Page 1

Fuel Management System
Programming Guide
T5 Series
Software Revision 1.7.4
Franklin Fueling Systems • 3760 Marsh Rd. • Madison, WI 53718 USA
Tel: +1 608 838 8786 • 800 225 9787 • Fax: +1 608 838 6433 • www.franklinfueling.com
Page 2

Notice
Franklin Fueling Systems (FFS) strives to produce the nest manual possible and to ensure that the information that it
contains is complete and accurate FFS periodically review the manuals. However, FFS reserves the rights to change this
document and specications at any time without notice. FFS makes no expressed or implied warranty with regard to the
contents of this manual. FFS assumes no liability for errors, omissions or for any damages, direct or consequential, that
may result from the use of this document or the equipment that it describes.
This manual is for use expressly with the T5, T550, and T5000 at their approved specications. No part of this document
may be reproduced in any form without the prior written consent of FFS.
Open Source Notice
The T5 series consoles implement open source software released under the General Public License (GPL) as well as
other open source licenses. As a customer, you are entitled to receive a copy of the licensed source code used within our
product, if so desired. Please contact our sales staff for more information.
Trademarks
FFS®, Tank Sentinel®, System Sentinel®, SCALD®, Brite®, BriteBox®, BriteBus®, and BriteSensors® are registered
trademarks of Intelligent Controls. All brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
Inspection of Materials
Visually inspect all components for defects or damage prior to installation. If any defect or damage is found, do not use the
product and contact FFS for further assistance.
Warranty Information
Please refer to the FFS Fuel Management Systems & Product Warranty Policy for all warranty information.
Contacting Franklin Fueling Systems (FFS)
Please feel free to contact us by mail at:
Franklin Fueling Systems
3760 Marsh Rd.
Madison, WI 53718 USA
Or contact us by phone, fax or e-mail:
Tel: +1 800 984 6266 E-mail: sales@franklinfueling.com
Fax: +1 608 838 6433 techserve@franklinfueling.com
Ofce and Sales Hours: 8am to 5pm CST - Monday through Friday
Technical Support Hours: 7am to 7pm CST - Monday through Friday
Please visit our website at www.franklinfueling.com
Copyright ©2011 by Franklin Fueling Systems. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the prior written consent of FFS. All
ii
rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
Notice..................................................................................................................................ii
Important Safety Messages ..............................................................................................1
Introduction ........................................................................................................................3
FMS Functions ..........................................................................................................................3
Denitions and Acronyms ......................................................................................................... 4
Related Documentation ............................................................................................................ 4
General ............................................................................................................................... 5
User Interfaces (UI) ..................................................................................................................5
LCD Touch Screen Interface .......................................................................................................... 5
Touch Screen Calibration .........................................................................................................................5
Web Browser Interface .................................................................................................................... 5
Access Control ................................................................................................................................ 5
Password Input................................................................................................................................ 6
Modifying Passwords ...................................................................................................................... 6
Connecting a PC or Laptop Computer ...................................................................................... 6
Conguring IP Settings for Communication .................................................................................... 7
Check Status of Connection ............................................................................................................ 9
Connecting a PC to the T5 series RS-232 Port ........................................................................ 10
Connecting a PC to the T5 series COMM 1 Port ............................................................................ 10
Conguring COMM 1 Settings for Communication ......................................................................... 11
Check Operation of Connection ...................................................................................................... 13
Initial Console Conguration ...........................................................................................13
Console Build Characteristics ................................................................................................... 13
Conguration and Preferences ................................................................................................. 14
Preferences Menu ........................................................................................................................... 14
Conguration Menu ..................................................................................................................16
Conguration Options...................................................................................................................... 16
Network Parameters ........................................................................................................................ 16
Date/Time Set ................................................................................................................................. 16
Time Zone ....................................................................................................................................... 17
Remote Logging Host ..................................................................................................................... 17
Modem ..............................................................................................................................17
Programming and Navigation ..........................................................................................18
Console Navigation ...................................................................................................................18
Navigation Buttons .......................................................................................................................... 18
Character Navigation Buttons ......................................................................................................... 19
Application Menus ............................................................................................................ 19
Programming System Parameters ............................................................................................20
System ID ........................................................................................................................................ 20
System Conguration ...................................................................................................................... 20
Programming Modules .................................................................................................................... 21
IO Modules .............................................................................................................. 21
AC Input Modules.....................................................................................................................................21
Probe Modules ......................................................................................................................................... 22
2-Wire Sensor Modules............................................................................................................................22
3-Wire Sensor Modules............................................................................................................................22
4-20 mA Input Modules ........................................................................................................................... 23
Power Supply ........................................................................................................................................... 24
Relay Modules .........................................................................................................................................26
Dispenser Interface .................................................................................................................................. 27
iii
Page 4

Programming Parameters ............................................................................................................... 28
Fuel Management System .......................................................................................................................28
Special Tanks ...........................................................................................................................................29
Manifold Tank System ..............................................................................................................................29
Vapor Recovery Monitoring .....................................................................................................................31
Secondary Containment Monitoring .......................................................................................................31
E-Mail ....................................................................................................................................................... 32
Events ......................................................................................................................................................32
Web Browser Interface ......................................................................................................33
Navigating Applications Remotely ............................................................................................ 33
Accessing Web Browser Interface .................................................................................................. 33
Making Changes to System Parameters .................................................................................. 33
Password Prompting .................................................................................................................33
Setup ........................................................................................................................................33
Backup Setup Files ...................................................................................................................34
Leak Testing .......................................................................................................................36
Leak Testing .............................................................................................................................. 36
Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 36
Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency .......................................................................................... 36
Static Tank Testing Requirements ............................................................................................................ 36
When to Force Static Tank Leak Tests ..................................................................................................... 36
Manually Forcing Static Leak Tests ..........................................................................................................37
Tank Leak Test Results ................................................................................................................... 38
Reasons Why Tank Leak Tests Fail .........................................................................................................38
Steps to Take When a Tank Leak Test Fails.............................................................................................38
SCALD Tank Leak Tests .................................................................................................................. 38
Reasons Why SCALD Tank Tests may Fail .............................................................................................38
TS-LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak Testing ......................................................................................... 39
Overview ..................................................................................................................................................39
Line Leak Test Requirements ...................................................................................................................39
When to Force Line Leak Tests ................................................................................................................39
Line Leak Test Results .............................................................................................................................39
Steps to Take When a Line Leak Test Fails .............................................................................................39
DTU (Data Transfer Unit) Setup and Programming ........................................................ 40
DIM Programming ..............................................................................................................42
Dual DIM Installation .................................................................................................................46
Hardware Conguration ............................................................................................................ 46
Device Address .........................................................................................................................46
Communication Settings ........................................................................................................... 46
TS-TPI Overview and Functionality .................................................................................47
TPI Setup ..................................................................................................................................48
List of Alarms and Troubleshooting ................................................................................ 49
System Alarms ..........................................................................................................................49
VRM Alarms ..............................................................................................................................51
FMS Alarms .............................................................................................................................. 52
SCM Alarms ..............................................................................................................................55
Wire Sensor Alarms .................................................................................................................. 55
Line Leak Detector (LLD) Alarms .............................................................................................. 56
TPI Alarms ................................................................................................................................ 57
Printer Alarms ........................................................................................................................... 58
Appendix A - Standard Tanks Table .................................................................................59
Appendix B - Standard Products Table ........................................................................... 61
Appendix C - Typical Tank Leak Test Times ...................................................................61
iv
Page 5

Important Safety Messages
FFS equipment is designed to be installed in association with volatile hydrocarbon liquids such as gasoline and diesel
fuel. Installing or working on this equipment means working in an environment in which these highly ammable liquids
may be present. Working in such a hazardous environment presents a risk of severe injury or death if these instructions
and standard industry practices are not followed. Read and follow all instructions thoroughly before installing or working
on this, or any other related, equipment.
As you read this guide, please be aware of the following symbols and their meanings:
Warning
Caution
Danger
Warning
This symbol identies a warning. A warning sign will appear in the text of this document when a potentially
hazardous situation may arise if the instructions that follow are not adhered to closely. A potentially hazardous
situation may involve the possibility of severe bodily harm or even death.
This is a caution symbol. A caution sign will appear in the text of this document when a potentially hazardous
environmental situation may arise if the instructions that follow are not adhered to closely. A potentially
hazardous environmental situation may involve the leakage of fuel from equipment that could severely harm
the environment.
This symbol identies an electrical danger. An electrical danger sign will appear in the text of this document
when a potentially hazardous situation involving large amounts of electricity may arise if the instructions that
follow are not adhered to closely. A potentially hazardous situation may involve the possibility of electrocution,
severe bodily harm, or even death.
Alarms and warnings are designed to alert you with specic details when a problem occurs so you can
take appropriate corrective action. System hardware failure warnings, tank related alarms, leak detection
sensor alarms, and line leak alarms can be custom programmed to do many things. The events that require
programming are denoted by a (p) below:
- cause the red Alarm light or yellow Warning light to ash (standard)
- activate / sound the console annunciator alarm horn (p)
- activate internal output relays for external alarm devices (p)
- print alarm reports automatically, either locally (internal printer), or remotely (USB - HP compatible printer) (p)
- send alarm and test reports to a specied e-mail address (p)
- send reports to remote location(s), via internal data/fax modem (p)
Follow all applicable codes governing the installation and servicing of this product and the
entire system. Always lock out and tag electrical circuit breakers while installing or servicing
this equipment and any related equipment. A potentially lethal electrical shock hazard and the
possibility of an explosion or re from a spark can result if the electrical circuit breakers are
accidentally turned on during installation or servicing. Please refer to the Installation and Owner’s
Manual for this equipment, and the appropriate documentation for any other related equipment, for
complete installation and safety information.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Follow all federal, state and local laws governing the installation of this product and its associated
systems. When no other regulations apply, follow NFPA codes 30, 30A and 70 from the National Fire
Protection Association. Failure to follow these codes could result in severe injury, death, serious
property damage and/or environmental contamination.
Always secure the work area from moving vehicles. The equipment in this manual is usually
mounted underground, so reduced visibility puts service personnel working on this equipment in
danger from moving vehicles entering the work area. To help eliminate these unsafe conditions,
secure the area by using a service truck to block access to the work environment, or by using any
other reasonable means available to ensure the safety of service personnel.
When the Fuel Management System is used to monitor tanks containing gasoline or other
ammable substances, you may create an explosion hazard if you do not follow the requirements in
this manual carefully.
All wiring must enter the console’s enclosure through the designated knockouts. An explosion
hazard may result if other openings are used.
You must run wiring from probes or sensors to the Fuel Management System console in conduits
which are separate from all other wiring. Failure to do so will create an explosion hazard.
1
Page 6

Warning
Certied Programmer/Service Person: Only an FFS certied programmer or service person is allowed to access both
the user interface keypad and areas internal to the Fuel Management System console.
Station Owner/Operator: The station owner or operator of the Fuel Management System console is only allowed to
access the user interface keypad. Access to areas internal to the console is strictly prohibited.
Substituting components could impair intrinsic safety. T5XXXs are intrinsically safe for sensors
installed in – Class I, Division 1, Group D – hazardous locations. Substitution of components could
make the energy limiting circuitry in the system ineffective and could cause an explosion hazard.
Repairs to a T5XXX console or attached components should only be performed by a qualied,
factory-trained technician.
Approvals
All Fuel Management System models are UL and cUL listed 6L79 as Liquid Level Gauge / Leak Detection
Systems. Third party approved leak detection — Pd (probability of detection) = 99.2 % for 0.1 or 0.2 gph leak tests
(0.1 = annual precision test, 0.2 is the monthly regulatory compliance test).
*The static tank test does not support Manifolded tanks.
**SCALD is 3rd party approved for ONLY two Manifolded tanks.
2
Page 7

Introduction
The purpose of this manual is to guide installers, operators and technicians through programming and troubleshooting
the T5 series console, so that it’s congured based on a site’s specic needs. The Fuel Management Systems (FMS)
application within the T5 Series consoles tie together the monitoring and alarm capabilities of preceding automatic tank
gauges with advanced technologies to supply tank and level data more accurately and efciently. This manual is also
designed to introduce technicians to the optional LCD Graphical User Interface, which is used as an input device to
program system conguration and maintain all applications from the front panel of the console as well as through a web
interface. Overall safety issues, troubleshooting information, warranty, service and return policies, as dened in this
manual, must be followed.
FMS Functions
The main function of the Fuel Management System is to represent levels for inventory and tank leak testing by monitoring
probe inputs and performing calculations based on those inputs. Line leak sensing devices also provide input signals.
Results from these calculations may be used for system monitoring and/or regulatory compliance. The console, in
conjunction with external fuel system equipment, may provide positive system shutdown, based on programmed rules.
Sites that utilize Fuel Management Systems have the ability to monitor and perform:
• Tank Inventory Level Information
• Tank Leak Detection
• Sensor Conguration
• Line Leak Detection
• Sump Leak Detection
• Compliance Line and Leak Testing
FMS also allows sites to generate and print the following reports:
• Inventory Reports
• Delivery Reports
• Tank Test Results
• SCALD Testing Reports
• Regulatory Reports
• Sensor Reports
3
Page 8

Denitions and Acronyms
Module – A module is a plug-in card within the T5 series console that is used to perform various functions of the console.
The modules are used for eld wiring of the input and / or output of electrical signals between different functional
equipment pieces.
RS-232 – An IEEE standard for serial communication using a 9-pin connector.
RS-485 – An IEEE standard for serial communication using Shielded Twisted Pair or Unshielded Twisted Pair wiring.
RJ-45 – An IEEE standard connector for use in communications with Shielded Twisted Pair wiring. Usually data.
RJ-11 – An IEEE standard connector for use in communications using Shielded Twisted Pair wiring. Usually voice and fax.
2SM – 2-Wire Sensor Module (Intrinsically Safe)
ACIM – AC Input Module
AIM – 4-20mA Analog Input Module (Intrinsically Safe)
AST – Aboveground Storage Tank
ATG – Automatic Tank Gauge
CARB – California Air Resources Board
CM – Controller Module
DCE – Data Communication Equipment
DIM – Dispenser Interface Module
DTE – Data Terminal Equipment
DTU – Data Transfer Unit
DW/DWT – Double Wall/Double Wall Tank
EVR – Enhanced Vapor Recovery
FMS – Fuel Management Systems
IS – Intrinsically Safe
ISD – In-Station Diagnostic
LCD – Liquid Crystal Display
LIM – LonWork Interface Module
LLD – Line Leak Detection
PC – Personal Computer
PM – Probe Module (Intrinsically Safe)
PSM – Power Supply Module
RTD – Resistance Temperature Detectors
RM – Relay Module
SCM – Secondary Containment Monitoring
SLLD - Statistical Line Leak Detection
STP – Submersible Turbine Pump
TPI – Turbine Pump Interface
TS-5 – T5 Series FMS Consoles (T5/608, T550/EMS, T5000/EXPC)
TS-EMS – Environmental Monitoring System
TS-EXPC – Expansion Console
URL – Uniform Resource Locator for the internet
USB – Universal Serial Bus
UST – Underground Storage Tank
VFM – Vapor Flow Meter
V/L – Vapor to Liquid ratio
VRM – Vapor Recovery Monitoring
XML – eXtensible Markup Language
Related Documentation
The system installation and operation instructions, troubleshooting guide and console maintenance manual are provided
for your use in separate documents. Detailed installation and testing instructions for each type of leak detection sensor
are present in the relevant manual, and, likewise, the installation, testing, and programming of various upgrade kits and
optional accessories are also contained in separate manuals, addenda or in one of this document’s appendices.
T5 Series Fuel Management Systems Installation Guide (000-2150)
T5 Series Fuel Management Systems Operators Guide (000-2151)
4
Page 9

General
After the Fuel Management System has been installed, typically your interaction with the system will be from the LCD
display, on-board printer; or using the Web Browser software to program and monitor the console remotely. Remote
operation can be performed from a PC, either attached directly or through a network connection to the console. All of the
features of the console are available through these input / output devices. Also, the console may be set up to generate and
send automated reports to e-mail accounts or print reports at a programmed time.
Occasionally you may need console information, such as model and serial numbers. The model number is located on the
face of the console. The serial number is located on a small plaque placed on the bottom of the left panel. This label also
shows the model number, voltage, manufacturer’s address, a warning symbol and the unit’s voltage specications.
User Interfaces (UI)
LCD Touch Screen Interface
An LCD touch screen is included with the T5 (TS-608) consoles and can be ordered as an option on the T550
(TS-EMS) and T5000. The “D” designation in the console’s model number indicates that a LCD display was ordered
with the system. This bright display, with an adjustable contrast setting, allows easy viewing in any lighting condition. A
programmable screen saver can be selected to automatically turn the backlight off after 5 minutes. This extends the life of
the display. To enable or disable the sleep mode select: Menu > Preferences > Toggle Sleep Mode
Touch Screen Calibration
During initial setup, it will be necessary to calibrate the touch screen function of the LCD display. Calibrating the
touch screen will enable the console to better recognize the area that you “touch,” so that you can accurately enter in
information. To calibrate the touch-screen function of the display, you must rst access the calibration application.
1. From the HOME MENU, press MAIN MENU > DOWN > TOOLS > TOUCHSCREEN CALIBRATION.
2. The console will ask if you are sure that you want to proceed, answer Yes.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the calibration process.
Web Browser Interface
Each T5 Series console includes an Ethernet port and programming options to eliminate the need for an Ethernet port
server or a external / internal modem (although both options are still available). The advantages to using an Ethernet
connection are: faster connection speeds, quicker data transfer rates, less data errors or quicker recovery of data when
errors occur, and it does not require extra software or drivers to be loaded. This means that console parameters can be
modied and that status/alarm reports can be printed from virtually anywhere.
Access Control
There are three access levels programmed into the console’s operating system: Guest, User, and Administrator. Each
level will allow an operator to access different features or change specic settings on the console. This security feature
prevents unauthorized tampering of console congurations.
The User Role icon will appear in the upper-right corner of the LCD display as one of the following:
• ONE BAR lled operates at the GUEST level. Guests are allowed to access menu options and check the system
congurations. The GUEST will not be able to modify the console settings.
• TWO BARS lled operates at the USER level. Users are given limited access to certain areas of the operating
system to make changes or print reports.
• THREE BARS lled operates as an ADMINISTRATOR. This level grants access to all areas of programming and
setup conguration. The administrator privilege is usually assigned to the designated technician of a site.
5
Page 10

