Page 1

Bulletin 71.2:310A
January 2009
Type 310A-32A Pressure Reducing Regulator and
Type 310A-32A-32A Working Monitor Regulator
Introduction
The Type 310A pilot-operated high-pressure regulator
(Figure 1) is used where high capacity and accurate
control are essential. This regulator includes one
Type 32A pilot assembly mounted on the main valve
for pressure reducing or wide-open monitoring
applications, or two Type 32A pilots mounted on the
main valve for working monitor applications.
Features
• Accurate Control—Molded pilot diaphragms
provide a narrow proportional band and
registration of outlet pressure on the main
diaphragm allows excellent control sensitivity.
• Tight Shutoff—Throttling-sleeve design with
Polytetrauoroethylene (PTFE) seat in the body
ensures positive shutoff.
• High Capacity—Straight-through ow passage
allows exceptionally high capacities and
stable operation.
• Reduced Relief Requirements—Optional restricted
trim helps reduce relief valve size requirements; the
regulator is easily converted to full capacity by
changing the trim, if ow conditions increase.
• Fast Speed of Response—Designed to meet
stringent speed of response requirements for
turbine startup and fuel gas applications.
W6278
Figure 1. Type 310A Regulator with Type 32A Pilot
• Minimum Installation Space Required—Since
main valve design incorporates actuator spring,
less installation space is needed for the Type 310A
than for other regulators of comparable capacity.
www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
D102066X012
Page 2

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Specications
Available Congurations
Type 310A-32A: Type 310A main valve with one
Type 32A pilot for standard pressure-reducing and
wide-open monitoring applications
Type 310A-32A-32A: Type 310A main valve with
two Type 32A pilots for working monitor applications
Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
1-inch body with NPT ends; and 1, 2, 3, 4, or
4 x 6-inch (DN 25, 50, 80, 100, and
100 x 150) body with CL300 RF or
CL600 RF anged ends
Maximum Inlet and Pilot Supply Pressures
(1)
NPT and CL600 RF: 1500 psig (103 bar)
CL300 RF: 750 psig (51,7 bar)
Maximum Pressure Drop
(1)
NPT and CL600 RF: 1425 psig (98,3 bar)
CL300 RF: 720 psig (49,6 bar)
Maximum Outlet Pressure
Operating: 700 psig (48,3 bar)
(1)
To Avoid Internal Part Damage: 800 psig (55,2 bar)
Exceeding this pressure may result in gas venting
from pilot spring case.
Emergency (Casing): 1500 psig (103 bar) or
maximum inlet pressure whichever is lower.
Outlet Pressure Ranges and Proportional Bands
See Table 1
Maximum Travel
See Table 3
Minimum Differential Pressure
(1)
15 psig (1,0 bar)
Flow Coefcients
See Tables 4, 5, and 6
IEC Sizing Coefcients
See Table 7
Flow Capacities
See Tables 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12
Maximum Temperature Capabilities
(1)
Nitrile (NBR) with Wiper Ring:
-20° to 150°F (-29° to 66°C)
Fluorocarbon (FKM) with Wiper Ring:
0° to 150°F (-18° to 66°C)
Fluorocarbon (FKM) without Wiper Ring:
0° to 300°F (-18° to 149°C)
External Pilot Supply Connection
1/4-inch NPT
Pilot Vent Connection
1/4-inch NPT
Pressure Connections
See Figure 9
Options
• Main valve body without pilot for on-off service
• Remote-mounted pilot
• Electrically controlled pilot using Type 662 Kixcel™
• Travel indicator
• Pressure loaded pilot
• Type 252 pilot supply filter
• Backpressure protection system
• Restricted Trim (30%, 50%, or 70%)
• NACE construction
• Inlet tap
Approximate Weights
1-inch (DN 25): 45 pounds (20 kg)
2-inch (DN 50): 90 pounds (41 kg)
3-inch (DN 80): 145 pounds (66 kg)
4-inch (DN 100): 190 pounds (86 kg)
4 x 6-inch (DN 100 x 150): 235 pounds (107 kg)
Construction Materials
Main Valve
Body: WCC steel
Throttling Sleeve: Stainless steel
Seat: PTFE
Diaphragm Plates: Steel
Diaphragm and O-rings: Nitrile (NBR) (standard)
or Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Main Spring: Steel
Valve Plug: Stainless steel
Travel Indicator Rod: Stainless steel
Wiper Ring: Nitrile (NBR)
Pilot
Spring Case, Diaphragm Spacer, Pilot Body, and
Spring Case Cap: Cast steel
Adjusting Screw and Diaphragm Plate: Plated steel
Diaphragm: Nitrile (NBR) (standard) or
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Orifice Assembly and Yoke: Stainless steel
Valve Disk Assembly: Stainless steel/Nitrile (NBR)
(standard) or Stainless steel/Fluorocarbon (FKM)
Bleed Valve and Orifice: Stainless steel
Piston and Piston Seat Assembly: Stainless steel
and Nylon (PA)
Pilot Main Spring: Plated steel
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this bulletin or any applicable standard limitation should not be exceeded.
2
Page 3
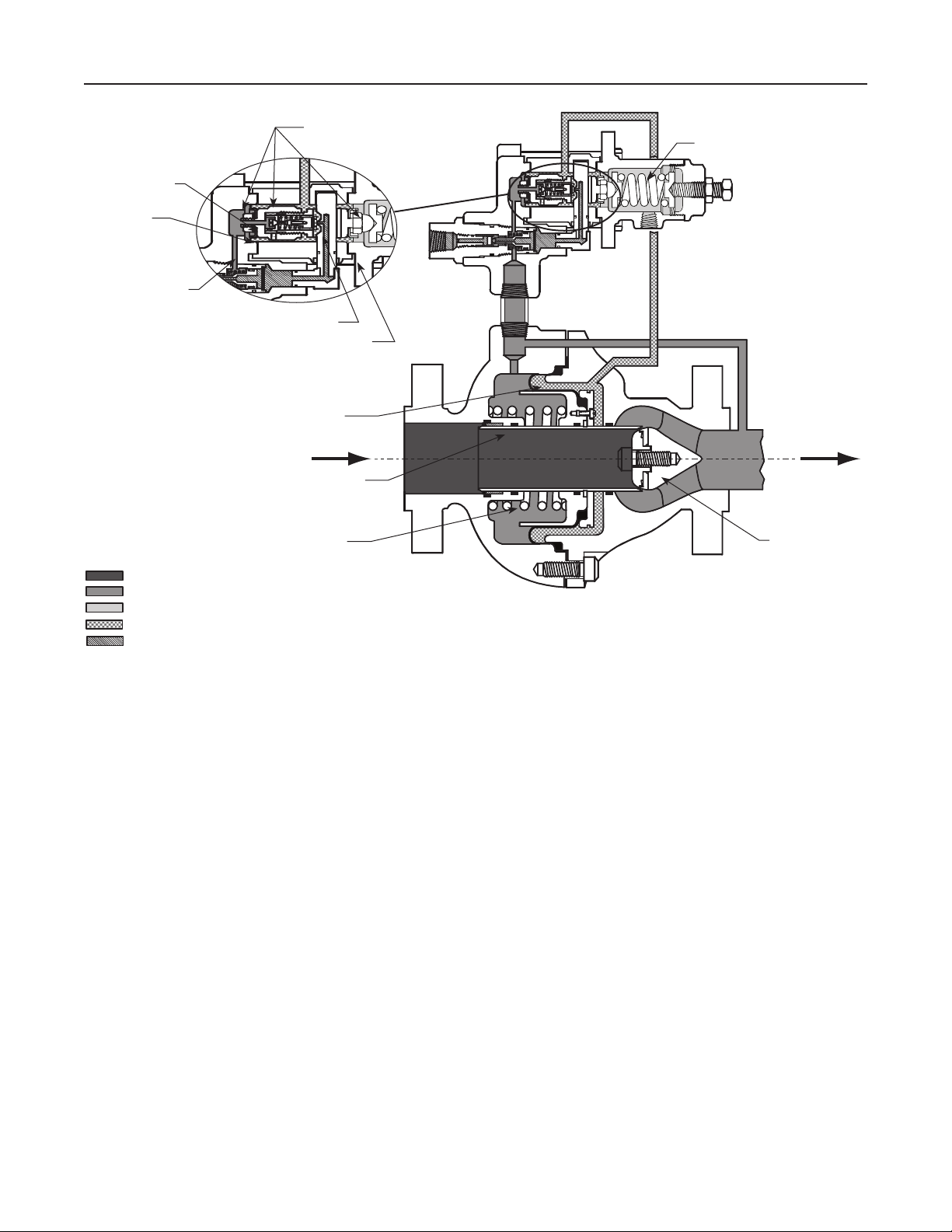
BLEED VALVE
FIXED
RESTRICTION
BOTTOM
DIAPHRAGM
PILOT DIAPHRAGM PLATE
AND YOKE ASSEMBLY
RELAY SEAT
TOP DIAPHRAGM
MAIN VALVE DIAPHRAGM
THROTTLING SLEEVE
Bulletin 71.2:310A
PILOT CONTROL
SPRING
E0696
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
PILOT SUPPLY PRESSURE
Figure 2. Type 310A-32A Regulator Operational Schematic
MAIN VALVE SPRING
Principle of Operation
Single-Pilot Regulator (Figure 2)
The regulator inlet pressure enters the pilot through
the external pilot supply line and is utilized as the
supply pressure for the pilot. The setting of the
pilot control spring determines the reduced outlet
(downstream) pressure.
