Page 1

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
I
Page 2

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Using Command Line Interface ........................................................................................... 1
Chapter 2 Basic Management Commands .......................................................................................... 8
Chapter 3 802.1X Commands............................................................................................................ 30
Chapter 4 Access Authentication Control (AAC) Commands ............................................................ 56
Chapter 5 Access Control List (ACL) Commands.............................................................................. 78
Chapter 6 Access Control List (ACL) Egress Command List .......................................................... 107
Chapter 7 ARP Commands.............................................................................................................. 126
Chapter 8 ARP Spoofing Prevention Commands ............................................................................ 131
Chapter 9 Asymmetric VLAN Commands ........................................................................................ 133
Chapter 10 Auto Configuration Commands ................................................................................... 135
Chapter 11 Basic IP Commands .................................................................................................... 138
Chapter 12 BPDU Attack Protection Commands........................................................................... 147
Chapter 13 Cable Diagnostics Commands .................................................................................... 152
Chapter 14 CFM Commands ......................................................................................................... 155
Chapter 15 Command List History Commands ............................................................................. 182
Chapter 16 Command Logging Command List.............................................................................. 185
Chapter 17 Common Unicast Routing Command List ................................................................... 187
Chapter 18 Compound Authentication Commands ....................................................................... 193
Chapter 19 Debug Software Command List .................................................................................. 203
Chapter 20 DHCP Local Relay Commands ................................................................................... 229
Chapter 21 DHCP Relay Commands ............................................................................................ 233
Chapter 22 DHCP Server Commands ........................................................................................... 248
Chapter 23 DHCPv6 Relay Command List .................................................................................... 274
Chapter 24 DHCPv6 Server Commands ....................................................................................... 279
Chapter 25 Domain Name System (DNS) Relay Commands ....................................................... 293
Chapter 26 Domain Name System (DNS) Resolver Commands .................................................. 298
Chapter 27 DoS Attack Prevention Commands............................................................................. 305
Chapter 28 D-Link Unidirectional Link Detection (DULD) Commands .......................................... 310
Chapter 29 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) Commands ............................................ 312
Chapter 30 External Alarm Commands ......................................................................................... 322
Chapter 31 FDB Commands .......................................................................................................... 324
Chapter 32 File System Management Commands ........................................................................ 333
Chapter 33 Filter Comm a nds ......................................................................................................... 343
Chapter 34 Gratuitous ARP Commands ........................................................................................ 350
II
Page 3

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 35
Chapter 36 IGMP Snooping Commands ....................................................................................... 360
Chapter 37 IGMP Snooping Multicast (ISM) VLA N Commands .................................................... 381
Chapter 38 IP Routing Commands ................................................................................................ 392
Chapter 39 IP Tunnel Commands ................................................................................................. 397
Chapter 40 IPv6 NDP Commands ................................................................................................. 406
Chapter 41 IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB) Commands ................................................................... 413
Chapter 42 Japanese Web-based Access Control (JWAC) Commands ....................................... 434
Chapter 43 Jumbo Frame Commands ........................................................................................... 458
Chapter 44 LACP Configuration Commands ................................................................................. 461
Chapter 45 Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT) Command List ..................................................... 463
Chapter 46 Limited Multicast IP Address Commands ................................................................... 468
Chapter 47 Link Aggregation Commands ...................................................................................... 477
Chapter 48 LLDP Commands ........................................................................................................ 482
Chapter 49 Loopback Detection Commands ................................................................................. 505
Chapter 50 Loopback Interface Commands .................................................................................. 512
IGMP Proxy Commands ............................................................................................. 355
Chapter 51 MAC Notification Commands ...................................................................................... 515
Chapter 52 MAC-based Access Control Commands .................................................................... 520
Chapter 53 Mirror Commands........................................................................................................ 536
Chapter 54 MLD Proxy Commands ............................................................................................... 542
Chapter 55 MLD Snooping Commands ......................................................................................... 547
Chapter 56 MLD Snooping Multicast (MSM) VLAN Com mands ................................................... 566
Chapter 57 Modify Login Banner and Prompt Commands ............................................................ 577
Chapter 58 Network Load Balancing (NLB) Commands ............................................................... 581
Chapter 59 Network Management Commands .............................................................................. 585
Chapter 60 Network Monitoring Commands .................................................................................. 602
Chapter 61 OAM Commands ......................................................................................................... 620
Chapter 62 Packet Storm Commands ........................................................................................... 627
Chapter 63 Password Recovery Commands ................................................................................. 632
Chapter 64 Port Security Commands ............................................................................................ 635
Chapter 65 Power over Ethernet (PoE) Commands ...................................................................... 643
Chapter 66 Power Saving Commands ........................................................................................... 648
Chapter 67 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) Commands ................................................................ 650
Chapter 68 Protocol VLAN Commands ......................................................................................... 668
Chapter 69 QoS Commands .......................................................................................................... 674
Chapter 70 Q-in-Q Command ........................................................................................................ 688
III
Page 4

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 71
Chapter 72 RIPng Commands ....................................................................................................... 701
Chapter 73 RSPAN Commands..................................................................................................... 705
Chapter 74 Safeguard Engine Commands .................................................................................... 711
Chapter 75 sFlow Commands........................................................................................................ 713
Chapter 76 Single IP Management Commands ............................................................................ 724
Chapter 77 SMTP Commands ....................................................................................................... 734
Chapter 78 SNMPv1/v2/v3 Commands ......................................................................................... 739
Chapter 79 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) commands ................................................................. 756
Chapter 80 SSH Commands.......................................................................................................... 769
Chapter 81 SSL Commands .......................................................................................................... 777
Chapter 82 Stacking Commands ................................................................................................... 783
Chapter 83 Static MAC-based VLAN Commands ......................................................................... 790
Chapter 84 Static Replication Commands ..................................................................................... 793
Chapter 85 Subnet VLAN Commands ........................................................................................... 800
Chapter 86 Switch Port Commands ............................................................................................... 806
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Command List ..................................................... 696
Chapter 87 System Severity Commands ....................................................................................... 810
Chapter 88 Tech Support Commands ........................................................................................... 812
Chapter 89 Time and SNTP Commands ....................................................................................... 815
Chapter 90 Traffic Segmentation Commands ................................................................................ 822
Chapter 91 UDP Helper Commands .............................................................................................. 824
Chapter 92 Utility Commands ........................................................................................................ 830
Chapter 93 Voice VLAN Commands ............................................................................................. 853
Chapter 94 VLAN Commands........................................................................................................ 863
Chapter 95 VLAN Trunking Commands ........................................................................................ 880
Chapter 96 Web-based Access Control (WAC) Commands ......................................................... 884
Appendix A Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet Content ACL .................................... 898
Appendix B Password Recovery Procedure ................................................................................... 906
Appendix C System Log Entries ..................................................................................................... 908
Appendix D Trap Entries ................................................................................................................. 927
Appendix E RADIUS Attributes Assignment ................................................................................... 931
IV
Page 5

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Chapter 1 Using Command Line
Interface
The DGS-3420 Layer 2+ stackable Gigabit Ethernet switch series are members of the D-Link
xStack® family. Ranging from 10/100/1000Mbps edge switches to core gigabit switches, the
xStack
tolerance, flexibility, port density, robust security and maximum throughput with a user-friendly
management interface for the networking professional.
The Switch can be managed through the Switch’s serial port, Telnet, SNMP or the Web-based
management agent. The Command Line Interface (CLI) can be used to configure and manage the
Switch via the serial port or Telnet interfaces.
This manual provides a reference for all of the commands contained in the CLI. Every command
will be introduced in terms of purpose, format, description, parameters, and examples.
Configuration and management of the Switch via the Web-based management agent are
discussed in the Web UI Reference Guide. For detailed information on installi ng h ardware please
also refer to the Harware Installation Guide.
®
switch family has been future-proof designed to provide a stacking architecture with fault
1-1 Accessing the Switch via the Ser ial Port
The Switch’s serial port’s default settings are as follows:
• 115200 baud
• no parity
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
A computer running a terminal emulation program capable of emulating a VT-100 terminal and a
serial port configured as above is then connected to the Switch’s serial port via an RJ-45 to RS232 DB-9 convertor cable.
With the serial port properly connected to a management computer, the following screen should be
visible.
DGS-3420-28SC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 1.00.024
Copyright(C) 2011 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
UserName:
There is no initial username or password. Just press the Enter key twice to display the CLI input
cursor − DGS-3420-28SC:admin#. This is the command line where all commands are input.
1
Page 6
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
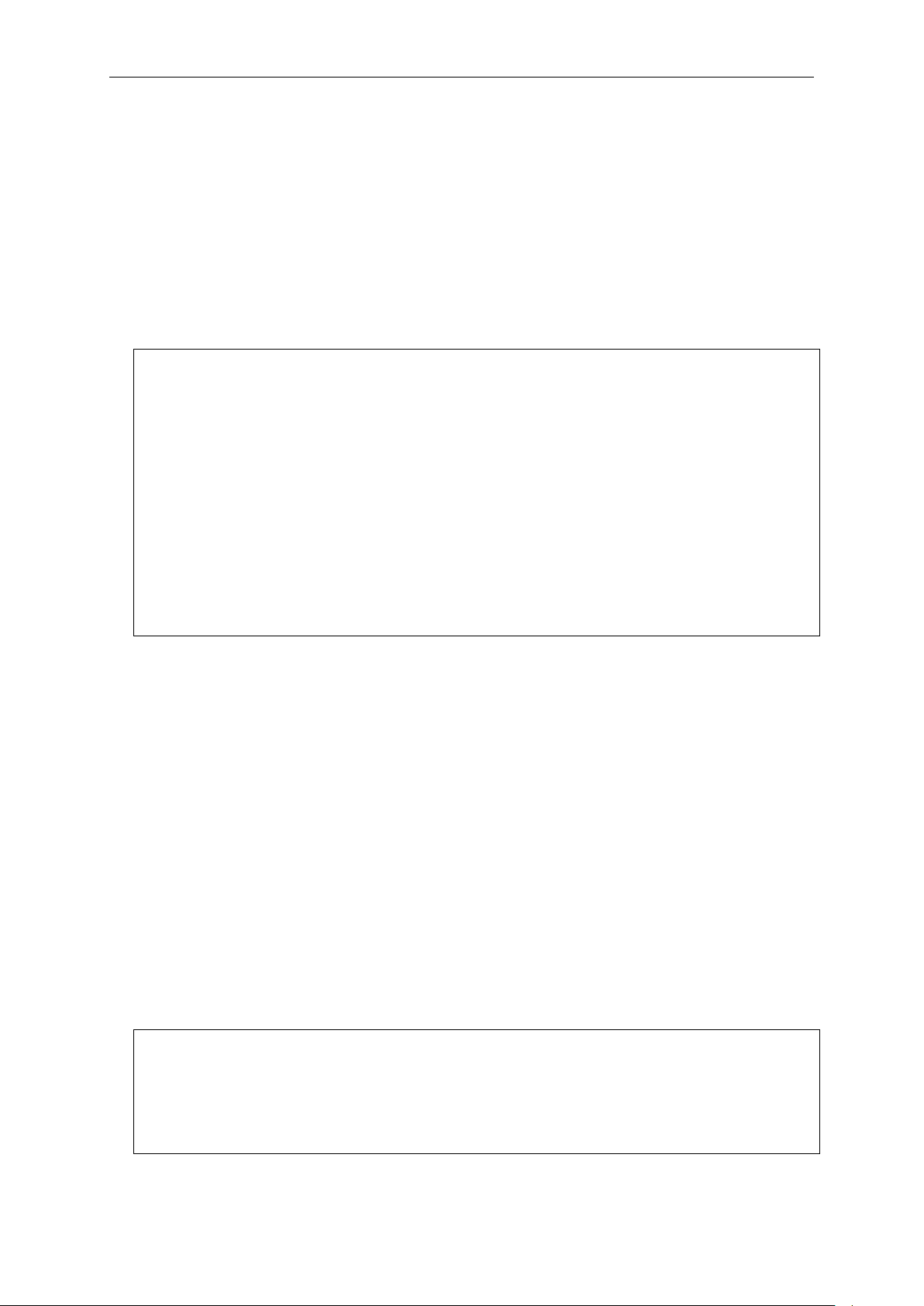
Boot Procedure V1.00.006
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config ipif System ipaddress 10.24.22.100/255.0.0.0
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
1-2 Setting the Switch’s IP Address
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an
SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The Switch’s
default IP address is 10.90.90.90. You can change the default Switch IP address to meet the
specification of your networking address scheme.
The Switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This MAC address cannot be
changed, and can be found on the initial boot console screen – shown below.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Power On Self Test ........................................ 100 %
MAC Address : 00-01-02-03-04-00
H/W Version : A1
Please Wait, Loading V1.00.024 Runtime Image .............. 100 %
UART init ................................................. 100 %
Starting runtime image
Device Discovery .......................................... 100 %
Configuration init ........................................ 100 %
The Switch’s MAC address can also be found in the Web management program on the Device
Information (Basic Settings) window on the Configuration menu.
The IP address for the S wit c h must be set before it ca n be managed with the Web-based manager.
The Switch IP address can be automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case
the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known.
Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the
IP interface named System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s
represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System a nd th e z represents
the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask
which can then be used to connect a management station to the Switch’s Telnet or Web-based
management agent.
Command: config ipif System ipaddress 10.24.22.100/8
Success.
2
Page 7

