Page 1

Detcon Model Series
DM-500IS OLED
Explosion Proof and Intrinsically Safe Toxic Gas Sensors
Operator’s Installation and Instruction Manual
DETCON, Inc.
4055 Technology Forest Blvd. Suite 100,
The Woodlands, Texas 77381
Ph.281.367.4100 / Fax 281.298.2868
www.detcon.com
August 17, 2015 • Document #4517 • Revision 0.1
Page 2

This page left intentionally blank
DM-500IS
DM-500IS Instruction Manual ii
Page 3

DM-500IS
Table of Contents
1.0 Description................................................................................................................................................ 2
1.1 Sensor Technology............................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Universal Microprocessor Control Transmitter Circuit........................................................................ 3
1.3 Base Connector Board.......................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Explosion Proof Enclosure................................................................................................................... 3
2.0 Principle Of Operation............................................................................................................................ 4
3.0 Application............................................................................................................................................... 5
3.1 Sensor Placement/Mounting................................................................................................................. 5
3.2 Interference Data.................................................................................................................................. 5
3.3 Interference Gas List ............................................................................................................................ 6
3.4 Interference Gas Table (page 1 of 5)....................................................................................................7
4.0 Specifications.......................................................................................................................................... 12
5.0 Installation.............................................................................................................................................. 13
5.1 Field Wiring Table (4-20 mA output) ................................................................................................ 13
5.2 Sensor Location.................................................................................................................................. 13
5.3 Local Electrical Codes........................................................................................................................ 15
5.4 Installation Procedure......................................................................................................................... 15
5.5 Remote Mounting Applications ......................................................................................................... 16
6.0 Startup.................................................................................................................................................... 17
6.1 Initial Operational Tests ..................................................................................................................... 17
7.0 Operating Software & Magnetic Interface.......................................................................................... 18
7.1 Normal Operation............................................................................................................................... 18
7.2 Calibration Mode................................................................................................................................ 18
7.2.1 Zero Adjustment ......................................................................................................................... 18
7.2.2 Span Adjustment......................................................................................................................... 18
7.3 Program Mode.................................................................................................................................... 18
7.3.1 Program Status........................................................................................................................... 18
7.3.2 Calibration Level Adjustment..................................................................................................... 18
7.4 Programming Magnet Operating Instructions.................................................................................... 19
8.0 Software Flow Chart ............................................................................................................................. 20
9.0 Calibration.............................................................................................................................................. 20
9.1 Calibration Procedure – Zero ............................................................................................................. 20
9.2 Calibration Procedure – Span............................................................................................................. 21
9.3 Additional Notes................................................................................................................................. 22
9.4 Calibration Frequency........................................................................................................................ 22
10.0 Status of Programming, Calibration Level and Sensor Life.............................................................. 22
11.0 Program Features.................................................................................................................................. 23
12.0 Universal Transmitter Feature (Re-Initialization)............................................................................. 24
13.0 Trouble Shooting ................................................................................................................................... 25
14.0 Spare Parts List...................................................................................................................................... 27
15.0 Warranty................................................................................................................................................ 29
16.0 Service Policy ......................................................................................................................................... 29
DM-500IS Instruction Manual iii
Page 4

DM-500IS
17.0 Revision History..................................................................................................................................... 30
Table of Figures
Figure 1 DM-500IS Sensor ...............................................................................................................................2
Figure 2 Construction of Electrochemical Sensor.............................................................................................2
Figure 3 Universal Microprocessor Control Transmitter circuit.......................................................................3
Figure 4 Base connector board..........................................................................................................................3
Figure 5 Explosion-Proof Enclosure .................................................................................................................4
Figure 6 Functional Block Diagram..................................................................................................................4
Figure 7 Typical Installation .............................................................................................................................14
Figure 8 Typical Outline and Mounting Dimensions........................................................................................15
Figure 9 Sensor wiring......................................................................................................................................16
Figure 10 Remote wiring diagram.....................................................................................................................16
Figure 11 Programming magnet........................................................................................................................ 19
Figure 12 Programming Switch locations.........................................................................................................19
Figure 13 Software Flow Chart.........................................................................................................................20
Figure 14 Spare parts diagram...........................................................................................................................27
List of Tables
Table 1 Model #, Gas Name and Symbol..........................................................................................................1
Table 2 Sensor cell specifications.....................................................................................................................12
Table 3 Field wiring Table................................................................................................................................13
Table 4 Over-current Protection per AWG .......................................................................................................13
Table 5 IS Sensor Head / Plug-in Replacement Sensor Cell............................................................................. 28
Shipping Address 4055 Technology ForestBlvd. Suite100,., TheWoodlands Texas 77381
Phone: 888.367.4286, 281.367.4100 • Fax:281.292.2860• www.detcon.com• sales@detcon.com
DM-500IS Instruction Manual iv
Mailing Address: P.O. Box 8067, The Woodlands Texas77387-8067
Page 5

This manual covers the following Models...
Table 1 Model #, Gas Name and Symbol
Model # Gas Name Symbol
DM-500-C2H3O Acetaldehyde C2H3O
DM-500-C2H2 Acetylene C2H2
DM-500-C3H3N Acrylonitrile C3H3N
DM-500-NH3 (-20°C) Ammonia NH3
DM-501-NH3 (-40°C) Ammonia NH3
DM-502-NH3 Ammonia (continuous exposure) NH3
DM-500-AsH3 Arsine AsH3
DM-500-Br2 Bromine Br2
DM-500-C4H6 Butadiene C4H6
DM-500-CS2 Carbon Disulfide CS2
DM-500-CO Carbon Monoxide CO
DM-500-COS Carbonyl Sulfide COS
DM-500-CL2 Chlorine CL2
DM-500-CLO2 Chlorine Dioxide (>50 ppm range) CLO2
DM-501-CLO2 Chlorine Dioxide (≤50 ppm range) CLO2
DM-500-B2H6 Diborane B2H6
DM-500-C2H6S Dimethyl Sulfide C2H6S
DM-500-C3H5OCL Epichlorohydrin C3H5OCL
DM-500-C2H5OH Ethanol C2H5OH
DM-500-C2H5SH Ethyl Mercaptan C2H5SH
DM-500-C2H4 Ethylene C2H4
DM-500-C2H4O Ethylene Oxide C2H4O
DM-500-F2 Fluorine F2
DM-500-CH2O Formaldehyde CH2O
DM-500-GeH4 Germane GeH4
DM-500-N2H4 Hydrazine N2H4
DM-500-H2 Hydrogen (ppm range) H2
DM-501-H2 Hydrogen (% LEL range) H2
DM-500-HBr Hydrogen Bromide HBr
DM-500-HCL Hydrogen Chloride HCL
DM-500-HCN Hydrogen Cyanide HCN
DM-500-HF Hydrogen Fluoride HF
DM-500-H2S Hydrogen Sulfide H2S
DM-500-CH3OH Methanol CH3OH
DM-500-CH3SH Methyl Mercaptan CH3SH
DM-500-NO Nitric Oxide NO
DM-500-NO2 Nitrogen Dioxide NO2
DM-500-O3 Ozone O3
DM-500-COCL2 Phosgene COCL2
DM-500-PH3 Phosphine PH3
DM-500-SiH4 Silane SiH4
DM-500-SO2 Sulfur Dioxide SO2
DM-500-C4H8S Tetrahydrothiophene C4H8S
DM-500-C4H4S Thiophane C4H4S
DM-500-C6H5CH3 Toluene C6H5CH3
DM-500-C4H6O2 Vinyl Acetate C4H6O2
DM-500-C2H3CL Vinyl Chloride C2H3CL
DM-500IS
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 1 of 30
Page 6

