Dell R530 User Manual

Dell PowerEdge R530
Owner's Manual
Regulatory Model: E29S Series
Regulatory Type: E29S001

Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you
how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2014 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. Dell™ and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2014 - 11
Rev. A00

Contents
1 About your system................................................................................................ 8
Front-panel features and indicators.....................................................................................................8
LCD panel features..............................................................................................................................10
Home screen................................................................................................................................. 10
Setup menu.................................................................................................................................... 11
View menu......................................................................................................................................11
Hard-drive indicator patterns..............................................................................................................12
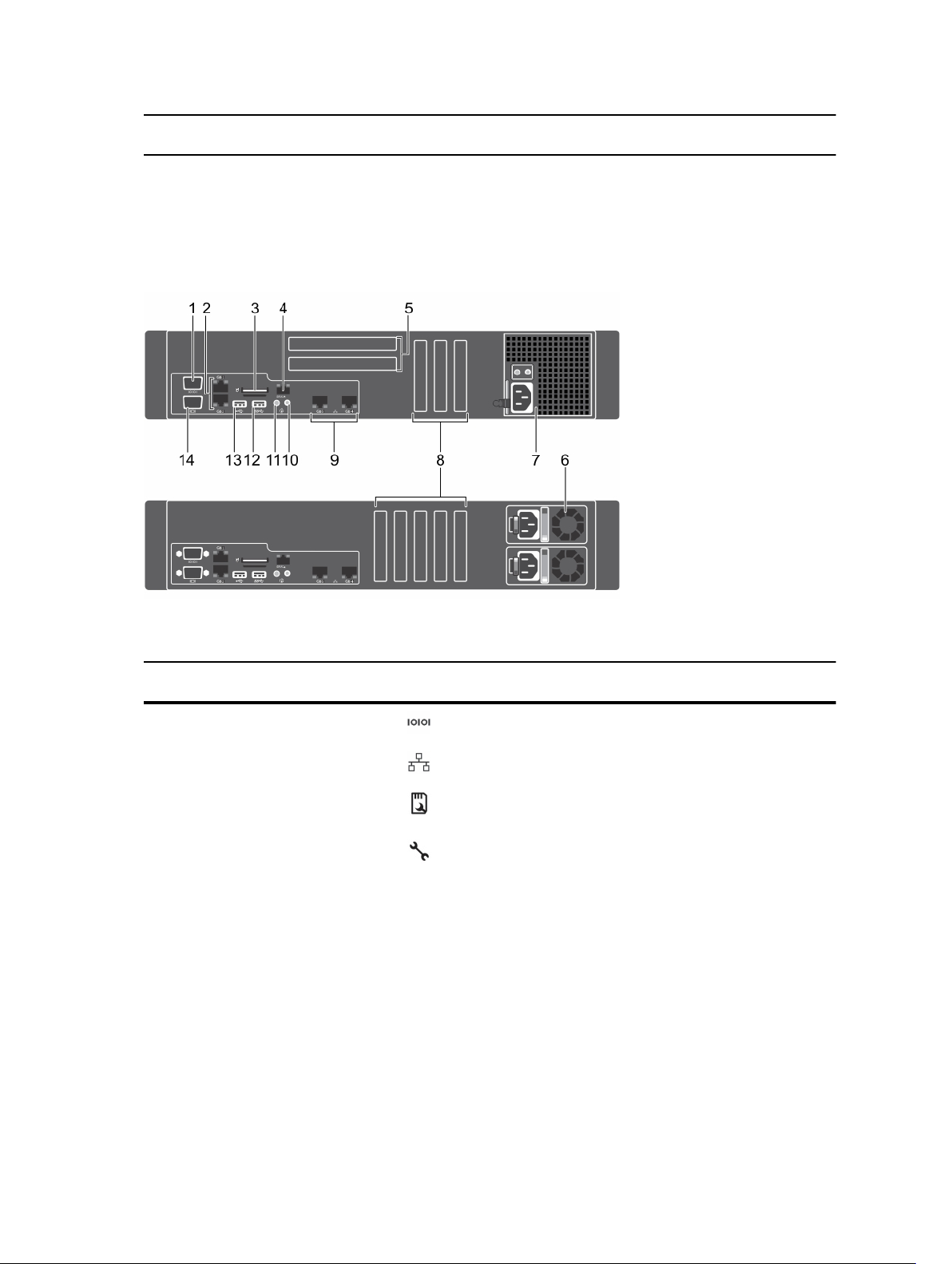
Back-panel features and indicators.................................................................................................... 13
NIC indicator codes.............................................................................................................................15
Power supply unit indicator codes..................................................................................................... 15
Power indicator codes for AC and DC redundant power supply unit.........................................15
Indicator codes for non-redundant power supply...................................................................... 18
Documentation matrix........................................................................................................................ 19
Quick Resource Locator (QRL)...........................................................................................................20
2 Performing initial system configuration ........................................................21
Setting up your system........................................................................................................................21
Setting up and configuring the iDRAC IP address .............................................................................21
Logging in to iDRAC............................................................................................................................ 21
Installing the operating system...........................................................................................................22
Managing your system remotely........................................................................................................ 22
Downloading and installing drivers and firmware............................................................................. 22
3 Pre-operating system management applications........................................24
Navigation keys................................................................................................................................... 24
About System Setup............................................................................................................................24
Entering System Setup.................................................................................................................. 25
System Setup Main Menu..............................................................................................................25
System BIOS screen...................................................................................................................... 25
System Information screen...........................................................................................................26
Memory Settings screen............................................................................................................... 26
Processor Settings screen.............................................................................................................27
SATA Settings screen.....................................................................................................................28
Boot Settings screen......................................................................................................................31
Network Settings screen............................................................................................................... 31
Integrated Devices screen details.................................................................................................32
Serial Communication screen...................................................................................................... 33
System Profile Settings screen......................................................................................................34

System Security Settings screen................................................................................................... 35
Miscellaneous Settings screen......................................................................................................37
About Boot Manager...........................................................................................................................38
Entering Boot Manager ................................................................................................................38
Boot Manager main menu............................................................................................................ 38
About Dell Lifecycle Controller.......................................................................................................... 38
Changing the boot order....................................................................................................................39
Choosing the system boot mode.......................................................................................................39
Assigning a system and setup password............................................................................................39
Using your system password to secure your system........................................................................40
Deleting or changing an existing system and/or setup password.................................................... 41
Operating with a setup password enabled.........................................................................................41
Embedded system management....................................................................................................... 42
iDRAC Settings utility.......................................................................................................................... 42
Entering the iDRAC Settings utility............................................................................................... 42
Changing the Thermal Settings.................................................................................................... 42
4 Installing and removing system components...............................................43
Safety instructions...............................................................................................................................43
Before working inside your system.................................................................................................... 43
After working inside your system....................................................................................................... 43
Recommended tools.......................................................................................................................... 44
Front bezel (optional)..........................................................................................................................44
Removing the front bezel............................................................................................................. 44
Installing the front bezel............................................................................................................... 45
Removing and installing the system cover........................................................................................ 45
Removing the system cover......................................................................................................... 46
Installing the system cover........................................................................................................... 46
Inside the system.................................................................................................................................47
Cooling shroud................................................................................................................................... 49
Removing the cooling shroud......................................................................................................49
Installing the cooling shroud.........................................................................................................51
System memory...................................................................................................................................51
General memory module installation guidelines.........................................................................53
Mode-specific guidelines..............................................................................................................53
Sample memory configurations................................................................................................... 54
Removing a memory module.......................................................................................................56
Installing memory modules.......................................................................................................... 58
Hard drives.......................................................................................................................................... 60
Removing a hot-swap hard drive.................................................................................................60
Installing a hot-swap hard drive....................................................................................................61
Removing a 3.5 inch hard-drive blank......................................................................................... 62