Password Login
1. Press the User Roll icon
2.
Enter Password for the desired level as described in the Access Control section on page 5.
Default passwords are as follows:
Guest: guest
User: user
Administrator: admin
Tapping twice on the User Role Icon will reset to guest level access.
Modifying Passwords
For initial settings and continuous security purposes, the console will allow you to change any password used for
accessing console functions. When changing passwords, make note of the password and keep it in a secure, memorable
place. The password you choose must be at least two characters long with a maximum of 16 characters — spaces and
special characters are allowed as part of your password.
The Administrator status is required to change passwords.
From the touch screen display, changing access passwords is done by navigating through menus to modify a password.
1. When the console is powered up, press the Main Menu button .
2. Press the Conguration Application button.
3. Press Passwords in the application window, and then press the corresponding button to change the password for that
access level.
4. Verify the correct password has been entered, and then press the Checkmark button.
Connecting a PC or Laptop Computer
To access the console using the Web Browser interface, connect a PC to the console through either the Ethernet port or
the COMM 1 serial port. If the console is connected to a local network, you can perform this setup from any PC on that
network by using a web browser application, such as Microsoft’s Internet Explorer or Mozilla’s FireFox (the console’s IP
address may need to be modied — see Conguration in Section 2).
The following instructions are written specically for Microsoft’s Windows XP operating system. For assistance with other
operating systems, please contact Franklin Fueling Systems Technical Services.
Connecting a PC to the T5 series Ethernet Port
1. Using an Ethernet Crossover, 10 Base-T cable, plug the RJ-45 connector on one end of the cable into the Ethernet
port of the console.
2. Plug the RJ-45 connector on the opposite end of the cable to the Network Interface Card of the computer.
3. Verify that the green POWER LED on the front panel of the console is lit, which indicates that the console has power.
4. Power up and log onto your PC.
Note: You may need to recongure your TCP / IP settings to allow the computer to communicate with the console.
6
Page 11
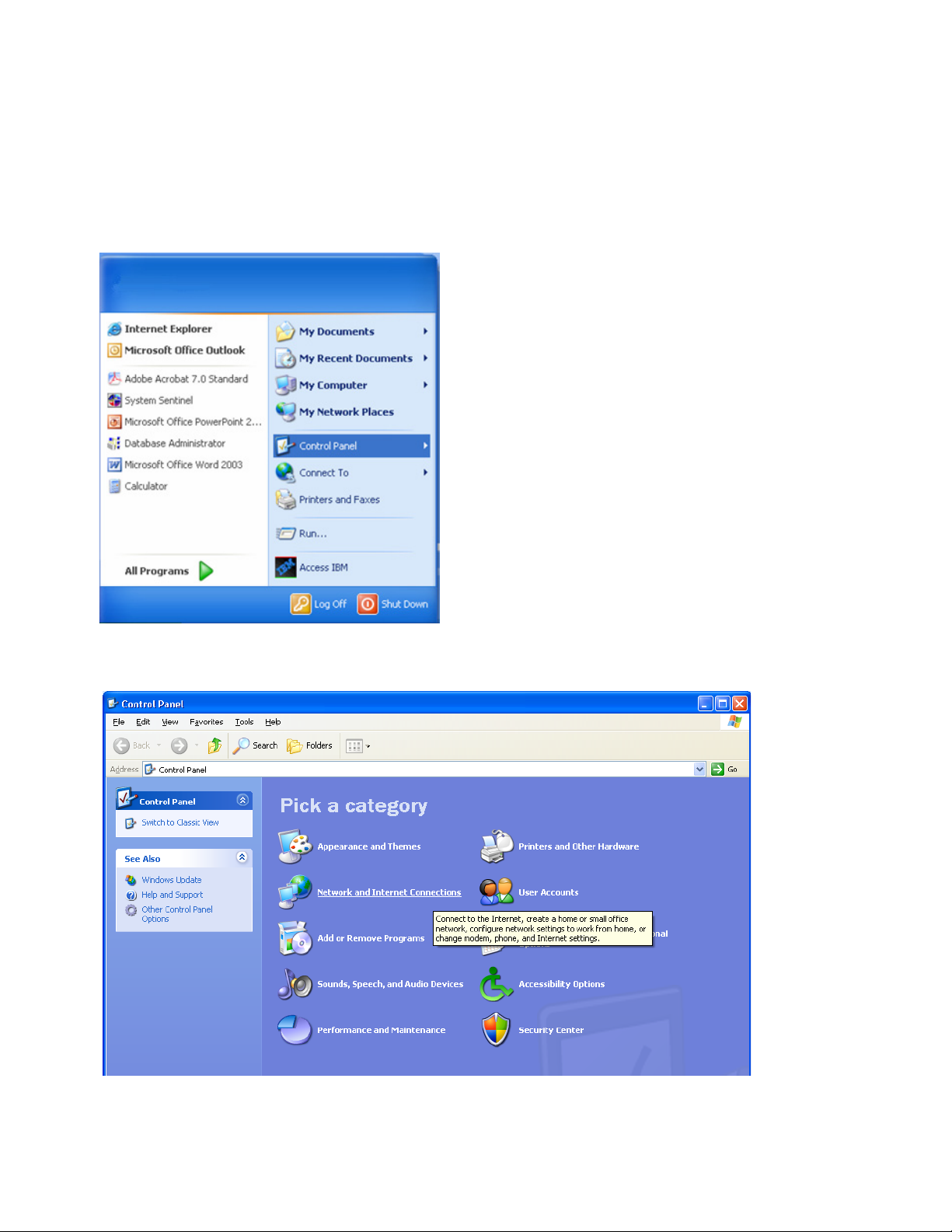
Conguring IP Settings for Communication
Before attempting to modify any computer settings, contact the Information Technologies department of your business, if
available. Some computer accounts may have restricted permissions to overcome before any changes are allowed to be
made to TCP / IP settings.
Note: If setting up a connection with a newer operating system (i.e. MS Vista or Widows 7), contact FFS Technical
Support for assistance.
At the PC:
1. Power up the PC and log into your Windows operating system.
2. Click on Start, then select Control Panel.
3. There are (2) two views settings possible when using Windows XP:
• In Category View, click on Network and Internet Connection, then click Network Connections.
7
Page 12
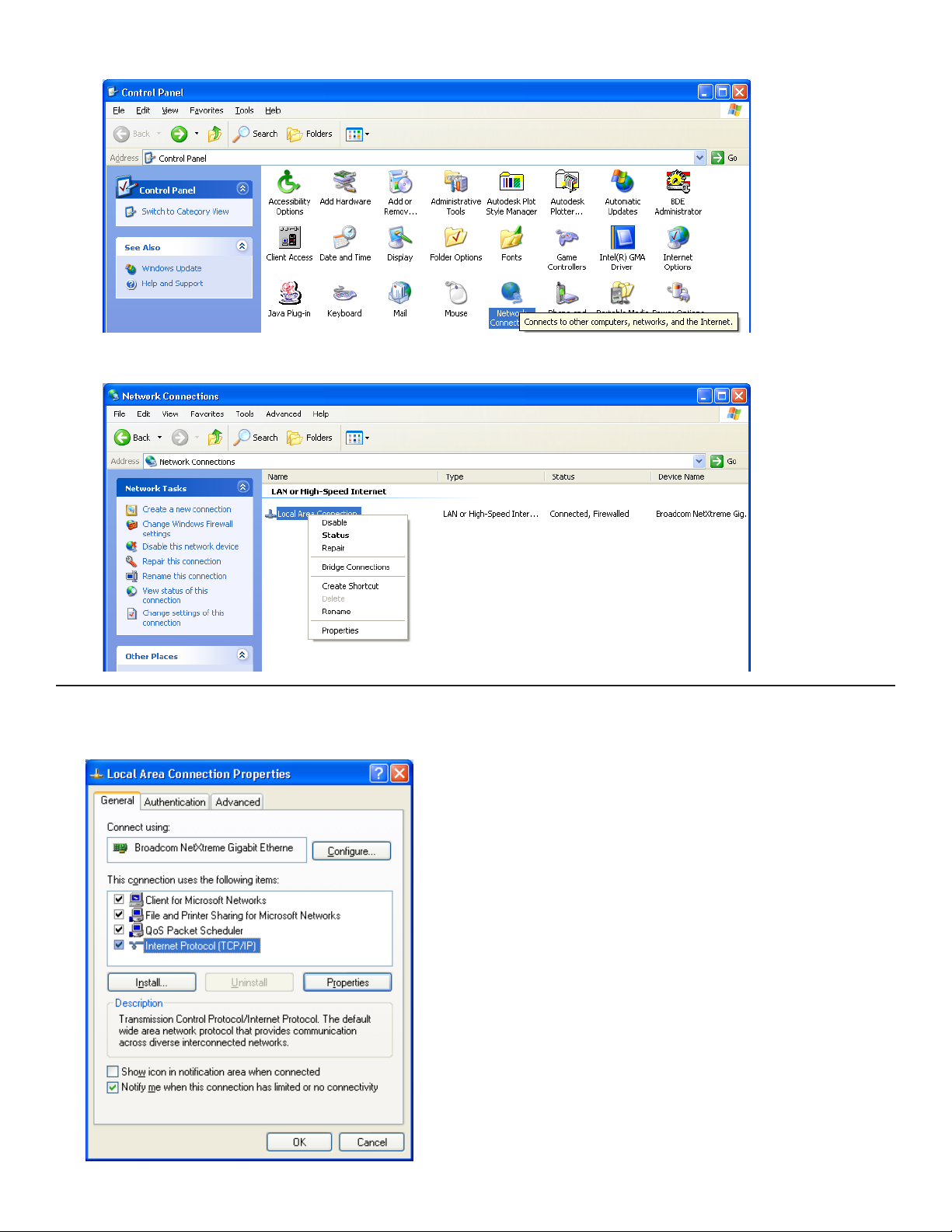
• In Classic View, click on Network Connections.
4. Right-click on Local Area Connection and select Properties.
5. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box,
under “This connection uses the following items,” select
Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) and click Properties.
There are many ways to congure a computer to
communicate with a T5 series console. These factors are
dependent on the user’s computer knowledge and how the
computer is currently congured.
To determine which method is best for your site, read the
instructions in the following section carefully. Make detailed
notes on the current conguration of the TCP / IP settings on
the PC you are using. Read both the “Obtain an IP address
automatically” and the “Use the following IP address”
methods before making a choice between the two.
8
Page 13
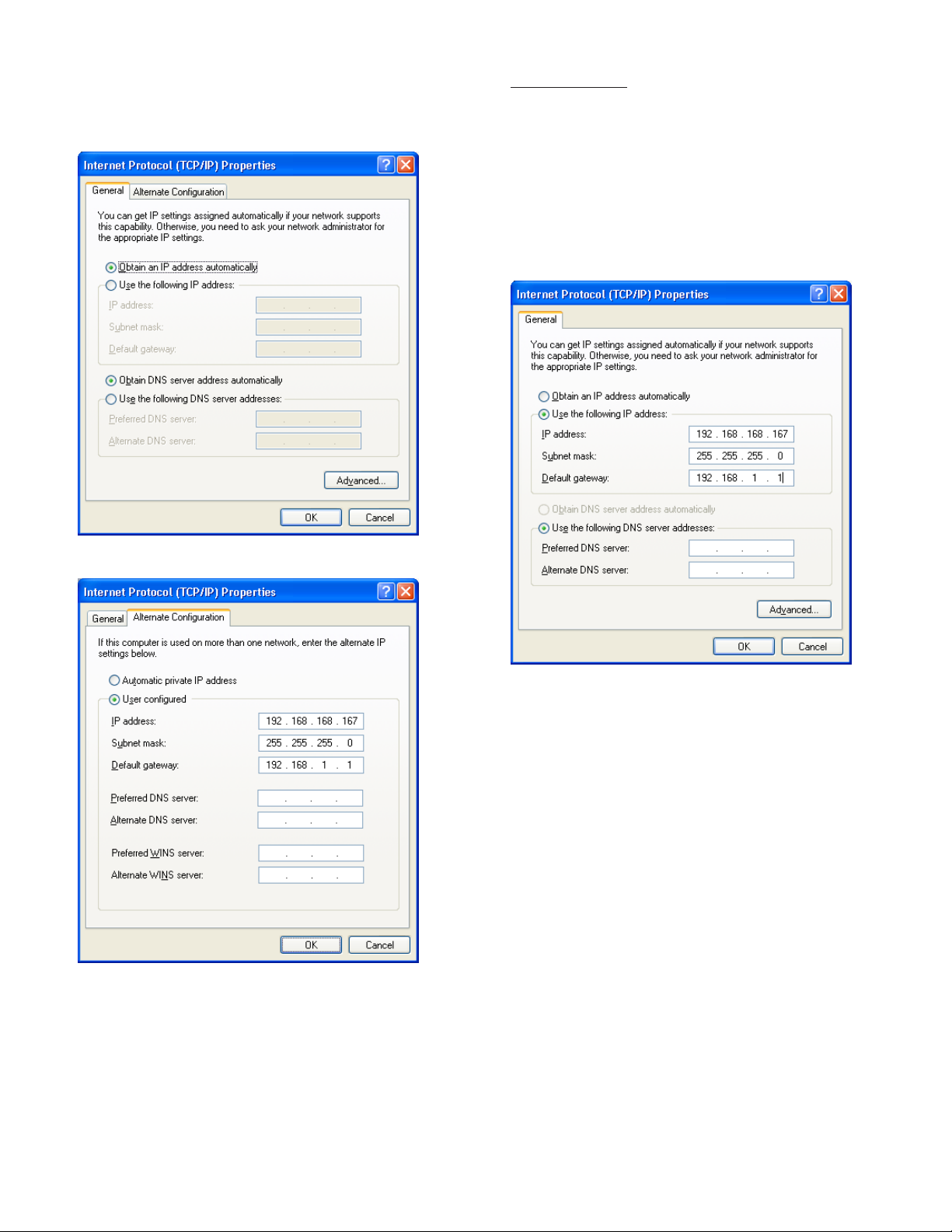
Obtain an IP Address Automatically
Computers commonly use this setting to obtain an IP
address automatically.
1. If Obtain an IP address automatically is selected, it
may be best to click the Alternate Conguration tab.
Note: The consoles default IP address is
192.168.168.168. If the PC is normally congured
to acquire an IP address automatically, Alternate
Conguration may be used, as mentioned above, to
allow a connection to be enabled without the necessity
of reconguring the computer each time it will be used
to connect to this console.
Use the Following IP Address
1.
If Use the following IP address is selected and the entry
boxes contain any information, record this information for
use when console programming is complete.
2. Select User Congured.
3. Enter an IP address. For simplicity, make the last
segment of the IP one number different than the IP
address of the console. Upon initial setup ONLY, the
numbers used in the gure may be used to congure
the TCP / IP settings of your PC.
4. Leave all other information blank and click OK.
5. Close the Local Area network for changes to take place.
2. Enter an IP address. For simplicity, make the last
segment of the IP one number different than the IP
address of the console. Upon initial setup ONLY, the
numbers used in the gure may be used to congure
the TCP / IP settings of your PC.
3. Leave the DNS information blank.
Note: The consoles default IP address is
192.168.168.168. If the PC is normally congured
to Use the following IP address, make sure that
all displayed information is recorded and kept prior
to making any changes. It may be necessary to use
this information to recongure the console once
programming is complete.
Check Status of Connection
1. Check the status of your connection by going to the
Network Connections window.
2. If the connection status is disabled, enable it by rightclicking on the Local Area Connection and selecting
Enable.
3. Verify link light is lit under Ethernet on Controller
module is lit and RX light is ashing.If technical
difculties arise, please contact Franklin Fueling
Systems Technical Support before proceeding.
More information on the Web Browser Interface is located
on page 33 of this manual.
9
Page 14
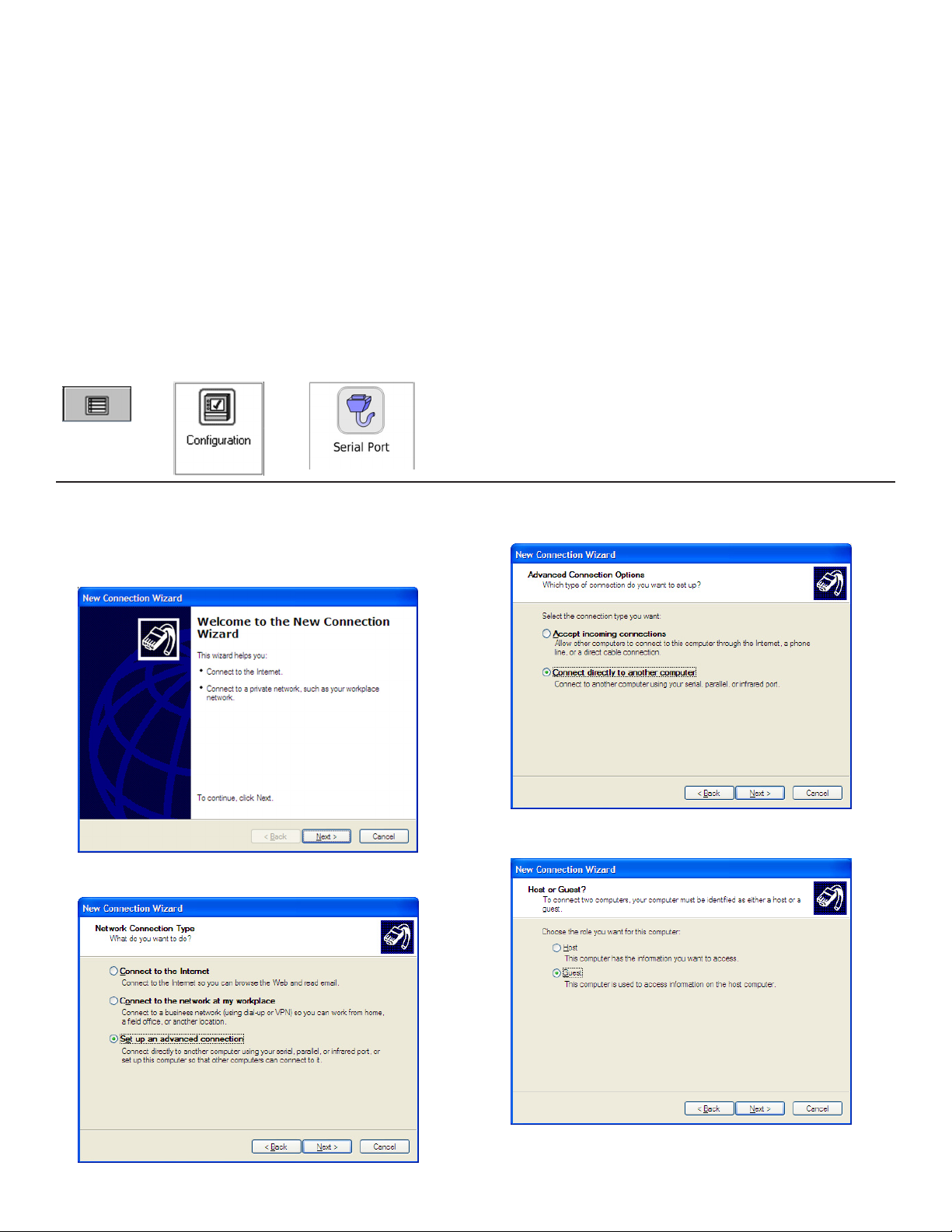
Connecting a PC to the T5 series RS-232 Port
COMM 1 is used to connect a PC or laptop with the console via the Web Browser Interface for programming or remote
monitoring. COMM 2 is used only for VRM to retrieve ullage data from an external ATG.
If serial connection to Point-Of-Sale (POS) is desired for report retrieval, then we suggest using COMM 1 in Veeder-Root
(VR) mode.
Note: The PC or laptop will recognize this serial connection as a network connection and will not allow the use of a Local
Area Connection simultaneously. While it is not necessary to disconnect the Local Area Connection to connect
using the Serial port, it will be necessary to disconnect the Serial Connection through the computers operating
system in order to use the Local Area Connection again.
Connecting a PC to the T5 series COMM 1 Port
1. Using a female to male DB-9 straight serial cable, connect the female end of the serial cable to the serial
communication (COM) port of the computer.
2. Connect the male end of the serial cable to COMM 1 on the bottom of the console.
Console Conguration
Mode: Network Connection (PPP)
Baud Rate: 57600
→
→
Conguring COMM 1 Settings for
Communication
1. Select Start > All Programs > Accessories >
Communications > New Connection Wizard.
→
Data Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
3. Select Connect Directly to Another Computer.
2. Select Set up an Advanced Connection.
10
4. Select Guest.
Page 15
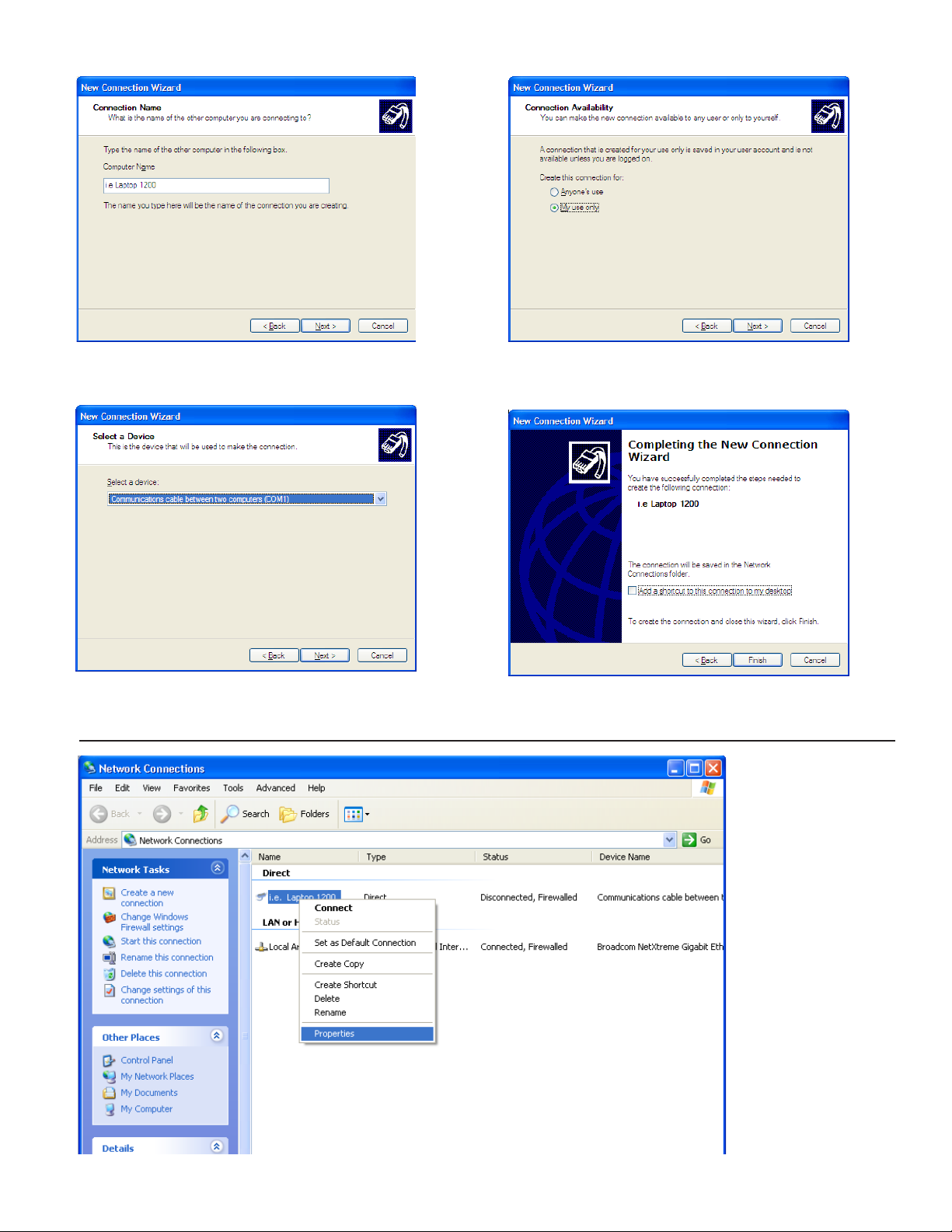
5. Enter a Computer Name (it can be the site name).
7. Select My use only.
6. Select the communication port to be used from the
Select a Device drop-down list.
8. For convenience, a shortcut may be created on your
desktop. Click Finish to complete the wizard.
9. In the Network Connections window, right-click the
new direct connection that was created and select
Properties.
11
Page 16
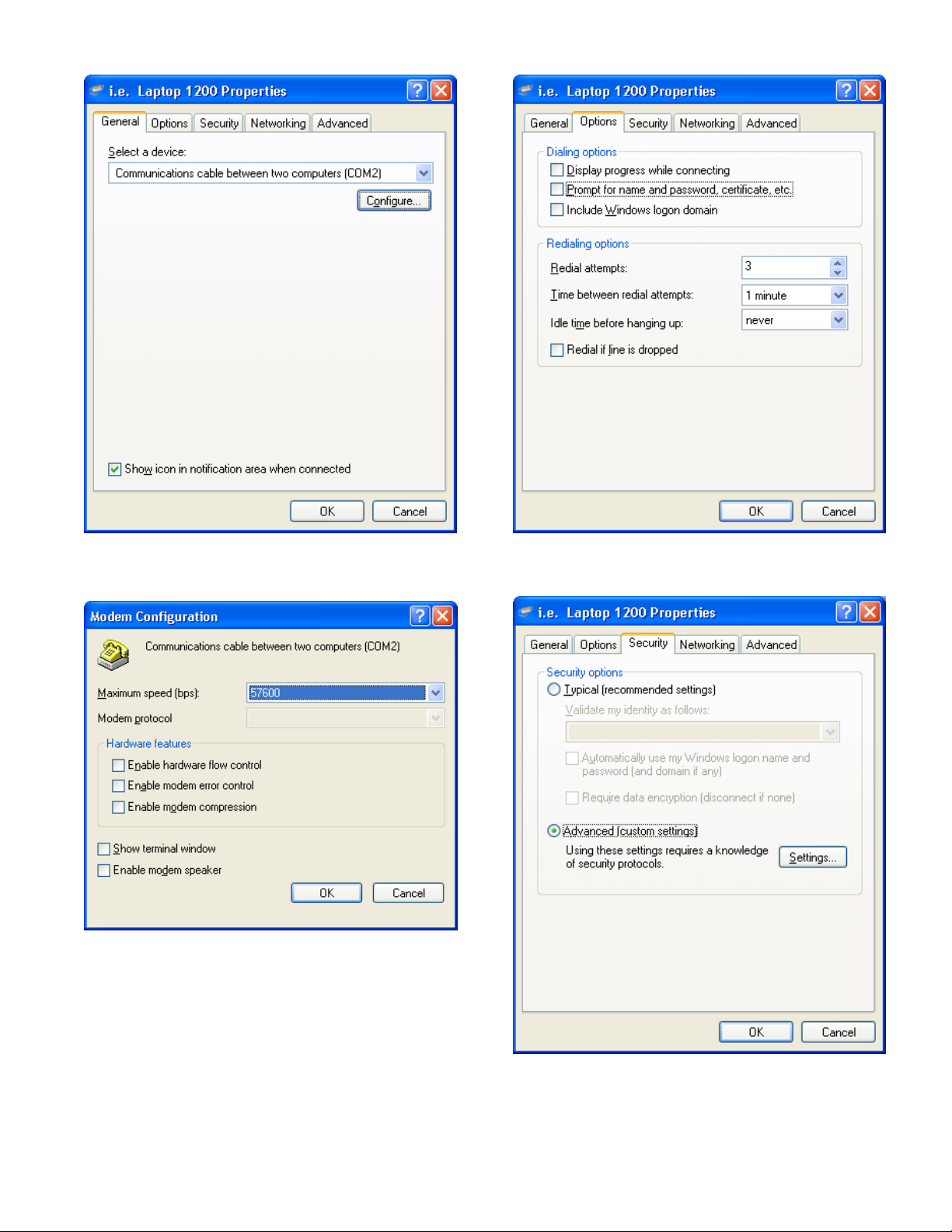
10. Under the General tab, select Congure.
15. Leave the existing Redialing Options as they are.
11. Change the Maximum speed (bps) to 57600.
12. Disable all of the Hardware Features and click OK.
13. Select the Options tab.
14. Disable all of the Dialing Options.
16. Select the Security tab.
17. Select Advanced (custom settings).
12
18. Select the Networking tab.
Page 17
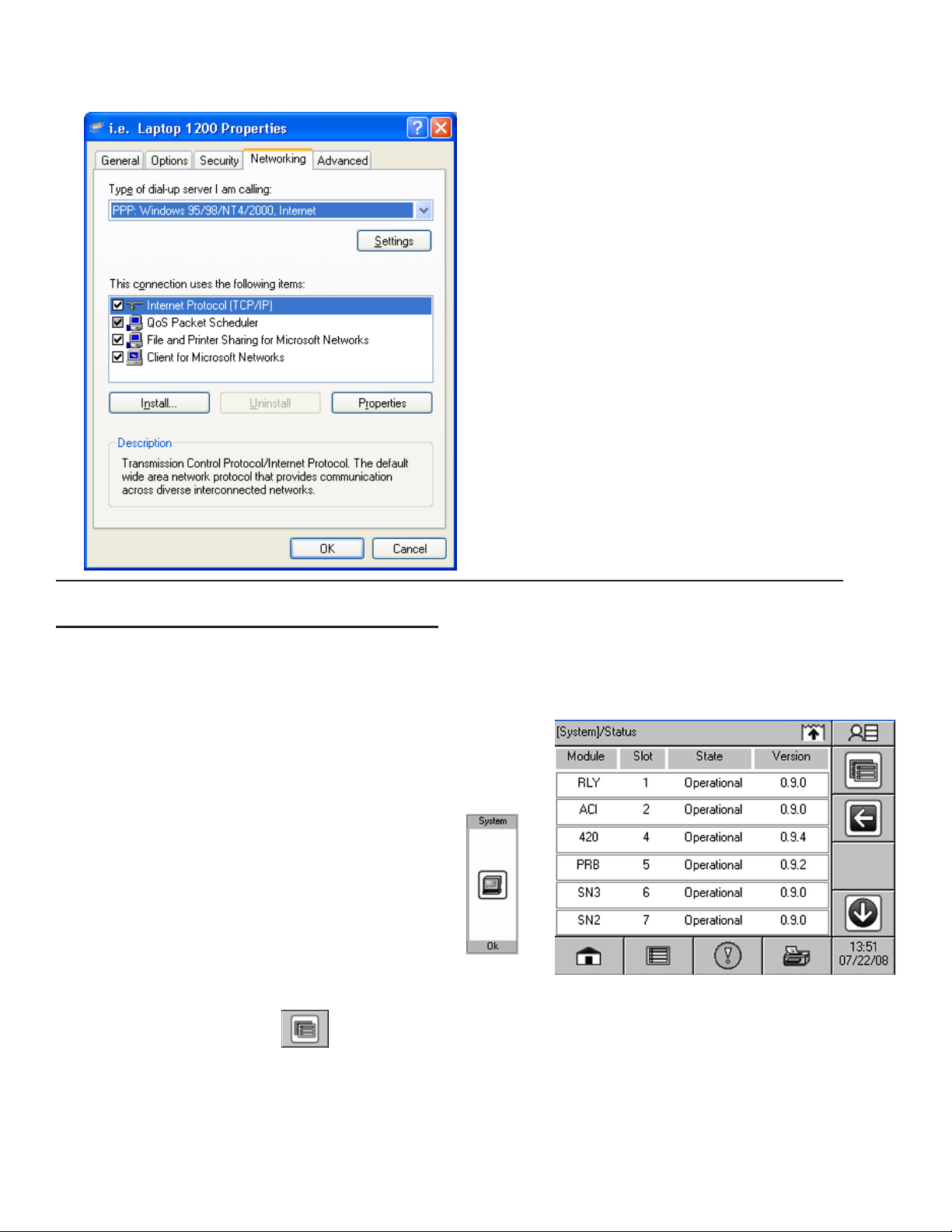
19. In the Type of dial-up server I am calling, select
PPP: Windows 95 / 98 / NT4 / 2000, Internet from the
drop-down list then click OK.
Check Operation of Connection
1. As before, open Network Connections.
2. Right-Click the new direct connection and select
Connect. The status should change to connected. At
this point, the computer is connected to the console.
If you experience technical difculties, please contact
Franklin Fueling Systems Technical Support before
proceeding.
At this point, more information on navigating the Web
Browser Interface is provided in Section 4: Web Browser
Interface of this manual.
Initial Console Conguration
Initial setup must be completed before the console can be used. This section will show how to set custom parameters by
navigating through the programming options and set up the T5 series console for the rst time.
Console Build Characteristics
Each console is custom ordered and built to customer specications.
That means that all of the hardware (modules) and software options
needed for your site are installed and tested. Before programming,
check the status and version of each module and verify that your
purchased options are present.
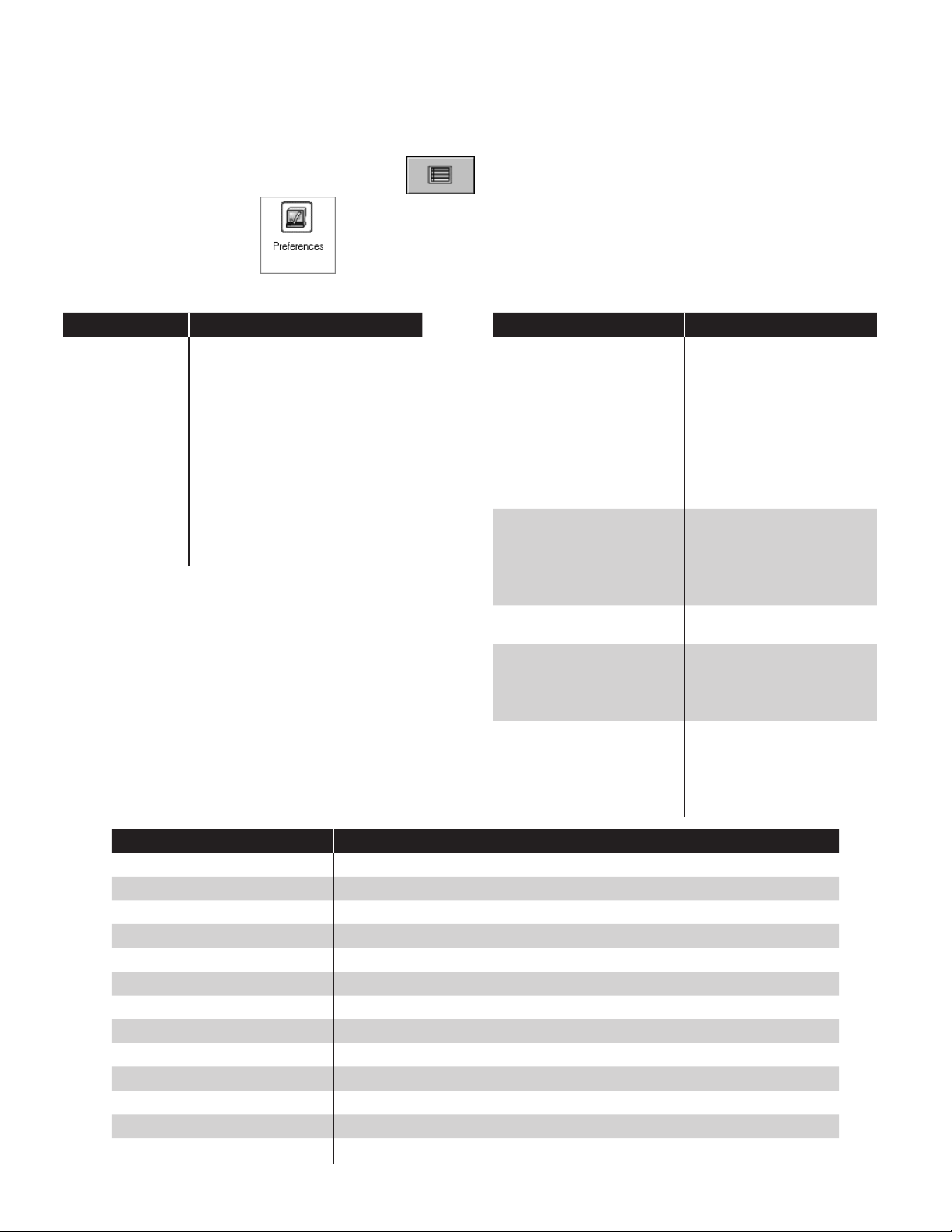
1. At the Home Status screen, press System Application.
2. The System Status screen will appear. Here you can see a
module’s description, installed slot, operational status, and version.
3. Press the Application Menu button.
Identication – View to locate the System Serial Number, Ethernet Address (not the same as IP address) Controller
Serial number and Date/Time of manufacture.
Options – Displays the current installed software options.
13
Page 18
Conguration and Preferences
Conguration and Preferences include how information will be displayed and conguring the console for its location and
communication and access options.
Preferences Menu
Starting at the Home Menu, press the Main Menu button.
And then select Preferences .
Use the Preference tables on the following pages to select the menu options to be changed.
Translation Options
Language English
Spanish
Russian
Chinese (Simplied)
Chinese (Traditional)
French
Portuguese
German
Russian
Polish
Slovakian
Hebrew
Date/Time Options
MM/dd/yyyy
M/d/yyyy
M/d/yy
MM/d/yy
Short date format
Long date format
Year/month date format
Short time format
Long time format
MM/dd/yy
Yy/MM/dd
yyyy-MM-dd
dd-MMM-yy
User Dened
EEEE, MMMM dd, yyyy
MMMM dd, yyyy
EEEE dd MMMM, yyyy
dd MMMM, yyyy
User Dened
MMMM, yyyy
User Dened
HH:mm
H:mm
hh:mm a
h:mm a
HH:mm:ss
H:mm:ss
hh:mm:ss a
h:mm:ss a
User dened
14
Symbol Representation
MM Two-digit month with leading zero (i.e. 01 for Jan…).
M Two-digit month, no leading zero (i.e. 1 for Jan…).
MMM Three-letter month (i.e. JAN, FEB, AUG…).
dd Two-digit day with leading zero (i.e. 01, 02…).
d Two-digit day, no leading zero (i.e. 1, 2…).
yyyy Four-digit year (i.e. 2006…).
yy Two-digit year (i.e. 06, 07…).
HH Two-digit hour with leading zero; 24-hour format.
hh Two-digit hour, no leading zero; 24-hour format.
mm Two-digit minute, with leading zero.
ss Two-digit second, with leading zero.
a A.M. or P.M. indicator.
EEEE
Page 19
Numbers Options
Digit grouping
Group digits by 103 using specied symbol (i.e. either “123456789” or
“123,456,789”).
Digit grouping symbol Symbol used to group digits (i.e. ‘, ’; ‘ _ ‘…). User dened option.
Decimal symbol Symbol used to separate decimal units (i.e. ‘.’; ‘,’). User dened option.
Display leading zeroes Displays decimals with leading zero (i.e. with ‘0.123’; without ‘.123’).
Units Options
Liters
Volume
Gallons
Imperial Gallons
Millimeters
Length
Centimeters
Meters
Inches
Temperature
Centigrade
Fahrenheit
Liters/Hour
Cubic Centimeters/Second
Flow
Cubic Feet/Hour
Gallons/Minute
Gallons/Hour
Pascal
Bar
FMS - Line Pressure
Pounds per square inch
Inches of Water
Inches of Mercury
Pascal
Bar
VRM-Tank Ullage
Pounds per square inch
Inches of Water
Inches of Mercury
Pascal
SCM - Containment
Vacuum
Bar
Pounds per square inch
Inches of Water
Inches of Mercury
Kilograms per Cubic Meter
Density Units
Grams per cubic centimeter
Pounds per cubic foot
Kilograms
Mass Units
Grams
Pounds
Other Options
Refresh Rate (web interface only) How often the systems information is updated.
Show XML Tool (web interface only) Displays the Tool in the upper right corner of the browser window.
Sleep Mode (console screen only) Toggles display sleep mode on or off
Printer Options (console screen only) Set external printer paper size
15
Page 20