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#?
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config account
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
In the above example, the Switch was assigned an IP address of 10.24.22.100 with a subnet mask
of 255.0.0.0. The system message Success indicates that the command was executed
successfully. The Switch can now be configured and managed via Telnet, SNMP MIB browser and
the CLI or via the Web-based management agent using the above IP address to connect to the
Switch.
There are a number of helpful features included in the CLI. Entering the ? c om mand will display a
list of all of the top-level commands.
Command: ?
..
?
cable_diag ports
cd
cfm linktrace
cfm lock md
cfm loopback
change drive
clear
clear address_binding dhcp_snoop binding_entry ports
clear address_binding nd_snoop binding_entry ports
clear arptable
clear attack_log
clear cfm pkt_cnt
clear counters
clear dhcp binding
clear dhcp conflict_ip
clear dhcpv6 binding
clear ethernet_oam ports
clear fdb
clear igmp_snooping data_driven_group
clear igmp_snooping statistics counter
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page ENTER Next Entry a All
When entering a command without its required parameters, the CLI will prompt you with a Next
possible completions: message.
Command: config account
Next possible completions:
<username>
In this case, the command config account was entered with the parameter <username>. The CLI
will then prompt to enter the <username> with the message, Next possible completions:. Every
command in the CLI has this feature, and complex commands have several layers of parameter
prompting.
3
Page 8
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
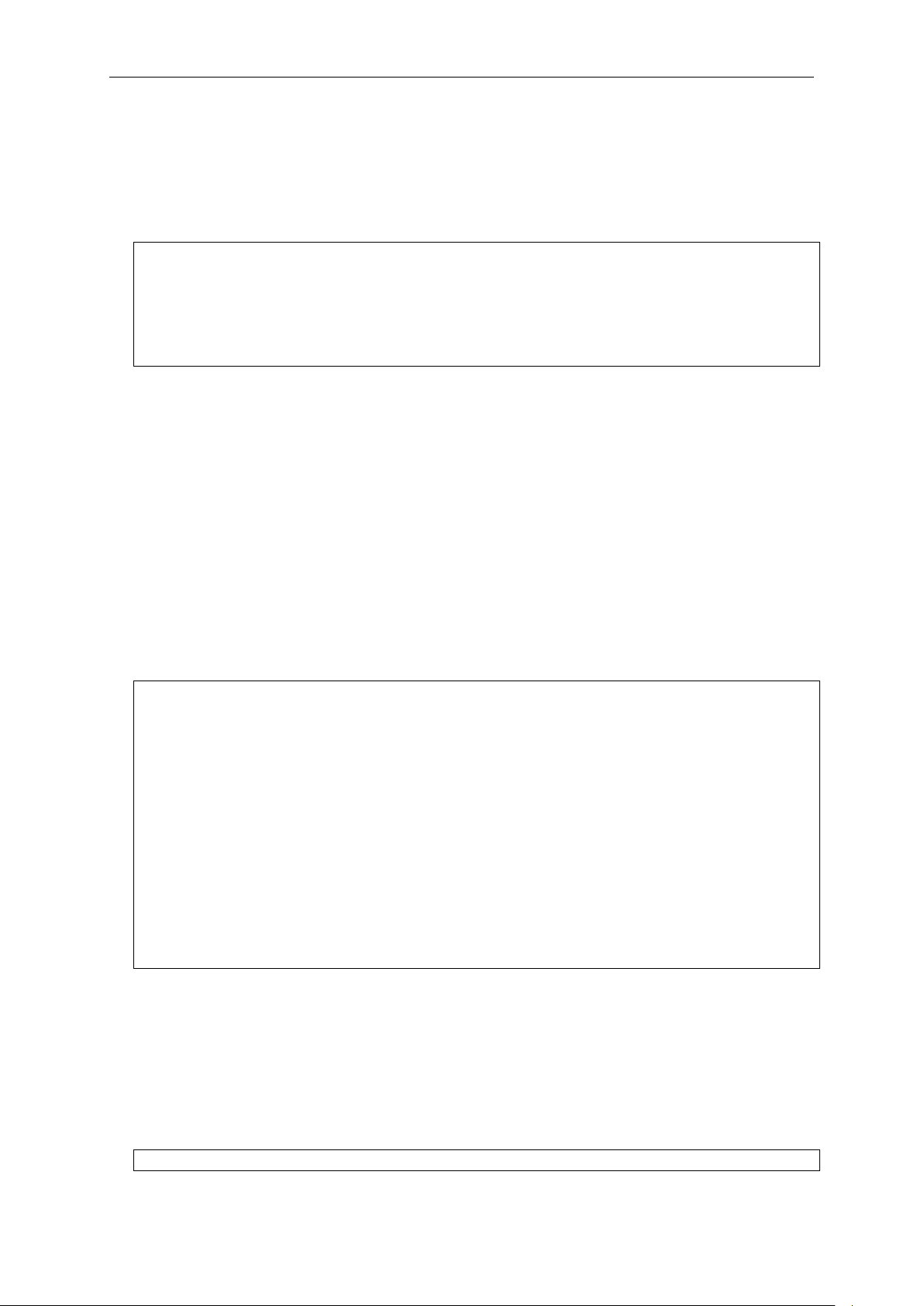
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config account
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config account
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#the
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show
In addition, after typing any given command plus one space, users can see all of the next possible
sub-commands, in sequential order, by repeatedly pressing the Tab key.
To re-enter the previous command at the command prompt, press the up arrow cursor key. The
previous command will appear at the command prompt.
Command: config account
Next possible completions:
<username>
In the above example, the command config account was entered without the required parameter
<username>, the CLI returned the Next possible completions: <username> prompt. The up
arrow cursor control key was pressed to re-enter the previous command (config account) at the
command prompt. Now the appropriate username can be entered and the config account
command re-executed.
All commands in the CLI function in this way. In addition, the syntax of the help prompts are the
same as presented in this manual − angle brackets < > indicate a numerical value or character
string, braces { } indicate optional parameters or a choice of parameters, and brackets [ ] indicate
required parameters.
If a command is entered that is unrecognized by the CLI, the top-level commands will be displayed
under the Available commands: prompt.
Available commands:
.. ? cable_diag cd
cfm change clear config
copy create debug del
delete dir disable download
enable erase format login
logout md move no
ping ping6 rd reboot
reconfig rename reset save
show smtp telnet traceroute
traceroute6 upload
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
The top-level commands consist of commands such as show or config. Most of these commands
require one or more param eter s to narr o w the top-level command. T his is equival ent to show what?
or config what? Where the what? is the next parameter.
For example, entering the show command with no additional parameters, the CLI will then display
all of the possible next parameters.
4
Page 9
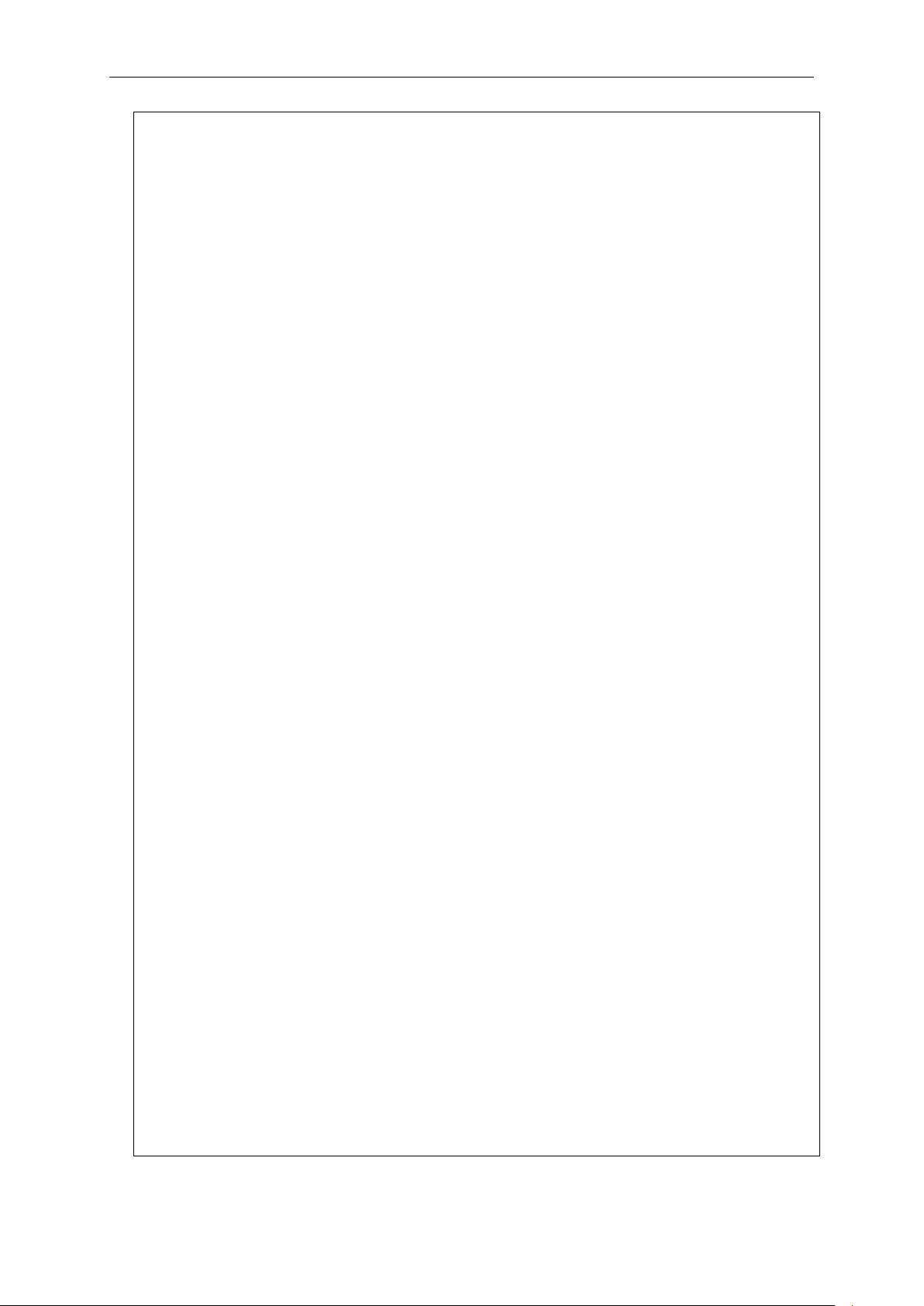
Command: show
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Next possible completions:
802.1p 802.1x access_profile account
accounting acct_client address_binding
arp_spoofing_prevention arpentry asymmetric_vlan
attack_log auth_client auth_diagnostics
auth_session_statistics auth_statistics authen
authen_enable authen_login authen_policy authentication
authorization autoconfig bandwidth_control boot_file
bpdu_protection broadcast_ping_reply cfm
command command_history community_encryption
config cpu current_config ddm
device_status dhcp dhcp_local_relay dhcp_relay
dhcp_server dhcpv6 dhcpv6_relay dhcpv6_server
dnsr dos_prevention dot1v_protocol_group
duld egress_access_profile egress_flow_meter
environment erps error ethernet_oam
external_alarm fdb filter flow_meter
gratuitous_arp greeting_message gvrp hol_prevention
host_name igmp_proxy igmp_snooping ip_tunnel
ipfdb ipif ipif_ipv6_link_local_auto
ipmc_vlan_replication ipmc_vlan_replication_entry
iproute ipv6 ipv6route jumbo_frame
jwac l2protocol_tunnel lacp_port
limited_multicast_addr link_aggregation lldp
lldp_med log log_save_timing
log_software_module loopback loopdetect
mac_based_access_control mac_based_access_control_local
mac_based_vlan mac_notification max_mcast_group
mcast_filter_profile mirror mld_proxy
mld_snooping multicast multicast_fdb name_server
nlb out_band_ipif packet password_recovery
per_queue port port_group port_security
port_security_entry port_vlan ports
power_saving private_vlan ptp pvid
qinq radius rcp rip
ripng rmon route router_ports
rspan safeguard_engine scheduling
scheduling_mechanism serial_port session
sflow sim smtp snmp
sntp ssh ssl stack_device
stack_information stacking_mode storage_media_info
stp subnet_vlan switch syslog
system_severity tech_support terminal time
time_range traffic traffic_segmentation
trap trusted_host udp_helper utilization
vlan vlan_precedence vlan_translation vlan_trunk
voice_vlan wac
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
5
Page 10
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
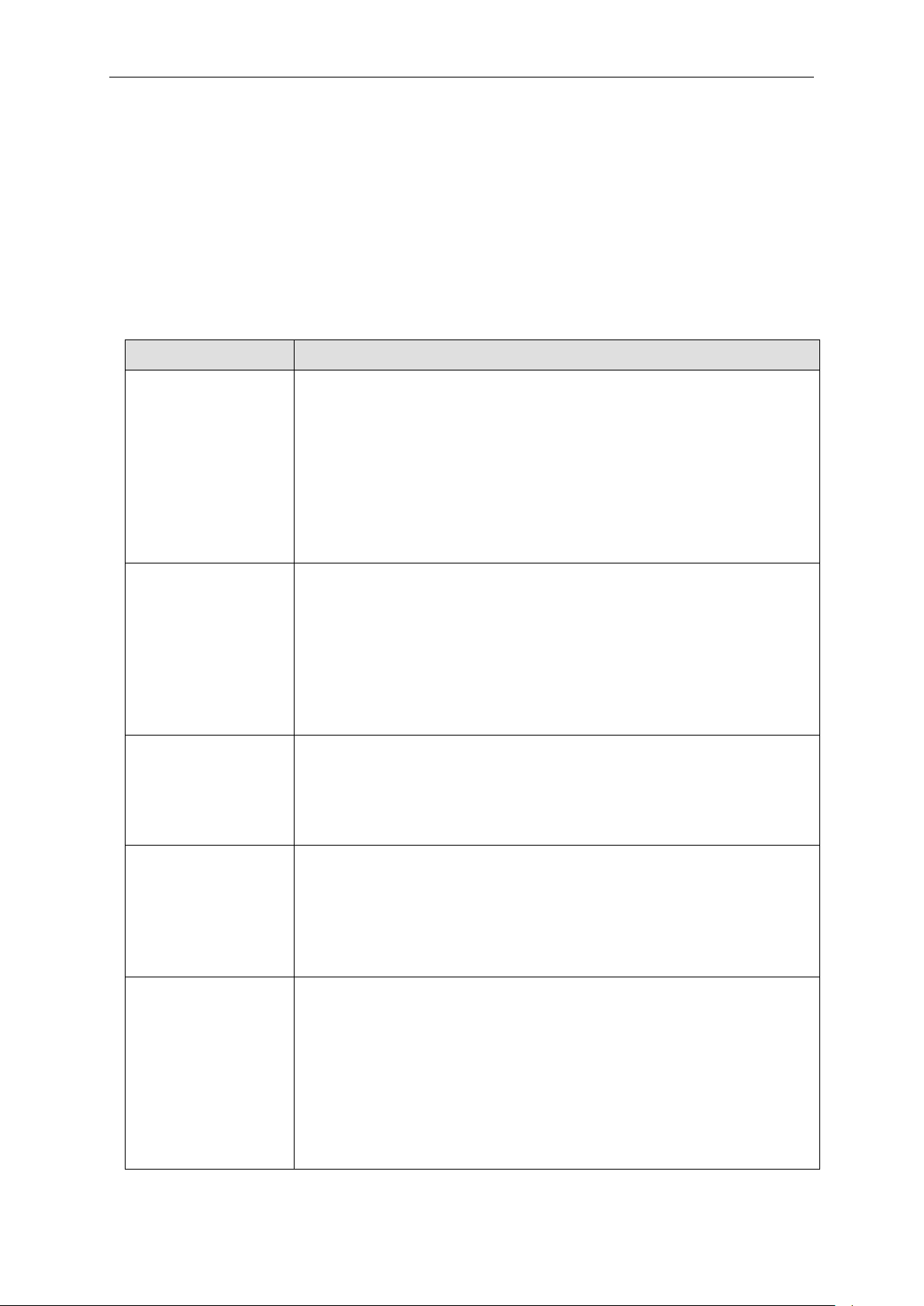
Syntax
Description
angle brackets < >
Encloses a variable or value. Users must specify the variable or value.
square brackets [ ]
Encloses a required value or list of required arguments. Only one
vertical bar |
Separates mutually exclusive items in a list. For example, in the syntax
parentheses ( )
Indicates at least one or more of the values or arguments in the
In the above example, all of the possible next parameters for the show command are displayed. At
the next command prompt, the up arrow was used to re-enter the show command, followed by the
account parameter. The CLI then displays the user accounts configured on the Switch.
1-3 Command Syntax Symbols
The following symbols are used to describe how command entries are made and values and
arguments are specified in this manual. The online help contained in the CLI and available through
the console interface uses the same syntax.
Note: All commands are case-sensitive. Be sure to disable Caps Lock or any other unwanted
function that changes text case.
For example, in the syntax
create ipif <ipif_name 12> {<network_address>} <vlan_name 32>
{secondary | state [enable | disable] | proxy_arp [enable | disable]
{local [enable | disable]}}
users must supply an IP interface name for <ipif_name 12> and a
VLAN name for <vlan_name 32> when entering the command. DO
NOT TYPE THE ANGLE BRACKETS.
value or argument must be specified. For example, in the syntax
create account [admin | operator | power_user | user] <username
15> {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
users must specify either the admin-, operator-, power_user-level or
user-level account when entering the command. DO NOT TYPE THE
SQUARE BRACKETS.
reset {[config |system]} {force_agree}
users may choose config or system in the command. DO NOT TYPE
THE VERTICAL BAR.
braces { } Encloses an optional value or a list of optional arguments. One or
more values or arguments can be specified. For example, in the syntax
reset {[config | system]} {force_agree}
users may choose config or system in the command. DO NOT TYPE
THE BRACES.
preceding syntax enclosed by braces must be specified. For example,
in the syntax
config dhcp_relay {hops <int 1-16> | time <sec 0-65535>}(1)
users have the option to specify hops or time or both of them. The "(1)"
following the set of braces indicates at least one argument or value
within the braces must be specified. DO NOT TYPE THE
PARENTHESES.
6
Page 11
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
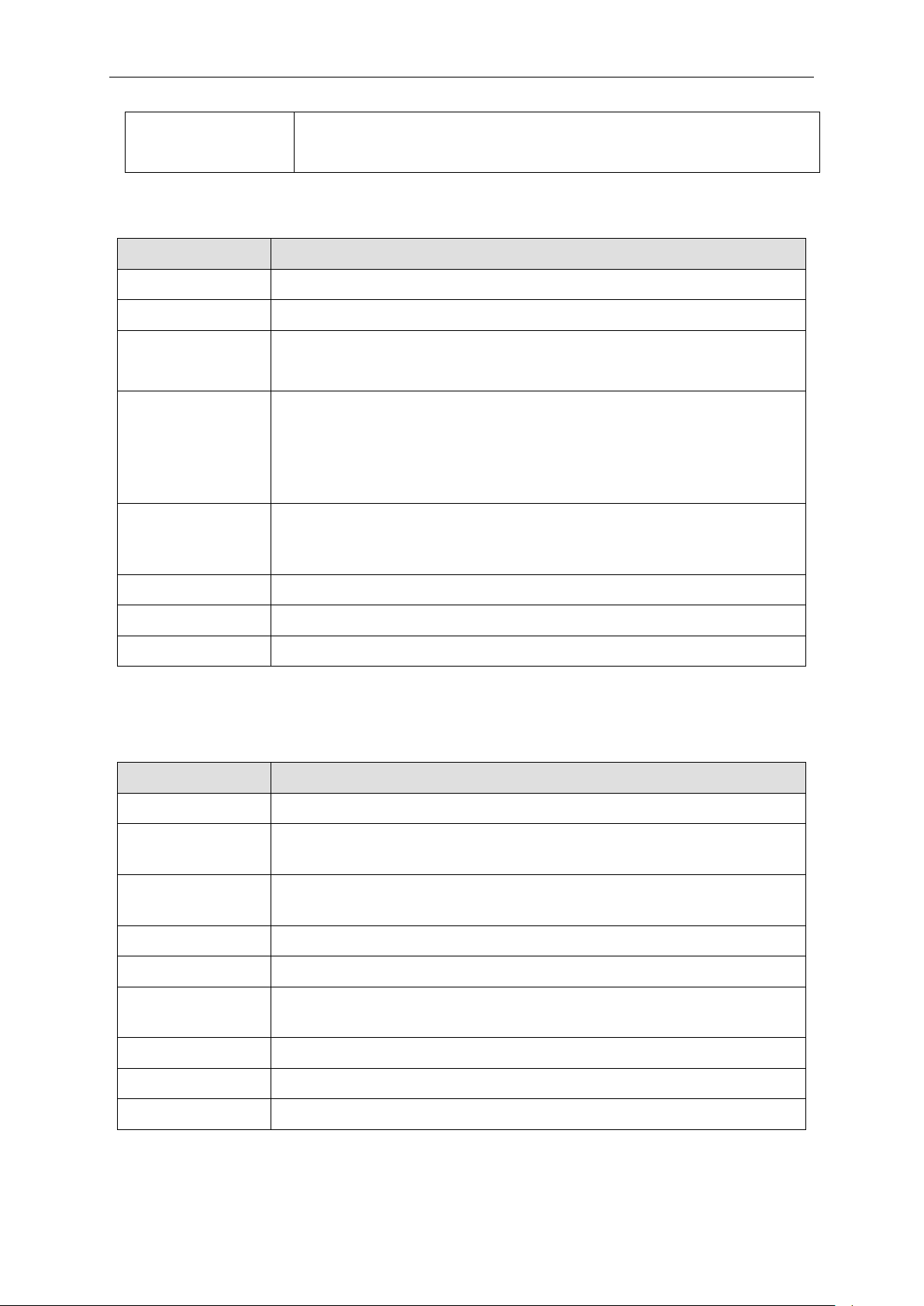
ipif <ipif_name 12>
12 means the maximum length of the IP interface name.
Keys
Description
Backspace
Delete character to left of cursor and shift remainder of line to left.
CTRL+R
Toggle on and off. When toggled on, inserts text and shifts previous
Up Arrow
Repeats the previously entered command. Each time the up arrow is
Left Arrow
Move cursor to left.
Tab
Help user to select appropriate token.
Keys
Description
CTRL+C
Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
ESC
Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
n
Displays the next page.
p
Displays the previous page.
a
Displays the remaining pages without pausing between pages.
Enter
Displays the next line or table entry.
metric <value 1-31>
1-31 means the legal range of the metric value.
1-4 Line Editing Keys
Delete Delete character under cursor and shift remainder of line to left.
text to right.
pressed, the command previous to that displayed appears. This way it is
possible to review the command history for the current session. Use the
down arrow to progress sequentially forward through the command
history list.
Down Arrow The down arrow will display the next command in the command history
entered in the current session. This displays each command sequentially
as it was entered. Use the up arrow to review previous commands.
Right Arrow Move cursor to right
The screen display pauses when the show command output reaches the end of the page.
1-5 Multiple Page Display Control Keys
Space Displays the next page.
displayed.
displayed.
q Stops the display of remaining pages when multiple pages are to be
displayed.
r Refreshes the pages currently displayed.
7
Page 12

