Page 1

Copyright Statement
Copyright ©1998 D-Link Corpor ation
No part of this p ublication may be r ep roduced in any form or by
any means or used to make any derivative such as translation,
transformation, or adaptation without permission from D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems Inc., as stipulated by the United
States Co pyright Act of 1976.
Trademarks
D-Link is a registered tr ademark of D-Link Corporat ion/D-Link
Systems, Inc.
All other tr ademarks belong to t heir respective owners.
Limited Warranty
This guide and the accompanying product ar e each provid ed “as
is,” without w arranty as to th eir perfor mance, merchantability or
fitness for any particular purpose. D-Link Corporation and D-Link
Systems, Inc. reserve the right to r evise this publication and to
make changes to its co nt ent s at any time, without obligation to
notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
Page 2

Page 3
Table of Contents
I
NTRODUCTION
.......................................................................1
Features .................................................................................................... 2
Ease of Installation..............................................................................................2
Built-in Hub.......................................................................................................2
ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI)......................................................................... 3
ISDN Leased Line...............................................................................................3
Multiple Networking Protocol Support................................................................4
Standard Phone Jacks..........................................................................................4
Dial On Demand................................................................................................. 4
Bandwidth On Demand.......................................................................................4
Full Network Management..................................................................................5
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) ......................................5
PPP Security....................................................................................................... 5
MS (Microsoft) CHAP........................................................................................5
RIP-1/RIP-2........................................................................................................6
DHCP Support (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol )....................................... 6
Call Control........................................................................................................6
Data Compression............................................................................................... 7
Networking Compatibility...................................................................................7
Applications For Your DI-106 or DI-106M................................................ 7
Internet Access....................................................................................................7
Internet Single User Account (SUA) .................................................................... 7
Multiprotocol LAN-to-LAN Connection .............................................................. 8
Telecommuting Server........................................................................................ 8
What This Manual Covers.......................................................................... 8
What This Manual Doesn’t Cover..............................................................9
Other Resources ........................................................................................ 9
Packing List............................................................................................... 9
Additional Install ati on R equi rement s.......................................................10
B
EFORE YOU BEGIN
.............................................................11
Page 4

Road Map and Flow.................................................................................11
Completing the Worksheet ....................................................................... 12
Ordering Your ISDN Line ................................................................................. 13
Collecting General Setup Information................................................................ 14
Collecting ISDN Phone Line Information .......................................................... 14
Collecting Ethernet Setup Information ............................................................... 17
I
NSTALLATION
.......................................................................23
A Warning On Connection Cables ........................................................... 24
Mounting the Route r................................................................................24
Connecting Your Computer and Your DI-106 or DI-106M....................... 24
Connecting the RS-232 Cable to the Router....................................................... 25
Connecting an ISDN Line to the Router............................................................. 25
Connecting a Telephone or Fax Machine to the Router...................................... 26
Connecting Ethernet Cables to the Router......................................................... 26
Important Notes on Ethernet Hub Connections.................................................. 27
Connecting a Power Adapter to the Router........................................................29
The DI-106 or DI-106M’s Front Panel .................................................... 30
Powering Up Your DI-106 or DI-106M.................................................... 31
Navigating Through the System Management Terminal Inte rfac e............. 32
System Management Terminal Interface Summary................................... 33
General Setup.......................................................................................... 34
ISDN Setup.............................................................................................. 35
North American ISDN....................................................................................... 36
DSS1 & 1TR6 ISDN......................................................................................... 38
Ethernet Setup......................................................................................... 42
General Ethernet Setup..................................................................................... 42
TCP/IP and DHCP Ethernet Setup .................................................................... 43
Novell IPX Ethernet Setup................................................................................45
Bridge Ethernet Setup....................................................................................... 46
C
ONFIGURING FOR INTERNET ACCESS
...................................47
Page 5

IP Addresses and the Internet .................................................................. 47
Internet Access Configuration.................................................................. 49
Single User Account ................................................................................ 52
Configuration for Single User Acc ount .................................................... 54
Configuring Backup ISP Account s ........................................................... 55
R
EMOTE NODE CONFIGURATION
............................................57
Bandwidth on Demand............................................................................. 63
Edi ting PPP Optio n s................................................................................ 65
D
IAL-IN CONFIGURATION
.......................................................68
Telecommuting ........................................................................................ 69
Dial-In Server Application....................................................................... 69
Default Dial-In Setup............................................................................... 70
Dial-In Users Setup ................................................................................. 75
More on CLID .................................................................................................. 77
TCP/IP C
ONFIGURA TI ON
......................................................79
IP Subnet Mask........................................................................................ 79
LAN-to-LAN Application ......................................................................... 80
Remote Node Setup .......................................................................................... 81
Static Route Setup............................................................................................83
N
OVELL
IPX C
ONFIGURATION
...............................................87
IPX Network Environment ....................................................................... 87
Frame Type....................................................................................................... 87
Network Numbers............................................................................................. 87
DI-106M on LAN with Server................................................................... 88
DI-106M on LAN without Server .............................................................. 88
Page 6

IPX Spoofing ........................................................................................... 89
IPX Ethernet Setup .................................................................................. 89
LAN-to-LAN Application ......................................................................... 91
Remote Node Setup .......................................................................................... 92
Static Route Setup.................................................................................... 94
B
RIDGING CONFIGURA TION
....................................................97
IPX Spoofing ........................................................................................... 97
Bridge Ethernet Setup.............................................................................. 98
LAN-to-LAN Application ......................................................................... 99
Remote Node Setup ........................................................................................ 100
Default Dial-In Setup for Bridge ..................................................................... 101
Bridge Static Route Setup............................................................................... 101
F
ILTER CONFIGURA TION
......................................................103
About Filtering...................................................................................... 103
DI-106’s Filter Structure....................................................................... 104
Configuring a Filter Set......................................................................... 104
Configuring a Filter Rule....................................................................... 107
TCP/IP Filter Rule .......................................................................................... 108
Generic Filter Rule......................................................................................... 112
Novell IPX Filter Rule....................................................................................114
SNMP...............................................................................116
About SNMP.......................................................................................... 116
Configuring Your DI-106M For SNMP Support..................................... 116
S
YSTEM SECURITY
..............................................................119
Configuring the SMT Password.............................................................. 120
Page 7

Using RADIUS Authentication............................................................... 121
Installing a RADIUS Server............................................................................ 121
Configuring the DI-106M for RADIUS Authentication.................................... 122
Adding Users to the RADIUS Database........................................................... 124
Using RADIUS Authentication for CLID......................................................... 124
T
ELNET CONFIGURA TI ON A ND CAPABILITIES
............................126
About Telnet Confi guration ................................................................... 126
Telnet Capabilities................................................................................. 127
Single Administrator....................................................................................... 127
System Timeout.............................................................................................. 127
S
YSTEM MAINTENANCE
.......................................................128
System Status ......................................................................................... 128
Terminal Baud Rate............................................................................... 132
Log and Trace ....................................................................................... 132
View Error Log............................................................................................... 133
Syslog And Accounting................................................................................... 133
Diagnostic............................................................................................. 135
Backup Configuration............................................................................ 138
Restore Configuration............................................................................ 138
Software Update.................................................................................... 139
Command Interpreter Mode................................................................... 140
Call Control .......................................................................................... 140
Call Control Parameters.................................................................................. 141
Blacklist......................................................................................................... 142
Budget Management ....................................................................................... 143
Call History.................................................................................................... 143
T
ROUBLESHOOTING
............................................................145
Problems Starting Up the DI-106 or DI-106M....................................... 145
None of the LEDs are on when you power up the router .................................. 145
Page 8

Connecting the RS-232 cable, cannot access the SMT..................................... 145
Problems With the ISDN Line................................................................ 146
The ISDN initialization failed......................................................................... 146
The ISDN loopback test failed......................................................................... 146
Problems with the LAN Interface ........................................................... 147
Can’t PING any station on the LAN ................................................................ 147
Problems Connecting to a Remote Node or ISP ..................................... 147
Problems Connecting to a Remote User ................................................. 148
ISDN S
WITCH TYPES
.........................................................149
Provisioning For U.S. Switches.............................................................. 149
Provisioning For the AT&T 5ESS Switches..................................................... 150
Provisioning For the Northern Telecom Switch ............................................... 151
G
LOSSARY
.........................................................................153
I
NDEX
................................................................................163
Page 9
ISDN Router
User’s Guide
Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of a D-Link DI-106 series
remote access router with integrated Ethernet hub. No larger than
an ordina ry mod em, your router offers inexpensiv e yet comp lete
telecommunication s and in terne twor king solutions for your home
or branch office. It is ideal for everything from Internet browsing to
receiving calls from Remote Dial-in Users and making LAN-toLAN connections to Remote No des.
Distinguishing features of the DI-106 series include support for a
full range of networking protocols such as TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, also known as IP), Novell IPX
(Internet P acket Exchange), and Transparent Bridging.
♦ DI-106: ISDN S/T interface, IP routing
♦ DI-106W: ISDN U interface, IP routing
♦ DI-106M: ISDN S/T interface, IP/IPX routing, bridging
♦ DI-106MW: ISDN U interface, IP/IPX r outing, bridging
This complete solution also includes r emote dial-in user support, an
Internet single-user account (Networ k Address T r anslation) option,
ex tensive network ma nagement capa bilities, and solid sec urity
features.
Page 10

2 Introduction
NOTE:
Throughout the remainder of this manual, the term
“DI-106” refers to any DI-106 or DI-106W, and the term
“DI-106M” ref ers t o any D I- 106M or DI- 106MW .
Features
Each DI-106 series router is packed with features that give it the
flex ibility to provid e a comp lete networ king solution for almost an y
user.
Ease of Installation
Your DI-106 or DI-106M is a self-contained unit that is quick and
easy to in stall. Phys ica lly, it resembles an exter n al mod em;
however, it is a combination ISDN rout er and 10BASE-T E thernet
hub, and it uses twisted-pair Ethernet cables to connect to the host
network.
Built-in Hub
As a 10BASE-T Ethernet hub, yo ur DI -106 or DI-106M pro vides
six ports for connection of standard 10- Mbps Ethernet devices.
Five ports ar e designed for connection of network end nodes—
single-u ser computers, ser vers, bridges, other r outer s, etc.—
through standard “straight-thro ugh” twisted-pair cables; the sixt h is
wired for making an “uplink” co nnection to a nother hub thro ugh
the same kind of cable for ne twork expa ns ion.
Page 11
Introduction 3
ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
Using a standard S/T or U I nt erface (t he DI-106 and DI-106M use
the S/T interface, while the DI-106W and DI-106MW use the U
interface) the DI-106 and DI-106M suppor t a full range of switch
types. The switch type depends on the CO (Centr al Office) switch
your ISDN line is connected to . S ee the
ISDN Switch Types
chapter
for more information on North American, Eu r opean, and Asian
ISDN firmware and swit ch types support ed by these routers.
The two B- channels can be used independently fo r two
destinations. Or they can be bundled fo r one connection to suppor t
bandwidth-on-demand.
ISDN Leased Line
If the router is set up for an ISDN leased line (t hat is, if any opt ion
but Switch/Switch or Switch/Unused is selected for the B Channel
Usage control in setup menu 2, ISDN Set up, and the Transfer Type
control is set to Leased in either set up menu 4, Internet Access
Setup, o r set up menu 11.1, Remote Node Pro file), the rout er will
auto matically initialize the leased-line connection each time it is
powered up o r the settings in setup menu 2, 4, or 11.1 are saved.
The DI-106 and DI-106M implement the PPP echo mechanism for
verifying ISDN leased line status. The setting of the Idle Timeout
con trol in setup menu 11.1 will be u sed a s the interval between t wo
LCP_Echo_Req messages. It is supposed that t here exists an echo
reply correspo nding to an echo request. Whenever an echo request
is sen t, the counter will be increme nt ed by one .
T h e s end counter will be r eset to zero after an ech o response is
received. The leased- line error reco very mechanism will be
Page 12
4 Introduction
triggered after the send counter r eaches 4. If the Idle Timeout
control is set to zero, the PPP echo mechanism will no t b e u se d.
Multiple Networking Protocol Support
The DI-106M is a multi-proto col router. It supports T CP/IP,
Novell I PX, and Transparent Bridging.
Standard Phone Jacks
The rout er is equipped wit h two standard phone jacks fo r
connecting t ele phones, fax ma chines, or modems. This allows the
ISDN line to be used for voice calls as well as data calls.
Dial On Demand
The Dial On Demand feature allows a DI-106 or DI - 106M t o
auto matically place a call to a Remote Node whenever there is
traffic coming fro m any workstation on the LAN (Local Area
Network) to that remote site.
Bandwidth On Demand
Your DI-106 or DI-106M support s bandwidth up to 128 kbps
(k ilobits—that is, tho usand s of bits—per second) o ve r a single
ISDN BRI line. It incorporates PPP/MP (Point-to -Po int Protoco l/
Multilink Protoc ol) to bundle two B channels ov er a BRI line. In
addition, the router dynamically allocates bandwidth between the
two B channels, increasing or decr easing bandwidt h as needed to
allo w for gr eater efficiency in data transfer. It supports BAP
(Ba ndwidth Allocation Pro tocol) and BA CP (Ban dw idth A llocation
Page 13

