Page 1

D-LINK
2.4GHz Wireless USB Adapter
Air DWL-120
Manual
(09/27/2002)
Building Networks for People
Page 2

Contents
Package Contents ................................................................................3
Introduction ..........................................................................................4
Wireless Basics ....................................................................................6
Getting Started ................................................................................... 10
Using the Configuration Utility ............................................................ 13
Networking Basics ..............................................................................19
Troubleshooting..................................................................................32
Technical Specifications .....................................................................35
Contacting Technical Support.............................................................36
Warranty and Registration.................................................................. 37
2
Page 3

Package Contents
Contents of Package:
D-Link Air DWL-120
2.4 GHz Wireless USB Adapter
Manual, Warranty and Drivers on CD
Quick Installation Guide
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
System Requirements:
A computer with an available USB port
Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows Me, or Windows 98SE
At least 32 MB of memory and a 300 MHz processor
An 802.11b Access Point or Router (e.g., DWL-900AP for
Infrastructure Mode) or another 802.11b wireless adapter
(e.g., DWL-650 for Ad-Hoc mode.)
3
Page 4

Introduction
The D-Link Air DWL-120 2.4GHz Wireless USB Adapter is an ideal way to
extend the reach and number of computers connected to your wireless network.
After completing the steps outlined in the Quick Installation Guide (included in
your package) you will have the ability to share information and resources,
such as files and printers, and take full advantage of a “connected” environment
for work or play!
This DWL-120 comes with software drivers for the most popular Microsoft
Windows operating systems and can be integrated into a larger network, running
Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows ME, or Windows 98SE in either Ad
Hoc mode (without an Access Point) or Infrastructure mode (with an Access
Point.) The IEEE 802.11b standards compliance means this adapter gives
you the flexibility to connect it to any 802.11b network. The IEEE 802.11b
Ethernet standard allows you to connect computers and devices at speeds up
to 11Mbps, dependent upon the distance between wireless adapters, the
configuration of your working environment, or the capabilities or limitations of
your computer systems.
This manual provides a quick introduction to wireless technology and its
application as it relates to networking. Take a moment to read through this
manual and familiarize yourself with wireless technology. You should also give
yourself some time to become familiar with your new wireless network.
4
Page 5

Features and Benefits
Provides high-speed wireless connection at up to 11Mbps
Operates in the 2.4 to 2.4835 GHz Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Supports wireless data encryption with 64-bit WEP and 128-bit
WEP for more secure networking
Supports infrastructure networks via an Access Point and peer-to-
peer communication in ad-hoc mode
User-friendly configuration and diagnostic utilities
Cost-effective wireless solution
IEEE 802.11b and Wi-Fi Certified
Connects at up to 328 feet indoors*
WHQL Certification for Windows XP
Easy installation
One year warranty
**
* Environmental factors may adversely affect range
5
Page 6
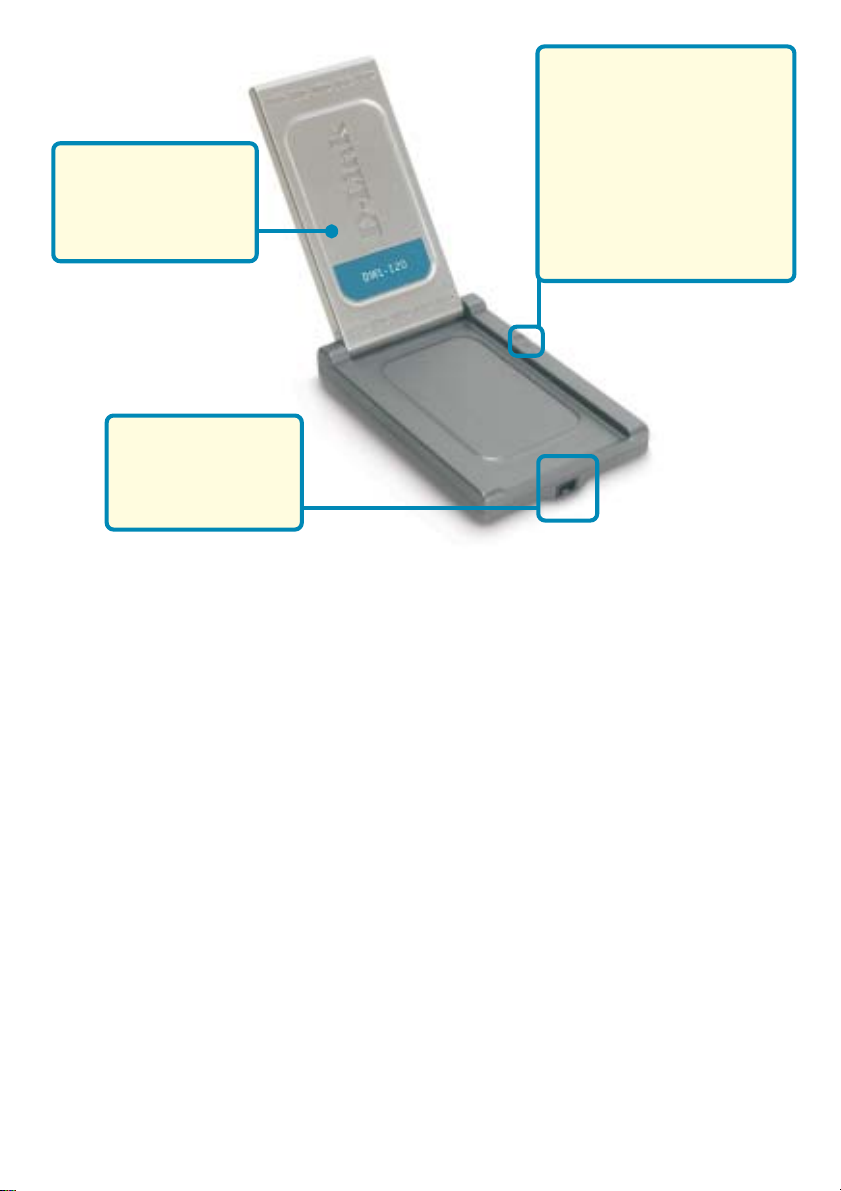
Features
Antenna
Used to wirelessly
connect to 802.11b
networks
Mini-USB port
Used to connect the
DWL-120 to your
computer
Link/Activity LED
Link - Indicates that the
DWL-120 is properly
installed in the computer.
Activity - Blinks when data
is being transmitted
through the wireless
connection.
Wireless Basics
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-touse and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home, business
or public access wireless networks. Strictly adhering to the IEEE standard, the
D-Link wireless family of products will allow you to securely access the data
you want, when and where you want it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom
that wireless networking delivers.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a cellular computer network that
transmits and receives data with radio signals instead of wires. Wireless LANs
are used increasingly in both home and office environments, and public areas
such as airports, coffee shops and universities. Innovative ways
to utilize WLAN technology are helping people to work and communicate
more efficiently. Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other fixed
infrastructure have proven to be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network.
Wireless adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems support the same
protocols as Ethernet adapter cards.
Under many circumstances, it may be desirable for mobile network devices to
link to a conventional Ethernet LAN in order to use servers, printers or an
Internet connection supplied through the wired LAN. A Wireless Router is a
device used to provide this link.
6
Page 7