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
create account [admin | operator | power_user | user] <username 15> {encrypt [plain_text |
sha_1] <password>}
enable password encryption
disable password encryption
config account <username> {encrypt [plain_t ex t | sha_1] <pas sw ord>}
show account
delete account <username>
show session
show switch
show environment
config temperature [trap | log] state [enable | disable]
config temperature threshold {high <temperature -500-500> | low <temperature -500-500>}(1)
show serial_port
config serial_port { bau d_r at e [960 0 | 19200 | 38400 | 1152 00] | auto_l ogo ut [never | 2_minutes |
5_minutes | 10_minutes | 15_m inutes ]}( 1)
enable clipaging
disable clipaging
enable telnet {<tcp_port_number 1-65535>}
disable telnet
enable web {<tcp_port_number 1-65535>}
disable web
save {[config <pathname> | log | all]}
reboot {force_agree}
reset {[config | system]} {force_agree}
login
logout
clear
config terminal width [default | <value 80-200>]
show terminal width
show device_status
admin - Specify the name of the admin account.
Chapter 2 Basic Management
Commands
2-1 create account
Description
This command creates user accounts. The username is between 1 and 15 characters, the
password is between 0 and 15 characters. The number of accounts (including admin, operator,
power-user and user) is up to eight.
Format
create account [admin | operator | power_user | user] <username 15> {encrypt [plain_text |
sha_1] <password>}
Parameters
8
Page 13

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
operator - Specify the name of the operator account.
power_user - Specify a power user level account. The power user level is lower than the
operator level and higher than the user level.
user - Specify the name of the user account.
<username 15> - Specify a username of up to 15 characters.
encrypt - Specifies the encryption used.
password, the length is fixed to 35 bytes long. The password is case-sensitive.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create account admin dlink
DGS-3420-28SC:admin##create account operator Sales
DGS-3420-28SC:admin##create account user System
plain_text - Specify the password in plain text form.
sha_1 - Specify the password in SHA-1 encrypted form.
<password> - The password for the user account. The length of a password in plain-text form
and encrypted form are different. For a plain-text form password, the password must be a
minimum of 0 characters and a maximum of 15 characters. For an encrypted form
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create the Administrator-level user “dlink”:
Command: create account admin dlink
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for confirmation:****
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
To create the Operator-level user “Sales”:
Command: create account operator Sales
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for confirmation:****
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
To create the User-lev el us er “System”:
Command: create account user System
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
Enter the new password again for confirmation:****
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
9
Page 14

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable password encryption
2-2 enable password encryption
Description
The user account configuration information will be stored in the configuration file, and can be
applied to the system later. If the password encryption is enabled, the password will be in
encrypted form when it is stored in the configuration file. When password encryption is disabled,
the password will be in plain text form when it is stored in the configuration file. However, if the
created user account directly uses the encrypted password, the password will still be in the
encrypted form.
Format
enable password encryption
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable password encryption:
Command: enable password encryption
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-3 disable password encryption
Description
The user account configuration information will be stored in the configuration file, and can be
applied to the system later. If the password encryption is enabled, the password will be in
encrypted form when it is stored in the configuration file. When password encryption is disabled,
the password will be in plain text form when it is stored in the configuration file. However, if the
created user account directly uses the encrypted password, the password will still be in the
encrypted form.
Format
disable password encryption
Parameters
None.
10
Page 15
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable password encryption
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<username> - Specify the name of the account. The account must already be defined.
encrypt - (Optional) Spec if y the enc r yption t ype, plain_text or sha_1.
the length is fixed to 35 bytes long. The password is case-sensitive.
<password> - Specify the password.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config account dlink
Enter the new password again for confirmation:****
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable password encryption:
Command: disable password encryption
Success.
2-4 config account
Description
When the password information is not specified in the command, the system will prompt the user
to input the password interactively. For this case, the user can only input the plain text password.
If the password is present in the command, the user can select to input the password in the plain
text form or in the encrypted form. The encryption algorithm is based on SHA-1.
Format
config account <username> {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
Parameters
plain_text - Specify the password in plain text form. For the plain text form, passwords must
have a minimum of 0 and a maximum of 15 characters. The password is case-sensitive
sha_1 - Specify the password in the SHA-1 encrypted form. For the encrypted form password,
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the user password of the “dlink” account:
Command: config account dlink
Enter a old password:****
Enter a case-sensitive new password:****
11
Page 16
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config account administrator encrypt sha_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show account
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
To configure the user password of the “administrator” account:
*@&NWoZK3kTsExUV00Ywo1G5jlUKKv+toYg
Command: config account administrator encrypt sha_1
*@&NWoZK3kTsExUV00Ywo1G5jlUKKv+toYg
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-5 show account
Description
This command is used to display user accounts that have been created.
Format
show account
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display accounts that have been created:
Command: show account
Current Accounts:
Username Access Level
--------------- -----------System User
Sales Operator
dlink Admin
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-6 delete account
Description
This command is used to delete an existing account.
12
Page 17
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<username> - Specify the name of the user who will b e deleted .
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete account System
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show session
8 23:37:42.270 Serial Port admin Anonymous
Format
delete account <username>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command. One active admin user must exist.
Example
To delete the user account “System”:
Command: delete account System
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-7 show session
Description
This command is used to display a list of current users which are logged in to CLI sessions.
Format
show session
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display accounts a list of currently logged-in users:
Command: show session
ID Live Time From Level User
-- ------------ ------------ ----- --------------------
13
Page 18

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show switch
Telnet : Enabled (TCP 23)
Total Entries: 1
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
2-8 show switch
Description
This command is used to display the switch information.
Format
show switch
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the switch information:
Command: show switch
Device Type : DGS-3420-28SC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
MAC Address : 00-01-02-03-04-00
IP Address : 10.90.90.90 (Manual)
VLAN Name : default
Subnet Mask : 255.0.0.0
Default Gateway : 0.0.0.0
Boot PROM Version : Build 1.00.006
Firmware Version : Build 1.00.024
Hardware Version : A1
Serial Number : D1234567890
System Name :
System Location :
System Uptime : 0 days, 0 hours, 38 minutes, 12 seconds
System Contact :
Spanning Tree : Disabled
GVRP : Disabled
IGMP Snooping : Disabled
MLD Snooping : Disabled
RIP : Disabled
RIPng : Disabled
VLAN Trunk : Disabled
14
Page 19

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Web : Enabled (TCP 80)
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show environment
High Warning Temperature Threshold(Celsius) : 79
SNMP : Disabled
SSL Status : Disabled
SSH Status : Disabled
802.1X : Disabled
Jumbo Frame : Off
CLI Paging : Enabled
MAC Notification : Disabled
Port Mirror : Disabled
SNTP : Disabled
HOL Prevention State : Enabled
Syslog Global State : Disabled
Single IP Management : Disabled
Password Encryption Status : Disabled
DNS Resolver : Disabled
2-9 show environment
Description
This command is used to display the device’s internal and external po wer and inter nal temperature
status.
Format
show environment
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the switch hardware status:
Command: show environment
Internal Power : Active
External Power : Fail
Right Fan 1 : Speed Low (3000 RPM)
Right Fan 2 : Speed Low (3000 RPM)
Current Temperature(Celsius) : 30
Fan High Temperature Threshold(Celsius) : 40
Fan Low Temperature Threshold(Celsius) : 35
15
Page 20

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Low Warning Temperature Threshold(Celsius) : 11
trap - Specify to configure the warning temperature trap.
log - Specify to configure the warning temperature log.
state - Enable or disable either the trap or log state for a warning temperature event. The default
disable - Disable either the trap or log state for a warning temperature event.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config temperature trap state enable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config temperature log state enable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-10 config temperature
Description
This command is used to configure the warning trap or log state of the system internal temperature.
Format
config temperature [trap | log] state [enable | disable]
Parameters
is enable.
enable - Enable either the trap or log state for a warning temperature event.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the warning temperature trap state:
Command: config temperature trap state enable
Success.
To enable the warning temperature log state:
Command: config temperature log state enable
Success.
16
Page 21
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
high - Specify the high threshold value. The high threshold must bigger than the low threshold.
and 500.
low - Specify the low threshold value.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config temperature threshold high 80
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-11 config temperature threshold
Description
This command is used to configure the warning temperature high threshold or low threshold. When
temperature is above the high threshold or below the low threshold, SW will send alarm traps or
keep the logs.
Format
config temperature threshold {high <temperature -500-500> | low <temp erat ure -500-500>}(1)
Parameters
<temperature -500-500> - Specify the high threshold value. This value must be between -500
<temperature -500-500> - Specify the low threshold value. This value must be between -500
and 500.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a warming temperature threshold high of 80:
Command: config temperature threshold high 80
Success.
2-12 show serial_port
Description
This command is used to display the current console port setting.
Format
show serial_port
Parameters
None.
17
Page 22
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show serial_port
baud_rate - Specify the baud rate value. The default baud rate is 115200.
115200 - Specify a baud rate of 115200.
auto_logout - Specify the timeout value. The default timeout is 10_minutes.
15_minutes - Specify when the idle value is over 15 minutes, the device will auto logout.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config serial_port baud_rate 9600
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the console port setting:
Command: show serial_port
Baud Rate : 115200
Data Bits : 8
Parity Bits : None
Stop Bits : 1
Auto-Logout : 10 mins
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-13 config serial_port
Description
This command is used to configure the serial bit rate that will be used to communicate with the
management host and the auto logout time for idle connections.
Format
config serial_port {baud_rate [9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 115200] | auto_logout [never |
2_minutes | 5_minutes | 10_minutes | 15_minutes]}(1)
Parameters
9600 - Specify a baud rate of 9600.
19200 - Specify a baud rate of 19200.
38400 - Specify a baud rate of 38400.
never - Specify to never timeout.
2_minutes - Specify when the idle value is over 2 minutes, the device will auto logout.
5_minutes - Specify when the idle value over 5 minutes, the device will auto logout.
10_minutes - Specify when the idle value is over 10 minutes, the device will auto logout.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the baud rate:
18
Page 23

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Command: config serial_port baud_rate 9600
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable clipaging
Success.
2-14 enable clipaging
Description
This command is used to enable pausing of the screen display when show command output
reaches the end of the page. The default setting is enabled.
Format
enable clipaging
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable pausing of the screen display when show command output reaches the end of the page:
Command: enable clipaging
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-15 disable clipaging
Description
This command is used to disable pausing of the screen display when show command output
reaches the end of the page. The default setting is enabled.
Format
disable clipaging
Parameters
None.
19
Page 24
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable clipaging
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<tcp_port_number 1-65535> - (Optional) Specify the TCP port number. TCP ports are
numbered between 1 and 65535. The “well-known” TCP port for the Telnet protocol is 23.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable telnet 23
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable pausing of the screen displa y when show comm and output r eaches th e end of the page:
Command: disable clipaging
Success.
2-16 enable telnet
Description
This command is used to enable Telnet and configure a port number. The default setting is
enabled and the port number is 23.
Format
enable telnet {<tcp_port_number 1-65535>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable Telnet and configure a port number:
Command: enable telnet 23
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-17 disable telnet
Description
This command is used to disable Telnet.
20
Page 25
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable telnet
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<tcp_port_number 1-65535> - (Optional) Specify the TCP port number. TCP ports are
numbered between 1 and 65535. The “well-know” TCP port for the Web protocol is 80.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable web 80
Format
disable telnet
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable Telnet:
Command: disable telnet
Success.
2-18 enable web
Description
This command is used to enable Web UI and configure the port number . The default setting is
enabled and the port number is 80.
Format
enable web {<tcp_port_number 1-65535>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable HTTP and configure port number:
Command: enable web 80
Note: SSL will be disabled if web is enabled.
Success.
21
Page 26

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable web
config - (Optional) Specify to save configuration.
<pathname> - Specify the path name of the indicated configuration
log - (Optional) Specify to save log.
all - (Optional) Specify to save changes to currently active configuration and save logs.
Note: If no keyword is specified, all changes will be saved to bootup configuration file.
2-19 disable web
Description
This command is used to disable Web UI.
Format
disable web
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable HTTP:
Command: disable web
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-20 save
Description
This command is used to save the current configuration or log in non-volatile RAM.
Format
save {[config <pathname> | log | all]}
Parameters
22
Page 27

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#save
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#save config 1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#save log
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#save all
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator and Operator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To save the current configuration to the bootup configuration file:
Command: save
Saving all configurations to NV-RAM.......... Done.
To save the current configuration to destination file, named 1:
Command: save config 1
Saving all configurations to NV-RAM.......... Done.
To save a log to NV-RAM:
Command: save log
Saving all system logs to NV-RAM............. Done.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
To save all the configurations and logs to NV-RAM:
Command: save all
Saving configuration and logs to NV-RAM...... Done.
2-21 reboot
Description
This command is used to restart the switch.
Format
reboot {force_agree}
23
Page 28

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
force_agree – (Optional) Specify to immediately execute the reboot command without further
confirmation.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#reboot
Please wait, the switch is rebooting…
config - (Optional) Specif y this ke yword and all parameters are reset to default settings.
However, the device will neither save nor reboot.
system - (Optional) Specify this keyword and all parameters are reset to default settings. Then
the switch will do factory reset, save, and reboot.
force_agree - (Optional) Specify and the reset command will be executed immediately without
further confirmation.
Note:
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#reset
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To restart the switch:
Command: reboot
Are you sure you want to proceed with the system reboot?(y/n)
2-22 reset
Description
This command is used to reset all switch parameters to the factory defaults.
Format
reset {[config | system]} {force_agree}
Parameters
If no keyword is specified, all parameters will be reset to default settings except IP
address, user account, and history log, but the device will neither save nor reboot.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To reset all the switch parameters except the IP address:
Command: reset
24
Page 29

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Are you sure you want to proceed with system reset
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#reset config
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#reset system
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#login
except IP address, log, user account and banner?(y/n) y
Success.
To reset the system configuration settings:
Command: reset config
Are you sure to proceed with system reset?(y/n)
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
To reset all system parameters, save, and restart the switch:
Command: reset system
Are you sure to proceed with system reset, save and reboot?(y/n)
Loading factory default configuration… Done.
Saving all configuration to NV-RAM… Done.
Please wait, the switch is rebooting…
2-23 login
Description
This command is used to log in to the switch.
Format
login
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To login to the switch:
Command: login
UserName:
25
Page 30

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#logout
2-24 logout
Description
This command is used to log out of the switch.
Format
logout
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To logout of the switch:
Command: logout
***********
* Logout *
***********
UserName:
2-25 clear
Description
DGS-3420-28SC Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Command Line Interface
Firmware: Build 1.00.024
Copyright(C) 2011 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
This command is used to clear the terminal screen.
Format
clear
26
Page 31