Conguration Menu
Conguration Options
Using the options in this menu, you can change:
• Console passwords • COM 1 parameters
• Network parameters • Modem Parameters
• Current time and date and set an accurate time zone.
For instructions on setting passwords, see pages 5 & 6: Access Control.
Once the console has been powered up, navigate the console by pressing the screen on the appropriate button.
1. Starting at the Home Status Menu, press the Main Menu button.
2. Select the Conguration button.
3. Select from the options in the Network Parameters section that follows to view or change console conguration settings
Network Parameters
To communicate with your network equipment (i.e. router, switch, hub, etc.) you will need to modify the network
parameters.
IP Address Settings:
IP Address – This is a logical (electronic) address, like a street address, that the console uses to route information.
This address will have to match your network, if connected to a network, in order to ‘talk’ to a remote
communication device, or your PC.
Network Mask – Masking is a way to diversify the use of multiple subnets. The mask must match that of the network the
console is connected to. Masks are used in networking to create ‘sub-networks’ within a whole, like slicing
and apple. You have separate slices that may be in different locations, but they are still from the same apple.
Administrators use this to make separate networks, to maximize bandwidth or capacity of medium resources
(cables or ber). Therefore, when your network uses static IP addressing (assigned by an administrator),
this mask must match the Network Mask of the router port that it is attached to. If the network uses a DHCP
server (automatically assigns IP addresses) then the mask should meet the specications set by your
administrator.
Gateway – The Gateway is the logical address to the nearest router port, commonly the one that is connected to the
console. Consult your administrator for details on this and other network parameters.
DNS Server Address:
Preferred DNS Server / Alternate DNS Server – The domain name system (DNS) is the way that internet domain names
are located and translated into Internet Protocol addresses. A domain name is a meaningful and easy-to-remember tag for
an internet address (used for e-mail functions).
Protocol Settings – Veeder Root, port 8001: Port used to connect to a network that uses VR Protocol
– Web Server Secondary Port, 10001: Port used for network as port to forward
Date / Time Set
To set the date and time, click the button that corresponds with your selection and then select the correct option from the
list. If your choice does not appear on the rst screen, use the up and down navigation buttons to scroll through more
options. When nished, conrm your selection by pressing the checkmark or OK button. It is important to enter the date
and time information correctly to ensure reports and alarms can be accurately tracked.
.
16
Page 21

Time Zone
Set the Time Zone according to your geographical location. If your choice does not appear on the rst screen, use the
navigation up and down buttons to scroll through more options. When nished, conrm your selection by pressing the
check-mark or OK button.
Remote Logging Host
Logging event information can be done remotely by using this option. Type the address of the remote host that the
console will communicate with.
Modem
Type:
External USB
External Serial
Mode:
Network Connections (PPP)
Veeder Root
Franklin Fueling (XML)
Data Bit: 5 to 8
Parity: Odd, Even or None
Stop Bits: 1 or 2
Country Code: (Country)
Serial Port (Comm 1)
Mode:
Network Connections (PPP) Point-to-Point Protocol is a commonly used data link protocol.
Veeder Root
Franklin Fueling (XML)
Baud Rate: 300 - 57600
Data Bit: 5-8
Parity: Odd, Even or None
Stop Bits: 1 or 2
17
Page 22