Wireless Basics (continued)
People use wireless LAN technology for many different purposes:
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any
location within the operating range of the WLAN. Management decisions based
on real-time information can significantly improve worker efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs – WLANs (Wireless Local Area Networks) are
easy to set up, manage, change and relocate. Networks that frequently change,
both physically and logically, can benefit from WLANs ease of implementation.
WLANs can operate in locations where installation of wiring may be impractical.
Installation Speed and Simplicity - Installing a wireless LAN system can
be fast and easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and
ceilings.
Network Expansion - Wireless technology allows the network to go
where wires cannot.
Scalability – Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) can be configured in a
variety of topologies to meet the needs of specific applications or existing
infrastructures. Configurations are easily changed and range from peer-topeer networks suitable for a small number of users to larger infrastructure
networks to accommodate hundreds or thousands of users, depending on the
number of wireless devices deployed.
7
Page 8

Wireless Basics (continued)
The DWL-120 is compatible with the D-Link Air 802.11b family of products
which include:
2.4GHz Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop
computers (DWL-650)
2.4GHz Wireless PCI cards used with desktop computers
(DWL-520)
Wireless Access Points (DWL-900AP)
Standards-Based Technology
Based on the IEEE 802.11b standard, the DWL-120 is interoperable with
existing compatible 2.4GHz wireless technology with data transfer speeds of
up to 11Mbps.
8
Page 9

Wireless Basics (continued)
Installation Considerations
The D-Link Air DWL-120 lets you access your network, using a wireless
connection, from virtually anywhere. Keep in mind, however, that the number,
thickness and location of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals
must pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges vary depending on the
types of materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise in your home or
business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic
guidelines:
1. Keep the antenna of the DWL-120 in an upright position.
2.
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the DWL-120 and
other network devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce
your D-Link Air Wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.)
Position your receiving devices so that the number of walls or ceilings is
minimized.
3. Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is
1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3
feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters)
thick! Try to make sure that devices are positioned so that the signal will
travel straight through a wall or ceiling for better reception.
4. Building Materials make a difference - a solid metal door or aluminum
studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless
devices and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal passes
through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
5. Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical
devices or appliances that generate RF noise.
9
Page 10
Getting Started
With its default settings, the DWL-120 will connect with other
D-Link Air products, right out of the box.
There are basically two modes of networking:
Infrastructure – using an Access Point, such as the DWL-900AP+.
Ad-Hoc – directly connecting to another computer, for peer-to-peer
communication, using wireless network adapters on each computer, such
as two or more DWL-120 wireless network USB adapters.
On the following pages we will show you an example of an Infrastructure
Network and an Ad-Hoc Network.
An Infrastructure network contains an Access Point or Router. The
Infrastructure Network example shown on the following page contains the
following D-Link network devices (your existing network may be comprised
of other devices):
A wireless Router - D-Link AirPro DI-764
A laptop computer with a wireless adapter -
D-Link AirPlus DWL-650+
A desktop computer with another D-Link Air DWL-120
A Cable modem - D-Link DCM-200
10
Page 11
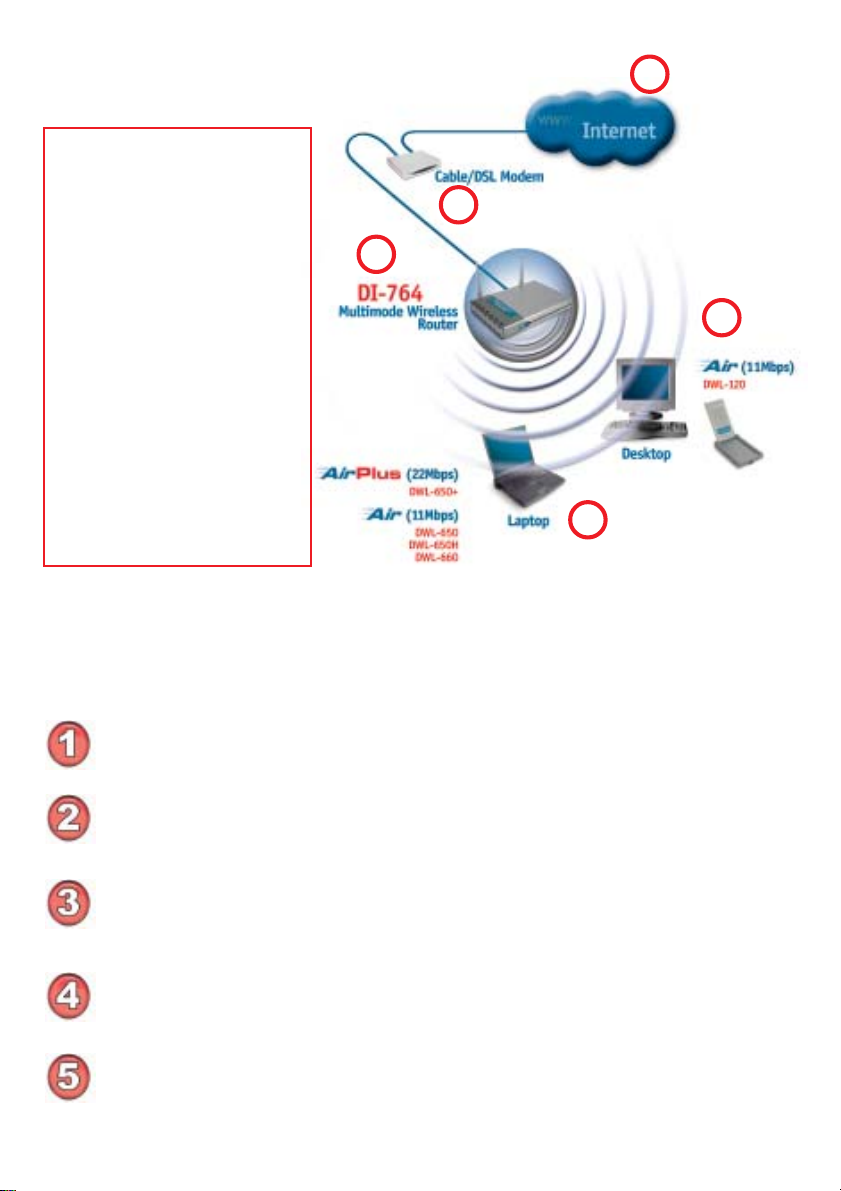
Getting Started
Setting up a Wireless Infrastructure Network
Please refer to the following
sections of this manual for
additional information about
setting up a network:
2
1
Networking Basics - learn
how to check and assign
your IP Address; share
printers and files.
Using the Configuration
Menu - learn the settings for
the DWL-120, using the
web-based interface.
Troubleshooting - learn
how to check for common
installation issues and other
tips for troubleshooting.
Please remember that D-Link Air wireless devices are pre-configured to connect
together, right out of the box, with their default settings.
3
4
5
For a typical wireless setup at home (as shown above), please do the
following:
You will need broadband Internet access (a Cable or DSL-subscriber line into
your home or office)
Consult with your Cable or DSL provider for proper installation of the modem
Connect the Cable or DSL modem to your broadband router (see the Quick
Installation Guide included with your router.)
Install the D-Link Air DWL-120 wireless USB adapter into an available USB
port on your desktop computer. (See the Quick Installation Guide included with
the DWL-120.)
If you are connecting a laptop computer to your network, install the drivers for
the wireless cardbus adapter (e.g., DWL-650+ or the DWL-650) into a laptop
computer. (See the Quick Installation Guide included with the DWL-A650,
DWL-650+, or DWL-650.)
11
Page 12