In operation, assume the outlet pressure is less than
the setting of the pilot control spring. Pilot control
spring force then overcomes the force resulting from
outlet pressure acting on the bottom diaphragm.
The spring pushes the diaphragm plate and yoke
assembly away from the relay seat, opening it and
supplying additional loading pressure to the main
valve diaphragm. When this additional loading
pressure exceeds the force resulting from outlet
pressure acting on the main valve diaphragm plus
STATIONARY
VALVE PLUG
the force of the main valve spring, the diaphragm is
pushed away from the stationary valve plug. The
throttling sleeve opens wider, and the required gas is
supplied to the downstream system.
When gas demand in the downstream system has
been satisfied, the outlet pressure tends to increase.
The increased outlet pressure acting on the bottom
diaphragm of the diaphragm plate and yoke assembly
results in a force that overcomes the pilot spring
setting and forces the assembly toward the relay
seat, closing it. The loading pressure acting on the
main valve diaphragm bleeds to the downstream
system through the fixed restriction in the diaphragm
plate and yoke assembly. When rapid main valve
closure is required by unusual control conditions,
the bleed valve opens for increased bleed rate. The
force of increased outlet pressure acting on the main
valve diaphragm plus the main valve spring force
overcomes the force of decreased loading pressure
acting on the main valve diaphragm and moves the
3
Page 4
Bulletin 71.2:310A
E0694
Figure 3. Typical Wide-Open Monitor Figure 4. Typical Working Monitor
throttling sleeve toward the stationary valve plug to
decrease the gas ow to the downstream system.
The top diaphragm in the pilot acts as a sealing
member for the loading chamber and as a balancing
member to the bottom diaphragm. The two
diaphragms are connected by a yoke. Pressure
change to the center chamber has little effect on the
positioning of the valve disk.
Monitor Systems
Wide-Open Monitors (Figure 3)
Monitoring regulators serve as overpressure protection
devices to limit system pressure in the event of failure
of working regulators feeding the system. The control
line of a wide-open monitoring regulator may be
connected downstream of the working regulator, so
that during normal operation the wide-open monitoring
regulator is standing wide open with the pressure
reduction being taken across the working regulator.
Only in case of working regulator failure does the
wide-open monitoring regulator operate.
E0695
of the Type 32A monitoring pilot. A plug in both the
working and monitoring pilots makes the internal
bleed nonfunctional. A restriction placed in the
external tubing between the diaphragm loading
pressure and the intermediate pressure acts as a
downstream bleed.
If the second-stage working regulator fails to open,
the distribution pressure increases to the setting of
the Type 32A monitoring pilot (slightly higher than
the original distribution pressure) and is controlled
at that level by the Type 310A-32A-32A. Thus,
downstream equipment is protected against a major
overpressure condition without disrupting service or
venting gas to atmosphere.
In the working pilot, the inlet pressure is reduced
to a pre-determined pilot supply pressure, which is
further reduced to loading pressure for the Type 310A
diaphragm. The loading pressure is piped through
the portion of the monitoring pilot blocked open by the
spacer and, as long as distribution pressure is below
the setting of the monitoring pilot, passes through the
relay orifice of the monitoring pilot to the diaphragm
case of the Type 310A body.
Working Monitors (Figures 4 and 5)
The Type 310A-32A-32A working monitor regulator
differs from wide-open monitors in that it has working
monitor capability. This means that it normally
reduces pressure and throttles while the second-stage
regulator is in operation. Should the second-stage
working regulator fail open, the Type 310A-32A-32A
will take over the entire pressure reduction function.
The working monitor pilots are adaptations of two
Type 32A pilots with special internal parts, due to
the pressure conditions in this piloting system. A
spacer blocks open the differential regulator portion
4
Distribution pressure is piped back to the monitoring
pilot. As long as the distribution pressure is less than
the monitoring pilot setting, the working pilot controls
the Type 310A to maintain intermediate pressure. If
the distribution pressure increases to the monitoring
pilot setting, the monitoring pilot relay orifice starts
to throttle the loading pressure to the Type 310A
diaphragm. This allows the Type 310A main spring
to move the throttling sleeve closer to the seat and
control distribution pressure at the monitoring pilot set
point. Therefore, failure of the second-stage working
regulator is controlled with only a slight increase in
distribution pressure, with the Type 310A-32A-32A
accomplishing the entire pressure reduction function.
