Dell Wyse 3030 LT User Manual

Dell Wyse 3030 LT
User Guide
Regulatory Model: N06D
Regulatory Type: N06D001

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2016 - 2018 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other
trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.
2016 - 07
Rev. A00

1
Welcome to Dell Wyse 3030 LT thin client
Dell Wyse 3030 LT thin client enhances the user’s multimedia experience with its integrated graphics engine and provides multiple
connectivity choices for an excellent virtual desktop solution. These thin clients have a dual core Intel 1.6GHz processer, which delivers high
performance experience to the end users and allows easy deployment of ready to connect to Citrix, Microsoft, VMware, and Dell
vWorkspace. The 3030 LT has various conguration options which support a wide variety of interfaces and peripherals. Wyse 3030 LT thin
clients are ideal choice for virtual desktop environments because of easy deployment and management across remote sites.
Topics:
• About this guide
• Dell Wyse external references
About this guide
This guide is intended for Wyse 3030 LT thin clients running either Dell Wyse ThinLinux or Dell Wyse ThinOS. It provides hardware
specications and OS specic congurations to help you work with Wyse 3030 LT thin clients.
Dell Wyse external references
This section provides links to technology related support and self-service sites for Dell Wyse Thin Clients.
• Dell reference guides — User, Administrator, Quick Start Guide, and related documentation
• Dell Wyse Technology End User License Agreement
• Dell service and support — Latest software images
• Dell Wyse Device Manager — Information about Dell remote management software
• Dell and the Environment — Information about Dell compliance with RoHS and with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
(WEEE)
• Dell and e-Recycling — Information about recycling and reuse of Dell products
• Dell product registration — Register your product
Welcome to Dell Wyse 3030 LT thin client 3

Installation and setup
This section describes about the following topics:
• Wyse 3030 LT thin client hardware setup.
• Wyse 3030 LT thin client BIOS conguration.
Topics:
• Wyse 3030 LT thin client hardware installation
• Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinOS
• Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinLinux
Wyse 3030 LT thin client hardware installation
2
For more information on the hardware installation, see
Dell Wyse 3030 LT thin client Quick Start Guide
.
Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinOS
After starting your thin client you will see a Dell logo for a short period of time. During this period you can press and hold the Delete key to
enter the BIOS with Fireport as the password to make necessary modications. For example, you can use the F7 key to use Optimized
Defaults (load optimal default values for all the items in the BIOS setup utility).
Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinLinux
This section describes about the 3030 LT thin client BIOS settings.
How to invoke BIOS settings and select boot source
The standard BIOS features and boot options are common to all platforms with the following boot options:
• Boot from HardDisk –Boots from the internal SSD storage.
• Boot from USB – Boots the USB storage from any of the USB ports (this option is disabled by default).
• Boot from PXE – Boots from the network through PXE.
• Boot from CLOUD – Not supported by ThinLinux.
The following are the BIOS Hot Key functions while booting:
• P-Key – The key invokes to the boot selection menu. It is used to select or alter the temporary boot order.
• Del-key – The key invokes to the BIOS settings. The BIOS settings is protected by a password and the default password is Fireport.
4 Installation and setup

3
Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT thin client
This section includes the following topics:
• Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinOS.
• Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinLinux.
Topics:
• Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinOS
• Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinLinux
Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinOS
What you see after logging on to the server depends on the administrator congurations.
• Users with a Classic Desktop - will see the classic ThinOS desktop with full taskbar, desktop, and Connect Manager familiar to ThinOS
users. This option is the default out-of-the-box experience and is recommended for terminal server environments with published
applications and for backward compatibility with ThinOS 6.x versions.
• Users with a Zero Desktop - will see the Zero Desktop with the Zero Toolbar showing the assigned list of connections from which to
select. This option is recommended for VDI and any full-screen only connections.
In any desktop case, you can select the desktop option you want (Classic Desktop or Zero Desktop) and create the connections you need
using the Visual Experience tab on the Remote Connections dialog box.
To open the Remote Connections dialog box, perform one of the following tasks:
• Classic Desktop — Click User Name , and then select System Setup > Remote Connections.
NOTE
: User Name is the user who is logged-on and is located at the lower-left pane of the taskbar
• Zero Desktop — Click the System Settings icon on the Zero Toolbar, and then select Remote Connections.
Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT running ThinLinux
On your initial conguration, Dell recommends that you connect by using a wired connection by plugging in the network connected
Ethernet cable to your thin client.
After you turn on your thin client, you are automatically logged in to the local thinuser account. By default, the password of the thinuser
account is set to thinuser.
: In cases where a GDM login is needed (for example, AD/Domain login, PNAgent login and so on), the auto-login option
NOTE
can be turned o through the GUI or by using the INI.