Getting Started
Setting up a Wireless Ad Hoc Network
Install the D-Link Air DWL-120 Wireless USB adapter into the desktop
computer. See the Quick Installation Guide included with the product for
installation instructions.
Install a wireless network adapter into the laptop computer. In the
example above the DWL-650+ or DWL-650 may be installed into a
laptop computer. See the Quick Installation Guide included with the
product.
Set the wireless configuration for the adapters to Ad-Hoc mode, set
the adapters to the same channel, and assign an IP Address to each
computer on the Ad-Hoc network. (See Box below)
IP Address
When assigning IP Addresses to the computers on the network, please
remember that the IP Address for each computer must be in the same
IP Address range as all the computers in the network, and the subnet
mask must be exactly the same for all the computers in the network.
For example: If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of 192.168.0.2
with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0, then the second computer can be
assigned an IP Address of 192.168.0.3 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0,
etc.
IMPORTANT: If computers or other devices are assigned the same IP
Address, one or more of the devices may not be visible on the network.
12
Page 13
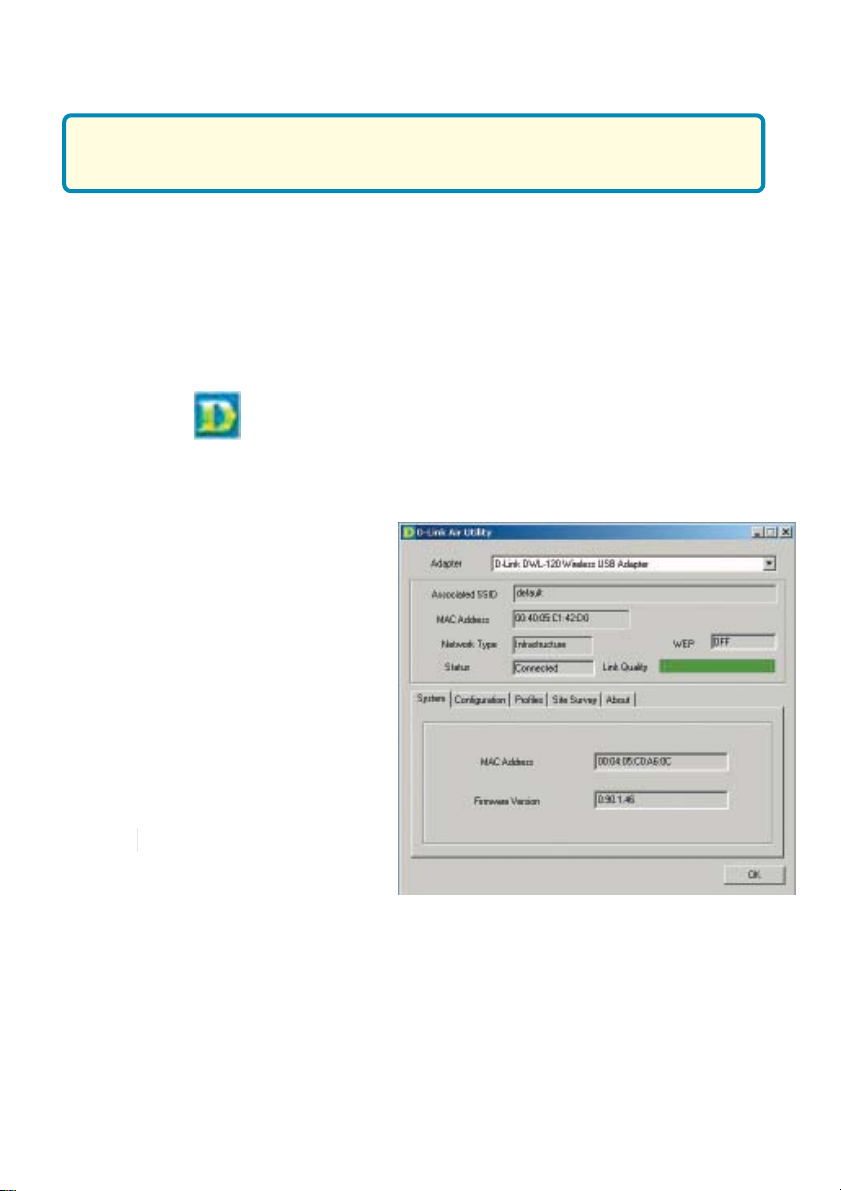
Using the Configuration Utility
With its default settings, the DWL-120 will connect
with other D-Link Air products, right out of the box.
D-Link Air DWL-120 uses the Configuration Utility as the management
software. The utility provides the user an easy interface to change any settings
related to the wireless adapter. When the computer is started, the
Configuration Utility starts automatically and the system tray icon is loaded
in the toolbar (see illustration below.) Clicking on the utility icon will start the
Configuration Utility. Another way to start the Configuration Utility is to
click on Start>Programs>D-Link DWL-120.
A new icon - will appear in your Icon tray. Double-click on the icon
shown above. The screen below will be displayed with the following default
settings:
System
Associated SSID:
The Service Set Identifier is the
name assigned to the wireless
network. The factory SSID setting
is set to default.
MAC Address:
Displays the MAC Address of the
Access Point that is associated