DM-500IS
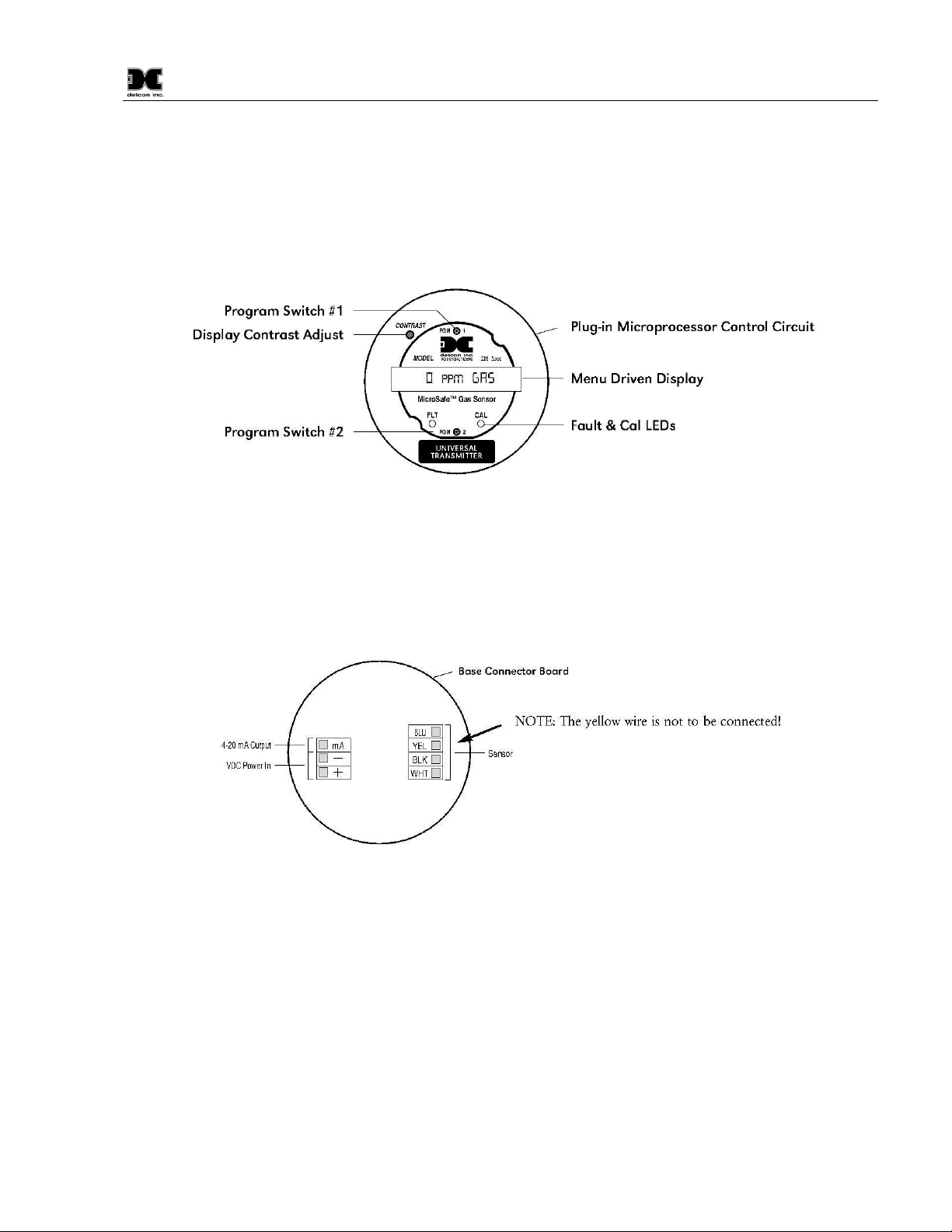
1.0 Description
Detcon MicroSafeTM Model DM-500IS, toxic sensors are non-intrusive “Smart” sensors designed to detect
and monitor for toxic gas in the ppm range. One of the primary features of the sensor is its method of
automatic calibration which guides the user through each step via instructions displayed on the OLED Display
The sensor features LED indicators for FAULT and CAL status and is equipped with a standard analog 4-20
mA output. The microprocessor supervised electronics are packaged as a universal plug-in transmitter module
that mates to a standard connector board. Both are housed in an explosion proof condulet that includes a glass
lens. A 16 character alpha/numeric indicator is used to display sensor readings as well as the sensor’s menu
driven features via a hand-held programming magnet.
Figure 1 DM-500IS Sensor
Typical ranges of detection are 0-10ppm, 0-25ppm, 0-50ppm and 0-100ppm. Other ranges are available and all
ranges are covered by this manual. To determine sensor model number, reference the label located on the
enclosure cover. To determine gas type and range, reference labeling on the intrinsically safe sensor head.
1.1 Sensor Technology
The sensors are electrolytic chemical cells. Each cell consists of three electrodes embedded in an electrolyte
solution all housed beneath a diffusion membrane. Sensitivity to specific target gases is achieved by varying
composition of any combination of the sensor components. Good specificity is achieved in each sensor type.
The cells are diffusion limited via small capillary barriers resulting in long service life of up to 3 or more
years. The fuel cell is packaged as a field replaceable plug-in sensor via gold plated pins. Pre-amplifier and
intrinsically safe barrier circuits are epoxy potted in the stainless steel housing and include the mating sockets
for the sensor.
Figure 2 Construction of Electrochemical Sensor
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 2 of 30
Page 7
DM-500IS
1.2 Universal Microprocessor Control Transmitter Circuit
The control circuit is microprocessor based and is packaged as a universal plug-in field replaceable module,
facilitating easy replacement and minimum down time. The universality includes the ability to set it for any
range concentration and for any gas type. These gas and range settings must be consistent with the IS Sensor
Head it is mated with. Circuit functions include a basic sensor pre-amplifier, on-board power supplies,
microprocessor, back lit alpha numeric display, fault and calibration status LED indicators, magnetic
programming switches, and a linear 4-20 mA DC output.
Figure 3 Universal Microprocessor Control Transmitter circuit
1.3 Base Connector Board
The base connector board is mounted in the explosion proof enclosure and includes: the mating connector for
the control circuit, reverse input and secondary transient suppression, input filter and lugless terminals for all
field wiring.
Figure 4 Base connector board
1.4 Explosion Proof Enclosure
The transmitter electronics are packaged in a cast metal explosion proof enclosure. The enclosure is fitted with
a threaded cover that has a glass lens window. Magnetic program switches located behind the transmitter
module face plate are activated through the lens window via a hand-held magnetic programming tool allowing
non-intrusive operator interface with the sensor. Calibration can be accomplished without removing the cover
or declassifying the area. Electrical classification is Class I; Groups B, C, D; Division 1 (explosion proof).
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 3 of 30
Page 8

DM-500IS
The sensor housing section employs an Intrinsically Safe Barrier circuit which allows for the safe usage of
plastic housing materials in the lower section. This design benefit avoids the requirement for stainless steel
flame arrestors which reduce the sensitivity and response time to “active” gas species such as NH3, CL2,
CLO2, and HCL...etc.
Transmitter Electronics in
Explosion-Proof Housing
Intrinsically Safe
Sensor Head
Figure 5 Explosion-Proof Enclosure
2.0 Principle Of Operation
Method of detection is by an electrochemical reaction at the surface of an electrode called the sensing
electrode. Air and gas diffuse through the capillary diffusion barrier. The controlling circuit maintains a small
external operating voltage between the sensing and counter electrodes of the proper bias and magnitude so that
no current flows to or from the reference electrode while its potential is maintained at the correct fixed voltage
- usually ground. The electrochemical reaction creates a change in current flow from the counter electrode to
the sensing electrode. This change in current is proportional to the gas concentration and is reversible. The
quick response of the sensor results in continuous monitoring of ambient air conditions. The Intrinsically Safe
Sensor Housing design allows direct contact of the target gas to the electrochemical sensor, thus maximizing
response time, detectability and repeatability.
Figure 6 Functional Block Diagram
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 4 of 30
Page 9

DM-500IS
NOTE
3.0 Application
3.1 Sensor Placement/Mounting
Sensor location should be reviewed by facility engineering and safety personnel. Area leak sources and
perimeter mounting are typically used to determine number and location of sensors. The sensors are generally
located 2 - 4 feet above grade.
3.2 Interference Data
Detcon Model DM-500IS series electrochemical sensors are subject to interference from other gases. This
interaction is shown in the table in section 3.4 as the relation between the amount of the interfering gas applied
to the sensor, and the corresponding reading that will occur. All measurements are in ppm unless otherwise
noted.
The table is laid out with the Model Number of each sensor in a column on the left side of the page. The
interfering gases are listed in a row across the top of the page. Each page lists all Model Numbers but 5 pages
are necessary to list all interfering gases, thus each page is a repeat of the full line of Detcon sensors. Be sure
to reference each page to ascertain the full listing of interfering gases for a particular sensor.
As an example, the first listing shows that the Model DM-500IS-C2H30 acetaldehyde sensor will have an
interference reading of 340 ppm if 40 ppm of C2H2 (Acetylene) is applied.
: Interference factors may differ from sensor to sensor and with life time. It is not
advisable to calibrate with interference gases. They should be used as a guide only
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 5 of 30
Page 10
3.3 Interference Gas List
Gas Name
Symbol
Gas Name
Symbol
Acetaldehyde C2H3O Hydrocarbons C-H’s
Acetylene C2H2 Hydrocarbons (unsaturated) C-H’s (u)
Acrylonitrile C3H3N Hydrogen H2
Alcohols Alcohols Hydrogen Bromide HBr
Amines Amines Hydrogen Chloride HCL
Ammonia NH3 Hydrogen Cyanide HCN
Arsenic Trifluoride AsF3 Hydrogen Fluoride HF
Arsenic Pentafluoride AsF5 Hydrogen Selenide HSe
Arsine AsH3 Hydrogen Sulfide H2S
Boron Trifluoride BF3 Iodine I2
Bromine Br2 Isopropanol C3H8O
Butadiene C4H6 Methane CH4
Buten-1 Buten-1 Methanol CH3OH
Carbon Dioxide CO2 Methyl-Ethyl-Ketone C4H8O
Carbon Disulfide CS2 Methyl Mercaptan CH3SH
Carbon Oxide Sulfide COS Nitric Oxide NO
Carbon Monoxide CO Nitrogen N2
Carbonyl Sulfide COS Nitrogen Dioxide NO2
Chlorine CL2 Ozone O3
Chlorine Dioxide CLO2 Phosgene COCL2
Chlorine Trifluoride CLF3 Phosphine PH3
Diborane B2H6 Phosphorous Trifluoride PF3
Dimethyl Sulfide C2H6S Silane SiH4
Disilane Si2H6 Silicon Si
Epichlorohydrin C3H5OCL Silicon Tetra Fluoride SiF4
Ethanol C2H5OH Sulfur Dioxide SO2
Ethyl Mercaptan C2H5SH Tetrahydrothiophene C4H8S
Ethylene C2H4 Thiophane C4H4S
Ethylene Oxide C2H4O Toluene C6H5CH3
Fluorine F2 Tungsten Hexafluoride WF6
Formaldehyde CH2O Vinyl Acetate C4H6O2
Germane GeH4 Vinyl Chloride C2H3CL
Hydrazine N2H4
DM-500IS
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 6 of 30
Page 11
DM-500IS
DM-500IS-C3H3N
DM-500IS-NH3(-
20°C)
DM-501IS-NH3(-
40°C)
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
DM-500IS-AsH3
DM-500IS-Br2
DM-500IS-C4H6
DM-500IS-CS2
DM-500IS-CO
DM-500IS-COS
DM-500IS-CL2
DM-500IS-CLO2 (>10ppm)
DM-501IS-CLO2 (
≤
10ppm)
DM-500IS-B2H6
DM-500IS-C2H6S
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL
DM-500IS-C2H5OH
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
DM-500IS-C2H4
DM-500IS-C2H4O
DM-500IS-F2
DM-500IS-CH2O
DM-500IS-GeH4
DM-500IS-N2H4
200=0.04
n/d
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm
)
n/d
n/d
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL)
100=0
n/d
DM-500IS-HBr
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-HCL
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-HCN
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-H
F
n/d
yes
n/d
DM-500IS-H2S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3OH
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3SH
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-NO
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-NO2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-O3
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-COCL2
50=0.5
n/d
DM-500IS-PH3
100=0.01
n/d
DM-500IS-SiH4
100=<1
n/d
DM-500IS-SO2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H8S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H4S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H6O2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C2H3CL
n/d
n/d
3.4 Interference Gas Table (page 1 of 5)
NOTE: Reference the listing in Table 1 to match model number with gas name. Reference the listing in section
3.3 to match the interfering gas symbol with the gas name.
Model Number C2H30 C2H2 C3H3N Alcohols Amines NH3 AsF3 AsF5 AsH3 BF3 Br2 C4H6 Buten-1
DM-500IS-C2H3O n/a 40=340 40=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 40=170 n/d
DM-500IS-C2H2 340=40 n/a 340=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 340=170 n/d
75=40 75=340 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 75=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 yes n/d n/a n/d n/d 1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d yes n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=0.01 n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d n/d
170=40 170=340 170=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d
140=40 140=340 140=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 140=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
135=40 135=340 135=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 135=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0.55 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0.18 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=0.013 n/d n/d 0.15=0.2 n/d n/d n/d n/d
150=40 150=340 150=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 150=170 n/d
50=40 50=340 50=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 50=170 n/d
180=40 180=340 180=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 180=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
220=40 220=340 220=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 220=170 n/d
275=40 275=40 275=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 275=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d 0.1=0 n/d yes n/d n/d n/d
330=40 330=340 330=75 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 330=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=<1 n/d n/d 0.2=0.14 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 No
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 No
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
415=40 415=340 415=75 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d 1000=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
45=40 45=340 45=75 n/d n/d
55=40 55=340 55=75 n/d n/d
200=40 200=340 200=75 n/d n/d
200=40 200=340 200=75 n/d n/d
n/a = not applicable
n/d = no data
n/d 0.1=0.1 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 0.1=0.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 0.1=0.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 0.1=0 n/d yes n/d n/d n/d
yes n/d 0.1=0 yes n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 415=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 275=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 0.1=0.05 n/d yes n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 1=1 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 0.2=0.14 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 45=170 1%=1.8
n/d n/d n/d n/d 55=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 200=170 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 200=170 n/d
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 7 of 30
Page 12