Introduction 5
Control Pr otocol) to manage the nu mber of links in multilin k
bundle.
Full Network Management
The DI-106M incorporates SNMP (Simple Net work Management
Prot ocol) support and menu-driven network management via an
RS-232 or T elnet connection. In addition, both the DI-106 and the
DI-106M offer the Call Detail Record ( CDR) function to help you
an alyz e a nd manage you r telephon e bill.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service)
The RADIUS feature allows you to use a cent r al external Unixbased server to suppo r t thousands of users (DI-106M only).
PPP Security
The DI-106 and DI-106M support PAP (Password Aut hentication
Protoco l) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol).
MS (Microsoft) CHAP
Your DI-106 or DI-106M and a Microsoft Windows 95 o r
Windows NT server can authenticate each other using Microsoft’s
proprietary CHAP algorithm. No special setup is needed to suppor t
MS CHAP. Everything is done through PPP negotiation between
the router and the server.
Page 14
6 Introduction
RIP-1/RIP-2
Your DI-106 or DI-106M support s bot h RIP-1 and RIP-2 (Routing
Information Pro toco l versions 1 and 2) exchanges with other
rout ers. RIP version controls in setup menus 3.2 (TCP/IP and
DHCP Ethernet Setup) and 11.3 (Remote Node Networ k Layer
Options ) le t you con trol R IP use, and offer th e following v er sion
opt ions: RIP- 1 ( accept and send RIP-1 messages only), RIP-2B
(accept RI P-1 and RIP-2 messages, both broadcast and multicast,
and send RIP-2 messages in broadcast format), and RIP-2M
(accept RI P-1 and RIP-2 messages, both broadcast and multicast,
an d send RIP-2 me ssages in multicast format) .
(The suggested choice in bot h menus is RIP-2B, except in
envir onments where there are r outers that do not understand RIP-2
packets at all.
Broadcast
, above, means a destination MAC or IP
hos t address consisting of all binary o nes;
multicast
means a MAC
address of 01:00:5E:00:00:09 hex or an IP destination address of
224.0.0.9.)
DHCP Support (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP (D yn amic Hos t Configuration Protocol) allows you to
dynamically and automatically assign IP addr ess settings to hosts on
your network.
Call Control
Your DI-106 or DI-106M pro vides budget management for
out going calls and maintains a “blacklist” of unreachable phone
number s in order to save you the expense of unnecessary charges.
Page 15
Introduction 7
Data Compression
The DI-106 and DI-106M incorporate St ac data compression and
CCP (Compression Control Protocol).
Networking Compatibility
The DI-106 and DI-106M are compatible with remote access
products from other companies such as Ascend, Cisco, and 3Com.
Furthermore, they support Microsoft Windows 95 and Windows
NT remote access capability.
Applications For Your DI-106 or DI-106M
Some applications for the DI-106 and DI-106M include:
Internet Access
Your DI-106 or DI-106M supports the TCP/IP protocol, which is
the language used for the Inter net . I t is also compatible with access
servers manufactured by major vendors such as Cisco and Ascend.
Internet Single User Account (SUA)
For small office environments, the DI-106 and DI-106M offer a
Single User Int er net Account ( also known as a Netwo r k Address
Translator, or NAT) from an ISP (Internet S er vice Provider). This
allows multiple users on t he LAN to access the Internet
concurrent ly for t he co st of a single user.
Single User Acco unt addr ess mapping can also be used for LAN to
LAN connections.
Page 16
8 Introduction
Multiprotocol LAN-to-LAN Connection
The DI-106 and DI-106M can dial to or answer calls from anot her
remote access ro uter connected t o a different network. The
DI-106M support s TCP/IP and Novell IPX, and has the capability
to bridge any Ethernet protocol.
Telecommuting Serve r
The DI-106 and DI-106M allow Remot e Dial-in Users to dial in
and gain access to your LAN. This feature enables users that have
workstations with remote access capabilities, e.g ., Win dow s 95, to
dial in using an ISDN terminal adapter (TA) to access the netwo r k
resources without physically being in the office.
What This Manual Covers
T h is ma n ua l is d ivided into five pa rts .
1. Part One, Getting Started, is stru ctured as a step- by-step guide
to help you connect, install, and set up your DI-106 or DI-106M
to operate on your LAN.
2. Part Two, The Internet , descr ibes how to configure the router
to connect to the Internet.
3. Part Three, Setting Up Advanced Applications, describes how
to use the router for more advanced applications, such as
TCP/IP routing and Bridging.
4. Part Four, Advanced Management, p rovides information on
adva nced mana gement features for ne twork manage rs.
Page 17
Introduction 9
5. Part Five, System Maintenance, describes maintenance features
for checking system stat us and logging errors.
Regardless of the ap plic ation, it is importan t th at you follow the
steps outlined in Part One to cor r ectly co nnect your DI-106 or
DI-106M to your LAN. You can then refer to other chapters of the
manual depending on which applications you wish to use.
What This Manual Doesn’t Cover
This manual assumes that you know how to use your computer and
are familiar with your co mmunication s software . If you hav e
questions about using either o ne, refer t o the manual for the
product .
Other Resources
For more info r mation about your DI-106 or DI-106M check the
fo llowing sources:
♦ Quick Start Guide.
♦ Support disk.
Packing List
Before you proceed further, check all items you r eceived with yo ur
DI-106 or DI - 106M against this list to make sure nothing is
missing. The complete package should include:
♦ One DI-106 or DI-106M IS DN r outer.
♦ One power adapter.
Page 18

10 Introduction
♦ One RS-232 cable.
♦ One “straight-thro ugh” t wisted-pair Ethernet cable.
♦ One Support Disk.
♦ This
User’s Guide
.
Additional Installation Requirements
In addition to the contents o f your package, there are other
hardware and software requirements you need before you can
install and use your router. These requirements include:
♦ An ISDN telep ho ne lin e.
♦ E thernet connection(s) to your computer(s).
♦ A computer equipped with an RS-232 por t and
communications software co nfigured to the following
parameters:
◊ VT100 terminal emulation.
◊ 9600 baud.
◊ No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit.
After the rout er has been successfully connected to your network,
you can make futur e changes to the configuration using a Telnet
client application.
Page 19
Before You Begin 11
Before You Begin
To ensure successful installation of your DI-106 or DI-106M, we
strongly recommend t hat you carefully follow the steps outlined in
the next two chapter s. T hese chapters ar e designed as a guide for
you to collect the necessary information about your I SDN pho ne
line and the LAN w hich you w ill b e c onne cted to. On ce th is
information has be en collected, it will be used to configure your
rout er.
After you have successfully configured your DI-106 or DI- 106M,
see the appropr iate chapter s to set up your applications. For
Internet Access, see the
Configuring for Internet A ccess
chapter
start ing on page 47.
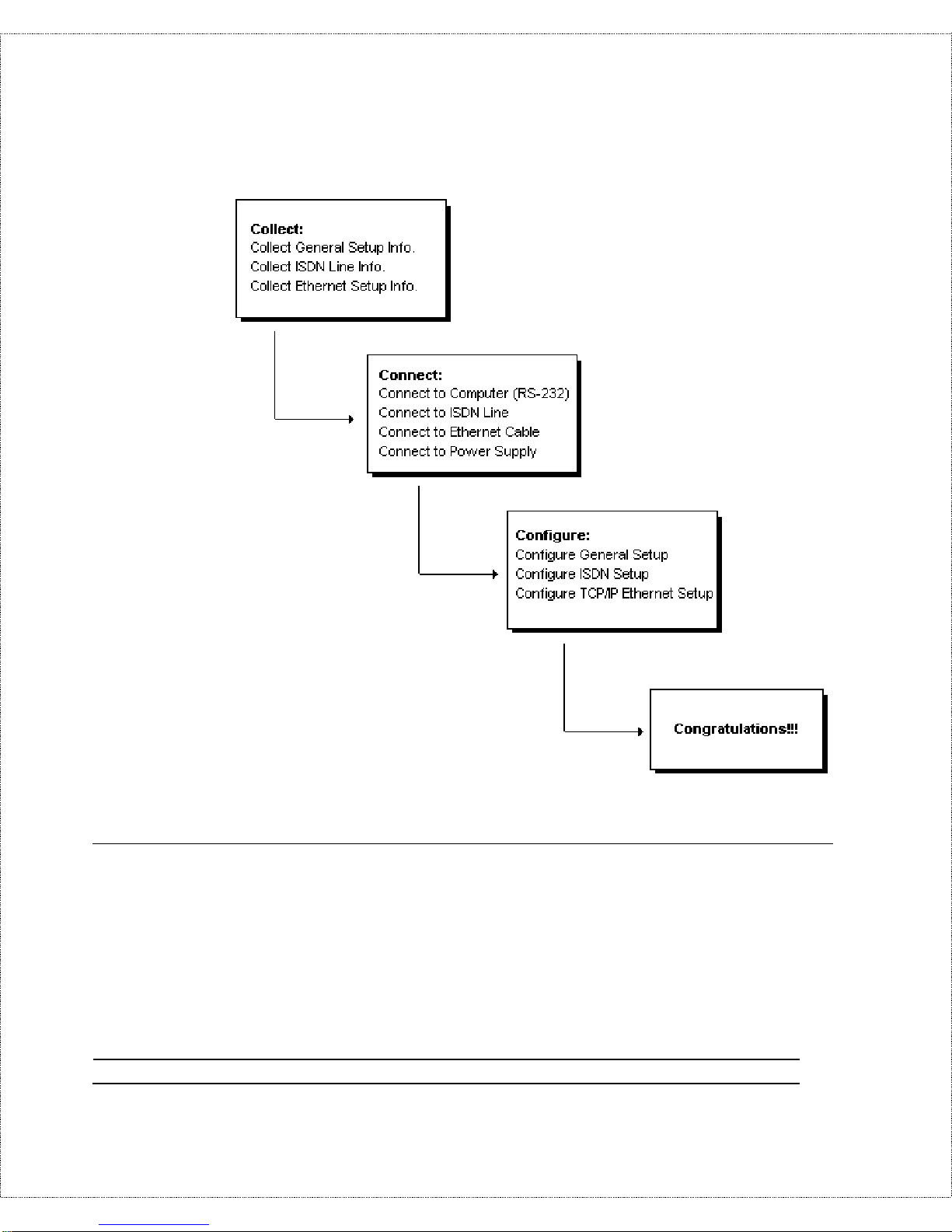
Road Map and Flow
The chart below is provided as a step by step guide to successfully
ins talling your DI -106 o r DI - 106M.
Page 20
12 Before You Begin
Completing the Worksheet
Before you continue, locate the wor k sheet at the end of this
chapter. T his information work sheet has been provided to help you
get thro ugh setup and installation of your DI-106 o r DI -106M as
easily as possible.
Page 21

Before You Begin 13
Ordering Your ISDN Line
If you do not have the ISDN line installed already, we suggest that
you order it from your telephone company as so on as possible t o
av oid the long wa iting pe riod common whe n orde ring a new line.
Use the information in t his section to place the or der ( see the
ISDN
Switch Types
ch ap ter for information on provis ioning your ISDN
line). I f you have already installed your I S DN line, yo u can check
the following section to make sure that you can use all the features
of your DI-106 or DI-106M.
1. Contact your local telephone company’s IS DN Or der ing Center.
2. Find out what type of ISDN service is available. Refer to the
ISDN Switch Types
chapter to find out the provisioning
information for the appro pr iate switch type and ISDN service.
For the U.S. , the DI-106W and DI-106MW (U Interface) have
been approved by Bellcore and have I OC ( I S DN Or der ing
Code) “S” Capability, EZ-ISDN 1.
3. P r ovid e your t elephone company with the proper pr ovisioning
information.
4. When the telephone company installs your ISDN line, be sure to
o btain the follow in g information :
◊ ISDN switch type.
◊ ISDN telephone number(s).
◊ ISDN Service Profile Identifier (SPID) number(s) (only for
North America).
Page 22
14 Before You Begin
Collecting General Setup Information
Your DI-106 or DI-106M requires the following system
information. Yo u c an obtain all the pe rtinent informa tion from you r
networ k administrato r . Record this information int o the wor ksheet
as it be comes av aila b le. This worksheet will later be r efe rred to as
you configure your router.
♦ System Name—T his is the name g iven to the router for
identification purposes . This name sh ould be n o more than 8
alphanumeric characters. Spaces ar e no t allowed, but “-” and
“_” are accepted. This name can be obtained remot ely via the
SNMP mana ge ment pr otocol an d w ill be displa yed as the
prompt when t he user enters Command Interpreter Mode.
♦ Route IP Field—For Int er net access, you will need to ena ble
the Rout e I P Field. See the
Configuring for Internet A ccess
chapter starting on page 47 for more details on configur ing
your rout er for Int er net access. T o support Novell IPX, or
Bridging, enable the appropriate pro toco l and reference the
related chapters for de tailed information.
You have now collected all of the general setup information you
need. Make sure that you have entered all the values onto t he
worksheet before proceeding to the next section.
Collecting ISDN Phone Line Information
Afte r you ha ve successfu lly installed the ISDN phone line or if you
already have one installed, you need to use the ISDN line
information to complete the worksheet and co nfigure your router.
Page 23
Before You Begin 15
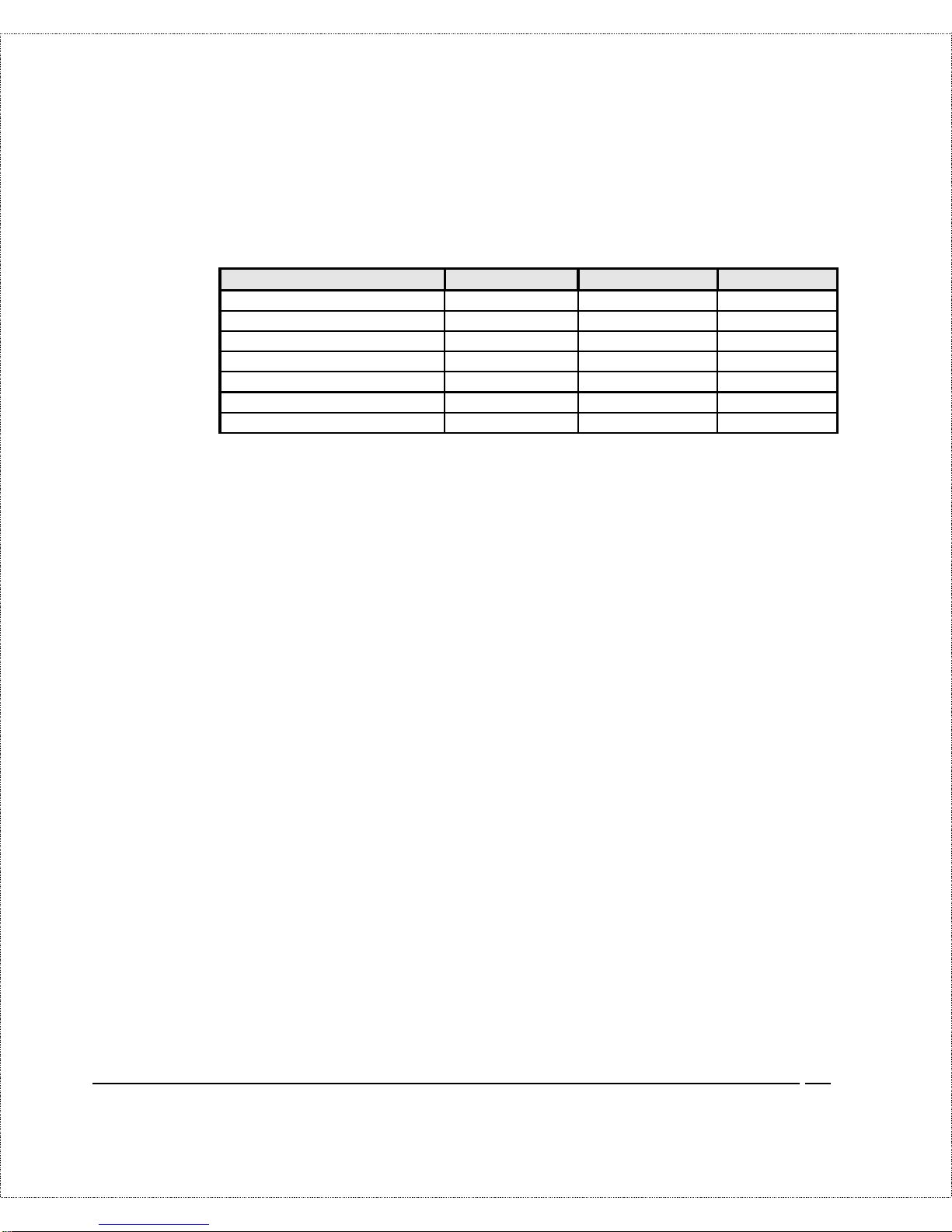
Your t elephone company can give you the following information to
configure the DI-106 or DI- 106M:
Switch Type Geography No. of Phone #s No. of SPIDs
AT&T 5ESS NI-1 North America 2 2
AT&T 5ESS Point to Point North America 1 0
AT&T 5ESS Multipoint North America 2 2
Northern Telecom NI-1 North America 2 2
Northern Telecom Custom North Am erica 2 2
DSS1 Europe, Asia 2 N/A
1TR6 Germany 2 N/A
♦ Switch Type—This is the type of switch used by your
telephone company. Check wit h your t elephone company and
choose t he appropriate option on the worksheet. For North
America, select your ISDN switch type. For DSS 1 and 1TR6,
verify this field to make sure that you have the proper
firmware loaded.
♦ B Channel Usage—De ter mine which c on nection is
appropriate for your B channel and check the corresponding
option on the worksheet.
If your DI-106 or DI - 106M is the only device using the ISDN
line, configure B Channel Usage to Switch/Switch so the router
device will u se bo th B cha nne ls to communicate. If th e r oute r is
sharing the ISDN line with other devices, configure B Channel
Usage to Switch/Unused. If your DI-106 or DI - 106M is on a
leased line, configure B channel usage t o Leased/Leased or
Leased/Switch, depending on the setting of the line.
♦ Telephone Number(s)—Record on the worksheet the
telephone number ( s) given to you by your ISDN provider.
Some switc h type s only have one tele phone number . These
phone numbers should be in a standard digit format (for
Page 24