Installing a 3.5 inch hard-drive blank........................................................................................... 63
Removing a 2.5 inch hard drive from a 3.5 inch hard-drive adapter..........................................64
Installing a 2.5 inch hard drive into a 3.5 inch hard-drive adapter..............................................65
Removing a hard-drive adapter from a hard-drive carrier..........................................................65
Installing a hard-drive adapter into a hard-drive carrier............................................................. 66
Removing a hard drive from a hard-drive carrier........................................................................ 66
Installing a hard drive into a hard-drive carrier............................................................................ 67
Optical drive (optional)........................................................................................................................67
Removing the optical drive........................................................................................................... 67
Installing the optical drive.............................................................................................................68
Cooling fans........................................................................................................................................ 69
Removing a cooling fan................................................................................................................69
Installing a cooling fan...................................................................................................................71
Internal USB memory key (optional)...................................................................................................71
Replacing the internal USB key..................................................................................................... 71
Expansion cards and expansion-card riser (optional)........................................................................72
Expansion-card installation guidelines.........................................................................................73
Removing an expansion card from the system board.................................................................75
Installing an expansion card on the system board...................................................................... 76
Removing the (optional) expansion-card riser.............................................................................77
Installing the (optional) expansion-card riser...............................................................................78
Removing an expansion card from the expansion-card riser..................................................... 79
Installing an expansion card into the expansion-card riser.........................................................81
iDRAC ports card (optional)................................................................................................................82
Removing the iDRAC ports card...................................................................................................82
Installing the iDRAC ports card.....................................................................................................84
SD vFlash media card..........................................................................................................................84
Replacing an SD vFlash media card..............................................................................................84
Internal dual SD module..................................................................................................................... 85
Removing an internal SD card...................................................................................................... 85
Installing an internal SD card........................................................................................................86
Removing the internal dual SD module ...................................................................................... 87
Installing the internal dual SD module ........................................................................................ 89
Integrated storage controller card.....................................................................................................90
Removing the integrated storage controller card....................................................................... 90
Installing the integrated storage controller card......................................................................... 92
Processors........................................................................................................................................... 92
Removing a processor.................................................................................................................. 93
Installing a processor.................................................................................................................... 97
Power supplies..................................................................................................................................100
Hot Spare feature........................................................................................................................100
Removing the power supply unit blank..................................................................................... 100

Installing the power supply unit blank........................................................................................101
Removing an AC power supply unit........................................................................................... 101
Installing an AC power supply unit.............................................................................................102
Non-redundant AC power supply (cabled)................................................................................103
Wiring instructions for a DC power supply unit.........................................................................105
Removing a DC power supply unit.............................................................................................108
Installing a DC power supply unit...............................................................................................109
Power interposer board.................................................................................................................... 110
Removing the power interposer board...................................................................................... 110
Installing the power interposer board.........................................................................................112
System battery................................................................................................................................... 112
Replacing the system battery...................................................................................................... 112
Hard-Drive Backplane....................................................................................................................... 114
Removing the hard-drive backplane.......................................................................................... 114
Installing the hard-drive backplane............................................................................................ 116
Control panel and I/O module..........................................................................................................117
Removing the control-panel board............................................................................................ 117
Installing the control-panel board..............................................................................................118
Removing the control panel........................................................................................................119
Installing the control panel.........................................................................................................120
System board..................................................................................................................................... 121
Removing the system board........................................................................................................121
Installing the system board......................................................................................................... 123
Restoring the Service Tag using Easy Restore............................................................................125
Entering the system Service Tag using System Setup................................................................125
Trusted Platform Module..................................................................................................................126
Installing the Trusted Platform Module .....................................................................................126
Re-enabling the TPM for BitLocker users...................................................................................127
Re-enabling the TPM for TXT users............................................................................................127
5 Troubleshooting your system........................................................................ 128
Safety first—for you and your system...............................................................................................128
Troubleshooting system startup failure........................................................................................... 128
Troubleshooting external connections............................................................................................128
Troubleshooting the video subsystem.............................................................................................128
Troubleshooting a USB device......................................................................................................... 128
Troubleshooting a serial I/O device................................................................................................. 129
Troubleshooting a NIC......................................................................................................................129
Troubleshooting a wet system......................................................................................................... 130
Troubleshooting a damaged system................................................................................................ 131
Troubleshooting the system battery.................................................................................................131
Troubleshooting power supply units................................................................................................132

Power source problems....................................................................................................................132
Power supply unit problems.............................................................................................................132
Troubleshooting cooling problems..................................................................................................133
Troubleshooting cooling fans...........................................................................................................133
Troubleshooting system memory.................................................................................................... 134
Troubleshooting an internal USB key...............................................................................................135
Troubleshooting an SD card.............................................................................................................135
Troubleshooting an optical drive..................................................................................................... 136
Troubleshooting a hard drive............................................................................................................137
Troubleshooting a storage controller...............................................................................................137
Troubleshooting expansion cards....................................................................................................138
Troubleshooting processors.............................................................................................................139
System messages.............................................................................................................................. 139
Warning messages.......................................................................................................................139
Diagnostic messages...................................................................................................................139
Alert messages............................................................................................................................ 140
6 Using system diagnostics................................................................................141
Dell Embedded System Diagnostics.................................................................................................141
When to use the Embedded System Diagnostics...................................................................... 141
Running the Embedded System Diagnostics............................................................................. 141
System diagnostic controls.........................................................................................................142
7 Jumpers and connectors................................................................................ 143
System board jumper settings.......................................................................................................... 143
System board connectors.................................................................................................................144
Disabling a forgotten password........................................................................................................145
8 Technical specifications..................................................................................147
9 Getting help.......................................................................................................153
Contacting Dell..................................................................................................................................153
Locating your system Service Tag....................................................................................................153
Documentation feedback................................................................................................................. 153
Quick Resource Locator (QRL).........................................................................................................153
1
About your system
The Dell PowerEdge R530 is a rack server that supports up to two processors based on the Intel E5-2600
v3 product family, up to 12 DIMMs, and up to eight drive bays for hard drives/ SSDs.
The PowerEdge R530 system is available in the following configurations:
• Redundant power supply configuration
• Non-redundant power supply configuration
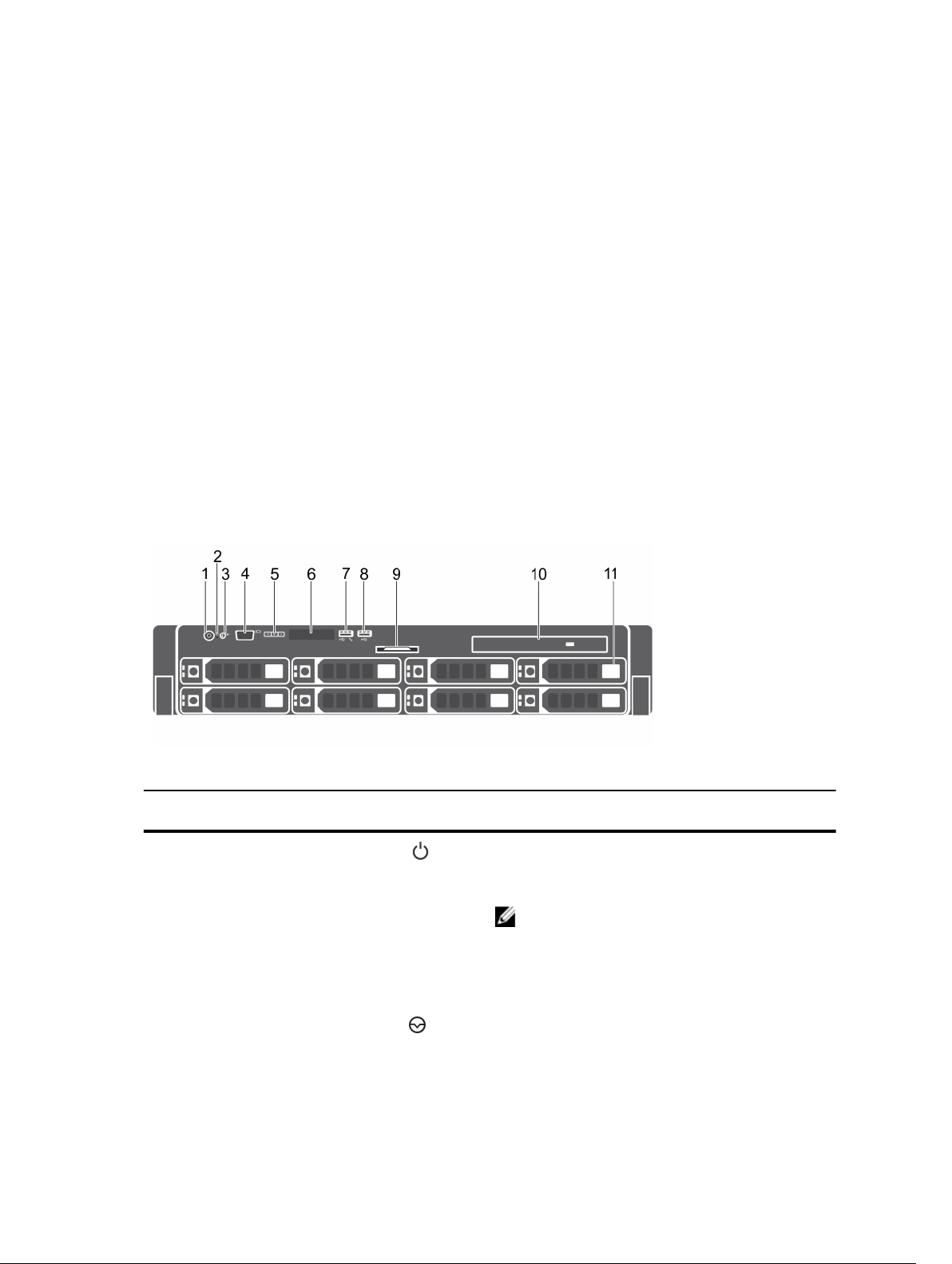
Front-panel features and indicators
Figure 1. Front-panel features and indicators
Item Indicator, Button, or
Connector
1 Power-on indicator,
power button
2 NMI button
8
Icon Description
The power-on indicator lights when the system is
powered on. The power button controls the power
supply output to the system.
NOTE: On ACPI-compliant operating systems,
turning off the system using the power button
causes the system to perform a graceful
shutdown before power to the system is
turned off.
Used to troubleshoot software and device driver
errors when using certain operating systems. This