with the DWL-120.
Network Type:
The default setting is Infrastructure.
Ad-Hoc mode is used for peer-to-
peer networking.
Status:
Displays the current connection state of the DWL-120.
WEP:
(Wireless Encryption Protocol)
Displays encryption status.
Link Quality:
Displays the wireless signal strength
for the DWL-120 wireless connection
to the access point.
13
Page 14
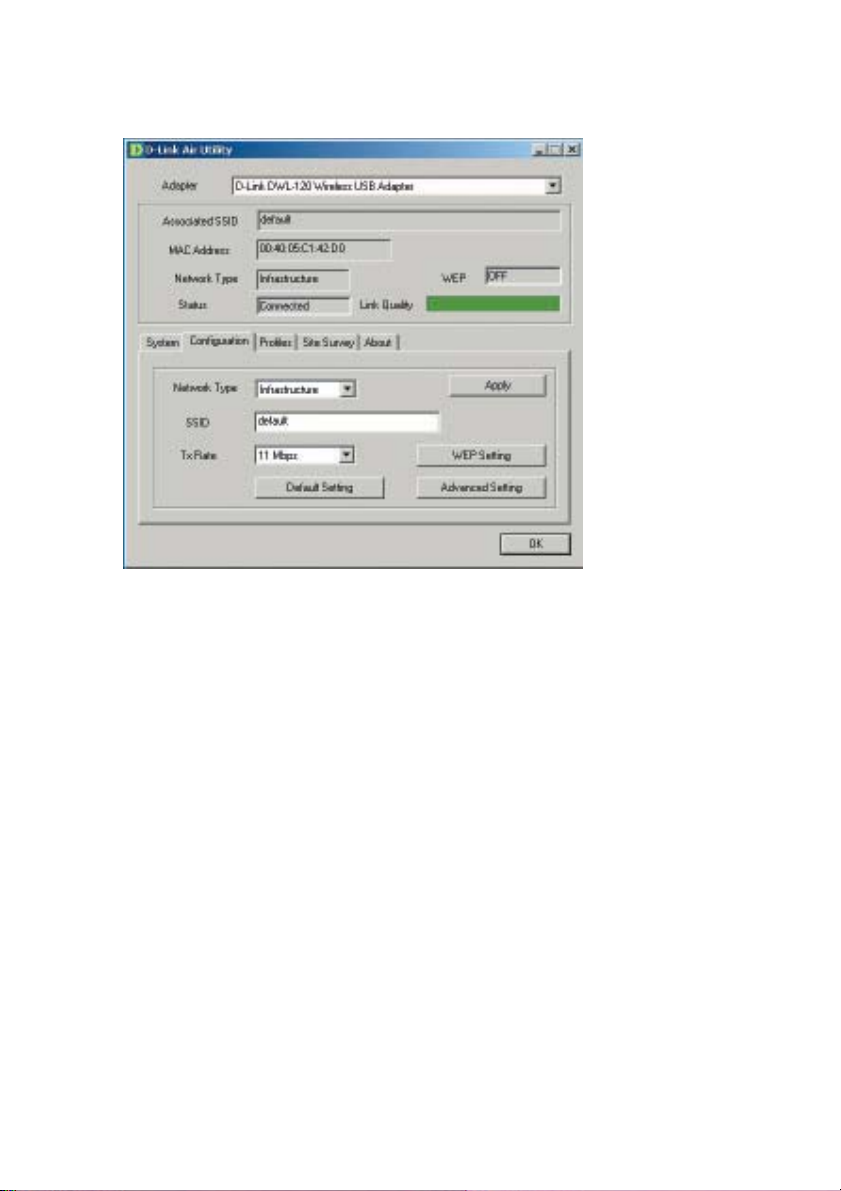
Using the Configuration Utility
Configuration
Network Type:
Infrastructure is the factory default setting. Ad-Hoc mode is used for peer
to peer networking. See the Getting Started section in this manual for
examples of these network types.
SSID:
The Service Set Identifier is the name assigned to the wireless network. The
factory SSID setting is set to default. Make changes here to match the
SSID on existing Wireless Router or Access Point.
Tx Rate:
You can adjust the transmission rate to get the best signal possible depending on your usage and your environment.
Default Setting:
Reverts the DWL-120 back to its factory default settings
WEP Setting:
Will allow you to configure the Encryption for your DWL-120. By default
WEP is disabled.
Advanced Setting:
To configure advanced settings for Power, RTS and Fragmentation Threshold.
14
Page 15
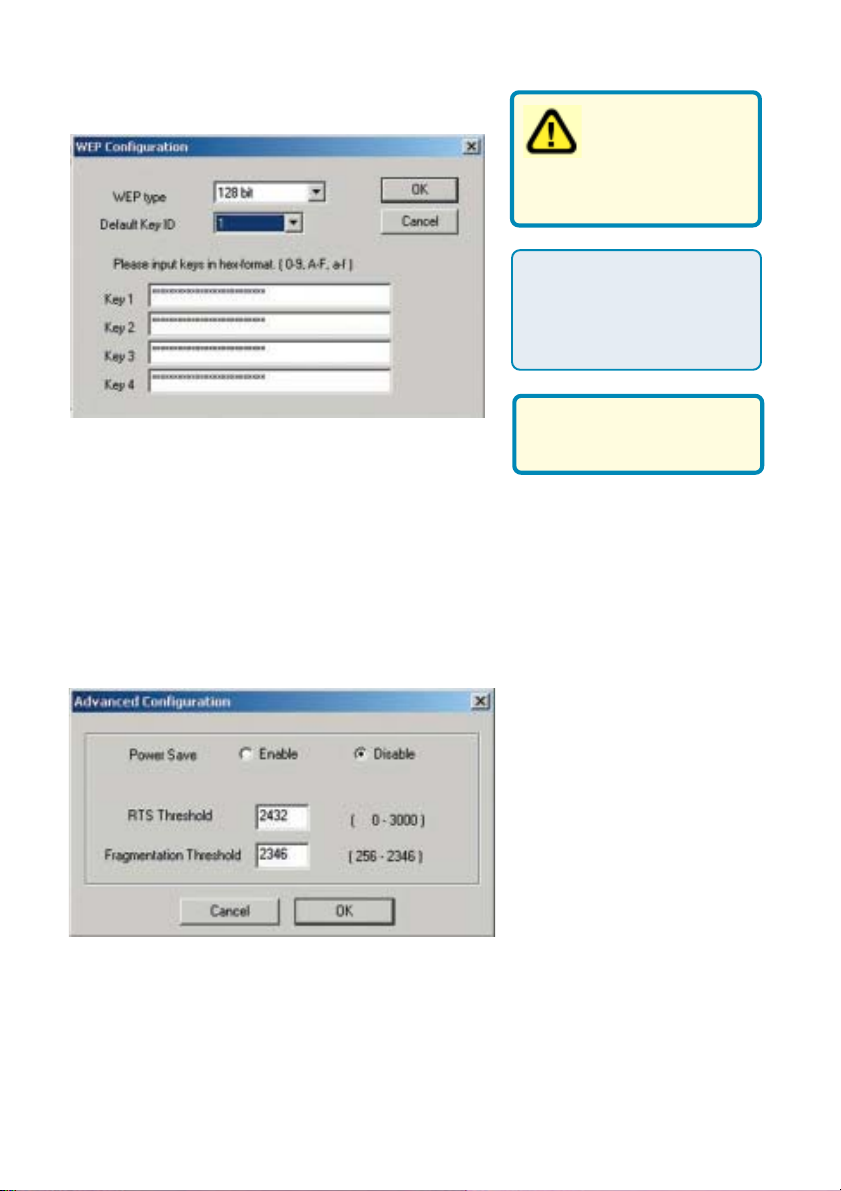
Using the Configuration Utility
Configuration>WEP Setting
WEP encryption on the
router or access point.
WEP stands for Wired
Equivalent Privacy. It is a
security protocol for
Wireless Local Area
Networks
Hexadecimal format
WEP type:
Select 128 bit WEP or 64 bit WEP encryption
consists of numbers 0-9
and letters a-f.
Default Key ID:
1 is the default key, or you may select a key from 1-4
Input WEP keys:
Input up to 4 WEP keys in hexadecimal format
Click OK if you have made any changes
Configuration>Advanced Setting
Power Save:
Select Enable or Disable;
Disable is the default setting
If you enable WEP
encryption make
sure to match the
RTS Threshold:
Request to Send threshold
measures the value in bytes.
Any packet size exceeding
2432 will trigger the DWL120 to use RTS/CTS
mechanism for transmission.
Fragmentation Threshold:
The fragmentation threshold, which is specified in bytes, determines whether
packets will be fragmented. Packets exceeding the 2346 byte setting will be
fragmented before transmission.
Click OK if you have made any changes
15
Page 16