16 Before You Begin
example, 5551212). Note that these fields will only accept
digits, so hyphens and spaces will not be accept ed.
♦ Analog Call—The router can direct an incoming analog call
to standard phone jack 1 or to st andard phone jack 2, or treat
it as a data call, on t he basis of the number being called. On
the work sheet , check t he way analog calls to each phone
number are to be hand led.
The Phone1 sett ing directs incoming analog calls for the
associated number to standard pho ne jack 1 (also referred to as
A/B adapter 1, POTS [Plain Old Telephone System] port 1, and
analog po r t 1). T he Phone2 set ting directs such calls t o standard
phone jack 2.
The DOVBS setting is used for Data Over Voice Bearer
Service, also known as Data Over S peech Bearer S er vice, or
DOS BS . This is a service availab le fro m some ISDN provide rs
that declares incoming ISDN data calls as analog. Check this
setting if your service contract specifies DOVBS on the
associated number.
♦ SPID Number(s)—(For North America only) T he SPI D
(Service Profile Ident ifier) is a number used by a central
office switch for identification purposes. With the switch
information, see the previous table for the number of SPIDs
you must enter .
You have now collected all of the necessary information about your
ISDN phone line. Make sure that these values are entered into your
worksheet before you cont inue to the next section. For DSS1 and
1TR6 ISDN, refer to the
Installation
chapter starting on page 23.
Page 25

Before You Begin 17
Collecting Ethernet Setup Information
This section assumes that you are setting up your router for a
TCP/IP connection. If you want to configur e the system for other
protocols (e.g., IPX), refer to t he appropriate chapters.
♦ Ethern et I nte rf ace —Your DI-106 or DI - 106M is equipped
with six Ethernet po r ts (input/output circuits). The jacks (that
is, the connectors) for por ts 1 through 5 are wired to let you
connect netwo r k end nodes—single-user computers, servers,
bridges, and other routers, for example—using easily
obtained “straight-through” twisted-pair Ethernet cables. The
jack for the six th port is labeled Up link and is wired to let
you c onnect a nother 10- M bps Ethernet hub us ing a straightthrough cable, or an end node using a cr oss-wired cable.
♦ IP Address—An IP Address is required for TCP/IP prot ocol.
The IP Address is a unique 32- bit number assigned to your
route r. I t is w ritte n in d otted decimal nota tion (four 8-bit
numbers, between 0 and 255, separated by per iods), e.g.,
192.68.203.5.
Record the IP Address into the worksheet as assigned by your
network administr ator. Note t hat every machine on a TCP/IP
network ( the global Internet, for example) must have a unique
IP address; do no t assign an arbitrar y address to any machine.
♦ IP Sub-net Mask—This field is required for TCP/IP
protocol. An IP address consists of two parts, the network ID
and the host ID. The IP Subnet Mask is used to specify the
network ID portion of the address, expressed in dot ted
decimal notation. Your DI -106 or DI-106M will
auto matically calculate this mask based on t he IP addr ess that
Page 26
18 Before You Begin
you assign. Unle ss you have special need for subnetting, use
the default mask as calculated by the router .
The table belo w lists some examples of IP subnet masks and the
number of hosts that are allo wed. Consult your network
administ rator if you a re unsure of this v alu e.
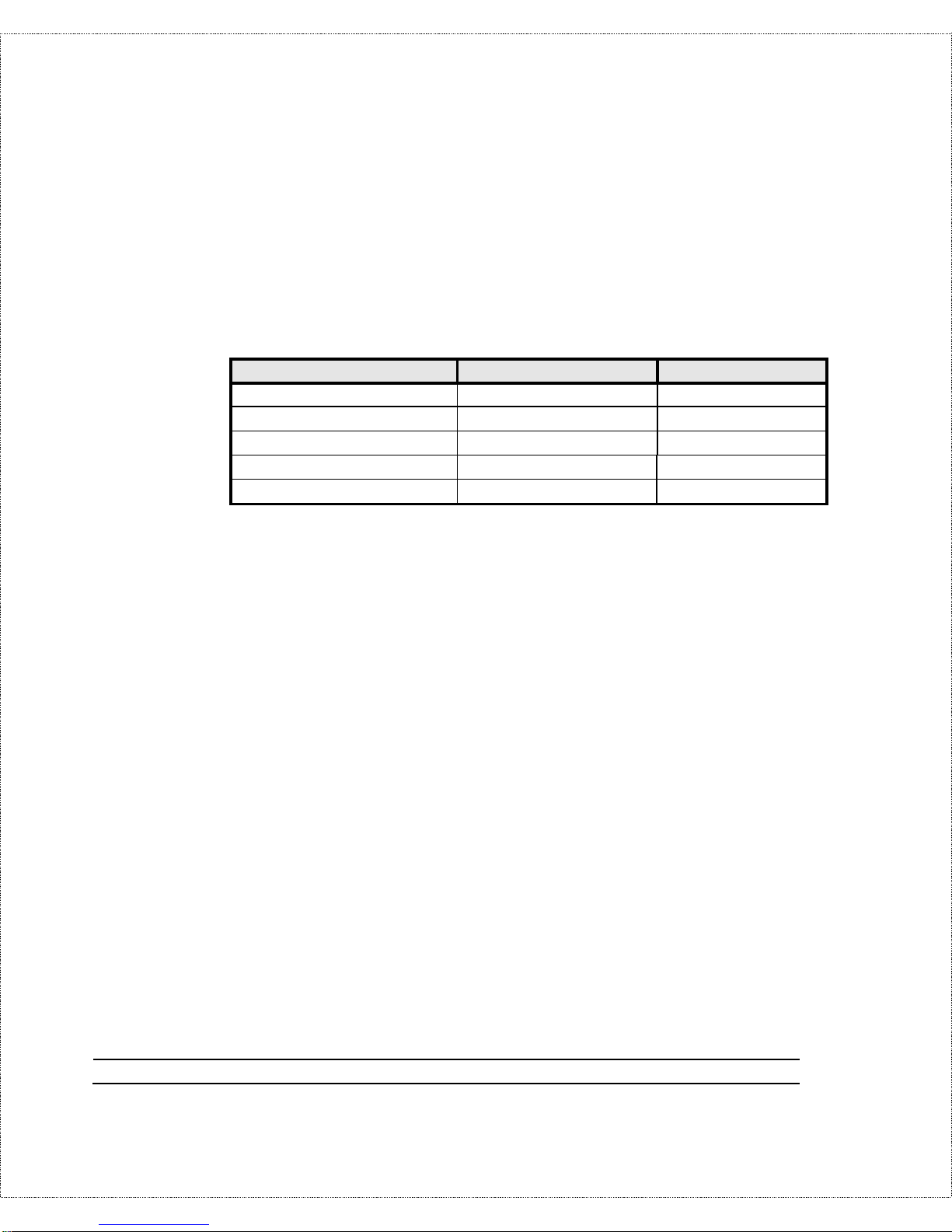
IP Subnet Mask Number of Host IDs Number of Bits
255.255.255.0 254 24
255.255.255.128 126 25
255.255.255.192 62 26
255.255.255.224 30 27
255.255.255.255 1 32
Page 27

Before You Begin 19
DI-106/DI-106M Setup and Installation Worksheet
*HQHUDO 6HWXS ,QIRUPDWLRQ
♦ System Name (for identification purposes):
_______________________________________
♦ Protocol(s):
___TCP/IP
___IPX (DI-106M only)
___Bridging (DI-106M only)
,6'1 6HWXS ,QIRUPDWLRQ
♦ Switch Typ e ( ch eck one):
___AT&T 5ESS NI-1
___AT&T Point to Po int
___AT&T 5ESS Mult ipoint
___Nort hern Telecom NI-1
___Nort hern Telecom Custom
___DSS1
___1TR6
♦ B-Channel Usage (check one):
___Switch/Swit ch
___Switch/Leased
___Leased/Switch
___Leased/Unused
Page 28

20 Before You Begin
___Unused/Leased
___Leased/Leased
___Leased128
___Switch/Unus ed
North American ISDN
♦ 1st Telephone Number:
_________________________________________________
Analog Call (check one): __Phone1 __Phone2 __DOVBS
♦ 1st SPID Number:
_________________________________________________
♦ 2nd Telephone Number:
_________________________________________________
Analog Call (check one): __Phone1 __Phone2 __DOVBS
♦ 2nd SPID Number:
_________________________________________________
DSS1 ISDN
♦ ISDN Data Number & Subaddress:
_________________________________________________
♦ A/B Adapter 1 Number & Subaddress:
_________________________________________________
♦ A/B Adapter 2 Number & Subaddress:
_________________________________________________
♦ Outside Line Prefix Number:
_________________________________________________
Page 29

Before You Begin 21
♦ PBX Nu mber (S/T Bu s Number):
_________________________________________________
♦ Incoming Number Matching:
___MSN
___Calling Party Subaddress
___Don’t Care
♦ Analog Call Rout ing:
__A/B #1 __A/B #2 __Ignore
♦ Global Analog Call:
__Accept __Ignore
1TR6 ISDN:
♦ ISDN Data Number:
_________________________________________________
♦ A/B Adapter 1 Number:
_________________________________________________
♦ A/B Adapter 2 Number:
_________________________________________________
♦ Outside Line Prefix Number:
_________________________________________________
♦ PBX Number (S/T Bus Number):
_________________________________________________
♦ Incoming Number Matching:
___EAZ ___Don’t Care
♦ Analog Call Routing:
__A/B #1 __A/B #2 __Ignore
Page 30

22 Before You Begin
(WKHUQHW 6HWXS ,QIRUPDWLRQ
♦ IP Address:
_______._______._______._______
♦ IP Subnet Mask:
_______._______._______._______
1RWHV=
Page 31

Installation 23
Installation
This chapter outlines how to connect your DI-106 or DI - 106M t o
your LAN and ISDN line. Refer to t he diagram below to identify all
of the ports on your device when yo u make connections.
Page 32

24 Installation
A Warning On Connection Cables
ISDN and E th erne t ca b les ar e ver y similar to each ot her. I t is
important that you use the correct cable for each connection;
otherwise, your rout er could be damaged.
Before connecting or disconnecting an RS-232 cable between two
devices, tur n bot h devices off to avoid any chance of damaging
them.
Mounting the Router
The rout er can be placed on a desktop or mounted o n a wall,
depending on your needs. Two mounting holes are provided on the
bottom of the unit for wall mounting . The rec ommended moun ting
position is with the cable jacks facing sideways or downward t o
help keep dust off the contact s.
Regardless of how you mou nt the rou ter, mak e sure its cable jacks
are accessible, its LED indicators are visible, and its ventilation
holes a re never blocked .
Connecting Your Computer and Your DI-106 or DI-106M
For init ial setup of your DI-106 or DI -106M, you must use an
RS-232 connection, either to a computer running serial
communications software or to a serial data t er minal.
After the rout er has been successfully installed, you can mo dify the
configur ation through a remote Telnet connection. See the chapter
Page 33