Admin mode enables you to perform system administration tasks such as adding or removing connections and setting up specic device
settings. To enter into the Admin mode, click the Switch to Admin button from Setting application screen to admin mode and then enter
the default root password in the Password Needed window. The default root password is admin.
Logging on to the Wyse 3030 LT thin client 5

4
Displays
This section provides information about the multiple monitor congurations.
Multiple monitor congurations
Wyse 3030 LT thin clients running ThinOS
Depending on your thin client model, connections to monitors can be made using either a DisplayPort, or a proper Dell monitor cables/
splitters/adapters.
For information about conguring dual head display settings, see Conguring the Dual Head display setting on ThinOS.
Wyse 3030 LT thin clients running ThinLinux.
In a Dual-monitor conguration, if both monitors are connected, then by default, the monitors are in span mode. The primary monitor is on
the left (monitor 1) and the secondary monitor is on the right (monitor 2). The resolutions of the monitors are auto detected by the system
by analyzing the monitor’s capabilities.
For information about conguring dual head display settings, see Customizing your display on ThinLinux.
Conguring dual Head display settings on Wyse ThinOS
To congure the Dual head display settings:
1 From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Display.
The Display dialog box is displayed.
2 Click Dual Head tab, and use the following guidelines:
6 Displays
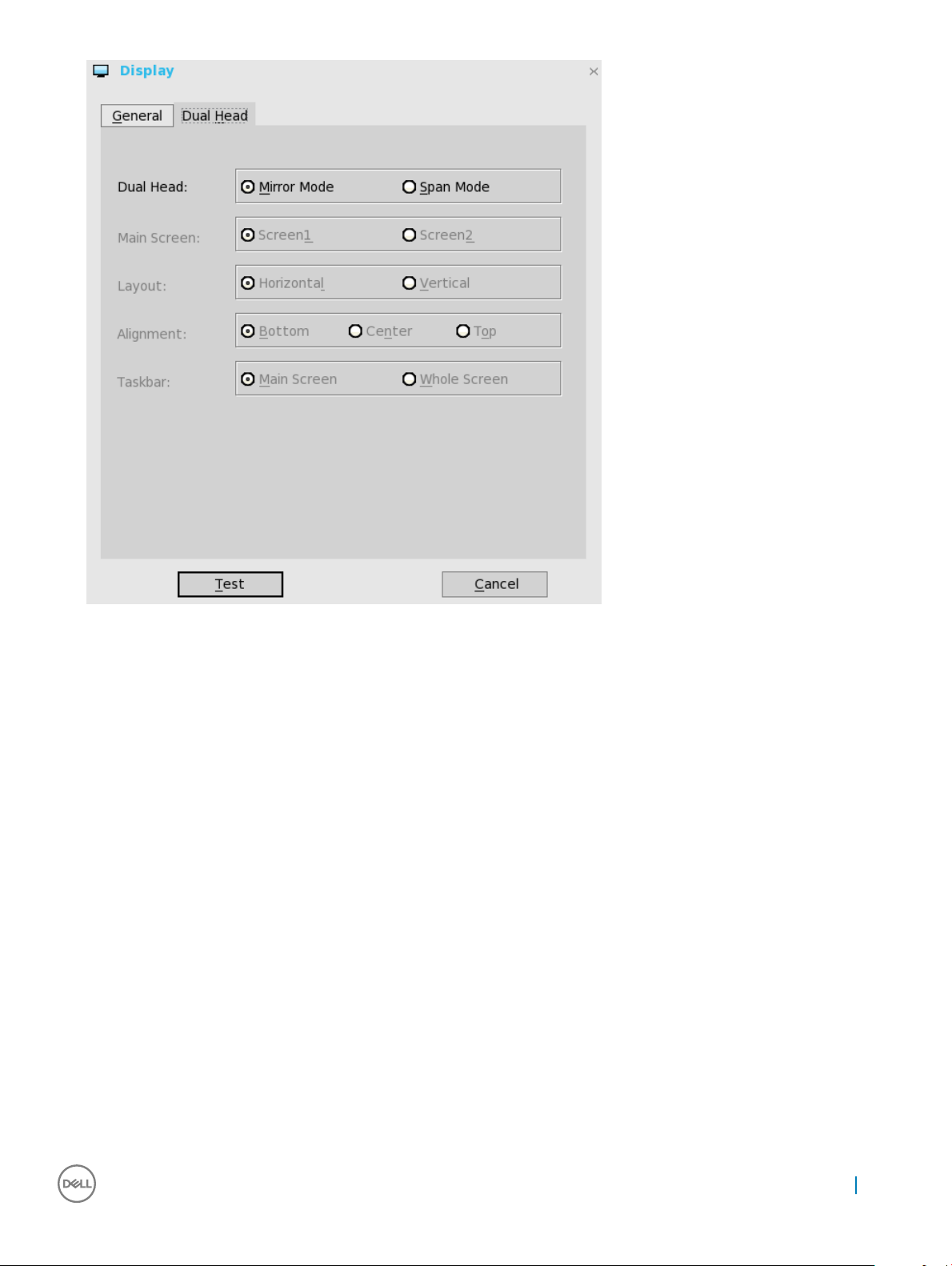
This feature is applicable for supported Dual Monitor Capable Thin Clients Only.