Page 5
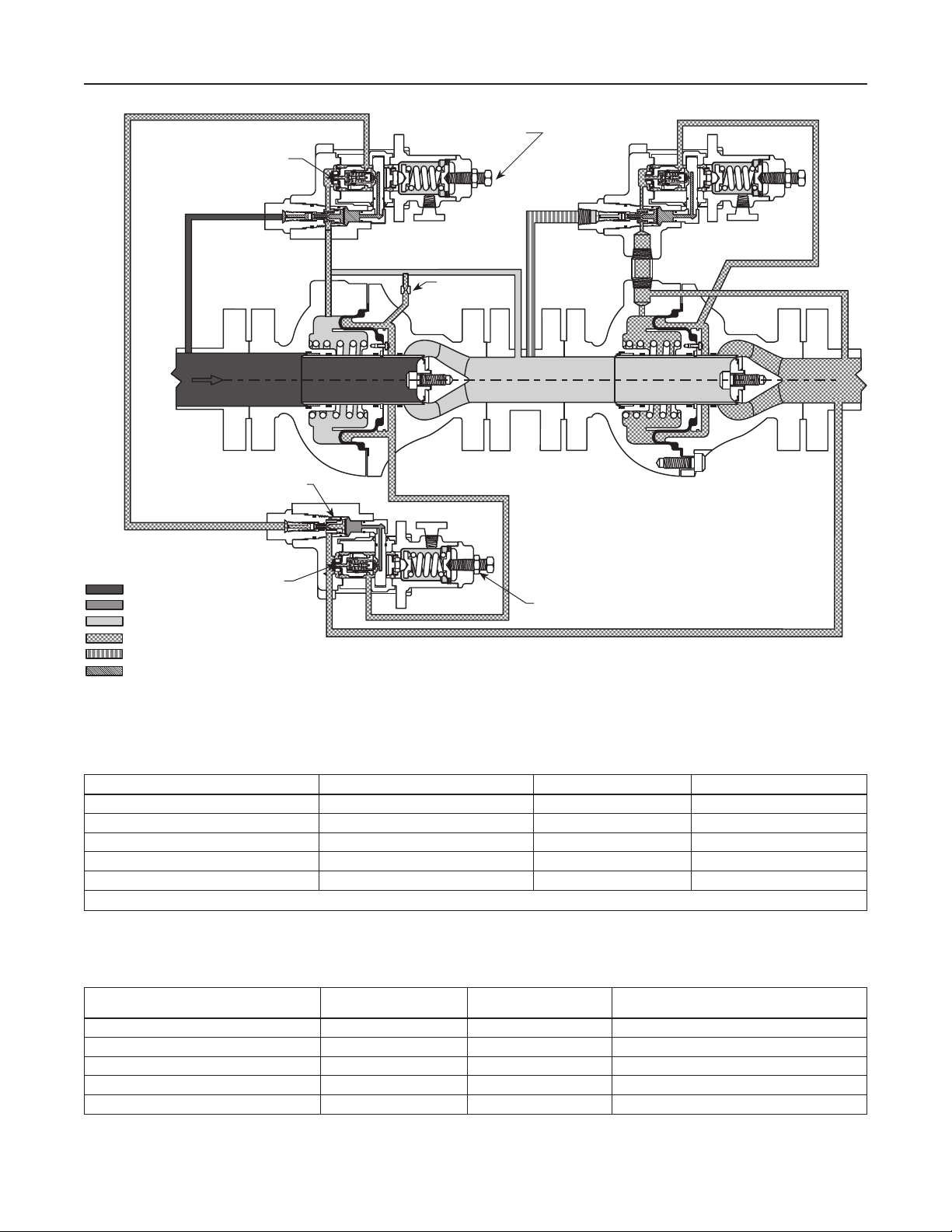
PLUG
SPACER
Bulletin 71.2:310A
WORKING PILOT
RESTRICTION
E0693
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
INTERMEDIATE PRESSURE
PILOT SUPPLY PRESSURE
PLUG
MONITORING PILOT
Figure 5. Type 310A-32A-32A Working Monitor Regulator Operational Schematic
Table 1. Outlet Pressure Ranges
OUTLET PRESSURE RANGE, PSIG (bar) PROPORTIONAL BAND, PSIG (bar) SPRING COLOR SPRING PART NUMBER
10 to 20 (0,69 to 1,4) 0.5 (0,03) Silver 1D809627022
10 to 100 (0,69 to 6,9) 2 (0,14) Yellow 1E392527022
100 to 250 (6,9 to 17,2) 5 (0,34) Blue 1D387227022
250 to 600 (17,2 to 41,4) 12 (0,83) Red 1D465127142
400 to 700 (27,6 to 48,3)
(1)
20 (1,4) Green 13A5543X012
1. Available with Nitrile (NBR) pilot diaphragm only.
Table 2. Recommended Minimum Differential Between Monitoring Pilot Setting and Distribution Pressure
OUTLET PRESSURE RANGE, PSIG (bar) SPRING COLOR
10 to 20 (0,69 to 1,4) Silver 1D809627022 3.0 (0,21) over normal distribution pressure
10 to 100 (0,69 to 6,9) Yellow 1E392527022 5.0 (0,34) over normal distribution pressure
100 to 250 (6,9 to 17,2) Blue 1D387227022 10 (0,69) over normal distribution pressure
250 to 600 (17,2 to 41,4) Red 1D465127142 15 (1,0) over normal distribution pressure
400 to 700 (27,6 to 48,3) Green 13A5543X012 20 (1,4) over normal distribution pressure
SPRING
PART NUMBER
MINIMUM PRESSURE AT WHICH
MONITORING PILOT CAN BE SET, PSIG (bar)
5
Page 6

Bulletin 71.2:310A
HAND VALVE
1/4-INCH NPT PILOT
SUPPLY CONNECTION
VENT VALVE
BLOCK VALVE
BYPASS VALVE
BYPASS LINE
24B4134
B2444
Figure 6. Typical Pressure Reducing Installation
HAND VALVE
Installation
The Type 310A may be installed in any position, but is
normally installed in a horizontal pipeline with the pilot
or pilots above the body. See Figures 6, 7, and 8 for
typical piping installation.
Capacity Information
Note
Type 310A regulator flow capacities
are laboratory verified; therefore, they
may be sized for 100% flow using
capacities as shown in Tables 8, 9,
10, 11, and 12. It is not necessary to
reduce published capacities.
Tables 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 show the natural gas
regulating capacities of the Type 310A regulator at
selected inlet pressures and outlet pressure settings.
Flows are in thousands of SCFH at 60°F and 14.7 psia
(and in thousands of Nm3/h at 0°C and 1,01325 bar) of
0.6 specific gravity natural gas.
To determine equivalent capacities for air, propane,
butane, or nitrogen, multiply the capacity by the
following appropriate conversion factor: 0.775 for
air, 0.628 for propane, 0.548 for butane, or 0.789
for nitrogen. For gases of other specific gravities,
multiply the given capacity by 0.775, and divide by the
square root of the appropriate specific gravity. Then,
LOADING TUBING
VENT VALVE
LOCATE 6 TO 10 PIPE
DIAMETERS FROM
VALVE OUTLET
1/2-INCH (13 mm)
DOWNSTREAM CONTROL LINE
VENT VALVE
BLOCK VALVE
ALTERNATE
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE TAP
if capacity is desired in normal cubic meters per hour
at 0°C and 1,01325 bar, multiply SCFH by 0.0268.
To find approximate regulating capacities at pressure
settings not given in Tables 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 or
to find wide-open ow capacities for relief sizing
at any inlet pressure, perform one of the following
procedures. Then, if necessary, convert using the
factors provided above.
For critical pressure drops (absolute outlet pressure
equal to or less than one-half of absolute inlet
pressure), use the following formula:
Q = (P1)(Cg)(1.29)
For pressure drops lower than critical (absolute
outlet pressure greater than one-half of absolute
inlet pressure).