DM-500IS
DM-500IS-C3H3N
DM-500IS-NH3(-
20°C)
DM-501IS-NH3(-
40°C)
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
DM-500IS-AsH3
DM-500IS-Br2
DM-500IS-C4H6
DM-500IS-CS2
DM-500IS-CO
DM-500IS-COS
DM-500IS-CL2
DM-500IS-CLO2 (>10ppm)
DM-501IS-CLO2 (
≤
10ppm)
DM-500IS-B2H6
DM-500IS-C2H6S
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL
DM-500IS-C2H5OH
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
DM-500IS-C2H4
DM-500IS-C2H4O
DM-500IS-F2
DM-500IS-CH2O
DM-500IS-GeH4
DM-500IS-N2H4
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm
)
n/d
n/d
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL)
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-HBr
n/d
yes n
/d
DM-500IS-HCL
n/d
1=yes n/d
DM-500IS-HCN
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-H
F
n/d
yes
n/d
DM-500IS-H2S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3OH
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3SH
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-NO
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-NO2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-O3
0.1=0.12
1=1(theor.)
DM-500IS-COCL2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-PH3
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-SiH4
300=0
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-SO2
300=
<5
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H8S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H4S
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H6O2
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C2H3CL
n/d
n/d
Interference Gas Table (page 2 of 5)
Model Number CO2 CS2 CO COS CL2 CL02 CLF3 B2H6 C2H6S Si2H6 C3H5OCL C2H5OH
DM-500IS-C2H3O n/d 40=140 40=100 40=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 40=150 n/d 40=50 40=180
DM-500IS-C2H2 n/d 340=140 340=100 340=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 340=150 n/d 340=50 340=180
n/d 75=140 75=100 75=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 75=150 n/d 75=50 75=180
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=0 n/d n/d 0.1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
5000=0 n/d 300=100 n/d 5=0 n/d n/d 0.1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 300=8 n/d 1=1 10%=15 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
5000=0 n/d 300=0 n/d 0.5 = -0.04 n/d n/d 0.2=0.15 n/d 5=yes n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 300=0 n/d 1=2 1=6 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d
n/d 170=140 170=100 170=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 170=150 n/d 170=50 170=180
n/d n/a 140=100 140=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 140=150 n/d 140=50 140=180
n/d n/d n/a n/d 1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 200=0
n/d 135=140 135=100 n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d 135=150 n/d 135=50 135=180
n/d n/d 300=0 n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 300=0 n/d 3=1 n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=0.9 n/a yes n/d 0.1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
5000=0 n/d 300=0 n/d 0.5 = -0.06 n/d n/d n/a n/d 5=yes n/d n/d n/d
n/d 150=140 150=100 150=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d 150=50 150=180
n/d 50=140 50=100 50=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 50=150 n/d n/a 50=180
n/d 180=140 180=100 180=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 180=150 n/d 180=50 n/a
n/d n/d 300≤5 n/d 1 = -0.6 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 220=140 220=100 220=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 220=150 n/d 220=50 220=180
n/d 275=100 275=100 275=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 275=150 n/d 275=50 275=180
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=1.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 330=140 330=100 330=135 n/d n/d n/d n/d 330=150 n/d 330=50 330=180
5000=0 n/d 300=0 n/d 0.5 = -0.04 n/d n/d 0.2=0.11 n/d 5=yes n/d n/d n/d
n/a = not applicable
n/d = no data
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=0
n/d n/d 300=<30 n/d 1=0
1000-0 n/d 50=6 n/d 5=0
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 5=1
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 5=1
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 5 = -1
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=0.4
n/d n/d 300=≤1.5 n/d 1 = ≈ -0.2
n/d 415=140 415=100 415=135 n/d
n/d n/d 300 ≤ 3 n/d 1 = --0.4
n/d n/d 300=0 n/d 1=0
n/d n/d 300=0 n/d 1= ≈1
5000=0 n/d 300=0 n/d 1=1.4
5000=0 n/d 1000=0 n/d 1=0
5000=0 n/d 300=0 n/d 0.5 = -0.04
5000=0 n/d
n/d n/d
5000=0 n/d 0.1%=1.2 1%=10 n/d
n/d 45=140 45=100 45=135 n/d
n/d 55=140 55=100 55=135 n/d
n/d 200=140 200=100 200=135 n/d
n/d 200=140 200=100 200=135 n/d
n/d 0.5 = -0.04
n/d 1=<0.5
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 415=150 n/d 415=50 415=180
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.2=0.15 n/d 5=yes n/d n/d n/d
0.2=0.11 n/d 5=yes n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 45=150 n/d 45=50 45=180
n/d 55=150 n/d 55=50 55=180
n/d 200=150 n/d 200=50 200=180
n/d 200=150 n/d 200=50 200=180
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 8 of 30
Page 13