Installation 25
entitled
Telnet Configuration and Capabilities
fo r detailed
instructions on using T elnet to configure your DI-106 or DI -106M.
Connecting the RS-232 Cable to the Router
An RS-232 cable is included in your package. To connect t his
cable, plug its nine- pin connector into the DCE port on the rout er ’s
side panel, t hen connect the o ther end to an RS-232 serial port on
your computer or data terminal (on IBM-type microco mputers,
serial ports are usually labeled COM1, COM2, etc.).
Connecting an ISDN Line to the Router
Plug one end of your I S DN phone line into the socket on the rear
panel of the rout er labeled ISDN and the other end into the ISDN
wall jack .
♦ S/ T i nt erface—This can only connect to your NT-1
(Network Termination) device.
NOTE:
Do not under any circumstances connect directly to the ISDN
wall jack.
♦ U interface—This allows you to co nnect directly to your
ISDN wall jack.
NOTE:
The ISDN jack is for ISDN line connection only. Connection of
a phone line may r es ult i n dam age to your D I- 106 or D I- 106M .
Page 34

26 Installation
Connecting a Telephone or Fax Machine to the Router
You can connect a regular telephone, fax machine, or modem to
your rout er to be used for analog calls, just as you can do on a
conventional telephone line. No te that the router ’s o ther functions
all wo r k the same whether you connect an analog device or not.
To connect an analo g device, just plug one end of the device’s line
cord into the socket on t he back of the router marked PHONE 1 or
PHONE 2.
To have incoming calls directed to a device on a PHONE po r t, you
must select Phone1 or Phone2 for t he desired telephone number’s
Analog Call contro l in setup menu 2, ISDN Setup.
Connecting Ethernet Cables to the Router
Your DI-106 or DI-106M has six ports for connecting 10BASE-T
Ethernet devices to form a LAN. The jacks for ports 1 through 5
are wired to let you connect netwo r k end nodes (single-user
computers, ser vers, bridges, other routers, et c. ) using standard
“straight-through” EI A (E lectronic Industries Association)
Category 3 or higher-grade twisted-pair data cables. The jack fo r
the sixth p or t is labeled Up link and is wired t o let you co nnect
ano ther 10 -Mbps Et hernet hub using a str a ight- thr ough cable, or an
end node using a cross-wired cable.
The jacks for the ro uter’s Ethernet ports ar e of the type known as
EIA RJ-45 (Recommended Jack No. 45). Note that when you
make a n uplink connection to another hub us ing a st raight-throug h
cable, you must use an uplink-type jack at one end and an endnode-type jack at the ot her.
Page 35

Installation 27
The follo wing figure sho ws ho w to make an Ethernet co nnection
between the rout er and a netwo r k end node.
Important Notes on Ethernet Hub Connections
Observe the following r ules when connecting devices with twistedpair Ethernet cables:
♦ For bot h end-node and uplink connections, use only EIA
Category 3 or higher-grade twisted-pair data cables with
RJ-45 plugs. In almost all cases, only st andard st r aightthrough cables are needed.
♦ Make sure no cable is more than 100 meters (328 feet) long.
Page 36

28 Installation
♦ When u plinking tw o hubs together with a s tr a ig ht-thr ough
cable, use an uplink-t ype jack at one end and an end-nodetype jack at t he o ther.
Not e that you can connect an end node through t he Uplink
jack, but to do so you must use a cro ss- wired cable or cable
converter.
Page 37

Installation 29
♦ If uplinking more than two hubs together, observe the 5-4-3
rule: no signal, in order t o go from one end node t o another,
must ev er pass through more than fiv e tw isted-pair ca bles,
four repeater s ( that is, hubs), and three uplink connections.
T h is is the maximum signa l pa th in tw isted-pair Eth er net.
Also be sure never to allow a signal loop to form.
Connecting a Power Adapter to the Router
Plug an 18V DC, 750 mA power adapt er into t he po wer jack on
the router’s rear panel.
At this point, you should have connected the RS-232 cable, the
ISDN phone line, one or more Et hernet cables, and the power
adapter. You can now power up your DI-106 or DI - 106M.
Page 38

30 Installation
The DI-106 or DI-106M’s Front Panel
Names and descriptions of your router’s front panel LEDs are
given belo w:
POWER—Comes on as soon as you connect the router to t he
power adapt er and plug the power adapt er into a suitable AC
outlet.
TEST—Should be blinking if the router is functioning properly.
ISDN – LINK—Indicates that the rout er has an ISDN line
connected to the WAN interface and it has been successfully
initialized.
ISDN – B1 and ISDN – B2—On if there is an active WAN session
on that channel or if that channel is making or r eceiving a call.
ETHERNET – COL— Shines yellow when a collision oc cu rs o n
the LAN, that is, when two devices have attempted to transmit at
the same time .
ETHERNET – Uplink and ETHERNET – 1 through
ETHERNET – 5—Each of these indicators shines green when a
connection to an Et hernet device is detect ed. The indicato r blinks
when a transmission is received from the device, and shines yellow
when the device has been partitioned, that is, temporar ily isolated
Page 39

Installation 31
from the LAN because of excessive collis ion s (par tition ing is a
req uired c ap ability of all E th erne t hub s) .
PHONE – 1—Light s up when standard phone port 1 is in use.
PHONE – 2—Light s up when standard phone port 2 is in use. .
Powering Up Your DI-106 or DI-106M
When you power up your DI- 106 or DI-106M, t he ro uter will
per f orm s ever al internal tests an d d o an ISDN line initializa tion .
Afte r IS DN line in itialization, the r outer will ask you to p re ss
ENTER to continue.
When you press ENTER, th e r oute r will display a login s creen and
ask you to enter the password, as shown belo w:
Enter t he default password, 1234, to get into the main menu of the
System Management Ter minal (S MT ) . Note that once you are in
the SMT, if there is no activity for more than 5 minutes, the router
Page 40

32 Installation
will au tomatically log you ou t and d isp lay a blan k s creen. If you see
a blank screen, press ENTER to bring up the password screen.
Navigating Through the System Management Terminal
Interface
The SMT is the interface that you use to configure your DI-106 or
DI-106M. Several operations that you should be familiar with
before you attempt to modify the co nfiguration of your router ar e
listed b elow :
♦ M oving Forward to Another Menu. To move forward to a
sub-menu belo w the current one, type in the number of the
sub-menu and press ENTER.
♦ Moving Backward to a Previous Menu. Press the Escape
key to move back to the previous menu.
♦ Moving the Cursor. Within a menu, press ENTER (carriage
retur n) to move to the next field. You can also use the Up
and Down keys to move to the previous and the next field,
respectively.
♦ En teri ng I nform ation . There are two t ypes of fields that
you will need to fill in. T he firs t re quires you to type in th e
appropr iate information. The second gives you choices to
choose from. In the seco nd case, pr ess the space bar to cycle
through t he available choices.
♦ Required Fields. Some of the fields in t he SMT ar e essent ial
in order to configure the DI-106 or DI-106M. T hese fields
will in itially show qu estion marks, indicating th at the
infor mation must be fille d in befor e that men u c an be saved.
Page 41

Installation 33
♦ N/A Fields. Some of th e fie lds in the SM T will show a N/ A.
This symbol r efers to an op tion th at is no t availab le or n ot
applicable.
♦ Saving Your Configuration. You can save your
co nfigu ration by pr essing ENTER at the message ‘Press
ENTER to co nfirm or ESC to cancel’. Saving t he dat a on the
scr een will take you in mo st cases to th e p re vious men u.
T h e SMT main men u is shown below.
System Management Terminal Interface Summary
T h is sec tion summarizes all major SMT me nus:
#
Menu Title Description
1 General Setup Set up general information and enable routing or bridging
of specific protocols
2 ISDN Setup Set up ISDN configuration
3 Ethernet Setup Set up Ethernet c o n figuration
4 Internet Access Setup A quick and easy way to setup Internet connection
11 Remote Node Setup Set up Remote Nod e for LAN- to -LAN connection
Page 42

34 Installation
#
Menu Title Description
includi ng Inte r net connecti on. A DI-106 or DI-106M can
have up to four Remote Nodes.
12 Static Routing Setup Set up static routes for different protocols. Up to four static
routes can be set for each protocol.
13 Default Dial-in Setup Set up default dial-in parameters such that your DI-106 o r
DI-106M can be a dial-in server for the Remote Node and
Remote Dial-in User.
14 Dial-in User Setup Set up Remot e Dial-in User. Your DI-106 or DI-106M
can directly support up to eight Remote Dial-in Users.
21 Filter Set Configuration Set up filters to b e used in men u 3 and men u 11 to provide
security, call control, etc.
22 SN MP Conf iguration S et up SNMP -relate d paramet ers (DI- 106M only)
23 System Security Set up security related parameters
24 System Maintenance Provide system status, diagnostics, firmware upload, etc.
99 Exit To exit from S MT and return to th e blank screen
General Setup
This menu contains ad ministrativ e and system-re late d information .
Enter 1 in the main me nu to go to men u 1, Ge nera l Setup.
Page 43

Installation 35
1. System Name—Give the ro uter a descriptive name for
identification purposes, e.g., AB CD. This na me should be no
more than 8 alphanumeric characters. Spaces ar e not allowed,
but “-” and “_” are accepted. This name can be retrieved
remotely via SNMP , used for CHAP authentic ation, and will be
displaye d a s the promp t in command inte rprete r mode. See the
Dial-In Configuration
chapter starting on page 68 for more
information on CHAP; see the
System Maintenance
chapter
start ing on page 128 for more information on command
interpreter mode.
2. Location—Enter the geographic location (up to 31 characters)
of your DI- 106 or DI-106M, e.g. , San Jose.
3. Contact Person’s Name—Enter t he name (up to 8 charact er s)
of the person in char ge of the router . The Location and the
Contact Person fields are optional.
4. Protocols—Turn on or off the individual protocols for your
particular application. Unsupported proto cols will have a N /A in
their fields.
ISDN Setup
Menu 2 is for entering information about your ISDN line. Different
telephone companies deploy different types of switches for IS DN
ser v ice . Depending on th e s witch for your par ticu lar installa tion ,
yo u w ill hav e a diffe re nt nu mber of telep h on e numbers, and if you
are in North America, you may also have SPIDs. Make sur e that
you have correct and complete t elephone numbers and SPIDs. You
need to pass the ISDN setup before your system can make an
out g oing call or answer an incoming call.
Page 44

36 Installation
North American ISDN
1. Switch Type—Verify the switch type information with your
telephone company. Fo r North America, select the type of
switch used by your telephone company. I f your switch type is
not curr e ntly show n, press the space b a r to change to the next
switch; repeat until you see the co r r ect switch type. The router
will n ot be able to place or to receive calls if the wrong switch
type is specified. If you are not sure, contact your telephone
company to confirm the exact switch type.
2. B Channel Usage—If yo u ar e using one B channel of your
router with another device on the S/T bus, then select
Switch/Unused. If not choose Switch/Switch. The fo llowing
table shows the relationship between the B Channel Usage
sett ing and ISDN B channels.
B Channel Usage B1 B2
Switch/Sw itc h Switch Switch
Switch/Lease d Switch Leased
Leased/Switc h Leased Switch
Leased/Un use d Leased N/A
Unused/Leased N/A Leased
Leased/Leased* Leased Leased
Page 45

Installation 37
B Channel Usage B1 B2
Leased128** Leased Leased
Switch/U nuse d Switc h N/A
*Leased/Leased = B1 and B2 channels connect to different remote nodes.
**Leased128 = B1 an d B2 channels connect to the same remote node.
3. Telephone Number(s)—Ent er the telephone number(s)
assigned to your IS DN by your telephone company. Some
switch type s allow only one telep hone numb er. In Nor th
America, each number should be in standard seven-digit format,
for example, 5551212. Note t hat the router accepts only digits;
do not include hyphens or spaces in this field. This field should
be no longer than 19 digits.
4. Analog Call—This tells the router where t o direct incoming
analog calls fo r the associated phone number. Set to P ho ne1 t o
direct such calls to the PHONE 1 port, Phone2 to direct them
to the PHONE 2 port, or DOVBS to have them handled as Data
Over Voice Bearer Service (also known as Data Over S peech
Bearer Service, or DOSBS) data calls. ( T he PHONE 1 and
PHONE 2 por ts are known as Plain Old Telepho ne Service
[POTS] ports in North America and A/B Adapter ports in
Europe.)
5. SPID Number(s)—SPIDs are numbers used by a switch for
identificat ion purposes. Depending on yo ur switch type, you
may have zero, one, or two SPI Ds assigned to your line. For
example, if your switch type is Nort hern Telecom Custom, you
will h ave to en ter two SP ID nu mbers .
Page 46

38 Installation
DSS1 & 1TR6 ISDN
1. Switch Type—This field is fixed as DSS1 or 1TR6.
2. B Channel Usage—This field is fixed as Switch/Switch.
Page 47

Installation 39
3. ISDN Data & Subaddress—Enter the telephone number and
subaddress assigned to the ISDN data call for the ro uter. It will
be us ed as th e ou tgoing C GPN (C alling P arty Number ) s etting
for ISDN data calls. Note that the router only accepts digits; do
not include hyphens or spaces in this field. T his field should be
no longer than 19 digits for the number and 5 digit s for the
subaddress. The subaddress is only available for DSS 1.
4. A/B Adapter 1 & Subaddress—Enter the telephone number
and subaddress assigned to analog port 1 ( PHONE 1, also
known as A/B Adapter 1 and POTS port 1) calls. T his setting
will b e u sed a t the Callin g Party N umber for outgoin g c alls mad e
through this port.
5. A/B Adapter 2 & Subaddress—Enter the telephone number
and subaddress assigned to analog port 2 ( PHONE 2, also
known as A/B Adapter 2 and POTS port 2) calls. T his setting
will b e u sed a t the Callin g Party N umber for outgoin g c alls mad e
through this port.
6. Dial Prefix to Access Outsid e Lin e—E nt er the prefix number
if the router is connected to an ISDN PABX. This number will
be ad de d to a ll outg oin g c alls and sho uld be n o lon ger th an 3
digit s. Otherwise, leave this field blank.
7. PABX Number (with S/T Bus Number)—Ent er the S/T bus
number if the router is connected to an ISDN PABX. If this field
is left as blank th en the loopback test will be skipped.
8. In comin g Phon e Nu mber Mat ch in g —The setting of this
con trol d ete rmines what inco ming calls w ill b e a nswere d. T here
are three possible settings:
◊ Multiple Subscriber Number (MSN)—Dig ital c alls will be
answered only when there is a match for the ISDN data
nu mber; analog calls w ill b e a nswere d only when ther e is a
Page 48