Item Indicator, Button, or
Connector
Icon Description
button can be pressed using the end of a paper
clip.
Use this button only if directed to do so by
qualified support personnel or by the operating
system's documentation.
3 System identification
button
4 Video connector Connects a VGA display to the system.
5 LCD menu buttons Allows you to navigate the control panel LCD
6 LCD panel Displays system ID, status information, and system
7 USB management port/
iDRAC Direct
The identification buttons on the front and back
panels can be used to locate a particular system
within a rack. When one of these buttons is
pushed, the LCD panel on the front and the system
status indicator on the back flash blue until one of
the buttons is pushed again.
Press to toggle the system ID ON and OFF. If the
system hangs during POST, press and hold the
system ID button for more than five seconds to
enter BIOS progress mode.
To reset the iDRAC (if not disabled in F2 iDRAC
setup) press and hold for more than 15 seconds.
menu.
error messages. See LCD panel features.
Allows you to connect USB devices to the system
or provides access to the iDRAC Direct features.
For more information, see the Integrated Dell
Remote Access Controller User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals. The USB management port
is USB 2.0-compliant.
8 USB connector Allows you to connect USB devices to the system.
The ports are USB 2.0 compliant.
9 Information tag A slide-out label panel, which allows you to record
system information, such as Service Tag, NIC
addresses, MAC address, and so on, for your
reference.
10 Optical drive (optional) One optional SATA DVD-ROM drive or DVD+/-RW
drive.
NOTE: DVD devices are data only.
11 Hard drives/SSDs bay Up to eight 2.5 inch or 3.5 inch hot-swappable
hard drives/SSDs.
9
LCD panel features
The system's LCD panel provides system information and status and error messages to indicate if the
system is operating correctly or if the system needs attention. For more information on error messages,
see the Dell Event and Error Messages Reference Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• The LCD backlight lights blue during normal operating conditions.
• When the system needs attention, the LCD lights amber, and displays an error code followed by
descriptive text.
NOTE: If the system is connected to a power source and an error is detected, the LCD lights
amber regardless of whether the system is turned on or off.
• The LCD backlight turns OFF when the system is in standby mode and can be turned on by pressing
either the Select, Left, or Right button on the LCD panel.
• The LCD backlight remains OFF if LCD messaging is turned off through the iDRAC utility, the LCD
panel, or other tools.
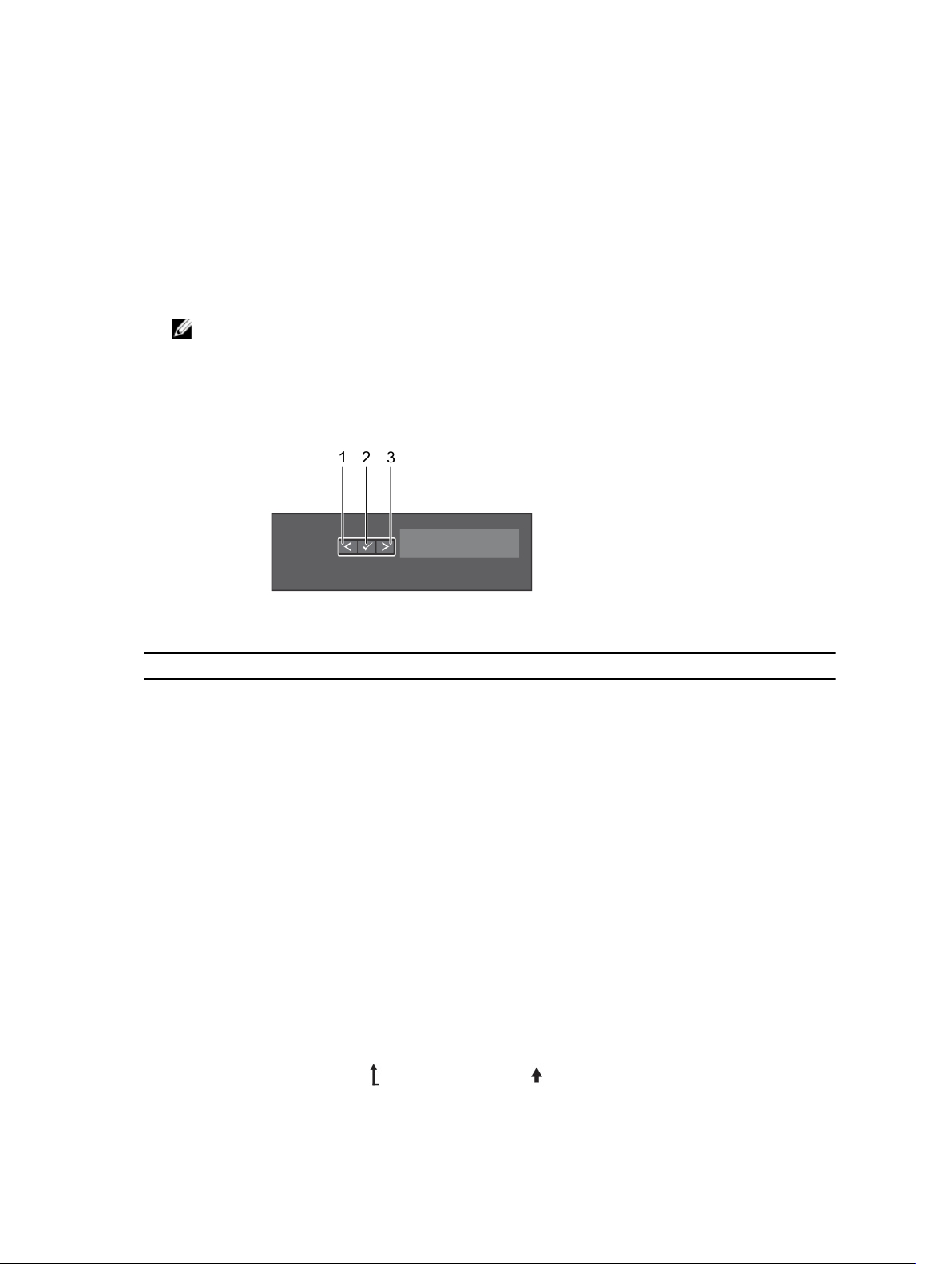
Figure 2. LCD panel features
Item Button Description
1 Left Moves the cursor back in one-step increments.
2 Select Selects the menu item highlighted by the cursor.
3 Right Moves the cursor forward in one-step increments.
During message scrolling:
• Press once to increase scrolling speed
• Press again to stop
• Press again to return to the default scrolling speed
• Press again to repeat the cycle
Home screen
The Home screen displays user-configurable information about the system. This screen is displayed
during normal system operation when there are no status messages or errors. When the system is in
standby mode, the LCD backlight turns off after five minutes of inactivity if there are no error messages.
Press one of the three navigation buttons (Select, Left, or Right) to view the Home screen.
To navigate to the Home screen from another menu, follow the steps below.
1. Press and hold the up arrow until the Home icon is displayed.
10
2. Select the Home icon.
3. From the Home screen, press the Select button to enter the main menu.
Setup menu
NOTE: When you select an option in the Setup menu, you must confirm the option before
proceeding to the next action.
Option Description
iDRAC Select DHCP or Static IP to configure the network mode. If Static IP is selected,
the available fields are IP, Subnet (Sub), and Gateway (Gtw). Select Setup DNS to
enable DNS and to view domain addresses. Two separate DNS entries are available.
Set error Select SEL to display LCD error messages in a format that matches the IPMI
description in the SEL. This is useful when trying to match an LCD message with an
SEL entry.
Select Simple to display LCD error messages in a simplified user-friendly
description. For more information on error messages, see the Dell Event and Error
Messages Reference Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
Set home Select the default information to be displayed on the LCD Home screen. See View
menu to see the options and option items that can be set as the default on the
Home screen.
View menu
NOTE: When you select an option in the View menu, you must confirm the option before
proceeding to the next action.
Option Description
iDRAC IP Displays the IPv4 or IPv6 addresses for iDRAC8. Addresses include DNS (Primary
and Secondary), Gateway, IP, and Subnet (IPv6 does not have Subnet).
MAC Displays the MAC addresses for iDRAC, iSCSI, or Network devices.
Name Displays the name of the Host, Model, or User String for the system.
Number Displays the Asset tag or the Service tag for the system.
Power Displays the power output of the system in BTU/hr or Watts. The display format can
be configured in the Set home submenu of the Setup menu.
Temperature Displays the temperature of the system in Celsius or Fahrenheit. The display format
can be configured in the Set home submenu of the Setup menu.
11
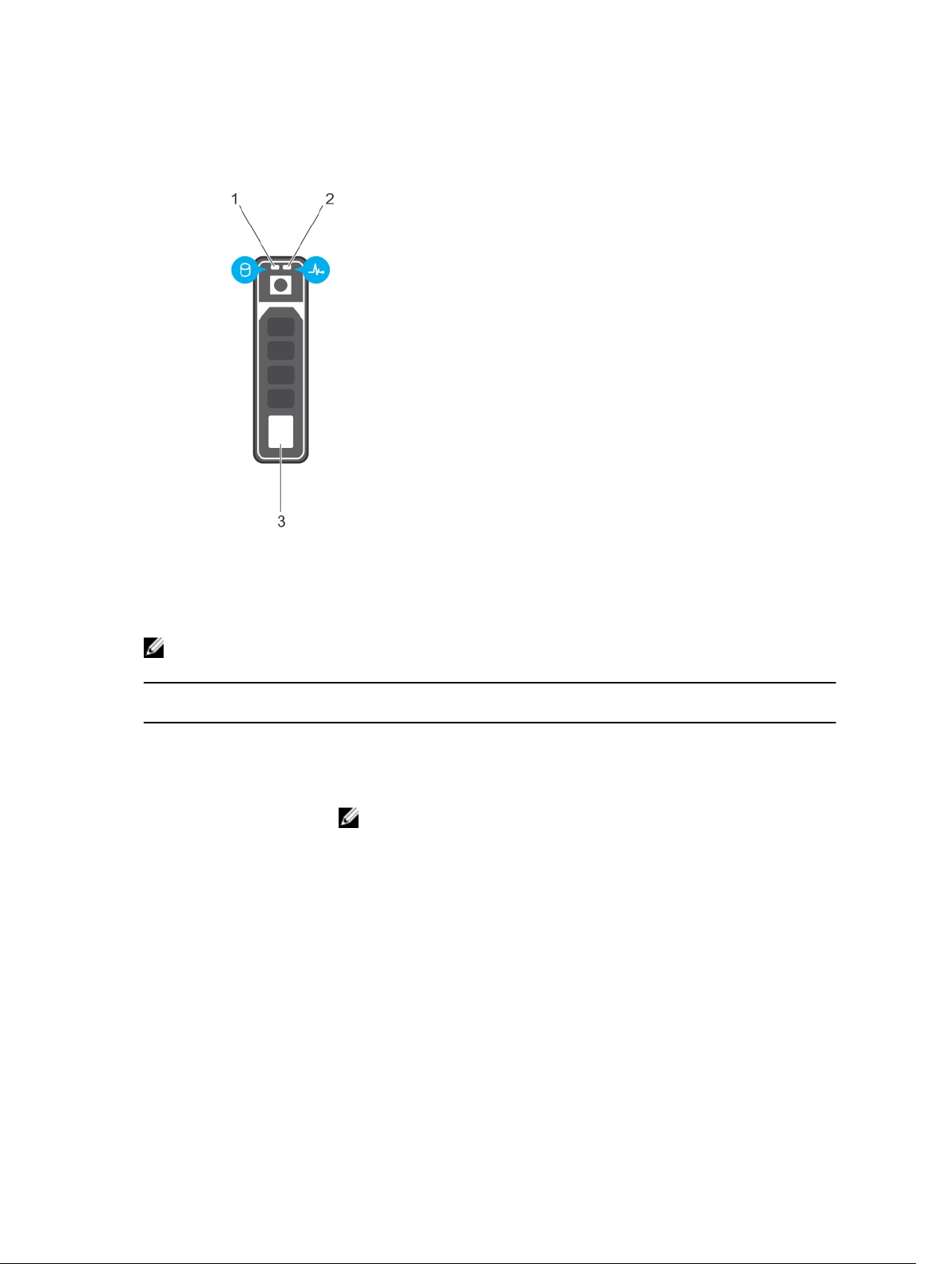
Hard-drive indicator patterns
Figure 3. Hard-drive indicators
1. hard-drive activity indicator 2. hard-drive status indicator
3. hard drive
NOTE: If the hard drive is in Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) mode, the status indicator
(on the right side) does not function and remains OFF.
Drive-status indicator
pattern (RAID only)
Blinks green two times per
second
OFF Drive ready for insertion or removal.
Blinks green, amber, and
off
Blinks amber four times per
second
Blinks green slowly Drive rebuilding
Steady green Drive online
Condition
Identifying the drive or preparing for removal.
NOTE: The drive status indicator remains OFF until all hard drives are
initialized after the system is turned on. Drives are not ready for
insertion or removal during this time.
Predicted drive failure
Drive failed
12
Drive-status indicator
pattern (RAID only)
Condition
Blinks green three seconds,
amber three seconds, and
OFF six seconds
Rebuild aborted
Back-panel features and indicators
Figure 4. Back-panel features and indicators for a non-redundant power supply unit chassis and a redundant
power supply unit chassis
Item Indicator, button, or
connector
1 Serial connector Connects a serial device to the system.
2 Ethernet connectors (2)
3 vFlash media card slot
(Optional)
4 iDRAC port (Optional) Dedicated management port for the iDRAC Ports
5 Full Height PCIe
expansion card slots (2)
6 Redundant Power
Supply Unit
Icon Description
Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps NIC connector
Allows you to insert a vFlash media card.
Card.
PCIe cards located on the optional expansion-card
riser
AC 495 W EPP, 750 W EPP or
1100 W EPP
Or
DC 750 W
13