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#clear
Command: clear
default - Specify the default terminal width value.
<value 80-200> - Specify a terminal width value between 80 and 200 characters. The default
value is 80.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config terminal width 90
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To clear the terminal screan:
2-26 config terminal width
Description
This command is used to configure the terminal width.
Format
config terminal width [defa ult | < value 8 0-200>]
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To configure the terminal width:
Command: config terminal width 90
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-27 show terminal width
Description
This command is used to display the configuration of the current terminal width.
27
Page 32

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show terminal width
Format
show terminal width
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the configuration of the current terminal width:
Command: show terminal width
Global terminal width : 80
Current terminal width : 80
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
2-28 show device_status
Description
This command displays current status of power(s) and fan(s) on the system.
Within fan(s) status display, for example, there are three fans on the left of the switch, if three fans
is working normally, there will display “OK” in the Left Fan field. If some fans work failed, such as
fan 1,3 , there will only display the failed fans in the Left Fan field, such as “1,3 Fail”.
In the same way, the Right Fan, Back Fan is same to Left Fan. Because there is only one CPU
Fan, if it is working failed, display “Fail”, otherwise display “OK”.
Format
show device_status
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
28
Page 33

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show device_status
Example
To show device status, the number 1, 2, 3 etc represent the fan number:
Command: show device_status
Unit 1:
Internal Power: Active
External Power: Fail
Right Fan : OK
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
29
Page 34

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
enable 802.1x
disable 802.1x
create 802.1x user <username 15>
delete 802.1x user <username 15>
show 802.1x user
config 802.1x auth_protocol [local | radius_eap]
show 802.1x {[auth_state | auth_configuration] ports {<portlist>}}
config 802.1x capability ports [<portlist> | all] [authenticator | none]
config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports [<portlist> | all] [enable | disable]
config 802.1x fwd_pdu system [enable | disable]
config 802.1x auth_parameter ports [<portlist> | all] [default | {direction [both | in] | port_contr o l
| disable]}(1)]
config 802.1x authorization attributes radius [enable | disable]
config 802.1x init
{mac_address <macaddr>}]
config 802.1x max_users [<value 1-448> | no_limit]
config 802.1x reauth [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] |mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr>}]
create 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
delete 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
config 802.1x guest_vlan ports [<portlist> | all] state [enable | disable]
show 802.1x guest_vlan
config radius add <server_index 1-3> [<server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] key <password 32> [default |
<sec 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}(1)]
config radius delete <server_index 1-3>
config radius
default] | timeout [<sec 1-255> | default] | retransm it [<int 1-20> | default]}(1)
show radius
show auth_statistics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_diagnostics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_session_statistics {ports <portlist>}
show auth_client
show acct_client
config accounting service [network | shell | system] state [enable | disable]
show accounting service
Chapter 3 802.1X Commands
[force_unauth | auto | force_auth] | quiet_period <sec 0-65535> | tx_period <sec 1-65535 > |
supp_timeout <sec 1-65535> | server_timeout <sec 1-65535> | max_req <value 1-10> |
reauth_period <sec 1-65535> | max_users [<value 1-448> | no_lim it] | enable_reauth [enable
[port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{auth_port <udp_port_number 1-65535> | acct_port <udp_port_number 1-65535> | timeout
<server_index 1-3> {ipaddress [<server_ip > | <ipv6addr>] | key <password 32> |
auth_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535> | default] | acct_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535> |
3-1 enable 802.1x
Description
This command is used to enable the 802.1X function.
Format
enable 802.1x
30
Page 35

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable 802.1x
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable 802.1x
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable the 802.1X function:
Command: enable 802.1x
Success.
3-2 disable 802.1x
Description
This command is used to disable the 802.1X functio n.
Format
disable 802.1x
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable the 802.1Xfunction:
Command: disable 802.1x
Success.
31
Page 36

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<username 15> - Specify to add a user name.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create 802.1x user ctsnow
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<username 15> - Specify to delete a user name.
3-3 create 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to create an 802.1X user.
Format
create 802.1x user <username 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user named “ctsnow”:
Command: create 802.1x user ctsnow
Enter a case-sensitive new password:
Enter the new password again for confirmation:
Success.
3-4 delete 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to delete a specified user.
Format
delete 802.1x user <username 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
32
Page 37

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete 802.1x user Tiberius
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show 802.1x user
Example
To delete the user named “Tiberius”:
Command: delete 802.1x user Tiberius
Success.
3-5 show 802.1x user
Description
This command is used to display 802.1X local user account information.
Format
show 802.1x user
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display 802.1X user information:
Command: show 802.1x user
Current Accounts:
Username Password
--------------- -----------ctsnow gallinari
Total Entries : 1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-6 config 802.1x auth_protocol
Description
This command is used to configure the 802.1X authentication protocol.
33
Page 38

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
local - Specifiy the authentication protocol as local.
radius_eap - Specify the authentication protocol as RADIUS EAP.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config 802.1x auth_protocol radius_eap
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
auth_state - (Optional) Specify to display the 802.1X authentication state of some or all ports.
auth_configuration - (Optional) Specify to display 802.1X configuration of some or all ports.
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show 802.1x
Format
config 802.1x auth_protocol [local | radius_eap]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 802.1X RADIUS EAP:
Command: config 802.1x auth_protocol radius_eap
Success.
3-7 show 802.1x
Description
This command is used to display the 802.1X state or configurations.
Format
show 802.1x {[auth_state | auth_configuration] ports {<portlist>}}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display 802.1X information:
Command: show 802.1x
802.1X : Disabled
34
Page 39

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Authentication Protocol : RADIUS_EAP
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show 802.1x auth_state ports 1-4
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show 802.1x auth_configuration ports 1:1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Forward EAPOL PDU : Disabled
Max User : 448
RADIUS Authorization : Enabled
To display the 802.1x state for ports 1 to 5:
Command: show 802.1x auth_state ports 1-4
Status: A – Authorized; U – Unauthorized; (P): Port-Based 802.1X Pri: Priority
Port MAC Address Auth PAE State Backend Status VID Pri
VID State
----- -------------------- ------- -------------- ---------- ------ ----- ----1 00-00-00-00-00-01 10 Authenticated Idle A 4004 3
1 00-00-00-00-00-02 10 Authenticated Idle A 1234 1 00-00-00-00-00-04 30 Authenticating Response U - 2 - (P) - Authenticating Request U - 3 - (P) - Connecting Idle U - 4 - (P) - Held Fail U - -
Total Authenticating Hosts: 3
Total Authenticated Hosts : 2
To display the 802.1x configuration for port 1:
Command: show 802.1x auth_configuration ports 1:1
Port number : 1:1
Capability : None
AdminCrlDir : Both
OpenCrlDir : Both
Port Control : Auto
QuietPeriod : 60 Seconds
TxPeriod : 30 Seconds
SuppTimeout : 30 Seconds
ServerTimeout : 30 Seconds
MaxReq : 2 Times
ReAuthPeriod : 3600 Seconds
ReAuthenticate : Disabled
Forward EAPOL PDU On Port : Enabled
Max User On Port : 10
35
Page 40

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
authenticator - The port that wishes to enforce authentication before allowing access to services
that are accessible via that port adopts the authenticator role.
none – Disable authentication on specified port.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config 802.1x capability ports 1-10 authenticator
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify all ports.
enable - Enable the 802.1X PDU forwarding state.
disable - Disable the 802.1X PDU forwarding state.
3-8 config 802.1x capability port s
Description
This command is used to configure port capability.
Format
config 802.1x capability ports [< p o rtlist> | all] [authenticator | none]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure port capability for ports 1 to 10:
Command: config 802.1x capability ports 1-10 authenticator
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-9 config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports
Description
This command is used to configure the 802.1X PDU forwarding state on specific ports of the
switch.
Format
config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports [<portlist> | all] [enable | disable]
Parameters
36
Page 41

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports 1-2 enable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
enable - Enable the 802.1X PDU forwarding state.
disable - Disable the 802.1X PDU forwarding state.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config 802.1x fwd_pdu system enable
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 802.1X PDU forwarding state on ports 1 to 2:
Command: config 802.1x fwd_pdu ports 1-2 enable
Success.
3-10 config 802.1x fwd_pdu system
Description
This command is used to configure the 802.1X PDU forwarding state.
Format
config 802.1x fwd_pdu system [enable | disable]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 802.1X PDU forwarding state:
Command: config 802.1x fwd_pdu system enable
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-11 config 802.1x auth_parameter ports
Description
This command is used to configure the parameters that control the operation of the authenticator
associated with a port.
37
Page 42

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
default - Set all parameters to the default value.
direction - (Optional) Set the direction of access control.
in
port_control - (Optional) Force a specific port to be unconditionally authorized or unauthorized
the client to authenticate.
quiet_period
<sec 0-65535> - The quiet period value must be between 0 an 65535 seconds.
tx_period - (Optional) The initialization value of the txWhen timer. The default value is 30 s and
<sec 1-65535> - The transmit period value must be between 1 an 65535 seconds.
supp_timeout - (Optional) The initialization value of the aWhile timer when timing out the
<sec 1-65535> - The timeout value must be between 1 an 65535 seconds.
server_timeout - (Optional) The initialization value of the aWhile timer when timing out the
<sec 1-65535> - The server timeout value must be between 1 an 65535 seconds.
max_req - (Optional) The maximum number of times that the authenitcation PAE state machine
<value 1-10> - The maximum require number must be between 1 and 10.
reauth_period - (Optional) It's a non-zero number of seconds, which is used to be the re-
<sec 1-65535> - The reauthentication period value must be between 1 an 65535 seconds.
max_users - (Optional) Set the maximum number of users between 1 and 448.
no_limit - Set an unlimited number of users.
enable_reauth - (Optional) Enable or disable the re-authentication mechanism for a specific port.
disable - Disable the re-authentication mechanism for a specific port.
Format
config 802.1x auth_parameter ports [<portlist> | all] [default | {direction [both | in] |
port_control [force_unauth | auto | force_auth] | quiet_period <sec 0-65535> | tx_period
<sec 1-65535> | supp_timeout <sec 1-65535> | server_timeout <sec 1-65535> | max_req
<value 1-10> | reauth_period <sec 1-65535> | max_users [<value 1-448> | no_limit] |
enable_reauth [enable | disable]}(1)]
Parameters
both - For bidirectional access control.
- For ingress access control.
by setting the parameter of port_control to be force_authorized or force_unauthorized.
Besides, the controlled port will reflect the outcome of authentication if port_control is auto.
force_authorized - The port transmits and receives normal traffic without 802.1X-based
authentication of the client.
auto - The port begins in the unauthorized state, and relays authentication messages between
the client and the authentication server.
force_unauthorized - The port will remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all attempts by
- (Optional) The initialization value of the quietWhile timer. The default value is 60 s
and can be any value from 0 to 65535.
can be any value from 1 to 65535.
supplicant. Its default value is 30 s and can be any value from 1 to 65535.
authentication server. Its default value is 30 and can be any value from 1 to 65535.
will retransmit an EAP Request packet to the supplicant. Its default value is 2 and can be any
number from 1 to 10.
authentication timer. The default value is 3600.
<value 1-448> - The maximum users value must be between 1 and 448.
enable - Enable the re-authentication mechanism for a specific port.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
38
Page 43

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config 802.1x auth_parameter ports 1-20 direction both
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
enable - The authorization attributes such as VLAN, 802.1p default priority, and ACL assigned by
state is enabled.
disable - The authorization attributes assigned by the RADUIS server will not be accepted.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config 802.1x authorization attributes radius enable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Example
To configure the parameters that control the operation of the authenticator associated with a port:
Command: config 802.1x auth_parameter ports 1-20 direction both
Success.
3-12 config 802.1x authorization attributes radius
Description
This command is used to enable or disable the acceptation of an authorized configuration. (To
configure that attributes, regarding VLAN, 802.1p, ACL and Ingress/Egress Bandwidth, please
refer to the Appendix section at the end of this document.)
Format
config 802.1x authorization attributes radius [enable | disable]
Parameters
the RADUIS server will be accepted if the global authorization status is enabled. The default
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 802.1X state of acceptation of an authorized configuration:
Command: config 802.1x authorization attributes radius enable
Success.
3-13 config 802.1x init
Description
This command is used to initialize the authentication state machine of some or all.
39
Page 44

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
port_based ports - Used to configure authentication in port-based mode.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
mac_based ports - To configure authentication in host-based 802.1X mode.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
mac_address - (Optional) Specify the MAC address of the host.
<macaddr>
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config 802.1x init port_based ports all
<value 1-448> - Specify the maximum number of users.
no_limit - Specify an unlimited number of users.
Format
config 802.1x init [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] | mac_base d ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr >}]
Parameters
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
- Enter the MAC address here.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To initialize the authentication state machine of some or all:
Command: config 802.1x init port_based ports all
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-14 config 802.1x max_users
Description
This command is used to configure the 802.1X maximum number of users of the system.
Format
config 802.1x max_users [<value 1-448> | no_limit]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the 820.1X maximum numbers of the system:
40
Page 45

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config 802.1x max_users 2
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
port_based ports - The switch passes data based on its authenticated port.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
mac_based ports
all - Specify to configure all ports.
mac_address - (Optional) Specify the MAC address of the authenticated RADIUS client.
<macaddr> - Enter the MAC address here.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config 802.1x reauth port_based ports all
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Command: config 802.1x max_users 2
Success.
3-15 config 802.1x reauth
Description
This command is used to reauthenticate the device connected with the port. During the
reauthentication period, the port status remains authorized until failed reauthentication.
Format
config 802.1x reauth [port_based ports [<portlist> | all] |mac_based ports [<portlist> | all]
{mac_address <macaddr >}]
Parameters
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
- The switch passes data based on the MAC address of authenticated
RADIUS client.
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To reauthenticate the device connected with the port:
Command: config 802.1x reauth port_based ports all
Success.
3-16 create 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to assign a static VLAN to be a guest VLAN. The specific VLAN which is
assigned to a guest VLAN must already exist. The specific VLAN which is assigned to the guest
VLAN can’t be deleted.
41
Page 46

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the static VLAN to be a guest VLAN.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# create 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the guest VLAN name.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# delete 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
Format
create 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To assign a static VLAN to be a guest VLAN:
Command: create 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-17 delete 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to delete a guest VLAN setting, but not to delete the static VLAN itself.
Format
delete 802.1x guest_vlan <vlan_name 32>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a guest VLAN configuration:
Command: delete 802.1x guest_vlan guestVLAN
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
42
Page 47

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be configured.
all - Specify to configure all ports.
state - Specify the guest VLAN port state of the configured ports.
disable - Remove from guest VLAN.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config 802.1x guest_vlan ports 1-8 state enable
3-18 config 802.1x guest_vlan ports
Description
This command is used to configure a guest VLAN setting.
Format
config 802.1x guest_vlan ports [<portlist> | all] state [enable | disable]
Parameters
enable - Join the guest VLAN.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a guest VLAN setting for ports 1 to 8:
Command: config 802.1x guest_vlan ports 1-8 state enable
Warning, The ports are moved to Guest VLAN.
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-19 show 802.1x guest_vlan
Description
This command is used to display guest VLAN information.
Format
show 802.1x guest_vlan
Parameters
None.
43
Page 48

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show 802.1x guest_vlan
<server_index 1-3> - Specify the RADIUS server index.
<server_ip> - Specify the IP address of the RADIUS server.
<ipv6add> - Specifies the IPv6 address used.
key
<passwd 32> - The maximum length of the password is 32 characters long.
default - Sets the auth_port to be 1812 and acct_port to be 1813.
auth_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS authentication data
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - The authentication port value must be between 1 and 65535.
acct_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS accounting statistics
65535.
timeout - Specify the time, in seconds ,for waiting server reply. The default value is 5 seconds.
<int 1-255> - The timeout value must be between 1 and 255.
retransmit - Specify the count for re-transmit. The default value is 2.
<int 1-20> - The re-transmit value must be between 1 and 20.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display guest VLAN information:
Command: show 802.1x guest_vlan
Guest Vlan Setting
----------------------------------------------------------Guest vlan : guest
Enable guest vlan ports : 1-10
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-20 config radius add
Description
This command is used to add a new RADIUS server. The server with a lower index has higher
authenticative priority.
Format
config radius add <server_index 1-3> [<server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] key <password 32>
[default | {auth_port <udp_port_number 1-65535> | acct_port <udp_port_number 1-65535> |
timeout <sec 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}(1)]
Parameters
- Specify the key pre-negotiated between switch and the RADIUS server. It is used to encrypt
user’s authentication data before being transmitted over the Internet. The maximum length of
the key is 32.
between the switch and the RADIUS server.The range is 1 to 65535.
between the switch and the RADIUS server. The range is 1 to 65535.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - The accounting statistics value must be between 1 and
44
Page 49

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config radius add 1 10.48.74.121 key dlink default
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<server_index 1-3> - Specify the RADIUS server index. The range is from 1 to 3.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config radius delete 1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To add a new RADIUS server:
Command: config radius add 1 10.48.74.121 key dlink default
Success.
3-21 config radius delete
Description
This command is used to delete a RADIUS server.
Format
config radius delete <server_index 1-3>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a RADIUS server:
Command: config radius delete 1
Success.
3-22 config radius
Description
This command is used to configure a RADIUS server.
45
Page 50