Using the Configuration Utility
Profiles
New:
Click New to create a new profile; a pop-up window will appear allowing
you to configure the new profile. (See the example on the next page.)
Remove:
Highlight the profile you wish to remove; click Remove
Edit:
Highlight the profile you wish to edit; click Edit; a pop-up window will appear allowing you to edit the profile. (See the example on the next page.)
Duplicate:
Highlight the profile you wish to duplicate; click Duplicate
Configuration >Save:
Click Save to save the new profile
Configuration >Apply:
Click Apply to use a selected profile for your network configuration
File >Import:
Click on Import to select an existing profile on your hard drive
File >Export:
Click on Export to save a selected profile to your hard drive
Click OK if you have made any changes
16
Page 17

Using the Configuration Utility
Network Type:
Select Infrastructure or
Ad-Hoc
SSID:
All devices on the network must
share the same SSID to be able
to communicate
TxRate:
Choose the data rate speed
WEP:
Choose Enable or Disable. Disable is the default setting. If you enable
WEP, you must Enable WEP on all devices on the network, in order to
communicate.
Advanced Setting:
Click to access Advanced
configuration
Click OK if you have made any changes
Edit/Create new profile
WEP Setting:
Click to configure the WEP setting
Site Survey
View all the devices in the network from the Site Survey tab.
17
Page 18

Using the Configuration Utility
About
The About tab displays the utility (firmware) version.
18
Page 19

Networking Basics
Using the Network Setup Wizard in Windows XP
In this section you will learn how to establish a network at home or work,
using Microsoft Windows XP.
Note: Please refer to websites such as
and http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000 for information about
networking computers using Windows 2000, ME or 98SE.
Go to Start>Control Panel>Network Connections
Select Set up a home or small office network
http://www.homenethelp.com
When this screen appears, Click Next.
19
Page 20

Networking Basics
Please follow all the instructions in this window:
Click Next
In the following window, select the best description of your computer. If your
computer connects to the internet through a gateway/router, select the
second option as shown.
Click Next
20
Page 21

Networking Basics
Enter a Computer description and a Computer name (optional.)
Click Next
Enter a Workgroup name. All computers on your network should have the
same Workgroup name.
Click Next
21
Page 22

Networking Basics
Please wait while the Network Setup Wizard applies the changes.
When the changes are complete, click Next.
Please wait while the Network Setup Wizard configures the computer.
This may take a few minutes.
22
Page 23

Networking Basics
In the window below, select the option that fits your needs. In this example, Create
a Network Setup Disk has been selected. You will run this disk on each of the
computers on your network. Click Next.
Insert a disk into the Floppy Disk Drive, in this case drive A.
23
Page 24

Networking Basics
Please read the information under Here’s how in the screen below. After you complete the Network Setup Wizard you will use the Network Setup Disk to run the
Network Setup Wizard once on each of the computers on your network. To continue
click Next.
24
Page 25

Networking Basics
Please read the information on this screen, then click Finish to complete the
Network Setup Wizard.
The new settings will take effect when you restart the computer. Click Yes to
restart the computer.
You have completed configuring this computer. Next, you will need to run the
Network Setup Disk on all the other computers on your network. After running the Network Setup Disk on all your computers, your new wireless network will be ready to use.
25
Page 26

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
To name your computer, please follow these directions:In Windows XP:
Click Start (in the lower left corner of the screen)
Right-click on My Computer
Select Properties and click
Select the Computer
Name Tab in the System
Properties window.
You may enter a Computer Description if you
wish; this field is optional.
To rename the computer
and join a domain, Click
Change.
26
Page 27

Networking Basics
Naming your Computer
In this window, enter the
Computer name
Select Workgroup and enter
the name of the Workgroup
All computers on your network
must have the same
Workgroup name.
Click OK
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP
The wireless adapter-equipped computers in your network must be in the same IP
Address range (see Getting Started in this manual for a definition of IP Address Range.)
To check on the IP Address of the adapter, please do the following:
Right-click on the
Local Area
Connection icon
in the task bar
Click on Status
27
Page 28

Networking Basics
Checking the IP Address in Windows XP
This window will appear.
Click the
Support tab
Click Close
Assigning a Static IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Note: Residential Gateways/Broadband Routers will automatically assign IP Addresses to the computers on the network, using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) technology. If you are using a DHCP-capable Gateway/Router you
will not need to assign Static IP Addresses.
If you are not using a DHCP capable Gateway/Router, or you need to assign a Static IP
Address, please follow these instructions:
Go to Start
Double-click on
Control Panel
28
Page 29

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address in Windows XP/2000
Double-click on
Network
Connections
Right-click on Local Area
Connections
Double-click on
Properties
29
Page 30

Networking Basics
Assigning a Static IP Address
in Windows XP/2000
Click on Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP)
Click Properties
Input your IP address and
subnet mask. (The IP
Addresses on your network
must be within the same
range. For example, if one
computer has an IP Address
of 192.168.0.2, the other
computers should have IP
Addresses that are
sequential, like 192.168.0.3
and 192.168.0.4. The
subnet mask must be the
same for all the computers
on the network.)
Input your DNS server
addresses. (Note: If you
are entering a DNS server,
you must enter the IP
Address of the Default
Gateway.)
The DNS server information will be supplied
by your ISP (Internet Service Provider.)
Click OK
30
Page 31