Programming and Navigation
Console Navigation
The operating system is designed for easy navigation. Applications allow the user to modify programming options by
responding to on-screen commands. The following instructions show various operating system functions, so that issues
can be corrected efciently without interrupting dispensing or sales.
Access application sub-menus within the console by pressing the corresponding menu option button on the display.
Graphical icons are used to navigate the console. Console application menus / sub-menus are outlined in the next section
of this manual.
User Role – Displays the access level
Path Bar – Shows the path/description
of information displayed.
Application Window –
Displays the current
application content.
Form Feed Button
of the current user (determined by the
password input).
Back – Returns you to the
previous screen.
Home – This button will bring
you back from any application
to the home status screen.
Main Menu – Access the
Main Menu application.
Status – Displays a check for OK
or an exclamation for alarm. When
alarms exist, pressing this will bring
you to an alarms page.
Date/Time – The current date
and time. This will let you
congure Time/Date settings.
Print Report – Pressing this
button will take you to a menu
of reports.
Navigation Buttons
There are many ways to navigate the applications of the T5 series console. Listed below are buttons that will help you
navigate the functions of the console.
Exit: Takes you back to the Main Menu.
Scroll Up: When this button appears on the right side of the screen it indicates more menu options are available
and pressing this button will scroll up through the options.
Scroll Down: When this button appears on the right side of the screen it indicates more menu options are
available and pressing this button will scroll down through the options.
18
Page 23
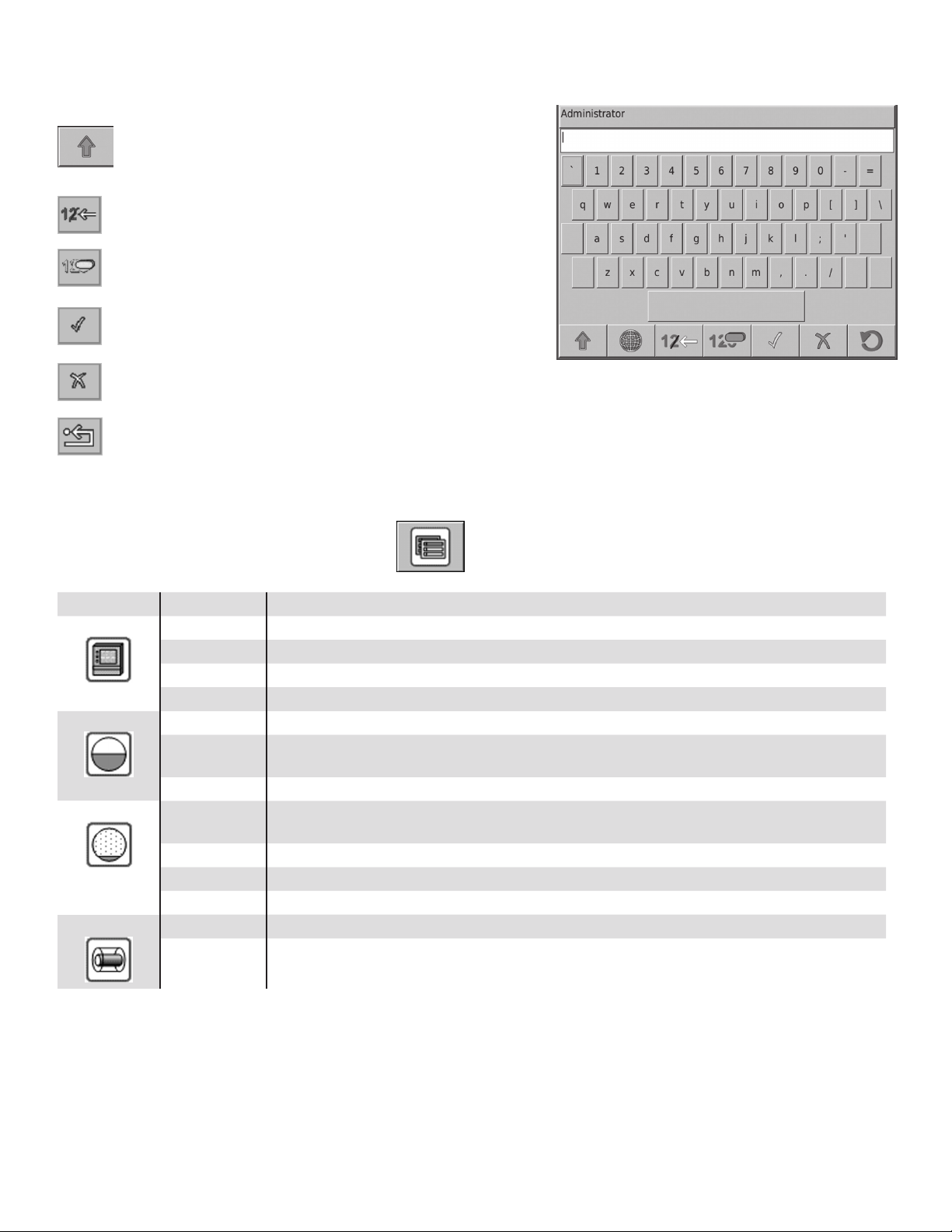
Character Navigation Buttons
When prompted to enter system information, press the corresponding keys.
Character Selection: Selects between upper case letters,
lower case letters and numerals. Note how the characters
on the input buttons change as you scroll through the
options.
Backspace: This will move the cursor one space to the left
and delete the last character.
Clear: Deletes all of the data on the entry line.
Enter: Allows the data to be accepted. When this button is
pushed, the conguration will be set for the item you are
changing.
Cancel: Will return to the application you were changing. No changes will be made to console settings.
Restore Default: This button will restore the original settings programmed into the console during manufacture.
Application Menus
Each Application has an application menu button
application have selected. These are listed below:
Application Menu Topic Description
System Status Shows status of installed modules including slot#, state and software version
About Shows system software version and copyright information
Identication Shows system and controller serial #, Ethernet address, and date created
Options Shows which options are installed
FMS Status Show status of Tanks, Lines, Sensors, Pumps and Deliveries
Control Allows controlling Tanks, Lines, Sensors, Pumps and Probes including initiating test and
to re-enable retest condition
Reports Allows printing various FMS reports
VRM Ullage
Pressure
Dispensers Shows status of the dispensers
Control Allows running manual tests, calibrating sensors and clearing monitoring
Reports Allows printing, e-mailing or faxing of Monthly and Daily Vapor Recovery reports
SCM Status Shows pressure reading and enabled status of each containment area
Control Allows controlling the Secondary containment, including resetting alarms and
Shows current ullage pressure as well as Operational Statistics and Compliance status
re-enabling containment.
This will bring up different options depending upon which
.
19
Page 24

Programming System Parameters
Using the touch screen function of the console to program, navigate from the Home Status screen by pressing the Main
Menu button.
At the Main Menu, press the Setup button, and select System ID.
The System ID screen looks like this:
To make a modication, select the parameter that you want to change.
Type the new setting in using the characters available. When nished,
press the check-mark. When Conrmation is displayed, press Yes to
save and apply, or No to exit without saving — you may press cancel
to continue making changes. Changes will not be applied until you
return to the main menu.
Refer to the programming tables on the following pages for a more
descriptive representation of each option including the submenus of
each menu item. The console will update the menus as additional
data or information is required during programming.
Please note, features appearing in this guide may not be available,
unless the option is purchased with your console. Default parameters
are noted by the use of parentheses ().
You should have the following items ready before beginning console programming:
• Site location information to setup Site ID
• Communications parameters for external equipment to match console settings
• Wiring diagrams of site if necessary; to identify sensor and/or probe location
• Manufacturers Tank Charts for “special” tank correction tables
• Probe stickers with gradient and RTD location for “special” probes
System ID
Group Name
System ID
Parameter
Name
Site Name (Site Name) Physical name of site. 40
Web UI URL (http://localhost/tsa) URL address of site. 40
ID Line 1 (blank)
ID Line 2 (blank) 40
ID Line 3 (blank) 40
ID Line 4 (blank) 40
ID Line 5 (blank) 40
Parameter
Value
Description
These lines should contain the physical address of the site. This
information will be used in the header of reports and to identify
site properties when using web UI.
Max
Characters
40
System Conguration
Group Name Parameter Name
System Conguration
Modules Expected
20
Technical Support Key (0) Enter the appropriate key number. 0-1
Enable Log Files (No) Enables the logging option. Yes/No
IO (0) These settings are preset by ordered options. This
AC Input (0) 0-6
Relay (0) 0-6
Probe (0) 0-6
2-Wire Sensor (0) 0-6
3-Wire Sensor (0) 0-6
4-20mA Input (0) 0-6
Printer (0) 0-1
LON (0) 0-1
DIM (0) 0-2
Console DTU (0) 0-1
Parameter
Default
Description
value represents the number of each module installed.
When a module is installed, the console will open more
options base on which module will be utilized.
Parameter
Input
0-6
Page 25

Programming Modules
The Fuel Management System is composed of a custom set of modules. Each module maintains individual characteristics.
Parameters must be set to match the site conguration. The programming table below will assist in this setup.
Remote Data Transfer Units (DTU’s)
Remote Data Transfer Units (DTU’s) are used in California for the purpose of relaying information from various sensors
mounted in dispensers to the FFS console.
Group Name Parameter Name
Remote Data Transfer Units
Parameter
Default
Description
Parameter
Input
DTU 1 Unit ID (0) Insert the Serial number of the rst DTU. abc#
Network ID (1) The I.D. of the network. #
Number of units (0) The number of DTUs in the eld. 1-16
For Further DIM or DTU Setup information, refer to the Web Browser Interface Section.
IO Modules
The Low Voltage Input / Output Module is a non-intrinsically safe module that provides eight separate AC or DC voltage inputs
that can range from 0 to 240 volts. In addition to the AC / DC inputs, the IO module also includes four 4-20mA signal outputs.
Group Name
IO Modules
Module #
Inputs Channels (0) The number of A/C or D/C inputs physically wired to the gauge. 0-8
Channel #
Outputs Channels (0) Number of 4-20mA channels in use per module. 0-4
Channel #
Parameter
Name
Name (Input 1) Descriptive name used to identify the input. abc#
Enabled (Yes) Enables the input.
Active State (High)
Action (None) Create an alarm or event timestamp . None
Name (output 1) Descriptive name used to identify the output
Enable (Yes) Yes if the channel is in use
Parameter
Default
Description Parameter Input
High will activate channel when high voltage is present.
Low will activate channel with no voltage present.
Yes / No
High / Low
Alarm
Event
abc
Yes / No
AC Input Modules
The AC Input Module is a non-intrinsically safe module that has 12 identical optically isolated AC input channels that can
be used for dispenser hook isolation, vapor processor input, or as generic AC inputs.
Group Name Parameter Default
AC Input Modules
Module # Channels (0) Number of channels in use per module. 0-12
Channel #
Number Gasoline Hooks per
Dispenser
Name (AC Input 1) Given name of channel. abc#
Enabled (Yes) Yes if channel is used. Yes / No
Active State (High)
Action Setup None Create an alarm or event timestamp None, Alarm,
Parameter
Default
(0)
Description
Including diesel. This is for reference only
except on VRM applications.
High will activate channel when high voltage
is present. Low will activate channel with no
voltage present.
Parameter
Input
0-8
High / Low
Event
21
Page 26

Probe Modules
The Probe Module gather data from probes, vapor ow meter and TS-DMS sensors. This information is processed by
the Controller Module for use in inventory, reconciliation, V/L Ratio calculation, TS-DMS sensor alarms and to provide
information for reports.
If a DTU is being used there will be an option for a “virtual module” labeled Remote Module. The Remote Module gathers
information from the vapor ow meter when a DTU is used. (see DTU Programming for further details on page 31 in this manual.)
Group Name Parameter Name
Probe Modules
Module # Channels (0)
Channel #
Remote Module 2 Channels (6) Number of DTU devices in use 0-12
Channel 1 (TS-DTU 1) Name DTU 1-VFM 1 Unique name given to channel abc#
Name (Probe 1) Given Name of Probe. abc#
Type (TS-LL2) Type of device connected.
Type TS-VFM Type of device connected. TS-VFM
Parameter
Default
Description
Number of channels in use per module.
Parameter
Input
0-12
TS-VFM
TS-LL2
TS-DMS
2-Wire Sensor Modules
The 2-Wire Sensor Module is designed to accept 12 sensor inputs per module, and the system as a whole can accept a
total of 36 sensors (3 modules with 12 inputs each). The module only supports standard sensors, and does not accept
inputs from 3-wire BriteSensors®.
Group Name Parameter Name
2-Wire Sensor Modules
Module # Channels (0) Number of channels in use per module. 0-12
Channel #
Name
Monthly Compliance (Yes)
Parameter
Default
(2-Wire Sensor
1)
Description
Given name of channel. abc#
Select Yes if this sensor is to appear on the
Compliance page and in the Regulatory report
Parameter
Input
Yes/No
3-Wire Sensor Modules
The 3-Wire Sensor Module is designed to accept 8 sensor inputs per module, and the system as a whole can accept a
total of 24 sensors (3 modules with 8 inputs each). The 3WSNS can support standard sensors and BriteSensors®.
Note: When the number of 3-wire sensor channels is selected, the system will automatically detect the connected
sensors and populate the setup with the detected types.
Group Name
3-Wire Sensor Modules
Module # Channels (0)
Channel #
Parameter
Name
Name
Type
Monthly
Compliance
Parameter
Default
(3-Wire Sensor 1)
(Interstitial
(EIS) or 2-Wire
Sensor)
(Yes)
Description Parameter Input
Number of channels in use
per module.
Given name of channel. abc#
Unknown,
The type of sensor
connected to the channel.
After the Channels are
entered this will ll in
automatically.
Select Yes if this sensor
is to appear on the
Compliance page and in
the Regulatory report
Interstitial (EIS) or 2-Wire Sensor
Discriminating Interstitial Sensor (DIS)
Discriminating Dispenser Sump Sensor (DDS)
Discriminating Turbine Sump Sensor (DTS)
Monitoring Well Sensor (MWS)
Hydrostatic Interstitial Brine Reservoir Sensor (HIS)
Discriminating Monitoring Well Vapor Sensor (DVS)
0-12
Yes / No
22
Page 27

4-20 mA and 4-20 mA EXP Input Modules
The Analog Input Module has 8 identical channels for loop powered IS sensors with a 4-20 mA interface.
The 4-20 mA EXP module is programmed in the same manner. The 420 EXP module is located on the hazardous side of
the console, must have the wires enclosed in explosion-proof conduit, and has a red front. If a DTU is being used there
will be an option for a “virtual module” labeled Remote Module. The Remote Module gathers information from the vapor
pressure sensor when a DTU is used. (see DTU Programming for further details on page 31 in this manual.)
Group Name
4-20mA Input Modules
Module # Channels (0) Number of channels in use per module. 0-8
Channel #
#3 Remote
Module 2 (DTU)
Parameter
Name
Name (4-20mA Input 1) Given name of the channel. abc#
Service Type (Analog) Determines the input signal.
Low Range -8.00 Low range of mA input - #
High Range 8.00 High range of mA input + #
Channels (0) Number of channels in use 0-5
Name 4-20 mA input 6 Given name of the channel abc#
Service Type (Vapor Recovery) Determines the output signal Vapor Recovery Monitoring
Parameter
Default
Description Parameter Input
Analog
Secondary Containment Monitoring
Line Leak Detection
Vapor Recovery Monitoring
FMS Level Probe
23
Page 28

Power Supply Module
The Power Supply is a non-intrinsically safe module that provides power to the T5 series console from line voltage rated 110 - 240
VAC. This module is two inches wide, occupies two slots and is located immediately to the right of the Controller Module.
The Power Supply Module has two AC / DC switching power supplies: one power supply is +5 V and the other is +24 V.
The Power Supply also has two relay outputs for use with remote annunciators and two low voltage inputs for emergency
generator applications.
Group Name Parameter Name
Power Supply
RS-485 Enable Interface (Yes) Enables RS-485 options Yes / No
TS-TPI
Controllers
Controller #
Groups
Group #
Comm 2
Enable Interface (Yes)
Number of Controllers (0)
Name Pump 1
Enabled (Yes)
Type (Unknown)
Address (0)
Group (0)
Tank (0) The tank number (where this Pump is located). 0 - 29
Height (5.00)
Number of inputs (0)
Number of groups (0)
Name Group 1
Mode (None)
Mode: None
Master / Slave (No)
Alternating (No)
Fault Shutdown (No)
Mode: Leveling
Master / Slave (No)
Fault shutdown (No)
Mode: Priority
Reserve (20)
Master / Slave (No)
Fault shutdown (No)
Baud rate (9600) Data transmission speed in bits per second. 1200-57600
Data Bits (8) Number of bits that represent data. 7-8
Parity (None) Value of parity (error check) bit. None, Even, Odd
Stop Bits (1)
Response Time-out (8)
Parameter
Default
Description
Enables TS-TPI options.
The number of controllers being monitored
Descriptive name used to identify input
Enables the output
The type of FE Petro Smart Controller • Variable
The slave address of the controller as congured by the
DIP switches on the Smart Controller.
The Group number this pump is in. Put Pumps located
in similar products into the same group for Leveling or
Priority mode.
The height of the Pump Motor Assembly off of the bottom
of the tank in inches.
The number of inputs that will have control over activating
and deactivating this Pump.
The number of Groups as assigned under controllers.
Descriptive name used to identify input.
Select the mode you want. (Refer to the TPI section for
more details).
Select yes if you want both pumps to run during periods of
high demand.
Select yes if you want the pumps to alternate when hook
signals drop out.
Select yes if you want both pumps to shutdown upon an
alarm.
Select yes if you want both pumps to run during periods of
high demand.
Select yes if you want both pumps to shutdown upon an
alarm.
The percent of volume that the pump will switch to the
next in the group.
Select yes if you want all pumps to run during periods of
high demand.
Select yes if you want all pumps to shutdown upon an
alarm.
Number of stop bits, noties receiving device of end of
data packet.
Period of time the device will wait until transmission stops
in seconds.
Parameter
Input
Yes / No
1-31
abc#
Yes / No
Frequency
• Smart
• Smart 1
• 3 Phase Smart
208/380V
• Mag/Eco
• Unknown
0 - 30
0 - 15
#
0 - 32
0 - 15
abc#
Leveling
Priority
None
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
# %
Yes / No
Yes / No
1-2
1-10
24
Page 29

Group Name Parameter Name
RS-232
Relays
Channel #
Input # Type (Unknown
Low Voltage Inputs
Channel #
LON
Baud Rate (9600) Data transmission speed in bits per second. 1200-57600
Data Bits (8) Number of bits that represent data. 7-8
Parity (None) Value of parity (error check) bit. None, Even, Odd
Stop Bits (1)
Response Time-out (8)
Name (Relay 1) Given name of the relay. abc#
Enabled (Yes) Whether the Relay is Enabled or not. Yes/No
Type (Unknown) Equipment connected to the relays output. Unknown
Polarity (Normal) Allows the polarity to be inverted. Normal, Invert
Logic (OR Logic) The type of logic that the gate will use to process incoming
Physically Wired As
Number of inputs (0) Number of devices that can control the relay. 0-32
Name (LV Input 1) Given name of input. abc#
Enabled (Yes) Whether the input is Enabled or not. Yes/No
Active State (high)
Action (None)
IFSF Node ID (1)
Parameter
Default
(Normally
Module)
Open)
Description
Number of stop bits, noties receiving device of end of
data packet.
Period of time the console will wait for a response from a
remote device.
signals. In OR, if any combination of inputs is active, the
relay is active. With AND, when all inputs are active, the
relay is active. In XOR, if all inputs are in the same state
(on / off), the relay is inactive.
How the relay is wired internally.
Chooses which module is inputting the signal to the relay. Unknown
High will activate channel when high voltage is present.
Low will activate channel with no voltage present.
Create an alarm or event timestamp None
Allows the T5 Series console to communicate with an
IFSF POS (Point of Sale) System
Parameter
Input
1-2
0-10
Submersible
Alarm
Solenoid
Dispenser
Other
OR, AND, XOR
NO, NC
Controller
Power Supply
IO
AE
4-20
Probe
2-wire Sensor
3-wire Sensor
High / Low
Alarm
Event
0-127
25
Page 30

Relay Modules
The Relay Module is a non-intrinsically safe module that has 8 identical Form C output channels. Each channel has a fuse
and three terminals. Each channel can be congured as NO or NC with the power off by wiring to the appropriate terminals.
Group Name Parameter Name
Relay Modules
Module # 10 Amp
Channel #
Input # Type (Unknown) Type of module that is sending the signal. Unknown
Channels
Name (Relay 1) Given name of the channel.
Enabled (Yes) Yes if the channel is in use.
Type (Unknown) Equipment connected to the relays output. Unknown
Polarity (Normal) Allows the polarity to be inverted.
Logic (OR Logic)
Physically Wired As (Normally Open) How the relay is wired externally.
Number of inputs (0) Number of devices that can control the relay.
Parameter
Default
(No)
(0)
Description
Select Yes if this is the 10 Amp relay module.
Number of relays used on this module.
The type of logic that the gate will use to process incoming signals.
Parameter
Input
Yes / No
0-8 (2 Amp
module)
0-6 (10 Amp
Module)
abc#
Yes / No
Submersible
Alarm
Solenoid
Dispenser
Other
Normal, Invert
OR, AND, XOR
NO, NC
1-32
Controller
Power Supply
AC Input
IO
Probe
2-wire Sensor
3-wire Sensor
4-20 mA
26
Page 31