a Select Mirror Mode option from Dual Head to have the two monitors work in a matching state, or Span Mode to have the two
monitors work separately second is extended from rst.
b Select which of the two monitors you want to be the main screen - Screen1 or Screen2 from Main Screen option. The other
screen is extended from the main screen.
c Select how you want the two monitors to be oriented to each other through the Layout option.
Horizontal—where you move between the monitors from the left and right of the screens.
Vertical—where you move between the monitors from the top and bottom of the screens.
d Alignment—Select how you want the monitors to be aligned Bottom, Center, or Top.
Bottom means that screens are bottom-aligned in a horizontal orientation; Center means that screens are center-aligned; Top
means screens are top-aligned in a horizontal orientation.
e Taskbar (Classic Desktop Only)—Select under which screen you want the Taskbar to appear Whole Screen or Main Screen
Gamma Supported Monitors Only—Use the Gamma Setup tab to adjust the saturation values for Red, Green, and Blue on
VGA connected monitors supporting ggamma settings, if you feel the default settings are too light. The Gamma Setup tab is
disabled once you click Save+Exit. You can enable it again by setting gamma={1-100} ggamma={1-100} bgamma={1-100} in the
Resolution INI parameter. For more information, see Dell Wyse ThinOS INI Guide.
Displays
7
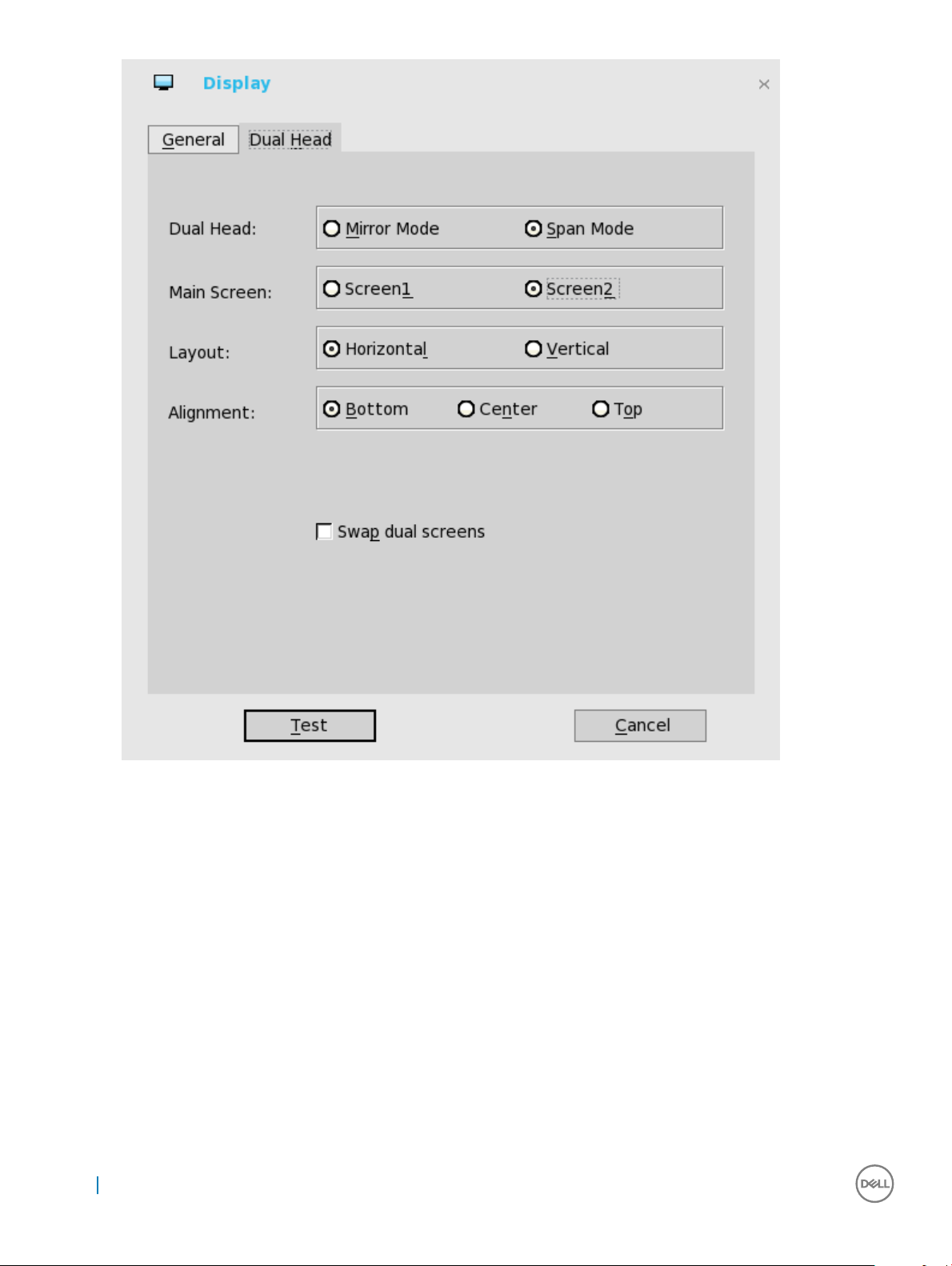
For Swap dual screens, when you set Main Screen to Screen2, an extra check box is displayed at the bottom of the tab that
allows you to swap dual screens. If you clear the check box, the Screen1 is usually the left one or the top one in dual display.