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<server_index 1-3> - Specify the RADIUS server index.
ipaddress - Specify the IP address of the RADIUS server.
<ipv6addr> - Enter the IPv6 address here.
key - Specify the key pre-negotiated between the switch and the RADIUS server. It is used to
The maximum length of the key is 32.
auth_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS authentication data
default - Specify to use the default value.
acct_port - Specify the UDP port number which is used to transmit RADIUS accounting statistics
default - Specify to use the default value.
timeout - Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The default value is 5
default - Specify to use the default value.
retransmit - Specify the count for re-transmission. The default value is 2.
default - Specify to use the default value.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config radius 1 ipaddress 10.48.74.121 key dlink
Format
config radius <server_index 1-3> {ipaddress [<server_ip> | <ipv6addr>] | key <password
32> | auth_port [<udp_port_number 1-65535> | default] | acct_port [<udp_port_number 165535> | default] | timeout [<sec 1-255> | default] | retransmit [<int 1-20> | default]}(1)
Parameters
<server_ip> - Enter the RADIUS server IP address here.
encrypt user’s authentication data before being transmitted over the Internet. The maximum
length of the key is 32.
<passwd 32> - Specify the key pre-negotiated between the switch and the RADIUS server. It
is used to encrypt user’s authentication data before being transmitted over the Internet.
between the switch and the RADIUS server. The default is 1812.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - The authentication port value must be between 1 and 65535.
between the switch and the RADIUS server. The default is 1813.
<udp_port_number 1-65535> - The accounting statistics value must be between 1 and
65535.
seconds.
<int 1-255> - Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The timeout value
must be between 1 and 255. The default value is 5 seconds.
<int 1-20> - The re-transmit value must be between 1 and 20.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a RADIUS server:
Command: config radius 1 ipaddress 10.48.74.121 key dlink
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-23 show radius
Description
This command is used to display RADIUS server configurations.
46
Page 51

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show radius
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
Format
show radius
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display RADIUS server configurations:
Command: show radius
Index 1
IP Address : 192.168.69.1
Auth-Port : 1812
Acct-Port : 1813
Timeout : 5
Retransmit : 2
Key : 123456
Total Entries : 1
3-24 show auth_statistics
Description
This command is used to display authenticator statistics information
Format
show auth_statistics {ports <portlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
47
Page 52

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show auth_statistics ports 3
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist> - Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show auth_diagnostics ports 3
Auth VID 100
Example
To display authenticator statistics information for port 3:
Command: show auth_statistics ports 3
Auth VID :100
MAC Address :00-00-00-00-00-03
Port number : 3
EapolFramesRx 0
EapolFramesTx 6
EapolStartFramesRx 0
EapolReqIdFramesTx 6
EapolLogoffFramesRx 0
EapolReqFramesTx 0
EapolRespIdFramesRx 0
EapolRespFramesRx 0
InvalidEapolFramesRx 0
EapLengthErrorFramesRx 0
LastEapolFrameVersion 0
LastEapolFrameSource 00-00-00-00-00-03
3-25 show auth_diagnostics
Description
This command is used to display authenticator diagnostics information.
Format
show auth_diagnostics {ports < p o rtlist>}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authenticator diagnostics information for port 3:
Command: show auth_diagnostics ports 3
48
Page 53

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
MAC Address 00-00-00-00-00-03
ports - (Optional) Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
<portlist>
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show auth_session_statistics ports 3
Port number : 1
EntersConnecting 20
EapLogoffsWhileConnecting 0
EntersAuthenticating 0
SuccessWhileAuthenticating 0
TimeoutsWhileAuthenticating 0
FailWhileAuthenticating 0
ReauthsWhileAuthenticating 0
EapStartsWhileAuthenticating 0
EapLogoffWhileAuthenticating 0
ReauthsWhileAuthenticated 0
EapStartsWhileAuthenticated 0
EapLogoffWhileAuthenticated 0
BackendResponses 0
BackendAccessChallenges 0
BackendOtherRequestsToSupplicant 0
BackendNonNakResponsesFromSupplicant 0
BackendAuthSuccesses 0
BackendAuthFails 0
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
3-26 show auth_session_statistics
Description
This command is used to display authenticator session statistics information.
Format
show auth_session_stat istics {p ort s <portl ist >}
Parameters
- Specify a range of ports to be displayed.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authenticator session statistics information for port 1:
Command: show auth_session_statistics ports 3
Auth VID : 100
MAC Address : 00-00-00-00-00-03
49
Page 54

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Port number : 3
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show auth_client
radiusAuthClientAccessRetransmissions 0
SessionOctetsRx 0
SessionOctetsTx 0
SessionFramesRx 0
SessionFramesTx 0
SessionId
SessionAuthenticMethod Remote Authentication Server
SessionTime 0
SessionTerminateCause SupplicantLogoff
SessionUserName
CTRL+C ESC q Quit SPACE n Next Page p Previous Page r Refresh
3-27 show auth_client
Description
This command is used to display authentication client information.
Format
show auth_client
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display authentication client information:
Command: show auth_client
radiusAuthClient ==>
radiusAuthClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAuthClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAuthServerIndex :1
radiusAuthServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAuthClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAuthClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRequests 0
50
Page 55

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
radiusAuthClientAccessAccepts 0
radiusAuthClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRejects 0
radiusAuthClientAccessChallenges 0
radiusAuthClientMalformedAccessResponses 0
radiusAuthClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAuthClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAuthClientTimeouts 0
radiusAuthClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAuthClientPacketsDropped 0
radiusAuthClient ==>
radiusAuthClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAuthClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAuthServerIndex :2
radiusAuthServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAuthClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAuthClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRequests 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRetransmissions 0
radiusAuthClientAccessAccepts 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRejects 0
radiusAuthClientAccessChallenges 0
radiusAuthClientMalformedAccessResponses 0
radiusAuthClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAuthClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAuthClientTimeouts 0
radiusAuthClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAuthClientPacketsDropped 0
radiusAuthClient ==>
radiusAuthClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAuthClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAuthServerIndex :3
radiusAuthServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAuthClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAuthClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRequests 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRetransmissions 0
radiusAuthClientAccessAccepts 0
radiusAuthClientAccessRejects 0
radiusAuthClientAccessChallenges 0
radiusAuthClientMalformedAccessResponses 0
radiusAuthClientBadAuthenticators 0
51
Page 56

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
radiusAuthClientTimeouts 0
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show acct_client
radiusAuthClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAuthClientPacketsDropped 0
3-28 show acct_client
Description
This command is used to display account client information
Format
show acct_client
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display account client information:
Command: show acct_client
radiusAcctClient ==>
radiusAcctClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAcctClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAccServerIndex : 1
radiusAccServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAccClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAccClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAccClientRequests 0
radiusAccClientRetransmissions 0
radiusAccClientResponses 0
radiusAccClientMalformedResponses 0
radiusAccClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAccClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAccClientTimeouts 0
radiusAccClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAccClientPacketsDropped 0
52
Page 57

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
radiusAcctClient ==>
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
radiusAcctClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAcctClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAccServerIndex : 2
radiusAccServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAccClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAccClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAccClientRequests 0
radiusAccClientRetransmissions 0
radiusAccClientResponses 0
radiusAccClientMalformedResponses 0
radiusAccClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAccClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAccClientTimeouts 0
radiusAccClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAccClientPacketsDropped 0
radiusAcctClient ==>
radiusAcctClientInvalidServerAddresses 0
radiusAcctClientIdentifier D-Link
radiusAuthServerEntry ==>
radiusAccServerIndex : 3
radiusAccServerAddress 0.0.0.0
radiusAccClientServerPortNumber X
radiusAccClientRoundTripTime 0
radiusAccClientRequests 0
radiusAccClientRetransmissions 0
radiusAccClientResponses 0
radiusAccClientMalformedResponses 0
radiusAccClientBadAuthenticators 0
radiusAccClientPendingRequests 0
radiusAccClientTimeouts 0
radiusAccClientUnknownTypes 0
radiusAccClientPacketsDropped 0
3-29 config accounting service
Description
This command is used to configure the state of the specified RADIUS accounting service.
53
Page 58

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
network - Specifies that when enabled, the Switch will send informational packets to a remote
Switch. By default, the service is disabled.
shell - Specifies that when enabled, the Switch will send informational packets to a remote
console, Telnet, or SSH. By default, the service is disabl ed.
system - Specifies that when enabled, the Switch will send informational packets to a remote
boot. By default, the service is disabled.
state - Specify the state of the accounting service.
disable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config accounting service shell state enable
Format
config accounting service [network | shell | system] state [enable | disable]
Parameters
RADIUS server when 802.1X, WAC and JWAC port access control events occur on the
RADIUS server when a user either logs in, logs out or times out on the Switch, using the
RADIUS server when system events occur on the Switch, such as a system reset or system
enable - Enable the specified accounting service.
- Disable the specified accounting service.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the state of the RADIUS accounting service shell to enable:
Command: config accounting service shell state enable
Success
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
3-30 show accounting service
Description
This command is used to display RADIUS accounting service information.
Format
show accounting service
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
54
Page 59

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show accounting service
Example
To display accounting service information:
Command: show accounting service
Accounting State
------------------Network : Disabled
Shell : Disabled
System : Disabled
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
55
Page 60

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
enable authen_policy
disable authen_policy
show authen_policy
create authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
config authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+
| radius | server_group <string 15> | local | none}(1)
delete authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
show authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
create authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
config authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | loca l_e na ble | none} (1)
delete authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
show authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
config authen application [console | telnet | ssh | http | all] [login | enable] [default |
method_list_name <string 15>]
show authen application
create authen server_group <string 15>
config authen server_group [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius | <string 15>] [add | delete]
server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
delete authen server_group <string 15>
show authen server_group {<string 15>}
create authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int 1-
65535> | key [<key_string 254> | none] | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
config authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int 1-
65535> | key [<key_string 254> | none] | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}(1)
delete authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
show authen server_host
config authen parameter response_ti meout <int 0-255>
config authen parameter attempt <int 1-255>
show authen parameter
enable admin
config admin local_enable {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
Chapter 4 Access Authenticat ion
Control (AAC)
Commands
The TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS commands allows secure access to the Switch
using the TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS protocols. When a user logs in to the
Switch or tries to access the administrator level privilege, he or she is prompted for a password. If
TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS authentication is enabled on the Switch, it will contact
a TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS server to verify the user. If the user is verified, he or
she is granted access to the Switch.
There are currently three versions of the TACACS security protocol, each a separate entity. The
Switch’s software supports the following versions of TACACS:
1. TACACS (Terminal Access Con troller Access Control System) —Provides password
checking and authentication, and notification of user actions for security purposes utilizing
56
Page 61

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Note: User granted access to the Switch will be granted normal user privileges on the
via one or more centralized TACACS servers, utilizing the UDP protocol for packet
transmission.
2. Extended TACACS (XTACACS) — An extension of the TACACS protocol with the ability
to provide more types of authentication requests and more types of response codes than
TACACS. This protocol also uses UDP to transmit packets.
3. TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access Control System plus) — Provides
detailed access control for authentication for network devices. TACACS+ is facilitated
through Authentication commands via one or more centralized servers. The TACACS+
protocol encrypts all traffic between the Switch and the TACACS+ daemon, using the TCP
protocol to ensure reliable delivery.
The Switch also supports the RADIUS protocol for authentication using the Access Authentication
Control commands. RADIUS or Remote Authentication Dial In User Server also uses a remote
server for authentication and can be responsible for receiving user connection requests,
authenticating the user and returning all configuration information necessary for the client to deliver
service through the user. RADIUS may be facilitated on this Switch using the commands listed in
this section.
In order for the TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS security function to work properly, a
TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS server must be configured on a device other than the
Switch, called a server host and it must include usernames and passwords for authentication.
When the user is prompted by the Switch to enter usernames and passwords for authentication,
the Switch contacts the TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS server to verify, and the
server will respond with one of three messages:
The server verifies the username and password, and the user is granted normal user privileges on
the Switch. The server will not accept the username and password and the user is denied access
to the Switch.
The server doesn’t respond to the verification query. At this point, the Switch receives the timeout
from the server and then moves to the next method of verification configured in the method list.
The Switch has four built-in server groups, one for each of the TACACS, XTACACS, TACACS+
and RADIUS protocols. These built-in server groups are used to authenticate users trying to
access the Switch. The users will set server hosts in a preferable order in the built-in server group
and when a user tries to gain access to the Switch, the Switch will ask the first server host for
authentication. If no authentication is made, the second server host in the list will be queried, and
so on. The built-in server group can only have hosts that are running the specified protocol. For
example, the TACACS server group can only have TACACS server hosts.
The administrator for the Switch may set up five different authentication techniques per userdefined method list (TACACS / XTACACS / TACACS+ / RADIUS / local / none) for authentication.
These techniques will be listed in an order preferable, and defined by the user for normal user
authentication on the Switch, and may contain up to eight authentication techniques. When a user
attempts to access the Switch, the Switch will select the first technique listed for authentication. If
the first technique goes through its server hosts and no authentication is returned, the Switch will
then go to the next technique listed in the server group for authentication, until the authentication
has been verified or denied, or the list is exhausted.
Switch. To gain access to admin level privileges, the user must enter the enable
admin command and then enter a password, which was previously configured by
the administrator of the Switch.
57
Page 62

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Note: This Switch also support the assignment of user privilege by a TACACS+ server.
Note: TACACS, XTACACS and TACACS+ are separate entities and are not compatible.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#enable authen_policy
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
The Switch and the server must be configured exactly the same, using the same
protocol. (For example, if the Switch is set up for TACACS authentication, so must
be the host server.)
4-1 enable authen_policy
Description
This command is used to enable system access authentication policy. When enabled, the device
will adopt the login authentication method list to authenticate the user for login, and adopt the
enable authentication mothod list to authenticate the enable password for promoting the user‘s
privilege to Administrator leve l.
Format
enable authen_policy
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To enable system access authentication policy:
Command: enable authen_policy
Success.
4-2 disable authen_policy
Description
This command is used to disable system access authentication policy. When authentication is
disabled, the device will adopt the local user account database to authenticate the user for login,
and adopt the local enable password to authenticate the enable password for promoting the user‘s
privilege to Administrator leve l.
Format
disable authen_policy
58
Page 63

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#disable authen_policy
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen_policy
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To disable system access authentication policy:
Command: disable authen_policy
Success.
4-3 show authen_policy
Description
This command is used to display whether system access authentication policy is enabled or
disabled.
Format
show authen_policy
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display system access authentication policy:
Command: show authen_policy
Authentication Policy : Enabled
59
Page 64

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined m ethod list na me.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
4-4 create authen_login method_list_name
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined method list of authentication methods for user
login. The maximum supported number of the login method lists is eight.
Format
create authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: create authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-5 config authen_login
Description
This command is used to configure a user-defined or default method list of authentication methods
for user login. The sequence of methods will affect the authentication result. For example, if the
sequence is TACACS+ first, then TACACS and local, when a user trys to login, the authentication
request will be sent to the first server host in the TACACS+ built-in server group. If the first server
host in the TACACS+ group is missing, the authentication request will be sent to the second server
host in the TACACS+ group, and so on. If all server hosts in the TACACS+ group are missing, the
authentication request will be sent to the first server host in the TACACS group. If all server hosts
in a TACACS group are missing, the local account database in the device is used to authenticate
this user. When a user logs in to the device successfully while using methods like
TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+/RADIUS built-in or user-defined server groups or none, the “user”
privilege level is assigned only. If a user wants to get admin privilege level, the user must use the
“enable admin” command to promote his privilege level. But when the local method is used, the
privilege level will depend on this account privilege level stored in the local device.
Format
config authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | local | none}(1)
60
Page 65

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
default – Specify the default method list of authentication methods.
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list of authentication methods.
name can be up to 15 characters long.
method - Choose the desired authentication method:
none - Specify no authentication.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen_login method_list_name login_list_1 method
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined m ethod list na me.
Parameters
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined method list of authentication methods. The method list
tacacs - Specify authentication by the built-in server group TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify authentication by the built-in server group XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify authentication by the built-in server group TACACS+.
radius - Specify authentication by the built-in server group RADIUS.
server_group - Specify authentication by the user-defined server group.
<string 15> - Specify authentication by the user-defined server group. The server group
value can be up to 15 characters long.
local - Specify authentication by local user account databas e in the de vice.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a user-defined method list for user login:
tacacs+ tacacs local
Command: config authen_login method_list_name login_list_1 method tacacs+
tacacs local
Success.
4-6 delete authen_login method_list_name
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined method list of authentication methods for user login.
Format
delete authen_login method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
61
Page 66