520 3417
P
Q = CgP1SIN DEG
GT C1 P
1
where,
Q = gas ow rate, SCFH
P1 = absolute inlet pressure, psia
(P1 gauge + 14.7)
Cg = regulating or wide-open gas sizing
coefficient from Table 4, 5, or 6
G = gas specific gravity of the gas
T = absolute temperature of gas at inlet, °Rankine
C1 = ow coefficient
P = pressure drop across the regulator, psi
6
Page 7

24B4134
B2445_2
Bulletin 71.2:310A
FLEXIBLE WIDE-OPEN MONITOR ARRANGEMENT THAT PERMITS
WIDE-OPEN MONITOR TO BE EITHER UPSTREAM OR
DOWNSTREAM OF THE WORKING REGULATOR
Figure 7. Typical Wide-Open Monitor Installation
A0714_2
Figure 8. Typical Working Monitor Installation
MINIMUM PIPING WIDE-OPEN MONITOR ARRANGEMENT THAT
REQUIRES WIDE-OPEN MONITOR ALWAYS TO BE
UPSTREAM OF WORKING REGULATOR
Table 3. Maximum Travel
BODY SIZE, INCHES (DN) MAXIMUM TRAVEL, INCH (mm)
1 (25) 0.5 (13)
2 (50) 0.875 (22)
3 (80) 1 (25)
4 (100) 1.125 (28)
4 x 6 (100 x 150) 1.5 (38)
Table 4. Wide-Open Flow Coefficients for Relief Valve Sizing with Body Size Piping for Relief Valve Sizing
BODY SIZE, INCHES (DN)
30%
50%
70%
100%
TRIM SIZE
1 (25) 2 (50) 3 (80) 4 (100) 4 x 6 (100 x 150)
C
g
C
v
C
1
C
g
C
v
C
1
C
g
C
v
C
1
C
g
C
v
C
1
238 835 1810 3080 4400
8.6 30.6 64.6 114.9 181.8
27.7 27.3 28 26.8 24.2
313 1240 2810 4620 6600
10.3 46.3 99.3 172.4 280.9
30.4 26.8 28.3 26.8 23.5
- - - - 1800 3780 6660 9000
- - - - 69 129 213 360
- - - - 26.2 29.3 31.3 25
612 2610 5510 8830 16200
22 95 200 322 661
28.1 27.5 27.5 27.4 24.5
7
Page 8

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 5. Regulating Flow Coefficients for Body Size Piping
COEFFICIENT
AT PERCENT
OF MAXIMUM
TRAVEL
C
10%
Cv2.2 2.0 2.0 7.6 7.5 6.9 7.0 12.5 11.6 11.3 10.8 29.6 24.0 22.6 19.2 41.6 32.0 33.2 31.4
Cg115 93 83 460 396 311 260 810 735 615 460 1800 1310 1040 705 2235 1680 1420 1160
20%
Cv4.0 3.2 3.0 16.6 14.9 11.3 9.8 29.3 25.2 21.4 16.3 66.2 43.4 38.2 26.6 104.0 67.2 60.4 47.9
Cg210 124 107 810 583 430 325 1520 1120 85 606 3100 1990 1480 917 3800 2550 2050 1550
30%
Cv7.3 4.2 3.8 29.2 21.9 15.6 12.3 55.1 38.4 3.0 21.4 114.0 65.9 54.4 34.6 176.7 102.0 87.2 64.0
Cg343 151 126 1120 758 540 385 2380 1480 1130 755 4350 2650 1900 1130 5510 3300 2650 1940
40%
Cv11.9 5.1 4.5 40.4 28.5 19.6 14.6 86.2 50.7 39.4 26.7 159.9 87.7 69.9 42.6 256.3 132.0 112.8 80.2
Cg427 178 140 1440 925 646 444 3270 1840 1380 902 5480 3280 2300 1340 7300 4150 3250 2330
50%
Cv14.8 6.0 5.0 52.0 34.8 23.4 16.8 118.5 63.0 48.1 31.9 201.5 108.6 84.6 50.6 339.5 166.0 138.3 96.3
Cg485 204 150 1750 1090 744 502 3890 2190 1630 1060 6310 3950 2730 1540 9010 5010 3840 2720
60%
Cv16.8 6.9 5.4 63.2 41.0 27.0 19.0 140.9 75.0 56.8 37.5 232.0 130.8 110.4 58.1 419.1 200.4 163.4 112.4
Cg523 226 159 2040 1240 841 561 4410 2540 1880 1210 7040 4550 3140 1740 10580 5870 4430 3110
70%
Cv18.2 7.7 5.7 73.6 46.6 30.5 21.3 159.8 87.0 65.5 42.8 258.8 150.7 115.4 65.7 492.1 234.8 188.5 128.5
Cg549 250 168 2260 1400 946 624 4820 2900 2130 1360 7640 5110 3540 1950 12100 6720 5030 3500
80%
C
Cg573 272 177 2430 1550 1040 690 5080 3210 2380 1510 8140 5700 3950 2200 13600 7570 5650 3870
90%
C
100%
Cg597 289 184 2520 1700 1130 761 5330 3530 2640 1670 8670 6390 4390 2680 14900 8450 6320 4120
C
C
1
1 (25) 2 (50) 3 (80) 4 (100) 4 x 6 (100 x 150)
100% 50% 30% 100% 70% 50% 30% 100% 70% 50% 30% 100% 70% 50% 30% 100% 70% 50% 30%
65 60 56 210 200 190 185 346 340 325 305 805 725 615 510 895 800 780 760
g
19 8 6 82 53 34 24 175 99 74 48 281 169 130 74 563 269 214 145
v
20 9 6 88 58 38 26 184 110 83 53 299 189 145 83 633 303 240 160
v
21 10 7 91 64 41 29 193 121 92 59 319 212 161 101 693 338 269 174
v
28.8 29.5 28 27.7 26.6 27.6 26.4 27.6 29.2 28.7 28.3 27.2 30.2 27.2 26.5 24.5 25 23.5 24.2
TRIM SIZE (PERCENT OF FLOW CAPACITY) BY BODY SIZE, INCHES (DN)
Table 6. Regulating Flow Coefficients for 2:1 Swaged Piping and 100% Trim
COEFFICIENT AT PERCENT
OF MAXIMUM TRAVEL
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
C
1
1 (25) 2 (50) 3 (80) 4 (100) 4 x 6 (100 x 150)
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
C
g
C
v
60 210 340 810 850
2.0 7.1 11.6 28.1 29.8
115 450 825 1700 2050
3.8 15.2 28.3 59.0 71.9
205 795 1540 3050 3300
6.7 26.8 52.7 105.9 115.8
330 1110 2350 4300 4650
10.8 37.4 80.5 149.3 163.2
395 1380 3025 5400 6050
13.0 46.5 103.6 187.5 212.3
450 1610 3550 6200 7430
14.8 54.2 121.6 215.3 260.7
490 1800 3900 3900 8700
16.1 60.6 133.6 135.4 305.3
515 1960 4200 7400 9860
17 66 144 257 346
533 2055 4440 7800 10800
17 69 152 271 379
548 2140 4610 8150 11600
18 72 158 283 407
30.5 29.7 29.2 28.8 28.5
TRIM SIZE (PERCENT OF FLOW CAPACITY) BY BODY SIZE, INCHES (DN)
Table 7. IEC Sizing Coefficients
BODY SIZE, INCHES (DN) 1 (25) 2 (50) 3 (80) 4 (100) 4 x 6 (100 x 150)
X
T
F
D
F
L
8
0.53 0.49 0.48 0.47 0.29
0.66 0.59 0.56 0.48 0.58
0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74 0.74
Page 9

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 8. 1-inch (DN 25) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (Thousands of SCFH (Nm3/h)) of 0.6 Specific Gravity Gas)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5) 48 (1,3)
75 (5,2) 69 (1,8) 61 (1,6)
100 (6,9) 88 (2,4) 87 (2,3) 73 (1,9)
150 (10,3) 127 (3,4) 127 (3,4) 125 (3,4) 115 (3,1) 92 (2,5)
200 (13,8) 165 (4,4) 165 (4,4) 165 (4,4) 163 (4,4) 156 (4,2) 139 (3,7) 107 (2,9)
250 (17,2) 204 (5,5) 204 (5,5) 204 (5,5) 204 (5,5) 202 (5,4) 195 (5,2) 182 (4,9) 160 (4,3) 121 (3,2)
300 (20,7) 243 (6,5) 243 (6,5) 243 (6,5) 243 (6,5) 242 (6,5) 240 (6,4) 234 (6,3) 223 (6,0) 206 (5,5) 178 (4,8)
350 (24,1) 281 (7,5) 281 (7,5) 281 (7,5) 281 (7,5) 281 (7,5) 281 (7,5) 278 (7,5) 273 (7,3) 263 (7,1) 248 (6,6) 195 (5,2)
400 (27,6) 320 (8,6) 320 (8,6) 320 (8,6) 320 (8,6) 320 (8,6) 320 (8,6) 319 (8,5) 317 (8,5) 312 (8,4 303 (8,1) 272 (7,3)
450 (31,0) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 358 (9,6) 355 (9,5) 350 (9,4) 331 (8,9)
500 (34,5) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 397 (10,6) 396 (10,6) 393 (10,5) 381 (10,2)
550 (38,0) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 435 (11,7) 434 (11,6) 427 (11,4)
600 (41,4) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 474 (12,7) 470 (12,6)
650 (44,8) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 512 (13,7) 511 (13,7)
700 (48,3) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8) 551 (14,8)
750 (51,7) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8) 589 (15,8)
800 (55,2) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8)
850 (58,6) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8)
900 (62,1) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9)
950 (65,5) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9)
1000 (68,9) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0)