Item Indicator, button, or
connector
Icon Description
7 Non-Redundant Power
Supply Unit
8 Half Height PCIe
expansion card slots (5)
9 Ethernet connectors (2)
10 System identification
connector
11 System identification
button
12 USB connector Connects USB devices to the system. This port is
450 W
Allows you to connect PCIe expansion cards.
Integrated 10/100/1000 Mbps NIC connector
Connects the optional system status indicator
assembly through the optional cable management
arm.
The identification buttons on the front and back
panels can be used to locate a particular system
within a rack. When one of these buttons is
pushed, the LCD panel on the front and the system
status indicator on the back blink until one of the
buttons is pushed again.
Press to toggle the system ID on and off. If the
system hangs during POST, press and hold the
system ID button for more than five seconds to
enter BIOS progress mode.
To reset the iDRAC (if not disabled in System
Setup) press and hold for more than 15 seconds.
USB 3.0-compliant.
13 USB connector Connects USB devices to the system. This port is
USB 2.0-compliant.
14 Video connector Connects a VGA display to the system.
14
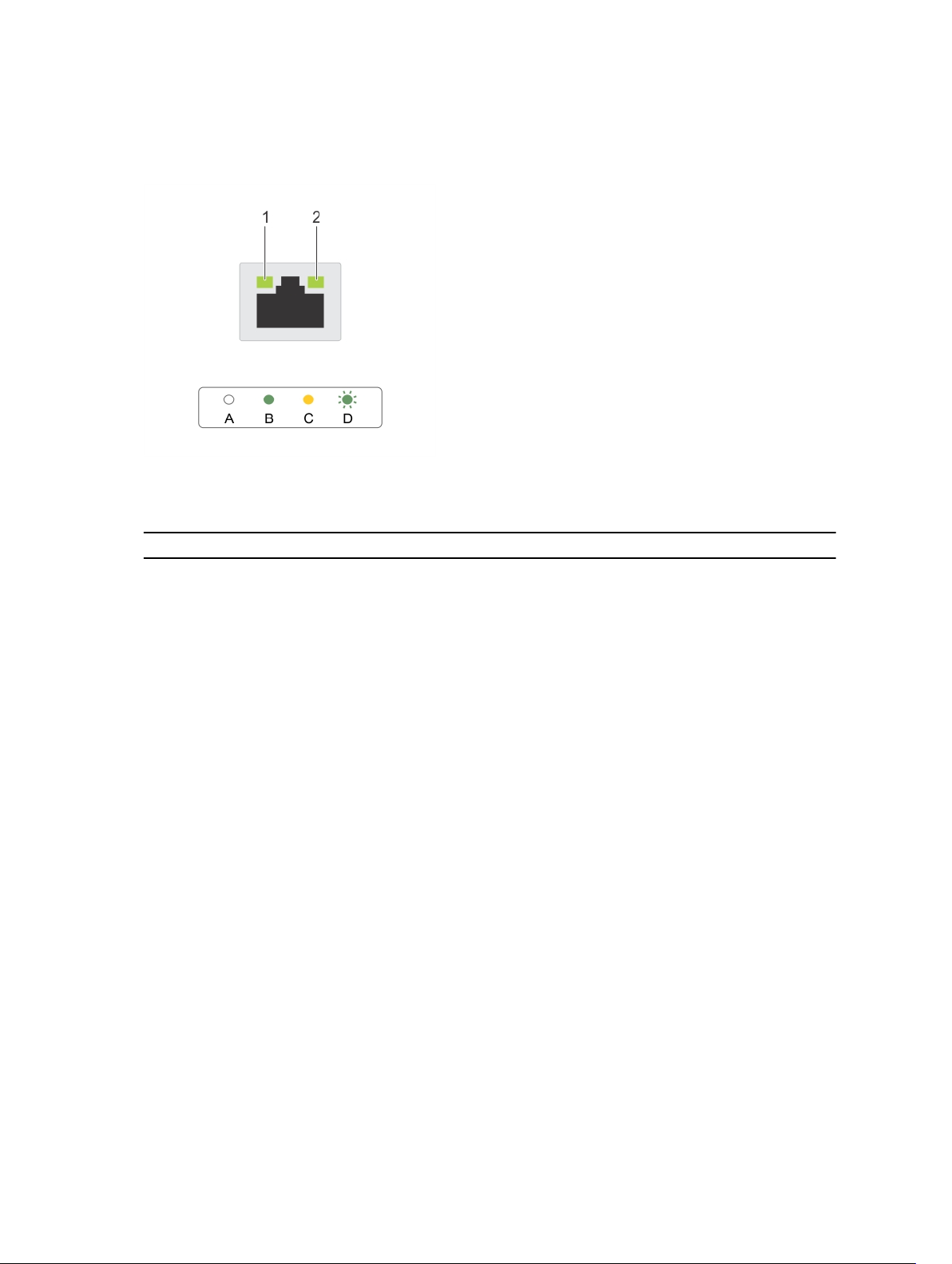
NIC indicator codes
Figure 5. NIC indicators
1. link indicator 2. activity indicator
Convention Indicator pattern Description
A Link and activity indicators
are OFF
B Link indicator is green The NIC is connected to a valid network at its maximum
C Link indicator is yellow The NIC is connected to a valid network at less than its
D Activity indicator is blinking
green
The NIC is not connected to the network.
port speed (1 Gbps).
maximum port speed.
Network data is being sent or received.
Power supply unit indicator codes
Power indicator codes for AC and DC redundant power supply unit
Each AC power supply unit (PSU) has an illuminated translucent handle and each DC PSU (when
available) has an LED that serves as an indicator to show whether power is present or a power fault has
occurred.
15
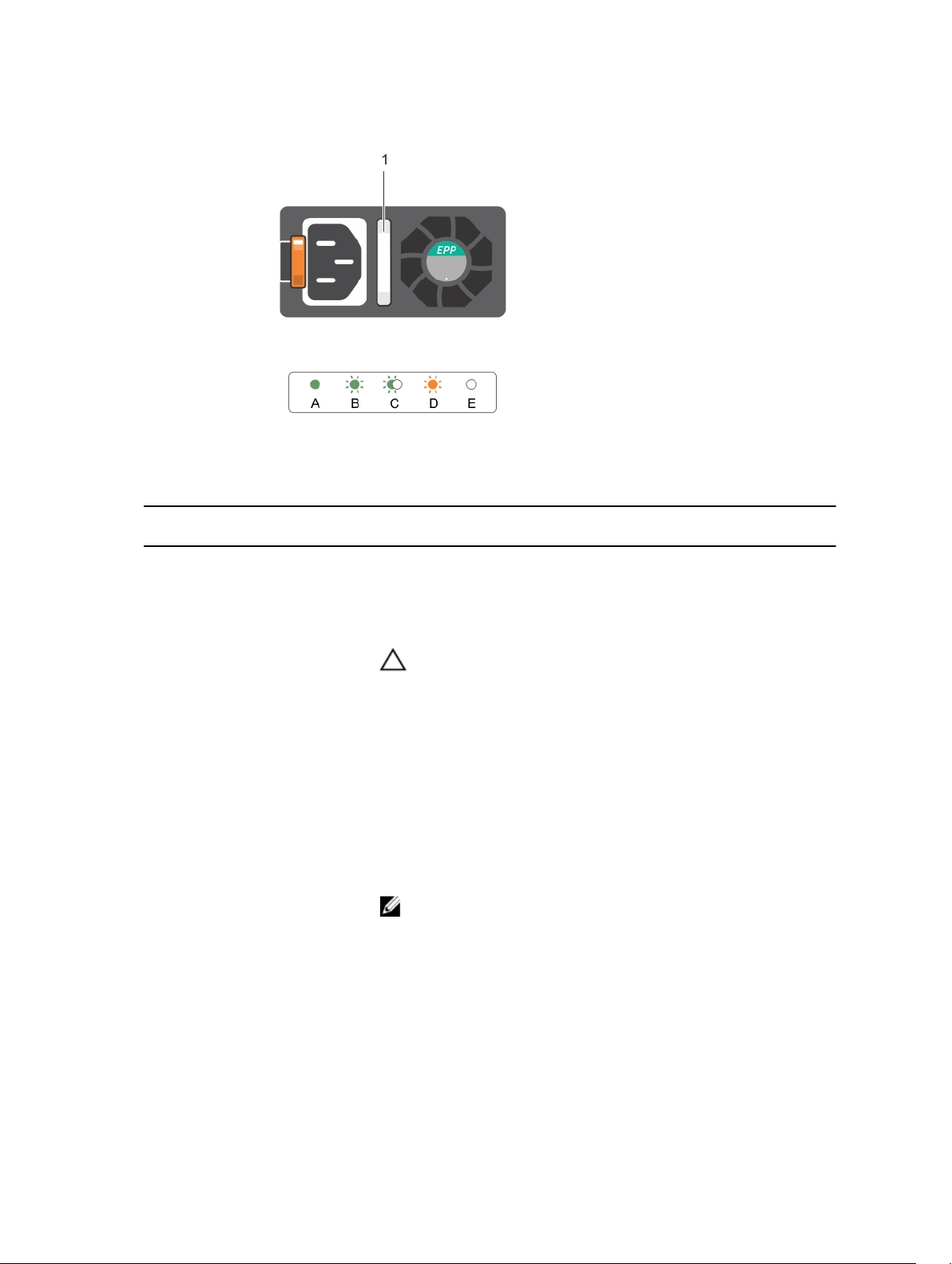
Figure 6. AC power supply unit status indicator
Convention Power indicator
Condition
pattern
A Green The handle indicator lights green indicating that a valid power
source is connected to the PSU and that the PSU is operational.
B Flashing green When updating the firmware of thePSU, the PSU handle flashes
green.
CAUTION:
Do not disconnect the power cord or unplug the PSU when
updating firmware. If firmware update is interrupted, the PSUs will
not function. You must roll back the power supply firmware by using
Life cycle controller. See Dell Lifecycle Controller User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals
C Flashes green
and turns off
When hot-adding a PSU, the handle of the new power supply unit
flashes green five times at 4 Hz rate and turns off. This indicates that
the new PSU is mismatched with the PSU that is installed (in terms of
efficiency, feature set, health status, and supported voltage). Use a
PSU that matches the capacity of the PSU that is installed.
NOTE: For AC power supplies, use only PSUs with the Extended
Power Performance (EPP) label on the back. Mixing PSUs from
previous generations of servers can result in a PSU mismatch
condition or failure to power on.
D Flashing amber Indicates a problem with the power supply unit.
16
Convention Power indicator
Condition
pattern
CAUTION: When correcting a PSU mismatch, replace only the
PSU with the flashing indicator. Swapping the opposite power
supply unit to make a matched pair can result in an error
condition and unexpected system shutdown. To change from
a High Output configuration to a Low Output configuration or
vice versa, you must power down the system.
CAUTION: AC power supplies support both 220 V and 110 V
input voltages with the exception of Titanium power supplies,
which support only 220 V. When two identical power supplies
receive different input voltages, they can output different
wattages, and trigger a mismatch.
CAUTION: If two power supplies are used, they must be of the
same type and have the same maximum output power.
CAUTION: Combining AC and DC power supplies is not
supported and triggers a mismatch.
E Not lit Power is not connected.
Figure 7. DC power supply unit status indicator
17
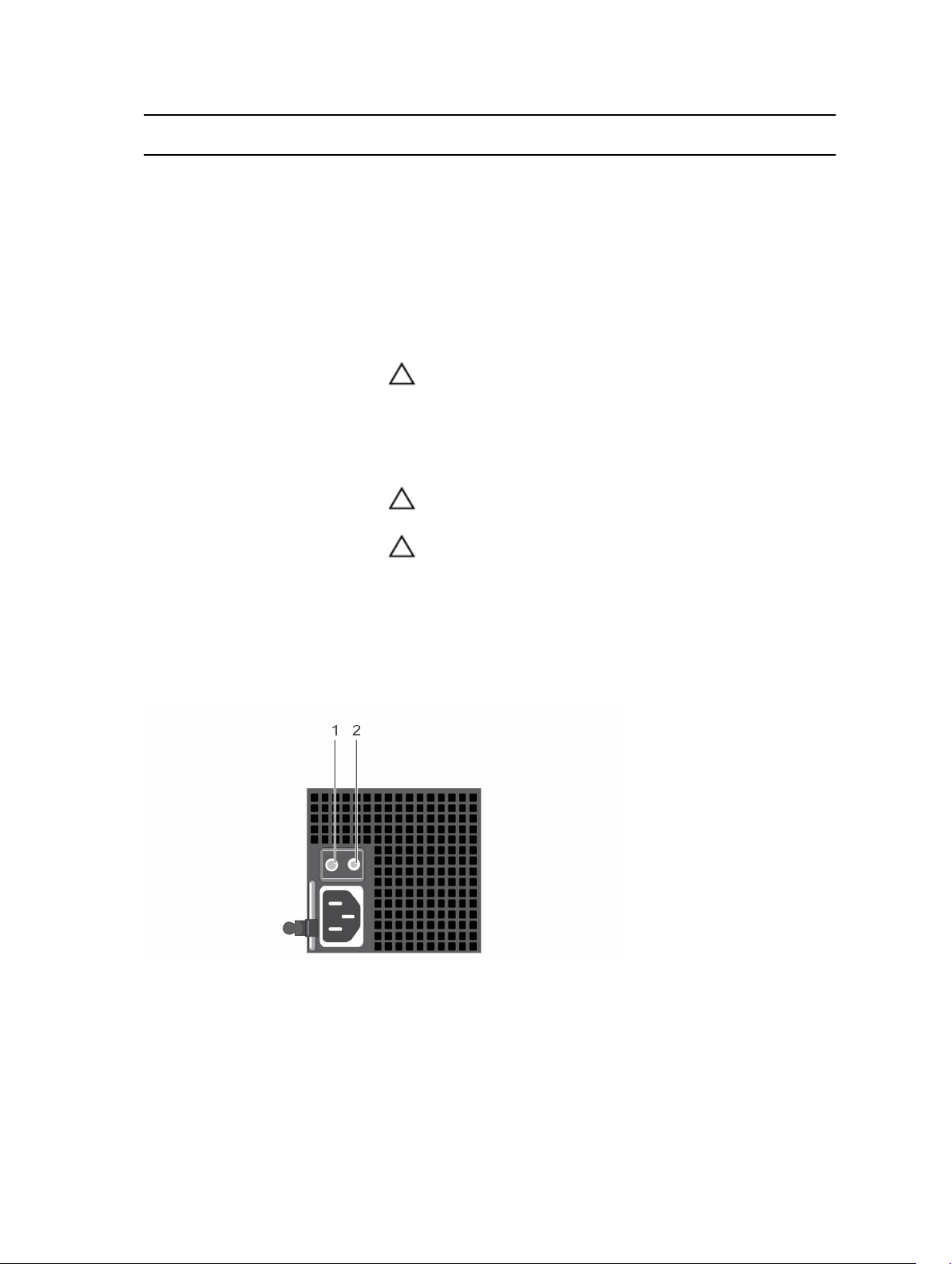
Convention Power indicator
pattern
A Green The handle/LED indicator lights green indicating that a valid power
B Flashing green When hot-adding a PSU, the handle of the new power supply unit
C Flashing amber Indicates a problem with the PSU.
Condition
source is connected to the PSU and that the PSU is operational.
flashes green five times at 4 Hz rate and turns off. This indicates
that the new PSU is mismatched with the PSU that is installed (in
terms of efficiency, feature set, health status, and supported
voltage). Use a PSU that matches the capacity of the PSU that is
installed.
CAUTION: When correcting a PSU mismatch, replace only
the PSU with the flashing indicator. Swapping the opposite
PSU to make a matched pair can result in an error condition
and unexpected system shutdown. To change from a High
Output configuration to a Low Output configuration or vice
versa, you must power down the system.
CAUTION: If two power supplies are used, they must be of
the same type and have the same maximum output power.
CAUTION: Combining AC and DC power supplies is not
supported and triggers a mismatch.
D Not lit Power is not connected.
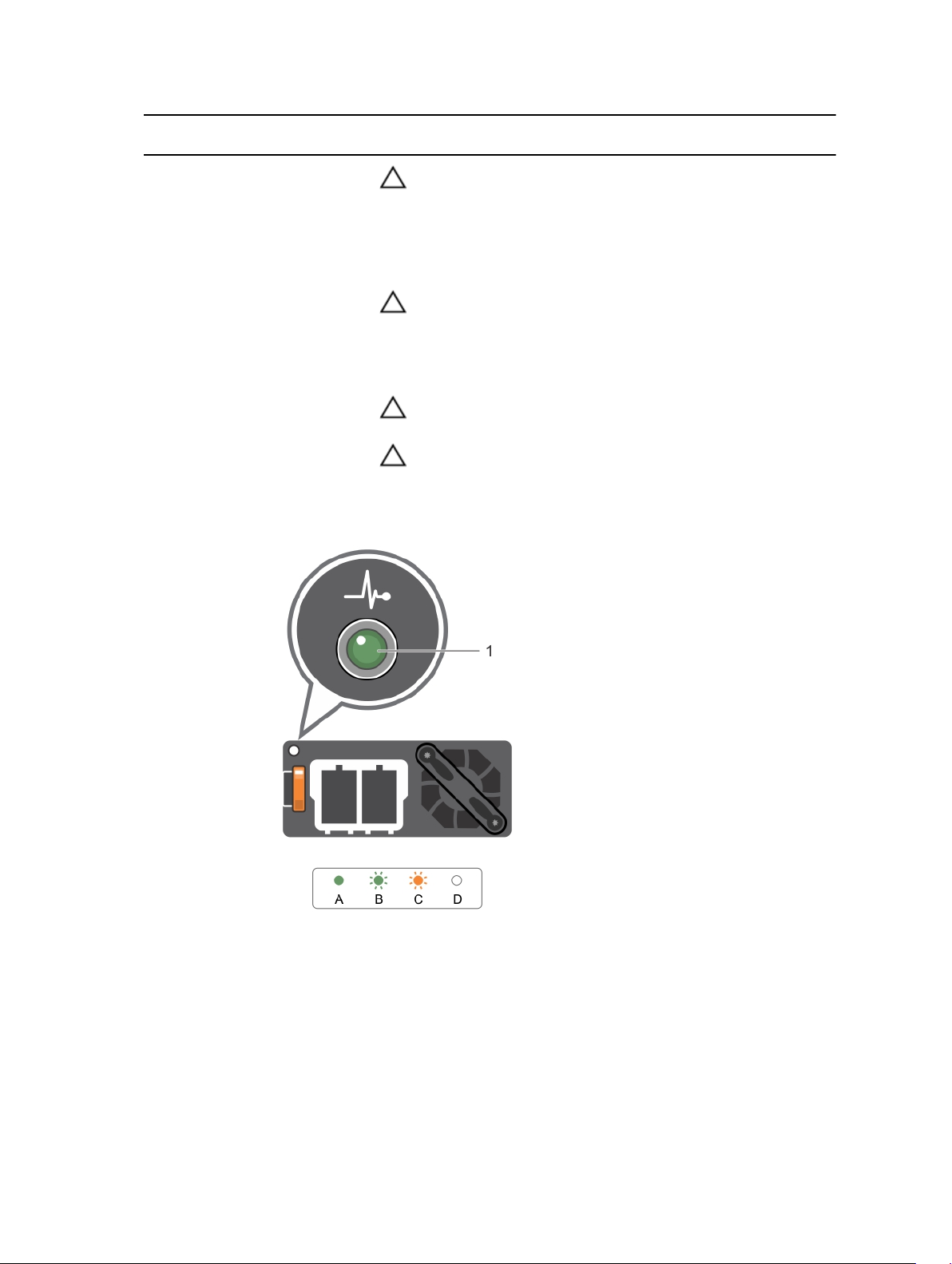
Indicator codes for non-redundant power supply
Press the self-diagnostic button to perform a quick health check on the non-redundant power supply of
the system.
Figure 8. Non-redundant AC power supply status indicator and self-diagnostic button
1. self-diagnostic button 2. AC power supply status indicator
18