When you set Main Screen to Screen2, the main screen is changed to the right screen or bottom screen. If you select the swap
dual screens check box, you are able to set Main Screen to Screen2, but still have it at the left side or the top side, which is
considered more user friendly.
Customizing your display on ThinLinux
By default, the Customize your display screen is available in both User mode and Admin mode. Any changes to display preferences made
through this screen is saved and available for the built-in thinuser. In a Dual-monitor conguration, if both monitors are connected, then by
default, the monitors are in extended mode. The primary monitor is on the left (monitor 1) and the secondary monitor is on the right
(monitor 2). The resolutions of the monitors are auto detected by the system by analyzing the monitor’s capabilities.
1 Click the Display tab.
The Customize Your Display page is displayed.
Displays
8
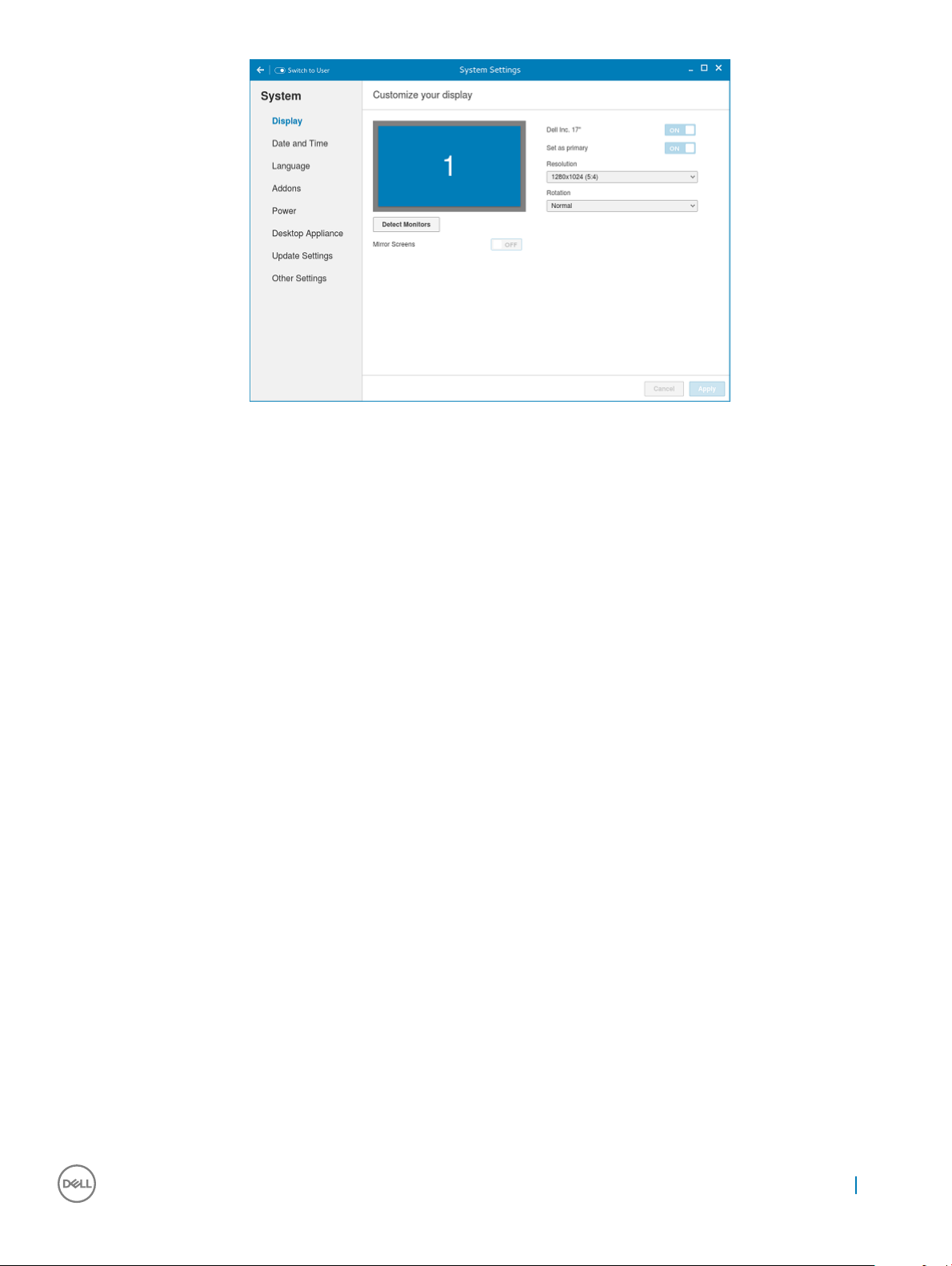
Figure 1. Display Settings
2 Select the preferred Resolution from the drop-down list.
3 Select the Rotation type from the drop-down list.
• Normal
• Right
• Left
• Upside-down
4 Click the ON/OFF button to switch between dual display and mirror mode in a dual monitor conguration.
5 Click the ON/OFF button to enable the Set as primary option. This option allows you to set the selected monitor as primary.
6 Click the ON/OFF button to enable the Monitor On/O option. This option allows you to switch o and switch on the preferred
monitor in a dual monitor conguration.
Displays
9

This section describes about the network congurations of Wyse 3030 LT running either ThinOS or ThinLinux.
• For network congurations on ThinOS, see Conguring the network settings on ThinOS.
• For network congurations on ThinLinux, see Conguring the network settings on ThinLinux.