1100 (75,8) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0)
1200 (82,7) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1)
1300 (89,6) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1)
1400 (96,5) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2)
25 (1,7) 50 (3,5) 75 (5,2) 100 (6,9) 125 (8,6) 150 (10,3) 175 (12,1) 200 (13,8) 225 (15,5) 250 (17,2) 300 (20,7)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
Table 8. 1-inch (DN 25) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (continued)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5)
75 (5,2)
100 (6,9)
150 (10,3)
200 (13,8)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7)
350 (24,1) 145 (3,9)
400 (27,6) 246 (6,6) 211 (5,7)
450 (31,0) 315 (8,4) 294 (7,9) 225 (6,0) 165 (4,4)
500 (34,5) 371 (9,9) 357 (9,6) 314 (8,4) 282 (7,6) 239 (6,4)
550 (38,0) 420 (11,3) 411 (11,0) 381 (10,2) 360 (9,6) 333 (8,9) 252 (6,7)
600 (41,4) 466 (12,5) 459 (12,3) 438 (11,7) 423 (11,3) 404 (10,8) 351 (9,4) 264 (7,1)
650 (44,8) 508 (13,6) 504 (13,5) 489 (13,1) 478 (12,8) 465 (12,5) 427 (11,4) 369 (9,9) 276 (7,4)
700 (48,3) 549 (14,7) 547 (14,7) 536 (14,4) 528 (14,2) 518 (13,9) 490 (13,1) 448 (12,0) 385 (10,3) 287 (7,7)
750 (51,7) 589 (15,8) 588 (15,8) 581 (15,6) 575 (15,4) 567 (15,2) 546 (14,6) 514 (13,8) 468 (12,5) 401 (10,7) 297 (8,0)
800 (55,2) 628 (16,8) 628 (16,8) 623 (16,7) 619 (16,6) 614 (16,5) 597 (16,0) 572 (15,3) 537 (14,4) 487 (13,1) 416 (11,1)
850 (58,6) 666 (17,8) 666 (17,8) 664 (17,8) 662 (17,7) 658 (17,6) 645 (17,3) 626 (16,8) 598 (16,0) 559 (15,0) 506 (13,6)
900 (62,1) 705 (18,9) 705 (18,9) 704 (18,9) 703 (18,8) 700 (18,8) 691 (18,5) 676 (18,1) 653 (17,5) 622 (16,7) 580 (15,5)
950 (65,5) 744 (19,9) 744 (19,9) 743 (19,9) 743 (19,9) 741 (19,9) 734 (19,7) 723 (19,4) 705 (18,9) 680 (18,2) 646 (17,3)
1000 (68,9) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 782 (21,0) 781 (20,9) 777 (20,8) 768 (20,6) 754 (20,2) 733 (19,6) 705 (18,9)
1100 (75,8) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 859 (23,0) 858 (23,0) 853 (22,9) 845 (22,6) 831 (22,3) 812 (21,8)
1200 (82,7) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 936 (25,1) 935 (25,1) 930 (24,9) 921 (24,7) 908 (24,3)
1300 (89,6) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1013 (27,1) 1011 (27,1) 1006 (27,0) 998 (26,7)
1400 (96,5) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1090 (29,2) 1082 (29,0)
325 (22,4) 350 (24,1) 400 (27,6) 425 (29,3) 450 (31,0) 500 (34,5) 550 (38,0) 600 (41,4) 650 (44,8) 700 (48,3)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
9
Page 10

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 9. 2-inch (DN 50) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (Thousands of SCFH (Nm3/h)) of 0.6 Specific Gravity Gas)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5) 205 (5,5)
75 (5,2) 292 (7,8) 265 (7,1)
100 (6,9) 373 (10,0) 369 (9,9) 315 (8,4)
150 (10,3) 536 (14,4) 536 (14,4) 532 (14,3) 497 (13,3) 399 (10,7)
200 (13,8) 698 (18,7) 698 (18,7) 698 (18,7) 695 (18,6) 668 (17,9) 602 (16,1) 468 (12,5)
250 (17,2) 861 (23,1) 861 (23,1) 861 (23,1) 861 (23,1) 858 (23,0) 835 (22,4) 785 (21,0) 693 (18,6) 529 (14,2)
300 (20,7) 1024 (27,4) 1024 (27,4) 1024 (27,4) 1024 (27,4) 1024 (27,4) 1020 (27,3) 1000 (26,8) 959 (25,7) 889 (23,8) 775 (20,8)
350 (24,1) 1186 (31,8) 1186 (31,8) 1186 (31,8) 1186 (31,8) 1186 (31,8) 1186 (31,8) 1183 (31,7) 1165 (31.2) 1130 (30,3) 1072 (28,7) 849 (22,8)
400 (27,6) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1349 (36,2) 1345 (36,0) 1329 (35,6) 1298 (34,8) 1175 (31,5)
450 (31,0) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1512 (40,5) 1508 (40,4) 1493 (40,0) 1421 (38,1)
500 (34,5) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1674 (44,9) 1670 (44,8) 1631 (43,7)
550 (38,0) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1837 (49,2) 1820 (48,8)
600 (41,4) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 2000 (53,6) 1995 (53,5)
650 (44,8) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9) 2162 (57,9)
700 (48,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3) 2325 (62,3)
750 (51,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7)
800 (55,2) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0)
850 (58,6) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4)
900 (62,1) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8)
950 (65,5) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1)
1000 (68,9) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5)
1100 (75,8) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2)
1200 (82,7) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106)
1300 (89,6) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115)
1400 (96,5) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123)
25 (1,7) 50 (3,5) 75 (5,2) 100 (6,9) 125 (8,6) 150 (10,3) 175 (12,1) 200 (13,8) 225 (15,5) 250 (17,2) 300 (20,7)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
Table 9. 2-inch (DN 50) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (continued)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5)
75 (5,2)
100 (6,9)
150 (10,3)
200 (13,8)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7)
350 (24,1) 634 (17,0)
400 (27,6) 1070 (28,7) 917 (24,6)
450 (31,0) 1359 (36,4) 1271 (34,1) 981 (26,3) 724 (19,4)
500 (34,5) 1592 (42,7) 1537 (41,2) 1361 (36,5) 1226 (32,9) 1041 (27,9)
550 (38,0) 1796 (48,1) 1761 (47,2) 1645 (44,1) 1559 (41,8) 1446 (38,8) 1098 (29,4)
600 (41,4) 1983 (53,1) 1961 (52,6) 1884 (50,5) 1824 (48,9) 1748 (46,8) 1526 (40,9) 1152 (30,9)
650 (44,8) 2158 (57,8) 2146 (57,5) 2095 (56,1) 2054 (55,0) 2000 (53,6) 1846 (49,5) 1603 (43,0) 1204 (32,3)
700 (48,3) 2325 (62,3) 2320 (62,2) 2289 (61,3) 2261 (60,6) 2223 (59,6) 2112 (56,6) 1939 (52,0) 1677 (44,9) 1253 (33,6)
750 (51,7) 2488 (66,7) 2488 (66,7) 2472 (66,3) 2453 (65,7) 2427 (65,0) 2346 (62,9) 2218 (59,4) 2029 (54,4) 1746 (46,8) 1301 (34,9)
800 (55,2) 2650 (71,0) 2650 (71,0) 2645 (70,9) 2634 (70,6) 2617 (70,1) 2558 (68,6) 2463 (66,0) 2321 (62,2) 2113 (56,6) 1814 (48,6)
850 (58,6) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2813 (75,4) 2808 (75,3) 2797 (75,0) 2756 (73,9) 2685 (72,0) 2576 (69,0) 2418 (64,8) 2196 (58,9)
900 (62,1) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2976 (79,8) 2975 (79,7) 2970 (79,6) 2944 (78,9) 2891 (77,5) 2808 (75,3) 2684 (71,9) 2513 (67,3)
950 (65,5) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3138 (84,1) 3123 (83,7) 3085 (82,7) 3021 (81,0) 2924 (78,4) 2789 (74,7)
1000 (68,9) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3301 (88,5) 3295 (88,3) 3270 (87,6) 3222 (86,4) 3145 (84,3) 3038 (81,4)