40 Installation
match for the number assigned to an analog phone port , and
the y will be directed to th e p ort to w hich th e number is
assigned (if no number is assigned to analog phone port 1 or
2, ana log calls will not be a n sw ered) . This o ption is av aila ble
as EAZ (Endgeraete Auswahl Ziffer) for 1TR6.
◊ Called Party Sub-Address (CDSA)— Digital calls will be
answered only when there is a match for the ISDN data
subaddr es s; ana log calls will be answere d only when ther e is a
match for the subaddress assigned to an analog phone port ,
an d they will be dir ec ted to th e p ort to w h ich th e subad dress
is assigned (if no subaddress is assigned to analog phone port
1 or 2 , analo g c alls will not b e answered). T his optio n is
available only for DSS1.
◊ Don’t care – all numbers accepted—All dig ital c alls to any
Called P arty Number , inclu ding g lob al c alls (those without
CDP N or CD SA in the call setup ), w ill b e a nswere d. All
an alog calls w ill be dir ec ted to analog por t 1 or an alog por t 2,
or (if Analog Call Routing is set to Ignore) not answered.
♦ Analog Call Rou tin g—All ana log c alls will be directed
to analog phone port 1 if the setting is A/B Adapter 1,
or to analog phone port 2 if the setting is A/B Adapter
2. If the setting is Ign ore , analo g c alls will not b e
answered.
♦ Global Analog Call—If the setting is Accept, all
an alog calls w ill be ans we re d a nd directed to analog
port 1 or analog port 2, as specified by setting of the
Analog Call Routing control. If Global Analog Call
is set to Ignore, no a nalog calls will be an sw er ed .
Page 49

Installation 41
9. Enter the S/T bus number if the ro uter is connected to an ISDN
PA BX . If this field is left as b lank the n the loopba ck test will be
skipped.
When you are finished, press ENTER at the message ‘Pre ss
ENTER to Confirm...’ to save your selections, or press ESC to
cancel. Wh en you press ENT ER, the rou ter will use the in formatio n
that you entered to initialize the ISDN link to the telephone
company switch. It should be noted that whenever the switch type
is cha nged , the ISDN init ializ ation will take slig ht ly longer . In
addition, if you are using the U-interface, the system will also tak e
slightly longe r to initialize.
At this poin t, you will b e a sked if you w ish to che ck if your ISDN
line has been successfully connected to your r outer. I f you select
Yes, the ro ute r will per f orm a loop-ba ck test to che ck the ISDN
line. I f the loop-back test fails, note the error message that you
receive and take the appro pr iate t r oubleshoot ing action.
Page 50

42 Installation
Ethernet Setup
Menu 3 is used to ente r Ethe rnet r ela ted information. Dep ending o n
the protocols ( TC P/I P or I PX) on your L A N, you will need to
configur e each proto col separately.
General Ethernet Setup
This menu deter mines the type of Ethernet interface you are using
as well as the filter sets you w ish to implement to monitor your
Ethernet traffic. From menu 3, Ethernet Setup, ent er 1 to go to
menu 3. 1, General E thernet Setup.
Input and Output Filter Sets—Filter sets are used to block
certain packets to r educe traffic and to prevent a security br each.
Filt er ing is a very involved subject , so leave these fields blank for
the time being. After you have studied the
Filter Configuration
chapter starting on page 103, come back and define the filter sets.
Page 51

Installation 43
TCP/IP and DHCP Ethernet Setup
If you are setting up your network for the first time, read the
chapter entitled
Configuring for Internet A ccess
before proceeding.
The chapter cont ains important information on how t o assign IP
addresses for your networ k.
From menu 3, Ethernet Setup, enter 2 to go t o menu 3. 2, TCP/IP
and DHCP Ethernet Setup.
1. DHCP—This field determines whethe r the r outer will act as a
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. If this
con trol is se t to None , DHCP will not be u se d. If it is set to
Serve r, the route r will act as a DHCP server, cap able of
automatically assigning IP addresses to Windows 95, Windows
NT, and ot her systems that support the DHCP client. When
DHCP is used, the follo wing four items need to be set.
Do not set t his field to S er ver if there is already a DHCP server
on your network.
Page 52

44 Installation
2. Client IP Pool Starting Address—DHCP can assign IP
addresses to hosts dynamically instead of requiring t hat each
system have a fixed IP address. IP addresses are allocated from a
block of addresses, usually assigned by your Internet provider.
The Client I P P ool Starting Address gives the first addr ess in the
reserved block, which is also used as the LAN network addr ess
of the rou ter itself. This ad dress will also serv e a s the de fau lt
gateway for DHCP clients.
3. Size of Client IP Pool—Gives the size of the block of addresses
reserved for DHCP address assignment. The default is 6
address es; the maximum is 32. The router its elf u ses the firs t
address in the blo ck, and t he remaining addresses in the po ol are
assigned to clients.
4. Primary DNS Server/Secondary DNS Server—T hese two
fields are used by DHCP clients (such as Windows 95 and
Wind ows NT systems) for Domain Name Servers. Usua lly your
Internet provide r will provide one or mor e name service ho sts.
5. IP A d d ress—E nt er the IP address of the DI-106 or DI-106M in
dotted decimal notat ion (four 8-bit numbers, between 0 and 255,
separated by perio ds), e. g. , 192.68.135.5. No te that every
machine on the TCP/ I P net work must have a unique IP addr ess.
6. IP Subnet Mask—An IP address consists of two parts, the
networ k I D and t he host ID. The IP S ubnet Mask is used to
specify the networ k I D portion of the address, expressed in
dotted decimal notation. Your DI - 106 or DI-106M will
auto matically calculate this mask based on t he IP addr ess that
you assign. Unless you have special need for subnett ing, use the
default subnet mask calculated by the router.
7. RIP Direction—This parameter determines how the DI-106 or
DI-106M handles RIP (Routing Info rmation Proto co l). If set to
Page 53

Installation 45
Both (defau lt), the route r will broadcast its r outing tab le on th e
LAN, and inco r porate RI P broadcasts by other ro uters into its
routing table. If set to In Onl y, th e router will not broadcast its
routing table on the LAN, if set to Out Only, the ro uter will
broadcast its r outing table but ignore any RIP broadcast packet s
that it receives. If set to None, t he router will n ot participate in
any RIP exchange with other routers.
Usually, you shou ld le ave this pa rameter at its de fau lt of Both
and let RIP pr opagate the routing information auto matically.
8. RIP Version—Determines what versions of the RIP Rout ing
Information Protocol the router accepts. Cho ices are:
◊ RIP-1 The router w ill accept and send RIP version 1
messages only.
◊ RIP-2B The r outer will accept RIP - 1 and RIP- 2 messages
(bot h broa dcast and multicast), and sends RIP-2 messages in
broadcast for mat.
◊ RIP-2M The r outer will accept RIP - 1 and RIP- 2 messages
(bot h broa dcast and multicast), and sends RIP-2 messages in
multicast format.
Unless there are routers in your environment that do not
understand RIP-2 packets, you should probably set this field to
RIP-2B.
When you are finished, press ENTER at the message ‘Pre ss
ENTER to Confirm...’ to save your selections, or press ESC at any
time to cancel them.
Novell IPX Ethernet Setup
Refer to t he chapter on Novell IPX configuration.
Page 54

46 Installation
Bridge Ethernet Setup
Refer to t he chapter on Bridging configuration.
Page 55

Configuring for Internet Access 47
Configuring for Internet Access
Menu 4 of the SMT allows you to configure I nt er net access on one
screen. Before you configure yo ur DI - 106 or DI-106M for Internet
access, you need to collect the following info r mation from your I SP
(Internet Service Provider).
♦ IP address of the ISP’s gateway (optional) .
♦ Telephone number(s) of your ISP.
♦ Login name.
♦ Passwo r d for I S P authentication
For yo ur Workstation:
♦ Domain Name Server (DNS)
IP Addresses and the Internet
Conventionally, the Internet ( with a capital I) refers the large-scale
interconnected networks acr oss the wor ld that was originally
Page 56

48 Configuring for Internet Access
developed by the US Department of Defense. The Internet uses
exclusively the TCP/IP suite o f protoco ls. The t er m “internet”
(lower case i), however, refers to any interconnected networks
using any protocol. An inter net can be as simple as two hosts on a
LAN, or it can be as complex as the Internet itself.
Every machine on the Internet must have a unique address within
that internet. If your networ ks ar e isolated from the Internet, e. g. ,
only bet ween your t wo branch offices, you can assign any IP
addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the Internet
Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following
three blocks of IP addresses specifically for private netwo r ks:
10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
For this reason, it is recommended that you choo se your network
number fro m the above list.
You can o btain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP, or
assigned from a private netwo r k. If you belong to a small
organization and yo ur I nt ernet access is through an ISP, the ISP
can provide yo u with the Inter net addr esses for your local
networks. On t he o ther hand, if you are part of a much larger
organization, you should consult your network administrator for
the approp r iate IP addr esses.
NOTE:
Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an
arbitrary IP address; always follow the guidelines above. For
more information on address assignment, refer to RFC 1597,
Page 57

Configuring for Internet Access 49
Address Allocation for Private Internets
and RFC 1466,
Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space
.
Once you have determined the IP address range for your local
network, you may want to use DHCP ( Dynamic Host
Configuration Protoco l) to assign addresses to individual hosts o n
the network, as an alternative to manually configuring each host’s
IP settings. See the TCP/IP and DHCP section on page 43 for more
infor mation a bo ut DHC P.
Internet Access Configuration
This section describes how to co nfigure yo ur DI - 106 or DI-106M
for Internet access. T he information you will need to pro vide will
be indicated in bold type.
Not e that configuring the router for I nter net access will
auto matically create a new entry in the Remote Node Setup menu
(menu 11). Before carr ying out the following steps, check t he
Remote Node Setup menu to make sure there is space for a new
entry. In order for you to be able to configure the router for
Internet access, there must be no more than three entr ies in the
Remote Node Setup menu befo r e you start.
Page 58

50 Configuring for Internet Access
1. From the main menu, enter 4 to go to menu 4, Internet Access
Setu p. T his menu is sho wn above.
2. IS P’s Name—Enter the name of your Internet S er vice Provider,
e.g ., myisp. T his informa tion is for ide ntificatio n purpos es only.
3. ISP IP Addr—Enter the IP Address of the remote gateway at
the ISP’s site. If you do not have this data, just leave it blank.
4. Pri(mary) Phone # and Sec(ondary) Phone Number—Both
the Primary and t he Seco ndary Phone number refer to the
number that your DI-106 or DI -106M will dial to connec t to th e
ISP. The rou ter will alw ays ca ll your ISP u sing the Primary
Phone number first. If the Primary P ho ne number is busy or do es
not a n sw er , th e r oute r will call the Seconda ry Phone number if
av aila ble. O nce con nected, the rout er will use the BA CP
(Ba ndwidth Allocation Contro l Protocol) to establish the second
B-channel if PPP/MP is enabled, and the ISP also supports MP
and BACP.
Page 59

Configuring for Internet Access 51
5. My Login Name—Enter the lo gin name given to you by your
ISP.
6. My Password—Enter t he passwo r d associated with the login
na me a bo ve. N ote that this login n ame /p as sword pair is only for
the router t o connect to the ISP’s gateway. When you use
TCP/IP applications, e.g., FTP, to access t he Int er net from your
work station , you will need a sep arate login name and pa sswor d
for each server.
7. Single User Account—See the following section for a more
detailed discussion on the Single User Account feature. The
default is No.
8. Telco Options: Transfer Rate—This field (whic h only app lies
to outgoing calls) controls the rate at which the data is
transferred between your rout er and t he Inter net . T he o ptions
for this field are:
◊ 64K—The router w ill place 64-kbps (kilobit s per second)
digit al data calls.
◊ 56K—(For the North Amer ica only) The router will p lac e
56-kbps digital data calls.
◊ Lease—The route r will place leased-line calls.
◊ DOVBS—T his option is for Nor th America only. The router
will place 56-kbps Data Over Voice Bearer Ser vice
(DOVBS) calls. So me phone companies in North America
charge less if calls are made with the DOVBS o ption.
9. Multilink—Determines whethe r or not Multilink PPP should be
used. Available o ptions are:
◊ Off—The base transfer rate and maximum transfer rate will
be 64 kbps.
Page 60

52 Configuring for Internet Access
◊ BOD (Bandwidth On Demand)—T he base tr ansfer rate will
be 64 kb ps, and the maximum tr ansfer rate will be 128 kbps.
◊ Always—Multilin k w ill alw ays be on ; both the base tr ansfer
rate and maximum tra nsfer ra te w ill be 128 kbps.
10. Press ENTER at the message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to
con firm your selec tion s, or press ESC at any time to cancel
your selections.
11. A t this point, the SM T will ask if you w ish to te st the Internet
con nection. If you sele ct Yes, th e r oute r will call the ISP to test
the Inter net connection. If the test fails, not e the error message
that you receive and take the appropriate t r oubleshoot ing steps.
Single User Account
T ypically, if the re are multip le u sers o n the LAN wanting to
concurrent ly access the Internet, they will have to subscribe to
multiple IP addresses o r a Class C subnetwork from the IS P . In
eith er case, these two app roa ches will cost more than a single us er
account.
The Single User Account ( S UA) feature allows custo mers to have
the same bene fits as ha ving a Class C address, but still only pa y for
one IP address, thus saving significantly on subscription fees.
(Check with your ISP before you enable this feature).
This feature may also be used to connect t o TCP/IP r emote nodes
ot her than Internet Service Providers. For example this feature can
be used to simplify the allo cation of IP addresses when connecting
branch offices to the corpo r ate networ k.
Page 61