Dispenser Interface
The Dispenser Interface is used in VRM and Reconciliation applications to communicate sales data from the dispensers
to the console.
Group Name
Dispenser Interface
Precision
Grades
Dispenser Interface Modules: DIM 1
Parameter
Name
Volume Precision (3) The number of digits to the right of the decimal point. 0-6
Dispenser Volume (Gross) Select Gross if the dispenser volume is not temperature
Number of Grades (0) The number of grades that are on site. 0 - 32
Name (1) Given name of Grade abc#
Include in Vapor
Recovery
Type (Wayne) The type of communication from the dispensers. None
Communication (Currant Loop) The communication protocol of the distribution box. None
Fueling Points
Number of fueling
points*
Number of hoses (0) The number of grades on this dispenser. 0 - 8
Hose # (1)
Grade
Association
Position (0) The number that was detected from the Query function after a
Parameter
Default
compensated.
(Yes) Select yes if this grade will be used in VRM.
(0) The number of possible fueling points on site
(Unknown) The grade that is associated with the rst hose you dispensed
from.
dispense.
Description Parameter Input
Gross / Net
Yes / No
Gilbarco
Wayne
Tokheim
G Site
Bennett 515
Current Loop
RS422 / 485
Tokheim STD
RS232 Duplex
RS232 RxD x 1
RS232 RxD x 2
0 - 32
Select the correct
grade from the
Grades menu.
0 - 9
* Q The query function is used to determine the Position number from the dispensers.
C Will copy the Position numbers and Grade associations to all like number of hoses fueling points.
The copy and query functions are available only via the Web Browser Interface.
If using the console touch-screen, the “Auto-congure” button
will initiate the query function.
27
Page 32

Programming FMS Parameters
Here is where specic equipment parameters will be modied to match the site setup.
Fuel Management System
Group Name Parameter Name
Ullage Percent (95) Percent of tank level used to calculate space left. 70-100 %
Fuel Management
System
Static Tank Testing
Tanks Number of Tanks (0) Number of tanks in fuel system. 0-48
Tank #
Probe Channel (Probe 1) Channel used for the probe in tank. Probe
Generator
Mode
SCALD
Delivery Delay (15 min) Time after delivery when increase is reported. # min.
Correction Temperature (60.00 °F) Product temperature correction. # °
High Product Limit (Level)
Region (United States) The region in which the gauge is located
Monthly Leak Test Threshold (0.20 gph) Static leak tolerance for testing tanks. # gph
Yearly Leak Test Threshold (0.10 gph) Static leak tolerance for testing tanks. # gph
Sentinel Mode Threshold (3.00 gph)
Condence (99%) Leak testing condence.
Minimum Leak Test Time (2 hr) Minimum amount of time used to test. 0-8
Maximum Leak Test Time (8 hr) Maximum amount of time used to test. 1-8
Alarm On Precision Leak Test
Failure
Name (Tank 1) Given name of tank. abc#
Type (Special 1) Type of tank. Std./Spcl.
Manifolded (No) Used for Manifolded tanks. Yes / No
Manifold # (1)
Product # ( 1) Type of product in tank. 1-48
Delivery Threshold (200.0 gal) Amount of increase to report delivery. # gal
Theft Threshold (5.0 gal) Amount of decrease to report theft. # gal
4-20 mA Output (None)
Monthly Compliance (Yes)
Annual Compliance (Yes)
Type (Standard 101) Type of probe used in this tank. Std./Spcl.
Ratio
Float Type (4 in gas) Type of oat(s) used on probe. 4, 3, or 2 in.
Water Float (Yes) Select Yes if water oat is present. Yes /No
Gradient
Product Offset (0.00 in)
Water Offset (0.00 in) # in
Enable (No) If generator testing is being used, select yes. Yes / No
Enable (No) Enables SCALD tank testing. Yes / No
Qualify (14 %) Required percent full to run SCALD test. # %
Parameter
Default
(No)
(1 to 1 tip to
head)
(9.03000 µs / in)
Description
Select whether the High Product alarm will be triggered
by high product Level or high product Volume.
If Sentinel Mode is congured, this is the amount of
volume that would trigger an alarm.
Used to produce an alarm upon failure.
If Manifold is selected, this option will allow you to
select a manifold number. Tanks that are Manifolded
should have the same manifold number.
If an IO module is used and the outputs are congured,
this option will appear. Select the correct output that
correlates to this tank.
Select Yes if this tank is to appear on the Compliance
page and in the Regulatory report.
Select Yes if this tank is to appear on the Compliance
page and in the Regulatory report for annual tank testing.
Ratio of oat movement in proportion to product level.
1:7-9 for use with Moorman gauge interface.
Speed of probe wire. # µs/in
Used for compensation of tank tilt. (See Appendix xx:
Calculating Tank Tilt).
Parameter
Input
Level / Volume
Other
United States
Spain
#
90, 95, 97.5,
99 %
Yes/No
1 - 24
None
Output 1-4
Yes / No
Yes / No
1:1; 1:7; 1:9
Gas/Diesel,
Stainless,
Propane
Gas density
Diesel Density
# in
28
Page 33

FMS Parameters Continued
Group Name Parameter Name
Fuel Management System
Special Tanks
Special #
Special Probes
Special # Length (101 in) The length of the special probe #
Shape (Horizontal
Length (160.00 in) Length of tank in inches. # in
Diameter (96.00 in) Diameter of tank in inches. # in
End Type (Cylinder)
Dome style (Spherical)
Dome Radius (0.00 in)
Correction table
Maximum number of points (0)
Data # Enter known volume for a designated level Level / Volume
RTD Table (0.00 in)
Parameter
Default
cylinder)
Description
Physical shape of the tank.
Type of the end of the tank Cylinder
The type of dome end Spherical
Radius of domed end
The number of strapping data points that will be
entered. Begin with 0 inches and 0 volume and end
with maximum diameter and capacity.
The distance to the rst RTD location. (+ adds
positions, typically 5 in total)
Manifold Tank System
Group Name Parameter Name
Fuel Management System
Manifolds
Name (Manifold 1) Given name of manifold. abc#
Product # (1) Number of product in tanks. 1-48
Delivery Threshold (200.0 gal) Amount of increase to detect delivery. # gal
Theft Threshold (5.0 gal) Amount of decrease to detect theft. # gal
Monthly Compliance (Yes)
Low Product Volume Limit (0.0)
Low Low Product Volume
Limit
Enable (No) Enables SCALD tank testing Yes / No
Qualify (14%) Required percent full to run SCALD test #%
Name (Product 1) Given name of product abc#
Type
Manifold #
Limits
SCALD
Products
Parameter
Default
(0.0)
(Unleaded
Regular)
Description
Select Yes if this manifold is to appear on the
Compliance page and in the Regulatory report
The volume that will trigger the Low Product alarm.
The volume that will trigger the Low Low Product
alarm.
The type of product
Parameter
Input
• Horizontal
Cylinder
• Vertical
Cylinder
• Rectangular
One domed end
Two domed ends
Ellipsoidal
0-600
0-100
# In
Parameter
Input
Yes / No
# gal
$ gal
Unleaded regular
Unleaded plus
Unleaded extra
Unleaded super
Diesel
Kerosene
#2 Fuel Oil
Ethanol
Special Product N
29
Page 34

Manifold Continued
Group Name Parameter Name
Special Products
Special N
Lines Number of lines (1) Number of tanks in the fuel system 0-48
Line# Name (Line 1) Given name of line abc#
Gross Test Enable
Monthly Tests
Annual Tests
Grades
Grade 1
Correction Type (Table 6A) As dened by the fuel provider
API Gravity (63-500)
Alpha (600.000) As dened by the fuel provider #
Density (500.0) As dened by the fuel provider #
Mole Weight (130.000) As dened by the fuel provider #
Vapor A (12.101) As dened by the fuel provider #
Vapor B (8,907.000) As dened by the fuel provider #
Submersible Pump module (Relay Module) The module where the STP is connected
TPI (Yes)
Submersible Pump Channel (Relay 1) Select the Relay that is associated with this line.
Transducer (4-20mA Input 1) Select the correct transducer for this line LLD#
Enable SLLD (Yes)
Product (None) Select the Product associated with this input. Product N
Enable (No) Select Yes to enable line leak detection. Yes / No
Monthly Compliance (Yes)
Annual Compliance (Yes)
Pressure Up Test Wait Time
Catch Pressure Wait Time
Dispenser Pressure Test
Catch and Sudden Pressure
Test
Enable
Shutdown on Test Fail
Fails Before Shutdown
Enable
Wait Period Between Passed
Tests
Shutdown on Test Fail
Fails Before Shutdown
First Tank
Second Tank
Blending Ratio
Parameter
Default
(4 sec)
(2 sec)
(Yes)
(Yes)
(Yes)
(Yes)
(Yes)
(1)
(Yes)
(0 Days)
(Yes)
(1)
(Tank 1)
(None)
(100.00%)
Description
As dened by the fuel provider
This option will appear if you select the Power Supply
Module or controller # and TPI is being used.
Select yes to enable Statistical Line Leak Detection
software.
Select Yes if this Line is to appear on the Compliance
page and in the Regulatory report.
Select Yes if this Line is to appear on the Compliance
page and in the Regulatory report for annual tank
testing.
The amount of time to wait for Pressure to develop
after demand has been made
The amount of time to wait for the pressure to stabilize
after dispensing has nished
Select Yes if dispenser Pressure Test should be
performed.
Select Yes if Catch and Sudden Pressure Tests should
be performed.
Select Yes to Enable Gross leak test of 3 gph.
Select Yes to Enable monthly leak tests of 0.2 gph.
Select Yes to disable dispensing upon a failed test.
The number of fails before the system will disable
dispensing.
Select Yes to Enable Annual leak tests of 0.1 gph.
The amount of time the system will wait after a passed
annual test before starting another one.
Select Yes to disable dispensing upon a failed test.
The number of fails before the system will disable
dispensing.
Select the tank that Grade 1 is associated to.
Dependent on how many tanks and the tank names
Select a second tank if this grade is blended
Select the amount of product is blended from the rst
tank
Parameter
Input
Table 6a
Table 6b
Table 6c
Relay Module
Power Supply
Module
Yes / No
Relays
Pumps
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
1-8 sec
1-4 sec
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
Yes / No
0, 7, 30, 90
Yes / No
#
1-3
1-3
abc
abc
#%
30
Page 35

Group Name Parameter Name
Over Short Limit Percent (1.00%) Gives the allowed amount on variance report 0-100%
Over Short Limit Volume (130.0 gal)
Reconciliation
Autocalibration
Sales (Yes)
Deliveries (Yes) Yes / No
Tank Volume (Yes) Yes / No
Autostop Volume Coverage (100%)
Autostop Level Coverage (80%)
Autostop Number of Points
Coverage
Vapor Recovery Monitoring
Group Name Parameter Name
Vapor Recovery Monitoring
Method Type
Hour Assessment
Week Day Assessment
Parameter
Default
Combines with the Over Short % to give allowed
variance
Select what info is Included to create variance report
How much volume must be used before the
Autocalibration stops.
How much level must be used before the
Autocalibration stops
(100)
How many tank chart points must be created before
Autocalibration stops.
Parameter
Default
(Assist) Select Assist if vacuum pumps are used or Balance if
(0) Select the time of day the site wishes to have the daily
(Sunday)
a balance system is used.
calculations.
Select the day of the week the site wishes to have the
weekly results calculated.
Description
Description
Parameter
Input
#
Yes / No
#%
#%
#
Parameter
Input
Assist
Balance
0-23
Sunday - Saturday
Dispenser
Conguration Dispenser Type
Multihose Dispenser Site (Yes) Select yes if the site is using mulithose dispensers. Yes / No
Number of Dispensers (0) Select how many dispensers are on site. 0-16
Dispenser N
Ullage Pressure Input Sensor (4-20mA Input 1) Select the 4-20mA input that the TS-VPS is associated with. 4-20mA input
Ullage Volume Input
Tank # Ullage Enable (Yes)
First Fueling Point (1)
Second Fueling Point (2) Select the second Fueling Point that is associated with
Third Fueling Point (3) Select the third Fueling Point that is associated with
Flow Meter (Probe 1) Select the Flow Meter that is associated with this
Acquire Ullage (Internal)
Security Code (Blank) Enter external ATG’s Comport security code. abc#
Number of Tanks (0)
(Wayne)
Select the type of dispensers.
Select the Fueling Point that is associated with this
dispenser.
this dispenser.
this dispenser.
dispenser.
Select Internal if system has FMS software. Select
External if system acquires Ullage input from another
tank monitor.
Enter the number of tanks as programmed in the
external ATG.
Select yes if Vapor Recovery is to be enabled on this
tank.
Wayne
Gilbarco
Other
Probe 1 - 12
Internal / External
Secondary Containment Monitoring
Group Name Parameter Name
Secondary Containment
Monitoring
Containment N Name (Containment 1) Given name of the containment abc#
Number of Containments
Enabled (Yes) Select Yes if this containment will be monitored. Yes / No
Pump Shutdown on Alarm (No)
Submersible Pump Module
TPI (No) Select Yes if TPI is controlling the STP. Yes / No
Submersible Pump
Channel
Transducer (4-20mA Input 1) Select the transducer that is associated with this
Parameter
Default
(0)
(Relay module)
(Relay 1) Select the channel that has control of the STP that is
Select the number of containments present. 0 - 48
Do you want to disable the pump on a containment alarm?.
Select the module that has control of the STP that is
associated with this containment.
associated with this containment.
containment.
Description
Parameter
Relay Module
Power Supply
None
1-32
None
1-32
None
1-32
0 - 48
Yes / No
Input
Yes / No
Module
Relay #
Pump #
4-20mA
#
31
Page 36

E-Mail
Group Name Parameter Name
E-Mail
“From” Address
SMTP Host
SMTP Port 25 Port address of SMTP. #
Enable Authentication No Data authentication (if required). Yes / No
Maximum Queue Size 20 Maximum size of queue in Megabytes.
Retry Timeout 3600 Time, in seconds, that the console will wait before attempting
Watchdog Timeout 30
Enable Debugging (No) Select Yes if you would like more status information to be
Parameter
Default
your_from@address.
com
your_smtp_host_
address
Description
Address of sender (console). abc
IP address of SMTP Host. #
to resend the message.
Time, in seconds, that the console self-monitoring program
waits when it expects and error due to software or power
quality problems.
stored in the Messages le.
Parameter
Input
Yes / No
System Sentinel Anyware
This section will be lled out automatically upon the initial polling by System Sentinel Anyware.
Events
Group Name Parameter Name Parameter Default Description Options
Rules: Rules are a logic-based programming that are driven off of “If” based Events and “Then” Based actions. Essentially: “If” this event occurs
“Then” the console will perform a specied action.
Rule – New Rule # Name (New Rule #) Given name of rule. abc#
Events: Events can be both “If” logic and “Or” Logic. Therefore you can have several events trigger the same action. “If” Event 1 “Or” Event 2
occurs the console will perform a specied action.
Event
Action: Actions are sequentially “Then” / ”And” driven. Therefore, “If” an Event occurs “Then” the console will perform Action 1 and then Action
2 and then Action 3.
Action Type (e-mail) Action that will occur upon event E-mail, Report, Relay, Tank
Enabled (No) Yes to enable rule. Yes/No
Type (New Alarm Occurred) Event type that triggers action. New Alarm Occurred;
Category (Any) System that event occurs in to trigger
action.
Code (Any) Error/Trouble Event Code that triggers
action.
Device (Any) Device that created the alarm
condition.
State (Any) State of alarm to trigger action. Various
Address your,email@address.com Where it will send e-mail
Contact Generated What e-mail format is used Generated, Text, HTML, Other
Template Text E-mail Template HTML, Text, short text
Alarm Status Changed;
Application Event;
Scheduled
Any;
System;
FMS;
VRM;
SCM;
Other
(see below)
Various
Testing, Line Testing, Sentinel
mode, Reconciliation, sound,
Notify SSA, Sample input,
STP Control, Generator
32
Page 37

Web Browser Interface
Navigating Applications Remotely
The Web Browser Interface offers several ways to navigate through applications:
• Easy-to-read web pages that use hyperlink text (words or characters that, when clicked, take you to another page) to
move through the menus,
• Text and drop boxes and buttons allow inputs to be made efciently,
• On-screen prompts automatically pop-up instructions to verify each step.
Not all application functions, like Network Congurations, are available at all levels. To access these options, you need to
be logged in at a high enough User Role.
Accessing the Web Browser Interface
1. To access the console using a computer, open a web browsing application.
2. Type the IP address (the default IP Address is 192.168.168.168) into the address bar of the browser window. To
access the console using a remote PC, setup communications per Section 2 of this manual. When using a PC to
access console applications through a direct or network connection, a T5 console incorporates a XML (eXtensible
Markup Language) based access method. If the console is equipped with an optional LCD screen, the connection
settings may be modied using the touch screen function of the console.
Making Changes to System Parameters
1. To make any changes on a settings page, click Edit.
2. Once the preferred selections have been altered, click the conrmation option Yes in the yellow shaded area near the
top of the window.
3. At this point, the system may prompt for a password.
Password Prompting
After changes have been made to the consoles parameters, if the appropriate access level has not been entered, the
system will prompt for a password.
If you haven’t obtained the appropriate access level, you will be prompted “Error: Insufcient privileges” in a red shaded
area, near the top of the window.
1. Type the password for the access level required to save changes into the text-box and click Apply.
2. You will then be prompted again to save your changes; click the conrmation option Yes in the yellow shaded area
near the top of the window.
When you’ve nished conguring your programming options, keep system security in mind and, to prevent unauthorized
personnel from gaining access to console congurations, lower the access level to Guest. To do this from the Web
Browser Interface, click T550 System - Guest access level. Notice that the User Role changes back to Guest.
Setup
The programming options for the Web Browser Interface are identical to the LCD interface; however, they are represented
differently due to their respective graphical interfaces. Use the programming tables in Section 3 as a reference in
programming your console with a web browser.
33
Page 38

Backup Setup Files
Download
Backup allows you to download the setup le and store it on any PC connected to the console. This le can be uploaded
to the console to recover lost settings or copy settings from one site to another.
1. Open a web browsing application, type the IP address (the default IP address is 192.168.168.168) into the address bar
of the browser window.
2. The console will navigate to the Home Status page, indicated by the word Status displayed in the header.
3. Left-Click once on Setup.
4. To download a site conguration, click Download. A File Download dialog box may appear, and, if it does, select Save
to open an explorer window.
5. Select a location to save the conguration le.
Then, type the File Name you want to create. Use
something that identies the le with the site and
represents the date saved. Click Save.
The le is now stored in the location of your
choice and ready to upload when necessary. It is
recommended that a backup copy of this le is
created and stored on another medium, to ensure
that the le’s integrity is maintained.
34
Page 39

Upload
When required, the backup conguration le will need to be reloaded onto the console to restore a previous setup. When
uploading, it is important to remember that network parameters may be affected by the change, rendering it unreachable
from a remote location. If the downloaded le contains an IP address different from the one currently in use, someone will
need to locally reprogram the correct address into the console in order to communicate remotely.
1. Open a web browsing application, type the IP address (the default IP Address is 192.168.168.168) into the address bar
of the browser window. The console will navigate to the Home Status page, indicated by the word Status in the header.
2. Left-click once on Setup.
3. To upload a conguration le, click Upload on the Setup page. At this point, the console may prompt for a password if
the proper access level has not been obtained.
4. An Upload Conrmation window will open. Left-Click Browse to locate the correct le. Click on the le name, and then
click Open.
This process may take a few moments for the console to apply the settings and reboot. To indicate that the update was
successful, you will see this notication window.
35
Page 40

Leak Testing
All T5 series console models meet (or exceed) the
requirements of the U.S. Environment Protection Agency
(EPA / 530 / UST-90 / 006 test protocol) for Automatic Tank
Gauging Systems (ATGS) for Monthly Monitoring for 0.2
gal/hr leaks of Underground Storage Tanks. The system(s)
also meet (or exceed) the requirements for Annual Tank
Tightness Testing for 0.1 gal / hr leaks of the National Work
Group on Leak Detection Evaluations (NWGLDE). For the
most recent third-party documentation, visit the NWGLDE
website at www.nwglde.org.
Overview
Tank and / or line leak tests are performed on a regular
schedule according to test type. In addition, leak tests
can be started manually from the console display or web
interface.
To obtain valid results, leak tests should be started when
conditions in the tank or line are stable and will remain
stable throughout the test (such as during non-business
hours). A test will not and can not pass if tank and/or line
conditions are disturbed. Deliveries and dispenses will
cause thermal instability or product turbulence, which
will interfere with tank leak testing. These disturbances
may cause the test to report a failure, an increased
result, or cause the test to run for 8 hours and report an
indeterminate test result. Wait at least 6 hours after a
product delivery, and 2 hours after product dispensing
stops, before forcing Tank Leak Tests.
Generally, tank tests take about 4 to 5 hours to nish (the
exact time required depends on the type of test being
performed, size of the tank, volume of product in the tank,
and the product temperature).
The best time to test the tank integrity (leak test) is when it
is full or nearly full. Regulatory requirements in some areas
insist on having a certain percentage of product in the tank
before a test can be considered valid and in compliance.
Try to run tests on tanks that are 50% full or greater.
SCALD leak tests can run only when tank levels are at or
above the set “Qualify” value.
Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency
Tank Testing software (option T) includes Static and
SCALD tank testing. Both tests comply with federal, state
and local codes and regulatory agencies, which specify
how often to run these tests. Consult and comply with
these rules and regulations.
Caution
Static Tank Testing Requirements
• Print a leak test Estimate Report.
• There must be enough quiet time to nish the test
with no product dispensing.
Note: A 10,000 gallon tank requires about 5 or 6 hours to
nish.
• Wait at least 6 hours after a product delivery – or
– 2 hours after a product dispense. Active tanks
without Stage II vapor recovery may require longer
stabilization periods.
FFS does not recommend running both Line & Tank
Leak Tests at the same time.
When to Force Static Tank Leak Tests
• To comply with federal, state, and local regulatory
agency requirements.
• To comply with the policy and procedures of your site.
• Whenever a leak detection sensor alarms — this
is especially important when a discriminating
BriteSensor detects a liquid / vapor hydrocarbon
(product). A failed leak test and BriteSensor product
alarm indicates a tank or product-line leak.
Note: Standard / product alarms may be caused by
motor oil runoff during heavy rains, or because a
BriteSensor has detected a product leak from a
tank. Take a sample from the area for chemical
analysis.
It is the tank owner’s obligation to
comply with the procedures and the
reporting requirements of federal, state
and local regulations. You are legally
bound to follow these regulations
explicitly. When policies conict with
this manual, follow the regulations.
36
Page 41

