
No. (Hex)
Description
-
28
Data
format
-
Page 35

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
29
M27 41 (29) Frequency (Motor speed) setting at alarm final 2
- 42 (2A) - -
- 43 (2B) - -
- 44 (2C) - M31 45 (2D) Frequency setting at alarm final 5
M32 46 (2E) Actual frequency at alarm 2
M33 47 (2F) Actual value of torque at alarm 6
M34 48 (30) Torque current at alarm 6
M35 49 (31) Output frequency at alarm 5
M36 50 (32) Motor output at alarm 5
M37 51 (33) Output voltage (rms) at alarm 5
M38 52 (34) Output voltage effective value at alatm 3
M39 53 (35) Operation command at alarm 14
M40 54 (36) Operation state at alarm 16
M41 55 (37) General-purpose output terminal at alarm 15
M42 56 (38) Total operation time at alarm 1
M43 57 (39) DC link voltage at alarm 1
M44 58 (3A) Internal temperature of inverter at alarm 1
M45 59 (3B) Temperature of cooling fin at alarm 1
M46 60 (3C) Lifetime of main circuit capacitor 3
M47 61 (3D) Lifetime of capacitor on PCB 1
M48 62 (3E) Lifetime of cooling fan 1
- 63 (3F) - -
- 64 (40) - -
- 65 (41) - -
- 66 (42) - -
- 67 (43) - -
- 68 (44) - -
- 69 (45) - F00 70 (46) Data protection 1
F01 71 (47) Frequency command 1 1
F02 72 (48) Operation method 1
F03 73 (49) Maximum frequency 1 1
F04 74 (4A) Base frequency 1 1
F05 75 (4B) Rated voltage 1 1
F06 76 (4C) Maximum voltage 1 1
F07 77 (4D) Acceleration time 1 12
F08 78 (4E) Deceleration time 1 12
F09 79 (4F) Torque boost 1 12
F10 80 (50) Electronic Thermal 1 (Select) 3
F11 81 (51) Electronic Thermal 1 (Level) 1
F12 82 (52) Electronic Thermal 1 (Time constant) 16
F13 83 (53) Electronic thermal overload relay (for DB resistor) 3
F14 84 (54) Restart mode after momentary power failure 1
F15 85 (55) Frequency limiter (High) 1
F16 86 (56) Frequency limiter (Low) 1
F17 87 (57) Gain (for freq set signal) 1
F18 88 (58) Bias frequency 1
F20 89 (59) DC brake (Starting freq.) 3
F21 90 (5A) DC brake (Braking level) 1
F22 91 (5B) DC brake (Braking time) 3
F23 92 (5C) Starting frequency (Freq.) 3
F24 93 (5D) Starting frequency (Holding time) 3
F25 94 (5E) Stop frequency 1
Page 36

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
30
F26 95 (5F) Motor sound (Carrier freq.) 1
F27 96 (60) Motor sound (Sound tone) 1
F30 97 (61) FMA (Voltage adjust) 1
F31 98 (62) FMA (Function) 1
F33 99 (63) FMP (Pulse rate) 1
F34 100 (64) FMP (Voltage adjust) 1
F35 101 (65) FMP (Function) 1
F36 102 (66) 30RY operation mode 1
F40 103 (67) Torque limiter 1 (Driving) 1
F41 104 (68) Torque limiter 1 (braking) 1
F42 105 (69) Torque vector control 1 1
E01 106 (6A) X1 terminal function X1 1
E02 107 (6B) X2 terminal function X2 1
E03 108 (6C) X3 terminal function X3 1
E04 109 (6D) X4 terminal function X4 1
E05 110 (6E) X5 terminal function X5 1
E06 111 (6F) X6 terminal function X6 1
E07 112 (70) X7 terminal function X7 1
E08 113 (71) X8 terminal function X8 1
E09 114 (72) X9 terminal function X9 1
E10 115 (73) Acceleration time 2 12
E11 116 (74) Deceleration time 2 12
E12 117 (75) Acceleration time 3 12
E13 118 (76) Deceleration time 3 12
E14 119 (77) Acceleration time 4 12
E15 120 (78) Deceleration time 4 12
E16 121 (79) Torque limiter 2 (Driving) 1
E17 122 (7A) Torque limiter 2 (braking) 1
E20 123 (7B) Y1 terminal function 1
E21 124 (7C) Y2 terminal function 1
E22 125 (7D) Y3 terminal function 1
E23 126 (7E) Y4 terminal function 1
E24 127 (7F) Y5A, Y5C terminal func. 1
E30 128 (80) FAR function (Hysteresis) 3
E31 129 (81) FDT function (Level) 1
E32 130 (82) FDT signal (Hysteresis) 3
E33 131 (83) OL function (Mode select) 1
E34 132 (84) OL function signal (Level) 19
E35 133 (85) OL function signal (Timer) 3
E36 134 (86) FDT2 function (Level) 1
E37 135 (87) OL2 function (Level) 19
E40 136 (88) Display coefficient A 12
E41 137 (89) Display coefficient B 12
E43 138 (8A) LED Monitor (Function) 1
E44 139 (8B) LED Monitor (Display in STOP mode) 1
E45 140 (8C) LCD Monitor (Function) 1
C01 141 (8D) Jump frequency (Jump freq 1) 1
C02 142 (8E) Jump frequency (Jump freq 2) 1
C03 143 (8F) Jump frequency (Jump freq 3) 1
C04 144 (90) Jump frequency (Hysteresis) 1
C05 145 (91) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 1) 5
C06 146 (92) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 2) 5
C07 147 (93) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 3) 5
C08 148 (94) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 4) 5
Page 37