Interference Gas Table (page 3 of 5)
DM-500IS-C3H3N
DM-500IS-NH3
(-20°C)
n/d
DM-501IS-NH3
(-40°C)
yes
n/d
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
DM-500IS-AsH3
5=0
DM-500IS-Br2
5=0
DM-500IS-C4H6
DM-500IS-CS2
DM-500IS-CO
DM-500IS-COS
DM-500IS-CL2
5=0
10=0
DM-500IS-CLO2 (>10ppm)
5=0
10=0
DM-501IS-CLO2 (
≤
10ppm)
n/d
DM-500IS-B2H6
n/d
DM-500IS-C2H6S
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL
DM-500IS-C2H5OH
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
DM-500IS-C2H4
DM-500IS-C2H4O
DM-500IS-F2
n/d
DM-500IS-CH2O
n/d
DM-500IS-GeH4
n/d
5=0
DM-500IS-N2H4
n/d
%range=0
n/d
5=0
.1
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm
)
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=0
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL)
n/d
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-HBr
n/d
%range=0
n/d
1%=0
15=
1
DM-500IS-HCL
n/d
%range=0
n/d
1%=0
15=
1
DM-500IS-HCN
n/d
%range=0
n/d1000
=0
5=0
DM-500IS-H
F
n/d
%range=0
n/d
5=
3.3
DM-500IS-H2S
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=0
DM-500IS-CH3OH
n/d
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3SH
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=0
10=0
DM-500IS-NO
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=<110=0
DM-500IS-NO2
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=0
10=0
DM-500IS-O3
n/d
n/d
n/d
10
=0
DM-500IS-COCL2
n/d
%range=0
n/d
5=0
DM-500IS-PH3
n/d
%range=0
n/d
5=0
10=0
.1
DM-500IS-SiH4
n/d
%range=0
n/d
5=0
10=
1
DM-500IS-SO2
n/d
n/d
n/d
5=0
10=
<5
DM-500IS-C4H8S
n/d
%range=0
yes
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H4S
n/d
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3
n/d
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H6O2
n/d
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C2H3CL
n/d
n/d
n/d
Model Number C2H4 C2H4O F2 CH2O GeH4 N2H4 C-H’s C-H’s (U) H2 HBr HCL HCN HF
DM-500IS-C2H3O 40=220 40=275 n/d 40=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
DM-500IS-C2H2 340=220 340=275 n/d 340=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
75=220 75=275 n/d 75=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0 n/d %range=0
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0 n/d %range=0
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 200=4 n/d 5 = -3 10=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0.4 n/d %range=0 n/d 3000=0 n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=0 n/d
170=220 170=275 n/d 170=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
140=220 140=275 n/d 140=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
100=<100 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100 = <60 n/d 5=0 10 = -2 n/d
135=220 135=275 n/d 135=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=0 n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100=0 n/d
n/d n/d yes n/d n/d 1=0 n/d %range=0
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0.53 n/d %range=0
150=220 150=275 n/d 150=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
50=220 50=275 n/d 50=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
180=220 180=275 n/d 180=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 1%=<15 n/d 5=0 10=0 n/d
n/a 220=275 n/d 220=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
275=200 n/a n/d 275=330 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d %range=0
330=220 330=275 n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d %range=0
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
100= ≈80 n/d n/d n/d n/d
yes n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d yes n/d n/d 1=0
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
415=220 415=275 n/d 415=330 n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 0.1=0.07 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=0.4
n/d n/d n/d n/d 1=1.0
100=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
1%=2.4 n/d n/d n/d n/d
45=220 45=275 n/d 45=330 n/d
55=220 55=275 n/d 55=330 n/d
200=220 200=275 n/d 200=330 n/d
200=220 200=275 n/d 200=330 n/d
n/a = not applicable
n/d = no data
1%=0 n/d 5=0 10=0 4=0
1000=35 n/d yes n/d 10 = -18 n/d
1%=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
3000=0 n/d 5=0 10=0.13 4=0
1%=0 n/d 5=0 1 = -3 3=0
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
3000=0 n/d
1000=0 n/d
n/a n/d
n/a n/d n/d 10=0 n/d
n/a 1=1
1=1 n/a
n/d
1%=0 n/d
1%=<5 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
1%=<10 n/d
100=0 n/d
100=0 n/d
1%=0.003 n/d
1%=0 n/d
3000=0 n/d
3000=0 n/d
100=0 n/d
0.1%=0.3 n/d yes n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
DM-500IS
10=0.1 4=0
10=0 n/d
n/d
n/d
10=1 4=0
n/d 3=0
10 = ≈3 n/d
3=0
3=0
n/a 3=0
n/d n/a
10=0 n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
10=0.33 5=0
5=0 3=0
4=0
4=0
n/d
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 9 of 30
Page 14

DM-500IS
DM-500IS-C3H3N
DM-500IS-NH3(-
20°C)
DM-501IS-NH3(-
40°C)
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
DM-500IS-AsH3
DM-500IS-Br2
DM-500IS-C4H6
170
=275
DM-500IS-CS2
140
=275
DM-500IS-CO
DM-500IS-COS
DM-500IS-CL2
15
=-0.75
35=
0
DM-500IS-CLO2 (>
10ppm)
15=
0.25
DM-501IS-CLO2 (
≤
10ppm)
DM-500IS-B2H6
DM-500IS-C2H6S
150
=415
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL
50
=415
50
=275
DM-500IS-C2H5OH
180
=415
180
=275
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
n/d
DM-500IS-C2H4
220
=415
220
=275
DM-500IS-C2H4O
275
=415
275
=275
DM-500IS-F2
n/d
DM-500IS-CH2O
330
=415
DM-500IS-GeH4
1=0
100%=0
DM-500IS-N2H4
1=0
.1
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm
)
15=
<3
n/d
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL)
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-HBr
10=
2.75
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-HCL
10=
2.75
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-HCN
10=0
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-H
F
10=0
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-H2S
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3OH
n/d
DM-500IS-CH3SH
n/d
5 =-1.0
DM-500IS-NO
15=
≈5
n/d
5
=<1.5
DM-500IS-NO2
15=-0.75
n/d
DM-500IS-O3
1
=-.015
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-COCL2
1=0
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-PH3
1=0
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-SiH4
1=0
n/d
n/d
100%=0
DM-500IS-SO2
15=0
n/d
35=
0
DM-500IS-C4H8S
20=0.3
1300=64
n/d
10=7.5
DM-500IS-C4H4S
45
=415
n/d45=275
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3
55
=415
n/d55=275
DM-500IS-C4H6O2
200
=415
n/d
200=27
5
DM-500IS-C2H3CL
200
=415
n/d
200=27
5
Interference Gas Table (page 4 of 5)
Model Number HSe H2S I2 C3H8O CH4 CH3OH C4H8O CH3SH NO N2 NO2 03 COCL2
DM-500IS-C2H3O n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 40=415 n/d 40=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
DM-500IS-C2H2 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 340=415 n/d 340=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 75=415 n/d 75=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0 10=0 n/d n/d n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d 100%=0 n/d n/d n/d
n/d 14=18 n/d n/d n/d yes n/d n/d n/d n/d 100%=0 10 = -5 n/d n/d
n/d 15=30 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 35=6 n/d 5 = -1 n/d n/d
0.05=0.005 1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100%=0 n/d n/d n/d
n/d 15 = -1.5 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 35=0 n/d 5 = ≈10 n/d n/d
n/a = not applicable
n/d = no data
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 170=415 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 140=415 n/d
n/d 15=<0.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 35=≤7 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 135=415 n/d 135=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d 10 = -0.015 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d yes n/d yes n/d n/d
0.05=0.006 1=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 100%=0 n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 1:3 n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 1 = -1.5 n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.05=0.005
n/d
n/d
n/d
0.1=0
0.1=0
n/d
n/d
n/d n/a n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 1:2 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
0.05=0.005
0.05=0.005
n/d
n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 35=0 n/d 5=1.66 n/d n/d
n/d 1:15 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d 5=8 35=<6 n/d 5 = -1.5 n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d n/d n/d 100%=0 1=0.05 0.1=0.2 n/d
n/d 330=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d yes n/d 1%=0 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
yes n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 100%=0
n/d n/d
n/d 35= ≈10 n/d 5=0 n/d n/d
n/d yes n/d n/d 10=0 n/d n/d
n/d n/d
n/d n/d
n/d n/d
n/d n/d
2:1 35=<2 n/d 5 = -0.5 n/d n/d
415=275 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/a 35=<4 n/d
n/d 100=0 n/d
n/d 35=0 n/d n/a n/d n/d
n/d 10=0
n/d n/d
n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d 5 = ≈5 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d
1 = -0.25 0.1 = -0.1 n/d
n/d n/d 0.1=0
n/d n/d 0.1=0
10 = -12 0.1=0 n/d
10=0.1 n/d n/d
n/d n/d
n/d n/d
1=0.7 n/a n/d
n/d n/d n/a
n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d
n/d 5 = ≈ -5 n/d n/d
100%=0 10=0.9 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 10 of 30
Page 15

DM-500IS
DM-500IS-C3H3N
DM-500IS-NH3
DM-501IS-NH3
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
DM-500IS-AsH3
DM-500IS-Br2
DM-500IS-C4H6
17
0=45
170=55DM-
500IS-CS2
1
40=45
1
40=55DM-500IS-CO
DM-500IS-COS
DM-500IS-CL2
DM-500IS-CLO2
DM-501IS-CLO2
DM-500IS-B2H6
DM-500IS-C2H6S
150=45
150=55DM-
500IS-C3H5OCL
50=45
50=55DM-
500IS-C2H5OH
180=45
180=55
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
DM-500IS-C2H4
22
0=45
220=55DM-
500IS-C2H4O
275
=45
275=55DM-
500IS-F2
DM-500IS-CH2O
DM-500IS-GeH4
DM-500IS-N2H4
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-H2 (ppm
)
5
=0
n/d
n/dDM-
501IS-H2 (LEL)
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-HBr
5=2.5
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-HCL
5=2.5
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-HCN
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-H
F
yes
n/d
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-H2S
5=<1
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-CH3OH
n/d
415=45
415=55
DM-500IS-CH3SH
5=<2
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-NO
5
=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-NO2
5
=-0.025
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-O3
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-COCL2
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-PH3
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-SiH4
2=0
n/d
n/dDM-
500IS-SO2
n/
a
n/d
n/d
DM-500IS-C4H8S
2=0.6
n/
d
n/
a
DM-500IS-C4H4S
n/d
n/
a
45=55DM-
500IS-C6H5CH3
n/d
55
=45
n/dDM-
500IS-C4H6O2
n/d
20
0=45
200=55DM-
500IS-C2H3CL
n/d
20
0=45
200=55
Interference Gas Table (page 5 of 5)
Model Number PH3 PF3 SiH4 Si SiF4 SO2 C4H8S C4H4S C6H5CH3 WF6 C4H6O2 C2H3CL C2H5SH C6H5CH3
DM-500IS-C2H3O n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 40=45 n/d n/d 40=200 40=200 n/d 40=55
DM-500IS-C2H2 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 340=45 n/d n/d 340=200 340=200 n/d 340=55
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 75=45 n/d n/d 75=200 75=200 n/d 75=55
(-20°C)
(-40°C)
(>10ppm)
(≤10ppm)
n/a = not applicable
n/d = no data
300=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d 2=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.3=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d yes n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5= --0.5 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1-0.11 n/d 1=0.56 n/d n/d 2=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5= -0.1 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 135=45 n/d n/d 135=200 135=200 n/d 135=55
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5=- 0.05 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5=-0.016 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0.14 n/d 1=0.72 n/d n/d 2=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 5=<3 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 2=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d 330=45 n/d n/d 330=200 330=200 n/d 330=55
0.1=0.13 n/d n/d n/d n/d 2=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.3=0.1 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0.3 n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.3=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.1=0 yes n/d n/d n/d 3=4
(theor.)
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
0.3=0.03 n/d 1=0.015 n/d n/d
0.3=0 n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/a n/d 1=0.56 n/d n/d
0.1=0.13 n/a n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/a
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d
n/d n/d 170=200 170=200 n/d
n/d n/d 140=200 140=200 n/d
n/d n/d 150=200 150=200 n/d
n/d n/d 50=200 50=200 n/d
n/d n/d 180=200 180=200 n/d
n/d n/d 220=200 220=200 n/d
n/d n/d 275=200 275=200 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d yes n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 3=1
n/d n/d 415=200 415=200 n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d 2=1
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/d n/d n/d
n/d n/d 45=200 45=200 n/d
n/d n/d 55=200 n/d n/d
n/d n/d n/a 200=200 n/d
n/d n/d 200=200 n/a n/d
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 11 of 30
Page 16