Networking Basics
Checking the Wireless Connection by Pinging in Windows XP and
2000
Go to Start > Run >
type cmd. A window
similar to this one
will appear. Type
ping
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx,
where xxx is the IP
Address of the
Wireless Router or
Access Point. A
good wireless
connection will show
four replies from the
Wireless Router or
Acess Point, as
shown.
Checking the Wireless Connection by Pinging in Windows Me
and 98
Go to Start > Run
> type command.
A window similar to
this will appear.
Type ping
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
where xxx is the IP
Address of the
Wireless Router or
Access Point. A
good wireless
connection will
show four replies
from the wireless
router or access
point, as shown.
31
Page 32

Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems that can occur during the installation and
operation of the DWL-120. Read the following descriptions if you are having problems.
(The examples below are illustrated in Windows XP. If you have another operating
system, these solutions will still apply although the appearance on your computer screen
may differ.)
1. Check that the drivers for the DWL-120 are installed properly.
Go to Start >
My Computer >
Properties
Select the
Hardware
Tab
Click Device
Manager
32
Page 33

Troubleshooting
Double-click
on Network
Adapters
Right-click on D-Link Air
DWL-120 Wireless USB
Adapter
Select Properties
to check that the
drivers are
installed properly
D-Link Air DWL-120 Wireless USB Adapter
Look under Device
Status to check that the
device is working
properly
Click OK
D-Link Air DWL-120 Wireless USB Adapter
D-Link Air DWL-120 Wireless USB Adapter
33
Page 34

Troubleshooting
2. What variables may cause my wireless products to lose reception?
D-Link products let you access your network from virtually anywhere you want.
However, the positioning of the products within your environment will affect the
wireless range. Please refer to Installation Considerations in the Wireless
Basics section of this manual for further information about the most advantageous placement of your D-Link wireless products.
3. Why does my wireless connection keep dropping?
Antenna Orientation- Try different antenna orientations for the DWL-
120. Try to keep the antenna at least 6 inches away from the wall or
other objects.
If you are using 2.4GHz cordless phones, X-10 equipment or other home
security systems, ceiling fans, and lights, your wireless connection will
degrade dramatically or drop altogether. Try changing the Channel on
your Router, Access Point and Wireless adapter to a different Channel
to avoid interference.
Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet) from electrical devices that
generate RF noise, like microwaves, Monitors, electric motors, etc.
4. Why can’t I get a wireless connection?
If you have enabled Encryption on the DWL-120, you must also enable encryption on all wireless devices in the network in order to establish a wireless connection.
The Encryption settings are: 64 or 128 bit. Make sure that the encryp-
tion bit level is the same on the Router and the DWL-120.
Make sure that the SSID on the Router (if you have one in your network)
and the DWL-120 are exactly the same. If they are not, wireless connection will not be established. The default SSID is default.
34
Page 35

Technical Specifications
Standard
IEEE 802.11b
WIFI Certified
Diagnostic LED
Power
Link Status
Temperature
Operating: 0ºC to 55ºC (32ºF to 131ºF)
Storing: -20ºC to 75ºC (-4ºF to 167ºF)
Humidity:
95%, non-condensing
Antenna Type:
Integrated
Modulation Technique:
DSSS
WHQL Certified
Physical Dimensions:
L = 3.3 inches
W = 2.1 inches
H = 0.2 inches
Data Rates:
1,2,5.5,11 Mbps (with Automatic Fallback)
Interface:
USB 1.1
Available Channels:
Eleven channels for North America
Media Access Protocol:
CSMA/CA with ACK
35
Page 36

Contacting Technical Support
You can find the most recent software and user documentation on the
D-Link website.
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
When contacting technical support, please provide the following
information:
• Serial number of the unit
• Model number or product name
• Software type and version number
Page 37

Warranty and Registration
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
1. Bitte lesen Sie sich diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den spätern Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen.
Vervenden Sie keine Flüssig- oder Aerosolreiniger. Am besten dient
ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung.
4. Um eine Beschädigung des Gerätes zu vermeiden sollten Sie nur
Zubehörteile verwenden, die vom Hersteller zugelassen sind.
5. Das Gerät is vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sichern Stand zu achten. Ein
Kippen oder Fallen könnte Verletzungen hervorrufen. Verwenden Sie
nur sichere Standorte und beachten Sie die Aufstellhinweise des
Herstellers.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen zur Luftzirkulation die das Gerät vor
Überhitzung schützt. Sorgen Sie dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht
abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose muß aus Gründen der elektrischen
Sicherheit einen Schutzleiterkontakt haben.
10.Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen
kann. Es sollete auch nichts auf der Leitung abgestellt werden.
11.Alle Hinweise und Warnungen die sich am Geräten befinden sind zu
beachten.
12.Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten
Sie es vom Stromnetz trennen. Somit wird im Falle einer
Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
13.Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder
Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät gelangen. Dies könnte einen Brand bzw.
Elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
14.Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der
elektrischen Sicherheit nur von authorisiertem Servicepersonal
geöffnet werden.
Page 38

15.Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu
trennen und von einer qualifizierten Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a –Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sint beschädigt.
b –Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c –Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
d –Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung ensprechend
funktioniert oder Sie mit Hilfe dieser Anleitung keine Verbesserung
erzielen.
e –Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f – Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
16.Bei Reparaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile bzw. den Orginalteilen
entsprechende Teile verwendet werden. Der Einsatz von
ungeeigneten Ersatzteilen kann eine weitere Beschädigung
hervorrufen.
17. Wenden Sie sich mit allen Fragen die Service und Repartur betreffen
an Ihren Servicepartner. Somit stellen Sie die Betriebssicherheit des
Gerätes sicher.
Page 39

Limited Warranty
Hardware:
D-Link warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in
workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the
following periods measured from date of purchase from D-Link or its
Authorized Reseller:
Product Type Warranty Period
Complete products One year
Spare parts and spare kits 90 days
The one-year period of warranty on complete products applies on
condition that the product's Registration Card is filled out and returned to
a D-Link office within ninety (90) days of purchase. A list of D-Link
offices is provided at the back of this manual, together with a copy of the
Registration Card. Failing such timely registration of purchase, the
warranty period shall be limited to 90 days.
If the product proves defective within the applicable warranty period,
D-Link will provide repair or replacement of the product. D-Link shall
have the sole discretion whether to repair or replace, and replacement
product may be new or reconditioned. Replacement product shall be of
equivalent or better specifications, relative to the defective product, but
need not be identical. Any product or part repaired by D-Link pursuant
to this warranty shall have a warranty period of not less than 90 days,
from date of such repair, irrespective of any earlier expiration of original
warranty period. When D-Link provides replacement, then the
defective product becomes the property of D-Link.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting a D-Link office within
the applicable warranty period, and requesting a Return Material
Authorization (RMA) number. If a Registration Card for the product in
question has not been returned to D-Link, then a proof of purchase (such
as a copy of the dated purchase invoice) must be provided. If
Purchaser's circumstances require special handling of warranty
correction, then at the time of requesting RMA number, Purchaser may
also propose special procedure as may be suitable to the case.
Page 40