Topics:
• Conguring the network settings on ThinOS
• Conguring the network settings on ThinLinux
Conguring the network settings on ThinOS
To congure the network settings use the following options:
• Conguring the General settings.
• Conguring the Options settings.
• Conguring the ENET settings.
• Conguring the WLAN settings.
5
Networks
Conguring general settings
To congure the general network settings:
1 From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
10 Networks
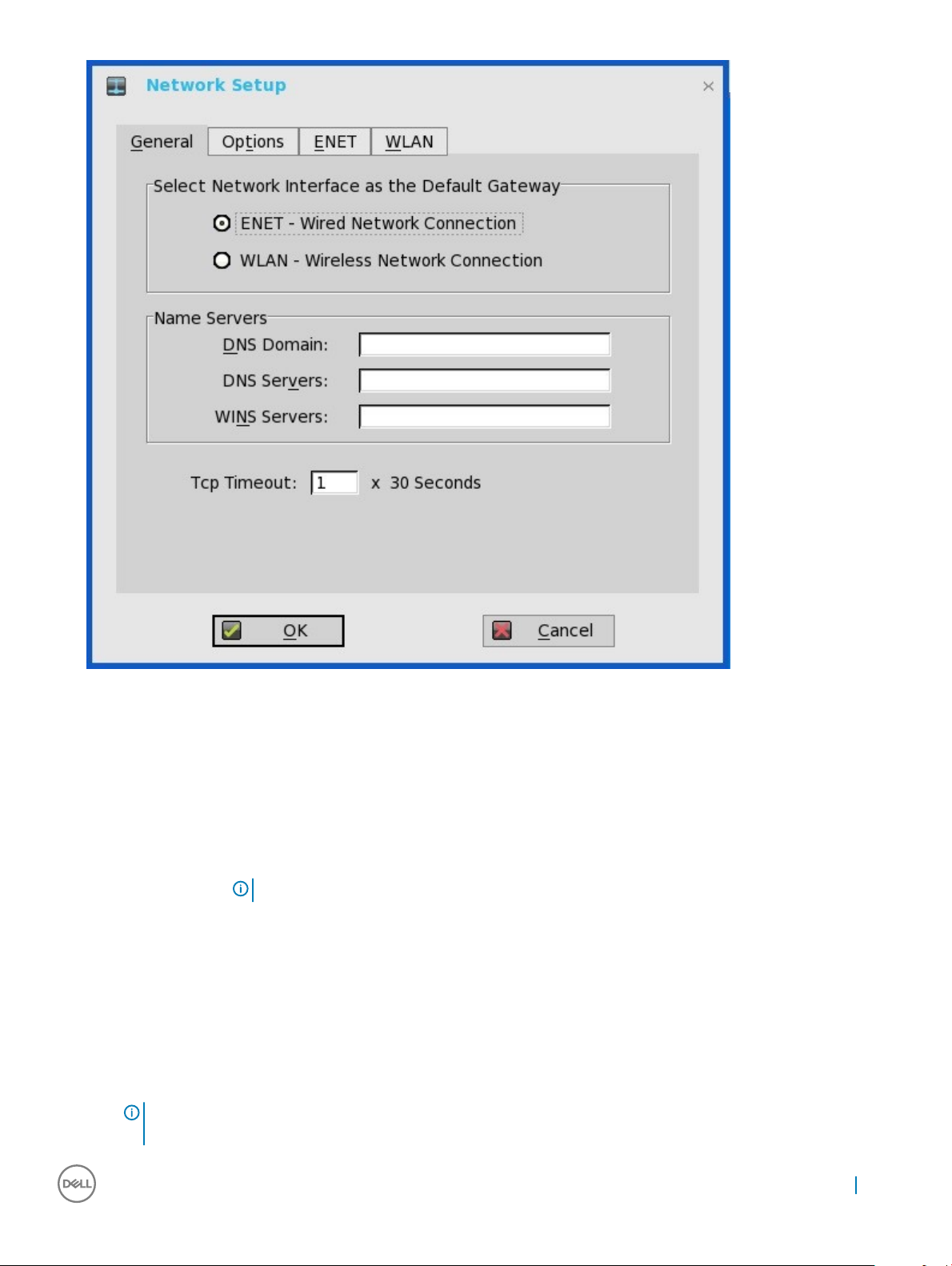
2 Click the General tab, and use the following guidelines:
a To set the default gateway, select the type of network interface from the available options.
1 Single Network support—Either wireless or wired network is connected.
• ENET—Click this option, if you want set up the Ethernet Wired Network Connection.
• WLAN—Click this option, if you want set up the Wireless Network Connection.
• If the user use wireless network after selecting ENET connection or wired network after selecting WLAN connection,
then the system log "WLAN: Set default gate way xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"for rst case and"ENET: Set default gate way
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx" for second case are printed to ensure that the UI setting reects the actual usage.
NOTE
: The User Interface (UI) will not be changed automatically.
2 Dual Network support — Both wireless and wired networks are connected. The default gateway is determined by the UI
settings.
b Enter the URL address of the DNS Domain in the DNS Domain box.
c Enter the IP address of the DNS Server in the DNS Server box.
Use of DNS is optional. DNS allows you to specify remote systems by their host names rather than IP addresses. If a specic IP