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
C09 149 (95) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 5) 5
C10 150 (96) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 6) 5
C11 151 (97) Multistep frequency setting (Freq. 7) 5
C20 152 (98) JOG frequency 5
C30 153 (99) Frequency command 2 1
C31 154 (9A) Offset adjust (terminal [12]) 4
C32 155 (9B) Offset adjust (terminal [C1]) 3
C33 156 (9C) Analog setting signal filter 5
P01 157 (9D) Number of motor 1 poles 1
P02 158 (9E) Motor 1 (Capacity) 5
P03 159 (9F) Motor 1 (Rated current) 19
P04 160 (A0) Motor 1 (Tuning) 21
P05 161 (A1) Motor 1 (On-line Tuning) 1
P06 162 (A2) Motor 1 (No-load current) 19
P07 163 (A3) Motor 1 (%R1 setting) 5
P08 164 (A4) Motor 1 (%X setting) 5
P09 165 (A5) Slip compensation control 5
H03 166 (A6) Data initializing 1
H04 167 (A7) Auto-reset (Times) 1
H05 168 (A8) Auto-reset (Reset interval) 1
H06 169 (A9) Fan stop operation 1
H07 170 (AA) ACC/DEC pattern (select) 1
H08 171 (AB) Rev. phase sequence lock 1
H09 172 (AC) Start mode 1
H10 173 (AD) Energy-saving operation 1
H11 174 (AE) DEC mode 1
H12 175 (AF) Instantaneous OC limiting 1
H13 176 (B0) Auto-restart (restart time) 3
H14 177 (B1) Auto-restart (freq. fall rate) 5
H15 178 (B2) Auto-restart (holding DC voltage) 1
H16 179 (B3) Auto-restart (OPR command self hold time) 3
H18 180 (B4) Torque control 1
H19 181 (B5) Active drive 1
H20 182 (B6) PID control (Mode select) 1
H21 183 (B7) PID control (Feedback signal) 1
H22 184 (B8) PID control (P-gain) 5
H23 185 (B9) PID control (I-gain) 3
H24 186 (BA) PID control (D-gain) 1
H25 187 (BB) PID control (Feedback filter) 5
H26 188 (BC) PTC thermistor (Mode select) 1
H27 189 (BD) PTC thermistor (Level) 5
H28 190 (BE) Droop operation 4
H30 191 (BF) Serial link (Function select) 1
H31 192 (C0) Modbus-RTU (Address) 1
H32 193 (C1) Modbus-RTU (Mode select on no response error) 1
H33 194 (C2) Modbus-RTU (Timer) 3
H34 195 (C3) Modbus-RTU (Baud rate) 1
H35 196 (C4) Modbus-RTU (Data length) 1
H36 197 (C5) Modbus-RTU (Parity check) 1
H37 198 (C6) Modbus-RTU (Stop bits) 1
H38 199 (C7) Modbus-RTU (No resp. error detection time) 1
H39 200 (C8) Modbus-RTU (Response interval) 5
A01 201 (C9) Maximum frequency 2 1
A02 202 (CA) Base frequency 2 1
31
Page 38