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
default – Specify to display the default method list for user login.
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list for user login.
up to 15 characters long.
all – Specify to display all method lists for user login.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Example
To delete a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: delete authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
4-7 show authen_login
Description
This command is used to display the method list of authentication methods for user login.
Format
show authen_login [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
Parameters
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined method list for user login. The method list name can be
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display a user-defined method list for user login:
Command: show authen_login method_list_name login_list_1
Method List Name Priority Method Name Comment
---------------- -------- --------------- -----------------login_list_1 1 tacacs+ Built-in Group
2 tacacs Built-in Group
3 mix_1 User-defined Group
4 local Keyword
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
62
Page 67

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined m ethod list na me.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-8 create authen_enable method_list_name
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined method list of authentication methods for
promoting a user's privilege to Admin level. The maximum supported number of the enable method
lists is eight.
Format
create authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined method list for promoting a user's privilege to Admin level:
Command: create authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
Success.
4-9 config authen_enable
Description
This command is used to configure a user-defined or default method list of authentication methods
for promoting a user's privilege to Admin level. The sequence of methods will effect the
authencation result. For example, if the sequence is TACACS+ first, then TACACS and
local_enable, when a user tries to promote a user's privilege to Admin level, the authentication
request will be sent to the first server host in the TACACS+ built-in server group. If the first server
host in the TACACS+ group is missing, the authentication request will be sent to the second server
host in the TACACS+ group, and so on. If all server hosts in the TACACS+ group are missing, the
authentication request will be sent to the first server host in the TACACS group. If all server hosts
in the TACACS group are missing, the local enable password in the device is used to authenticate
this user’s password. The local enable password in the device can be configured by the CLI
command config admin local_enable.
Format
config authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15>] method {tacacs | xtacacs |
tacacs+ | radius | server_group <string 15> | local_enable | none}(1)
63
Page 68

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
default - Specify the default method list of authentication methods.
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list of authentication methods.
name can be up to 15 characters long.
method - Choose the desired authentication method:
none - Specify no authentication.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1 method
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined m ethod list name.
Parameters
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined method list of authentication methods. The method list
tacacs - Specify authentication by the built-in server group TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify authentication by the built-in server group XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify authentication by the built-in server group TACACS+.
radius - Specify authentication by the built-in server group RADIUS.
server_group - Specify authenticati on b y the user -defined server group.
<string 15> - Specify authentication by the user-defined server group. The server group
value can be up to 15 characters long.
local_enable - Specify authentication by local enab le pass wor d in the device.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a user-defined method list for promoting a user's privilege to Admin level:
tacacs+ tacacs local_enable
Command: config authen_ enable method_list_name enable_list_1 method tacacs+
tacacs local_enable
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-10 delete authen_enable method_list_name
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined method list of authentication methods for
promoting a user's privilege to Administrator level.
Format
delete authen_enable method_list_name <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
64
Page 69

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
default - Specify to display the default method list for promoting a user's privilege to
Administrator level.
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list for promoting a user's privilege to
Administrator level . The method list name value can be up to 15 characters long.
all - Specify to display all method lists for promoting a user's privilege to Administrator level.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen_enable all
Example
To delete a user-defined method list for promoting a user's privilege to Admin level:
Command: delete authen_enable method_list_name enable_list_1
Success.
4-11 show authen_enable
Description
This command is used to display the method list of authentication methods for promoting a user's
privilege to Administrator leve l.
Format
show authen_enable [default | method_list_name <string 15> | all]
Parameters
Administrator level.
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined method list for a promoting a user's privilege to
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all method lists for promoting a user's privilege to Administrator level:
Command: show authen_enable all
Method List Name Priority Method Name Comment
---------------- -------- --------------- -----------------default 1 local_enable Keyword
enable_list_1 1 tacacs+ Built-in Group
2 tacacs Built-in Group
3 mix_1 User-defined Group
4 loca_enable Keyword
enable_list_2 1 tacacs+ Built-in Group
2 radius Built-in Group
65
Page 70

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Total Entries : 3
console - Specify an application: console.
all - Specify all applications: console, Telnet, SSH, and Web.
login - Specify the method list of authentication methods for user login.
Administrator level.
default - Specify the default method list.
up to 15 characters long.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen application telnet login method_list_name
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-12 config authen application
Description
This command is used to configure login or enable method list for all or the specified application.
Format
config authen application [console | telnet | ssh | http | all] [login | enable] [default |
method_list_name <string 15>]
Parameters
telnet - Specify an application: Telnet.
ssh - Specify an application: SSH.
http - Specify an application: Web.
enable - Specify the method list of authentication methods for promoting user privilege to
method_list_name - Specify the user-defined method list name.
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined method list name. The method list name value can be
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the login method list for Telnet:
login_list_1
Command: config authen application telnet login method_list_name login_list_1
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-13 show authen application
Description
This command is used to display the login/enable method list for all applications.
66
Page 71

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen application
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined server group name.
Format
show authen application
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display the login and enable method list for all applications:
Command: show authen application
Application Login Method List Enable Method List
----------- ----------------- -----------------Console default default
Telnet login_list_1 default
SSH default default
HTTP default default
4-14 create authen server_group
Description
This command is used to create a user-defined authentication server group. The maximum
supported number of server groups including built-in server groups is eight. Each group consists of
eight server hosts as maximum.
Format
create authen server_group <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a user-defined authentication server group:
67
Page 72

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create authen server_group mix_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
tacacs - Specify the built-in server group TACACS.
<string 15> - Specify a user-defined server group.
add - Specify to add a server host to a server group.
delete - Specify to remove a server host from a server group.
server_host - Specify the server host’s IP address.
<ipaddr> - Specify the server host’s IP address.
protocol - Specify the server host’s type of authentication protocol.
radius - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol RADIUS.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen server_group mix_1 add server_host 10.1.1.222
Command: create authen server_group mix_1
Success.
4-15 config authen server_group
Description
This command is used to add or remove an authentication server host to or from the specified
server group. Built-in server group tacacs, xtacacs, tacacs+, and RADIUS accept the server host
with the same protocol only, but user-defined server group can accept server hosts with different
protocols. The server host must be created first by using the CLI command create authen
server_host.
Format
config authen server_group [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius | <string 15>] [add | delete]
server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
Parameters
xtacacs - Specify the built-in server group XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify the built-in server group TACACS+.
radius – Specify the built-in server group RADIUS.
tacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS+.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To add an authentication server host to a server group:
protocol tacacs+
Command: config authen server_group mix_1 add server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol
tacacs+
Success.
68
Page 73

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<string 15> - Specify the user-defined server group name.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete authen server_group mix_1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<string 15> - (Optional) Specify the built-in or user-defined server group name.
4-16 delete authen server_group
Description
This command is used to delete a user-defined authentication server group.
Format
delete authen server_group <string 15>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete a user-defined authentication server group:
Command: delete authen server_group mix_1
Success.
4-17 show authen server_group
Description
This command is used to display the authentication server groups.
Format
show authen server_group {<string 15>}
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
69
Page 74

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen server_group
<ipaddr> - Specify the server host’s IP address.
protocol - Specify the server host’s type of authentication protocol.
radius - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol RADIUS.
port - (Optional) Specify the port number of the authentication protocol for the server host. The
key - (Optional) Specify the key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication.
for TACACS and XTACACS.
timeout
seconds. The timeout value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
Example
To display all authentication server groups:
Command: show authen server_group
Group Name IP Address Protocol
--------------- --------------- -------mix_1 10.1.1.222 TACACS+
radius 10.1.1.224 RADIUS
tacacs 10.1.1.225 TACACS
tacacs+ 10.1.1.226 TACACS+
xtacacs 10.1.1.227 XTACACS
Total Entries : 5
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-18 create authen server_host
Description
This command is used to create an authentication server host. When an authentication server host
is created, the IP address and protocol are the index. That means more than one authentication
protocol service can be run on the same physical host. The maximum supported number of server
hosts is 16.
Format
create authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int
1-65535> | key [<key_string 254> | none] | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}
Parameters
tacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS+.
default value for TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. The default value for RADIUS is 1812.
<int 1-65535> - Specify the port number of the authentication protocol for the server host. The
default value for TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. The default value for RADIUS is
1812. The port number must be between 1 and 65535.
<key_string 254> - Specify the key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authenticaiton. If the value is
null, no encryption will apply. This value is meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
none - No encryption for TACACS+ and RADIUS authenticaiton. This value is meaningless
- (Optional) Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The default value
is 5 seconds.
<int 1-255> - Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The default value is 5
70
Page 75

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
retransmit - (Optional) Specify the count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for
default value is 2. The re-transmit value must be between 1 and 20.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ port
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<ipaddr> - Specify the server host’s IP address.
protocol - Specify the server host’s type of authentication protocol.
radius - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol RADIUS.
port - Specify the port number of the authentication protocol for the server host. The default value
1812. The port number must be between 1 and 65535.
key
meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
timeout - Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The default value is 5
<int 1-255> - Specify the time in seconds for waiting for a server reply. The default value is 5
TACACS+. The default value is 2.
<int 1-20> - Specify the count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for TACACS+. The
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To create a TACACS+ authentication server host with a listening port number of 15555 and a
timeout value of 10 seconds:
15555 key "123" timeout 10
Command: create authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ port 15555 key
"123" timeout 10
Success.
4-19 config authen server_host
Description
This command is used to configure an authentication server host.
Format
config authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius] {port <int
1-65535> | key [<key_string 254> | none] | timeout <int 1-255> | retransmit <int 1-20>}(1)
Parameters
tacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS+.
for TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. The default value for RADIUS is 1812.
<int 1-65535> - Specify the port number of the authentication protocol for the server host. The
default value for TACACS/XTACACS/TACACS+ is 49. The default value for RADIUS is
- Specify the key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication.
<key_string 254> - Specify the key for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. If the value is
null, no encryption will apply. This value is meaningless for TACACS and XTACACS.
none - Specify no encryption for TACACS+ and RADIUS authentication. This value is
seconds.
71
Page 76

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
seconds. The timeout value must be between 1 and 255 seconds.
retransmit - Specify the count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for TACACS+. The
default value is 2. The re-transmit value must be between 1 and 20.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ key
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<ipaddr> - Specify the server host’s IP address.
protocol - Specify the server host’s type of authentication protocol.
radius
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
default value is 2.
<int 1-20> - Specify the count for re-transmit. This value is meaningless for TACACS+. The
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure a TACACS+ authentication server host’s key value:
"abc123"
Command: config authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+ key "abc123"
Success.
4-20 delete authen server_host
Description
This command is used to delete an authentication server host.
Format
delete authen server_host <ipaddr> protocol [tacacs | xtacacs | tacacs+ | radius]
Parameters
tacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS.
xtacacs - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol XTACACS.
tacacs+ - Specify the server host’s authentication protocol TACACS+.
- Specify the server host’s authentication protocol RADIUS.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete an authentication server host:
Command: delete authen server_host 10.1.1.222 protocol tacacs+
Success.
72
Page 77

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show authen server_host
<int 0-255> - Specify the amount of time for user input on console or Telnet or SSH. 0 means
there is no time out. The default value is 30 seconds.
4-21 show authen server_host
Description
This command is used to display authentication server hosts.
Format
show authen server_host
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display all authentication server hosts:
Command: show authen server_host
IP Address Protocol Port Timeout Retransmit Key
--------------- -------- ----- ------- ---------- -----------------------
10.1.1.222 TACACS+ 15555 10 ------ 123
Total Entries : 1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-22 config authen parameter response_timeout
Description
This command is used to configure the amount of time waiting for user to input on console, Telnet,
and SSH applications.
Format
config authen parameter response_ti meout <int 0-255>
Parameters
73
Page 78

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen parameter response_timeout 60
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
<int 1-255> - Specify the amount of attempts for users trying to login or promote the privilege on
console, Telnet, or SSH. The default value is 3.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config authen parameter attempt 9
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure 60 seconds for user to input:
Command: config authen parameter response_timeout 60
Success.
4-23 config authen parameter attempt
Description
This command is used to configure the maximum attempts for users trying to login or promote the
privilege on console, Telnet, or SSH applications. If the failure value is exceeded, connection or
access will be locked.
Format
config authen parameter attempt <int 1-255>
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the maximum attempts for users trying to login or promote the privilege to be 9:
Command: config authen parameter attempt 9
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-24 show authen parameter
Description
This command is used to display the authentication parameters.
74
Page 79

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# show authen parameter
Format
show authen parameter
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To display the authentication parameters:
Command: show authen parameter
Response Timeout : 60 seconds
User Attempts : 9
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-25 enable admin
Description
This command is used to promote the "user" privilege level to "admin" level. When the user enters
this command, the authentication method TACACS, XTACAS, TACACS+, user-defined server
groups, local enable, or none will be used to authenticate the user. Because TACACS, XTACACS
and RADIUS don't support the enable function by themselves, if a user wants to use either one of
these three protocols to enable authentication, the user must create a special account on the
server host first, which has a username enable and then configure its password as the enable
password to support the "enable" function. This command cannot be used when authentic ati on
policy is disabled.
Format
enable admin
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To enable administrator lever privilege:
75
Page 80

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# enable admin
encrypt - (Optional) Specifies the encryption type to be used for the password.
sha_1 - Specifies that the password entered should be in SHA-1 encrypted form.
<password> - (Optional) Enter the password value used here. Note that for plain_text
passwords, the password must be 35 bytes long.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config admin local_enable
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Password:********
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
4-26 config admin local_enable
Description
This command is used to configure the local enable password for the enable command. When the
user chooses the local_enable method to promote the privilege level, the enable password of the
local device is needed.
Format
config admin local_enable {encrypt [plain_text | sha_1] <password>}
Parameters
plain_text - Specifies that the password entered should be in plain text form.
passwords, the password can be up to 15 characters long. Note that for SHA-1 encrypted
Restrictions
Only Administrator-level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the administrator password:
Command: config admin local_ebable
Enter the old password:
Enter the case-sensitive new password:******
Enter the new password again for confirmation:******
Success.
To configure the administrator password, specifying an SHA-1 encrypted password of
“*@&cRDtpNCeBiq15KOQsKVyrA0sAiCIZQwq”:
76
Page 81

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin# config admin local_enable encrypt sha_1
*@&cRDtpNCeBiq15KOQsKVyrA0sAiCIZQwq
Command: config admin local_enable encrypt sha_1
*@&cRDtpNCeBiq15KOQsKVyrA0sAiCIZQwq
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
77
Page 82

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
create access_profile profile_id <value 1-6> profile_name <name 1-32> [ethernet {vlan {<hex
dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | icmp {type | code}]}(1)]
delete access_profile [profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32> | all]
config access_profile [profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>] [add access_id
delete access_id <value 1-256>]
show access_profile {[profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>]}
config time_range <range_name 32> [hours start_time <time hh:mm:ss> end_time <time
hh:mm:ss> weekdays <daylist> | delete]
show time_range
show current_config access_profile
delete cpu access_profile [profile_id <value 1-5> | all]
create cpu access_profile profile_id < va lue 1-5> [ethernet {vlan | source_mac <macmask
{user_define_mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}]}(1) | packet_content_mask {offset_0-15 <hex 0x0-
Chapter 5 Access Control List
(ACL) Commands
0x0-0x0fff>} | source_mac <macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> | destination_mac <macmask
000000000000-ffffffffffff> | 802.1p | ethernet_type}(1) | ip {vlan {<hex 0x0-0x0fff>} |
source_ip_mask <netmask> | destination_ip_mask <netmask> | dscp | [icmp {type | code} |
igmp {type} | tcp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
flag_mask [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | protocol_id_mask <hex 0x0-0xff> {user_define_mask <hex
0x0-0xffffffff>}]}(1) | packet_content_mask {offset_chunk_1 <value 0-31> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff > |
offset_chunk_2 <value 0-31> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_chunk_3 <value 0-31> <hex 0x00xffffffff> | offset_chunk_4 <value 0-31> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}(1) | ipv6 {class | flowlabel |
source_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | destination_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | [tcp {src_port_mask
<hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | udp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
[auto_assign | <value 1-256>] [ethernet {[vlan <vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>]
{mask <hex 0x0-0x0fff>} | source_mac <macaddr> {mask <macmask>} | destination_mac
<macaddr> {mask <macmask>} | 802.1p <value 0-7> | ethernet_type <hex 0x0-0xffff>}(1) | ip
{[vlan <vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>] {mask <hex 0x0-0x0fff>} | source_ip
<ipaddr> {mask <netmask>} | destination_ip <ipaddr> {mask <netmask>} | dscp <value 0-63>
| [icmp {type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>} | igmp {type <value 0-255>} | tcp {src_port
<value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>}
| flag [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x00xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>}} | protocol_id <value 0-255>
{user_define <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}}]}(1) | packet_content
{offset_chunk_1 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | offset_chunk_2 <hex 0x00xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | offset_chunk_3 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x00xffffffff>} | offset_chunk_4 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}}(1) | ipv6 {class
<value 0-255> | flowlabel <hex 0x0-0xfffff> | source_ipv6 <ipv6addr> {mask <ipv6mask>} |
destination_ipv6 <ipv6addr> {mask <ipv6mask>} | [tcp {src_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex
0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>}} | udp {src_port <value 065535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0x f fff>}} | icm p
{type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>}]}(1)] [port [<portlist> | all] | vlan_based [vlan
<vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>]] [permit {priority <value 0-7> {replace_priority} |
[replace_dscp_with <value 0-63> | replace_t os _prec ed enc e_ with < value 0-7>] | counter
[enable | disable]} | mirror {group_id <value 1-4>} | deny] {time_r ang e <rang e_n a me 32>} |
000000000000-ffffffffffff> | destination_mac <macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> | 802.1p |
ethernet_type}(1) | ip {vlan | source_ip_mask <netmask> | destination_ip_mask <netmask> |
dscp | [icmp {type | code} | igmp {type} | tcp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask
<hex 0x0-0xffff> | flag_mask [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port_mask <hex
0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | protocol_id_mask <hex 0x0-0xff>
78
Page 83