Diagnostic Indicator Pattern Description
Not lit Power is not connected or power supply is faulty.
Green A valid power source is connected to the power supply and
the power supply is operational.
Documentation matrix
The documentation matrix provides information on documents that you can refer to for setting up and
managing your system.
To... Refer to...
Install your system into a rack Rack documentation included with your rack
solution
Set up your system and know the system technical
specifications
Install the operating system Operating system documentation at dell.com/
Get an overview of the Dell Systems Management
offerings
Configure and log in to iDRAC, set up managed
and management system, know the iDRAC
features and troubleshoot using iDRAC
Know about the RACADM subcommands and
supported RACADM interfaces
Launch, enable and disable Lifecycle Controller,
know the features, use and troubleshoot Lifecycle
Controller
Use Lifecycle Controller Remote Services Dell Lifecycle Controller Remote Services Quick
Set up, use, and troubleshoot OpenManage Server
Administrator
Install, use and troubleshoot OpenManage
Essentials
Getting Started With Your System that shipped with
your system or see dell.com/poweredgemanuals
operatingsystemmanuals
Dell OpenManage Systems Management Overview
Guide at dell.com/openmanagemanuals
Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's
Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals
RACADM Command Line Reference Guide for
iDRAC and CMC at dell.com/esmmanuals
Dell Lifecycle Controller User’s Guide at dell.com/
esmmanuals
Start Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals
Dell OpenManage Server Administrator User’s
Guide at dell.com/openmanagemanuals
Dell OpenManage Essentials User’s Guide at
dell.com/openmanagemanuals
Know the features of the storage controller cards,
deploy the cards, and manage the storage
subsystem
Check the event and error messages generated by
the system firmware and agents that monitor
system components
Storage controller documentation at dell.com/
storagecontrollermanuals
Dell Event and Error Messages Reference Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals
19
Quick Resource Locator (QRL)
Use the Quick Resource Locator (QRL) to get immediate access to system information and how-to
videos. This can be done by visiting www.dell.com/QRL or by using your smartphone or tablet and a
model specific Quick Resource (QR) code located on your Dell PowerEdge system. To try out the QR
code, scan the following image.
20