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
32
A03 203 (CB) Rated voltage 2 (at Base frequency 2)
A04 204 (CC) Maximum voltage 2
A05 205 (CD) Torque boost 2
A06 206 (CE) Electronic thermal 2 (Select)
A07 207 (CF) Electronic thermal 2 (Level)
A08 208 (D0) Electronic thermal 2 (Thermal time constant)
A09 209 (D1) Torque vector control 2
A10 210 (D2) Number of motor 2 poles
A11 211 (D3) Motor 2 (Capacity)
A12 212 (D4) Motor 2 (Rated current)
A13 213 (D5) Motor 2 (Tuning)
A14 214 (D6) Motor 2 (On-line Tuning)
A15 215 (D7) Motor 2 (No-load current)
A16 216 (D8) Motor 2 (%R1 setting)
A17
217 (D9) Motor 2 (%X setting) 5
1
1
1
1
19
3
1
1
5
19
21
1
19
5
A18 218 (DA) Motor 2 (Slip compensation control 2) 5
o01 219 (DB) Control method selection 1
o02 220 (DC) Speed filter time constant 1
o03 221 (DD) Number of feedback pulses 1
o04 222 (DE) P-gain of feedback 1
o05 I-gain of feedback 1
223 (DF)
o06 224 (E0) Feedback speed detection filter 1
o07 225 (E1) Feedback pulse correction coeff 1 1
o08 226 (E2) Feedback pulse correction coeff 2 1
o27 227 (E3) Bus loss behaviour 1
o28 228 (E4) Bus loss timer 1
o30 229 (E5) Communication rate 1
o31 230 (E6) Disable FTP 1
o32 231 (E7) Reserved 1
o33 232 (E8) Idle action 1
o34 233 (E9) Modbus/TCP timeout 1
o35 234 (EA) - 1
o36 235 (EB) - 1
o37 236 (EC) - 1
o38 237 (ED) - 1
o39 238 (EE) - 1
o40 239 (EF) - 1
o41 240 (F0) - 1
o42 241 (F1) - 1
o43 242 (F2) - 1
o44 243 (F3) - 1
o45 244 (F4) - 1
o46 245 (F5) - 1
o47 246 (F6) - 1
o48 247 (F7) - 1
o49 248 (F8) - 1
o50 249 (F9) - 1
o51 250 (FA) - 1
o52 251 (FB) - 1
o53 252 (FC) - 1
o54 253 (FD) - 1
o55 254 (FE) - 1
- 255 (FF) - -
Page 39

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
Data Format Specification
All data within the data field of the communication frame consist of 16 bits binary data.
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
16-bits binary data
(Negative data is treated with two’s complement)
Data Format [1]: Integer Data (Positive): Min. Unit 1
Example) If F15 (Frequency limiter, high limit) = 60 Hz,
33
60 * 1 = 60 = 003C
H
Data Format [2]: Integer Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 1
Example) If F18 (Bias frequency) = -20 Hz,
-20 * 1 = -20 = FFEC
(two’s complement)
H
Data Format [3]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.1
Example) If F17 Gain (for frequency setting signal) = 100.0%,
100.0 * 10 = 1000 = 03E8
H
Data Format [4]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.1
Example) If H28 (Droop operation) = -5.0Hz,
-5.0 * 10 = -50 = FFCE
(two’s complement)
H
Data Format [5]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.01
Example) If C05 (Multi-step frequency 1) = 50.25 Hz,
50.25 * 100 = 5025 = 13A1
H
Data Format [6]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.01
Example) If M07 (Actual torque value) = -85.38%,
-85.38 * 100 = -8538 = DEA6
(two’s complement)
H
Data Format [7]: Decimal Data (Positive): Min. Unit 0.001
Example) If o05 (Constant I of feedback speed controller) = 0.105s,
0.105 * 1000 = 105 = 0069
H
Page 40