Configuring for Internet Access 53
The IP address for the Sing le User Account can be either fixed or
dynamically assigned by the ISP (or other remo te node). In
addition, you can also configur e a ser ver, e.g., a Web server, on
your local network and make it accessible by outside users.
If you do not set a server IP addr ess, SUA offers the additional
benefit o f firewall pr otect ion. This is because if no server is defined,
all in coming inquirie s w ill b e filte red out by the r oute r eve n if you
do have a server on your network. This can prevent intruders from
probing your system.
The router accomplishes this address sharing by translating the
internal LAN IP addresses to a single address that is globally
unique on the Internet. For more information on IP address
translation, refer to RFC 1631,
The IP Network Address Translator
(NAT)
.
In summary:
1. SUA is an ideal, cost-effective solution for small offices with
less than 20 host s using a LAN to co ncurr ent ly access the
Internet or ot her remote TCP/IP network.
2. SUA can provide one server address to be accessed by Remote
Dial- in Users , thus controlling the in coming pac ke ts.
3. S UA can provide firewall protection if you do not configure a
ser v er IP address. All incoming inquiries will be filtered out by
the DI-106 or DI - 106M. T herefore, servers o n your networ k ar e
prot ected.
4. UDP and TCP datagrams can be routed. I n addition, ICMP echo
can also be routed.
Page 62

54 Configuring for Internet Access
The figur e below shows an example o f a small office connected to
the Internet via a Single User Account using a DI-106 or DI- 106M.
Not e that if you enable the Single User Account feature, your local
IP address MUST be selected from the list o f IP addresses for
private networks as defined by the IANA.
Configuration for Single User Account
The steps for configuring your DI-106 or DI-106M for Single User
Internet Access are identical to conventional Internet Access, with
the exception that yo u need to fill in thre e e xt ra fields.
Follow st eps 1- 4 from the previous section, Inter net Access
Configuration.
1. Single User Account—Enter Yes t o enable the Single User
Account feature. Use the space bar to toggle between Yes and
No.
Page 63

Configuring for Internet Access 55
2. Single User Account: IP Addr—I f your ISP assigns you a
dynamic IP address, enter 0.0. 0. 0 here. If your ISP assigns you a
stat ic IP address enter that I P addr ess here.
3. Single User Account: Server IP Addr—If you want t o make a
single server, e.g., a Web server, accessible to outside users,
enter t hat ser ver’s IP addr ess here.
Press ENTER at t he message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to
con firm your selec tion s or press ESC at any time to cancel your
selections.
At this poin t, the router will a sk if you w ish to te st the Internet
con nection. If you sele ct Yes, th e r oute r will call the ISP to test
the Inter net connection. If the test fails, not e the error message
that you receive and take the appropriate t r oubleshoot ing steps.
Configuring Backup ISP Accounts
Sometimes it may be desir able to con f igu re mo re tha n o ne ISP
account for backup purposes. T he Single User Account feature can
be enabled for all of these accounts, making it co nvenient to switch
Internet S er vice Providers in the event of a failure.
To co nfigure a backup I SP,
1. Configure your primary ISP using menu 4, as described earlier in
this chapter.
2. Enter menu 11, then select t he number of an unused remot e
node.
3. In menu 11.1, choose a name for your backup ISP account, set
the Active field to No, and enter your outgoing login name,
password, and phone number(s). The Remote IP Address field
should be set to 1.1. 1. 1.
Page 64

56 Configuring for Internet Access
4. In menu 11. 3, set the remote node’s subnet mask to 0.0.0. 0, and
set RIP to None.
5. S a ve the new configurat ion.
Once you have done this, if you need to change from yo ur pr imary
ISP to a backup ISP follow the steps below:
1. Enter menu 11 and select your Primary ISP.
2. In menu 11.1, set the Active field to No.
3. Enter menu 11 again and select your backup ISP.
4. In menu 11.1, set the Active field to Yes.
You will now b e a b le to access the Internet through the backup ISP
Remote Node.
Page 65

Remote Node Configuration 57
Remote Node Configuration
A Remote Node represents both a remote gateway and the internet
behind it, across an ISDN connection. A Remote Node is required
for placing calls to or answering calls from a remote netwo r k. Note
that when you use menu 4 t o configur e the Internet, your DI-106
or DI-106M will au tomatically add a Remote Node for you . Once a
Remote Node is configur ed pr operly, traffic to t he remote LAN
will trig ge r the router to mak e a ca ll au tomatically ( i.e. , Dial On
Demand). S imilar ly, calls fr om th e remote LAN w ill be ans we red
automatically and security will b e c hecked .
In this chapter , we will d iscus s the pa rameter s that are pro tocol
ind epen de n t. The protoc ol de pe ndent c onfiguration will be cov ered
in subsequent chapters. For TCP/IP, see the
TCP/IP Configuration
chapter on page 79. For I P X, see the
Novell IPX Configuration
chapter on page 87. For bridging, see the
Bridging Configuration
chapter on page 97.
From the main menu, enter 11 t o go to menu 11, Remote Node
Setup. When in menu 11, enter the number of the Remote No des ( 1
to 4) that you wish to configur e as sho wn below:
Page 66

58 Remote Node Configuration
E n ter the Remote Node numb er to edit an d you will go to the nex t
submenu: 11.1, Remote Node Profile, shown below:
1. Rem Node Name—This is a required field. E nt er a descriptive
name for the Remote Node, e.g., SJHQ. The name can be up to
Page 67

Remote Node Configuration 59
eight charact er s long, and must be different from any ot her
Remote Node name or R emote Dia l-in User na me.
2. Act ive—Press the space bar to t oggle between Yes and No.
When a Remote Node is deactivated, it has no effect o n t he
oper ation of the router , eve n thou gh it is still kept in the
database, and can be activated in the future. Deact ivated nodes
are displayed with a minus sign [-] at the beginning of the name
in me nu 11 .
3. Call Direction—If this parameter is set to Both, your DI-106 or
DI-106M can both place and receive calls to/from this Remote
Node. If s et to I n coming, the rou ter will n ot place a call to this
Remote Nod e. If set to Ou tgoing, the route r will drop an y ca ll
from th is Remot e N ode.
Sever al other field s in this menu de pe nd on th is p arameter. For
example, in order to enable Call Back, the Call Direction mu st
be Bot h.
4. Incoming: Rem Node Login Name—Ent er the login name tha t
this Re mote Node will u se when it calls into the route r. T he
login name in this field c omb ined w ith the Rem Node Password
will b e u sed to authenticate th e inco ming calls fr om th is nod e.
5. Incoming: Rem Node Pa sswo rd —E nter the password used
wh en th is Remote Nod e calls in to th e router .
6. Incoming : Rem CLID—This control is active on ly if th e C all
Direction control is set to either Bo th or Incoming. Otherwise,
N/A appe ars here. This is the Calling Line ID (the telep h one
numbe r of the c alling p arty) of th is Remote Nod e. If you e nab le
the CLID Authen field in menu 13, Default Dial I n, the router
will check this number a ga in st the CLID in th e incoming ca ll. If
they do not match and the CLID Authen control is set to
Required, the rou ter will re jec t th e c all.
Page 68

60 Remote Node Configuration
7. Incoming: Call Back—T h is field w ill be v alid on ly if Call
Direction is Both. Ot herwise, an N/A appears in the field. This
field determines whether or not you wish the rout er to call back
after receiving a call from this Remote Node. I f this option is
en abled, the router will d isconne ct the initia l call from this node
and call it back at the Outgoing Primary Phone Number (see
below).
8. Outgoing: My Login Name—This is a required field if Call
Direction is either Both or Out. Enter the login name for the
route r whe n it ca lls this Re mote Node . If the login name is
long er tha n 24 chara cters, only the firs t 23 will be disp laye d,
with a + displayed at the end.
9. Outgoing: My Password—This is a requir ed field if Call
Direction is either Both or Out. Enter the password for the
route r whe n it ca lls this Re mote Node . If the password is longe r
tha n 20 c hara cte rs then a + will be disp laye d a t the end.
10. Outgoing: Authen—This field set s t he aut hentication prot ocol
used for outgoing calls.
Your DI-106 or DI-106M supports two authentication
protocols: PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP
(Challenge Handshake Authentication Pro tocol).
◊ PAP sends the user name and password in plain text.
◊ CHAP scrambles the password before it is sent over the
wire.
Gene rally speak ing, C HAP is more se cu re than PAP; h owe ver,
PA P is re ad ily availab le on more platforms. The
recommendation is to use CHAP whenever possible. Turning
off the authentication is STRONGLY disco u r aged.
Page 69

Remote Node Configuration 61
Opt ions for this field are:
◊ CHAP/PAP—The ro uter will try CHAP when CH AP is
requested by the Remote Node o r PAP when PAP is
requested by the Remo te Node.
◊ CHAP—use CHAP only.
◊ PAP—use PAP only.
11. O ut goi ng: Pri(mary) Phone Sec(ondary) Phone Number—
Bot h t he Primary Phone number and t he Secondary Phone
nu mber refer to th e numbe r that the router will dial to connect
to t he Remote Node . The r outer will always call the Remote
Node us ing th e P rimar y Phon e number firs t. If the P rimary
Phone numb er is bus y or do es not an swer, the rou ter will call
the Secondary Phone number if available. Once connected, the
route r will use th e B A CP (Ban dw idth A llocation Control
Protoc ol) to e stablish the second B-chan nel if Multilin k PPP is
enabled, and t he Remote Node supports MP and BACP.
Some areas require dialing # before the phone number for local
calls. A # symbol may be included at the beginning of the
Primary Phone number o r S econdary Phone number.
12. Rout e—This fields determines the pro toco ls that your DI-106
or DI-106M will rou te. The choices for this field are
determined by the features enabled on your r outer.
13. Bridge—Bridging is used (on the DI-106M only) for protocols
that are not support ed or not turned on in the previous Route
field, e.g., SNA. When bridging is enabled, the DI-106M will
forward any packet that it does not recognize to t his Remot e
Node; ot herwise, the unrecognized packets are discarded. The
disadvantage of bridging is that it usually generates large
Page 70

62 Remote Node Configuration
amounts of traffic. Press the space bar to select either Yes o r
No.
14. Ed i t PPP Opti o ns—To edit the PPP options for t his Remote
Node, move the curso r to this field, use the space bar to select
Yes and press ENTER. This will bring you to menu 11 .2,
Remo te Node PPP Options. For mo re info rmation on
configuring PPP options, see the section entitled “E diting PPP
Options.”
15. IP Addr—This is a required field if Route is set to I P. E nt er
the IP address of this Remote Node.
16. Edit IP/IPX/B ridge Options—To edit the parameters of the
prot ocols, go to this field, select Yes and press ENTER. This
will b rin g you to menu 1 1.3, Remote Node Ne twork Layer
Options . For more in forma tion on filling out this screen, re fer
to the chapter pertaining to your specific proto col.
17. Telco Options: Transfer Rate —T his field (which only applies
to outgoing calls) controls the rate at which the data is
transferred between your rout er and t he Remote Node. The
opt ions for t his field are:
◊ 64K—The router will place 64- kbps (kilobits per second)
digit al data calls.
◊ 56K—(For North A merica only) T he rou ter will p lace 56-
kbps digital data calls.
◊ Lease line—The rou ter will place leased-line calls.
◊ DOVBS—This option is for North America only. The
route r will place 56-kbps Dat a Over Voice Bearer Service
(DOVBS) calls. So me phone companies in North America
charge less if calls are made with the DOVBS o ption.
Page 71

Remote Node Configuration 63
18. Telco Options: Allocated Budget (min)—This field will s et a
budget out going call time for t he Remote No de. T he default for
this field is 0 for no budget co nt r ol.
19. Telco Options: Period (hr)—Th is fie ld w ill set th e time
interval to reset the above outg oing call budget control.
20. Session Option: Input Filter Sets, Output Filter Sets and
Call Filter S ets—In t hese fields, select which filter set( s) you
would like to implement to filter the in coming an d ou tgoing
traffic bet ween t his Remot e Node and the rout er . You can
choose from 12 differ ent filter sets. In addition, you can link up
to 4 filter sets together for further customization (e.g., 1, 5, 9,
12). Note that spaces and co mmas are accepted in this field.
For mo re infor mation on cu stomizing you r filte r s ets, s ee th e
Filter Configuration
chapter starting on page 103. The default
is blank, i.e. , no filter s defined.
21. Session Option: Idle Timeout (sec)—This value specifies the
number of idle seconds that elapses before the Remote Node is
auto matically disconnected. Idle seconds is the period of time
where no data is passed between the Remot e Node and your
DI-106 or DI - 106M. Administrat ive packets such as RIP are
not co unted as data. The default is 300 seconds (5 minut es).
On ce you have finish ed filling in menu 11.1 , R emote Nod e Profile,
press ENTER at the message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to
confirm your selections, or press E S C at any time to cancel yo ur
selections.
Bandwidth on Demand
The Bandw idth on Demand (BOD) feature allows you to bundle
both B channels in one connection. The second channel is added
Page 72

64 Remote Node Configuration
and subtracted dynamically according to traffic demand. The router
uses the Bandwidth Allocation Cont r ol Protocol (BACP) and the
Multilink Protoc ol (M P) to implement ban dwidth on de mand.
The configu ration of bandwidth on demand focu s e s on the Ba s e
Transmission Rate (BTR) and the Maximum Transmission Rat e
(MTR). T he relationship between BTR and MTR are shown below:
BTR & MTR Setting No. of channel(s)
used to initiate call
Max No. of
channel(s) used
Bandwidth on
demand
BTR = 64, MTR = 64 1 1 Off
BTR = 64, MTR = 128 1 2 On
BTR = 128, MTR = 128 2 2 Off
When bandwidth on de mand is enable d, a second ch ann el w ill be
bro ught u p if tr affic on th e initial ch annel is high er th an th e high
Target Utility n umber for longer than the specifie d Add Pe rs ist
va lue . Similarly, the second channel will be dr opp ed if th e tr affic
lev el falls belo w the low Ta rget Utility nu mb er fo r longe r than the
Subtract Persist value.
T h e Target Utility specifies the line utiliz ation range at which you
want your DI-106 or DI -106M to add or subtract bandwidt h. The
range is 30 to 64 kbps (kilobits per second). The parameters are
separated by a hyphen [-]. For example, 30-60 means the add
threshold is 60 kbps and subtract threshold is 30 kbps. The rout er
will pe rform band wid th o n dema n d only if it in itiates the call.
Addition and subtraction are based on the value set in the BOD
Calculation field. I f this field is set t o Transmit o r Receive, then
traffic in eith er direction w ill b e c alcula ted to deter mine if a link
should be adde d or dropped. T ra nsmit will o nly use outgoin g traffic
Page 73