2
Performing initial system configuration
After you receive your PowerEdge system, you must set up your system, install the operating system if it
is not pre-installed, and set up and configure the system iDRAC IP address.
Setting up your system
1. Unpack the server.
2. Install the server into the rack. For more information on installing the server into the rack, see your
system Rack Installation Placemat at dell.com/poweredgemanuals.
3. Connect the peripherals to the system.
4. Connect the system to its electrical outlet.
5. Turn the system on by pressing the power button or using iDRAC.
6. Turn on the attached peripherals.
Setting up and configuring the iDRAC IP address
You can set up the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC) IP address by using one of the
following interfaces:
• iDRAC Settings utility
• Lifecycle Controller
• Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit
• Server LCD panel
You can configure iDRAC IP address by using the following interfaces:
• iDRAC Web interface. For more information, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's
Guide.
• Remote Access Controller ADMin (RACADM). For more information, see the RACADM Command Line
Interface Reference Guide and the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide.
• Remote Services that includes Web Services Management (WS-Man). For more information, see the
Lifecycle Controller Remote Services Quick Start Guide.
For more information on setting up and configuring iDRAC, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access
Controller User's Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
Logging in to iDRAC
You can log in to iDRAC as an iDRAC local user, a Microsoft Active Directory user, or a Lightweight
Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user. You can also log in by using Single Sign-On or a Smart Card. The
21