address (instead of a name) is entered for a connection, it is used to make the connection. Enter the DNS Domain and the
network address of an available DNS Server. The function of the DNS Domain entry is to provide a default sux is used in name
resolution. The values for these two boxes may be supplied by a DHCP server. If the DHCP server supplies these values, they
replace any locally congured values. If the DHCP server does not supply these values, the locally congured values are used.
: You can enter up to 16 DNS Server addresses, separated by a semicolon, comma, or space. The rst address is
NOTE
for the primary DNS server, and the rest are secondary DNS servers or backup DNS servers.
Networks 11
d Enter the IP address of the WINS Server in the WINS Server box.
Use of WINS is optional. Enter the network address of an available WINS name server. WINS allows you to specify remote
systems by their host names rather than IP addresses. If a specic IP address (instead of a name) is entered for a connection, it
is used to make the connection. These entries can be supplied through DHCP, if DHCP is used. DNS and WINS provide
essentially the same function, name resolution. If both DNS and WINS are available, the thin client attempts to resolve the name
using DNS rst and then WINS.
You can enter two WINS Server addresses (primary and secondary), separated by a semicolon, comma, or space.
e Enter the digit multiplier of 30 seconds in the TCP Timeout box to set the time-out value of a TCP connection. The value must
be 1 or 2 which means the connection time-out value is from 1x30= 30 seconds to 2x30= 60 seconds. If the data for connecting
to the server is not acknowledged and the connection is time out, setting the time-out period retransmits the sent data and
again tries to connect to the server until the connection is established.