After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged
securely in the original or other suitable shipping package to ensure that
it will not be damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be
prominently marked on the outside of the package. The package must
be mailed or otherwise shipped to D-Link with all costs of
mailing/shipping/insurance prepaid; D-Link will ordinarily reimburse
Purchaser for mailing/shipping/insurance expenses incurred for return of
defective product in accordance with this warranty. D-Link shall never
be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory data
of Purchaser contained in, stored on, or integrated with any product
returned to D-Link pursuant to this warranty.
Any package returned to D-Link without an RMA number will be rejected
and shipped back to Purchaser at Purchaser's expense, and D-Link
reserves the right in such a case to levy a reasonable handling
charge in addition mailing or shipping costs.
Page 41

Software:
Warranty service for software products may be obtained by contacting a
D-Link office within the applicable warranty period. A list of D-Link
offices is provided at the back of this manual, together with a copy of the
Registration Card. If a Registration Card for the product in question has
not been returned to a D-Link office, then a proof of purchase (such as a
copy of the dated purchase invoice) must be provided when requesting
warranty service. The term "purchase" in this software warranty refers
to the purchase transaction and resulting licence to use such software.
D-Link warrants that its software products will perform in substantial
conformance with the applicable product documentation provided by
D-Link with such software product, for a period of ninety (90) days from
the date of purchase from D-Link or its Authorized Reseller. D-Link
warrants the magnetic media, on which D-Link provides its software
product, against failure during the same warranty period. This warranty
applies to purchased software, and to replacement software provided by
D-Link pursuant to this warranty, but shall not apply to any update or
replacement which may be provided for download via the Internet, or to
any update which may otherwise be provided free of charge.
D-Link's sole obligation under this software warranty shall be to replace
any defective software product with product which substantially conforms
to D-Link's applicable product documentation. Purchaser assumes
responsibility for the selection of appropriate application and
system/platform software and associated reference materials. D-Link
makes no warranty that its software products will work in combination
with any hardware, or any application or system/platform software
product provided by any third party, excepting only such products as are
expressly represented, in D-Link's applicable product documentation as
being compatible. D-Link's obligation under this warranty shall be a
reasonable effort to provide compatibility, but D-Link shall have no
obligation to provide compatibility when there is fault in the third-party
hardware or software. D-Link makes no warranty that operation of its
software products will be uninterrupted or absolutely error-free, and no
warranty that all defects in the software product, within or without the
scope of D-Link's applicable product documentation, will be corrected.
Page 42

LIMITATION OF WARRANTIES
IF THE D-LINK PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTED
ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER'S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT D-LINK'S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT. THE FOREGOING
WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, EITHER
IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE,
INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. D-LINK NEITHER ASSUMES NOR
AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY
OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION
MAINTENANCE OR USE OF D-LINK'S PRODUCTS.
D-LINK SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS
TESTING AND EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED
DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY
THE CUSTOMER'S OR ANY THIRD PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED
ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE
RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE,
LIGHTNING OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT WILL D-LINK BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES,
INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA, LOSS OF PROFITS, COST OF COVER
OR OTHER INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INDIRECT
DAMAGES ARISING OUT THE INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE, USE,
PERFORMANCE, FAILURE OR INTERRUPTION OF A D- LINK
PRODUCT, HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY.
THIS LIMITATION WILL APPLY EVEN IF D-LINK HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
IF YOU PURCHASED A D-LINK PRODUCT IN THE UNITED STATES,
SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION
OF LIABILITY FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES,
SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
D-Link Offices for Registration and Warranty Service
The product's Registration Card, provided at the back of this manual,
must be sent to a D-Link office. To obtain an RMA number for warranty
Page 43

service as to a hardware product, or to obtain warranty service as to a
software product, contact the D-Link office nearest you. An
addresses/telephone/fax list of D-Link offices is provided in the back of
this manual.
Trademarks
Copyright 2002 D-Link Corporation.
Contents subject to change without prior notice.
D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc.
All other trademarks belong to their respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative
such as translation, transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link
Systems Inc., as stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976
Page 44

FCC Warning
Federal Communication Commission Interference
Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by
the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for
an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and
operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
Page 45

CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause
radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures.
Warnung!
Dies ist ein Produkt der Klasse A. Im Wohnbereich kann dieses Produkt
Funkstoerungen verursachen. In diesem Fall kann vom Benutzer verlangt
werden, angemessene Massnahmen zu ergreifen.
Precaución!
Este es un producto de Clase A. En un entorno doméstico, puede causar
interferencias de radio, en cuyo case, puede requerirse al usuario para que
adopte las medidas adecuadas.
Attention!
Ceci est un produit de classe A. Dans un environnement domestique, ce
produit pourrait causer des interférences radio, auquel cas l`utilisateur devrait
prendre les mesures adéquates.
Attenzione!
Il presente prodotto appartiene alla classe A. Se utilizzato in ambiente
domestico il prodotto può causare interferenze radio, nel cui caso è possibile
che l`utente debba assumere provvedimenti adeguati.
BSMI Warning
Page 46

AVERTISSEMENT AUX UTILISATEURS
La décision N° 01-480 en date du 23 mai 2001 prise
par l’Autorité de Régulation des Télécommunications
(ART) autorise l’utilisation d’une partie de la bande de
fréquences 2400-2483,5 MHz pour les réseaux locaux
radioéléctriques (RLAN)
Au niveau national, seule la bande 2446,5-2483,5 MHz
est autorisée pour des produits ayant une puissance
limitée à 100 mW
Cette bande de fréquences correspond aux canaux
10,11,12 et 13.
En installant et utilisant les produits réseaux sans fils
de la gamme proposée par D-Link, vous vous engagez
donc à respecter cette réglementation et à n’utiliser
que ces 4 canaux.
WARNING
The Decision N° 01-480 taken by ART (Autorité de Régulation
de Télécommunications) on May 23, 2001 authorizes the
utilisation of a part of the 2400-2483.5MHz band for Radio
Local Area Network (RLAN) in France.
Only the 2446.5-2483.5MHz band is authorized for RLAN with
products with a limited power to 100mW.
This band concerns the channels 10, 11, 12 and 13.
Using and installing D-Link Wireless solutions for RLAN, you
commit to respect this regulation et to use only these four
channels.
Page 47