default user name is root and password is calvin. For more information on logging in to iDRAC and
iDRAC licenses, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
You can also access iDRAC using RACADM. For more information, see the RACADM Command Line
Interface Reference Guide and the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User's Guide available at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
Installing the operating system
If the server is shipped without an operating system, install the supported operating system on the server
by using one of the following methods:
• Dell Systems Management Tools and Documentation media. See the operating system
documentation at dell.com/operatingsystemmanuals.
• Dell Lifecycle Controller. See the Lifecycle Controller documentation at dell.com/esmmanuals.
• Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit. See the OpenManage documentation at dell.com/
openmanagemanuals.
For information on the list of operating systems supported on your system, see the operating systems
support matrix at dell.com/ossupport.
Managing your system remotely
To perform out-of-band systems management using iDRAC, you must configure iDRAC for remote
accessibility, set up the management station and managed system, and configure the supported Web
browsers. For more information, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller User’s Guide at
dell.com/esmmanuals.
You can also remotely monitor and manage the server by using the Dell OpenManage Server
Administrator (OMSA) software and OpenManage Essentials (OME) systems management console. For
more information, see dell.com/openmanagemanuals.
Downloading and installing drivers and firmware
It is recommended that you download and install the latest BIOS, drivers, and systems management
firmware on your system.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you clear the web browser cache.
Steps
1. Go to dell.com/support/drivers.
2. In the Product Selection section, enter the Service Tag of your system in the Service Tag or Express
Service Code field.
NOTE: If you do not have the Service Tag, select Automatically detect my Service Tag for me
to allow the system to automatically detect your Service Tag, or select Choose from a list of all
Dell products to select your product from the Product Selection page.
3. Click Get drivers and downloads.
The drivers that are applicable to your selection are displayed.
22