3 Click OK to save the settings.
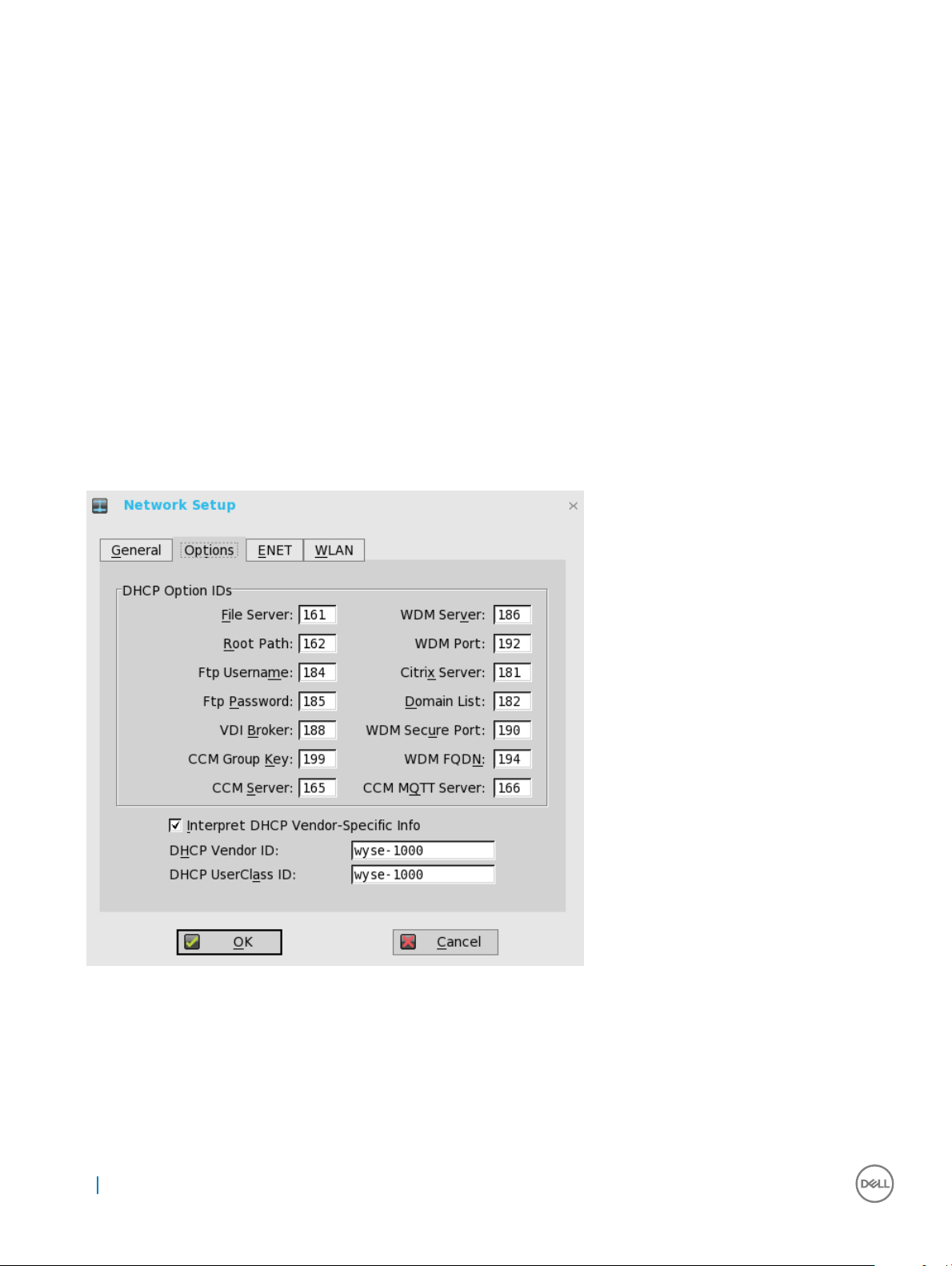
Conguring the DHCP Options Settings
To congure the options settings:
1 From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
2 Click the Options tab, and use the following guidelines:
a DHCP Option IDs — Enter the supported DHCP options. Each value can only be used once and must be between 128 and 254.
b Interpret DHCP Vendor-Specic Info — Select this check box for automatic interpretation of the vendor information.
c DHCP Vendor ID — Shows the DHCP Vendor ID when the dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP option is selected.
d DHCP UserClass ID — Shows the DHCP UserClass ID when the dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP option is selected.