Manually Forcing Static Leak Tests
1. To force a Static Tank Leak test, press the FMS button
in the Application Window.
4. The FMS Control Menu will display the systems
available for testing. To view control options for the
tanks system, press the Tanks button.
2. Press the Application Menu button.
3. Select the Control button in the FMS Menu.
5. On the FMS Tank Control Screen, press the button that
corresponds with the tank to be tested.
6. Touch the screen to highlight the desired test, then
press the Checkmark button to begin the testing
process.
37
Page 42

Tank Leak Test Results
Leak test results are either increase, passed, failed, or
indeterminate.
Reasons Why Tank Leak Tests Fail
• The tank leaks.
• Temperature instability – temperature variations of the
product within the tank after a delivery is the most common source of interference and failed leak tests / false
alarms (a failure to detect real leaks can also result).
Look at the hourly temperature data on the leak test report and retest if the variation is more than a few tenths
of a degree.
• Large changes in product temperature from the start to
the end of the test.
• Water Level changes during the test.
• Evaporation and loss of product through the vent
stack will look exactly like a leak. Evaporation can be
a problem during high seasonal temperatures and/or
high winds, and when liquid level exposes the greatest
surface area for evaporation (half full tanks are worse).
Seasonal variations in product composition, size of the
tank (larger is worse), and tank vent conguration are
also evaporation factors.
• Tank Deformation -- the tank changes shape after a
large product delivery.
• Tidal Action – in coastal communities, groundwater levels maybe be affected, and, as a result, may deform the
tank. During certain times of the day, the tide changes
inconsistently.
• Tank Cross-Talk – level changes in one tank causes a
level change in an adjacent tank or compartment.
• Product is being dispensed during a test.
Steps to Take When a Tank Leak Test Fails
Leak tests do occasionally fail and a single failed leak test
should not be a cause for great concern. Remember, if the
condence level of the test is 99%, there is a 1% chance
that the system will give a false answer.
Caution
If you fail a leak test, review the leak test report to
determine if there is an obvious source of interference with
the test (see the Causes of Leak Test Failures section for
an example of a Tank Leak Test Report). If such a source
of interference is identied, retest the tank as soon as
possible. Retest the tank to validate or invalidate the rst
test result if no source of interference can be identied. If
necessary, run several tests.
If repeated tests indicate a leak and no obvious source
of interference is found, then immediately have the
tank precision / pressure tested. If the precision test
conrms the presence of a leak, then the tank owner
must take corrective action in accordance with federal,
state and local regulations.
Don’t excavate / repair a tank because
of a single failed leak test. Reference
your site policy and procedures plan.
Warning
The owner of the tank is legally
obligated to comply with reporting and
procedural requirements of federal,
state and local regulations. These
must be followed explicitly. Serious
legal, health and safety hazards could
result from not taking immediate and
proper action. If codes and regulations
conict with this manual, follow the
regulations set by governing agencies.
SCALD Tank Leak Tests
SCALD (Statistical Continuous Automatic Leak Detection)
is optional on Franklin Fueling Systems tank gauges. It
runs 24 hours a day and is used to perform 0.2 gph tests
on tanks that are always in use.
SCALD works by collecting Quiet Intervals (QIs) in
between dispensing. A QI is obtained when a thermally
stable tank is idle for 20 minutes with no dispensing, no
deliveries and no other movement of the probe oats.
Once four QIs are collected, the Automatic Tank Gauge
(ATG) will analyze the data and either Pass, Fail, Increase
or discard that test because the data is not statistically
sound. Four QIs can be collected over a period of several
days or weeks.
• If the result is a Pass, then a test result of Pass will be
generated.
• If the result is Fail or Increase, then another test will be
run to ensure that this is not a false alarm. Three Failed
or Increase tests in a row will produce a test result of
Failed or Increase.
• If the data is not statistically sound, then the test is discarded. No new test result will be generated and SCALD
will continue to run. The fact that a result was discarded
is recorded and can be seen in the Status number that
accompanies the next generated test result.
•
On rare occasions certain conditions can arise that can
prevent SCALD from getting enough QIs to complete a test.
Reasons Why SCALD Tank Tests may Fail
• Temperature
• If a site receives deliveries where the temperature of the
fuel being delivered is several degrees different then the
fuel in the tank, then SCALD will not be able to collect
QIs due to thermal instability. The temperature of the
fuel can not change more than .01°F during a 20 min QI.
• If a pump control relay is stuck closed and the pump is
running all of the time, the temperature in the tank can
be much higher than the other tanks. Due to this high
temperature and the fact that the pump is running and
causing turbulence in the tank, no QIs will be collected.
• No Quiet Time
• SCALD needs four 20 minute QIs in order to complete
a test. These QIs are normally found in the early morning hours. If a site is so busy that there are no 20 minute
periods of no dispensing, then SCALD will not be able to
complete a test.
38
Page 43

TS-LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak Testing
Overview
A 0.2 gph and a 0.1 gph test line leak tests can be started
from the console. Some jurisdictions recommend that a
0.1 gph annual precision line leak test be run yearly.
The 0.2 gph test runs automatically on a daily basis.
The coarse 3 gph line test runs automatically after every
dispense. State and local regulations may require more
frequent tests and inspections. Make sure your site
personnel are aware of all of the issues and requirements
comply with these regulations.
Caution
Line Leak Test Requirements
• Create adequate quiet time – Prevent and stop all
dispensing, on the line to be tested, before and
during a test (bag or tape poly over dispenser and
dispenser lever).
• GPH precision tests normally need 4 hours of quiet
time (where no dispensing occurs) before the test is
started. Usually the test takes 13 minutes to complete.
• 0.2 GPH monthly tests normally need 13 minutes to 4
hours of quiet time to nish.
When to Force Line Leak Tests
• To comply with Federal, State, and local Regulatory
Agency requirements.
• To comply with the policy and procedures of your site.
• When a leak detection sensor alarms – per policy
and procedures at your site.
Manually Forcing Line Leak Tests
Lines MUST be calibrated and enabled before forcing
leak tests.
1. To force a Line Leak test, press the FMS button in
the Application Window.
2. Touch the screen to highlight the desired test,
then press the check-mark to begin the testing
process.
It is the tank owner’s obligation to
comply with the procedures and the
reporting requirements of federal,
state and local regulations. You are
legally bound to follow these explicitly.
Where they conict with this manual,
follow the regulations.
Line Leak Test Results
Line Leak test results are either increase, passed, failed,
or indeterminate.
Reasons Why Line Leak Tests Fail
• The tank leaks.
• Temperature instability – temperature variations
of the product within the line is the most common
source of interference and failed leak tests / false
alarms (a failure to detect real leaks can also result).
Look at the hourly temperature data on the leak test
report and retest if the variation is more than a few
tenths of a degree.
• Large changes in product temperature from the start
to the end of the test.
• Water Level changes from the start to the end of the
test.
• Product is being dispensed during a test.
Steps to Take When a Line Leak Test Fails
Leak tests do occasionally fail. A single failed leak test
should not be a cause for great concern – don’t panic.
Caution
If a site fails a leak test, review the leak test report to
determine if there is an obvious source of interference with
the test. If such a source of interference is identied, retest
the tank as soon as possible. (Retest the tank to check the
rst test result if no source of interference can be identied.
If necessary, run several tests.)
If repeated tests indicate a leak and no obvious source of
interference is found, then immediately have the tank
precision / pressure tested. If the precision test conrms
the presence of a leak then the tank owner must take
corrective action in accordance with federal, state and
local regulations.
Don’t excavate / repair a line because
of a single failed leak test. Reference
your site policy and procedures plan.
39
Page 44

DTU (Data Transfer Unit) Setup and Programming
1. Under Setup / System Conguration/Modules Expected, set Console DTU to 1.
2. Under Setup, locate Remote DTUs. The Network ID number will be defaulted to 1.
3. Enter the number of Remote DTUs installed in Number of Units.
Note: Remote DTUs refers to the units in dispensers only.
4. For each Remote Data Transfer Unit, you must enter the unique Unit ID #. This number can be found on the label
included with each Remote DTU. Enter this number for each one.
5. Under PROBE MODULES, locate REMOTE MODULE (DTU) and enter the number of Remote Data Transfer
Units installed. Each Probe channel refers to the VFM channel on the Remote DTU. The maximum number of
channels per REMOTE MODULE is 12.
6. For each Channel, enter a name for the Vapor Flow Meter connected to the channel.
7. Select TS-VFM for the type.
8. If more than 12 channels are necessary, program REMOTE MODULE (DTU). If there are no internal Probe
Modules congured then the rst Remote Module will be 1. Follow Steps 5 through 7 to complete all DTUs in the
system.
40
Page 45

9. Under Setup/4-20mA Input Modules (DTU) / locate Remote Module 2 and enter the number of DTUs installed.
The maximum number of channels per a 4-20mA Input Module is 8.
10. If more than 8 DTUs are used, program the next Remote Module. Follow steps 8 and 9 to complete the
Remote Data Transfer Units
11. For the 4-20mA Input Module programming, one channel will correspond to the dispenser that houses the ISD
Pressure Sensor. This channel is setup as follows;
12. Enter a Name for the ISD Pressure Sensor
13. Select Service Type Vapor Recovery Monitoring
Diagnostic Page
The diagnostic page can give information about the functionality of the installed DTUs. The page can be viewed from
Home / System / Diagnostic / DTU Status
The Remote DTU column will list each DTU in the system. The Software Version column will identify the current
software version is each of the installed Remote DTUs. Verify that each DTU has a software version listed. A software
version listed as ?.?.? is an indication of a problem with the DTU.
Software Version
In rare cases, network trafc from other stations or companies may cause communication conicts. In these cases,
Network ID numbers will need to be changed. To help identify the possibility of network interference, locate Network
Packages section of the DTU Status Diagnostic page. If a number other than 0 is listed under From Other Network, a
conict may exist. In this case, the Network ID number should be changed. Call Tech Support for more information.
41
Page 46

DIM Programming
1. For Web Browser programming capability, connect a computer to the T5 series tank gauge. (See programming
section of this manual for connection information)
2. From the Home screen, click Setup
3. Click System Conguration, then Modules Expected.
Note: The TS550 and TS5000 tank gauge systems can be built with the DIM module installed in the console. It is also
possible to have DIM capability installed by a technician in the eld. For information on installing the DIM module in
the eld, refer to DIM Module Installation Guide (part 000-2044)
4. If the TS550 / TS5000 was sent with DIM capability, verify that under Modules Expected, DIM is set to 1.
5. If the DIM module was installed in the eld, you may need to set DIM to 1. Click on Edit in the upper right corner
of the screen to allow the DIM setting to be changed to 1.
6. Under Setup, click on Dispenser Interface / Precision.
7. Volume Precision refers to the number of digits to the right of the decimal. It will only affect how the information
is displayed. Default is 3.
8. Dispenser Volume can be entered as Gross or Net.
a. Gross-not temperature compensated (typical US)
b. Net-temperature compensated (typical Canada)
9. Under Dispenser Interface, click Dispenser Interface Modules
10. Type refers to the manufacturer of the Dispenser Distribution box. Select the type from the drop down list.
Some typical examples:
• Gilbarco-Universal D-Box (PA0261 Series)
• Wayne-Wayne/Dresser D-Box
• GSite-Gilbarco MOC G-Site and Passport Systems
• Tokheim-M98, M94 Power Center, 67 DBoxes
42
Page 47

11. Communication refers to the method of communication used by the corresponding distribution box.
Some typical examples:
• Current loop-Gilbarco PA0261x000011-PA0261x00020, Wayne/Dresser D-Box
• RS422/485-Gilbarco PA0261x000011-PA0261x000021
• RS232 Duplex-Gilbarco MOC G-Site Systems
12. Under Dispenser Interface, select Grades.
13. Number of Grades refers to the number of grades used at the site. Select the appropriate number from the drop
down list.
14. Enter a Name for each grade entered in Number of Grades. This text box will allow entries of specic names per
customer request.
43
Page 48

15. Under Dispenser Interface, select Fueling Points.
Note: A Fueling Point is anywhere a vehicle can stop and dispense fuel. Most dispensers have two fueling points. (front
and back).
16. Select the Number of Fueling points from the drop down list.
17. Under Fueling Points, select Fueling Point 1.
18. Select the Number of Hoses from the drop down list.
Note: Hose is dened as “each type of product that can be dispensed from a fueling point” A fueling point with only one
physical hose, but three available grades, would be entered as Number of Hoses = 3.
19. Under Fueling Point 1, select Hose 1, then Grade Association.
20. Select from the drop down menu the grade associated with Hose 1. Click OK.
21. Select Position.
44
Page 49

There are two ways to program the Hose Position:
• Manually-If you know the D-Box grade position you can manually select the Position number from the drop down
list.
Query Button
• By selecting Q next to the Fueling Point, the gauge will automatically Query the D-Box and ll in the information. For
the Query function to work, all equipment must be installed and connected, and all positions must be set to 0.
After hitting the Query button, you will be prompted that programming for that fueling point will be overwritten. Select OK.
You will then be prompted to dispense a small amount of product (approximately 0.03 gal.) Follow the on-screen instructions.
The positions will then be automatically entered into the programming. If other fueling points are identical, simply hit the
Copy button © and the positions will ll in. There is no need to re-query and dispense fuel if fueling points are identical.
Rules
Rules can be used to generate the DIM reports.
The following is an example of generating a daily reconciliation report:
In the example above, two rules are used. The rst rule Rule-Reconciliation Report is used to dene the start time of the
reconciliation period. In this case , 5:00 a.m. The two actions are used to 1) Open a new period, which closes the last one,
and 2) Generate a Summation Report. When a summation report is generated, it is stored, but not printed.
To print the report, a second rule is established. In the example, this is the Print Reconciliation Report rule. A DIM
reconciliation report can be printed per the customer’s request.
45
Page 50

Dual DIM Installation
W1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
BR 1
BR 2
DB (7/8) Host 1
P 1
P 2
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Jumper Detail
W2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
BR 1
BR 2
DB (7/8)
P 1
P 2
A1
A2
A3
Aux
Device
Address
Some sites and dispenser congurations may require
the use of a second DIM module that would be installed
externally to perform reconciliation or VRM. This section
outlines the special installation steps required to install a
second TS-DIM on a T5 series console.
Hardware Conguration
In order for the external TS-DIM module to communicate
properly with the T5 series console a few jumpers will
need to be adjusted. To make these adjustments the cover
of the TS-DIM will need to be removed to access the
jumpers.
Top View of TS-DIM Main Board
J3
AC pwr
Diagnostic Port
J4
Host1/
Rs485
J5
RS485
Link to
next box
J2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Auxilliary/RS232
J1
Host1/RS232
W2
2 10
1 9
Pinouts for
J4 & J5
A 1
B 3
GND 2
W1
1
2 10
1 9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
RTS
W3
+
-
Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx
Diag Host1 Aux
J6
1 Adapter Connector
J8
Device Address
The internal DIM module in the T5 series console will
always be addressed as zero. By default an external TSDIM will come shipped with an address of zero also. For
these two devices to exist on the same system the external
TS-DIM will need to have it’s address changed to one. Set
the external TS-DIM’s address to one by placing a jumper
on row 6 of W2.
Communication Settings
Once the external DIM has been addressed properly
the communications for the Host 1 port will need to
be changed to match the internal DIM communication
settings. The internal DIM’s communication settings
are: 9600 Baud Rate, 8 Data Bits, No Parity. To
properly congure the communication setting
on the external DIM you will need to place
jumpers on the following rows 1, 2, and 3 of W1.
Wiring the TS-DIM to a T5 Series Console
Turn off the main power source / all
Warning
1. Make sure all power to the T5 Series console is
turned off at the power source.
2. Locate the Communication Ports on the T5 series
console.
3. Terminate the wires as follows:
a. Wire 485A to Terminal 485A
b. Wire 485B to Terminal 485B
c. Wire S.RTN to Terminal GND
Note: There may be RS-485 interface wires already
connected to the terminals. In this case, remove
the wire(s) and splice them with the appropriate TSDIM wire. Reinsert these into the correct terminal
and tighten the screw.
power sources that terminate in the
console before working on or servicing
this equipment. Failure to do so will
create a lethal electrical shock hazard.
46
Page 51

TS-TPI Overview and Functionality
Tank fuel management can be achieved using a Franklin
Fueling Systems T5 Series Fuel Management Systems
and an FE Petro Turbine Pump Controllers (STP-SC1,
EcoVFC or MagVFC). Refer to Bulletin TB1010-04 for
connecting to an STP-SCIII controller.
Tank Fuel Management looks at percent (%) full volume of
individual tanks and gives priority to the submersible pump
needed to control tank inventories. Additional features and
benets of the Tank Fuel Management system include:
• Tank Overll Protection
• Dry Tank Indication
• Automatic pump controller reset
• Clogged Intake Indication
• Pump in Water Indication.
Tank Fuel Management can be used to keep tank levels
similar, eliminating the need for a syphon system. Tank
Fuel Management can also be used to pump down one
tank to a user dened level, and then switch over to the
other tank for fuel dispensing. In either case, there must be
at least one submersible pump in each tank.
TS-TPI Overview
The TS-TPI programming function allows the controllers
to be “grouped” together, and be programmed for specic
fuel management options. These options are NONE,
LEVELING, and PRIORITY
• NONE means NO level management for the selected
pump group. (Default setting.)
• LEVELING mode seeks to maintain an equal level
of fuel in each tank by placing pump controllers
associated with the tank containing the most amount
of fuel to priority. This will force the pump installed in
the tank with the highest level of fuel to activate with
the next activation of a dispenser switch.
Note: Leveling is achieved using level as percentage
volume full. The tank gauge will look at levels
in a tank as % full, and will attempt to keep that
number equal between all tanks in LEVELING
mode. If tanks are different sizes, the levels in
tanks may not be equal, but the % full for each
tank will be similar.
• PRIORITY mode tries to pump down one tank before
switching to other tank(s). After choosing PRIORITY
mode, the technician will program the RESERVE
setting. The reserve level is input as a percent full in
the tank. When the RESERVE level is reached for
that tank, priority will switch to the pump in the other
tank. If both tanks are below RESERVE level the ATG
will automatically use Leveling until tanks receive a
delivery of fuel or reach Dry Tank Indication Levels.
Note: In both Leveling and Priority modes, the ATG
chooses which pump will take priority. Because
of this, the pump controllers should be set to
Master-Slave, not Master-Slave / Alternating
Circuit. If the pump controllers are congured for
Master-Slave / Alternating Circuit, the pumps will
not turn on in a predicable manner. Tanks that
are in Leveling or Priority mode are monitored
and tested as separate tanks and should NOT be
siphoned.
Other T5 series TS-TPI functions include;
Overll Protection: when the LEVELING and PRIORITY
modes are chosen, if a tank level rises above its high level
limit, that tank will become the priority tank, regardless
of what leveling mode is active. If the level in that tank
continues to rise and reaches the high-high limit, all
pumps in the group will be shutdown, except for the pump
in the tank with the high-high alarm. In-line check valves
used to prevent overll conditions in manifolded tanks,
such as those used with Red Jacket submersible pumps,
are not required or recommended.
Note: The Overll Protection feature will work correctly
ONLY when the high and high-high level alarms
are programmed correctly. Failure to set high
and high-high level alarms will result in a loss of
overll protection.
Dry Tank Indication: TS-TPI programming enables the
user to enter a PUMP HEIGHT measurement (default is
5"). This is the distance between the bottom of the pump
motor to the bottom of the tank. When the pump controller
indicates an Under - Load condition and the product
level is within 3" of the programmed PUMP HEIGHT
measurement, an alarm on the tank gauge will indicate
DRY TANK. When a delivery is made, the pump controller
will automatically be reset.
Note: Because the TS-TPI resets the pump controller
after a delivery is made, the Auto Restart feature
on the pump controller must be disabled.
Clogged Intake Indication: The combination of a pump
controller Under-load condition and a tank level that is
at least 3" greater than the programmed PUMP HEIGHT
measurement will cause a BLOCKED INTAKE indication.
Because the tank gauge is able to conrm that there is
fuel in the tank, this alarm indicates a motor intake that is
being blocked by a foreign object.
Pump in Water Indication: If the tank gauge records
a water level that is within 2” of the programmed PUMP
HEIGHT measurement, the pump will become disabled.
The tank gauge will indicate a PUMP IN WATER alarm.
47
Page 52