4. Download the drivers you require to a diskette drive, USB drive, CD, or DVD.
23

Pre-operating system management applications
The pre-operating system management applications for your PowerEdge system help you manage
different settings and features of your system without booting to the operating system.
Your PowerEdge system has the following pre-operating system management applications:
• System Setup
• Boot Manager
• Dell Lifecycle Controller
Navigation keys
The navigation keys can help you access the pre-operating system management applications.
Key Description
<Page Up> Moves to the previous screen.
3
<Page
Down>
Up arrow Moves to the previous field.
Down
arrow
<Enter> Enables you to type a value in the selected field (if applicable) or follow the link in the field.
Spacebar Expands or collapses a drop-down list, if applicable.
<Tab> Moves to the next focus area.
<Esc> Moves to the previous page until you view the main screen. Pressing <Esc> in the main
<F1> Displays the System Setup help.
Moves to the next screen.
Moves to the next field.
NOTE: This feature is applicable for the standard graphical browser only.
screen exits System BIOS/iDRAC Settings/Device Settings/Service Tag Settings and
proceeds with system boot.
About System Setup
Using System Setup, you can configure the BIOS settings, iDRAC settings, and device settings of your
system.
You can access System Setup in two ways:
24
• Standard Graphical Browser — This is enabled by default.
• Text Browser — This is enabled using Console Redirection.
NOTE: By default, help text for the selected field is displayed in the graphical browser. To view the
help text in the text browser, press <F1>.
Entering System Setup
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Press <F2> immediately after you see the following message:
<F2> = System Setup
If your operating system begins to load before you press <F2>, allow the system to finish booting,
and then restart your system and try again.
System Setup Main Menu
Option Description
System BIOS Enables you to configure BIOS settings.
iDRAC Settings Enables you to configure iDRAC settings.
The iDRAC Settings utility is an interface to set up and configure the
iDRAC parameters by using UEFI. You can enable or disable various
iDRAC parameters by using the iDRAC Settings utility. For more
information about this utility, see the Integrated Dell Remote Access
Controller User’s Guide at dell.com/esmmanuals.
Device Settings Enables you to configure device settings.
System BIOS screen
By using the System BIOS screen you can view the BIOS settings as well as edit specific functions such as
Boot Order, System Password, Setup Password, setting the RAID mode, and enabling or disabling USB
ports.
In the System Setup Main Menu, click System BIOS.
Menu Item Description
System Information Displays information about the system such as the system model name,
BIOS version and Service Tag.
Memory Settings Displays information and options related to the installed memory.
Processor Settings Displays information and options related to the processor such as speed,
cache size, and so on.
SATA Settings Displays options to enable or disable the integrated SATA controller and
ports.
Boot Settings Displays options to specify the boot mode (BIOS or UEFI). Enables you to
modify UEFI and BIOS boot settings.
Network Settings Displays options to change the network settings.
Integrated Devices Displays options to enable or disable integrated device controllers and
ports, and to specify related features and options.
25
Menu Item Description
Serial Communication Displays options to enable or disable the serial ports and specify related
features and options.
System Profile Settings Displays options to change the processor power management settings,
memory frequency, and so on.
System Security Displays options to configure the system security settings like, system
password, setup password, TPM security, and so on. It also enables or
disables support for the power and NMI buttons on the system.
Miscellaneous Settings Displays options to change the system date, time, and so on.
System Information screen
You can use the System Information screen to view system properties such as Service Tag, system
model, and the BIOS version.
To view the System Information click System Setup Main Menu → System BIOS → System Information.
Menu Item Description
System Model Name Displays the system model name.
System BIOS Version Displays the BIOS version installed on the system.
System Management
Engine Version
System Service Tag Displays the system Service Tag.
System Manufacturer Displays the name of the system manufacturer.
System Manufacturer
Contact Information
System CPLD Version Displays the current revision of the system CPLD firmware.
UEFI Compliance Version Displays the system firmware UEFI compliance level.
Displays the current revision of the Management Engine firmware.
Displays the contact information of the system manufacturer.
Memory Settings screen
You can use the Memory Settings screen to view all the memory settings as well as enable or disable
specific memory functions such as system memory testing and node interleaving.
To view theMemory Setting screen, click System Setup Main Menu → System BIOS → Memory Settings.
Menu Item Description
System Memory Size Displays the amount of memory installed in the system.
System Memory Type Displays the type of memory installed in the system.
System Memory Speed Displays the system memory speed.
System Memory Voltage Displays the system memory voltage.
Video Memory Displays the amount of video memory utilized.
System Memory Testing Specifies whether system memory tests are run during system boot.
Options are Enabled and Disabled. By default, the System Memory
Testing option is set to Disabled.
Memory Operating Mode Specifies the memory operating mode. The options available are
Optimizer Mode, Advanced ECC Mode, Mirror Mode, Spare Mode, and
26
Menu Item Description
Spare with Advanced ECC Mode. By default, the Memory Operating
Mode option is set to Optimizer Mode.
NOTE: The Memory Operating Mode can have different defaults
and available options based on the memory configuration of your
system.
Node Interleaving Specifies if Non-Uniform Memory architecture (NUMA) is supported. If
this field is Enabled, memory interleaving is supported if a symmetric
memory configuration is installed. If Disabled, the system supports
NUMA (asymmetric) memory configurations. By default, Node
Interleaving
Snoop Mode Specifies the Snoop Mode options. Snoop Mode options available are
Home Snoop, Early Snoop, and Cluster on Die. By default, the Snoop
Mode option is set to Early Snoop. The field is only available when Node
Interleaving is Disabled.
option is set to Disabled.
Processor Settings screen
You can use the Processor Settings screen to view the processor settings and perform specific functions
such as enabling virtualization technology, hardware prefetcher, and logical processor idling.
To view the Processor Settings screen, click System Setup Main Menu → System BIOS → Processor
Settings.
Menu Item Description
Logical Processor Enables or disables the logical processors and displays the number of
logical processors. If the Logical Processor option is set to Enabled, the
BIOS displays all the logical processors. If this option is set to Disabled,
the BIOS displays only one logical processor per core. By default, the
Logical Processor option is set to Enabled.
Alternate RTID (Requestor
Transaction ID) Setting
Virtualization Technology Enables or disables the additional hardware capabilities provided for
Address Translation Service
(ATS)
Adjacent Cache Line
Prefetch
Hardware Prefetcher Enables or disables the hardware prefetcher. By default, the Hardware
DCU Streamer Prefetcher Allows you to enable or disable the Data Cache Unit (DCU) streamer
Enables you to allocate more RTIDs to the remote socket, thereby
increasing cache performance between the sockets or easing work in
normal mode for NUMA. By default, the Alternate RTID (Requestor
Transaction ID) Setting is set to Disabled.
virtualization. By default, the Virtualization Technology option is set to
Enabled.
Defines the Address Translation Cache (ATC) for devices to cache the
DMA transactions. This field provides an interface to a chipset's Address
Translation and Protection Table to translate DMA addresses to host
addresses. By default, the option is set to Enabled.
Optimizes the system for applications that require high utilization of
sequential memory access. By default, the Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
option is set to Enabled. You can disable this option for applications that
require high utilization of random memory access.
Prefetcher option is set to Enabled.
prefetcher. By default, the DCU Streamer Prefetcher option is set to
Enabled.
27
Menu Item Description
DCU IP Prefetcher Enables or disables the Data Cache Unit (DCU) IP prefetcher. By default,
the DCU IP Prefetcher option is set to Enabled.
Execute Disable Enables or disables the execute disable memory protection technology.
By default, the Execute Disable option is set to Enabled.
Logical Processor Idling Enables or disables the operating system capability to put logical
processors in the idling state in order to reduce power consumption. By
default, the option is set to Disabled.
Configurable TDP Allows reconfiguration of Thermal Design Power (TDP) to lower levels.
TDP refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system is
required to dissipate.
X2Apic Mode Enables or disables the X2Apic mode.
Number of Cores per
Processor
Processor 64-bit Support Specifies if the processor(s) support 64-bit extensions.
Processor Core Speed Displays the maximum core frequency of the processor.
Processor Bus Speed Displays the bus speed of the processor.
Controls the number of enabled cores in each processor. By default, the
Number of Cores per Processor option is set to All.
NOTE: The processor bus speed option displays only when both
processors are installed.
Processor 1
Family-Model-Stepping Displays the family, model and stepping of the processor as defined by
Brand Displays the brand name reported by the processor.
Level 2 Cache Displays the total L2 cache.
Level 3 Cache Displays the total L3 cache.
Number of Cores Displays the number of cores per processor.
NOTE: Depending on the number of installed CPUs, there may be
up to two processor listings. The following settings are displayed for
each processor installed in the system.
Intel.
SATA Settings screen
You can use the SATA Settings screen to view the SATA settings of SATA devices and enable RAID on
your system.
To view the SATA Settings screen click System Setup Main Menu → System BIOS → SATA Settings.
Menu Item Description
Embedded SATA Enables the embedded SATA to be set to Off, ATA, AHCI, or RAID modes.
By default, the Embedded SATA option is set to AHCI.
Security Freeze Lock Sends Security Freeze Lock command to the Embedded SATA drives
during POST. This option is applicable only to ATA and AHCI mode.
Write Cache Enables or disables the command for Embedded SATA drives during
POST.
28

Menu Item Description
Port A Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port B Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port C Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port D Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port E Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
29

Menu Item Description
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port F Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port G Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port H Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port I Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
Drive Type Displays the type of drive attached to the SATA port.
Capacity Displays the total capacity of the hard drive. The field is undefined for
removable media devices such as optical drives.
Port J Sets the drive type of the selected device. For Embedded SATA settings
in ATA mode, set this field to Auto to enable BIOS support. Set it to OFF
to turn off BIOS support.
For AHCI mode or RAID mode, BIOS always enables support.
Model Displays the drive model of the selected device.
30
 Loading...
Loading...