4.0 Specifications
Model Number
Gas Name
Response
Span Drift
Temperature
Temperature
Humidity
SensorCell
DM-500IS-C2H3O
Acetaldehyde
T90 <140
<5%
signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H2
Acetylene
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C3H3N
Acrylonitrile
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-NH3 (-20°C)
Ammonia
T90 <60
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
10 to 95
2 years
DM-501IS-NH3 (-40°C)
Ammonia
T90 <90
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +40
-
40 to +104
5 to 95
2 years
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE)
Ammonia
T90 <90
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +50
-
40 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-AsH3
Arsine
T90 <60
<5% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
20 to 95
11/2
yearsDM-
500IS-Br2
Bromine
T90 <60
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C4H6
Butadiene
T90 <
140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-CS2
Carbon Disulfide
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-CO
Carbon Monoxide
T90≤30
<5% signal loss/year
-
40 to +50
-
40 to +122
15 to 90
3
yearsDM-
500IS-COS
Carbonyl Sulfide
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-CL2
Chlorine
T90 <60
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-CLO2(>10ppm)Chlorine Dioxide
T90 <60
<2%
signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-501IS-CLO2(≤10ppm)
Chlorine Dioxide
T90 <120
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
10 to 95
2 years
DM-500IS-B2H6
Diborane
T90 <60
<5% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
20 to 95
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-C2H6S
Dimethyl Sulfide
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL
Epichlorohydrin
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H5OH
Ethanol
T90 <140
<5%
signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H5SH
Ethyl Mercaptan
T90 <45
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +50
-
40 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H4
Ethylene
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H4O
Ethylene Oxide
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-F2
Fluorine
T90 <80
<5% signal loss/year
-
10 to +40
+14 to +104
10 to 95
1-1/2
years
DM-500IS-CH2O
Formaldehyde
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-20to +50-4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-GeH4
Germane
T90 <60
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
20 to 95
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-N2H4
Hydrazine
T90 <120
<5% signal loss/month
-
10 to +40
+14 to +104
10 to 95
1 year
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm)
Hydrogen
T90≤30
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL)*
Hydrogen
T90 <60
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +40
-
40 to +104
5 to 95
2 years
DM-500IS-HBr
Hydrogen Bromide
T90 <70
<3% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
10 to951-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-HCL
Hydrogen Chloride
T90 <70
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
10 to 95
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-HCN
Hydrogen Cyanide
T90 <40
<5% signal loss/month
-
40 to +40
-
40 to +104
5 to 95
2 years
DM-500IS-HF
Hydrogen Fluoride
T90 <90<10%
signal loss/month
-
20 to +35
-
4 to +95
10 to 80
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-H2S
Hydrogen Sulfide
T90≤30
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +50
-
40 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-CH3OH
Methanol
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2
yearsDM-
500IS-CH3SH
Methyl Mercaptan
T90 <45
<2% signal loss/month
-
40 to +50
-
40 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-NO
Nitric Oxide
T90≤10
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
3 years
DM-500IS-NO2
Nitrogen Dioxide
T90 <40
<2% signal
loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-O3
Ozone
T90 <120
<1% signal loss/month
-
10 to +40
+14 to +104
10 to 95
2 years
DM-500IS-COCL2
Phosgene
T90 <120
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
10 to 95
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-PH3
Phosphine
T90 <30
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
20 to 95
1-1/2
yearsDM-
500IS-SiH4
Silane
T90 <60
<1% signal loss/month
-
20 to +40
-
4 to +104
20 to 95
1-1/2
years
Method of Detection
Electrochemical Cell
Electrical Classification
CSA-NRTL (US OSHA) approved* Class 1; Groups B, C, D; Div. 1.
Input Voltage
11.5-28 VDC
Power Consumption
Normal operation = 29.5 mA @ 24VDC
Maximum 50mA @ 24VDC
Maximum 70mA @ 11.5VDC
Output
Linear 4-20 mA DC
Repeatability
± 2% FS
Table 2 Sensor cell specifications
DM-500IS
Time(seconds)
Range °C
Range °F
Range %
Warranty
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 12 of 30
Page 17

DM-500IS
DM-500IS-SO2
Sulfur Dioxide
T90≤20
<2% signal loss/month
-
20 to +50
-
4 to
+122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C4H8S
Tetrahydrothiophene
T90 <30
<2% signal loss/month
-
10 to +40
+14 to +104
10 to 95
2 years
DM-500IS-C4H4S
Thiophane
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3
Toluene
T90 <
140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C4H6O2
Vinyl Acetate
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
DM-500IS-C2H3CL
Vinyl Chloride
T90 <140
<5% signal loss/year
-
20 to +50
-
4 to +122
15 to 90
2 years
Note
1
Note
Note
3
*LELrangeH2isnotCSAapproved.
5.0 Installation
Optimum performance of ambient air/gas sensor devices is directly relative to proper location and installation
practice.
5.1 Field Wiring Table (4-20 mA output)
Detcon Model DM-500IS toxic gas sensor assemblies require three conductor connection between power
supplies and host electronic controllers. Wiring designators are + (DC), – (DC), and mA (sensor signal).
Maximum single conductor resistance between sensor and controller is 10 ohms. Maximum wire size for
termination in the sensor assembly terminal board is 14 gauge.
AWG Meters Feet
18 360 1200
16 600 2000
14 900 3000
Table 3 Field wiring Table
: This wiring table is based on stranded tinned copper wire and is designed to serve as a
reference only.
2: Shielded cable may be required in installations where cable trays or conduit runs
include high voltage lines or other sources of induced interference.
: The supply of power must be from an isolating source with over-current protection as
follows:
AWG Over-current Protection AWG Over-current Protection
22 3A 16 10A
20 5A 14 20A
18 7A 12 25A
Table 4 Over-current Protection per AWG
5.2 Sensor Location
Selection of sensor location is critical to the overall safe performance of the product. Five factors play an
important role in selection of sensor locations:
1) Density of the gas to be detected
2) Most probable leak sources within the industrial process
3) Ventilation or prevailing wind conditions
4) Personnel exposure
5) Maintenance access
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 13 of 30
Page 18

DM-500IS
Density - Placement of sensors relative to the density of the target gas is such that sensors for the detection of
heavier than air gases should be located within 2-4 feet of grade as these heavy gases will tend to settle in low
lying areas. For gases lighter than air, sensor placement should be 4-8 feet above grade in open areas or in
pitched areas of enclosed spaces.
Leak Sources - Most probable leak sources within an industrial process include flanges, valves, and tubing
connections of the sealed type where seals may either fail or wear. Other leak sources are best determined by
facility engineers with experience in similar processes.
Ventilation - Normal ventilation or prevailing wind conditions can dictate efficient location of gas sensors in a
manner where the migration of gas clouds is quickly detected.
Personnel Exposure - The undetected migration of gas clouds should not be allowed to approach
concentrated personnel areas such as control rooms, maintenance or warehouse buildings. A more general and
applicable thought toward selecting sensor location is combining leak source and perimeter protection in the
best possible configuration.
Maintenance Access
Consideration should be given to easy access by maintenance personnel as well as the consequences of close
proximity to contaminants that may foul the sensor prematurely.
Note: In all installations, the sensor element in SS housing points down relative to grade (Figure 7). Improper
sensor orientation may result in false reading and permanent sensor damage.
Conduit
Drain
"T"
EYS Seal Fitting
PGM 1
MODEL DM-5xxHOUSTON,TEXAS
TM
MicroSafe Gas Sensor
ALM ALM
FLT CAL
PGM 2
Figure 7 Typical Installation
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 14 of 30
Page 19

DM-500IS
5.3 Local Electrical Codes
Sensor and transmitter assemblies should be installed in accordance with all local electrical codes. Use
appropriate conduit seals. Drains & breathers are recommended. The sensor assemblies are CSA-NRTL
approved for Class I; Groups B, C, D; Div. 1 environments.
5.4 Installation Procedure
3/4" NPT Ports
6.1"
5.5"
5.825"
4.65"
8-32 tapped
ground point
8.985"
Wall (or other
mounting surface
1/4" Mounting holes
Intrinsically Safe
Sensor Head
Splash Guard
2"
0.5"
Cal Port
Figure 8 Typical Outline and Mounting Dimensions
a. Securely mount the sensor junction box in accordance with recommended practice. See dimensional
drawing (Figure 8).
b. Remove the junction box cover and un-plug the control circuit by grasping the two thumb screws and
pulling outward. Observing correct polarity, connect the loop power field wiring to the terminals
labeled “+” and “–” 4-20 mA. (Figure 9) Reinstall cover.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 15 of 30
Page 20