1100 (75,8) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3626 (97,2) 3620 (97,0) 3596 (96,4) 3549 (95,1) 3482 (93,3)
1200 (82,7) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3952 (106) 3945 (106) 3919 (105) 3878 (104)
1300 (89,6) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4277 (115) 4245 (114)
1400 (96,5) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123) 4602 (123)
325 (22,4) 350 (24,1) 400 (27,6) 425 (29,3) 450 (31,0) 500 (34,5) 550 (38,0) 600 (41,4) 650 (44,8) 700 (48,3)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
10
Page 11

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 10. 3-inch (DN 80) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (Thousands of SCFH (Nm3/h)) of 0.6 Specific Gravity Gas)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5) 434 (11,6)
75 (5,2) 617 (16,5) 561 (15,0)
100 (6,9) 739 (19,8) 781 (20,9) 668 (17,9)
150 (10,3) 1133 (30,4) 1133 (30,4) 1126 (30,2) 1052 (28,2) 845 (22,6)
200 (13,8) 1477 (39,6) 1477 (39,6) 1477 (39,6) 1471 (39,4) 1414 (37,9) 1276 (34,2) 993 (26,6)
250 (17,2) 1821 (48,8) 1821 (48,8) 1821 (48,8) 1821 (48,8) 1815 (48,6) 1768 (47,4) 1663 (44,6) 1470 (39,4) 1123 (30,1)
300 (20,7) 2165 (58,0) 2165 (58,0) 2165 (58,0) 2165 (58,0) 2165 (58,0) 2159 (57,9) 2118 (56,8) 2032 (54,5) 1884 (50,5) 1643 (44,0)
350 (24,1) 2510 (67,3) 2510 (67,3) 2510 (67,3) 2510 (67,3) 2510 (67,3) 2510 (67,3) 2503 (67,1) 2467 (66,1) 2393 (64,1) 2271 (60,9) 1800 (48,2)
400 (27,6) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2854 (76,5) 2847 (76,3) 2814 (75,4) 2749 (73,7) 2491 (66,8)
450 (31,0) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3198 (85,7) 3190 (85,5) 3160 (84,7) 3011 (80,7)
500 (34,5) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3542 (94,9) 3534 (94,7) 3453 (92,5)
550 (38,0) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3886 (104) 3851 (103)
600 (41,4) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4230 (113) 4222 (113)
650 (44,8) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123) 4574 (123)
700 (48,3) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132) 4918 (132)
750 (51,7) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5262 (141)
800 (55,2) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5606 (150)
850 (58,6) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159)
900 (62,1) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169)
950 (65,5) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178)
1000 (68,9) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187)
1100 (75,8) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206)
1200 (82,7) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224)
1300 (89,6) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242)
1400 (96,5) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261)
25 (1,7) 50 (3,5) 75 (5,2) 100 (6,9) 125 (8,6) 150 (10,3) 175 (12,1) 200 (13,8) 225 (15,5) 250 (17,2) 300 (20,7)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
Table 10. 3-inch (DN 80) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (continued)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5)
75 (5,2)
100 (6,9)
150 (10,3)
200 (13,8)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7)
350 (24,1) 1345 (36,0)
400 (27,6) 2268 (60,8) 1946 (52,2)
450 (31,0) 2879 (77,2) 2695 (72,2) 2081 (55,8) 1536 (41,2)
500 (34,5) 3372 (90,4) 3256 (87,3) 2886 (77,3) 2601 (69,7) 2209 (59,2)
550 (38,0) 3803 (102) 3729 (100) 3487 (93,5) 3304 (88,5) 3066 (82,2) 2330 (62,4)
600 (41,4) 4196 (112) 4151 (111) 3990 (107) 3866 (104) 3705 (99,3) 3237 (86,8) 2445 (65,5)
650 (44,8) 4566 (122) 4541 (122) 4437 (119) 4351 (117) 4238 (114) 3913 (105) 3400 (91,1) 2555 (68,5)
700 (48,3) 4918 (132) 4909 (132) 4846 (130) 4788 (128) 4709 (126) 4475 (120) 4111 (110) 3556 (95,3) 2658 (71,2)
750 (51,7) 5262 (141) 5262 (141) 5231 (140) 5193 (139) 5138 (138) 4969 (133) 4701 (126) 4301 (115) 3703 (99,2) 2760 (74,0)
800 (55,2) 5606 (150) 5606 (150) 5597 (150) 5575 (149) 5539 (148) 5418 (145) 5219 (140) 4919 (132) 4481 (120) 3847 (103)
850 (58,6) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5950 (159) 5941 (159) 5920 (159) 5836 (156) 5688 (152) 5459 (146) 5125 (137) 4657 (125)
900 (62,1) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6294 (169) 6293 (169) 6284 (168) 6231 (167) 6122 (164) 5948 (159) 5687 (152) 5327 (143)
950 (65,5) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6638 (178) 6637 (178) 6608 (177) 6532 (175) 6399 (171) 6194 (166) 5911 (158)
1000 (68,9) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6982 (187) 6972 (187) 6922 (186) 6823 (183) 6662 (179) 6437 (173)
1100 (75,8) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7670 (206) 7659 (205) 7612 (204) 7515 (201) 7374 (198)
1200 (82,7) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8358 (224) 8347 (224) 8295 (222) 8210 (220)
1300 (89,6) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 9046 (242) 8984 (241)
1400 (96,5) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9735 (261) 9375 (251) 9375 (251)
325 (22,4) 350 (24,1) 400 (27,6) 425 (29,3) 450 (31,0) 500 (34,5) 550 (38,0) 600 (41,4) 650 (44,8) 700 (48,3)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
11
Page 12

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 11. 4-inch (DN 100) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (Thousands of SCFH (Nm3/h)) of 0.6 Specific Gravity Gas)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5) 709 (19,0)
75 (5,2) 1004 (26,9) 919 (24,6)
100 (6,9) 1284 (34,4) 1274 (34,1) 1096 (29,4)
150 (10,3) 1843 (49,4) 1843 (49,4) 1836 (49,2) 1724 (46,2) 1390 (37,3)
200 (13,8) 2403 (64,4) 2403 (64,4) 2403 (64,4) 2396 (64,2) 2313 (62,0) 2094 (56,1) 1635 (43,8)
250 (17,2) 2963 (79,4) 2963 (79,4) 2963 (79,4) 2963 (79,4) 2957 (79,2) 2889 (77,4) 2725 (73,0) 2415 (64,7) 1849 (49,6)
300 (20,7) 3522 (94,4) 3522 (94,4) 3522 (94,4) 3522 (94,4) 3522 (94,4) 3517 (94,3) 3460 (92,7) 3327 (89,2) 3090 (82,8) 2701 (72,4)
350 (24,1) 4082 (109) 4082 (109) 4082 (109) 4082 (109) 4082 (109) 4082 (109) 4077 (109) 4027 (108) 3915 (105) 3723 (99,8) 2962 (79,4)
400 (27,6) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4642 (124) 4636 (124) 4592 (123) 4495 (120) 4087 (110)
450 (31,0) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5201 (139) 5196 (139) 5156 (138) 4929 (132)
500 (34,5) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5761 (154) 5756 (154) 5641 (151)
550 (38,0) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6321 (169) 6281 (168)
600 (41,4) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6880 (184) 6875 (184)
650 (44,8) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199) 7440 (199)