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_16-31 <hex 0x0-
| source_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | destination_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask>}(1)]
config cpu access_profile profile_id <value 1-5> [add access_id [auto_assign | <value 1-100>]
1-100>]
show cpu access_profile {profile_id <val ue 1-5>}
enable cpu_interface_filt erin g
disable cpu_interface_f ilterin g
config flow_meter [profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>] access_id <value 1-256>
show flow_meter {[pr of ile _id <va lue 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>] {access_id <value 1-
256>}}
Note: Please see the “Appendix A Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet
0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_32-47 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_48-63 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_64-79 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}(1) | ipv6 {class | flowlabel
[ethernet {[vlan <vlan_nam e 32> | vlan_id <v lani d 1-4094>] | source_mac <macaddr> |
destination_mac <macaddr> | 802.1p <value 0-7> | ethernet_t ype <hex 0x 0-0xffff>} | ip {[vlan
<vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-40 94 >] | source_ i p <ipa ddr > | destinat io n_i p <ipad dr > |
dscp <value 0-63> | [icmp {type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>} | igmp {type <value 0255>} | tcp {src_port <value 0-65535> | dst_port <value 0-65535> | flag [all | {urg | ack | psh |
rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port <value 0-65535> | dst_port <value 0-65535>} | protocol_id
<value 0-255> {user_define <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}]} | packet_content {offset_0-15 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_16-31 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_32-47 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_48-63 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_64-79 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | ipv6 {class <value 0255> | flowlabel <hex 0x0-0xfffff> | source_ipv6 <ipv6addr> | destination_ipv6 <ipv6addr>}]
port [<portlist> | all] [permit | deny] {time_range <range_name 32>} | delete access_id <value
[rate [<value 0-1048576>] {burst_size [<value 0-131072>]} rate_exceed [drop_packet |
remark_dscp <value 0-63>] | tr_tcm cir <value 0-1048576> {cbs <value 0-131072>} pir <value
0-1048576> {pbs <value 0-131072>} {[color_blind | color_aware]} {conform [permit |
replace_dscp <value 0-63>] {counter [enable | disable]}} exceed [permit {replace_dscp <value
0-63>} | drop] {counter [enable | disable]} v iolate [ permit {replace_dscp <value 0-63>} | drop]
{counter [enable | disable]} | sr_tcm cir <value 0-1048576> cbs <value 0-131072> ebs <value
0-131072> {[color_blind | color_aware]} {conform [permit | replace_dscp <value 0-63>]
{counter [enable | disable]}} exceed [permit {replace_dscp <value 0-63>} | drop] {counter
[enable | disable]} violate [permit {replace_dscp <value 0-63>} | drop] {counter [enable |
disable]} | delete]
5-1 create access_profile profile_id
Description
This command is used to create access list profiles.
Format
Content ACL” section for a configuration example and further information.
create access_profile profile_id <value 1-6> profile_name <name 1-32> [ethernet {vlan
{<hex 0x0-0x0fff>} | source_mac <macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> | destination_mac
<macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> | 802.1p | ethernet_type}(1) | ip {vlan {<hex 0x0-0x0fff>}
| source_ip_mask <netmask> | destination_ip_mask <netmask> | dscp | [icmp {type | code} |
igmp {type} | tcp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_ma sk <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
flag_mask [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
79
Page 84

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<value 1-6>
<name 1-32>
ethernet - Specify an Ethernet access control list rule.
ethernet_type - Specify the Ethernet type.
ip
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the L4 part mask.
dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | protocol_id_mask <hex 0x0-0xff> {user_define_mask
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}]}(1) | packet_content_ma sk {offset_chunk_1 <value 0-31> <hex 0x00xffffffff> | offset_chunk_2 <value 0-31> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_chunk_3 <value 0-31>
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_chunk_4 <value 0-31> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}(1) | ipv6 {class |
flowlabel | source_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | destination_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | [tcp
{src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | udp {src_port_mask
<hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | icmp {type | code}]}(1)]
Parameters
- Specify the profile ID between 1 and 6. The lower the profile ID, the higher the
priority.
profile_name - Specify a profile name.
- The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlan - Specify a VLAN mask. Only the last 12 bits of the mask will be considered.
<hex 0x0-0x0fff> - (Optional) Specify a VLAN mask.
source_mac - Specify the source MAC mask.
<macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> - Specify the source MAC mask.
destination_mac - Specify the destination MAC mask.
<macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> - Specify the destination MAC mask.
802.1p - Speciy the 802.1p priority tag mask.
- Specify an IP access control list rule.
vlan - Specify a VLAN mask. Only the last 12 bits of the mask will be considered.
<hex 0x0-0x0fff> - (Optional) Specify a VLAN mask.
source_ip_mask - Specify an IP source submask.
<netmask> - Specify an IP source submask.
destination_ip_mask - Specify an IP destination submask.
<netmask> - Specify an IP destination submask.
dscp - Specify the DSCP mask.
icmp - Specify that the rule applies to ICMP traffic.
type - (Optional) Specify the ICMP packet type.
code - (Optional) Specify the ICMP code.
igmp - Specify that the rule applies to IGMP traffic.
type - (Optional) Specify the IGMP packet type.
tcp - Specify that the rule applies to TCP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP destination port mask.
flag_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP flag field mask.
all – Specify to check all paramenters below.
urg - (Optional) Specify Urgent Pointer field significant.
ack - (Optional) Specify Acknowledgment field significant.
psh - (Optional) Specify Push Function.
rst - (Optional) Specify to reset the connection.
syn - (Optional) Specify to synchronize sequence numbers.
fin - (Optional) No more data from sender.
udp - Specify that the rule applies to UDP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP destination port mask.
protocol_id_mask - Specify that the rule applies to the IP protocol ID traffic.
<hex 0x0-0xff> - Specify that the rule applies to the IP protocol ID traffic.
user_define_mask - (Optional) Specify the L4 part mask.
80
Page 85

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
packet_content_mask - A maximum of six offsets can be specified. Each offset defines one byte
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the offset chunk 4 mask value here.
ipv6 - Specify the IPv6 filtering mask.
code - (Optional) Specify the ICMP code.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create access_profile profile_id 1 profile_name 1 ethernet
of data which is identified as a single UDF field. The offset reference is also configurable. It
can be defined to start at the end of the tag, the end of the Ethernet type, or the end of the IP
header.
offset_chunk_1 - Specifies the offset chunk 1 that allows users to examine the specified
offset_chunks within a packet at one time and specifies the frame content offset and mask.
<value 0-31> - Enter the offset chunk 1 value here. This value must be between 0 and 31.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the offset chunk 1 mask value here.
offset_chunk_2 - Specifies the offset chunk 2 that allows users to examine the specified
offset_chunks within a packet at one time and specifies the frame content offset and mask.
<value 0-31> - Enter the offset chunk 2 value here. This value must be between 0 and 31.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the offset chunk 2 mask value here.
offset_chunk_3 - Specifies the offset chunk 3 that allows users to examine the specified
offset_chunks within a packet at one time and specifies the frame content offset and mask.
<value 0-31> - Enter the offset chunk 3 value here. This value must be between 0 and 31.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the offset chunk 3 mask value here.
offset_chunk_4 - Specifies the offset chunk 4 that allows users to examine the specified
offset_chunks within a packet at one time and specifies the frame content offset and mask.
<value 0-31> - Enter the offset chunk 4 value here. This value must be between 0 and 31.
class - Specify the IPv6 class mask.
flowlabel - Specify the IPv6 flow label mask.
source_ipv6_mask - Specify the IPv6 source IP mask.
<ipv6mask> - Specify the IPv6 source IP mask.
destination_ipv6_mask - Specify the IPv6 destinat io n IP mask.
<ipv6mask> - Specify the IPv6 destination IP mask.
tcp - Specify that the rule applies to TCP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP destination port mask.
udp - Specify that the rule applies to UDP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP destination port mask.
icmp - Specify that the rule applies to ICMP traffic.
type - (Optional) Specify the ICMP packet type.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create access list profiles:
vlan source_mac FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF destination_mac 00-00-00-FF-FF-FF 802.1p
ethernet_type
Command: create access_profile profile_id 1 profile_name 1 ethernet vlan
source_mac FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF destination_mac 00-00-00-FF-FF-FF 802.1p
ethernet_type
Success.
81
Page 86

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
profile_id - Specify the index of the access list profile.
<value 1-6> - Specify the index of the access list profile. Enter a value between 1 and 6.
profile_name - Specify the profile name.
<name 1-32> - Specify the profile name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
all - Specify the whole access list profile to delete.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete access_profile profile_id 1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Note: Please see the “Appendix A Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attack s Using Packet
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create access_profile profile_id 2 profile_name 2 ip vlan
source_ip_mask 255.255.255.255 destination_ip_mask 255.255.255.0 dscp icmp
Command: create access_profile profile_id 2 profile_name 2 ip vlan
source_ip_mask 255.255.255.255 destination_ip_mask 255.255.255.0 dscp icmp
Success.
5-2 delete access_profile
Description
This command is used to delete access list profiles.
Format
delete access_profile [profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32> | all]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete access list profiles:
Command: delete access_profile profile_id 1
Success.
5-3 config access_profile
Description
This command is used to configure access list entries.
Content ACL” section for a configuration example and further information.
82
Page 87

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
profile_id - Specify the index of the access list profile.
<value 1-6> - Specify the value between 1 and 6.
profile_name - Specify the profile name.
<name 1-32> - Specify the profile name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
add access_id - Specify the index of the access list entry. The lower the access ID, the higher
<value 1-256> - Specify a value between 1 and 256.
ethernet - Specify an Ethernet access control list rule.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the Ethernet type.
Format
config access_profile [profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>] [add access_id
[auto_assign | <value 1-256>] [ethernet {[vlan <vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>]
{mask <hex 0x0-0x0fff>} | source_mac <macaddr> {mask <macmask>} | destination_mac
<macaddr> {mask <macmask>} | 802.1p <value 0-7> | ethernet_type <hex 0x0-0xffff>}(1) | ip
{[vlan <vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>] {mask <hex 0x0-0x0fff>} | source_ip
<ipaddr> {mask <netmask>} | destin atio n_ip <ipaddr> {mask <netmask>} | dscp <value 063> | [icmp {type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>} | igmp {type <value 0-255>} | tcp
{src_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex
0x0-0xffff>} | flag [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port <value 0-65535>
{mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>}} | protocol_id
<value 0-255> {user_define <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}}]}(1) |
packet_content {offset_c hu nk_1 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} |
offset_chunk_2 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | offs et_chunk_3 <hex 0x00xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | offset_chunk_4 <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> {mask <hex 0x00xffffffff>}}(1) | ipv6 {class <value 0-255> | flowlabel <hex 0x0-0xfffff> | source_ipv6
<ipv6addr> {mask <ipv6mask>} | destination_ipv6 <ipv6addr> {mask <ipv6mask>} | [tcp
{src_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex
0x0-0xffff>}} | udp {src_port <value 0-65535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | dst_port <value 065535> {mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>}} | icmp {type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>}]}(1)] [port
[<portlist> | all] | vlan_based [vlan <vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>]] [permit
{priority <value 0-7> {replace_priority} | [replace_dscp_with <value 0-63> |
replace_tos_precedence_with <value 0-7>] | counter [enable | disable]} | mirror {group_id
<value 1-4>} | deny] {time_range <range_name 32>} | delete access_id <value 1-256>]
Parameters
the priority.
auto_assign - Specify to automatically assign the access ID.
vlan - Specify the VLAN name.
<vlan_name 32> -Specify the VLAN name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlanid - Specify the VLAN ID.
<vlanid 1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0x0fff> - Specify the mask.
source_mac - Specify the source MAC address.
<macaddr> - Specify the source MAC address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<macmask> - Specify the mask.
destination_mac - Specify the destination MAC address.
<macaddr> - Specify the destination MAC address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<macmask> - Specify the mask.
802.1p - Specify the value of the 802.1p priority tag.
<value 0-7> - Specify the value of the 802.1p priority tag. The priority tag ranges from 1 to
7.
ethernet_type - Specify the Ethernet type.
83
Page 88

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
ip - Specify an IP access control list rule.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask.
packet_content - Specify the packet content for the user defined mask.
vlan - Specify the VLAN name.
<vlan_name 32> -Specify the VLAN name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlanid - Specify the VLAN ID.
<vlanid 1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
mask - (Optional)Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0x0fff> - Specify the mask.
source_ip - Specify an IP source address.
<ipaddr> - Specify an IP source address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<netmask> - Specify the mask.
destination_ip - Specify an IP destination address.
<ipaddr> - Specify an IP destination address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<netmask> - Specify the mask.
dscp - Specify the value of DSCP.
<value 0-63> - Specify the value of DSCP. The DSCP value ranges from 0 to 63.
icmp - Specify the ICMP.
type - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the ICMP Type traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
code - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the ICMP Code traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
igmp - Specify the IGMP.
type - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the IGMP Type traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
tcp - Specify TCP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to a range of TCP source ports.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to a range of TCP destination ports.
<value 0-65535> - Specif y the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
flag - Specify the TCP flag field value.
all – Specify to check all paramenters below.
urg - (Optional) Specify Urgent Pointer field significant.
ack - (Optional) Specify Acknowledgment field significant.
psh - (Optional) Specify Push Function.
rst - (Optional) Specify to reset the connection.
syn - (Optional) Specify to synchronize sequence numbers.
fin - (Optional) No more data from sender.
udp - Specify UDP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP source port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP destination port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
protocol_id - Specify that the rule will apply to the value of IP protocol ID traffic.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
user_define - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the IP protocol ID and that the mask
options behind the IP header, which has a length of 4 bytes.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify that the rule will apply to the IP protocol ID and that the
mask options behind the IP header, which has a length of 4 bytes.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
84
Page 89

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
offset_chunk_1 - Specifies the contents of the offset trunk 1 to be monitored.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the additional mask value used here.
ipv6 - Specify that the rule applies to IPv6 fields.
and 255.
port - The access profile rule may be defined for each port on the switch. The port list is specified
all - Specify that the access rule will apply to all ports.
vlan_based - Specify the VLAN-based ACL rule. There are two conditions: this rule will apply to
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the contents of the offset trunk 1 to be monitored here.
mask - Specifies an additional mask for each field.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the additional mask value used here.
offset_chunk_2 - Specifies the contents of the offset trunk 2 to be monitored.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the contents of the offset trunk 2 to be monitored here.
mask - Specifies an additional mask for each field.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the additional mask value used here.
offset_chunk_3 - Specifies the contents of the offset trunk 3 to be monitored.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the contents of the offset trunk 3 to be monitored here.
mask - Specifies an additional mask for each field.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the additional mask value used here.
offset_chunk_4 - Specifies the contents of the offset trunk 4 to be monitored.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Enter the contents of the offset trunk 4 to be monitored here.
mask - Specifies an additional mask for each field.
class - Specify the value of the IPv6 class.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
flowlabel - Specify the value of the IPv6 flow label.
<hex 0x0-0xfffff> - Specify the value of the IPv6 flow label.
source_ipv6 - Specify the value of the IPv6 source address.
<ipv6addr> - Specify the value of the IPv6 source address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<ipv6mask> - Specify the mask.
destination_ipv6 - Specify the value of the IPv6 destination address.
<ipv6addr> - Specify the value of the IPv6 destination address.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<ipv6mask> - Specify the mask.
tcp - Specify TCP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port range.
<value 0-65535> - Specif y the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
udp - Specify UDP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP source port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - (Optional) Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP destination port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
mask - Specify the mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the mask.
icmp - Specifies that the rule applies to the value of ICMP traffic.
type - Specifies that the rule applies to the value of ICMP type traffic.
<value 0-255> - Enter the ICMP type value used here. This value must be between 0
and 255.
code - Specifies that the rule applies to the value of ICMP code traffic.
<value 0-255> - Enter the ICMP code value used here. This value must be between 0
by listing the lowest switch number and the beginning port number on that switch, separated
by a colon.
<portlist> - Specify a list of ports.
85
Page 90