Offices
Australia D-Link Australasia
Unit 16, 390 Eastern Valley Way, Roseville, NSW 2069 Australia
TEL: 61-2-9417-7100 FAX: 61-2-9417-1077 TOLL FREE (Australia): 1800-177100
TOLL FREE (New Zealand): 0800-900900
URL: www.dlink.com.au E-MAIL: support@dlink.com.au & info@dlink.com.au
Level 1, 434 St. Kilda Road, Melbourne, Victoria 3004 Australia
TEL: 61-3-9281-3232 FAX: 61-3-9281-3229 MOBILE: 0412-660-064
Canada D-Link Canada
2180 Winston Park Drive, Oakville, Ontario, L6H 5W1 Canada
TEL: 1-905-829-5033 FAX: 1-905-829-5095 BBS: 1-965-279-8732
TOLL FREE: 1-800-354-6522 URL: www.dlink.ca
FTP: ftp.dlinknet.com E-MAIL: techsup@dlink.ca
Chile D-Link South America
Isidora Goyeechea 2934 of 702, Las Condes, Santiago, Chile, S. A.
TEL: 56-2-232-3185 FAX: 56-2-232-0923 URL: www.dlink.cl
E-MAIL: ccasassu@dlink.cl & tsilva@dlink.cl
China D-Link China
2F, Sigma Building, 49 Zhichun Road, Haidan District, 100080 Beijing, China
TEL: 86-10-88097777 FAX: 86-10-88096789 URL: www.dlink.com.cn
E-MAIL: liweii@digitalchina.com.cn
Denmark D-Link Denmark
Naverland 2, DK-2600 Glostrup, Copenhagen, Denmark
TEL: 45-43-969040 FAX:45-43-424347 URL: www.dlink.dk E-MAIL: info@dlink.dk
Egypt D-Link Middle East
7 Assem Ebn Sabet Street, Heliopolis, Cairo, Egypt
TEL: 20-2-635-6176 FAX: 20-2-635-6192 URL: www.dlink-me.com
E-MAIL: support@dlink-me.com & fateen@dlink-me.com
Finland D-Link Finland
Thlli-ja Pakkahuone Katajanokanlaituri 5, FIN– 00160 Helsinki
TEL: 358-9-622-91660 FAX: 358-9-622-91661 URL: www.dlink-fi.com
France D-Link France
Le Florilege #2, Allee de la Fresnerie, 78330 Fontenay le Fleury, France
TEL: 33-1-3023-8688 FAX: 33-1-3023-8689 URL: www.dlink-france.fr
E-MAIL: info@dlink-france.fr
Germany D-Link Central Europe/D-Link Deutschland GmbH
Schwalbacher Strasse 74, D-65760 Eschborn, Germany
TEL: 49-6196-77990 FAX: 49-6196-7799300 URL: www.dlink.de
BBS: 49-(0) 6192-971199 (analog) BBS: 49-(0) 6192-971198 (ISDN)
INFO: 00800-7250-0000 (toll free) HELP: 00800-7250-4000 (toll free)
REPAIR: 00800-7250-8000 E-MAIL: info@dlink.de
India D-Link India
Plot No.5, Kurla-Bandra Complex Rd., Off Cst Rd., Santacruz (E), Bombay, 400 098
India
Page 48

TEL: 91-22-652-6696 FAX: 91-22-652-8914 URL: www.dlink-india.com
E-MAIL: service@dlink.india.com
Italy D-Link Mediterraneo Srl/D-Link Italia
Via Nino Bonnet n. 6/b, 20154, Milano, Italy
TEL: 39-02-2900-0676 FAX: 39-02-2900-1723 URL: www.dlink.it E-MAIL:
info@dlink.it
Japan D-Link Japan
10F, 8-8-15 Nishi-Gotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141, Japan
TEL: 81-3-5434-9678 FAX: 81-3-5434-9868 URL: www.d-link.co.jp
E-MAIL: kida@d-link.co.jp
Netherlands D-Link Benelux
Fellenoord 1305611 ZB, Eindhoven, the Netherlands
TEL: 31-40-2668713 FAX: 31-40-2668666 URL: www.d-link-benelux.n
Norway D-Link Norway
Waldemar Thranesgt. 77, 0175 Oslo, Norway
TEL: 47-22-991890 FAX: 47-22-207039
Russia D-Link Russia
Michurinski Prospekt 49, 117607 Moscow, Russia
TEL: 7-095-737-3389 & 7-095-737-3492 FAX: 7-095-737-3390 URL: www.dlink.ru
E-MAIL: vl@dlink.ru
Singapore D-Link International
1 International Business Park, #03-12 The Synergy, Singapore 609917
TEL: 65-774-6233 FAX: 65-774-6322 E-MAIL: info@dlink.com.sg
URL: www.dlink-intl.com
South Africa D-Link South Africa
102 – 106 Witchhazel Avenue, Einstein Park 2, Block B, Highveld Technopark,
Centurion, South Africa
TEL: 27 (0) 12-665-2165 FAX: 27 (0) 12-665-2186 URL: www.d-link.co.za
E-MAIL: attie@d-link.co.za
Spain D-Link Iberia
C/Sabino De Arana, 56 Bajos, 08028 Barcelona, Spain
TEL: 34 93 4090770 FAX: 34 93 4910795 URL: www.dlinkiberia.es
E-MAIL: info@dlinkiberia.es
Sweden D-Link Sweden
P. O. Box 15036, S-167 15 Bromma, Sweden
TEL: 46-(0) 8-564-61900 FAX: 46-(0) 8-564-61901 E-MAIL: info@dlink.se
URL: www.dlink.se
Taiwan D-Link Taiwan
2F, No. 119 Pao-Chung Rd, Hsin-Tien, Taipei, Taiwan
TEL: 886-2-2910-2626 FAX: 886-2-2910-1515 URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
E-MAIL: dssqa@tsc.dlinktw.com.tw
Turkey D-Link Middle East
Deniz Bilgisayar, Buyukdere Cad. Naci Kasim Sk., No. 5 Mecidiyekoy, Istanbul, Turkey
TEL: 90-212-213-3400 FAX: 90-212-213-3420 E-MAIL: smorovati@dlink-me.com
U.A.E. D-Link Middle East
CHS Aptec (Dubai), P.O. Box 33550 Dubai U.A.E.
Page 49

TEL: 971-4-366-885 FAX: 971-4-355-941 E-MAIL: Wxavier@dlink-me.com
U.K. D-Link Europe
4th Floor, Merit House, Edgware Road, Colindale, London NW9 5AB United Kingdom
TEL: 44 (0) 20-8731-5555 FAX: 44 (0) 20-8731-5511 BBS: 44 (0) 181-235-5511
URL: www.dlink.co.uk E-MAIL: info@dlink.co.uk
U.S.A. D-Link U.S.A.
53 Discovery Drive, Irvine, CA 92618, USA
TEL: 1-949-788-0805 FAX: 1-949-753-7033 BBS: 1-949-455-1779 & 1-949-455-9616
INFO: 1-800-326-1688 URL: www.dlink.com
E-MAIL: tech@dlink.com & support@dlink.com
 Loading...
Loading...