700 (48,3) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214) 8000 (214)
750 (51,7) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8559 (229)
800 (55,2) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9119 (244)
850 (58,6) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259)
900 (62,1) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274)
950 (65,5) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289)
1000 (68,9) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304)
1100 (75,8) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334)
1200 (82,7) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364)
1300 (89,6) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394)
1400 (96,5) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424)
25 (1,7) 50 (3,5) 75 (5,2) 100 (6,9) 125 (8,6) 150 (10,3) 175 (12,1) 200 (13,8) 225 (15,5) 250 (17,2) 300 (20,7)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
Table 11. 4-inch (DN 100) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and Body Size Piping (continued)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5)
75 (5,2)
100 (6,9)
150 (10,3)
200 (13,8)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7)
350 (24,1) 2217 (59,4)
400 (27,6) 3728 (99,9) 3202 (85,8)
450 (31,0) 4720 (126) 4424 (119) 3427 (91,8) 2533 (67,9)
500 (34,5) 5517 (148) 5335 (143) 4741 (127) 4278 (115) 3638 (97,5)
550 (38,0) 6211 (166) 6098 (163) 5717 (153) 5424 (145) 5039 (135) 3837 (103)
600 (41,4) 6843 (183) 6778 (182) 6531 (175) 6335 (170) 6078 (163) 5322 (143) 4027 (108)
650 (44,8) 7435 (199) 7404 (198) 7251 (194) 7118 (191) 6942 (186) 6422 (172) 5592 (150) 4209 (113)
700 (48,3) 8000 (214) 7994 (214) 7909 (212) 7823 (210) 7701 (206) 7334 (197) 6751 (181) 5850 (157) 4380 (117)
750 (51,7) 8559 (229) 8559 (229) 8527 (229) 8474 (227) 8393 (225) 8132 (218) 7709 (207) 7066 (189) 6093 (163) 4548 (122)
800 (55,2) 9119 (244) 9119 (244) 9113 (244) 9087 (244) 9038 (242) 8857 (237) 8546 (229) 8070 (216) 7363 (197) 6331 (170)
850 (58,6) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9679 (259) 9673 (259) 9648 (259) 9529 (255) 9303 (249) 8945 (240) 8411 (225) 7654 (205)
900 (62,1) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 238 (274) 10 233 (274) 10 163 (272) 10 003 (268) 9734 (261) 9322 (250) 8745 (234)
950 (65,5) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 798 (289) 10 769 (289) 10 662 (286) 10 462 (280) 10 143 (272) 9694 (260)
1000 (68,9) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 357 (304) 11 352 (304) 11 288 (303) 11 144 (299) 10 897 (292) 10 545 (283)
1100 (75,8) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 477 (334) 12 471 (334) 12 411 (333) 12 271 (329) 12 057 (323)
1200 (82,7) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 596 (364) 13 590 (364) 13 524 (362) 13 403 (359)
1300 (89,6) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 715 (394) 14 645 (392)
1400 (96,5) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424) 15 835 (424)
325 (22,4) 350 (24,1) 400 (27,6) 425 (29,3) 450 (31,0) 500 (34,5) 550 (38,0) 600 (41,4) 650 (44,8) 700 (48,3)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
12
Page 13

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Table 12. 4 x 6-inch (DN 100 x 150) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and 2:1 Swaged Piping (Thousands of SCFH (Nm3/h)) of
0.6 Specific Gravity Gas)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5) 933 (25,0)
75 (5,2) 1342 (36,0) 1199 (32,1)
100 (6,9) 1716 (46,0) 1686 (45,2) 1423 (38,1)
150 (10,3) 2465 (66,1) 2465 (66,1) 2434 (65,2) 2253 (60,4) 1794 (48,1)
200 (13,8) 3213 (86,1) 3213 (86,1) 3213 (86,1) 3180 (85,2) 3035 (81,3) 2720 (72,9) 2104 (56,4)
250 (17,2) 3961 (106) 3961 (106) 3961 (106) 3961 (106) 3926 (105) 3802 (102) 3555 (95,3) 3126 (83,8) 2375 (63,7)
300 (20,7) 4709 (126) 4709 (126) 4709 (126) 4709 (126) 4709 (126) 4672 (125) 4561 (122) 4353 (117) 4017 (108) 3488 (93,5)
350 (24,1) 5457 (146) 5457 (146) 5457 (146) 5457 (146) 5457 (146) 5456 (146) 5417 (145) 5315 (142) 5135 (138) 4835 (130) 3818 (102)
400 (27,6) 6206 (166) 6206 (166) 6206 (166) 6206 (166) 6206 (166) 6206 (166) 6203 (166) 6163 (165) 6067 (163) 5906 (158) 5312 (142)
450 (31,0) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6954 (186) 6949 (186) 6908 (185) 6818 (183) 6453 (173)
500 (34,5) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7702 (206) 7695 (206) 7653 (205) 7430 (199)
550 (38,0) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8450 (226) 8441 (226) 8316 (223)
600 (41,4) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9198 (247) 9144 (245)
650 (44,8) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9947 (267) 9933 (266)
700 (48,3) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287) 10 695 (287)
750 (51,7) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307) 11 443 (307)
800 (55,2) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327) 12 191 (327)
850 (58,6) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347)
900 (62,1) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367)
950 (65,5) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387)
1000 (68,9) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407)
1100 (75,8) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447)
1200 (82,7) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487)
1300 (89,6) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527)
1400 (96,5) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567)
25 (1,7) 50 (3,5) 75 (5,2) 100 (6,9) 125 (8,6) 150 (10,3) 175 (12,1) 200 (13,8) 225 (15,5) 250 (17,2) 300 (20,7)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
Table 12. 4 x 6-inch (DN 100 x 150) Body Capacities with 100% Trim and 2:1 Swaged Piping (continued)
INLET
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
50 (3,5)
75 (5,2)
100 (6,9)
150 (10,3)
200 (13,8)
250 (17,2)
300 (20,7)
350 (24,1) 2843 (76,2)
400 (27,6) 4822 (129) 4123 (110)
450 (31,0) 6150 (165) 5739 (154) 4407 (118) 3244 (87,0)
500 (34,5) 7233 (194) 6965 (187) 6139 (165) 5519 (148) 4675 (125)
550 (38,0) 8188 (219) 8007 (215) 7447 (200) 7039 (189) 6516 (175) 4928 (132)
600 (41,4) 9064 (243) 8943 (240) 8552 (229) 8266 (222) 7903 (212) 6874 (184) 5170 (139)
650 (44,8) 9889 (265) 9812 (263) 9539 (256) 9332 (250) 9070 (243) 8338 (223) 7216 (193) 5400 (145)
700 (48,3) 10 679 (286) 10 634 (285) 10 449 (280) 10 299 (276) 10 107 (271) 9565 (256) 8753 (235) 7542 (202) 5622 (151)
750 (51,7) 11 442 (307) 11 424 (306) 11 306 (303) 11 200 (300) 11 058 (296) 10 651 (285) 10 039 (269) 9151 (245) 7856 (211) 5835 (156)
800 (55,2) 12 191 (327) 12 190 (327) 12 125 (325) 12 052 (323) 11 950 (320) 11 643 (312) 11 173 (299) 10 494 (281) 9534 (256) 8159 (219)