DM-500IS
NOTE:
The Yellow wire from the IS
Sensor Head is not used.
Customer Supplied
Wiring
+24VDC Power In
Common DC Power In
4-20 mA Output
Blue to Remote Sensor
Not Used
Black to Remote Sensor
White to Remote Sensor
Figure 9 Sensor wiring
5.5 Remote Mounting Applications
Some sensor mounting applications require that the gas sensor head be remotely mounted away from the
sensor transmitter. This is usually true in instances where the gas sensor head must be mounted in a location
that is difficult to access. Such a location creates problems for maintenance and calibration activities. Detcon
provides the DM-500IS sensor in a remote-mount configuration in which the sensor (Model DM-500IS-RS)
and the transmitter (Model DM-500IS-RT) are provided in their own condulet housing and are interfaced
together with a three conductor shielded cable. Sensor can be separate from transmitter up to 50 feet using
shielded twisted pair cable. Reference Figure 10 for wiring diagram.
Customer Wiring
BLU
WHT
BLK
Remote Sensor
DM-500IS-RS
Remote Transmitter
DM-500-RT
Figure 10 Remote wiring diagram
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 16 of 30
Page 21

DM-500IS
6.0 Startup
Upon completion of all mechanical mounting and termination of all field wiring, apply system power and
observe the following normal conditions:
a. DM-5xxIS “Fault” LED is off.
b. A temporary upscale reading will occur as the sensor powers up. This upscale reading will clear to “0”
ppm within approximately 30 minutes of turn-on, assuming there is no gas in the area of the sensor.
NOTE: Zero Clearing with Biased Cells
Some electrochemical sensors are biased with an excitation voltage. When power to the sensor
is lost, this bias voltage slowly decays. When power is restored after long periods (multiple
hours) of being unpowered, a surge in sensor output takes place and a long and slow reestablishing of the sensor’s zero baseline takes place. This re-stabilization time may range from
1 hour to 24 hours depending on the type of sensor and range of operation. The sensor types
that this applies to are the following: HCl, NO, plus all the VOC sensors, C2H30, C2H2,
C3H3N, C4H6, CS2, COS, C2H6S, C3H5OCL, C2H5OH, C2H4, C2H4O, CH2O, CH3OH,
C4H4S, C4H6O2, C6H5CH3 and C2H3CL.
If this characteristic is problematic for your specific application, a battery backup or uninterruptible power
supply is recommended.
6.1 Initial Operational Tests
After a warm up period has been allowed for, the sensor should be checked to verify sensitivity to its target
gas.
Material Requirements
Detcon PN 943-000006-132 Calibration Adapter
Span gas containing the target gas in air or nitrogen. It is recommended that the target gas
concentration be 50% of scale at a controlled flow rate of 500 ml/min. For example, a Model DM500IS-H2S sensor in the range 0-100ppm would require a test gas of 50ppm H2S. For a sensor with a
range of 0-10ppm a test gas of 5ppm is recommended, etc.
a. Attach the calibration adapter to the sensor housing. Apply the test gas at a controlled flow rate of 500
ml/m. Observe that the display increases to a level of 20% of range or higher.
b. Remove the test gas and observe that the display decreases to “0 PPM”.
Initial operational tests are complete. Detcon toxic gas sensors are pre-calibrated prior to shipment and will, in
most cases, not require significant adjustment on start up. However, it is recommended that a complete
calibration test and adjustment be performed within 24 hours of installation. Refer to calibration instructions in
Section 9.0.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 17 of 30
Page 22

DM-500IS
7.0 Operating Software & Magnetic Interface
Operating software is menu listed with operator interface via the two magnetic program switches located under
the face plate. The two switches are referred to as “PGM 1” and “PGM 2”. The menu list consists of 3 items
which include submenus as indicated below. (Note: see section 8.0 for a complete software flow chart.)
1. Normal Operation
a) Current Status
2. Calibration Mode
a) Zero
b) Span
3. Program Menu
a) View Program Status
b) Set Calibration Level
7.1 Normal Operation
In normal operation, the display tracks the current status of the sensor and gas concentration and appears as:
“0 PPM xxx” (the “xxx” is the abbreviated gas type, i.e. “0 PPM H2S”). The mA current output corresponds
to the monitoring level of 0-100% of range = 4-20 mA.
7.2 Calibration Mode
Calibration mode allows for sensor zero and span adjustments. “1-ZERO 2-SPAN”
7.2.1 Zero Adjustment
Zero is set in ambient air with no target gas present or with zero gas applied to the sensor. “AUTO ZERO”
7.2.2 Span Adjustment
Span adjustment is performed with a target gas concentration of 50% of range in air or nitrogen. Span gas
concentrations other than 50% of range may be used. Refer to section 7.3.2 for details. “AUTO SPAN”
7.3 Program Mode
The program mode provides a program status menu (View Program Status) to check operational parameters. It
also allows for the adjustment of the calibration gas level setting.
7.3.1 Program Status
The program status scrolls through a menu that displays:
The software version number.
Range is ###
The calibration gas level setting. The menu item appears as: “CalLevel @ xxPPM”
The estimated remaining sensor life. The menu item appears as: “SENSOR LIFE 100%”
7.3.2 Calibration Level Adjustment
The calibration level is adjustable from 10% to 90% of range. The menu item appears as: “CalLevel @
##PPM”
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 18 of 30
Page 23

DM-500IS
NOTE:
7.4 Programming Magnet Operating Instructions
Operator interface to MicroSafeTM gas detection products is via magnetic switches located behind the
transmitter face plate. DO NOT remove the glass lens cover to calibrate or change programming parameters.
Two switches labeled “PGM 1” and “PGM 2” allow for complete calibration and programming without
removing the enclosure cover, thereby eliminating the need for area de-classification or the use of hot permits.
Figure 11 Programming magnet
A magnetic programming tool (see Figure 11) is used to operate the switches. Switch action is defined as
momentary contact, 3-second hold, and 30-second hold. In momentary contact use, the programming magnet
is waved over a switch location. In 3 second hold, the programming magnet is held in place over a switch
location for 3 or more seconds. In 30 second hold, the programming magnet is held in place over a switch
location for 30 or more seconds. Three and thirty second hold is used to enter or exit calibration and program
menus while momentary contact is used to make adjustments. The location of “PGM 1” and “PGM 2” are
shown in Figure 12.
If, after entering the calibration or program menus, there is no interaction with the
menu items for more than 30 seconds, the sensor will return to its normal operating condition.
Figure 12 Programming Switch locations
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 19 of 30
Page 24

8.0 Software Flow Chart
NOTE
DM-500IS
Figure 13 Software Flow Chart
9.0 Calibration
Material Requirements
Detcon PN 327-000000-000 MicroSafeTM Programming Magnet
Detcon PN 943-000006-132 Calibration Adapter
Span gas containing the target gas in air or nitrogen. The target gas concentration is recommended at
50% of range (which is the factory default) at a controlled flow rate of 500 ml/min. Example: for a
Model DM-500IS-H2S sensor with a range of 0-100ppm, a test gas of 50 ppm is recommended. For a
sensor with a range of 0-10 ppm a test gas of 5 ppm is recommended, etc. Other concentrations can be
used as long as they fall within 10% to 90% of range. See section 9.2 for details. Reference section 10
-2) -b) if you do not know the sensor target gas or range of detection.
9.1 Calibration Procedure – Zero
: Before performing a zero calibration, be sure there is no background gas present or
apply a zero gas standard prior to performing zero calibration.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 20 of 30
Page 25

DM-500IS
CAUTION:
a. Enter the calibration menu by holding the programming magnet stationary over “PGM 1” (see Figure
12) for 3 seconds until the display reads “1-ZERO 2-SPAN” then withdraw the magnet. Note that the
“CAL” LED is on.
b. Next, enter the zero menu by holding the magnet stationary over “PGM 1” for 3 seconds until the
display reads: “SETTING ZERO”, then withdraw the magnet. The sensor has now entered the auto
zero mode. When it is complete the display will read “ZERO COMPLETE” for 5 seconds and then
return to the normal operations menu reading “(0 PPM)”.
Zero calibration is complete.
9.2 Calibration Procedure – Span
Verification of the correct calibration gas level setting and calibration span gas
concentration is required before “span” calibration. These two numbers must be equal.
Calibration consists of entering the calibration function and following the menu-displayed instructions. The
display will ask for the application of span gas in a specific concentration. This concentration must be equal to
the calibration gas level setting. The factory default setting for span gas concentration is 50% of range. In this
instance, a span gas containing a concentration equal to 50% of range is required. If a span gas containing 50%
of range is not available, other concentrations may be used as long as they fall within 10% to 90% of range.
However, any alternate span gas concentration value must be programmed via the calibration gas level menu
before proceeding with span calibration. Follow the instructions below for span calibration.
a. Verify the current calibration gas level setting as indicated by the programming status menu. To do
this, follow the instructions in section 11.0 and make note of the setting found in section 10- 2) -c).
The item appears as “GasLevel @ xxPPM”.
b. If the calibration gas level setting is equal to your calibration span gas concentration, proceed to item
“f”. If not, adjust the calibration gas level setting so that it is equal to your calibration span gas
concentration, as instructed in items “c” through “e”.
c. Enter the programming menu by holding the programming magnet stationary over “PGM 2” for 30
seconds until the display reads “VIEW PROG STATUS” then withdraw the magnet. At this point
you can scroll through the programming menu by momentarily waving the programming magnet over
“PGM 1” or “PGM 2”. The menu options are: View Program Status, and Set Cal Level.
d. From the programming menu scroll to the calibration level listing. The menu item appears as: “SET
CAL LEVEL”. Enter the menu by holding the programming magnet stationary over “PGM 1” for 3
seconds until the display reads “CalGas @ ##PPM”, then withdraw the magnet. Use the
programming magnet to make an adjustment to “PGM 1” to increase or “PGM 2” to decrease the
display reading until the reading is equal to the desired calibration span gas concentration. Exit to the
programming menu by holding the programming magnet over “PGM1” for 3 seconds.
e. Exit back to normal operation by holding the programming magnet over “PGM 2” for 3 seconds, or
automatically return to normal operation in 30 seconds.
f. From the calibration menu “1-ZERO 2-SPAN” (section 9.1a) proceed into the span adjust function by
holding the programming magnet stationary over “PGM 2” for 3 seconds then withdraw the
programming magnet. At this point the display will ask for the application of the target gas and
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 21 of 30
Page 26