Remote Node Configuration 65
to make this determination, and Receive will only use incoming
traffic to mak e this de ter min ation.
If, after making the call to bring up a second channel, t he second
channel does not succeed in joining the Multilink Protocol bundle
(because the remote device does not r ecognize the second call as
coming from the same d evice), the rou ter will h ang up the second
channel and continue with the first channel alone.
Editing PPP Option s
1. Encapsulation—Select CCP (Compression Control Protocol)
for the PPP or MP link. There are two options in this field.
◊ Standard PPP—Standard PPP options will be us ed .
◊ CISCO PPP— Cisco PPP options will be used .
2. C ompressi on— Turn o n Stac Compression. The default set ting
for th is con trol is No.
Page 74

66 Remote Node Configuration
3. M ultiple Li nk Options: BOD Calcu lation—Select the
direction of the traffic yo u wish to calculate in order t o
determine when to add or subtr act a link. T he default for this
field is Transmit or Receive.
4. Multi p le Link Option s: Base Trans Rate—Select the base
data transfer rate for this Remote Node. This parameter is in
kbps (kilobits per seco nd). There are two options for this field:
◊ 64—On ly one channel w ill be used .
◊ 128—Two ch ann els will be used w hen a p ac ke t trigger s a
call.
5. Multiple Link Options: Max Trans Rate—Enter the
max imum d ata transfer rate allowed for this Remote Node. This
parameter is in kilobits per second. T here are two options for
this field:
◊ 64—At most one channel can be used.
◊ 128—A ma x imum of two channels ca n be used .
6. M u ltiple Link Options: Target Utility—E nt er the two
thresholds, separated by a hyphen [-], for subtracting and adding
the second channel. The default is 32-48.
7. Multiple Link Options: Add Persist—This parameter specifies
the number of seconds where tr affic is above the adding
threshold before the router will b ring u p the second c han n el. T h e
default is 5 seconds.
8. Multiple Link Options: Subtract Persist—This paramet er
specifies the number of seconds where traffic is below the
subtract ion threshold before the router dro ps the second
channel. The default is 5 seconds.
Page 75

Remote Node Configuration 67
Once yo u have completed menu 11.2, Remo te Node PPP Options,
press ENTER at t he message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to
con firm your selec tion s, or press ESC to cancel your selections.
Page 76

68 Dial-In Configuration
Dial-In Configuration
You can configur e your DI- 106 or DI-106M t o receive calls from
Remote Dial-in Users (e.g., t elecommuters) and Remote Nodes.
There are several differ ences between Remote Dial-in Users and
Remote No de s:
1. The rout er can make calls t o or answer calls from a Remote
Node. Ho we ver, it will only ans wer calls from Remote Dial- in
Users.
2. Each Remot e Node can have its own set of parameters such as
Bandwidth On Demand, Proto col, Security, etc., while all
Remote Dial-in Users share o ne co mmon set, as defined in the
Default Dial In Setup (menu 13).
3. Generally, Remote Dial-in Users are individual users who dial in
to the DI-106 or DI - 106M directly from their workstat ions,
while Remote No des r epr esent net works and are used for LANto - LAN connections.
This chapter discusses how to set up Default Dial-in parameters for
both Remote Node and Remot e Dial-in Users. The following
sections give t wo examples of how a DI-106 or DI - 106M can be
configur ed as a dial-in server for either or both.
By default, your DI-106 o r DI - 106M allows information for up to
eight users to be kept. To let more than eight remot e dial-in users
access a DI-106M, you can use a separate RADIUS server to
provide remote authentication services. Fo r details o n using a
Page 77

Dial-In Configuration 69
separate RADIUS ser ver, see the
Using RADIUS Authentication
section on page 124.
Telecommuting
T ele commuting enable s peop le to work at re mote sites and still
have access to t he resources in the business o ffice. Typically, a
telecommuter will use a c lient works tation w ith T CP /IP or IP X
an d dial-ou t capa bilities, e.g., a W indows 95 PC or a Ma cintos h
and an ISDN Terminal Adapter (TA). For telecommut er s to call
in to your LAN, you need to configure a Dial-In User Profile for
each telecommut er. Additionally, you need to co nfigure the
Default Dial-In Setup to set the operational parameters for all
dial-in users. You can configure up to eight Remote Dial- in
Users for your DI- 106 or DI-106M.
An example o f Remote Dial-in User application, telecommuting,
is shown below:
Dial-In Server Application
A DI-106 or DI - 106M can also be used as a dial-in server. This
application allows the router to provide services for
Page 78

70 Dial-In Configuration
workstations on a remote network. For the router to be set up as
a dial-in server, you need to co nfigure the Default Dial-In Setup
to set the operatio nal parameter s for in coming call. Ad ditionally,
yo u w ill hav e to cre ate a Remote Nod e for th e r outer on th e
remote network (see the
Remote Node Configuration
chapter
start ing on page 57). An example of a DI-106 or DI- 106M being
used as a dial-in server is shown below:
Default Dial-In Setup
This section covers the default dial-in parameters. The
par ame ter s in me nu 13 affect incoming calls fr om all Remote
Dial-in Users and Remote Nodes before aut hentication is
completed . Onc e a uthentic ation is completed, and if it matche s a
Remot e N ode, the ro ute r w ill us e parameters from that
particular Remo te Node.
Page 79

Dial-In Configuration 71
From the main menu, enter 13 t o go to menu 13, Default Dial-in
Setu p. T his s ec tion will d es cr ibe h ow to configure th e p rotoc olindependent fields in this menu. For the pro tocol-dependent fields,
refer to the appropriate chapters.
1. Telco Options: CLID Authen.—This field sets the CLID
authentication parameter for all incoming calls. There are three
options for this field:
◊ None—No CLID is required.
◊ Required—Must provide CLID, or call is disconnected.
◊ Preferred—If the CLI D is availab le then CLI D w ill be used
to do authentication. If the CLID is not available the call will
continue.
2. PPP Opti o ns: Recv. Auth e n .—This field sets the
authentication prot ocol used for incoming calls. User names and
passwords are configured in the next section (Remote
users/Dial-in Users Setup). Options for this field are:
Page 80

72 Dial-In Configuration
◊ CHAP/PAP— The ro ute r will try CH A P first, but PAP will
be used if CHAP is not a v ailable.
◊ CHAP—Use CHAP only.
◊ None—No authentication required.
3. PPP Opti o ns: Comp ressio n —The setting in this field
determines if Sta c compr ession will be used . The default setting
is Yes.
4. PPP O ption s: Mut ual Auth e n .—Some vendors, e.g. Cisco,
implement a t ype of mutual authentication. That is, the node that
initia tes th e call w ill re ques t a u ser name and password from th e
far end that they are dialing to. If the Remote Node that is
dialing in implements this type of authen tication, set this field to
Yes.
5. PA P Lo g i n—T his field will only be enabled if the Mutual
Authen. field is set to Yes. Enter in the login name to be used to
respond to the far end’s PAP authentication request . T his field
does not apply to CHAP authentication.
6. PAP Password—T his field will only be enab led if the Mutual
Authen. field is set to Yes. Enter in the PAP password to be
used to r espond to the far end’s authentication request. This
field does not apply t o CHAP authentication.
7. Multiple Link Options: Max Trans Rat e—Enter the
maximum data t r ansfer rate between your ro uter and the Remote
Dial-in User. The unit is kbps (kilobits per second). There are
two options for this field:
◊ 64—At most, one B channel will be used .
◊ 128—A ma ximum of two chan nels can be u sed.
Page 81

Dial-In Configuration 73
When the DI-106 or DI - 106M calls back to t he Remote Dial-in
User the maximum data transfer rate is always 64.
8. Callback Budget Management: Allocated Budget (min)—
This field will set a b udget callback t ime for all the Remote Dialin Users. The default for this field is 0 for no budget co nt r ol.
9. Callback Budget Management: Period (hr)—T h is field w ill
set the t ime inter val to r eset the above callback budget cont r ol.
10. Dial-In IP Address Supplied By: Dial-in User—If set to Yes,
it tells the DI-106 or DI-106M to allow a remote host to
specify its own IP addr ess. T his is to prevent the remote host
from using an invalid IP address and potentially disrupting the
whole network. If set to No, the remote host must use the IP
address assigned by the DI-106 or DI-106M from the IP pool,
configur ed below. The default is Yes.
11. Dial-In IP Address Supplied By: IP Pool—This field te lls
your DI-106 or DI- 106M t o provide the remot e host with an IP
address from the pool. This field is required if Dial- I n IP
Address Supplied By: Dial-in User is set to No. You can
configure this field even if Dial-in User is set to Yes, in which
case the DI-106 or DI -106M will accept the IP address if the
remote peer specifies one; otherwise, an IP address is assigned
from the pool. If Dial-in User is Yes and this field is No, the
remote peer
must
supply its own IP address, o r communication
will n ot b e p ossible. T h e d efa ult is No.
12. IP Pool: IP Start Addr—This field is active on ly if you
selected Yes in the Dial-I n IP Address Supplied By: I P P ool
field. The IP po ol contains contiguous IP addresses and t his
field specifies the first one in the pool.
13. IP Count (1,2)—In this field, enter t he number (1 or 2) of the
addresses in the IP Pool. For example, if the star ting address is
Page 82

74 Dial-In Configuration
192.168.135.5 and the count is 2, then the pool will ha ve
192.68.135.5 and 192.68.135.6
14. Dial-In IPX Net. Num. Supplied By: IPX Pool—This field
tells the DI-106M to provide the remot e host with an IPX
network number from the pool. Otherwise, the router will
generate a random IPX network number. The default is No.
15. IPX Start Net. Num.—This field is active only if you selected
Yes in the Dial-In IPX Net. Num. Supplied By: IPX Pool field.
The IPX pool contains contiguous IPX networ k numbers and
this field specifies the first one in the pool.
16. IPX Count (1 , 16) —In t his field, enter the number (1–16) of
networ k numbers in the IPX Po ol. For example, if the start ing
number is 12345678, and the count is 2, then the pool will have
12345678 and 12345679.
17. Session Options: Input Filter Sets and Sessi o n Options:
Output Filter Sets—In these fields, you need to select the
filter set(s) t o filter the incoming and outg oing traffic between
your DI-106 or DI - 106M and the Remote Dial-in User. Keep in
mind that th ese filter set(s) will only a pp ly to all Remote Dia l-in
Users but not the Remote Nodes.
You can choose from 12 differ ent filter sets. I n addition, you
can link up to 4 filter sets together for furt her cust omization
(e.g., 1, 5, 9, 12) . Note that spaces and commas are accepted in
this field . For more in forma tion on cu stomizin g you r filte r s ets,
see the
Filter Configuration
chapter on page 103. The default
is blank, i.e. , no filter s.
18. Session Options: Idle Timeou t—This value is the nu mber of
idle seconds that elapses before the dial-in user is automatically
disconnected. Idle Timeout is the period of time when there is
no data t r affic between the dial-in user or Remot e Node and the
Page 83

Dial-In Configuration 75
router. This field will only be u sed if Rec v. Auth en is set to
Non e a nd th e c all is no t map pe d to a ny Remote Node or
Remote Dial-in User, or t he router calls back to the Remot e
Dial-in User.
On ce you are finished filling in menu 13, Default D ial- in Setup,
press ENTER at the message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ t o save
your selections, or press ESC at any time to cancel your selections.
Dial-In Users Setup
The following steps describe the setup pro cedure for adding a
Remote Dial-in User. From the main menu, enter 14 to go to menu
14, Dial-in User S e tup. This menu is shown belo w:
Sele ct one o f th e e ight possible us ers by numb er. This will bring
you to the next screen, menu 14.1, Edit Dial- in User.
Page 84

76 Dial-In Configuration
1. User Name—T his is a re qu ired field . This will b e u sed a s the
login name for authentication. Choo se a descriptive word for
login, e.g., kathyg.
2. Active—You can disallo w dial-in access to this user by setting
this field to Inact ive. When set t o inactive, the user record is still
kept in the database for later activation. Deactivated users are
displayed wit h a hyphen [-] at the beginning of the name in menu
14.
3. Password—Enter the password for the Remote Dial-in User.
4. Callback—This field determines if the DI-106 or DI- 106M will
allo w callback to the Remote Dial-in User upo n dial-in. If this
con trol is se t to Option al, the router w ill be able to ca ll b ac k to
the Remote Dial-in User if so requested by that user’s system; if
the control is set to Man da tory, the router w ill attempt c allback
in all cases. Callback entails disconnecting the call and dialing
the specified callback number (see belo w) . T he default setting of
this control is No.
Page 85

Dial-In Configuration 77
5. Phone # Supplied by Caller—This control allows the Remote
Dial-in User to specify the callback t elephone number on a callby-call basis. This is useful for when the DI-106 or DI- 106M
retur ns a callback to a mobile user at different numbers, e.g., a
sales rep in a hotel. Note that the default is No, i.e., the router
always calls back to the fixed callback number.
6. Callback Phone #—I f Ca llback is Yes, th en this is a required
field. Other wise, N/ A will appe ar in the field. Enter th e
telephone n umber t o which the ro ute r will call back.
7. Rem CLID—If you have enabled the CLID Authen field in
menu 13, you need to specify the t elephone number from which
this Remote Dial-in User calls. The DI-106 or DI-106M will
check this number against the CLID in the incoming call. If they
do not match and the CLID Authen is Required, the rout er will
reject the call.
8. Idle Time-ou t — Enter the idle time ( in secon ds). This time- out
determines how long the dial-in user can be idle before t he DI106 or DI- 106M disconnects the call. I dle time is defined as the
period of time where there is no data traffic bet ween t he dial-in
user and the router . The default is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
More on CLID
CLID allo ws your DI-106 or DI-106M t o authenticate the caller
before a call is answered, thus saving the cost o f a connection. The
router uses the caller ID in the ISDN call setup message to match
against t he CLID in the database.
Howeve r, CL ID may not be available due to your switch
configur ation.
Page 86