850 (58,6) 12 939 (347) 12 939 (347) 12 915 (346) 12 870 (345) 12 799 (343) 12 570 (337) 12 206 (327) 11 676 (313) 10 933 (293) 9903 (265)
900 (62,1) 13 688 (367) 13 688 (367) 13 684 (367) 13 661 (366) 13 615 (365) 13 449 (360) 13 168 (353) 12 750 (342) 12 161 (326) 11 356 (304)
950 (65,5) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 436 (387) 14 430 (387) 14 430 (387) 14 291 (383) 14 077 (377) 13 746 (368) 13 275 (356) 12 630 (338)
1000 (68,9) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 184 (407) 15 177 (407) 15 105 (405) 14 946 (401) 14 686 (394) 14 306 (383) 13 783 (369)
1100 (75,8) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 680 (447) 16 670 (447) 16 596 (445) 16 442 (441) 16 198 (434) 15 848 (425)
1200 (82,7) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 177 (487) 18 162 (487) 18 086 (485) 17 937 (481) 17 706 (475)
1300 (89,6) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 673 (527) 19 654 (527) 19 576 (525) 19 431 (521)
1400 (96,5) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 170 (567) 21 146 (567) 21 066 (565)
325 (22,4) 350 (24,1) 400 (27,6) 425 (29,3) 450 (31,0) 500 (34,5) 550 (38,0) 600 (41,4) 650 (44,8) 700 (48,3)
OUTLET PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
13
Page 14

Bulletin 71.2:310A
TYPE 32A
1/4-INCH NPT
SUPPLY
CONNECTION
8.31
(211)
E
G
B
A
1/2-INCH NPT
CONTROL
CONNECTION
BOTH SIDES
M
L
TYPE 310A REGULATOR WITH TYPE 32A PILOT
9.62
(244)
F
1/2-INCH NPT
DISTRIBUTION
PRESSURE
CONNECTION
8.75
(222)
1/4-INCH NPT
PILOT SUPPLY
CONNECTION
MONITORING PILOT
C
14B0914-K
44B4135-B
BODY SIZE,
INCHES (DN)
1
(25)
2
(50)
3
(80)
4
(100)
4 x 6
(100 x 150)
CL150 RF CL300 RF CL600 RF CL150 RF CL300 RF CL600 RF
- - - -
10.06
(256)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Figure 9. Dimensions
D
G
A
WORKING
PILOT
TYPE 310A REGULATOR WITH TWO TYPE 32A PILOTS FOR WORKING MONITOR SERVICE
DIMENSIONS, INCHES (mm)
A B
7.78
(198)
10.53
(267)
12.53
(318)
14.53
(369)
16.19
(411)
8.28
(210)
11.28
(287)
13.28
(337)
15.53
(394)
17.38
(441)
- - - -
3.19
(81)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
2.94
(75)
3.44
(87)
3.81
(97)
4.88
(124)
4.88
(124)
3.19
(81)
3.81
(97)
4.19
(106)
5.38
(137)
5.38
(137)
C D E F G L M
9.62
(244)
10.68
(271)
11.50
(292)
13.38
(340)
13.38
(340)
8.25
(210)
11.25
(286)
13.25
(337)
15.50
(394)
15.50
(394)
10.56
(268)
11.56
(294)
12.38
(314)
14.25
(362)
14.25
(362)
2.25
(57)
3.12
(79)
3.12
(79)
3.88
(99)
3.88
(99)
3.06
(78)
4.44
(113)
5.25
(133)
7.12
(181)
7.12
(181)
1/2-INCH NPT
INTERMEDIATE
PRESSURE
CONNECTION
INCHES
(mm)
3.56
(90)
4.56
(116)
5.38
(137)
7.25
(184)
7.25
(184)
4.00
(102)
5.44
(138)
6.25
(159)
8.12
(206)
8.00
(203)
14
Page 15

Ordering Guide
Bulletin 71.2:310A
Type (Select One)
310A-32A (one pilot for standard pressure
reducing and wide-open monitor applications)***
310A-32A-32A (two pilots for working
monitor applications)***
Body Size and End Connection Style (Select One)
1-inch (DN 25) Body
NPT***
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
2-inch (DN 50) Body
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
3-inch (DN 80) Body
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
4-inch (DN 100) Body
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
4 x 6-inch (DN 100 x 150) Body
CL300 RF***
CL600 RF***
Outlet Pressure Range (Select One)
10 to 20 psig (0,69 to 1,4 bar)***
10 to 100 psig (0,69 to 6,9 bar)***
100 to 250 psig (6,9 to 17,2 bar)***
250 to 600 psig (17,2 to 41,4 bar)***
400 to 700 psig (27,6 to 48,3 bar)
(1)
***
Main Valve Trim Size (Select One)
100% (standard)***
70% (not available on 1-inch (DN 25) body)
50%
30%
Main Valve Diaphragm and O-Rings (Select One)
Nitrile (NBR) (standard)***
Fluorocarbon (FKM)**
Pilot Diaphragm (Select One)
Stainless Steel/Nitrile (NBR) (standard)***
Stainless Steel/Fluorocarbon (FKM)**
Pilot Valve Disk Assembly (Select One)
Nitrile (NBR) (standard)***
Fluorocarbon (FKM)
(2)
**
Main Valve Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one replacement parts kit to match
this order.
Pilot Replacement Parts Kit (Optional)
Yes, send one replacement parts kit to match
this order.
1. Only available in Nitrile (NBR).
2. Maximum Operating Pressure of 600 psig (41,4 bar).
Regulators Quick Order Guide
* * * Standard - Readily Available for Shipment
* * Non-Standard - Allow Additional Time for Shipment
Special Order, Constructed from Non-Stocked Parts.
*
Consult your local Sales Office for Availability.
Availability of the product being ordered is determined by the component with the
longest shipping time for the requested construction.
Specication Worksheet
Application (Please designate units):
Specific Use
Line Size
Gas Type and Specific Gravity
Gas Temperature
Does the Application Require Overpressure Protection?
No Yes, if so, which is preferred:
Relief Valve Monitor Regulator Shutoff Device
Is overpressure protection equipment selection assistance
desired?
Pressure (Please designate units):
Maximum Inlet Pressure (P
Minimum Inlet Pressure (P
Downstream Pressure Setting(s) (P2)
Maximum Flow (Q
Performance Required:
Accuracy Requirements?
Need for Extremely Fast Response?
Other Requirements:
max
)
1min
1max
)
)
15
Page 16

Bulletin 71.2:310A
Industrial Regulators
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacific
Shanghai, China 201206
Tel: +86 21 2892 9000
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Tel: +971 4811 8100
For further information visit www.emersonprocess.com/regulators
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners. Fisher is a mark owned by Fisher Controls, Inc., a
business of Emerson Process Management.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be construed as warranties or
guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to modify or improve the designs or specifications of such
products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any Emerson
Process Management product remains solely with the purchaser.
Natural Gas Technologies
Emerson Process Management
Regulator Technologies, Inc.
USA - Headquarters
McKinney, Texas 75069-1872 USA
Tel: 1-800-558-5853
Outside U.S. 1-972-548-3574
Asia-Pacific
Singapore, Singapore 128461
Tel: +65 6777 8211
Europe
Bologna, Italy 40013
Tel: +39 051 4190611
Gallardon, France 28320
Tel: +33 (0)2 37 33 47 00
TESCOM
Emerson Process Management
Tescom Corporation
USA - Headquarters
Elk River, Minnesota 55330-2445 USA
Tel: 1-763-241-3238
Europe
Selmsdorf, Germany 23923
Tel: +49 (0) 38823 31 0
©Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc., 1994, 2009; All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...