DM-500IS
NOTE 1
NOTE 2:
concentration. The display reads “APPLY xxPPM xxx” The x’s here will indicate the actual
concentration requested.
g. Apply the calibration test gas at a flow rate of 500 milliliters per minute. As the sensor signal changes,
the display will change to “AutoSpan xxPPM”. The “xx” part of the reading indicates the actual gas
reading which will increase until the sensor stabilizes. When the sensor signal is stable it will auto
span to the correct ppm reading and the display will change to “SPAN COMPLETE” for 3 seconds,
then to “SENSOR LIFE: xxx%” and then “REMOVE GAS”. Remove the gas. When the signal
level has fallen below 10% of full scale, the display will return to the normal operating mode.
: If there is not a minimal response to the cal gas in the first minute, the sensor
will enter into the calibration fault mode which will cause the display to alternate between
the sensor’s current status reading and the calibration fault screen which appears as:
“SPAN FAULT #1” (see section 9.3)
If during the auto-span function the sensor fails to meet a minimum signal
stability criteria, the sensor will enter the calibration fault mode which will cause the
display to alternate between the sensor’s current status reading and the calibration fault
screen which appears as: “SPAN FAULT #2” (see section 9.3).
9.3 Additional Notes
1. Upon entering the calibration menu, the 4-20 mA signal drops to 2 mA and is held at this level until
you return to normal operation.
2. If during calibration the sensor circuitry is unable to attain the proper adjustment for zero or span, the
sensor will enter into the calibration fault mode which will activate the fault LED (see section 11.0)
and will cause the display to alternate between the sensor’s current status reading and the calibration
fault description. In these cases, the previous calibration points will remain in memory. If this occurs
you may attempt to recalibrate by entering the calibration menu as described in section 9.1-a. If the
sensor fails again, defer to technical trouble shooting (see section 13.0).
9.4 Calibration Frequency
In most applications, monthly to quarterly calibration intervals will assure reliable detection. However,
industrial environments differ. Upon initial installation and commissioning, close frequency tests should be
performed, weekly to monthly. Test results should be recorded and reviewed to determine a suitable
calibration interval.
10.0 Status of Programming, Calibration Level and
Sensor Life
The programming menu has a “View Program Status” listing that allows the operator to view the gas, range,
and software version number of the program, as well as the calibration gas level setting, and estimated
remaining sensor life. The programming menu also allows the changing of the calibration gas level setting (see
section 9.2).
The following procedure is used to view the programming status of the sensor:
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 22 of 30
Page 27

DM-500IS
1) First, enter the programming menu by holding the programming magnet stationary over “PGM 2” for 30
seconds until the display reads “VIEW PROG STATUS”, then withdraw the magnet. At this point you
can scroll through the programming menu by momentarily waving the programming magnet over “PGM
1” or “PGM 2”. The menu options are: View Program Status, and Set Cal Level.
2) Next, scroll to the “VIEW PROG STATUS” listing and then hold the programming magnet over “PGM
1” for 3 seconds. The menu will then automatically scroll, at five second intervals, through the following
information before returning back to the “VIEW PROG STATUS” listing.
a) The software version number.
b) Range is ###.
c) Calibration gas level setting. The menu item appears as: “CalLevel @ xxPPM”
d) The estimated remaining sensor life. The menu item appears as: “SENSOR LIFE 100%”
3) Exit back to normal operations by holding the programming magnet over “PGM 2” for 3 seconds, or
automatically return to normal operation in 30 seconds.
11.0 Program Features
Detcon MicroSafeTM toxic gas sensors incorporate a comprehensive program to accommodate easy operator
interface and fail-safe operation. Program features are detailed in this section. Each sensor is factory tested,
programmed, and calibrated prior to shipment.
Over Range
When the sensor detects gas greater than 100% of range, it will cause the display to flash the highest reading
of its range on and off.
Under Range Fault(s)
If the sensor should drift below a zero baseline of -10% of range, the display will indicate a fault: “ZERO
FAULT”. This is typically fixed by performing another zero cal. When the total negative zero drift exceeds
the acceptable threshold the display will indicate “SENSOR FAULT” and you will longer be able to zero
calibrate.
Span Fault #1
If during span calibration the sensor circuitry is unable to attain a minimum defined response to span gas, the
sensor will enter into the calibration fault mode and cause the display to alternate between the sensor’s current
status reading and the calibration fault screen which appears as: “SPAN FAULT #1”. The previous calibration
settings will remain saved in memory. Previous span calibration is retained.
Span Fault #2
If during the span routine, the sensor circuitry is unable to attain a minimum defined stabilization point, the
sensor will enter into the calibration fault mode and cause the display to alternate between the sensor’s current
status reading and the calibration fault screen which appears as “SPAN FAULT #2”. Previous span calibration
is retained.
Memory Fault
If new data points cannot successfully be stored to memory the display will indicate: “MEMORY FAULT”.
Fail-Safe/Fault Supervision
Detcon MicroSafeTM sensors are programmed for fail-safe operation. All fault conditions will illuminate the
fault LED, and cause the display to read its corresponding fault condition: “ZERO FAULT”, “SENSOR
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 23 of 30
Page 28

DM-500IS
NOTE
NOTE 1
NOTE 2
FAULT”, “SPAN FAULT #1”, or “SPAN FAULT #2”. A “SENSOR FAULT” and “ZERO FAULT” will
cause the mA output to drop to zero (0) mA.
Sensor Life
The “Sensor Life” feature gauges the remaining sensor life based on signal output from the sensor cell. When
sensor life of 25% or less remains the sensor cell should be replaced within a reasonable maintenance
schedule.
12.0 Universal Transmitter Feature (Re-Initialization)
The Model DM500IS uses a universal transmitter design that allows the transmitter to be set up for any target
gas and any toxic concentration range. The original transmitter set-up is done at Detcon Inc. as part of the
sensor test and calibration procedure, but it may also be changed in the field if necessary. The Universal
Transmitter feature is a significant convenience to the user because it allows hardware flexibility and
minimizes the spare parts requirements to handle unexpected transmitter failures of different gas/ranges. It is
however, absolutely critical that changes to gas/range set-up of the Universal Transmitter be consistent with
the gas type and range of the Intrinsically Safe Sensor Head that it is connected to.
: If the Universal Transmitter is changed for gas type and range, it must be consistent
with the Intrinsically Safe sensor head it is mated with.
If the Universal Transmitter needs to be changed for gas type and range follow this procedure. First, unplug
the transmitter temporarily and then plug it back in. While the message “Universal Transmitter” appears, take
the program magnet and swipe it over magnet PGM1. This will reveal the set-up options for gas range and gas
type.
Swipe over PGM1to advance through the options for gas range which include:
1, 2, 3....10 ppm
10, 15, 20...100 ppm
100, 200, 300...1000 ppm
1000, 2000, 3000 …10,000 ppm
When the correct range is displayed, hold magnet over PGM1 for 3 seconds to accept the selection.
Next is your selection for the gas type. In this set-up you will enter the alpha-numeric characters of the gas
type. See Table 1 for correct symbols. There is space for the chemical formula up to six characters. Use PGM1
and PGM2 swipes to advance through the alphabet and numbers 0-9 selection (there is a blank space after 9).
When the correct alphanumeric character is highlighted, hold the magnet over PGM1 for 3 seconds to lock it
in. This moves you to the next blank and the procedure is repeated until the chemical formula is completed.
After the 6th character is locked in the transmitter will proceed to normal operation.
: If the gas symbol has more than 6 characters, the symbol can be replaced by an
abbreviated version of the target gas name such as TOL or TOLUEN for Toluene which has
the symbol C6H5CH3. For Epichlorohydrin (symbol C3H5OCL) you can substitute the name
EPI or EPICHL etc.
: When the Universal Transmitter is re-initialized and a new gas and range is entered,
the previous customer settings span gas value is reset to default levels. This must be reprogrammed back to the customer specific settings.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 24 of 30
Page 29