78 Dial-In Configuration
Besides authentication, another application of CLID is to
combine
it with callback. For instance, your company pays for the
connection charges for telecommu ting employees, and you are
using the DI-106 or DI- 106M as t he dial-in server. You can tu r n on
both the CLID authentication and callback options for the dial-in
users. By doing so, all usage ar e charged to t he company instead of
the employees, and yo ur accounting department can avoid the
hassles of accountability a nd reimbu rs eme nt.
On ce you a re finish ed fillin g in menu 14.1, Ed it Dia l-in Us er , pr ess
ENTER at the message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ t o save your
selections, or pr ess ES C at any time to cancel your selections.
Page 87

TCP/IP Configuration 79
TCP/IP Configuration
This chapter shows you how to configure your DI-106 o r
DI-106M for TCP/IP. Depending on your par ticular
applica tion s, you w ill n ee d to con f igu re diffe rent menus. Fo r
instance, Int e r net access is the most common application of
T CP /IP. F or this app lica tion , you sh ould configure men u 4 . We
will illustra te the configuratio n fo r other ap plications in the
fo llowing section s.
IP Subnet Mask
A subnet mask is a 32-bit quantity that, wh en logically ANDed with
an IP address, yields t he network number. For instance, the subnet
masks for class A, B and C netwo rks without su bnet ting are
255.0.0.0, 255. 255. 0.0 and 255.255.255.0, respectively.
To cr eate more netwo r k numbers, you shift some bits from the host
ID to the network ID. Fo r instance, t o partition a class C network
number 192.68.135.0 into two , you shift 1 bit from the host ID to
the network ID. Thus th e new subne t mask w ill be
255.255.255.128; the first subnet will have networ k number
192.68.135.0 with hosts 192.68.135.1 t o 129.68.135.126 and the
secon d subnet will ha ve n etw ork nu mber 192.68.135.128 with
hosts 192.68.135.129 t o 192.68.135.254.
It is recommended that you use t he same subnet mask fo r all
physical networks that share an IP net work number. The t able
below lists the additional subnet mask bits in dot decimal notations.
To use to following table, write down the o r iginal subnet mask and
substitute the higher order 0s with the dot decimal of the additional
Page 88

80 TCP/IP Configuration
subnet bits . Fo r insta nc e, to p artitio n yo ur clas s C ne twork
204.247.203.0 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 into 16 subnets (4
bits), t he new subnet mask becomes 255.255.255.240.
Number of Bits Dot Decimal
1 128
2 192
3 224
4 240
5 248
6 252
7 254
8 255
LAN-to-LAN Application
A typical LAN-to-LAN application is t o use the DI-106 or
DI-106M to call from a branch office to t he headquarter s, as
depicted in the following diagram.
For the branch office, you need to configure a Remote Node in
order to dial out to t he headquarter s. Additionally, you may also
need to configure Static Routes if some services reside beyond the
immediate remote LAN.
Page 89

TCP/IP Configuration 81
Remote Node Setup
Follow the pro cedur e in the
Remote Node Configuration
chapter
startin g on page 57 to fill th e protoc ol-indepe n de nt par ameter s
in me nu 11 , Remote Node Profile. F or the p rotocol-depe ndent
parameters, follow the instructions be low. If you are con figuring
the router t o receive an incoming call, you also need to set the
default dial-in parameters in menu 13 (see t he chapter entitled
Dial-In Configuration
, starting on page 68).
1. Route—Make sure IP is among the proto cols in t he Route field.
2. IP Address—Enter the IP address of the gat eway at t he remote
site (in this case, headquarters). I f the remote router is using a
different IP address t han the one entered here, your DI-106 or
DI-106M will drop the ca ll.
3. Edit IP/IPX/Bridge—Press t he space bar to change the setting
to Yes and press Enter t o go to menu 11.3, Remote Node
Network Layer O ptions. Th is menu is sh own below :
Page 90

82 TCP/IP Configuration
1. Rem IP Address—This will s how th e IP ad dress you e ntere d
for th is Remote Node in the p reviou s men u.
2. Rem IP Subnet Mask—Enter the subnet mask for the remote
network.
3. My WAN Ad dr—Some imp leme n tations, espe cia lly the UNIX
derivatives , re quire hosts on both ends o f the I SDN link to have
separat e ad dresses from the LAN, and that the addresses must
have the same network number. If this is t he case, ent er the IP
address assigned to the WAN port of your DI-106 or DI - 106M.
Note that this is the address assigned to the local DI-106 or
DI-106M, not the remote router.
1. Single User Account—This field should be set to yes to enable
the Single User Acco unt ( Network Address T r anslator ) featur e
for this site. Use t he space bar to toggle between yes and no.
See page 52 for more info r mation on the Single User Account
feature.
2. Server IP address—If you are using the Single User Account
feature and you want to make a server accessible on yo ur LAN,
e.g., a web server, accessible to outside users, enter that servers
IP address here.
Page 91

TCP/IP Configuration 83
3. Metric—The metric represents the “cost” of transmission for
rout ing purpose. IP r outing uses hop count as the measurement
of cost, with a minimum of 1 for directly connected networks.
Enter a number that appro ximates the cost for this link. T he
number need not be pr e cise, but it must be between 1 and 16. In
practice, 2 or 3 is usually a good number.
4. Private—This parameter determines if yo ur DI- 106 or
DI-106M will include th e route to this Re mote Node in its RIP
broadcasts. If set t o yes, this route is kept private and not
included in RIP broadcasts. If no, the route to this Remote Node
will b e p ropagated to oth er hosts through RI P broa dc asts.
5. RIP—This parameter determines how your DI-106 or DI-106M
handles RIP (Ro uting Information Pr otoc ol), and the d e fa ult is
Both. If s et to Both , your router w ill b roadcast its rou ting table
on the WAN and incor porate RIP broadcast s from the other
route r into its r outing tab le. If set to In Only, you r router will
not broadcast its routing table on the WAN; if set to Out Only, it
will b roadcast its rou ting table bu t ignore any RIP broa dc ast
packets that it receives. If set t o None, your DI-106 o r DI - 106M
will n ot pa rtic ipa te in any R IP exch ange with other route rs .
Usually, you shou ld le ave this pa rameter at its de fau lt of Both
and let RIP pr opagate the routing information auto matically.
On ce you have comp lete d filling in the N etw ork Layer Options
menu, press ENTER to return to menu 11. Press ENTER at the
message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to save your selections, or
press ESC at any time to cancel your selections.
Static Route Setup
On a directly connected internet, RI P usually handles the rout ing
auto matically. However, RI P cannot propagate across isolated
Page 92

84 TCP/IP Configuration
networ ks, as in the case before a connection is made between the
two subnetwo r ks using one Class C IP address. Without a route, no
packets can be forwarded to their destinations. A static route is
used to reso lve this problem by providing the DI-106 or DI - 106M
with some static routing information. As a matter of fa ct, wh en you
configure the Inter net Access o r a Remot e Node, a st atic route is
implicitly created. An example is given below. In the example,
stations on the 204.5.1. 0/24 subnetwor k can access the remote
statio ns usin g the static route. The route will have a d estination of
204.5.1.64/26 with the gateway address being that o f the Remote
Node (204.5. 1. 150) .
Note that in normal circumstances, your DI- 106 or DI-106M will
have adequate routing information after you co nfigure it for
Internet access and Remote No des; you do not need to configure
add ition al static routes. You will need to con f igu re static rou tes
only for unusual cases, e.g., subnetting. To create additional static
rout es for IP, use menu 12, Static Route Setup, as shown below:
Page 93

TCP/IP Configuration 85
1. Route Name— Enter a descrip tive n ame for this route. This is
for ide n tification purpose only.
2. Act ive—This fields allows you t o activate/deactivate this static
route.
3. Destination IP Address—This parameter specifies the IP
network
add re ss of the fin al d estination. Routin g is alw ays based
Page 94

86 TCP/IP Configuration
on networ k number. If you need to specify a route t o a single
host, use a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 in the subnet mask
field to for ce the network number to be identical to t he host ID.
4. IP Subnet Mask—Ente r the subnet ma sk for this destin ation.
Follow the discussion on IP subnet mask in this chapter.
5. Gateway IP Address—Enter the IP addr ess of the gateway.
The gateway is an
immediate
neighbor of the DI-106 or
DI-106M that w ill forw ar d packets to the d estin ation. On the
LAN, the gateway must be a router on the same segment as the
DI-106 or DI - 106M; over ISDN, the gateway must be the IP
address of one of the Remote Nodes.
6. The Metric and the Private parameters hav e the same mea n ing
as those in the Remote Node Setup.
On ce you a re finish ed fillin g in the menu, press ENTER at the
message ‘Press ENTER to Confirm...’ to save your selections, or
press ESC at any time to cancel your selections.
Page 95

Novell IPX Configuration 87
Novell IPX Configuration
This chapter shows you how to configure the DI-106M for IPX.
Dep ending on your pa rticular app lica tion s, you will need to
conf igu re differ ent me nus. W e w ill illustrat e the conf igu rat ion
for some applic ations in t he following sections .
IPX Network Environment
Frame Type
The stat ions on an IPX netw ork (both clients and servers) can run
on four different frame types existing on one physical Ethernet
cable. These frame types are 802.2, 802.3, Et hernet II ( DI X) , and
SNAP.
Network Numbers
Whenever you are setting up an IPX routing environment, it is
important to co r r ectly co nfigure the network numbers on t he LAN.
On any IP X network, t here is an external network number, that is,
the number associated with the frame type on the Ethernet cable to
which the stations on the netwo r k ar e joined. In addition to this
external network number, each NetWare server has its own internal
ne twor k number . It is import ant to remember that eve ry netw ork
number has t o be unique for that entire internet work. So if a ser ver
station has an internal network number of 00000011, there must be
no ot her netwo r k number (internal or external) of 00000011
anywhere on the entire network.
Page 96

88 Novell IPX Configuration
There are two different scenarios in which you wo uld connect your
DI-106M to a LAN: one with a server (server side), and o ne
without a server (client side).
DI-106M on LAN with Server
If the DI-106M will be con nected to a LAN with an exis tin g
NetWare s er ver, you will not n ee d to c on f igu re the DI-106M as
a seed rou ter , a nd h ence ther e w ill b e no need for a network
number parameter in the Ethernet Setup menu for the DI-106M.
Rather, the DI-106M will learn th e network nu mber of the
network it is attached t o through t he regular RIP broadcasts sent
by the ser ver, an d it w ill ad d this r oute to its r outing tab le.
DI-106M on LAN without Server
If the DI-106M is connected to a LAN without an existing
NetWare server st ation, then it needs to create a unique external
network number to apply to that frame on the LAN. This
DI-106M must then be configured as a Seed Router , and the
network number can be configured in t he Ethernet Setup menu.
Page 97

Novell IPX Configuration 89
The network number must be unique and no t used anywhere else
on the entire internetwork.
IPX Spoofing
The DI-106M comes with several pre-defined call filters
designed to pr event certain IPX packets fro m triggering a call to
a Remote Node. These filter s should inform yo ur DI - 106M
which packets should be ignored as t r affic.
When you are rout ing IPX packets, the default call filt er s ar e
defined as follo ws:
♦ Block periodical SAP and RIP respo nse messages.
♦ Block NetWare serializat ion packets.
♦ Allow SAP and RIP inquiry packets.
These call filt er s prevent the DI-106M from making a call to the
Remote Node, thus preventing the expense of an unnecessary
phone call.
IPX Ethernet Setup
The fir st step is to set up t he DI-106M on the LAN. From menu
3, select option 3 to go to menu 3.3, Novell IP X E thernet Setup.
T h is me n u is shown below:
Page 98

90 Novell IPX Configuration
1. Seed Router—Det er mine if the DI-106M is to act as a seed
router. This value depends on the existing network. If there is a
NetWare server pro viding the network number, select No . I f
there is no NetWare server providing the network number,
select Yes.
2. Frame Type—For every frame type that the DI-106M needs to
support , you need to set the corresponding field to Yes. The
frame type(s) selected here must be the same frame type(s) as
the server or client stations on that net work. Ot herwise, the
devices will n ot be able to commu n ica te. You can select on e or
more of these four frame types:
◊ 802.2
◊ 802.3
◊ Ethernet II
◊ SNAP
3. IPX Network #—If you selected t he DI-106M to act as a seed
rout er , you need to provide a unique netwo r k number to be
Page 99

Novell IPX Configuration 91
associated with the network t hat the DI-106M has joined. Keep
in mind that this number mu st not be u sed a nywh ere else on the
entire internetwork.
On ce you a re finish ed fillin g in menu 3.3, press ENTER at the Save
message to save your selections, or press ESC at any time to cancel
your selections.
LAN-to-LAN Application
A typical LAN-to-LAN application is t o use the DI-106M to call
from a branch office t o headquarters such that all of the stations on
the branch office networ k have access to the server at the
headquarters, as depicted in the fo llowing diagram:
For the branch office, you need to configure a Remote Node in
order to dial out to headquarter s.
Page 100

92 Novell IPX Configuration
Remote Node Setup
Follow t he instructions in the chapter ent itled
Remote Node
Configuration
, starting on p ag e 5 7, to fill in the pro tocolindependent para meters in me nu 11 , Remote Node Profile. For the
protocol-d ep enden t pa rameters, follow the instructions below. If
the DI-106M is configured to receive incoming calls, you can
configur e the default dial-in parameters in menu 13 (see the chapter
entitled
Dial-In Configuration
, starting on page 68).
1. Route—Make sure IP X is among the proto cols in the Rout e
field.
2. Edit IP/IP X/ Br idge—Press t he space bar to change the setting
to Yes, then press Enter to go to the Remote Node Network
Layer Opt ions menu.
1. Dial-On-Query—This field is necessary fo r the DI-106M on
the client side LAN. When set to Yes, any “Get Service” SAP or
RIP broad casts coming from the LA N will trigger the DI-106M
 Loading...
Loading...