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
Data Format [8]: Decimal Data (Positive, Negative): Min. Unit 0.001
Example) If value -1.234,
-1.234 * 1000 = -1234 = FB2EH(two’s complement)
Data Format [10]: Alarm Code
Code Description Code Description
0 No alarm 22 Overheat, DB resistor
1
2
3
5 Ground fault 27 Overspeed
6 Overvoltage, during acceleration 28 PG wire break
7 Over voltage, during deceleration 31 Memory error
8
10 DC undervoltage 33 CPU error
11 Power supply open phase 34 Option comm error
14 Blown DC fuse 35 Option error
16 Output wiring error 36 PL error
17 Overheat, heat sink, inverter 37 Output wiring error
18 Overheat, outside thermal 38 RS485 comm error
19 Overheat, unit inside temp - -
Overcurrent, during acceleration (INV
output)
Overcurrent, during deceleration (INV
output)
Overcurrent, during steady state
operation (INV output)
Overvoltage, during steady state
operation
23 Overload, motor 1
24 Overload, motor 2
25 Overload, drive
32 Keypad error
34
Data Format [11]: Capacity Code
Code Capacity (HP) Code Capacity (HP) Code Capacity (HP)
7 0.07 (spare) 2000 20 17500 175
15 0.15 (spare) 2500 25 20000 200
25 0.15 3000 30 25000 250
50 0.15 4000 40 30000 300
100 1 5000 50 35000 350
200 2 6000 60 40000 400
300 3 7500 75 45000 450
500 5 10000 100 50000 500
750 7.5 12500 125 60600 600
1000 10 15000 150 60700 700
1500 15 - - 60800 800
Page 41