DM-500IS
13.0 Trouble Shooting
Sensor reads Over-range after Power-up
Probable Cause: Biased sensor requiring additional stabilization time.
1. Verify if this is a biased sensor (see section 6.0).
2. Wait up to 8 hours for unit to come on-scale if using a low range biased sensor.
3. Verify that there are not large amounts of target gas or interfering gases in background.
Reading Higher than Anticipated
Probable Causes: Target or Interfering gases in background, Incorrect calibration for Zero or Span, Biased
sensor still stabilizing.
1. Verify no target or interfering gases are present.
2. Redo Zero and Span calibrations with validated Zero Gas and Span Gas standards.
3. If recovering after a start-up, give more time to stabilize.
Reading Lower than Anticipated
Probable Causes: Target gas or Interfering gases in background during Zero Calibration, Zero Calibration done
before unit finished stabilizing, or Incorrect Span Calibration.
1. Redo Zero and Span calibrations with validated Zero Gas and Span Gas standards.
Sensor Fault
Probable Causes: Yellow wire is connected. Sensor has drifted since last zero cal.
1. Perform Zero calibration
2. Re-calibrate sensor
Zero Calibration Fault
Probable Causes: Target gas or Interfering gases in background during Zero Calibration, Failed
electrochemical sensor.
1. Verify no target or interfering gases are present.
2. Redo Zero and Span calibrations with validated Zero Gas and Span Gas standards.
3. If recovering after a start-up, give more time to stabilize.
Span Calibration Fault
Probable Causes: Failed electrochemical sensor, ice/mud/dust blocking sensor membrane, invalid span
calibration gas do to age and contamination or insufficient flow rate.
1. Verify there is no ice/mud/dust blocking sensor membrane.
2. Redo Span Calibration with validated Span Gas standard (check with Pull Tube).
3. Reinitialize unit by plugging in transmitter while holding the magnet on PGM1. Scroll through and select
the correct gas type. Make sure all customer settings are re-entered after “re-initialization”.
4. Replace with new electrochemical sensor.
Noisy Sensor (continuous drift) or suddenly Spiking
Probable Cause: Unstable power source, inadequate grounding, Inadequate RFI protection.
1. Verify power Source output and stability.
2. Contact Detcon for assistance in optimizing shielding and grounding.
3. Add RFI Protection accessory available from Detcon.
Reporting “ERROR @ XXXXXXX”
Probable Cause: Span calibration calculation error.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 25 of 30
Page 30

DM-500IS
1. Reinitialize unit by plugging in transmitter and the swiping the magnet over PGM1 while “Universal
Transmitter” is displayed. Scroll through and select the correct gas type and range (see section 12.0). Make
sure all customer specific settings are re-entered after “re-initialization”.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 26 of 30
Page 31

14.0 Spare Parts List
943-000006-132 Calibration Adapter
500-005065-007 Connector board
327-000000-000 Programming Magnet
897-850901-010 Aluminum Condulet
897-850901-316 Stainless Steel Condulet
960-202200-000 Condensation prevention packet (replace annually).
925-9954S0-000 DM-5xx Series Universal Plug-in Control Circuit w/OLED
925-8454S0-04P* DM-5xx-H2 LEL range Series Universal Plug-in Control Circuit w/OLED
* The H2 LEL range transmitter is not universal but is discrete to Hydrogen in the 0-4% by volume range.
Aluminum ConduletLid with
window, partof Assembly
DM-500IS
Customer Supplied
Wiring
4-20 mA Output
+24VDC Power IN
Standard Connector Board
P/N 500-005065-007
DM Plug-InSensor Replacement Cell
Where XXXXrepresents GAS codeand Cell code
O'ring 11/4"ID X 17/16OD 0.103W
O'ring 19/16" ID X1 3/4"OD 0.103W
P/N 370-XXXX00-000
Toxic Is Hsg Gasket
P/N 027-02364-1
P/N 173
P/N 171
Splashguard with
Calibration Adapter
P/N:613-120000-700
Sensor Head Wiring Connection
N/A (Noconnection)
Sensor Head Wiring Connection
Sensor Head Wiring Connection
The yellowwire from the
Sensor Housingis not
used.
Condensation PreventionPacket
IS SensorHead
P/N 394-XXXX00-Range
Where XXXXrepresents
GAS codeand Cell code
Figure 14 Spare parts diagram
Transmitter ModuleDM-500IS
Transmitter ModuleDM5xx H2 LEL
STANDARD CONNECTORBOARD
P/N:960-202200-000
P/N 925-9954S0-000
P/N 925-8454S0-04P
P/N:500-005065-007
Condulet Base,part of
Condulet Assembly
6/32 X3/8 Screw (2ea.)
#6 internalStar Washer(2ea.)
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 27 of 30
Page 32

DM-500IS
Table 5 IS Sensor Head / Plug-in Replacement Sensor Cell
Model Number GasName IS Sensor Head Plug-in Replacement
Sensor Cell
DM-500IS-C2H3O Acetaldehyde 394-12EA00-Range 370-12EA00-000
DM-500IS-C2H2 Acetylene 394-12EG00-Range 370-12EG00-000
DM-500IS-C3H3N Acrylonitrile 394-12EM00-Range 370-12EM00-000
DM-500IS-NH3 (-20°C) Ammonia 394-171700-Range 370-171700-000
DM-501IS-NH3 (-40°C) Ammonia 394-151500-Range 370-151500-000
DM-502IS-NH3 (CE) Ammonia 394-505000-Range 370-505000-000
DM-500IS-AsH3 Arsine 394-191900-Range 370-191900-000
DM-500IS-Br2 Bromine 394-747500-Range 370-747500-000
DM-500IS-C4H6 Butadiene 394-12EB00-Range 370-12EB00-000
DM-500IS-CS2 Carbon Disulfide 394-12EH00-Range 370-12EH00-000
DM-500IS-CO Carbon Monoxide 394-444400-Range 370-444400-000
DM-500IS-COS Carbonyl Sulfide 394-12EN00-Range 370-12EN00-000
DM-500IS-CL2 Chlorine 394-747400-Range 370-747400-000
DM-500IS-CLO2 (>10ppm) Chlorine Dioxide 394-747600-Range 370-747600-000
DM-501IS-CLO2 (≤10ppm) Chlorine Dioxide 394-777700-Range 370-777700-000
DM-500IS-B2H6 Diborane 394-192100-Range 370-192100-000
DM-500IS-C2H6S Dimethyl Sulfide 394-12EC00-Range 370-12EC00-000
DM-500IS-C3H5OCL Epichlorohydrin 394-12EI00-Range 370-12EI00-000
DM-500IS-C2H5OH Ethanol 394-12EO00-Range 370-12EO00-000
DM-500IS-C2H5SH Ethyl Mercaptan 394-24EZ00-Range 370-24EZ00-000
DM-500IS-C2H4 Ethylene 394-12ED00-Range 370-12ED00-000
DM-500IS-C2H4O Ethylene Oxide 394-12EJ00-Range 370-12EJ00-000
DM-500IS-F2 Fluorine 394-272700-Range 370-272700-000
DM-500IS-CH2O Formaldehyde 394-12EP00-Range 370-12EP00-000
DM-500IS-GeH4 Germane 394-232500-Range 370-232500-000
DM-500IS-N2H4 Hydrazine 394-262600-Range 370-262600-000
DM-500IS-H2 (ppm) Hydrogen 394-848400-Range 370-848400-000
DM-501IS-H2 (LEL) Hydrogen 394-050500-Range 370-050500-000
DM-500IS-HBr Hydrogen Bromide 394-090800-Range 370-090800-000
DM-500IS-HCL Hydrogen Chloride 394-090900-Range 370-090900-000
DM-500IS-HCN Hydrogen Cyanide 394-131300-Range 370-131300-000
DM-500IS-HF Hydrogen Fluoride 394-333300-Range 370-333300-000
DM-500IS-H2S Hydrogen Sulfide 394-242400-Range 370-242400-000
DM-500IS-CH3OH Methanol 394-12EE00-Range 370-12EE00-000
DM-500IS-CH3SH Methyl Mercaptan 394-24EK00-Range 370-24EK00-000
DM-500IS-NO Nitric Oxide 394-949400-Range 370-949400-000
DM-500IS-NO2 Nitrogen Dioxide 394-646400-Range 370-646400-000
DM-500IS-O3 Ozone 394-393900-Range 370-393900-000
DM-500IS-COCL2 Phosgene 394-414100-Range 370-414100-000
DM-500IS-PH3 Phosphine 394-192000-Range 370-192000-000
DM-500IS-SiH4 Silane 394-232300-Range 370-232300-000
DM-500IS-SO2 Sulfur Dioxide 394-555500-Range 370-555500-000
DM-500IS-C4H8S Tetrahydrothiophene 394-434300-Range 370-434300-000
DM-500IS-C4H4S Thiophane 394-12EQ00-Range 370-12EQ00-000
DM-500IS-C6H5CH3 Toluene 394-12ER00-Range 370-12ER00-000
DM-500IS-C4H6O2 Vinyl Acetate 394-12EF00-Range 370-12EF00-000
DM-500IS-C2H3CL Vinyl Chloride 394-12EL00-Range 370-12EL00-000
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 28 of 30
Page 33

DM-500IS
15.0 Warranty
Detcon, Inc., as manufacturer, warrants each new electrochemical toxic gas plug-in sensor cell, for a specified
period under the conditions described as follows: The warranty period begins on the date of shipment to the
original purchaser and ends after the specified period as listed in the table in Section 4.0. The sensor cell is
warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship. Should any sensor cell fail to perform in
accordance with published specifications within the warranty period, return the defective part to Detcon, Inc.,
4055 Technology Forest Blvd. Suite 100, The Woodlands, Texas 77381, for necessary repairs or replacement.
16.0 Service Policy
Detcon, Inc., as manufacturer, warrants under intended normal use each new DM-500IS series plug-in signal
transmitter Control Circuit and intrinsically safe Sensor Head circuit to be free from defects in material and
workmanship for a period of two years from the date of shipment to the original purchaser. All warranties and
service policies are FOB the Detcon facility located in The Woodlands, Texas.
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 29 of 30
Page 34

17.0 Revision History
Revision Date Changes made Approval
0 09/11/06 Initial Release LU
0.1 08/17/15 Update wiring of Sensor and Remote Sensor, update Spare Parts LU
DM-500IS
Shipping Address 4055 Technology ForestBlvd. Suite100,., TheWoodlands Texas 77381
Phone: 888.367.4286, 281.367.4100 • Fax:281.292.2860• www.detcon.com• sales@detcon.com
DM-500IS Instruction Manual Rev 0.1 Page 30 of 30
Mailing Address: P.O. Box 8067, The Woodlands Texas77387-8067
 Loading...
Loading...