TPI Setup
Group Name Parameter Name
Power Supply
RS-485
TS-TPI
Controllers A* Number of Controllers (2) Number of controllers to be connected 31
Parameter
Default
Enable Interface (Yes)
Controller 1 Name Unlead Pump 1 Given Name of the pump controller abc#
Enabled (Yes) Enables the controller. Yes / No
Type (Mag/ECO)
Address (1)
Group (0)
Tank (1)
Height (5.00 in)
Number of Inputs (1) Number of inputs that will activate controller 32
Input 1
Controller 2
Input 1
Type AC Input Module
Channel Disp. 1/2 Unleaded
Name Unlead Pump 2
Enabled (Yes)
Type (Mag/ECO)
Address (1)
Group (0)
Tank (1)
Height (5.00 in)
Number of Inputs (1)
Type AC Input Module
Channel Disp. 1/2 Unleaded
Enables TS-TPI options.
Type of controller used
Unique address of the controller
Controller group number (if a member of a group)
Tank associated with controller
Approximate distance of pump motor from tank
bottom
Select module that contains the input
Specic input that will activate the controller
Given Name of the pump controller
Enables the controller.
Type of controller used
Unique address of the controller
Controller group number (if a member of a group)
Tank associated with controller
Approximate distance of pump motor from tank
bottom
Number of inputs that will activate controller
Select module that contains the input
Specic input that will activate the controller
Description Max Value
Yes/No
Variable Frequency
Smart
3 phase smart
Smart I
Mag / Eco
unknown
30
15
48
#
Modules listed
12
abc#
Yes / No
Variable Frequency
Smart
3 phase smart
Smart I
Mag / Eco
unknown
30
15
48
#
32
Modules listed
12
* When in the Edit mode of Setup, an A will appear for AutoCongure. When the AutoCongure Option is used, the tank
gauge will locate all of the controllers that are properly wired in the system and identify them.
Note: All DIP switch settings for the FE Petro controllers should be set as stand alone controllers, with the exception of
the addressing. All controllers need to have a unique address that is NOT set to 0).
48
Page 53

List of Alarms and Troubleshooting
For all alarms conditions, the troubleshooting steps provided in this chapter are suggested actions to take in the event of
an alarm. Follow all site policy procedures set by local governing agencies in the case of a spill, leak, or malfunction. If
the steps provided by this manual or the site policy are followed and the system still requires additional support, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems Technical Services.
Alarms are listed in sections for System Alarms, VRM Alarms, FMS Alarms, SCM Alarms, Wire Sensor Alarms, LLD
Alarms, TPI Alarms, Printer Alarms and Miscellaneous Alarms.
System Alarms
Displayed Alarm /
Warning
2-Wire Sensor Module is
Ofine
2-Wire Sensor Module
Setup Error
2-Wire Sensor module
number mismatch
3-Wire Sensor Module is
Ofine
3-Wire Sensor Module
Setup Error
3-Wire Sensor Module
Mismatch
4-20mA Module is Ofine Slot 4-20mA Module is ofine due to
4-20mA Module Number
Mismatch
4-20mA Module Setup
Error
Device Description Recommended Actions
Slot 2-Wire Sensor Module is ofine
due to unknown causes.
None Programming errors made during
setup of the 2-Wire Sensor
Module.
Slot 2-Wire Sensor Modules detected
does not match the number
programmed.
Slot 3-Wire Sensor Module is ofine
due to unknown causes.
None Programming errors made during
setup of the 3-Wire Sensor
Module.
Slot 3-Wire Sensor Modules detected
does not match the number
programmed.
unknown causes.
Slot 4-20 mA Modules detected
does not match the number
programmed.
None Programming errors made during
setup of the 4-20mA Module.
Follow safety procedures before working inside of the console.
Visually verify a steady, green “Run” light. If a red “Err” light is ashing
or steady, try to reboot the system. If the condition still exists, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on
this issue.
Verify 2-Wire Sensor Module programming parameters. If the
condition still exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical
Services Dept. for support on this issue.
At startup check that the number of 2-Wire Sensor Modules installed
matches the number programmed under System Conguration >
Modules Expected. On machines that are in service: Check for a
ashing green light or no light at all on the 2-Wire Sensor Module and
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Follow safety procedures before working inside of the console.
Visually verify a steady, green “Run” light. If a red “Err” light is ashing
or steady, try to reboot the system. If the condition still exists, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on
this issue.
Verify 3-Wire Sensor Module programming parameters. If the
condition still exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical
Services Dept. for support on this issue.
At startup check that the number of 3-Wire Sensor Modules installed
matches the number programmed under System Conguration >
Modules Expected. On machines that are in service: Check for a
ashing green light or no light at all on the 3-Wire Sensor Module and
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Follow safety procedures before working inside the console. Visually
verify a steady green “Run” light. If a red “Err” light is ashing or
steady, try to reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on
this issue.
Check that the number of 4-20mA Modules installed matches
the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules
Expected. Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the
4-20mA Module and contact FFS Technical Services for support
Verify 4-20mA Module programming. If the condition still exists,
contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept.
4-20mA Input Error ChannelANA Errors have been detected in the
AC Input Module is Ofine Slot AC Input Module is ofine due to
AC Input module number
mismatch
AC Input Module Setup
Error
AC Input Alarm None An input on the AC input module
Slot AC Input Modules detected
None Programming errors made during
an analog input channel
unknown causes.
does not match the number
programmed.
setup of the AC Input Module.
has been congured as an
alarm and is active.
If the input is not being used, set the programming to reect proper
input type. If the input is being used as an analog signal, inspect the
wiring and redo connections.
Follow safety procedures before working inside of the console.
Visually verify a steady green “Run” light. If a red “Err” light is ashing
or steady, try to reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on
this issue.
Check that the number of AC Input Modules installed matches
the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules
Expected. Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the AC
Input Module and contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Verify AC Input Module programming parameters. If the condition still
exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for
support on this issue.
Check the programming and voltage inputs for the specied Input
channel on the AC Input module.
49
Page 54

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
Console DTU is ofine Slot The Console DTU is not
Console DTU number
mismatch
Controller Module is
Ofine
DIM module number
mismatch
Internal Error #1 System There is an internal buffer error
Invalid Conguration None The conguration that has been
Invalid Registration None The registration that is loaded is
IO Input Alarm None An input on the Input/Output
IO Module is ofine Slot The IO Module is not
IO module number
mismatch
IS Barrier Violation None Non-Intrinsically Safe module
LON module number
mismatch
Power Supply Input Alarm None An input on the Power Supply has
Power Supply Module
number mismatch
Power Supply Module is
Ofine
Power Supply Module
Setup Error
Printer Module Number
Mismatch
Probe Module is Ofine Slot Probe Module is not
Probe Module Number
Mismatch
Probe Module Setup Error None Programming errors made during
Relay Module is Ofine Slot Relay Module is ofine due to
Slot
Slot Controller Module is ofine due to
Slot DIM modules detected does not
Slot IO Modules detected does not
Slot Lon Modules detected does not
Slot Power Supply Modules detected
Slot Power Supply Module is ofine
None Errors in the setup of the listed
Slot Printer Modules detected does not
Slot Probe Modules detected does
communicating with the Console
The number of DTU Modules
detected does not match the
number programmed.
unknown causes.
match the number programmed.
occurring in the gauge.
loaded is not valid.
not valid.
module has been congured as an
alarm and is active.
communicating with the Console
match the number programmed.
placed in IS area; or IS Barrier is
removed.
match the number of Lon Modules
programmed.
been congured as an alarm and
is active.
does not match the number
programmed.
due to unknown causes.
module.
match the number programmed.
communicating with the console.
not match the number of Probe
Modules programmed.
setup of the Probe Module.
unknown causes.
Check for proper wire connection between the console and the
Console DTU. Verify DTU input power. Replace DTU
Ensure that a console DTU is being used. Possible bad bus
connection. Not powered. Replace DTU if connections and settings
check good.
Follow safety procedures before working inside the console. Visually
verify a steady green “Run” light. If red “Err” light is ashing or steady
try to reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact Franklin
Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on this issue.
Check that the number of DIM Modules installed matches the number
programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected. If
problem persists, contact FFS Technical Services for support
Contact FFS Technical Services for support
Verify the le type of the conguration which is being uploaded
If you have upgraded the site before, use the upgrade tool to restore
the former registration. If you have not upgraded the site before,
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Check the programming and voltage inputs for the specied Input
channel on the IO module.
Inspect the IO module for error lights. If green light is ashing,
recover the module. If the lights are off: Power down, remove / reseat the module and power back up. If problem persists, contact FFS
Technical Services for support
Check that the number of IO Modules installed matches the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected.
Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the IO Module and
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Check the module conguration to ensure that a module has not
been improperly placed. Power down and then remove / re-seat the IS
barrier. If problem persists contact FFS Technical Services for support
Check that the number of LON Modules installed matches the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected.
If problem persists, contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Check the programming and voltage inputs for the specied Low
Voltage Input channel on the Power Supply module.
Check that the number of Power Supply Modules installed matches
the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected. Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the Power
Supply Module and contact FFS Technical Services for support
Follow safety procedures before working inside the console. Visually
verify a steady green “Run” light. If red “Err” light is ashing or steady
try to reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact Franklin
Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on this issue.
The console may need to be reprogrammed.
Check that the number of Printer Modules installed matches the
number programmed under System Conguration > Modules
Expected. If problem persists, contact FFS Technical Support.
Follow safety procedures before working inside the console. Visually
verify a steady green “Run” light. If red “Err” light is ashing or steady,
re-seat module and reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Support for help on this issue.
Check that the number of Probe Modules installed matches the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected.
Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the Probe Module
and contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Verify Probe Module programming parameters. If the condition still
exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Support for help
on this issue.
Follow safety procedures before working inside the console. Visually
verify a steady green “Run” light. If red “Err” light is ashing or steady
try to reboot system. If the condition still exists, contact Franklin
Fueling Systems’ Technical Support for help on this issue.
50
Page 55

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
Relay module number
mismatch
Relay Module Setup Error None An error exists in the Relay
Secondary Containment
Monitor Setup Error
System bus error Slot Data transfer errors occurred in
System Setup Error None There is an error in the Setup
Vapor Recovery Monitor
Setup Error
slot Relay Modules detected does not
match the number programmed.
Module conguration
None An error exists in the conguration
of the Secondary Containment
Monitoring Setup.
the System Bus.
conguration.
None An error exists in the conguration
of the Vapor Recovery Monitoring
Setup.
VRM Alarms
Daily Vapor Collection
Failure
Daily Vapor Collection
Warning
External ATG Connection
Down Error
External ATG Connection
Down Warning
Monthly Ullage Pressure
Warning
Monthly Ullage Pressure
Failure
Pressure Out of Range for
Ullage Pressure Leak Test
Pressure Sensor Open
Circuit
TS-DIM Connection Down VRM The TS-DIMIB is not receiving
Ullage Volume Insufcient VRM The Ullage Volume as reported
Vapor Processor Input VRM Processor run time exceeds
VRM A Daily Vapor Collection Warning
VRM V / L average for Non-ORVR
VRM
VRM An External ATG Connection
VRM Ullage pressure is greater than
VRM A Monthly Ullage Pressure
VRM Pressure is out of specication to
VRM Communication has been partially
has occurred for 2 consecutive
days.
transactions is greater than 1.90
or less than 0.33.
The TS-EMS is no longer
communicating to the External ATG.
Down Error has occurred for 2
consecutive days.
+0.3” WC for 25% of time.
Warning has occurred for 2
consecutive months .
perform the Ullage Pressure Leak
test.
or entire lost.
communications from the
dispensers.
by either the internal probes or
the external Tank Gauge is not
adequate.
62 continuous minutes (as
determined by the Hirt Processor),
or processor is shutoff or input to
ISD console is disconnected
Check that the number of Relay Modules installed matches the number programmed under System Conguration > Modules Expected.
Check for a ashing green light or no light at all on the AC Input
Module and contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Inspect the Relay Module setup conguration for possible errors. Pay
particular attention to if the module is congured for 10amps or not.
Inspect the Secondary Containment Monitor setup conguration for
possible errors.
Upgrade to the latest version of rmware available at:
www.franklinfueling.com
Inspect the System setup conguration for possible errors.
Inspect the Vapor Recovery Monitory setup conguration for possible
errors.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
An External ATG Connection Down Error has occurred for 2
consecutive days.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Verify TSP-VPS for proper calibration. Contact FFS Technical
Services for more information.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Verify ullage volume and check programming.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Vapor Processor Warning VRM The ullage pressure exceeds
2.00 inches water column gauge
(WCG) for 144 minutes in one day
(90th percentile > 2.00” WCG as
determined by the VPS sensor).
Vapor Processor Failure VRM A Vapor Processor Warning alarm
has lasted 48 hours.
VFM Error VRM The Vapor Flow Meter is only
partially communicating with the
Console
VFM Missing VRM The Vapor Flow Meter is not
detected by the Console
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help
51
Page 56

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
VFM No Data VRM
Weekly Vapor Collection
Failure
Weekly Vapor Collection
Warning
Weekly Ullage Pressure
Warning
Weekly Ullage Pressure
Failure
Weekly Ullage Pressure
Leak Test Failure
Weekly Ullage Pressure
Leak Test Warning
Remote DTU is Ofine DTU The console cannot detect the
DTU FFS Interference DTU Two networks have the same
DTU Non FFS
Interference
VRM A Weekly Vapor Collection
VRM V / L average for Non-ORVR
VRM Ullage pressure is greater than
VRM A Weekly Ullage Pressure
VRM The leak rate of the vapor
VRM A Weekly Ullage Pressure Leak
DTU Non-FFS equipment is causing
The Vapor Flow Meter is detected
but is not communicating with the
Console
Warning has occurred for 2
consecutive weeks.
transactions is greater than 1.32
or less than 0.81.
+1.3” WC for 5% of time.
Warning has occurred for 2
consecutive weeks.
recovery system is two times the
allowable rate as stated in TP-
201.3 for one week.
Test Warning has occurred for 2
consecutive weeks
specied DTU.
Network ID or nearby FFS
equipment is causing interference
with the system.
interference with the DTU signals.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Refer to Vapor Recovery Monitoring Alarm and Troubleshooting
identication guide 000-0529 for troubleshooting help.
Wrong ID Number
Dispenser Powered Off
Not installed correctly
Not on same phase voltage as console DTU
Verify Network ID programming in Setup Menu. DTU’s may be in
service at a nearby location that is causing interference. Contact
FFS Technical Services for support
Contact FFS Technical Services for support.
FMS Alarms
Alpha volume correction
error
API volume correction
error
Correction table error Tank Level and Volume mismatch
Density oat error Tank A communication error has
Density error Tank The density of the product is not
Float height error Tank This error could indicate that the
Float Missing Tank Probe detects a lesser number of
FMS conguration error None Conicts exist within FMS
High product level Tank Product level exceeded High limit
High high product level Tank Product level exceeded High High
Tank This error is caused by a
programming mistake in the
Special Products section.
Tank This error is caused by a
programming mistake in the
Special Products section.
detected in Correction table
programming.
occurred involving the density
oat.
within specications.
wrong oat type is installed or that
a programming error has occurred.
oats than programmed.
Application programming.
set. Possible close to tank overll
condition
limit set. Possible tank overll
condition.
Verify Special Product Alpha volume correction program parameters.
Contact FFS Technical Services Department for assistance.
Verify Special Product API volume correction program parameters.
Contact FFS Technical Services Department for assistance.
Verify that all levels and volumes are entered accurately into the
Correction Table programming.
Verify programming and contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Enter setup and verify the information under density in the probe
programming.
Review probe programming for proper oat type, number of oats in
the tank. (This would be an idea time to clean the probe and oats).
Review probe programming for correct number of oats. If correct
then inspect probe shaft, oats, and oat magnets. With the probes
out of the tank, this would be an idea time to clean the probe and
oats. If pressures meets requirements specied, contact Franklin
Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support on this issue.
Verify FMS setting are correct in accordance with the site
specications.
Acquire an accurate product level. If actual product level in tank does
not match the consoles displayed current level, verify programming is
correct.
Acquire an accurate product level. If actual product level in tank does
not match the consoles displayed current level, verify programming is
correct.
52
Page 57

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
High product volume Tank The specied tank has reached
High High product volume Tank The specied tank has reached
High water level Tank Water level exceeded High limit
Level error Tank Product level exceeds tank
Line monitor disabled Line Specied line is not enabled, so
Low battery Tank Backup battery is low. See Installation Guide for replacement instructions.
Low product volume Tank/Manifold Product volume below Low limit
Low low product volume Tank/Manifold Product volume below Low
Mag installation error Sensor The specied TSP-DMS has an
Mag product alarm Sensor The specied TSP-DMS has
Mag sensor conguration
error
Mag sensor data error Sensor There is an error with the reported
Mag sensor oat height
error
Mag sensor oat missing Sensor The specied TSP-DMS is not
Mag sensor missing Sensor The console is not receiving any
Mag sensor not learned
error
Sensor An error has been detected in the
Sensor The oat height has exceeded the
Sensor The specied TSP-DMS was not
the programmed High Product
Volume.
the programmed High High
Product Volume.
set.
diameter due to an error in
console of programming.
line leak test will not be performed.
set. The tank / manifold specied
may be near empty
Low limit. The tank or manifold
specied may be near empty.
installation error
detected product.
conguration of the specied TSPDMS.
data from the specied TSP-DMS
limits as learned.
reporting the level information for
one or more oat.
information from the specied
TSP-DMS.
properly learned.
.
Check product volume and compare to the programmed High Volume
alarm Limit in the setup menu. Acquire an accurate product level and
compare to the ATG. If levels differ, verify programming is correct. If
alarm persists, contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Check product volume and compare to the programmed High High
Volume alarm Limit in the setup menu. Get an accurate product
volume and compare to the ATG. If levels differ, verify programming is
correct. If alarm persists, contact FFS Technical Services.
Verify programmed level. If water is too high consult you local site
policy procedures for corrective actions.
Verify tank, offset, and probe programming.
Verify line programming. If necessary enable line.
Acquire an accurate product volume. If actual product volume in
tank does not match the consoles displayed current volume, verify
programming.
Acquire an accurate product volume, and if does not match the
consoles displayed current volume, verify programming.
Check the installation of the TSP-DMS, the sensor must be plumb.
If installation is correct, then try to relearn the sensor. If the problem
persist, the sensor may need to be replaced
Inspect the sump for the presence of product.
Enter into the setup and inspect the TSP-DMS setup.
Inspect wire connections at the Mag sensor. If the problem persists,
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Inspect wire connections at the Mag sensor. If the problem persists,
contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Inspect the Mag sensor for damage and redo the connections. If the
Problem persists, contact FFS Technical Services.
Inspect wire connections at the Mag sensor. If the problem persists,
contact FFS Technical Services.
Enter into the Control > Mag Sensor screen and have the console
learn the sensor.
Mag sensor
synchronization error
Mag water alarm Sensor The specied TSP-DMS has
Mag water warning Sensor The TSP-DMS has detected water
Manifold Delivery
Detected
Manifold Gross Leak
Detected
Manifold Leak Detected Tank A leak in the specied manifolded
Manifold low product
volume
Sensor The console is receiving
incomplete or improperly timed
data from the specied
TSP-DMS
detected water.
above the preset limit.
Tank A delivery has been detected on
the specied manifold.
Tank A leak in the specied manifolded
tanks has been detected via a
SCALD test. Suspect possible
leak.
tanks has been detected via a
SCALD test. Suspect possible leak
Tank The specied manifold has
reached the programmed Low
Product Volume
Inspect wire connections at the Mag sensor. If the problem persists,
contact FFS Technical Services.
Inspect the sump for water.
Inspect the sump for water.
This is not an alarm and should only be a concern if there was not a
delivery to the site at the specied date and time.
Review Tank Leak Test History and programming.
Refer to Section 5: Misc / Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for
instructions on manually starting line leak tests.
Review Tank Leak Test History and programming.
Refer to Section 5: Misc/Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for
instructions on manually starting line leak tests.
Check product volume and compare to the programmed Low Volume
alarm Limit in the setup menu. Acquire an accurate product volume
and compare to the ATG. If levels differ, verify programming is correct.
If alarm persists, contact FFS Technical Services for support.
53
Page 58