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
all ports and packets must belong to the configured VLAN. It can be specified by VLAN name
<vlanid 1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
permit - Specify the packets that match the access profile are permit by the switch.
priority - (Optional) Specify the packets that match the access profile are remap the 802.1p
<value 0-7>
replace_priority - (Optional) Specify the packets that match the access profile remarking the
<value 0-7> - Specify the value between 0 and 7.
counter - (Optional) Specifies whether the ACL counter feature will be enabled or disabled.
disable - Specify whether the ACL counter feature is disabled. The default option is disabled.
mirror - Specify that packets matching the access profile are copied to the mirror port.
group_id - Specifies the group ID used.
<value 1-4> - Enter the group ID used here. This value must be between 1 and 4.
deny - Specify the packets that match the access profile are filtered by the switch.
time_range - (Optional) Specify the name of this time range entry.
characters.
delete access_id - Specify to delete the access ID.
<value 1-256> - Specify the value between 1 and 256.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config access_profile profile_id 1 add access_id 1 ip vlan
or VLAN ID.
vlan - Specify the VLAN name.
<vlan_name 32> - Specify the VLAN name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlan_id - Specify the VLAN ID.
priority tag field by the switch.
- Specify the value between 0 and 7.
802.1p priority tag field by the switch.
replace_dscp_with - (Optional) Specify the DSCP of the packets that match the access profile
are modified according to the value.
<value 0-63> - Specify the value between 0 and 63.
replace_tos_precedence_with - (Optional) Specify that the IP precedence of the outgoing
packet is changed with the new value. If used without an action priority, the packet is sent to
the default TC.
enable - Specify whether the ACL counter feature is enabled. If the rule is not bound with the
flow meter, all matching packets are counted. If the rule is bound with the flow meter, then
the “counter” is overridden.
<range_name 32> - Specify the name of this time range entry. The maximum length is 32
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure an access list entry:
default source_ip 20.2.2.3 destination_ip 10.1.1.252 dscp 3 icmp port 1 permit
Command: config access_profile profile_id 1 add access_id 1 ip vlan default
source_ip 20.2.2.3 destination_ip 10.1.1.252 dscp 3 icmp port 1 permit
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
86
Page 91

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
profile_id - (Optional) Specify the index of the access list profile.
<value 1-6> - Specify the profile ID between 1 and 6.
profile_name - (Optional) Specify the name of the access list profile.
<name 1-32> - Specify the profile name between 1 and 32.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show access_profile
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5-4 show access_profile
Description
This command is used to display the current access list table.
Format
show access_profile {[profile_id <value 1-6> | profile_name <name 1-32>]}
Parameters
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display the current access list table:
Command: show access_profile
Access Profile Table
Total User Set Rule Entries : 3
Total Used HW Entries : 19
Total Available HW Entries : 1005
===============================================================================
=
Profile ID: 1 Profile Name: 1 Type: Ethernet
Mask on
VLAN ID : 0xFF
Source MAC: FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-00
802.1p
Available HW Entries: 254
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Rule ID : 1 Ports: 1-10
Match on:
VLAN ID : 2 Mask : 0xFFF
Source MAC : 00-01-02-03-04-00
Action:
Permit
Replaced Priority to 2
Replace DSCP to 33
Matched Count: 0 packets
87
Page 92

--
xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Rule ID : 256 (auto assign) Ports: Match on:
VLAN ID : 8
Source MAC : 00-01-02-03-04-00
802.1p
Action:
Deny
===============================================================================
====
Profile ID: 3 Profile Name: 3 Type: IPv4
Mask on
Source IP : 255.255.255.0
TCP
Source Port : 0x00FF
Available HW Entries: 254
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Rule ID : 4 Ports: 1-28
Match on:
Source IP : 192.168.1.0
TCP
Source Port: 210 Mask : 0x0FFF
Action:
Mirror
===============================================================================
====
Profile ID: 2 Profile Name: IMPBv4
Mask
Source MAC : FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Source IP : 255.255.255.255
Consumed HW Entries: 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--Rule ID : 1 Ports: 1
Match on
Source MAC : 00-05-04-03-02-01 Mask : FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Source Ip : 10.10.10.1 Mask : 255.255.255.255
Action:
Permit
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---Rule ID : 2 Ports: 1
Match on
Any
Action:
Deny
===============================================================================
===
Profile ID: 3 Profile Name: VLAN Counter
Consumed HW Entries: 9
88
Page 93

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
Profile ID: 4 Profile Name: System
Note: “Total User Set Entries” indicates the total number of ACL rules created by the
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show access_profile profile_id 2
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show access_profile profile_id 5
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Consumed HW Entries: 4
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
user. “Total Used HW Entries” indicates the total number of hardware entries used
in the device. “Available HW Entries” indicates the total number of available
hardware entries in the device.
To display an access profile that supports an entry mask for each rule:
Command: show access_profile profile_id 2
Access Profile Table
Profile ID: 2 Profile Name: 2 Type: Ethernet
Mask on
VLAN : 0xF
Source MAC : FF-FF-FF-00-00-00
Destination MAC : 00-00-00-FF-FF-FF
Available HW Entries: 255
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-Rule ID : 22 Ports: 1-7
Match on:
VLAN ID : 8 Mask : 0xFFF
Source MAC : 00-01-02-03-04-05 Mask : FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Destination MAC : 00-05-04-03-02-00 Mask : FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-00
Action:
Deny
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Command: show access_profile profile_id 5
Access Profile Table
=============================================================================
Profile ID: 5 Profile name: 5 Type: User Defined
MASK on
offset_chunk_1 : 0 value : 0x0000FFFF
Available HW Entries : 256
=============================================================================
89
To display the packet content mask profile for the profile with an ID of 5:
Page 94

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<range_name 32> - Sp ec if y the name of the time range settings.
hours start_time - Specify the starting time in a day. (24-hr time). For example, 19:00 means
< hh:mm:ss> - Specify the time.
end_time
< hh:mm:ss>
weekdays - Specify the list of days contained in the time range. Use a dash to define a period of
<daylist> - Specify a list of days.
delete - Delete a time range profile. When a time range profile has been associated with ACL
entries, the deletion of this time range profile will fail.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#config time_range testdaily hours start_time 12:0:0
5-5 config time_range
Description
This command is used to define a specific range of time to activate a function on the Switch by
specifying which time range in a day and which days in a week are covered in the time range. Note
that the specified time range is based on SNTP time or configured time. If this time is not available,
then the time range will not be met.
Format
config time_range <range _nam e 32> [ hours start_time < hh:mm:ss> end_time< h h :m m :ss>
weekdays <daylist> | delete]
Parameters
7PM. 19 is also acceptable. The start_time must be smaller than the end_time.
- Specify the ending time in a day. (24-hr time)
- Specify the time.
days. Use a comma to separate specific days. For example, mon-fri (Monday to Friday)
sun, mon, fri (Sunday, Monday, and Friday)
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To configure the range of time to activate a function on the switch:
end_time 13:0:0 weekdays mon,fri
Command: config time_range testdaily hours start_time 12:0:0 end_time 13:0:0
weekdays mon,fri
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
5-6 show time_range
Description
This command is used to display current time range settings.
90
Page 95

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show time_range
Format
show time_range
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
Example
To display current time range setting:
Command: show time_range
Time Range Information
------------------------Range Name : testdaily
Weekdays : Mon,Fri
Start Time : 12:00:00
End Time : 13:00:00
Total Entries :1
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
5-7 show current_config access_profile
Description
This command is used to display the ACL part of the current configuration, when logged in with
user level privileges. The overall current configuration can be displayed by using the show config
command, which is accessible with administrator level privileges.
Format
show current_config access_profile
Parameters
None.
Restrictions
None.
91
Page 96

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#show current_config access_profile
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
profile_id - Specify the index of the access list profile.
<value 1-5> - Specify the value between 1 and 5.
all - Specify to delete all the access list profiles.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#delete cpu access_profile profile_id 3
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
Example
To display the ACL part of the current configuration:
Command: show current_config access_profile
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------# ACL
create access_profile Ethernet vlan profile_id 1
config access_profile profile_id 1 add access_id 1 ethernet vlan default port 1
permit
create access_profile ip source_ip_mask 255.255.255 profile_id 2
config access_profile profile_id 2 add access_id 1 ip source_ip 10.10.10.10
port 2 deny
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5-8 delete cpu access_profile
Description
This command is used to delete CPU access list profiles.
Format
delete cpu access_profile [profile_id <value 1-5> | all]
Parameters
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To delete access list rules:
Command: delete cpu access_profile profile_id 3
Success.
92
Page 97

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
<value 1-5> - Specify a value between 1 and 5.
ethernet - Specify an Ethernet CPU access control list rule.
ethernet_type - Specify the Ethernet type mask.
ip - Specify an IP CPU access control list rule.
rst - (Optional) Specify to reset the connection.
5-9 create cpu access_profile profile_id
Description
This command is used to create CPU access list profiles.
Format
create cpu access_profile profile_id <value 1-5> [ethernet {vlan | source_mac <macmask
000000000000-ffffffffffff> | destination_mac <macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> | 802.1p |
ethernet_type}(1) | ip {vlan | source_ip_mask <netmask> | destination_ip_mask <netmask> |
dscp | [icmp {type | code} | igmp {type} | tcp {src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> |
dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | flag_mask [all | {urg | ack | psh | rst | syn | fin}]} | udp
{src_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff> | dst_port_mask <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | protocol_id_mask <hex
0x0-0xff> {user_define_mask <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}]}(1) | packet_content_mask {offset_0-15
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_16-31
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_32-47
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_48-63
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_64-79
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}(1) | i p v6
{class | flowlabel | source_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask> | destination_ipv6_mask <ipv6mask>}(1)]
Parameters
vlan - Specify a VLAN mask.
source_mac - Specify the source MAC mask.
<macmask000000000000-ffffffffffff> - Specify the source MAC mask.
destination_mac - Specify the destination MAC mask.
<macmask 000000000000-ffffffffffff> - Specify the destination MAC mask.
802.1p - Specify the 802.1p priority tag mask.
vlan - Specify a VLAN mask.
source_ip_mask - Specify an IP source submask.
<netmask> - Specify an IP source submask.
destination_ip_mask - Specify an IP destination submask.
<netmask> - Specify an IP destination submask.
dscp - Specify the DSCP mask.
icmp - Specify that the rule applies to ICMP traffic.
type - (Optional) Specify the ICMP packet type.
code - (Optional) Specify the ICMP code.
igmp - Specify that the rule applies to IGMP traffic.
type - (Optional) Specify the IGMP packet type.
tcp - Specify that the rule applies to TCP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the TCP destination port mask.
flag_mask - (Optional) Specify the TCP flag field mask.
all – Specify to check all paramenters below.
urg - (Optional) Specify Urgent Pointer field significant.
ack - (Optional) Specify Acknowledgment field significant.
psh - (Optional) Specify Push Function.
93
Page 98

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
syn - (Optional) Specify to synchronize sequence numbers.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff>
packet_content_mask - Specify the packet content mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 76-79.
ipv6 - Specify the IPv6 mask.
<ipv6mask>
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create cpu access_profile profile_id 1 ethernet vlan
fin - (Optional) No more data from sender.
udp - Specify that the rule applies to UDP traffic.
src_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the UDP source port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the UDP source port mask.
dst_port_mask - (Optional) Specify the UDP destination port mask.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the UDP destination port mask.
protocol_id_mask - Specify that the rule applies to the IP protocol ID traffic.
<hex 0x0-0xff> - Specify that the rule applies to the IP protocol ID traffic.
user_define_mask - (Optional) Specify the L4 part mask
- Specify the L4 part mask
offset_0-15 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 0-15.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 0-3.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 4-7.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 8-11.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 12-15.
offset_16-31 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 16-31.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 16-19.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 20-23.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 24-27.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 28-31.
offset_32-47 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 32-47
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 32-35.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 36-39.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 40-43.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 44-47.
offset_48-63 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 48-63.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 48-51.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 52-55.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 56-59.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 60-63.
offset_64-79 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 64-79.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 64-67.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 68-71.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 72-75.
class - Specify the IPv6 class mask.
flowlabel - Specify the IPv6 flow label mask.
source_ipv6_mask - Specify the IPv6 source IP mask.
<ipv6mask> - Specify the IPv6 source IP mask.
destination_ipv6_mask - Specify the IPv6 destination IP mask.
- Specify the IPv6 destination IP mask.
Restrictions
Only Administrator, Operator and Power-User level users can issue this command.
Example
To create CPU access list profiles:
Command: create cpu access_profile profile_id 1 ethernet vlan
Success.
94
Page 99

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#create cpu access_profile profile_id 2 ip source_ip_mask
<value 1-5> - Specify the index of the CPU access list profile.
add access_id - Specify the index of an access list entry to add. The range of this value is 1 to
<value 1-100> - Specify an access ID between 1 and 100.
ethernet - Specify an Ethernet CPU access control list rule.
7.
255.255.255.255
Command: create cpu access_profile profile_id 2 ip source_ip_mask
255.255.255.25
5
Success.
DGS-3420-28SC:admin#
5-10 config cpu access_profile profile_id
Description
This command is used to configure CPU access list entries.
Format
config cpu access_profile profi le_id <value 1-5> [add access_id [auto_assign | <value 1100>] [ethernet {[vlan <vlan_name 32> | vla n_id <vlanid 1-4094>] | source_mac <macaddr> |
destination_mac <macaddr> | 802.1p <value 0-7> | ethernet_type <hex 0x0-0xffff>} | ip {[vlan
<vlan_name 32> | vlan_id <vlanid 1-4094>] | source_ip <ipaddr> | destination_ip <ipaddr> |
dscp <value 0-63> | [icmp {type <value 0-255> | code <value 0-255>} | igmp {type <value 0255>} | tcp {src_port <value 0-65535> | dst_port <value 0-65535> | flag [all | {urg | ack | psh |
rst | syn | fin}]} | udp {src_port <value 0-65535> | dst_port <value 0-65535>} | protocol_id
<value 0-255> {user_define <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>}]} | packet_content {offset_0-15 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_16-31 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_32-47 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_48-63 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> | offset_64-79 <hex 0x00xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff> <hex 0x0-0xffffffff>} | ipv6 {class <value 0255> | flowlabel <hex 0x0-0xfffff> | source_ipv6 <ipv6addr> | destination_ipv6 <ipv6addr>}]
port [<portlist> | all] [permit | deny] {time_range <range_name 32>} | delete access_id
<value 1-100>]
Parameters
100.
auto_assign - Specify to a utomatically assign the acces s ID.
vlan - Specify the VLAN name.
<vlan_name 32> -Specify the VLAN name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlanid - Specify the VLAN ID.
<vlanid 1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
source_mac - Specify the source MAC address.
<macaddr> - Specify the source MAC address.
destination_mac - Specify the destination MAC address.
<macaddr> - Specify the destination MAC address.
802.1p - Specify the value of the 802.1p priority tag.
<value 0-7> - Specify the value of the 802.1p priority tag. The priority tag ranges from 1 to
95
Page 100

xStack® DGS-3420 Series Layer 2 Managed Stackable Gigabit Switch CLI Reference Guide
ethernet_type - Specify the Ethernet type.
<hex 0x0-0xffff> - Specify the Ethernet type.
ip - Specify an IP access control list rule.
mask options behind the IP header , which has a length of 4 bytes.
packet_content - Specifies that the access control list rule will be set to packet content.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 40-43.
vlan - Specify the VLAN name.
<vlan_name 32> -Specify the VLAN name. The maximum length is 32 characters.
vlanid - Specify the VLAN ID.
<vlanid 1-4094> - Specify the VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
source_ip - Specify an IP source address.
<ipaddr> - Specify an IP source address.
destination_ip - Specify an IP destination address.
<ipaddr> - Specify an IP destination address.
dscp - Specify the value of DSCP.
<value 0-63> - Specify the value of DSCP. The DSCP value ranges from 0 to 63.
icmp - Specify the ICMP.
type - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the ICMP Type traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
code - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the ICMP Code traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
igmp - Specify the IGMP.
type - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the IGMP Type traffic value.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
tcp - Specify TCP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to a range of TCP source ports.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to a range of TCP destination ports.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
flag - Specify the TCP flag field value.
all – Specify to check all paramenters below.
urg - (Optional) Specify Urgent Pointer field significant.
ack - (Optional) Specify Acknowledgment field significant.
psh - (Optional) Specify Push Function.
rst - (Optional) Specify to reset the connection.
syn - (Optional) Specify to synchronize sequence numbers.
fin - (Optional) No more data from sender.
udp - Specify UDP.
src_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP source port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
dst_port - (Optional) Specify the UDP destination port range.
<value 0-65535> - Spec ify the value between 0 and 65535.
protocol_id - Specify that the rule will apply to the value of IP protocol ID traffic.
<value 0-255> - Specify the value between 0 and 255.
user_define - (Optional) Specify that the rule will apply to the IP protocol ID and that the mask
options behind the IP header, which has a length of 4 bytes.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify that the rule will apply to the IP protocol ID and that the
offset_0-15 - Specify the mask for packet byt es 0-15.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 0-3.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 4-7.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 8-11.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 12-15.
offset_16-31 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 16-31.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 16-19.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 20-23.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 24-27.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 28-31.
offset_32-47 - Specify the mask for packet bytes 32-47
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 32-35.
<hex 0x0-0xffffffff> - Specify the mask for packet bytes 36-39.
96
 Loading...
Loading...