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
35
Data Format [12]: Index Data (ACC/DEC Time, Display Coefficient)
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Polarity 0 0 0 Index portion Data portion
Field Description
Polarity
0: Positive (+)
1: Negative (-)
Index portion 0: 0.01 * 001–999 (0.00 – 9.99)
1: 0.1 * 100–999 (10.0 – 99.9)
2: 1 * 100–999 (100 – 999)
3: 10 * 100–999 (1000 – 9990)
Data portion Value
Example) F07 (Acceleration time 1) = 20.0 s,
20.0 = 0.1 * 200 = 0400
+ 00C8H = 04C8H
H
Data Format [14]: Operation Command
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RST 0 0 0 0 X9 X8 X7 X6 X5 X4 X3 X2 X1 REV FWD
(All bits are ON or active by 1)
Field Description
RST Alarm
X9-X1 Multi function command
REV Reverse rotation command
FWD Forward rotation command
Example) If M13 (Operation command, Final command) = FWD, X1, X5 = ON
0000 0000 0100 0101b = 0045H
Data Format [15]: Universal Output Terminal
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Y5 Y4 Y3 Y2 Y1
Y5-Y1 = Universal command (All bits are ON by 1)
Example) If M15 (Universal output terminal) = Y1, Y5 = ON,
0000 0000 0001 0001
.= 0011H
b
Page 42
Appendix B - Drive Parameters
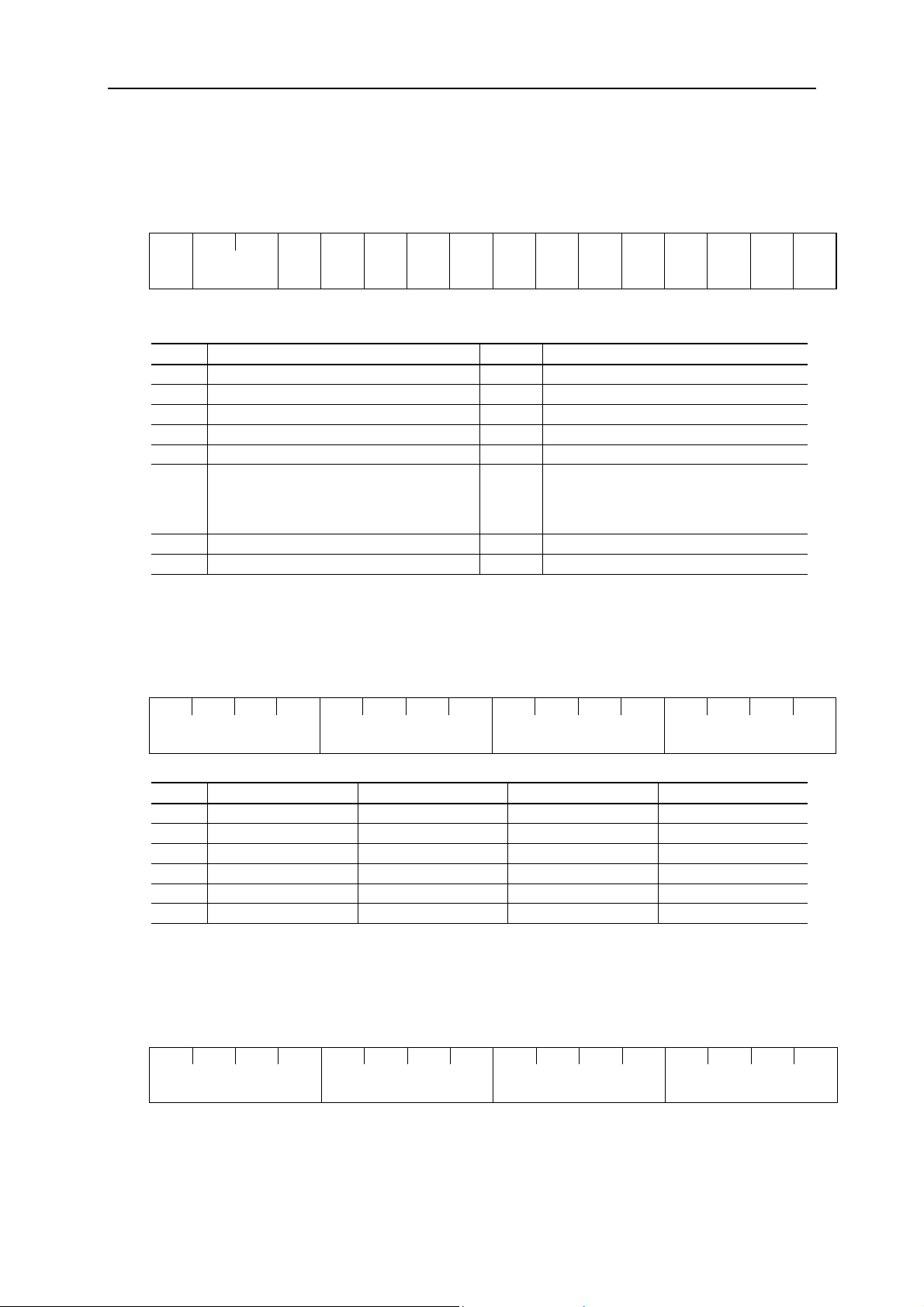
Data Format [16]: Operating State
36
(MSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
BUSY WR RL ALM DEC ACC IL VL TL NUV BRK INT EXT REV FWD
(LSB)
(All bits are ON or active by 1)
Field Description Field Description
FWD In forward operation IL In current limiting
REV In reverse operation ACC In acceleration
EXT In DC braking (or in pre-excitation) DEC In deceleration
INT No output ALM Drive fault
BRK In braking RL Transmission valid
NUV
DC link voltage is establishment
(Under voltage at 0)
WR Function writing right
0: Keypad panel
1: RS485
2: Fieldbus (Option)
TL In torque limiting BUSY Processing data write
VL In voltage limiting - -
Data Format [17]: Type Code
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Unit type Generation Series Voltage series
Code Type Generation Series Voltage series
1 VG 11th series For Japan 100V single phase
2 G 7 th series For Asia 200V single phase
3 P - For China 200V three phase
4 E - For Europe 400V three phase
5 C - For USA 575V three phase
6 S - - -
Data Format [18]: Code Setting (1 – 4 Figures)
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Data 4 Data 3 Data 2 Data 1
Page 43

Appendix B - Drive Parameters
Data Format [19]: Amperage Value Decimal Data (Positive)
Min unit 0.01, inverter capacity 30HP or below
Min unit 0.1, for 40 HP and over
Example) If F11 (electronics thermal overload relay 1 level) 107.0 A (40 HP)
37
107.0 x 10 = 1070 =042E
H
If F11 (electronics thermal overload relay 1 level) 3.60A (1 HP)
3.60 x 100 = 360 =0168
H
Data Format [20]: Transmission Error Code
Field Description Code Description
1 FC (Function code) error 71 CRC error (no response)
2 Illegal address 72 Parity error (no response)
3 Illegal address (Data range error) 73
7
NAK
- Priority for comm.
- No privilege for writing error
- Forbidden writing error
- -
Other errors (no response)
- Framing error
- Overrun error
- Buffer full error
Data Format [21]: Auto Tuning
(MSB) (LSB)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 REV FWD Data portion
0: Without forward rotation command
1: With forward rotation command
0: Without reverse rotation command
1: With reverse rotation command
Example) If P04 (Motor 1 auto tuning) = 1 : Forward rotation
0000 0001 0000 0001
= 0101H
B
Page 44

Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
The following EtherNet/IP objects are implemented and can be accessed by EtherNet/IP explicit messaging.
For more information about these objects, see the EtherNet/IP specification.
• Identity object, Class 0x01
• Message router, Class 0x02
• Assembly object, Class 0x04
• Connection Manager, Class 0x06
• Fuji Vendor Specific Object, Class 0x64
• TCP/IP Interface object, Class 0xF5
• Ethernet Link object, Class 0xF6
38
Page 45

Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
Identity Object, Class 0x01
Services
39
Class services
Instance services
Class Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001 Revision 1
Instance Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Vendor ID UINT 0x005A HMS Industrial Networks AB
2 Get Device type UINT 0x000C Communication Adapter
3 Get Product code UINT 0x012C OPC-G11S-ETN drive adapter
4 Get Revision
5 Get Status WORD -
6 Get Serial number UDINT
7 Get Product name
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Reset
Struct of: - Version X.YY
USINT XX
USINT YY
SHORT_S
TRING
Serial
number
“OPCG11SETN”
Major product version of this
communication module.
Minor product version of this
communication module
Status of the device, see table
below.
This is the serial number of the
product, assigned when the module
is produced.
The module’s product name.
Status Attribute Extended Device Status (Bit 4-7)
Bit 0 Owned, shall be set when at least one
connection is configured.
Bit 1 Reserved, set to 0.
Bit 2 Configured, is always set to 1.
Bit 3 Reserved, set to 0.
Bit 4-7 See extended device status
0000 = Unknown
0010 = Faulted I/O connection
0011 = No I/O connection established
0100 = Non volatile configuration bad
0110 = Connection in run mode
0111 = Connection in idle mode
Bit 8 Is set for minor recoverable faults.
Bit 9 Is set for minor recoverable faults.
Bit 10 Is set for major recoverable faults.
Bit 11 Is set for major unrecoverable faults.
Bit 12-15 Reserved, set to 0.
Page 46

Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
Assembly Object (Class 0x04)
The Assembly object uses static assemblies. The assembly instance IDs used are in the vendor specific range.
Services
Class services Get Attribute Single
Instance services
Class Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0002 Revision 2
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0x0096 The highest initiated instance number
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x03 (3d)
Get Attribute Single
Set Attribute Single
40
# Access Name Type Value Description
3 Get Data - - Heart beat instance
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x64 (100d)
# Access Name Type Value Description
3 Get Data
ARRAY of
BYTES
- Data produced by module
See “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP
IO Format”
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x65 (101d)
# Access Name Type Value Description
3 Get Data
ARRAY of
BYTES
-
Contains the same data as in EGD
exchange P2.
Instance Attributes, Instance/Connection Point 0x96 (150d)
# Access Name Type Value Description
3 Set Data
ARRAY of
BYTES
- Data consumed by module
See “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP
IO Format”
Page 47
Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
Fuji Vendor Specific Object (Class 0x64)
This is a vendor specific object that makes it possible to read/write all Communication No. in the drive.
Services
Class services Get Attribute All
Instance services Get Attribute Single
Set Attribute Single
Class Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001 Revision 1
Instance Attributes
41
If a Communication No is reporting ”Non existing error” the attribute does not exist.
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get/Set Parameter 1 UINT N/A
… Get/Set Parameter n UINT N/A
255 Get/Set Parameter 255 UINT N/A
Communication No 1 in the Fuji
Parameter List
Communication No n in the Fuji
Parameter List
Communication No 255 in the Fuji
Parameter List
Page 48

Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
TCP/IP Interface Object (Class 0xF5)
Services
42
Class services
Instance services
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Set Attribute Single
Class Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0001 Revision 1
Instance Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Status DWORD 0x00000001
2 Get
3 Get/Set
4 Get
5 Get/Set
6 Get/Set Host Name STRING - Host name
Configuration
capability
Configuration
control
Physical Link
Object
Path size UINT 0x0002 2 words
Path
Interface
configuration
IP Address UDINT - Module’s IP address
Network Mask UDINT - Module’s Network mask
Gateway Address UDINT - Module’s Gateway address
Name Server UDINT - Not used
Name Server 2 UDINT - Not used
Domain Name STRING - Not used
DWORD 0x00000014
DWORD -
Struct of:
Padded
EPATH
Struct of:
- Physical link -> Ethernet object
20 F6 24 01 Ethernet Class, Instance 1
1 = The interface configuration
attribute contains valid
configuration.
Interface configuration attribute is
settable.
Capable of obtaining network
configuration via DHCP.
0 – Configuration from nonvolatile memory 2 –
Configuration from DHCP
Page 49

Appendix C – Ethernet/IP Objects
Ethernet Link Object (Class 0xF6)
Services
43
Class services
Instance services
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Get Attribute All
Get Attribute Single
Set Attribute Single
Class Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Revision UINT 0x0002 Revision 2
Instance Attributes
# Access Name Type Value Description
1 Get Interface Speed UDINT 10 or 100
2 Get Interface Flags DWORD See EIP specification
3 Get Physical Address
6 Set
Interface control Struct of:
Control Bits WORD
Forced Interface
Speed
ARRAY of
6 USINTs
UINT -
MAC
address
0x01
(Default)
The actual speed of the Ethernet
connection
The module’s MAC address
Bit 0=1: Auto negotiation enabled
Bit 1: When auto negotiation is
disabled, this bit selects full- (1)
or half- (0) duplex.
When auto negotiation is
disabled, this word selects 100
(0x0064) or 10 (0x000A) Mbps.
Page 50

Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
Exchange C1
Exchange C1 is described in “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format”.
Exchange P1
Exchange P1 is described in “Appendix A - EGD, EtherNet/IP IO Format”.
Exchange P2
44
G11/P11
Register
S05 5 0 R/W
S07 7 2 R/W
S08 8 4 R/W
S09 9 6 R/W
S10 10 8 R/W
S11 11 10 R/W
S12 12 12 R/W
- 14 14
M01 15 16 R
- 16 18 R
- 17 20 R
- 18 22 R
M05 19 24 R
M07 21 26 R
M08 22 28 R
M09 23 30 R
M10 24 32 R
M11 25 34 R
M12 26 36 R
M13 27 38 R
M15 29 40 R
M16 30 42 R
M17 31 44 R
M18 32 46 R
M19 33 48 R
M20 34 50 R
M21 35 52 R
- 36 54 R
Comm.
Index
EGD Offset Read/Write
Page 51

Exchange P3
Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
45
G11/P11
Register
M23 37 0 R
M24 38 2 R
M25 39 4 R
M26 40 6 R
M27 41 8 R
- 42 10 -
- 43 12 -
- 44 14 M31 45 16 R
M32 46 18 R
M33 47 20 R
M34 48 22 R
M35 49 24 R
M36 50 26 R
M37 51 28 R
M38 52 30 R
M39 53 32 R
M40 54 34 R
M41 55 36 R
M42 56 38 R
M43 57 40 R
M44 58 42 R
M45 59 44 R
M46 60 46 R
M47 61 48 R
M48 62 50 R
- 63 52 -
- 64 54 -
- 65 56 -
- 66 58 -
- 67 60 -
- 68 62 -
- 69 64 F00 70 66 R/W
F01 71 68 R/W
F02 72 70 R/W
F03 73 72 R/W
F04 74 74 R/W
F05 75 76 R/W
F06 76 78 R/W
F07 77 80 R/W
F08 78 82 R/W
F09 79 84 R/W
F10 80 86 R/W
F11 81 88 R/W
F12 82 90 R/W
F13 83 92 R/W
F14 84 94 R/W
Comm.
Index
EGD Offset Read/Write
Page 52

Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
F15 85 96 R/W
F16 86 98 R/W
F17 87 100 R/W
F18 88 102 R/W
F20 89 104 R/W
F21 90 106 R/W
F22 91 108 R/W
F23 92 110 R/W
F24 93 112 R/W
F25 94 114 R/W
F26 95 116 R/W
F27 96 118 R/W
F30 97 120 R/W
F31 98 122 R/W
F33 99 124 R/W
F34 100 126 R/W
F35 101 128 R/W
F36 102 130 R/W
F40 103 132 R/W
F41 104 134 R/W
F42 105 136 R/W
E01 106 138 R/W
E02 107 140 R/W
E03 108 142 R/W
E04 109 144 R/W
E05 110 146 R/W
E06 111 148 R/W
E07 112 150 R/W
E08 113 152 R/W
E09 114 154 R/W
E10 115 156 R/W
E11 116 158 R/W
E12 117 160 R/W
E13 118 162 R/W
E14 119 164 R/W
E15 120 166 R/W
E16 121 168 R/W
E17 122 170 R/W
E20 123 172 R/W
E21 124 174 R/W
E22 125 176 R/W
E23 126 178 R/W
E24 127 180 R/W
E30 128 182 R/W
E31 129 184 R/W
E32 130 186 R/W
E33 131 188 R/W
E34 132 190 R/W
E35 133 192 R/W
E36 134 194 R/W
E37 135 196 R/W
E40 136 198 R/W
E41 137 200 R/W
E43 138 202 R/W
46
Page 53

Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
E44 139 204 R/W
E45 140 206 R/W
C01 141 208 R/W
C02 142 210 R/W
C03 143 212 R/W
C04 144 214 R/W
C05 145 216 R/W
C06 146 218 R/W
C07 147 220 R/W
C08 148 222 R/W
C09 149 224 R/W
C10 150 226 R/W
C11 151 228 R/W
C20 152 230 R/W
C30 153 232 R/W
C31 154 234 R/W
C32 155 236 R/W
C33 156 238 R/W
P01 157 240 R/W
P02 158 242 R/W
P03 159 244 R/W
P04 160 246 R/W
P05 161 248 R/W
P06 162 250 R/W
P07 163 252 R/W
P08 164 254 R/W
P09 165 256 R/W
H03 166 258 R/W
H04 167 260 R/W
H05 168 262 R/W
H06 169 264 R/W
H07 170 266 R/W
H08 171 268 R/W
H09 172 270 R/W
H10 173 272 R/W
H11 174 274 R/W
H12 175 276 R/W
H13 176 278 H14 177 280 H15 178 282 H16 179 284 H18 180 286 R/W
H19 181 288 H20 182 290 R/W
H21 183 292 R/W
H22 184 294 R/W
H23 185 296 R/W
H24 186 298 R/W
H25 187 300 R/W
H26 188 302 R/W
H27 189 304 R/W
H28 190 306 R/W
H30 191 308 R/W
H31 192 310 R/W
47
Page 54

Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
H32 193 312 R/W
H33 194 314 R/W
H34 195 316 R/W
H35 196 318 R/W
H36 197 320 R/W
H37 198 322 R/W
H38 199 324 R/W
H39 200 326 R/W
A01 201 328 R/W
A02 202 330 R/W
A03 203 332 R/W
A04 204 334 R/W
A05 205 R/W
336
A06 206 338 R/W
A07 207 340 R/W
A08 208 342 R/W
A09 209 344 R/W
A10 210 346 R/W
A11 211 348 R/W
A12 212 350 R/W
A13 213 352 R/W
A14 214 354 R/W
A15 215 356 R/W
A16 216 358 R/W
A17 217 360 R/W
A18 218 362 R/W
o01 219 364 R/W
o02 220 366 R/W
o03 221 368 R/W
o04 222 370 R/W
o05 223 372 R/W
o06 224 374 R/W
o07 225 376 R/W
o08 226 378 R/W
o27 227 380 R/W
o28 228 382 R/W
o30 229 384 R/W
o31 230 386 R/W
o32 231 388 R/W
o33 232 390 R/W
o34 233 392 R/W
o35 234 394 R/W
o36 235 396 R/W
o37 236 398 R/W
o38 237 400 R/W
o39 238 402 R/W
o40 239 404 R/W
o41 240 406 R/W
o42 241 408 R/W
o43 242 410 R/W
o44 243 412 R/W
o45 244 414 R/W
o46 245 416 R/W
o47 246 418 R/W
48
Page 55

Appendix D - EGD Exchanges
o48 247 420 R/W
o49 248 422 R/W
o50 249 424 R/W
o51 250 426 R/W
o52 251 428 R/W
o53 252 430 R/W
o54 253 432 R/W
o55 254 434 R/W
49
 Loading...
Loading...