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
Manifold low low product
volume
Manifold Leak Detected Tank A leak in the specied manifolded
Manifold Theft Detected Tank The specied manifold has entered
Modem Error None Indicates that a modem
Net error Tank Product net levels exceed tank
No data available System A communication issue has
No probe detected Tank The Console is not receiving any
Probe synchronization
error
Product volume error Tank The Product Volume as reported
RTD table error Tank RTD distance error; Special Probe
System memory error System The system has detected a low
Tank Gross Leak Detected Tank Tank Gross leak test detected
Tank Leak Detected Tank Tank leak detected. Suspect
Tank Product Density
High Limit Exceeded
Tank Product Density Low
Limit Exceeded
Tank SCALD Leak
Detected
Tank Delivery Detected Tank A delivery has been detected on
Tank Theft Detected Tank Product used in Sentinel Mode
Temperature error Tank Special Probe RTD temperature
Ullage error Tank Ullage reported has exceeded
Unstable probe Tank LL Liquid Level probes can send
Water volume error Tank Water volume has exceeded tank
Tank The specied manifold has
Tank Communication between the
Tank The Product Density exceeds the
Tank
Tank SCALD leak test detected tank
reached the programmed Low
Low Product Volume
tanks has been detected via a
SCALD test. Suspect possible
leak.
Sentinel Mode and detects product
leaving the tank that exceeds the
programmed theft limits.
malfunction has occurred.
diameter
occurred between the probe and
the console
communication from the probe.
probe and the Console is either
incomplete or ill timed.
by the probe has exceeded the
limits of the tank.
programming error.
memory situation.
tank. Suspect possible leak.
possible leak.
programmed high limit.
The Product Density has exceeded
the programmed low limit.
leak. Suspect possible leak.
the specied tank.
exceeds theft limit set. Suspect
theft, and then verify theft limit in
programming.
error detected.
tank capacity.
FFSsistent data back to console.
capacity.
Check product volume and compare to the programmed Low Low
Volume alarm Limit in the setup menu. Acquire an accurate product
volume and compare to the ATG. If levels differ, verify programming is
correct. If alarm persists, contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Review Tank Leak Test History and programming. Refer to Section
5: Misc/Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for instructions on
manually starting line leak tests.
Verify programming and accurate level / volume readings.
Try to recycle power on the console. Verify modem programming. If
the alarm does not clear, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical
Services Dept. for support on this issue.
Verify tank, product offset and probe programming
Check for proper probe programming at the console and inspect
wire connections at the probe. If the problem persists, contact FFS
Technical Services for support.
Check for proper probe programming at the console and inspect
wire connections at the probe. If the problem persists, contact FFS
Technical Services for support.
Check for proper probe programming at the console and inspect
wire connections at the probe. If the problem persists, contact FFS
Technical Services for support.
Check for proper probe and tank programming at the console. If
programming is correct, inspect the probe to ensure that the oat is
not stuck in the riser or is otherwise obstructed.
Verify correct RTD programming. If issue still exists, inspect wiring to
probe.If the condition still exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’
Technical Services for support.
Contact FFS Technical Services for support.
Review tank leak test history and programming.
Refer to Section 5: Misc. / Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for
instructions on manually starting line leak tests.
Review tank leak test history and programming.
Refer to Section 5: Misc. / Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for
instructions on manually starting line leak tests.
Verify programming if correct this alarm may be an indication of
improper density of the fuel.
Verify programming if correct this alarm may be an indication of
improper density of the fuel.
Review Tank Leak Test History and programming.
Refer to Section 5: Misc. /Tank Leak Tests – Type and Frequency for
more information on SCALD tests.
This is not an alarm and should only be a concern if there was not a
delivery to the site at the specied date and time.
Verify theft limit in programming. Also obtain an accurate product level
and compare to inventory.
Verify correct RTD table programming. If problem still exists, suspect
wiring or faulty probe.
Check for proper probe and tank programming at the console. If
programming is correct, inspect the probe to ensure that the oat is not
stuck in the riser or obstructed. Bring the probe inside and wire directly
to the gauge to eliminate possible problems with the eld wiring.
Check for proper probe programming at the console and inspect
wire connections at the probe. If the problem persists, contact FFS
Technical Services for support.
Check for proper probe and tank programming at the console. If
programming is correct, inspect the probe to ensure that the colored
water oat is on the bottom.
54
Page 59

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
SCM Alarms
Containment Not Learned SCM The learning process has not been
Containment Program
Error Detected
Containment Program
Error Warning
Containment Pump
Request Ignored
Failed to Hold Vacuum SCM The rate of vacuum decay faster
Failed to Reach Target
Vacuum
Low Vacuum SCM The vacuum level has dropped
Low Vacuum And Pump
Request Ignored
Not Congured SCM Containment programming has not
Unstable Vacuum SCM Vacuum level is uctuating at a
Vacuum Sensor Failed SCM The 4-20mA vacuum transducer
Vacuum Too High SCM The vacuum level has reached
SCM An error has been detected in the
SCM An error has been detected in the
Engineering T
SCM 6”hg could not be reached in the
Engineering Low vacuum level due to Pump
completed.
containment programming.
containment programming
he containment called for the
STP to turn on but has not seen an
increase in vacuum level.
than the learned rate.
learned time.
below 1”hg.
Request Ignored.
been completed
rate that is FFSsistent with the
learned parameters.
has failed and is no longer
detected
above 10”hg
Refer to Secondary Containment Monitoring Installation and User’s
Guide 000-0528 for more information.
Wire Sensor Alarms
Displayed Alarm /
Warning
SN2 Sensor On ChannelSN2 Sensor shows alarm status. Inspect location for presence of liquid. In the case of a leak, follow
SN2 Fuse Blown ChannelSN2 2-Wire Sensor Module fuse blown
SN3 Data Error ChannelSN3 Console has received erroneous
SN3 Dry Well ChannelSN3 Monitoring well is dry. Visually verify that the alarm is correct.
SN3 Fuse Blown ChannelSN3 3-Wire Sensor Module fuse blown
SN3 High Brine ChannelSN3 Brine solution has tripped high
SN3 Low Brine ChannelSN3 Brine solution has tripped low level
SN3 ID Error ChannelSN3 Discriminating sensor is given an
SN3 No Signal ChannelSN3 Console is not receiving data from
SN3 Product ChannelSN3 Discriminating sensor has
Device Description Recommended Actions
site policy procedures. If no liquid is present, and alarm still exists,
sensor may be tripped on error. Check wiring continuity from sensor
to console. Test sensor at console, trip sensor on purpose. Verify
console terminal wiring. If issue still exists, inspect wiring to sensor.
Contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services for support.
due to unknown causes.
data from sensor.
due to unknown causes.
level brine sensor.
brine sensor.
improper ID.
a discriminating sensor.
detected product present at
location.
The fuses on the Sensor boards are non-serviceable per UL listing
standards. The module must be replaced if the fuse is blown.
Check wiring continuity from sensor to console. Test sensor at
console, trip sensor on purpose. Verify console terminal wiring. If
issue still exists, inspect wiring to sensor. If the condition still exists,
contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services for support.
The fuses on the Sensor boards are non-serviceable per UL listing
standards. The module must be replaced if the fuse is blown.
Verify actual level of solution and sensor installed location.
Verify brine level and sensor location.
Verify sensor programming and Auto conguration.
Verify programming of sensor type and wiring connection.
Visually inspect location carefully for presence of liquid. In the case of
a leak, follow site policy procedures. If no liquid is present, and alarm
still exists, sensor may be tripped on error. Check wiring continuity
from sensor to console.
55
Page 60

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
SN3 Pwr Short Slot 3-Wire sensor malfunction. If a 2-Wire sensor is used on a 3-wire module ensure that the
SN3 Sensor On ChannelSN3 Discriminating sensor shows
alarm status.
SN3 Sump Full ChannelSN3 3-wire sensor detected sump full
of liquid.
SN3 Sync Error ChannelSN3 3-wire sensor data signals not in
sync with module.
red / pwr terminal is not used. If a 3-wire sensor is used, disconnect
wires and see if alarm clears. If alarm clears inspect shorts in wiring.
If alarm stays at PWR short replace module. Contact Franklin Fueling
Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support.
Inspect location for presence of liquid. In the case of a leak, follow
site policy procedures. If no liquid is present, and alarm still exists,
sensor may be tripped on error. Check wiring continuity from sensor
to console. Test sensor at console, trip sensor on purpose. Verify
console terminal wiring. If issue still exists, inspect wiring to probe. If
the condition still exists, contact Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical
Services for support.
Inspect location for presence of liquid. In the case of a leak, follow
site policy procedures. If in alarm with no liquid is present, sensor
may be tripped on error. Check wiring continuity from sensor to
console.
Verify correct wiring and re-make the connections. Verify sensor type.
SN3 Vapor ChannelSN3 3-wire discriminate sensor
detecting vapors at location.
SN3 Water ChannelSN3 3-wire discriminate sensor
detecting water at location.
Visually inspect area for product presence. Verify the vapor level has
been calibrated correctly.
Visually inspect area for water presence.
Line Leak Detector (LLD) Alarms
Displayed Alarm /
Warning
0.1 GPH Compliance
Expired
0.2 GPH Compliance
Expired
3 GPH Compliance
Expired
Air in Line Line Air has been detected in the line. Purge all air from the line starting at the furthest dispenser and
Dispensing Pressure Test
Failed
Extended Hook Signal Line A hook signal has been detected
Failed to Catch Pressure Line The pump OFF pressure has
Failed to Pressure Up Line The Line has called for the pump
Gross Leak Detected Line The console has detected a line
High Pump Pressure Line The Pump Off pressure has
Line is not congured Line Specied line is not congured,
56
Device Description Recommended Actions
Line
Line A 0.2 gph test has not been
Line The required daily 3 GPH test has
Line Pressure during dispensing
A 0.1 gph test has not been
completed within the last 365
days.
completed within the last 30 days.
not been completed.
dropped below 7.5 psi. This is
seen as a catastrophic leak during
dispensing.
for more than 60 minutes with the
line pressure staying the same.
dropped below 7 psi within
1 second after the pump was
turned off
to turn on but did not see the
pressure increase
leak greater than 3 gph.
stayed above 49 psi for 3
consecutive times.
therefore line leak test will not be
performed.
Verify that no pertinent alarm conditions have been reoccurring.
Ensure that there is enough time to pass the test.
Verify that no pertinent alarm conditions have been reoccurring.
Ensure proper seating pressure. If Firmware revision is older
than 1.7.4.5535, upgrade to make use of the Statistical Line Leak
Detection enhancement.
Check for continuous pump on conditions that could be caused by a
sticky handle switch or relay.
working in toward the STP. Verify tightness of lines and investigate
other sources for air inltration.
Inspect all sumps for product. Use a pressure gauge to test line
pressure during dispensing. See “LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak
Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145. Contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support.
Check for voltage to the AC-Input module. If issue still exists contact
Franklin Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support.
Inspect all sumps for product. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line
Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more
information.
Inspect all sumps for product. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line
Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more
information.
Inspect all sumps for product. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line
Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more
information.
Inspect all sumps for product. Ensure that no other check valves are
used within the system. Observe multi-point line pressure readings
during pump on and off using a pressure gauge in the line. If line
pressure is high, there may be a blockage in the line. Refer to “LS500
Auto Learn Line Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide”
FFS 000-2145 for more information.
Verify line programming. If necessary congure line.
Page 61

Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
Line Not Learned Line Specied line not learned. Complete learn process, if any learn alarms occur follow the
Line Program Error
Detected
Line Pump Request
Ignored
Marginal Pass of Gross
Leak Test
Monthly Leak Test Failed Line The Console has detected a line
Not Enabled Line Line testing has not been enabled. Verify no other alarm is present then enter the line control menu and
Precision Leak Test Failed Line 0.1 GPH Line leak test failed. Follow site policy on line leak procedures.
Pressure Transducer Fail Line The transducer is not being
Sudden Pressure Loss Line During a 45 minute quite period
Line An error has been detected in the
programming of the specied line.
Engineering The line has called for the pump
to be turned on but another
application is currently using the
STP
Line The last passed gross test
detected a leak just under the
3 gph threshold.
leak greater than 0.2 gph.
detected by the console.
the pressure was seen to drop by
a 2 times the learned 3 gph slope.
proper procedure. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak Detection
Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more information.
Verify programming of line under the setup menu.
Verify that other applications are operating properly. Contact Franklin
Fueling Systems’ Technical Services Dept. for support.
Verify there is no sign of leaks within any of the sumps. Run
additional tests. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak Detection
Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more information.
Inspect all sumps for product. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line
Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more
information.
enable the line testing feature.
Inspect the wiring to the specied transducer and the channel it
terminates at. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line Leak Detection
Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more information.
Inspect all sumps for product. Refer to “LS500 Auto Learn Line
Leak Detection Installation & User’s Guide” FFS 000-2145 for more
information.
TPI Alarms
Displayed Alarm /
Warning
Capacitor Failing TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Clogged Intake TPI The STP controller has reported
Communication Failure TPI Communication from the TPI to
Controller Type Error TPI The programmed controller type
Dry Tank TPI The STP Controller has reported
Extended Run TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Hardware Fault TPI The STP controller is reporting
High Temperature TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Locked Rotor TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Not Calibrated TPI The STP controller is reporting
Open Circuit TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Over Speed TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Over Voltage TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Device Description Recommended Actions
capacitor failure.
a dry run condition but the
associated tank shows a product
level above the intake.
the STP controller has failed. The
Console is seeing the controller
but the controller is not responding
to commands.
does not match what the console
is detecting.
a dry run condition and the
tank level is at or below the
programmed intake.
extended run condition.
is reporting a hardware fault
condition.
high temperature condition.
locked rotor rating.
that it has not been calibrated.
open circuit condition.
over speed condition.
over voltage condition.
Refer to the applicable Smart controller Installation guide for details.
Ensure proper programming of the TPI and calibration of the Smart
Controller. If correct, check for an obstruction on the PMA.
Verify all wiring connections. Call FFS Technical Services Department
for support.
Verify proper programming of the TPI as well as the Smart controller
type and address.
Ensure proper programming of the TPI and calibration of the Smart
Controller. If correct, add fuel.
Refer to the applicable Smart Controller Installation guide for details.
Refer to the applicable Smart Controller Installation guide for details
57
Page 62
Displayed Alarm /
Device Description Recommended Actions
Warning
Pump Communication Fail TPI Communication from the TPI to
Pump In Water TPI The water level has risen to within
Relay Fault TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Short Circuit TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Unbalanced Load TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Unbalanced Voltage TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Under Voltage TPI The STP controller is reporting a
Under Load TPI The STP controller is reporting an
Unknown Fault TPI The STP controller is reporting an
the STP controller has failed.
3 inches of the programmed intake
level.
relay fault error.
short circuit condition.
unbalanced load condition.
unbalanced voltage condition.
voltage level under 200VAC.
underload condition.
unknown fault code.
Printer Alarms
Check Printer
(Thermal Printer Only)
Printer Door Open
(Impact Printer Only)
Printer Head
Temperature
(Thermal Printer Only)
Printer Motor
Temperature
Printer Paper Jam
(Impact Printer Only)
Printer Printer is out of paper, or the
printer door is open.
Printer The system has detected the
printer door is open
Printer Print head high temperature
persists for at least 2 minutes
Printer Printer motor has exceeded
temperature limit
Printer Indicates that paper is jammed in
printer.
Check all wiring connections and ensure that there is power supplied
to the Smart Controller.
Ensure proper programming of the TPI and calibration of the Smart
Controller. If correct, have water removed from the tank
Refer to the applicable Smart Controller Installation guide for details.
Check fault condition on Smart controller and contact FFS Technical
Services for more information
Make sure the printer has paper, and the printer door is closed
completely.
Check to make sure the printer door is closed.
Printer will resume printing and the alarm will clear after a short cooldown period. Keep the console area cool and ventilated. If the alarm
does not clear, contact FFS Technical Support.
Allow printer to cool. Keep the console area cool and ventilated. If the
alarm does not clear, contact FFS Technical Support.
Carefully lift printer cover to inspect and remove the jammed paper.
58
Page 63
Appendix A - Standard Tanks Table
Legend
O/C = Owens Corning / FC Fluid Containment
D = Diameter (Dia.)
L = Length
S = Single Wall
DW = Double Wall Tank (DWT)
Type #
01 O/C Tanks D5
02 O/C Tanks D-5
03 O/C Tanks D-2B
04 O/C Tanks DWT-2 (6) 2,500 75 x 151 DW
05 O/C Tanks D-6
06 O/C Tanks G-5
07 O/C Tanks G-3 4,000 92 x 165 S
08 O/C Tanks D-6
09 O/C Tanks G-3 6,000 92 x 231 S
10 O/C Tanks DWT-2 (8) 6,000 95 x 237 DW
11 O/C Tanks G-3 8,000 92 x 300 S
12 O/C Tanks G-5
13 O/C Tanks DWT-2 (6) 8,000 75 x 472 DW
14 O/C Tanks G-3 10,000 92 x 362 S
15 O/C Tanks G-5
16 O/C Tanks D-6 10,000 120 x 245 S
17 O/C Tanks DWT-2(6) 10,000 75 x 570 DW
18 O/C Tanks G-3 12,000 92 x 432 S
19 O/C Tanks G-5
20 O/C Tanks DWT-2(10) 15,000 124 x 348 DW
21 O/C Tanks DWT-2(10) 20,000 124 x 458 DW
22 O/C Tanks DWT-2(10) 25,000 125 x 554 DW
23 Xerxes DWT-2(10) 30,000 124 x 656 DW
24 Xerxes — 2,000 96 x 108 S
25 Xerxes — 2,000 76 x 166 DW
26 Xerxes — 2,000 75 x 144 S
Manufacturer Model Capacity
(Gallons)
550
DWT-4 (4)
DWT-4 (4)
D-6
DWT-2 (6)
G-6
DWT-2 (6)
G-6
DWT-2 (8)
G-6
G-6
DWT-2(8)
550
1,000
1,000
2,000
2,000
4,000
4,000
4,000
4,000
6,000
6,000
8,000
8,000
8,000
10,000
10,000
12,000
12,000
12,000
Dimensions
D x L (inches)
48 x 78
51 x 83
50 x 132
53 x 138
74 x 133
74 x 133
74 x 236
75 x 239
92 x 167
95 x 167
74 x 354
75 x 357
92 x 299
95 x 299
95 x 303
92 x 365
95 x 365
92 x 431
95 x 431
95 x 435
S / DW
Wall
S
DW
S
DW
S
S
S
DW
S
S
S
DW
S
S
DW
S
S
S
S
DW
59
Page 64

Type #
Manufacturer Model Capacity
(Gallons)
Dimensions
D x L (inches)
27 Xerxes — 3,000 96 x 147 S
28 Xerxes — 4,000 75 x 263 S
29 Xerxes — 4,000 96 x 180 S
30 Xerxes — 4,000 76 x 252 DW
31 Xerxes — 6,000 75 x 353 S
32 Xerxes — 6,000
6,000
33 Xerxes —
—
34 Xerxes —
—
35 Xerxes —
—
36 Xerxes —
—
37 Xerxes —
—
38 Xerxes —
—
39 Xerxes —
—
8,000
8,000
10,000
10,000
10,000
10,000
12,000
12,000
12,000
12,000
15,000
15,000
20,000
20,000
96 x 246
97 x 251
96 x 312
97 x 317
96 x 378
97 x 383
124 x 257
125 x 262
96 x 444
97 x 449
124 x 288
125 x 293
124 x 353
125 x 359
124 x 452
125 x 458
40 Corespan — 4,000 99 x 162 DW
41 Corespan — 5,000 99 x 192 DW
42 Corespan — 6,000 99 x 216 DW
43 Corespan — 8,000 99 x 282 DW
44 Corespan — 10,000 99 x 342 DW
45 Corespan — 12,000 99 x 402 DW
46 Corespan — 15,000 99 x 576 DW
47 — — 275 44 Vertical S
48 — — 550 44 Vertical
(Dual 275
gal.)
49 — — 275 44 Horizontal S
S / DW
Wall
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
DW
S
60
Page 65

Appendix B - Standard Products Table
Product Name API Gravity (6B Compensation)
Leaded Regular 63.5
Unleaded Regular 63.5
Unleaded Plus 62.8
Unleaded Extra 62.8
Unleaded Super 51.3
Diesel 32.8
Kerosene 41.8
#2 Fuel Oil 32.8
Appendix C - Typical Tank Leak Test Times
For 7 Tank Sizes at Half Capacity ( Worst Case is 50% Full )
Tank Size in Gallons Typical - Tank Leak Test Times (to Finish)
4,000 2.0 hours
6,000 3.0 hours
8,000 4.0 hours
10,000 5.0 hours
12,000 6.0 hours
15,000 7.5 hours
20,000 8.0 hours
Note: The Leak Threshold value is one half of the Leak Test value.
61
Page 66

©2011 FFS 000-2142 Rev. E
 Loading...
Loading...