3 Click OK to save the settings.
12
Networks
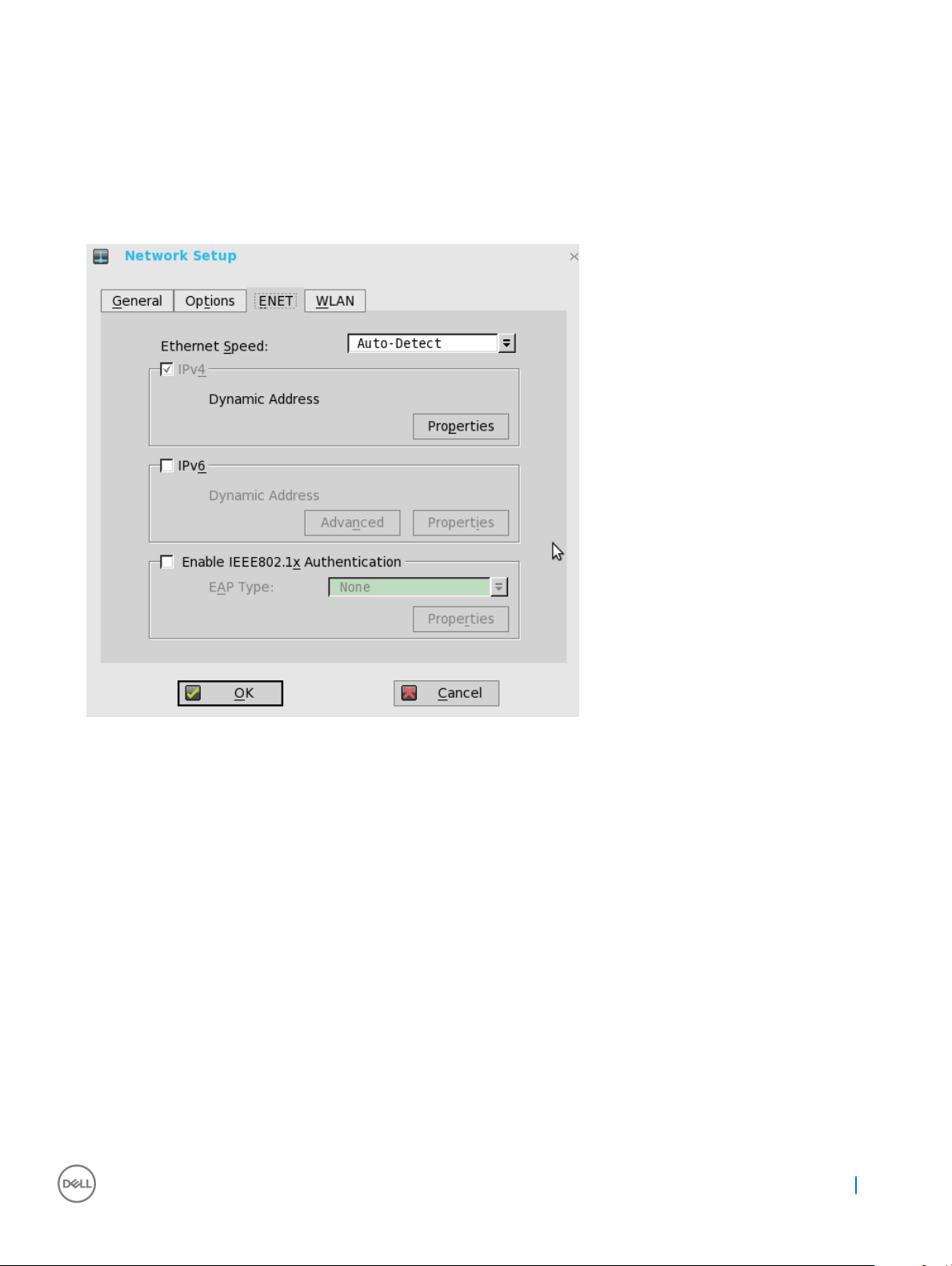
Conguring ENET settings
To congure the ENET settings:
1 From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
2 Click the ENET tab, and use the following guidelines:
a Ethernet Speed—Normally the default (Auto-Detect) should be selected, but another selection can be made if automatic
negotiation is not supported by your network equipment. The selections include Auto-Detect, 10 MB Half-Duplex, 10 MB Full-
, 100 MB Half-Duplex, 100 MB Full-Duplex, and 1 GB Full-Duplex.
Duplex
The 10 MB Full-Duplex option can be selected locally at the device, however, this mode may need to be negotiated through
AutoDetect.
b The IPV4 check box is selected by default. Click Properties to set various options supported by IPV4.
• Dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP—Selecting this option enables your thin client to automatically receive
information from the DHCP server. The network administrator must congure the DHCP server using DHCP options to
provide information. Any value provided by the DHCP server replaces any value entered locally on the Options tab, however,
locally entered values are used if the DHCP server fails to provide replacement values.
• Statically specied IP Address—Select this option to manually enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway:
• IP Address—Must be a valid network address in the server environment. The network administrator must provide this
information.
• Subnet Mask—Enter the value of the subnet mask. A subnet mask is used to gain access to machines on other subnets.
The subnet mask is used to dierentiate the location of other IP addresses with two choices: Same subnet or other
subnet. If the location is other subnet, messages sent to that address must be sent through the Default Gateway,
whether specied through local conguration or through DHCP. The network administrator must provide this value.
Networks
13
 Loading...
Loading...